⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-25 更新
Evaluation and optimization of deep learning models for enhanced detection of brain cancer using transmission optical microscopy of thin brain tissue samples
Authors:Mohnish Sao, Mousa Alrubayan, Prabhakar Pradhan
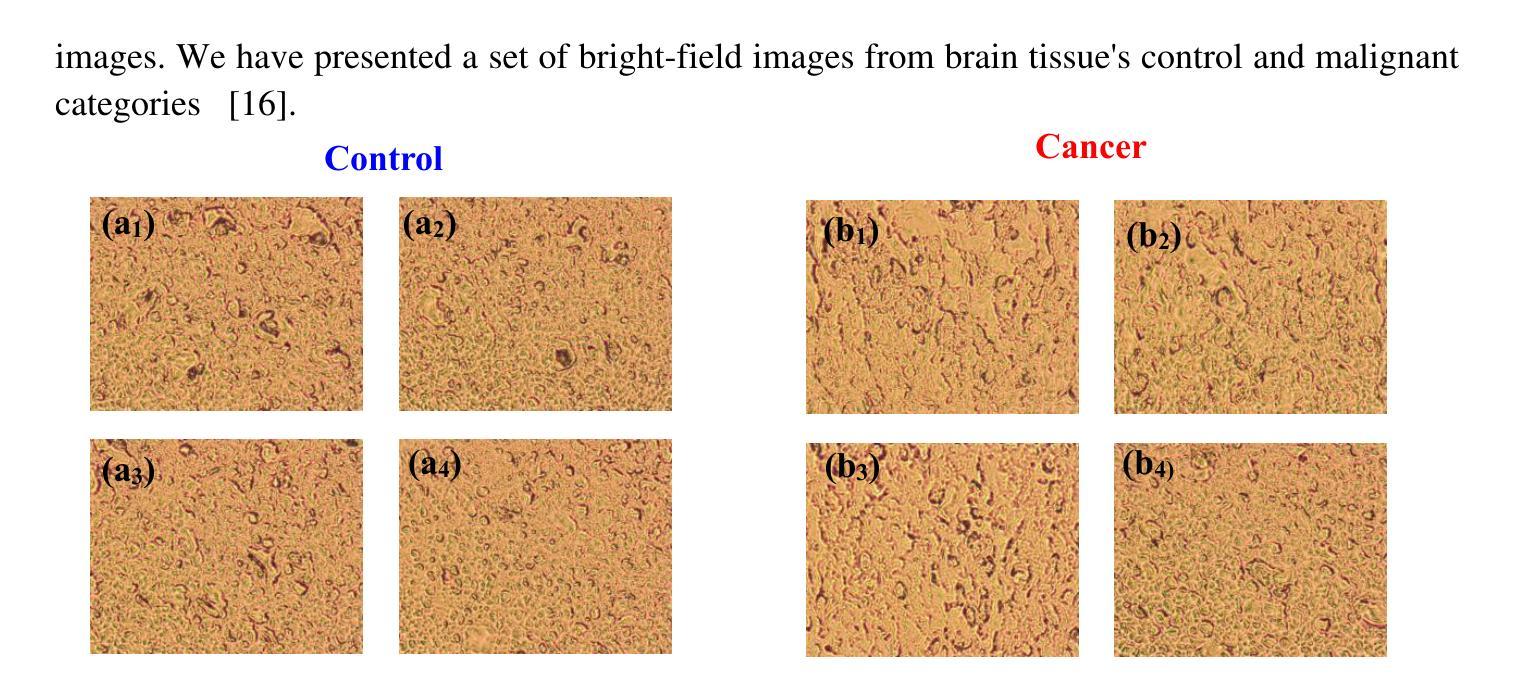
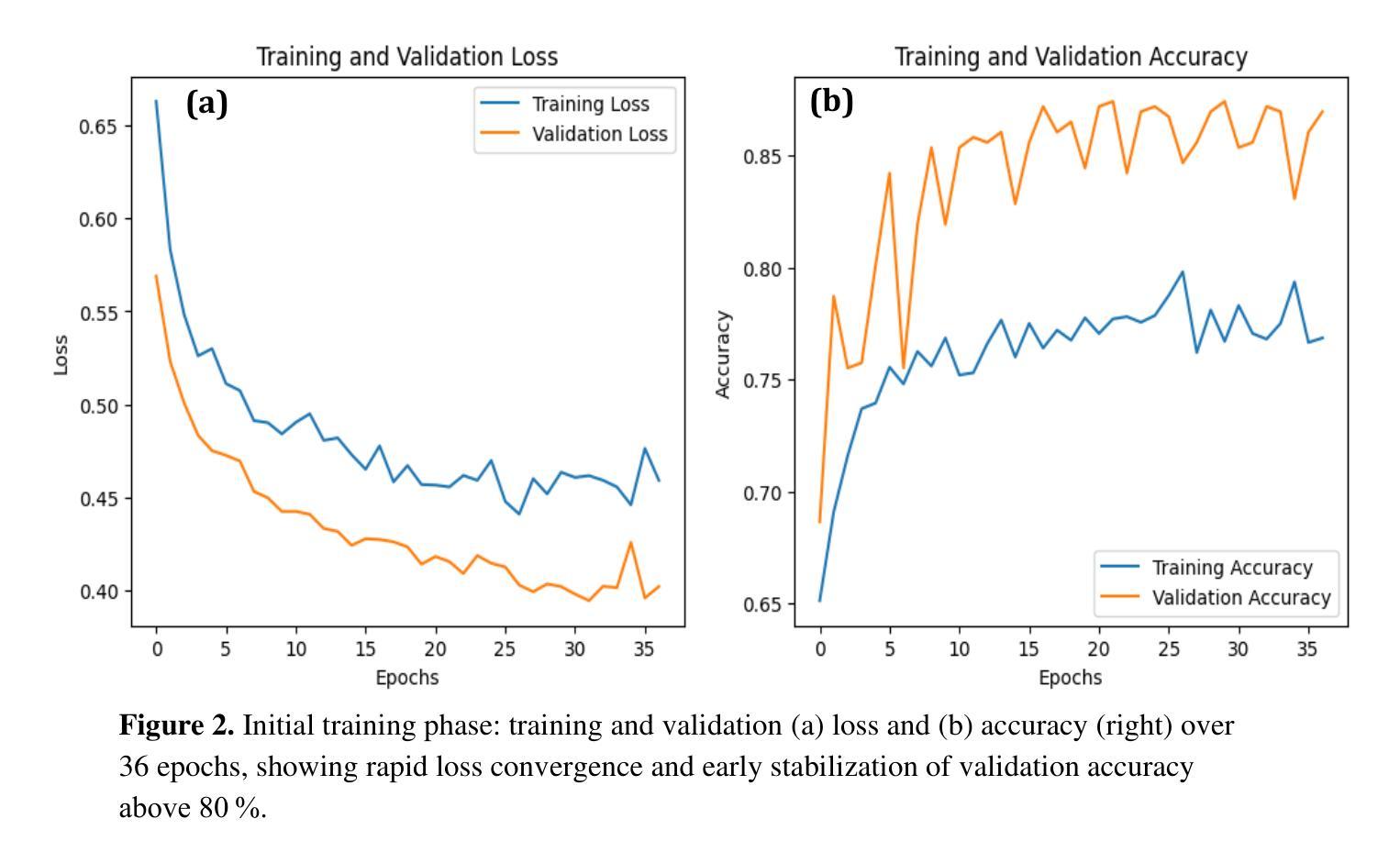
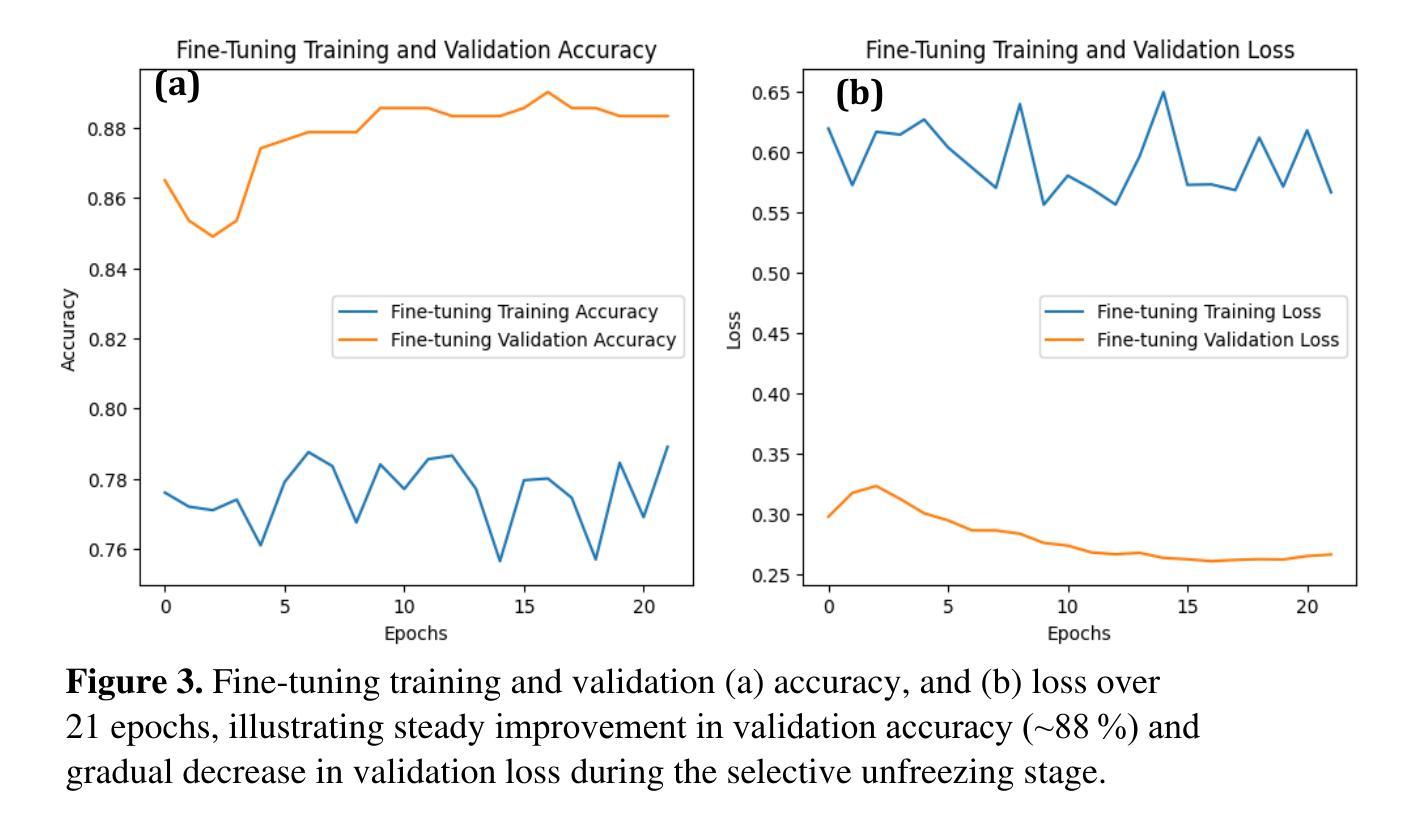
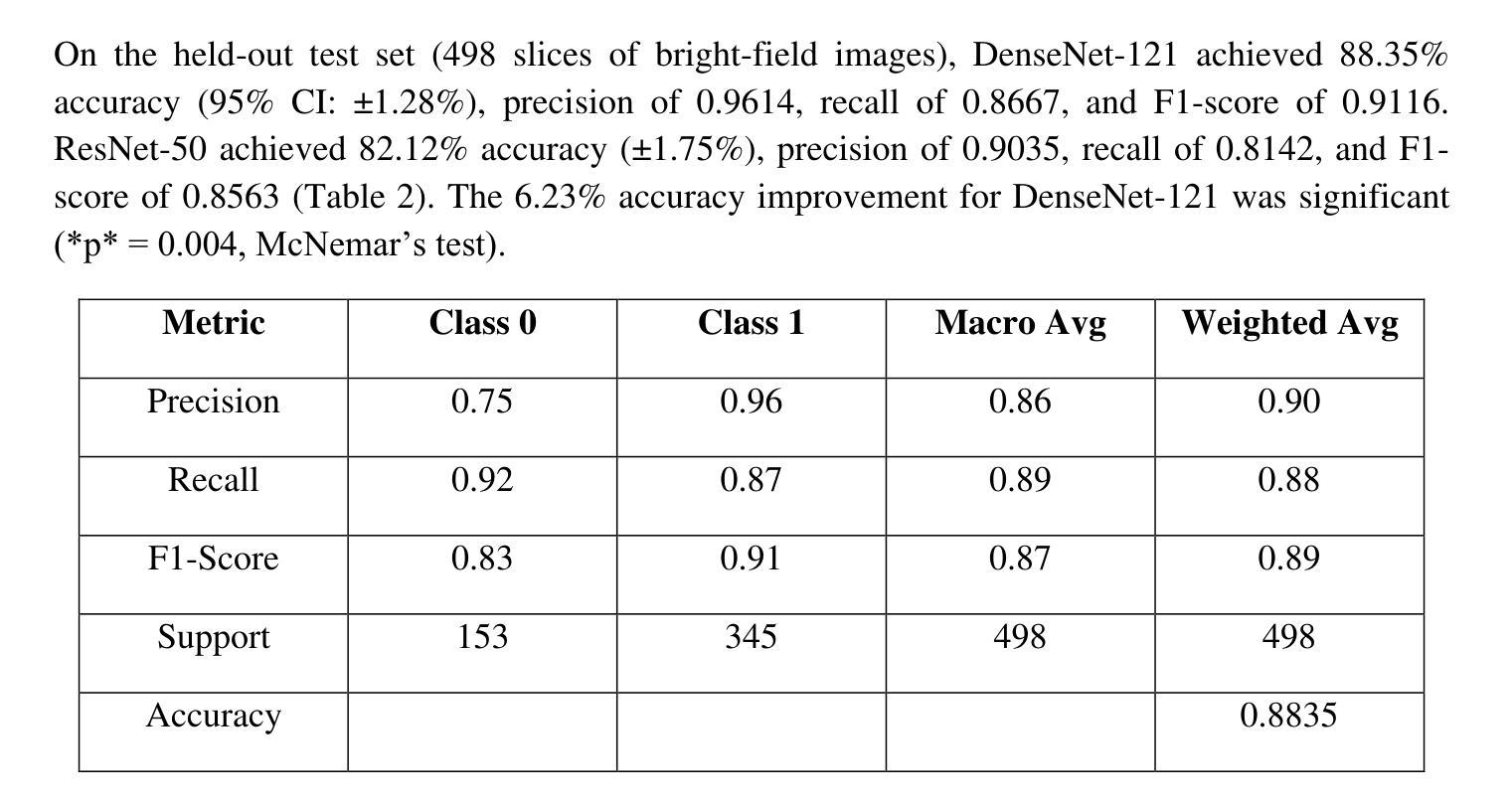
Optical transmission spectroscopy is one method to understand brain tissue structural properties from brain tissue biopsy samples, yet manual interpretation is resource intensive and prone to inter observer variability. Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) offer automated feature learning directly from raw brightfield images. Here, we evaluate ResNet50 and DenseNet121 on a curated dataset of 2,931 bright-field transmission optical microscopy images of thin brain tissue, split into 1,996 for training, 437 for validation, and 498 for testing. Our two stage transfer learning protocol involves initial training of a classifier head on frozen pretrained feature extractors, followed by fine tuning of deeper convolutional blocks with extensive data augmentation (rotations, flips, intensity jitter) and early stopping. DenseNet121 achieves 88.35 percent test accuracy, 0.9614 precision, 0.8667 recall, and 0.9116 F1 score the best performance compared to ResNet50 (82.12 percent, 0.9035, 0.8142, 0.8563). Detailed analysis of confusion matrices, training and validation curves, and classwise prediction distributions illustrates robust convergence and minimal bias. These findings demonstrate the superior generalization of dense connectivity on limited medical datasets and outline future directions for multi-class tumor grading and clinical translation.
光学传输光谱法是一种通过脑组织活检样本了解脑组织结构性质的方法,但人工解读需要大量资源,且易出现观察者间差异。深度卷积神经网络(CNN)可以直接从原始明场图像中实现自动化特征学习。在此,我们对包含2931张脑组织薄片明场透射光学显微镜图像的定制数据集进行了ResNet50和DenseNet121的评估,其中1996张用于训练,437张用于验证,498张用于测试。我们的两阶段迁移学习协议涉及首先在冻结的预训练特征提取器上训练分类器头部,随后通过丰富的数据增强(旋转、翻转、强度抖动)进行深层卷积块的微调,并早期停止训练。DenseNet121达到了88.35%的测试准确率、0.9614的精确度、0.8667的召回率和0.9116的F1分数,与ResNet50相比表现出最佳性能(分别为82.12%、0.9035、0.8142和0.8563)。对混淆矩阵、训练和验证曲线以及类别预测分布的详细分析,证明了其稳健的收敛性和较低的偏见。这些发现表明密集连接在有限医疗数据集上的优越泛化能力,并指出了多类肿瘤分级和临床转化的未来研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
深度学习中的卷积神经网络(CNN)可自动学习脑组织活检样本的结构特性,减轻人工解读的负担并减少观察者间的差异。本研究对ResNet50和DenseNet121网络在脑组织薄切片透射光学显微镜图像上进行评估,结果显示DenseNet121在测试集上的准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数均高于ResNet50。这表明在有限的医学数据集中,密集连接网络具有更好的泛化能力,并为多类肿瘤分级和临床转化提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- Optical transmission spectroscopy可用于通过脑组织活检样本了解脑组织结构性特征。
- 手动解读这些特征资源消耗大且存在观察者间差异。
- Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs)能自动从原始明场图像中学习特征。
- 本研究对比了ResNet50和DenseNet121网络在脑组织薄切片图像数据集上的表现。
- DenseNet121在准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数等评估指标上表现更佳。
- 详细分析表明DenseNet121在有限医学数据集上具有较好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

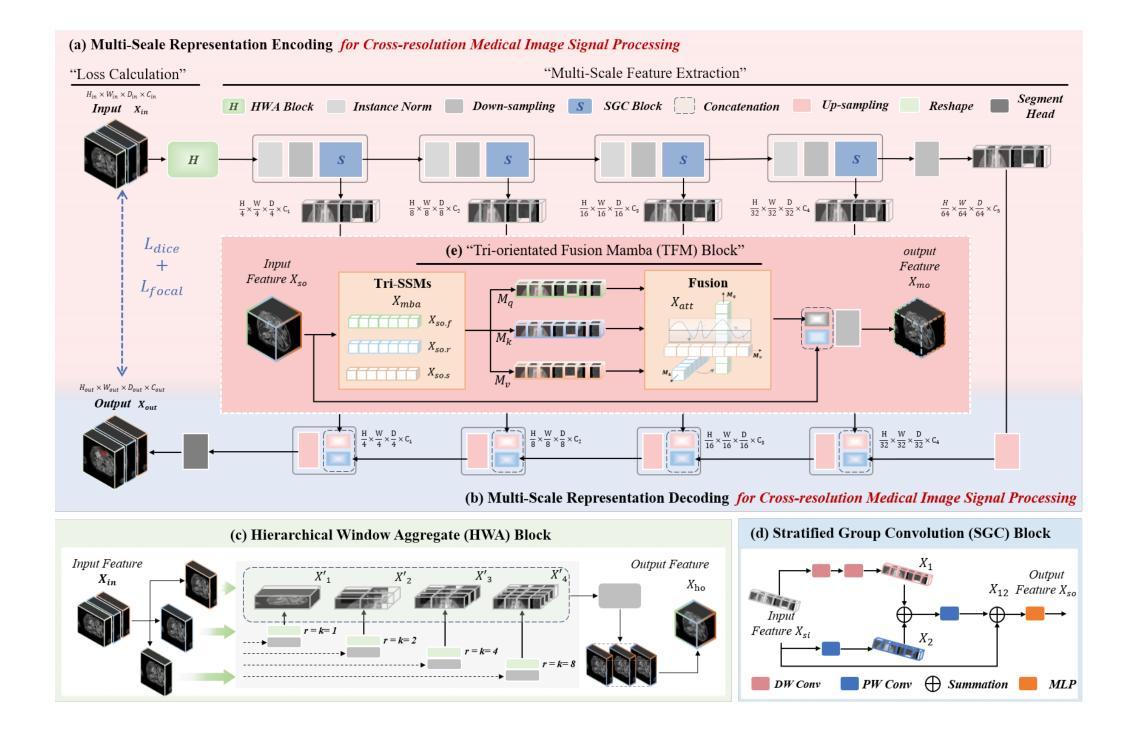
HWA-UNETR: Hierarchical Window Aggregate UNETR for 3D Multimodal Gastric Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Jiaming Liang, Lihuan Dai, Xiaoqi Sheng, Xiangguang Chen, Chun Yao, Guihua Tao, Qibin Leng, Hongmin Cai, Xi Zhong
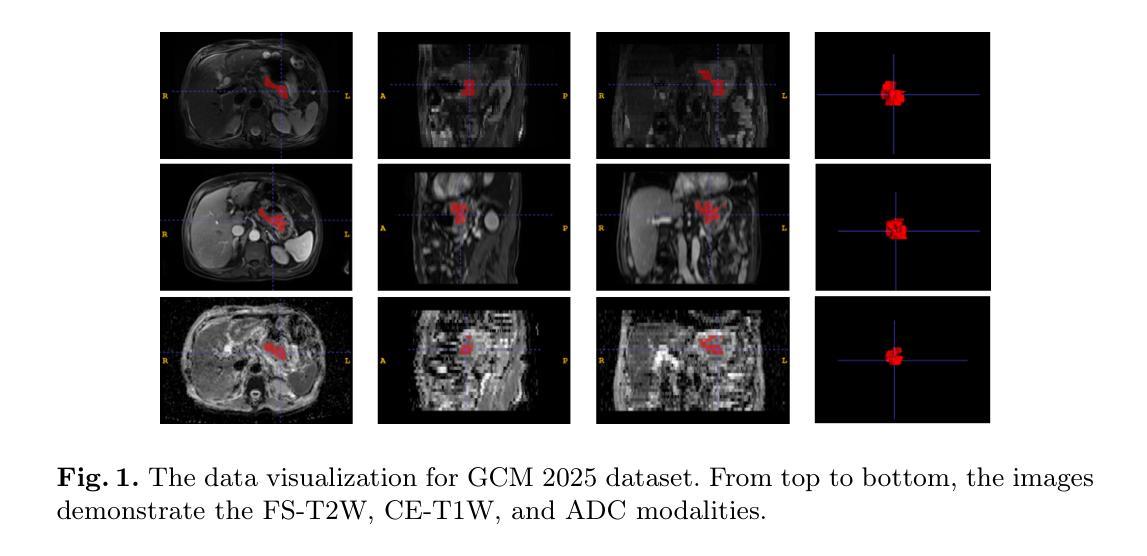
Multimodal medical image segmentation faces significant challenges in the context of gastric cancer lesion analysis. This clinical context is defined by the scarcity of independent multimodal datasets and the imperative to amalgamate inherently misaligned modalities. As a result, algorithms are constrained to train on approximate data and depend on application migration, leading to substantial resource expenditure and a potential decline in analysis accuracy. To address those challenges, we have made two major contributions: First, we publicly disseminate the GCM 2025 dataset, which serves as the first large-scale, open-source collection of gastric cancer multimodal MRI scans, featuring professionally annotated FS-T2W, CE-T1W, and ADC images from 500 patients. Second, we introduce HWA-UNETR, a novel 3D segmentation framework that employs an original HWA block with learnable window aggregation layers to establish dynamic feature correspondences between different modalities’ anatomical structures, and leverages the innovative tri-orientated fusion mamba mechanism for context modeling and capturing long-range spatial dependencies. Extensive experiments on our GCM 2025 dataset and the publicly BraTS 2021 dataset validate the performance of our framework, demonstrating that the new approach surpasses existing methods by up to 1.68% in the Dice score while maintaining solid robustness. The dataset and code are public via https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR.
在胃癌病灶分析的背景下,多模态医学图像分割面临着巨大的挑战。这种临床背景的特点是缺乏独立的多模态数据集,以及迫切需要融合内在不一致的模态。因此,算法受到训练数据近似性的限制,并依赖于应用迁移,导致资源消耗巨大,分析精度可能下降。为了应对这些挑战,我们做出了两大贡献:首先,我们公开传播了GCM 2025数据集,该数据集是首个大规模的、开源的胃癌多模态MRI扫描集合,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像。其次,我们介绍了HWA-UNETR,这是一种新型的3D分割框架,采用原始HWA块和可学习的窗口聚合层来建立不同模态解剖结构之间的动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的三角定向融合妈妈机制进行上下文建模和捕获长程空间依赖性。在我们的GCM 2025数据集和公开的BraTS 2021数据集上的广泛实验验证了我们的框架的性能,结果表明,新方法在Dice得分上比现有方法高出1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been provisionally accepted for MICCAI 2025
摘要
胃癌病灶分析的多模态医学图像分割面临诸多挑战。缺乏独立多模态数据集以及需要对固有错配模态进行融合的临床环境,限制了算法的训练数据并依赖于应用迁移,导致了资源消耗大且分析精度可能下降。为应对这些挑战,我们做出了两大贡献:首先,我们公开发布了GCM 2025数据集,这是首个大规模公开的胃癌多模态MRI扫描数据集,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像;其次,我们引入了HWA-UNETR,这是一种新型的3D分割框架,采用可学习的窗口聚合层建立不同模态解剖结构之间的动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的三角融合mama机制进行上下文建模和捕获长期空间依赖性。在我们的GCM 2025数据集和公开的BraTS 2021数据集上的实验验证了该框架的性能,新方法的Dice得分高出现有方法高达1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码公开在https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR。
关键见解
- 多模态医学图像分割在胃癌病灶分析中存在挑战,缺乏独立多模态数据集和模态融合的需求是主要原因。
- GCM 2025数据集的公开解决了这一问题,它包含了大量经过专业注释的胃癌多模态MRI扫描数据。
- HWA-UNETR框架被引入以解决多模态医学图像分割的挑战,它采用可学习的窗口聚合层建立不同模态之间的动态特征对应关系。
- HWA-UNETR框架在GCM 2025数据集和BraTS 2021数据集上的实验表现优异,相比现有方法Dice得分提高1.68%。
- 该框架具备强大的上下文建模能力,能够捕获长期空间依赖性。
- HWA-UNETR框架具备稳健性,能够应对不同数据集的挑战。
- 数据集和代码已经公开,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

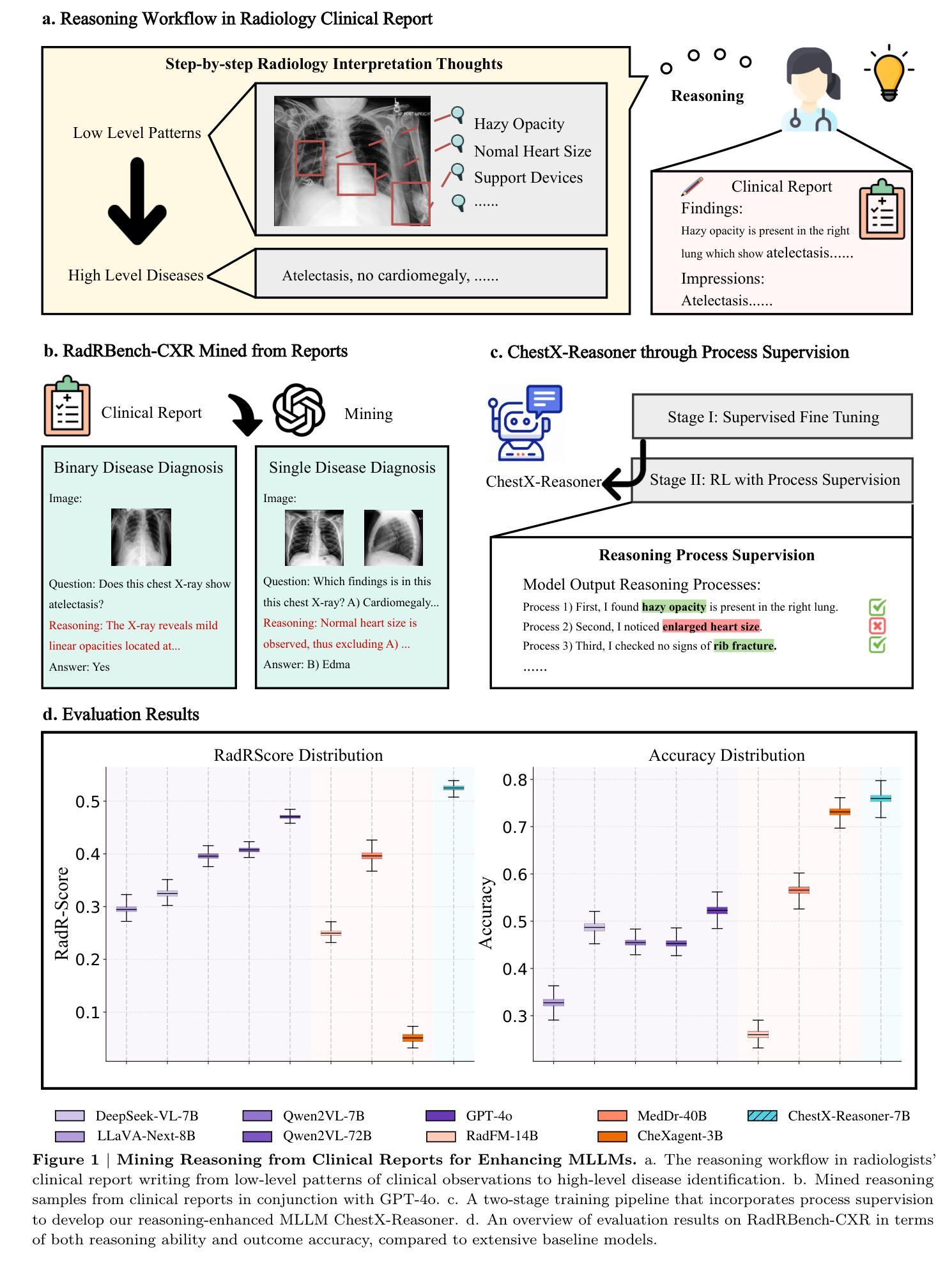
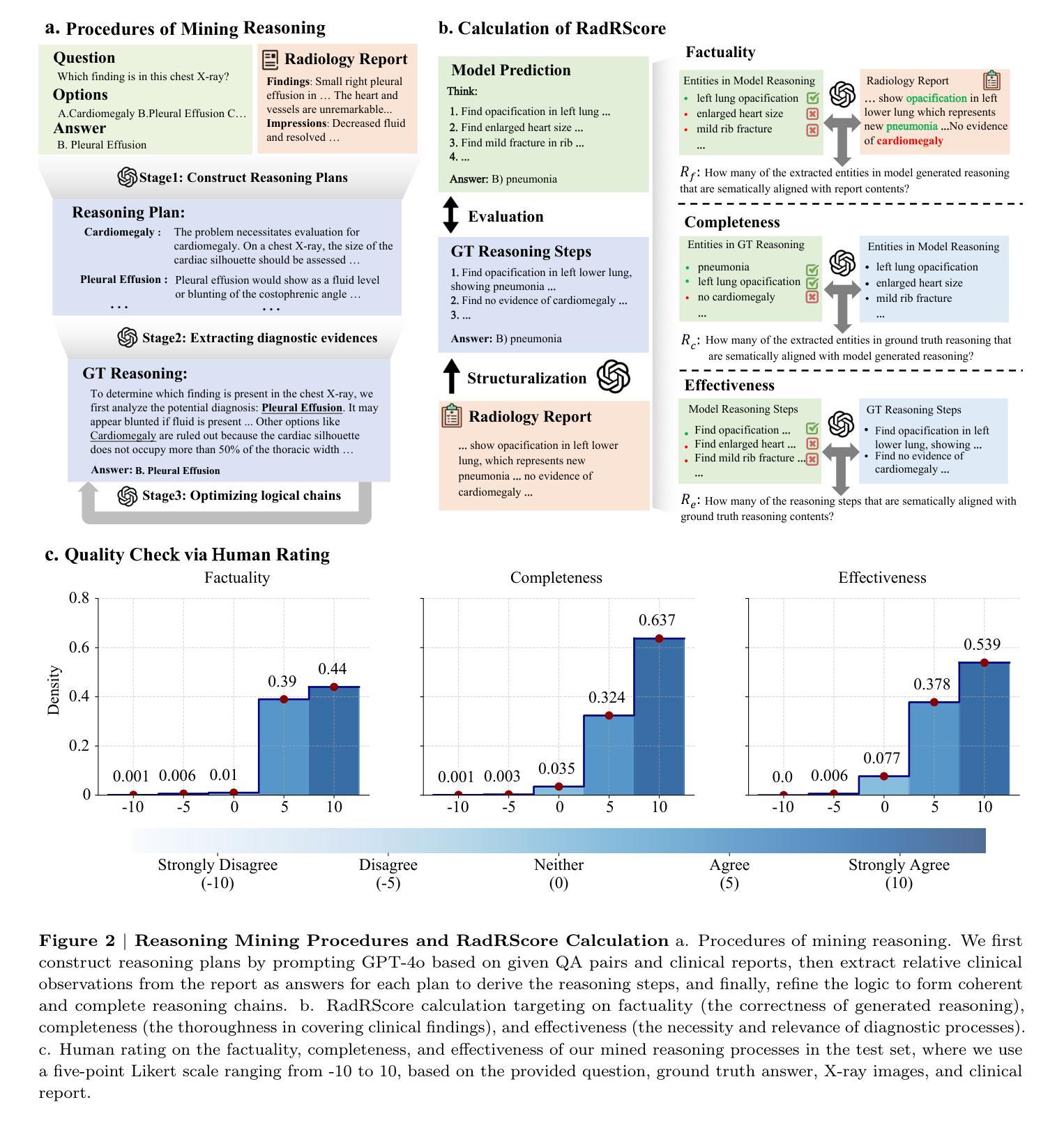
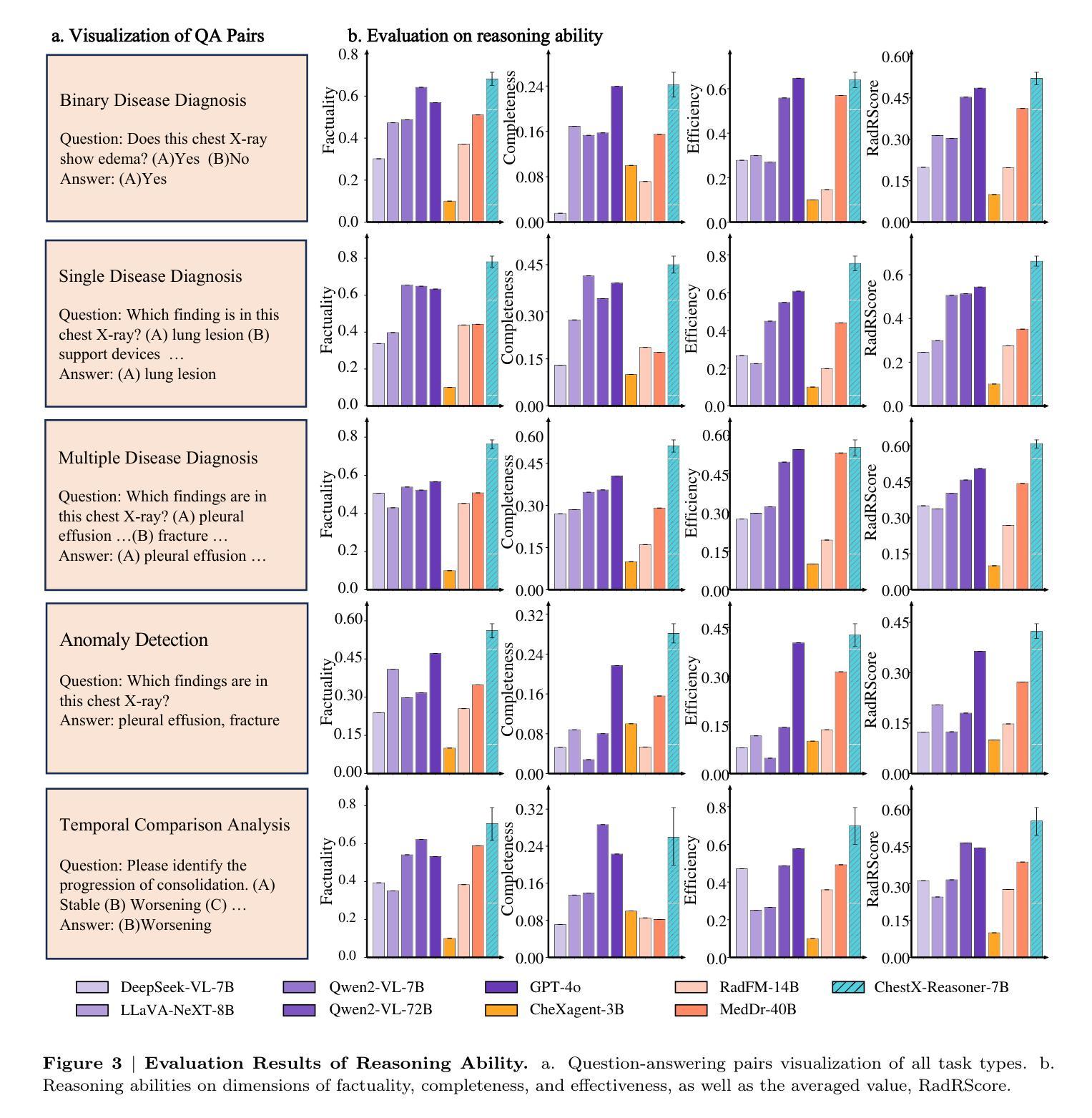
ChestX-Reasoner: Advancing Radiology Foundation Models with Reasoning through Step-by-Step Verification
Authors:Ziqing Fan, Cheng Liang, Chaoyi Wu, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
Recent advances in reasoning-enhanced large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) have significantly improved performance in complex tasks, yet medical AI models often overlook the structured reasoning processes inherent in clinical practice. In this work, we present ChestX-Reasoner, a radiology diagnosis MLLM designed to leverage process supervision mined directly from clinical reports, reflecting the step-by-step reasoning followed by radiologists. We construct a large dataset by extracting and refining reasoning chains from routine radiology reports. Our two-stage training framework combines supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning guided by process rewards to better align model reasoning with clinical standards. We introduce RadRBench-CXR, a comprehensive benchmark featuring 59K visual question answering samples with 301K clinically validated reasoning steps, and propose RadRScore, a metric evaluating reasoning factuality, completeness, and effectiveness. ChestX-Reasoner outperforms existing medical and general-domain MLLMs in both diagnostic accuracy and reasoning ability, achieving 16%, 5.9%, and 18% improvements in reasoning ability compared to the best medical MLLM, the best general MLLM, and its base model, respectively, as well as 3.3%, 24%, and 27% improvements in outcome accuracy. All resources are open-sourced to facilitate further research in medical reasoning MLLMs.
最近,在推理增强大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLM(MLLMs)方面的进展,已经在复杂任务中显著提高性能。然而,医疗AI模型往往忽略了临床实践中的结构化推理过程。在这项工作中,我们提出了ChestX-Reasoner,这是一种设计用于利用直接从临床报告中挖掘的过程监督的放射学诊断MLLM,反映了放射医师遵循的逐步推理。我们通过从常规放射报告中提取和精炼推理链来构建大型数据集。我们的两阶段训练框架结合了监督微调与由过程奖励引导的自我强化学习,以更好地使模型推理与临床标准保持一致。我们介绍了RadRBench-CXR,这是一个包含59K视觉问答样本和301K临床验证推理步骤的综合基准测试,并提出了RadRScore,一个评估推理真实性、完整性和有效性的指标。ChestX-Reasoner在诊断和治疗准确度以及推理能力方面均优于现有的医疗和通用领域MLLMs。相较于最佳的医疗MLLM、通用MLLM及其基础模型,在推理能力方面分别提高了16%、5.9%和18%;在结果准确性方面分别提高了3.3%、24%和27%。所有资源均开源,以促进在医疗推理MLLM方面的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作提出了ChestX-Reasoner,这是一种结合临床报告中的推理过程监督设计的放射学诊断多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。通过从常规放射报告中提取和精炼推理链,构建大型数据集。采用两阶段训练框架,结合监督微调与以过程奖励引导的强化学习,使模型推理更符合临床标准。同时引入了RadRBench-CXR基准测试和RadRScore评估指标,以评估推理的真实性、完整性和有效性。ChestX-Reasoner在诊断准确性和推理能力方面超越了现有的医学和通用MLLMs模型,实现了显著的提升并公开所有资源以促进医学推理MLLM的进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- ChestX-Reasoner是一个结合临床推理过程监督设计的放射学诊断多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。
- 通过从常规放射报告中提取和精炼推理链构建大型数据集。
- 采用两阶段训练框架,结合监督微调与强化学习,使模型推理更符合临床标准。
- 引入了RadRBench-CXR基准测试和RadRScore评估指标。
- ChestX-Reasoner在诊断准确性和推理能力方面表现出显著的提升。
- 与现有医学和通用MLLMs相比,ChestX-Reasoner有更高的诊断准确性和推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

Multiobjective optimization for scattering mitigation and scattering screen reconstruction in VLBI observations of the Galactic Center
Authors:Alejandro Mus, Teresa Toscano, Hendrik Müller, Guang-Yao Zhao, Andrei Lobanov, Ciriaco Goddi
Imaging reconstruction of interferometric data is a hard ill-posed inverse problem. Its difficulty is increased when observing the Galactic Center, which is obscured by a scattering screen. This is because the scattering breaks the one-to-one correspondence between images and visibilities. Solving the scattering problem is one of the biggest challenges in radio imaging of the Galactic Center. In this work we present a novel strategy to mitigate its effect and constrain the screen itself using multiobjective optimization. We exploit the potential of evolutionary algorithms to describe the optimization landscape to recover the intrinsic source structure and the scattering screen affecting the data. We successfully recover both the screen and the source in a wide range of simulated cases, including the speed of a moving screen at 230 GHz. Particularly, we can recover a ring structure in scattered data at 86 GHz. Our analysis demonstrates the huge potential that recent advancements in imaging and optimization algorithms offer to recover image structures, even in weakly constrained and degenerated, possibly multi-modal settings. The successful reconstruction of the scattering screen opens the window to event horizon scale works on the Galactic Center at 86G Hz up to 116 GHz, and the study of the scattering screen itself.
成像重建干涉数据是一个难度较大的反问题。在观测银河系中心时难度更大,因为银河系中心被一个散射屏所遮蔽。散射破坏了图像和可见度之间的一一对应关系。解决散射问题是银河系中心射电成像面临的最大挑战之一。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的策略,利用多目标优化来缓解散射效应并约束散射屏本身。我们利用进化算法描述优化景观的潜力,以恢复影响数据的固有源结构和散射屏。我们在广泛的模拟案例中成功地恢复了屏幕和源,包括以230 GHz移动的屏幕速度。尤其值得一提的是,我们能够在散射数据中恢复环状结构(如在86 GHz的数据)。我们的分析证明了成像和优化算法的最新进展在恢复图像结构方面的巨大潜力,即使在弱约束和退化、可能是多模态的环境中也是如此。成功重建散射屏为在86 GHz至116 GHz上对银河系中心的事件视界规模工作打开了窗口,以及对散射屏本身的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in A&A
Summary
针对干涉数据的成像重建是一个病态的逆问题,尤其在对银河系中心进行观测时难度更大,因为散射破坏了图像与可见度之间的一一对应关系。本研究提出了一种新的策略,利用多目标优化来减轻散射的影响并约束散射屏本身。我们利用进化算法描述优化景观,以恢复影响数据的内在源结构和散射屏。在多种模拟情况下,我们成功恢复了屏幕和源,包括移动屏幕的速度(在230 GHz下)。特别是在86 GHz的散射数据中,我们成功恢复了环形结构。我们的分析展示了最新的成像和优化算法在恢复图像结构方面的巨大潜力,即使在弱约束和退化的可能多模态环境中也是如此。成功重建散射屏为在86 GHz至116 GHz上对银河系中心的事件视界规模工作打开了窗口,并对散射屏本身进行了研究。
Key Takeaways
- 干涉数据成像重建是一个病态的逆问题,尤其在观测银河系中心时难度更大。
- 散射破坏了图像与可见度之间的一一对应关系,是射电成像中面临的最大挑战之一。
- 研究提出了一种新的策略,利用多目标优化减轻散射影响并约束散射屏。
- 通过进化算法描述优化景观,可以恢复内在源结构和影响数据的散射屏。
- 在多种模拟情况下成功恢复了屏幕和源,包括移动屏幕的速度。
- 成功在86 GHz的散射数据中恢复环形结构。
点此查看论文截图

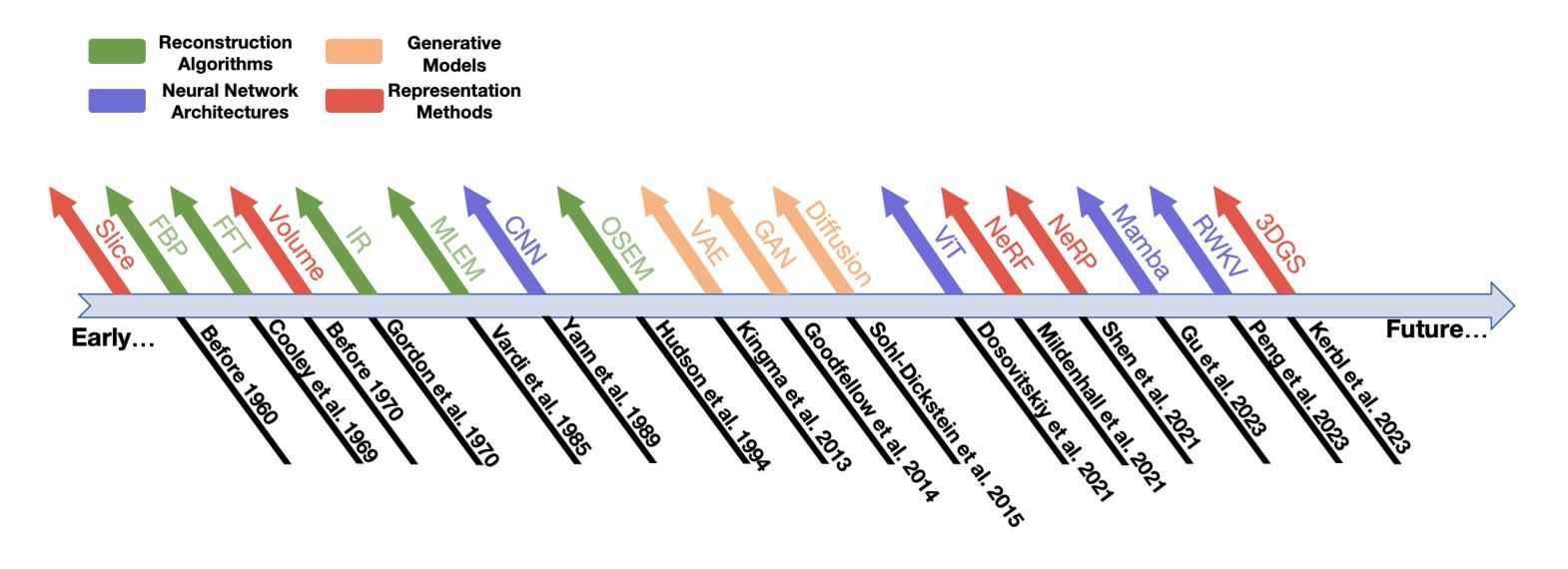
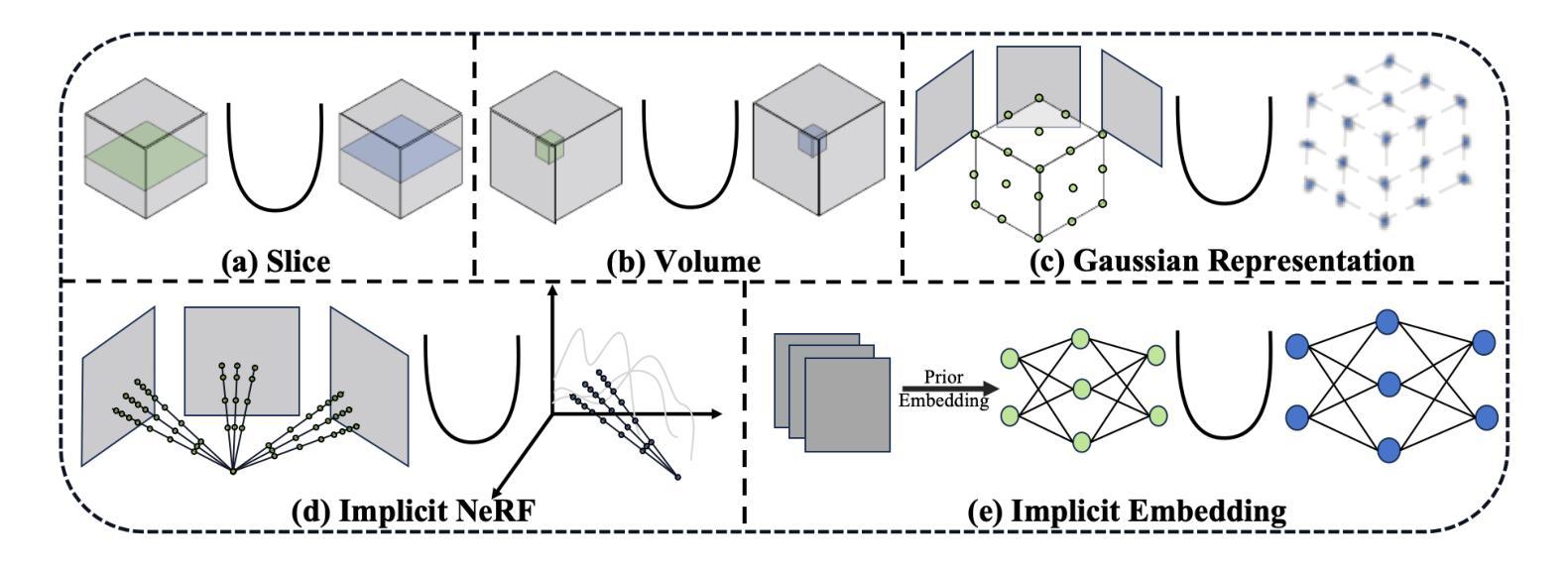
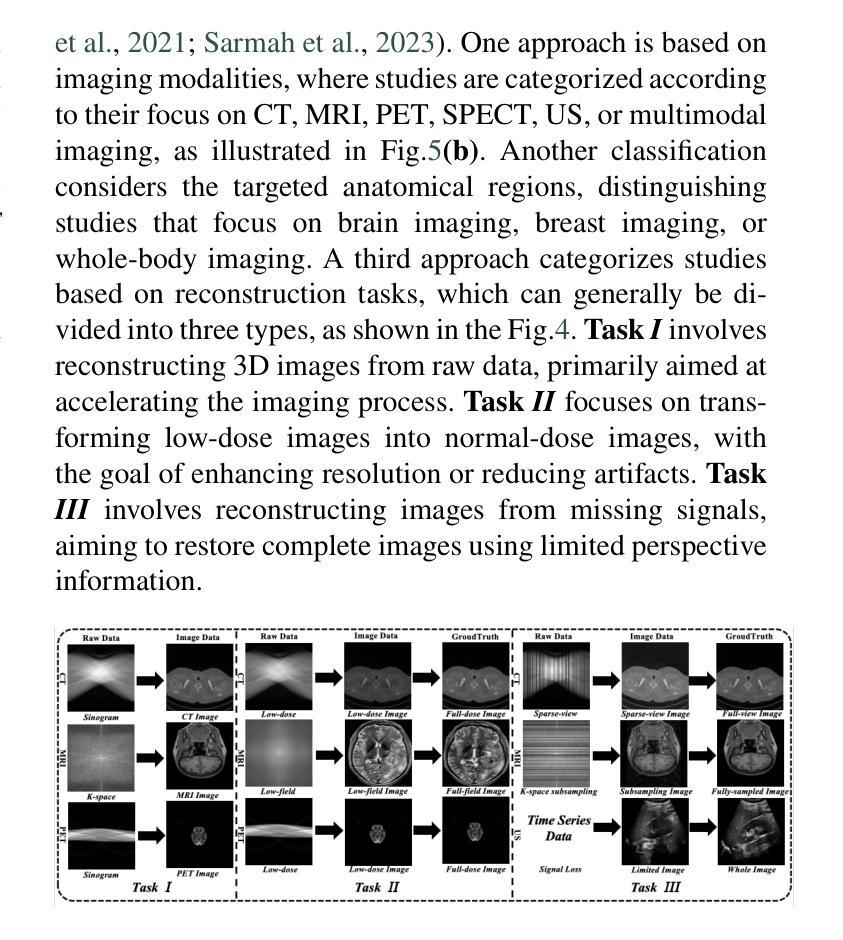
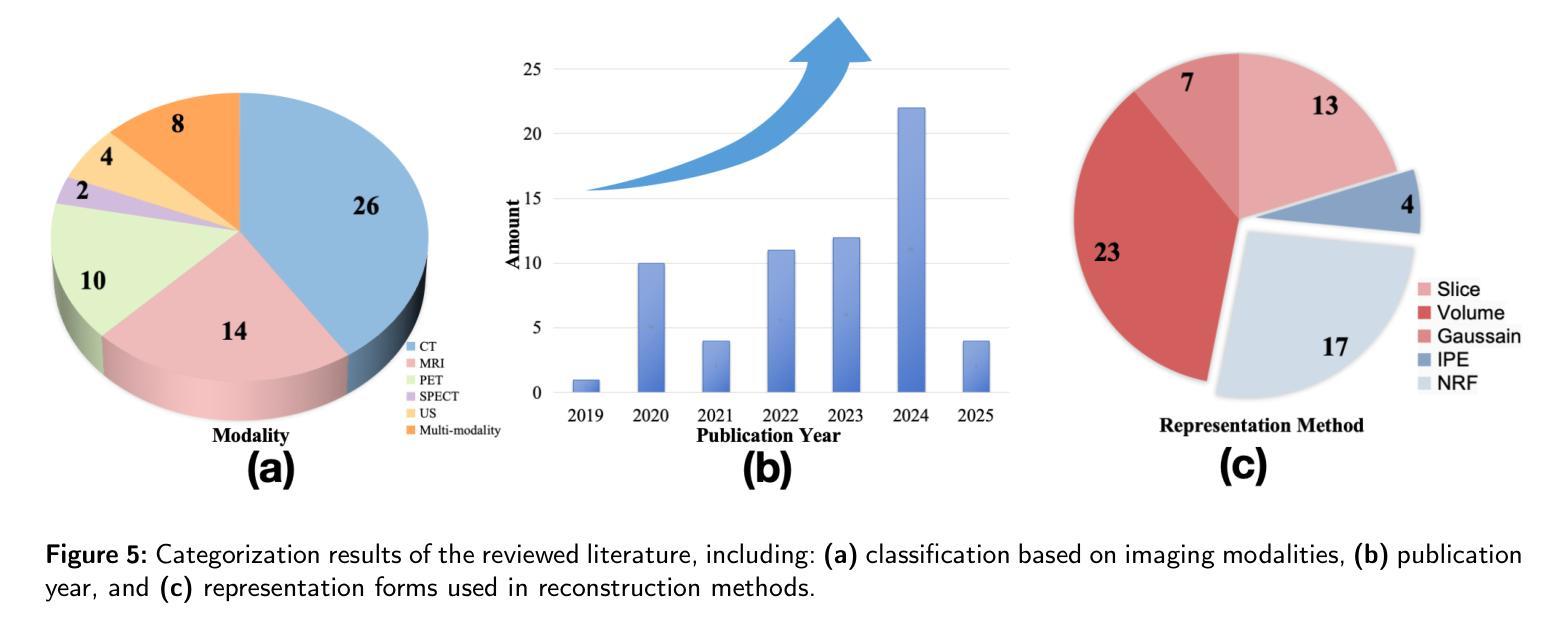
Explicit and Implicit Representations in AI-based 3D Reconstruction for Radiology: A Systematic Review
Authors:Yuezhe Yang, Boyu Yang, Yaqian Wang, Yang He, Xingbo Dong, Zhe Jin
The demand for high-quality medical imaging in clinical practice and assisted diagnosis has made 3D reconstruction in radiological imaging a key research focus. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising approach to enhancing reconstruction accuracy while reducing acquisition and processing time, thereby minimizing patient radiation exposure and discomfort and ultimately benefiting clinical diagnosis. This review explores state-of-the-art AI-based 3D reconstruction algorithms in radiological imaging, categorizing them into explicit and implicit approaches based on their underlying principles. Explicit methods include point-based, volume-based, and Gaussian representations, while implicit methods encompass implicit prior embedding and neural radiance fields. Additionally, we examine commonly used evaluation metrics and benchmark datasets. Finally, we discuss the current state of development, key challenges, and future research directions in this evolving field. Our project available on: https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology.
临床实践和对辅助诊断的高质量医学成像的需求使得放射成像中的3D重建成为关键的研究重点。人工智能(AI)已成为一种有前途的方法,可以提高重建精度,同时减少采集和处理时间,从而最小化患者的辐射暴露和不适感,并最终有益于临床诊断。本文综述了基于人工智能的放射成像3D重建算法的最新进展,根据它们的基本原理将它们分为显式方法和隐式方法。显式方法包括点基、体积基和高斯表示法,而隐式方法包括隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场。此外,我们还介绍了常用的评估指标和基准数据集。最后,我们讨论了该领域的当前开发状态、关键挑战和未来研究方向。我们的项目可用在:https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 5 figures, submit to Medical Image Analysis
Summary
本文主要探讨了人工智能在医学影像学三维重建中的重要作用和应用。介绍了基于人工智能的三维重建算法的前沿进展,包括显式方法和隐式方法。显式方法主要包括点基、体积基和高斯表示法,隐式方法包括隐式先验嵌入和神经辐射场。文章还介绍了常用的评估指标和基准数据集,并讨论了当前的发展状况、关键挑战以及未来的研究方向。项目代码可通过链接访问:https://github.com/Bean-Young/AI4Radiology。
Key Takeaways
- 医学影像学中三维重建的重要性及其在临床实践和辅助诊断中的需求。
- 人工智能在提升三维重建准确性、减少采集和处理时间方面的潜力。
- 人工智能在医学影像学三维重建中的显式方法和隐式方法,包括各自的优点和挑战。
- 常用的评估三维重建效果的评价指标和基准数据集。
- 当前医学影像学三维重建领域的发展状况。
- 面临的关键挑战,如算法复杂性、数据获取和处理难度等。
点此查看论文截图

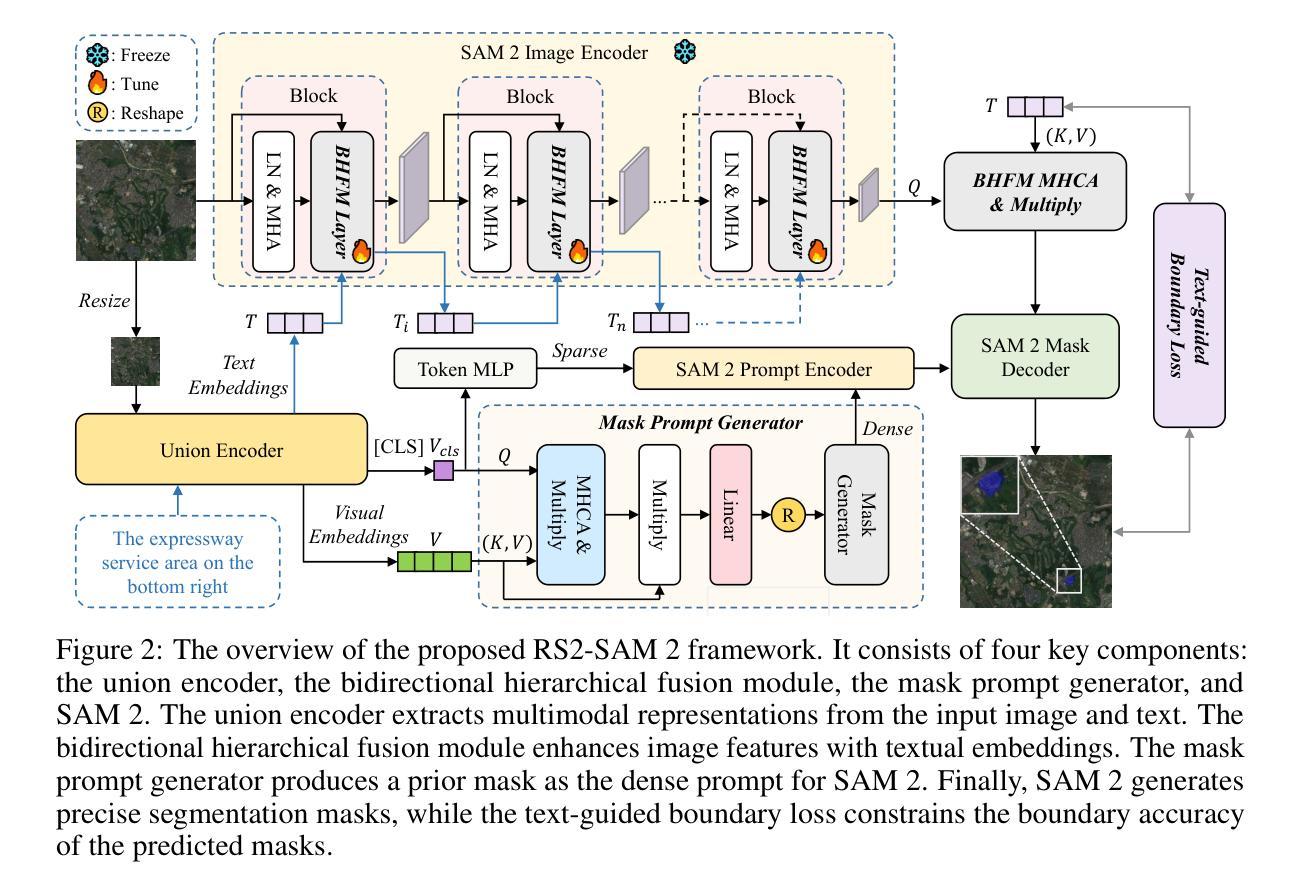
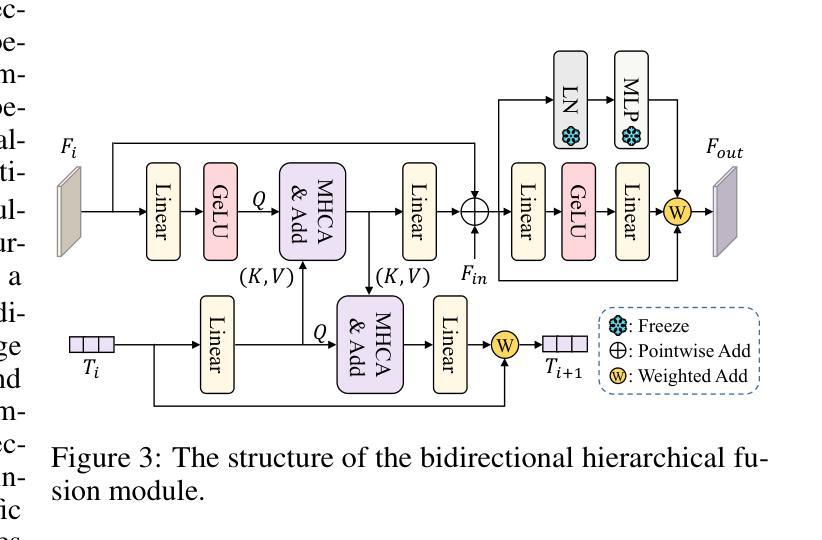
Customized SAM 2 for Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Fu Rong, Meng Lan, Qian Zhang, Lefei Zhang
Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation (RRSIS) aims to segment target objects in remote sensing (RS) images based on textual descriptions. Although Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) has shown remarkable performance in various segmentation tasks, its application to RRSIS presents several challenges, including understanding the text-described RS scenes and generating effective prompts from text descriptions. To address these issues, we propose RS2-SAM 2, a novel framework that adapts SAM 2 to RRSIS by aligning the adapted RS features and textual features, providing pseudo-mask-based dense prompts, and enforcing boundary constraints. Specifically, we first employ a union encoder to jointly encode the visual and textual inputs, generating aligned visual and text embeddings as well as multimodal class tokens. Then, we design a bidirectional hierarchical fusion module to adapt SAM 2 to RS scenes and align adapted visual features with the visually enhanced text embeddings, improving the model’s interpretation of text-described RS scenes. Additionally, a mask prompt generator is introduced to take the visual embeddings and class tokens as input and produce a pseudo-mask as the dense prompt of SAM 2. To further refine segmentation, we introduce a text-guided boundary loss to optimize segmentation boundaries by computing text-weighted gradient differences. Experimental results on several RRSIS benchmarks demonstrate that RS2-SAM 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance.
远程遥感图像分割(RRSIS)旨在根据文本描述对遥感(RS)图像中的目标对象进行分割。尽管Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)在各种分割任务中表现出卓越的性能,但将其应用于RRSIS面临一些挑战,包括理解文本描述的RS场景和从文本描述中产生有效的提示。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了RS2-SAM 2,这是一个新型框架,通过适应SAM 2到RRSIS,通过对齐适应的RS特征和文本特征、提供基于伪掩码的密集提示和执行边界约束来适应RRSIS。具体来说,我们首先采用联合编码器对视觉和文本输入进行编码,生成对齐的视觉和文本嵌入以及多模式类别标记。然后,我们设计了一个双向层次融合模块,使SAM 2适应RS场景,并使适应后的视觉特征与增强的文本嵌入对齐,提高模型对文本描述的RS场景的解释能力。此外,我们还引入了一个掩膜提示生成器,以视觉嵌入和类别标记为输入,生成一个伪掩膜作为SAM 2的密集提示。为了进一步细化分割,我们引入了一种文本引导边界损失,通过计算文本加权的梯度差异来优化分割边界。在多个RRSIS基准测试上的实验结果表明,RS2-SAM 2达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本描述的遥感图像分割(RRSIS)旨在实现对遥感图像中目标对象的分割。尽管SAM 2模型在各种分割任务中表现出卓越的性能,但将其应用于RRSIS面临一些挑战,如理解文本描述的遥感场景和从文本描述中产生有效的提示。为解决这些问题,我们提出了RS2-SAM 2框架,该框架通过对齐遥感特征和文本特征、提供基于伪掩码的密集提示和执行边界约束,使SAM 2适应RRSIS。实验结果表明,RS2-SAM 2在多个RRSIS基准测试上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- RS2-SAM 2框架旨在使SAM 2模型适应基于文本描述的遥感图像分割(RRSIS)。
- RS2-SAM 2通过联合编码视觉和文本输入,生成对齐的视觉和文本嵌入以及多模态类令牌来解决理解文本描述的遥感场景和生成有效提示的挑战。
- 框架设计了一个双向层次融合模块,使SAM 2适应遥感场景,并将适应后的视觉特征与增强文本嵌入对齐。
- 引入了一个掩膜提示生成器,以视觉嵌入和类令牌为输入,生成伪掩膜作为SAM 2的密集提示。
- 为进一步优化分割边界,引入了文本引导边界损失,通过计算文本加权的梯度差异来优化分割边界。
- 实验结果表明,RS2-SAM 2在多个RRSIS基准测试上实现了最先进的性能。
- RS2-SAM 2框架的应用为遥感图像分割提供了一种新的、有效的方法。
点此查看论文截图


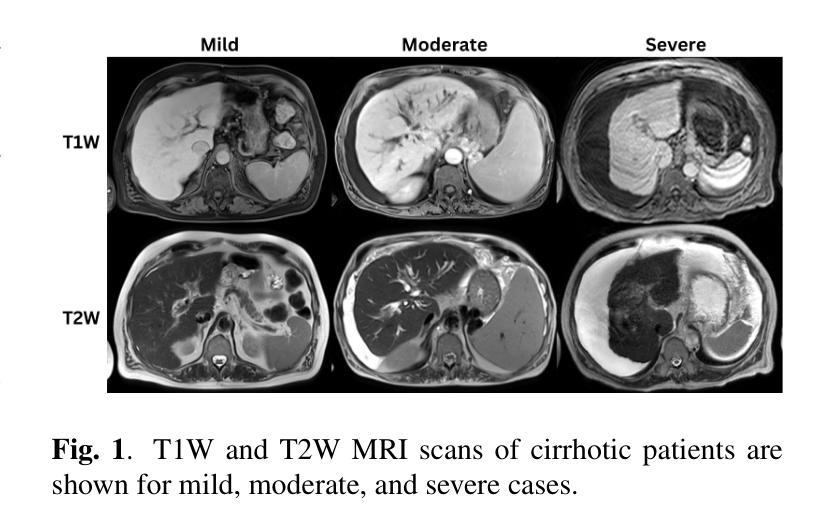
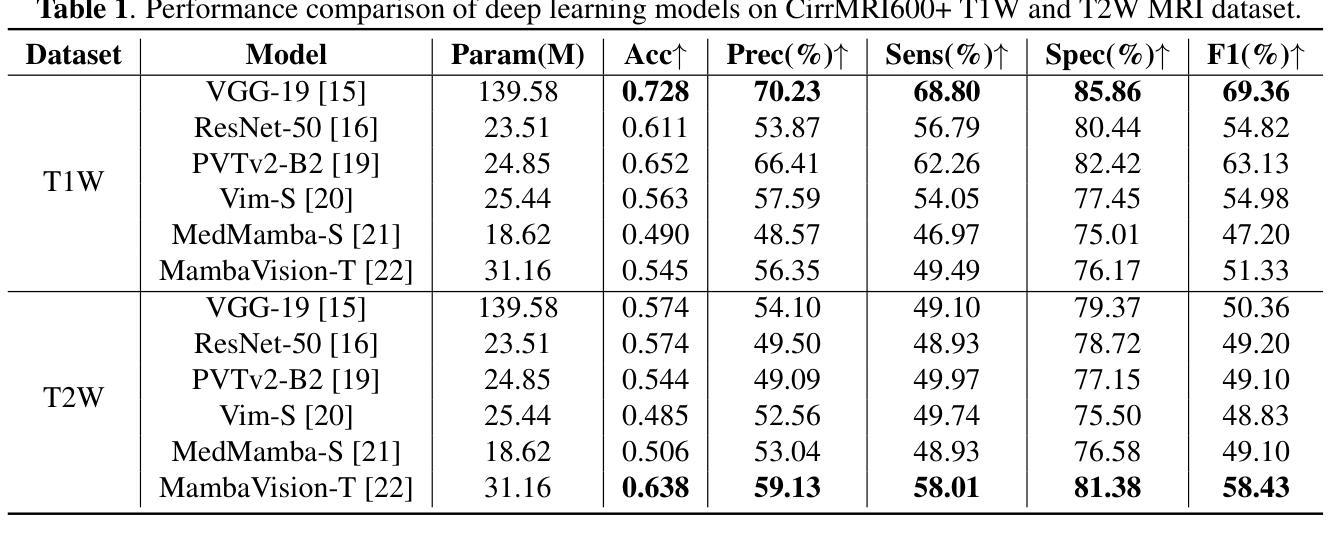
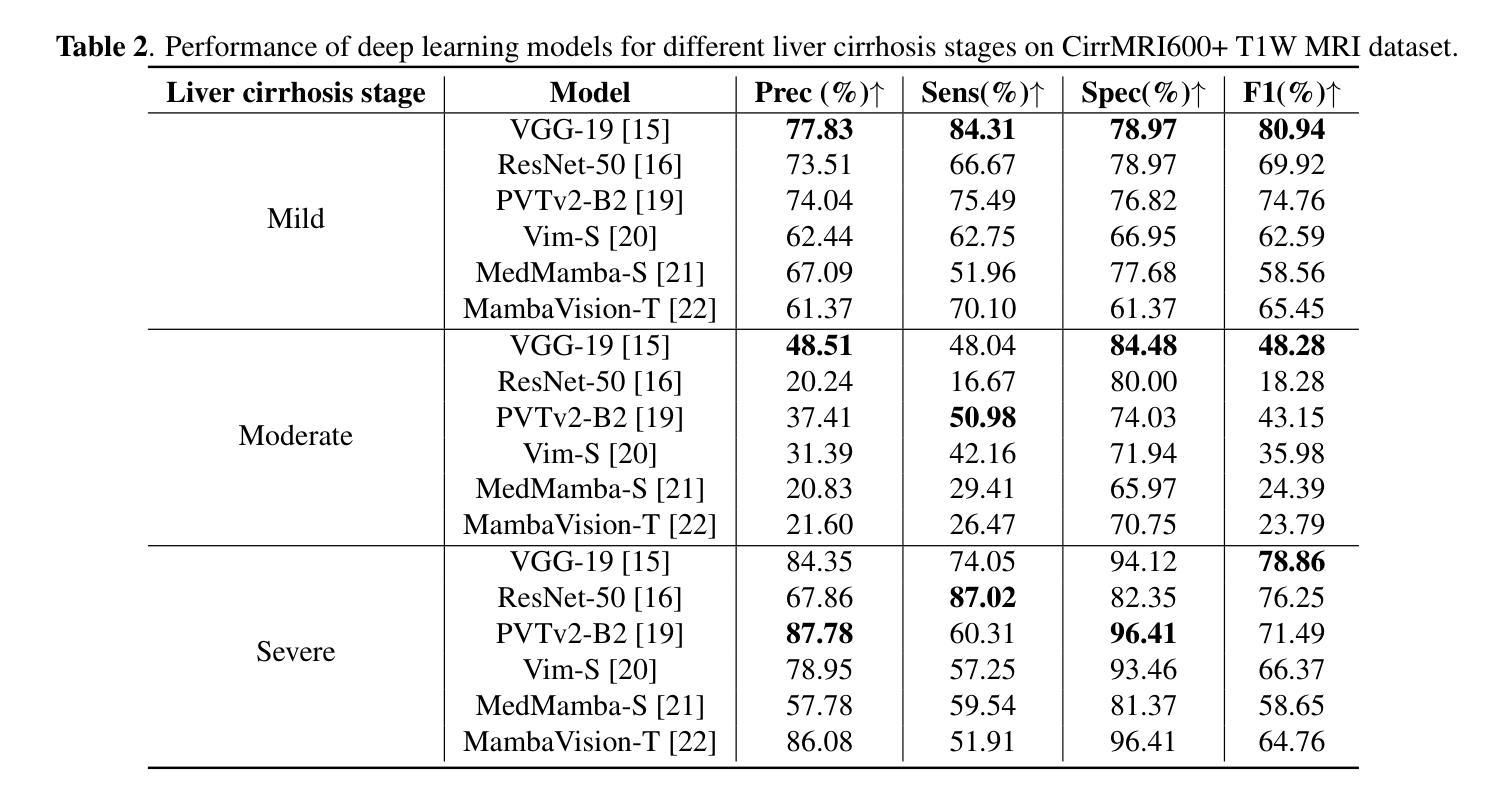
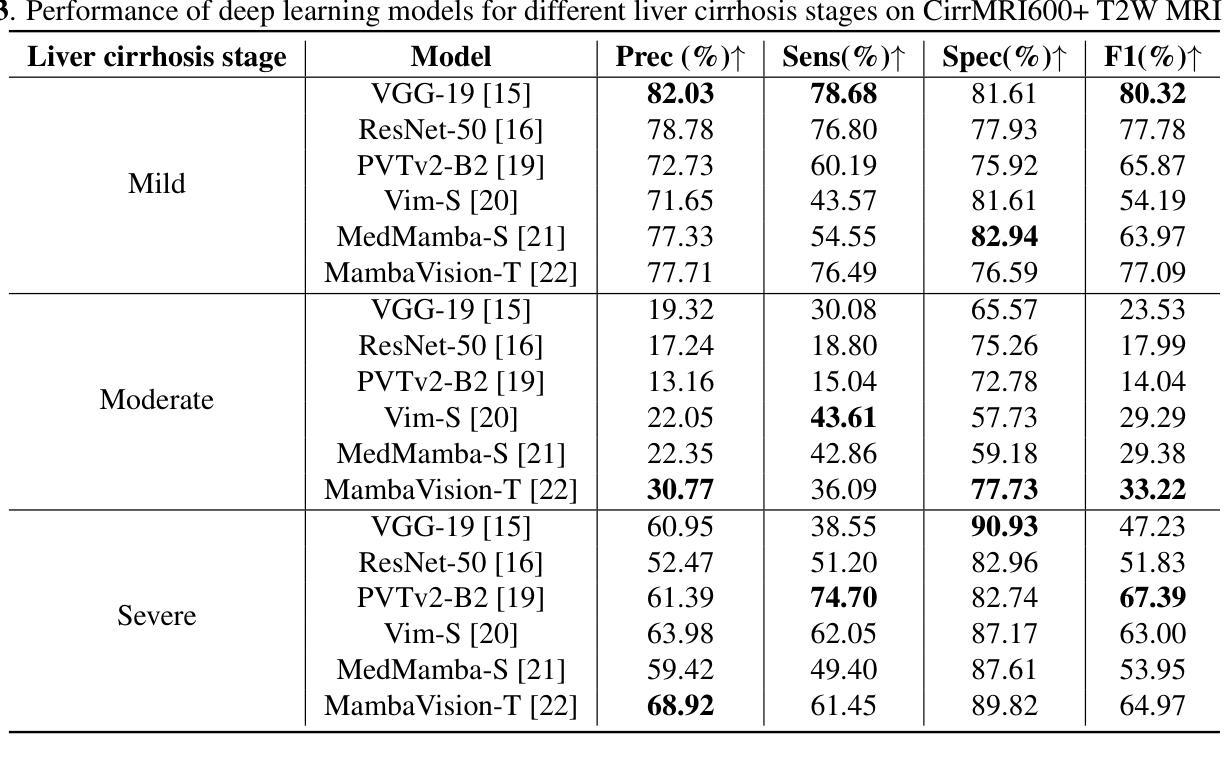
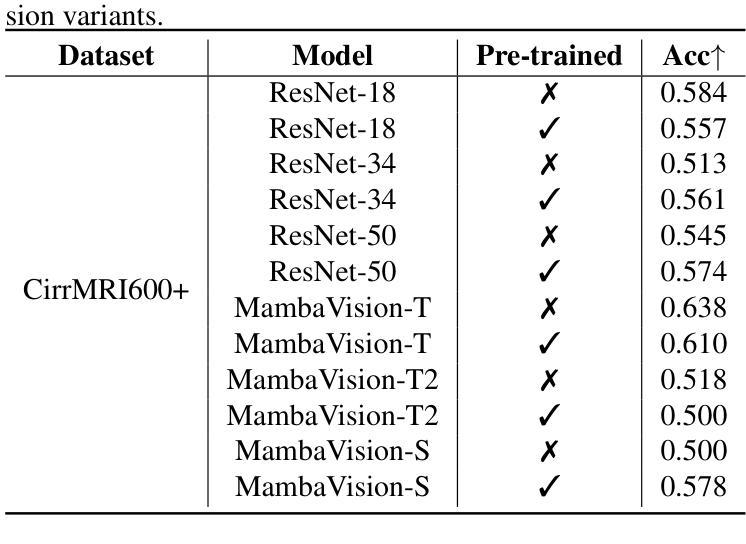
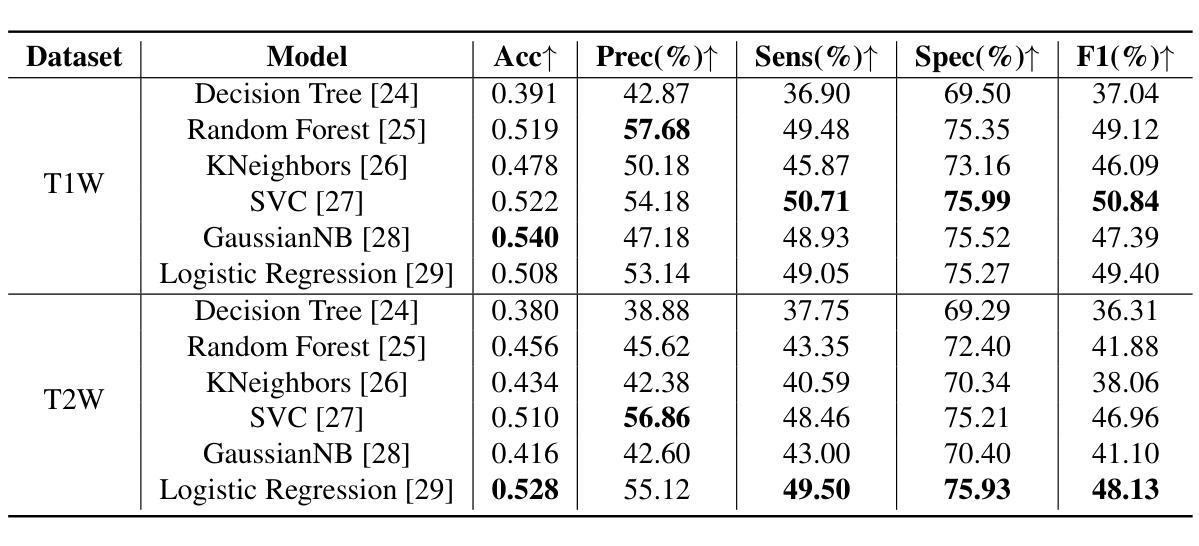
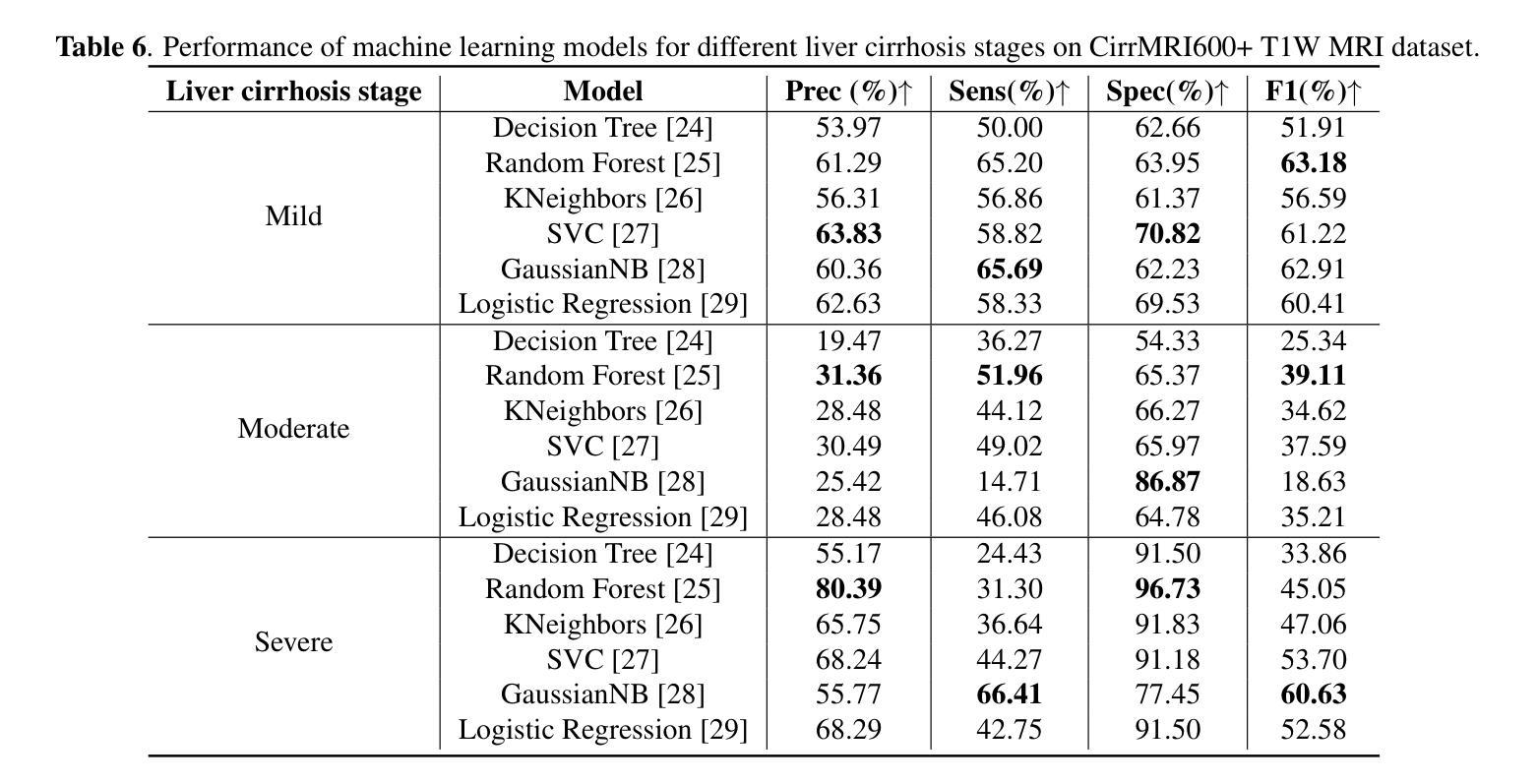
Liver Cirrhosis Stage Estimation from MRI with Deep Learning
Authors:Jun Zeng, Debesh Jha, Ertugrul Aktas, Elif Keles, Alpay Medetalibeyoglu, Matthew Antalek, Federica Proietto Salanitri, Amir A. Borhani, Daniela P. Ladner, Gorkem Durak, Ulas Bagci
We present an end-to-end deep learning framework for automated liver cirrhosis stage estimation from multi-sequence MRI. Cirrhosis is the severe scarring (fibrosis) of the liver and a common endpoint of various chronic liver diseases. Early diagnosis is vital to prevent complications such as decompensation and cancer, which significantly decreases life expectancy. However, diagnosing cirrhosis in its early stages is challenging, and patients often present with life-threatening complications. Our approach integrates multi-scale feature learning with sequence-specific attention mechanisms to capture subtle tissue variations across cirrhosis progression stages. Using CirrMRI600+, a large-scale publicly available dataset of 628 high-resolution MRI scans from 339 patients, we demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in three-stage cirrhosis classification. Our best model achieves 72.8% accuracy on T1W and 63.8% on T2W sequences, significantly outperforming traditional radiomics-based approaches. Through extensive ablation studies, we show that our architecture effectively learns stage-specific imaging biomarkers. We establish new benchmarks for automated cirrhosis staging and provide insights for developing clinically applicable deep learning systems. The source code will be available at https://github.com/JunZengz/CirrhosisStage.
我们提出了一种端到端的深度学习框架,用于从多序列MRI自动估计肝硬化分期。肝硬化是肝脏的严重瘢痕(纤维化)形成,是多种慢性肝病的常见终点。早期诊断对于预防并发症(如失代偿和癌症)至关重要,这些并发症会显著降低预期寿命。然而,在肝硬化早期进行诊断具有挑战性,患者通常会出现危及生命的并发症。我们的方法将多尺度特征学习与序列特定的注意力机制相结合,以捕捉肝硬化进展阶段中细微的组织变化。我们使用CirrMRI600+数据集,该数据集包含来自339名患者的628个高分辨率MRI扫描,展示了在三期肝硬化分类中的最新性能。我们的最佳模型在T1W上达到了72.8%的准确率,在T2W序列上达到了63.8%的准确率,显著优于传统的基于放射组学的方法。通过广泛的消融研究,我们证明了我们的架构有效地学习了与阶段相关的成像生物标志物。我们为自动化肝硬化分期设定了新的基准,并为开发临床适用的深度学习系统提供了见解。源代码将在https://github.com/JunZengz/CirrhosisStage上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 1 figure
Summary
本文介绍了一个基于深度学习的端到端框架,用于从多序列MRI中自动估计肝硬化分期。该研究利用大规模公开数据集CirrMRI600+进行三阶段肝硬化分类,并实现了先进性能,最佳模型在T1W和T2W序列上的准确率分别为72.8%和63.8%,显著优于传统基于放射学的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用深度学习方法进行肝硬化分期的自动估计。
- 利用多序列MRI数据进行肝硬化分期。
- 使用大规模公开数据集CirrMRI600+进行实验研究。
- 最佳模型在T1W和T2W序列上的准确率分别为72.8%和63.8%。
- 深度学习方法显著优于传统基于放射学的方法。
- 通过消融研究,证明该方法能有效学习阶段特定的成像生物标志物。
点此查看论文截图

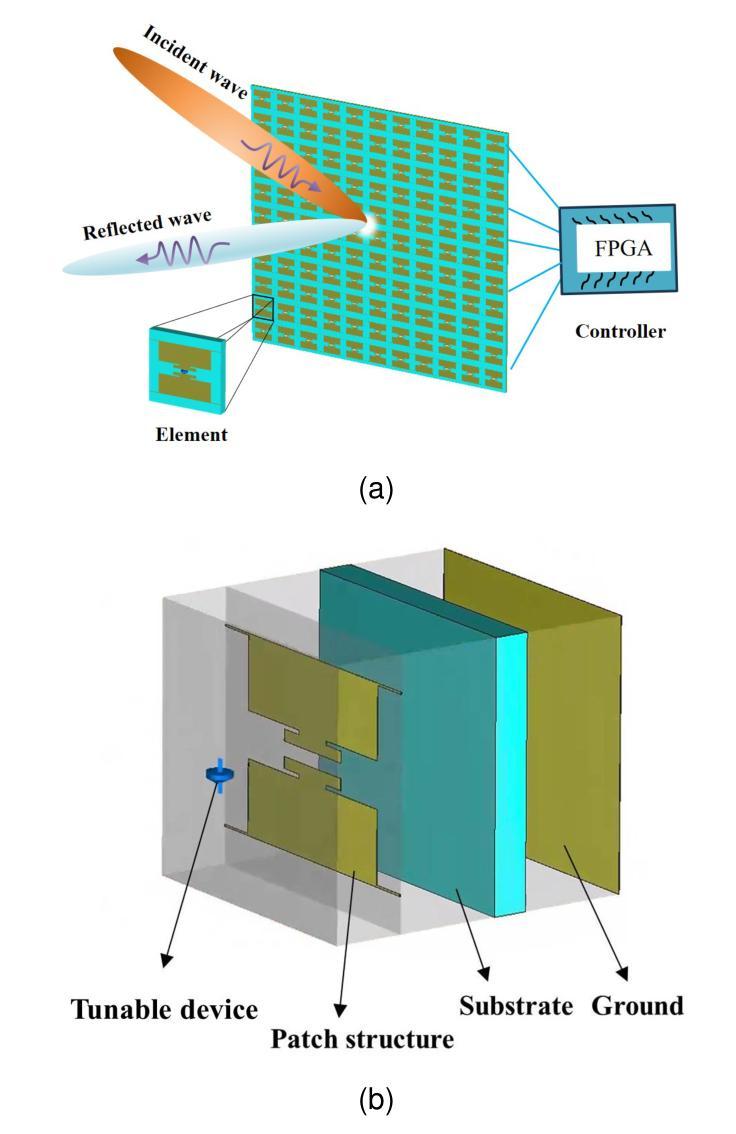
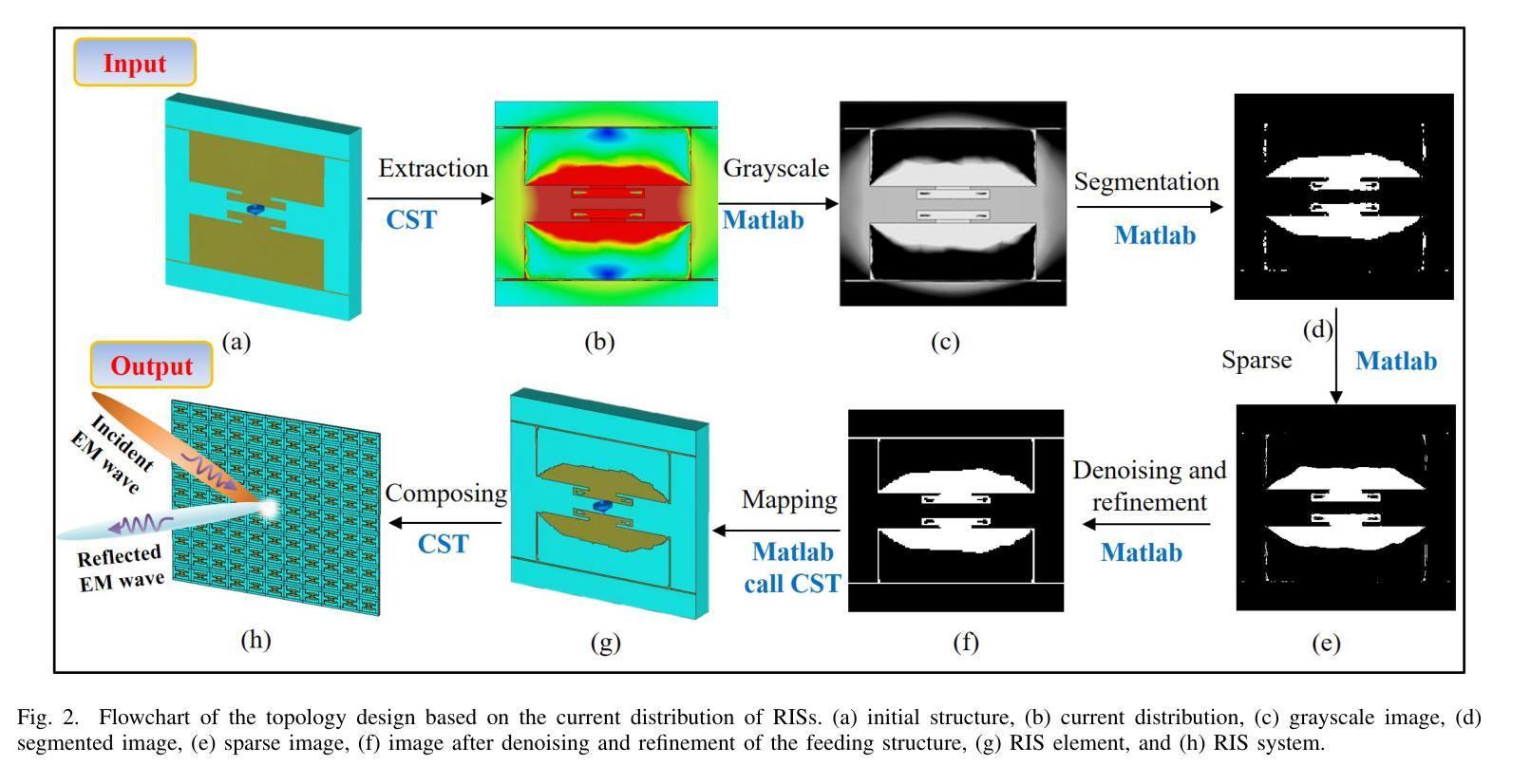
Topology Design of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Based on Current Distribution and Otsu Image Segmentation
Authors:Zhen Zhang, Jun Wei Zhang, Hui Dong Li, Junhui Qiu, Lijie Wu, Wan Wan Cao, Ren Wang, Jia Nan Zhang, Qiang Cheng
Miniaturization of reconffgurable intelligent surface RIS) elements is a crucial trend in the development of RISs. It not only facilitates the attainment of multifunctional integration but also promotes seamless amalgamation with other elements. The current on the RIS element plays a crucial role in determining the characteristics of the induced electromagnetic ffeld components. Segments with high current intensity determine the performance of RIS elements. Carving the parts with strong current distribution density into the metal patch of RIS element structure can achieve miniaturization. Based on this insight, this work proposes a topology design method that leverages current distribution and image processing techniques to achieve efffcient miniaturization of the RIS elements. In this proposed method, we ffrst obtain the current distribution across different operational states and the period of the working frequency. Next, we employ the Otsu image segmentation method to extract relevant image information from the current distribution images of the RIS elements. Subsequently, we utilize linear mapping techniques to convert this image information into the structure of RIS elements. Then, based on the structure of the RIS elements, the Quasi-Newton optimization algorithm is utilized to obtain the parameters of the tunable device that correspond to various operational states. As a result, we successfully construct the structural topology of the RIS elements based on their current distribution, designing areas with strong current distribution as metal patches. To validate the performance of the proposed method, a 16 by 16 3-bit RIS was developed, fabricated and measured. Compared with existing RIS designs, the proportion of the top-layer metal patches is smaller, which provides the possibility for integrating other functions and devices.
可重构智能表面(RIS)元素的微型化是RIS发展的重要趋势。它不仅有利于实现多功能集成,而且促进了与其他元素的无缝融合。RIS元件上的电流在决定感应电磁场组件的特性方面起着至关重要的作用。高电流强度的区域决定了RIS元件的性能。通过将电流分布密度较大的部分雕刻成RIS元件结构的金属贴片,可以实现微型化。基于这一见解,这项工作提出了一种利用电流分布和图像处理技术来实现RIS元素高效微型化的拓扑设计方法。在该方法中,我们首先获得不同工作状态下和工作频率周期的电流分布。接下来,我们采用Otsu图像分割方法从RIS元件的电流分布图像中提取相关图像信息。然后,我们利用线性映射技术将图像信息转换为RIS元件的结构。随后,基于RIS元件的结构,利用拟牛顿优化算法获得对应于各种工作状态的可调设备的参数。因此,我们成功构建了基于电流分布的RIS元素结构拓扑,设计电流分布强烈的区域作为金属贴片。为了验证所提方法的性能,开发、制作并测量了一个16x16 3位RIS。与现有的RIS设计相比,顶层金属贴片的比例较小,这为集成其他功能和设备提供了可能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了可重构智能表面(RIS)元素的微型化趋势,指出微型化有助于实现多功能集成和与其他元素的无缝融合。文章提出了基于电流分布和图像处理技术的拓扑设计方法,以实现RIS元素的高效微型化。该方法首先获取不同工作状态下和工作频率周期的电流分布,然后采用Otsu图像分割方法提取RIS元素的电流分布图像的相关信息,再利用线性映射技术将图像信息转换为RIS元素的结构。最后,基于Quasi-Newton优化算法获取与各种工作状态相对应的可调设备的参数。研究结果表明,该方法成功构建了基于电流分布的RIS元素结构拓扑,并验证了所提出方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 可重构智能表面(RIS)元素的微型化是发展的关键趋势,有助于实现多功能集成和与其他元素的融合。
- 电流分布在决定RIS元素特性方面起着关键作用,高电流强度区域影响RIS元素性能。
- 通过在金属贴片结构中精细雕刻强电流分布的部分来实现微型化。
- 提出了一种基于电流分布和图像处理技术的拓扑设计方法。
- 该方法涉及获取不同工作状态和工作频率周期的电流分布,并采用Otsu图像分割法提取相关信息。
- 使用线性映射技术和Quasi-Newton优化算法将图像信息转换为RIS元素的结构并获取可调设备参数。
点此查看论文截图

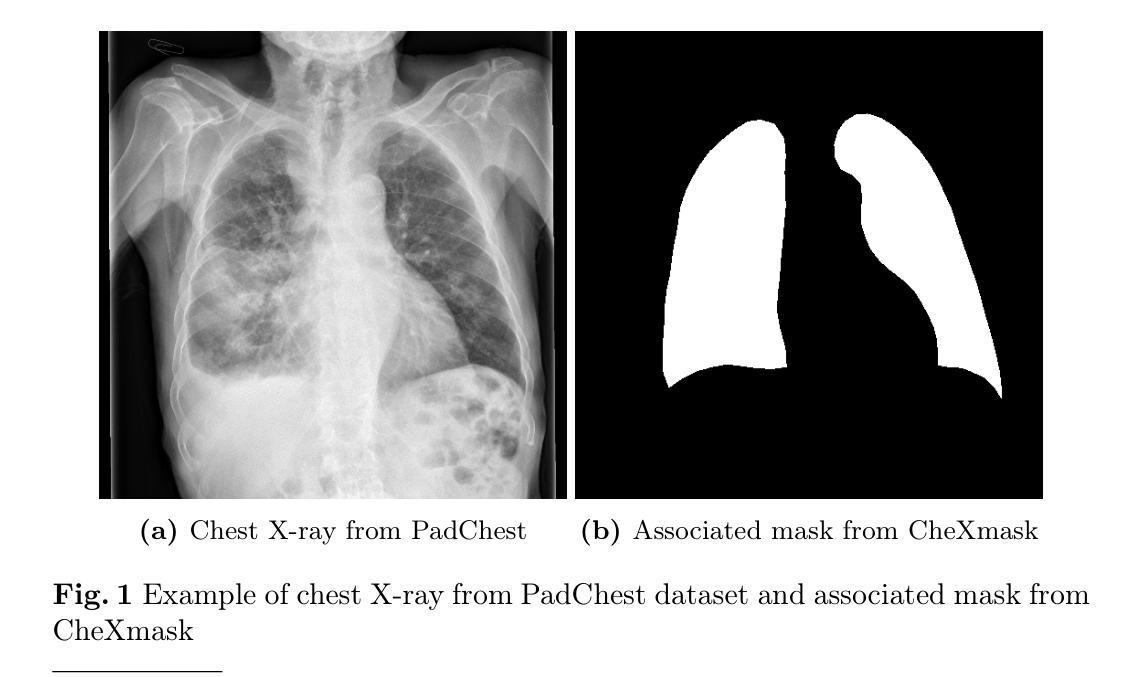
Mask of truth: model sensitivity to unexpected regions of medical images
Authors:Théo Sourget, Michelle Hestbek-Møller, Amelia Jiménez-Sánchez, Jack Junchi Xu, Veronika Cheplygina
The development of larger models for medical image analysis has led to increased performance. However, it also affected our ability to explain and validate model decisions. Models can use non-relevant parts of images, also called spurious correlations or shortcuts, to obtain high performance on benchmark datasets but fail in real-world scenarios. In this work, we challenge the capacity of convolutional neural networks (CNN) to classify chest X-rays and eye fundus images while masking out clinically relevant parts of the image. We show that all models trained on the PadChest dataset, irrespective of the masking strategy, are able to obtain an Area Under the Curve (AUC) above random. Moreover, the models trained on full images obtain good performance on images without the region of interest (ROI), even superior to the one obtained on images only containing the ROI. We also reveal a possible spurious correlation in the Chaksu dataset while the performances are more aligned with the expectation of an unbiased model. We go beyond the performance analysis with the usage of the explainability method SHAP and the analysis of embeddings. We asked a radiology resident to interpret chest X-rays under different masking to complement our findings with clinical knowledge. Our code is available at https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking and https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking_EyeFundus
开发用于医学图像分析的大型模型已经提高了性能。然而,这也影响了我们解释和验证模型决策的能力。模型可能会使用与图像不相关的部分(也称为偶然关联或捷径)来获得基准数据集上的高性能,但在现实世界的场景中却会失败。在这项工作中,我们通过遮挡医学上重要的图像部分来挑战卷积神经网络(CNN)对胸部X射线和眼底图像的分类能力。我们显示,在PadChest数据集上训练的所有模型,无论采用何种遮挡策略,都能获得高于随机的曲线下面积(AUC)。此外,在完整图像上训练的模型在没有感兴趣区域(ROI)的图像上也能获得良好的性能,甚至优于仅在包含ROI的图像上获得的性能。我们还揭示了Chaksu数据集中可能存在的偶然关联,同时其性能更符合无偏见模型的预期。除了性能分析,我们还使用了SHAP解释方法和嵌入分析。我们邀请了一位放射科住院医师在不同遮挡条件下解读胸部X射线,以结合我们的临床知识发现。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking 和 https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking_EyeFundus。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Updated after publication in the Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine
Summary
医学图像分析模型发展提升性能,但难以解释和验证决策。模型可能利用图像的非关键部分获得高基准数据集性能,但在真实场景中失败。研究挑战卷积神经网络对胸部X光和眼底图像的分类能力,同时掩盖临床上关键部分。模型在无关区域上表现良好,甚至优于仅包含ROI的图像。代码公开。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析模型性能提升同时,存在解释和验证决策困难的问题。
- 模型可能利用图像的非相关部分(即偶然关联或捷径)获得高基准数据集性能,但在真实场景中应用时可能失败。
- 研究评估了卷积神经网络对胸部X光和眼底图像分类的能力,并在掩盖临床关键部分的情况下进行了测试。
- 所有在PadChest数据集上训练的模型,无论采用何种掩盖策略,都能获得超过随机的AUC性能。
- 在无关区域上训练的模型表现出良好的性能,甚至在某些情况下优于仅包含ROI的图像。
- 研究发现了Chaksu数据集中的一种可能的偶然关联。
点此查看论文截图

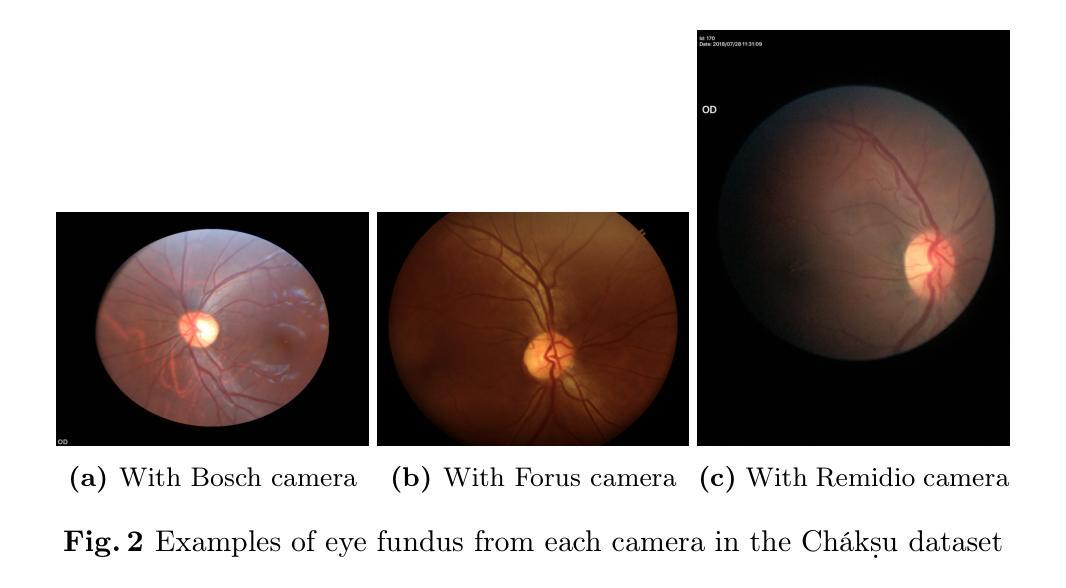
KAN-Mamba FusionNet: Redefining Medical Image Segmentation with Non-Linear Modeling
Authors:Akansh Agrawal, Akshan Agrawal, Shashwat Gupta, Priyanka Bagade
Medical image segmentation is essential for applications like robotic surgeries, disease diagnosis, and treatment planning. Recently, various deep-learning models have been proposed to enhance medical image segmentation. One promising approach utilizes Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs), which better capture non-linearity in input data. However, they are unable to effectively capture long-range dependencies, which are required to accurately segment complex medical images and, by that, improve diagnostic accuracy in clinical settings. Neural networks such as Mamba can handle long-range dependencies. However, they have a limited ability to accurately capture non-linearities in the images as compared to KANs. Thus, we propose a novel architecture, the KAN-Mamba FusionNet, which improves segmentation accuracy by effectively capturing the non-linearities from input and handling long-range dependencies with the newly proposed KAMBA block. We evaluated the proposed KAN-Mamba FusionNet on three distinct medical image segmentation datasets: BUSI, Kvasir-Seg, and GlaS - and found it consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in IoU and F1 scores. Further, we examined the effects of various components and assessed their contributions to the overall model performance via ablation studies. The findings highlight the effectiveness of this methodology for reliable medical image segmentation, providing a unique approach to address intricate visual data issues in healthcare.
医学图像分割对于机器人手术、疾病诊断和治疗计划等应用至关重要。最近,为了提升医学图像分割的效果,已经提出了各种深度学习模型。一种有前途的方法是利用Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs),它能更好地捕捉输入数据中的非线性。然而,它们无法有效地捕捉长距离依赖关系,这对于准确分割复杂的医学图像以及在临床环境中提高诊断准确性是必要的。神经网络(如Mamba)能够处理长距离依赖关系,但与KANs相比,它们在准确捕捉图像非线性方面的能力有限。因此,我们提出了一种新型架构,即KAN-Mamba FusionNet,它通过有效捕捉输入的非线性和使用新提出的KAMBA块来处理长距离依赖关系,提高了分割准确性。我们在三个不同的医学图像分割数据集上评估了所提出的KAN-Mamba FusionNet:BUSI、Kvasir-Seg和GlaS,发现它在IoU和F1分数上均优于最先进的方法。此外,我们研究了各种组件的影响,并通过消融研究评估了它们对整体模型性能的贡献。研究结果表明,该方法在可靠的医学图像分割方面的有效性,为医疗保健中复杂的视觉数据问题提供了独特的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables
Summary
基于Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)和Mamba神经网络的优势,提出了一种新的医学图像分割网络架构——KAN-Mamba FusionNet。该架构融合了KANs对非线性的捕捉能力和Mamba对长距离依赖的处理能力,通过新提出的KAMBA模块,提高了分割准确度和诊断准确性。在多个数据集上的评估证明了其表现优于其他前沿方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在机器人手术、疾病诊断和治疗计划等应用中至关重要。
- 最近提出的深度学习模型如Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KANs)和Mamba神经网络在医学图像分割中有潜力。
- KANs能够更好地捕捉输入数据的非线性,但无法有效捕捉长距离依赖关系。
- Mamba神经网络能够处理长距离依赖关系,但在捕捉图像非线性方面能力有限。
- 提出的KAN-Mamba FusionNet结合了KANs和Mamba的优势,通过KAMBA模块提高了分割准确性。
- 在三个不同的医学图像分割数据集上评估,KAN-Mamba FusionNet的表现优于其他最新方法。
- 通过消融研究,证实了架构中各个组件的有效性及其对模型性能的贡献。
点此查看论文截图

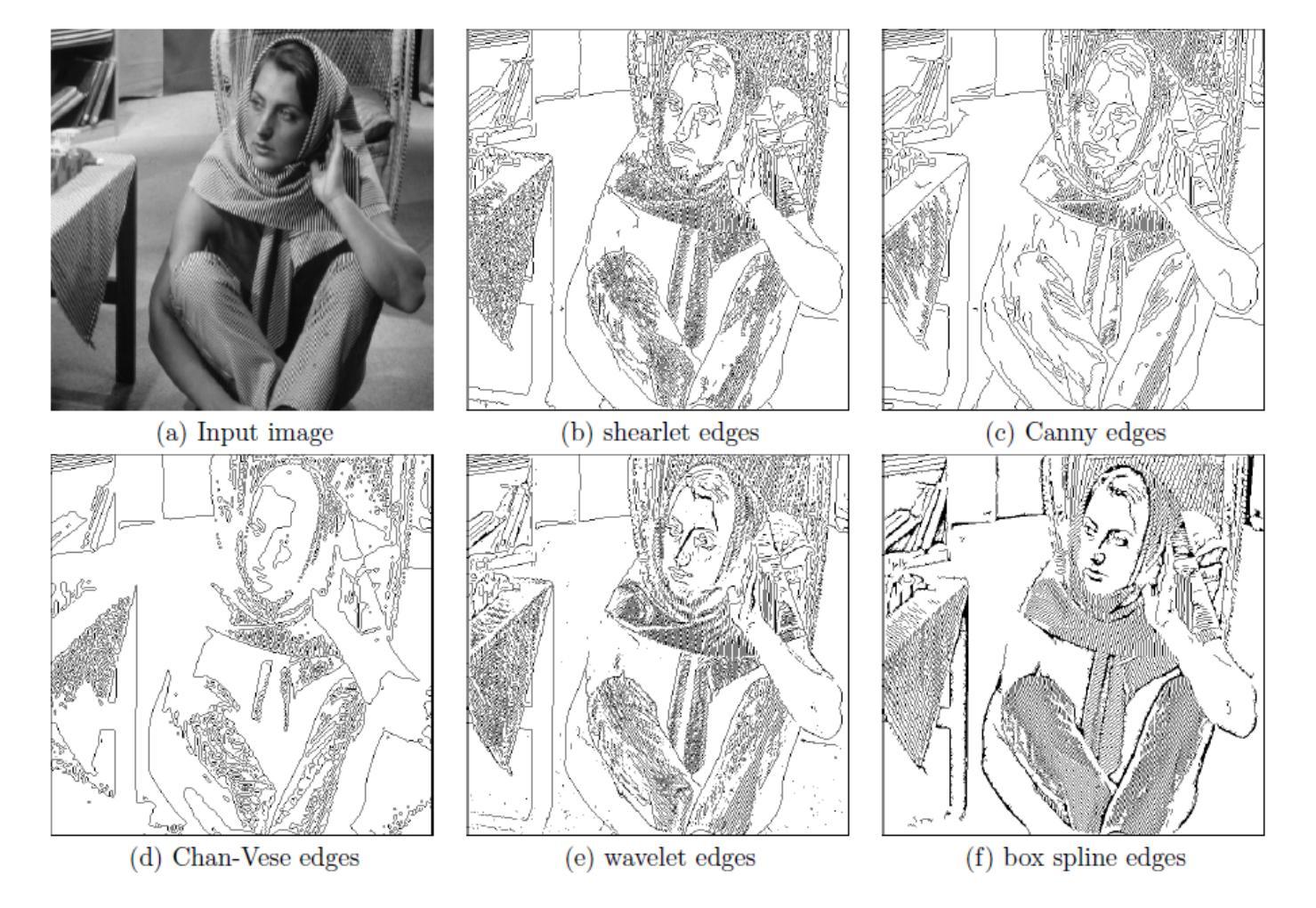
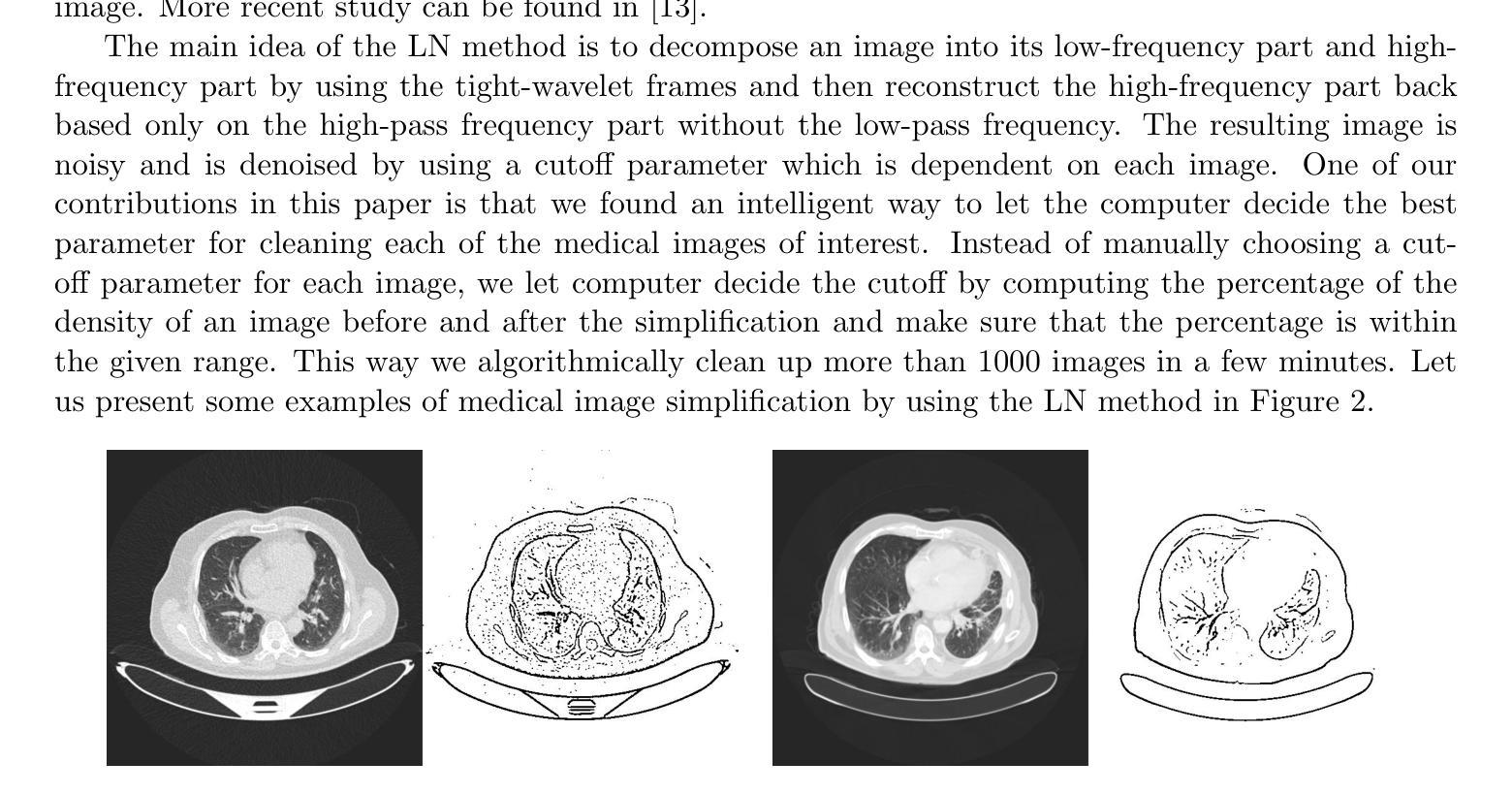
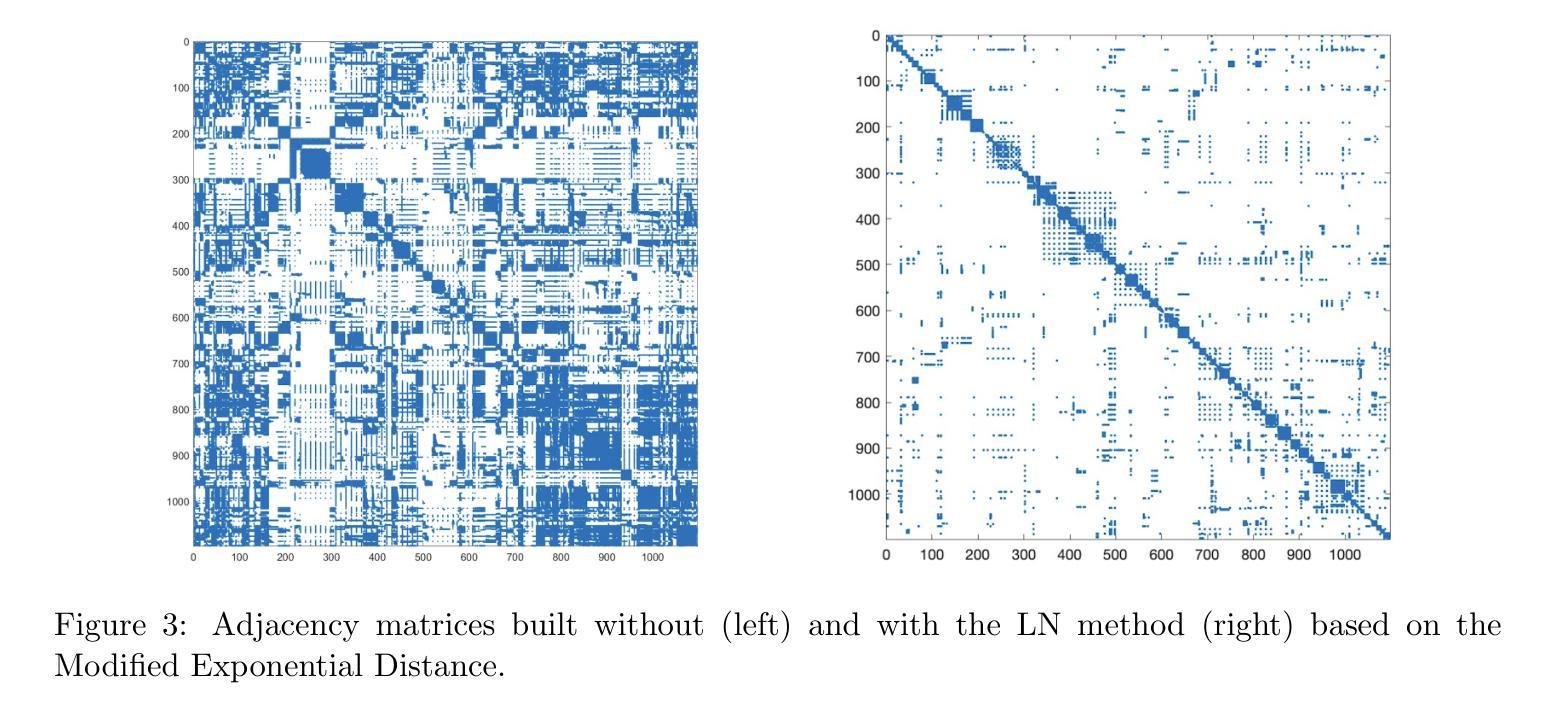
Local Clustering for Lung Cancer Image Classification via Sparse Solution Technique
Authors:Jackson Hamel, Ming-Jun Lai, Zhaiming Shen, Ye Tian
In this work, we propose to use a local clustering approach based on the sparse solution technique to study the medical image, especially the lung cancer image classification task. We view images as the vertices in a weighted graph and the similarity between a pair of images as the edges in the graph. The vertices within the same cluster can be assumed to share similar features and properties, thus making the applications of graph clustering techniques very useful for image classification. Recently, the approach based on the sparse solutions of linear systems for graph clustering has been found to identify clusters more efficiently than traditional clustering methods such as spectral clustering. We propose to use the two newly developed local clustering methods based on sparse solution of linear system for image classification. In addition, we employ a box spline-based tight-wavelet-framelet method to clean these images and help build a better adjacency matrix before clustering. The performance of our methods is shown to be very effective in classifying images. Our approach is significantly more efficient and either favorable or equally effective compared with other state-of-the-art approaches. Finally, we shall make a remark by pointing out two image deformation methods to build up more artificial image data to increase the number of labeled images.
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于稀疏解技术的局部聚类方法,用于医学图像的研究,特别是在肺癌图像分类任务中的应用。我们将图像视为加权图中的顶点,将图像之间的相似性视为图中的边。同一聚类中的顶点可以假定具有相似的特征和属性,这使得图聚类技术在图像分类中的应用非常有用。最近发现,基于线性系统稀疏解的聚类方法比传统的聚类方法(如谱聚类)更能有效地识别聚类。我们建议使用两种新开发的基于线性系统稀疏解的局部聚类方法进行图像分类。此外,我们还采用基于箱线紧小波框架的方法对图像进行清理,帮助在聚类之前建立更好的邻接矩阵。我们的方法在图像分类方面的表现非常有效,与其他最新方法相比,我们的方法更有效率,要么具有优势,要么同样有效。最后,我们应该指出两种图像变形方法来建立更多的人工图像数据,以增加标记图像的数量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出利用基于稀疏解技术的局部聚类方法,针对医学图像尤其是肺癌图像分类任务进行研究。将图像视为加权图中的顶点,图像间的相似性视为图中的边。同一聚类中的顶点可视为具有相似特征和属性,因此图聚类技术对于图像分类非常有用。基于线性系统稀疏解的图聚类方法能更有效地识别聚类。此外,还采用了基于盒状样条的紧小波框架方法对图像进行清洗,帮助建立更好的邻接矩阵进行聚类。该方法在图像分类方面表现出非常有效的性能,与其他最新方法相比,具有更高的效率,要么优越,要么相当。最后提出了两种生成更多人工图像数据的方法以增加标注图像的数量。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用基于稀疏解技术的局部聚类方法用于医学图像分类,特别是肺癌图像分类。
- 将图像视为加权图中的顶点,图像间的相似性视为图中的边,应用图聚类技术进行分类。
- 基于线性系统稀疏解的图聚类方法能更有效地识别聚类,提高图像分类性能。
- 采用盒状样条的紧小波框架方法对图像进行清洗,优化邻接矩阵的建立。
- 该方法相较于其他最新方法具有显著优势,表现为高效率、优越或相当有效。
- 提出了通过图像变形方法生成更多人工图像数据以增加标注图像数量的策略。
- 该研究为医学图像分类提供了新的视角和技术手段。
点此查看论文截图


DEFT: Efficient Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Models by Learning the Generalised $h$-transform
Authors:Alexander Denker, Francisco Vargas, Shreyas Padhy, Kieran Didi, Simon Mathis, Vincent Dutordoir, Riccardo Barbano, Emile Mathieu, Urszula Julia Komorowska, Pietro Lio
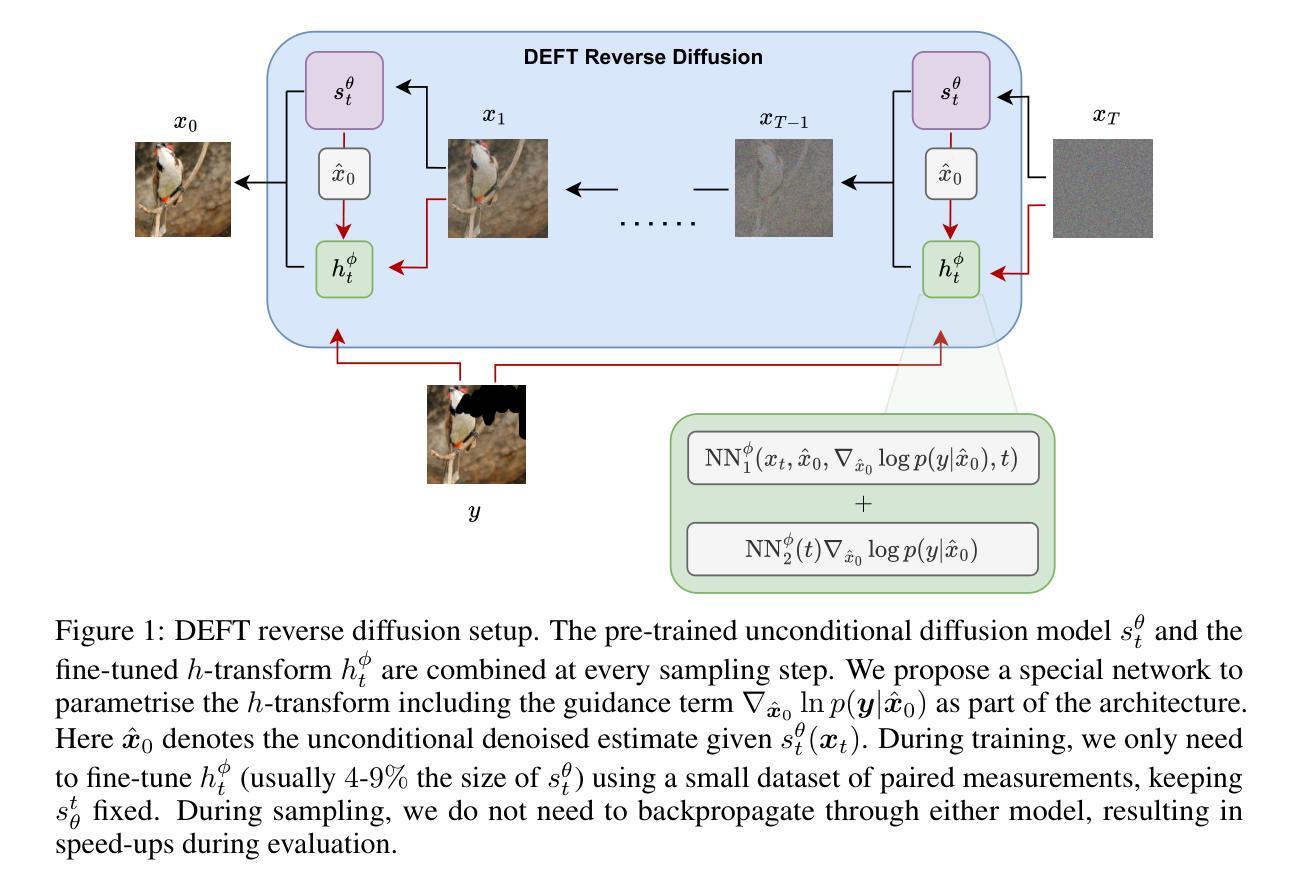
Generative modelling paradigms based on denoising diffusion processes have emerged as a leading candidate for conditional sampling in inverse problems. In many real-world applications, we often have access to large, expensively trained unconditional diffusion models, which we aim to exploit for improving conditional sampling. Most recent approaches are motivated heuristically and lack a unifying framework, obscuring connections between them. Further, they often suffer from issues such as being very sensitive to hyperparameters, being expensive to train or needing access to weights hidden behind a closed API. In this work, we unify conditional training and sampling using the mathematically well-understood Doob’s h-transform. This new perspective allows us to unify many existing methods under a common umbrella. Under this framework, we propose DEFT (Doob’s h-transform Efficient FineTuning), a new approach for conditional generation that simply fine-tunes a very small network to quickly learn the conditional $h$-transform, while keeping the larger unconditional network unchanged. DEFT is much faster than existing baselines while achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of linear and non-linear benchmarks. On image reconstruction tasks, we achieve speedups of up to 1.6$\times$, while having the best perceptual quality on natural images and reconstruction performance on medical images. Further, we also provide initial experiments on protein motif scaffolding and outperform reconstruction guidance methods.
基于去噪扩散过程的生成建模范式已成为逆问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。在许多实际应用中,我们通常可以访问大型且经过昂贵训练的无条件扩散模型,我们旨在利用这些模型来改善条件采样。最近的方法大多是启发式且缺乏统一框架,导致它们之间的联系模糊。此外,它们经常面临诸如对超参数非常敏感、训练成本高昂或需要访问封闭API后面的权重等问题。在这项工作中,我们使用数学上理解良好的Doob的h转换来统一条件训练和采样。这个新视角允许我们将许多现有方法纳入同一框架下。在这个框架下,我们提出了DEFT(Doob的h转换高效微调),这是一种新的条件生成方法,它只需微调一个非常小的网络,即可快速学习条件h转换,同时保持较大的无条件网络不变。DEFT相比现有基准测试速度更快,同时在各种线性和非线性基准测试中实现了最先进的性能。在图像重建任务上,我们实现了最高达1.6倍的加速,同时在自然图像上获得最佳的感知质量和在医学图像上的重建性能。此外,我们还进行了初步的蛋白质基序支架实验,并在重建指导方法上表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2312.09236
Summary
基于去噪扩散过程的生成建模范式已成为解决反问题中条件采样的领先候选方法。本文利用数学上理解良好的Doob的h-变换统一了条件训练和采样。在此基础上,提出了DEFT(Doob的h-变换高效微调)这一新的条件生成方法,只需微调一个非常小的网络即可快速学习条件h-变换,同时保持较大的无条件网络不变。DEFT在多种线性和非线性基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,在图像重建任务上实现了最高达1.6倍的速度提升,同时在自然图像上具有最佳的感知质量和医疗图像的重建性能。此外,还在蛋白质基序支架方面进行了初步实验,并超越了重建指导方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成建模范式在解决反问题的条件采样中占据领先地位,其中基于去噪扩散过程的方法受到关注。
- 现有方法缺乏统一框架,且存在超参数敏感、训练成本高昂、依赖封闭API等问题。
- 引入Doob的h-变换来统一条件训练和采样,提供了一个新的视角。
- 提出DEFT方法,通过微调小网络快速学习条件h-变换,保持大网络不变,实现快速且高质量的条件生成。
- DEFT在图像重建任务上实现了显著的速度提升和感知质量改进。
- DEFT在医疗图像重建方面表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Breast Cancer Classification Using Gradient Boosting Algorithms Focusing on Reducing the False Negative and SHAP for Explainability
Authors:João Manoel Herrera Pinheiro, Marcelo Becker
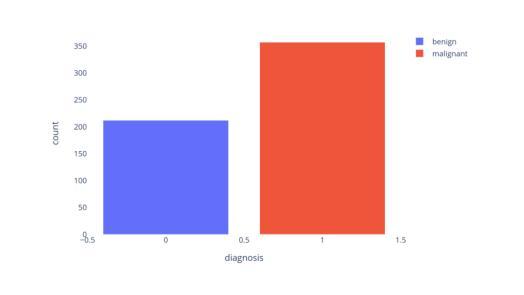
Cancer is one of the diseases that kill the most women in the world, with breast cancer being responsible for the highest number of cancer cases and consequently deaths. However, it can be prevented by early detection and, consequently, early treatment. Any development for detection or perdition this kind of cancer is important for a better healthy life. Many studies focus on a model with high accuracy in cancer prediction, but sometimes accuracy alone may not always be a reliable metric. This study implies an investigative approach to studying the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on boosting to predict breast cancer focusing on the recall metric. Boosting machine learning algorithms has been proven to be an effective tool for detecting medical diseases. The dataset of the University of California, Irvine (UCI) repository has been utilized to train and test the model classifier that contains their attributes. The main objective of this study is to use state-of-the-art boosting algorithms such as AdaBoost, XGBoost, CatBoost and LightGBM to predict and diagnose breast cancer and to find the most effective metric regarding recall, ROC-AUC, and confusion matrix. Furthermore, our study is the first to use these four boosting algorithms with Optuna, a library for hyperparameter optimization, and the SHAP method to improve the interpretability of our model, which can be used as a support to identify and predict breast cancer. We were able to improve AUC or recall for all the models and reduce the False Negative for AdaBoost and LigthGBM the final AUC were more than 99.41% for all models.
癌症是世界上导致女性死亡的主要疾病之一,其中乳腺癌病例数和死亡人数均居首位。然而,通过早期发现和早期治疗,癌症是可以预防的。任何有助于检测或预防这类癌症的发展对于更好地生活具有重要意义。许多研究集中在开发具有高精度预测癌症的模型上,但有时仅依靠准确性可能并不是一个可靠的指标。本研究采用一种基于boosting的机器学习方法来研究预测乳腺癌的性能,重点研究召回率指标。已有研究证明,使用boosting算法的机器学习是检测医学疾病的有效工具。本研究使用了加利福尼亚大学欧文分校(UCI)存储库的数据集来训练和测试分类模型,该模型包含了各种属性。本研究的主要目标是使用最新的boosting算法(如AdaBoost、XGBoost、CatBoost和LightGBM)来预测和诊断乳腺癌,并找到关于召回率、ROC-AUC和混淆矩阵的最有效指标。此外,我们的研究是首次将这四个boosting算法与用于超参数优化的Optuna库以及SHAP方法相结合,以提高我们模型的解释性,可作为检测和预测乳腺癌的辅助工具。我们成功提高了所有模型的AUC或召回率,并降低了AdaBoost和LightGBM的假阴性结果。所有模型的最终AUC均超过99.41%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文研究了利用机器学习算法预测乳腺癌的问题。研究通过使用AdaBoost、XGBoost、CatBoost和LightGBM等先进算法进行训练和测试模型分类器,并利用数据集找出最有效的评价指标关于召回率、ROC-AUC和混淆矩阵。该研究首次结合Optuna库进行超参数优化和SHAP方法改善模型的可解释性,从而有效改善乳腺癌的诊断与预测效果。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是世界范围内导致女性死亡的主要疾病之一,早期检测和预防是关键。
- 仅依赖准确性作为评估指标可能不足够可靠,因此本研究关注召回率等评价指标。
- 研究使用了加州大学欧文分校(UCI)的数据集进行模型训练和测试。
- AdaBoost、XGBoost、CatBoost和LightGBM等算法被应用于预测和诊断乳腺癌。
- 结合Optuna库进行超参数优化,并使用SHAP方法提高模型的可解释性。
- 所有模型的AUC或召回率均有所提升,AdaBoost和LightGBM的假阴性结果有所降低。
点此查看论文截图

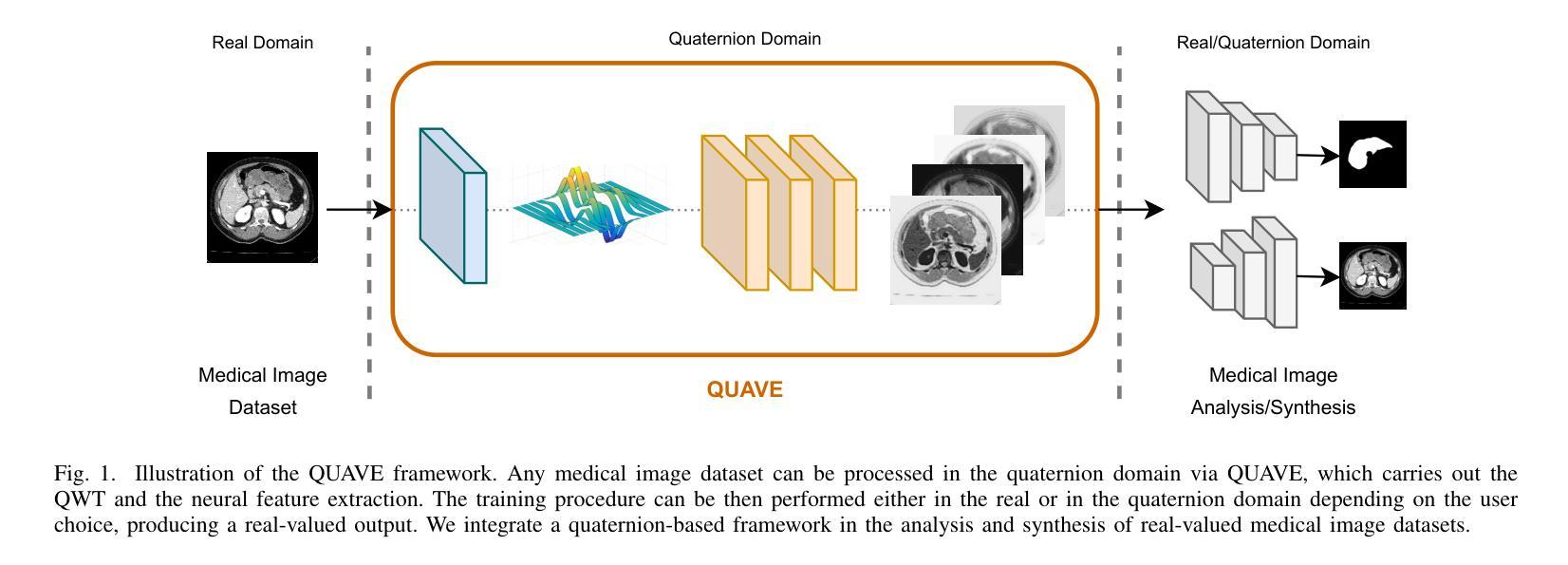
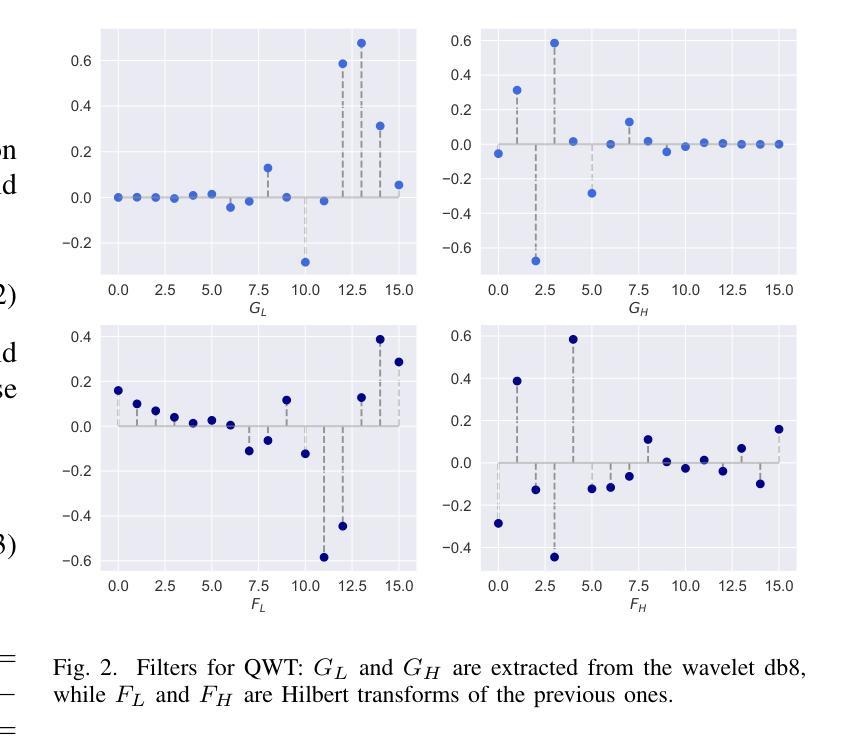
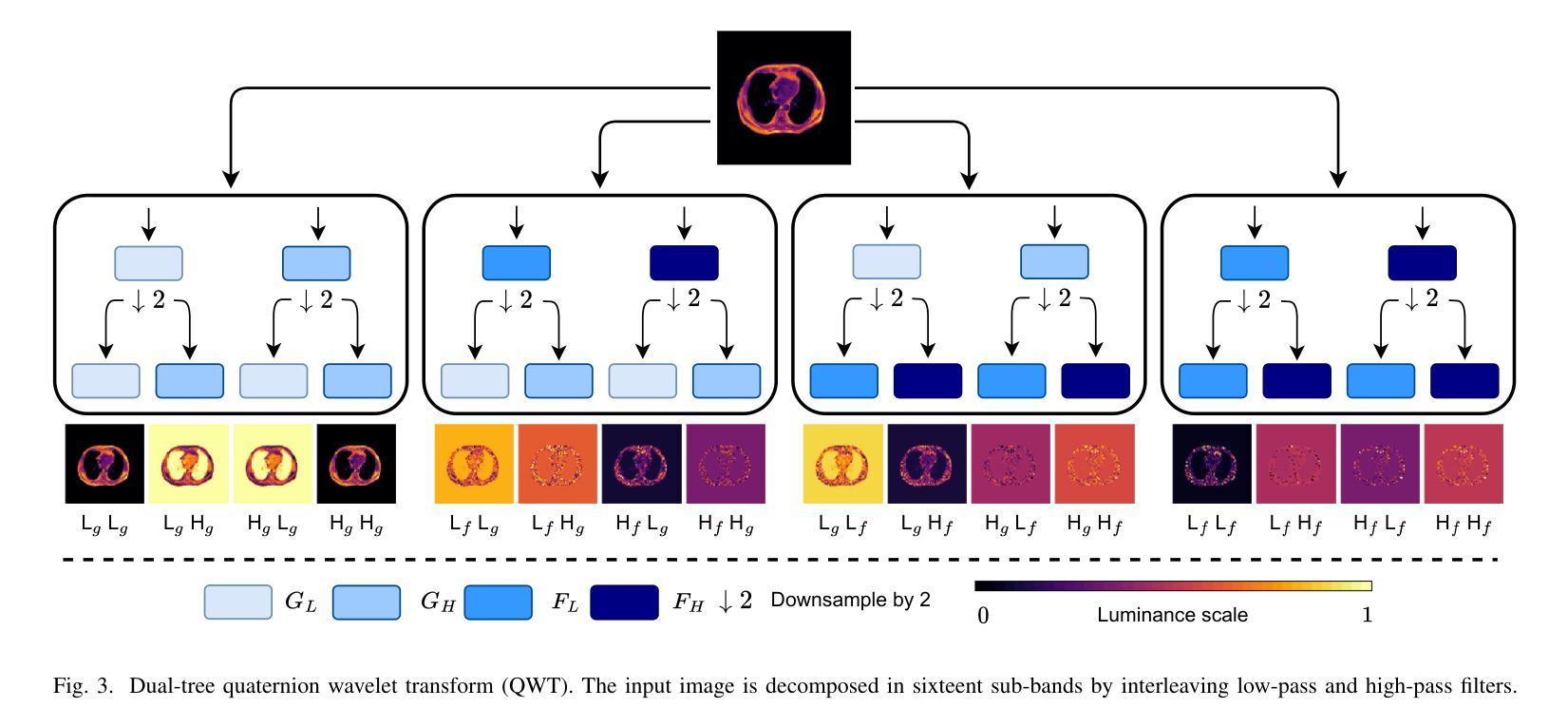
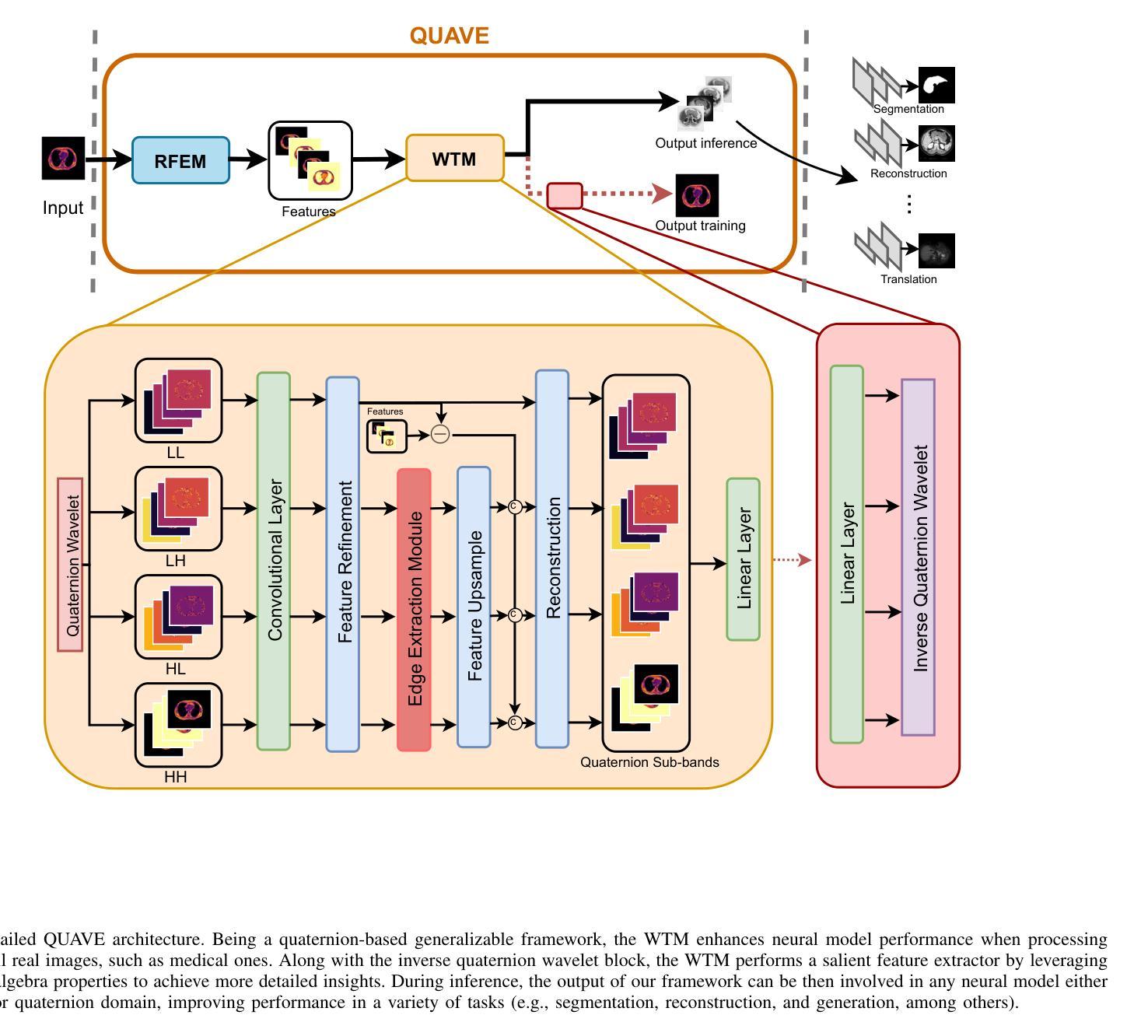
Generalizing Medical Image Representations via Quaternion Wavelet Networks
Authors:Luigi Sigillo, Eleonora Grassucci, Aurelio Uncini, Danilo Comminiello
Neural network generalizability is becoming a broad research field due to the increasing availability of datasets from different sources and for various tasks. This issue is even wider when processing medical data, where a lack of methodological standards causes large variations being provided by different imaging centers or acquired with various devices and cofactors. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel, generalizable, data- and task-agnostic framework able to extract salient features from medical images. The proposed quaternion wavelet network (QUAVE) can be easily integrated with any pre-existing medical image analysis or synthesis task, and it can be involved with real, quaternion, or hypercomplex-valued models, generalizing their adoption to single-channel data. QUAVE first extracts different sub-bands through the quaternion wavelet transform, resulting in both low-frequency/approximation bands and high-frequency/fine-grained features. Then, it weighs the most representative set of sub-bands to be involved as input to any other neural model for image processing, replacing standard data samples. We conduct an extensive experimental evaluation comprising different datasets, diverse image analysis, and synthesis tasks including reconstruction, segmentation, and modality translation. We also evaluate QUAVE in combination with both real and quaternion-valued models. Results demonstrate the effectiveness and the generalizability of the proposed framework that improves network performance while being flexible to be adopted in manifold scenarios and robust to domain shifts. The full code is available at: https://github.com/ispamm/QWT.
神经网络泛化性因不同来源和任务的数据集日益增多而成为一个广泛的研究领域。在处理医疗数据时,这个问题更为突出,因为缺乏方法论标准导致由不同成像中心或通过各种设备和辅助因素获得的数据存在很大差异。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了一种新型、可泛化的、独立于数据和任务的分析框架,能够从医学图像中提取重要特征。所提出的四元小波网络(QUAVE)可以轻松地与任何现有的医学图像分析或合成任务集成,并且可以涉及实数、四元数或超复数模型,将其推广到单通道数据。QUAVE首先通过四元小波变换提取不同的子带,得到低频/近似带和高频/精细特征。然后,它权衡最具代表性的子带集作为其他神经网络模型处理图像的输入,代替标准数据样本。我们进行了广泛的实验评估,包括不同的数据集、多样的图像分析和合成任务,如重建、分割和模态转换。我们还评估了QUAVE与实数和四元数值模型的组合。结果表明,所提出框架的有效性和泛化能力,在提高网络性能的同时,能够在多种场景中被灵活采用,并对领域偏移具有鲁棒性。完整代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ispamm/QWT 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted to Neurocomputing Journal
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型、通用、针对数据和任务的无偏见的框架,能够从医学图像中提取重要特征。提出的四元小波网络(QUAVE)可轻松集成到任何现有的医学图像分析或合成任务中,并可与实数、四元数或超复数模型结合,将其推广到单通道数据。QUAVE首先通过四元小波变换提取不同的子带,得到低频/近似带和高频/精细特征,然后加权最具代表性的子带集作为其他神经网络模型处理图像的输入,替代标准数据样本。实验评估表明,该框架有效且通用,可提高网络性能,可灵活应用于多种场景,对领域变化具有鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络的通用性在医学图像处理领域变得越来越重要,由于不同来源和任务的数据集日益增多。
- 处理医学数据时缺乏方法论标准导致大变化。
- 提出了一种新型通用框架——四元小波网络(QUAVE),能够提取医学图像的重要特征,可轻松集成到现有任务中。
- QUAVE可进行四元小波变换以提取子带,包括低频和高频特征。
- QUAVE可与其他神经网络模型结合,用于图像处理和替代标准数据样本。
- 通过广泛实验评估,证明QUAVE框架有效且通用,可提高网络性能,灵活应用于多种场景,并对领域变化具有鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图