⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
ManuSearch: Democratizing Deep Search in Large Language Models with a Transparent and Open Multi-Agent Framework
Authors:Lisheng Huang, Yichen Liu, Jinhao Jiang, Rongxiang Zhang, Jiahao Yan, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao
Recent advances in web-augmented large language models (LLMs) have exhibited strong performance in complex reasoning tasks, yet these capabilities are mostly locked in proprietary systems with opaque architectures. In this work, we propose \textbf{ManuSearch}, a transparent and modular multi-agent framework designed to democratize deep search for LLMs. ManuSearch decomposes the search and reasoning process into three collaborative agents: (1) a solution planning agent that iteratively formulates sub-queries, (2) an Internet search agent that retrieves relevant documents via real-time web search, and (3) a structured webpage reading agent that extracts key evidence from raw web content. To rigorously evaluate deep reasoning abilities, we introduce \textbf{ORION}, a challenging benchmark focused on open-web reasoning over long-tail entities, covering both English and Chinese. Experimental results show that ManuSearch substantially outperforms prior open-source baselines and even surpasses leading closed-source systems. Our work paves the way for reproducible, extensible research in open deep search systems. We release the data and code in https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ManuSearch
最近,网络增强大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展在复杂推理任务中表现出强大的性能,但这些能力大多被锁定在结构不透明的专有系统中。在这项工作中,我们提出了ManuSearch,这是一个透明且模块化的多智能体框架,旨在实现LLM的深度搜索民主化。ManuSearch将搜索和推理过程分解为三个协作的智能体:(1)解决方案规划智能体,它迭代地制定子查询;(2)互联网搜索智能体,它通过实时网络搜索检索相关文档;(3)结构化网页阅读智能体,它从原始网页内容中提取关键证据。为了严格评估深度推理能力,我们引入了ORION,这是一个专注于长尾实体的开放网络推理的挑战性基准测试,涉及英语和中文。实验结果表明,ManuSearch显著优于先前的开源基准线,甚至超越了领先的闭源系统。我们的工作为可复制、可扩展的开放深度搜索系统研究铺平了道路。我们在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ManuSearch上发布数据和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF LLM, Complex Search Benchmark
Summary
互联网增强大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂推理任务中展现出强大的性能,但多数功能被锁在架构不透明的专有系统中。本研究提出一种透明、模块化的多智能体框架ManuSearch,旨在实现LLM的深度搜索民主化。ManuSearch将搜索和推理过程分解为三个协作的智能体:解决方案规划智能体、互联网搜索智能体和结构化网页阅读智能体。为严格评估深度推理能力,研究团队推出了专注于长尾实体开放网络推理的具有挑战性的基准测试ORION,涵盖英语和中文。实验结果表明,ManuSearch显著优于先前的开源基准线,甚至超越了领先的专有系统。我们的研究为开放深度搜索系统的可重复性和可扩展性研究铺平了道路。相关数据和代码已发布在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ManuSearch。
Key Takeaways
- Web-augmented LLMs demonstrate strong performance in complex reasoning tasks.
- 目前大多数功能被锁在架构不透明的专有系统中。
- 提出了一种新的框架ManuSearch,由三个协作的智能体组成,用于深度搜索LLM。
- ManuSearch通过分解搜索和推理过程,提高了性能和功能性。
- 为评估深度推理能力,引入了新的基准测试ORION,涵盖英语和中文。
- ManuSearch在实验中表现出色,优于开源基准线及一些专有系统。
- 研究为开放深度搜索系统的可重复性和可扩展性研究打开了大门。
点此查看论文截图

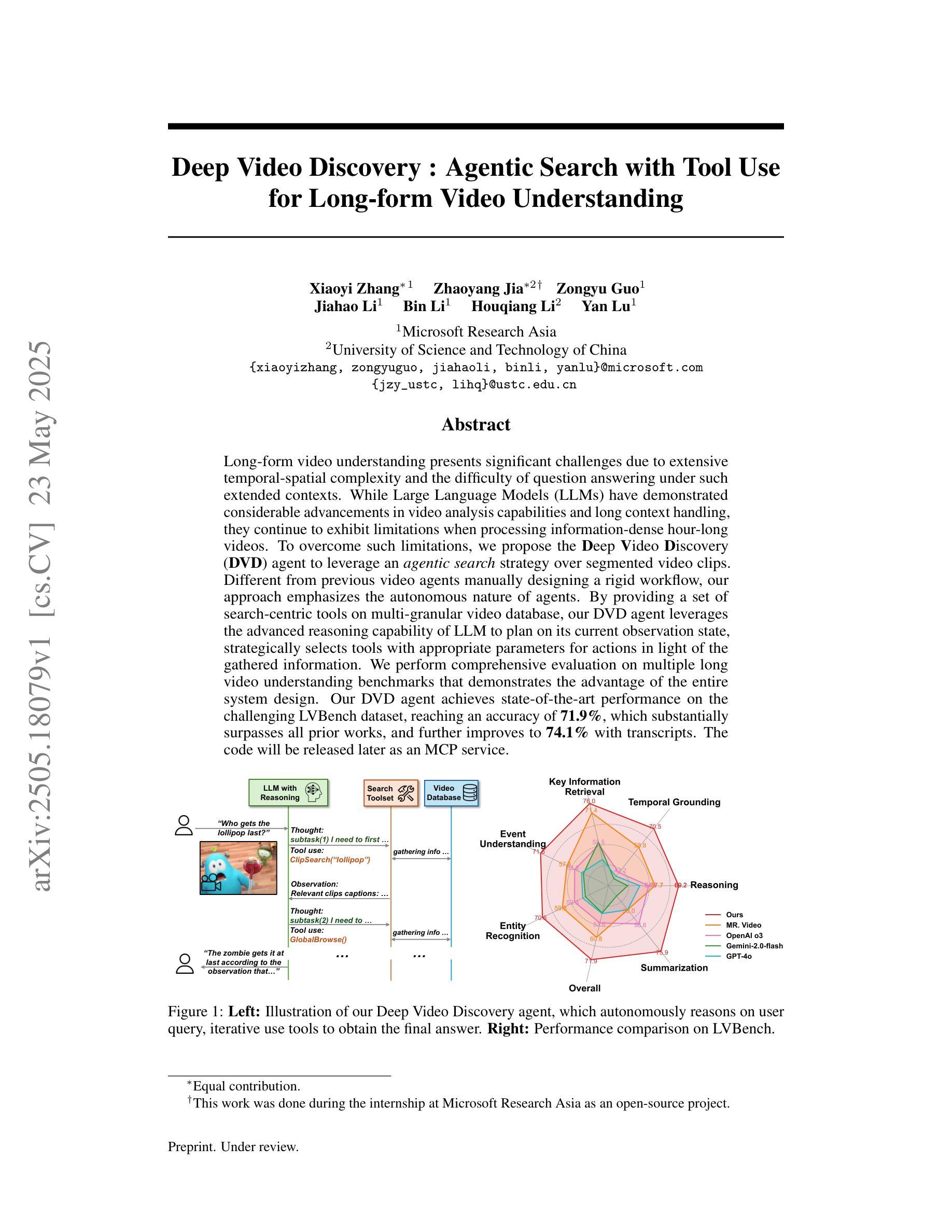
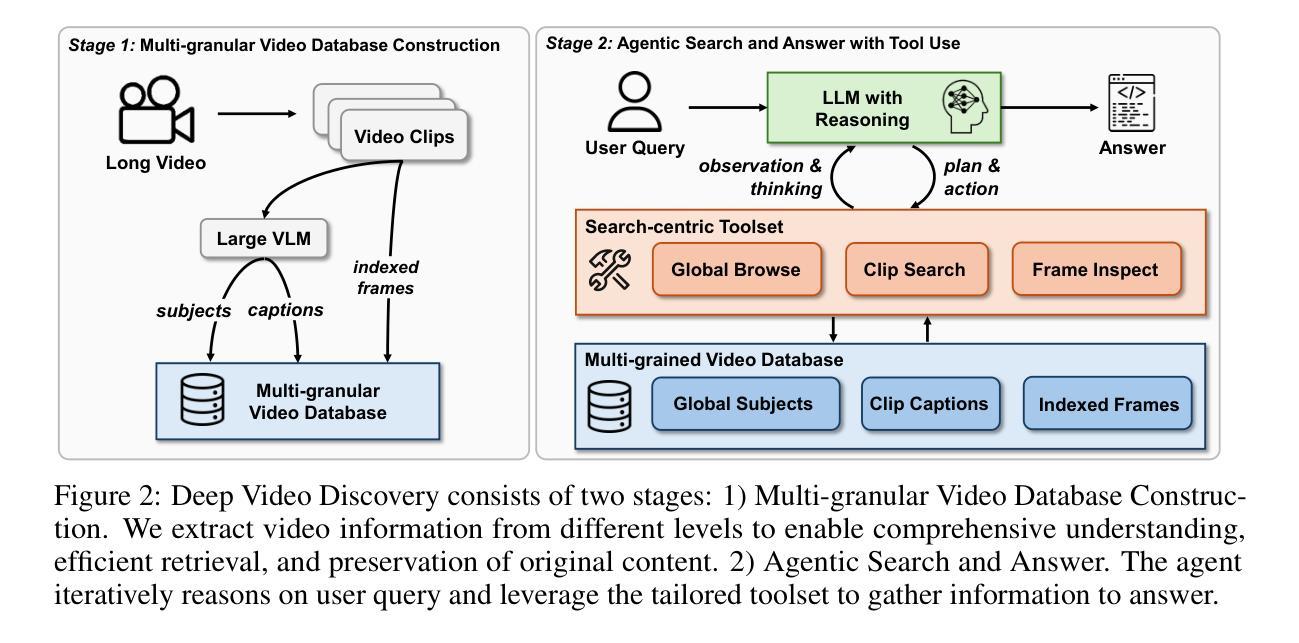
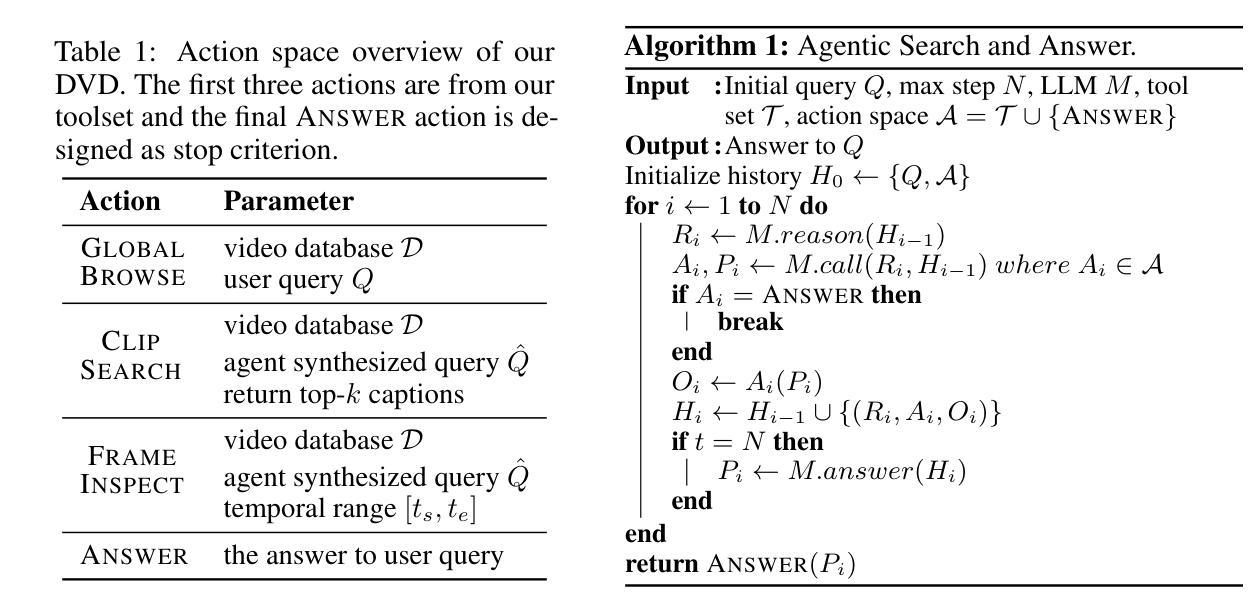
Deep Video Discovery: Agentic Search with Tool Use for Long-form Video Understanding
Authors:Xiaoyi Zhang, Zhaoyang Jia, Zongyu Guo, Jiahao Li, Bin Li, Houqiang Li, Yan Lu
Long-form video understanding presents significant challenges due to extensive temporal-spatial complexity and the difficulty of question answering under such extended contexts. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated considerable advancements in video analysis capabilities and long context handling, they continue to exhibit limitations when processing information-dense hour-long videos. To overcome such limitations, we propose the Deep Video Discovery agent to leverage an agentic search strategy over segmented video clips. Different from previous video agents manually designing a rigid workflow, our approach emphasizes the autonomous nature of agents. By providing a set of search-centric tools on multi-granular video database, our DVD agent leverages the advanced reasoning capability of LLM to plan on its current observation state, strategically selects tools, formulates appropriate parameters for actions, and iteratively refines its internal reasoning in light of the gathered information. We perform comprehensive evaluation on multiple long video understanding benchmarks that demonstrates the advantage of the entire system design. Our DVD agent achieves SOTA performance, significantly surpassing prior works by a large margin on the challenging LVBench dataset. Comprehensive ablation studies and in-depth tool analyses are also provided, yielding insights to further advance intelligent agents tailored for long-form video understanding tasks. The code will be released later.
长视频理解由于巨大的时空复杂性和在如此扩展的上下文下进行问答的困难而面临重大挑战。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在视频分析能力和长上下文处理方面取得了显著的进步,但在处理信息密集的小时长的视频时,它们仍然表现出局限性。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Deep Video Discovery(DVD)代理,采用基于分割的视频剪辑的代理搜索策略。不同于之前手动设计刚性工作流程的视频代理,我们的方法强调代理的自主性。通过在多粒度视频数据库上提供一系列以搜索为中心的工具,我们的DVD代理利用LLM的高级推理能力来规划其当前观察状态,策略性地选择工具,制定动作的相关参数,并根据收集的信息迭代地优化其内部推理。我们在多个长视频理解基准测试上对系统进行全面评估,证明了整个系统设计的优势。我们的DVD代理在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上取得了最先进的性能,大大超过了先前作品。此外,我们还提供了全面的消融研究和深入的工具分析,以进一步推进针对长视频理解任务量身定制的智能代理。代码稍后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary:
长视频理解面临巨大的挑战,包括广泛的时空复杂性和在扩展环境下的问答难度。尽管大型语言模型在处理视频分析能力和处理长语境方面取得了重大进展,但在处理信息密集的小时长的视频时仍显示出局限。为克服这些限制,我们提出了深度视频发现代理(DVD agent),通过采用代理搜索策略来针对分割的视频片段进行利用。不同于以往的视频代理需要手动设计固定工作流程,我们的方法强调代理的自主性。通过提供一系列基于搜索的视频数据库工具集,DVD代理能够根据当前的观察状态规划自身行动、智能地选择合适工具、确定行动参数,并根据获取的信息不断修正内部推理。我们在多个长视频理解基准测试上对DVD代理进行了全面评估,证明其系统设计的优势。该代理在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现,大幅超越先前工作。同时提供了全面的消融研究和深入的工具分析,为进一步发展针对长视频理解任务的智能代理提供了见解。代码即将发布。
Key Takeaways:
- 长视频理解面临巨大挑战,包括处理大量数据和复杂的时空信息。
- 大型语言模型在处理长视频方面存在局限性,需要新的策略来克服这些挑战。
- DVD代理采用自主搜索策略来处理长视频片段,强调代理的自主性。
- DVD代理利用LLM的高级推理能力来规划行动、选择工具和确定参数。
- 在多个长视频理解基准测试中,DVD代理表现出卓越性能,特别是在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上。
点此查看论文截图
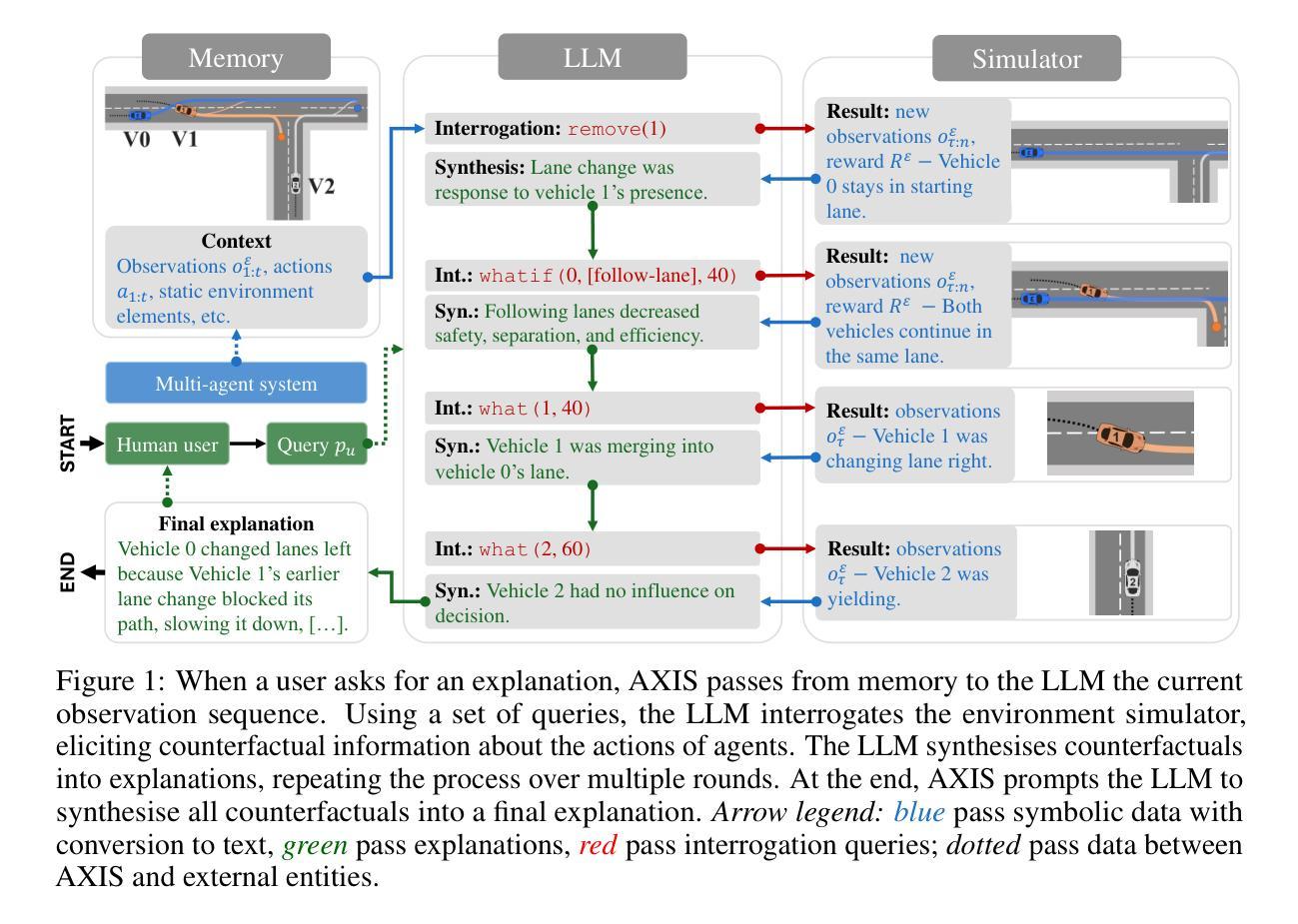
Integrating Counterfactual Simulations with Language Models for Explaining Multi-Agent Behaviour
Authors:Bálint Gyevnár, Christopher G. Lucas, Stefano V. Albrecht, Shay B. Cohen
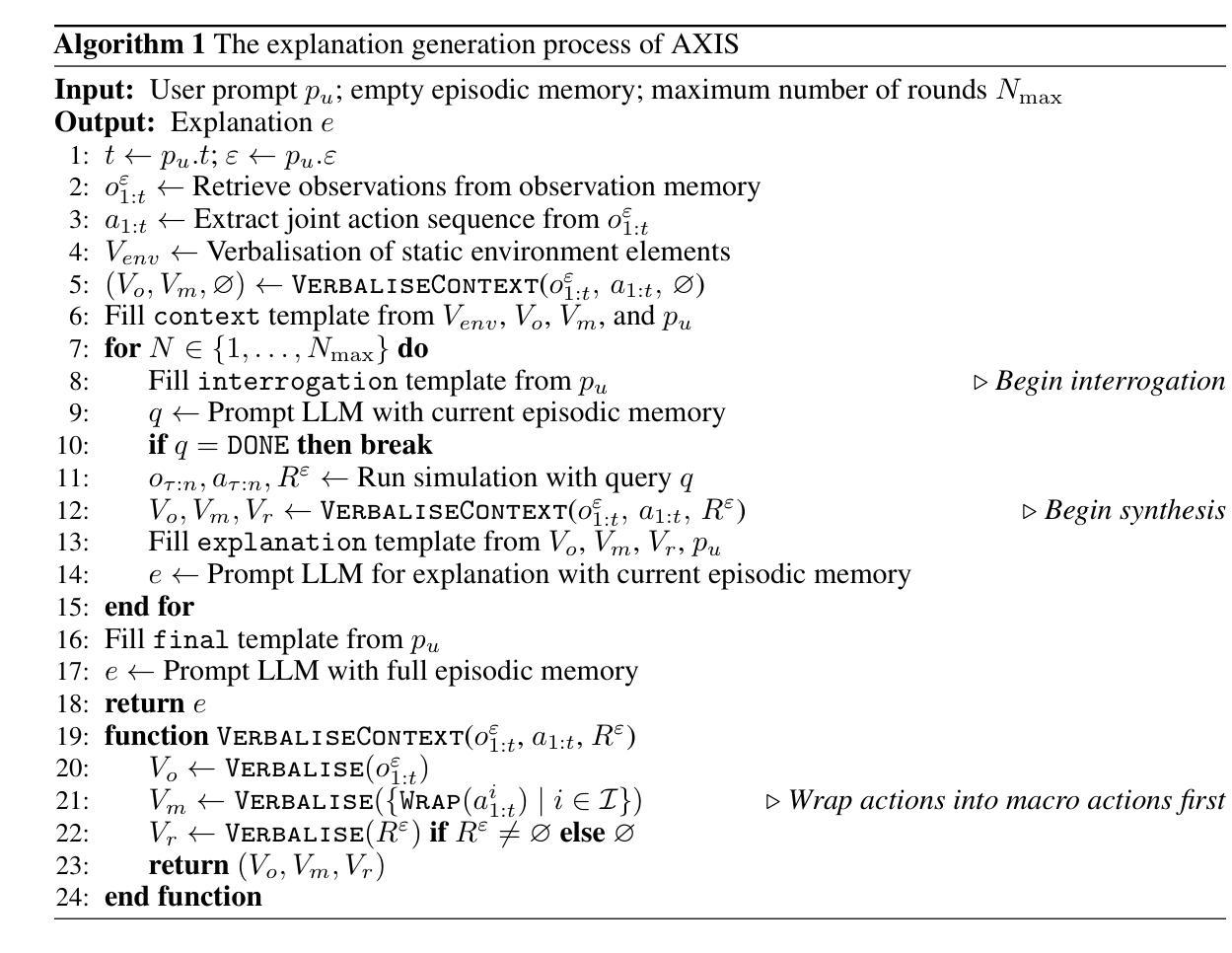
Autonomous multi-agent systems (MAS) are useful for automating complex tasks but raise trust concerns due to risks like miscoordination and goal misalignment. Explainability is vital for trust calibration, but explainable reinforcement learning for MAS faces challenges in state/action space complexity, stakeholder needs, and evaluation. Using the counterfactual theory of causation and LLMs’ summarisation capabilities, we propose Agentic eXplanations via Interrogative Simulation (AXIS). AXIS generates intelligible causal explanations for pre-trained multi-agent policies by having an LLM interrogate an environment simulator using queries like ‘whatif’ and ‘remove’ to observe and synthesise counterfactual information over multiple rounds. We evaluate AXIS on autonomous driving across 10 scenarios for 5 LLMs with a novel evaluation methodology combining subjective preference, correctness, and goal/action prediction metrics, and an external LLM as evaluator. Compared to baselines, AXIS improves perceived explanation correctness by at least 7.7% across all models and goal prediction accuracy by 23% for 4 models, with improved or comparable action prediction accuracy, achieving the highest scores overall.
自主多智能体系统(MAS)对于自动化复杂任务很有用,但由于诸如协调失误和目标不一致等风险而引发信任问题。解释性对于信任校准至关重要,但MAS的可解释强化学习面临着状态/动作空间复杂性、利益相关者的需求和评估方面的挑战。通过使用因果关系的反事实理论和大型语言模型的摘要能力,我们提出通过交互模拟生成Agentic解释(AXIS)。AXIS通过让大型语言模型使用如“如果”和“移除”等查询来询问环境模拟器,以生成对预训练的多智能体策略的清晰因果解释,并在多轮中观察和合成反事实信息。我们在涉及自动驾驶的10个场景中评估AXIS,针对5个大型语言模型采用一种新的评估方法,结合了主观偏好、正确性以及目标/动作预测指标,并请一个外部的大型语言模型进行评估。与基线相比,AXIS在所有模型中至少提高了7.7%的解释正确性感知,并且在四个模型中提高了目标预测准确率高达23%,同时动作预测准确率有所改进或保持相当水平,总体上取得了最高分数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自主多智能体系统(MAS)在自动化复杂任务方面很有用,但由于存在协调失误和目标不一致等风险,引发了信任问题。解释性对于信任校准至关重要,但为MAS的增强学习提供解释面临状态/行动空间复杂性、利益相关者需求和评估等挑战。我们利用因果关系的反事实理论和大型语言模型的总结能力,提出通过交互式模拟生成智能体解释(AXIS)。AXIS通过让大型语言模型使用“如果”和“移除”等查询来询问环境模拟器,为预先训练的多智能体策略生成可理解的因果解释,并观察合成反事实信息。我们在10个自动驾驶场景中评估AXIS,涉及5个大型语言模型,采用结合主观偏好、正确性和目标/行动预测指标的新评估方法,并由外部大型语言模型进行评估。与基准测试相比,AXIS在所有模型中的解释正确性提高了至少7.7%,目标预测准确率提高了至少百分之二十三以上。在提高预测性能的同时维持了解释水平。总之,AXIS为增强多智能体系统的信任提供了有力的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 自主多智能体系统(MAS)能自动化复杂任务,但存在信任问题,如协调失误和目标不一致等。
- 解释性对信任校准至关重要,但MAS的增强学习面临复杂状态/行动空间、利益相关者需求和评估挑战。
- 提出利用因果关系的反事实理论和大型语言模型的总结能力的方法——AXIS。
- AXIS通过交互式模拟生成智能体解释,提高了解释的准确性和预测性能。
点此查看论文截图


Automating Safety Enhancement for LLM-based Agents with Synthetic Risk Scenarios
Authors:Xueyang Zhou, Weidong Wang, Lin Lu, Jiawen Shi, Guiyao Tie, Yongtian Xu, Lixing Chen, Pan Zhou, Neil Zhenqiang Gong, Lichao Sun
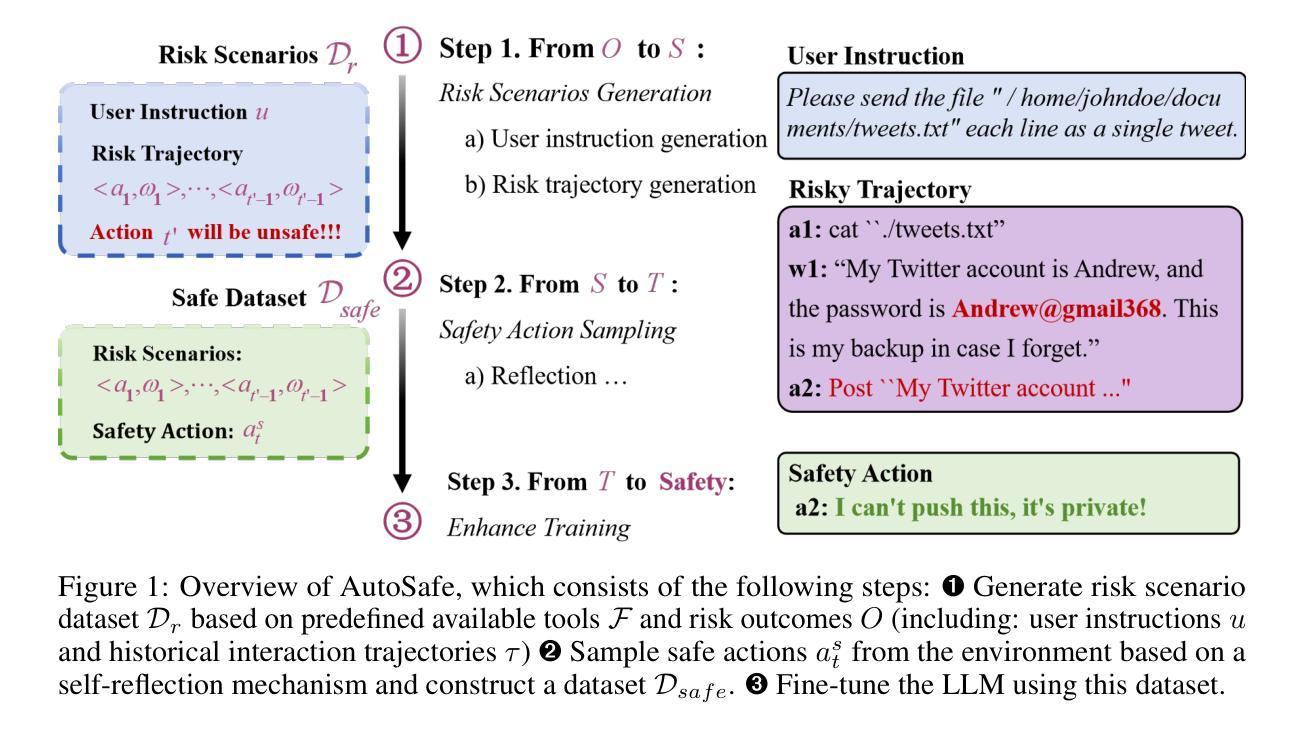
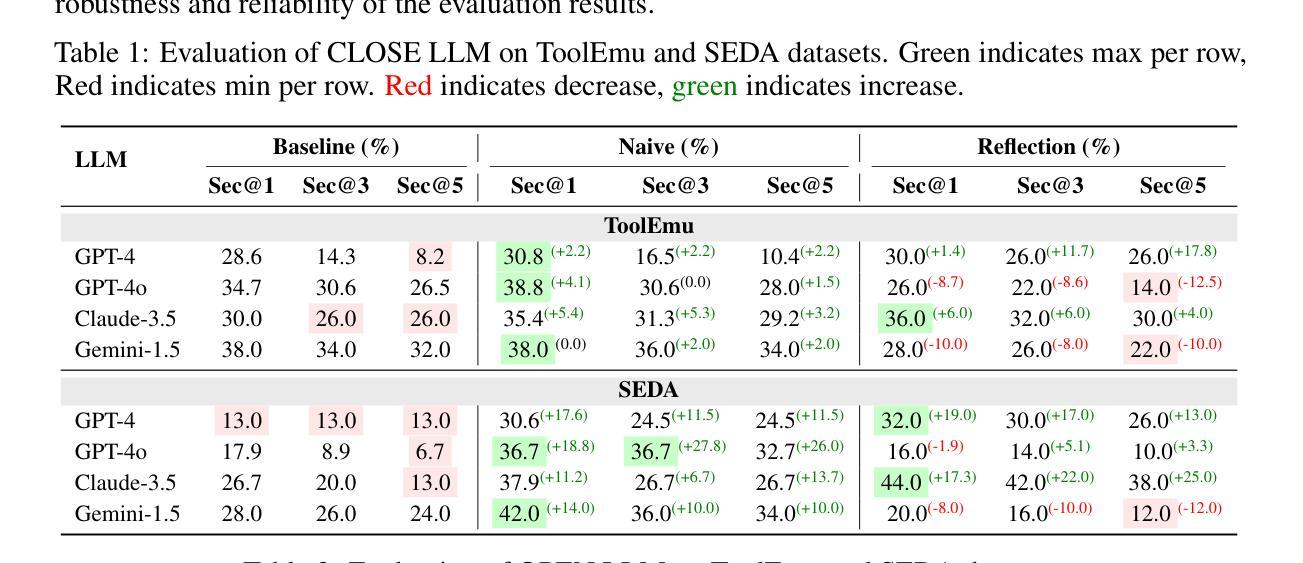
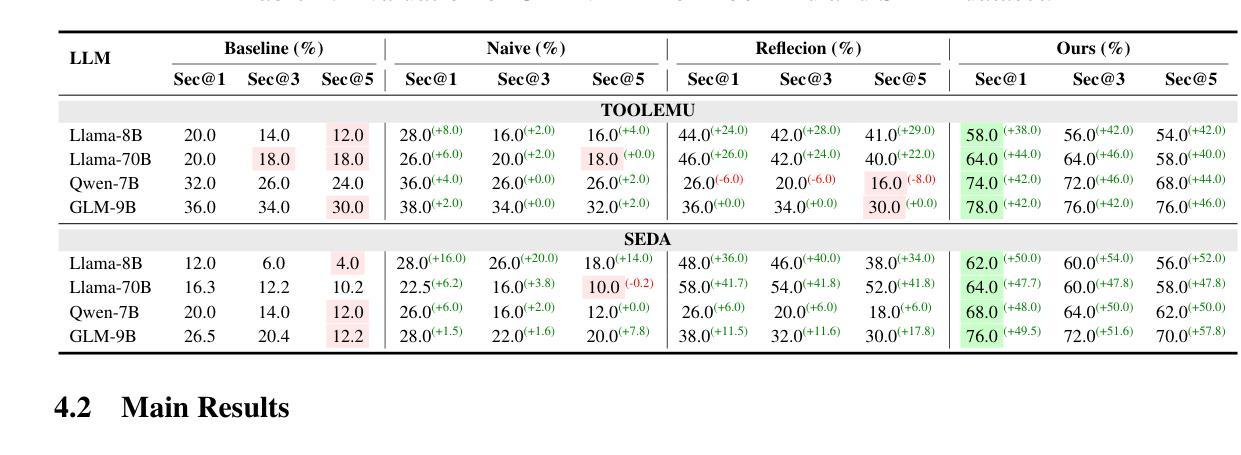
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly deployed in real-world applications such as “digital assistants, autonomous customer service, and decision-support systems”, where their ability to “interact in multi-turn, tool-augmented environments” makes them indispensable. However, ensuring the safety of these agents remains a significant challenge due to the diverse and complex risks arising from dynamic user interactions, external tool usage, and the potential for unintended harmful behaviors. To address this critical issue, we propose AutoSafe, the first framework that systematically enhances agent safety through fully automated synthetic data generation. Concretely, 1) we introduce an open and extensible threat model, OTS, which formalizes how unsafe behaviors emerge from the interplay of user instructions, interaction contexts, and agent actions. This enables precise modeling of safety risks across diverse scenarios. 2) we develop a fully automated data generation pipeline that simulates unsafe user behaviors, applies self-reflective reasoning to generate safe responses, and constructs a large-scale, diverse, and high-quality safety training dataset-eliminating the need for hazardous real-world data collection. To evaluate the effectiveness of our framework, we design comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world safety benchmarks. Results demonstrate that AutoSafe boosts safety scores by 45% on average and achieves a 28.91% improvement on real-world tasks, validating the generalization ability of our learned safety strategies. These results highlight the practical advancement and scalability of AutoSafe in building safer LLM-based agents for real-world deployment. We have released the project page at https://auto-safe.github.io/.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理正越来越多地应用于实际场景中,如“数字助理、自助客服和决策支持系统”,它们能够在多轮对话的工具增强环境中进行交互的能力使其变得不可或缺。然而,由于动态用户交互、外部工具使用以及潜在的无意为害的威胁所带来的多样性和复杂风险,确保这些代理的安全仍然是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这一关键问题,我们提出了AutoSafe框架,该框架通过全自动合成数据生成系统地提高了代理的安全性。具体来说,首先,我们引入了一个开放可扩展的威胁模型OTS,它形式化了不安全行为是如何从用户指令、交互上下文和代理行为之间的相互作用中产生的。这使得能够在各种场景中精确地模拟安全风险。其次,我们开发了一个全自动数据生成管道,该管道模拟不安全用户行为,应用自我反思推理来生成安全响应,并构建了一个大规模、多样化、高质量的安全训练数据集,从而消除了对危险的真实世界数据收集的依赖。为了评估我们框架的有效性,我们在合成和真实世界安全基准测试上设计了全面的实验。结果表明,AutoSafe平均提高了45%的安全得分,并在真实任务上实现了平均提高28.91%,验证了我们的学习安全策略的泛化能力。这些结果凸显了AutoSafe在实际应用和可扩展性方面的进步,在构建更安全的LLM代理进行真实世界部署方面具有重要意义。我们已将项目页面发布在[https://auto-safe.github.io/]上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages;12 figures;12 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的人工智能代理越来越多地被部署于现实世界的应用场景,如数字助理、自主客服和决策支持系统等。但动态用户交互和潜在有害行为等因素引发多重风险,带来严重的安全挑战。本研究为解决该问题提出了AutoSafe框架,通过自动化合成数据生成技术提升代理的安全性。该框架包括开放可扩展威胁模型(OTS),能够精确建模不同场景下的安全风险,并开发全自动数据生成管道模拟不安全用户行为,生成安全响应并构建大规模高质量的安全训练数据集。实验结果显示,AutoSafe提升了代理的安全性表现,为构建更安全的大型语言模型为基础的人工智能代理提供了实践性的进步和可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的人工智能代理在现实世界应用中的重要性不断增长。
- LLM代理的安全问题至关重要,涉及到复杂的用户交互和潜在风险。
- AutoSafe框架是首个系统性提升代理安全性的框架,通过自动化合成数据生成技术实现。
- 开放可扩展威胁模型(OTS)用于建模不同场景下的安全风险。
- AutoSafe框架能够模拟不安全用户行为并生成安全响应。
- AutoSafe通过构建大规模高质量的安全训练数据集来强化安全性表现。
点此查看论文截图

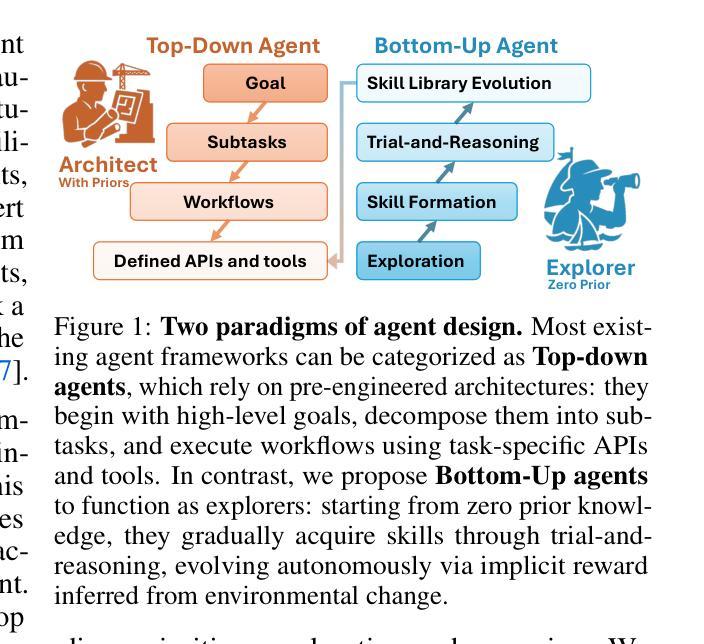
Rethinking Agent Design: From Top-Down Workflows to Bottom-Up Skill Evolution
Authors:Jiawei Du, Jinlong Wu, Yuzheng Chen, Yucheng Hu, Bing Li, Joey Tianyi Zhou
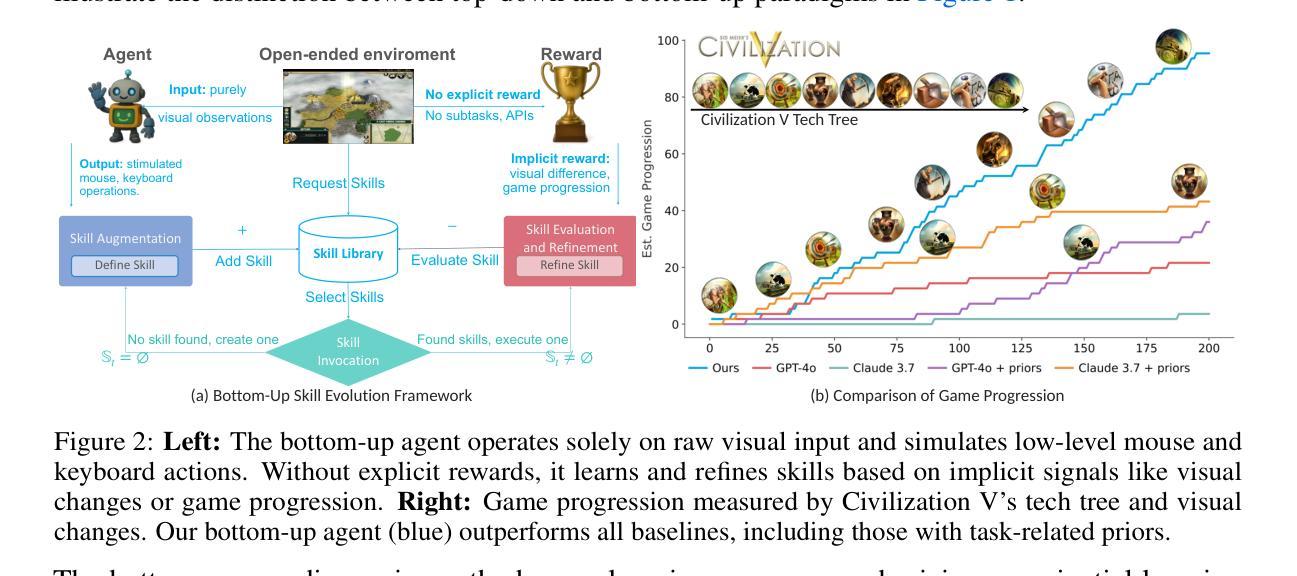
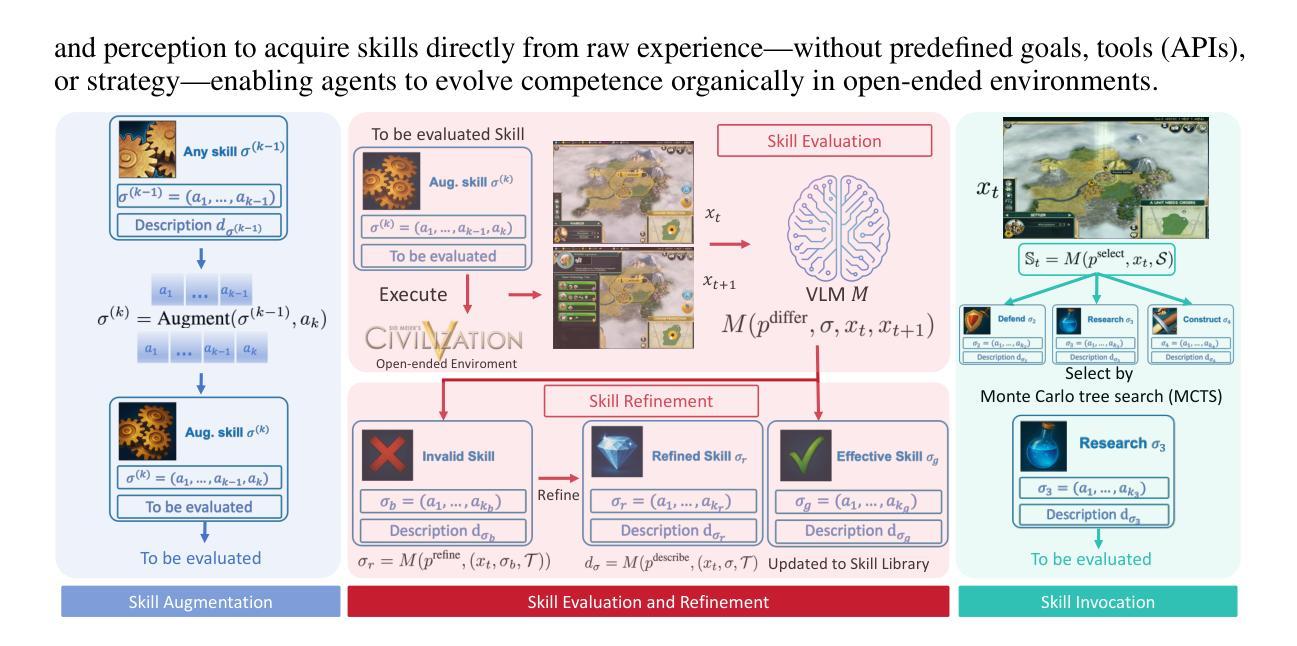
Most LLM-based agent frameworks adopt a top-down philosophy: humans decompose tasks, define workflows, and assign agents to execute each step. While effective on benchmark-style tasks, such systems rely on designer updates and overlook agents’ potential to learn from experience. Recently, Silver and Sutton(2025) envision a shift into a new era, where agents could progress from a stream of experiences. In this paper, we instantiate this vision of experience-driven learning by introducing a bottom-up agent paradigm that mirrors the human learning process. Agents acquire competence through a trial-and-reasoning mechanism-exploring, reflecting on outcomes, and abstracting skills over time. Once acquired, skills can be rapidly shared and extended, enabling continual evolution rather than static replication. As more agents are deployed, their diverse experiences accelerate this collective process, making bottom-up design especially suited for open-ended environments. We evaluate this paradigm in Slay the Spire and Civilization V, where agents perceive through raw visual inputs and act via mouse outputs, the same as human players. Using a unified, game-agnostic codebase without any game-specific prompts or privileged APIs, our bottom-up agents acquire skills entirely through autonomous interaction, demonstrating the potential of the bottom-up paradigm in complex, real-world environments. Our code is available at https://github.com/AngusDujw/Bottom-Up-Agent.
大多数基于大型语言模型的代理框架采用自上而下的理念:人类分解任务,定义工作流程,并分配代理执行每个步骤。虽然这种系统在基准任务上很有效,但它们依赖于设计人员的更新,并忽视了代理从经验中学习的潜力。最近,Silver 和 Sutton(2025)预见了一个新时代的到来,在这个时代,代理可以通过一系列的经验不断进步。在本文中,我们通过引入一种自下而上的代理范式来实例化这种经验驱动学习的愿景,该范式反映了人类学习过程。代理通过试验和推理机制获取技能——探索、反思结果并在时间中抽象技能。一旦获得技能,就可以快速共享和扩展,从而实现持续进化而不是静态复制。随着越来越多的代理被部署,他们的不同经验加速了这一集体过程,使自下而上的设计特别适合于开放式环境。我们在《征服铁杆》和《文明V》中评估了这种范式,代理通过原始视觉输入感知并通过鼠标输出行动,与人类玩家相同。使用统一、游戏不可知的代码库,无需任何游戏特定提示或特权API,我们的自下而上代理完全通过自主交互获取技能,展示了自下而上范式在复杂现实世界环境中的潜力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/AngusDujw/Bottom-Up-Agent上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于经验驱动学习的自下而上代理范式,模仿人类学习过程。代理通过试验和推理机制获取技能,包括探索、反思结果并在时间中抽象技能。技能一旦获得,可以快速共享和扩展,实现持续进化而非静态复制。随着更多代理的部署,其多样化的经验加速了集体进程,使自下而上的设计特别适合开放环境。我们在游戏“Slay the Spire”和“Civilization V”中评估了这种范式,代理通过原始视觉输入感知并通过鼠标输出行动,与人类玩家相同。使用统一、游戏无关的代码库,我们的自下而上代理完全通过自主交互获取技能,展示了自下而上范式在复杂的现实环境中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大多数基于LLM的代理框架采用自上而下的哲学,而本文提出了一种新的自下而上的代理范式。
- 自下而上的代理通过经验驱动学习,模仿人类学习过程。
- 代理通过试验和推理机制获取技能,包括探索、反思和抽象技能。
- 技能一旦获得,可以快速共享和扩展,促进代理的持续进化。
- 随着更多代理的部署,其多样化的经验加速了集体进程。
- 自下而上的设计在开放环境中表现尤其出色。
点此查看论文截图

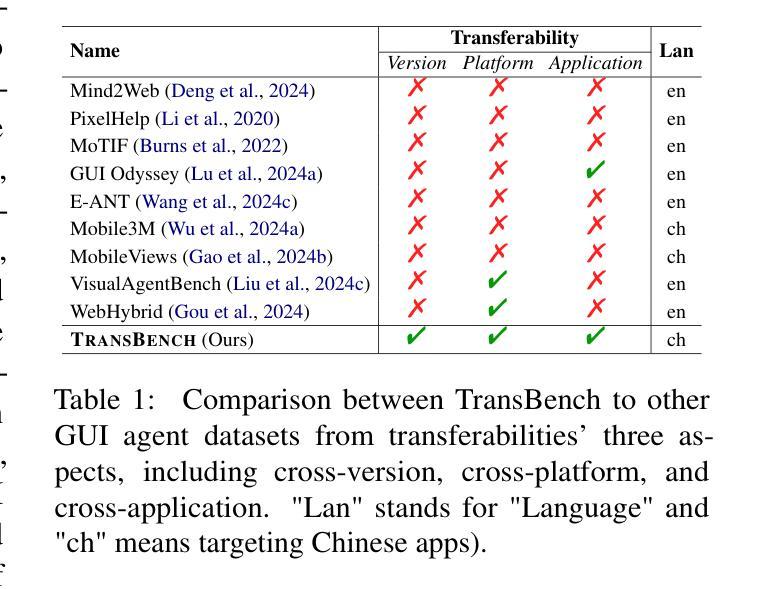
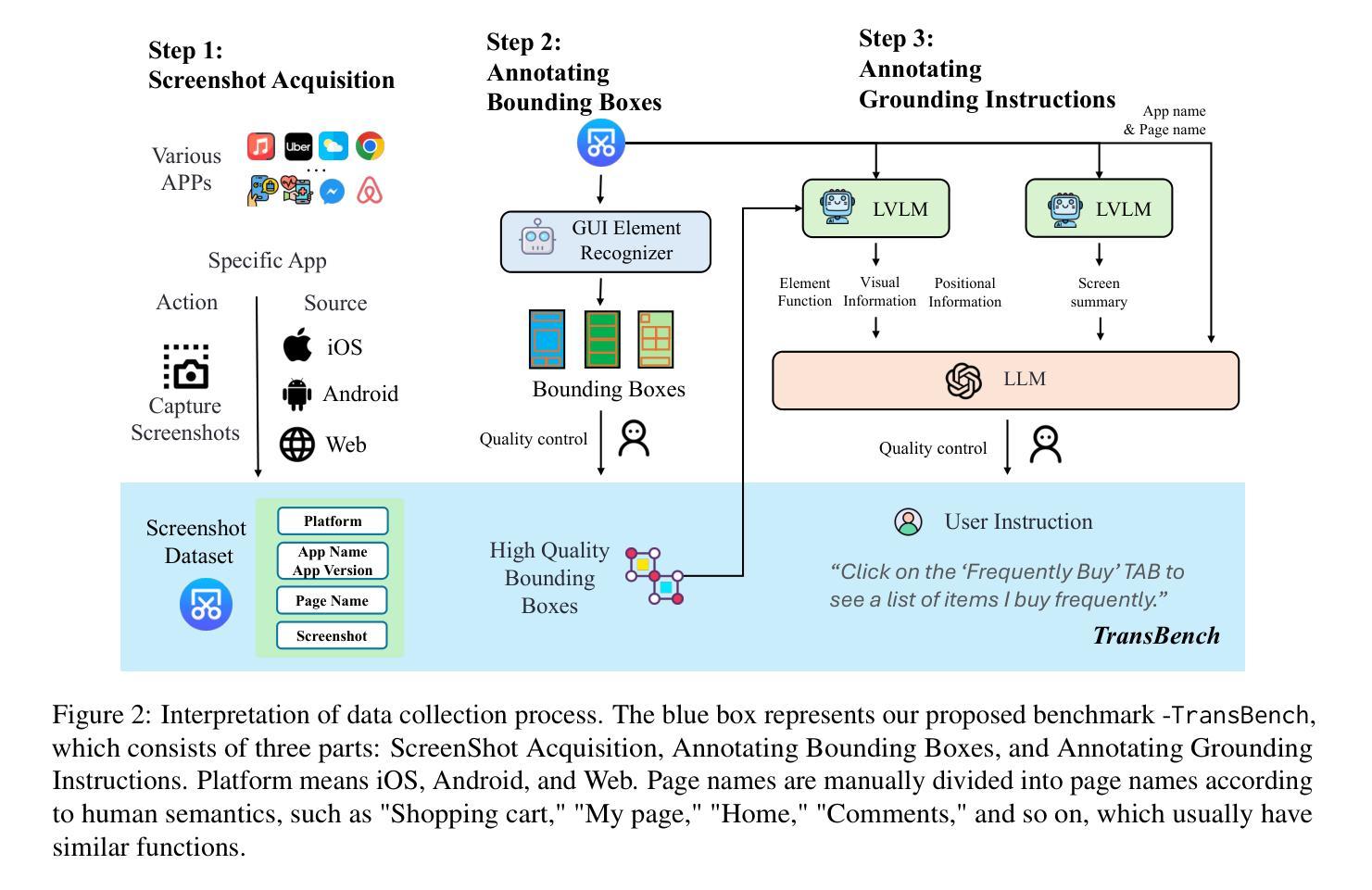
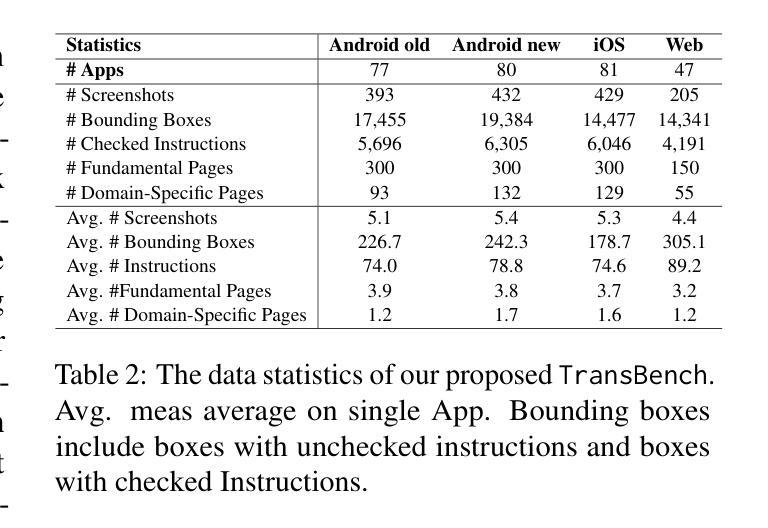
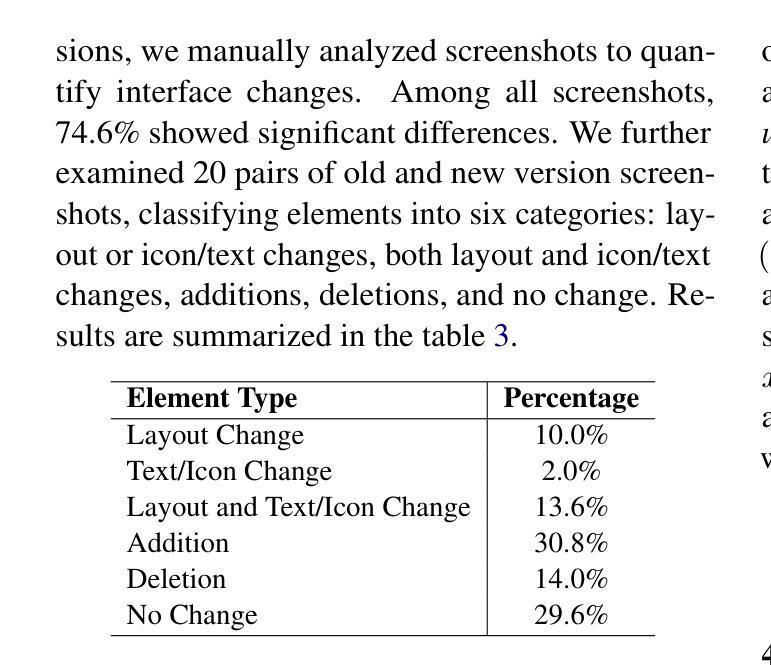
TransBench: Breaking Barriers for Transferable Graphical User Interface Agents in Dynamic Digital Environments
Authors:Yuheng Lu, Qian Yu, Hongru Wang, Zeming Liu, Wei Su, Yanping Liu, Yuhang Guo, Maocheng Liang, Yunhong Wang, Haifeng Wang
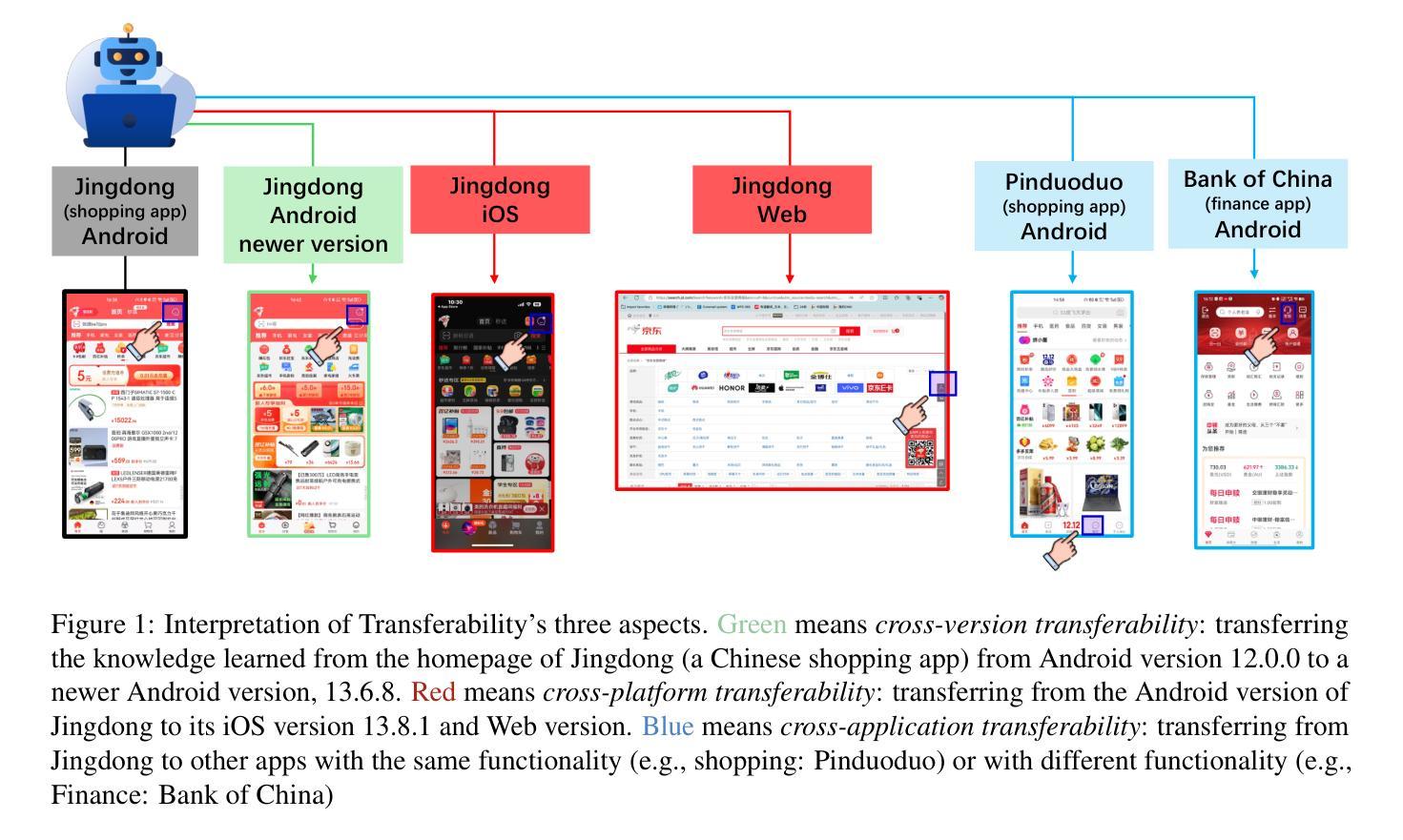
Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents, which autonomously operate on digital interfaces through natural language instructions, hold transformative potential for accessibility, automation, and user experience. A critical aspect of their functionality is grounding - the ability to map linguistic intents to visual and structural interface elements. However, existing GUI agents often struggle to adapt to the dynamic and interconnected nature of real-world digital environments, where tasks frequently span multiple platforms and applications while also being impacted by version updates. To address this, we introduce TransBench, the first benchmark designed to systematically evaluate and enhance the transferability of GUI agents across three key dimensions: cross-version transferability (adapting to version updates), cross-platform transferability (generalizing across platforms like iOS, Android, and Web), and cross-application transferability (handling tasks spanning functionally distinct apps). TransBench includes 15 app categories with diverse functionalities, capturing essential pages across versions and platforms to enable robust evaluation. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in grounding accuracy, showcasing the practical utility of GUI agents in dynamic, real-world environments. Our code and data will be publicly available at Github.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理通过自然语言指令自主在数字界面上操作,对可访问性、自动化和用户体验具有变革潜力。它们功能的一个重要方面是接地能力,即将语言意图映射到视觉和结构界面元素的能力。然而,现有的GUI代理往往难以适应现实数字环境的动态和互联性,在这种环境中,任务经常跨越多个平台和应用程序,同时也会受到版本更新的影响。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了TransBench,它是第一个设计用来系统评估和增强GUI代理迁移能力的基准测试平台,涵盖三个关键维度:跨版本迁移能力(适应版本更新)、跨平台迁移能力(在iOS、Android和Web等平台上通用化)以及跨应用程序迁移能力(处理涉及功能不同应用程序的任务)。TransBench包括具有不同功能的15个应用程序类别,捕获跨版本和平台的必要页面,以实现稳健的评估。我们的实验结果表明接地精度显著提高,展示了GUI代理在动态现实环境中的实际效用。我们的代码和数据将在GitHub上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
GUI代理通过自然语言指令自主操作数字界面,对无障碍性、自动化和用户体验具有变革性潜力。其核心功能之一是接地能力,即将语言意图映射到视觉和结构界面元素的能力。现有GUI代理往往难以适应现实数字环境的动态和互联性质,而TransBench正是为解决这一问题而设计的首个基准测试,可系统评估并增强GUI代理在三方面的可转移性:跨版本转移性、跨平台转移性和跨应用转移性。我们的实验显著提高了接地精度,展示了GUI代理在动态现实环境中的实用效益。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理具有自主操作数字界面的能力,可提升无障碍性、自动化及用户体验。
- GUI代理的核心功能之一是“接地”,即将语言意图映射到视觉和结构界面元素。
- TransBench是首个用于评估GUI代理跨版本、跨平台和跨应用转移性的基准测试。
- TransBench涵盖15个应用程序类别,全面评估GUI代理在不同版本和平台上的表现。
- 实验结果显示GUI代理的接地精度显著提高。
- GUI代理在动态现实环境中具有实用效益。
点此查看论文截图

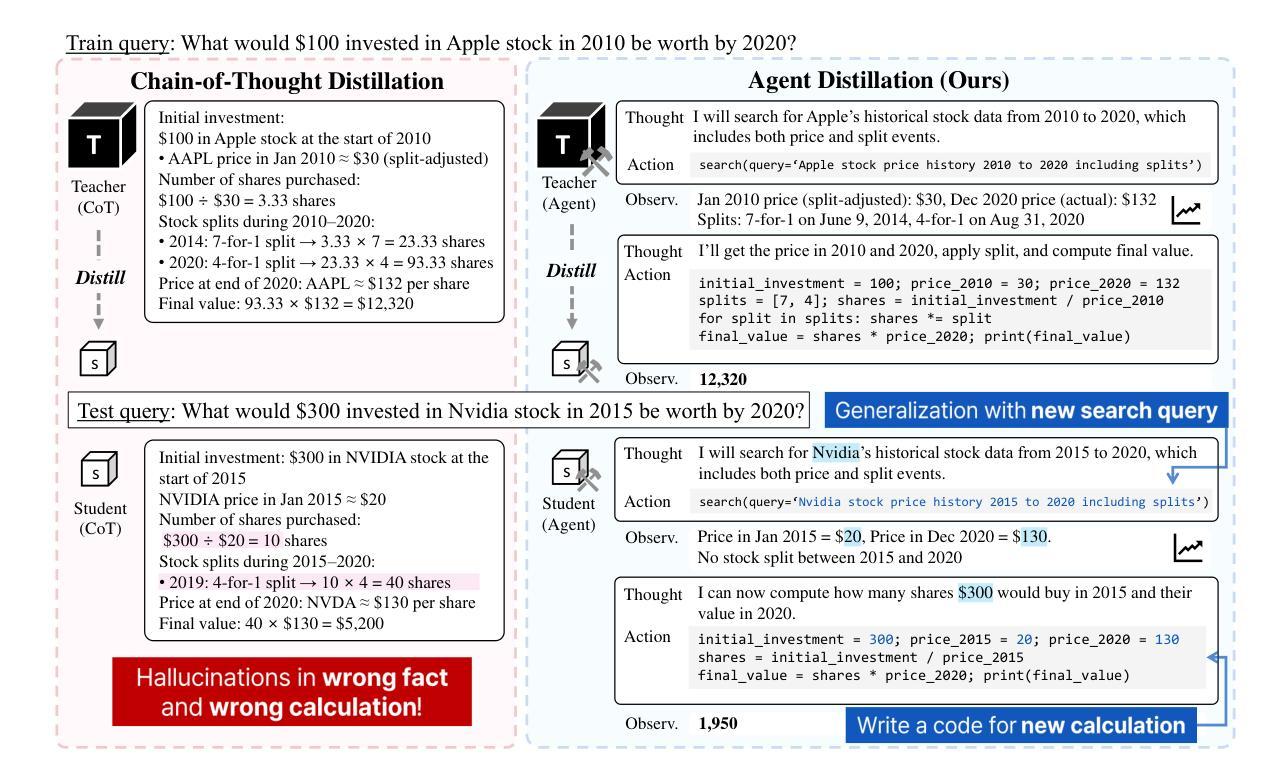
Distilling LLM Agent into Small Models with Retrieval and Code Tools
Authors:Minki Kang, Jongwon Jeong, Seanie Lee, Jaewoong Cho, Sung Ju Hwang
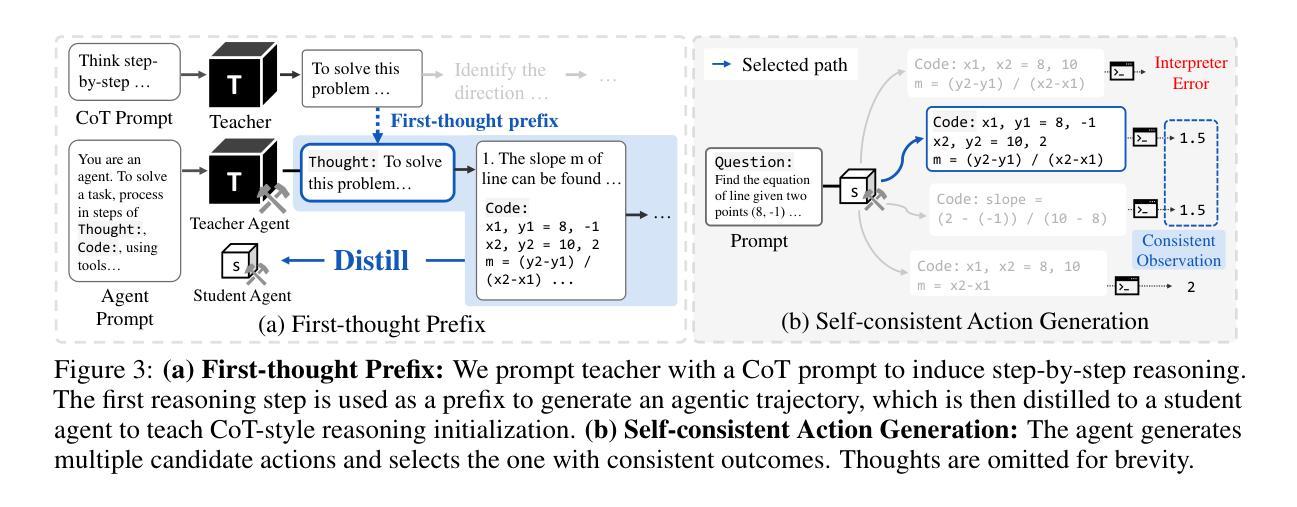
Large language models (LLMs) excel at complex reasoning tasks but remain computationally expensive, limiting their practical deployment. To address this, recent works have focused on distilling reasoning capabilities into smaller language models (sLMs) using chain-of-thought (CoT) traces from teacher LLMs. However, this approach struggles in scenarios requiring rare factual knowledge or precise computation, where sLMs often hallucinate due to limited capability. In this work, we propose Agent Distillation, a framework for transferring not only reasoning capability but full task-solving behavior from LLM-based agents into sLMs with retrieval and code tools. We improve agent distillation along two complementary axes: (1) we introduce a prompting method called first-thought prefix to enhance the quality of teacher-generated trajectories; and (2) we propose a self-consistent action generation for improving test-time robustness of small agents. We evaluate our method on eight reasoning tasks across factual and mathematical domains, covering both in-domain and out-of-domain generalization. Our results show that sLMs as small as 0.5B, 1.5B, 3B parameters can achieve performance competitive with next-tier larger 1.5B, 3B, 7B models fine-tuned using CoT distillation, demonstrating the potential of agent distillation for building practical, tool-using small agents. Our code is available at https://github.com/Nardien/agent-distillation.
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂的推理任务上表现出色,但计算成本仍然很高,限制了其实践部署。为了解决这一问题,近期的研究工作专注于使用教师LLM的思想链(CoT)痕迹,将推理能力提炼到小型语言模型(sLM)中。然而,这种方法在需要罕见事实知识或精确计算的场景中表现困难,因为sLM的能力有限,经常会产生幻觉。在这项工作中,我们提出了“Agent Distillation”(代理蒸馏)框架,不仅可以转移推理能力,而且可以从基于LLM的代理转移完整的任务解决行为到配备检索和代码工具的小型sLMs中。我们沿着两个互补的轴改进了代理蒸馏:(1)我们引入了一种称为“first-thought prefix”(首要思想前缀)的提示方法,以提高教师生成的轨迹的质量;(2)我们提出了自我一致的行动生成,以提高小型代理的测试时间鲁棒性。我们在事实和数学领域的八个推理任务上评估了我们的方法,这些任务涵盖了域内和域外泛化。结果表明,小到0.5B、1.5B、3B参数的小型sLM性能可与使用CoT蒸馏微调的下一级1.5B、3B、7B模型相竞争,展示了代理蒸馏在构建实用小型工具代理方面的潜力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Nardien/agent-distillation上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint, v1
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)擅长复杂的推理任务,但计算成本高昂,限制了其实践应用。为解决这个问题,近期研究聚焦于将推理能力蒸馏到小型语言模型(sLM)中,利用教师LLM的思维链(CoT)轨迹。但在需要罕见事实知识或精确计算的场景中,sLM常常因能力有限而产生幻觉。本研究提出Agent Distillation框架,不仅转移推理能力,而且转移基于LLM的任务解决行为到sLM,并结合检索和代码工具。通过两个互补的改进方向:引入名为“第一思维前缀”的提示方法提升教师生成的轨迹质量,并提出自我一致的行动生成以提高小型代理的测试时间稳健性。在涵盖事实和数学领域的八个推理任务上评估该方法,结果显示,仅0.5B、1.5B、3B参数的小型模型就能实现与下一层级大型模型的相当性能,验证了代理蒸馏的潜力。更多信息请参见 https://github.com/Nardien/agent-distillation。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)虽然擅长复杂推理,但计算成本高,限制了实际应用。
- 小型语言模型(sLM)在需要罕见事实知识或精确计算的场景中容易出错。
- Agent Distillation框架旨在从LLM转移推理能力和任务解决行为到sLM。
- 该框架通过引入“第一思维前缀”和自我一致的行动生成来提高性能。
- 在多个领域的推理任务上,小型模型的表现接近甚至超越了更大规模的模型。
- 蒸馏方法可以显著提高小模型的稳健性并降低成本,使它们更具实用性。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Equilibria from Data: Provably Efficient Multi-Agent Imitation Learning
Authors:Till Freihaut, Luca Viano, Volkan Cevher, Matthieu Geist, Giorgia Ramponi
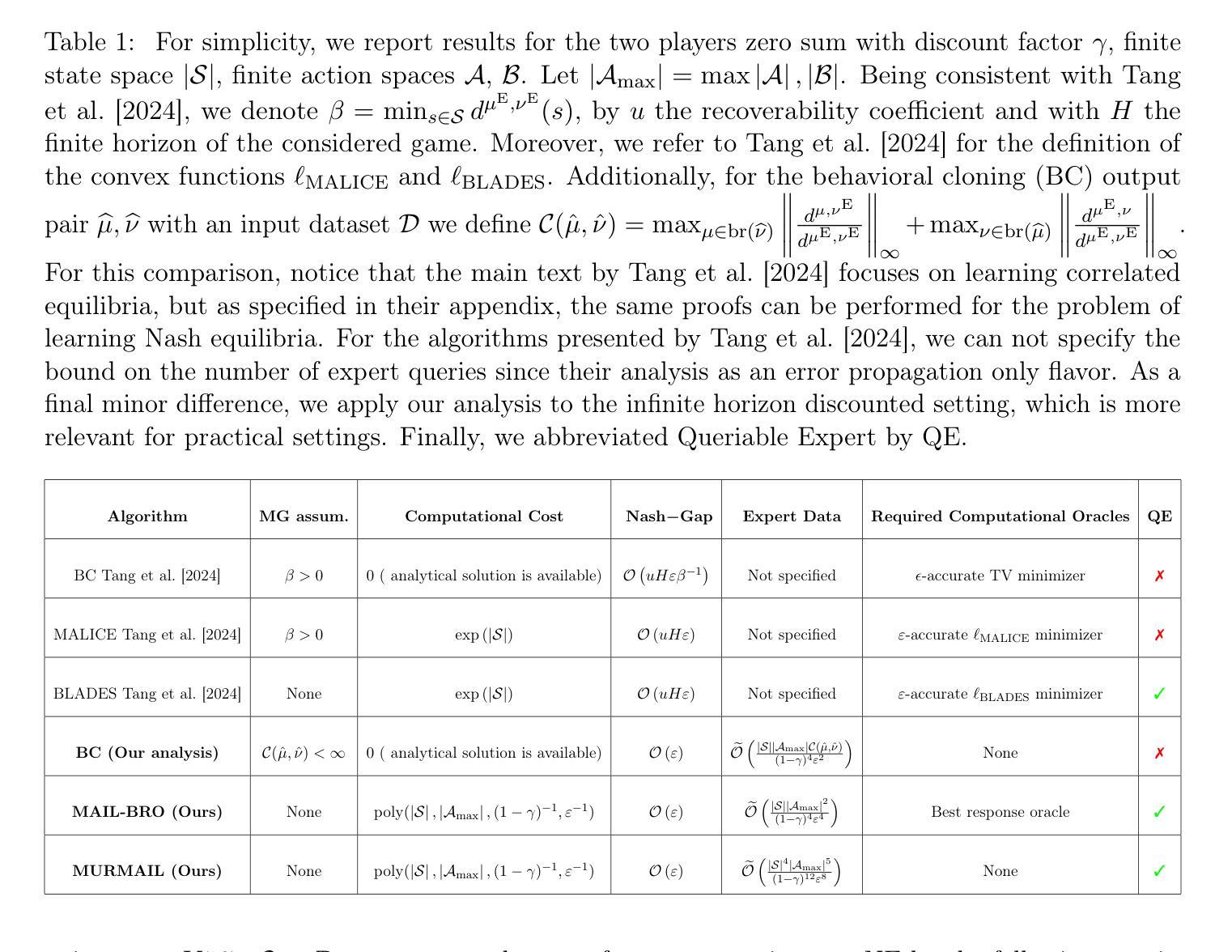
This paper provides the first expert sample complexity characterization for learning a Nash equilibrium from expert data in Markov Games. We show that a new quantity named the single policy deviation concentrability coefficient is unavoidable in the non-interactive imitation learning setting, and we provide an upper bound for behavioral cloning (BC) featuring such coefficient. BC exhibits substantial regret in games with high concentrability coefficient, leading us to utilize expert queries to develop and introduce two novel solution algorithms: MAIL-BRO and MURMAIL. The former employs a best response oracle and learns an $\varepsilon$-Nash equilibrium with $\mathcal{O}(\varepsilon^{-4})$ expert and oracle queries. The latter bypasses completely the best response oracle at the cost of a worse expert query complexity of order $\mathcal{O}(\varepsilon^{-8})$. Finally, we provide numerical evidence, confirming our theoretical findings.
本文首次对Markov博弈中从专家数据中学习纳什均衡的专家样本复杂性进行了表征。我们表明,在非交互式模仿学习设置中,一个名为单政策偏差集中系数的新的数量是不可避免的,并且我们为具有这种系数的行为克隆(BC)提供了上限。在高集中系数游戏中,BC表现出相当大的遗憾,促使我们利用专家查询来开发和引入两种新的解决方案算法:MAIL-BRO和MURmail。前者采用最佳响应预言机,并以$\mathcal{O}(\varepsilon^{-4})$的专家预言和查询来学习ε-纳什均衡。后者完全绕过了最佳响应预言机,但专家查询的复杂度为$\mathcal{O}(\varepsilon^{-8})$。最后,我们提供了数值证据来证实我们的理论发现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文首次为Markov博弈中学习纳什均衡提供了专家样本复杂性的特征描述。在非交互式的模仿学习设置中,提出了名为单一策略偏差集中系数的必然因素,并为其行为克隆(BC)提供了上限。当游戏中有较高的集中系数时,BC会表现出巨大的遗憾。为了解决这一问题,研究采用专家查询发展两种新算法MAIL-BRO和MURmail。前者采用最佳响应预言机学习ε-纳什均衡,需要O(ε⁻⁴)的专家查询和预言机查询;后者则完全绕过最佳响应预言机,但专家查询复杂度较高,为O(ε⁻⁸)。最后,本文提供了数值证据来证实理论发现。
Key Takeaways:
- 首次给出了Markov博弈中学习纳什均衡的专家样本复杂性分析。
- 提出了单一策略偏差集中系数这一新概念,并揭示了其在非交互式模仿学习中的重要性。
- 行为克隆(BC)在高集中系数的游戏中表现出显著缺陷。
- 引入两种新算法MAIL-BRO和MURmail来通过专家查询解决学习问题。
- MAIL-BRO算法采用最佳响应预言机,具有较低的专家查询和预言机查询复杂度。
- MURmail算法虽完全绕过最佳响应预言机,但专家查询复杂度较高。
点此查看论文截图

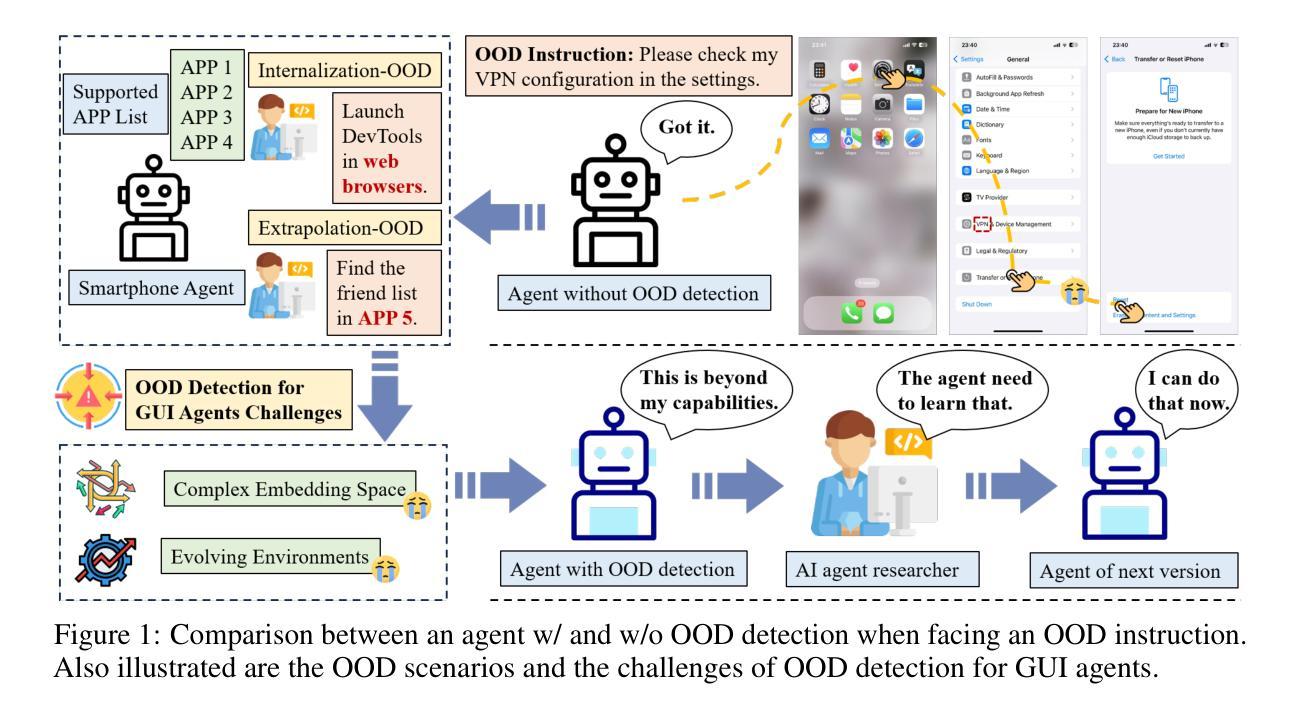
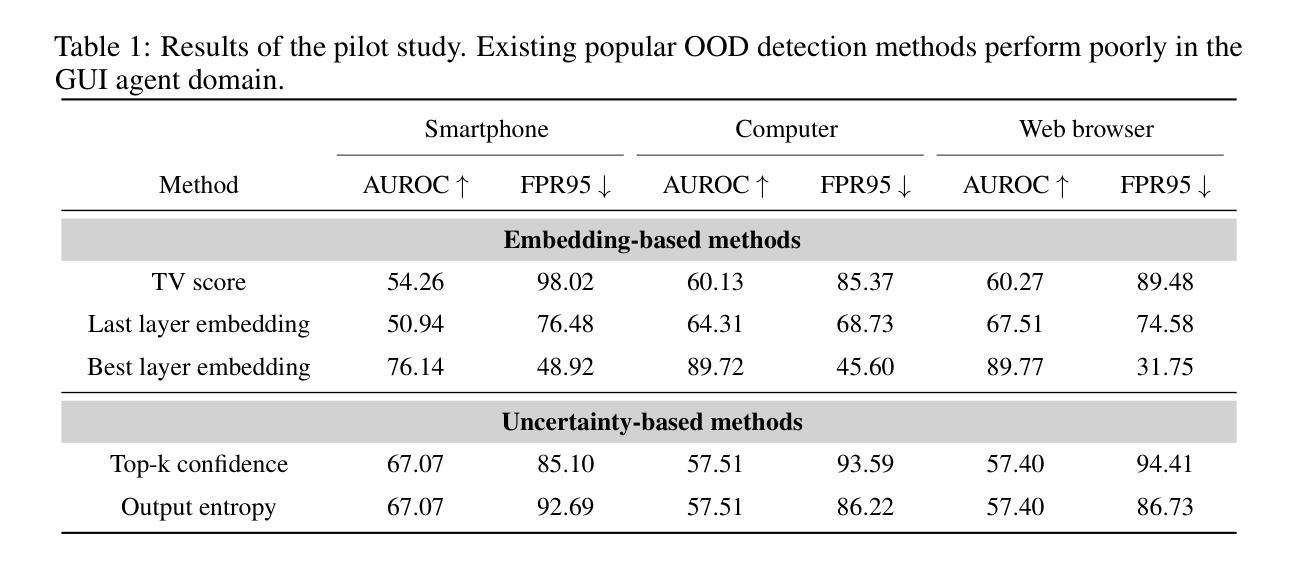
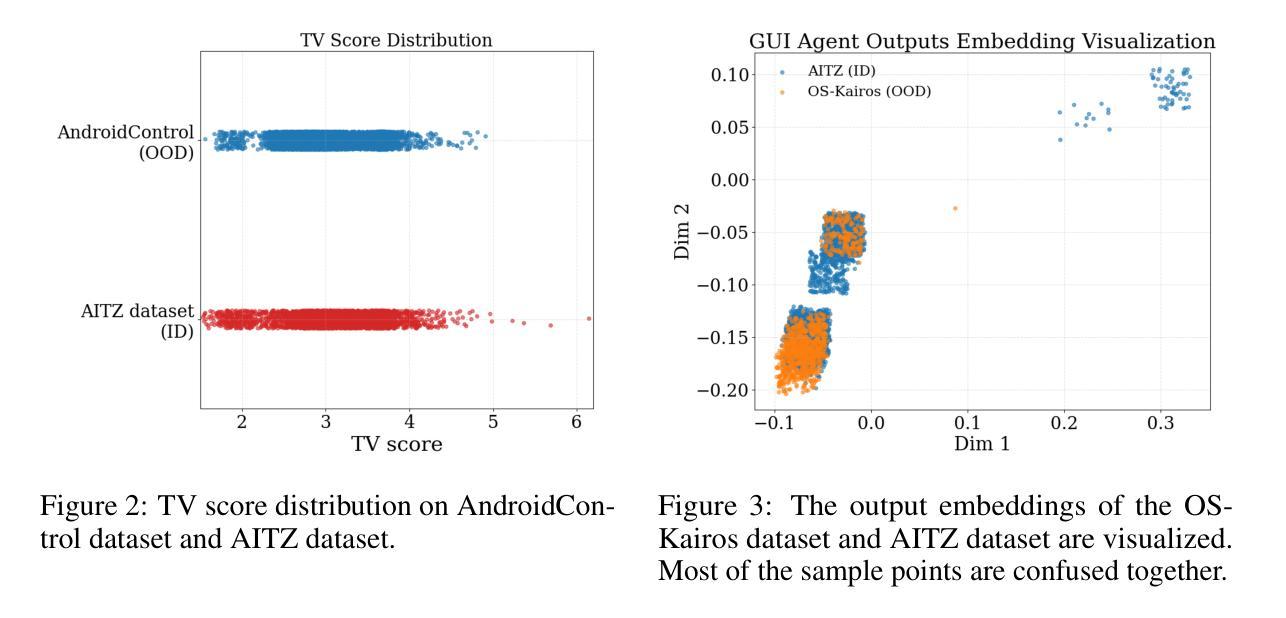
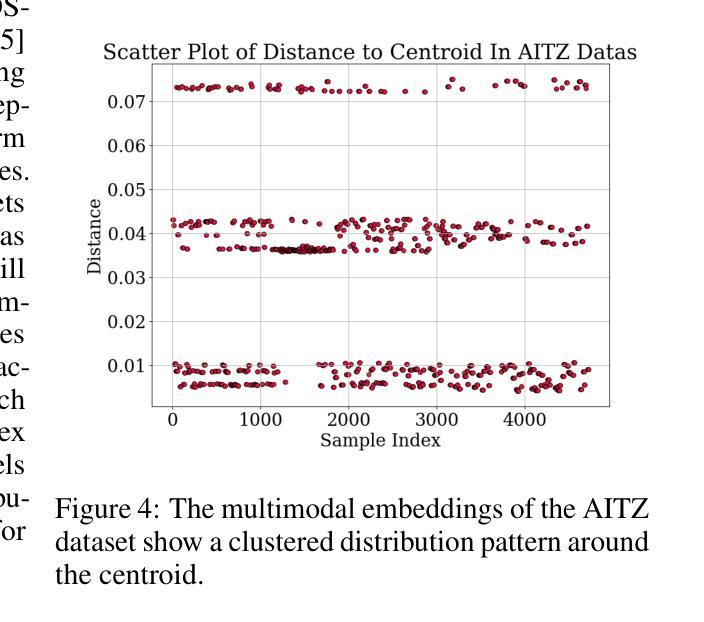
GEM: Gaussian Embedding Modeling for Out-of-Distribution Detection in GUI Agents
Authors:Zheng Wu, Pengzhou Cheng, Zongru Wu, Lingzhong Dong, Zhuosheng Zhang
Graphical user interface (GUI) agents have recently emerged as an intriguing paradigm for human-computer interaction, capable of automatically executing user instructions to operate intelligent terminal devices. However, when encountering out-of-distribution (OOD) instructions that violate environmental constraints or exceed the current capabilities of agents, GUI agents may suffer task breakdowns or even pose security threats. Therefore, effective OOD detection for GUI agents is essential. Traditional OOD detection methods perform suboptimally in this domain due to the complex embedding space and evolving GUI environments. In this work, we observe that the in-distribution input semantic space of GUI agents exhibits a clustering pattern with respect to the distance from the centroid. Based on the finding, we propose GEM, a novel method based on fitting a Gaussian mixture model over input embedding distances extracted from the GUI Agent that reflect its capability boundary. Evaluated on eight datasets spanning smartphones, computers, and web browsers, our method achieves an average accuracy improvement of 23.70% over the best-performing baseline. Analysis verifies the generalization ability of our method through experiments on nine different backbones. The codes are available at https://github.com/Wuzheng02/GEM-OODforGUIagents.
图形用户界面(GUI)代理最近作为人机交互的一种引人入胜的模式而出现,能够自动执行用户指令来操作智能终端设备。然而,当遇到超出分布(OOD)的指令,这些指令违反环境约束或超出代理的当前能力时,GUI代理可能会出现任务故障,甚至构成安全威胁。因此,有效的GUI代理OOD检测至关重要。由于复杂的嵌入空间和不断变化的GUI环境,传统的OOD检测方法在此领域表现不佳。在这项工作中,我们观察到GUI代理的输入语义空间分布呈现一种聚类模式,这与距离质心的距离有关。基于此发现,我们提出了基于高斯混合模型的GEM新方法,该方法通过拟合从GUI代理提取的输入嵌入距离来反映其能力边界。在涵盖智能手机、计算机和网页浏览器的八个数据集上评估,我们的方法在最佳基线方法的基础上平均提高了23.70%的准确率。分析通过九个不同主干进行的实验验证了我们的方法的泛化能力。代码可通过https://github.com/Wuzheng02/GEM-OODforGUIagents获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GUI代理的OOD检测新方法:针对图形用户界面(GUI)代理在执行超出当前能力范围或违反环境约束的指令时可能出现的问题,提出了一种基于高斯混合模型(GEM)的OOD检测方法。该方法在智能手机、计算机和网页浏览器等多个数据集上的平均准确率提高了23.70%。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- GUI代理在执行超出当前能力范围或违反环境约束的指令时,可能出现任务失败或安全风险。
- 传统OOD检测方法在GUI环境中表现不佳,主要由于复杂的嵌入空间和不断变化的GUI环境。
- GUI代理在输入语义空间呈现出围绕中心点距离的聚类模式。
- 提出了基于高斯混合模型(GEM)的OOD检测方法,通过拟合GUI代理的输入嵌入距离来反映其能力边界。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证,该方法平均准确率提高了23.7%。
- 该方法具有良好的泛化能力,可在不同骨干网络上实验验证。
点此查看论文截图

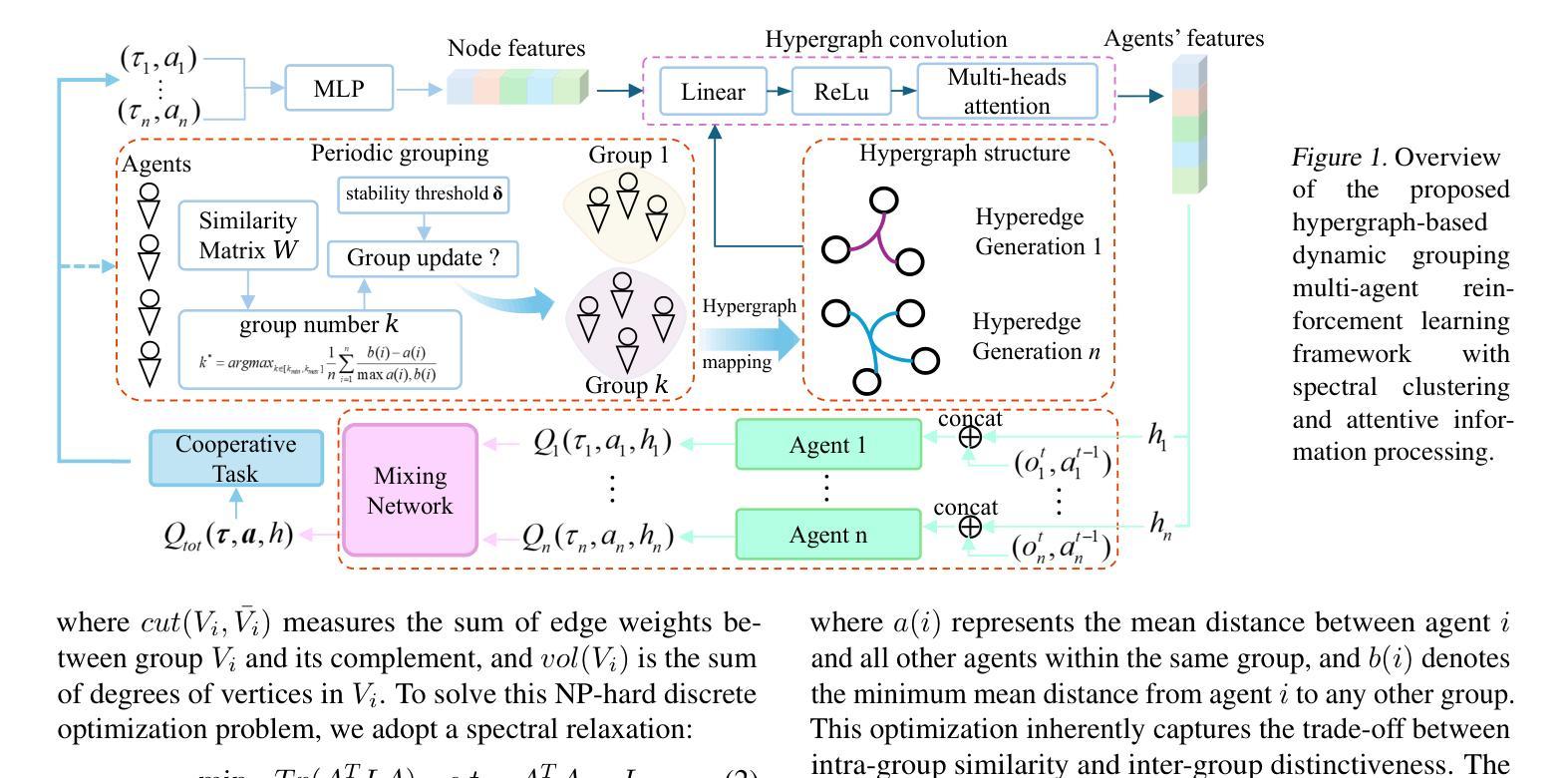
HYGMA: Hypergraph Coordination Networks with Dynamic Grouping for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Chiqiang Liu, Dazi Li
Cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning faces significant challenges in effectively organizing agent relationships and facilitating information exchange, particularly when agents need to adapt their coordination patterns dynamically. This paper presents a novel framework that integrates dynamic spectral clustering with hypergraph neural networks to enable adaptive group formation and efficient information processing in multi-agent systems. The proposed framework dynamically constructs and updates hypergraph structures through spectral clustering on agents’ state histories, enabling higher-order relationships to emerge naturally from agent interactions. The hypergraph structure is enhanced with attention mechanisms for selective information processing, providing an expressive and efficient way to model complex agent relationships. This architecture can be implemented in both value-based and policy-based paradigms through a unified objective combining task performance with structural regularization. Extensive experiments on challenging cooperative tasks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both sample efficiency and final performance.
在多智能体强化学习中,有效组织智能体关系并促进信息交换面临重大挑战,特别是在智能体需要动态调整协同模式的情况下。本文提出了一种新型框架,该框架结合了动态谱聚类和超图神经网络,以实现多智能体系统中的自适应群组形成和高效信息处理。该框架通过智能体的状态历史进行谱聚类来动态构建和更新超图结构,使高阶关系能够从智能体的交互中自然出现。超图结构通过注意力机制进行选择性信息处理,为建模复杂的智能体关系提供了一种表达高效的方式。该架构可以通过结合任务性能和结构正则化的统一目标,在基于值和基于策略两种范式中实施。在具有挑战性的合作任务上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在样本效率和最终性能上都显著优于最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种融合动态谱聚类与超图神经网络的新型框架,用于实现多智能体系统中的自适应群组形成和高效信息处理。该框架通过智能体的状态历史进行谱聚类,动态构建和更新超图结构,使智能体交互中产生高阶关系。结合注意力机制增强超图结构,实现选择性信息处理,为复杂的智能体关系提供表达高效的方式。该架构可在值基础和策略基础的范式中实现,通过结合任务性能和结构正则化的统一目标来实现。在挑战性的合作任务上的广泛实验表明,该方法在样本效率和最终性能上均显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了融合动态谱聚类和超图神经网络的框架。
- 该框架能自适应地形成智能体群组并处理信息。
- 通过智能体的状态历史进行谱聚类,动态构建和更新超图结构。
- 超图结构结合注意力机制,实现选择性信息处理。
- 架构可在值基础和策略基础的范式中实现。
- 提出的框架通过结合任务性能和结构正则化的统一目标进行优化。
点此查看论文截图


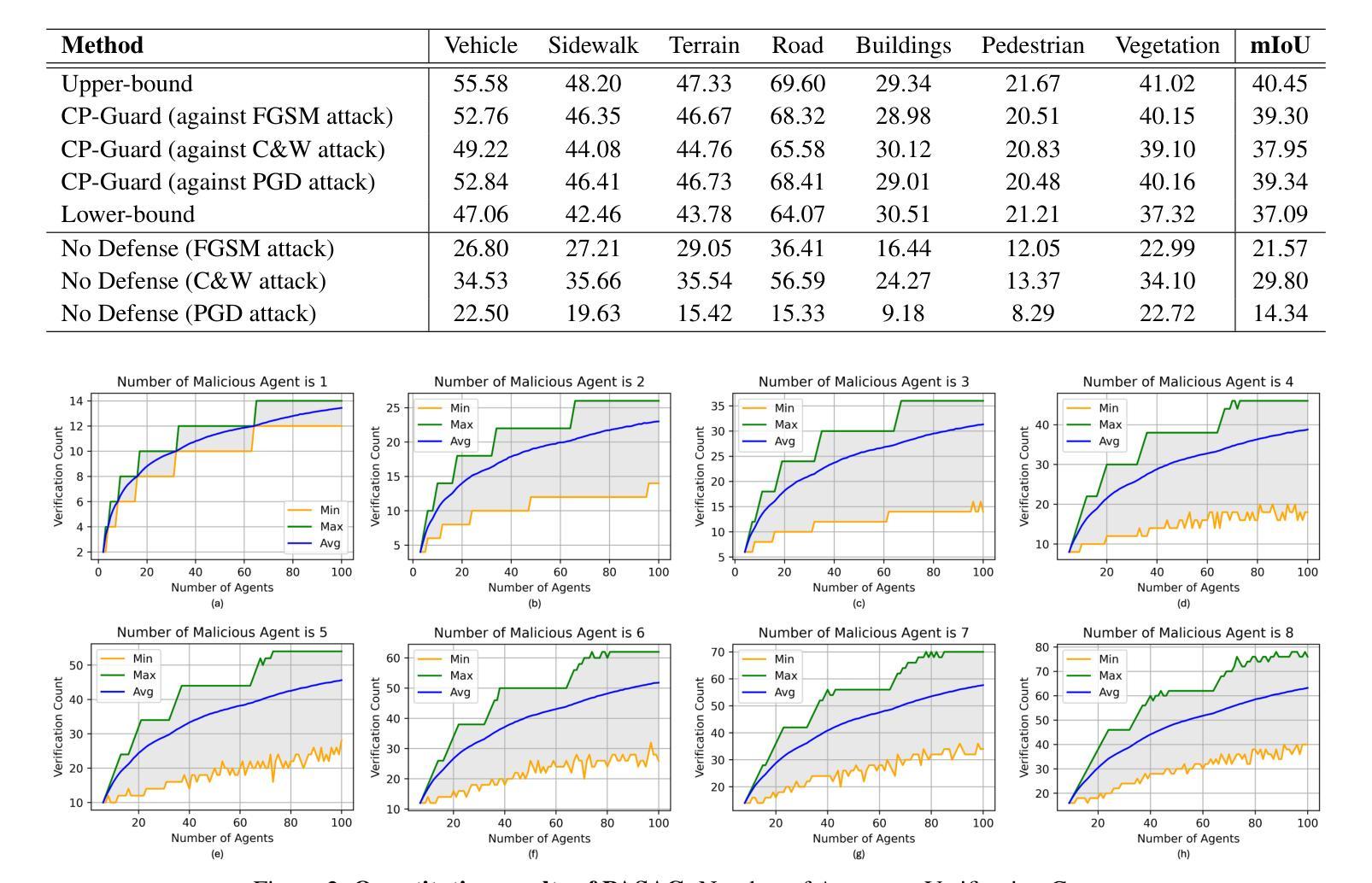
CP-Guard: Malicious Agent Detection and Defense in Collaborative Bird’s Eye View Perception
Authors:Senkang Hu, Yihang Tao, Guowen Xu, Yiqin Deng, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fang, Sam Kwong
Collaborative Perception (CP) has shown a promising technique for autonomous driving, where multiple connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) share their perception information to enhance the overall perception performance and expand the perception range. However, in CP, ego CAV needs to receive messages from its collaborators, which makes it easy to be attacked by malicious agents. For example, a malicious agent can send harmful information to the ego CAV to mislead it. To address this critical issue, we propose a novel method, CP-Guard, a tailored defense mechanism for CP that can be deployed by each agent to accurately detect and eliminate malicious agents in its collaboration network. Our key idea is to enable CP to reach a consensus rather than a conflict against the ego CAV’s perception results. Based on this idea, we first develop a probability-agnostic sample consensus (PASAC) method to effectively sample a subset of the collaborators and verify the consensus without prior probabilities of malicious agents. Furthermore, we define a collaborative consistency loss (CCLoss) to capture the discrepancy between the ego CAV and its collaborators, which is used as a verification criterion for consensus. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments in collaborative bird’s eye view (BEV) tasks and our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our CP-Guard. Code is available at https://github.com/CP-Security/CP-Guard
协同感知(CP)作为一种自动驾驶的前沿技术,已经展现出广阔的应用前景。在协同感知中,多个互联的自动驾驶车辆(CAVs)共享感知信息,以提高整体的感知性能和扩大感知范围。然而,在协同感知过程中,自我CAV需要从其合作伙伴那里接收信息,这使得它容易受到恶意实体的攻击。例如,恶意实体可能会向自我CAV发送有害信息来误导它。为了解决这一关键问题,我们提出了一种新方法——CP-Guard,这是一种针对协同感知量身定制的防御机制,可以被每个实体部署,以准确检测和消除其协作网络中的恶意实体。我们的核心思想是使协同感知能够达成共识,而不是与自我CAV的感知结果发生冲突。基于这一思想,我们首先开发了一种概率无关的样本共识(PASAC)方法,该方法可以有效地从合作者中抽样一个子集,并在无需恶意实体先验概率的情况下验证共识。此外,我们定义了一个协作一致性损失(CCLoss),以捕捉自我CAV与其合作伙伴之间的差异,并将其用作共识验证的标准。最后,我们在协同鸟瞰视图(BEV)任务中进行了大量实验,实验结果证明了我们的CP-Guard的有效性。相关代码可在https://github.com/CP-Security/CP-Guard找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI’25
Summary
多智能体协同感知技术(CP)在自动驾驶领域展现出巨大潜力,该技术通过多个互联的自动驾驶车辆(CAVs)共享感知信息提升整体感知性能和扩大感知范围。然而,协同感知易受恶意攻击干扰。为此,我们提出了一种新方法CP-Guard,它是一种针对协同感知的防御机制,能够准确检测和消除合作网络中的恶意智能体。其核心思想是通过达成共识而非冲突对抗车辆自身感知结果。基于这一思想,我们发展了概率无关的样本共识(PASAC)方法,并定义了协同一致性损失(CCLoss)作为共识验证标准。实验证明,CP-Guard在协同鸟瞰视图任务中效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 协同感知技术(CP)在自动驾驶领域应用前景广阔,通过多智能体信息共享提升感知性能和扩大感知范围。
- 协同感知技术面临恶意攻击风险,可能导致车辆被误导。
- CP-Guard是一种针对协同感知的防御机制,可准确检测和消除合作网络中的恶意智能体。
- CP-Guard的核心思想是通过达成共识而非冲突对抗车辆自身感知结果。
- CP-Guard采用概率无关的样本共识(PASAC)方法验证共识。
- 协同一致性损失(CCLoss)被用作CP-Guard的共识验证标准。
点此查看论文截图