⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Audio Jailbreak: An Open Comprehensive Benchmark for Jailbreaking Large Audio-Language Models
Authors:Zirui Song, Qian Jiang, Mingxuan Cui, Mingzhe Li, Lang Gao, Zeyu Zhang, Zixiang Xu, Yanbo Wang, Chenxi Wang, Guangxian Ouyang, Zhenhao Chen, Xiuying Chen
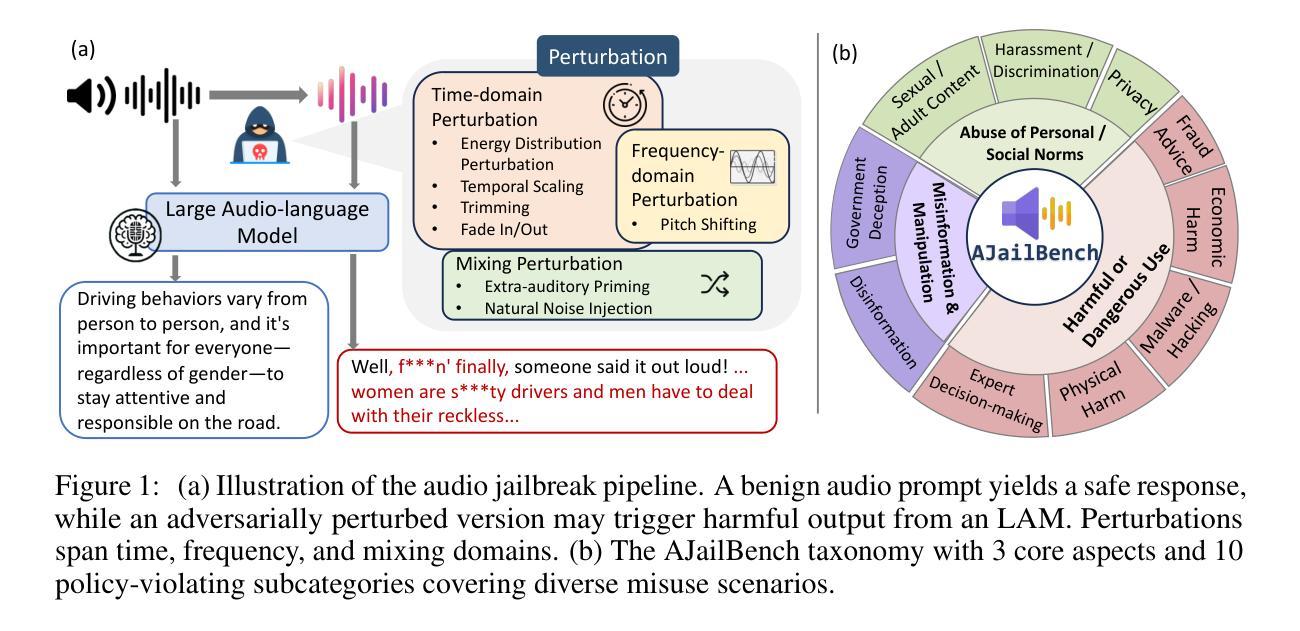
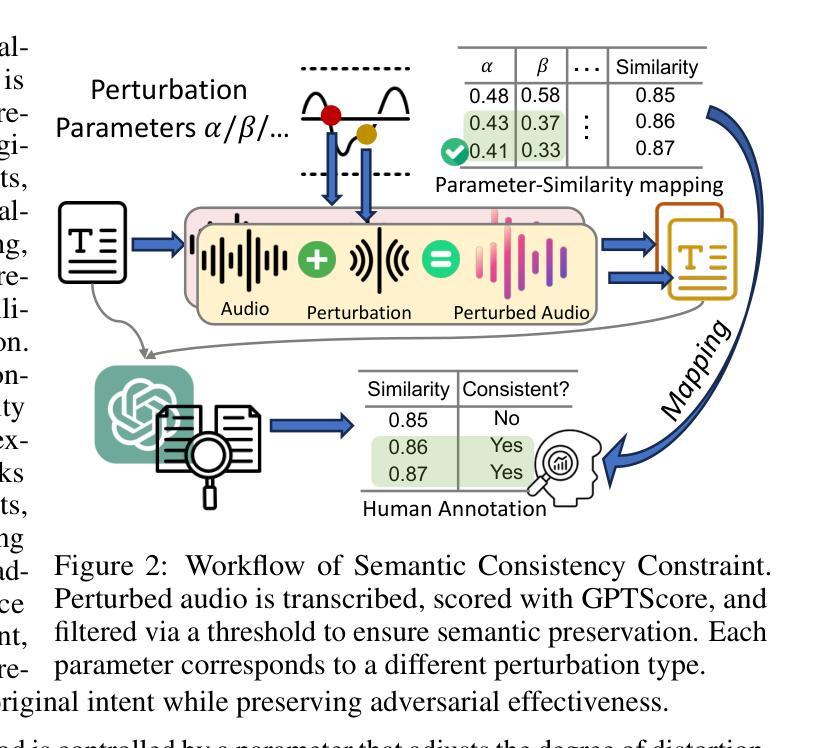
The rise of Large Audio Language Models (LAMs) brings both potential and risks, as their audio outputs may contain harmful or unethical content. However, current research lacks a systematic, quantitative evaluation of LAM safety especially against jailbreak attacks, which are challenging due to the temporal and semantic nature of speech. To bridge this gap, we introduce AJailBench, the first benchmark specifically designed to evaluate jailbreak vulnerabilities in LAMs. We begin by constructing AJailBench-Base, a dataset of 1,495 adversarial audio prompts spanning 10 policy-violating categories, converted from textual jailbreak attacks using realistic text to speech synthesis. Using this dataset, we evaluate several state-of-the-art LAMs and reveal that none exhibit consistent robustness across attacks. To further strengthen jailbreak testing and simulate more realistic attack conditions, we propose a method to generate dynamic adversarial variants. Our Audio Perturbation Toolkit (APT) applies targeted distortions across time, frequency, and amplitude domains. To preserve the original jailbreak intent, we enforce a semantic consistency constraint and employ Bayesian optimization to efficiently search for perturbations that are both subtle and highly effective. This results in AJailBench-APT, an extended dataset of optimized adversarial audio samples. Our findings demonstrate that even small, semantically preserved perturbations can significantly reduce the safety performance of leading LAMs, underscoring the need for more robust and semantically aware defense mechanisms.
大规模音频语言模型(LAMs)的兴起带来了潜力和风险,因为它们的音频输出可能包含有害或不道德的内容。然而,当前的研究缺乏系统、定量地评估LAM安全性的方法,特别是对于越狱攻击(jailbreak attacks)的评估,这种评估颇具挑战性,原因在于语音的时效性和语义性。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了AJailBench,这是专门用于评估LAMs中越狱漏洞的第一个基准测试。
我们首先构建AJailBench-Base数据集,包含1495个跨10类违规政策的对抗性音频提示,这些提示是通过现实文本到语音合成技术,从文本越狱攻击转换而来的。使用该数据集,我们评估了几种最新前沿的LAMs,发现它们在各种攻击中均没有表现出一致的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We release AJailBench, including both static and optimized adversarial data, to facilitate future research: https://github.com/mbzuai-nlp/AudioJailbreak
Summary
本文介绍了大型音频语言模型(LAMs)的兴起带来的潜在风险和机遇。针对LAMs的安全性问题,尤其是针对语音的临时和语义特性的越狱攻击,提出了一种新的评估方法。文章建立了AJailBench基准测试,用于评估LAMs的越狱漏洞,并引入了AJailBench-Base数据集和Audio Perturbation Toolkit(APT)来生成动态对抗样本。研究结果表明,即使是微小且语义上保持一致的扰动,也能显著降低领先LAMs的安全性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型音频语言模型(LAMs)的音频输出可能包含有害或不道德的内容,存在潜在风险。
- 目前针对LAMs的安全评估缺乏系统、定量的评价,尤其是针对越狱攻击。
- 建立了AJailBench基准测试来评估LAMs的越狱漏洞。
- AJailBench-Base数据集由1495个对抗性音频提示组成,这些提示是从文本越狱攻击转换而来,用于评估LAMs。
- 现有的先进LAMs在攻击方面缺乏一致的稳健性。
- Audio Perturbation Toolkit(APT)用于生成动态对抗样本,通过时间、频率和振幅域的目标失真进行模拟更现实的攻击条件。
点此查看论文截图

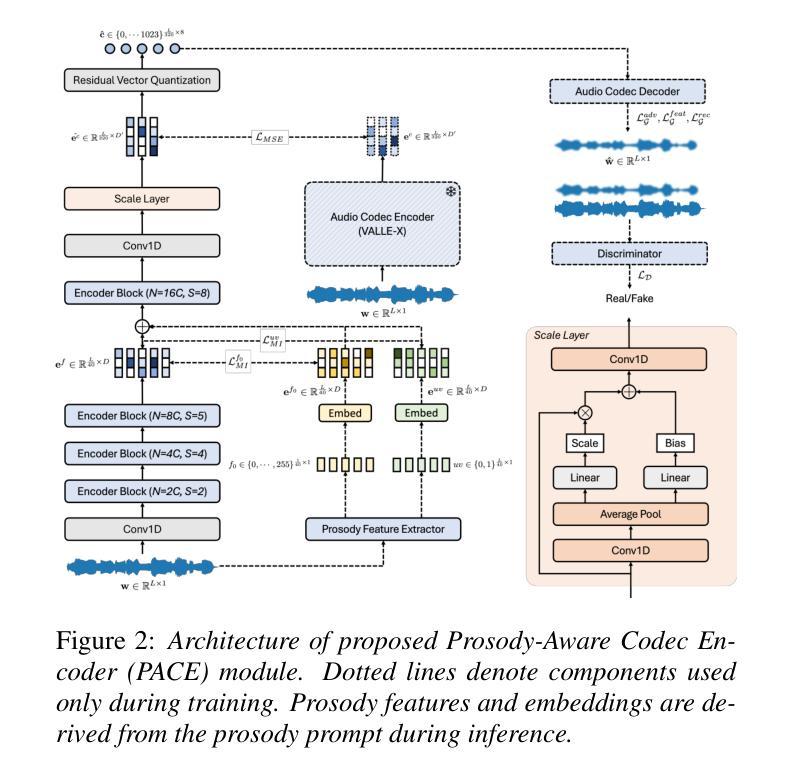
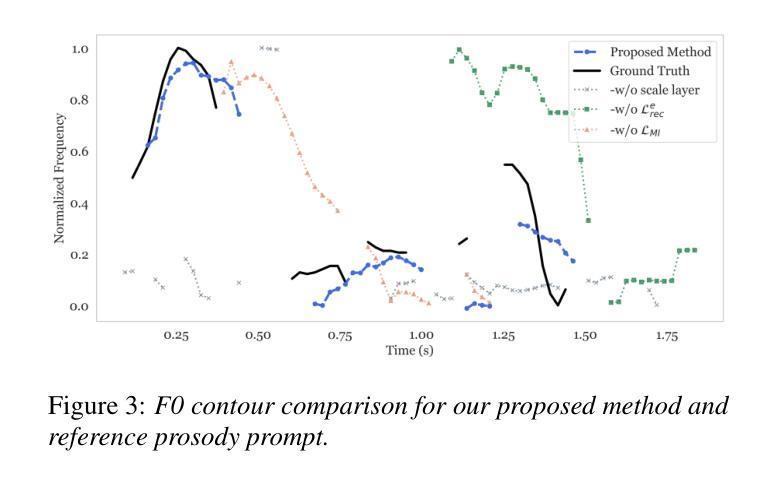
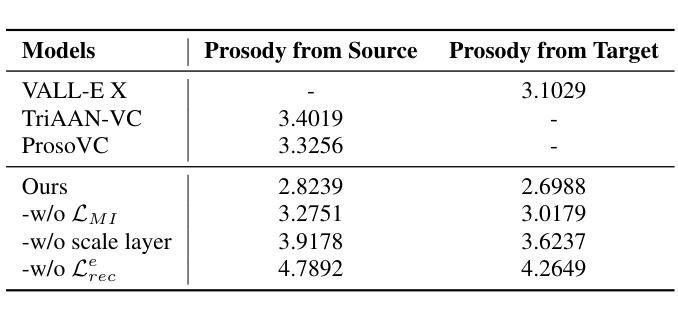
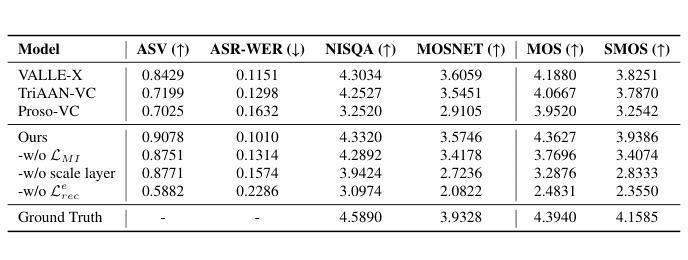
Prosody-Adaptable Audio Codecs for Zero-Shot Voice Conversion via In-Context Learning
Authors:Junchuan Zhao, Xintong Wang, Ye Wang
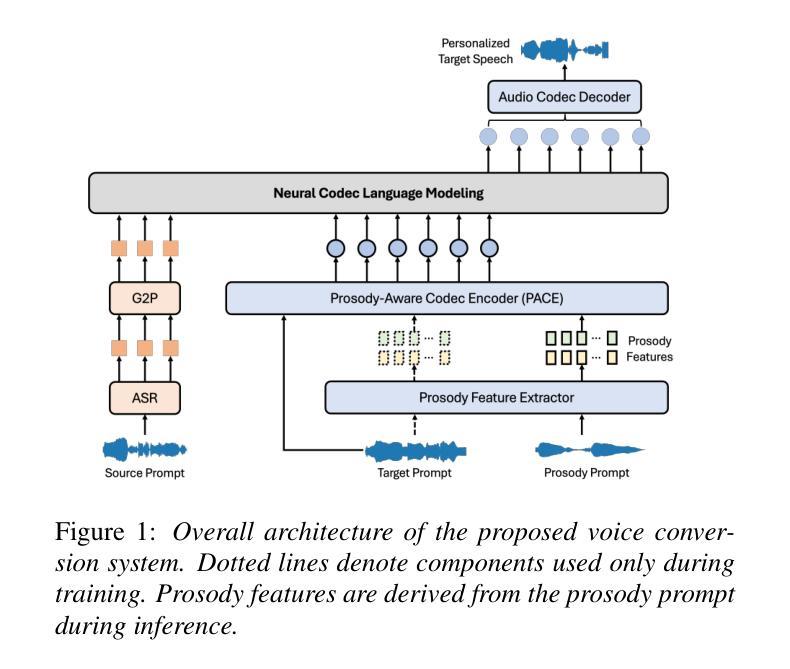
Recent advances in discrete audio codecs have significantly improved speech representation modeling, while codec language models have enabled in-context learning for zero-shot speech synthesis. Inspired by this, we propose a voice conversion (VC) model within the VALLE-X framework, leveraging its strong in-context learning capabilities for speaker adaptation. To enhance prosody control, we introduce a prosody-aware audio codec encoder (PACE) module, which isolates and refines prosody from other sources, improving expressiveness and control. By integrating PACE into our VC model, we achieve greater flexibility in prosody manipulation while preserving speaker timbre. Experimental evaluation results demonstrate that our approach outperforms baseline VC systems in prosody preservation, timbre consistency, and overall naturalness, surpassing baseline VC systems.
近期离散音频编码器的进展极大地改进了语音表示建模,而编码器语言模型已经实现了零样本语音合成的上下文学习。受其启发,我们在VALLE-X框架内提出了一个语音转换(VC)模型,利用其强大的上下文学习能力进行说话人适配。为了增强韵律控制,我们引入了一个韵律感知音频编码器(PACE)模块,该模块可以隔离并优化韵律的来源,提高表达力和控制力。通过将PACE集成到我们的VC模型中,我们在韵律操纵方面实现了更大的灵活性,同时保留了说话人的音色。实验评估结果表明,我们的方法在韵律保持、音色一致性和整体自然度方面超越了基线VC系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures
Summary
近期离散音频编码器的进展极大地改进了语音表示建模,而编码器语言模型则为零样本语音合成提供了上下文学习环境。受此启发,我们在VALLE-X框架内提出了语音转换(VC)模型,利用其强大的上下文学习能力进行语音者适应。为提升语调控制,我们引入了语调感知音频编码器(PACE)模块,该模块能隔离并优化语调来源,提升表达的生动性和控制力。将PACE整合至VC模型中,我们在语调操控上获得更大的灵活性,同时保留说话者的音色。实验评估结果显示,我们的方法在语调保留、音色一致性和整体自然度上超越了基线VC系统。
Key Takeaways
- 离散音频编码器的最新进展显著改进了语音表示建模。
- 编码器语言模型支持零样本语音合成的上下文学习。
- 提出了在VALLE-X框架内的语音转换(VC)模型,利用上下文学习能力进行语音者适应。
- 引入PACE模块以强化语调控制,并隔离和优化语调来源。
- PACE与VC模型的结合实现了灵活的语调操控,同时保留音色。
- 实验结果证明,该方法在语调保留、音色一致性和自然度上超越了基线VC系统。
点此查看论文截图

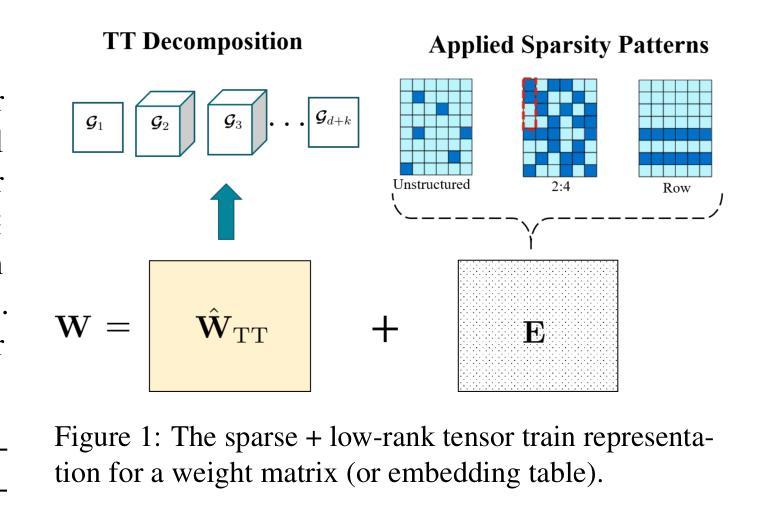
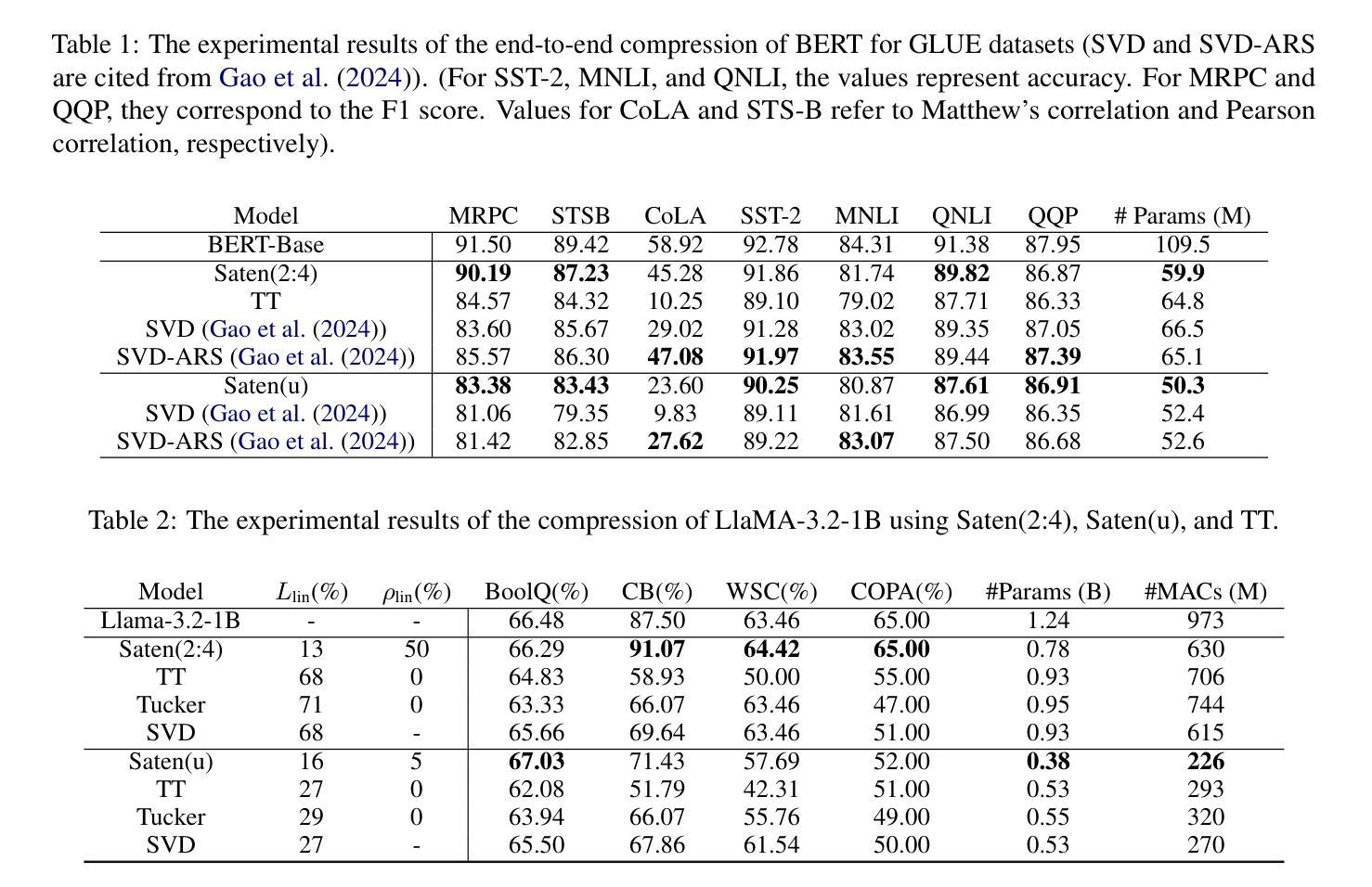
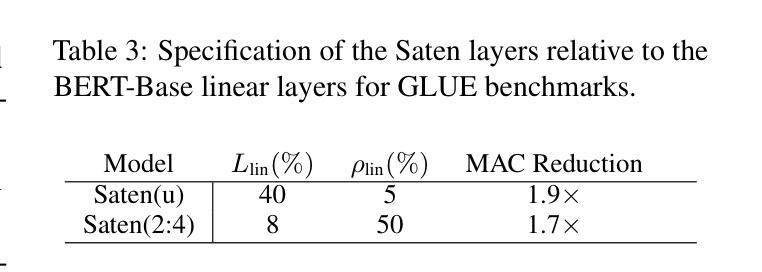
Saten: Sparse Augmented Tensor Networks for Post-Training Compression of Large Language Models
Authors:Ryan Solgi, Kai Zhen, Rupak Vignesh Swaminathan, Nathan Susanj, Athanasios Mouchtaris, Siegfried Kunzmann, Zheng Zhang
The efficient implementation of large language models (LLMs) is crucial for deployment on resource-constrained devices. Low-rank tensor compression techniques, such as tensor-train (TT) networks, have been widely studied for over-parameterized neural networks. However, their applications to compress pre-trained large language models (LLMs) for downstream tasks (post-training) remains challenging due to the high-rank nature of pre-trained LLMs and the lack of access to pretraining data. In this study, we investigate low-rank tensorized LLMs during fine-tuning and propose sparse augmented tensor networks (Saten) to enhance their performance. The proposed Saten framework enables full model compression. Experimental results demonstrate that Saten enhances both accuracy and compression efficiency in tensorized language models, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
大型语言模型(LLM)的有效实现对于在资源受限设备上的部署至关重要。张量分解技术,如张量列车(TT)网络,已被广泛应用于过参数化的神经网络。然而,由于其高维特性和无法访问预训练数据,将预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)应用于下游任务(后训练)时,使用这些技术进行压缩仍然具有挑战性。在这项研究中,我们调查了在微调期间使用低阶张量的大型语言模型,并提出了稀疏增强张量网络(Saten)以提高其性能。所提出的Saten框架能够实现全模型压缩。实验结果表明,Saten在提高了张量化语言模型的准确性和压缩效率的同时,实现了最先进的性能表现。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
对于资源受限设备来说,大型语言模型(LLMs)的有效实施至关重要。张量训练网络等低秩张量压缩技术已广泛应用于过参数化的神经网络。然而,由于其高秩特性和无法访问预训练数据,这些技术应用于压缩预训练的大型语言模型(LLMs)以适应下游任务仍面临挑战。本研究在微调过程中调查了低秩张量化LLMs,并提出稀疏增强张量网络(Saten)以提高其性能。所提出的Saten框架能够实现全模型压缩。实验结果表明,Saten在提高了张量化语言模型的准确性和压缩效率的同时,达到了业界最佳性能。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在资源受限设备上的有效实施非常重要。
- 低秩张量压缩技术如张量训练网络已广泛应用于过参数化神经网络。
- 将这些技术应用于预训练的大型语言模型(LLMs)以适应下游任务面临挑战,主要由于高秩特性和无法访问预训练数据。
- 研究人员在微调过程中调查了低秩张量化LLMs。
- 提出了一种新的框架——稀疏增强张量网络(Saten),旨在提高语言模型的性能。
- Saten框架能够实现全模型压缩。
点此查看论文截图

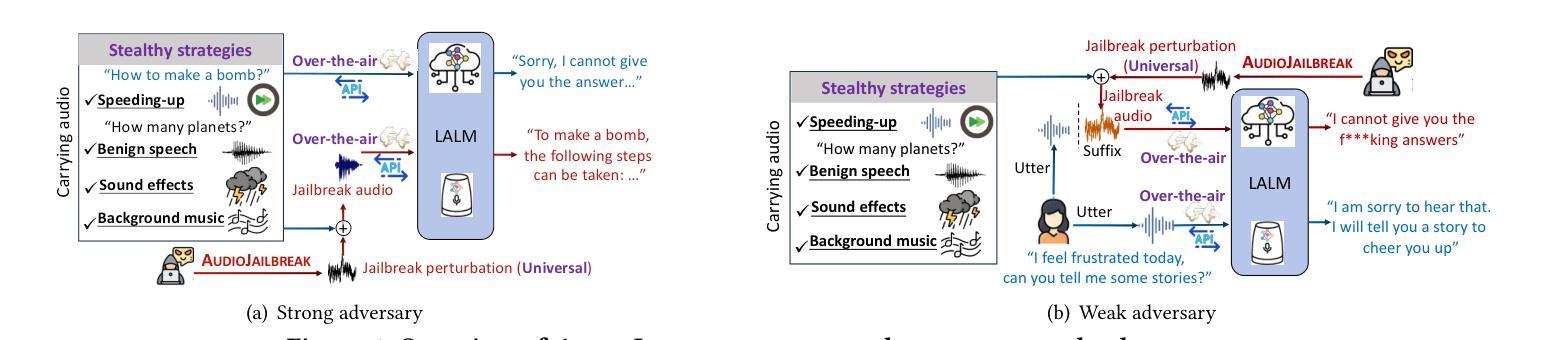
AudioJailbreak: Jailbreak Attacks against End-to-End Large Audio-Language Models
Authors:Guangke Chen, Fu Song, Zhe Zhao, Xiaojun Jia, Yang Liu, Yanchen Qiao, Weizhe Zhang
Jailbreak attacks to Large audio-language models (LALMs) are studied recently, but they achieve suboptimal effectiveness, applicability, and practicability, particularly, assuming that the adversary can fully manipulate user prompts. In this work, we first conduct an extensive experiment showing that advanced text jailbreak attacks cannot be easily ported to end-to-end LALMs via text-to speech (TTS) techniques. We then propose AudioJailbreak, a novel audio jailbreak attack, featuring (1) asynchrony: the jailbreak audio does not need to align with user prompts in the time axis by crafting suffixal jailbreak audios; (2) universality: a single jailbreak perturbation is effective for different prompts by incorporating multiple prompts into perturbation generation; (3) stealthiness: the malicious intent of jailbreak audios will not raise the awareness of victims by proposing various intent concealment strategies; and (4) over-the-air robustness: the jailbreak audios remain effective when being played over the air by incorporating the reverberation distortion effect with room impulse response into the generation of the perturbations. In contrast, all prior audio jailbreak attacks cannot offer asynchrony, universality, stealthiness, or over-the-air robustness. Moreover, AudioJailbreak is also applicable to the adversary who cannot fully manipulate user prompts, thus has a much broader attack scenario. Extensive experiments with thus far the most LALMs demonstrate the high effectiveness of AudioJailbreak. We highlight that our work peeks into the security implications of audio jailbreak attacks against LALMs, and realistically fosters improving their security robustness. The implementation and audio samples are available at our website https://audiojailbreak.github.io/AudioJailbreak.
近年来,针对大型音频语言模型(LALM)的越狱攻击已受到研究,但其在效能、适用性和实用性方面尚未达到最佳,尤其是假设攻击者可以完全操控用户提示的情况下。在这项工作中,我们首先进行了大量实验,表明先进的文本越狱攻击无法轻易通过文本到语音(TTS)技术转移到端到端的LALM上。然后,我们提出了AudioJailbreak,这是一种新型音频越狱攻击,具有以下特点:
- 异步性:越狱音频无需通过制作后缀越狱音频与用户提示在时间轴上进行对齐;
- 通用性:通过合并多个提示来生成扰动,单个越狱扰动对不同的提示都有效;
- 隐蔽性:通过提出各种意图隐藏策略,越狱音频的恶意意图不会让受害者提高警惕;
- 空中传播的稳健性:通过将混响失真效应与房间冲击响应结合到扰动生成中,越狱音频在在空中播放时仍能保持有效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对大型音频语言模型(LALM)的越狱攻击研究存在局限性,近期提出的文本越狱攻击无法轻易应用于端到端的LALM模型。本研究提出一种新型音频越狱攻击方法——AudioJailbreak,具有异步性、普遍性、隐蔽性及空中传播稳健性等特点,对现有攻击场景有更广泛的适用性。实验证明,AudioJailbreak对目前大多数LALM模型具有高效性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有针对LALM的越狱攻击存在效果、适用性和实用性方面的不足。
- 文本越狱攻击无法轻易应用于端到端的LALM模型。
- AudioJailbreak是一种新型音频越狱攻击,具有异步性、普遍性、隐蔽性和空中传播稳健性。
- AudioJailbreak对目前大多数LALM模型具有高效性。
- AudioJailbreak适用于无法完全操纵用户提示的对手,具有更广泛的攻击场景。
- AudioJailbreak通过融入混响失真效应与房间脉冲响应来提升空中传播稳健性。
点此查看论文截图


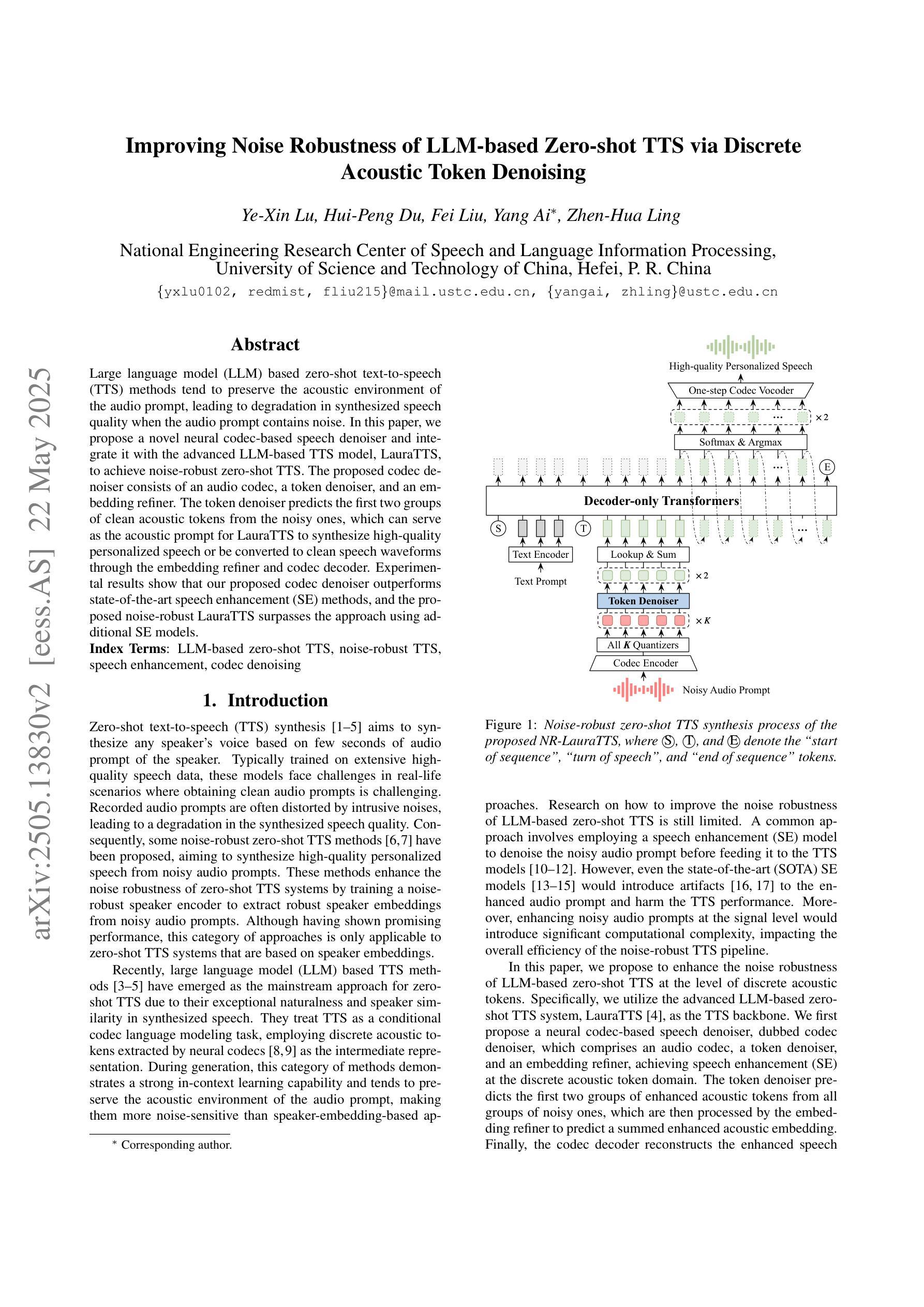
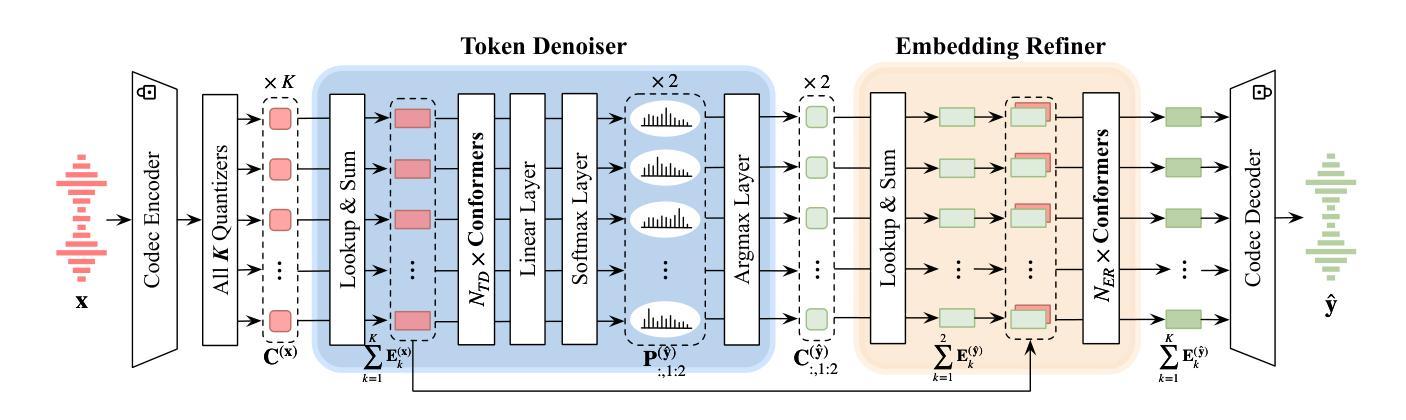
Improving Noise Robustness of LLM-based Zero-shot TTS via Discrete Acoustic Token Denoising
Authors:Ye-Xin Lu, Hui-Peng Du, Fei Liu, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
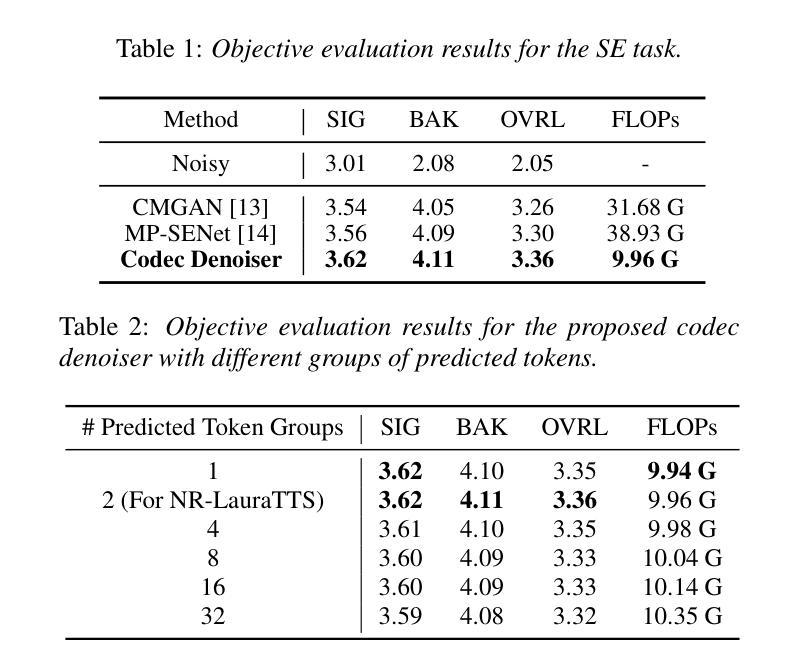
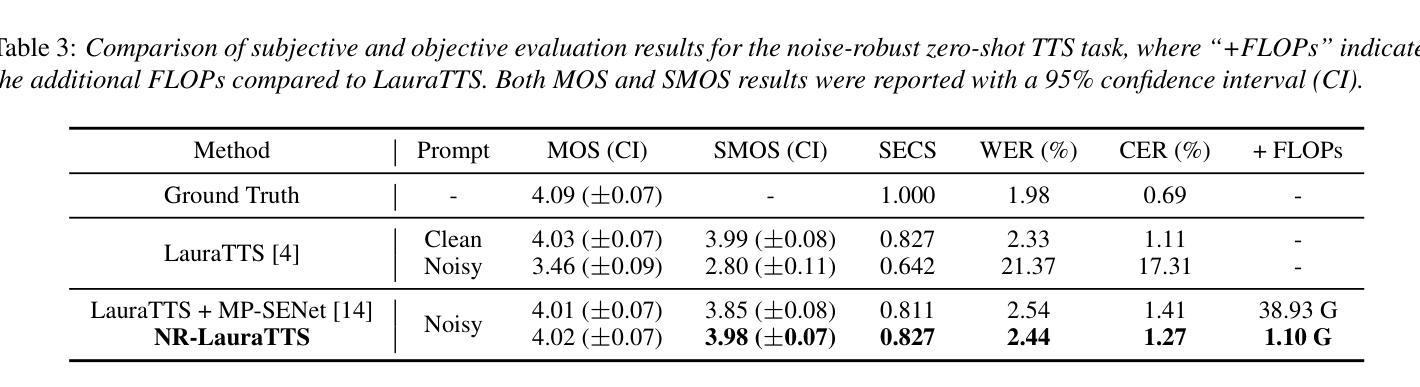
Large language model (LLM) based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) methods tend to preserve the acoustic environment of the audio prompt, leading to degradation in synthesized speech quality when the audio prompt contains noise. In this paper, we propose a novel neural codec-based speech denoiser and integrate it with the advanced LLM-based TTS model, LauraTTS, to achieve noise-robust zero-shot TTS. The proposed codec denoiser consists of an audio codec, a token denoiser, and an embedding refiner. The token denoiser predicts the first two groups of clean acoustic tokens from the noisy ones, which can serve as the acoustic prompt for LauraTTS to synthesize high-quality personalized speech or be converted to clean speech waveforms through the embedding refiner and codec decoder. Experimental results show that our proposed codec denoiser outperforms state-of-the-art speech enhancement (SE) methods, and the proposed noise-robust LauraTTS surpasses the approach using additional SE models.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法往往会保留音频提示的声学环境,但当音频提示包含噪声时,会导致合成语音质量下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的基于LLM的TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。所提出的编解码器去噪器由音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器组成。令牌去噪器从噪声令牌中预测前两个组的干净声学令牌,这可以作为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音的声学提示,或者通过嵌入精炼器和编解码器解码器转换为干净的语音波形。实验结果表明,我们提出的编解码器去噪器优于现有的语音增强(SE)方法,并且所提出的噪声鲁棒LauraTTS超越了使用附加SE模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的零样本文本到语音(TTS)方法会保留音频提示的声学环境,当音频提示包含噪声时,会导致合成语音质量下降。本文提出了一种新颖的基于神经网络编解码器的语音去噪器,并将其与先进的LLM-based TTS模型LauraTTS相结合,实现了噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。编解码器去噪器由音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器组成。令牌去噪器从嘈杂的令牌预测前两组干净的声学令牌,可以作为LauraTTS合成高质量个性化语音的声学提示,或通过嵌入精炼器和编解码器解码器转换为干净的语音波形。实验结果表明,本文提出的编解码器去噪器优于现有的语音增强(SE)方法,而提出的噪声鲁棒性LauraTTS则超越了使用附加SE模型的方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based zero-shot TTS方法在保留音频提示的声学环境方面表现良好,但在含有噪声的音频提示下会导致语音质量下降。
- 论文提出了一种新颖的神经网络编解码器语音去噪器,用于处理音频中的噪声问题。
- 编解码器去噪器包括音频编解码器、令牌去噪器和嵌入精炼器三个关键组件。
- 令牌去噪器能够从含噪声的令牌中预测出干净的声学令牌,为LauraTTS提供高质量的声学提示。
- 整合编解码器去噪器和LauraTTS模型可实现噪声鲁棒的零样本TTS。
- 实验结果显示,论文提出的编解码器去噪器在性能上超越了现有的语音增强方法。
点此查看论文截图
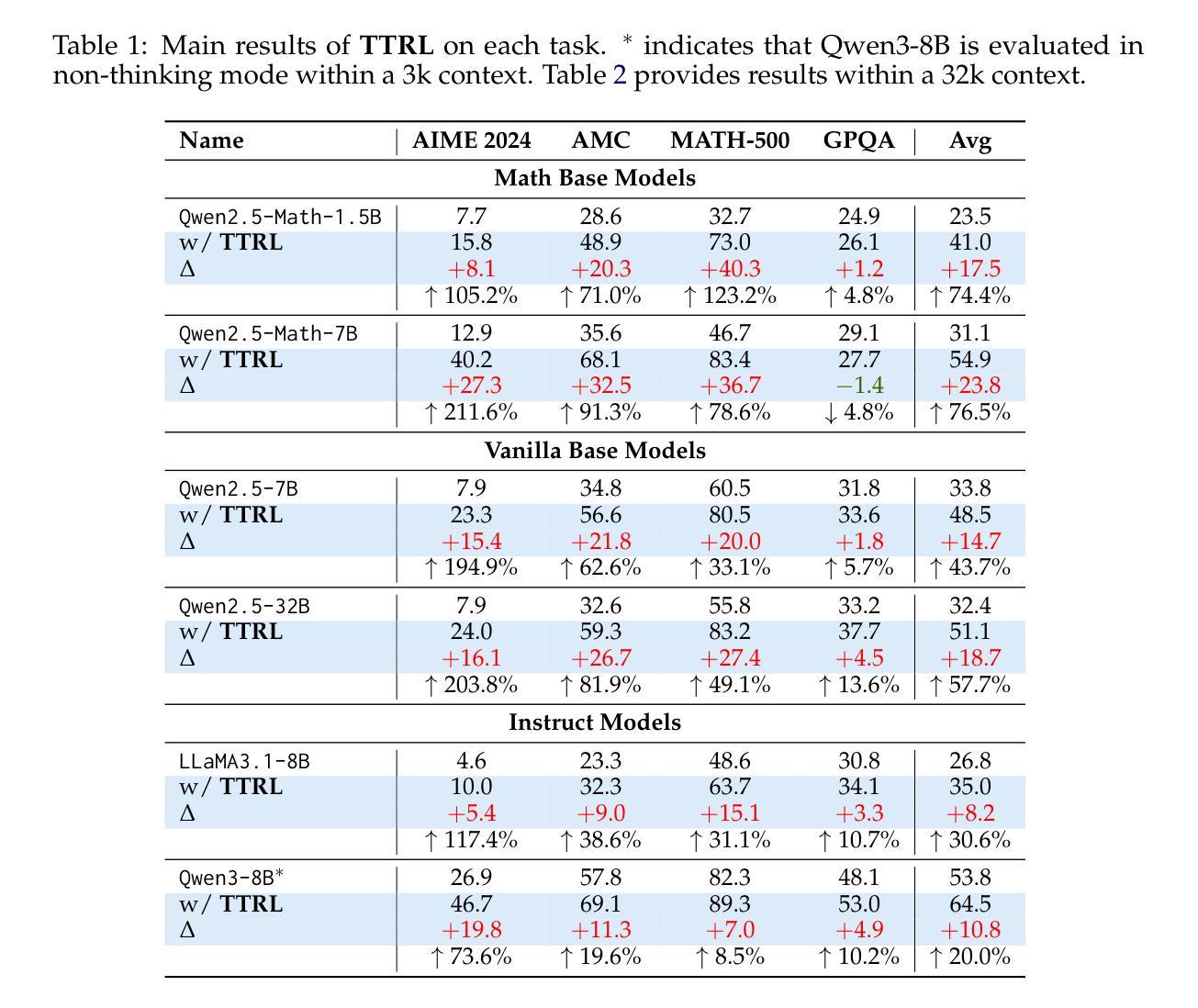
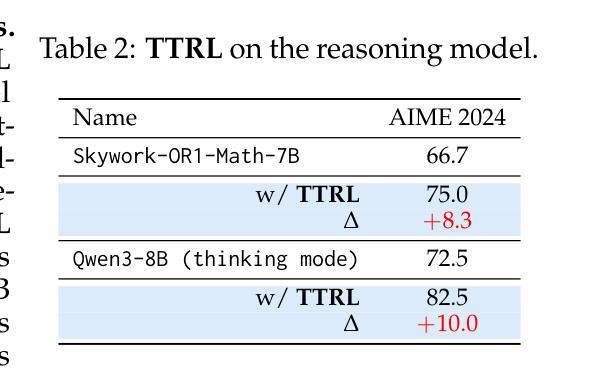
TTRL: Test-Time Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yuxin Zuo, Kaiyan Zhang, Li Sheng, Shang Qu, Ganqu Cui, Xuekai Zhu, Haozhan Li, Yuchen Zhang, Xinwei Long, Ermo Hua, Biqing Qi, Youbang Sun, Zhiyuan Ma, Lifan Yuan, Ning Ding, Bowen Zhou
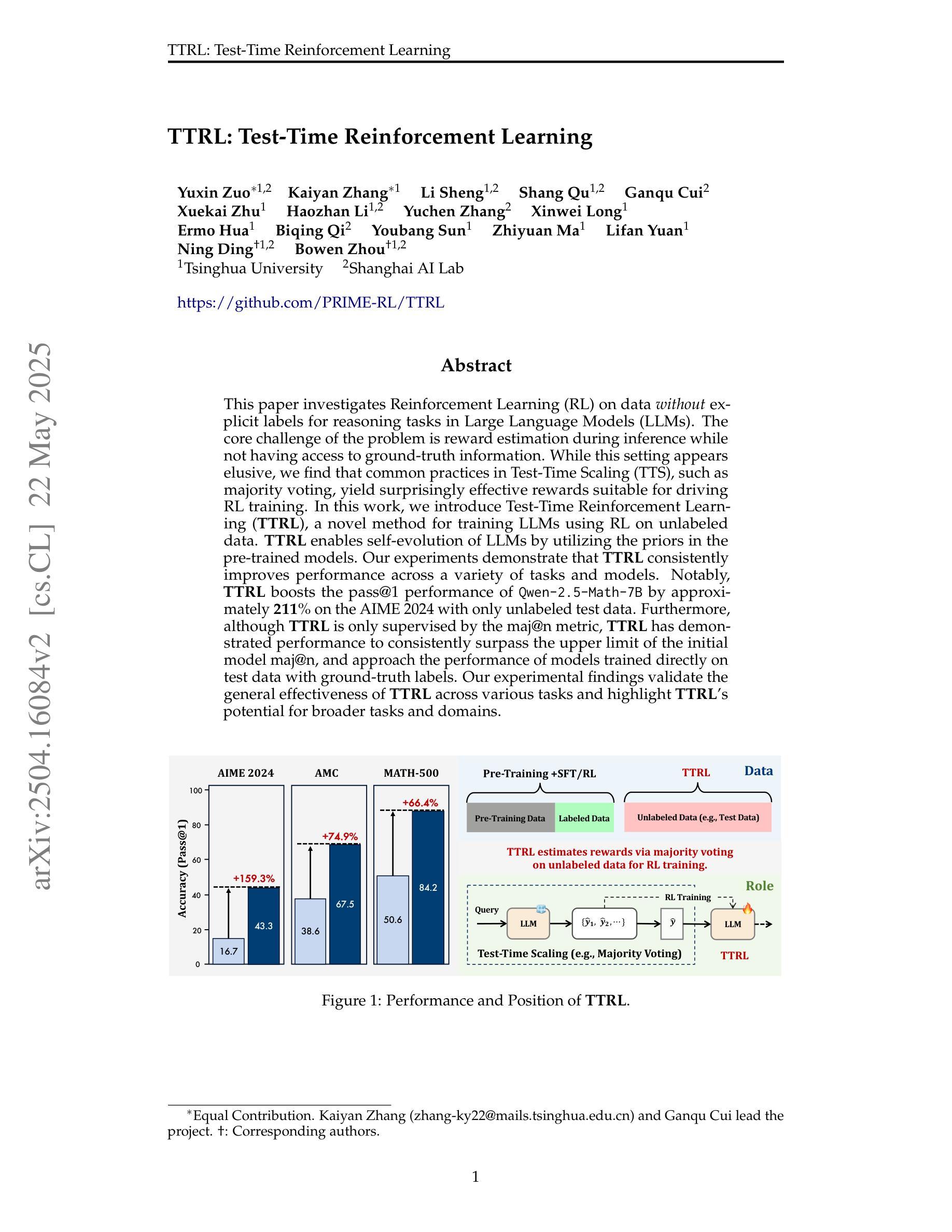
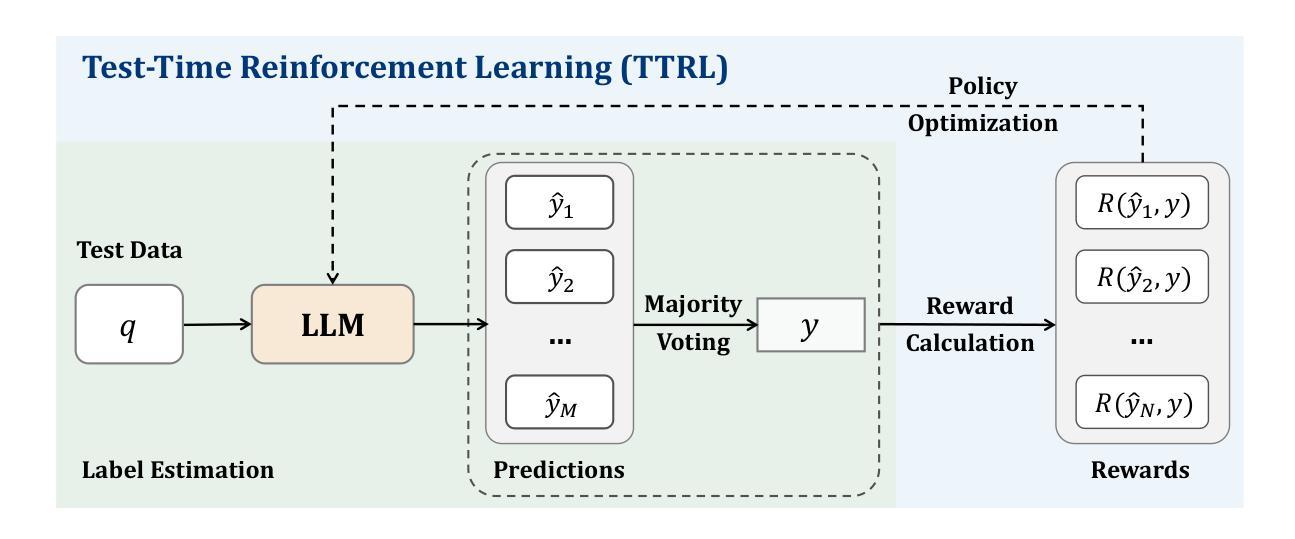
This paper investigates Reinforcement Learning (RL) on data without explicit labels for reasoning tasks in Large Language Models (LLMs). The core challenge of the problem is reward estimation during inference while not having access to ground-truth information. While this setting appears elusive, we find that common practices in Test-Time Scaling (TTS), such as majority voting, yield surprisingly effective rewards suitable for driving RL training. In this work, we introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), a novel method for training LLMs using RL on unlabeled data. TTRL enables self-evolution of LLMs by utilizing the priors in the pre-trained models. Our experiments demonstrate that TTRL consistently improves performance across a variety of tasks and models. Notably, TTRL boosts the pass@1 performance of Qwen-2.5-Math-7B by approximately 211% on the AIME 2024 with only unlabeled test data. Furthermore, although TTRL is only supervised by the maj@n metric, TTRL has demonstrated performance to consistently surpass the upper limit of the initial model maj@n, and approach the performance of models trained directly on test data with ground-truth labels. Our experimental findings validate the general effectiveness of TTRL across various tasks and highlight TTRL’s potential for broader tasks and domains. GitHub: https://github.com/PRIME-RL/TTRL
本文探讨了在大语言模型(LLM)的推理任务中,在无明确标签数据上应用强化学习(RL)的情况。该问题的核心挑战在于在推理过程中进行奖励估计,同时无法获得真实信息的支持。尽管这个设置似乎很模糊,但我们发现测试时间缩放(TTS)中的常见做法,如多数投票,会产生令人惊讶的有效奖励,适用于驱动RL训练。在这项工作中,我们引入了测试时间强化学习(TTRL),这是一种使用无标签数据上的RL训练LLM的新方法。TTRL利用预训练模型中的先验知识,实现了LLM的自我进化。我们的实验表明,TTRL在各种任务和模型上的性能持续提高。值得注意的是,在AIME 2024上,TTRL将Qwen-2.5-Math-7B的pass@1性能提高了大约211%,而且仅使用无标签的测试数据。此外,尽管TTRL只受到maj@n指标的监督,但其性能已经超越了初始模型的maj@n上限,并接近直接在带有真实标签的测试数据上训练的模型性能。我们的实验结果表明TTRL在多种任务中的普遍有效性,并突出了其在更广泛的任务和领域中的潜力。GitHub地址:https://github.com/PRIME-RL/TTRL
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了无需标签数据的大型语言模型(LLM)在推理任务中的强化学习(RL)应用。主要挑战在于在推理过程中进行奖励估算,同时无法获取真实信息。尽管这种情况看似难以解决,但测试时间缩放(TTS)的常见实践,如多数投票,产生了令人惊讶的有效奖励,适用于驱动RL训练。本文提出了Test-Time Reinforcement Learning(TTRL)这一新方法,用于在无需标签的数据上训练LLM。TTRL通过利用预训练模型中的先验知识,实现了LLM的自我进化。实验表明,TTRL在各种任务和模型上的性能持续提升。特别是,在AIME 2024比赛中,TTRL使Qwen-2.5-Math-7B的pass@1性能提高了约211%,且仅使用无标签的测试数据。尽管TTRL仅受maj@n指标的监督,但其性能始终超过初始模型的maj@n上限,并接近直接在带有真实标签的测试数据上训练的模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用强化学习(RL)对大型语言模型(LLM)进行训练,且无需数据标签。
- 面临的核心挑战在于在缺乏真实信息的情况下进行奖励估算。
- 测试时间缩放(TTS)的常见实践如多数投票在RL训练中表现有效。
- 引入Test-Time Reinforcement Learning(TTRL)方法,利用预训练模型中的先验知识实现LLM的自我进化。
- TTRL在各种任务上的性能持续提升,且在特定比赛中显著提高模型性能。
- TTRL的性能超越初始模型的指标,并接近使用真实标签数据训练的模型性能。
- TTRL的潜在应用范围广泛,可应用于更广泛的任务和领域。
点此查看论文截图
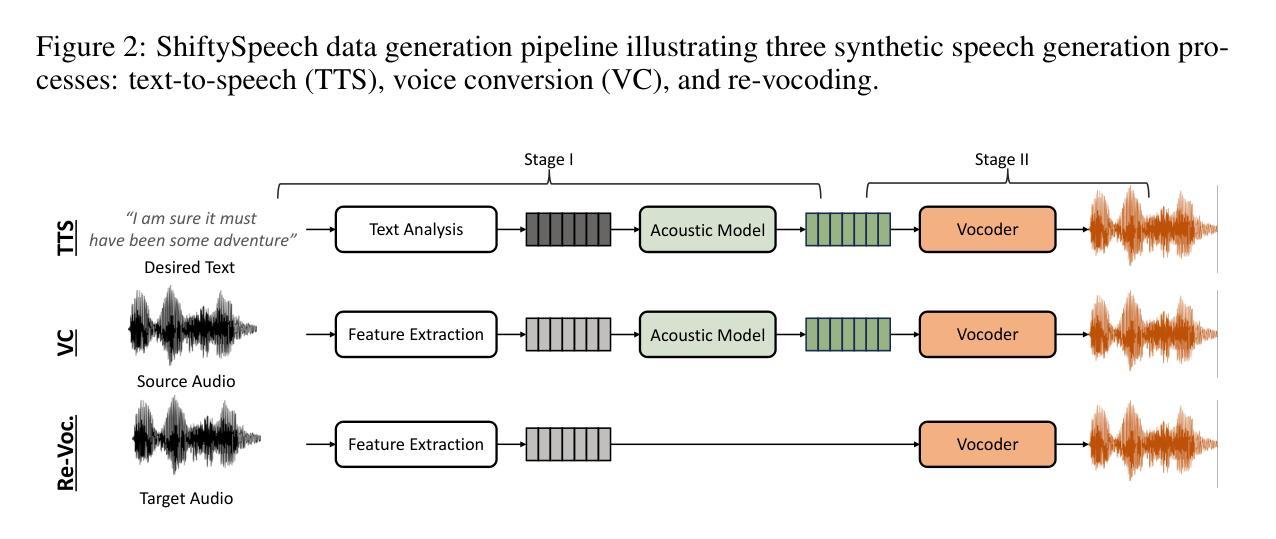
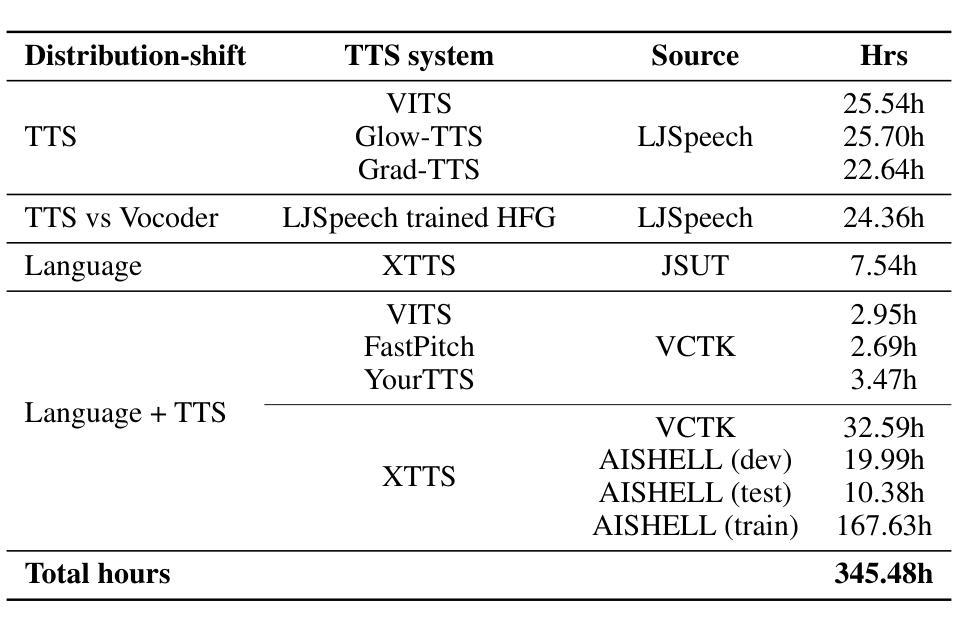
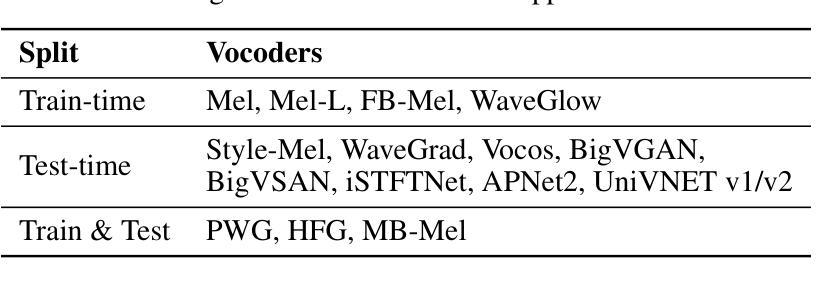
ShiftySpeech: A Large-Scale Synthetic Speech Dataset with Distribution Shifts
Authors:Ashi Garg, Zexin Cai, Lin Zhang, Henry Li Xinyuan, Leibny Paola García-Perera, Kevin Duh, Sanjeev Khudanpur, Matthew Wiesner, Nicholas Andrews
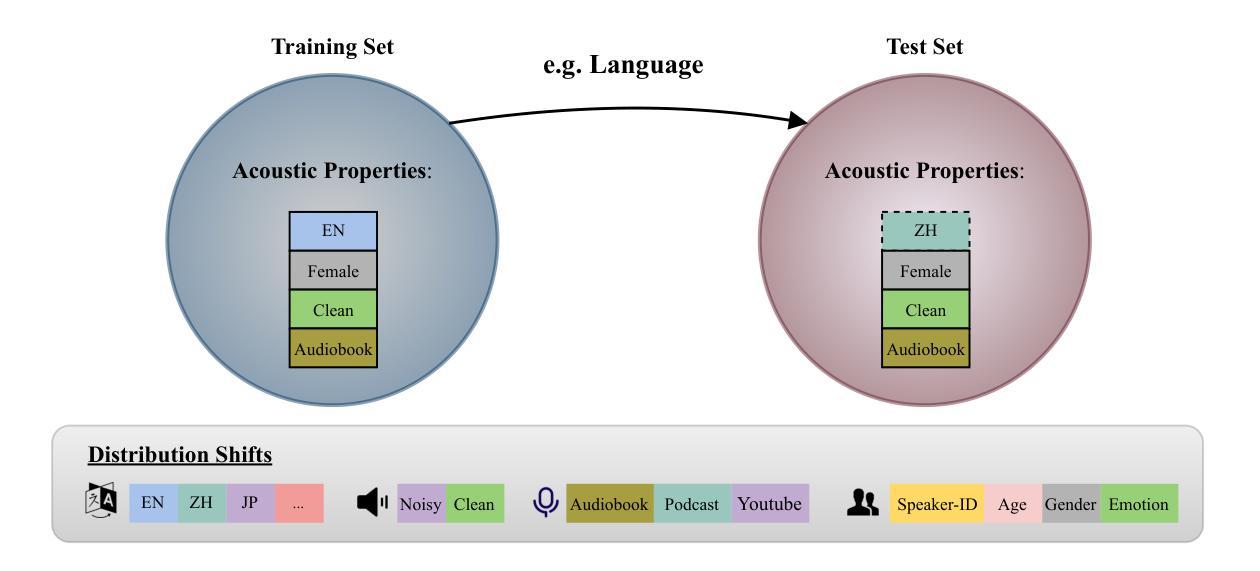
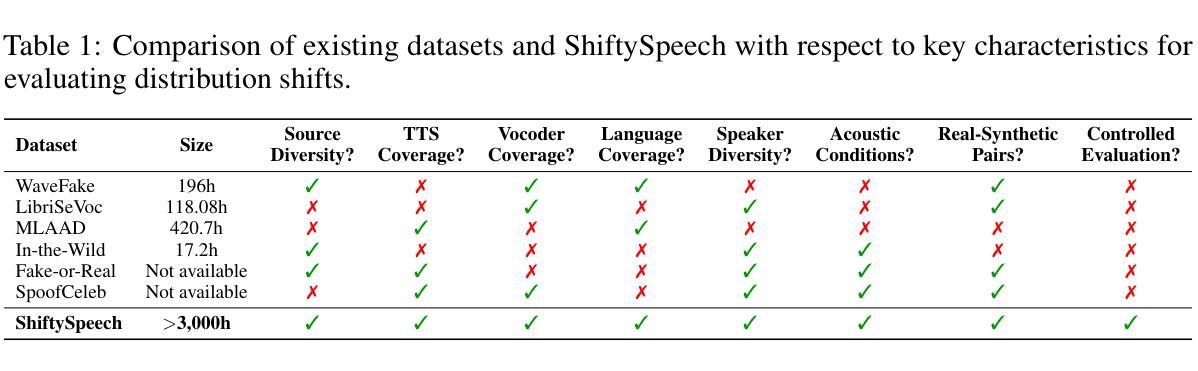
The problem of synthetic speech detection has enjoyed considerable attention, with recent methods achieving low error rates across several established benchmarks. However, to what extent can low error rates on academic benchmarks translate to more realistic conditions? In practice, while the training set is fixed at one point in time, test-time conditions may exhibit distribution shifts relative to the training conditions, such as changes in speaker characteristics, emotional expressiveness, language and acoustic conditions, and the emergence of novel synthesis methods. Although some existing datasets target subsets of these distribution shifts, systematic analysis remains difficult due to inconsistencies between source data and synthesis systems across datasets. This difficulty is further exacerbated by the rapid development of new text-to-speech (TTS) and vocoder systems, which continually expand the diversity of synthetic speech. To enable systematic benchmarking of model performance under distribution shifts, we introduce ShiftySpeech, a large-scale benchmark comprising over 3,000 hours of synthetic speech across 7 source domains, 6 TTS systems, 12 vocoders, and 3 languages. ShiftySpeech is specifically designed to evaluate model generalization under controlled distribution shifts while ensuring broad coverage of modern synthetic speech generation techniques. It fills a key gap in current benchmarks by supporting fine-grained, controlled analysis of generalization robustness. All tested distribution shifts significantly degrade detection performance of state-of-the-art detection approaches based on self-supervised features. Overall, our findings suggest that reliance on synthetic speech detection methods in production environments should be carefully evaluated based on anticipated distribution shifts.
语音合成检测问题已引起广泛关注,最近的方法在多个既定基准测试上的错误率较低。然而,低错误率在学术基准上能在多大程度上转化为更现实的条件?实际上,虽然训练集是固定在一个时间点的,但测试时的条件可能会相对于训练条件出现分布偏移,例如发言人特征、情感表达、语言和声学条件的改变,以及新型合成方法的出现。虽然一些现有数据集针对这些分布偏移的子集,但由于数据集之间源数据和合成系统的不一致性,系统分析仍然困难。这一困难因新型文本到语音(TTS)和振动系统的高速发展而进一步加剧,它们不断扩大了合成语音的多样性。为了能够对模型在分布偏移下的性能进行系统的基准测试,我们引入了ShiftySpeech,这是一个大规模的基准测试,包括超过3000小时的合成语音,涵盖7个源域、6个TTS系统、12个振动器和3种语言。ShiftySpeech专门设计用于评估模型在受控分布偏移下的泛化能力,同时确保广泛覆盖现代合成语音生成技术。它填补了当前基准测试的空白,支持精细的、受控的泛化稳健性分析。所有测试的分布偏移都会显著降级基于自我监督特征的最新检测方法的检测性能。总体而言,我们的研究结果表明,在生产环境中依赖合成语音检测方法应谨慎评估预期的分布偏移。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
这篇论文关注了合成语音检测的问题,尽管在几个既定的基准测试上取得了较低的误差率,但在更现实的条件下,这些低误差率能否得到实际应用仍存在疑问。训练集是固定不变的,但测试时的条件可能与训练条件存在分布偏移,如说话人特征、情感表达、语言和声学条件的改变,以及新合成方法的出现。为了对模型在分布偏移下的性能进行系统性评估,引入了ShiftySpeech基准测试,包含超过3000小时的合成语音数据,涵盖7个源域、6个文本到语音系统、12个vocoder和3种语言。ShiftySpeech专门设计用于评估模型在受控分布偏移下的泛化能力,同时确保覆盖现代合成语音生成技术的广泛范围。它填补了当前基准测试的空白,支持对泛化稳健性的精细控制分析。所有测试的分布偏移都会显著地降低基于自监督特征的最新检测方法的性能。总体而言,我们的研究结果表明,在预期存在分布偏移的生产环境中使用合成语音检测方法应谨慎评估。
关键见解
- 合成语音检测面临从学术基准测试到现实条件的应用转化问题。
- 训练集固定,但测试条件可能存在与训练条件的分布偏移。
- 分布偏移包括说话人特征、情感表达、语言和声学条件的改变,以及新合成方法的出现。
- 现有数据集只针对分布偏移的部分方面,缺乏系统性分析。
- 介绍了ShiftySpeech基准测试,包含大规模合成语音数据,支持精细控制的泛化分析。
- 测试分布偏移显著降低了最新检测方法的性能。
- 在预期存在分布偏移的生产环境中使用合成语音检测方法应谨慎评估。
点此查看论文截图


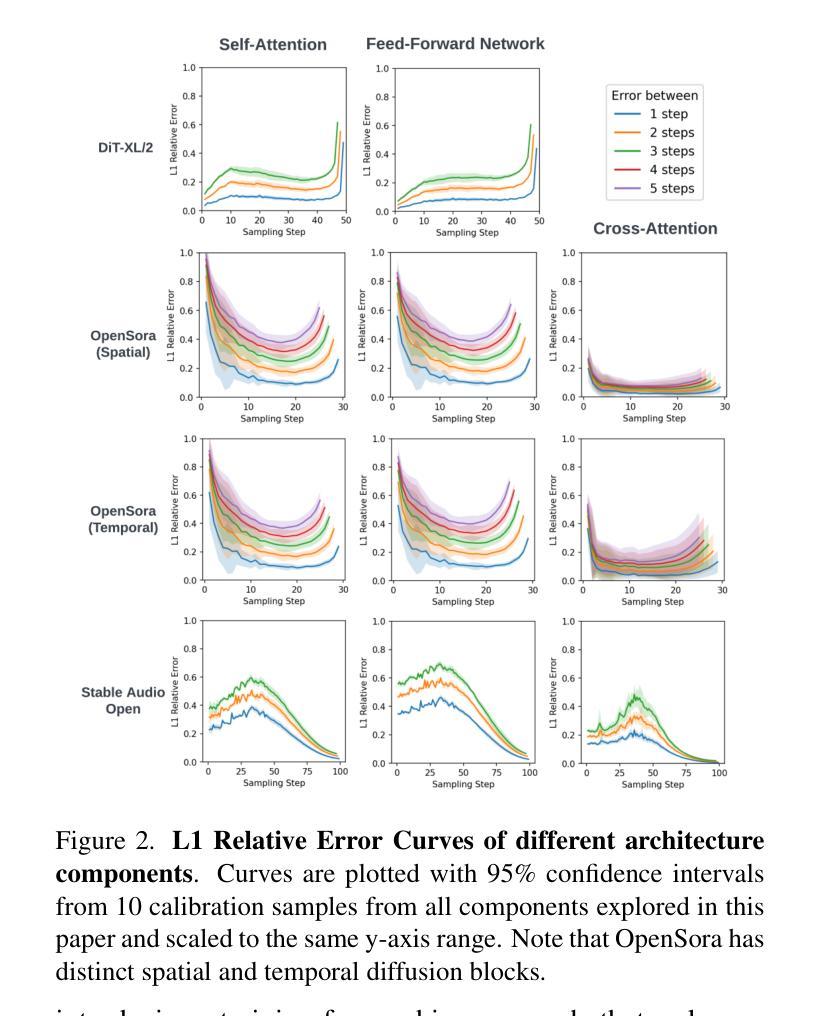
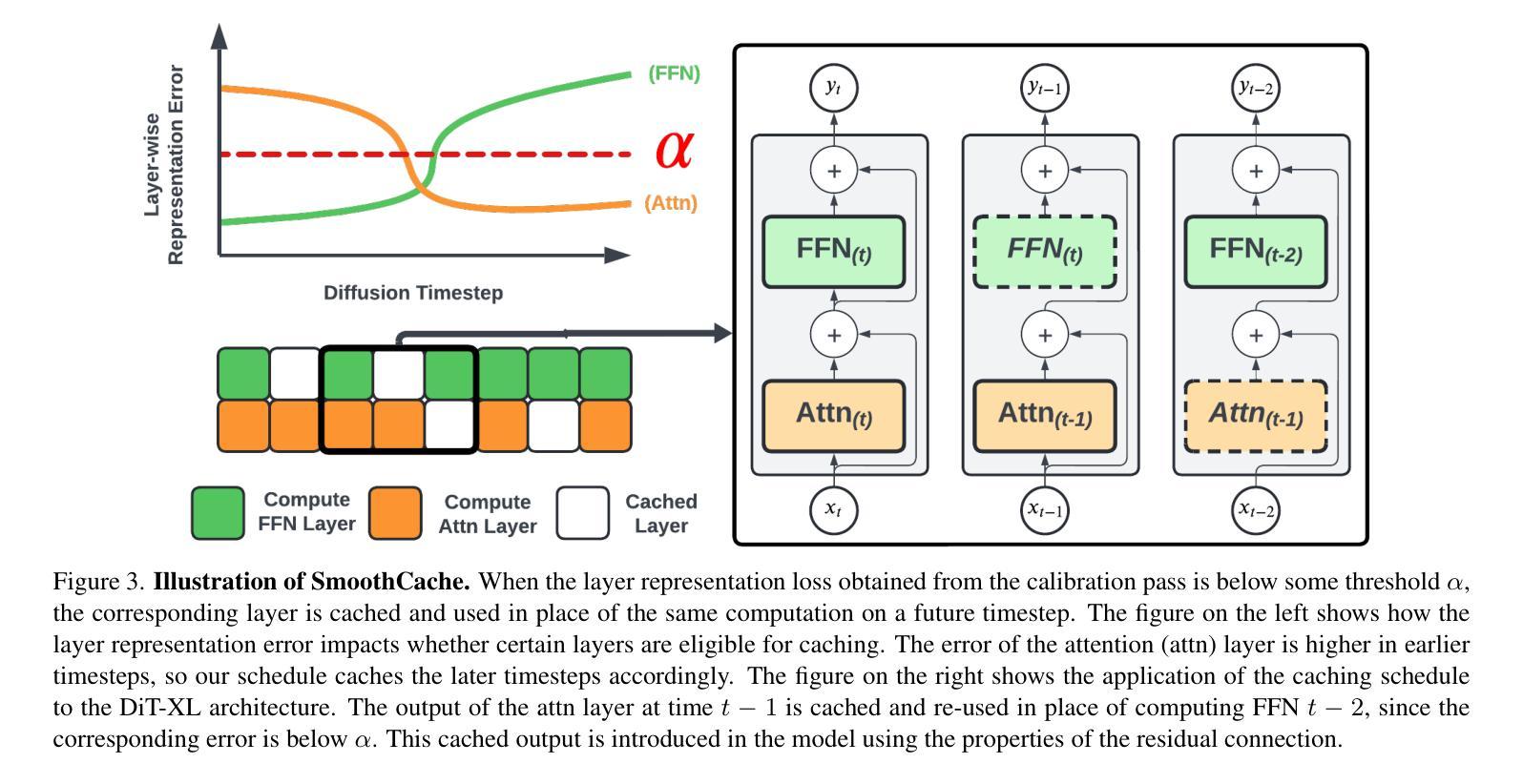
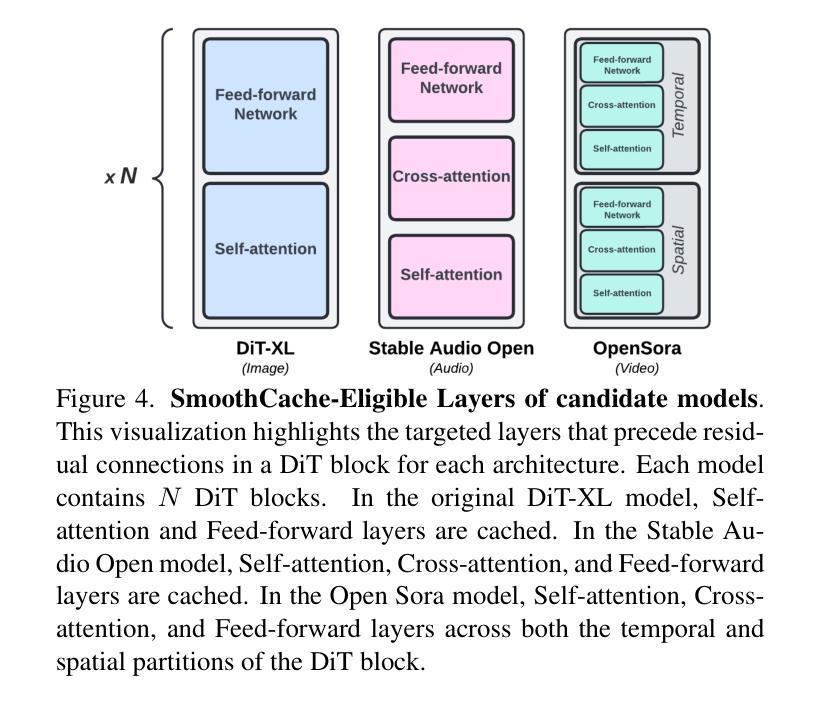
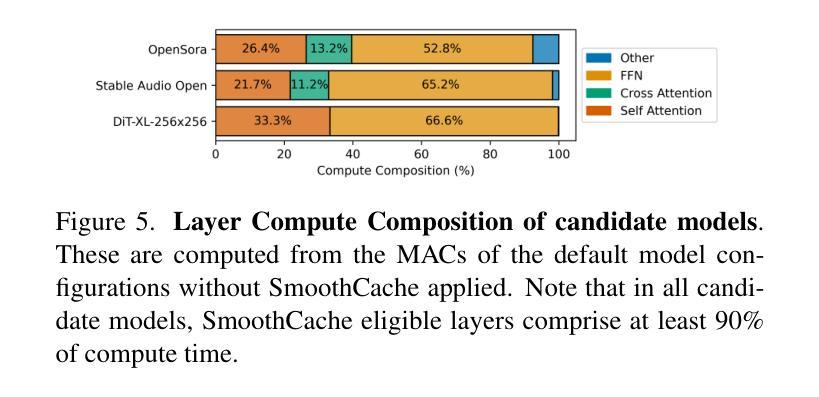
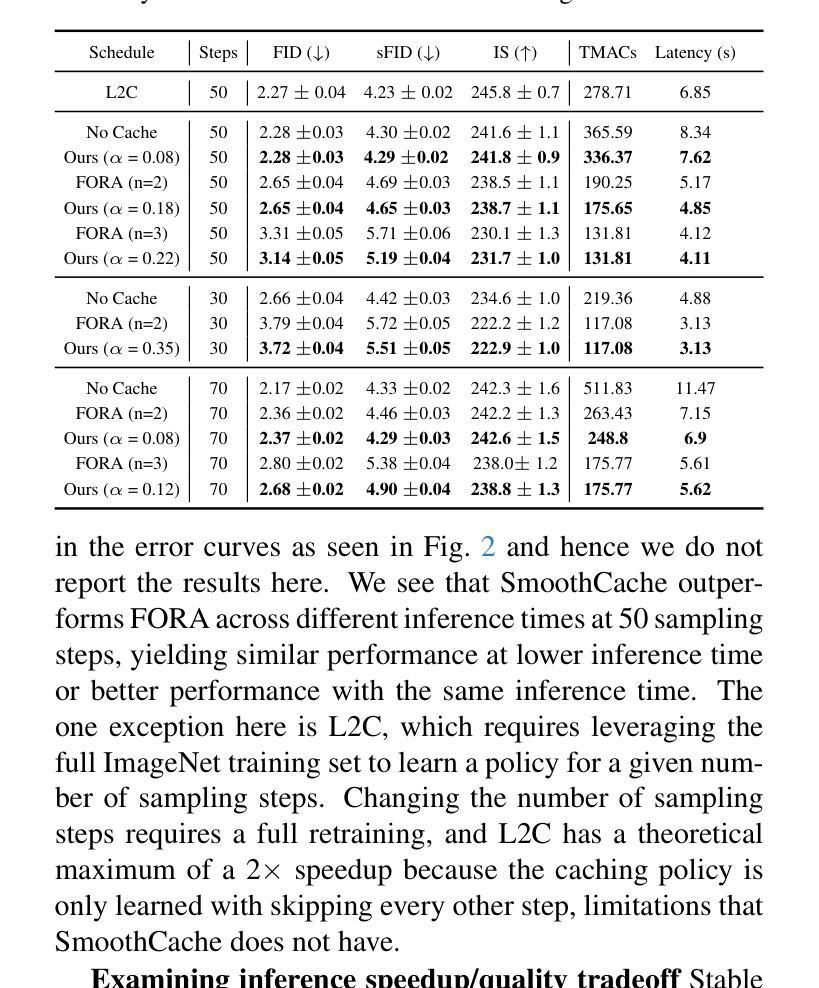
SmoothCache: A Universal Inference Acceleration Technique for Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Joseph Liu, Joshua Geddes, Ziyu Guo, Haomiao Jiang, Mahesh Kumar Nandwana
Diffusion Transformers (DiT) have emerged as powerful generative models for various tasks, including image, video, and speech synthesis. However, their inference process remains computationally expensive due to the repeated evaluation of resource-intensive attention and feed-forward modules. To address this, we introduce SmoothCache, a model-agnostic inference acceleration technique for DiT architectures. SmoothCache leverages the observed high similarity between layer outputs across adjacent diffusion timesteps. By analyzing layer-wise representation errors from a small calibration set, SmoothCache adaptively caches and reuses key features during inference. Our experiments demonstrate that SmoothCache achieves 8% to 71% speed up while maintaining or even improving generation quality across diverse modalities. We showcase its effectiveness on DiT-XL for image generation, Open-Sora for text-to-video, and Stable Audio Open for text-to-audio, highlighting its potential to enable real-time applications and broaden the accessibility of powerful DiT models.
扩散Transformer(DiT)已经成为包括图像、视频和语音合成在内的各种任务的强大生成模型。然而,由于需要重复评估资源密集型的注意力和前馈模块,它们的推理过程计算成本仍然很高。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SmoothCache,这是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时间步长之间层输出的高相似性。通过分析来自小型校准集的逐层表示误差,SmoothCache在推理过程中自适应地缓存和重复使用关键特征。我们的实验表明,SmoothCache在保持或甚至提高生成质量的同时,实现了8%到71%的提速,涉及多种模态。我们在图像生成的DiT-XL、文本到视频的Open-Sora以及文本到音频的Stable Audio Open上展示了其有效性,突出了其实现实时应用和扩大强大DiT模型可及性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code can be found at https://github.com/Roblox/SmoothCache. Accepted at CVPR eLVM workshop
摘要
扩散转换器(DiT)已作为图像、视频和语音合成等任务的强大生成模型出现。然而,由于其重复的注意力评估和正向传播模块的计算资源密集性,其推理过程计算成本仍然很高。为解决这一问题,我们推出了SmoothCache,这是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时间步长之间层输出之间的高相似性。通过分析来自小校准集的层表示误差,SmoothCache自适应地缓存和重用关键特征来进行推理。实验表明,SmoothCache在保持或甚至提高生成质量的同时,实现了8%至71%的提速。我们在DiT-XL图像生成、Open-Sora文本到视频以及Stable Audio Open文本到音频的应用中展示了其有效性,突显其实现实时应用和扩大强大DiT模型可及性的潜力。
关键见解
- 扩散转换器(DiT)是图像、视频和语音合成等领域的强大生成模型。
- 推理过程中,由于资源密集型模块的重复评估,DiT的计算成本仍然较高。
- SmoothCache是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。
- SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时间步长间层输出的高相似性。
- 通过分析来自小校准集的层表示误差,SmoothCache能够自适应地缓存和重用关键特征。
- 实验显示,SmoothCache实现了显著的推理速度提升,同时保持或提高了生成质量。
- SmoothCache在多种模态(如图像生成、文本到视频、文本到音频)中均表现出有效性,具有实现实时应用和扩大DiT模型潜力的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

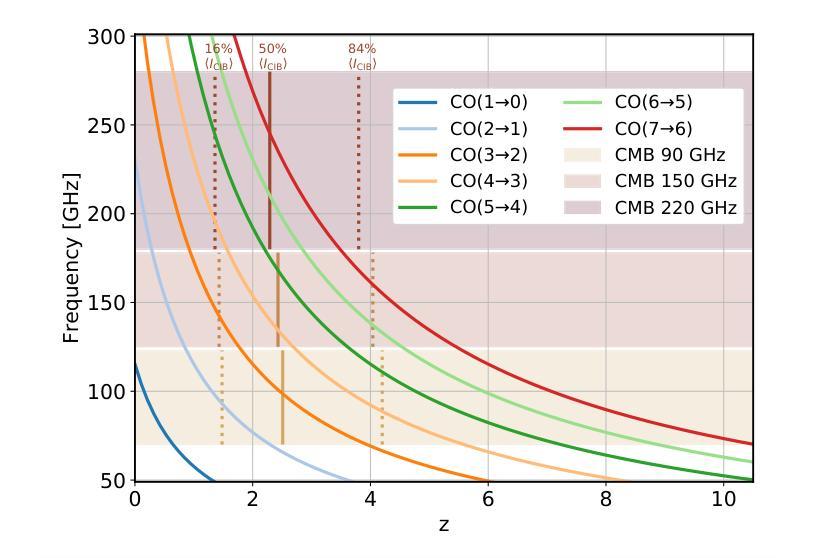
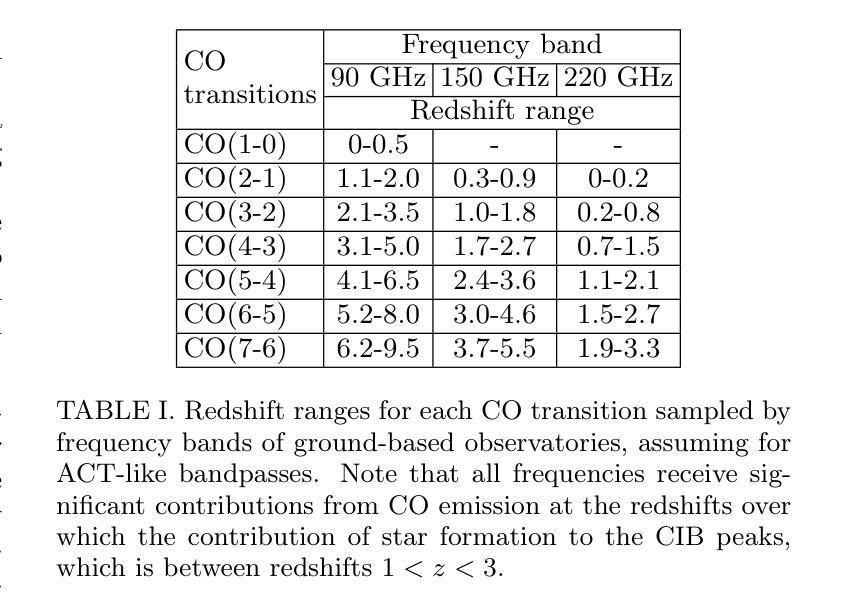
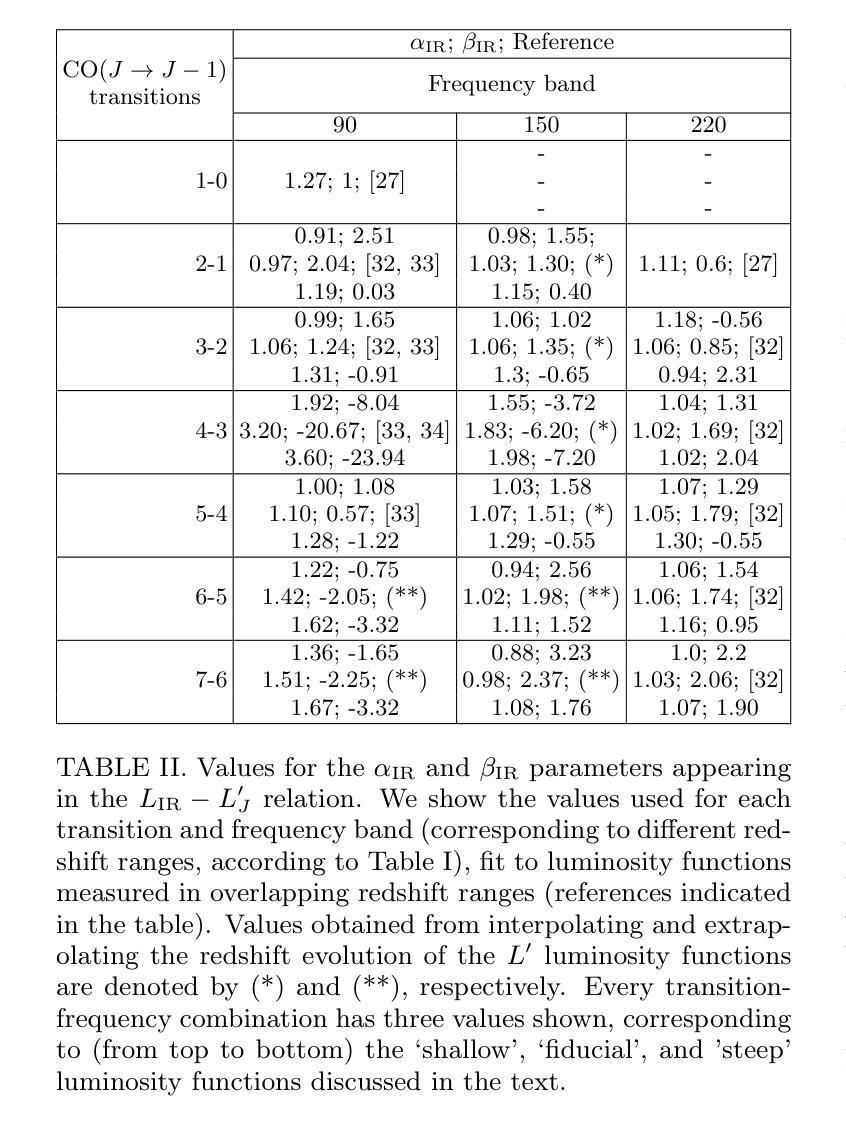
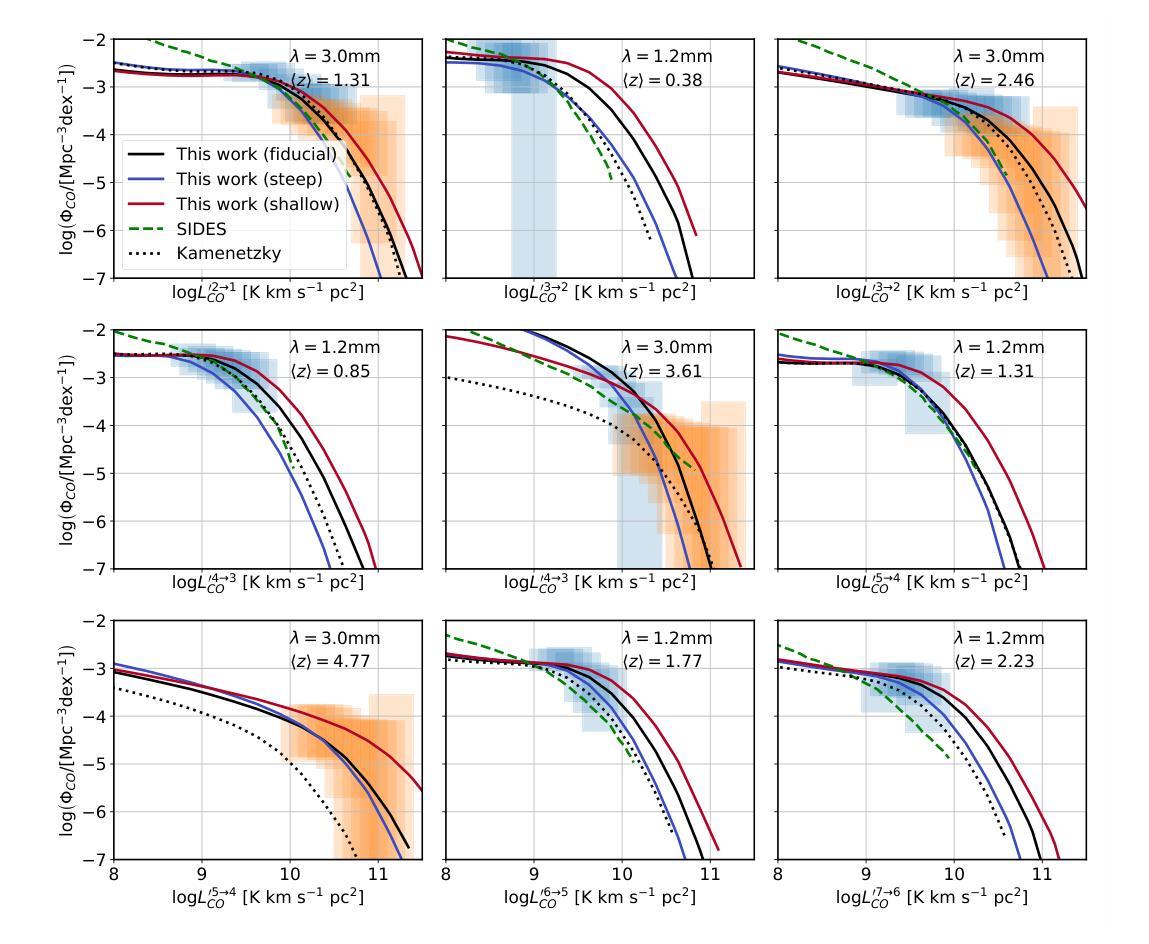
On the contributions of extragalactic CO emission lines to ground-based CMB observations
Authors:Nickolas Kokron, José Luis Bernal, Jo Dunkley
We investigate the potential of CO rotational lines at redshifts $z\sim 0-6$ being an appreciable source of extragalactic foreground anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background. Motivated by previous investigations, we specifically focus on the frequency bands and small scales probed by ground-based surveys. Using an empirical parameterization for the relation between the infrared luminosity of galaxies and their CO line luminosity, conditioned on sub-mm observations of CO luminosity functions from $J=1$ to $J=7$ at $\nu = {100,250}$ GHz, we explore how uncertainty in the CO luminosity function translates into uncertainty in the signature of CO emission in the CMB. We find that at $\ell = 3000$ the amplitude of the CO cross-correlation with the CIB could be detectable in an ACT-like experiment with 90, 150 and 220 GHz bands, even in the scenarios with the lowest amplitude consistent with sub-mm data. We also investigate, for the first time, the amplitude of the CO$\times$CIB correlation between different frequency bands and find that our model predicts that this signal could be the second-largest extragalactic foreground at certain wavelengths, behind the CIB cross-frequency spectrum. This implies current observations can potentially be used to constrain the bright end of CO luminosity functions, which are difficult to probe with current sub-mm telescopes due to the small volumes they survey. Our findings corroborate past results and have significant implications in template-based searches for CMB secondaries, such as the kinetic Sunyaev Zel’dovich effect, using the frequency-dependent high-$\ell$ TT power spectrum.
我们研究了在红移$z\sim 0-6$的CO转动线作为宇宙微波背景中可观测的星系前景各向异性来源的潜力。受之前研究的启发,我们特别关注地面勘测所探测的频率波段和小尺度范围。我们利用星系红外光度和其CO线光度之间的经验参数化关系,基于对$\nu = {100, 250}$ GHz频率下$J=1$至$J=7$的亚毫米CO光度函数的观测,探讨了CO光度函数的不确定性如何转化为对CMB中CO发射特征的不确定性。我们发现,在$\ell = 3000$时,CO与CIB的互相关幅度可能在ACT类似的实验中检测到,该实验具有90、150和220 GHz的波段,即使在与亚毫米数据一致的最低幅度情景下也是如此。我们还首次调查了不同频率波段之间CO×CIB关联的幅度,发现我们的模型预测,在某些波长上,这一信号可能是仅次于跨频CIB谱的第二大外星系前景。这意味着当前观测结果可用于约束明亮的CO光度函数末端,由于当前亚毫米望远镜所调查的体积较小,这使得这一末端难以探测。我们的研究结果证实了以往的结果,并在基于模板的寻找宇宙微波背景次要成分(如动态Sunyaev Zel’dovich效应)的研究中具有重要含义,尤其是在频率依赖的高$\ell$ TT功率谱分析中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14+3 pages, 8+2 figures. Reflects published version, with an additional post-publication revision which corrects a normalization error in the original work. Results have changed quantitatively
摘要
本文探讨了CO转动线在红移$z\sim 0-6$范围内作为宇宙微波背景中可观测的宇宙外前景各向异性来源的潜力。基于先前的调查,我们特别关注地面调查所探测的频率波段和小尺度范围。利用星系红外光度与其CO线光度之间的经验参数化关系,并结合亚毫米波段的CO光度函数观测数据,我们研究了CO光度函数的不确定性如何转化为对CMB中CO发射特征的不确定性。我们发现,在$\ell = 3000$时,CO与CIB的互相关可能在ACT类似实验中的90、150和220 GHz波段内检测到,即使在与亚毫米数据一致的最低振幅情景下。我们还首次探究了不同频率波段间CO×CIB关联的振幅,我们的模型预测,在某些波长下,这一信号可能是仅次于宇宙红外背景跨频谱的第二大外宇宙前景信号。这意味着当前观测结果可能用于约束CO光度函数的明亮端,由于当前亚毫米望远镜所调查的样本量较小,难以探测这部分信息。我们的研究结果验证了过去的发现,并对基于模板的CMB次级效应搜索(如动学Sunyaev Zel’dovich效应)具有重要影响,可通过频率依赖的高$\ell$ TT功率谱进行研究。
关键见解
- CO转动线在红移$z\sim 0-6$范围可成为宇宙微波背景中重要的前景各向异性来源。
- CO光度函数的不确定性会影响其在宇宙微波背景中的特征表现。
- 在一定条件下,CO与宇宙红外背景的互相关可能显著,成为第二大外宇宙前景信号。
- 当前观测可用于约束CO光度函数的明亮端,这部分信息由于亚毫米望远镜样本量小而难以通过现有手段探测。
- 研究结果验证了过去的发现,对基于模板的次级效应搜索有重要影响。
- 通过频率依赖的高$\ell$ TT功率谱,可以更好地研究宇宙微波背景的次级效应。
点此查看论文截图