⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Meta-PerSER: Few-Shot Listener Personalized Speech Emotion Recognition via Meta-learning
Authors:Liang-Yeh Shen, Shi-Xin Fang, Yi-Cheng Lin, Huang-Cheng Chou, Hung-yi Lee
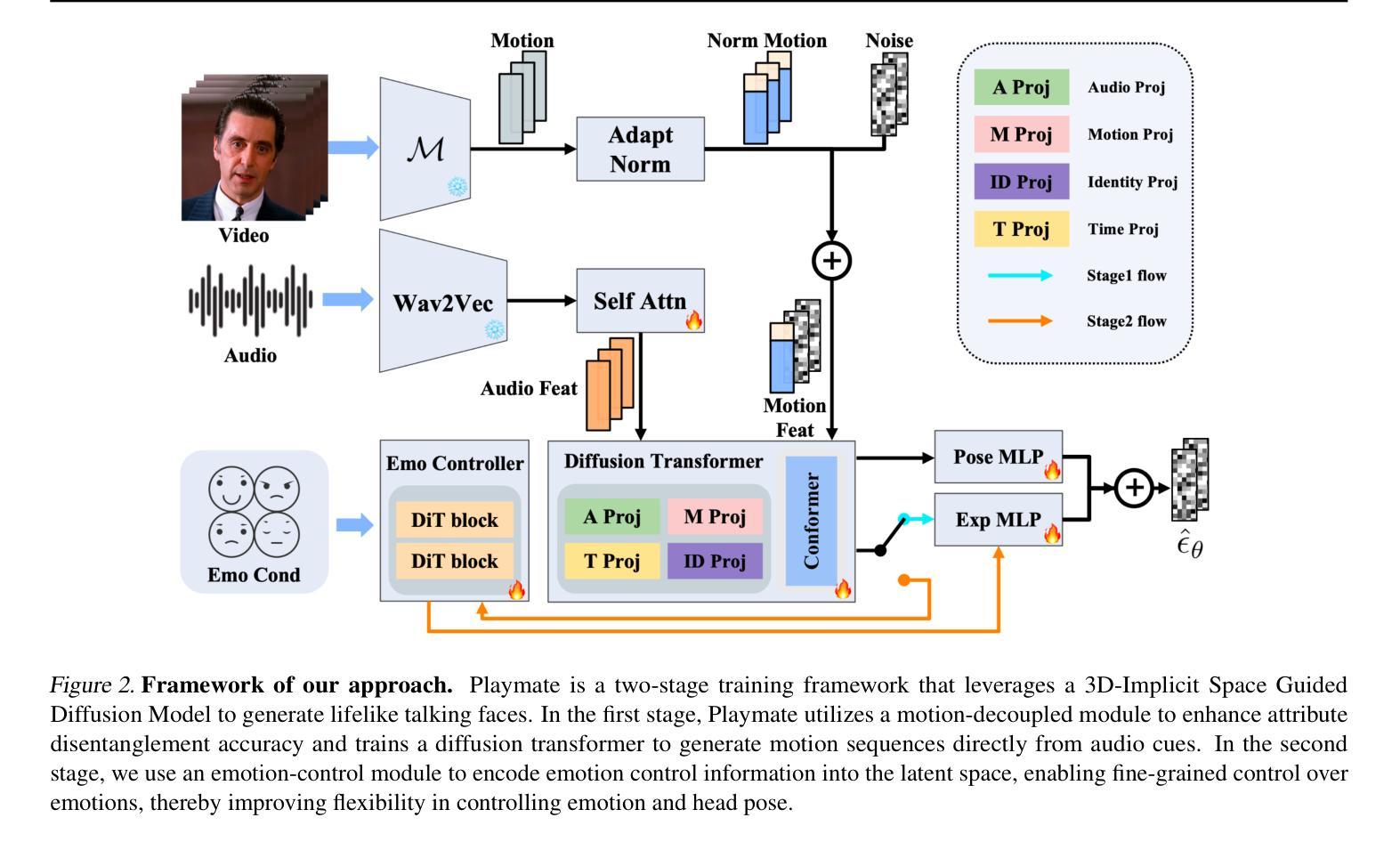
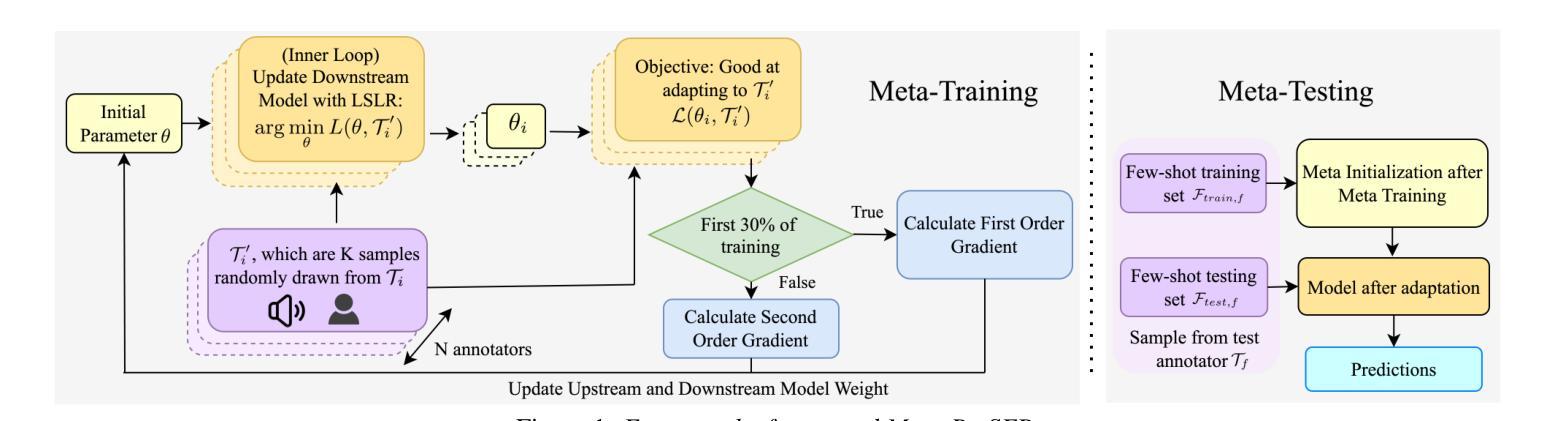
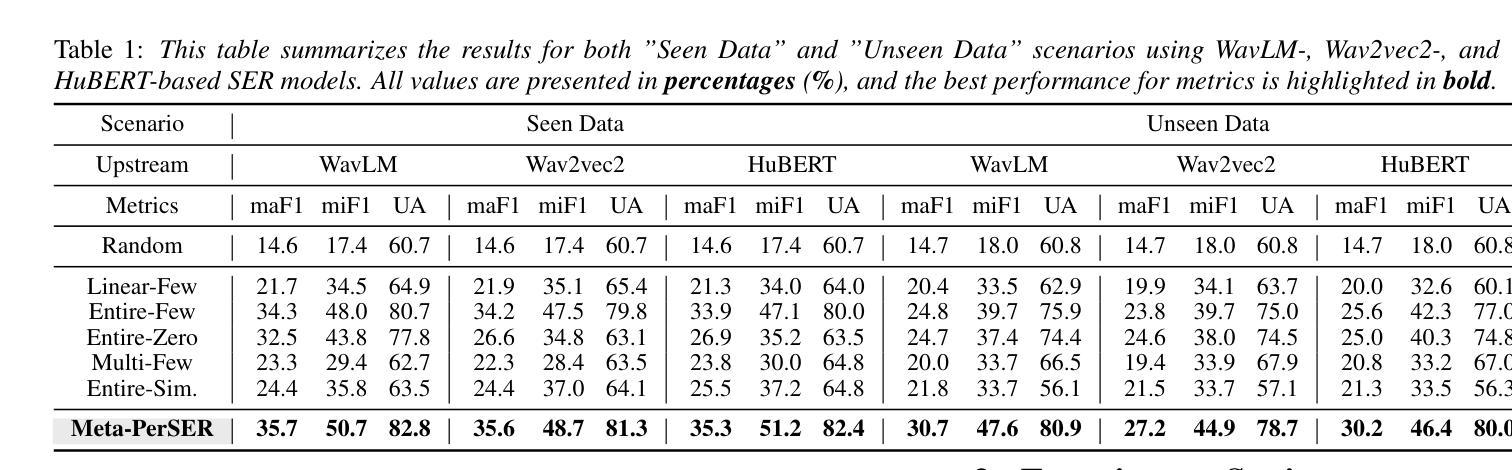
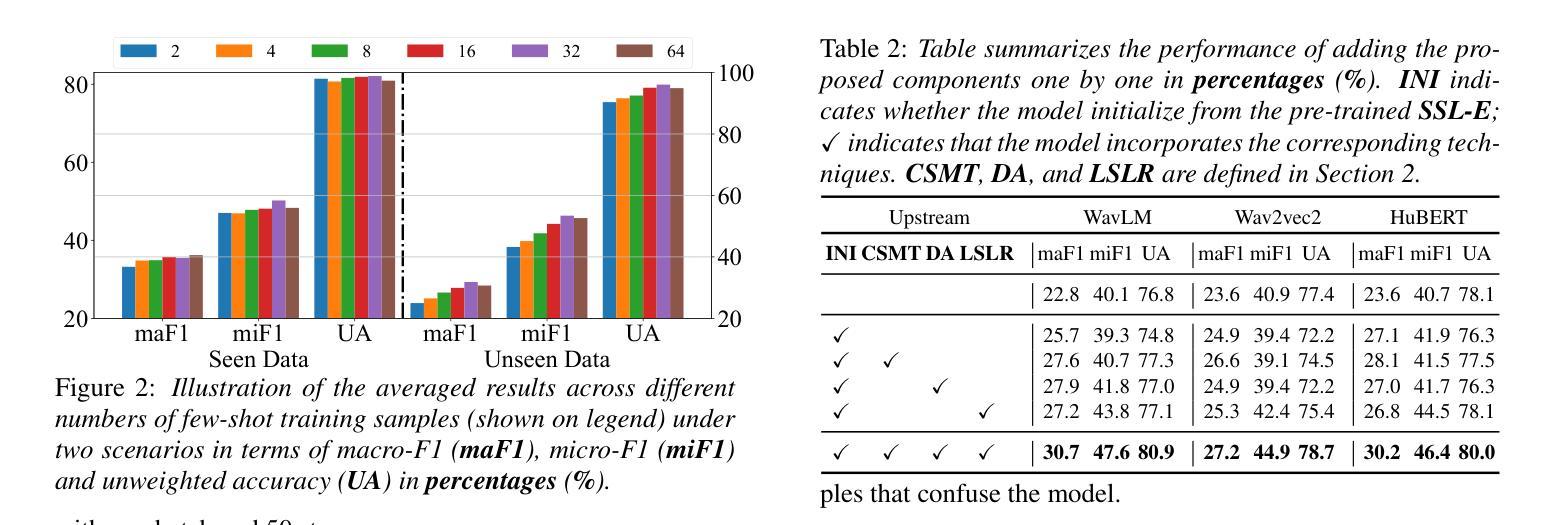
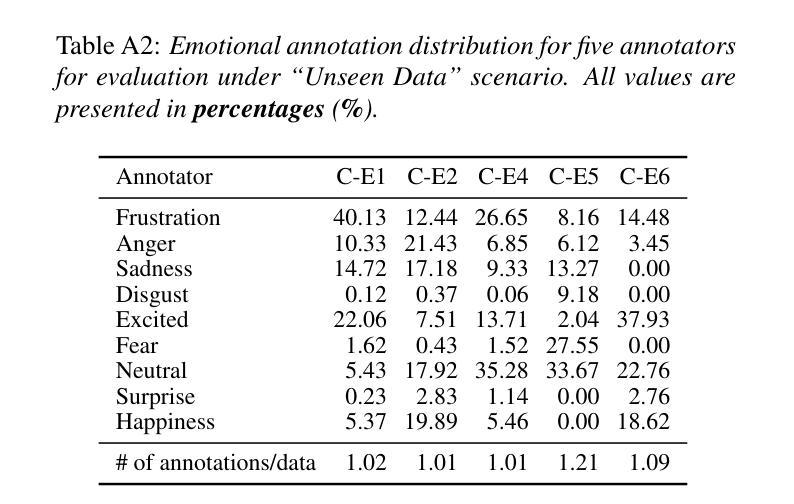
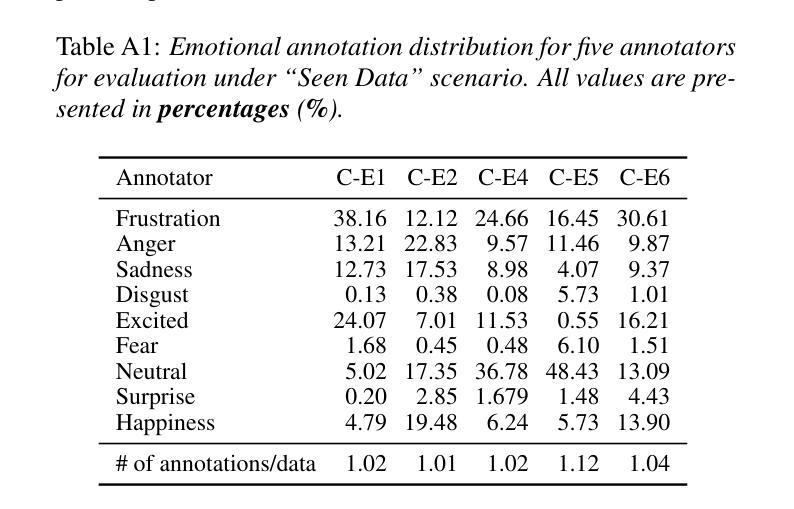
This paper introduces Meta-PerSER, a novel meta-learning framework that personalizes Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) by adapting to each listener’s unique way of interpreting emotion. Conventional SER systems rely on aggregated annotations, which often overlook individual subtleties and lead to inconsistent predictions. In contrast, Meta-PerSER leverages a Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) approach enhanced with Combined-Set Meta-Training, Derivative Annealing, and per-layer per-step learning rates, enabling rapid adaptation with only a few labeled examples. By integrating robust representations from pre-trained self-supervised models, our framework first captures general emotional cues and then fine-tunes itself to personal annotation styles. Experiments on the IEMOCAP corpus demonstrate that Meta-PerSER significantly outperforms baseline methods in both seen and unseen data scenarios, highlighting its promise for personalized emotion recognition.
本文介绍了Meta-PerSER,这是一种新型的元学习框架,通过适应每个听众独特的情感解读方式,对语音情感识别(SER)进行个性化处理。传统的SER系统依赖于聚合注释,这往往会忽略个体的细微差别,导致预测结果不一致。相比之下,Meta-PerSER利用模型无关元学习(MAML)方法,结合集合元训练、导数退火和每层每步学习率,仅通过少量有标签的样本即可实现快速适应。通过整合预训练自监督模型的稳健表示,我们的框架首先捕捉一般的情感线索,然后对自己进行微调,以适应个人注释风格。在IEMOCAP语料库上的实验表明,Meta-PerSER在已见和未见的数据场景中都显著优于基准方法,凸显了其在个性化情感识别方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by INTERSPEECH 2025. 7 pages, including 2 pages of appendix
Summary
本文介绍了Meta-PerSER,这是一种新型元学习框架,通过适应每个听众独特的情感解读方式,实现了个性化的语音情感识别(SER)。与传统的依赖于聚合注释的SER系统不同,Meta-PerSER采用模型无关的元学习方法,并结合组合集元训练、导数退火和逐层逐步的学习率,仅通过少量标注样本即可实现快速适应。通过整合预训练自监督模型的稳健表示,该框架首先捕捉一般情感线索,然后微调自身以适应个人注释风格。在IEMOCAP语料库上的实验表明,Meta-PerSER在可见和未见数据场景中均显著优于基准方法,展现出其在个性化情感识别方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Meta-PerSER是一种新的元学习框架,用于个性化语音情感识别(SER)。
- 不同于传统依赖于聚合注释的SER系统,Meta-PerSER通过模型无关的元学习方法,考虑每个听众独特的情感解读方式。
- Meta-PerSER采用多种技术,如组合集元训练、导数退火和逐层逐步的学习率,以实现快速适应,仅需要少量标注样本。
- 该框架整合了预训练自监督模型的稳健表示,先捕捉一般情感线索,再微调以适应个人注释风格。
- Meta-PerSER在IEMOCAP语料库上的实验表现优异,说明其在实际应用中的有效性。
- 该框架在可见和未见数据场景中均表现出色,显示出其强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


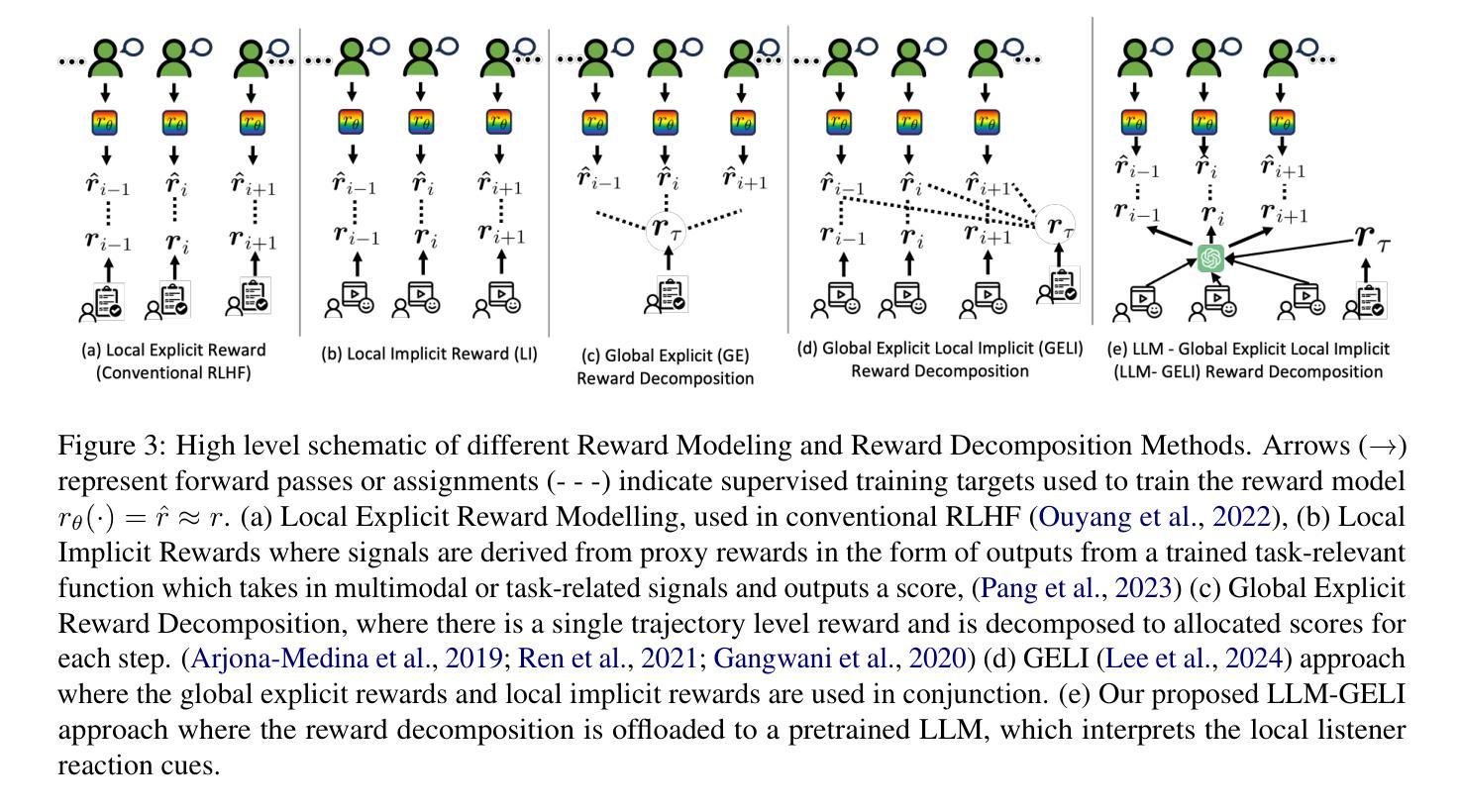
Aligning Dialogue Agents with Global Feedback via Large Language Model Reward Decomposition
Authors:Dong Won Lee, Hae Won Park, Cynthia Breazeal, Louis-Philippe Morency
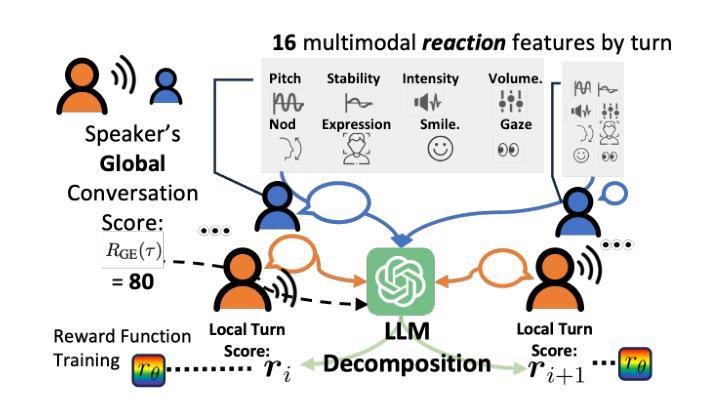
We propose a large language model based reward decomposition framework for aligning dialogue agents using only a single session-level feedback signal. We leverage the reasoning capabilities of a frozen, pretrained large language model (LLM) to infer fine-grained local implicit rewards by decomposing global, session-level feedback. Our first text-only variant prompts the LLM to perform reward decomposition using only the dialogue transcript. The second multimodal variant incorporates additional behavioral cues, such as pitch, gaze, and facial affect, expressed as natural language descriptions. These inferred turn-level rewards are distilled into a lightweight reward model, which we utilize for RL-based fine-tuning for dialogue generation. We evaluate both text-only and multimodal variants against state-of-the-art reward decomposition methods and demonstrate notable improvements in human evaluations of conversation quality, suggesting that LLMs are strong reward decomposers that obviate the need for manual reward shaping and granular human feedback.
我们提出了一种基于大型语言模型的奖励分解框架,该框架仅使用单个会话级别的反馈信号来对对话代理进行对齐。我们利用冻结的预训练大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,通过分解全局会话级反馈来推断精细的局部隐含奖励。我们的第一种纯文本变体提示LLM仅使用对话记录进行奖励分解。第二种多模式变体结合了额外的行为线索,例如音调、凝视和面部表情,表现为自然语言描述。这些推断的回合级奖励被提炼成轻量级的奖励模型,我们用于基于RL的微调对话生成。我们将文本和多模态变体与最新的奖励分解方法进行了评估对比,并在人类对话质量评估中取得了显著的改进,这表明LLM是强大的奖励分解器,可以省去手动奖励塑形和精细的人类反馈的步骤。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables
摘要
本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型的奖励分解框架,用于仅使用单个会话级别的反馈信号来对对话代理进行对齐。通过利用冻结的预训练大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,通过分解全局会话级别的反馈来推断精细的局部隐含奖励。我们的文本仅提示LLM进行奖励分解,使用对话记录。第二种多模式变体则结合了额外的行为线索,如音调、目光和面部表情,表现为自然语言描述。这些推断出的回合级奖励被提炼成轻量级的奖励模型,我们用于基于强化学习的对话生成微调。我们对文本仅和多模式变体进行了评估,并与最新的奖励分解方法进行了比较,在人类对话质量评价中取得了显著的改进,这表明LLM是强大的奖励分解器,不需要手动奖励塑形和详细的人类反馈。
要点
- 提出了一种基于大型语言模型的奖励分解框架,用于对话代理对齐。
- 利用预训练的大型语言模型的推理能力来推断精细的局部隐含奖励。
- 提出了文本仅和多模式两种变体进行奖励分解。
- 文本仅变体通过使用对话记录来进行奖励分解。
- 多模式变体结合了额外的行为线索,如音调、目光和面部表情。
- 推断的回合级奖励被提炼成轻量级的奖励模型。
点此查看论文截图


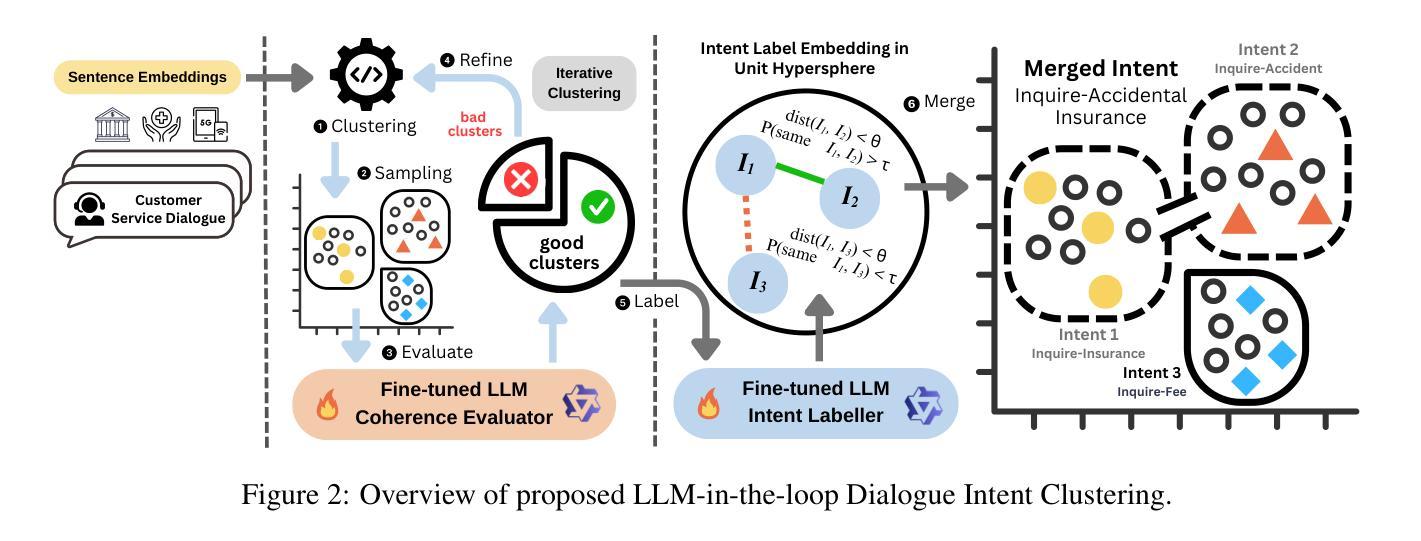
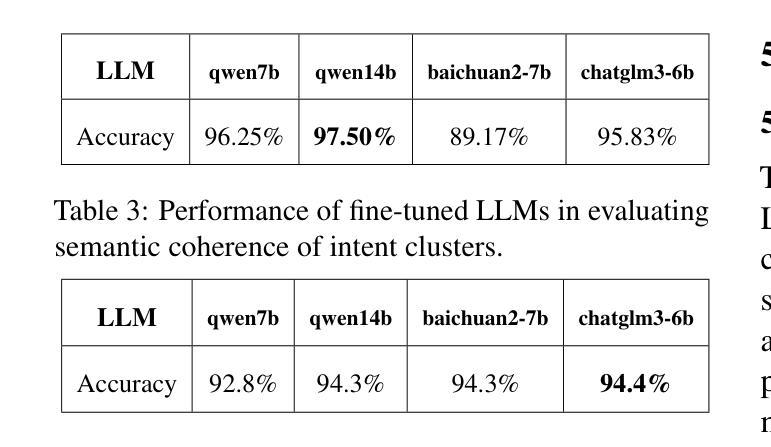
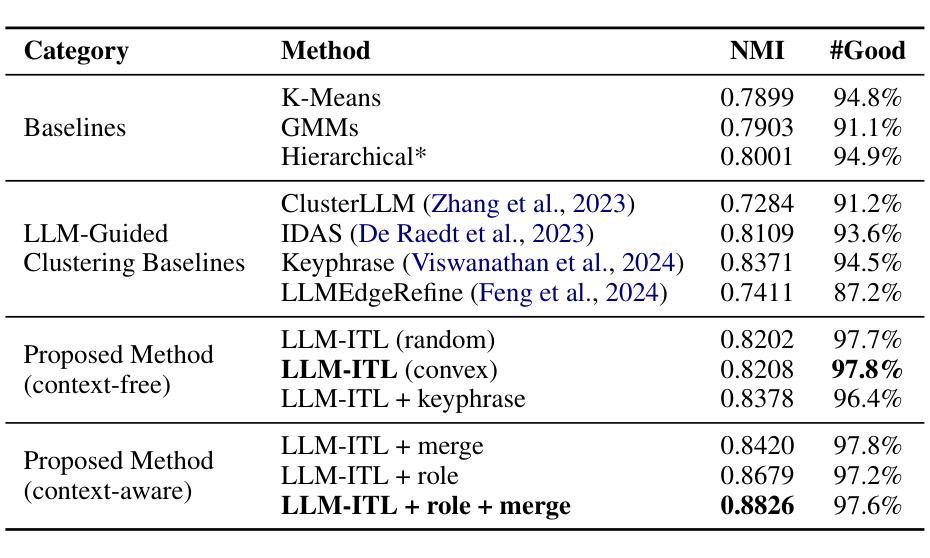
Dial-In LLM: Human-Aligned LLM-in-the-loop Intent Clustering for Customer Service Dialogues
Authors:Mengze Hong, Wailing Ng, Chen Jason Zhang, Yuanfeng Song, Di Jiang
Discovering customer intentions in dialogue conversations is crucial for automated service agents. However, existing intent clustering methods often fail to align with human perceptions due to a heavy reliance on embedding distance metrics and a tendency to overlook underlying semantic structures. This paper proposes an LLM-in-the-loop (LLM-ITL) intent clustering framework, integrating the semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs into conventional clustering algorithms. Specifically, this paper (1) investigates the effectiveness of fine-tuned LLMs in semantic coherence evaluation and intent cluster naming, achieving over 95% accuracy aligned with human judgments; (2) designs an LLM-ITL framework that facilitates the iterative discovery of coherent intent clusters and the optimal number of clusters; and (3) proposes context-aware techniques tailored for customer service dialogue. As existing English benchmarks offer limited semantic diversity and intent groups, we introduce a comprehensive Chinese dialogue intent dataset, comprising over 100k real customer service calls and 1,507 human-annotated intent clusters. The proposed approaches significantly outperform LLM-guided baselines, achieving notable enhancements in clustering quality and lower computational cost. Combined with several best practices, our findings highlight the potential of LLM-in-the-loop techniques for scalable and human-aligned intent clustering.
在对话中发现客户的意图对于自动化服务代理至关重要。然而,现有的意图聚类方法往往因过于依赖嵌入距离度量而忽略潜在语义结构,导致无法与人类感知相匹配。本文提出了一种LLM-in-the-loop(LLM-ITL)意图聚类框架,将LLM的语义理解能力集成到传统聚类算法中。具体来说,本文(1)研究了精细调整的LLM在语义连贯性评估和意图聚类命名中的有效性,与人类判断对齐的准确率超过95%;(2)设计了一个LLM-ITL框架,便于发现连贯的意图簇和最优簇数;并(3)提出了针对客户服务对话的上下文感知技术。由于现有的英语基准测试提供的语义多样性和意图群体有限,我们引入了一个全面的中文对话意图数据集,包含超过10万条真实的客户服务呼叫和1,507个人工注释的意图簇。所提出的方法显著优于LLM指导的基线,在聚类质量和计算成本方面取得了显著的改进。结合几种最佳实践,我们的研究突出了LLM-in-the-loop技术在可扩展性和人类对齐意图聚类方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出了一种结合大型语言模型(LLM)的意图聚类框架,用于在对话中识别客户意图。该框架通过对LLM进行微调,提高语义连贯性评估和意图聚类命名的准确性,并设计了一种迭代发现连贯意图聚类和最佳聚类数量的方法。同时,针对客户服务对话提出了上下文感知技术。此外,由于现有英语基准测试提供的语义多样性和意图组有限,研究团队还引入了一个包含超过十万个真实客户服务电话和一千多个手工标注意图聚类的中文对话意图数据集。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有的意图聚类方法常常无法与人类感知对齐,因为它们过于依赖嵌入距离度量并且容易忽略潜在的语义结构。
- LLM-in-the-loop(LLM-ITL)意图聚类框架结合了LLM的语义理解功能与传统聚类算法,提高了意图聚类的准确性。
- LLM微调后,在语义连贯性评估和意图聚类命名方面的准确性超过95%,与人类判断对齐。
- LLM-ITL框架设计用于迭代发现连贯的意图聚类和最佳聚类数量。
- 针对客户服务对话,提出了上下文感知技术。
- 引入了一个全面的中文对话意图数据集,包含超过十万个真实客户服务电话和一千多个手工标注的意图聚类,为相关研究提供了丰富的资源。
点此查看论文截图



Stability in Reaction Network Models via an Extension of the Next Generation Matrix Method
Authors:Florin Avram, Rim Adenane, Andrei D. Halanay, Matthew D. Johnston
In this essay, we investigate some relations between Chemical Reaction Networks (CRN) and Mathematical Epidemiology (ME) and report on several pleasant surprises which we had simply by putting these two topics together. Firstly, we propose a definition of ME models as a subset of CRN models. Secondly, we review a fundamental stability result for boundary points, known in ME as the NGM method since it replaces the investigation of the Jacobian by that of a matrix whose origins lie in probability (the theory of branching processes). This important result seems to be little known outside of ME; even in ME, it has not been made clear before that the method gets sometimes the right answer, even though the conditions of the NGM theorem are not all satisfied. Thus, beyond the theorem, there is a heuristic approach, the validity conditions for which are not sufficiently understood. Thirdly, we show that some simple CRN models with absolute concentration robustness (ACR), are close qualitatively to simple ME models, in the sense that they have an unique disease free equilibrium, and a unique interior fixed point, and the latter enters the positive domain and becomes stable precisely when $R_0:=s_{dfe} \mathcal{R}=\frac{s_{dfe}}{s_e}>1.$ (where $s$ denotes the “ACR species”). Thus, for these “ME type models”, a “relay phenomena” takes place: precisely when the DFE loses stability, a new fixed point enters the domain, and takes over. Last but not least, we offer in the associated GitHub repository https://github.com/adhalanay/epidemiology_crns a Mathematica package, Epid-CRN, which is addressed to researchers of both disciplines, and provide illustrative notebooks, which in particular solve a few minor open ME and CRN problems. Our package may also be used to study easy cases of analogue continuous time Markov chain (CTMC) ME and CRN models.
在这篇论文中,我们研究了化学反应网络(CRN)和数理流行病学(ME)之间的关系,并报告了将这两个主题结合起来所得到的几个令人愉快的惊喜。首先,我们提出了ME模型作为CRN模型子集的定义。其次,我们回顾了边界点的基本稳定性结果,在ME中被称为NGM方法,因为它用概率起源的矩阵取代了雅可比矩阵的研究(分支过程的理论)。这个重要的结果似乎在ME之外鲜为人知;即使在ME中,也没有弄清楚该方法有时会得到正确的答案,尽管NGM定理的条件并不都满足。因此,除了定理之外,还有一种启发式方法,其有效条件尚未充分理解。第三,我们表明,具有绝对浓度稳健性(ACR)的一些简单CRN模型在定性上类似于简单的ME模型,它们具有一个独特的无疾病平衡态和一个独特的内部固定点,当$R_0:=s_{dfe} \mathcal{R}=\frac{s_{dfe}}{s_e}>1$时,后者进入正域并变得稳定。(其中s表示“ACR物种”)。因此,对于这些“ME类型模型”,会发生一种“接力现象”:恰好当无疾病平衡态失去稳定性时,一个新的固定点进入域并接管。最后但并非最不重要的是,我们在相关的GitHub仓库https://github.com/adhalanay/epidemiology_crns中提供了一个名为Epid-CRN的Mathematica软件包,该软件包面向两个学科的研究人员,并提供说明性笔记本,特别解决了几个小的ME和CRN问题。我们的软件包也可用于研究类似连续时间马尔可夫链(CTMC)的ME和CRN模型的简单情况。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Major review. Title was changed
摘要
本文探讨了化学反应网络(CRN)与数学流行病学(ME)之间的关系,并报告了将这两个主题结合起来所得到的几个令人愉快的惊喜。首先,我们提出将ME模型定义为CRN模型的一个子集。其次,我们回顾了边界点的稳定性结果,在ME中被称为NGM方法,该方法通过概率理论中的分支过程替代雅可比矩阵的研究。这一重要结果似乎鲜为人知,即使在ME领域,也未明确说明该方法有时会在条件不满足的情况下得到正确答案。因此,除了定理之外,还存在一种启发式的做法,其有效性条件尚不足以充分理解。第三,我们展示了具有绝对浓度稳健性(ACR)的简单CRN模型在定性上与简单ME模型相近,其独特之处在于存在唯一的无疾病平衡点和唯一的内部固定点。当$R_0:=s_{dfe} \mathcal{R}=\frac{s_{dfe}}{s_e}>1$时,该固定点进入正域并变得稳定。对于这些“ME类型模型”,恰好当DFE失去稳定性时,一个新的固定点进入域并接管。最后,我们在GitHub存储库中提供了针对两个学科的研究人员的Epid-CRN Mathematica软件包,并提供说明笔记本,解决了一些轻微的ME和CRN问题。我们的软件包也可用于研究类似连续时间马尔可夫链(CTMC)的ME和CRN模型的简单情况。
关键见解
- ME模型可定义为CRN模型的一个子集。
- ME中的NGM方法是一种基于概率理论的分支过程替代雅可比矩阵研究的稳定性方法,但其有效性条件尚不充分理解。
- 具有ACR的简单CRN模型在定性上与简单ME模型相似,具有独特的无疾病平衡点和内部固定点。
- 当特定条件满足时,这些CRN模型的固定点会发生变化,表现出“接力现象”。
- 提供的Epid-CRN Mathematica软件包旨在帮助两个学科的研究人员,并解决了一些ME和CRN的开放问题。
- 软件包可用于研究类似CTMC的ME和CRN模型的简单情况。
点此查看论文截图