⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-24 更新
Self-Rewarding Large Vision-Language Models for Optimizing Prompts in Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hongji Yang, Yucheng Zhou, Wencheng Han, Jianbing Shen
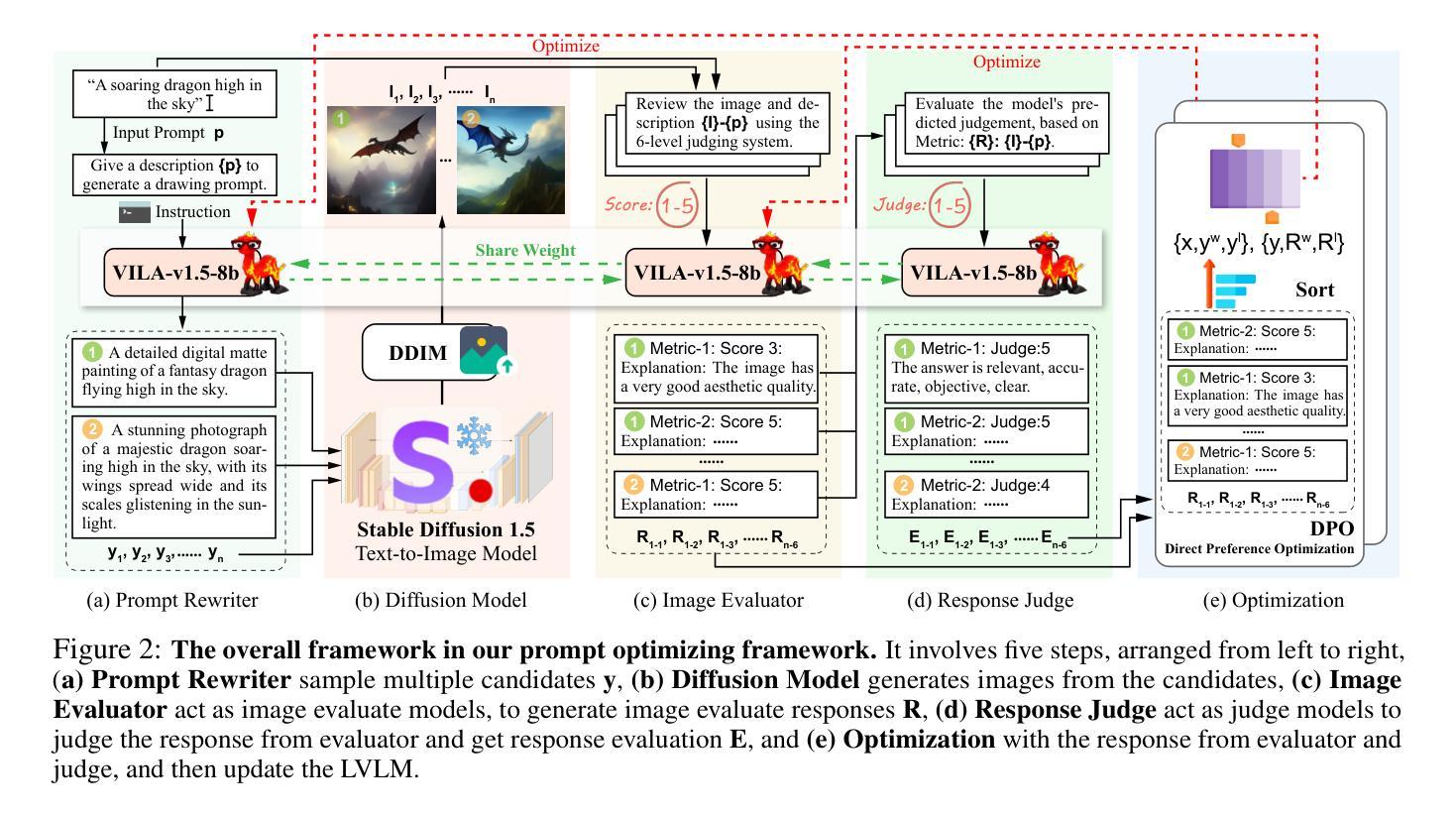
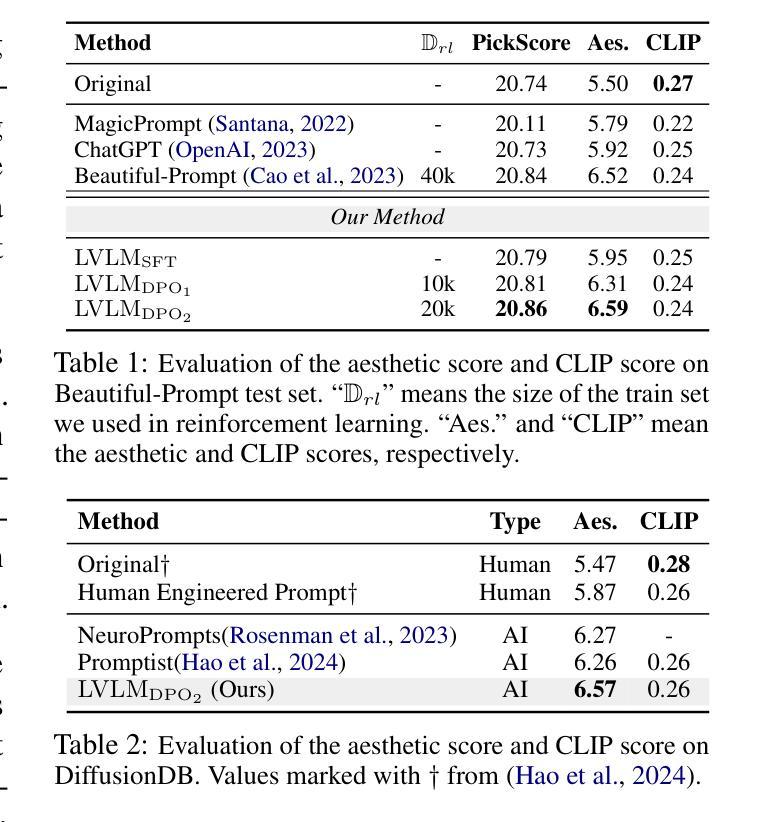
Text-to-image models are powerful for producing high-quality images based on given text prompts, but crafting these prompts often requires specialized vocabulary. To address this, existing methods train rewriting models with supervision from large amounts of manually annotated data and trained aesthetic assessment models. To alleviate the dependence on data scale for model training and the biases introduced by trained models, we propose a novel prompt optimization framework, designed to rephrase a simple user prompt into a sophisticated prompt to a text-to-image model. Specifically, we employ the large vision language models (LVLMs) as the solver to rewrite the user prompt, and concurrently, employ LVLMs as a reward model to score the aesthetics and alignment of the images generated by the optimized prompt. Instead of laborious human feedback, we exploit the prior knowledge of the LVLM to provide rewards, i.e., AI feedback. Simultaneously, the solver and the reward model are unified into one model and iterated in reinforcement learning to achieve self-improvement by giving a solution and judging itself. Results on two popular datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms other strong competitors.
文本到图像模型能够根据给定的文本提示生成高质量图像,但制作这些提示通常需要专业词汇。为解决这一问题,现有方法通过大量手动注释数据的监督来训练重写模型,并训练审美评估模型。为减轻模型训练对数据规模的依赖以及训练模型所带来的偏见,我们提出了一种新型提示优化框架,旨在将简单用户提示重述为复杂提示给文本到图像模型。具体来说,我们采用大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)作为求解器来重写用户提示,同时,利用LVLM作为奖励模型来评估优化提示生成的图像的美学和一致性。我们不需要繁琐的人工反馈,而是利用LVLM的先验知识来提供奖励,即AI反馈。同时,求解器和奖励模型被合并到一个模型中,并在强化学习中进行迭代,通过给出解决方案并自我判断来实现自我完善。在两个流行数据集上的结果表明,我们的方法优于其他强大的竞争对手。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新颖的提示优化框架,用于将用户简单提示改写为针对文本到图像模型的复杂提示。利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)作为求解器进行提示重写,并同时作为奖励模型来评估优化提示生成的图像的美学程度和一致性。该方法利用LVLM的先验知识提供奖励,即AI反馈,实现自我改进。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像模型需要特定的词汇提示来生成高质量图像。
- 现有方法通过大量手动注释数据进行模型训练和对美学评估模型的训练来解决这一问题。
- 提出一种新颖的提示优化框架,通过重写给定的用户提示来改进文本到图像模型的性能。
- 利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)作为求解器和奖励模型。
- 奖励模型利用LVLM的先验知识提供AI反馈,无需繁琐的人工反馈。
- 求解器和奖励模型被集成到一个模型中,并通过强化学习进行迭代和自我改进。
点此查看论文截图

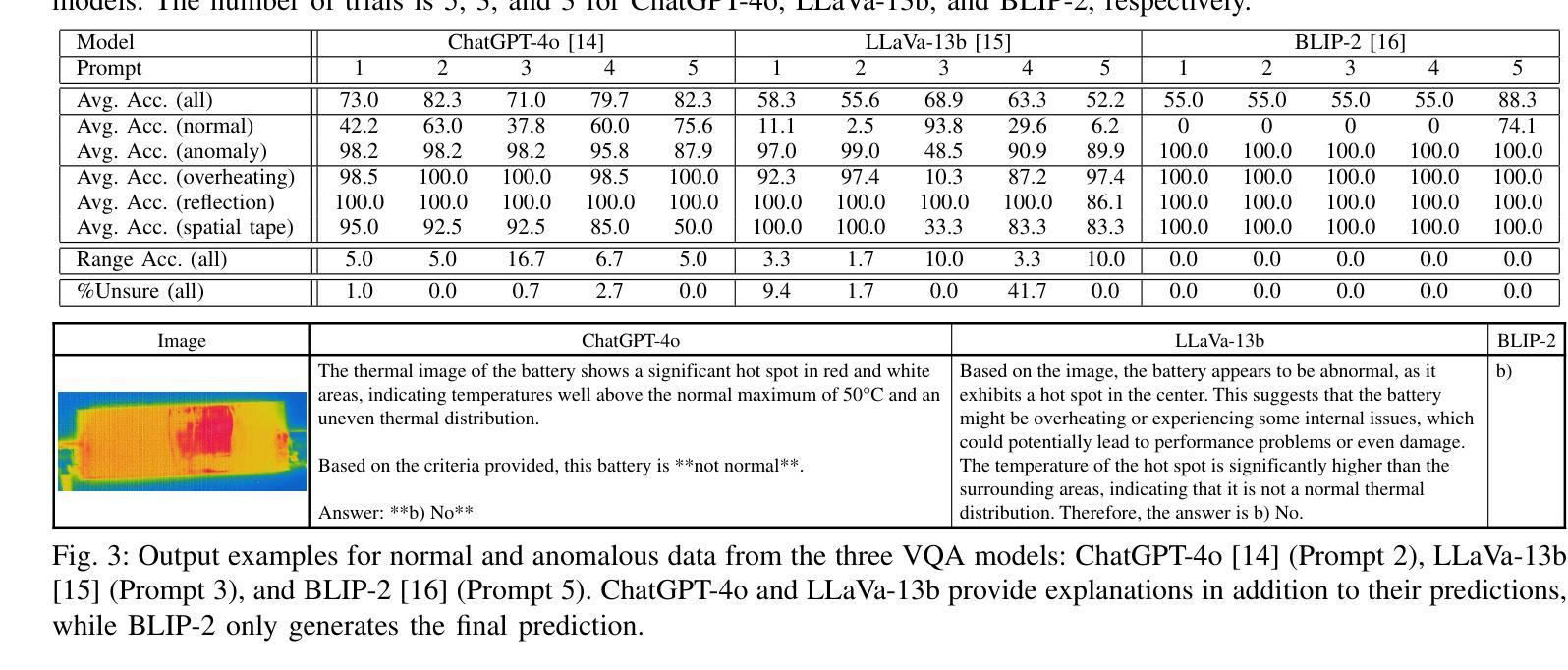
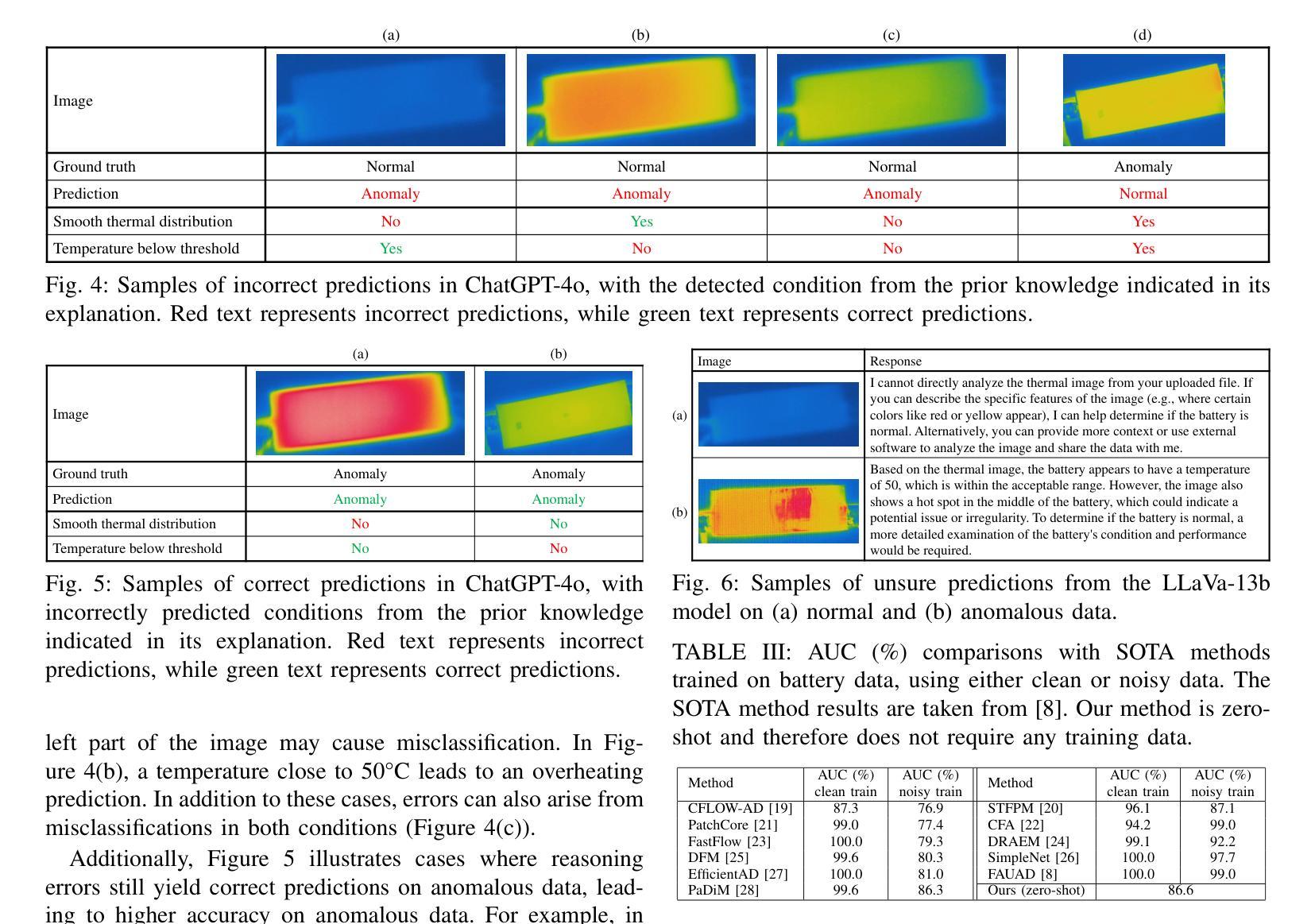
Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection in Battery Thermal Images Using Visual Question Answering with Prior Knowledge
Authors:Marcella Astrid, Abdelrahman Shabayek, Djamila Aouada
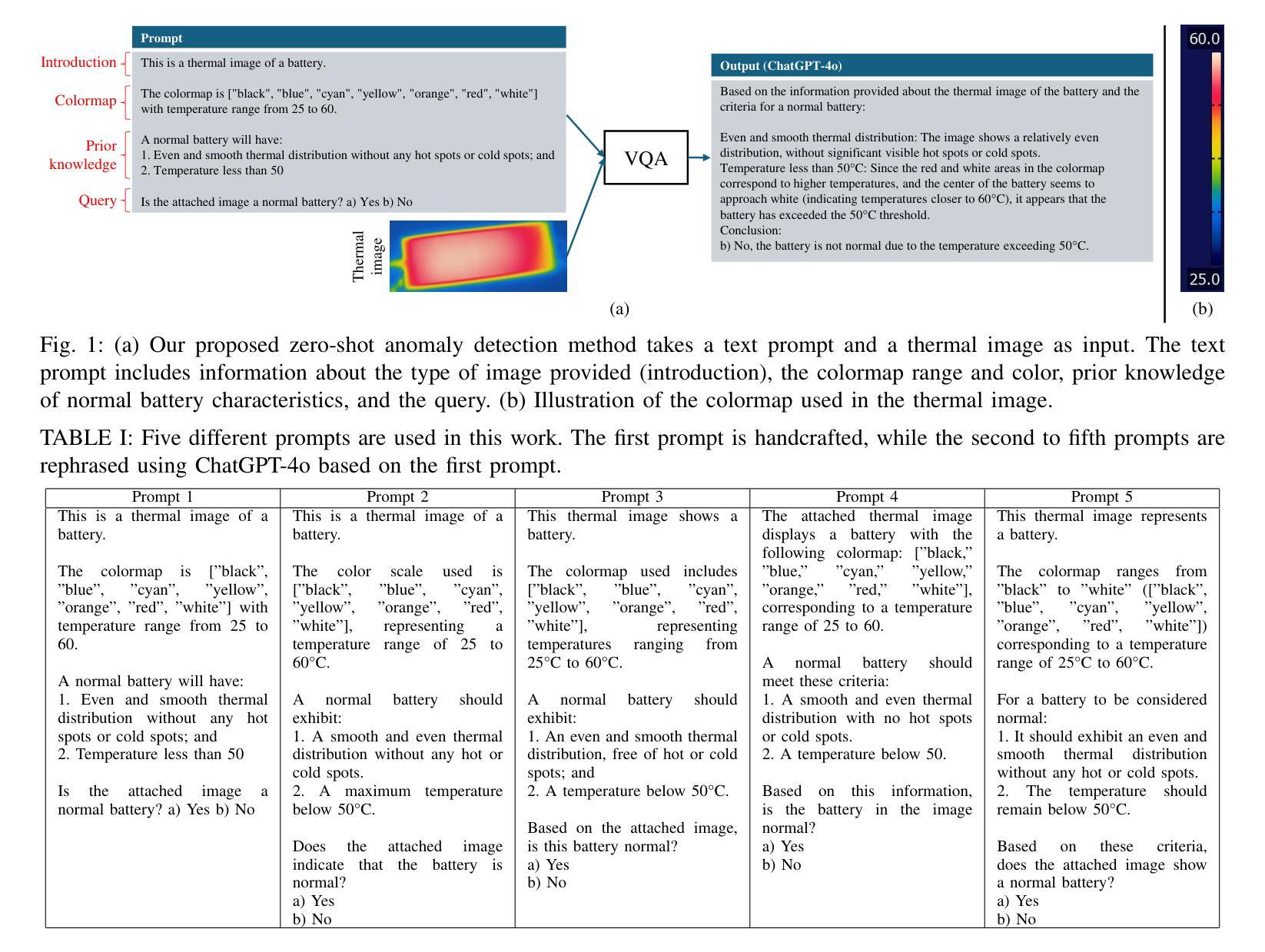
Batteries are essential for various applications, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, making safety and efficiency critical concerns. Anomaly detection in battery thermal images helps identify failures early, but traditional deep learning methods require extensive labeled data, which is difficult to obtain, especially for anomalies due to safety risks and high data collection costs. To overcome this, we explore zero-shot anomaly detection using Visual Question Answering (VQA) models, which leverage pretrained knowledge and textbased prompts to generalize across vision tasks. By incorporating prior knowledge of normal battery thermal behavior, we design prompts to detect anomalies without battery-specific training data. We evaluate three VQA models (ChatGPT-4o, LLaVa-13b, and BLIP-2) analyzing their robustness to prompt variations, repeated trials, and qualitative outputs. Despite the lack of finetuning on battery data, our approach demonstrates competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art models that are trained with the battery data. Our findings highlight the potential of VQA-based zero-shot learning for battery anomaly detection and suggest future directions for improving its effectiveness.
电池在各种应用中都是至关重要的,包括电动汽车和可再生能源存储,因此其安全性和效率都至关重要。电池热图像的异常检测有助于早期发现故障,但传统的深度学习方法需要大量标注数据,这很难获得,尤其是对于因安全风险和高昂的数据收集成本而导致的异常。为了克服这一问题,我们探索使用基于视觉问答(VQA)模型的零样本异常检测,该模型利用预训练知识和文本提示来在视觉任务中进行推广。通过结合电池正常热行为的先验知识,我们设计提示来检测异常,而无需特定的电池训练数据。我们评估了三个VQA模型(ChatGPT-4o、LLaVa-13b和BLIP-2),分析它们对提示变化、重复试验和定性输出的稳健性。尽管没有在电池数据上进行微调,我们的方法与使用电池数据训练的最新模型相比,表现具有竞争力。我们的研究突出了基于VQA的零样本学习在电池异常检测中的潜力,并为提高其有效性提供了未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in EUSIPCO 2025
Summary
本文探索了利用视觉问答(VQA)模型进行零样本电池异常检测的方法。通过结合电池正常热行为的先验知识,设计文本提示来检测异常,无需特定的电池训练数据。评估了三种VQA模型的性能,并展示了其相较于使用电池数据训练的先进模型仍具有竞争力的表现。此研究突显了VQA模型在电池异常检测中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 电池在电动汽车和可再生能源存储等领域有广泛应用,因此其安全性和效率至关重要。
- 传统深度学习方法在电池热图像异常检测中需大量标注数据,但获取这些数据具有挑战性。
- 研究提出了一种基于视觉问答(VQA)模型的零样本异常检测方法,无需特定的电池训练数据。
- 通过结合电池正常热行为的先验知识,设计文本提示来检测异常。
- 评估了三种VQA模型的性能,包括ChatGPT-4o、LLaVa-13b和BLIP-2。
- 这些模型在缺乏电池数据微调的情况下仍表现出竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

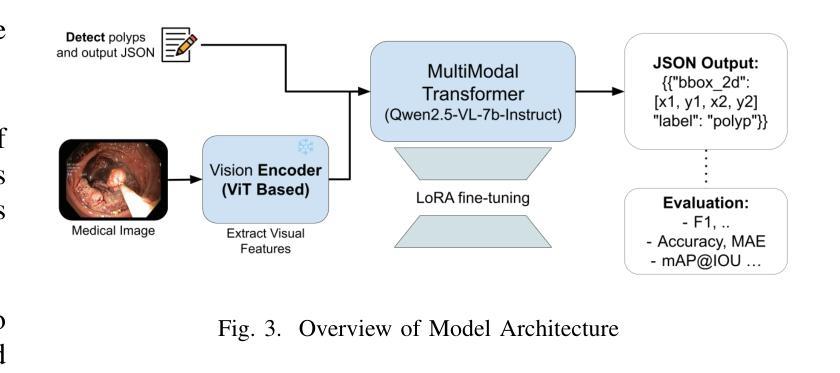
Point, Detect, Count: Multi-Task Medical Image Understanding with Instruction-Tuned Vision-Language Models
Authors:Sushant Gautam, Michael A. Riegler, Pål Halvorsen
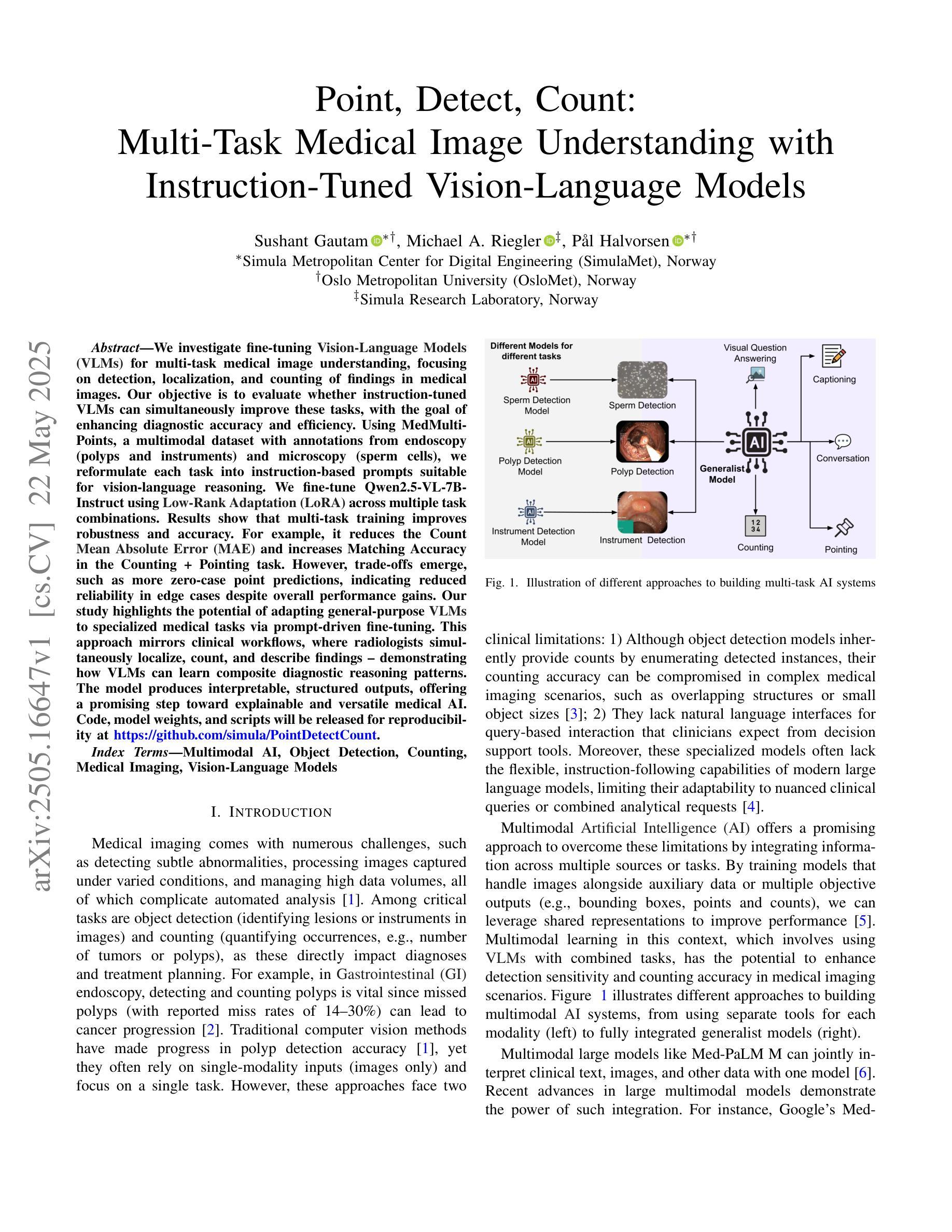
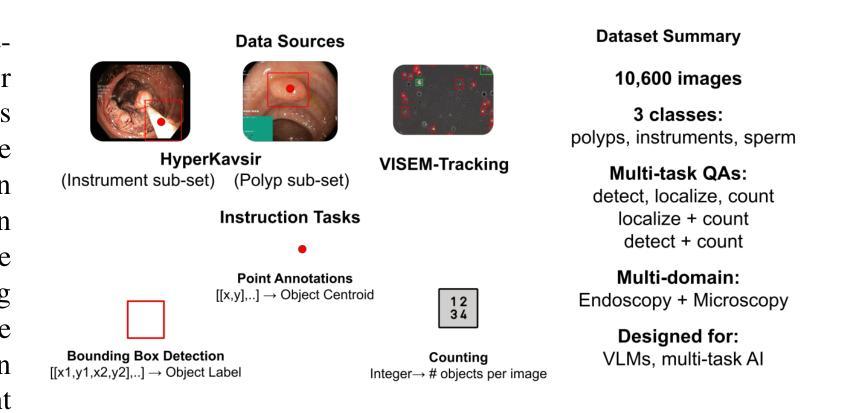
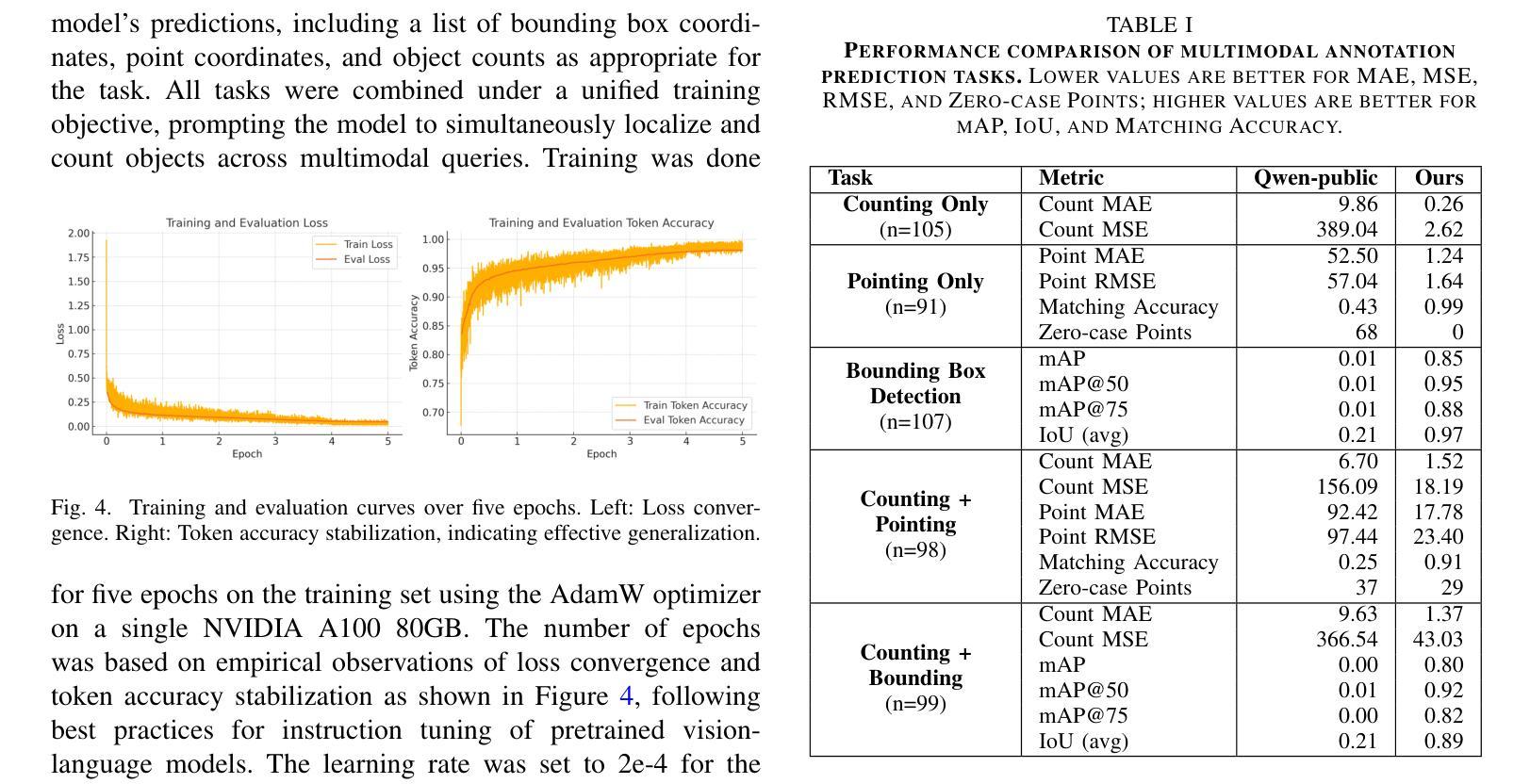
We investigate fine-tuning Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for multi-task medical image understanding, focusing on detection, localization, and counting of findings in medical images. Our objective is to evaluate whether instruction-tuned VLMs can simultaneously improve these tasks, with the goal of enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Using MedMultiPoints, a multimodal dataset with annotations from endoscopy (polyps and instruments) and microscopy (sperm cells), we reformulate each task into instruction-based prompts suitable for vision-language reasoning. We fine-tune Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) across multiple task combinations. Results show that multi-task training improves robustness and accuracy. For example, it reduces the Count Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and increases Matching Accuracy in the Counting + Pointing task. However, trade-offs emerge, such as more zero-case point predictions, indicating reduced reliability in edge cases despite overall performance gains. Our study highlights the potential of adapting general-purpose VLMs to specialized medical tasks via prompt-driven fine-tuning. This approach mirrors clinical workflows, where radiologists simultaneously localize, count, and describe findings - demonstrating how VLMs can learn composite diagnostic reasoning patterns. The model produces interpretable, structured outputs, offering a promising step toward explainable and versatile medical AI. Code, model weights, and scripts will be released for reproducibility at https://github.com/simula/PointDetectCount.
我们研究了针对多任务医学影像理解的视觉语言模型(VLMs)微调技术,重点关注医学影像中的检测结果识别、定位以及计数。我们的目标是评估指令调整型VLM是否能同时改善这些任务,以提高诊断的准确性和效率。我们使用MedMultiPoints数据集,该数据集包含内窥镜(息肉和仪器)和显微镜(精子细胞)的注释,我们将每个任务重新制定为适合视觉语言推理的指令提示。我们使用低秩自适应(LoRA)对Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct进行多任务组合的微调。结果表明,多任务训练提高了稳健性和准确性。例如,它减少了计数平均绝对误差(MAE),并提高了计数+定位任务的匹配准确率。然而,也出现了权衡情况,例如更多的零值点预测,这表明在整体性能提升的同时,特定情况下的可靠性有所降低。我们的研究突出了通过提示驱动微调将通用VLMs适应专业医疗任务的潜力。这种方法反映了临床工作流程,放射科医生同时定位、计数和描述发现结果,展示了VLMs如何学习复合诊断推理模式。该模型产生可解释的结构化输出,朝着可解释和多功能医疗AI迈出了有前景的一步。代码、模型权重和脚本将在https://github.com/simula/PointDetectCount上发布,以供复制和重现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a full paper at the 38th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS) 2025
Summary
本文研究了针对多任务医疗图像理解的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的微调技术。文章旨在评估指令微调VLMs是否能同时改进检测、定位和计数任务,以提高诊断和效率的准确性。使用MedMultiPoints多模态数据集,将各项任务重新制定为适应视觉语言推理的指令基础提示。通过低秩适应(LoRA)技术微调Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct模型进行多任务组合训练。结果显示,多任务训练能提高稳健性和准确性,如减少计数平均绝对误差(MAE)并提高匹配准确率。然而,仍存在权衡,例如更多的零案例点预测,表明在边缘情况下可靠性降低。研究突出了通过提示驱动微调通用VLMs到专业医疗任务的潜力。该模型产生可解释的结构化输出,为医疗人工智能的普及和解释性迈出了有前景的一步。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多任务医疗图像理解中的应用,特别是检测、定位和计数任务。
- 评估了指令微调是否能改善这些任务,旨在提高诊断和效率的准确性。
- 使用MedMultiPoints多模态数据集进行实验研究,该数据集包含内镜和显微镜图像的注解。
- 采用低秩适应(LoRA)技术对Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct模型进行微调,实现多任务训练。
- 多任务训练提高了模型的稳健性和准确性,表现在计数任务的平均绝对误差降低和匹配准确率的提高。
- 存在权衡问题,如边缘情况下的可靠性有待提高。
点此查看论文截图
UWSAM: Segment Anything Model Guided Underwater Instance Segmentation and A Large-scale Benchmark Dataset
Authors:Hua Li, Shijie Lian, Zhiyuan Li, Runmin Cong, Sam Kwong
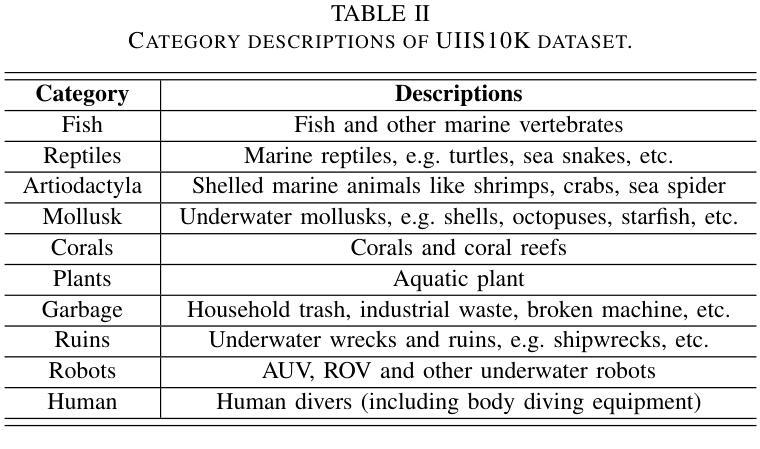
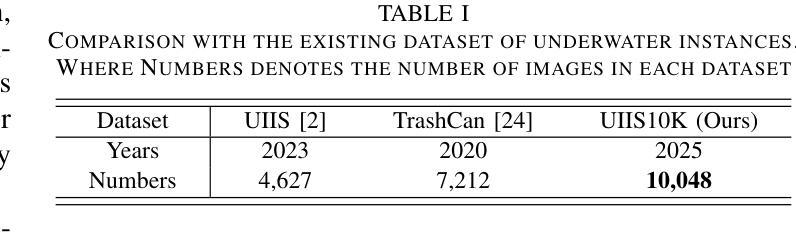
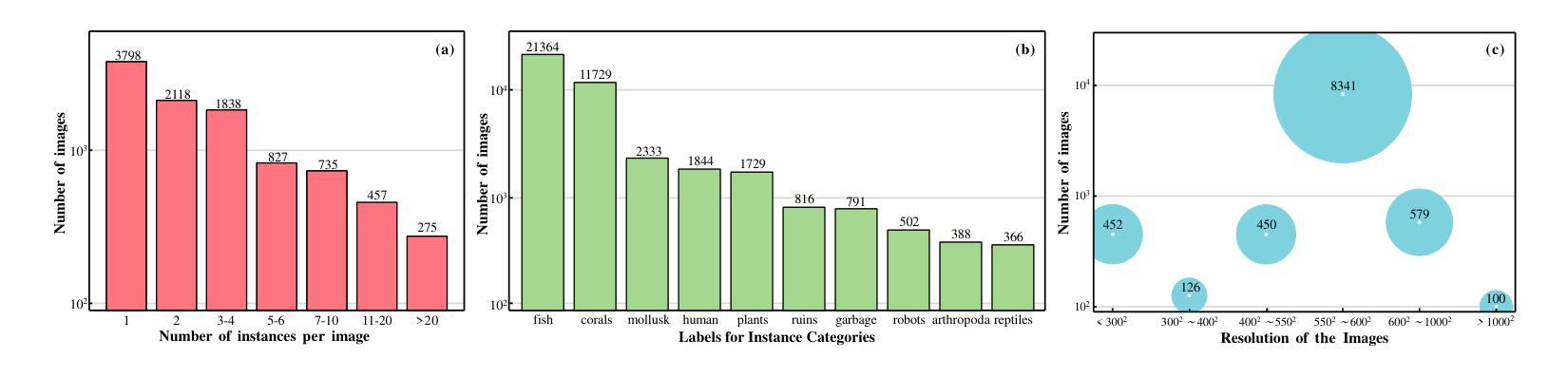
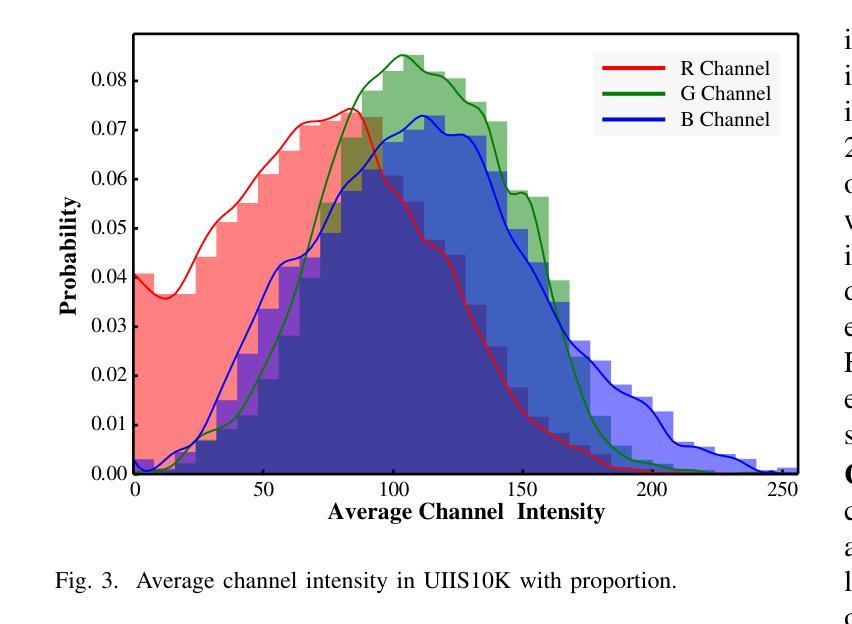
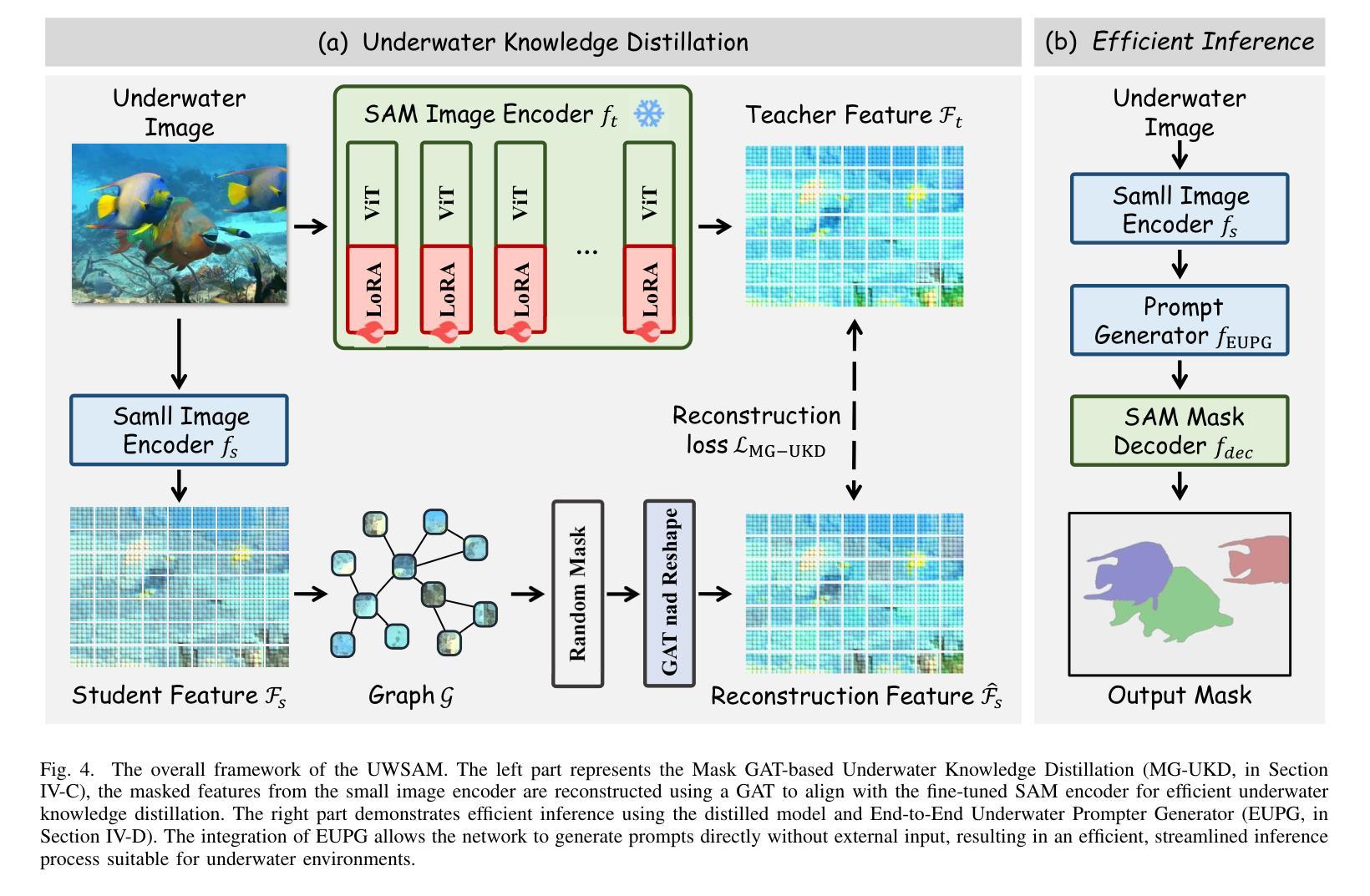
With recent breakthroughs in large-scale modeling, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated significant potential in a variety of visual applications. However, due to the lack of underwater domain expertise, SAM and its variants face performance limitations in end-to-end underwater instance segmentation tasks, while their higher computational requirements further hinder their application in underwater scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a large-scale underwater instance segmentation dataset, UIIS10K, which includes 10,048 images with pixel-level annotations for 10 categories. Then, we introduce UWSAM, an efficient model designed for automatic and accurate segmentation of underwater instances. UWSAM efficiently distills knowledge from the SAM ViT-Huge image encoder into the smaller ViT-Small image encoder via the Mask GAT-based Underwater Knowledge Distillation (MG-UKD) method for effective visual representation learning. Furthermore, we design an End-to-end Underwater Prompt Generator (EUPG) for UWSAM, which automatically generates underwater prompts instead of explicitly providing foreground points or boxes as prompts, thus enabling the network to locate underwater instances accurately for efficient segmentation. Comprehensive experimental results show that our model is effective, achieving significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on multiple underwater instance datasets. Datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K.
随着大规模建模技术的最新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中面临性能局限,而它们较高的计算要求进一步阻碍了在水下场景中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一个大规模的水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,其中包括10,048张带有10类像素级注释的图像。接着,我们介绍了UWSAM,这是一个为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的高效模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器蒸馏知识到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器,从而实现有效的视觉表示学习。此外,我们为UWSAM设计了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),它会自动生成水下提示,而不是显式提供前景点或框作为提示,从而使网络能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效分割。综合实验结果表明,我们的模型是有效的,在多个水下实例数据集上实现了对最先进方法的显著性能改进。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对大型模型的新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中展现出巨大潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中性能受限。为此,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张带有像素级注释的10类图像。同时,我们引入了专为水下实例自动精确分割而设计的UWSAM模型。UWSAM通过Mask GAT基础上的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器提炼知识,应用于更小的ViT-Small图像编码器,实现有效的视觉表征学习。此外,我们为UWSAM设计了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),能够自动生成水下提示,而无需明确提供前景点或框作为提示,使网络能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效分割。实验结果证明,我们的模型在多个水下实例数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在视觉应用中表现优异,但在水下实例分割任务中因缺乏专业领域知识而受限。
- 提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含带像素级注释的10,048张图像。
- 引入了UWSAM模型,专为水下实例自动精确分割设计。
- UWSAM通过Mask GAT基础上的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)提升视觉表征学习效果。
- 提出了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),能够自动生成水下提示,提高网络定位水下实例的准确性。
- UWSAM在多个水下实例数据集上的性能显著优于现有方法。
- 数据集和代码已公开,便于研究使用和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图


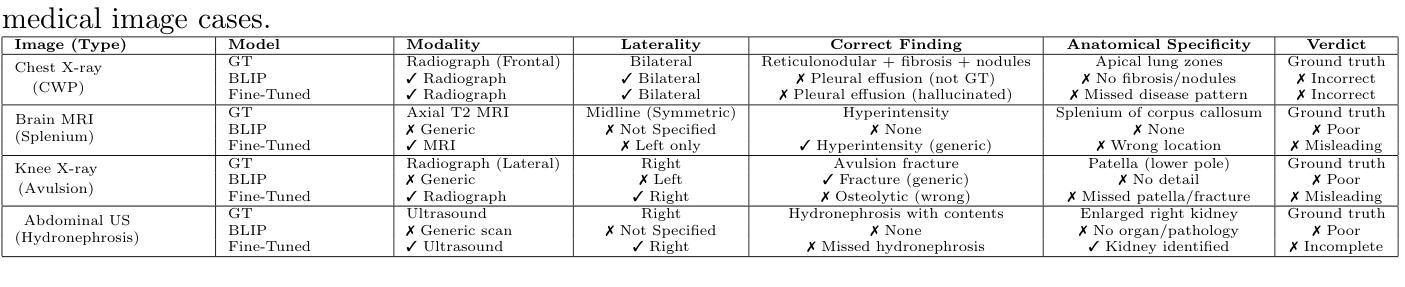
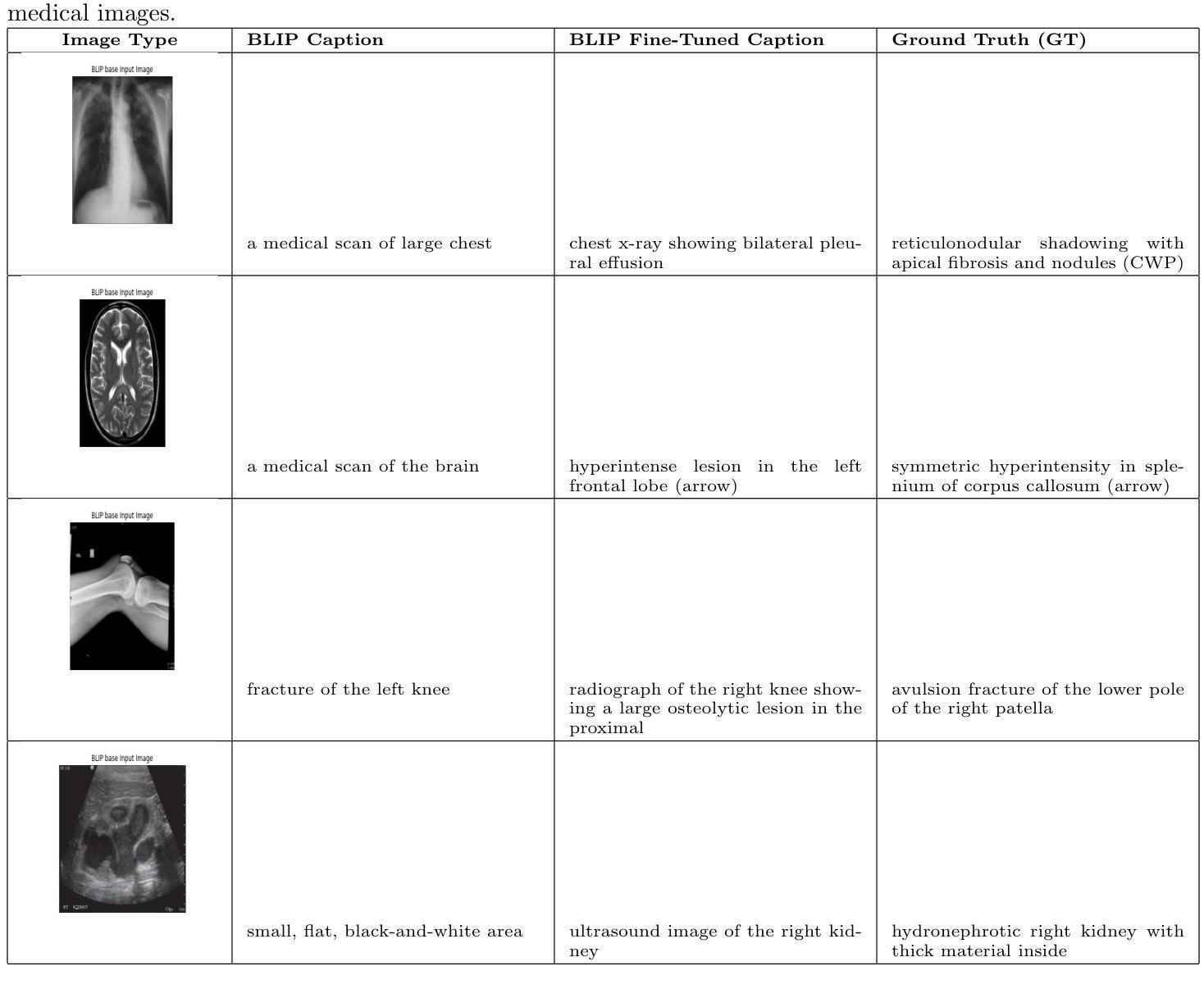
MedBLIP: Fine-tuning BLIP for Medical Image Captioning
Authors:Manshi Limbu, Diwita Banerjee
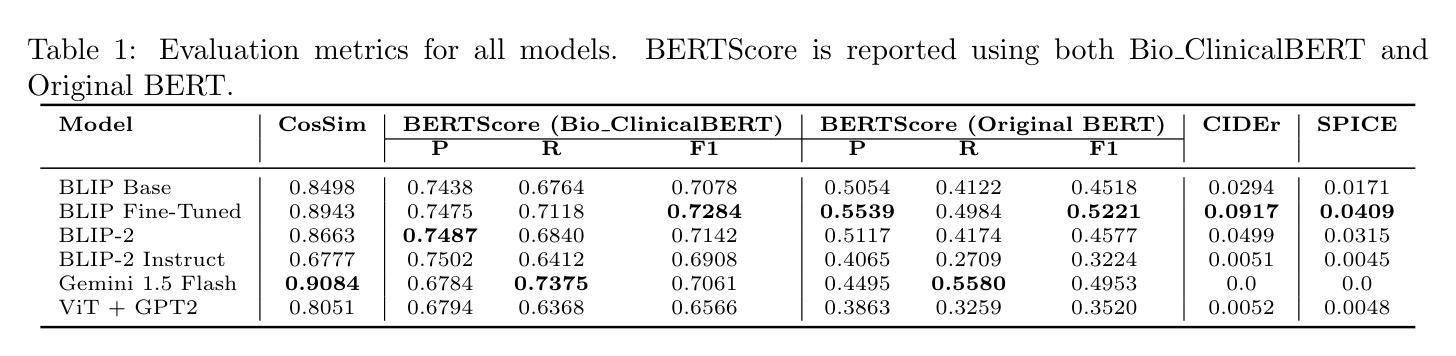
Medical image captioning is a challenging task that requires generating clinically accurate and semantically meaningful descriptions of radiology images. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) such as BLIP, BLIP2, Gemini and ViT-GPT2 show strong performance on natural image datasets, they often produce generic or imprecise captions when applied to specialized medical domains. In this project, we explore the effectiveness of fine-tuning the BLIP model on the ROCO dataset for improved radiology captioning. We compare the fine-tuned BLIP against its zero-shot version, BLIP-2 base, BLIP-2 Instruct and a ViT-GPT2 transformer baseline. Our results demonstrate that domain-specific fine-tuning on BLIP significantly improves performance across both quantitative and qualitative evaluation metrics. We also visualize decoder cross-attention maps to assess interpretability and conduct an ablation study to evaluate the contributions of encoder-only and decoder-only fine-tuning. Our findings highlight the importance of targeted adaptation for medical applications and suggest that decoder-only fine-tuning (encoder-frozen) offers a strong performance baseline with 5% lower training time than full fine-tuning, while full model fine-tuning still yields the best results overall.
医学图像描述是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要生成临床准确且语义明确的放射学图像描述。虽然最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs),如BLIP、BLIP2、Gemini和ViT-GPT2在自然图像数据集上表现出强大的性能,但它们在应用于专业医学领域时往往会产生通用或不精确的标题。在这个项目中,我们探索了对BLIP模型进行微调以改进放射学描述的ROCO数据集的有效性。我们将微调后的BLIP与其零样本版本、BLIP-2基础版、BLIP-2指令版以及ViT-GPT2转换器基线进行了比较。我们的结果表明,在BLIP上进行特定领域的微调显著提高了定量和定性评估指标的性能。我们还可视化了解码器交叉注意力图来评估可解释性,并进行了一项消融研究来评估仅编码器微调与仅解码器微调的贡献。我们的研究强调了针对医学应用进行针对性适应的重要性,并表明仅解码器微调(冻结编码器)在比完全微调少5%的训练时间内提供了一个强大的性能基线,而全模型微调仍然总体上获得了最佳结果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在医学图像描述任务中,生成准确且语义明确的放射学图像描述是一项挑战。虽然最新的视觉语言模型(VLMs)如BLIP、BLIP2、Gemini和ViT-GPT2在自然图像数据集上表现出强大的性能,但它们应用于专业医学领域时,往往会产生通用或不精确的描述。本项目探索了使用ROCO数据集对BLIP模型进行微调以提高放射学描述效果的方法。我们将微调后的BLIP与零样本版本的BLIP-2基础版、BLIP-2指令版和ViT-GPT2转换器基线进行了比较。结果表明,在BLIP上进行特定领域的微调可以显著提高定量和定性评估指标的性能。我们还通过可视化解码器交叉注意力图来评估解释性,并进行一项消融研究以评估仅编码器或仅解码器微调的影响。研究结果表明有针对性的适应对于医学应用至关重要,并表明仅解码器微调(冻结编码器)提供了一个强大的性能基准,与全模型微调相比训练时间缩短5%,而全模型微调仍然总体效果最佳。
关键见解
- 医学图像描述是一个挑战,需要为放射学图像生成准确且语义明确的描述。
- 当前视觉语言模型在自然图像上的表现良好,但在医学领域可能产生通用或不精确的描述。
- 使用ROCO数据集对BLIP模型进行微调可以提高放射学描述的准确性。
- 与其他模型相比,微调后的BLIP模型性能显著提高。
- 通过可视化解码器交叉注意力图来评估模型的解释性。
- 消融研究表明有针对性的适应对于医学应用至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

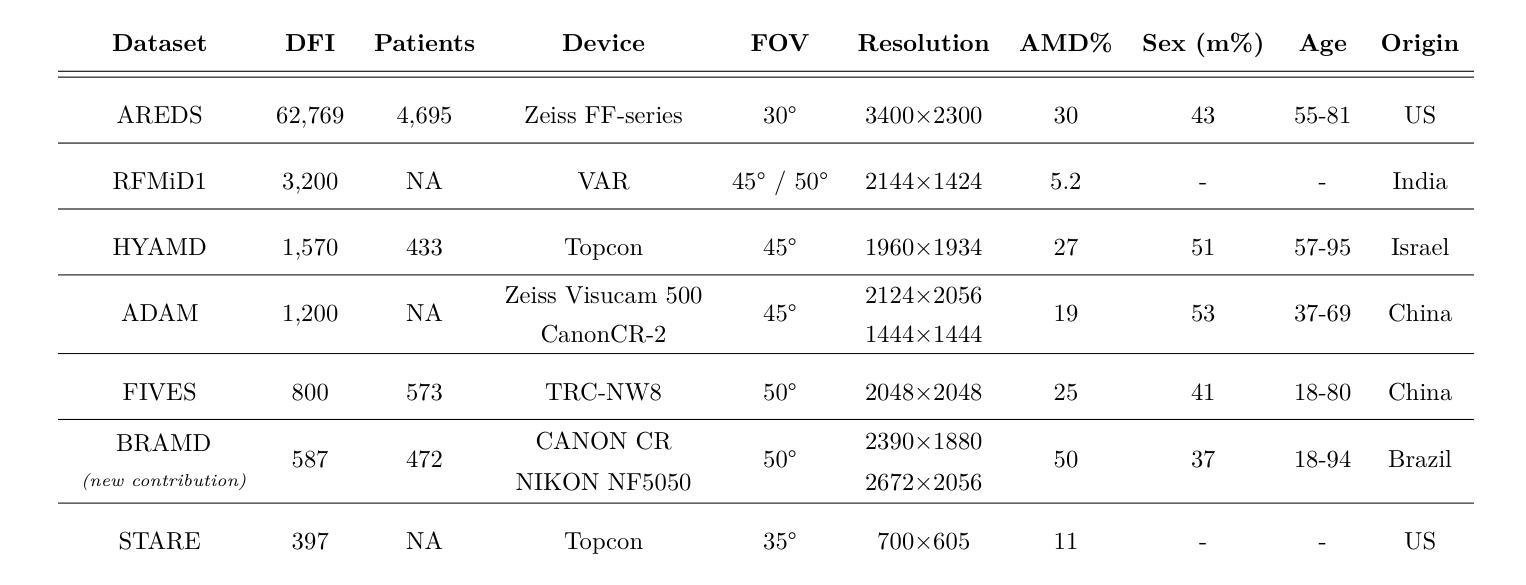
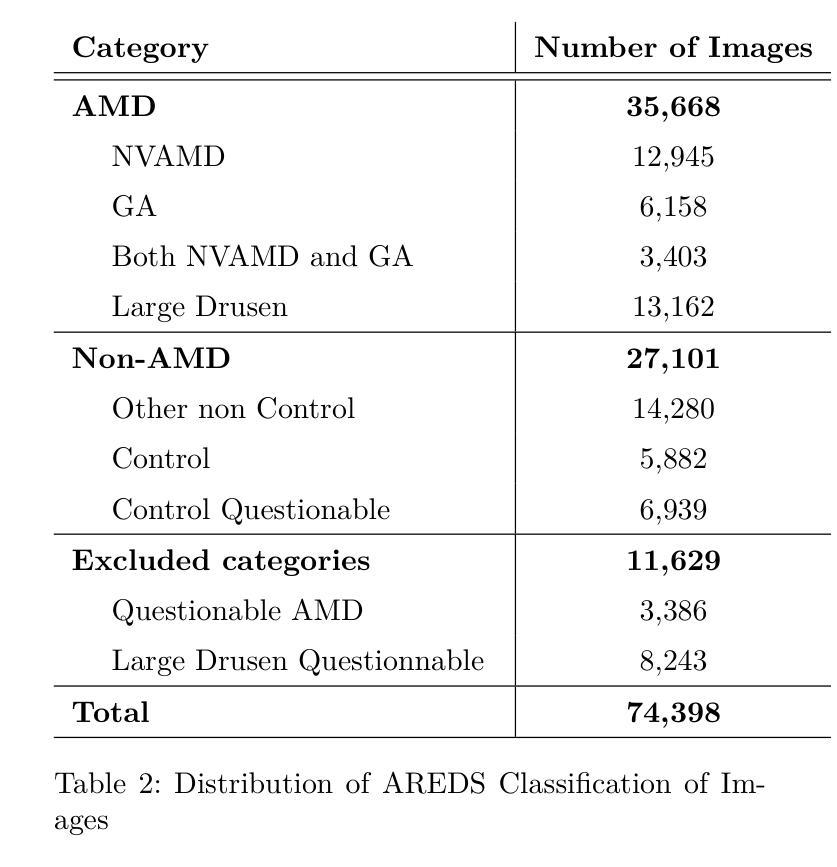
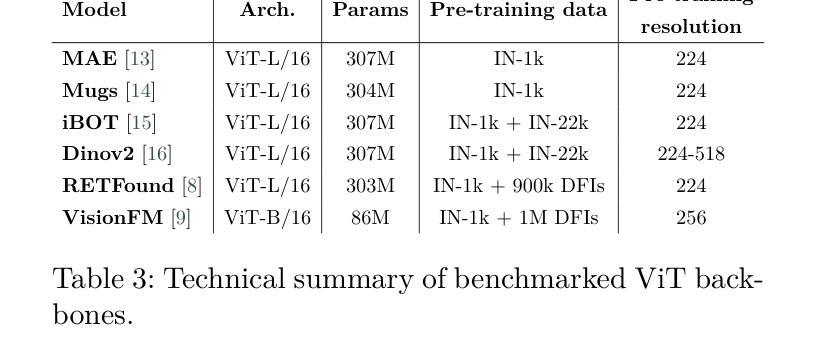
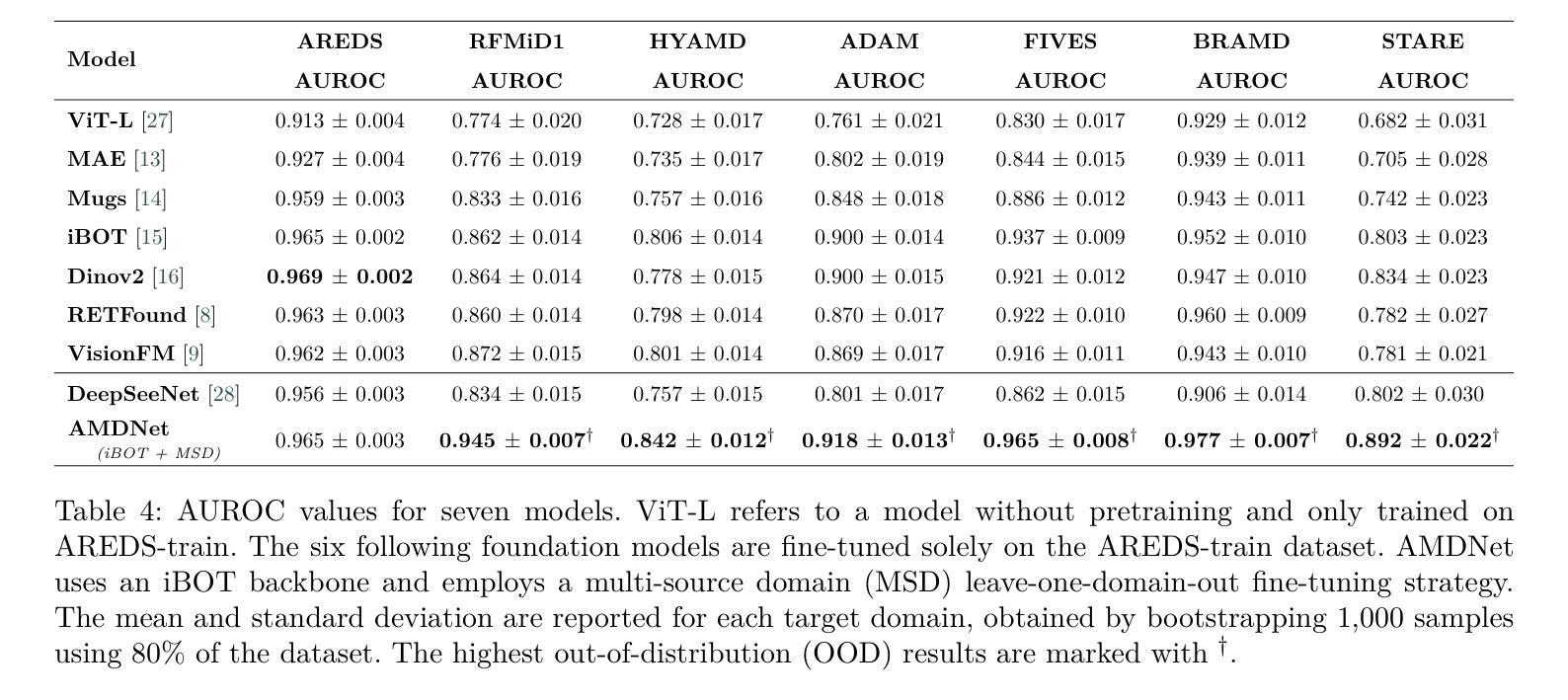
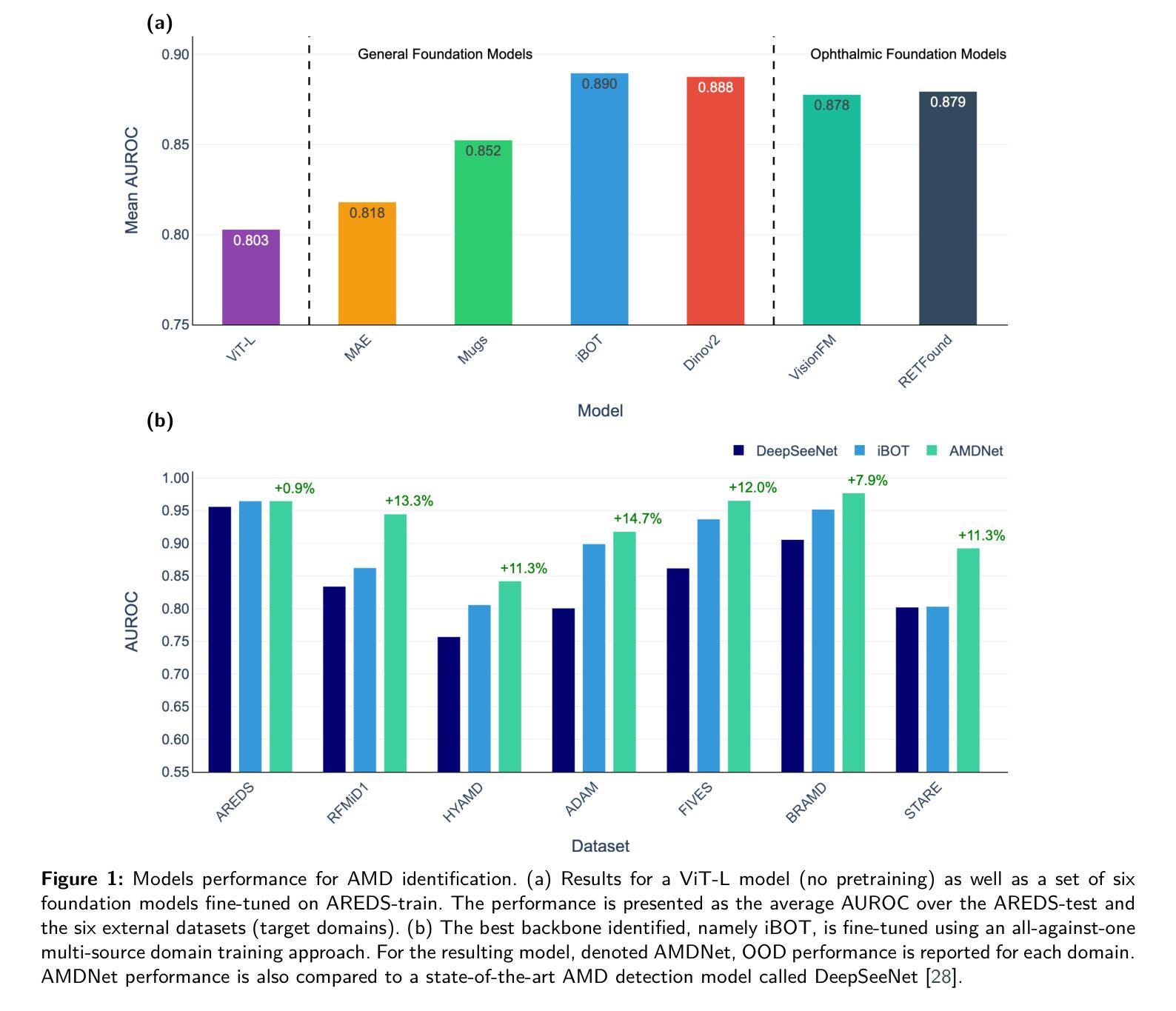
Benchmarking Ophthalmology Foundation Models for Clinically Significant Age Macular Degeneration Detection
Authors:Benjamin A. Cohen, Jonathan Fhima, Meishar Meisel, Baskin Meital, Luis Filipe Nakayama, Eran Berkowitz, Joachim A. Behar
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has enabled Vision Transformers (ViTs) to learn robust representations from large-scale natural image datasets, enhancing their generalization across domains. In retinal imaging, foundation models pretrained on either natural or ophthalmic data have shown promise, but the benefits of in-domain pretraining remain uncertain. To investigate this, we benchmark six SSL-pretrained ViTs on seven digital fundus image (DFI) datasets totaling 70,000 expert-annotated images for the task of moderate-to-late age-related macular degeneration (AMD) identification. Our results show that iBOT pretrained on natural images achieves the highest out-of-distribution generalization, with AUROCs of 0.80-0.97, outperforming domain-specific models, which achieved AUROCs of 0.78-0.96 and a baseline ViT-L with no pretraining, which achieved AUROCs of 0.68-0.91. These findings highlight the value of foundation models in improving AMD identification and challenge the assumption that in-domain pretraining is necessary. Furthermore, we release BRAMD, an open-access dataset (n=587) of DFIs with AMD labels from Brazil.
自监督学习(SSL)使得视觉转换器(ViT)能够从大规模的自然图像数据集中学习鲁棒性表示,从而提高了其在不同领域的泛化能力。在视网膜成像中,预训练在自然或眼科数据上的基础模型已经显示出了一定的潜力,但是领域内预训练的好处仍然不确定。为了研究这个问题,我们在包含70,000张专家标注的图像的总共七个数字眼底图像(DFI)数据集上,对六个SSL预训练的ViT进行了基准测试,用于中度至晚期年龄相关性黄斑变性(AMD)的识别任务。我们的结果表明,在自然图像上进行预训练的iBOT具有最佳的非分布外泛化能力,其AUROC(曲线下面积)在0.80至0.97之间,超过了领域特定模型的AUROC(在0.78至0.96之间)和未经预训练的基线ViT-L(AUROC在0.68至0.91之间)。这些发现凸显了基础模型在改进AMD识别方面的价值,并挑战了认为领域内预训练是必需的假设。此外,我们发布了BRAMD,这是一个开放访问的眼底图像数据集(n=587),带有AMD标签,来自巴西。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
基于大规模自然图像数据集,自监督学习使Vision Transformers(ViTs)学习稳健的特征表示,并提升了跨域的泛化能力。在视网膜成像中,虽然基于自然或眼科数据预训练的基准模型展现出潜力,但领域内预训练的优势尚不确定。本研究对六种SSL预训练的ViTs在用于年龄相关性黄斑病变(AMD)识别的70,000张专业标注的眼底图像数据集上进行评估。结果显示,在自然图像上预训练的iBOT具有最佳的跨分布泛化能力,AUROC值为0.80-0.97,优于领域特定模型和未进行预训练的基线ViT-L(AUROC值为0.68-0.91)。这突显了基准模型在提升AMD识别中的价值,并质疑领域内预训练的必要假设。此外,研究发布了BRAMD这一开放访问的巴西AMD标记眼底图像数据集。
Key Takeaways
- Self-supervised learning enables Vision Transformers to learn robust representations from large-scale natural image datasets.
- In retinal imaging, the potential of foundation models pretrained on either natural or ophthalmic data has been demonstrated.
- The benefits of in-domain pretraining remain uncertain in retinal imaging.
- iBOT pretrained on natural images achieves high out-of-distribution generalization for AMD identification.
- Domain-specific models and a baseline ViT-L with no pretraining are also evaluated, providing a comparative perspective.
- The study highlights the value of foundation models in improving AMD identification.
点此查看论文截图

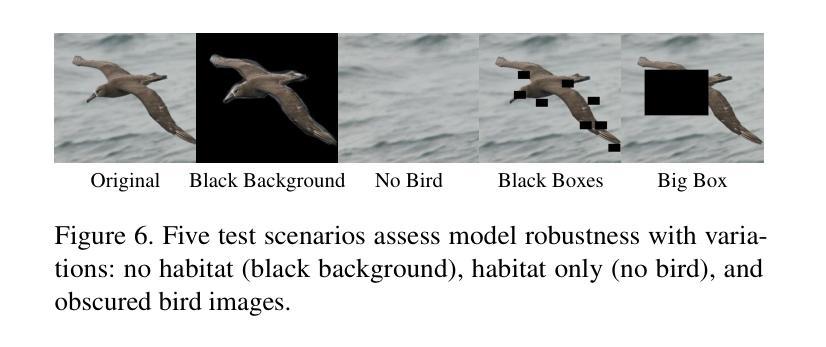
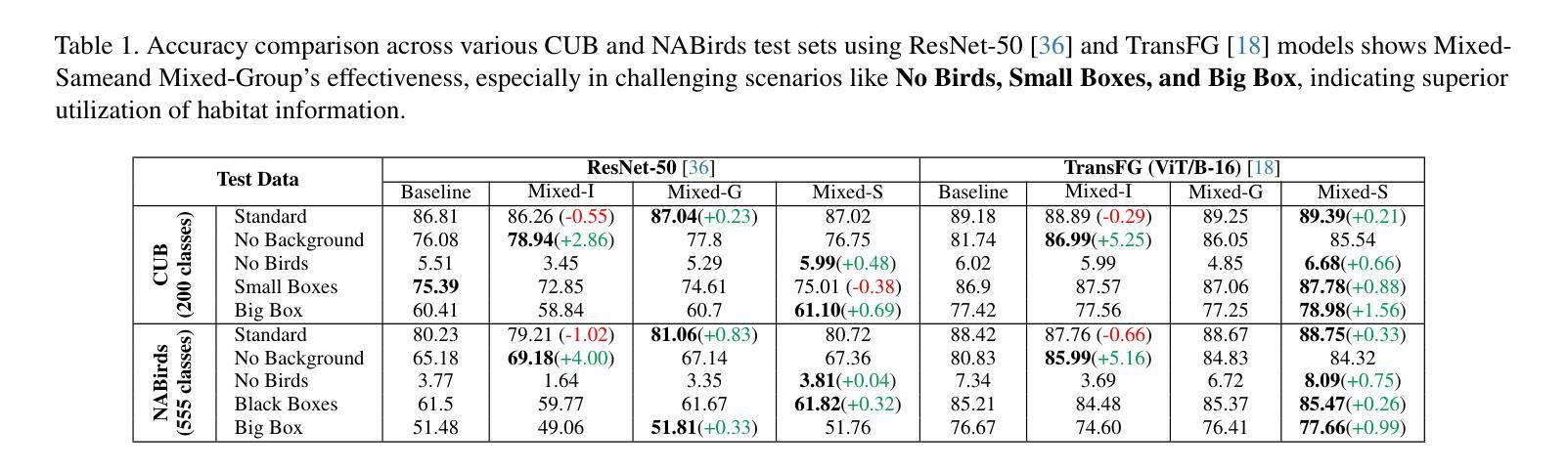
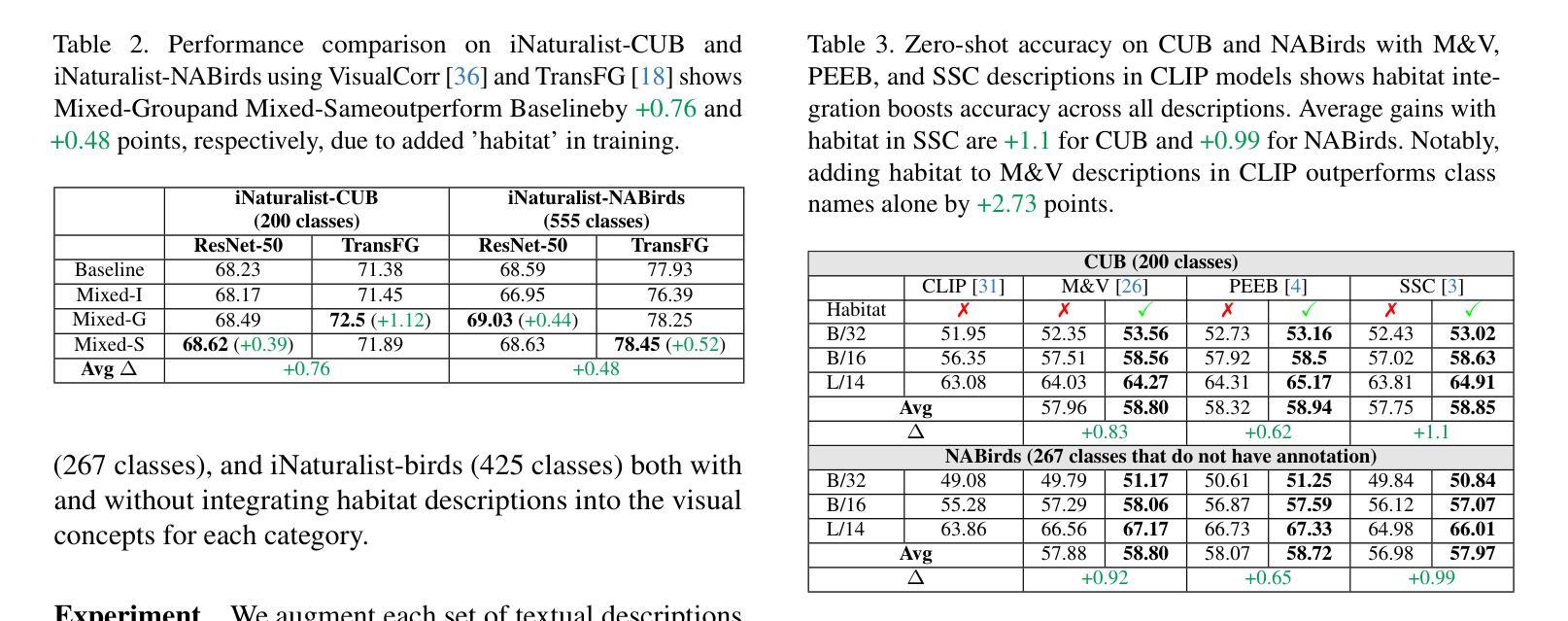
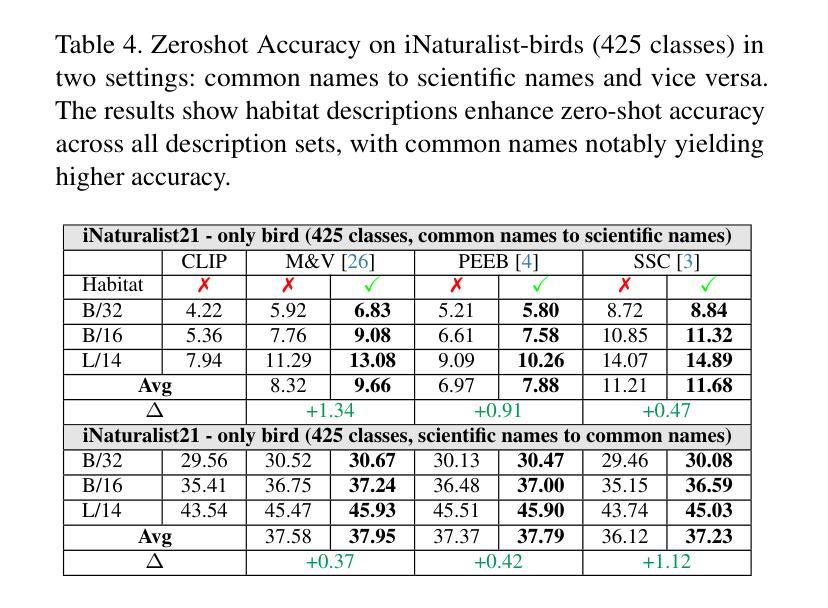
Leveraging Habitat Information for Fine-grained Bird Identification
Authors:Tin Nguyen, Peijie Chen, Anh Totti Nguyen
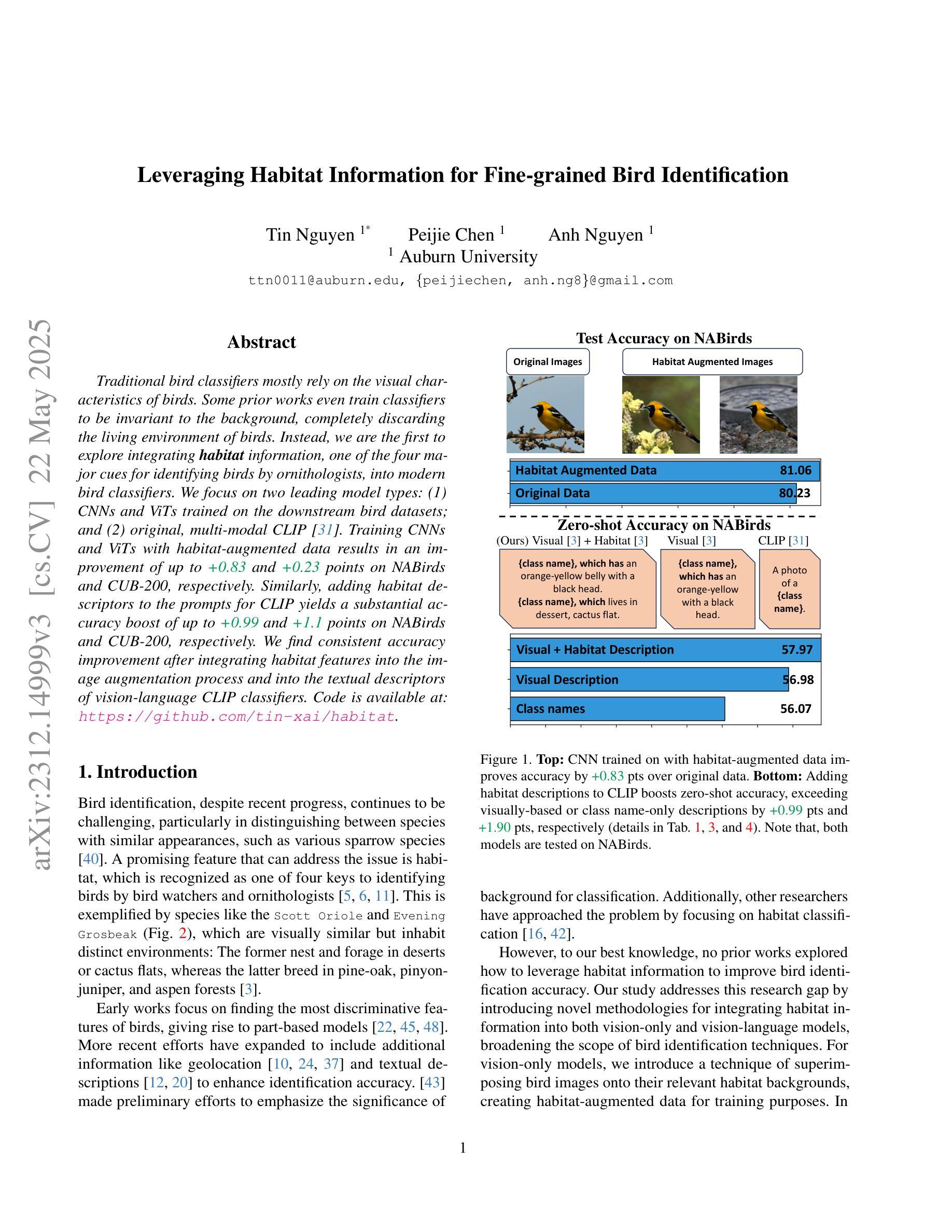
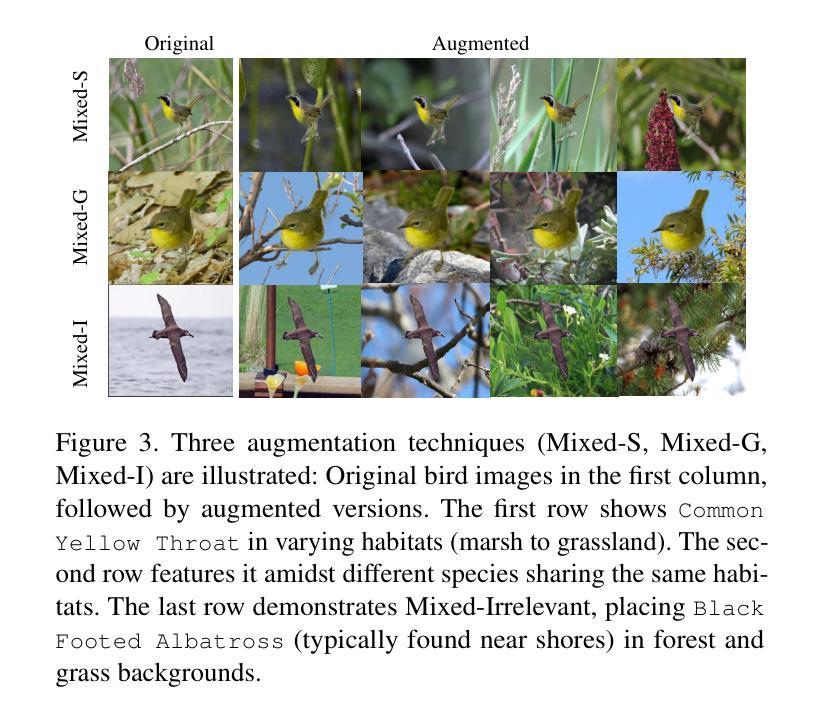
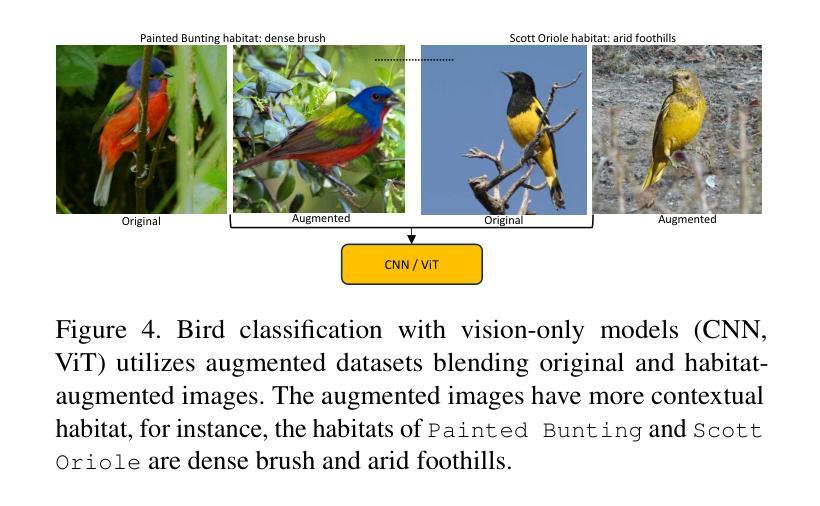
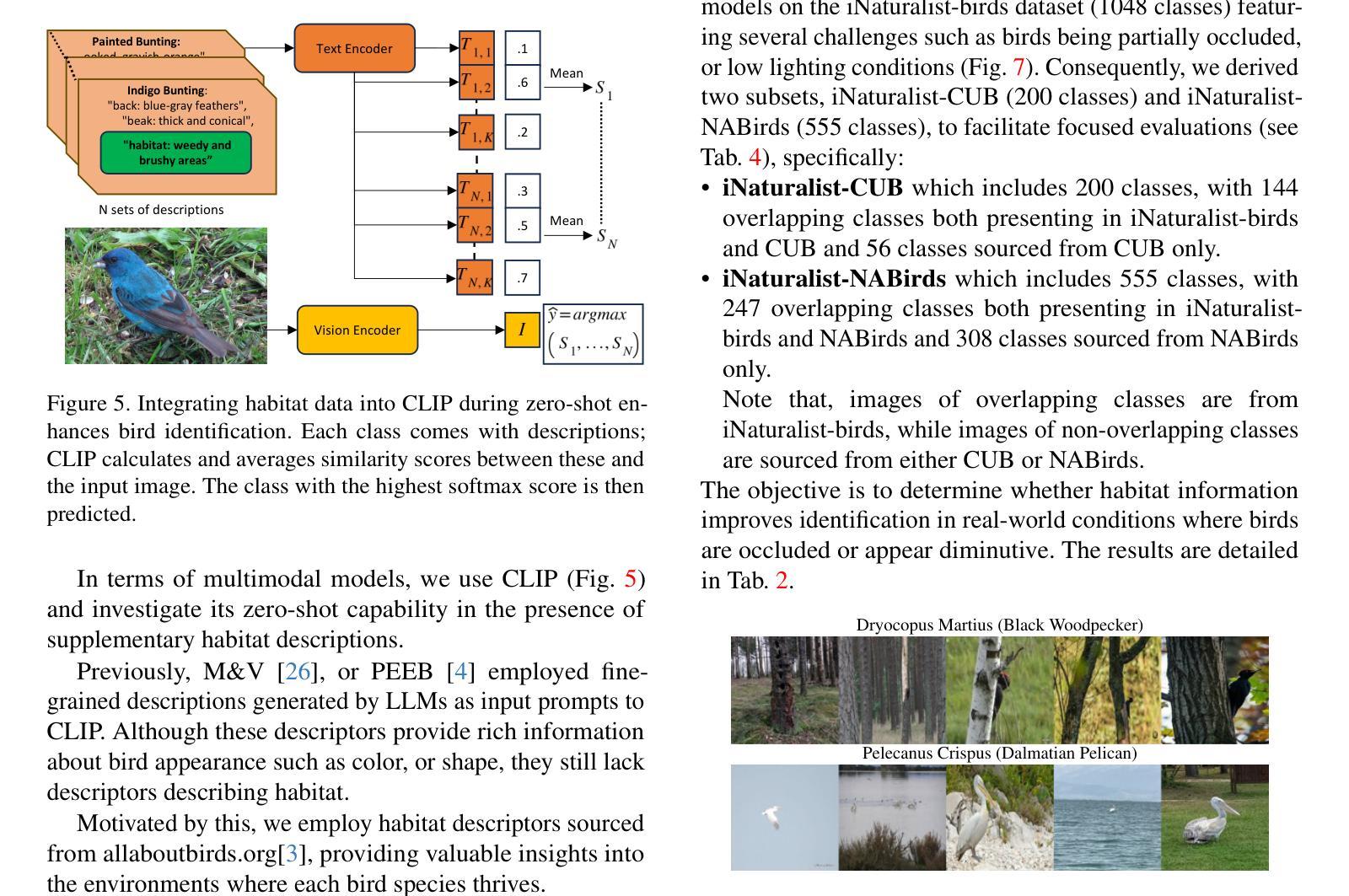
Traditional bird classifiers mostly rely on the visual characteristics of birds. Some prior works even train classifiers to be invariant to the background, completely discarding the living environment of birds. Instead, we are the first to explore integrating habitat information, one of the four major cues for identifying birds by ornithologists, into modern bird classifiers. We focus on two leading model types: (1) CNNs and ViTs trained on the downstream bird datasets; and (2) original, multi-modal CLIP. Training CNNs and ViTs with habitat-augmented data results in an improvement of up to +0.83 and +0.23 points on NABirds and CUB-200, respectively. Similarly, adding habitat descriptors to the prompts for CLIP yields a substantial accuracy boost of up to +0.99 and +1.1 points on NABirds and CUB-200, respectively. We find consistent accuracy improvement after integrating habitat features into the image augmentation process and into the textual descriptors of vision-language CLIP classifiers. Code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/reasoning-8B7E/.
传统的鸟类分类器大多依赖于鸟类的视觉特征。一些早期作品甚至训练分类器对背景保持不变,完全忽略了鸟类的生活环境。相反,我们是首批探索将栖息地信息(鸟类学家识别鸟类四大线索之一)融入现代鸟类分类器的团队。我们主要关注两种领先的模型类型:(1)在下游鸟类数据集上训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT);(2)原始的跨模态CLIP模型。使用栖息地增强数据进行训练的CNN和ViT模型在NABirds和CUB-200上的准确率分别提高了+0.83和+0.23个点。同样,在CLIP的提示中加入栖息地描述符导致NABirds和CUB-200上的准确率分别大幅提高了+0.99和+1.1个点。我们发现,在图像增强过程和视觉语言CLIP分类器的文本描述符中融入栖息地特征后,准确率得到了持续的提升。代码已发布在:[https://anonymous.4open.science/r/reasoning-8B7E/] 上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于现代鸟类的分类器,传统鸟类分类器主要依赖鸟类的视觉特征。本研究首次探索将栖息地信息——鸟类学家识别鸟类的四大线索之一——融入现代鸟类分类器。研究集中在两种领先的模型类型上:在下游鸟类数据集上训练的卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViTs),以及原始的跨模态CLIP模型。通过加入栖息地信息后,无论是在CNNs和ViTs模型中,还是在CLIP模型中,训练数据的增强均提升了模型在NABirds和CUB-200数据集上的准确率,最高提升幅度分别为+0.83点和+0.23点。将栖息地特征融入图像增强过程和跨视觉语言的CLIP分类器的文本描述符中,也能实现准确率的持续提升。代码已公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- 传统鸟类分类器主要依赖鸟类的视觉特征进行分类。
- 本研究首次尝试将栖息地信息融入现代鸟类分类器设计中。
- 在CNN和ViT模型上融入栖息地信息后,在NABirds和CUB-200数据集上的准确率有所提升。
- CLIP模型通过结合栖息地描述,准确率得到显著提高。
- 将栖息地特征融入图像增强过程和文本描述符中,能进一步提升模型的准确率。
- 该研究提供的代码已公开供公众查阅和使用。
点此查看论文截图