⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
Semantic segmentation with reward
Authors:Xie Ting, Ye Huang, Zhilin Liu, Lixin Duan
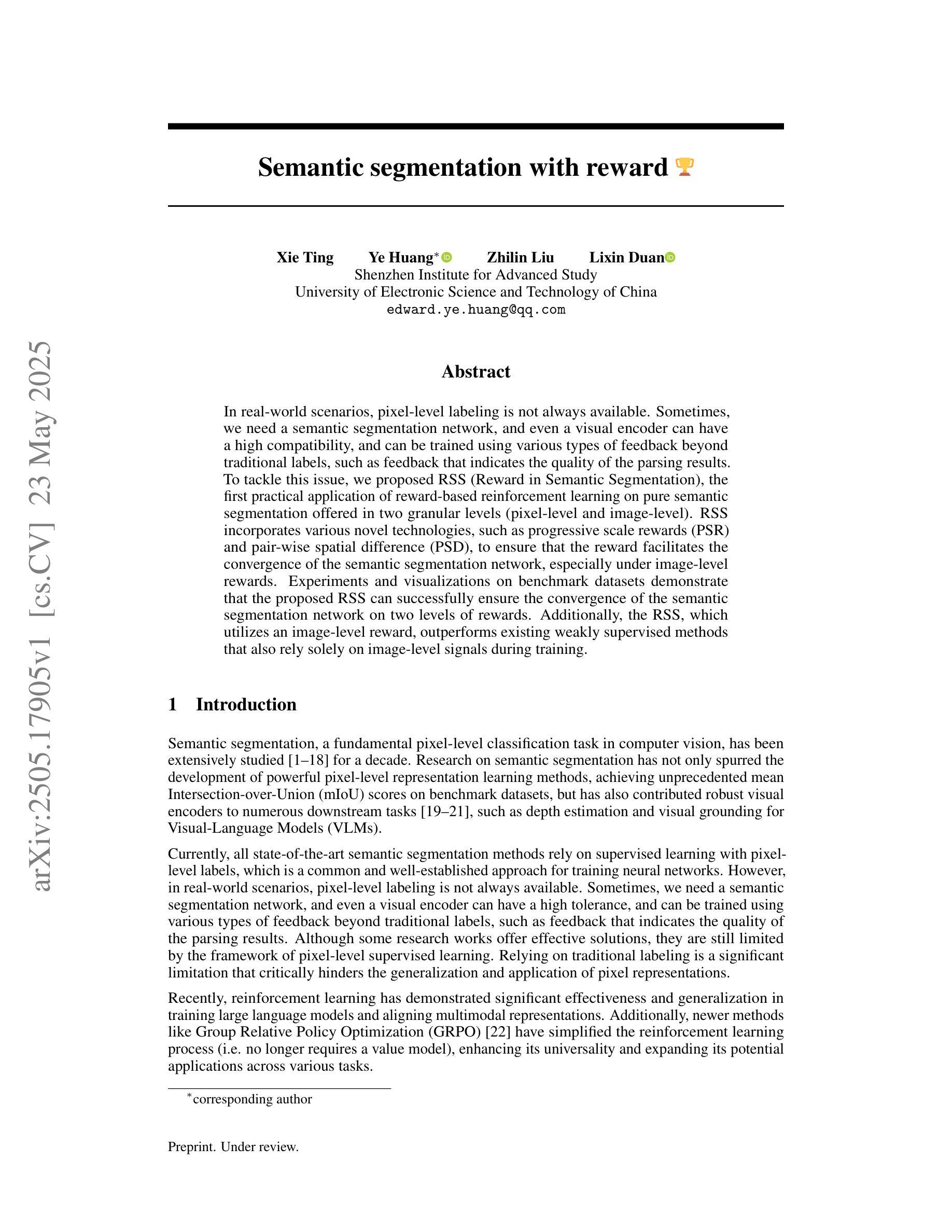
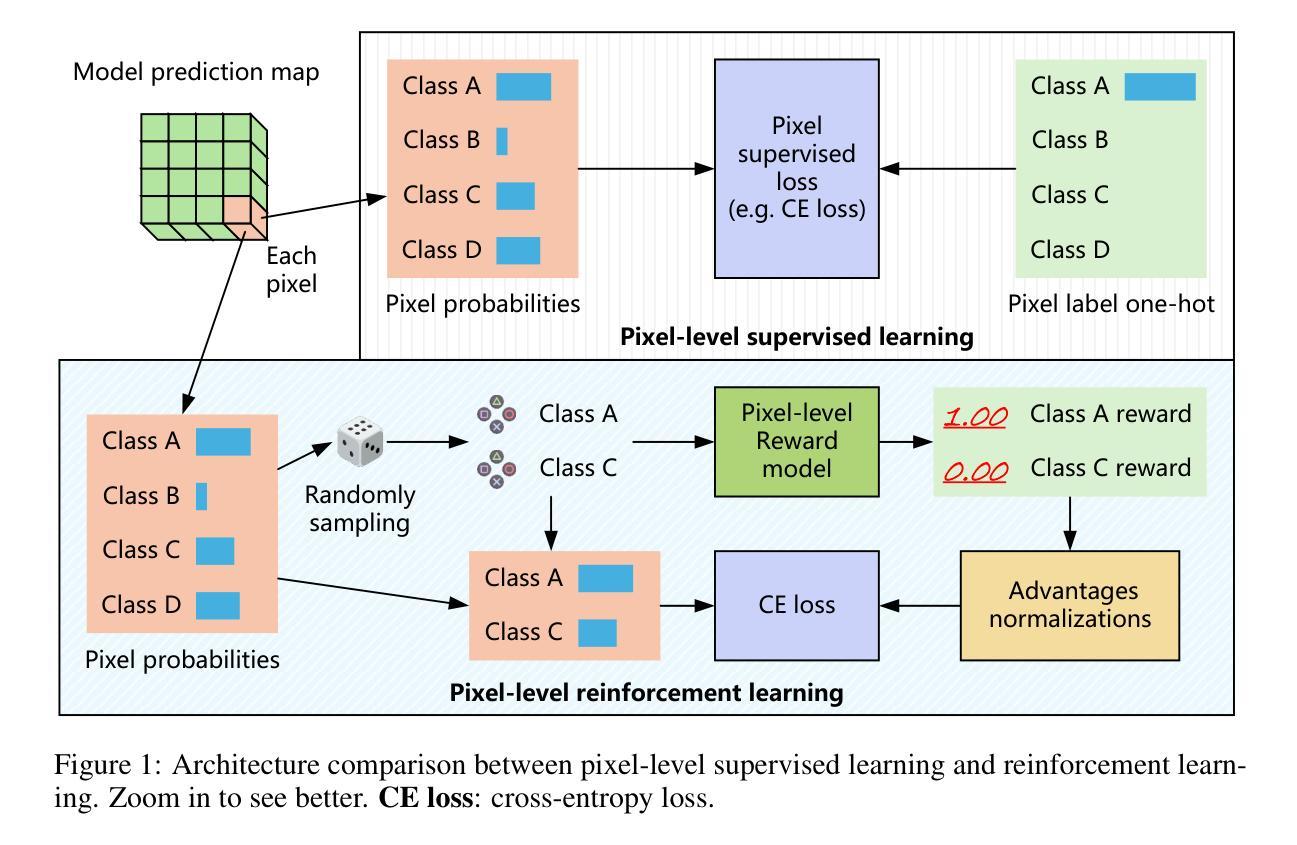
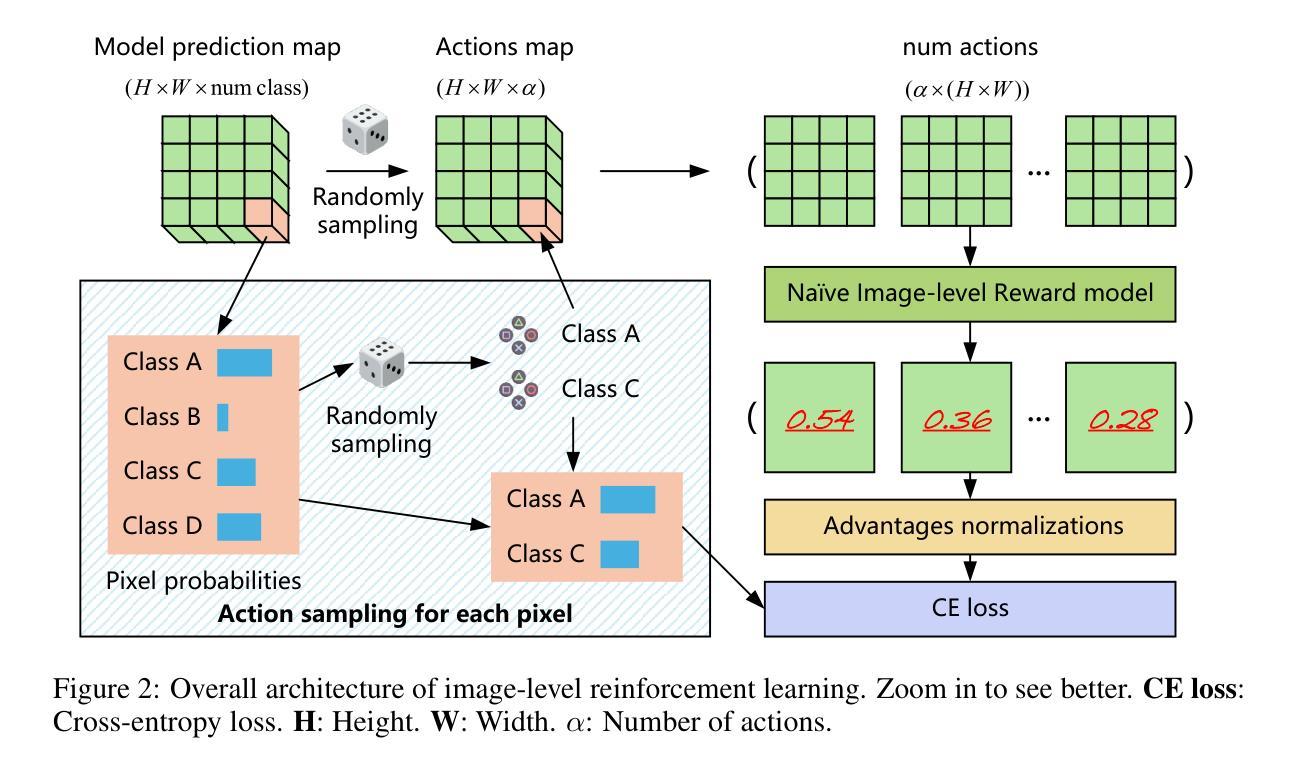
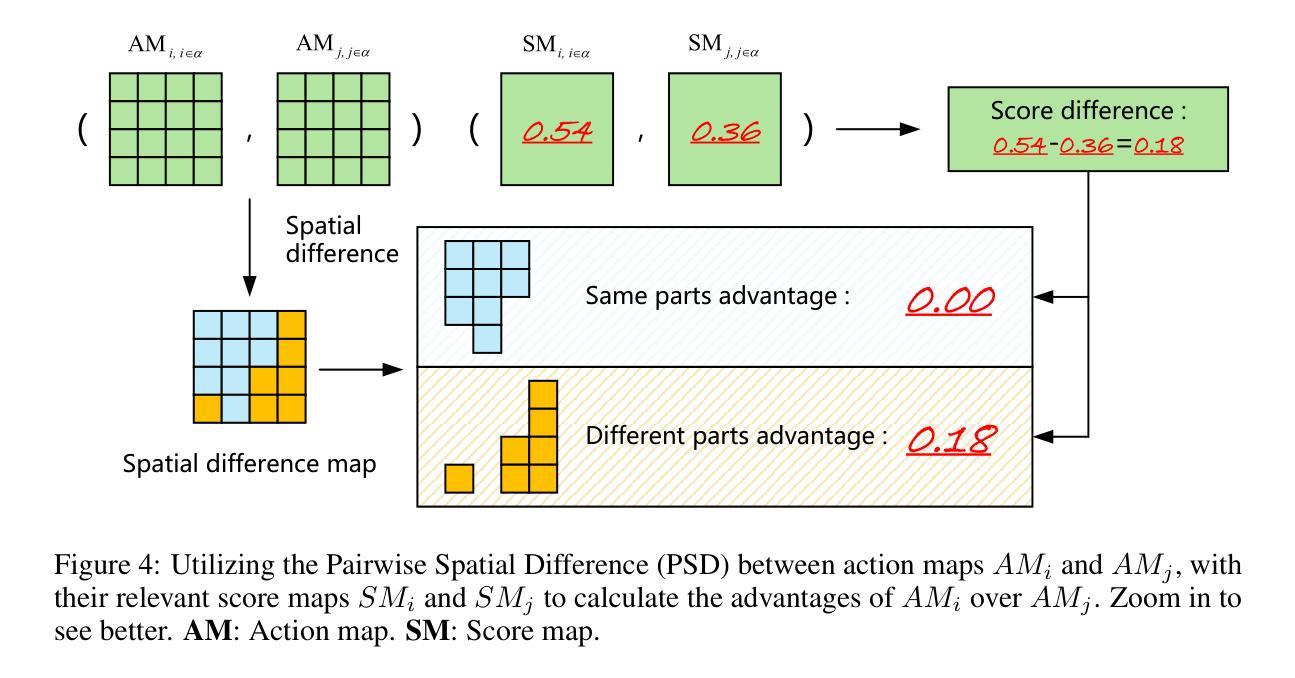
In real-world scenarios, pixel-level labeling is not always available. Sometimes, we need a semantic segmentation network, and even a visual encoder can have a high compatibility, and can be trained using various types of feedback beyond traditional labels, such as feedback that indicates the quality of the parsing results. To tackle this issue, we proposed RSS (Reward in Semantic Segmentation), the first practical application of reward-based reinforcement learning on pure semantic segmentation offered in two granular levels (pixel-level and image-level). RSS incorporates various novel technologies, such as progressive scale rewards (PSR) and pair-wise spatial difference (PSD), to ensure that the reward facilitates the convergence of the semantic segmentation network, especially under image-level rewards. Experiments and visualizations on benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed RSS can successfully ensure the convergence of the semantic segmentation network on two levels of rewards. Additionally, the RSS, which utilizes an image-level reward, outperforms existing weakly supervised methods that also rely solely on image-level signals during training.
在真实场景中,像素级标签并非总是可用。有时,我们需要语义分割网络,甚至视觉编码器可以具有很高的兼容性,并可以使用传统标签以外的各种反馈进行训练,例如指示解析结果质量的反馈。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了RSS(语义分割中的奖励),这是奖励型强化学习在纯语义分割上的首次实际应用,分为两个粒度级别(像素级和图像级)。RSS结合了多种新技术,如渐进尺度奖励(PSR)和配对空间差异(PSD),以确保奖励促进语义分割网络的收敛,特别是在图像级奖励下。在基准数据集上的实验和可视化证明,所提出的RSS可以成功确保语义分割网络在两个级别的奖励下收敛。此外,使用图像级奖励的RSS表现优于现有的弱监督方法,这些方法在训练期间也仅依赖于图像级信号。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech report
Summary
本文提出一种基于奖励的语义分割方法RSS,适用于无像素级标签的实际情况。RSS结合多种新技术,如渐进尺度奖励(PSR)和配对空间差异(PSD),确保奖励促进语义分割网络的收敛,尤其在图像级奖励下。实验和可视化结果表明,RSS可在两个奖励级别上成功确保语义分割网络的收敛,并且利用图像级奖励的RSS表现优于现有的仅依赖图像级信号的弱监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- RSS方法适用于无像素级标签的实际情况。
- RSS结合多种新技术,如PSR和PSD,促进语义分割网络的收敛。
- RSS方法在图像级奖励下表现出良好的性能。
- RSS方法在基准数据集上的实验和可视化结果证明了其有效性。
- RSS方法成功解决了语义分割网络在两种奖励级别上的收敛问题。
- 与现有的弱监督方法相比,RSS方法表现更优。
点此查看论文截图
EMRA-proxy: Enhancing Multi-Class Region Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images with Attention Proxy
Authors:Yichun Yu, Yuqing Lan, Zhihuan Xing, Xiaoyi Yang, Tingyue Tang, Dan Yu
High-resolution remote sensing (HRRS) image segmentation is challenging due to complex spatial layouts and diverse object appearances. While CNNs excel at capturing local features, they struggle with long-range dependencies, whereas Transformers can model global context but often neglect local details and are computationally expensive.We propose a novel approach, Region-Aware Proxy Network (RAPNet), which consists of two components: Contextual Region Attention (CRA) and Global Class Refinement (GCR). Unlike traditional methods that rely on grid-based layouts, RAPNet operates at the region level for more flexible segmentation. The CRA module uses a Transformer to capture region-level contextual dependencies, generating a Semantic Region Mask (SRM). The GCR module learns a global class attention map to refine multi-class information, combining the SRM and attention map for accurate segmentation.Experiments on three public datasets show that RAPNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior multi-class segmentation accuracy.
高分辨率遥感(HRRS)图像分割面临复杂空间布局和多样化目标外观的挑战。CNN擅长捕捉局部特征,但在处理长距离依赖时遇到困难,而Transformer可以建模全局上下文,但往往忽视局部细节且计算成本较高。我们提出了一种新方法,名为Region-Aware Proxy Network (RAPNet),由两部分组成:区域上下文注意力(CRA)和全局类别细化(GCR)。与传统的基于网格布局的方法不同,RAPNet在区域级别进行操作以实现更灵活的分割。CRA模块使用Transformer捕获区域级别的上下文依赖关系,生成语义区域掩码(SRM)。GCR模块学习全局类别注意力图以细化多类别信息,结合SRM和注意力图进行精确分割。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,RAPNet优于最新方法,实现了优越的多类别分割精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Intelligent Computing (ICIC 2024): Poster Volume I. Tianjin, China, 2024: 538-562
Summary
基于高分辨遥感图像分割的挑战性,如复杂空间布局和多样物体外观,提出一种新型方法Region-Aware Proxy Network (RAPNet)。该方法包括Contextual Region Attention (CRA)和Global Class Refinement (GCR)两个组件。RAPNet以区域级别操作,更灵活地进行分割,优于传统基于网格的布局方法。CRA模块使用Transformer捕捉区域级别的上下文依赖关系,生成Semantic Region Mask (SRM)。GCR模块学习全局类别注意力图,以精炼多类别信息,结合SRM和注意力图进行精确分割。在三个公共数据集上的实验显示,RAPNet的多类别分割精度优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率遥感图像分割面临复杂空间布局和多样物体外观的挑战。
- 现有CNNs和Transformers方法存在局限性,如忽略长程依赖、局部细节或计算成本高。
- 提出的新型方法RAPNet结合Contextual Region Attention (CRA)和Global Class Refinement (GCR)进行更灵活的分割。
- CRA模块使用Transformer捕捉区域级别上下文依赖。
- GCR模块通过学习全局类别注意力图来精炼多类别信息。
- RAPNet在三个公共数据集上实现优越的多类别分割精度。
点此查看论文截图



Extending Dataset Pruning to Object Detection: A Variance-based Approach
Authors:Ryota Yagi
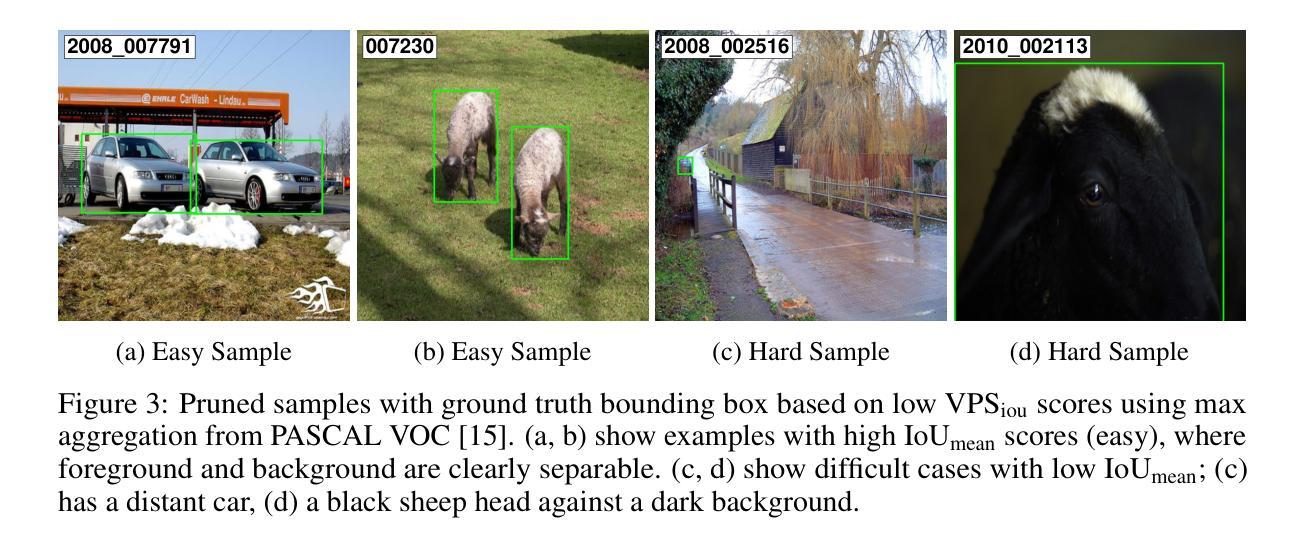
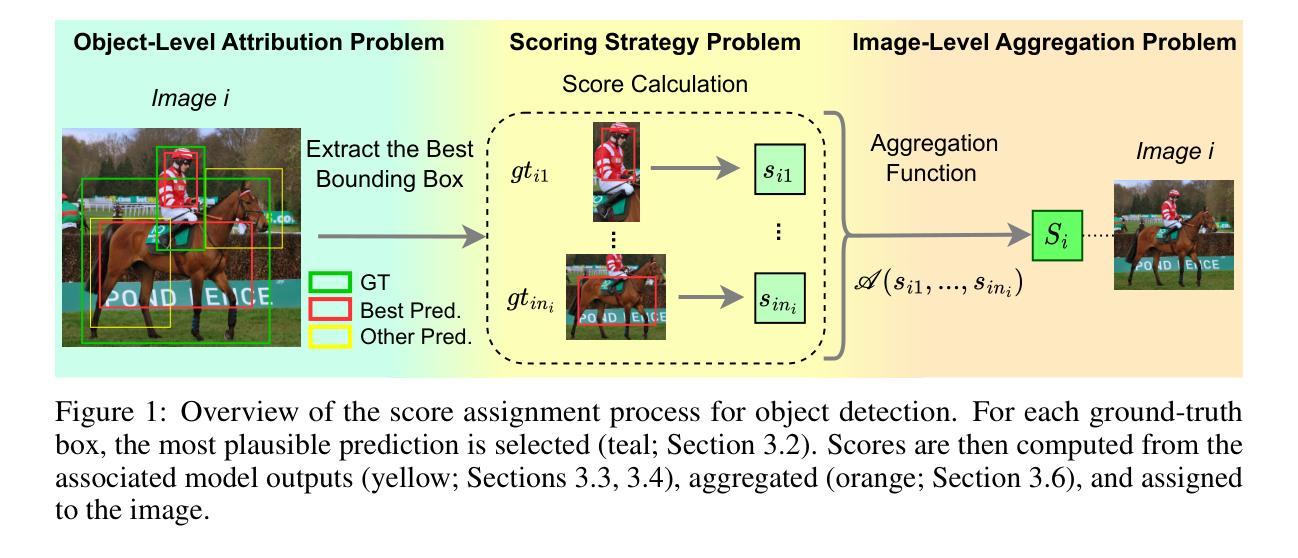
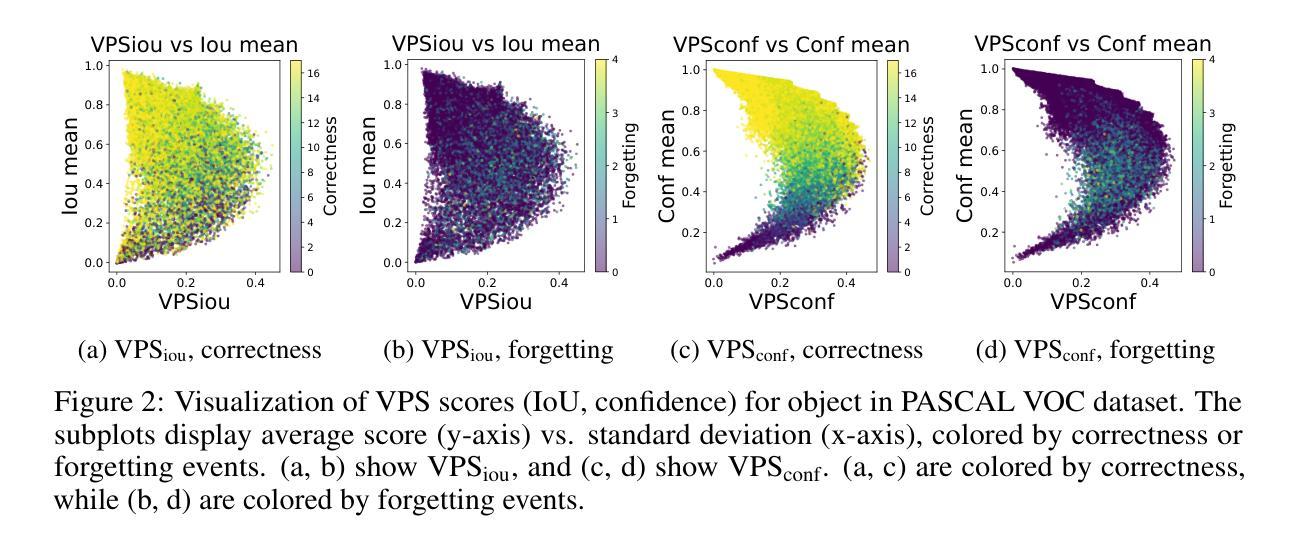
Dataset pruning – selecting a small yet informative subset of training data – has emerged as a promising strategy for efficient machine learning, offering significant reductions in computational cost and storage compared to alternatives like dataset distillation. While pruning methods have shown strong performance in image classification, their extension to more complex computer vision tasks, particularly object detection, remains relatively underexplored. In this paper, we present the first principled extension of classification pruning techniques to the object detection domain, to the best of our knowledge. We identify and address three key challenges that hinder this transition: the Object-Level Attribution Problem, the Scoring Strategy Problem, and the Image-Level Aggregation Problem. To overcome these, we propose tailored solutions, including a novel scoring method called Variance-based Prediction Score (VPS). VPS leverages both Intersection over Union (IoU) and confidence scores to effectively identify informative training samples specific to detection tasks. Extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms prior dataset pruning methods in terms of mean Average Precision (mAP). We also show that annotation count and class distribution shift can influence detection performance, but selecting informative examples is a more critical factor than dataset size or balance. Our work bridges dataset pruning and object detection, paving the way for dataset pruning in complex vision tasks.
数据集剪枝——选择训练数据的一个小而又有信息量的子集——已经作为一种高效的机器学习策略崭露头角,与数据集蒸馏等替代方案相比,它在计算成本和存储方面提供了显著的降低。虽然剪枝方法在图像分类方面表现出强大的性能,但它们在更复杂的计算机视觉任务,特别是目标检测方面的应用,仍然相对未被充分探索。在本文中,我们据我们所知,首次将分类剪枝技术原则性地扩展到目标检测领域。我们确定了阻碍这一转变的三个关键挑战,即对象级归因问题、评分策略问题和图像级聚合问题。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了量身定制的解决方案,包括一种新型评分方法,称为基于方差的预测评分(VPS)。VPS利用交集比联合(IoU)和置信度评分,有效地识别出针对检测任务的有信息量的训练样本。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在计算平均精度(mAP)方面始终优于以前的数据集剪枝方法。我们还表明,注释计数和类别分布变化会影响检测性能,但选择有信息的例子是一个比数据集大小或平衡更重要的因素。我们的工作架起了数据集剪枝和目标检测的桥梁,为复杂视觉任务的数据集剪枝铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了数据集修剪策略在对象检测领域的应用。针对对象检测面临的挑战,如对象级属性问题、评分策略问题和图像级聚合问题,提出了基于方差预测评分(VPS)的定制解决方案。实验证明,该方法在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上的平均精度(mAP)优于其他修剪方法,并指出标注数量和类别分布变化对检测性能的影响,而选择性实例的重要性大于数据集大小和平衡。该研究架起了数据集修剪和对象检测之间的桥梁,为复杂视觉任务的数据集修剪铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways:
- 数据集修剪策略在对象检测领域展现出前景,能有效降低计算成本和存储需求。
- 本文首次将分类修剪技术原理应用于对象检测领域。
- 面临对象级属性问题、评分策略问题和图像级聚合问题三大挑战。
- 提出基于方差预测评分(VPS)的定制解决方案,结合IoU和置信度评分有效识别检测任务的信息训练样本。
- 在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上的实验表明,该方法在平均精度(mAP)上优于其他修剪方法。
- 标注数量和类别分布变化会影响检测性能,但选择信息实例更为重要。
点此查看论文截图