⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
Effect of Fluorine doping on the electrocatalytic properties of Nb2O5 for H2O2 electrogeneration
Authors:Aline B. Trench, João Paulo C. Moura, Caio Machado Fernandes, Mauro C. Santos
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) via the 2-electron mechanism is an efficient way to produce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) under mild conditions. This study examines the modification of Vulcan XC72 carbon with fluorine (F)-doped niobium oxide (Nb2O5) nanoparticles at varying molar ratios (0, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02). The F-doped Nb2O5 nanoparticles were synthesized using the oxidizing peroxide method and then incorporated into Vulcan XC72 carbon via impregnation. Characterization techniques included X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), contact angle measurements, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Electrochemical evaluation using the rotating ring disk electrode method revealed that Vulcan XC72 modified with 1.0% F-doped Nb2O5 exhibited the best ORR performance. When used as a gas diffusion electrode, this electrocatalyst produced more H2O2 at all applied potentials than the pure and Nb2O5-modified Vulcan XC72 carbon. At potentials of -0.7 V and -1.3 V, the proposed electrocatalyst achieved H2O2 yields 65% and 98% higher than the Nb2O5-modified electrocatalyst. Furthermore, it presented lower energy consumption and higher current efficiency than the other electrocatalysts compared in this study. The enhanced performance is attributed to F doping, which increased Nb2O5 lattice distortion and disorder, improving electron availability for ORR. Additionally, F-doped electrocatalysts exhibited more oxygenated species and greater hydrophilicity, facilitating O2 adsorption, transport, and electron transfer. These properties significantly enhanced H2O2 electrogeneration efficiency while reducing energy consumption.
通过两电子机制进行的氧还原反应(ORR)是在温和条件下产生过氧化氢(H2O2)的有效方法。本研究以氟(F)掺杂的氧化铌(Nb2O5)纳米颗粒对Vulcan XC72碳进行了改性,并设置了不同的摩尔比(0、0.005、0.01、0.02)。采用氧化过氧化物法合成F掺杂的Nb2O5纳米颗粒,然后通过浸渍法将其掺入Vulcan XC72碳中。表征技术包括X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、接触角测量和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)。采用旋转圆盘电极法进行电化学评估,结果显示,用1.0% F掺杂Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72具有最佳的ORR性能。当用作气体扩散电极时,该电催化剂在所有施加的电位下产生的H2O2比纯Vulcan XC72和Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72碳更多。在-0.7V和-1.3V的电位下,所提电催化剂的H2O2产量比Nb2O5改性电催化剂高出65%和98%。此外,与本研究中比较的其他电催化剂相比,它表现出更低的能耗和更高的电流效率。性能提升的原因是F掺杂增加了Nb2O5的晶格畸变和无序性,提高了用于ORR的电子可用性。此外,F掺杂的电催化剂表现出更多的氧化物种和更大的亲水性,有利于O2的吸附、传输和电子转移。这些特性显著提高了H2O2的电生产效率,同时降低了能耗。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
氟掺杂二氧化铌改性的Vulcan XC72碳在氧还原反应中表现出更高的氢过氧化氢生产效率。研究通过对不同摩尔比例的氟掺杂二氧化铌改性的Vulcan XC72碳进行表征和电化学评估,发现1.0%氟掺杂二氧化铌改性的Vulcan XC72碳具有最佳性能。该催化剂能更有效地产生H2O2,降低能耗并提高电流效率。
Key Takeaways
- 氟掺杂二氧化铌改性的Vulcan XC72碳通过2电子机制有效地参与氧还原反应,生成氢过氧化氢。
- 通过XRD、SEM、TEM、接触角测量和XPS等技术对催化剂进行了表征。
- 1.0%氟掺杂Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72碳在氧还原反应中表现出最佳性能。
- 与纯和Nb2O5改性的Vulcan XC72碳相比,该催化剂在作为气体扩散电极使用时产生了更多的H2O2。
- 在-0.7V和-1.3V的电位下,该催化剂的H2O2产量分别比Nb2O5改性催化剂高65%和98%。
- 氟掺杂提高了Nb2O5的晶格失真和无序性,改善了电子在氧还原反应中的可用性。
点此查看论文截图

A Foundation Model Framework for Multi-View MRI Classification of Extramural Vascular Invasion and Mesorectal Fascia Invasion in Rectal Cancer
Authors:Yumeng Zhang, Zohaib Salahuddin, Danial Khan, Shruti Atul Mali, Henry C. Woodruff, Sina Amirrajab, Eduardo Ibor-Crespo, Ana Jimenez-Pastor, Luis Marti-Bonmati, Philippe Lambin
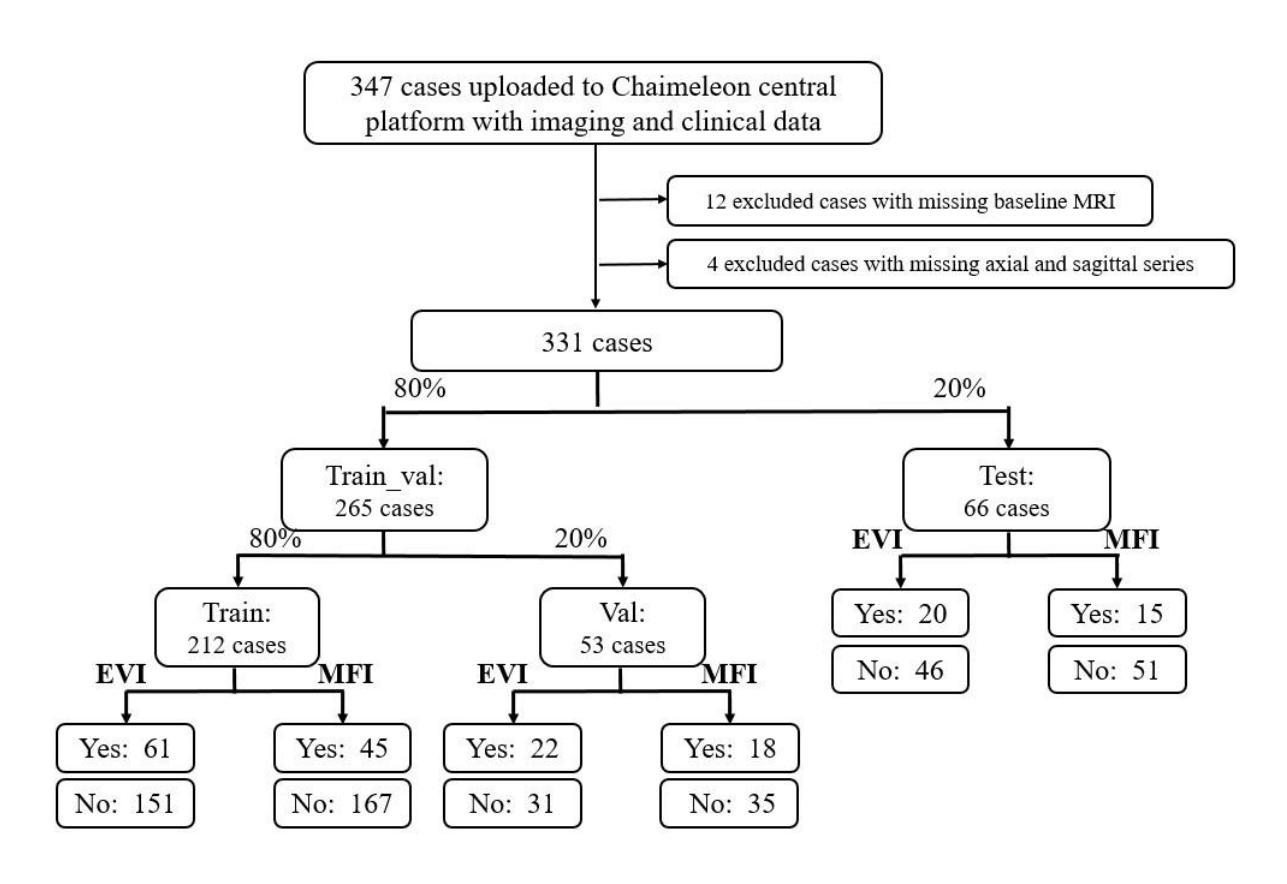
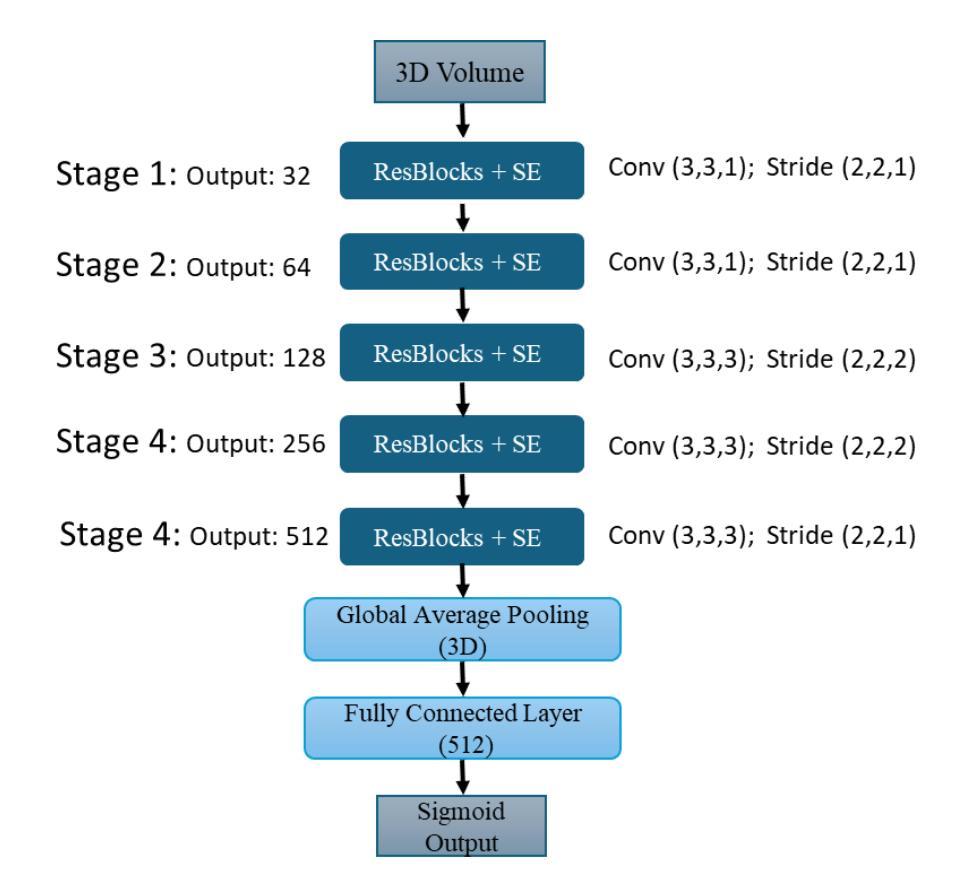
Background: Accurate MRI-based identification of extramural vascular invasion (EVI) and mesorectal fascia invasion (MFI) is pivotal for risk-stratified management of rectal cancer, yet visual assessment is subjective and vulnerable to inter-institutional variability. Purpose: To develop and externally evaluate a multicenter, foundation-model-driven framework that automatically classifies EVI and MFI on axial and sagittal T2-weighted MRI. Methods: This retrospective study used 331 pre-treatment rectal cancer MRI examinations from three European hospitals. After TotalSegmentator-guided rectal patch extraction, a self-supervised frequency-domain harmonization pipeline was trained to minimize scanner-related contrast shifts. Four classifiers were compared: ResNet50, SeResNet, the universal biomedical pretrained transformer (UMedPT) with a lightweight MLP head, and a logistic-regression variant using frozen UMedPT features (UMedPT_LR). Results: UMedPT_LR achieved the best EVI detection when axial and sagittal features were fused (AUC = 0.82; sensitivity = 0.75; F1 score = 0.73), surpassing the Chaimeleon Grand-Challenge winner (AUC = 0.74). The highest MFI performance was attained by UMedPT on axial harmonized images (AUC = 0.77), surpassing the Chaimeleon Grand-Challenge winner (AUC = 0.75). Frequency-domain harmonization improved MFI classification but variably affected EVI performance. Conventional CNNs (ResNet50, SeResNet) underperformed, especially in F1 score and balanced accuracy. Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that combining foundation model features, harmonization, and multi-view fusion significantly enhances diagnostic performance in rectal MRI.
背景:基于MRI的精准腹膜外血管浸润(EVI)和直肠系膜筋膜浸润(MFI)识别对于直肠癌的风险分层管理至关重要。然而,视觉评估具有主观性,容易受到机构间差异的影响。
目的:开发并外部评估一个多中心、基于基础模型的框架,该框架可在轴状和矢状T2加权MRI上自动分类EVI和MFI。
方法:这项回顾性研究使用了来自三家欧洲医院的331例直肠癌MRI检查。在TotalSegmentator引导的直肠补丁提取后,训练了一种自监督的频率域和谐管道,以最小化扫描仪相关的对比度变化。对比了四种分类器:ResNet50、SeResNet、带有轻量级MLP头的通用生物医学预训练转换器(UMedPT),以及使用冻结UMedPT特征的逻辑回归变体(UMedPT_LR)。
结果:当融合轴状和矢状特征时,UMedPT_LR在EVI检测方面表现最佳(AUC = 0.82;灵敏度= 0.75;F1分数= 0.73),超越了Chai本科挑战赛冠军(AUC = 0.74)。在轴状和谐图像上,UMedPT在MFI方面表现最佳(AUC = 0.77),也超越了挑战赛冠军(AUC = 0.75)。频率域和谐化改进了MFI分类,但对EVI性能的影响有所不同。传统的CNN(ResNet50,SeResNet)表现较差,尤其是在F1分数和平衡精度方面。
结论:这些发现表明,结合基础模型特征、和谐化以及多视图融合,可以显著提高直肠MRI的诊断性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 8 figures
摘要
基于MRI的自动分类技术对于直肠癌的额外血管侵袭(EVI)和系膜筋膜侵袭(MFI)的准确识别至关重要。本研究开发了一种多中心、基于基础模型的框架,用于在轴向和矢状T2加权MRI上自动分类EVI和MFI。结果显示,结合基础模型特征、谐波融合和多视角融合的方法显著提高了MRI的诊断性能。其中UMedPT_LR模型在融合轴向和矢状特征后,EVI检测效果最佳(AUC=0.82),超越Chaimeleon Grand Challenge冠军模型(AUC=0.74)。而UMedPT模型在轴向谐波图像上实现了最高的MFI性能(AUC=0.77)。此外,频率域谐波技术改善了MFI分类,但对EVI性能的影响存在差异。传统的CNN(如ResNet50和SeResNet)表现较差,特别是在F1分数和平衡精度上。
关键见解
- 基于MRI的自动分类技术在直肠癌风险分层管理中至关重要。
- 研究开发了一种多中心、基于基础模型的框架,用于自动分类EVI和MFI。
- UMedPT_LR模型在EVI检测方面表现最佳,UMedPT模型在MFI诊断中表现优秀。
- 频率域谐波技术有助于提高MFI分类性能,但对EVI的影响有所差异。
- 结合基础模型特征、谐波技术和多视角融合能显著提高MRI诊断性能。
- 传统CNN模型(如ResNet50和SeResNet)在EVI和MFI检测中的表现不如预期。
- 此研究为多中心、基于基础模型的框架在医学图像分析领域的应用提供了有价值的参考。
点此查看论文截图

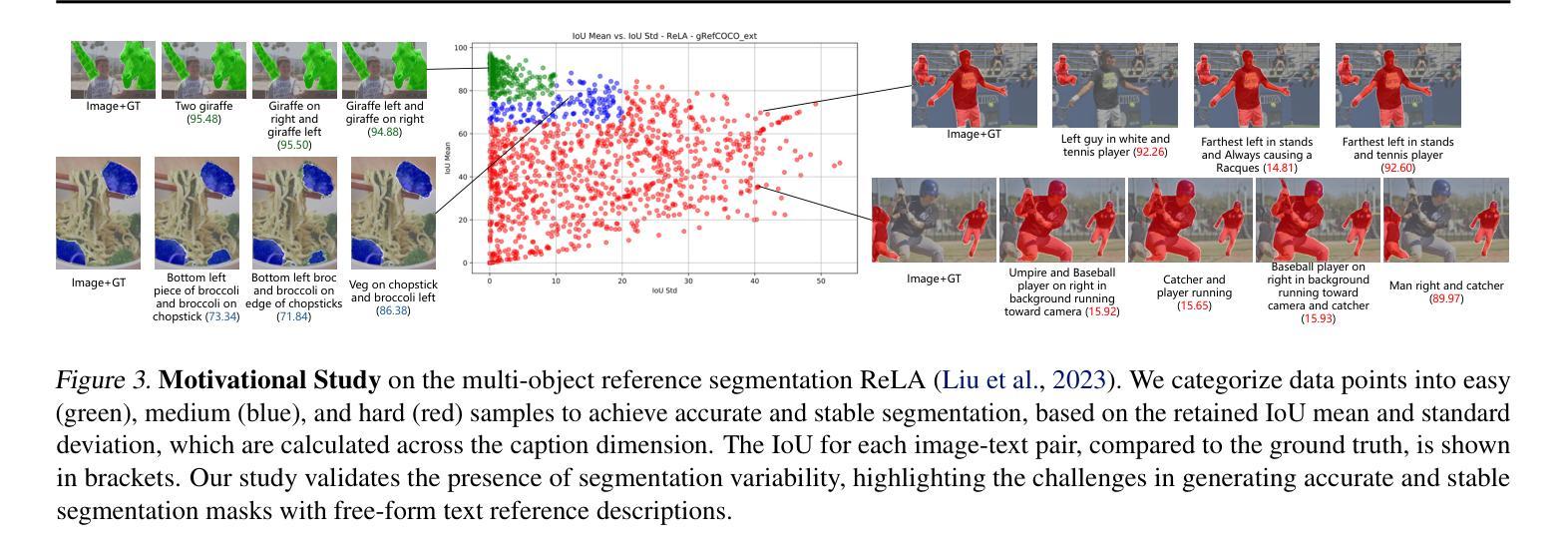
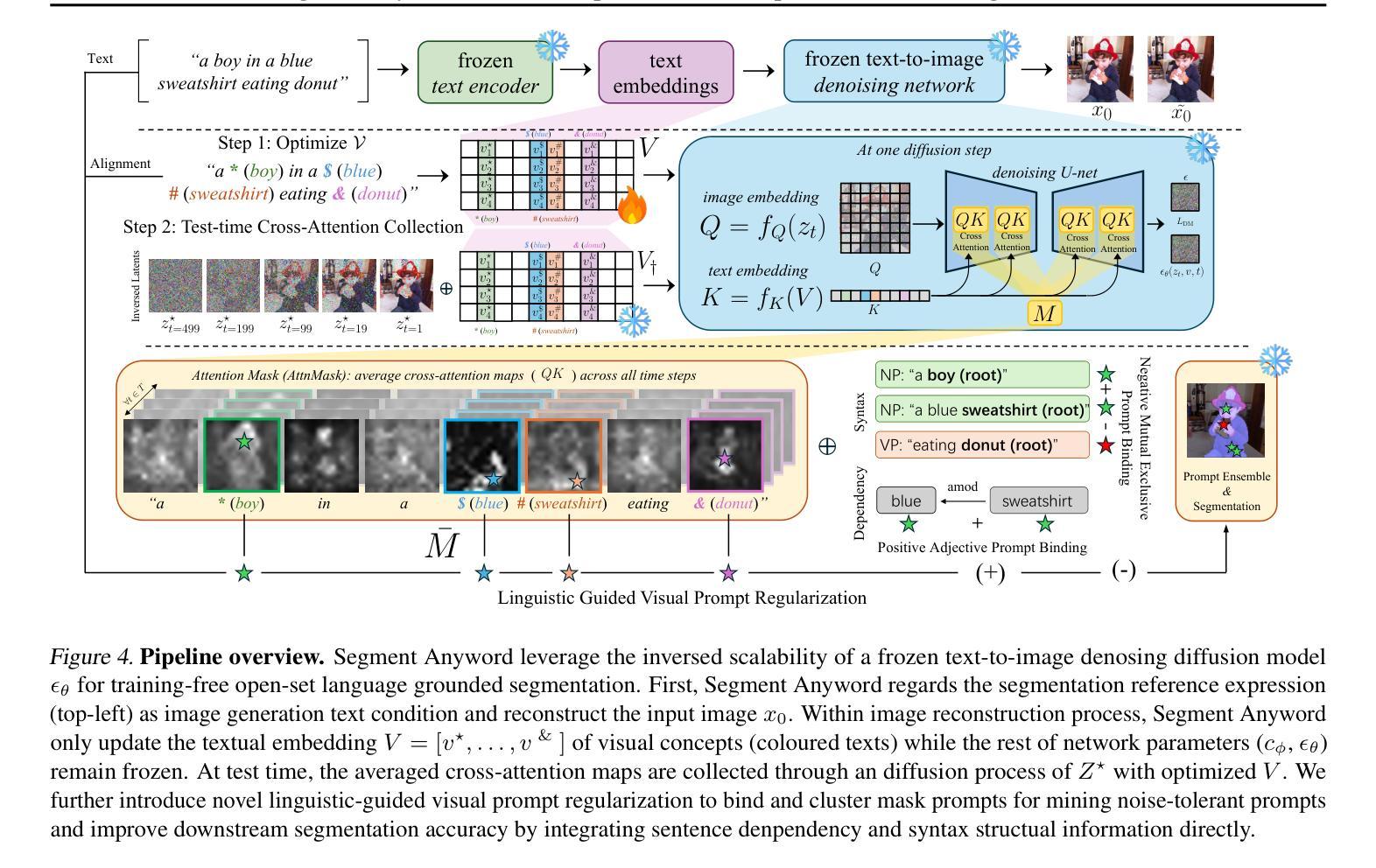
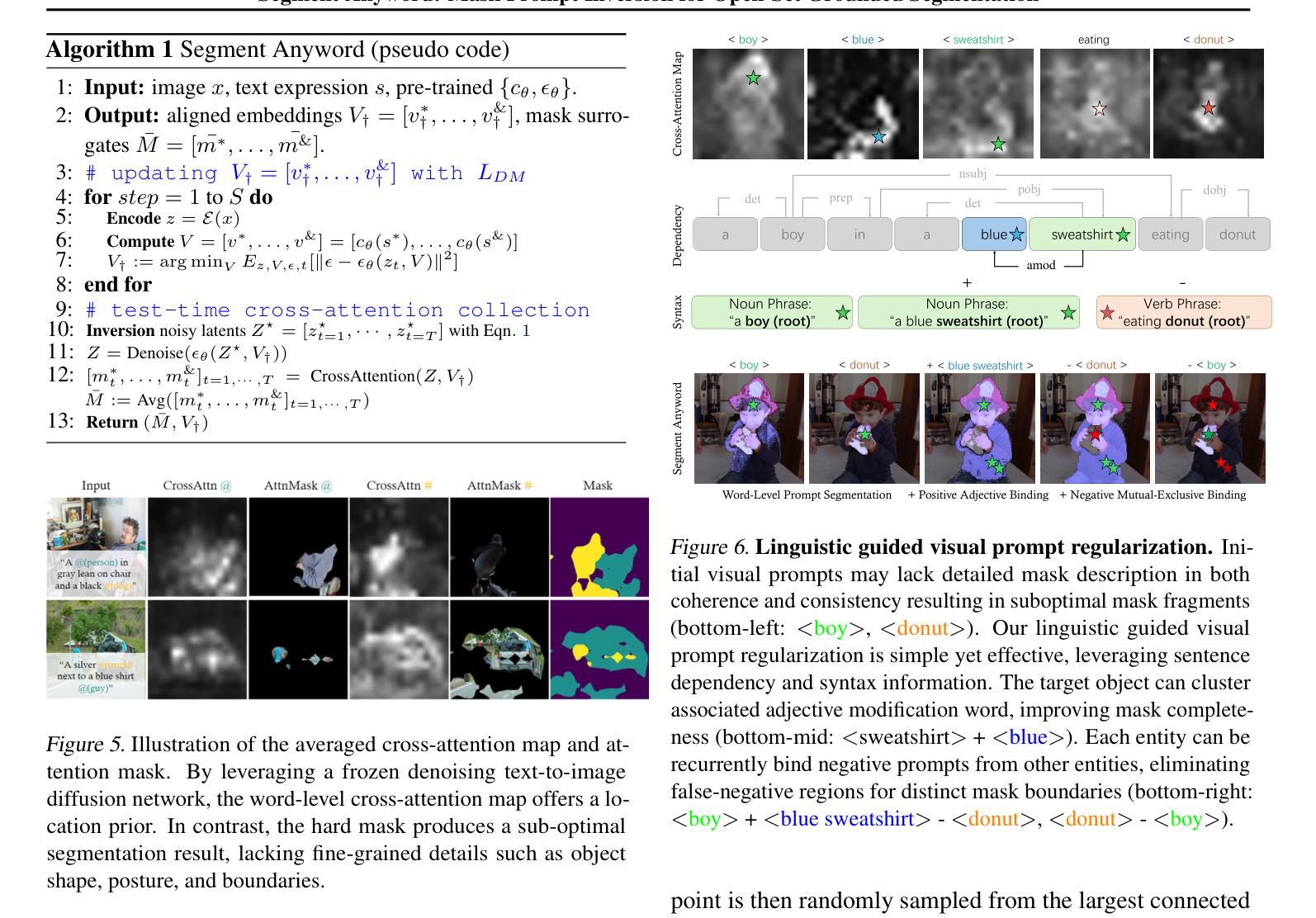
Segment Anyword: Mask Prompt Inversion for Open-Set Grounded Segmentation
Authors:Zhihua Liu, Amrutha Saseendran, Lei Tong, Xilin He, Fariba Yousefi, Nikolay Burlutskiy, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Huiyu Zhou, Chen Jin
Open-set image segmentation poses a significant challenge because existing methods often demand extensive training or fine-tuning and generally struggle to segment unified objects consistently across diverse text reference expressions. Motivated by this, we propose Segment Anyword, a novel training-free visual concept prompt learning approach for open-set language grounded segmentation that relies on token-level cross-attention maps from a frozen diffusion model to produce segmentation surrogates or mask prompts, which are then refined into targeted object masks. Initial prompts typically lack coherence and consistency as the complexity of the image-text increases, resulting in suboptimal mask fragments. To tackle this issue, we further introduce a novel linguistic-guided visual prompt regularization that binds and clusters visual prompts based on sentence dependency and syntactic structural information, enabling the extraction of robust, noise-tolerant mask prompts, and significant improvements in segmentation accuracy. The proposed approach is effective, generalizes across different open-set segmentation tasks, and achieves state-of-the-art results of 52.5 (+6.8 relative) mIoU on Pascal Context 59, 67.73 (+25.73 relative) cIoU on gRefCOCO, and 67.4 (+1.1 relative to fine-tuned methods) mIoU on GranDf, which is the most complex open-set grounded segmentation task in the field.
开放集图像分割是一个重大挑战,因为现有方法通常需要大量训练和微调,并且在跨不同文本参考表达时,一般难以一致地分割统一对象。受此启发,我们提出了Segment Anyword,这是一种新型的无训练视觉概念提示学习方法,用于开放集语言基础分割。它依赖于冻结的扩散模型的令牌级跨注意图来生成分割替代品或掩膜提示,然后将其细化为目标对象掩膜。随着图像文本复杂性的增加,初始提示通常缺乏连贯性和一致性,导致掩膜片段不佳。为解决此问题,我们进一步引入了一种新型的语言引导视觉提示正则化方法,该方法根据句子依赖关系和句法结构信息来绑定和聚类视觉提示,从而提取出稳健、耐噪声的掩膜提示,并显著提高分割精度。所提出的方法效果显著,可应用于不同的开放集分割任务,并在Pascal Context 59上实现了52.5(+6.8相对)mIoU,在gRefCOCO上实现了67.73(+25.73相对)cIoU,以及在领域中最复杂的开放集语言基础分割任务GranDf上实现了67.4(+1.1相对于微调方法)mIoU的业界最佳结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种无需训练的新型视觉概念提示学习方法,用于开放式语言基础分割。该方法利用冻结的扩散模型的token级跨注意力图生成分割替代方案或掩膜提示,并进行精细化处理,形成目标对象掩膜。通过引入语言指导的视觉提示正则化,提高掩膜提示的鲁棒性和噪声容忍度,显著提高分割精度。该方法在开放式分割任务中表现有效,具有跨任务泛化能力,并在多个数据集上达到最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 开放集图像分割面临挑战:现有方法需要大量训练或微调,难以在多种文本参考表达中一致地分割统一对象。
- Segment Anyword方法是一种新型训练免费的视觉概念提示学习方法,用于开放式语言基础分割。
- 该方法利用冻结的扩散模型的token级跨注意力图生成分割替代方案或掩膜提示。
- 初始提示缺乏连贯性和一致性,随着图像文本复杂性的增加,产生次优的掩膜片段。
- 引入语言指导的视觉提示正则化,通过句子依赖和句法结构信息绑定和聚集视觉提示,提高掩膜提示的鲁棒性和噪声容忍度。
- 该方法在多个数据集上实现显著改进的分割精度,包括Pascal Context 59、gRefCOCO和GranDf。
点此查看论文截图

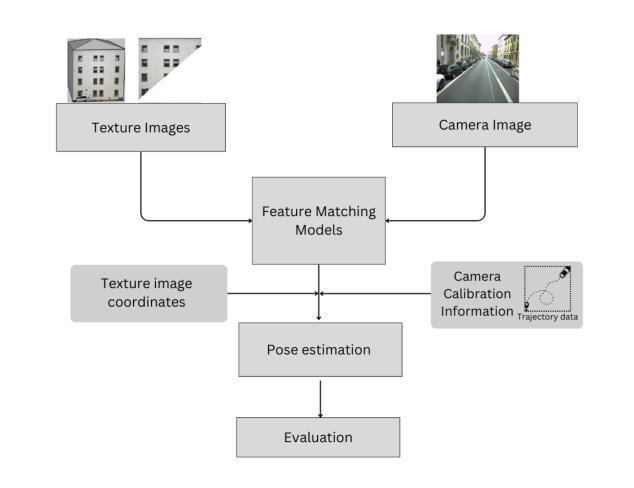
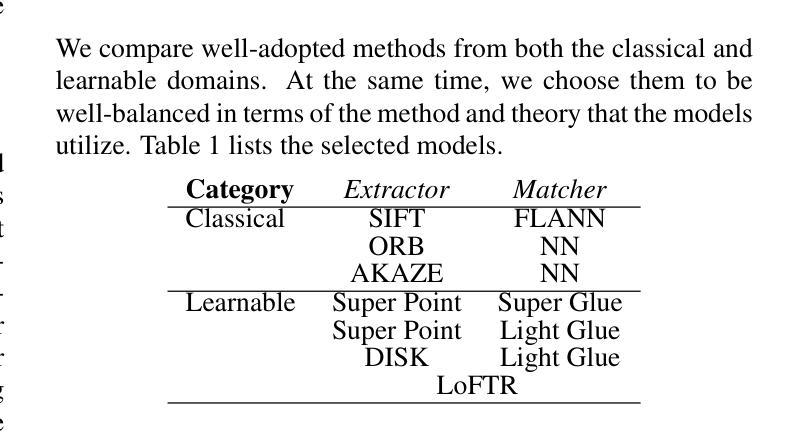
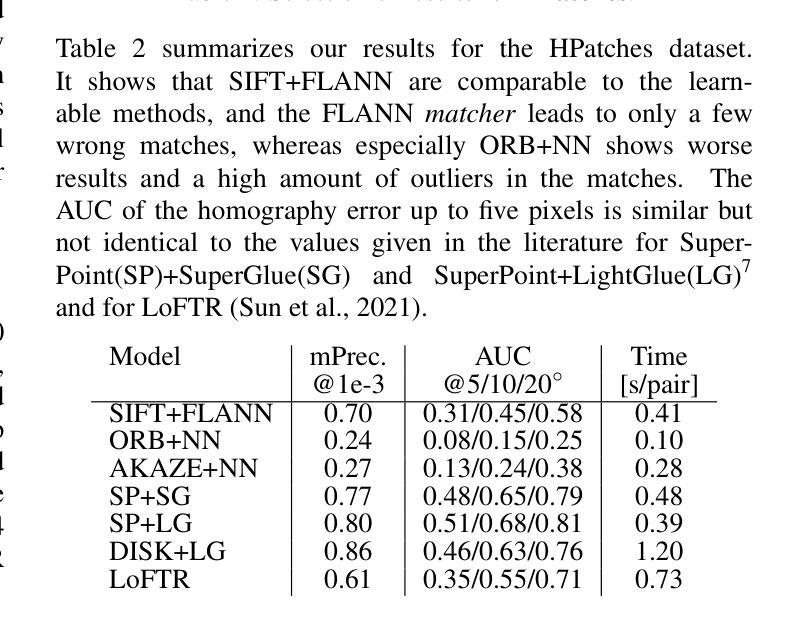
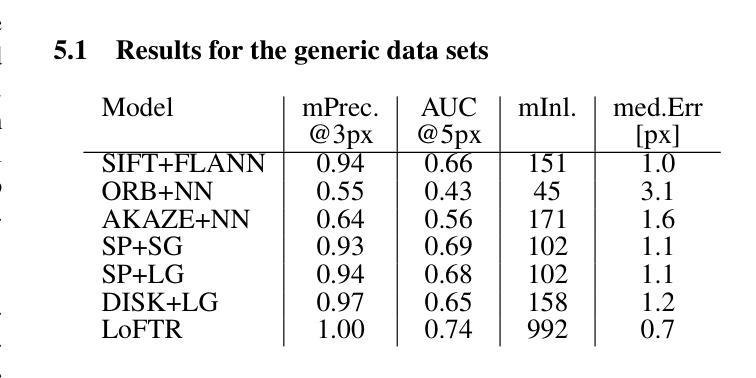
To Glue or Not to Glue? Classical vs Learned Image Matching for Mobile Mapping Cameras to Textured Semantic 3D Building Models
Authors:Simone Gaisbauer, Prabin Gyawali, Qilin Zhang, Olaf Wysocki, Boris Jutzi
Feature matching is a necessary step for many computer vision and photogrammetry applications such as image registration, structure-from-motion, and visual localization. Classical handcrafted methods such as SIFT feature detection and description combined with nearest neighbour matching and RANSAC outlier removal have been state-of-the-art for mobile mapping cameras. With recent advances in deep learning, learnable methods have been introduced and proven to have better robustness and performance under complex conditions. Despite their growing adoption, a comprehensive comparison between classical and learnable feature matching methods for the specific task of semantic 3D building camera-to-model matching is still missing. This submission systematically evaluates the effectiveness of different feature-matching techniques in visual localization using textured CityGML LoD2 models. We use standard benchmark datasets (HPatches, MegaDepth-1500) and custom datasets consisting of facade textures and corresponding camera images (terrestrial and drone). For the latter, we evaluate the achievable accuracy of the absolute pose estimated using a Perspective-n-Point (PnP) algorithm, with geometric ground truth derived from geo-referenced trajectory data. The results indicate that the learnable feature matching methods vastly outperform traditional approaches regarding accuracy and robustness on our challenging custom datasets with zero to 12 RANSAC-inliers and zero to 0.16 area under the curve. We believe that this work will foster the development of model-based visual localization methods. Link to the code: https://github.com/simBauer/To\_Glue\_or\_not\_to\_Glue
特征匹配是计算机视觉和摄影测量学等许多应用(如图像配准、从运动中获取结构以及视觉定位)中必不可少的一步。对于移动地图相机而言,经典的基于手工的方法(如SIFT特征检测和描述与最近邻匹配和RANSAC异常值去除相结合)一直处于最先进的状态。随着深度学习最近的进步,学习型方法的引入已被证明在复杂条件下具有更好的鲁棒性和性能。尽管它们的采用正在不断增加,但对于语义3D建筑相机与模型匹配的特定任务,经典的特征匹配方法和可学习的特征匹配方法之间的全面比较仍然缺失。本次提交系统地评估了使用纹理化的CityGML LoD2模型进行视觉定位的不同特征匹配技术的有效性。我们使用标准基准数据集(HPatches,MegaDepth-1500)以及自定义数据集(包括墙面纹理和相应的相机图像(地面和无人机拍摄))。对于后者,我们评估使用透视n点(PnP)算法估计的绝对姿态的可实现精度,该几何真实值是从地理参考轨迹数据得出的。结果表明,在具有零到12个RANSAC-inliers和零到0.16曲线下面积的我们具有挑战性的自定义数据集上,学习型特征匹配方法在准确性和鲁棒性方面大大优于传统方法。我们相信这项工作将促进基于模型的视觉定位方法的发展。代码链接:https://github.com/simBauer/To\_Glue\_or\_not\_to\_Glue
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MMT, Xiamen, China; ISPRS Annals
摘要
特征匹配是很多计算机视觉和摄影测量应用(如图像配准、运动结构分析和视觉定位)中的必要步骤。传统的基于手工设计的方法(如SIFT特征检测和描述,结合最近邻匹配和RANSAC异常值去除)对于移动映射相机而言一直是最先进的。随着深度学习的最新进展,引入的学习型方法已经证明在复杂条件下具有更好的稳健性和性能。尽管学习型特征匹配方法的采用日益普遍,但针对语义三维建筑相机与模型匹配的特定任务,对经典与可学习特征匹配方法的全面比较仍然缺失。本研究系统地评估了不同特征匹配技术在视觉定位中的有效性,使用了带纹理的CityGML LoD2模型。我们使用标准数据集(HPatches,MegaDepth-1500)以及包含墙面纹理和相应相机图像(地面和无人机)的自定义数据集。对于后者,我们评估了使用透视n点(PnP)算法估计的绝对姿态的精度,几何真实值来源于地理参考轨迹数据。结果表明,在具有零至12个RANSAC-inliers和零至0.16曲线下面积的挑战性自定义数据集上,可学习的特征匹配方法在精度和稳健性方面大大优于传统方法。我们相信这项工作将促进基于模型的视觉定位方法的发展。
要点
- 研究对多种特征匹配方法进行了系统的比较,包括经典的和可学习的特征匹配方法。
- 实验在视觉定位任务中评估了这些方法的有效性,特别是在语义三维建筑相机与模型匹配方面的应用。
- 研究使用了标准数据集以及包含墙面纹理和相应相机图像的自定义数据集。
- 可学习的特征匹配方法在挑战性的数据集上显著优于传统方法。
- 实验中使用了透视n点(PnP)算法来评估绝对姿态估计的精度。
- 几何真实值来源于地理参考轨迹数据,增强了实验的可靠性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

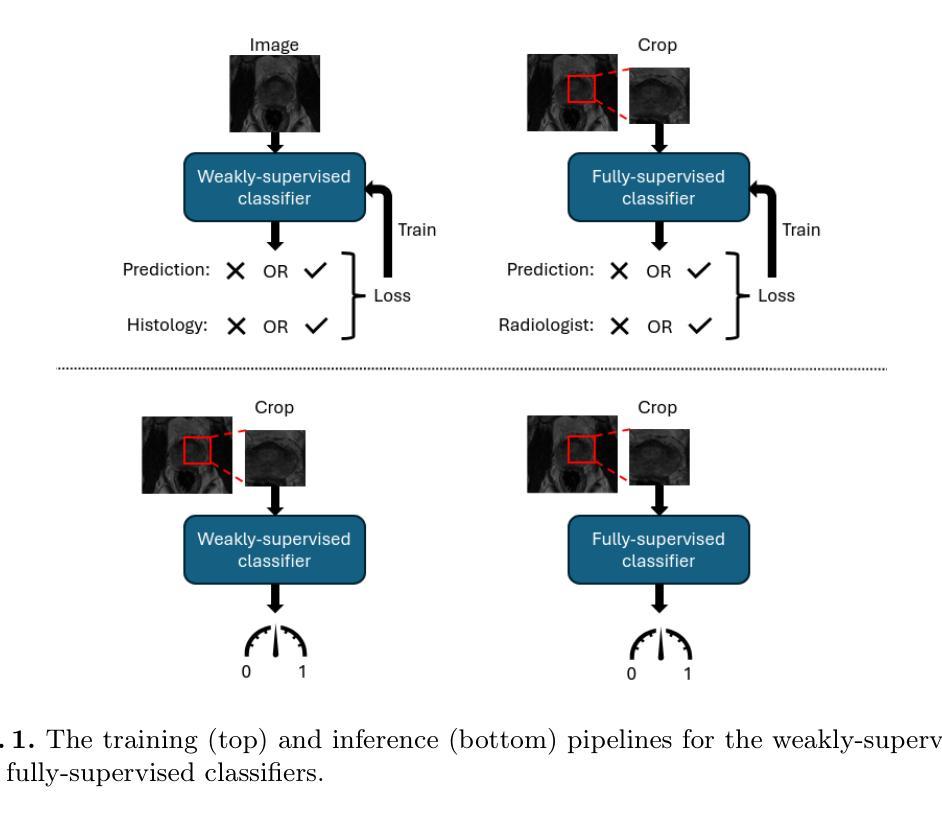
Promptable cancer segmentation using minimal expert-curated data
Authors:Lynn Karam, Yipei Wang, Veeru Kasivisvanathan, Mirabela Rusu, Yipeng Hu, Shaheer U. Saeed
Automated segmentation of cancer on medical images can aid targeted diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. However, its adoption is limited by the high cost of expert annotations required for training and inter-observer variability in datasets. While weakly-supervised methods mitigate some challenges, using binary histology labels for training as opposed to requiring full segmentation, they require large paired datasets of histology and images, which are difficult to curate. Similarly, promptable segmentation aims to allow segmentation with no re-training for new tasks at inference, however, existing models perform poorly on pathological regions, again necessitating large datasets for training. In this work we propose a novel approach for promptable segmentation requiring only 24 fully-segmented images, supplemented by 8 weakly-labelled images, for training. Curating this minimal data to a high standard is relatively feasible and thus issues with the cost and variability of obtaining labels can be mitigated. By leveraging two classifiers, one weakly-supervised and one fully-supervised, our method refines segmentation through a guided search process initiated by a single-point prompt. Our approach outperforms existing promptable segmentation methods, and performs comparably with fully-supervised methods, for the task of prostate cancer segmentation, while using substantially less annotated data (up to 100X less). This enables promptable segmentation with very minimal labelled data, such that the labels can be curated to a very high standard.
医学图像上的癌症自动分割有助于针对性的诊断和治疗方法。然而,其应用受限于训练所需专家标注的高成本和数据集之间的观察者间差异。虽然弱监督方法缓解了一些挑战,它们需要使用二元组织病理学标签进行训练,而不是需要完整的分割,但它们需要配对的大量组织病理学图像数据集,这些数据集很难编纂。同样,提示分割旨在实现在推理阶段无需针对新任务进行重新训练即可进行分割,然而,现有模型在病理区域的性能较差,同样需要大量数据集进行训练。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型提示分割方法,仅需要24张完全分割的图像和8张弱标签图像进行训练。将这些最少数据整理到高标准是相对可行的,因此可以缓解获取标签的成本和差异问题。通过利用一个弱监督和一个完全监督的分类器,我们的方法通过单点提示启动的引导搜索过程来完善分割。我们的方法表现优于现有的提示分割方法,并且在前列腺癌分割任务上的表现与完全监督的方法相当,同时使用的标注数据大大减少(最多减少100倍)。这能够实现用极少量的标注数据进行提示分割,使标签可以编纂到很高的标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Medical Image Understanding and Analysis (MIUA) 2025
Summary
医学图像自动化分割技术有助于精准诊断和治疗癌症,但其应用受限于专家标注成本高和数据集间观察者差异大等问题。本研究提出了一种新的提示分割方法,仅需少量全分割图像和弱标注图像进行训练,可缓解标注成本和数据差异问题。通过两个分类器,即一个弱监督分类器和一个全监督分类器,以单点提示引导搜索过程,对分割进行精细化处理。该方法在前列腺癌分割任务上的表现优于现有提示分割方法,与全监督方法相当,且使用的标注数据量大大减少。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像自动化分割在癌症诊断与治疗中有重要作用,但面临专家标注成本高昂和数据集间差异大的挑战。
- 弱监督方法虽然有助于缓解部分问题,但配对数据集难求。
- 提示分割方法旨在实现对新任务的无需再训练推理,但现有模型在病理区域表现欠佳。
- 本研究提出了一种新的提示分割方法,仅需要少量全分割图像和弱标注图像进行训练。
- 通过两个分类器的结合,即一个弱监督分类器和一个全监督分类器,以单点提示启动引导搜索过程,优化分割结果。
- 该方法在前列腺癌分割任务上的表现优于多数提示分割方法,并与全监督方法相当。
点此查看论文截图

UltraBoneUDF: Self-supervised Bone Surface Reconstruction from Ultrasound Based on Neural Unsigned Distance Functions
Authors:Luohong Wu, Matthias Seibold, Nicola A. Cavalcanti, Giuseppe Loggia, Lisa Reissner, Bastian Sigrist, Jonas Hein, Lilian Calvet, Arnd Viehöfer, Philipp Fürnstahl
Background: Bone surface reconstruction plays a critical role in computer-assisted orthopedic surgery. Compared to traditional imaging modalities such as CT and MRI, ultrasound offers a radiation-free, cost-effective, and portable alternative. Continuous bone surface reconstruction can be employed for many clinical applications. However, due to the inherent limitations of ultrasound imaging, B-mode ultrasound typically capture only partial bone surfaces. Existing reconstruction methods struggle with such incomplete data, leading to artifacts and increased reconstruction errors. Effective techniques for accurately reconstructing thin and open bone surfaces from real-world 3D ultrasound volumes remain lacking. Methods: We propose UltraBoneUDF, a self-supervised framework designed for reconstructing open bone surfaces from ultrasound using neural Unsigned Distance Functions. To enhance reconstruction quality, we introduce a novel global feature extractor that effectively fuses ultrasound-specific image characteristics. Additionally, we present a novel loss function based on local tangent plane optimization that substantially improves surface reconstruction quality. UltraBoneUDF and baseline models are extensively evaluated on four open-source datasets. Results: Qualitative results highlight the limitations of the state-of-the-art methods for open bone surface reconstruction and demonstrate the effectiveness of UltraBoneUDF. Quantitatively, UltraBoneUDF significantly outperforms competing methods across all evaluated datasets for both open and closed bone surface reconstruction in terms of mean Chamfer distance error: 1.10 mm on the UltraBones100k dataset (39.6% improvement compared to the SOTA), 0.23 mm on the OpenBoneCT dataset (69.3% improvement), 0.18 mm on the ClosedBoneCT dataset (70.2% improvement), and 0.05 mm on the Prostate dataset (55.3% improvement).
背景:骨表面重建在计算机辅助骨科手术中起着至关重要的作用。与CT和MRI等传统成像模式相比,超声提供了一种无辐射、成本低廉、便于携带的替代方案。骨表面连续重建可用于多种临床应用。然而,由于超声成像的固有局限性,B模式超声通常只能捕获部分骨表面。现有的重建方法在处理此类不完整数据时遇到困难,导致出现伪影和重建误差增加。从现实世界中的3D超声体积准确重建薄而开放的骨表面的有效技术仍然缺乏。方法:我们提出了UltraBoneUDF,这是一个用于从超声数据中重建开放骨表面的自监督框架,采用神经无符号距离函数。为了提高重建质量,我们引入了一种新型全局特征提取器,有效地融合了超声特定的图像特征。此外,我们还提出了一种基于局部切线平面优化的新型损失函数,这极大地提高了表面重建的质量。UltraBoneUDF和基线模型在四个开源数据集上进行了广泛评估。结果:定性结果突出了现有方法在开放骨表面重建方面的局限性,并证明了UltraBoneUDF的有效性。在定量方面,UltraBoneUDF在所有评估的数据集上均显著优于其他方法,无论是开放还是闭合骨表面重建,以平均Chamfer距离误差衡量:在UltraBones100k数据集上为1.10毫米(相比最新技术提高39.6%),在OpenBoneCT数据集上为0.23毫米(提高69.3%),在ClosedBoneCT数据集上为0.18毫米(提高70.2%),在前列腺数据集上为0.05毫米(提高55.3%)。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种利用神经网络 Unsigned Distance Functions 技术,从超声数据中重建开放骨表面的新方法 UltraBoneUDF。该方法通过引入全球特征提取器和基于局部切线平面优化的新型损失函数,提高了重建质量。在四个公开数据集上的实验结果表明,UltraBoneUDF 在开放和闭合骨表面重建方面均显著优于其他方法,特别是在超声骨表面重建数据集上,其平均 Chamfer 距离误差降低了 39.6%。
关键见解
- 骨表面重建在计算机辅助骨科手术中起着至关重要的作用。
- 超声成像作为替代传统 CT 和 MRI 的成像方式,具有无辐射、成本低和便携的优点。
- B模式超声通常只能捕获部分骨表面,现有重建方法在处理不完整数据时存在困难。
- UltraBoneUDF 是一个利用神经网络 Unsigned Distance Functions 技术从超声数据中重建开放骨表面的自监督框架。
- 全球特征提取器的引入有效融合了超声特有的图像特征,提高了重建质量。
- 基于局部切线平面优化的新型损失函数显著提高了表面重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

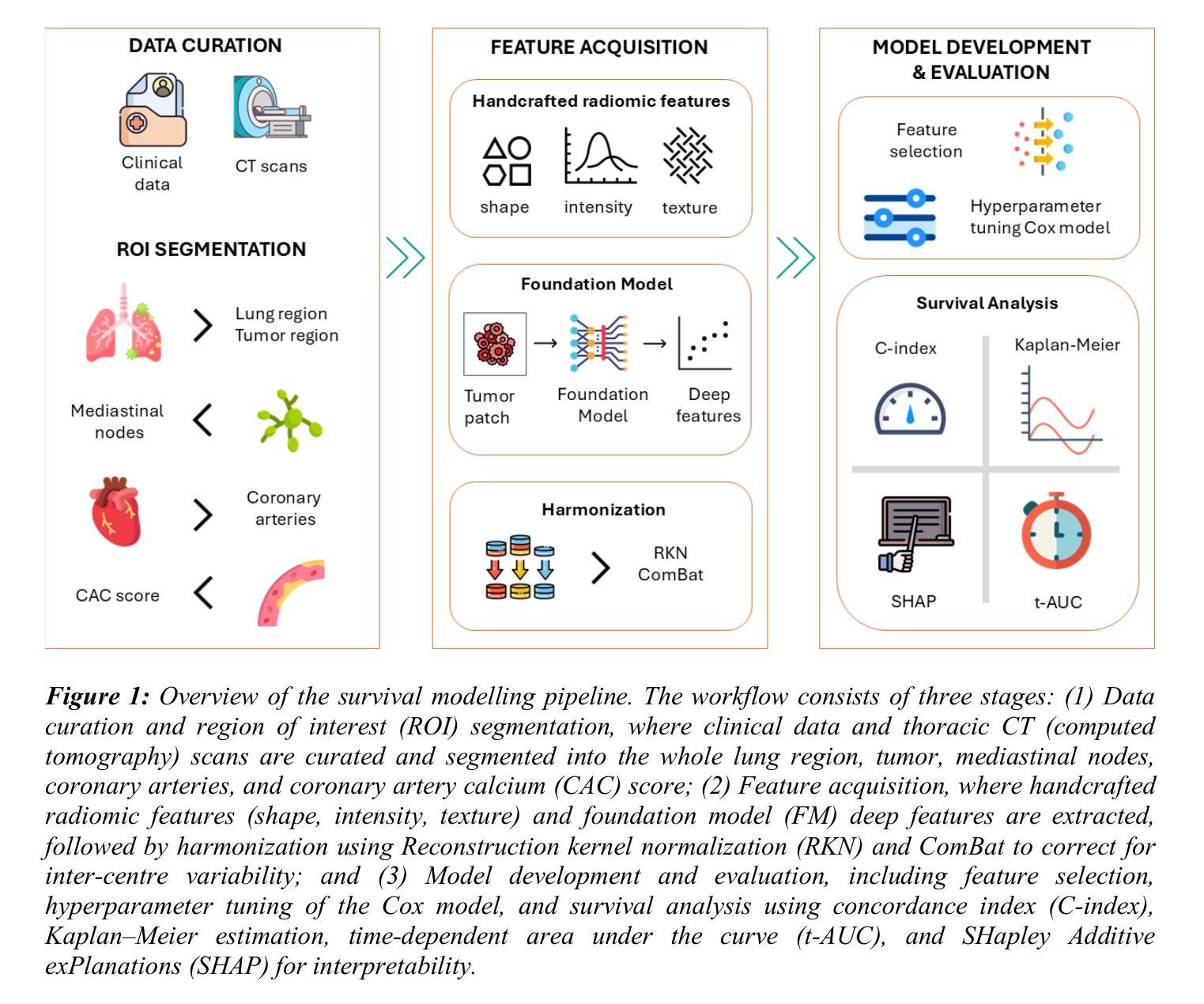
Pixels to Prognosis: Harmonized Multi-Region CT-Radiomics and Foundation-Model Signatures Across Multicentre NSCLC Data
Authors:Shruti Atul Mali, Zohaib Salahuddin, Danial Khan, Yumeng Zhang, Henry C. Woodruff, Eduardo Ibor-Crespo, Ana Jimenez-Pastor, Luis Marti-Bonmati, Philippe Lambin
Purpose: To evaluate the impact of harmonization and multi-region CT image feature integration on survival prediction in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, using handcrafted radiomics, pretrained foundation model (FM) features, and clinical data from a multicenter dataset. Methods: We analyzed CT scans and clinical data from 876 NSCLC patients (604 training, 272 test) across five centers. Features were extracted from the whole lung, tumor, mediastinal nodes, coronary arteries, and coronary artery calcium (CAC). Handcrafted radiomics and FM deep features were harmonized using ComBat, reconstruction kernel normalization (RKN), and RKN+ComBat. Regularized Cox models predicted overall survival; performance was assessed using the concordance index (C-index), 5-year time-dependent area under the curve (t-AUC), and hazard ratio (HR). SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) values explained feature contributions. A consensus model used agreement across top region of interest (ROI) models to stratify patient risk. Results: TNM staging showed prognostic utility (C-index = 0.67; HR = 2.70; t-AUC = 0.85). The clinical + tumor radiomics model with ComBat achieved a C-index of 0.7552 and t-AUC of 0.8820. FM features (50-voxel cubes) combined with clinical data yielded the highest performance (C-index = 0.7616; t-AUC = 0.8866). An ensemble of all ROIs and FM features reached a C-index of 0.7142 and t-AUC of 0.7885. The consensus model, covering 78% of valid test cases, achieved a t-AUC of 0.92, sensitivity of 97.6%, and specificity of 66.7%. Conclusion: Harmonization and multi-region feature integration improve survival prediction in multicenter NSCLC data. Combining interpretable radiomics, FM features, and consensus modeling enables robust risk stratification across imaging centers.
目的:本研究旨在利用手工制作的放射学特征、预训练的基石模型(FM)特征和来自多中心数据集的临床数据,评估和谐化以及多区域CT图像特征融合在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者生存预测中的影响。方法:我们分析了来自五个中心的876例NSCLC患者(604例训练,272例测试)的CT扫描和临床数据。特征从整个肺部、肿瘤、纵隔节点、冠状动脉和冠状动脉钙化(CAC)中提取。使用ComBat、重建核归一化(RKN)和RKN+ComBat对手工制作的放射学特征和FM深度特征进行和谐化处理。正则化Cox模型预测总体生存;性能评估采用一致性指数(C-index)、5年时间依赖曲线下面积(t-AUC)和危险比(HR)。SHapley Additive exPlanations(SHAP)值解释了特征贡献。共识模型利用顶级感兴趣区域(ROI)模型的共识来分层患者风险。结果:TNM分期具有预后作用(C-index = 0.67;HR = 2.70;t-AUC = 0.85)。使用ComBat的临床+肿瘤放射学模型达到C-index为0.7552和t-AUC为0.8820。FM特征(50体素立方体)与临床数据相结合取得了最佳性能(C-index = 0.7616;t-AUC = 0.8866)。所有ROI和FM特征的组合达到了C-index为0.7142和t-AUC为0.7885。共识模型覆盖78%的有效测试病例,达到t-AUC为0.92,敏感度为97.6%,特异度为66.7%。结论:和谐化与多区域特征融合可提高多中心NSCLC数据的生存预测能力。结合可解释的放射学特征、FM特征和共识建模,可在成像中心之间实现稳健的风险分层。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究多中心非小细胞肺癌患者的CT图像与临床数据融合,通过和谐化及多区域图像特征整合提高生存预测的准确性。结合手工放射学特征、预训练模型特征和临床数据,通过和谐化方法如ComBat、重建核归一化(RKN)等,利用正规化Cox模型预测总体生存情况。研究显示,多区域特征整合和谐化能提高非小细胞肺癌的生存预测准确性,结合解释性放射学特征、预训练模型特征和共识建模,可在跨影像中心实现稳健的风险分层。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目的:评价和谐化及多区域CT图像特征整合在非小细胞肺癌患者生存预测中的影响。
- 使用了手工放射学特征、预训练模型特征和临床数据。
- 通过ComBat、RKN及其组合进行特征和谐化。
- 利用正规化Cox模型进行生存预测,采用C-index、t-AUC和HR评估性能。
- TNM分期具有预后效用。
- 最佳的预测模型结合了临床数据、肿瘤放射学特征和预训练模型特征,达到较高的C-index和t-AUC。
点此查看论文截图

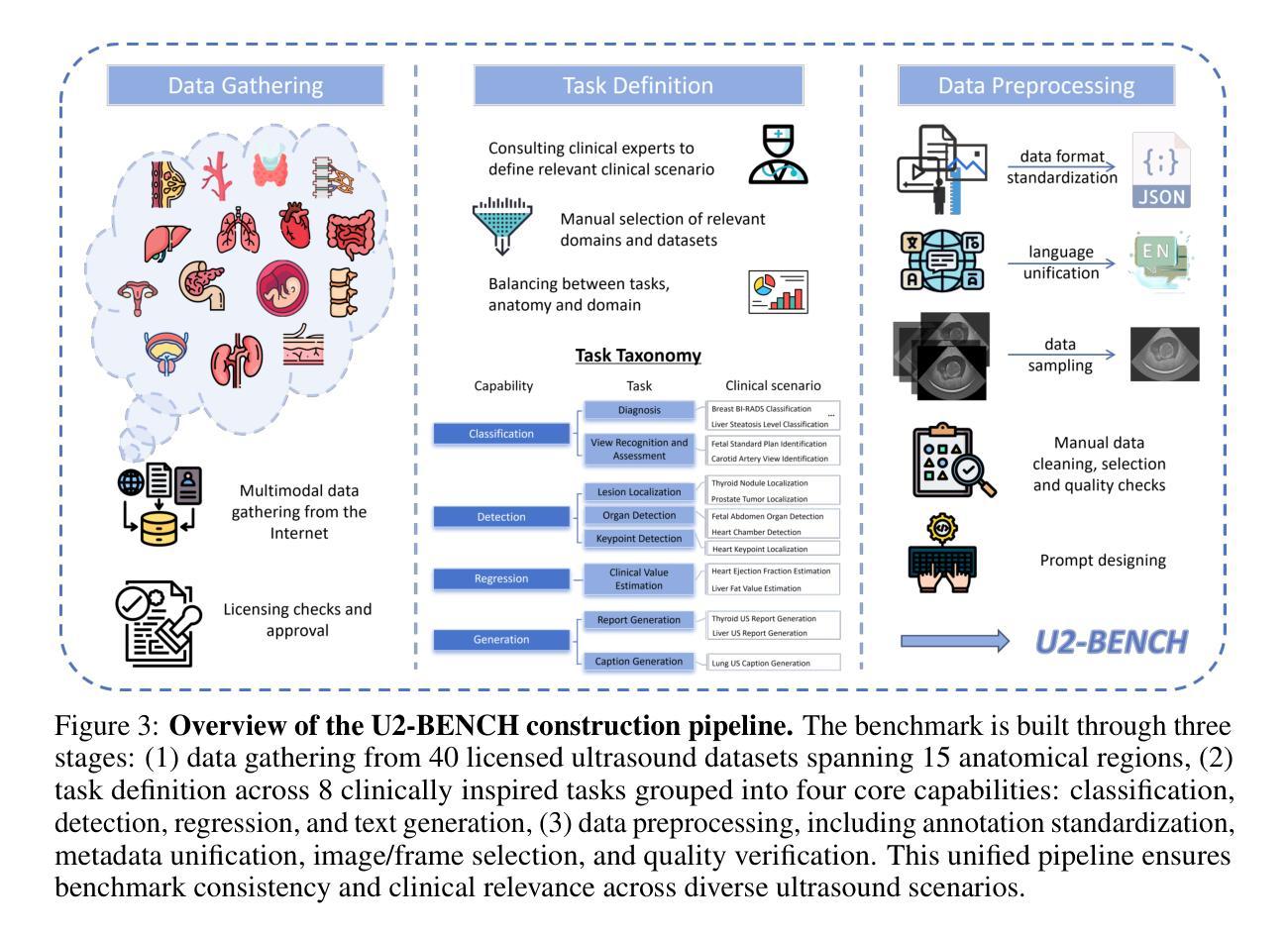
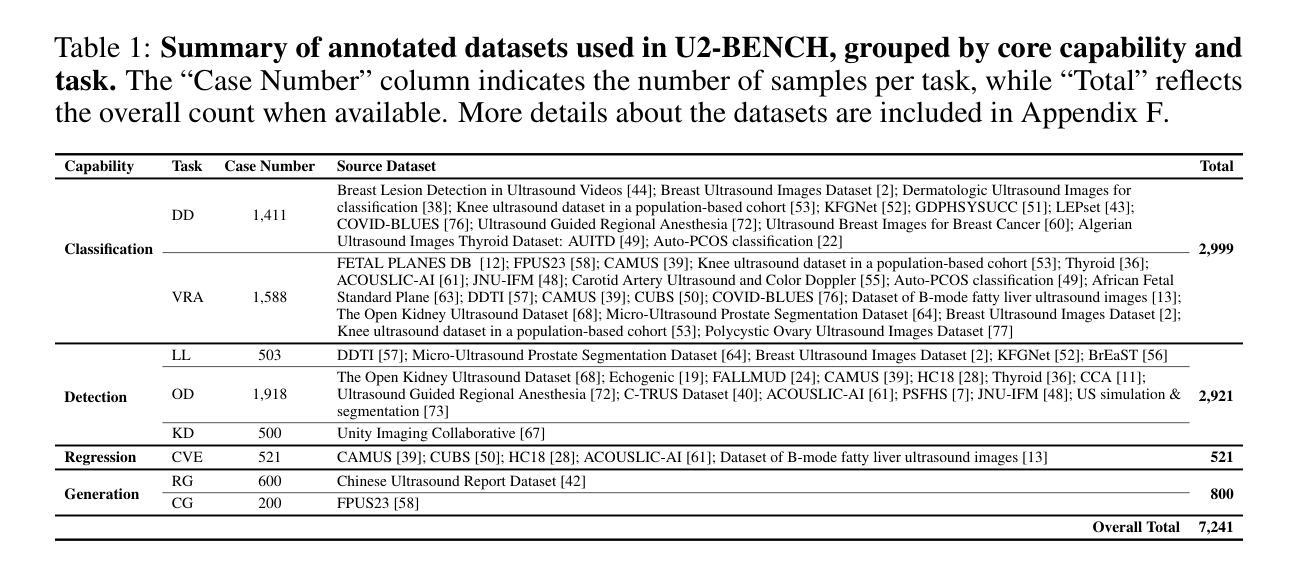
U2-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Vision-Language Models on Ultrasound Understanding
Authors:Anjie Le, Henan Liu, Yue Wang, Zhenyu Liu, Rongkun Zhu, Taohan Weng, Jinze Yu, Boyang Wang, Yalun Wu, Kaiwen Yan, Quanlin Sun, Meirui Jiang, Jialun Pei, Siya Liu, Haoyun Zheng, Zhoujun Li, Alison Noble, Jacques Souquet, Xiaoqing Guo, Manxi Lin, Hongcheng Guo
Ultrasound is a widely-used imaging modality critical to global healthcare, yet its interpretation remains challenging due to its varying image quality on operators, noises, and anatomical structures. Although large vision-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal capabilities across natural and medical domains, their performance on ultrasound remains largely unexplored. We introduce U2-BENCH, the first comprehensive benchmark to evaluate LVLMs on ultrasound understanding across classification, detection, regression, and text generation tasks. U2-BENCH aggregates 7,241 cases spanning 15 anatomical regions and defines 8 clinically inspired tasks, such as diagnosis, view recognition, lesion localization, clinical value estimation, and report generation, across 50 ultrasound application scenarios. We evaluate 20 state-of-the-art LVLMs, both open- and closed-source, general-purpose and medical-specific. Our results reveal strong performance on image-level classification, but persistent challenges in spatial reasoning and clinical language generation. U2-BENCH establishes a rigorous and unified testbed to assess and accelerate LVLM research in the uniquely multimodal domain of medical ultrasound imaging.
超声是全球医疗中广泛使用的成像方式,对其解读仍具有挑战性,因为其在操作者、噪声和解剖结构上的图像质量存在差异。虽然在自然语言与医疗领域的多模态能力方面,大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)已经表现出了令人印象深刻的性能,但它们在超声方面的表现仍鲜有研究。我们介绍了U2-BENCH,这是第一个全面评估LVLM在超声理解方面的基准测试,涵盖了分类、检测、回归和文本生成任务。U2-BENCH汇集了7241例病例,涉及15个解剖区域,并定义了8个受临床启发的任务,如诊断、视图识别、病灶定位、临床价值评估和报告生成等,涵盖50种超声应用场景。我们对20项最先进的大型视觉语言模型进行了评估,包括开源和闭源、通用型和医用特定型。我们的结果表明,在图像级别分类方面表现出强大的性能,但在空间推理和临床语言生成方面仍存在持续挑战。U2-BENCH建立了一个严格统一的测试平台,以评估和加速医用超声成像多模态领域的LVLM研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超声是全球卫生保健中广泛使用的成像方式,但其图像质量受操作人员、噪声和解剖结构等因素影响,解读具有挑战性。大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在医学领域表现卓越,但在超声上的性能尚待探索。引入U2-BENCH作为评估LVLMs在超声理解方面的首个综合基准测试,涵盖分类、检测、回归和文本生成任务。U2-BENCH包含7,241例,涵盖15个解剖区域,定义8个临床任务,如诊断、视图识别、病灶定位、临床价值评估和报告生成等。评估了20项先进的LVLMs,包括开源和闭源、通用和专用的模型。结果显示,图像分类性能强,但在空间推理和临床语言生成方面仍有挑战。U2-BENCH为评估和加速医学超声成像领域LVLM研究提供了严格、统一的测试平台。
Key Takeaways
- 超声是全球卫生保健中重要的成像方式,但其解读具有挑战性,需要更精确的视觉语言模型进行解读。
- U2-BENCH是首个针对视觉语言模型在超声理解方面的综合基准测试。
- U2-BENCH涵盖了多种任务,包括分类、检测、回归和文本生成等,并定义了8个临床任务。
- U2-BENCH包含大量病例数据,涵盖多种解剖区域和超声应用场景。
- 图像分类任务在超声理解方面表现良好,但在空间推理和临床语言生成方面仍存在挑战。
- 现有视觉语言模型在超声解读方面的性能有待提高。
点此查看论文截图

Star-like thermoresponsive microgels: a new class of soft nanocolloids
Authors:Elisa Ballin, Francesco Brasili, Tommaso Papetti, Jacopo Vialetto, Michael Sztucki, Simona Sennato, Marco Laurati, Emanuela Zaccarelli
We provide experimental and numerical evidence of a new class of soft nanocolloids: star-like microgels with thermoresponsive character. This is achieved by using the standard precipitation polymerization synthesis of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) microgels and replacing the usually employed crosslinking agent, N,N’-methylenebis(acrylamide) (BIS), with ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA). The fast reactivity of EGDMA combined with its strong tendency to self-bind produces colloidal networks with a central, crosslinker-rich core, surrounded by a corona of long, crosslinker-free arms. These novel star-like microgels fully retain PNIPAM thermoresponsivity and undergo a volume phase transition at a temperature of 32{\deg}C that is very sharp as compared to standard PNIPAM-BIS microgels, independently of crosslinker content. Dynamic light scattering and small angle X-ray scattering experiments are compared to extensive simulation results, based on ideal star polymers as well as on state-of-the-art monomer-resolved simulations, offering a microscopic evidence of the star-like internal structure of PNIPAM-EGDMA microgels. This can be described by a novel model for the form factors combining star and microgel features. The present work thus bridges the fields of star polymers and microgels, providing the former with the ability to respond to temperature via a facile synthetic route that can be routinely employed, opening the way to exploit these soft particles for a variety of fundamental studies and applicative purposes.
我们提供一类新型软纳米胶体物质——星形微凝胶的实验和数值证据,它具有热响应特性。这是通过采用N-异丙基丙烯酰胺(PNIPAM)微凝胶的标准沉淀聚合合成方法实现的,用乙二醇二甲丙烯酸酯(EGDMA)替代通常使用的交联剂N,N’-亚甲基双丙烯酰胺(BIS)。EGDMA的快速反应性与其自身强烈的自结合趋势相结合,产生了以富含交联剂的中央为核心,周围环绕着长而无交联剂的臂的胶体网络。这些新型的星形微凝胶完全保留了PNIPAM的热响应性,在32℃的温度下发生体积相变,与标准的PNIPAM-BIS微凝胶相比,无论交联剂含量如何,这种相变都非常尖锐。通过动态光散射和小角度X射线散射实验与基于理想星形聚合物以及最新的单体解析模拟的广泛模拟结果进行比较,为PNIPAM-EGDMA微凝胶的星形内部结构提供了微观证据。这可以通过结合星形和微凝胶特性的新型因子模型来描述。因此,本工作架起了星形聚合物和微凝胶之间的桥梁,赋予前者通过简便的合成途径对温度作出反应的能力,为这些软粒子在基础研究和应用方面开辟了新的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文实验和数值证明了一种新型软纳米胶体——星状微凝胶的热敏特性。通过采用沉淀聚合合成聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)(PNIPAM)微凝胶的标准方法,并改用乙二醇二甲酸酯(EGDMA)作为交联剂,实现了星状微凝胶的合成。EGDMA的快速反应性和强烈的自结合趋势,形成了以交联剂丰富的核心为中心,周围环绕着长而无交联剂的臂的胶体网络。这些新型的星状微凝胶完全保留了PNIPAM的热敏性,在32℃时经历了体积相变,与标准的PNIPAM-BIS微凝胶相比,无论交联剂含量如何,这种相变都非常锐利。通过动态光散射和小角度X射线散射实验与基于理想星形聚合物和最新单体解析模拟的广泛模拟结果进行比较,从微观上证明了PNIPAM-EGDMA微凝胶的星形内部结构。这可以通过结合星形和微凝胶特征的新模型来描述其形状因子。因此,本文结合了星形聚合物和微凝胶领域,为前者提供了一种可通过简便的合成路线实现对温度的响应能力,为这些软粒子在各种基础研究和应用目的中的利用打开了道路。
关键见解
- 成功合成了一种新型软纳米胶体——星状微凝胶,具有热敏特性。
- 通过使用EGDMA作为交联剂,实现了星状微凝胶的独特内部结构。
- 星状微凝胶在32℃时经历尖锐的体积相变,表现出高度的温度响应性。
- 通过动态光散射和小角度X射线散射实验验证了微凝胶的星形内部结构。
- 结合星形聚合物和微凝胶特性的新模型描述了其形状因子。
- 这种合成方法为制备温度响应性软粒子提供了一种简便途径。
点此查看论文截图

Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation via Dual Networks
Authors:Yunyao Lu, Yihang Wu, Reem Kateb, Ahmad Chaddad
Traditional supervised medical image segmentation models require large amounts of labeled data for training; however, obtaining such large-scale labeled datasets in the real world is extremely challenging. Recent semi-supervised segmentation models also suffer from noisy pseudo-label issue and limited supervision in feature space. To solve these challenges, we propose an innovative semi-supervised 3D medical image segmentation method to reduce the dependency on large, expert-labeled datasets. Furthermore, we introduce a dual-network architecture to address the limitations of existing methods in using contextual information and generating reliable pseudo-labels. In addition, a self-supervised contrastive learning strategy is used to enhance the representation of the network and reduce prediction uncertainty by distinguishing between reliable and unreliable predictions. Experiments on clinical magnetic resonance imaging demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art techniques. Our code is available at https://github.com/AIPMLab/Semi-supervised-Segmentation.
传统监督式医学图像分割模型需要大量的标记数据进行训练;然而,在现实世界中获取如此大规模的标记数据集极具挑战性。最近的半监督分割模型还面临着伪标签噪声问题和特征空间监督有限的问题。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种创新的半监督3D医学图像分割方法,以减少对大规模专家标记数据集的依赖。此外,我们引入了一种双网络架构,以解决现有方法在利用上下文信息和生成可靠伪标签方面的局限性。另外,我们还使用了一种自我监督的对比学习策略,以提高网络的表示能力,并通过区分可靠和不可靠的预测来减少预测的不确定性。对临床磁共振成像的实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进的技术。我们的代码可在https://github.com/AIPMLab/Semi-supervised-Segmentation获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ISBI2025
Summary
本文提出了一种创新的半监督3D医学图像分割方法,减少对大量专家标注数据集的依赖。采用双网络架构解决现有方法在使用上下文信息和生成可靠伪标签方面的局限性。同时,使用自监督对比学习策略增强网络表示,通过区分可靠和不可靠的预测来减少预测不确定性。在临床磁共振成像上的实验表明,该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割方法减少了对大规模专家标注数据集的依赖。
- 引入双网络架构,解决现有方法在利用上下文信息和生成可靠伪标签方面的不足。
- 采用自监督对比学习策略,提高网络表示能力。
- 该方法能够区分可靠和不可靠的预测,减少预测不确定性。
- 提出的方法在临床磁共振成像实验上表现出优异性能。
- 该方法的代码已公开提供,方便研究使用和进一步开发。
点此查看论文截图

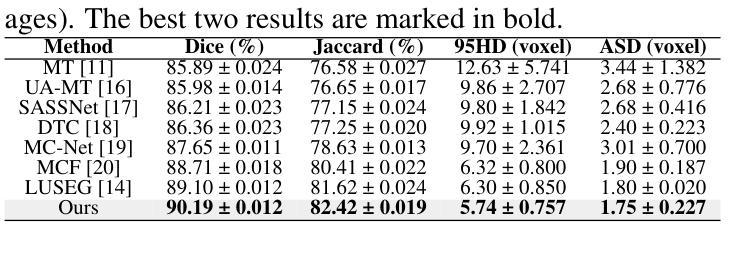
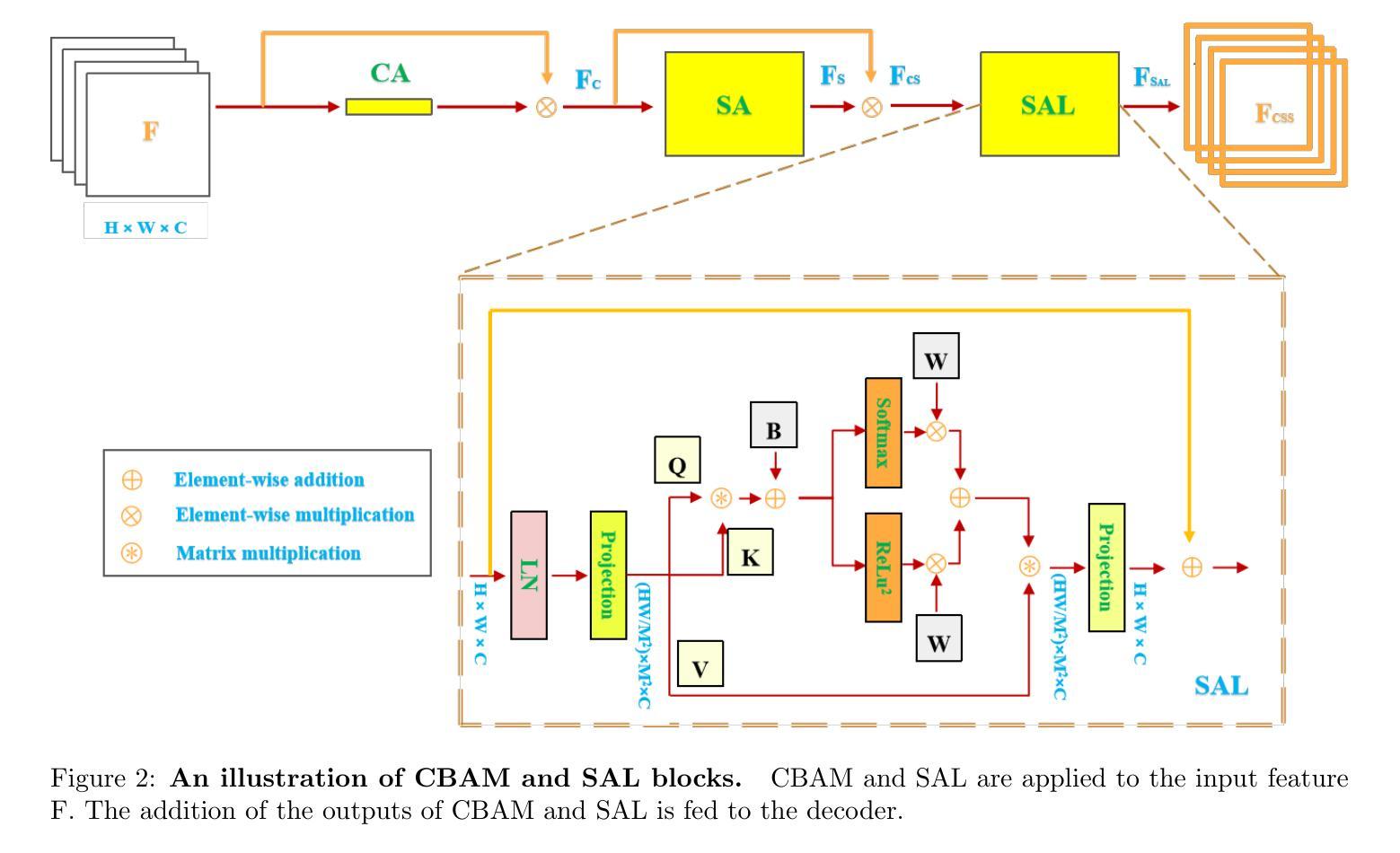
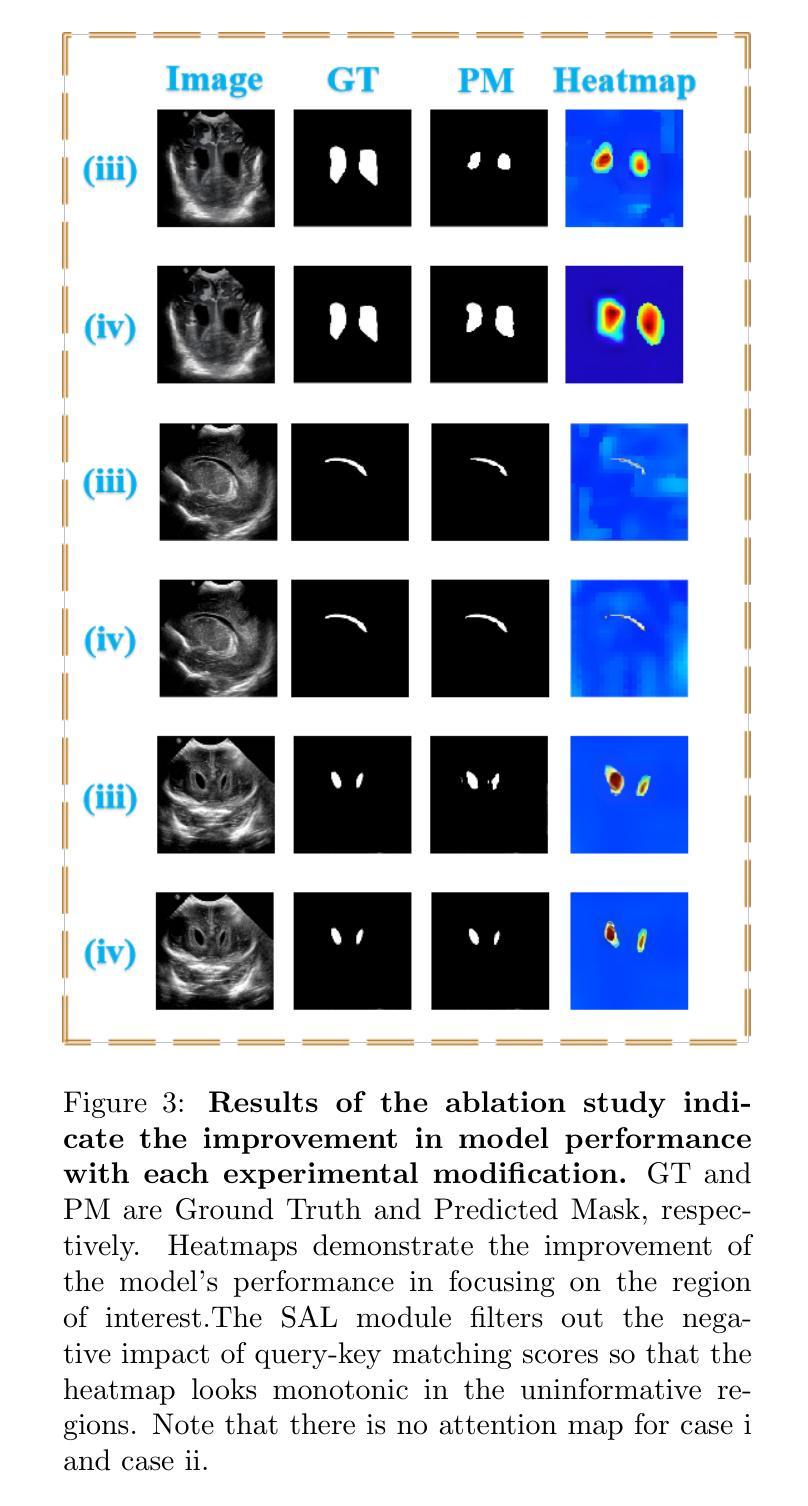
Dual Attention Residual U-Net for Accurate Brain Ultrasound Segmentation in IVH Detection
Authors:Dan Yuan, Yi Feng, Ziyun Tang
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is a severe neurological complication among premature infants, necessitating early and accurate detection from brain ultrasound (US) images to improve clinical outcomes. While recent deep learning methods offer promise for computer-aided diagnosis, challenges remain in capturing both local spatial details and global contextual dependencies critical for segmenting brain anatomies. In this work, we propose an enhanced Residual U-Net architecture incorporating two complementary attention mechanisms: the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and a Sparse Attention Layer (SAL). The CBAM improves the model’s ability to refine spatial and channel-wise features, while the SAL introduces a dual-branch design, sparse attention filters out low-confidence query-key pairs to suppress noise, and dense attention ensures comprehensive information propagation. Extensive experiments on the Brain US dataset demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art segmentation performance, with a Dice score of 89.04% and IoU of 81.84% for ventricle region segmentation. These results highlight the effectiveness of integrating spatial refinement and attention sparsity for robust brain anatomy detection. Code is available at: https://github.com/DanYuan001/BrainImgSegment.
室内出血(IVH)是早产儿中一种严重的神经并发症,需要通过脑部超声(US)图像进行早期和准确的检测,以改善临床治疗效果。虽然最近的深度学习方法在计算机辅助诊断方面显示出潜力,但仍然存在挑战,即捕获对分割大脑结构至关重要的局部空间细节和全局上下文依赖关系。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种增强的Residual U-Net架构,该架构结合了两种互补的注意力机制:卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)和稀疏注意力层(SAL)。CBAM提高了模型对空间和通道特征的精细处理能力,而SAL引入了双分支设计,其中稀疏注意力过滤掉低置信度的查询-键对以抑制噪声,而密集注意力确保全面信息传播。在Brain US数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的分割性能,对脑室区域分割的Dice得分为89.04%,IoU为81.84%。这些结果突出了整合空间精细化和注意力稀疏性对于稳健的大脑结构检测的有效性。代码可在:https://github.com/DanYuan001/BrainImgSegment找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages,6 figures and 3 tables
Summary
本摘要针对颅内出血的早产儿进行早期和准确的诊断,利用深度学习的增强Residual U-Net架构融合卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)和稀疏注意力层(SAL)实现高效诊断。在超声图像上取得了显著分割效果,具有89.04%的Dice系数和81.84%的IoU得分。该方法有效整合空间细节与注意力稀疏性,提高了脑部结构检测的稳健性。相关代码可通过特定链接获取。
Key Takeaways
- 针对早产儿颅内出血的早期和准确诊断至关重要。
- 增强Residual U-Net架构结合了卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)和稀疏注意力层(SAL),增强了计算机辅助诊断的准确性。
- 通过双重分支设计实现了空间和全局依赖的捕获。
点此查看论文截图

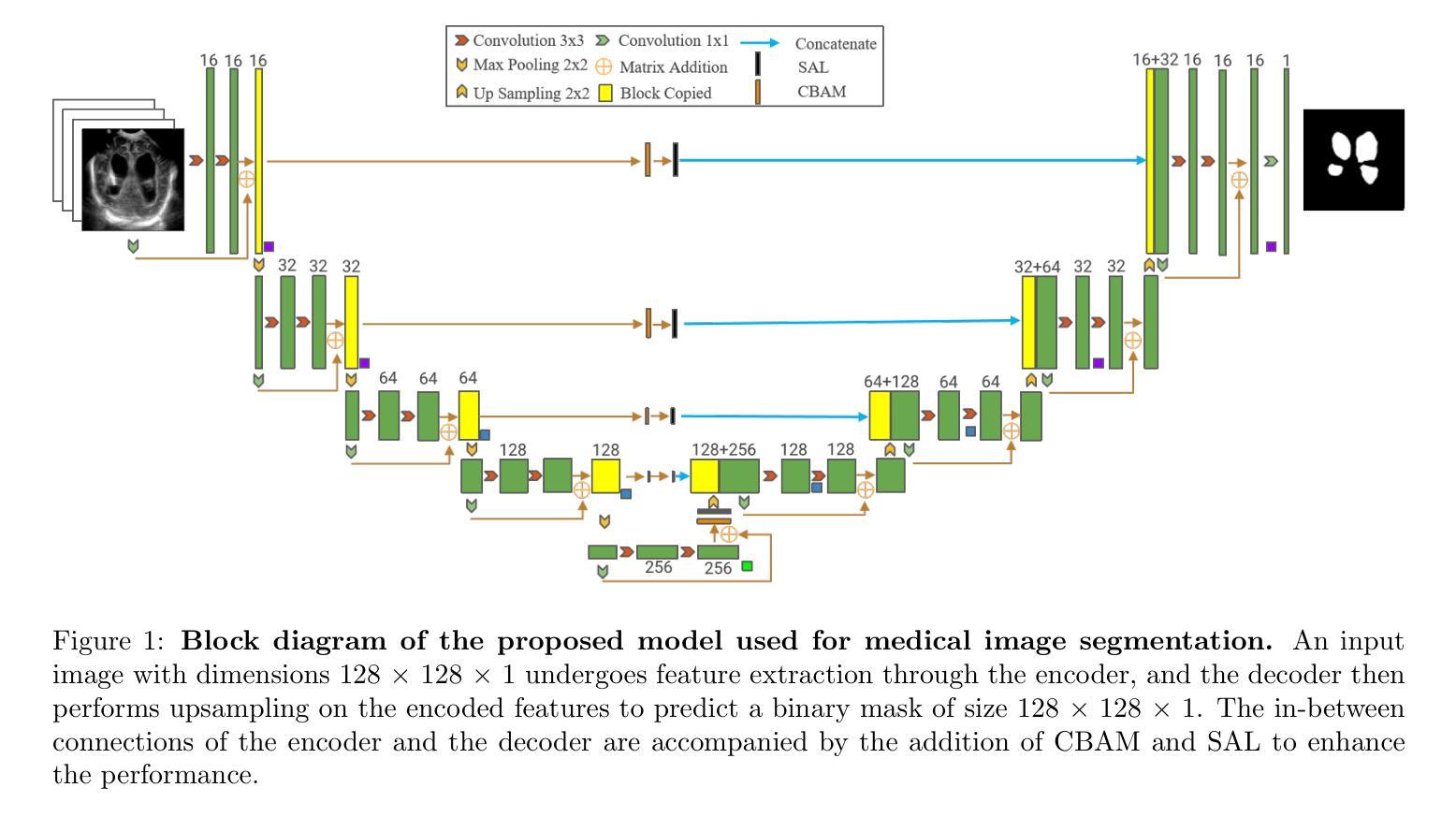
EMRA-proxy: Enhancing Multi-Class Region Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images with Attention Proxy
Authors:Yichun Yu, Yuqing Lan, Zhihuan Xing, Xiaoyi Yang, Tingyue Tang, Dan Yu
High-resolution remote sensing (HRRS) image segmentation is challenging due to complex spatial layouts and diverse object appearances. While CNNs excel at capturing local features, they struggle with long-range dependencies, whereas Transformers can model global context but often neglect local details and are computationally expensive.We propose a novel approach, Region-Aware Proxy Network (RAPNet), which consists of two components: Contextual Region Attention (CRA) and Global Class Refinement (GCR). Unlike traditional methods that rely on grid-based layouts, RAPNet operates at the region level for more flexible segmentation. The CRA module uses a Transformer to capture region-level contextual dependencies, generating a Semantic Region Mask (SRM). The GCR module learns a global class attention map to refine multi-class information, combining the SRM and attention map for accurate segmentation.Experiments on three public datasets show that RAPNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior multi-class segmentation accuracy.
高分辨率遥感(HRRS)图像分割由于复杂的空间布局和多样的对象外观而具有挑战性。虽然卷积神经网络(CNN)在捕捉局部特征方面表现出色,但在处理长距离依赖关系时却遇到困难,而Transformer能够建模全局上下文,但往往忽略了局部细节,且计算成本较高。我们提出了一种新方法,即区域感知代理网络(RAPNet),它由两部分组成:上下文区域注意力(CRA)和全局类别细化(GCR)。与传统的基于网格布局的方法不同,RAPNet在区域级别上进行操作,以实现更灵活的分割。CRA模块使用Transformer来捕获区域级别的上下文依赖关系,生成语义区域掩膜(SRM)。GCR模块学习全局类别注意力图来细化多类别信息,结合SRM和注意力图进行精确分割。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,RAPNet优于最新方法,实现了更高的多类别分割精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Intelligent Computing (ICIC 2024): Poster Volume I. Tianjin, China, 2024: 538-562
Summary
本文提出一种新型的高分辨率遥感图像分割方法——Region-Aware Proxy Network (RAPNet),包含Contextual Region Attention (CRA)和Global Class Refinement (GCR)两个组件。RAPNet以区域级别操作,更灵活地实现分割,通过Transformer捕捉区域级别的上下文依赖关系,生成Semantic Region Mask (SRM),并结合全局类注意力图进行多类信息修正,从而提高分割准确性。在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,RAPNet的多类分割精度优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率遥感图像分割面临复杂空间布局和多样物体外观的挑战。
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)擅长捕捉局部特征,但难以处理长距离依赖;而Transformer可以建模全局上下文,但忽略局部细节且计算成本高。
- RAPNet方法包括Contextual Region Attention (CRA)和Global Class Refinement (GCR)两个组件。
- RAPNet以区域级别操作,实现更灵活的分割。
- CRA模块使用Transformer捕捉区域级别的上下文依赖关系,生成Semantic Region Mask (SRM)。
- GCR模块学习全局类注意力图,用于修正多类信息。
点此查看论文截图



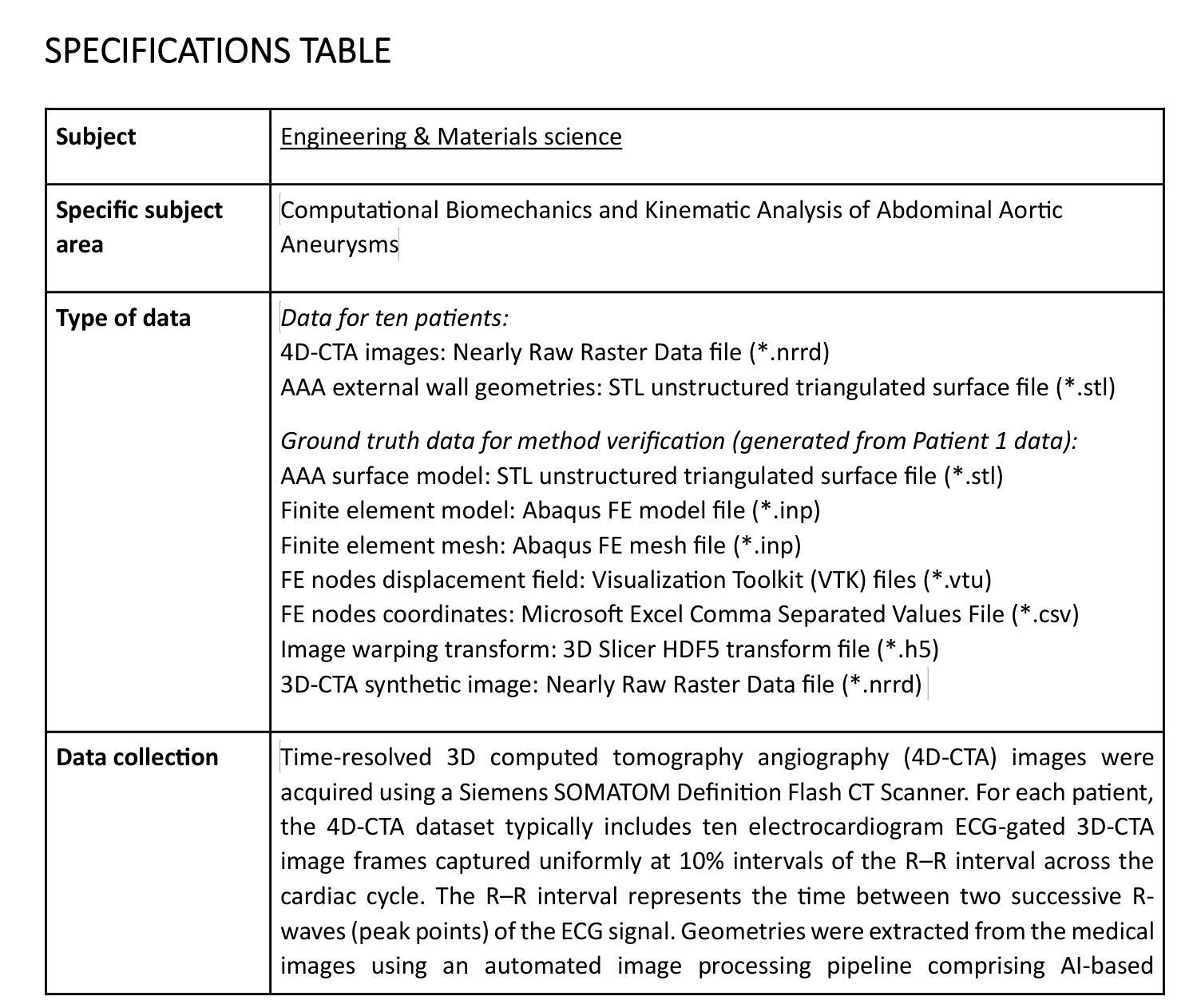
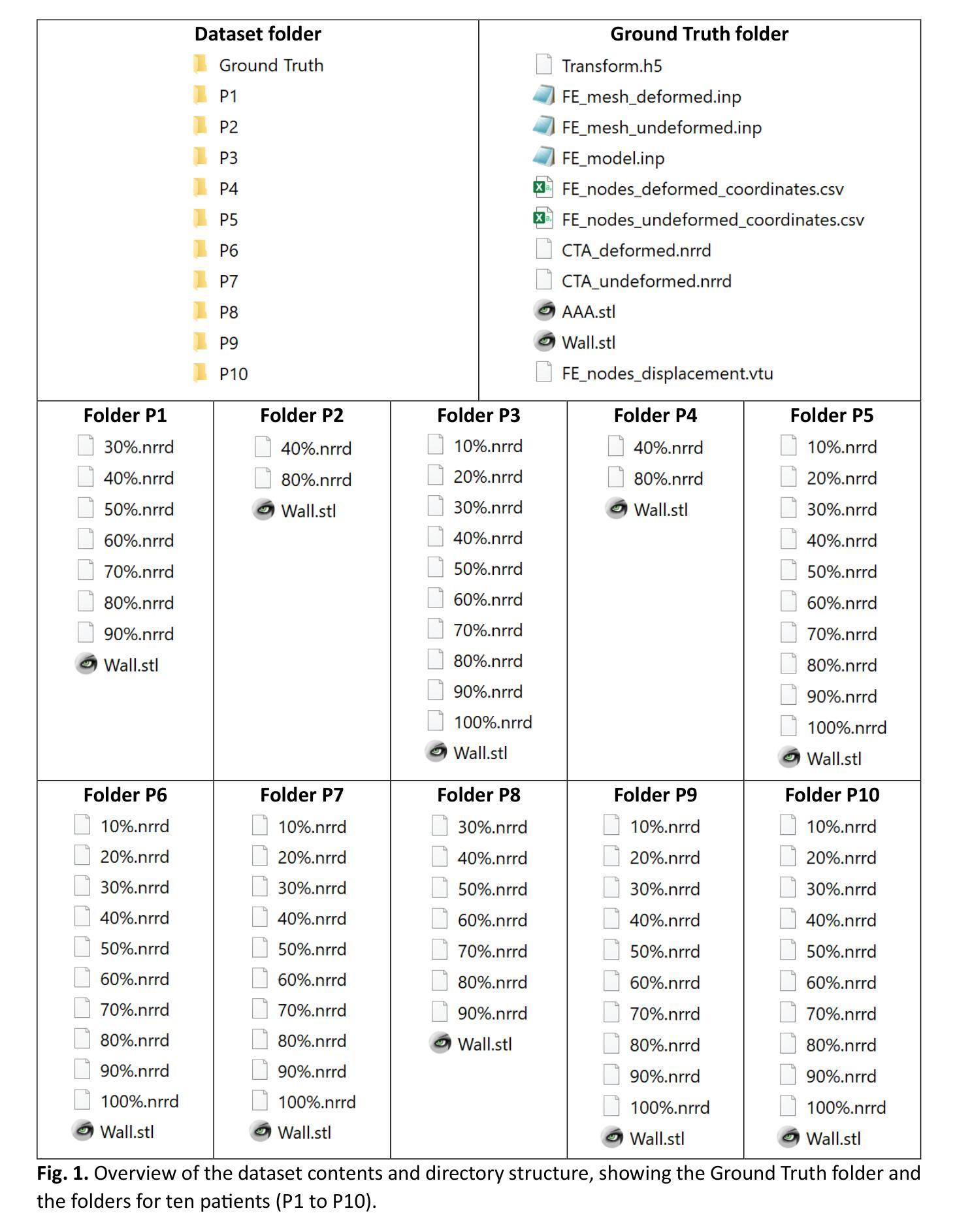
4D-CTA Image and geometry dataset for kinematic analysis of abdominal aortic aneurysms
Authors:Mostafa Jamshidian, Adam Wittek, Saeideh Sekhavat, Farah Alkhatib, Jens Carsten Ritter, Paul M. Parizel, Donatien Le Liepvre, Florian Bernard, Ludovic Minvielle, Antoine Fondanèche, Jane Polce, Christopher Wood, Karol Miller
This article presents a dataset used in the article “Kinematics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms” [arXiv:2405.13377], published in the Journal of Biomechanics. The dataset is publicly available for download from the Zenodo data repository (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15477710). The dataset includes time-resolved 3D computed tomography angiography (4D-CTA) images of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) captured throughout the cardiac cycle from ten patients diagnosed with AAA, along with ten patient-specific AAA geometries extracted from these images. Typically, the 4D-CTA dataset for each patient contains ten electrocardiogram (ECG)-gated 3D-CTA image frames acquired over a cardiac cycle, capturing both the systolic and diastolic phases of the AAA configuration. For method verification, the dataset also includes synthetic ground truth data generated from Patient 1’s 3D-CTA AAA image in the diastolic phase. The ground truth data includes the patient-specific finite element (FE) biomechanical model and a synthetic systolic 3D-CTA image. The synthetic systolic image was generated by warping Patient 1’s diastolic 3D-CTA image using the realistic displacement field obtained from the AAA biomechanical FE model. The images were acquired at Fiona Stanley Hospital in Western Australia and provided to the researchers at the Intelligent Systems for Medicine Laboratory at The University of Western Australia (ISML-UWA), where image-based AAA kinematic analysis was performed. Our dataset enabled the analysis of AAA wall displacement and strain throughout the cardiac cycle using a non-invasive, in vivo, image registration-based approach. The use of widely adopted, open-source file formats (NRRD for images and STL for geometries) facilitates broad applicability and reusability in AAA biomechanics studies that require patient-specific geometry and information about AAA kinematics during cardiac cycle.
本文介绍了在《生物力学杂志》上发表的“腹部主动脉瘤的运动学”一文(arXiv:2405.13377)中使用的数据集。该数据集可从Zenodo数据仓库(https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15477710)公开下载。数据集包含通过心脏周期捕获的腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)的时间分辨三维计算机断层血管造影(四维计算机断层血管造影图像),以及从这些图像中提取的十个患者特定的AAA几何形状。通常,每个患者的四维计算机断层扫描数据集包含十个心电图门控的三维计算机断层扫描图像帧,这些图像帧在整个心脏周期内捕获AAA配置的收缩期和舒张期。为了验证方法,数据集还包括由患者一号处于舒张期的三维计算机断层扫描AAA图像生成的合成基准数据。基准数据包括患者特定的有限元生物力学模型和一张合成收缩期的三维计算机断层扫描图像。合成收缩期图像是通过使用AAA生物力学有限元模型获得的现实位移场来扭曲患者一号的舒张期三维计算机断层扫描图像生成的。这些图像是在西澳大利亚的菲欧娜斯坦利医院获得的,并提供给西澳大利亚大学智能医学实验室的研究人员,在那里进行了基于图像的AAA运动学分析。我们的数据集能够使用一种无创、活体、基于图像配准的方法分析整个心脏周期内AAA壁位移和应变。使用广泛采用的开源文件格式(NRRD用于图像和STL用于几何形状)有助于在需要患者特定几何形状信息和心脏周期内AAA运动学信息的AAA生物力学研究中实现广泛的应用和再利用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个用于研究腹部主动脉瘤运动学的数据集。数据集包含从十个被诊断为腹部主动脉瘤的患者身上捕获的4D-CTA图像,以及从这些图像中提取的十个患者特定的AAA几何形状。数据集还包括由患者1的舒张期3D-CTA图像生成的合成基准数据。该数据集可促进对AAA壁位移和应变在整个心脏周期内的分析,并使用非侵入性、体内、基于图像配准的方法进行。
Key Takeaways
- 文章介绍了一个关于腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)的公开数据集,包含通过4D-CTA成像技术获取的患者图像和患者特定的AAA几何形状数据。
- 数据集包含十名AAA患者的图像数据,每个患者包含十个心电图门控的3D-CTA图像帧,涵盖整个心脏周期,可分析AAA配置在收缩期和舒张期的特点。
- 数据集还包括由患者1的舒张期3D-CTA图像生成的合成基准数据,包括患者特定的有限元生物力学模型和合成收缩期3D-CTA图像。
- 图像是在西澳大利亚的菲奥娜斯坦利医院获取的,并提供了智能系统医学实验室(ISML-UWA)的研究人员进行研究。
- 数据集的分析方法能够非侵入性地、在活体情况下,基于图像配准方法分析AAA壁位移和应变在整个心脏周期的变化。
- 数据集使用广泛采用的开放源文件格式(NRRD用于图像和STL用于几何),便于在需要患者特定几何信息和心脏周期内AAA运动学信息的AAA生物力学研究中使用和复用。
点此查看论文截图

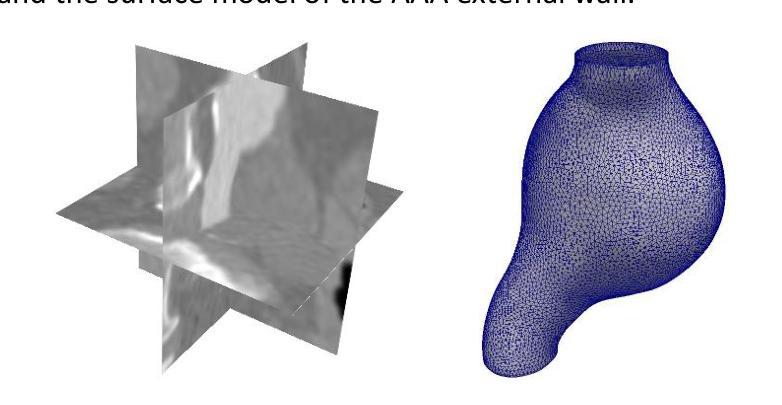
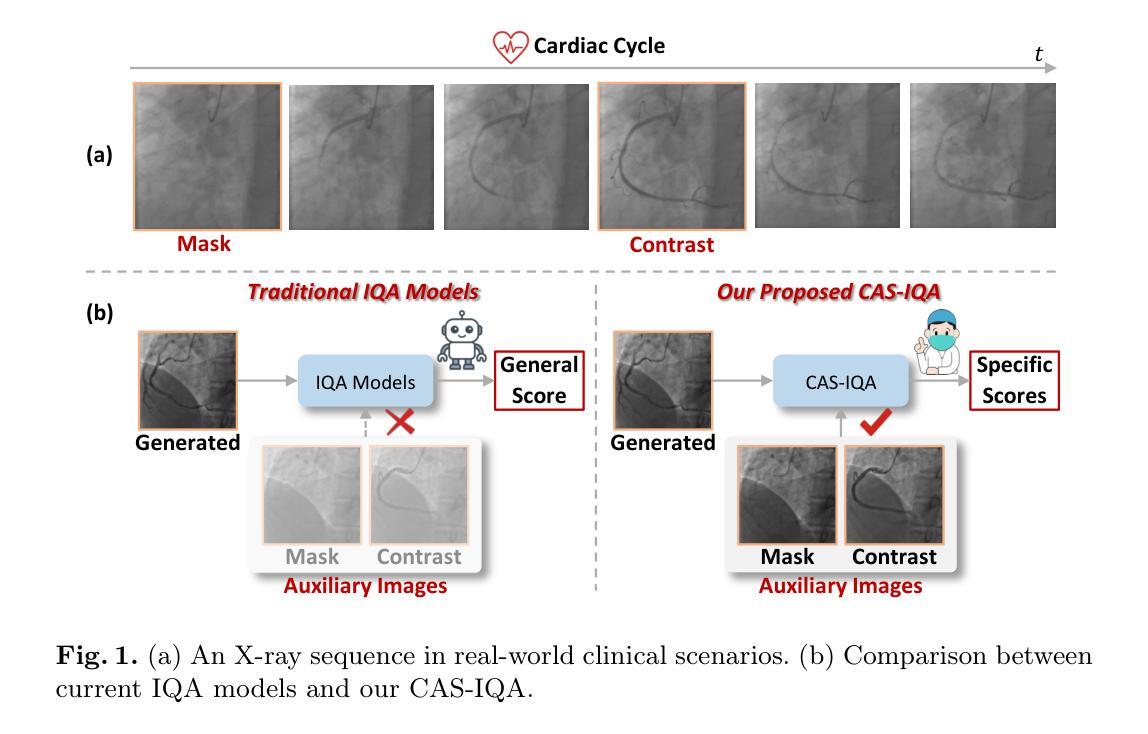
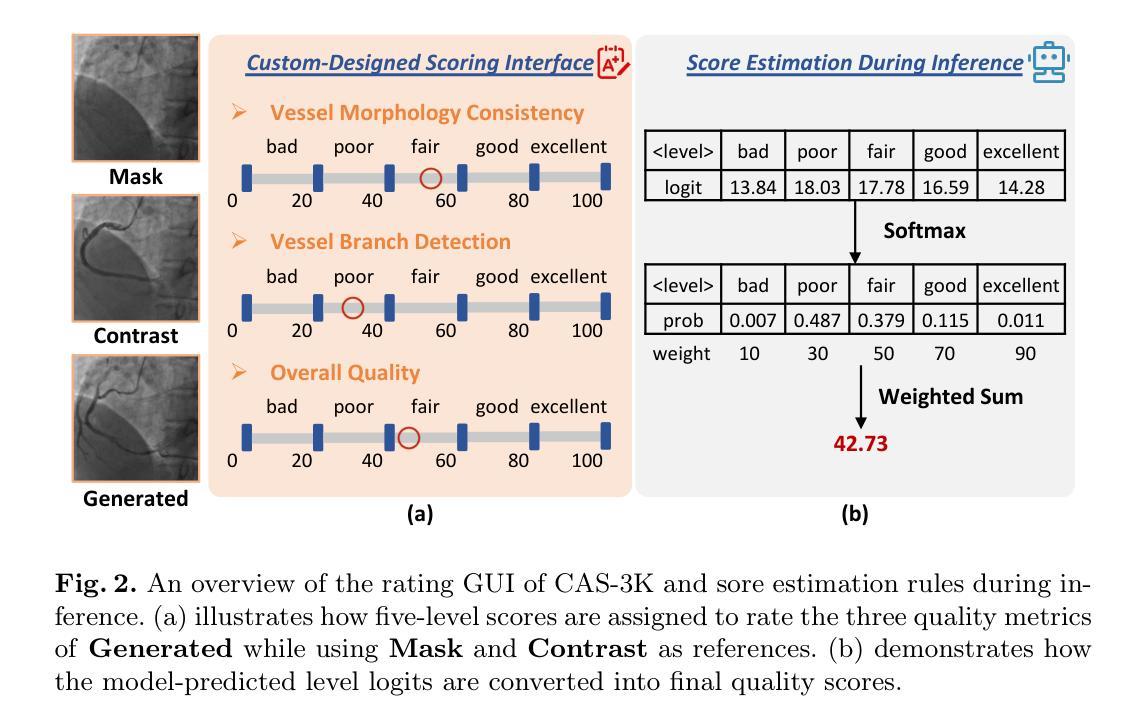
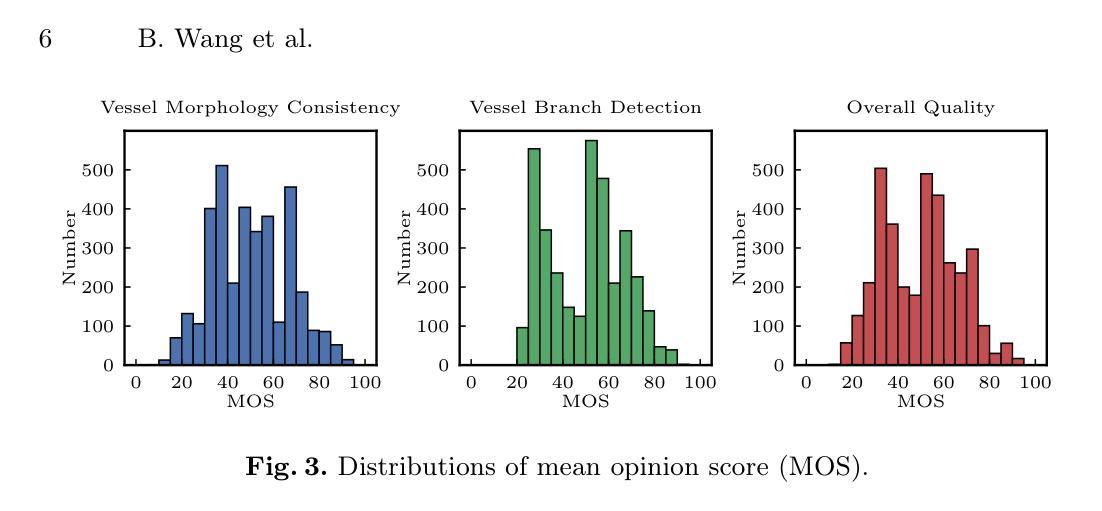
CAS-IQA: Teaching Vision-Language Models for Synthetic Angiography Quality Assessment
Authors:Bo Wang, De-Xing Huang, Xiao-Hu Zhou, Mei-Jiang Gui, Nu-Fang Xiao, Jian-Long Hao, Ming-Yuan Liu, Zeng-Guang Hou
Synthetic X-ray angiographies generated by modern generative models hold great potential to reduce the use of contrast agents in vascular interventional procedures. However, low-quality synthetic angiographies can significantly increase procedural risk, underscoring the need for reliable image quality assessment (IQA) methods. Existing IQA models, however, fail to leverage auxiliary images as references during evaluation and lack fine-grained, task-specific metrics necessary for clinical relevance. To address these limitations, this paper proposes CAS-IQA, a vision-language model (VLM)-based framework that predicts fine-grained quality scores by effectively incorporating auxiliary information from related images. In the absence of angiography datasets, CAS-3K is constructed, comprising 3,565 synthetic angiographies along with score annotations. To ensure clinically meaningful assessment, three task-specific evaluation metrics are defined. Furthermore, a Multi-path featUre fuSion and rouTing (MUST) module is designed to enhance image representations by adaptively fusing and routing visual tokens to metric-specific branches. Extensive experiments on the CAS-3K dataset demonstrate that CAS-IQA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art IQA methods by a considerable margin.
由现代生成模型生成的合成X射线血管造影图在很大程度上可以减少血管介入过程中对造影剂的使用,具有巨大潜力。然而,低质量的合成血管造影图可能会显著增加手术风险,这强调了需要可靠的图像质量评估(IQA)方法。然而,现有的IQA模型在评估过程中未能利用辅助图像作为参考,并且缺乏针对临床相关性的精细任务和特定指标。为了解决这些局限性,本文提出了CAS-IQA,这是一个基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的框架,通过有效地结合相关图像的辅助信息来预测精细的质量分数。在没有血管造影数据集的情况下,构建了CAS-3K,它包括3565张合成血管造影图像以及分数注释。为了确保临床上有意义的评估,定义了三个特定任务的评估指标。此外,设计了一个多路径特征融合和路由(MUST)模块,通过自适应融合和路由视觉令牌到特定指标的分支,以增强图像表示。在CAS-3K数据集上的广泛实验表明,CAS-IQA显著优于最新一代的IQA方法,差距相当明显。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
这篇文章探讨了基于现代生成模型的合成X射线血管造影图像质量评估的问题。由于低质量的合成血管造影图像可能增加手术风险,因此需要可靠的图像质量评估(IQA)方法。为解决现有IQA模型未能利用辅助图像作为参考以及缺乏针对临床相关的精细任务特定指标的局限性,本文提出了一种基于视觉语言模型的CAS-IQA框架,它能够有效地利用相关图像中的辅助信息来预测精细的质量分数。此外,为了进行临床上有意义的评估,定义了三个任务特定的评估指标,并设计了一个多路径特征融合和路由(MUST)模块来增强图像表示。在CAS-3K数据集上的实验表明,CAS-IQA显著优于现有最先进的IQA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 合成X射线血管造影图像在临床应用中有潜力减少造影剂的使用,但低质量图像可能增加手术风险。
- 现有的图像质量评估(IQA)模型未能充分利用辅助图像,缺乏针对临床任务的具体指标。
- CAS-IQA框架结合视觉语言模型(VLM)技术,能有效利用相关图像的辅助信息预测精细质量分数。
- 为确保临床相关的评估,定义了三个任务特定的评估指标。
- 设计了MUST模块来增强图像表示,通过自适应融合和路由视觉标记到特定指标分支。
- CAS-IQA在CAS-3K数据集上的实验表现显著优于当前最先进的IQA方法。
点此查看论文截图

A Unified Multi-Scale Attention-Based Network for Automatic 3D Segmentation of Lung Parenchyma & Nodules In Thoracic CT Images
Authors:Muhammad Abdullah, Furqan Shaukat
Lung cancer has been one of the major threats across the world with the highest mortalities. Computer-aided detection (CAD) can help in early detection and thus can help increase the survival rate. Accurate lung parenchyma segmentation (to include the juxta-pleural nodules) and lung nodule segmentation, the primary symptom of lung cancer, play a crucial role in the overall accuracy of the Lung CAD pipeline. Lung nodule segmentation is quite challenging because of the diverse nodule types and other inhibit structures present within the lung lobes. Traditional machine/deep learning methods suffer from generalization and robustness. Recent Vision Language Models/Foundation Models perform well on the anatomical level, but they suffer on fine-grained segmentation tasks, and their semi-automatic nature limits their effectiveness in real-time clinical scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel method for accurate 3D segmentation of lung parenchyma and lung nodules. The proposed architecture is an attention-based network with residual blocks at each encoder-decoder state. Max pooling is replaced by strided convolutions at the encoder, and trilinear interpolation is replaced by transposed convolutions at the decoder to maximize the number of learnable parameters. Dilated convolutions at each encoder-decoder stage allow the model to capture the larger context without increasing computational costs. The proposed method has been evaluated extensively on one of the largest publicly available datasets, namely LUNA16, and is compared with recent notable work in the domain using standard performance metrics like Dice score, IOU, etc. It can be seen from the results that the proposed method achieves better performance than state-of-the-art methods. The source code, datasets, and pre-processed data can be accessed using the link: https://github.com/EMeRALDsNRPU/Attention-Based-3D-ResUNet.
肺癌是世界上最大的威胁之一,致死率极高。计算机辅助检测(CAD)有助于早期发现,从而提高存活率。精确的肺实质分割(包括胸膜下结节)和肺结节分割(肺癌的主要症状)在肺CAD管道的整体准确性中起着至关重要的作用。肺结节分割具有挑战性,因为肺叶中存在各种类型的结节和其他抑制结构。传统的机器/深度学习方法存在通用性和稳健性问题。最近的视觉语言模型/基础模型在解剖水平上表现良好,但在精细分割任务上存在问题,其半自动性质限制了其在实时临床场景中的有效性。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于精确3D肺实质和肺结节分割的新方法。所提出的架构是一个基于注意力的网络,每个编码器-解码器状态都有残差块。编码器处的最大池化被步幅卷积所替代,解码器处的三线性插值被转置卷积所替代,以最大化可学习参数的数量。每个编码器-解码器阶段的膨胀卷积允许模型捕获更大的上下文,而不会增加计算成本。该方法已在最大的公开数据集之一LUNA16上进行了广泛评估,并使用Dice分数、IOU等标准性能指标与领域中的最新显著工作进行了比较。从结果可以看出,该方法比最新技术取得了更好的性能。源代码、数据集和预处理数据可通过以下链接访问:https://github.com/EMeRALDsNRPU/Attention-Based-3D-ResUNet。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的三维分割方法,用于准确地进行肺实质和肺结节分割。该方法基于注意力机制的网络架构,具有优秀的性能,特别是在大型公开数据集LUNA16上进行评估时表现出良好的结果。该方法的源代码、数据集和预处理数据均可在GitHub上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌是全球主要的健康威胁之一,计算机辅助检测(CAD)有助于早期发现和增加存活率。
- 肺实质和肺结节的准确分割在肺CAD流程中起到关键作用。
- 传统机器/深度学习方法在肺结节分割上面临挑战,因为结节类型多样且肺叶内存在其他抑制结构。
- 最近的视觉语言模型/基础模型在解剖水平上表现良好,但在精细分割任务上受限,且其半自动性质限制了它们在实时临床场景中的有效性。
- 本文提出了一种新型的三维分割方法,基于注意力机制的网络架构,具有优秀的性能。
- 该方法采用残差块和替换最大池化的步幅卷积以及替换三线性插值的转置卷积等技术,以最大化可学习参数的数量。
点此查看论文截图

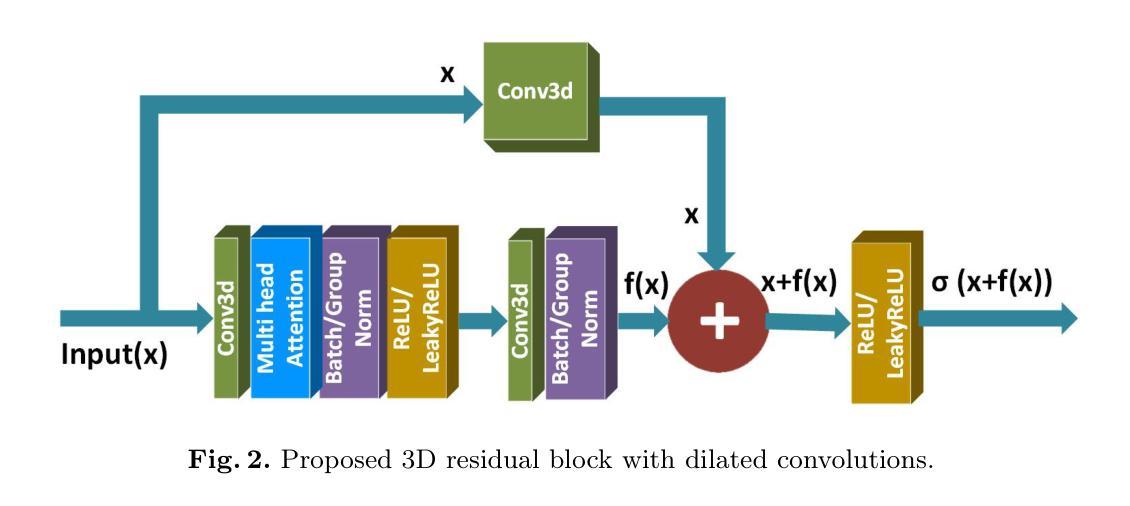
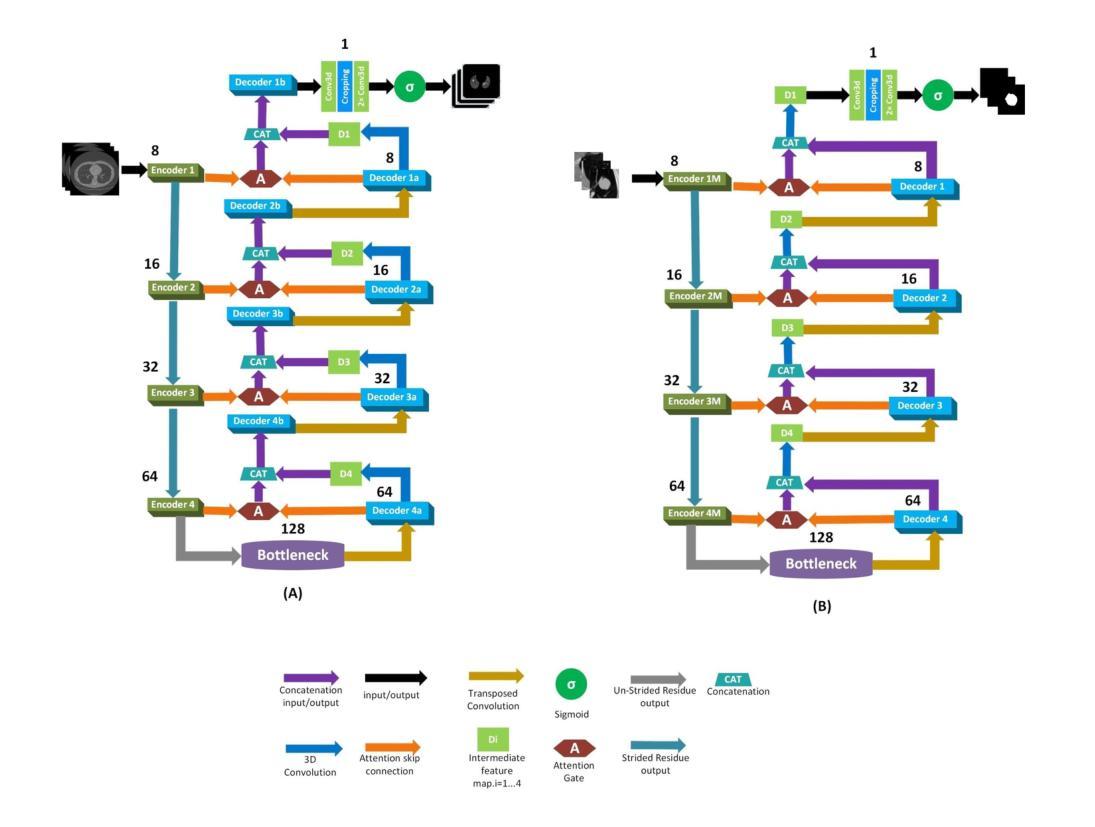
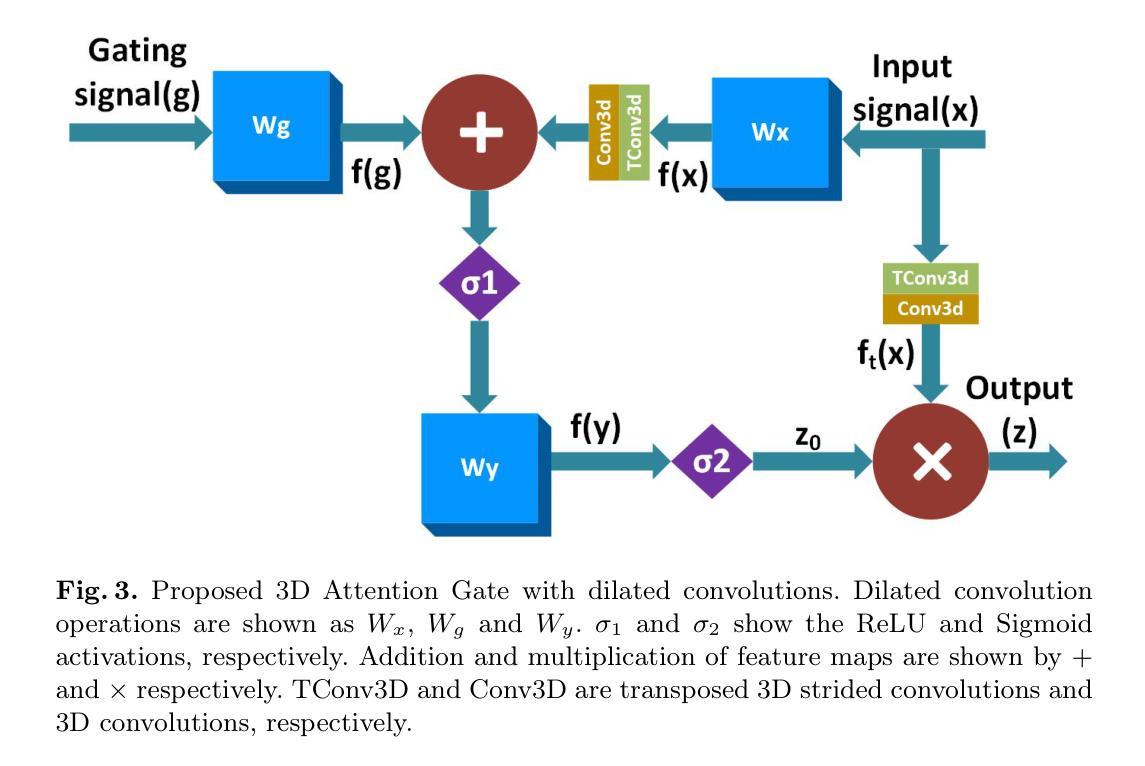
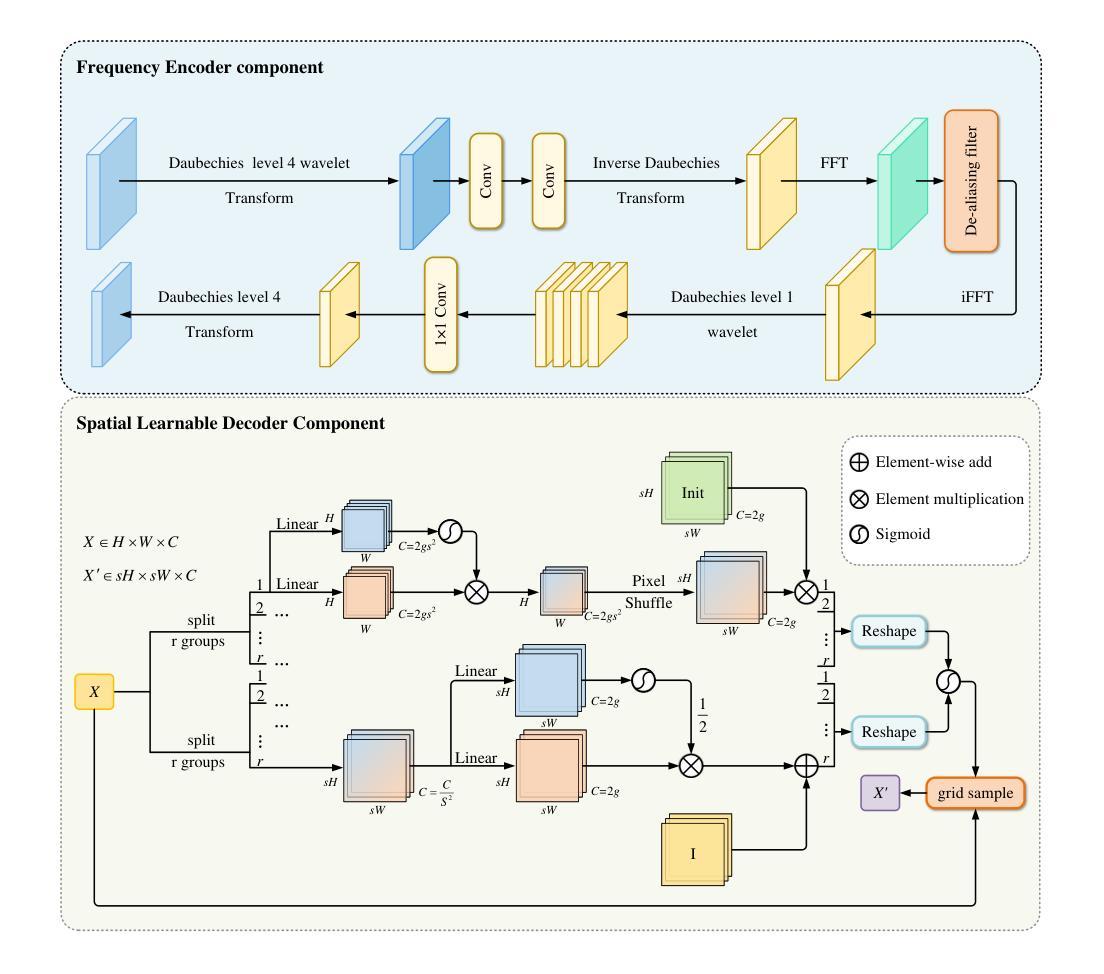
FreqU-FNet: Frequency-Aware U-Net for Imbalanced Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ruiqi Xing
Medical image segmentation faces persistent challenges due to severe class imbalance and the frequency-specific distribution of anatomical structures. Most conventional CNN-based methods operate in the spatial domain and struggle to capture minority class signals, often affected by frequency aliasing and limited spectral selectivity. Transformer-based models, while powerful in modeling global dependencies, tend to overlook critical local details necessary for fine-grained segmentation. To overcome these limitations, we propose FreqU-FNet, a novel U-shaped segmentation architecture operating in the frequency domain. Our framework incorporates a Frequency Encoder that leverages Low-Pass Frequency Convolution and Daubechies wavelet-based downsampling to extract multi-scale spectral features. To reconstruct fine spatial details, we introduce a Spatial Learnable Decoder (SLD) equipped with an adaptive multi-branch upsampling strategy. Furthermore, we design a frequency-aware loss (FAL) function to enhance minority class learning. Extensive experiments on multiple medical segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that FreqU-FNet consistently outperforms both CNN and Transformer baselines, particularly in handling under-represented classes, by effectively exploiting discriminative frequency bands.
医学图像分割面临着由于类别严重不平衡和解剖结构特定频率分布而带来的持续挑战。大多数传统的基于CNN的方法在空间域中操作,难以捕获少数类信号,常常受到频率混叠和有限谱选择性的影响。虽然基于Transformer的模型在建模全局依赖性方面非常强大,但它们往往忽略了用于精细分割所必需的关键局部细节。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了FreqU-FNet,这是一种新型的频率域U型分割架构。我们的框架结合了一个频率编码器,它利用低通频率卷积和基于Daubechies小波的降采样来提取多尺度谱特征。为了重建精细的空间细节,我们引入了一种配备有自适应多分支上采样策略的Spatial Learnable Decoder(SLD)。此外,我们设计了一种频率感知损失(FAL)函数,以增强对少数类的学习。在多个医学分割基准测试上的广泛实验表明,FreqU-FNet持续优于CNN和Transformer基线,特别是在处理表示不足的类别时,通过有效地利用判别频带。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 1 figure
Summary
针对医学图像分割中的类别不平衡和特定频率分布问题,文章提出了一种新型U型频域分割架构FreqU-FNet。该架构包括频率编码器、空间可学习解码器和频率感知损失函数。频率编码器利用低通频卷积和小波下采样提取多尺度频谱特征,解码器采用自适应多分支上采样策略以重建精细空间细节。在多个医学分割基准测试上,FreqU-FNet表现出出色的性能,特别是在处理代表性不足的类别时。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临类别不平衡和特定频率分布的挑战。
- 传统的CNN方法主要在空间域操作,难以捕捉少数类别的信号,并受到频率混叠和有限频谱选择性的影响。
- Transformer模型虽然擅长建模全局依赖性,但往往忽视关键的局部细节,这对于精细分割至关重要。
- 提出了一种新型频域分割架构FreqU-FNet,结合了频率编码器和空间可学习解码器。
- 频率编码器利用低通频卷积和小波下采样提取多尺度频谱特征。
- 空间可学习解码器通过自适应多分支上采样策略重建精细空间细节。
点此查看论文截图

Anatomy-Guided Multitask Learning for MRI-Based Classification of Placenta Accreta Spectrum and its Subtypes
Authors:Hai Jiang, Qiongting Liu, Yuanpin Zhou, Jiawei Pan, Ting Song, Yao Lu
Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders (PAS) pose significant risks during pregnancy, frequently leading to postpartum hemorrhage during cesarean deliveries and other severe clinical complications, with bleeding severity correlating to the degree of placental invasion. Consequently, accurate prenatal diagnosis of PAS and its subtypes-placenta accreta (PA), placenta increta (PI), and placenta percreta (PP)-is crucial. However, existing guidelines and methodologies predominantly focus on the presence of PAS, with limited research addressing subtype recognition. Additionally, previous multi-class diagnostic efforts have primarily relied on inefficient two-stage cascaded binary classification tasks. In this study, we propose a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture designed for efficient one-stage multiclass diagnosis of PAS and its subtypes, based on 4,140 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) slices. Our model features two branches: the main classification branch utilizes a residual block architecture comprising multiple residual blocks, while the second branch integrates anatomical features of the uteroplacental area and the adjacent uterine serous layer to enhance the model’s attention during classification. Furthermore, we implement a multitask learning strategy to leverage both branches effectively. Experiments conducted on a real clinical dataset demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
胎盘植入谱系疾病(PAS)在妊娠过程中存在重大风险,经常导致剖宫产术后出血和其他严重临床并发症,出血严重程度与胎盘侵犯程度有关。因此,对胎儿胎盘植入症及其亚型(胎盘植入(PA)、胎盘黏附(PI)和胎盘穿透(PP))的产前准确诊断至关重要。然而,现有的指南和方法主要关注PAS的存在,对亚型识别的研究有限。此外,以前的多类诊断工作主要依赖于效率低下的两阶段级联二元分类任务。本研究提出了一种新型的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构,该架构旨在基于4140个磁共振成像(MRI)切片,实现PAS及其亚型的一站式多类诊断。我们的模型有两个分支:主分类分支利用包含多个残差块的残差块架构,而第二个分支结合了子宫胎盘区域和邻近的子宫浆膜层的解剖特征,以增强模型在分类过程中的注意力。此外,我们实施了一种多任务学习策略,以有效利用这两个分支。在真实临床数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的模型达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本研究了胎盘植入症谱(PAS)及其亚型(胎盘植入、胎盘渗入和胎盘全层侵入)的产前诊断问题。由于PAS在妊娠期间存在显著风险,且出血严重程度与胎盘侵袭程度相关,因此准确诊断至关重要。现有研究多关注PAS的存在,对亚型识别的研究较少。本文提出了一种新型的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构,能够一次性进行PAS及其亚型的诊断,基于4140个磁共振成像(MRI)切片进行训练。模型包括两个分支,主分类分支使用残差块架构,第二分支整合子宫胎盘区域和邻近子宫浆膜层的解剖特征以增强分类时的注意力。同时采用多任务学习策略,有效利用两个分支的优势。实验表明,该模型在真实临床数据集上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 胎盘植入症谱(PAS)及亚型对孕妇存在显著风险,准确诊断至关重要。
- 当前研究多关注PAS的存在,而对亚型的识别研究较少。
- 提出了一种新型的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构,能一次性进行PAS及其亚型的诊断。
- 模型基于4140个磁共振成像(MRI)切片进行训练。
- 模型包括两个分支,主分类分支使用残差块架构,第二分支整合解剖特征以增强分类注意力。
- 采用多任务学习策略,有效利用两个分支的优势。
点此查看论文截图


SUFFICIENT: A scan-specific unsupervised deep learning framework for high-resolution 3D isotropic fetal brain MRI reconstruction
Authors:Jiangjie Wu, Lixuan Chen, Zhenghao Li, Xin Li, Saban Ozturk, Lihui Wang, Rongpin Wang, Hongjiang Wei, Yuyao Zhang
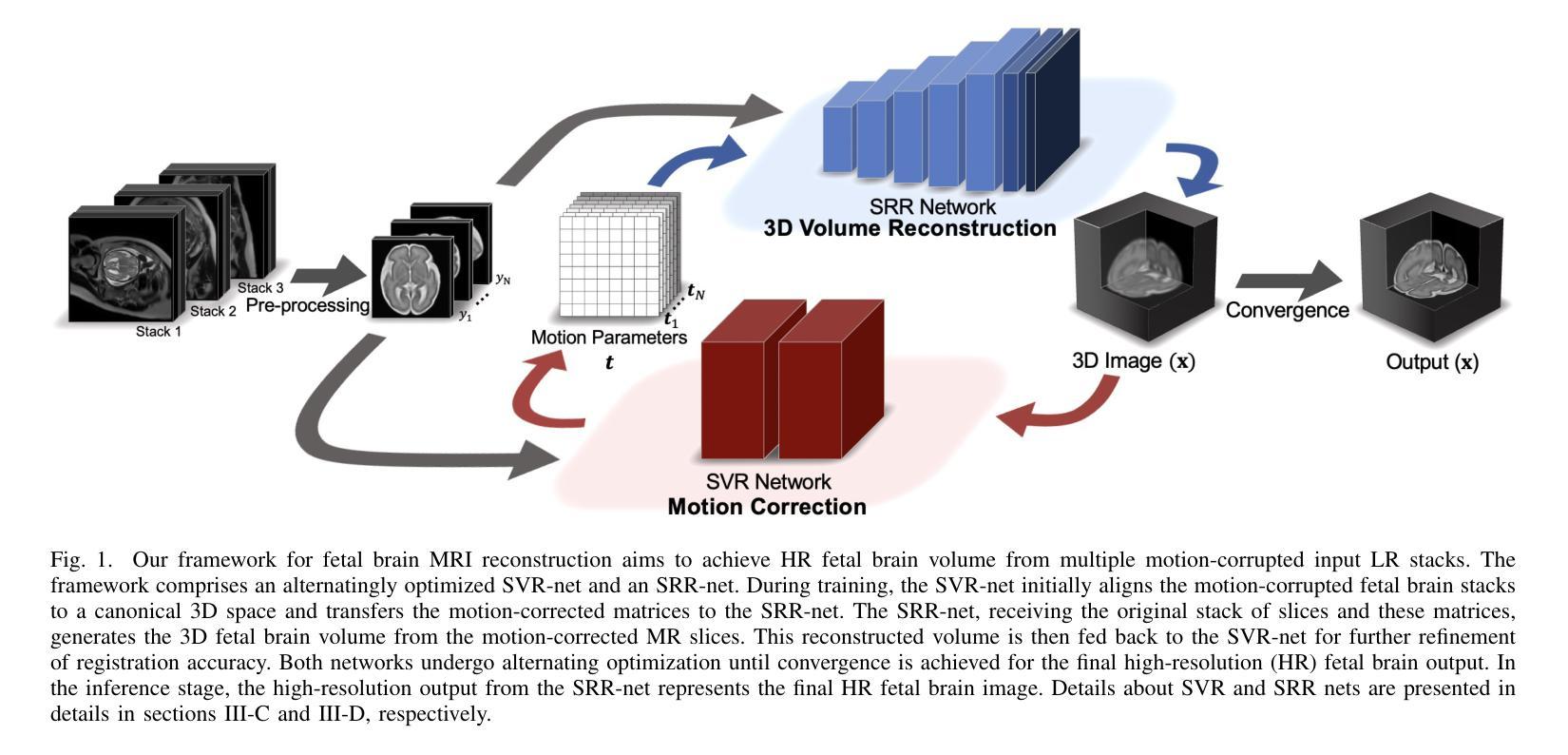
High-quality 3D fetal brain MRI reconstruction from motion-corrupted 2D slices is crucial for clinical diagnosis. Reliable slice-to-volume registration (SVR)-based motion correction and super-resolution reconstruction (SRR) methods are essential. Deep learning (DL) has demonstrated potential in enhancing SVR and SRR when compared to conventional methods. However, it requires large-scale external training datasets, which are difficult to obtain for clinical fetal MRI. To address this issue, we propose an unsupervised iterative SVR-SRR framework for isotropic HR volume reconstruction. Specifically, SVR is formulated as a function mapping a 2D slice and a 3D target volume to a rigid transformation matrix, which aligns the slice to the underlying location in the target volume. The function is parameterized by a convolutional neural network, which is trained by minimizing the difference between the volume slicing at the predicted position and the input slice. In SRR, a decoding network embedded within a deep image prior framework is incorporated with a comprehensive image degradation model to produce the high-resolution (HR) volume. The deep image prior framework offers a local consistency prior to guide the reconstruction of HR volumes. By performing a forward degradation model, the HR volume is optimized by minimizing loss between predicted slices and the observed slices. Comprehensive experiments conducted on large-magnitude motion-corrupted simulation data and clinical data demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed framework over state-of-the-art fetal brain reconstruction frameworks.
高质量的三维胎儿脑部MRI重建从受运动干扰的二维切片对临床诊断至关重要。可靠的基于切片到体积注册(SVR)的运动校正和超分辨率重建(SRR)方法至关重要。与常规方法相比,深度学习(DL)在提高SVR和SRR方面显示出潜力。然而,它需要大量外部训练数据集,这对于临床胎儿MRI来说很难获得。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种无监督迭代SVR-SRR框架,用于进行等分辨率的高分辨率体积重建。具体而言,SVR被制定为一个将二维切片和三维目标体积映射到刚性变换矩阵的函数,该矩阵将对齐切片到目标体积的潜在位置。该函数由卷积神经网络参数化,通过最小化预测位置处的体积切片与输入切片之间的差异来训练网络。在SRR中,嵌入深度图像先验框架中的解码网络结合全面的图像退化模型,生成高分辨率(HR)体积。深度图像先验框架提供了一个局部一致性先验来指导HR体积的重建。通过执行正向退化模型,HR体积通过最小化预测切片与观察切片之间的损失来进行优化。对大量运动干扰的模拟数据和临床数据进行的综合实验表明,所提出的框架优于最新的胎儿脑部重建框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种用于从受运动干扰的二维切片重建高质量三维胎儿脑部MRI图像的方法。该方法结合了无监督迭代切片到体积注册(SVR)和超分辨率重建(SRR)框架,以实现各向同性高分辨率体积重建。通过深度学习技术,该方法在胎儿脑部MRI重建方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量的三维胎儿脑部MRI重建对于临床诊断至关重要。
- 可靠的切片到体积注册(SVR)和超分辨率重建(SRR)方法是关键。
- 深度学习在增强SVR和SRR方面显示出潜力,但获取大规模外部训练数据集困难。
- 提出了一种无监督迭代SVR-SRR框架,用于各向同性高分辨率体积重建。
- SVR被制定为一个函数,将二维切片和三维目标体积映射到刚性变换矩阵,该矩阵将切片与底层目标体积的位置对齐。
- 使用卷积神经网络参数化该函数,通过最小化预测位置体积切片与输入切片之间的差异来训练网络。
- 在大量运动干扰的模拟数据和临床数据上进行的实验表明,该方法优于现有的胎儿脑部重建框架。
点此查看论文截图

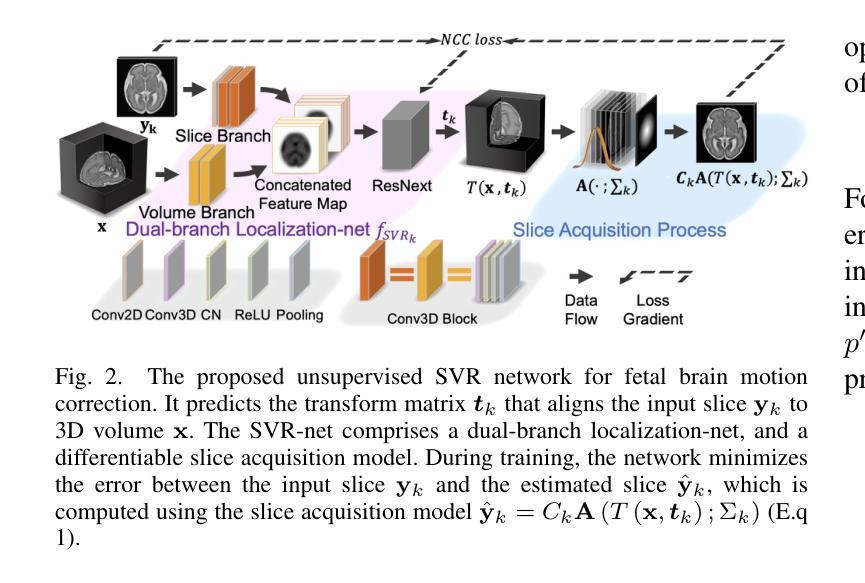
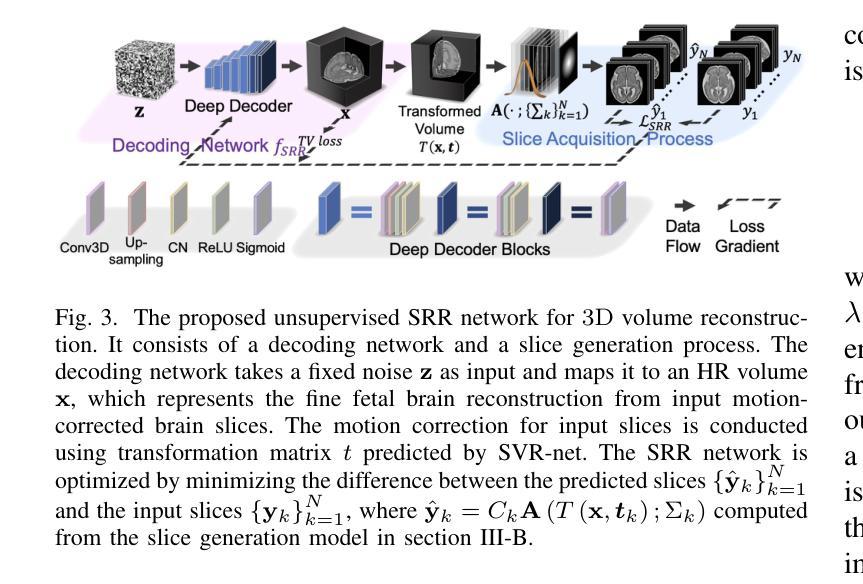
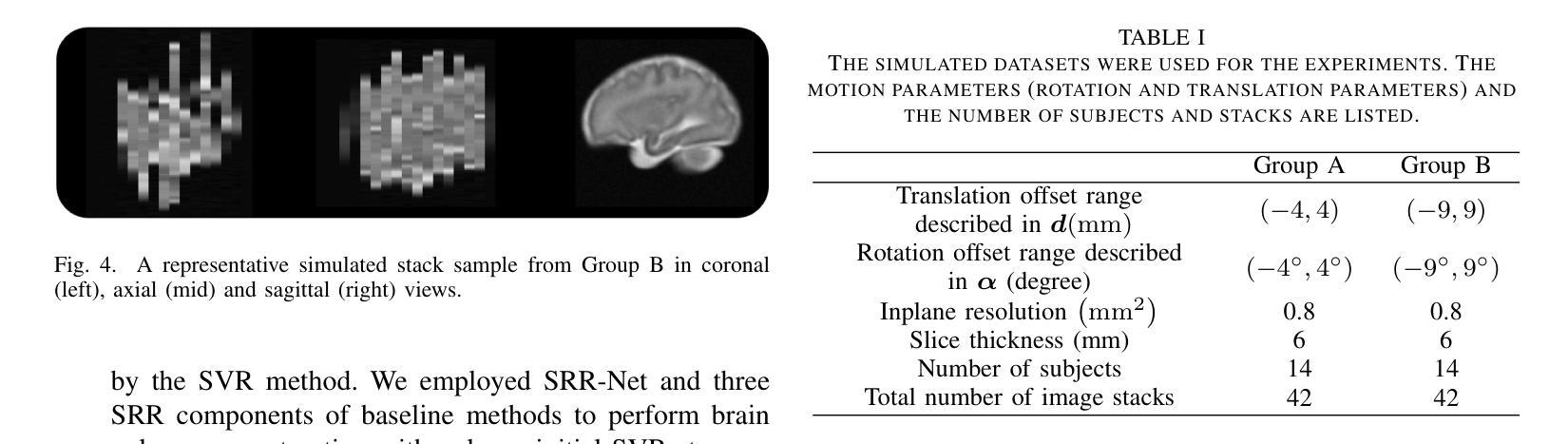
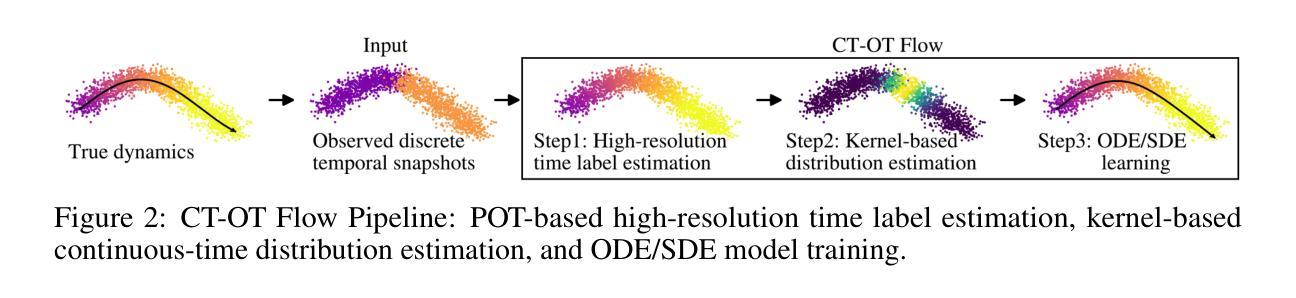
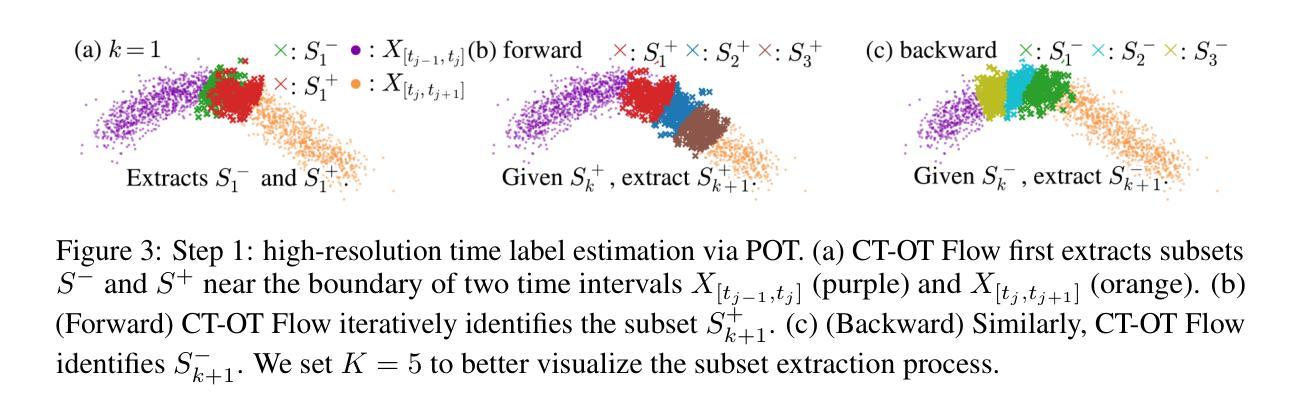
CT-OT Flow: Estimating Continuous-Time Dynamics from Discrete Temporal Snapshots
Authors:Keisuke Kawano, Takuro Kutsuna, Naoki Hayashi, Yasushi Esaki, Hidenori Tanaka
In many real-world scenarios, such as single-cell RNA sequencing, data are observed only as discrete-time snapshots spanning finite time intervals and subject to noisy timestamps, with no continuous trajectories available. Recovering the underlying continuous-time dynamics from these snapshots with coarse and noisy observation times is a critical and challenging task. We propose Continuous-Time Optimal Transport Flow (CT-OT Flow), which first infers high-resolution time labels via partial optimal transport and then reconstructs a continuous-time data distribution through a temporal kernel smoothing. This reconstruction enables accurate training of dynamics models such as ODEs and SDEs. CT-OT Flow consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on synthetic benchmarks and achieves lower reconstruction errors on real scRNA-seq and typhoon-track datasets. Our results highlight the benefits of explicitly modeling temporal discretization and timestamp uncertainty, offering an accurate and general framework for bridging discrete snapshots and continuous-time processes.
在现实世界中的许多场景中,例如单细胞RNA测序,数据仅被观察到作为跨越有限时间间隔的离散时间快照,并受到噪声时间戳的影响,无法获得连续轨迹。从具有粗糙和噪声观测时间的这些快照中恢复潜在的连续时间动力学是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务。我们提出了连续时间最优传输流(CT-OT Flow),它首先通过部分最优传输推断高分辨率时间标签,然后通过时间核平滑重建连续时间数据分布。这种重建使得动力学模型(如ODE和SDE)的训练更加准确。CT-OT Flow在合成基准测试上始终优于最新方法,并在真实scRNA-seq和台风轨迹数据集上实现了更低的重建误差。我们的结果强调了显式建模时间离散化和时间戳不确定性的好处,提供了一个准确且通用的框架,用于桥接离散快照和连续时间过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 28 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为Continuous-Time Optimal Transport Flow(CT-OT Flow)的方法,能够从离散时间快照中恢复出底层连续时间动态。该方法首先通过部分最优传输推断高分辨率时间标签,然后通过时间核平滑重建连续时间数据分布。此方法在合成基准测试和实际scRNA-seq和台风轨迹数据集上均表现优异,降低了重建误差,并强调显式建模时间离散化和时间戳不确定性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- CT-OT Flow能够从离散时间快照中恢复底层连续时间动态。
- 方法包括两个主要步骤:通过部分最优传输推断高分辨率时间标签,以及通过时间核平滑重建连续时间数据分布。
- CT-OT Flow在合成基准测试和实际数据集(如scRNA-seq和台风轨迹数据)上表现优异。
- 与现有方法相比,CT-OT Flow降低了重建误差。
- 显式建模时间离散化和时间戳不确定性对提高模型的准确性至关重要。
- CT-OT Flow为连接离散快照和连续时间过程提供了一个准确且通用的框架。
点此查看论文截图

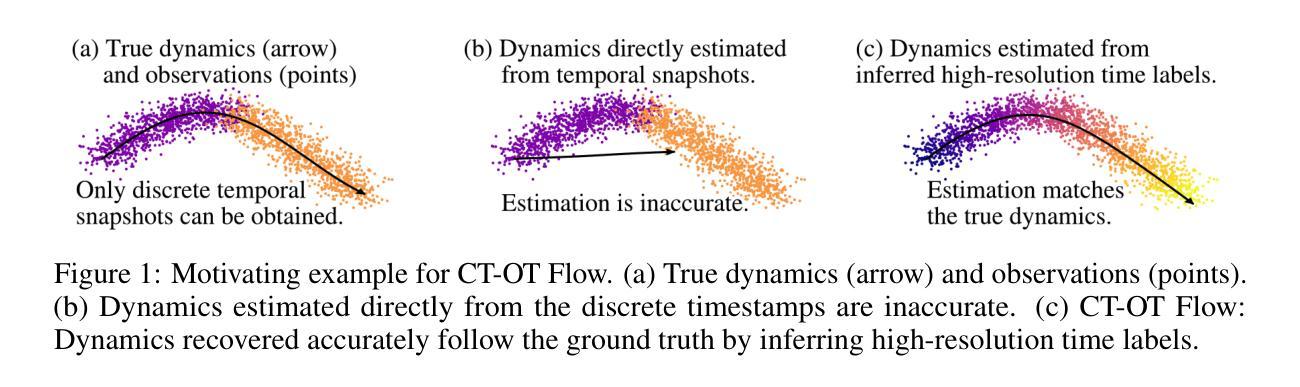
Temporal Differential Fields for 4D Motion Modeling via Image-to-Video Synthesis
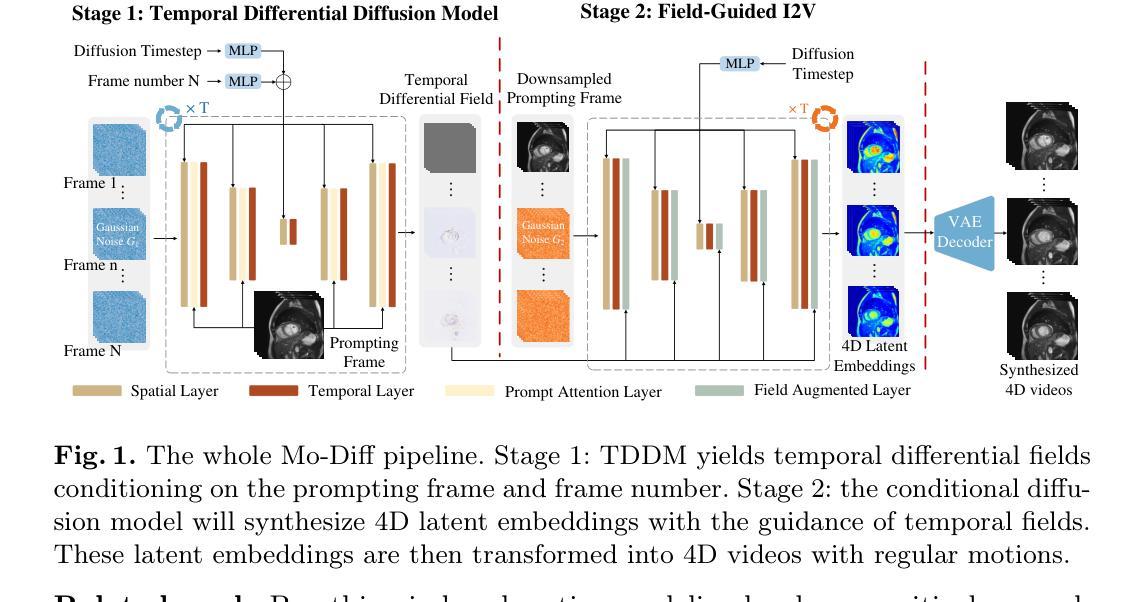
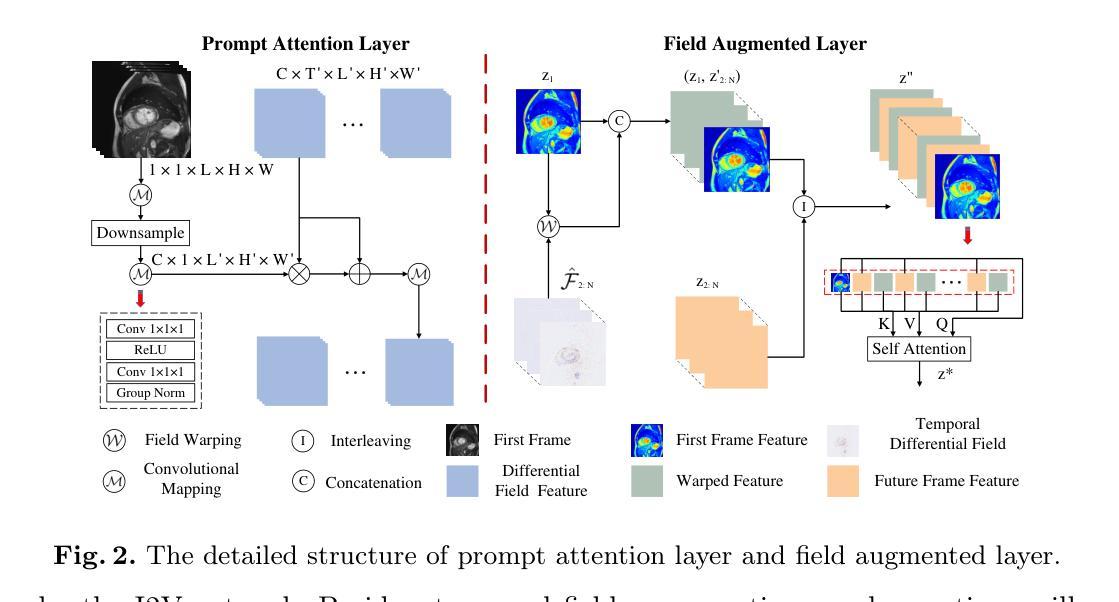
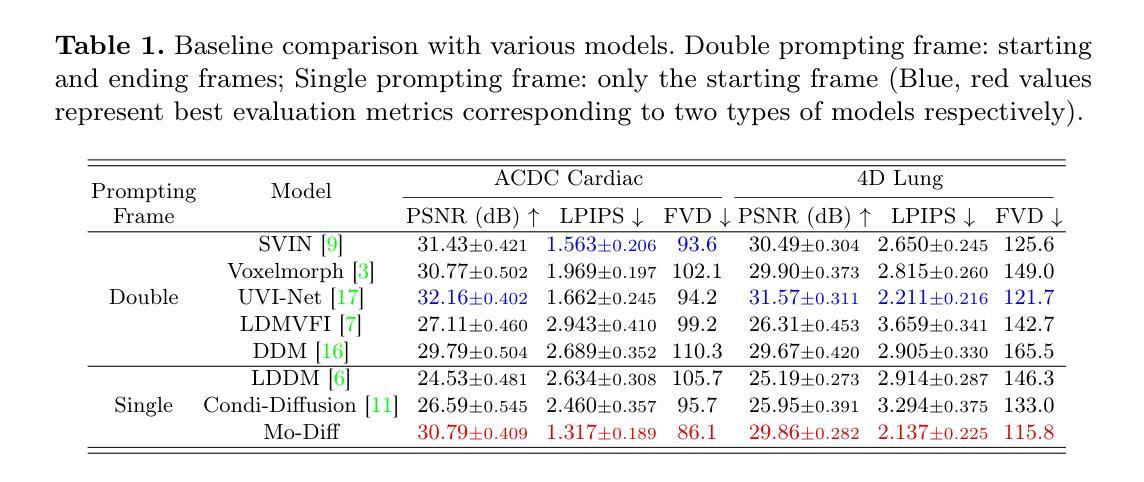
Authors:Xin You, Minghui Zhang, Hanxiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
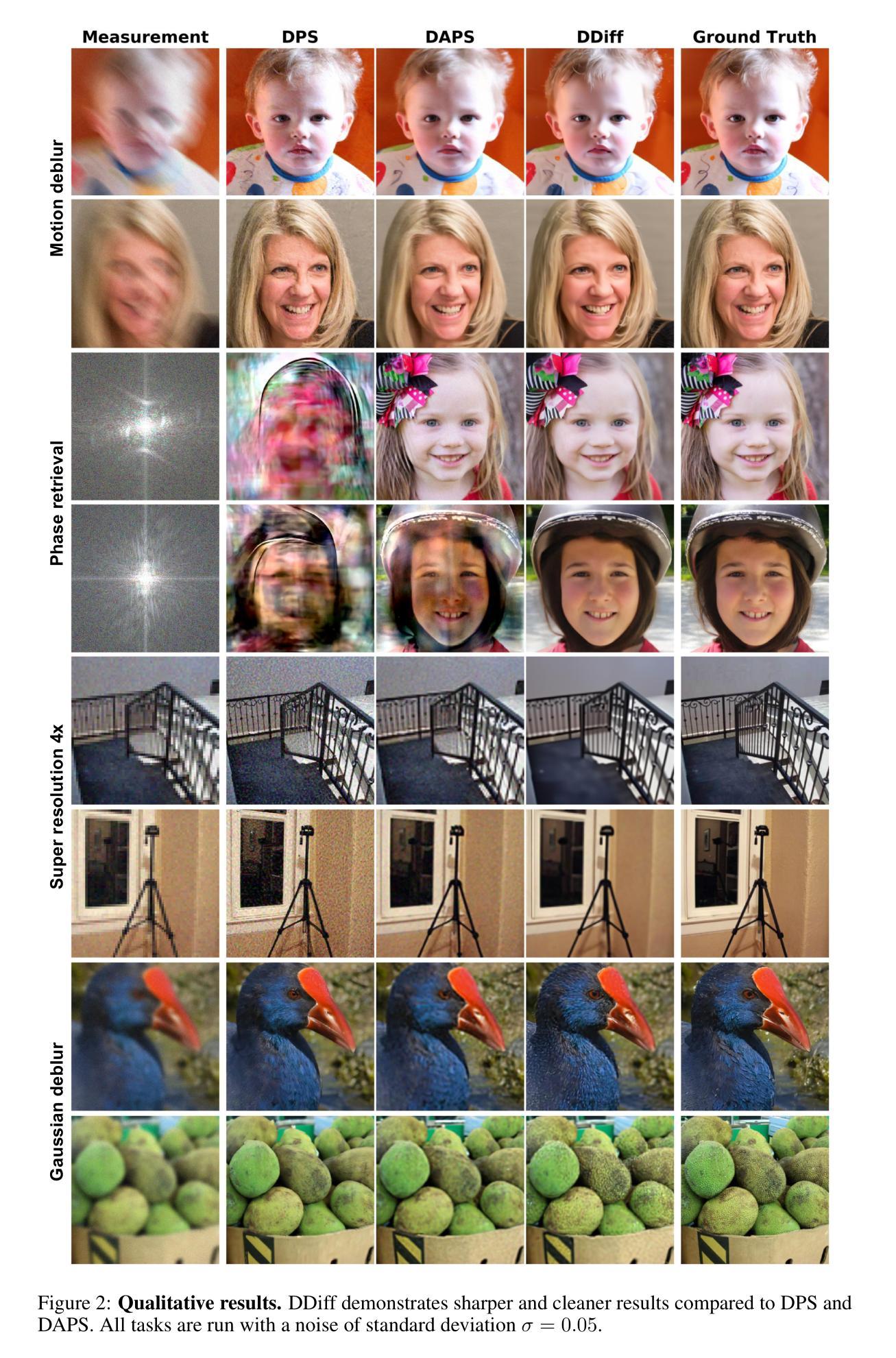
Temporal modeling on regular respiration-induced motions is crucial to image-guided clinical applications. Existing methods cannot simulate temporal motions unless high-dose imaging scans including starting and ending frames exist simultaneously. However, in the preoperative data acquisition stage, the slight movement of patients may result in dynamic backgrounds between the first and last frames in a respiratory period. This additional deviation can hardly be removed by image registration, thus affecting the temporal modeling. To address that limitation, we pioneeringly simulate the regular motion process via the image-to-video (I2V) synthesis framework, which animates with the first frame to forecast future frames of a given length. Besides, to promote the temporal consistency of animated videos, we devise the Temporal Differential Diffusion Model to generate temporal differential fields, which measure the relative differential representations between adjacent frames. The prompt attention layer is devised for fine-grained differential fields, and the field augmented layer is adopted to better interact these fields with the I2V framework, promoting more accurate temporal variation of synthesized videos. Extensive results on ACDC cardiac and 4D Lung datasets reveal that our approach simulates 4D videos along the intrinsic motion trajectory, rivaling other competitive methods on perceptual similarity and temporal consistency. Codes will be available soon.
对于受规律呼吸影响而发生的动态变化的建模对于图像导向的临床应用至关重要。现有的方法无法模拟时序运动,除非同时存在包括起始帧和结束帧在内的高剂量成像扫描。然而,在术前数据采集阶段,患者的轻微移动可能导致呼吸周期内第一帧和最后一帧之间的背景动态变化。这种额外的偏差几乎无法通过图像注册来消除,因此影响了时序建模。为了克服这一局限性,我们首创性地通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟规律的运动过程,该框架以第一帧动画预测给定长度的未来帧。此外,为了提高动画视频的时序一致性,我们设计了时序差分扩散模型,以生成时序差分场,该场测量相邻帧之间的相对差分表示。设计了即时注意层进行精细的差分场处理,并采用场增强层以更好地将这些字段与I2V框架进行交互,从而促进合成视频的时序变化更加准确。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集的大量结果显示,我们的方法模拟了沿内在运动轨迹的4D视频,在感知相似性和时序一致性方面与其他竞争方法相当。代码将很快提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI
Summary
该文强调时间建模在常规呼吸诱导运动中的图像引导临床应用的重要性。现有方法无法模拟时间运动,除非存在同时包含起始和结束帧的高剂量成像扫描。针对术前数据采集阶段患者轻微移动导致的动态背景问题,该文通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程,通过第一帧预测未来给定长度的帧。为提高动画视频的时空一致性,引入时间差分扩散模型,生成时间差分场,并利用即时注意力层进行精细差分场处理,通过场增强层优化这些场与I2V框架的互动,提高合成视频的时空变化准确性。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的大量实验结果表明,该方法模拟的4D视频沿着内在运动轨迹进行,在感知相似性和时间一致性方面与其他方法相比具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 时间建模在图像引导的临床应用中至关重要,尤其是在模拟常规呼吸诱导运动时。
- 现有方法受限于必须同时拥有起始和结束帧的高剂量成像扫描才能进行时间运动模拟。
- 术前数据采集阶段患者轻微移动可能导致动态背景,影响时间建模。
- 提出图像到视频(I2V)合成框架,通过第一帧预测未来帧以解决此问题。
- 为提高动画视频的时间一致性,引入时间差分扩散模型和即时注意力层。
- 提出场增强层来优化I2V框架与时空场的互动。
点此查看论文截图