⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Efficient Correlation Volume Sampling for Ultra-High-Resolution Optical Flow Estimation
Authors:Karlis Martins Briedis, Markus Gross, Christopher Schroers
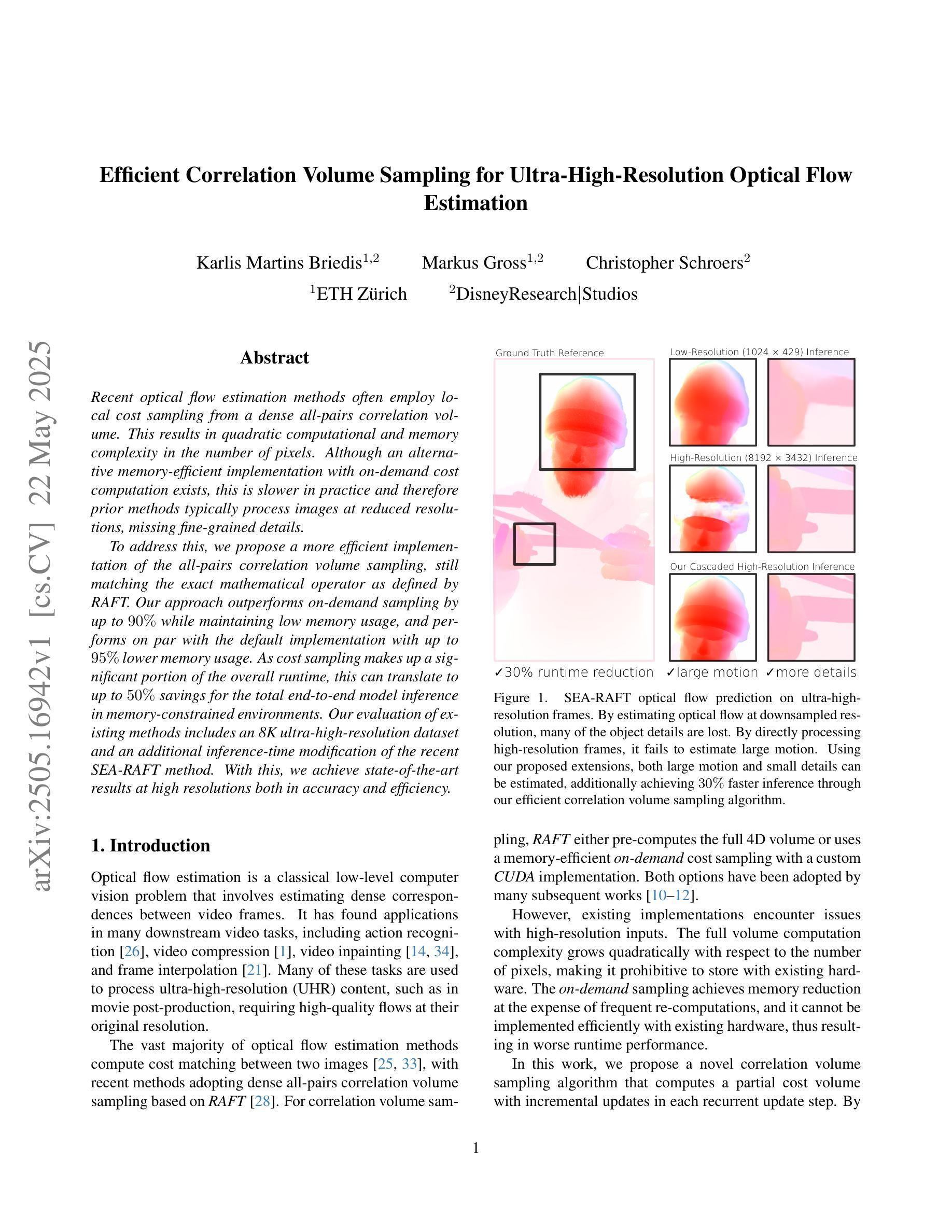
Recent optical flow estimation methods often employ local cost sampling from a dense all-pairs correlation volume. This results in quadratic computational and memory complexity in the number of pixels. Although an alternative memory-efficient implementation with on-demand cost computation exists, this is slower in practice and therefore prior methods typically process images at reduced resolutions, missing fine-grained details. To address this, we propose a more efficient implementation of the all-pairs correlation volume sampling, still matching the exact mathematical operator as defined by RAFT. Our approach outperforms on-demand sampling by up to 90% while maintaining low memory usage, and performs on par with the default implementation with up to 95% lower memory usage. As cost sampling makes up a significant portion of the overall runtime, this can translate to up to 50% savings for the total end-to-end model inference in memory-constrained environments. Our evaluation of existing methods includes an 8K ultra-high-resolution dataset and an additional inference-time modification of the recent SEA-RAFT method. With this, we achieve state-of-the-art results at high resolutions both in accuracy and efficiency.
近期光学流动估计方法经常采用从密集的全对相关性体积中进行局部成本采样。这导致了在像素数量上的二次计算和内存复杂性。尽管存在一种带有按需成本计算的内存高效实现方法,但在实践中这种方法较慢,因此先前的方法通常在降低的分辨率上处理图像,从而丢失了精细的颗粒细节。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了全对相关性体积采样的更高效实现方法,仍然匹配RAFT所定义的精确数学运算符。我们的方法在内存使用上优于按需采样高达90%,同时保持低内存使用,并且在内存受限的环境中与默认实现相比,性能相当,内存使用可降低高达95%。由于成本采样占总体运行时间的很大一部分,因此这可以转换为在内存受限的环境中端到端模型推理总时间的最高达50%的节省。我们对现有方法的评估包括一个8K超高分辨率数据集和最近SEA-RAFT方法的额外推理时间修改。借此,我们在准确度和效率方面都实现了业界领先水平的高分辨率结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出一种更高效的成对相关性体积采样方法,用于解决光学流动估计中的计算量大和内存复杂度高的问题。相较于传统方法,该方法能够在保持低内存使用的同时,加速采样过程,最高可达90%。此外,该方法能够在内存受限环境中节省高达50%的总端到端模型推理时间。对高清晰度数据集的评估显示了该方法在准确性和效率上的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种高效的成对相关性体积采样方法。
- 在保持低内存使用的同时,该方法可以显著加速光学流动估计的计算过程。
- 相较于传统的光学流动估计方法,该方法的运行速度最高可提高90%。
- 在内存受限的环境中,该方法可以节省高达50%的总端到端模型推理时间。
- 该方法能够在高清晰度数据集上实现最先进的性能和效率。
点此查看论文截图
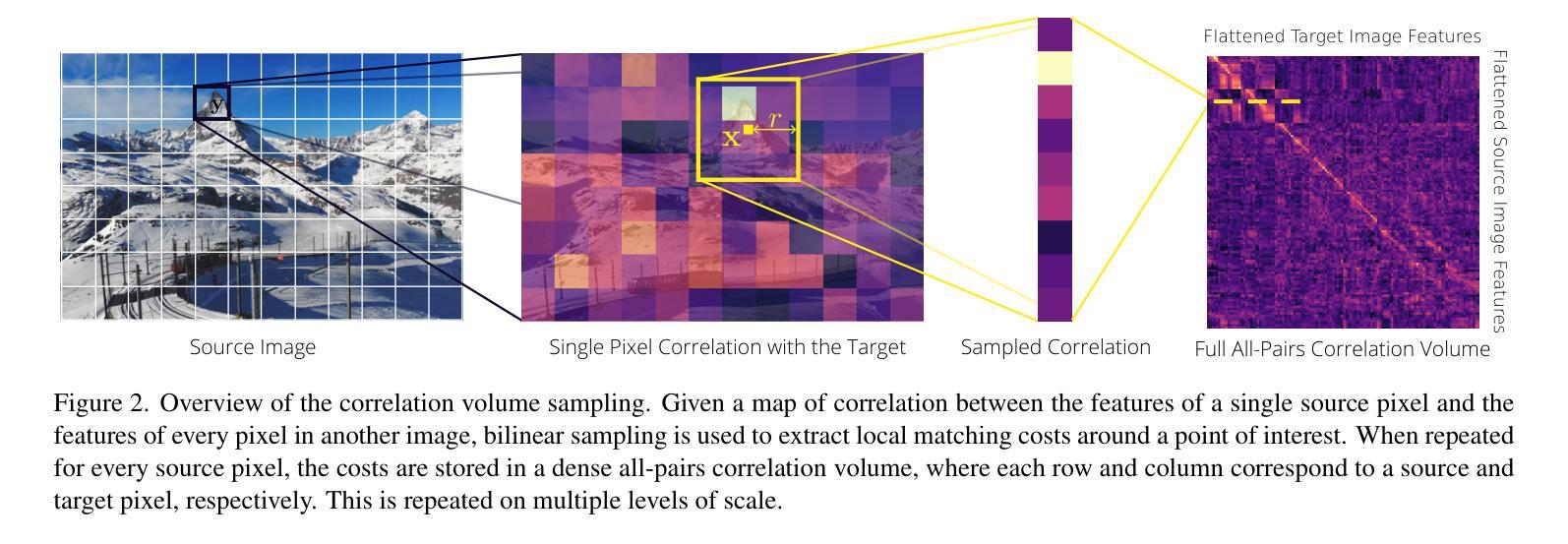
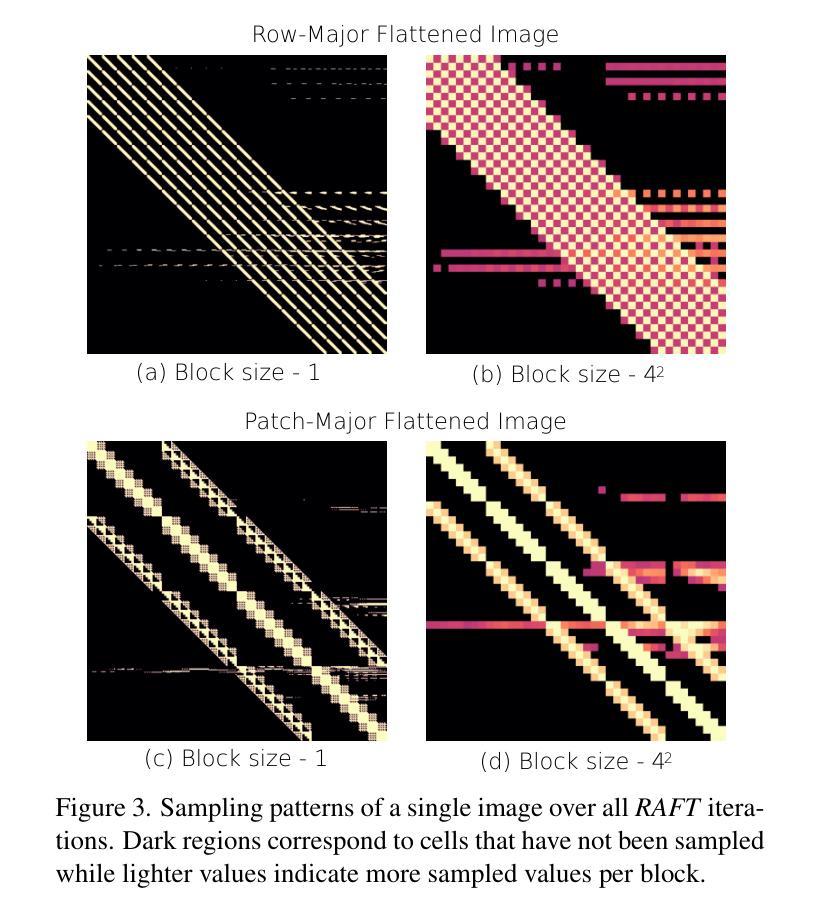
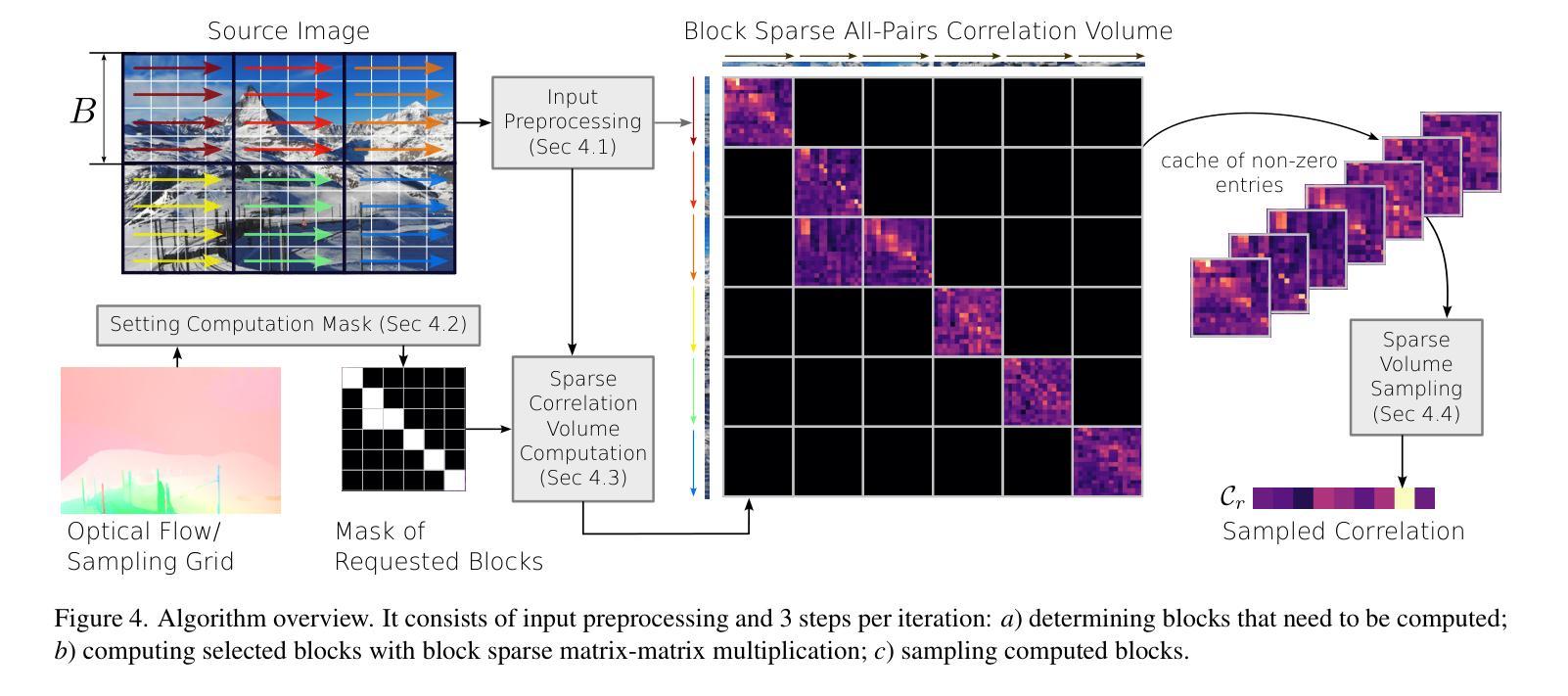
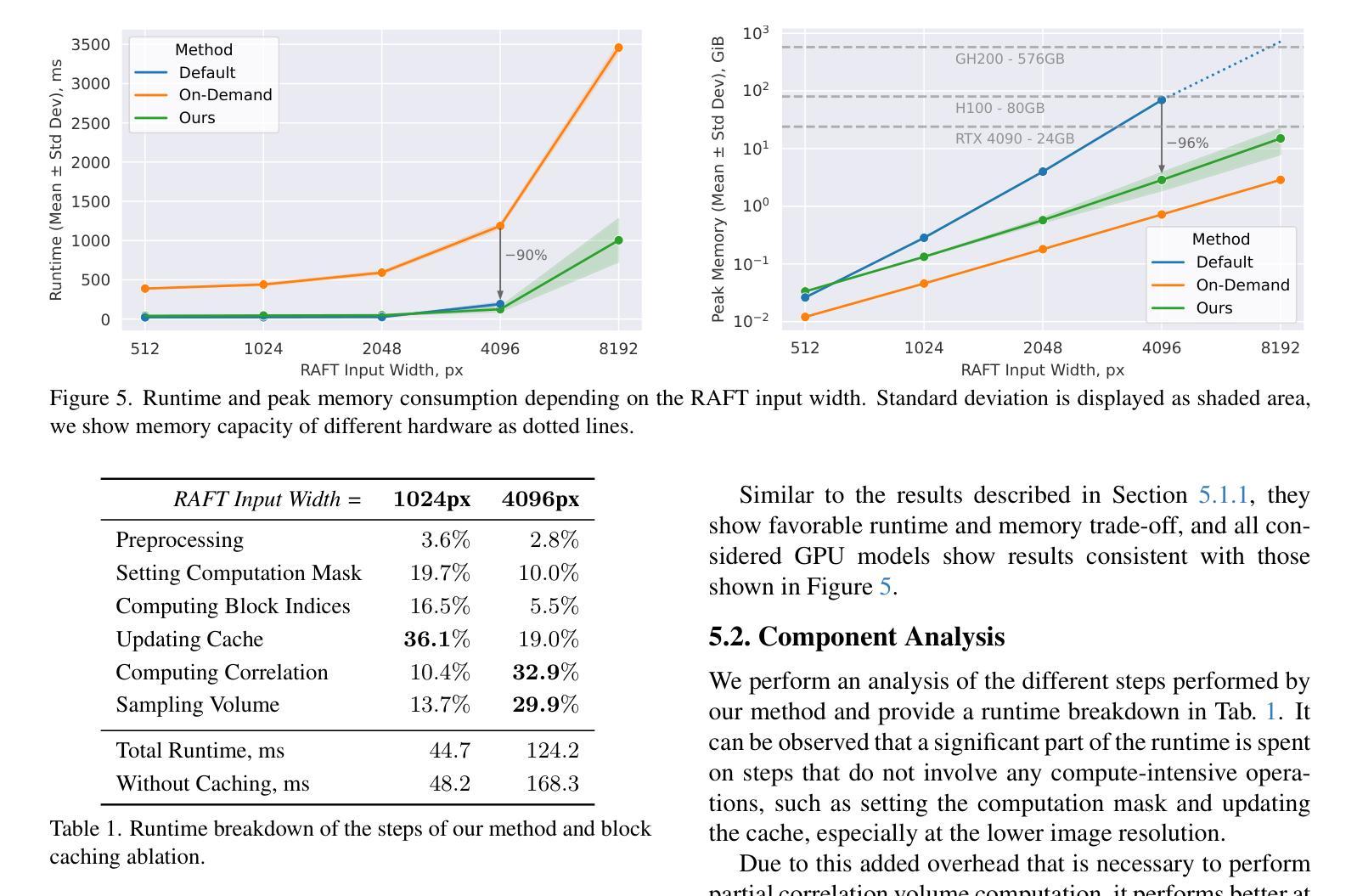
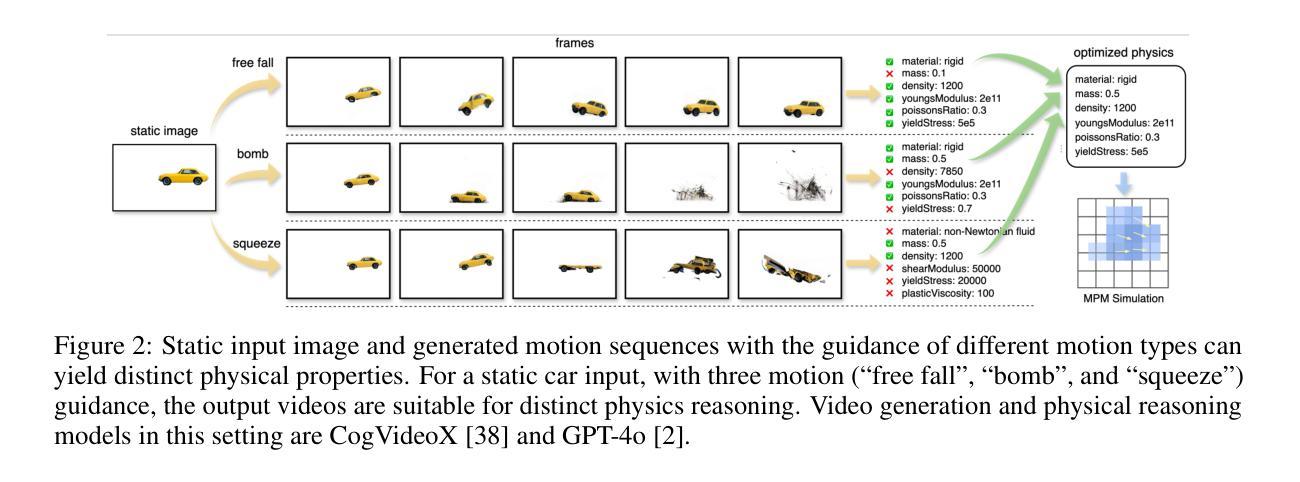
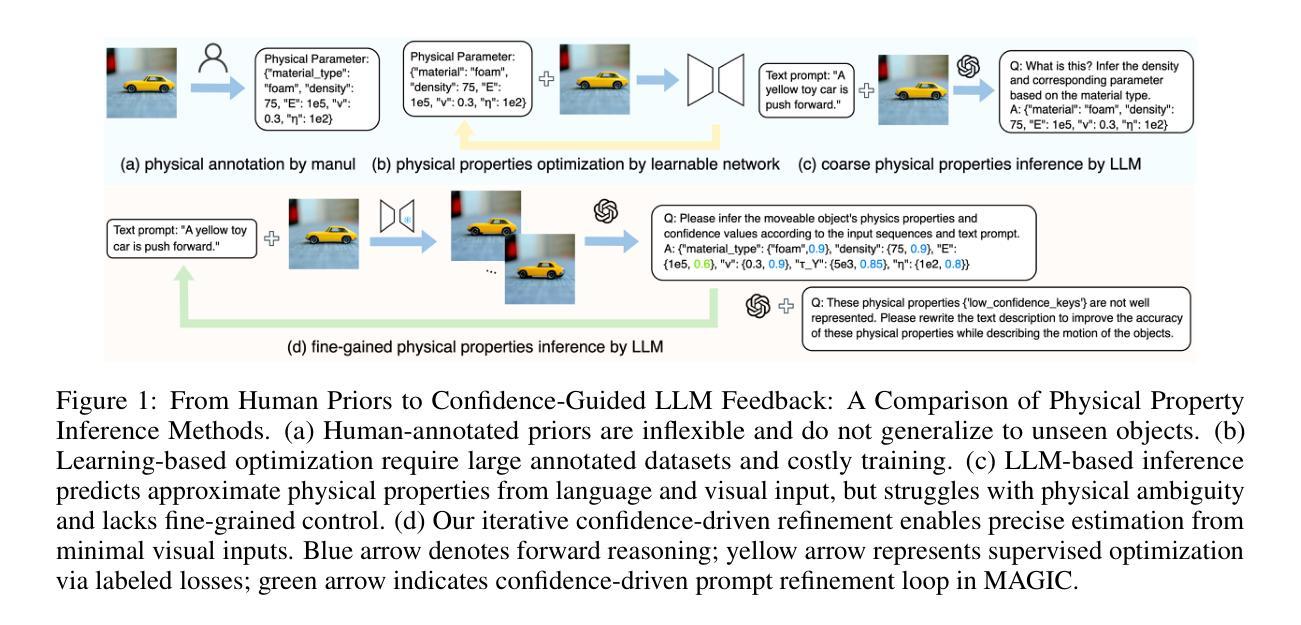
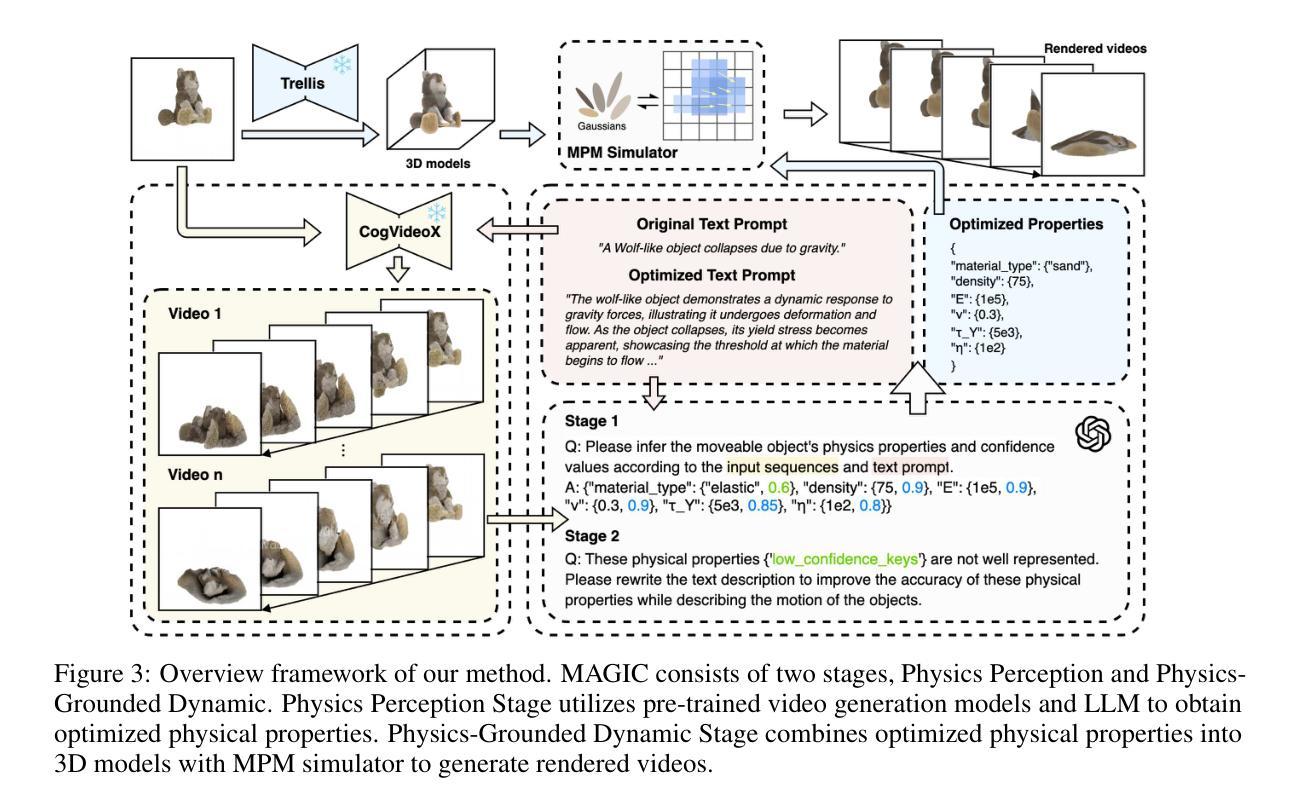
MAGIC: Motion-Aware Generative Inference via Confidence-Guided LLM
Authors:Siwei Meng, Yawei Luo, Ping Liu
Recent advances in static 3D generation have intensified the demand for physically consistent dynamic 3D content. However, existing video generation models, including diffusion-based methods, often prioritize visual realism while neglecting physical plausibility, resulting in implausible object dynamics. Prior approaches for physics-aware dynamic generation typically rely on large-scale annotated datasets or extensive model fine-tuning, which imposes significant computational and data collection burdens and limits scalability across scenarios. To address these challenges, we present MAGIC, a training-free framework for single-image physical property inference and dynamic generation, integrating pretrained image-to-video diffusion models with iterative LLM-based reasoning. Our framework generates motion-rich videos from a static image and closes the visual-to-physical gap through a confidence-driven LLM feedback loop that adaptively steers the diffusion model toward physics-relevant motion. To translate visual dynamics into controllable physical behavior, we further introduce a differentiable MPM simulator operating directly on 3D Gaussians reconstructed from the single image, enabling physically grounded, simulation-ready outputs without any supervision or model tuning. Experiments show that MAGIC outperforms existing physics-aware generative methods in inference accuracy and achieves greater temporal coherence than state-of-the-art video diffusion models.
近期静态3D生成技术的进展加剧了对物理一致性动态3D内容的需求。然而,现有的视频生成模型,包括基于扩散的方法,通常优先考虑视觉真实性,而忽略了物理可行性,导致物体动态不可信。以前对物理感知动态生成的方法通常依赖于大规模标注数据集或模型精细调整,这带来了很大的计算和数据采集负担,并限制了跨场景的扩展性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MAGIC,这是一个无需训练的单图像物理属性推断和动态生成框架,它整合了预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型与基于迭代的大型语言模型(LLM)推理。我们的框架从静态图像生成丰富的运动视频,并通过信心驱动的LLM反馈循环缩小了视觉到物理的差距,该循环自适应地引导扩散模型朝着物理相关的运动发展。为了将视觉动态转化为可控的物理行为,我们进一步引入了一个可微分的MPM模拟器,直接在从单张图像重建的3D高斯上运行,从而实现无需监督或模型调整的物理基础、模拟就绪输出。实验表明,MAGIC在推理准确性方面优于现有的物理感知生成方法,并且在时间连贯性方面优于最先进的视频扩散模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期静态3D技术的发展加剧了对物理一致性动态3D内容的需求。现有视频生成模型往往注重视觉真实性而忽视物理合理性,导致物体动态不合理。为解决此问题,提出MAGIC框架,无需训练即可进行单张图片物理属性推断和动态生成,整合预训练图像转视频扩散模型与迭代LLM推理。框架通过置信驱动LLM反馈环生成丰富动态视频,自适应引导扩散模型向物理相关运动发展。引入可微MPM模拟器,直接在单张图片重建的3D高斯上操作,产生物理基础、模拟准备输出,无需监督或模型调整。实验显示,MAGIC在推理准确性上优于现有物理感知生成方法,时间连贯性高于最先进视频扩散模型。
Key Takeaways
- 近期静态3D技术发展促进了对物理一致性动态内容的需求。
- 现有视频生成模型主要关注视觉真实性,忽略了物理合理性。
- MAGIC框架是一种无需训练的单图像物理属性推断和动态生成方法。
- MAGIC结合了预训练的图像到视频扩散模型与迭代LLM推理。
- 通过置信驱动LLM反馈环实现动态视频生成,引导扩散模型向物理相关运动发展。
- 引入可微MPM模拟器,直接操作单张图片上的3D高斯,产生物理基础输出。
点此查看论文截图



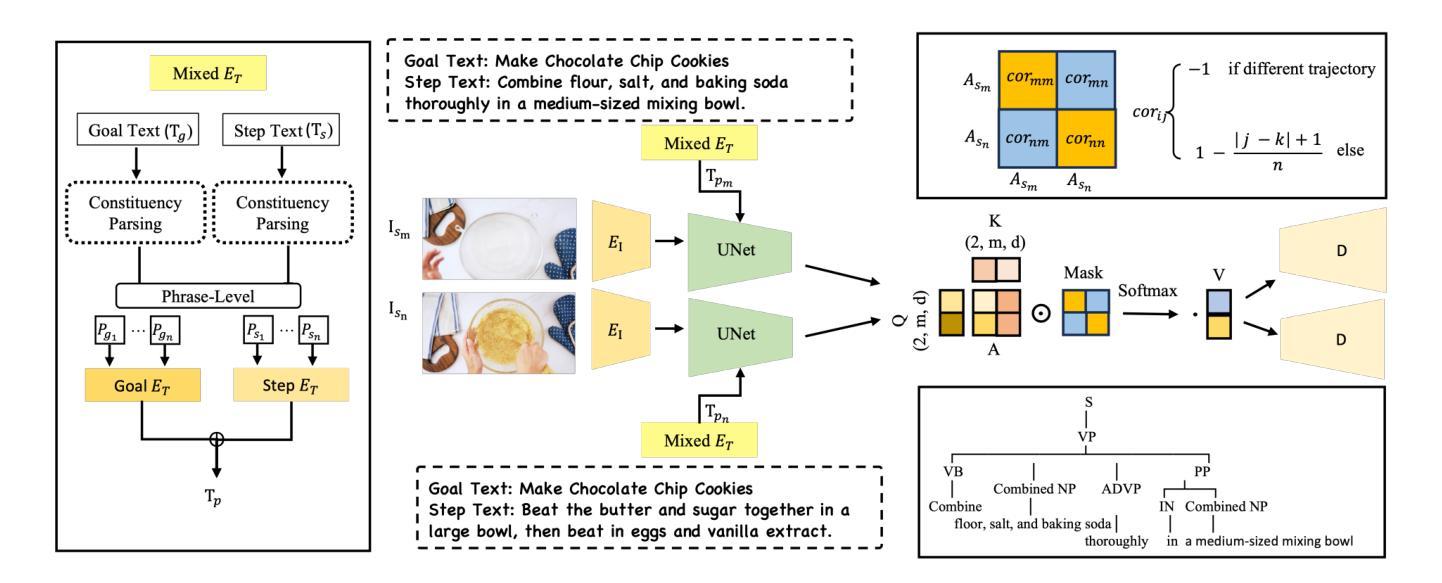
$I^2G$: Generating Instructional Illustrations via Text-Conditioned Diffusion
Authors:Jing Bi, Pinxin Liu, Ali Vosoughi, Jiarui Wu, Jinxi He, Chenliang Xu
The effective communication of procedural knowledge remains a significant challenge in natural language processing (NLP), as purely textual instructions often fail to convey complex physical actions and spatial relationships. We address this limitation by proposing a language-driven framework that translates procedural text into coherent visual instructions. Our approach models the linguistic structure of instructional content by decomposing it into goal statements and sequential steps, then conditioning visual generation on these linguistic elements. We introduce three key innovations: (1) a constituency parser-based text encoding mechanism that preserves semantic completeness even with lengthy instructions, (2) a pairwise discourse coherence model that maintains consistency across instruction sequences, and (3) a novel evaluation protocol specifically designed for procedural language-to-image alignment. Our experiments across three instructional datasets (HTStep, CaptainCook4D, and WikiAll) demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing baselines in generating visuals that accurately reflect the linguistic content and sequential nature of instructions. This work contributes to the growing body of research on grounding procedural language in visual content, with applications spanning education, task guidance, and multimodal language understanding.
在自然语言处理(NLP)中,过程性知识的有效沟通仍然是一个重大挑战,因为纯粹的文本指令往往无法传达复杂的物理动作和空间关系。我们通过提出一种语言驱动框架来解决这一局限性,该框架将过程性文本翻译成连贯的视觉指令。我们的方法通过分解指令内容为目标陈述和顺序步骤来建模指令内容的语言结构,然后根据这些语言元素进行视觉生成。我们引入了三项关键创新:(1)一种基于成分分析器的文本编码机制,即使在长篇指令的情况下也能保持语义完整性;(2)一种保持指令序列一致性的成对话语连贯性模型;(3)一种专为程序语言与图像对齐设计的全新评估协议。我们在三个指令数据集(HTStep、CaptainCook4D和WikiAll)上的实验表明,我们的方法在生成准确反映语言内容和指令顺序性的视觉图像方面显著优于现有基线。这项工作对教育、任务指导和跨模态语言理解等领域的过程性语言与视觉内容的结合研究做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures, under review
Summary:
程序性知识在自然语言处理中的有效传达仍是一大挑战,单纯文本指令往往无法传达复杂的物理动作和空间关系。本文提出了一种语言驱动框架,可将程序性文本转化为连贯的视觉指令。该方法通过分解目标陈述和顺序步骤对指令内容的语言结构进行建模,然后基于这些语言元素进行视觉生成。本文介绍了三个关键创新点:基于依存句法分析器的文本编码机制,即使在长篇指令下也能保持语义完整性;话语连贯性模型,保持指令序列的一致性;专为程序性语言与图像对齐设计的新型评估协议。实验表明,该方法在三个指令数据集上的表现均优于现有基线,生成的视觉图像能准确反映语言内容和指令的序列性。本文为将程序性语言根植于视觉内容的研究做出了贡献,应用范围涵盖教育、任务指导和多媒体语言理解。
Key Takeaways:
- 程序性知识在自然语言处理中的传达存在挑战,单纯文本指令难以表达复杂物理动作和空间关系。
- 提出了一种语言驱动框架,将程序性文本转化为视觉指令。
- 通过分解目标陈述和顺序步骤对指令内容的语言结构进行建模。
- 引入了基于依存句法分析器的文本编码机制,保持语义完整性。
- 采用了话语连贯性模型,确保指令序列的一致性。
- 设计了新的评估协议,专门用于程序性语言与图像的对齐。
- 实验在多个数据集上表现出优越性能,生成的视觉图像能反映语言内容和指令的序列性,对教育和多媒体语言理解等领域有贡献。
点此查看论文截图

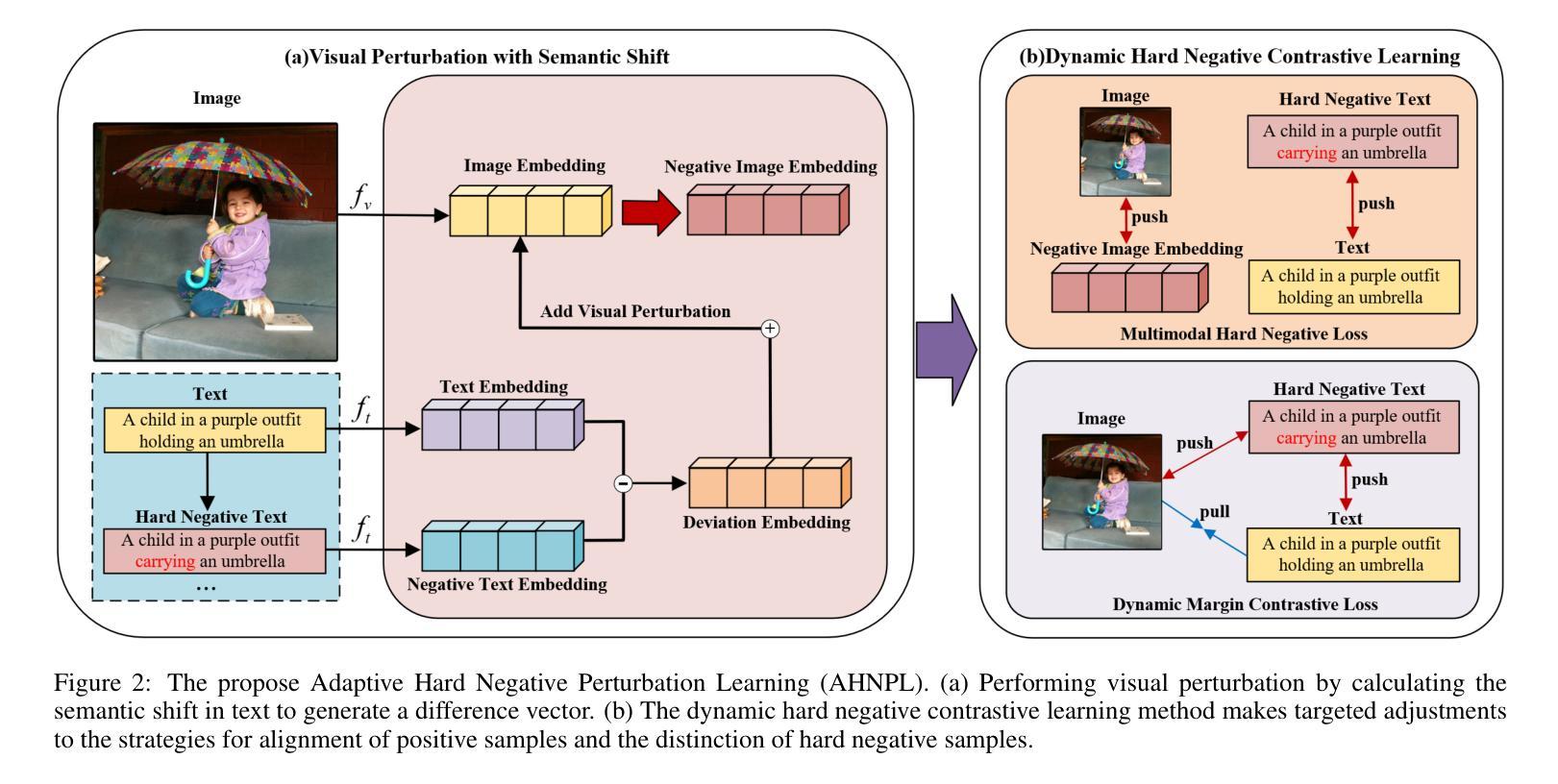
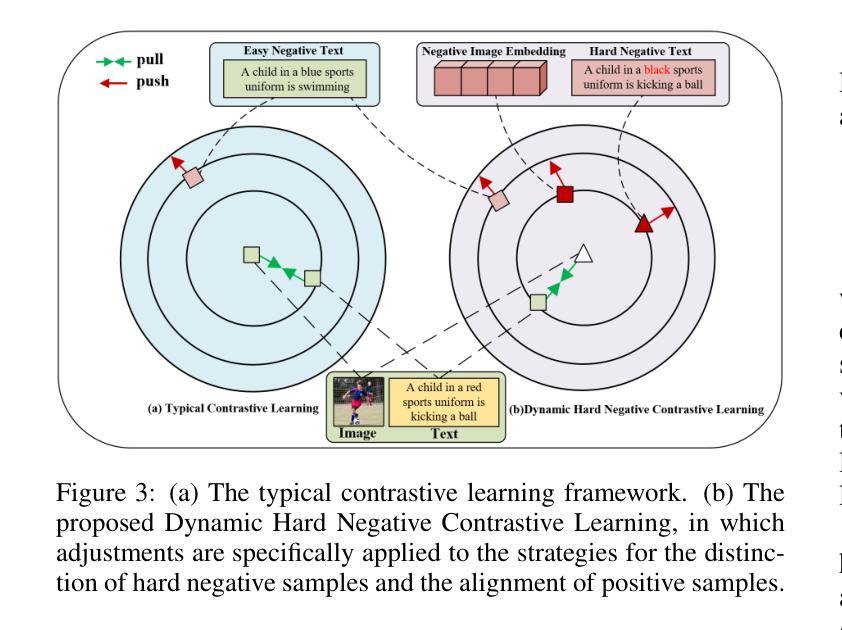
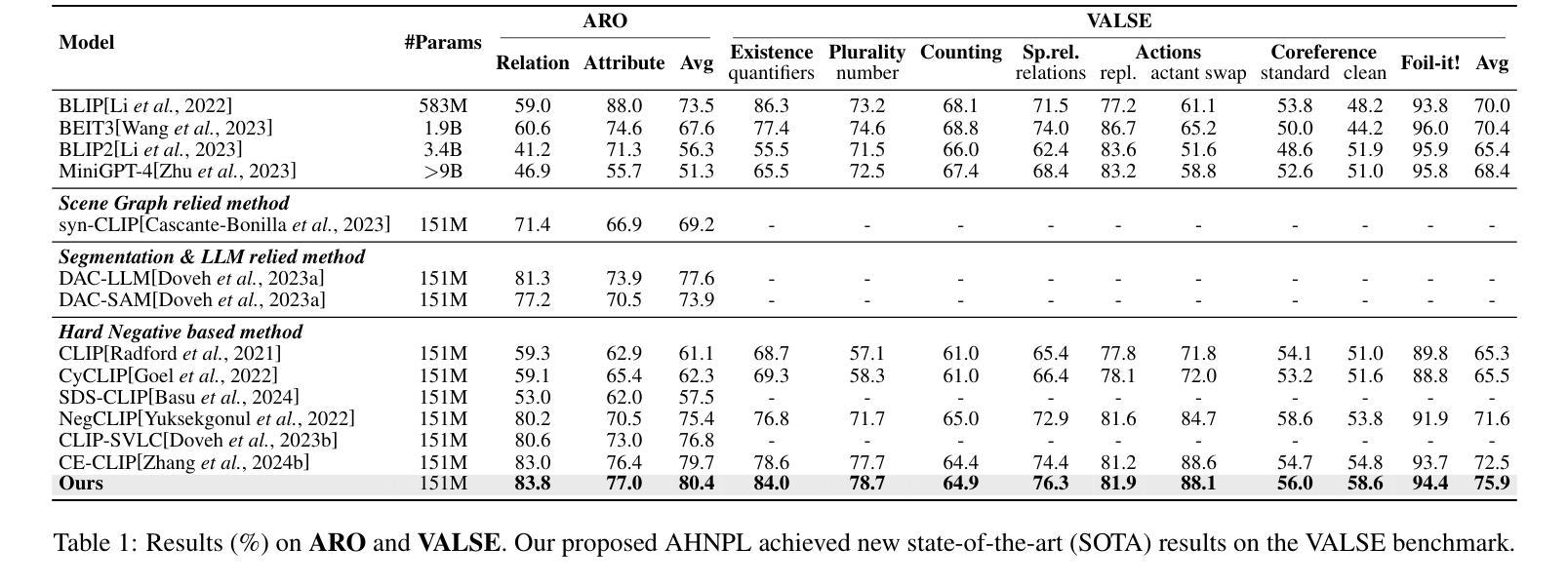
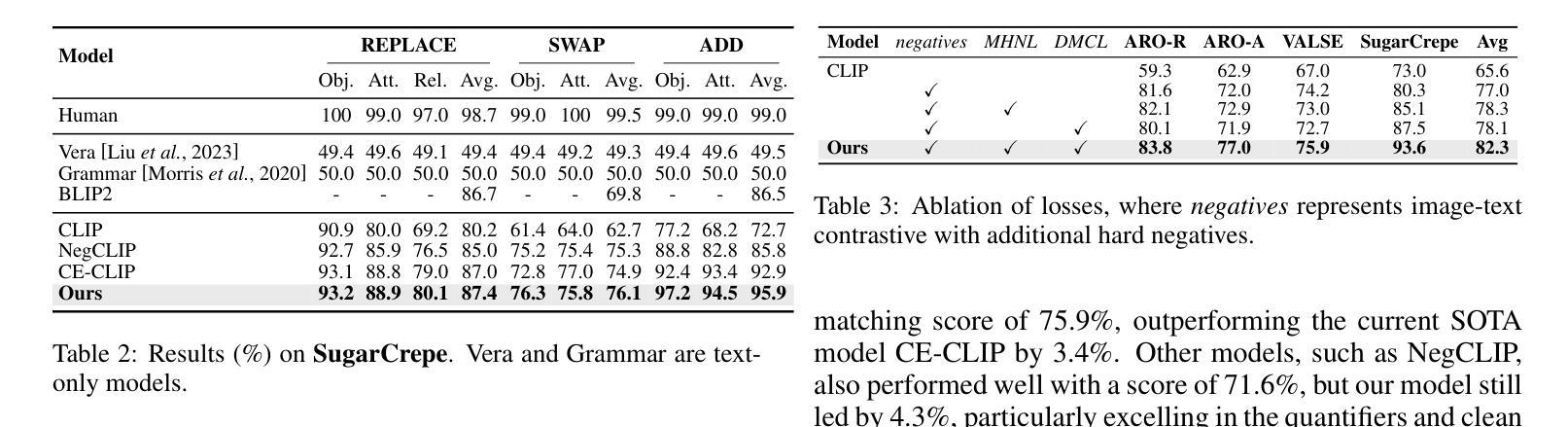
Visual Perturbation and Adaptive Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Compositional Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Xin Huang, Ruibin Li, Tong Jia, Wei Zheng, Ya Wang
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are essential for multimodal tasks, especially compositional reasoning (CR) tasks, which require distinguishing fine-grained semantic differences between visual and textual embeddings. However, existing methods primarily fine-tune the model by generating text-based hard negative samples, neglecting the importance of image-based negative samples, which results in insufficient training of the visual encoder and ultimately impacts the overall performance of the model. Moreover, negative samples are typically treated uniformly, without considering their difficulty levels, and the alignment of positive samples is insufficient, which leads to challenges in aligning difficult sample pairs. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Hard Negative Perturbation Learning (AHNPL). AHNPL translates text-based hard negatives into the visual domain to generate semantically disturbed image-based negatives for training the model, thereby enhancing its overall performance. AHNPL also introduces a contrastive learning approach using a multimodal hard negative loss to improve the model’s discrimination of hard negatives within each modality and a dynamic margin loss that adjusts the contrastive margin according to sample difficulty to enhance the distinction of challenging sample pairs. Experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that our method effectively boosts VLMs’ performance on complex CR tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)对于多模态任务,特别是需要区分视觉和文本嵌入之间细微语义差异的组合推理(CR)任务至关重要。然而,现有方法主要通过生成基于文本的硬负样本对模型进行微调,忽略了基于图像的负样本的重要性,导致视觉编码器训练不足,最终影响模型的总体性能。此外,负样本通常被一视同仁,没有考虑其难度水平,正样本的对齐也不足,这导致难以对齐困难样本对。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)。AHNPL将基于文本的硬负样本转换为视觉域,以生成用于训练模型的在语义上受到干扰的基于图像的负样本,从而提高模型的总体性能。AHNPL还引入了一种对比学习方法,使用多模态硬负损失来提高模型在每个模态内对硬负样本的辨别能力,以及一种动态边距损失,该损失会根据样本难度调整对比边距,以提高对困难样本对的区分能力。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法有效地提高了VLMs在复杂的CR任务上的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2025)
Summary
本文提出一种名为自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)的方法,用于改进视觉语言模型(VLMs)在组合推理任务上的性能。该方法解决了现有方法的缺陷,即忽略图像基负样本的重要性以及对正负样本的均匀处理和不足的排列问题。AHNPL通过翻译文本基硬负生成语义干扰的图像基负样本进行训练,并引入对比学习方法和多模态硬负损失来改进模型的区分能力。实验结果表明,该方法能有效提升VLMs在复杂CR任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在组合推理任务中面临区分视觉和文本嵌入中的细微语义差异的挑战。
- 现有方法主要通过对文本基硬负样本进行微调来优化模型,但忽略了图像基负样本的重要性,导致视觉编码器训练不足。
- AHNPL通过将文本基硬负样本转化为图像域来生成图像基负样本,从而提高模型的整体性能。
- AHNPL引入对比学习方法,使用多模态硬负损失改进模型对每种模态内硬负的区分能力。
- AHNPL还采用动态边际损失,根据样本难度调整对比边际,以提高对具有挑战性的样本对的区分能力。
- 在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,AHNPL方法能有效提升VLMs在复杂CR任务上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

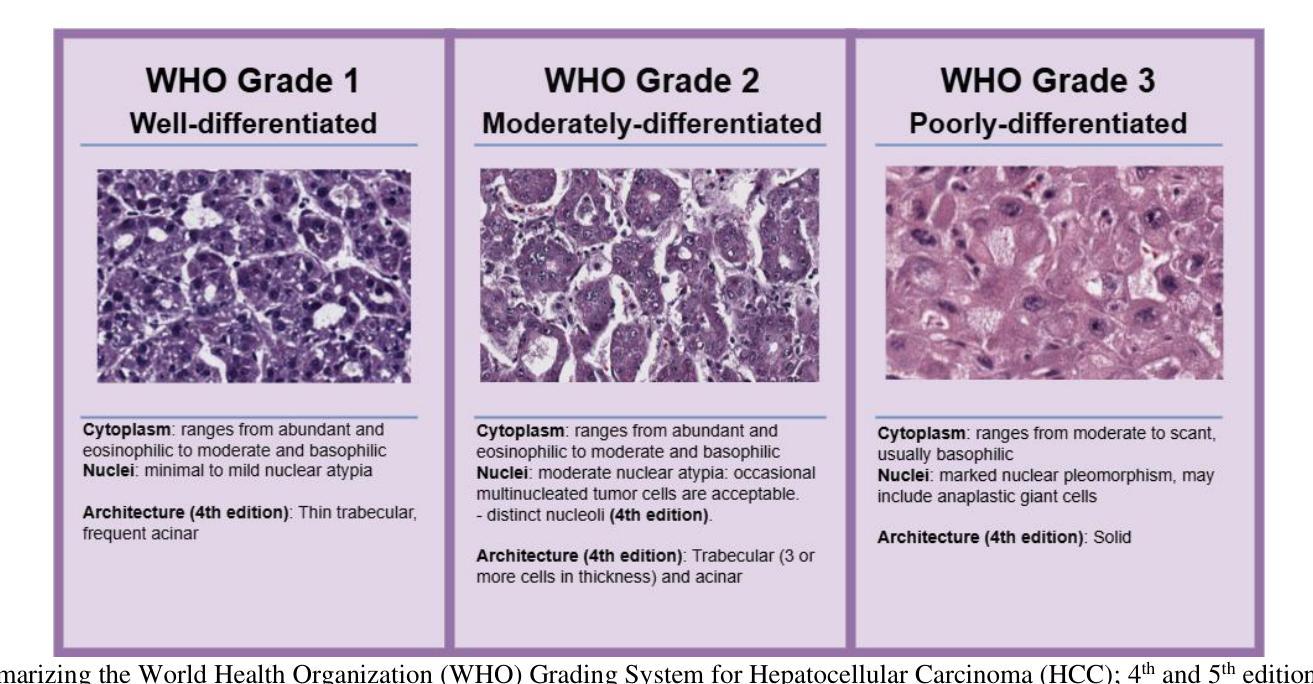
Pathobiological Dictionary Defining Pathomics and Texture Features: Addressing Understandable AI Issues in Personalized Liver Cancer; Dictionary Version LCP1.0
Authors:Mohammad R. Salmanpour, Seyed Mohammad Piri, Somayeh Sadat Mehrnia, Ahmad Shariftabrizi, Masume Allahmoradi, Venkata SK. Manem, Arman Rahmim, Ilker Hacihaliloglu
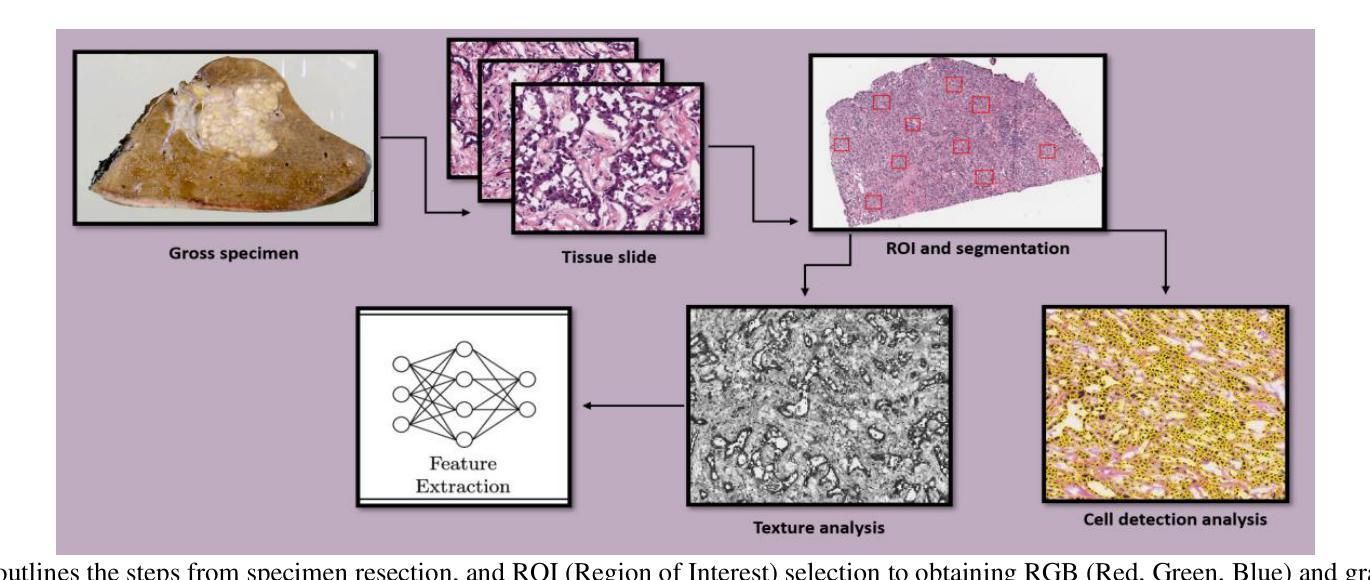
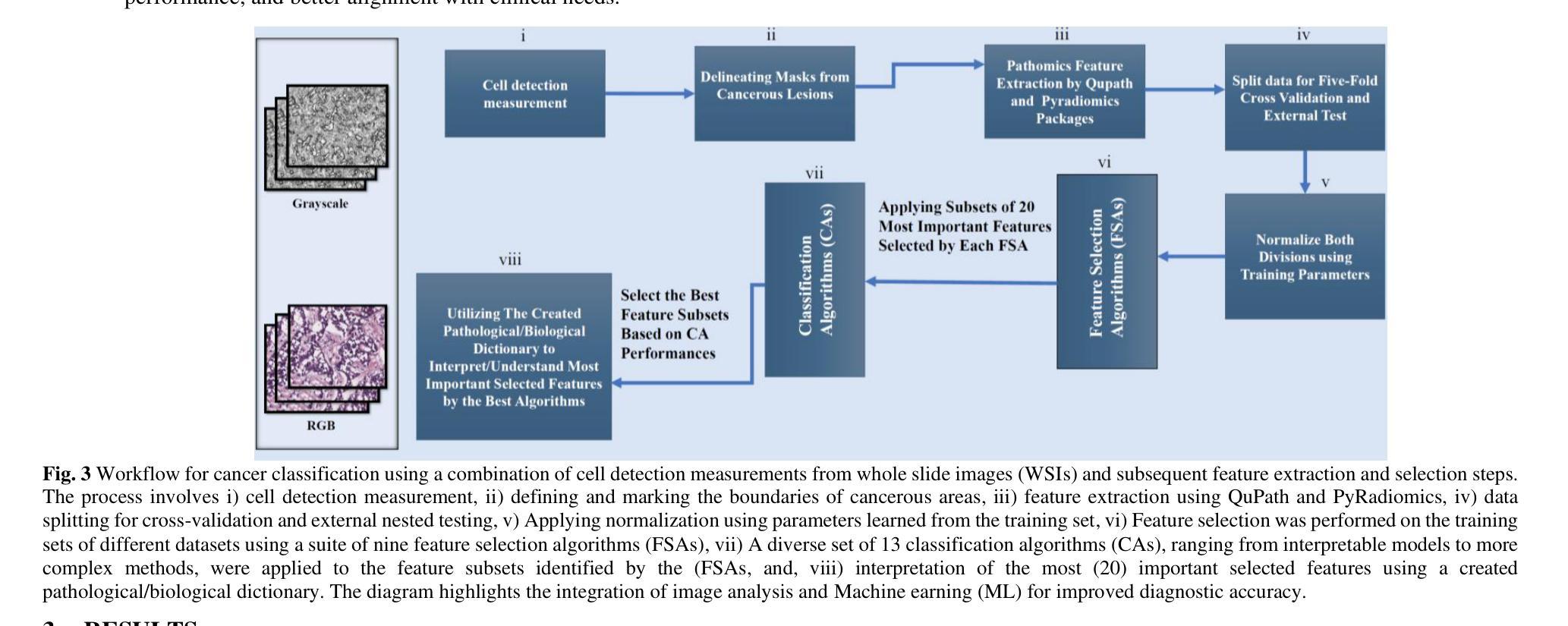
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds strong potential for medical diagnostics, yet its clinical adoption is limited by a lack of interpretability and generalizability. This study introduces the Pathobiological Dictionary for Liver Cancer (LCP1.0), a practical framework designed to translate complex Pathomics and Radiomics Features (PF and RF) into clinically meaningful insights aligned with existing diagnostic workflows. QuPath and PyRadiomics, standardized according to IBSI guidelines, were used to extract 333 imaging features from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue samples, including 240 PF-based-cell detection/intensity, 74 RF-based texture, and 19 RF-based first-order features. Expert-defined ROIs from the public dataset excluded artifact-prone areas, and features were aggregated at the case level. Their relevance to the WHO grading system was assessed using multiple classifiers linked with feature selectors. The resulting dictionary was validated by 8 experts in oncology and pathology. In collaboration with 10 domain experts, we developed a Pathobiological dictionary of imaging features such as PFs and RF. In our study, the Variable Threshold feature selection algorithm combined with the SVM model achieved the highest accuracy (0.80, P-value less than 0.05), selecting 20 key features, primarily clinical and pathomics traits such as Centroid, Cell Nucleus, and Cytoplasmic characteristics. These features, particularly nuclear and cytoplasmic, were strongly associated with tumor grading and prognosis, reflecting atypia indicators like pleomorphism, hyperchromasia, and cellular orientation.The LCP1.0 provides a clinically validated bridge between AI outputs and expert interpretation, enhancing model transparency and usability. Aligning AI-derived features with clinical semantics supports the development of interpretable, trustworthy diagnostic tools for liver cancer pathology.
人工智能(AI)在医学诊断方面具有巨大潜力,然而其临床应用却受限于解释性和通用性的缺乏。本研究引入了肝癌病理生物词典(LCP1.0),这是一个实用框架,旨在将复杂的病理学和放射学特征(PF和RF)转化为与现有诊断工作流相吻合的临床意义洞察。根据IBSI指南标准化了的QuPath和PyRadiomics被用于从肝细胞癌(HCC)组织样本中提取333个成像特征,包括240个基于PF的细胞检测/强度、74个基于RF的纹理和19个基于RF的一阶特征。来自公共数据集的专家定义ROI排除了易产生伪影的区域,特征被聚合到病例层面。它们与WHO分级系统的相关性通过使用与特征选择器相关联的多重分类器进行评估。该词典得到了8名肿瘤学和病理学专家的验证。我们与10名领域专家合作,开发了病理生物学词典,包括成像特征,例如PFs和RFs。在我们的研究中,结合支持向量机(SVM)模型的可变阈值特征选择算法达到了最高的准确性(0.80,P值小于0.05),选择了20个关键特征,主要是临床和病理特征,例如质心、细胞核和细胞质特性。这些特征,尤其是核和细胞质特征与肿瘤分级和预后密切相关,反映了诸如异型性、高色性和细胞定位等异常指标。LCP1.0提供了一个经过临床验证的桥梁,连接AI输出和专家解释,提高了模型的透明度和可用性。将AI衍生的特征与临床语义相结合,支持开发可解释、可信赖的肝癌病理诊断工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 4 figures and 1 table
Summary
该研究通过构建Pathobiological Dictionary for Liver Cancer(LCP1.0)框架,将复杂的Pathmics和Radiomics特征转化为与现有诊断工作流相匹配的、具有临床意义的见解,从而促进人工智能在肝脏癌症诊断中的应用。通过标准化提取影像特征并经过专家验证,开发出可解释性强、可信度高的肝癌病理诊断工具。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在医疗诊断中具有巨大潜力,但缺乏可解释性和通用性限制了其临床应用。
- Pathobiological Dictionary for Liver Cancer(LCP 1.0)框架能将复杂的Pathmics和Radiomics特征转化为具有临床意义的见解,与现有诊断流程相结合。
- 使用QuPath和PyRadiomics等工具,结合IBSI指南,从肝细胞癌组织样本中提取了333个成像特征。
- 通过专家定义的ROI排除易产生伪影的区域,并对特征进行病例水平汇总。
- 通过多分类器与特征选择器评估特征与WHO分级系统的相关性。
- Variable Threshold特征选择算法结合SVM模型达到最高准确率(0.80),选出的关键特征与肿瘤分级和预后密切相关,主要包括临床和病理特征。
点此查看论文截图

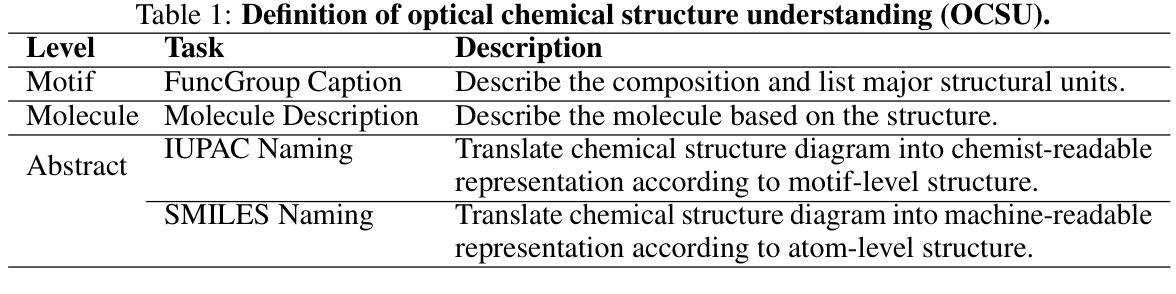
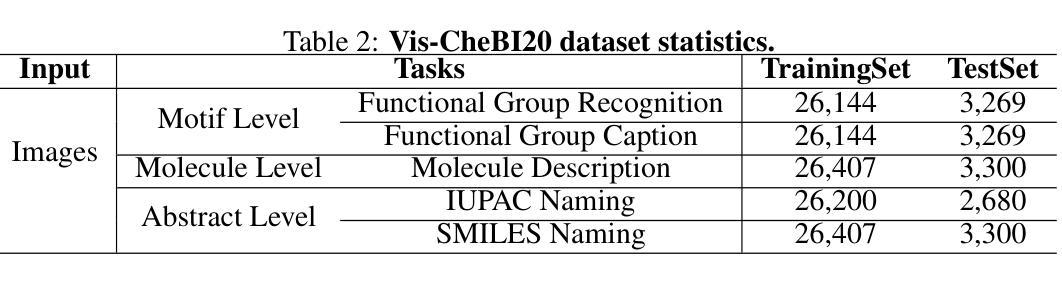
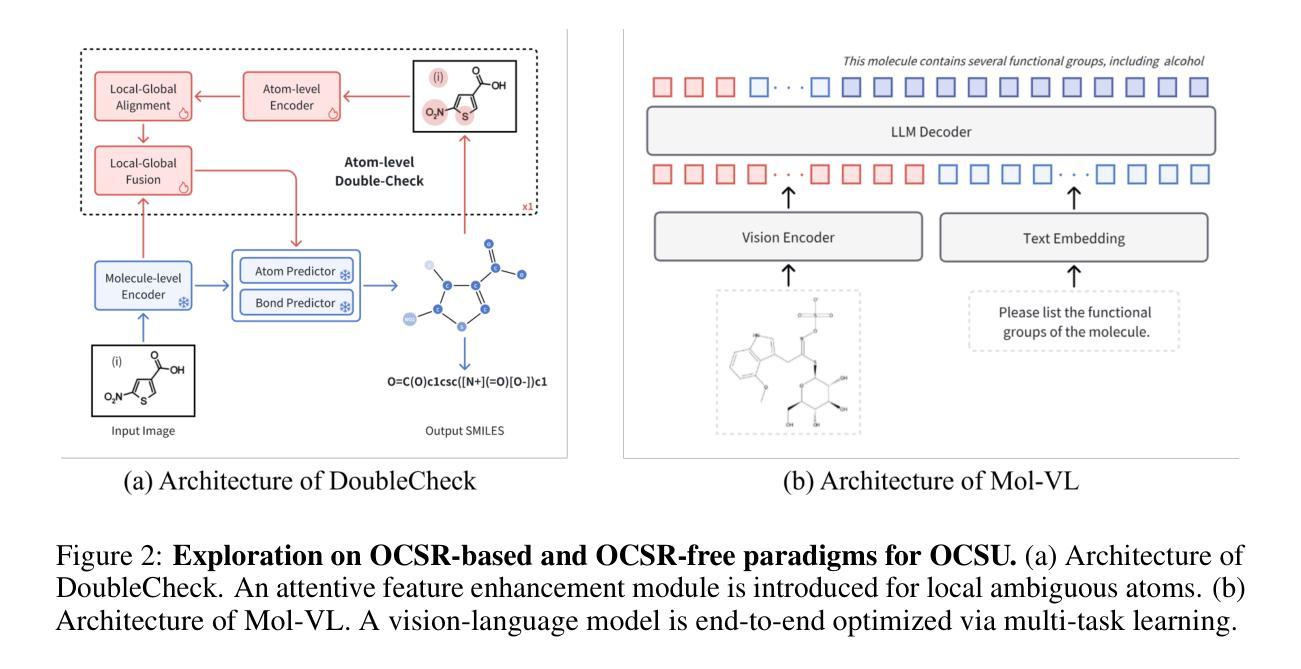
OCSU: Optical Chemical Structure Understanding for Molecule-centric Scientific Discovery
Authors:Siqi Fan, Yuguang Xie, Bowen Cai, Ailin Xie, Gaochao Liu, Mu Qiao, Jie Xing, Zaiqing Nie
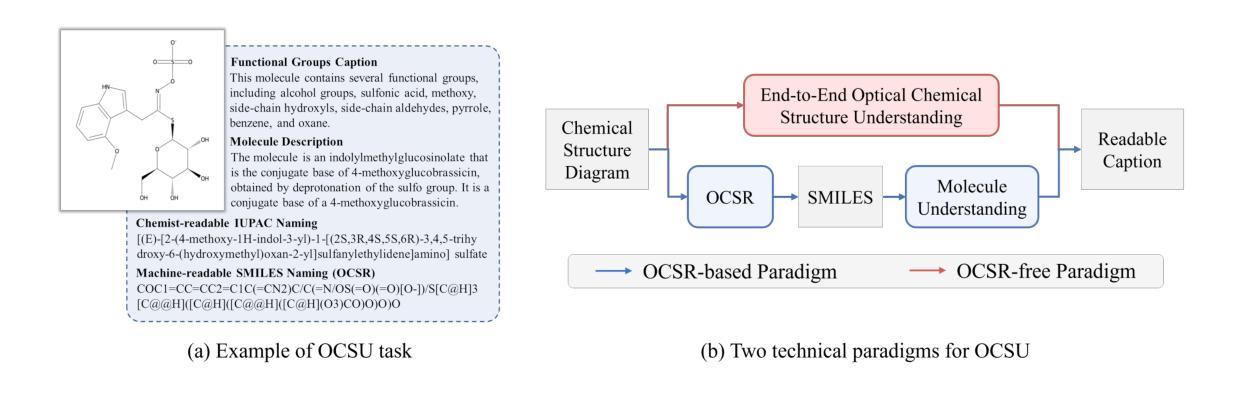
Understanding the chemical structure from a graphical representation of a molecule is a challenging image caption task that would greatly benefit molecule-centric scientific discovery. Variations in molecular images and caption subtasks pose a significant challenge in both image representation learning and task modeling. Yet, existing methods only focus on a specific caption task that translates a molecular image into its graph structure, i.e., OCSR. In this paper, we propose the Optical Chemical Structure Understanding (OCSU) task, which extends low-level recognition to multilevel understanding and aims to translate chemical structure diagrams into readable strings for both machine and chemist. To facilitate the development of OCSU technology, we explore both OCSR-based and OCSR-free paradigms. We propose DoubleCheck to enhance OCSR performance via attentive feature enhancement for local ambiguous atoms. It can be cascaded with existing SMILES-based molecule understanding methods to achieve OCSU. Meanwhile, Mol-VL is a vision-language model end-to-end optimized for OCSU. We also construct Vis-CheBI20, the first large-scale OCSU dataset. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate the proposed approaches excel at providing chemist-readable caption for chemical structure diagrams, which provide solid baselines for further research. Our code, model, and data are open-sourced at https://github.com/PharMolix/OCSU.
从分子图形的表示理解其化学结构是一项具有挑战性的图像描述任务,对以分子为中心的科研发现大有裨益。分子图像的多样性和描述的子任务对图像表示学习和任务建模都构成了重大挑战。然而,现有方法只关注特定的描述任务,即将分子图像转换为其图形结构,即OCSR(光学化学结构识别)。在本文中,我们提出了光学化学结构理解(OCSU)任务,它扩展了低级的识别功能到多级理解,旨在将化学结构图转化为机器和化学家都可读的字符串。为了促进OCSU技术的发展,我们探讨了基于OCSR的和不依赖OCSR的两种范式。我们提出DoubleCheck方法,通过注意力特征增强局部模糊原子,以提高OCSR性能。它可以与现有的基于SMILES的分子理解方法相结合,实现OCSU。同时,Mol-VL是一种针对OCSU进行端到端优化的视觉语言模型。我们还构建了Vis-CheBI20,这是首个大规模OCSU数据集。通过全面的实验,我们证明了所提出的方法在提供化学结构图的化学家可读描述方面表现出色,为进一步的研究提供了坚实的基准。我们的代码、模型和数据在https://github.com/PharMolix/OCSU上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
文中提出了一个全新的任务,名为光学化学结构理解(OCSU),旨在将化学结构图转化为机器和人类可读的字符串形式,促进分子图像的理解。文章介绍了两种实现方式:基于OCSR的方法和OCSR自由范式。通过双检查增强局部模糊原子的特征增强性能,并通过全面的实验验证方法的有效性。此外,构建了首个大规模OCSU数据集Vis-CheBI20,为未来的研究提供了坚实的基准。代码、模型和开源数据可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways:
- 文中提出了一个新的任务,即光学化学结构理解(OCSU),该任务旨在将化学结构图转化为可读的字符串形式,促进分子图像的理解。
- OCSU扩展了分子图像识别的任务范畴,涉及到多级理解问题,为分子科学发现提供了重要支持。
- 文章介绍了两种实现OCSU任务的方法:基于OCSR的方法和OCSR自由范式,展示了其技术细节和特点。
- 文章提出了一种双检查(DoubleCheck)技术来增强局部模糊原子的特征增强性能,从而提高化学结构识别的准确性。
- 构建了一个大规模数据集Vis-CheBI20用于OCSU任务的研究和实验验证。这对于研究具有重要意义,因为高质量的标注数据可以显著提高机器学习模型的性能。
- 通过全面的实验验证了提出的方法在化学结构图解析方面的优异性能,提供了准确和可靠的结果,为后续研究提供了坚实的基础。
点此查看论文截图
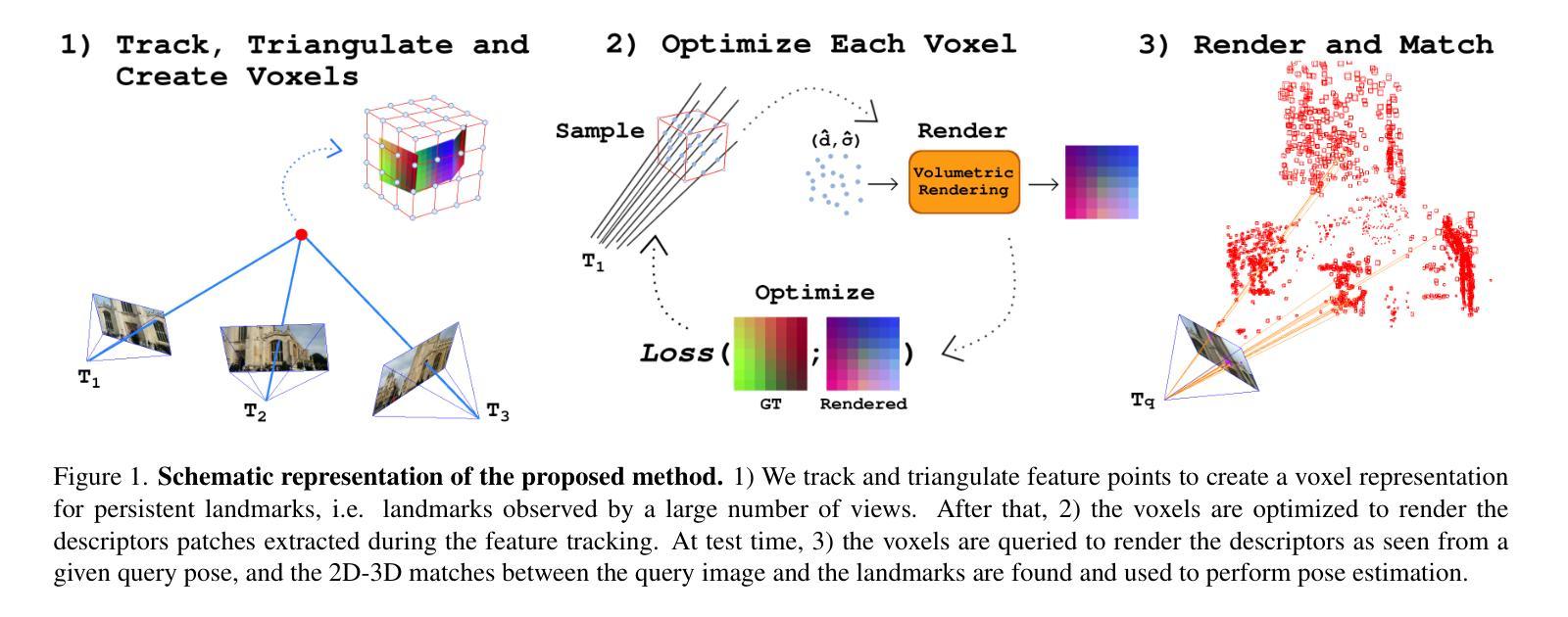
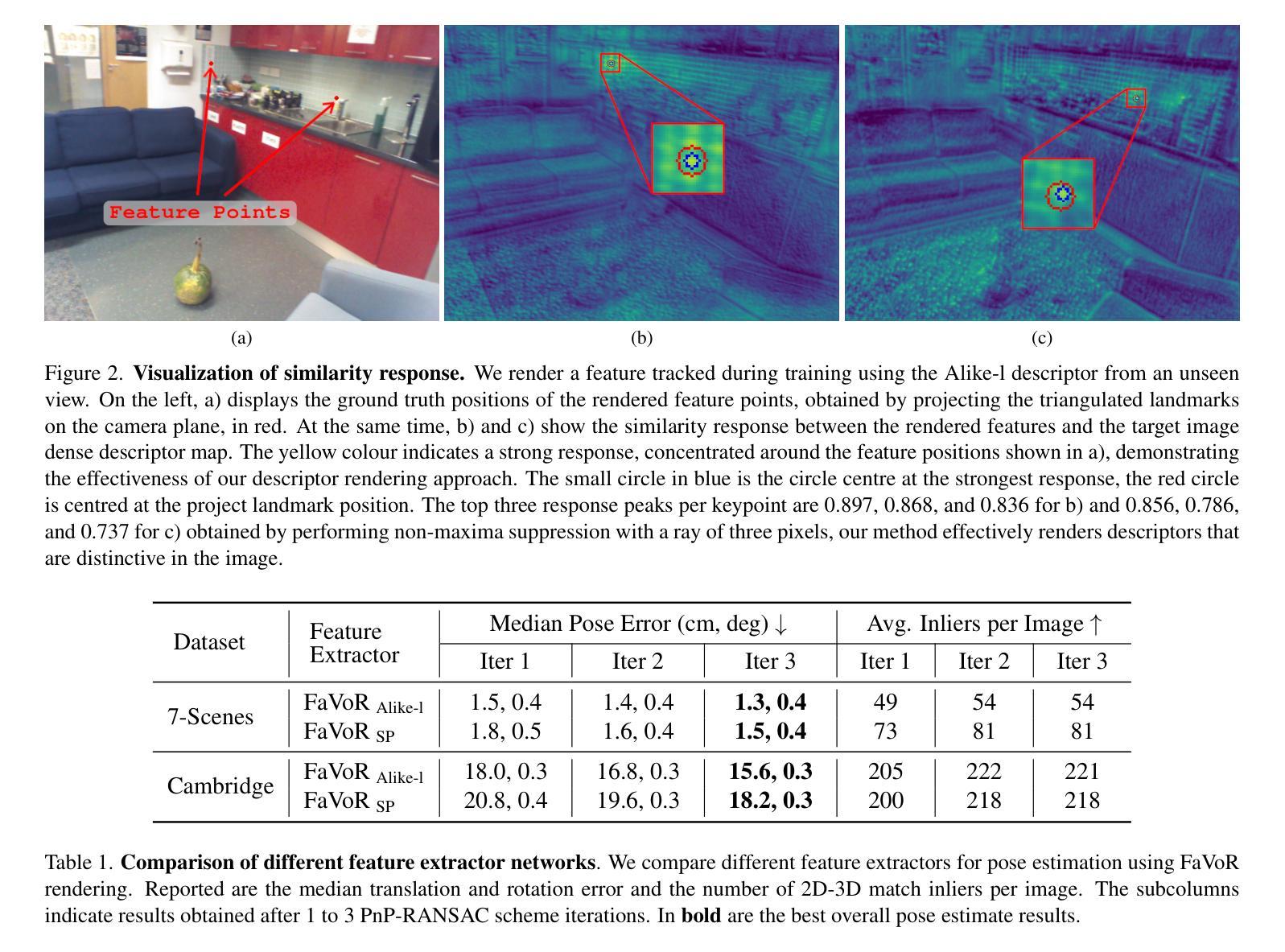
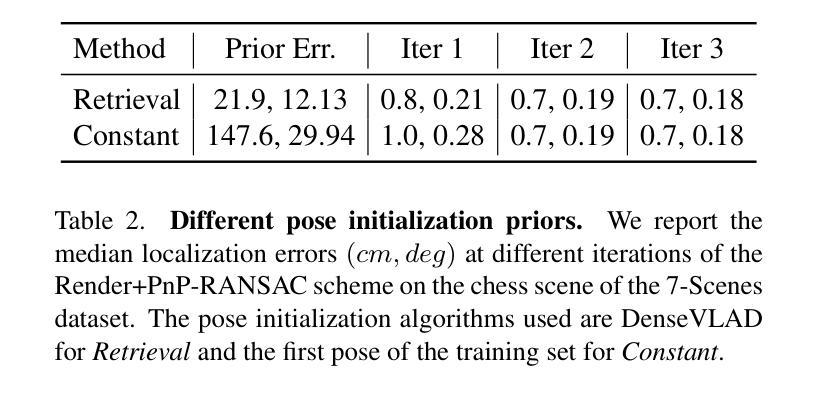
FaVoR: Features via Voxel Rendering for Camera Relocalization
Authors:Vincenzo Polizzi, Marco Cannici, Davide Scaramuzza, Jonathan Kelly
Camera relocalization methods range from dense image alignment to direct camera pose regression from a query image. Among these, sparse feature matching stands out as an efficient, versatile, and generally lightweight approach with numerous applications. However, feature-based methods often struggle with significant viewpoint and appearance changes, leading to matching failures and inaccurate pose estimates. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel approach that leverages a globally sparse yet locally dense 3D representation of 2D features. By tracking and triangulating landmarks over a sequence of frames, we construct a sparse voxel map optimized to render image patch descriptors observed during tracking. Given an initial pose estimate, we first synthesize descriptors from the voxels using volumetric rendering and then perform feature matching to estimate the camera pose. This methodology enables the generation of descriptors for unseen views, enhancing robustness to view changes. We extensively evaluate our method on the 7-Scenes and Cambridge Landmarks datasets. Our results show that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art feature representation techniques in indoor environments, achieving up to a 39% improvement in median translation error. Additionally, our approach yields comparable results to other methods for outdoor scenarios while maintaining lower memory and computational costs.
相机重定位方法包括从密集图像对齐到直接从查询图像进行相机姿态回归。其中,稀疏特征匹配以其高效、通用和通常较轻量级的方法以及众多应用而脱颖而出。然而,基于特征的方法通常在视角和外观变化显著时会出现困难,导致匹配失败和姿态估计不准确。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种新的方法,它利用了一种全局稀疏但局部密集的二维特征的三维表示。通过跟踪和三角测量一系列帧中的地标,我们构建了一个优化的稀疏体素地图,以呈现跟踪过程中观察到的图像块描述符。给定初始姿态估计,我们首先使用体积渲染技术从体素合成描述符,然后进行特征匹配以估计相机姿态。这种方法使得能够为未见过的视图生成描述符,提高了对视图变化的鲁棒性。我们在7场景和剑桥地标数据集上对我们的方法进行了广泛评估。结果表明,我们的方法在室内环境中显著优于现有的最先进的特征表示技术,在平均平移误差上最多提高了39%。此外,我们的方法在室外场景的结果与其他方法相当,同时降低了内存和计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tucson, Arizona, US, Feb 28-Mar 4, 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于稀疏特征匹配与局部密集三维表示的相机重定位新方法。该方法通过追踪和三角测量地标序列帧构建稀疏体素地图,优化渲染图像补丁描述符。利用初始姿态估计,通过体积渲染合成体素描述符,然后进行特征匹配估计相机姿态。此方法能生成未见视图的描述符,增强对视角变化的稳健性,并在室内环境下显著优于现有特征表示技术,其中位平移误差改进高达39%。
Key Takeaways
- 相机重定位方法包括从密集图像对齐到直接相机姿态回归查询图像等多种方法。
- 稀疏特征匹配是一种高效、通用、轻量级的方法,但面临视角和外观变化导致的匹配失败和姿态估计不准确的问题。
- 本文提出了一种基于稀疏特征匹配和局部密集三维表示的新方法,构建稀疏体素地图以优化渲染图像补丁描述符。
- 通过体积渲染合成体素描述符,进行特征匹配估计相机姿态。
- 该方法能生成未见视图的描述符,增强对视角变化的稳健性。
- 在室内环境下,该方法显著优于现有特征表示技术,并在中位平移误差上实现高达39%的改进。
点此查看论文截图

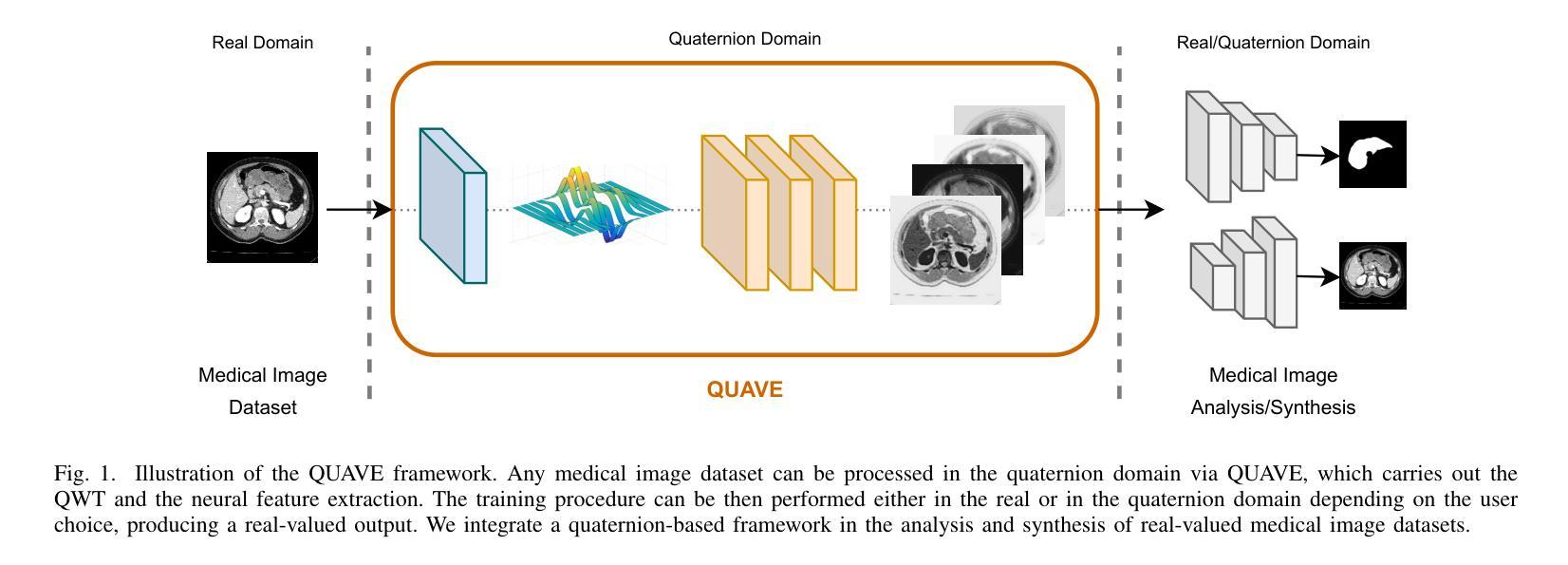
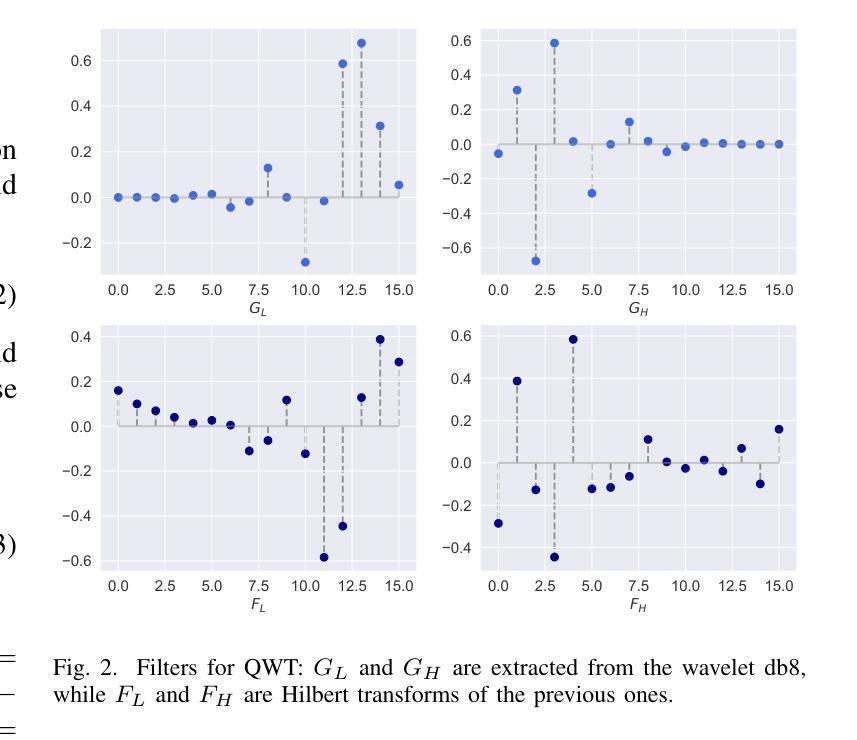
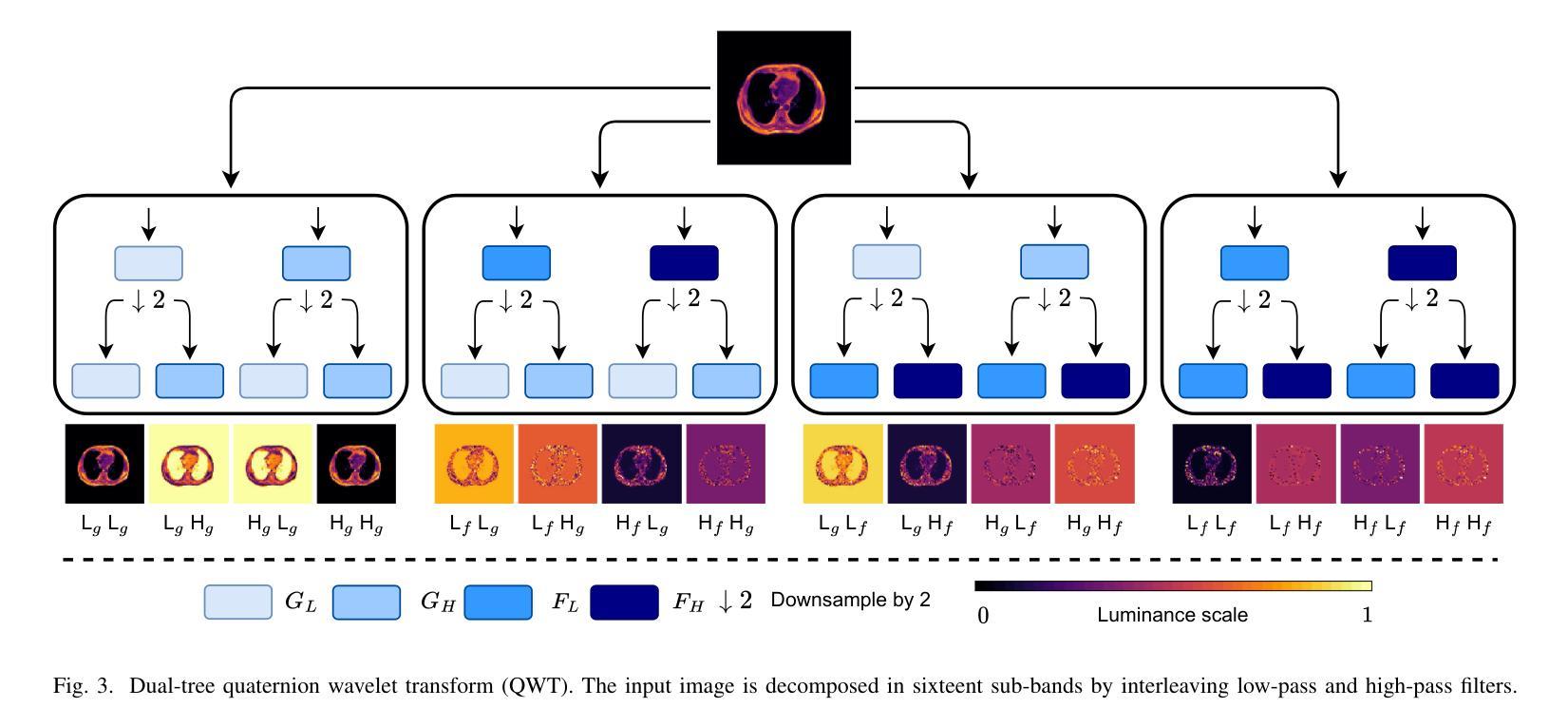
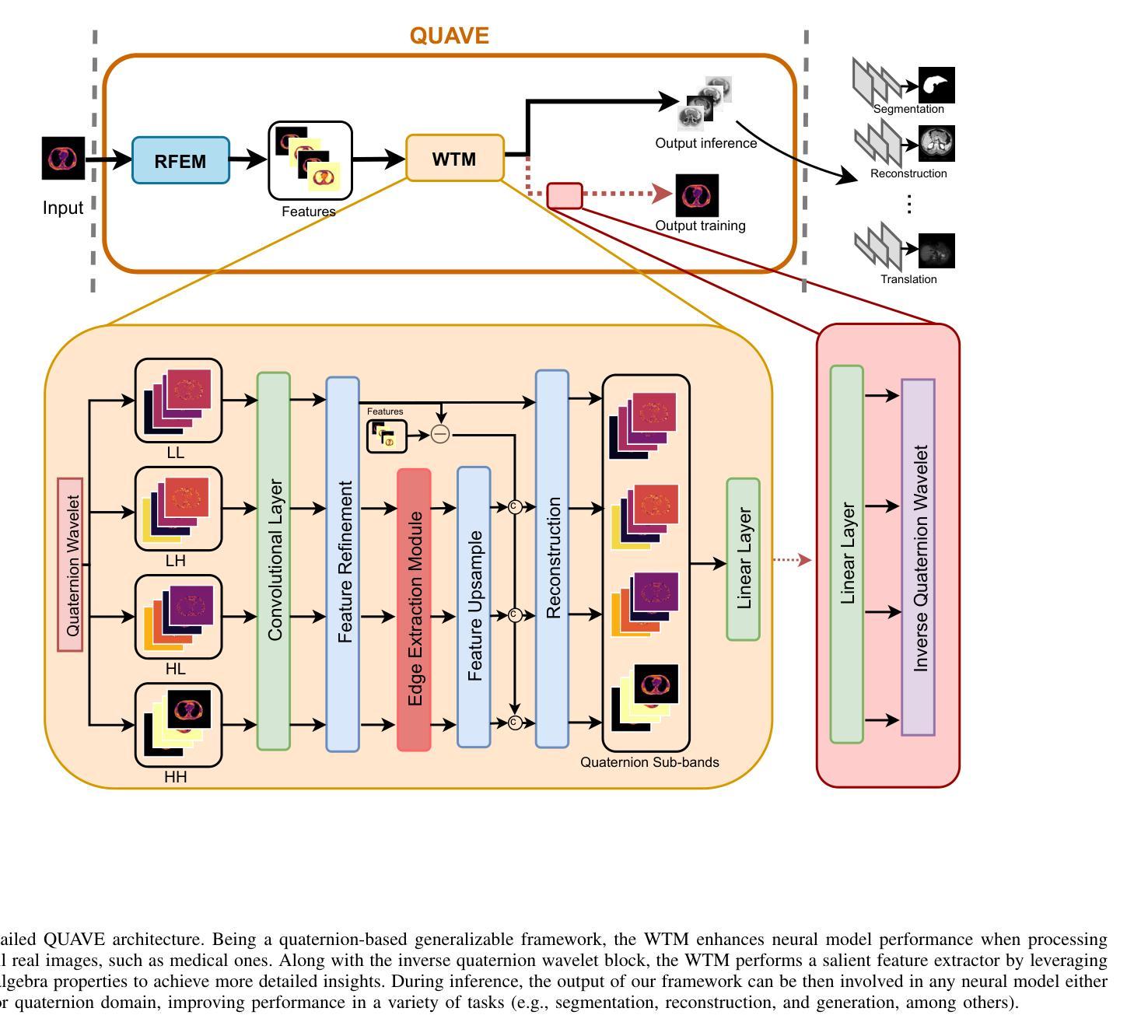
Generalizing Medical Image Representations via Quaternion Wavelet Networks
Authors:Luigi Sigillo, Eleonora Grassucci, Aurelio Uncini, Danilo Comminiello
Neural network generalizability is becoming a broad research field due to the increasing availability of datasets from different sources and for various tasks. This issue is even wider when processing medical data, where a lack of methodological standards causes large variations being provided by different imaging centers or acquired with various devices and cofactors. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel, generalizable, data- and task-agnostic framework able to extract salient features from medical images. The proposed quaternion wavelet network (QUAVE) can be easily integrated with any pre-existing medical image analysis or synthesis task, and it can be involved with real, quaternion, or hypercomplex-valued models, generalizing their adoption to single-channel data. QUAVE first extracts different sub-bands through the quaternion wavelet transform, resulting in both low-frequency/approximation bands and high-frequency/fine-grained features. Then, it weighs the most representative set of sub-bands to be involved as input to any other neural model for image processing, replacing standard data samples. We conduct an extensive experimental evaluation comprising different datasets, diverse image analysis, and synthesis tasks including reconstruction, segmentation, and modality translation. We also evaluate QUAVE in combination with both real and quaternion-valued models. Results demonstrate the effectiveness and the generalizability of the proposed framework that improves network performance while being flexible to be adopted in manifold scenarios and robust to domain shifts. The full code is available at: https://github.com/ispamm/QWT.
神经网络通用性由于不同来源和任务的数据集可用性增加而成为一个广泛的研究领域。在处理医疗数据时,这个问题更加突出,因为没有统一的方法学标准,导致不同成像中心或通过各种设备和辅助因素获得的数据存在很大差异。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了一种新型、通用、不受数据和任务限制的分析框架,能够从医学图像中提取重要特征。所提出的四元小波网络(QUAVE)可以轻松地与任何现有的医学图像分析或合成任务集成,并且可以与实数、四元数或超复数模型相结合,将其推广到单通道数据。QUAVE首先通过四元小波变换提取不同的子带,得到低频/近似带和高频/精细特征。然后,它加权最具代表性的子带集作为输入到其他神经网络模型进行图像处理,代替标准数据样本。我们进行了广泛的实验评估,包括不同的数据集、多样化的图像分析和合成任务,如重建、分割和模态转换。我们还评估了QUAVE与实数和四元数值模型的组合。结果表明,所提出框架的有效性和通用性,在提高网络性能的同时,能够灵活地应用于多种场景并对领域变化具有鲁棒性。完整代码可在:<https://github.com/ispamm/QWT 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to Neurocomputing Journal
Summary
针对神经网络泛化能力在医学数据处理上的不足,提出一种新型通用框架——四元小波网络(QUAVE)。该框架能够提取医学图像的重要特征,适用于不同来源和任务的多种数据集。QUAVE通过四元小波变换提取不同子带,并结合低频和高频特征,然后加权最具代表性的子带作为其他神经网络模型的输入进行图像处理。实验证明,QUAVE框架有效且通用,能提高网络性能,适用于多种场景,对领域变化具有鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络泛化能力已成为研究热点,尤其在处理来自不同来源和任务的医疗数据集时。
- QUAVE框架是一个针对医学图像数据的新型通用框架,旨在解决不同成像中心和设备获取的医疗数据差异问题。
- QUAVE能够轻松集成到任何现有的医学图像分析或合成任务中,并能与实值、四元数或超复数模型相结合,推广到单通道数据。
- QUAVE通过四元小波变换提取不同子带,包括低频和高频特征。
- QUAVE通过加权最具代表性的子带,作为其他神经网络模型的输入,进行图像处理。
- 实验证明QUAVE框架有效且通用,能够提高网络性能,并适应多种图像分析和合成任务,包括重建、分割和模态转换。
- QUAVE框架对领域变化具有鲁棒性,其完整代码已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图