⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
RestoreVAR: Visual Autoregressive Generation for All-in-One Image Restoration
Authors:Sudarshan Rajagopalan, Kartik Narayan, Vishal M. Patel
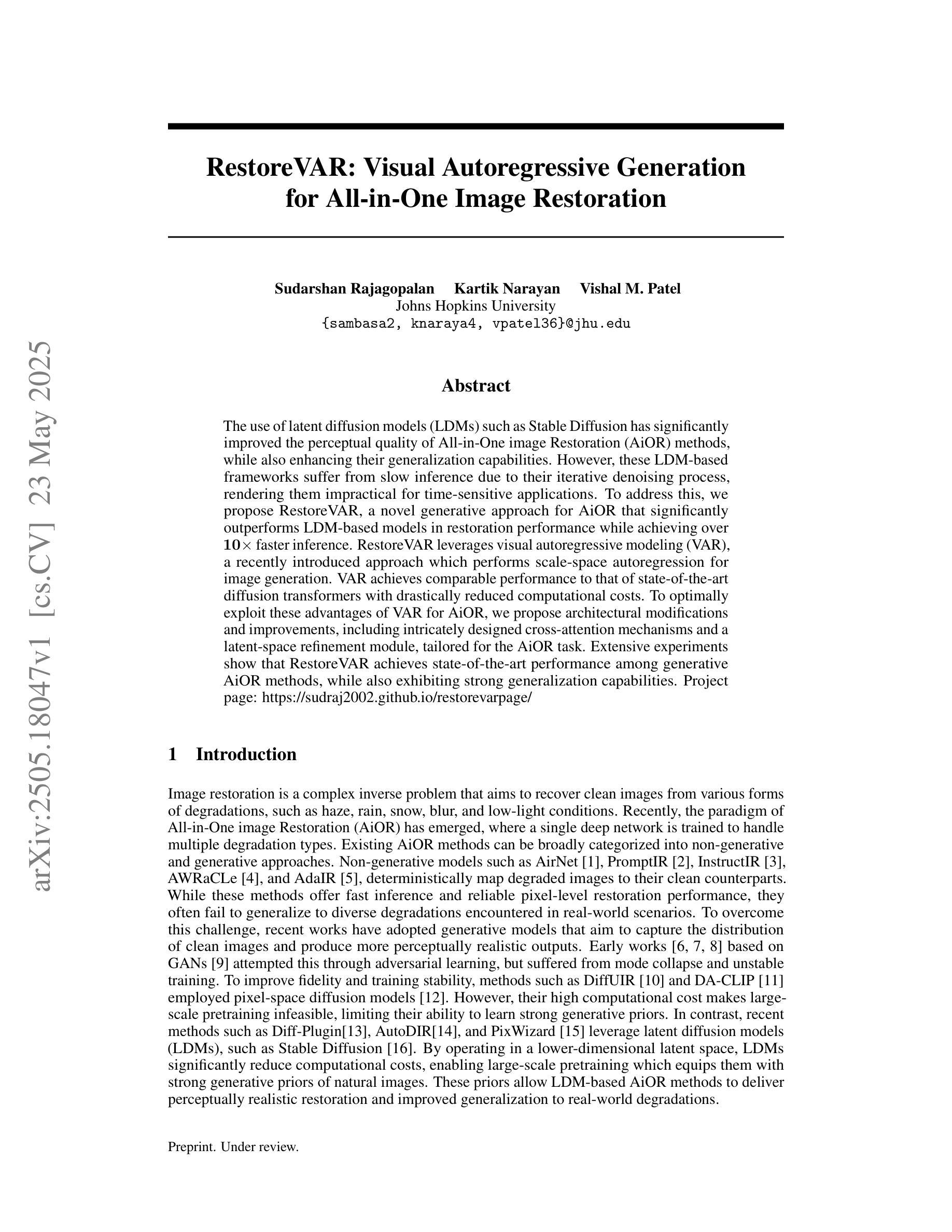
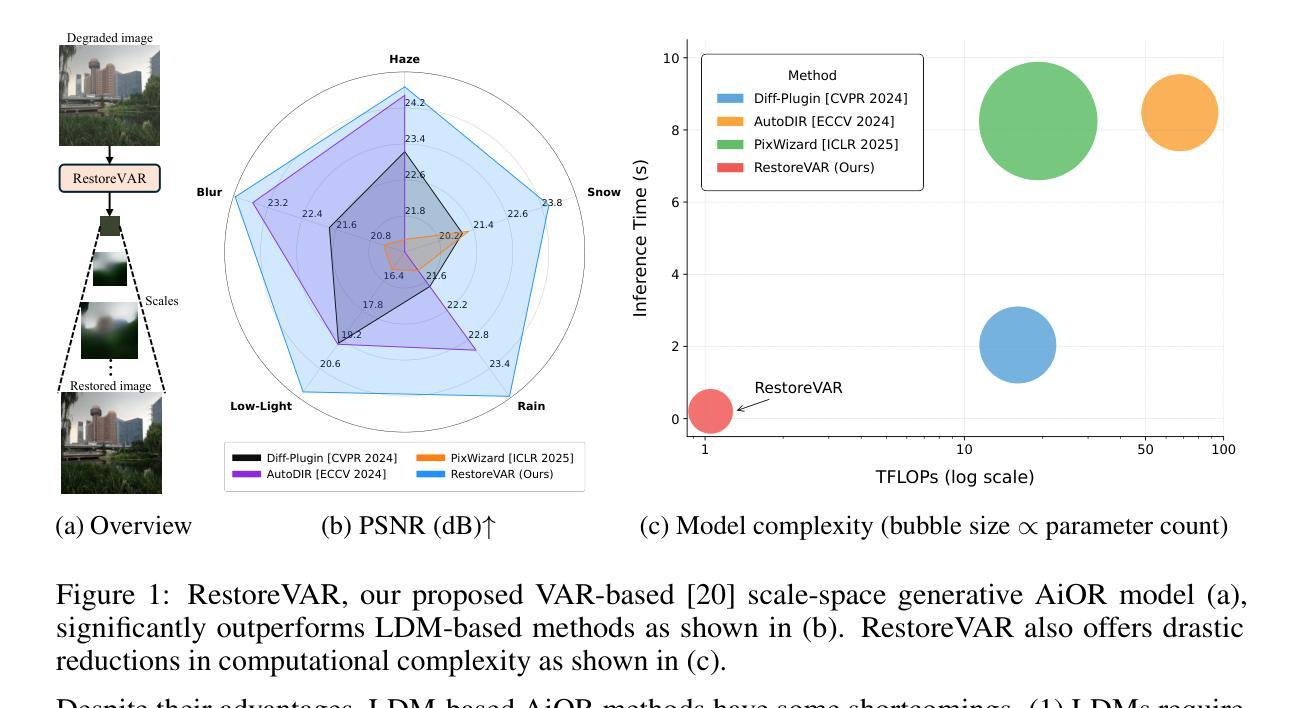
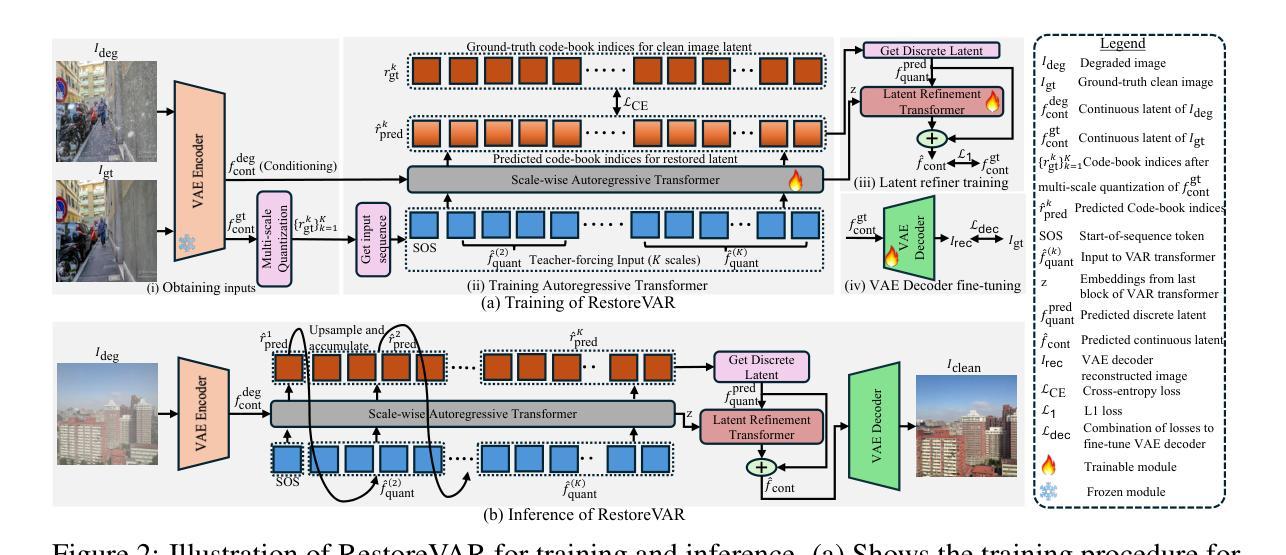
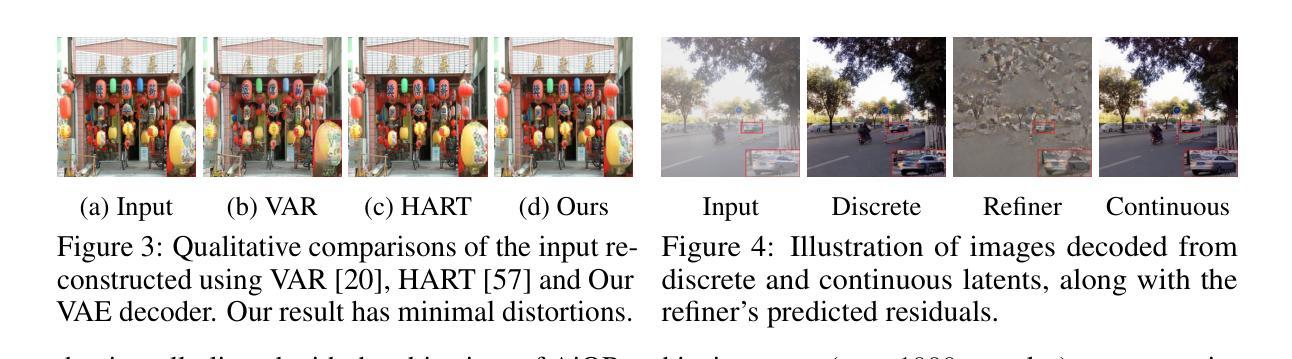
The use of latent diffusion models (LDMs) such as Stable Diffusion has significantly improved the perceptual quality of All-in-One image Restoration (AiOR) methods, while also enhancing their generalization capabilities. However, these LDM-based frameworks suffer from slow inference due to their iterative denoising process, rendering them impractical for time-sensitive applications. To address this, we propose RestoreVAR, a novel generative approach for AiOR that significantly outperforms LDM-based models in restoration performance while achieving over $\mathbf{10\times}$ faster inference. RestoreVAR leverages visual autoregressive modeling (VAR), a recently introduced approach which performs scale-space autoregression for image generation. VAR achieves comparable performance to that of state-of-the-art diffusion transformers with drastically reduced computational costs. To optimally exploit these advantages of VAR for AiOR, we propose architectural modifications and improvements, including intricately designed cross-attention mechanisms and a latent-space refinement module, tailored for the AiOR task. Extensive experiments show that RestoreVAR achieves state-of-the-art performance among generative AiOR methods, while also exhibiting strong generalization capabilities.
使用如Stable Diffusion之类的潜在扩散模型(LDM)已经显著提高了全合一图像恢复(AiOR)方法的感知质量,并增强了其泛化能力。然而,这些基于LDM的框架由于迭代去噪过程而导致推理速度较慢,对于时间敏感的应用程序来说并不实用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了RestoreVAR,这是一种新的用于AiOR的生成方法,在恢复性能上显著优于基于LDM的模型,同时实现了超过10倍的更快推理速度。RestoreVAR利用视觉自回归建模(VAR),这是一种最近推出的方法,用于执行尺度空间自回归以生成图像。VAR以大幅降低的计算成本实现了与国家最先进的扩散变压器相当的性能。为了充分利用VAR在AiOR中的这些优势,我们提出了架构修改和改进,包括精心设计用于AiOR任务的交叉注意机制和潜在空间细化模块。大量实验表明,RestoreVAR在生成AiOR方法中实现了最先进的性能,同时表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://sudraj2002.github.io/restorevarpage/
Summary
基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)如Stable Diffusion的应用已显著提高了一站式图像恢复(AiOR)方法的感知质量及其泛化能力。然而,这些LDM框架由于迭代去噪过程而导致推理速度较慢,不适合时间敏感型应用。为解决这一问题,我们提出了RestoreVAR,这是一种新型的AiOR生成方法,在恢复性能方面显著优于LDM模型,同时实现超过10倍加速推理。RestoreVAR利用视觉自回归建模(VAR),这是一种最近推出的图像生成尺度空间自回归方法,以较低的计算成本实现了与国家先进扩散变压器相当的性能。为了充分利用VAR在AiOR任务中的优势,我们提出了结构修改和改进,包括精心设计交叉注意机制和针对AiOR任务的潜在空间细化模块。大量实验表明,RestoreVAR在生成AiOR方法中达到最新技术水平,同时表现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- LDM模型如Stable Diffusion提升了AiOR方法的感知质量和泛化能力。
- LDM框架存在推理速度慢的问题,不适合时间敏感型应用。
- RestoreVAR是一种新型的AiOR生成方法,显著优于LDM模型,实现超过10倍加速推理。
- RestoreVAR利用视觉自回归建模(VAR),以较低的计算成本实现了与国家先进扩散变压器相当的性能。
- 为充分利用VAR在AiOR中的优势,进行了结构修改和改进,包括交叉注意机制和潜在空间细化模块的设计。
- RestoreVAR在生成AiOR方法中表现优秀,达到最新技术水平。
- RestoreVAR展现出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
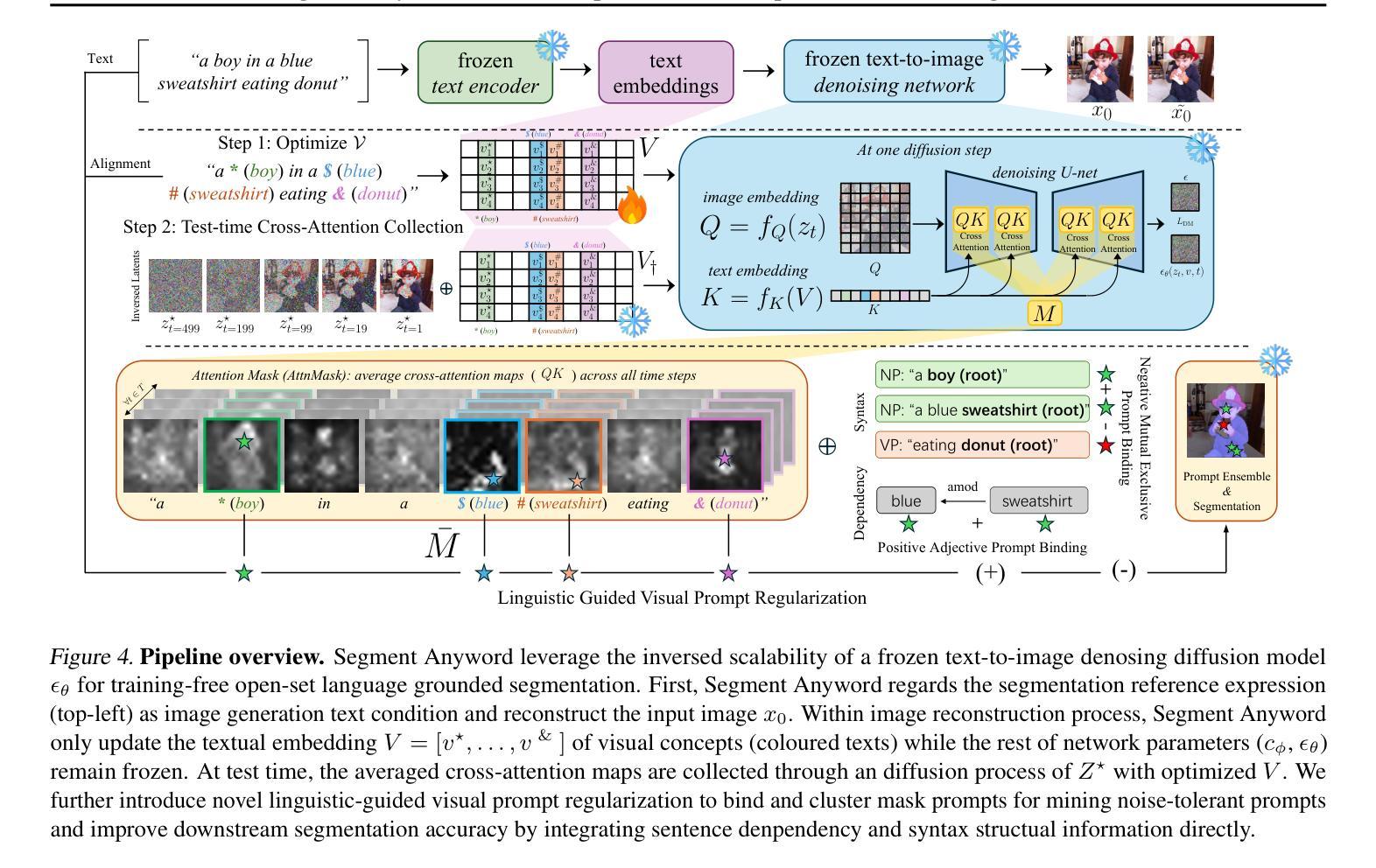
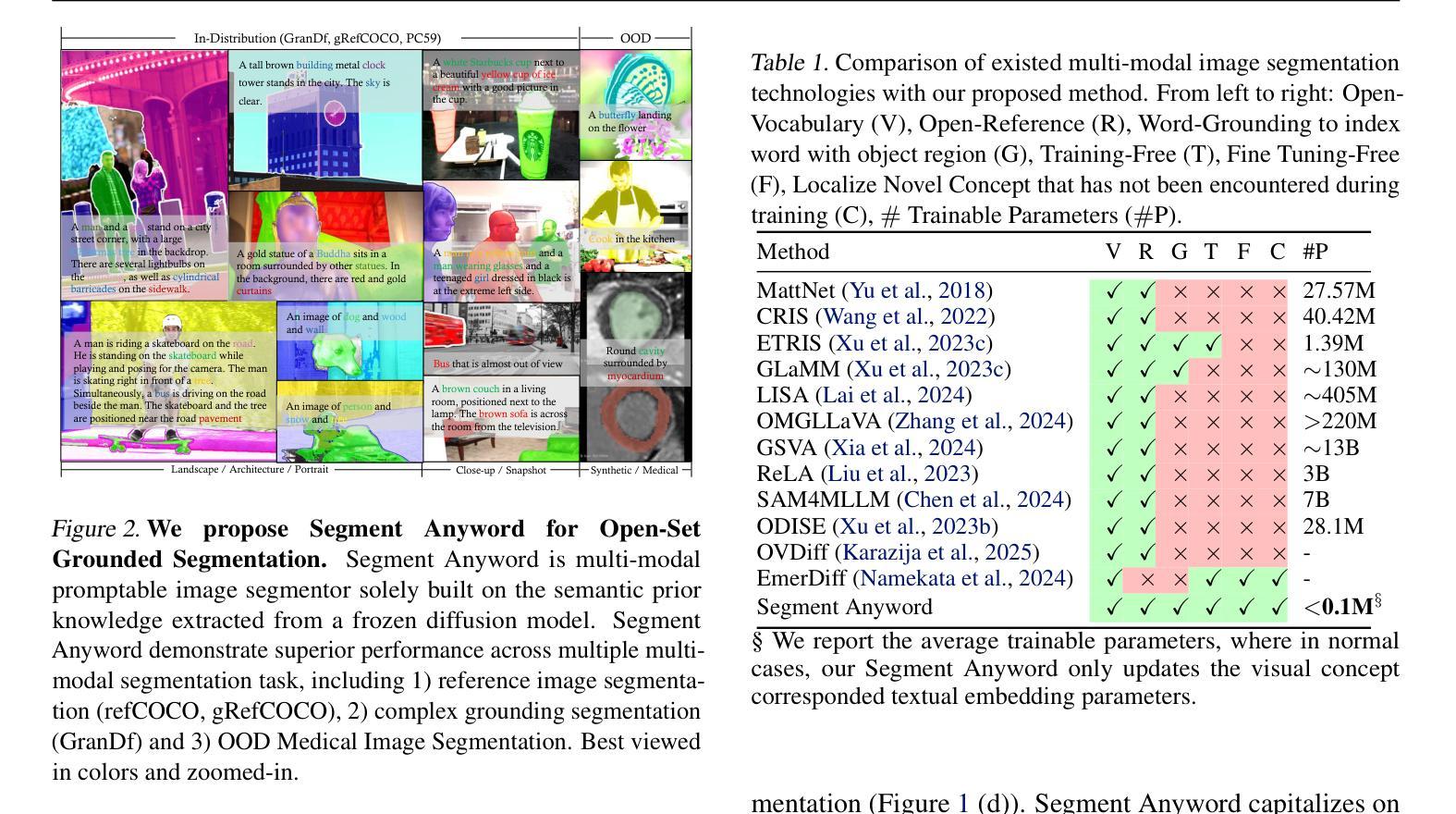
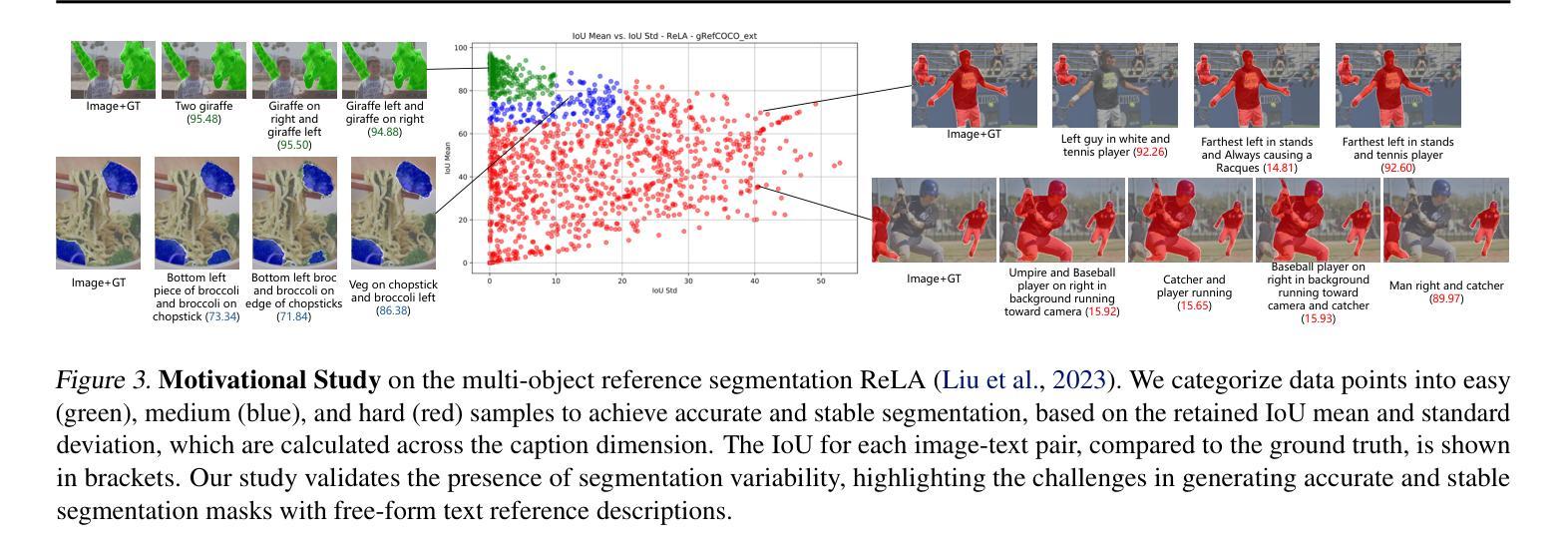
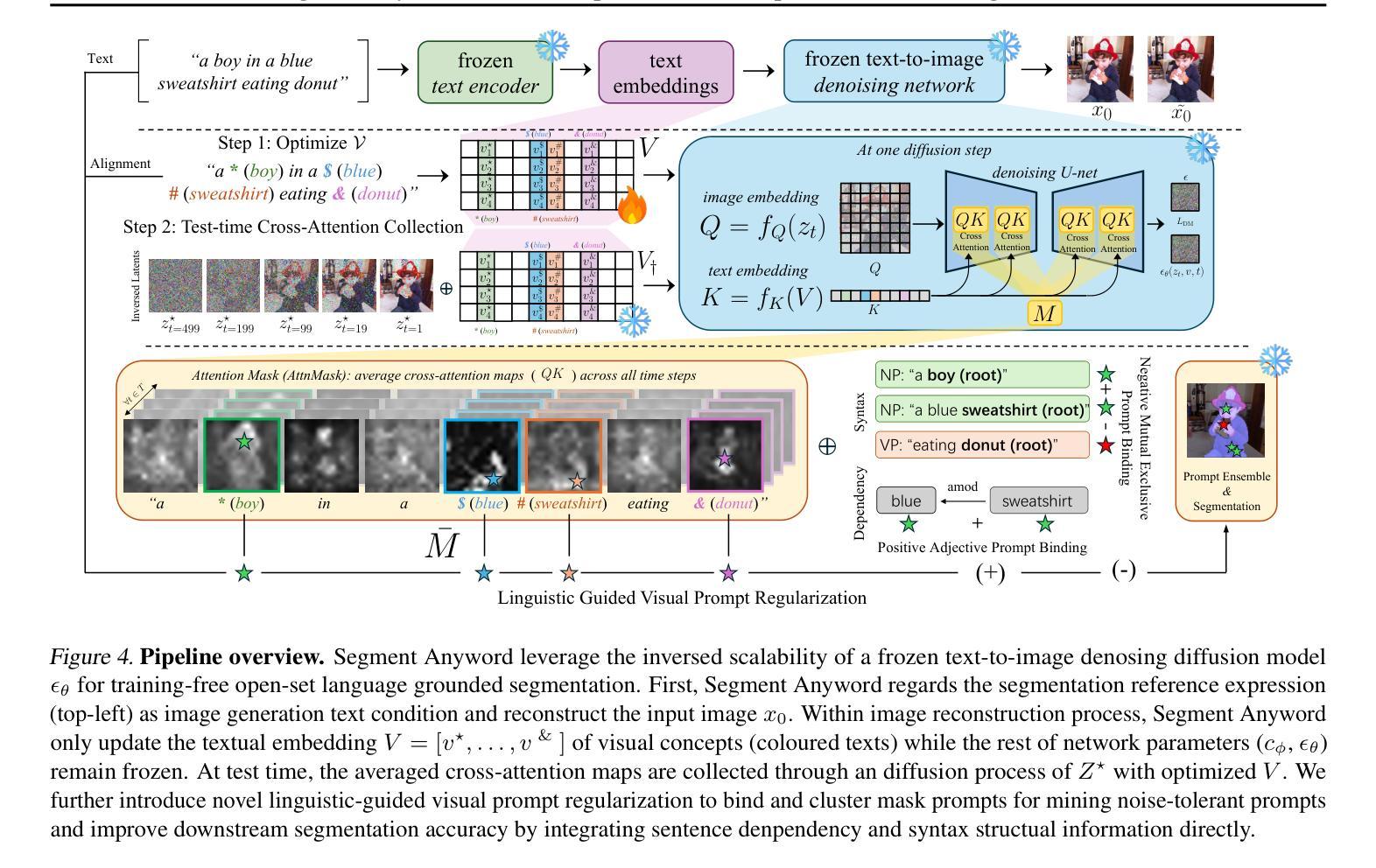
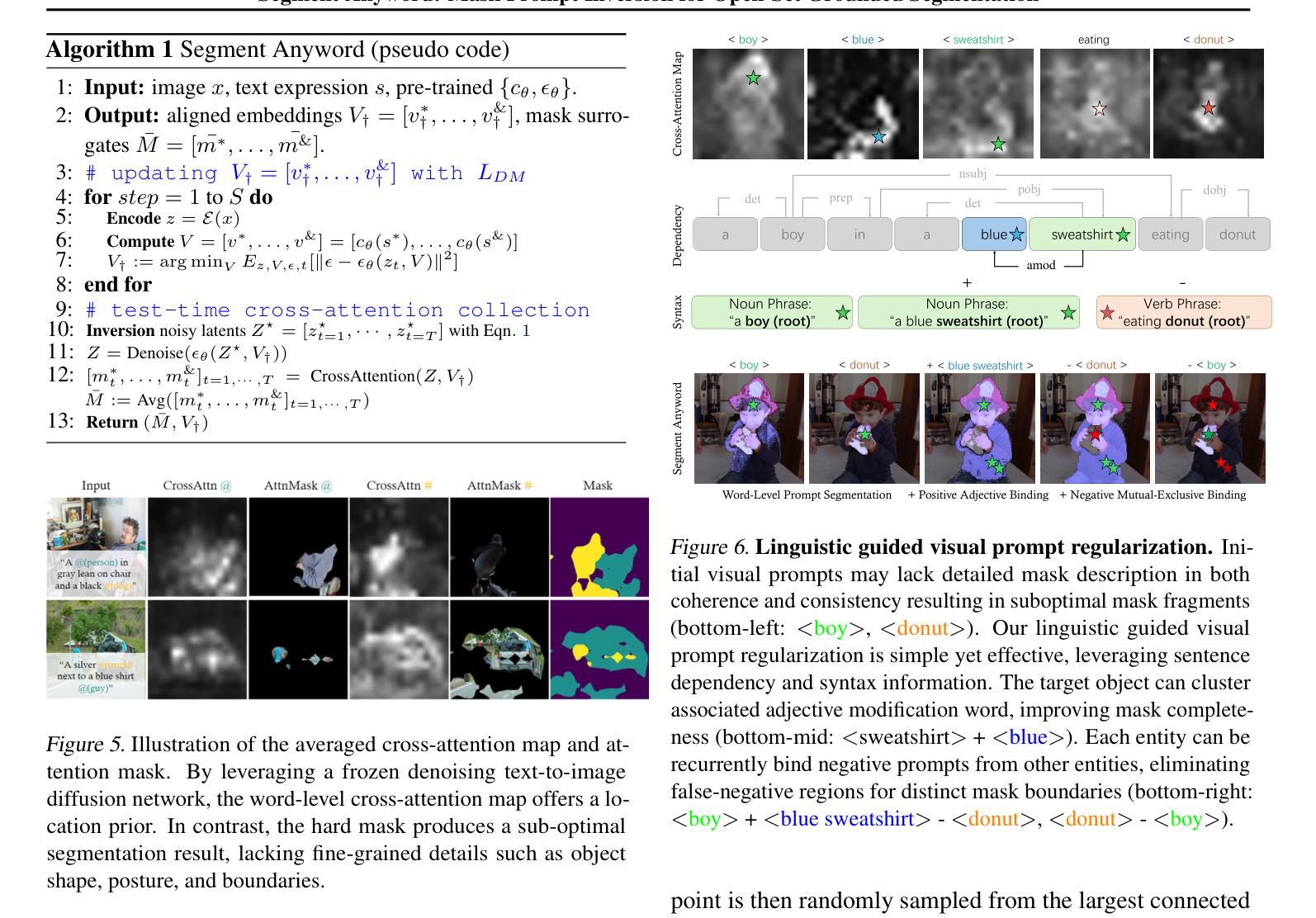
Segment Anyword: Mask Prompt Inversion for Open-Set Grounded Segmentation
Authors:Zhihua Liu, Amrutha Saseendran, Lei Tong, Xilin He, Fariba Yousefi, Nikolay Burlutskiy, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Huiyu Zhou, Chen Jin
Open-set image segmentation poses a significant challenge because existing methods often demand extensive training or fine-tuning and generally struggle to segment unified objects consistently across diverse text reference expressions. Motivated by this, we propose Segment Anyword, a novel training-free visual concept prompt learning approach for open-set language grounded segmentation that relies on token-level cross-attention maps from a frozen diffusion model to produce segmentation surrogates or mask prompts, which are then refined into targeted object masks. Initial prompts typically lack coherence and consistency as the complexity of the image-text increases, resulting in suboptimal mask fragments. To tackle this issue, we further introduce a novel linguistic-guided visual prompt regularization that binds and clusters visual prompts based on sentence dependency and syntactic structural information, enabling the extraction of robust, noise-tolerant mask prompts, and significant improvements in segmentation accuracy. The proposed approach is effective, generalizes across different open-set segmentation tasks, and achieves state-of-the-art results of 52.5 (+6.8 relative) mIoU on Pascal Context 59, 67.73 (+25.73 relative) cIoU on gRefCOCO, and 67.4 (+1.1 relative to fine-tuned methods) mIoU on GranDf, which is the most complex open-set grounded segmentation task in the field.
开放集图像分割构成了一个重大挑战,因为现有方法通常需要大量的训练或微调,并且在处理跨不同文本参考表达的一致对象分割时通常遇到困难。为此,我们提出了Segment Anyword,这是一种新型的无训练视觉概念提示学习方法,用于基于开放集语言的分割。该方法依赖于冻结的扩散模型的令牌级跨注意力图来生成分割代理或掩膜提示,然后将其细化为目标对象掩膜。随着图像文本复杂性的增加,初始提示通常缺乏连贯性和一致性,导致掩膜片段不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们进一步引入了一种新型的语言引导的视觉提示正则化方法,该方法根据句子依赖关系和句法结构信息来绑定和聚类视觉提示,从而提取出稳健、抗干扰的掩膜提示,并显著提高分割精度。所提出的方法效果显著,可应用于不同的开放集分割任务,并在Pascal Context 59上达到了52.5(+6.8相对)mIoU,在gRefCOCO上达到了67.73(+25.73相对)cIoU,以及在领域中最复杂的开放集基于语言的分割任务GranDf上达到了67.4(+相对于微调方法的1.1)mIoU。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种无需训练的新型视觉概念提示学习方法——Segment Anyword,用于开放式语言基础分割。该方法利用冻结的扩散模型的令牌级跨注意力图生成分割替代者或掩膜提示,并进行细化以形成目标对象掩膜。为解决初始提示缺乏连贯性和一致性的问题,引入了一种新型的语言引导视觉提示正则化方法,根据句子依赖和句法结构信息对视觉提示进行绑定和聚类,提高了掩膜提示的鲁棒性和噪声耐受性,以及分割精度。该方法有效、通用,并在多个开放式分割任务上达到最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anyword是一种新型训练免费的视觉概念提示学习方法,用于开放式语言基础分割。
- 该方法利用扩散模型的令牌级跨注意力图生成分割替代者或掩膜提示。
- 初始提示缺乏连贯性和一致性,因此引入语言引导的视觉提示正则化。
- 该方法根据句子依赖和句法结构信息对视觉提示进行绑定和聚类。
- 该方法提高了掩膜提示的鲁棒性和噪声耐受性。
- Segment Anyword方法在多个开放式分割任务上达到最佳结果,包括Pascal Context 59、gRefCOCO和GranDf。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Classifiers Understand Compositionality, but Conditions Apply
Authors:Yujin Jeong, Arnas Uselis, Seong Joon Oh, Anna Rohrbach
Understanding visual scenes is fundamental to human intelligence. While discriminative models have significantly advanced computer vision, they often struggle with compositional understanding. In contrast, recent generative text-to-image diffusion models excel at synthesizing complex scenes, suggesting inherent compositional capabilities. Building on this, zero-shot diffusion classifiers have been proposed to repurpose diffusion models for discriminative tasks. While prior work offered promising results in discriminative compositional scenarios, these results remain preliminary due to a small number of benchmarks and a relatively shallow analysis of conditions under which the models succeed. To address this, we present a comprehensive study of the discriminative capabilities of diffusion classifiers on a wide range of compositional tasks. Specifically, our study covers three diffusion models (SD 1.5, 2.0, and, for the first time, 3-m) spanning 10 datasets and over 30 tasks. Further, we shed light on the role that target dataset domains play in respective performance; to isolate the domain effects, we introduce a new diagnostic benchmark Self-Bench comprised of images created by diffusion models themselves. Finally, we explore the importance of timestep weighting and uncover a relationship between domain gap and timestep sensitivity, particularly for SD3-m. To sum up, diffusion classifiers understand compositionality, but conditions apply! Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/eugene6923/Diffusion-Classifiers-Compositionality.
理解视觉场景对人类智能至关重要。虽然判别模型在计算机视觉领域取得了显著进展,但在组合理解方面常常遇到困难。相比之下,最近的文本到图像的生成扩散模型在合成复杂场景方面表现出色,这表明其具有内在的组成能力。基于此,零样本扩散分类器被提出用于将扩散模型重新用于判别任务。虽然先前的工作在判别组合场景方面提供了有前景的结果,但由于基准测试的数量有限以及对模型成功的条件分析相对肤浅,这些结果仍然是初步的。为了解决这一问题,我们对扩散分类器在广泛组合任务上的判别能力进行了综合研究。具体来说,我们的研究涵盖了三个扩散模型(SD 1.5、2.0和首次推出的3-m),涉及10个数据集和30多个任务。此外,我们阐明了目标数据集领域对各自性能的作用;为了隔离领域效应,我们推出了一个新的诊断基准Self-Bench,由扩散模型本身创建的图像组成。最后,我们探讨了时间步长权重的重要性,并揭示了领域差距与时间步长敏感性之间的关系,特别是针对SD3-m。总之,扩散分类器能够理解组合性,但条件适用!相关代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/eugene6923/Diffusion-Classifiers-Compositionality获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视觉场景的理解对人类智能至关重要。虽然判别模型在计算机视觉领域取得了显著进展,但它们通常在组合理解方面遇到困难。相比之下,最新的文本到图像的生成扩散模型在合成复杂场景方面表现出色,表明其固有的组合能力。基于此,零样本扩散分类器被提出来将扩散模型用于判别任务。虽然先前的工作在判别组合场景中提供了有前景的结果,但由于基准测试的数量相对较少,以及对模型成功条件的分析相对肤浅,这些结果仍是初步的。为了解决这一问题,我们对扩散分类器在广泛组合任务上的判别能力进行了深入研究。具体地,我们的研究涵盖了三个扩散模型(SD 1.5、2.0和首次推出的3-m),涉及10个数据集和超过30个任务。此外,我们阐明了目标数据集领域在各自性能中的作用;为了隔离领域效应,我们推出了一个新的诊断基准Self-Bench,由扩散模型本身创建的图像组成。最后,我们探讨了时间步长权重的重要性,并揭示了领域差距与时间步长敏感性之间的关系,特别是针对SD3-m。总之,扩散分类器理解组合性,但条件适用!相关代码和数据集可在https://github.com/eugene6923/Diffusion-Classifiers-Compositionality找到。
要点
- 扩散模型在计算机视觉领域具有出色的合成复杂场景能力,表现出其固有的组合特性。
- 零样本扩散分类器被提出用于判别任务,这是基于扩散模型的新的应用方向。
- 当前研究在判别组合场景上的结果仍是初步的,主要由于基准测试数量少和对模型成功条件的分析不够深入。
- 本文对扩散分类器的判别能力进行了全面研究,覆盖了多个扩散模型和任务。
- 深入探讨了目标数据集领域对模型性能的影响,并推出了新的诊断基准Self-Bench。
- 研究了时间步长权重的重要性,并揭示了领域差距与时间步长敏感性之间的关系。
- 扩散分类器虽然理解组合性,但应用条件需考虑。
点此查看论文截图


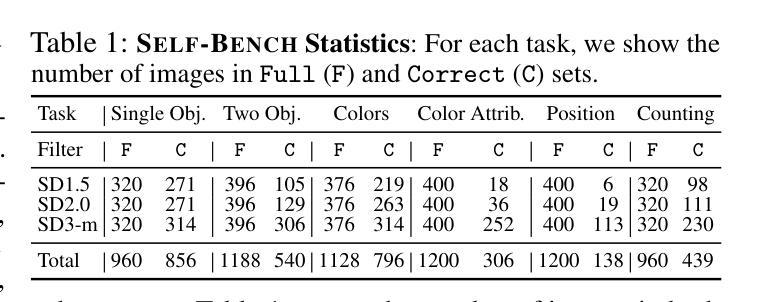
T2VUnlearning: A Concept Erasing Method for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Xiaoyu Ye, Songjie Cheng, Yongtao Wang, Yajiao Xiong, Yishen Li
Recent advances in text-to-video (T2V) diffusion models have significantly enhanced the quality of generated videos. However, their ability to produce explicit or harmful content raises concerns about misuse and potential rights violations. Inspired by the success of unlearning techniques in erasing undesirable concepts from text-to-image (T2I) models, we extend unlearning to T2V models and propose a robust and precise unlearning method. Specifically, we adopt negatively-guided velocity prediction fine-tuning and enhance it with prompt augmentation to ensure robustness against LLM-refined prompts. To achieve precise unlearning, we incorporate a localization and a preservation regularization to preserve the model’s ability to generate non-target concepts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively erases a specific concept while preserving the model’s generation capability for all other concepts, outperforming existing methods. We provide the unlearned models in \href{https://github.com/VDIGPKU/T2VUnlearning.git}{https://github.com/VDIGPKU/T2VUnlearning.git}.
近期文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型的进步极大地提高了生成视频的质量。然而,它们产生明确或有害内容的能力引发了关于误用和潜在权利侵犯的担忧。受文本到图像(T2I)模型中消除不良概念的去学习技术成功的启发,我们将去学习扩展到T2V模型,并提出了一种稳健且精确的去学习方法。具体来说,我们采用负导向速度预测微调,并通过提示增强来确保其对大型语言模型优化提示的稳健性。为了实现精确的去学习,我们结合了定位和保存正则化,以保留模型生成非目标概念的能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法在消除特定概念的同时,保留了模型对所有其他概念的生成能力,优于现有方法。我们提供去学习的模型在https://github.com/VDIGPKU/T2VUnlearning.git。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了近期文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型的进展,这些模型生成视频的质量得到了显著提升。然而,它们产生明确或有害内容的能力引发了关于误用和潜在权利侵犯的担忧。受文本到图像(T2I)模型中的去遗忘技术成功的启发,研究团队将去遗忘技术扩展到T2V模型,并提出了一种稳健且精确的去遗忘方法。该方法采用负导向速度预测微调,并通过提示增强技术来提高对大型语言模型优化提示的稳健性。为实现精确去遗忘,研究团队引入了定位和保护正则化来保留模型生成非目标概念的能力。实验证明,该方法在消除特定概念的同时,保留了模型对其他所有概念的生成能力,优于现有方法。研究团队提供了遗忘模型在GitHub上的链接:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型的最新进展显著提高了生成视频的质量。
- T2V模型产生有害内容的能力引发了对误用和潜在权利侵犯的担忧。
- 受文本到图像(T2I)模型去遗忘技术成功的启发,研究团队将其扩展到T2V模型。
- 提出了一种新的稳健且精确的去遗忘方法,包括负导向速度预测微调、提示增强、定位和保护正则化等技术。
- 实验证明该方法在消除特定概念的同时,能够保留模型对其他概念的生成能力。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

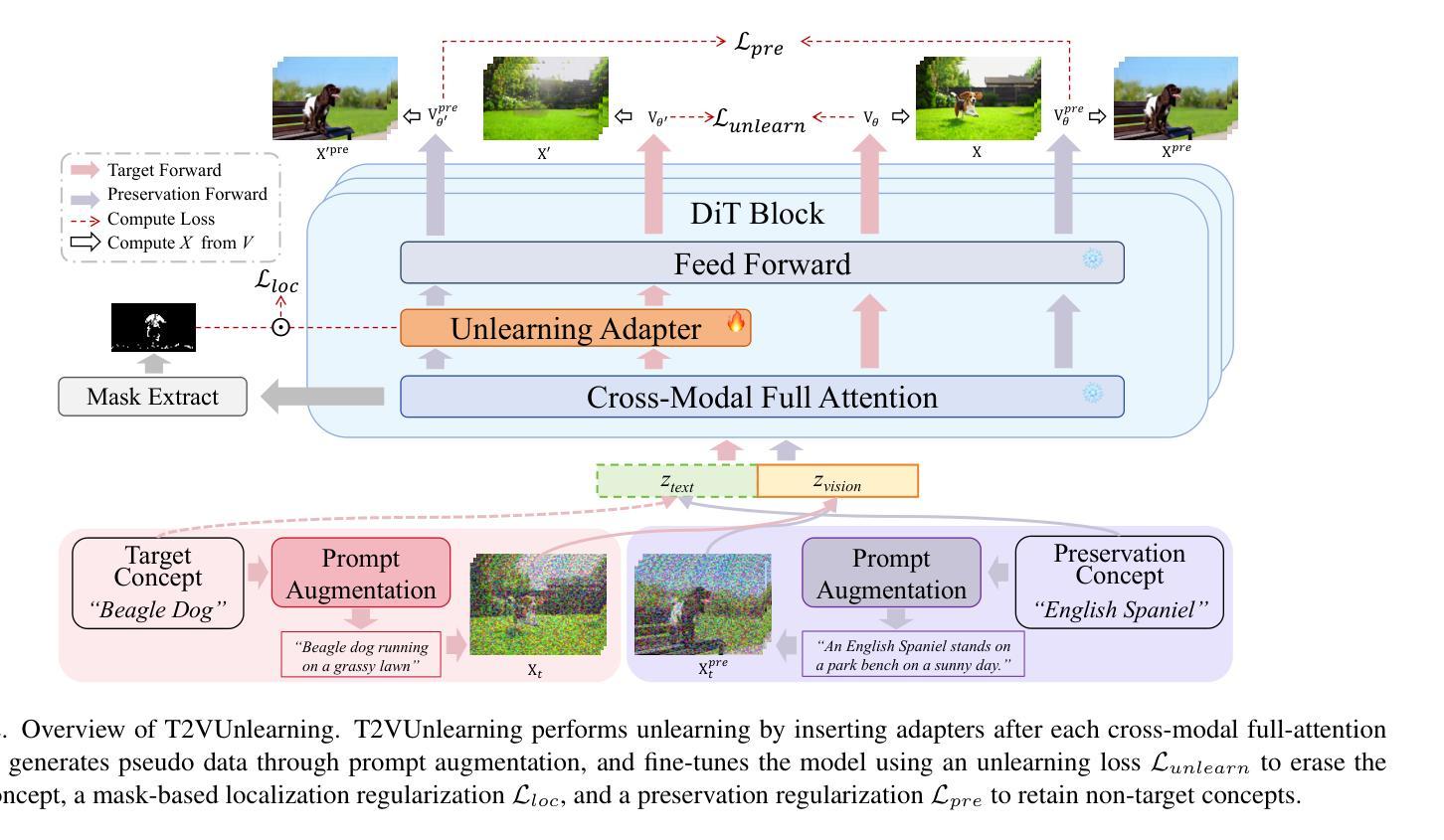
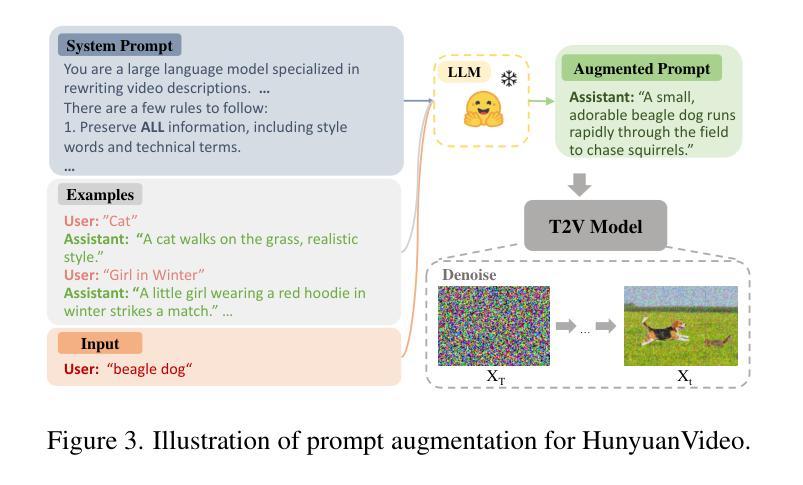
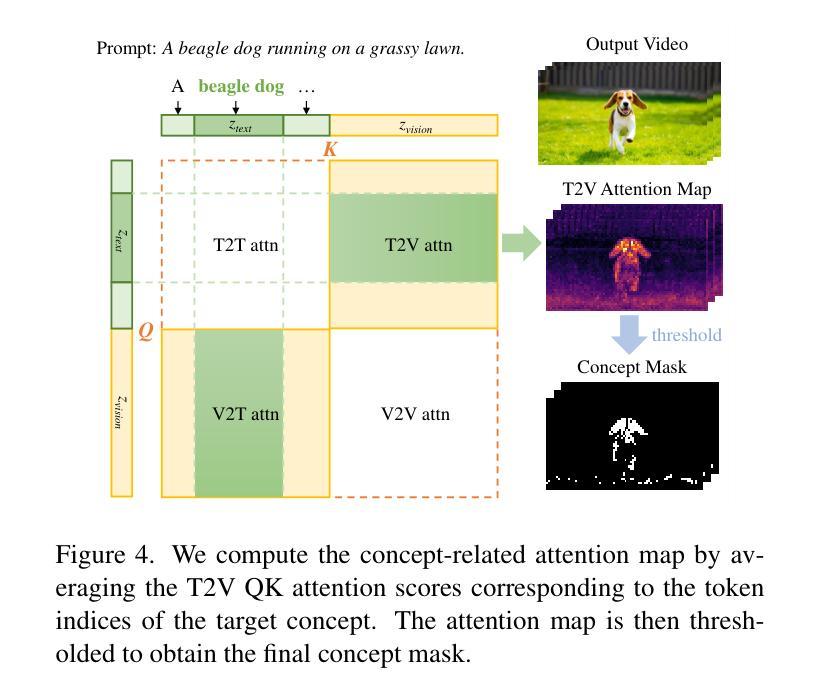
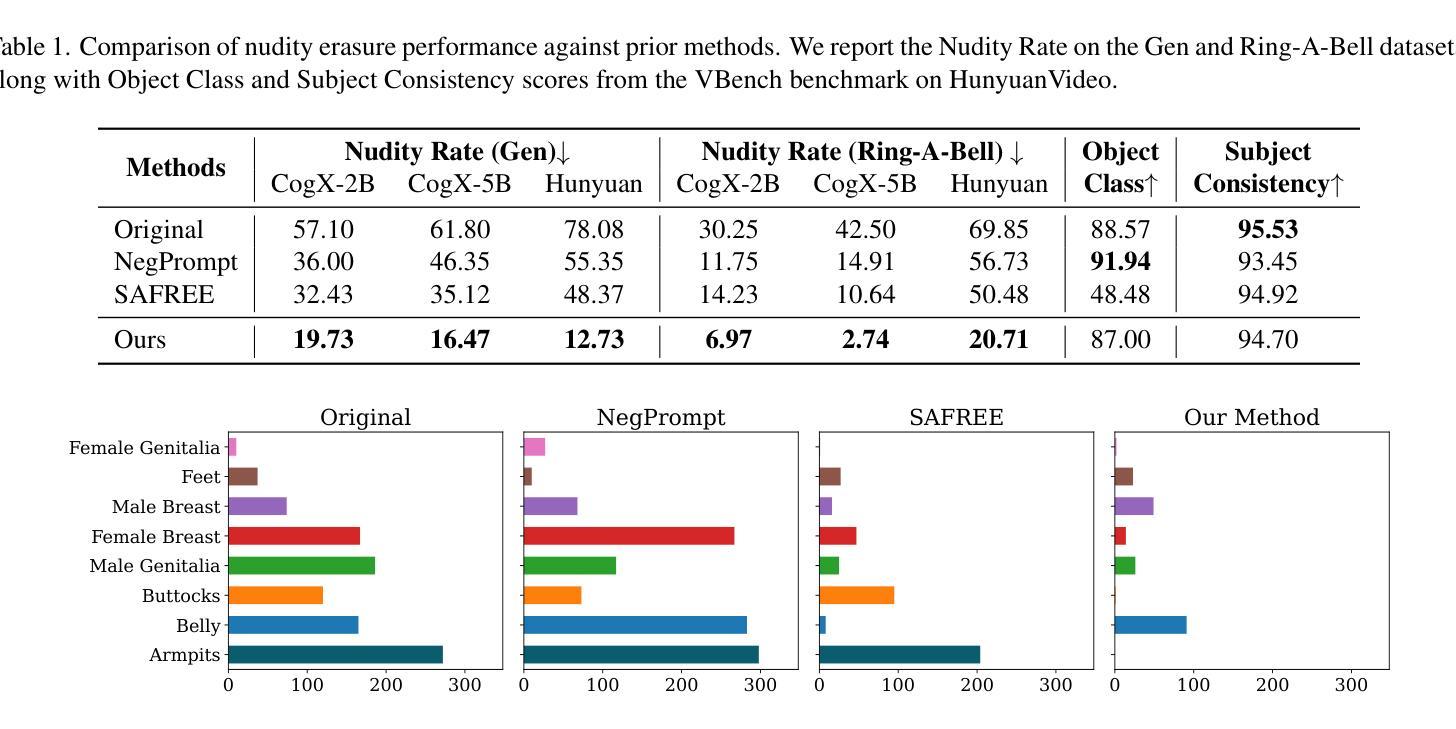
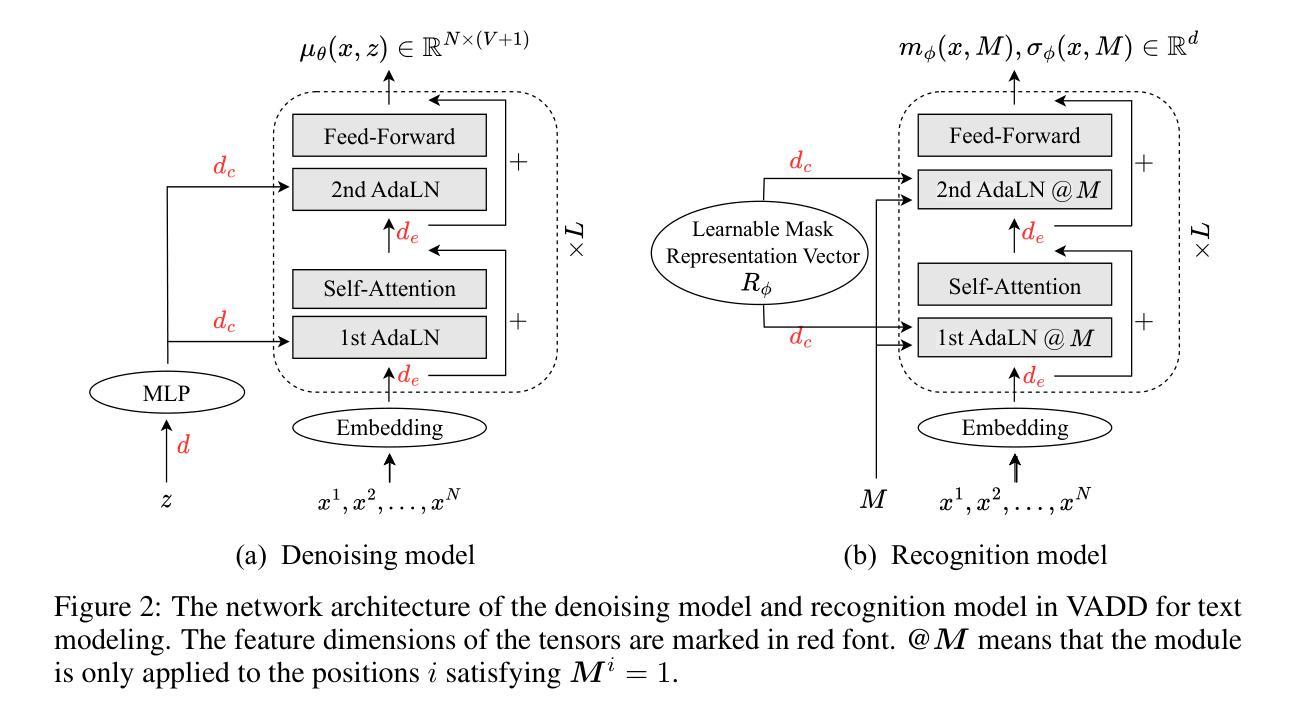
Variational Autoencoding Discrete Diffusion with Enhanced Dimensional Correlations Modeling
Authors:Tianyu Xie, Shuchen Xue, Zijin Feng, Tianyang Hu, Jiacheng Sun, Zhenguo Li, Cheng Zhang
Discrete diffusion models have recently shown great promise for modeling complex discrete data, with masked diffusion models (MDMs) offering a compelling trade-off between quality and generation speed. MDMs denoise by progressively unmasking multiple dimensions from an all-masked input, but their performance can degrade when using few denoising steps due to limited modeling of inter-dimensional dependencies. In this paper, we propose Variational Autoencoding Discrete Diffusion (VADD), a novel framework that enhances discrete diffusion with latent variable modeling to implicitly capture correlations among dimensions. By introducing an auxiliary recognition model, VADD enables stable training via variational lower bounds maximization and amortized inference over the training set. Our approach retains the efficiency of traditional MDMs while significantly improving sample quality, especially when the number of denoising steps is small. Empirical results on 2D toy data, pixel-level image generation, and text generation demonstrate that VADD consistently outperforms MDM baselines.
离散扩散模型最近在模拟复杂离散数据方面显示出巨大潜力,其中遮罩扩散模型(MDM)在质量和生成速度之间提供了令人信服的权衡。MDM通过从完全遮罩的输入中逐步去噪多个维度来实现去噪,但由于对维度间依赖性的建模有限,当使用较少的去噪步骤时,其性能可能会下降。在本文中,我们提出了变分自编码离散扩散(VADD)这一新型框架,它通过潜在变量建模增强离散扩散,以隐含地捕获维度之间的相关性。通过引入辅助识别模型,VADD能够通过变分下界最大化和训练集上的摊销推断来实现稳定训练。我们的方法保留了传统MDM的效率,同时显著提高了样本质量,尤其是当去噪步骤数量较少时。在二维玩具数据、像素级图像生成和文本生成方面的经验结果表明,VADD始终优于MDM基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 14 figures
Summary
离散扩散模型在处理复杂离散数据时展现出巨大潜力,其中掩模扩散模型(MDMs)在质量和生成速度之间达到了令人信服的平衡。然而,由于缺少对维度间依赖关系的建模,当使用较少的去噪步骤时,其性能可能会下降。本文提出一种新型框架——变分自编码离散扩散(VADD),通过引入潜在变量建模来捕获维度之间的相关性。此外,通过引入辅助识别模型,VADD能够通过变分下界最大化实现稳定训练,并在训练集上进行摊销推断。该方法保留了传统MDMs的效率,同时显著提高了样本质量,特别是在去噪步骤较少时。实验结果表明,无论是在二维玩具数据、像素级图像生成还是文本生成上,VADD均优于MDMs基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 离散扩散模型在建模复杂离散数据方面展现出巨大潜力。
- 掩模扩散模型(MDMs)在质量和生成速度之间取得了平衡。
- MDMs在较少去噪步骤时性能可能下降,因为缺乏对维度间依赖关系的建模。
- 变分自编码离散扩散(VADD)框架通过引入潜在变量建模来提高离散扩散的性能。
- VADD通过引入辅助识别模型实现了稳定训练,同时通过变分下界最大化进行了摊销推断。
- VADD在保留MDMs效率的同时,显著提高了样本质量,特别是在去噪步骤较少的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

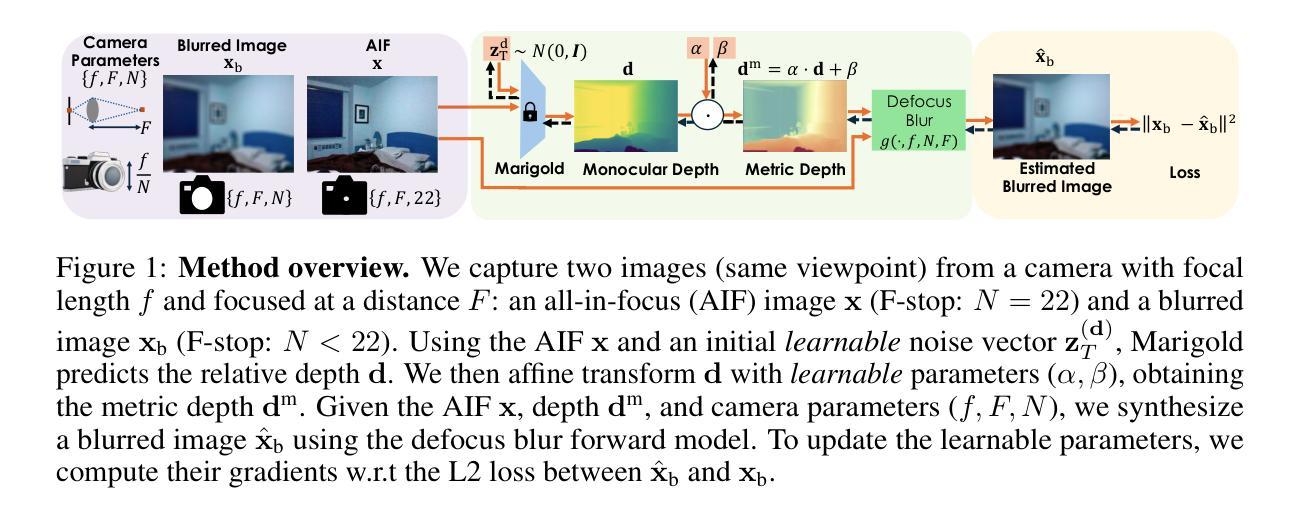
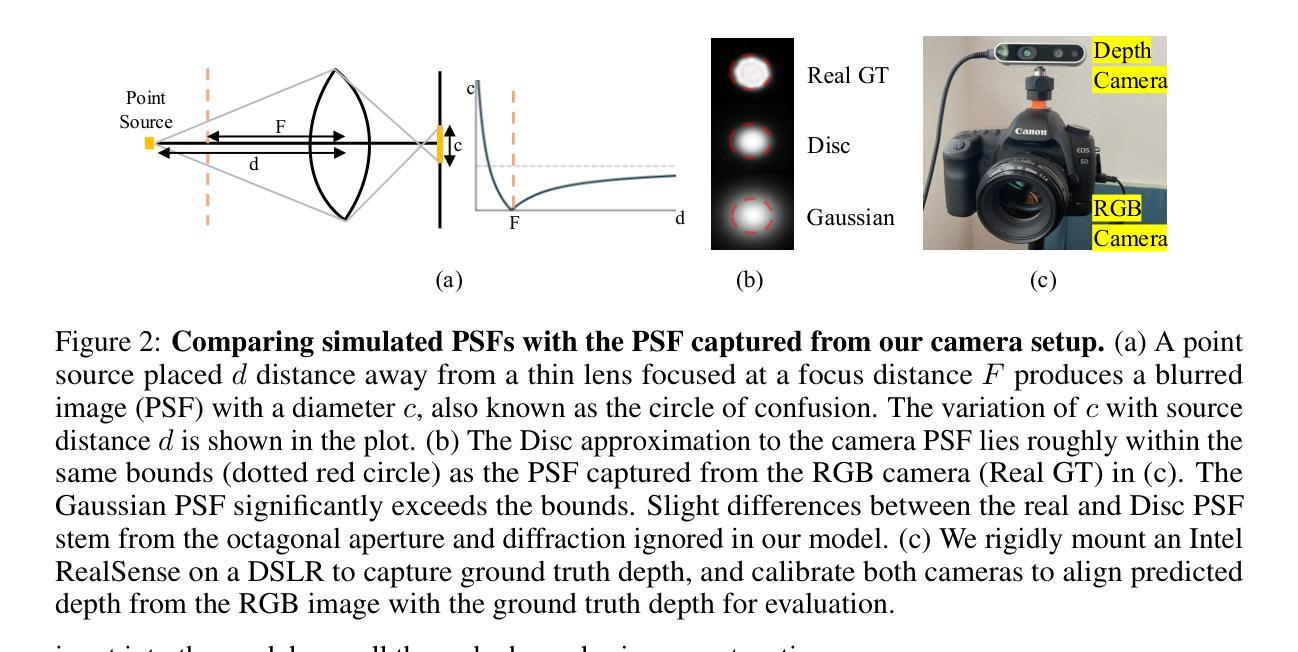
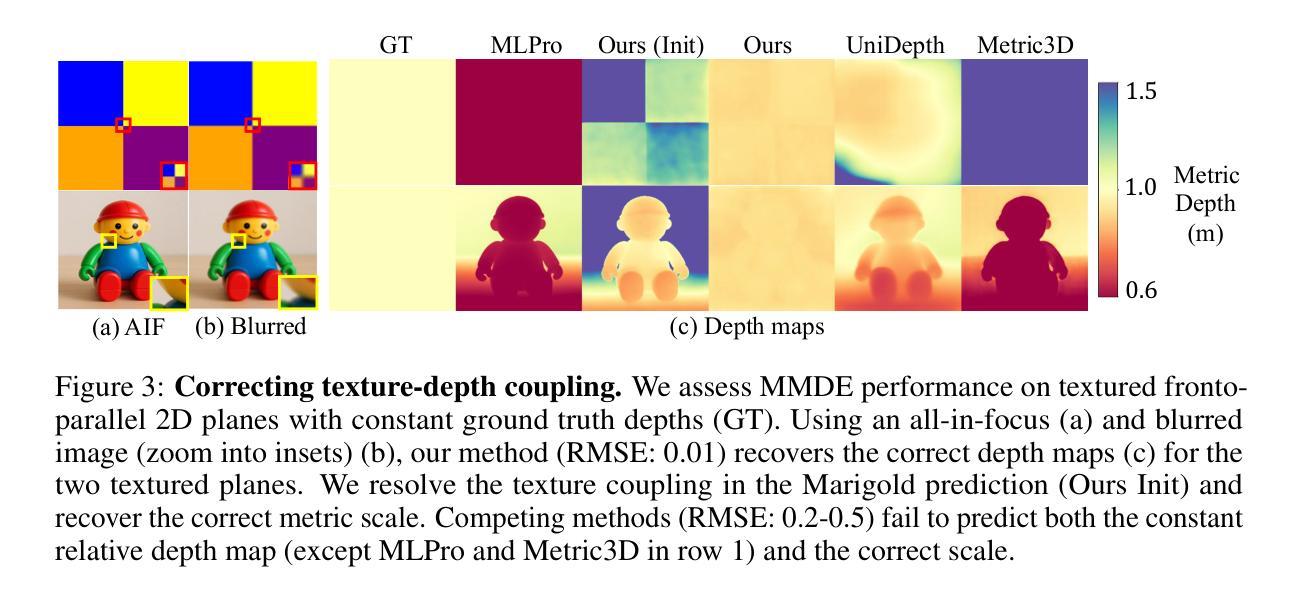
Repurposing Marigold for Zero-Shot Metric Depth Estimation via Defocus Blur Cues
Authors:Chinmay Talegaonkar, Nikhil Gandudi Suresh, Zachary Novack, Yash Belhe, Priyanka Nagasamudra, Nicholas Antipa
Recent monocular metric depth estimation (MMDE) methods have made notable progress towards zero-shot generalization. However, they still exhibit a significant performance drop on out-of-distribution datasets. We address this limitation by injecting defocus blur cues at inference time into Marigold, a \textit{pre-trained} diffusion model for zero-shot, scale-invariant monocular depth estimation (MDE). Our method effectively turns Marigold into a metric depth predictor in a training-free manner. To incorporate defocus cues, we capture two images with a small and a large aperture from the same viewpoint. To recover metric depth, we then optimize the metric depth scaling parameters and the noise latents of Marigold at inference time using gradients from a loss function based on the defocus-blur image formation model. We compare our method against existing state-of-the-art zero-shot MMDE methods on a self-collected real dataset, showing quantitative and qualitative improvements.
近期单眼度量深度估计(MMDE)方法在实现零样本泛化方面取得了显著进展。然而,它们在非分布数据集上仍然表现出显著的性能下降。我们通过推理时向Marigold注入失焦模糊线索来解决这一局限性,Marigold是一个用于零样本、尺度不变的单眼深度估计(MDE)的预训练扩散模型。我们的方法有效地以无训练的方式将Marigold转变为度量深度预测器。为了融入失焦线索,我们从同一视角捕获小孔和大孔的两张图像。然后,我们使用基于失焦模糊图像形成模型的损失函数的梯度,在推理时间优化度量深度缩放参数和Marigold的噪声潜在变量以恢复度量深度。我们在自我收集的真实数据集上将我们的方法与现有的最先进的零样本MMDE方法进行比较,从定量和定性两个方面展示了改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期单眼度量深度估计(MMDE)方法在零样本泛化方面取得了显著进展,但在跨分布数据集上性能下降。为解决这一问题,我们通过在推理阶段将散焦模糊线索注入到预先训练的扩散模型Marigold中,实现了零样本、尺度不变的单眼深度估计(MDE)。我们的方法以无需训练的方式使Marigold成为度量深度预测器。为融入散焦线索,我们从同一视角捕获小孔和大孔两张图像,然后使用基于散焦模糊图像形成模型的损失函数在推理阶段优化度量深度缩放参数和Marigold的噪声潜在变量。在自收集的真实数据集上,我们的方法与现有最先进的零样本MMDE方法相比,显示出定量和定性的改进。
Key Takeaways
- MMDE方法在零样本泛化方面取得进展,但在跨分布数据集上存在性能下降的问题。
- 提出一种将散焦模糊线索注入到预先训练的扩散模型Marigold中的方法,以提高深度估计性能。
- 通过优化度量深度缩放参数和噪声潜在变量,实现了零样本、尺度不变的单眼深度估计。
- 利用小孔和大孔图像来捕捉散焦线索,以提高深度估计的准确性。
- 采用基于散焦模糊图像形成模型的损失函数进行优化。
- 在自收集的真实数据集上进行了实验验证,与现有方法相比取得了定量和定性的改进。
点此查看论文截图

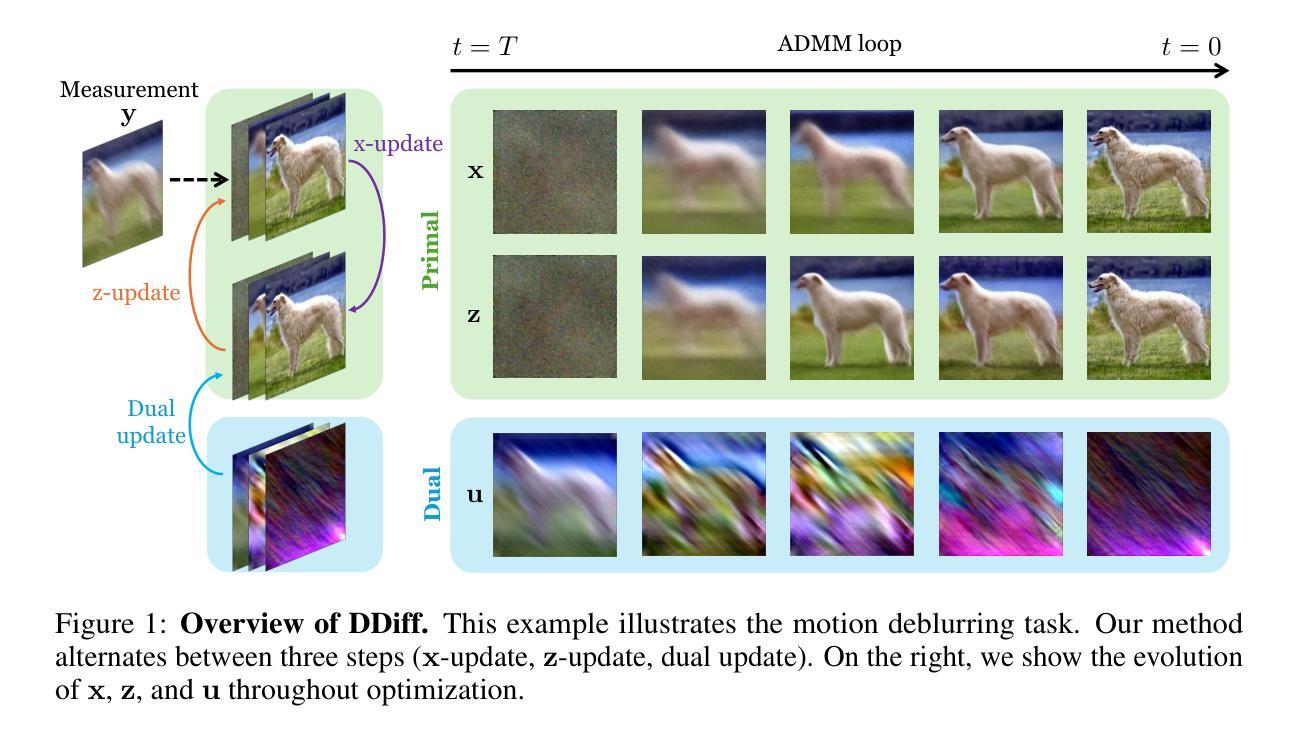
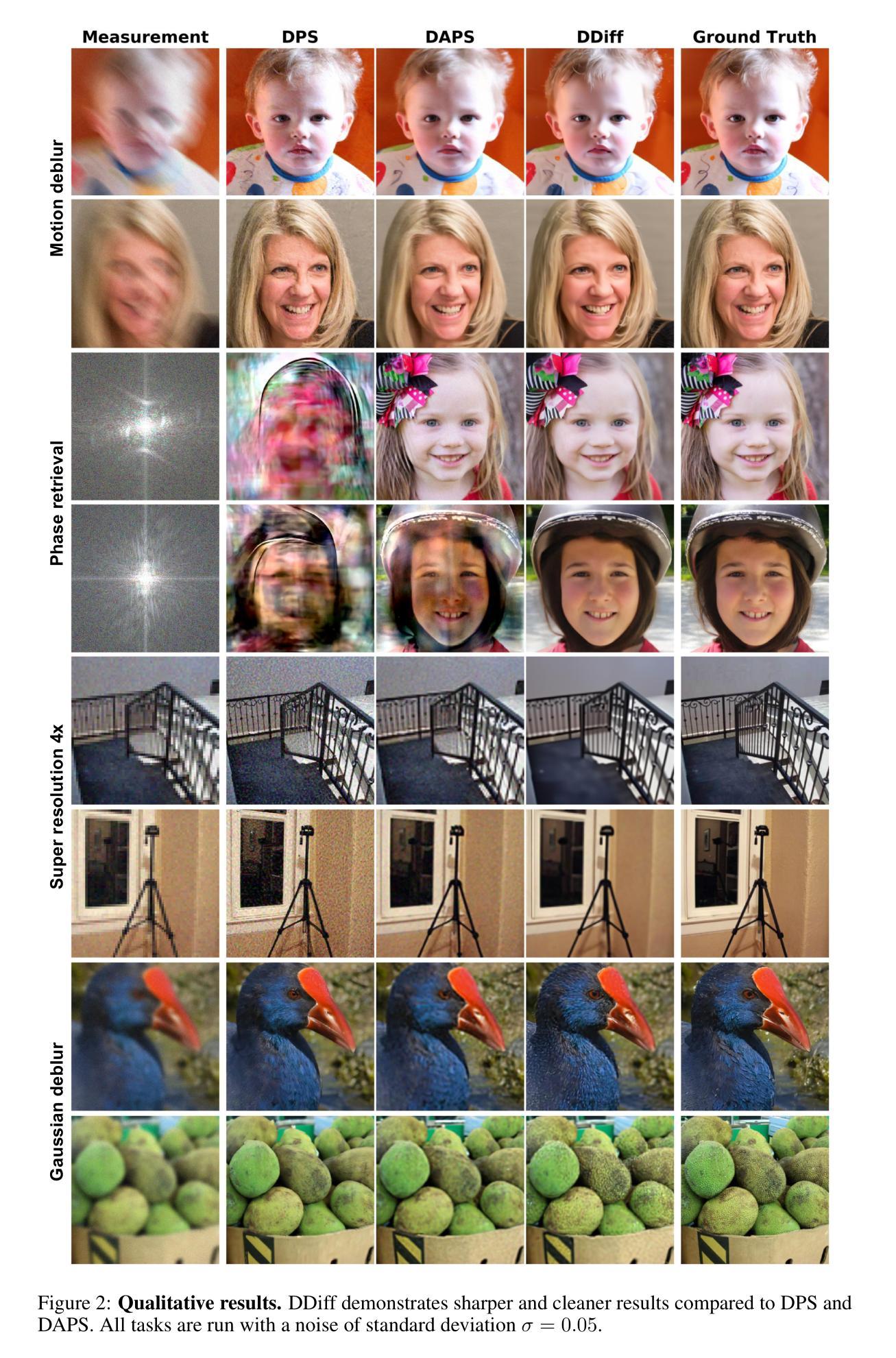
Dual Ascent Diffusion for Inverse Problems
Authors:Minseo Kim, Axel Levy, Gordon Wetzstein
Ill-posed inverse problems are fundamental in many domains, ranging from astrophysics to medical imaging. Emerging diffusion models provide a powerful prior for solving these problems. Existing maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) or posterior sampling approaches, however, rely on different computational approximations, leading to inaccurate or suboptimal samples. To address this issue, we introduce a new approach to solving MAP problems with diffusion model priors using a dual ascent optimization framework. Our framework achieves better image quality as measured by various metrics for image restoration problems, it is more robust to high levels of measurement noise, it is faster, and it estimates solutions that represent the observations more faithfully than the state of the art.
不适定反问题在许多领域都有广泛应用,从天文物理到医学影像。新兴的扩散模型为解决这些问题提供了强大的先验。然而,现有的最大后验概率(MAP)或后采样方法依赖于不同的计算近似方法,导致样本不准确或次优。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一种使用双上升优化框架解决带有扩散模型先验的MAP问题的新方法。我们的框架在图像恢复问题上以多种度量标准衡量图像质量更好,对高水平的测量噪声更具鲁棒性,速度更快,并且估计的解决方案比现有技术更真实地代表观察结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 15 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在解决不适定反问题中的应用。通过引入一种新的基于双重上升优化框架的MAP问题解决策略,新方法能够在图像修复等问题中提高图像质量,更好地应对高水平的测量噪声,估计出更为精准的解决方案。此外,该策略的速度也更快,能更好地还原观测结果。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图



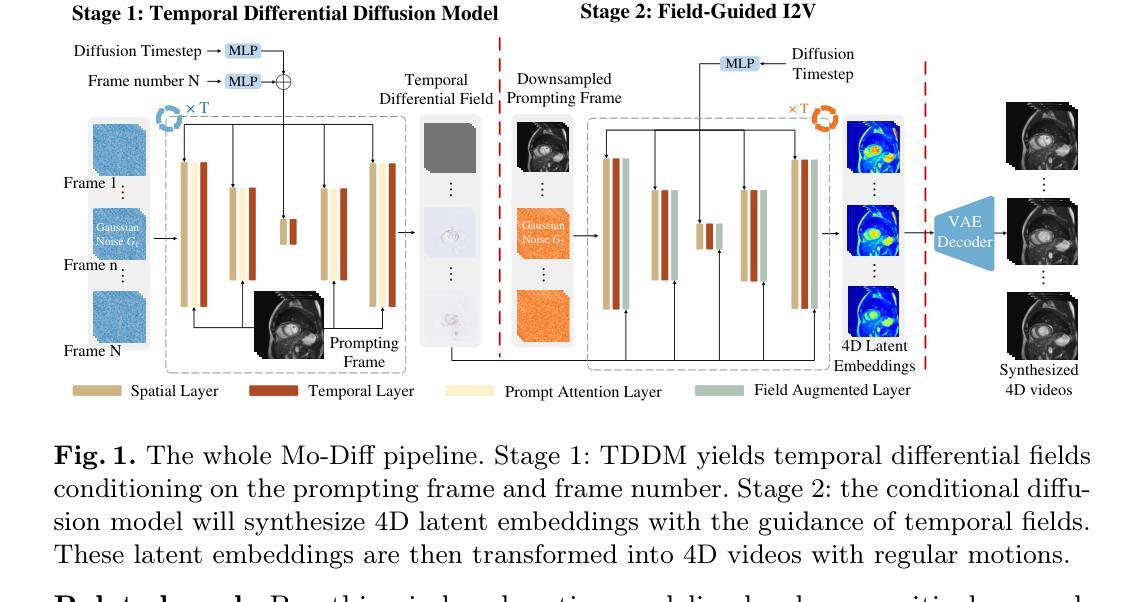
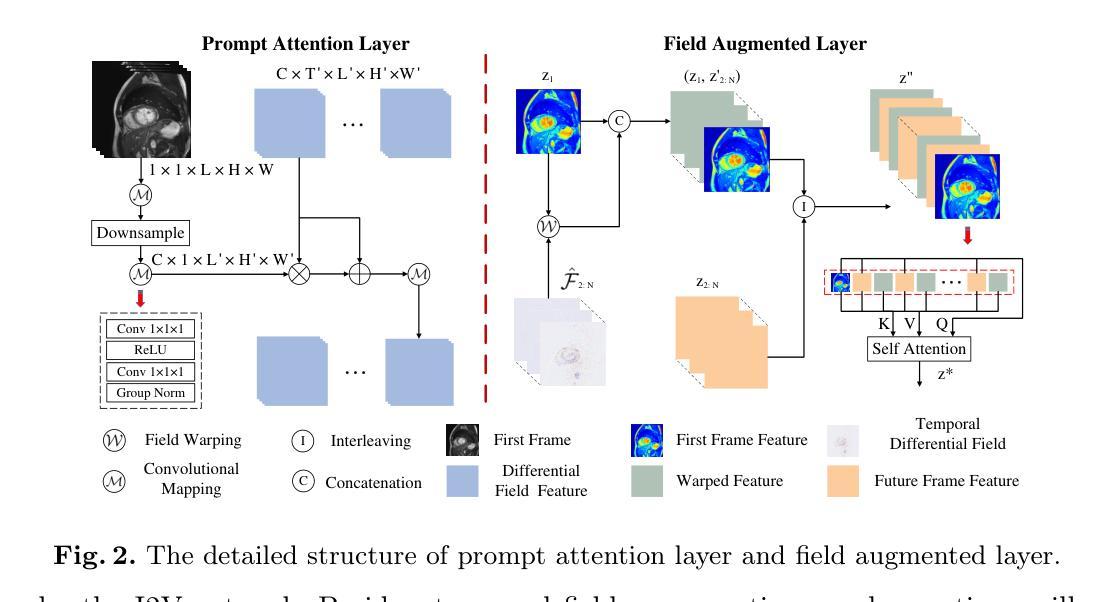
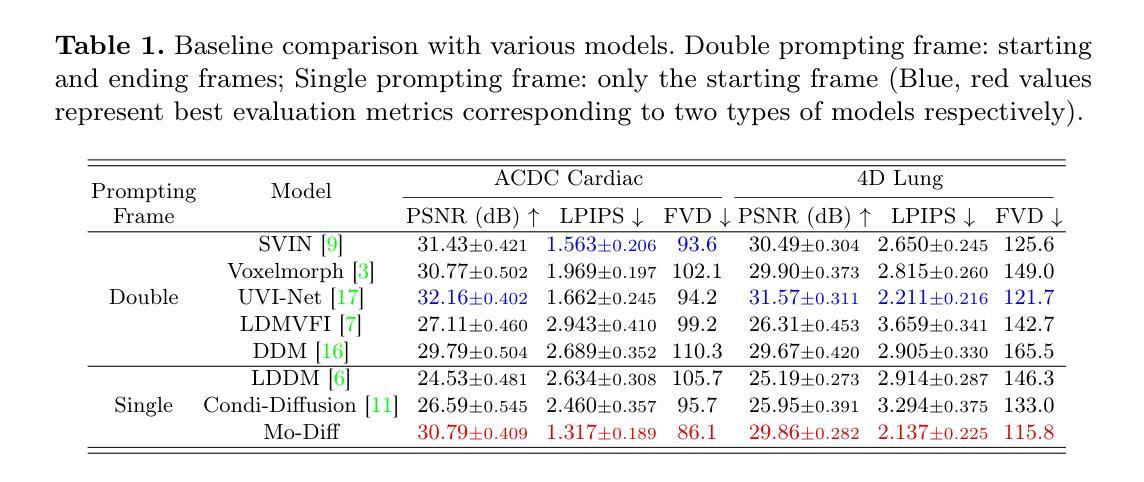
Temporal Differential Fields for 4D Motion Modeling via Image-to-Video Synthesis
Authors:Xin You, Minghui Zhang, Hanxiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Nassir Navab
Temporal modeling on regular respiration-induced motions is crucial to image-guided clinical applications. Existing methods cannot simulate temporal motions unless high-dose imaging scans including starting and ending frames exist simultaneously. However, in the preoperative data acquisition stage, the slight movement of patients may result in dynamic backgrounds between the first and last frames in a respiratory period. This additional deviation can hardly be removed by image registration, thus affecting the temporal modeling. To address that limitation, we pioneeringly simulate the regular motion process via the image-to-video (I2V) synthesis framework, which animates with the first frame to forecast future frames of a given length. Besides, to promote the temporal consistency of animated videos, we devise the Temporal Differential Diffusion Model to generate temporal differential fields, which measure the relative differential representations between adjacent frames. The prompt attention layer is devised for fine-grained differential fields, and the field augmented layer is adopted to better interact these fields with the I2V framework, promoting more accurate temporal variation of synthesized videos. Extensive results on ACDC cardiac and 4D Lung datasets reveal that our approach simulates 4D videos along the intrinsic motion trajectory, rivaling other competitive methods on perceptual similarity and temporal consistency. Codes will be available soon.
针对规律性的呼吸引起的运动进行时间建模,对图像引导的临床应用至关重要。现有方法无法模拟时间运动,除非同时存在包括起始帧和结束帧在内的高剂量成像扫描。然而,在术前数据采集阶段,患者轻微的移动可能会导致一个呼吸周期内第一帧和最后一帧之间的动态背景。这种额外的偏差几乎无法通过图像注册去除,从而影响时间建模。为了解决这个问题,我们首创性地通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程,该框架利用第一帧来预测给定长度的未来帧。此外,为了提升动画视频的时间一致性,我们设计了时间差分扩散模型,以生成时间差分场,它测量相邻帧之间的相对差分表示。设计了即时注意层用于精细的差分场,并采用场增强层来更好地将这些字段与I2V框架进行交互,从而促进合成视频的更加准确的时间变化。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集的大量结果表明,我们的方法能够沿着内在运动轨迹模拟4D视频,在感知相似性和时间一致性方面与其他竞争方法相比具有竞争力。代码将很快可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF early accepted by MICCAI
Summary
本文提出了一种通过图像到视频(I2V)合成框架模拟常规运动过程的方法,利用首帧预测未来指定长度的帧。为解决动态背景对时间建模的影响,引入时间差分扩散模型生成时间差分场,并设计了即时注意力层进行精细差分场的处理。在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的大量结果表明,该方法模拟的4D视频沿内在运动轨迹进行,感知相似性和时间一致性方面与其他方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 常规呼吸引起的运动在图像引导的临床应用中的时间建模是关键。
- 现有方法无法模拟时间运动,除非同时存在高剂量成像扫描的起始和结束帧。
- 患者轻微移动可能导致动态背景,影响时间建模。
- 提出了一种图像到视频(I2V)合成框架,通过首帧预测未来指定长度的帧来模拟常规运动过程。
- 引入时间差分扩散模型生成时间差分场,提高动画视频的时间一致性。
- 设计了即时注意力层来处理精细的差分场。
- 在ACDC心脏和4D肺部数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在感知相似性和时间一致性方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

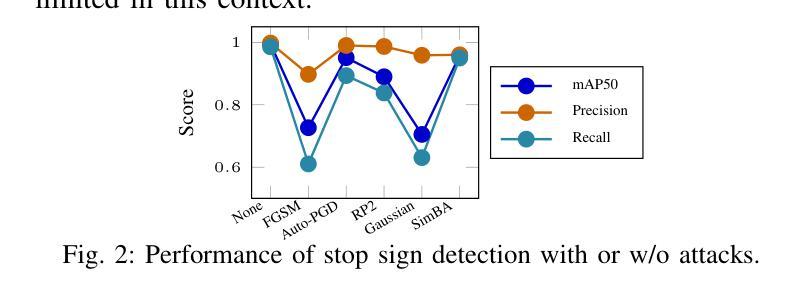
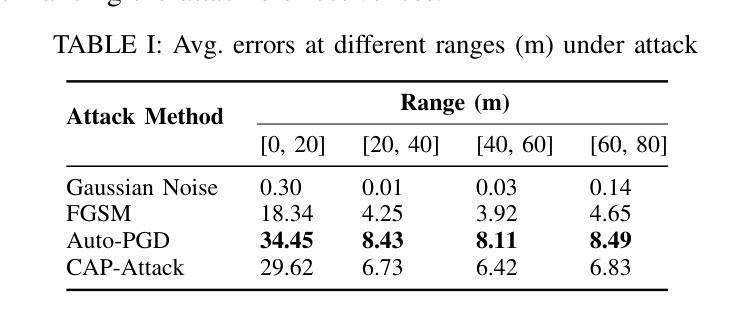
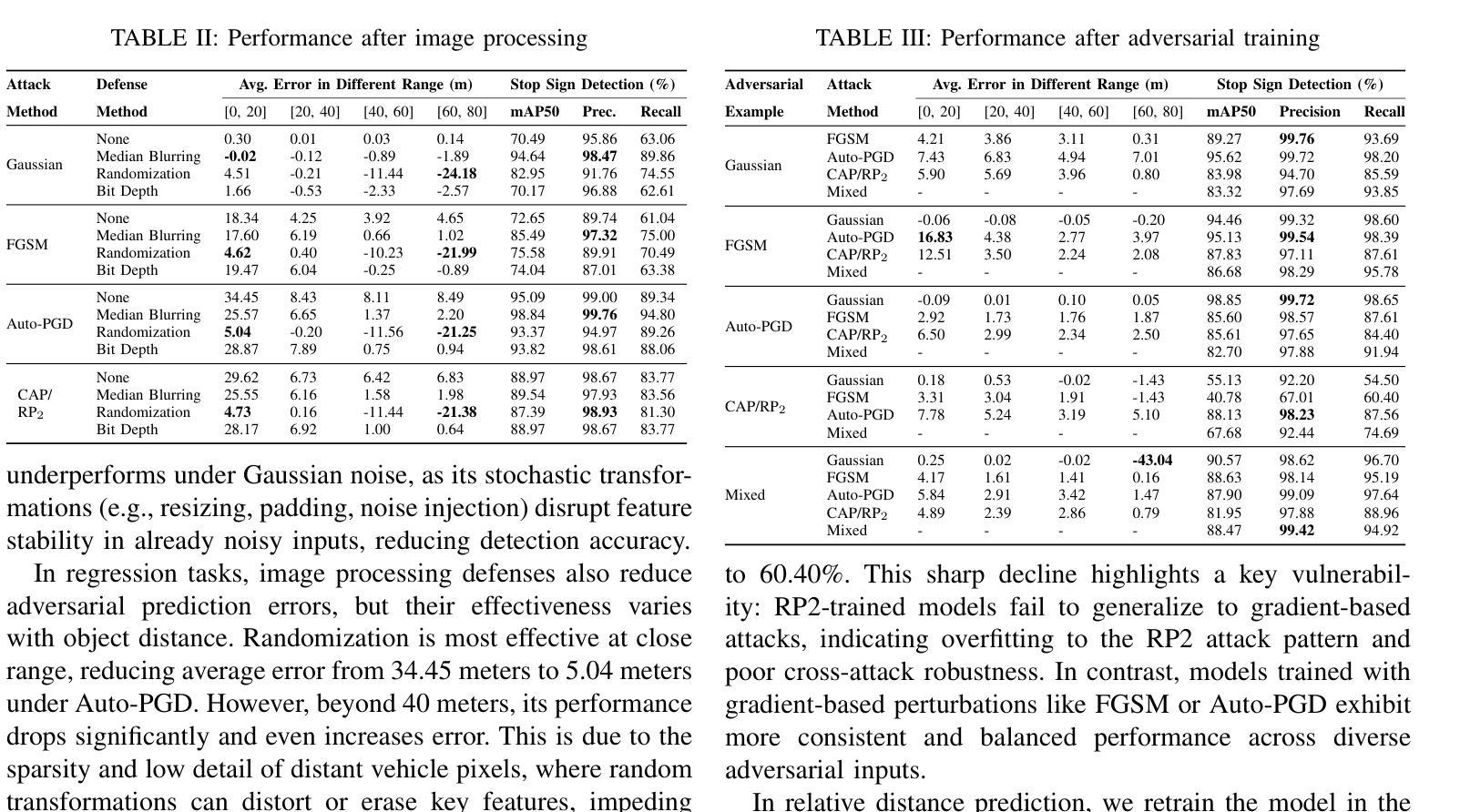
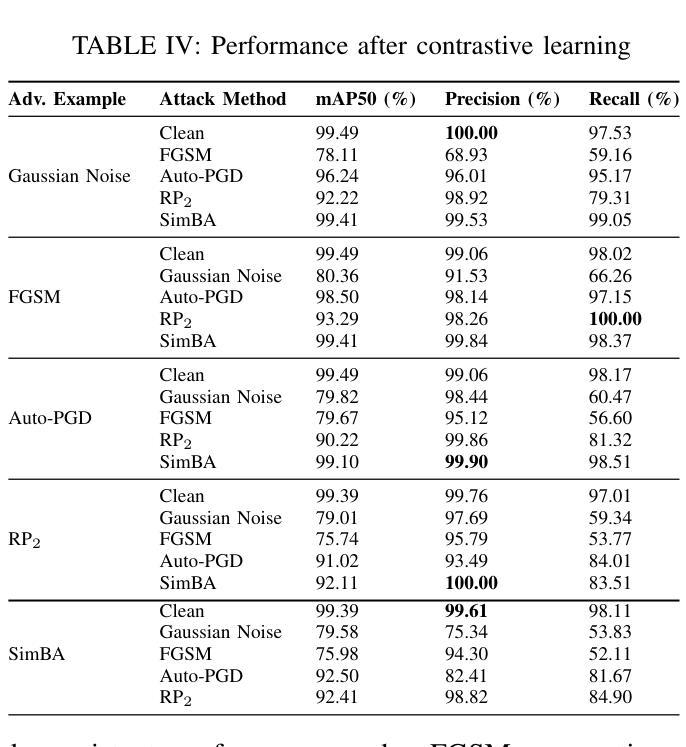
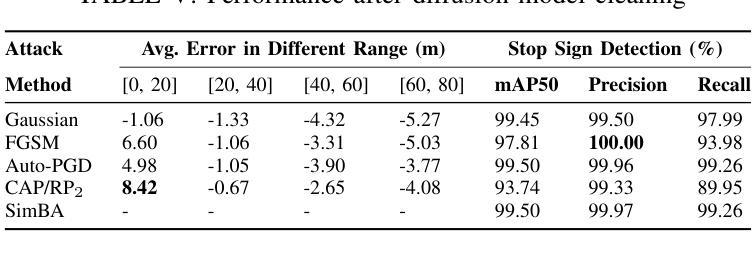
Revisiting Adversarial Perception Attacks and Defense Methods on Autonomous Driving Systems
Authors:Cheng Chen, Yuhong Wang, Nafis S Munir, Xiangwei Zhou, Xugui Zhou
Autonomous driving systems (ADS) increasingly rely on deep learning-based perception models, which remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In this paper, we revisit adversarial attacks and defense methods, focusing on road sign recognition and lead object detection and prediction (e.g., relative distance). Using a Level-2 production ADS, OpenPilot by Comma$.$ai, and the widely adopted YOLO model, we systematically examine the impact of adversarial perturbations and assess defense techniques, including adversarial training, image processing, contrastive learning, and diffusion models. Our experiments highlight both the strengths and limitations of these methods in mitigating complex attacks. Through targeted evaluations of model robustness, we aim to provide deeper insights into the vulnerabilities of ADS perception systems and contribute guidance for developing more resilient defense strategies.
自动驾驶系统(ADS)越来越依赖于基于深度学习的感知模型,而这些模型仍然容易受到对抗性攻击的威胁。本文重新审视了对抗性攻击和防御方法,重点关注道路标志识别以及前方物体的检测和预测(例如相对距离)。我们利用Comma.ai的Level-2生产型ADS和广泛采用的YOLO模型,系统地研究了对抗性扰动的影响,并评估了防御技术,包括对抗性训练、图像处理、对比学习和扩散模型。我们的实验突出了这些方法在缓解复杂攻击方面的优势和局限性。通过对模型稳健性的有针对性的评估,我们旨在深入了解ADS感知系统的漏洞,并为开发更具韧性的防御策略提供指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, To appear in the 8th Dependable and Secure Machine Learning Workshop (DSML 2025)
Summary
本文重点探讨了自主驾驶系统(ADS)中的对抗性攻击与防御方法,特别是针对道路标志识别以及前方目标检测和预测。研究使用了Comma.ai的OpenPilot水平2生产型ADS系统和广泛采用的YOLO模型,系统评估了对抗性扰动的影响,并测试了包括对抗性训练、图像处理、对比学习和扩散模型在内的防御技术。实验揭示了这些方法在应对复杂攻击时的优缺点,为深入了解ADS感知系统的脆弱性并为开发更稳健的防御策略提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- 自主驾驶系统(ADS)依赖深度学习感知模型,但易受对抗性攻击影响。
- 研究重点考察了道路标志识别及前方目标检测和预测中的对抗性攻击。
- 使用了OpenPilot和YOLO模型进行实验研究。
- 系统评估了对抗性扰动对模型的影响。
- 测试了多种防御方法,包括对抗性训练、图像处理、对比学习和扩散模型。
- 实验揭示了这些方法在应对复杂攻击时的优缺点。
点此查看论文截图


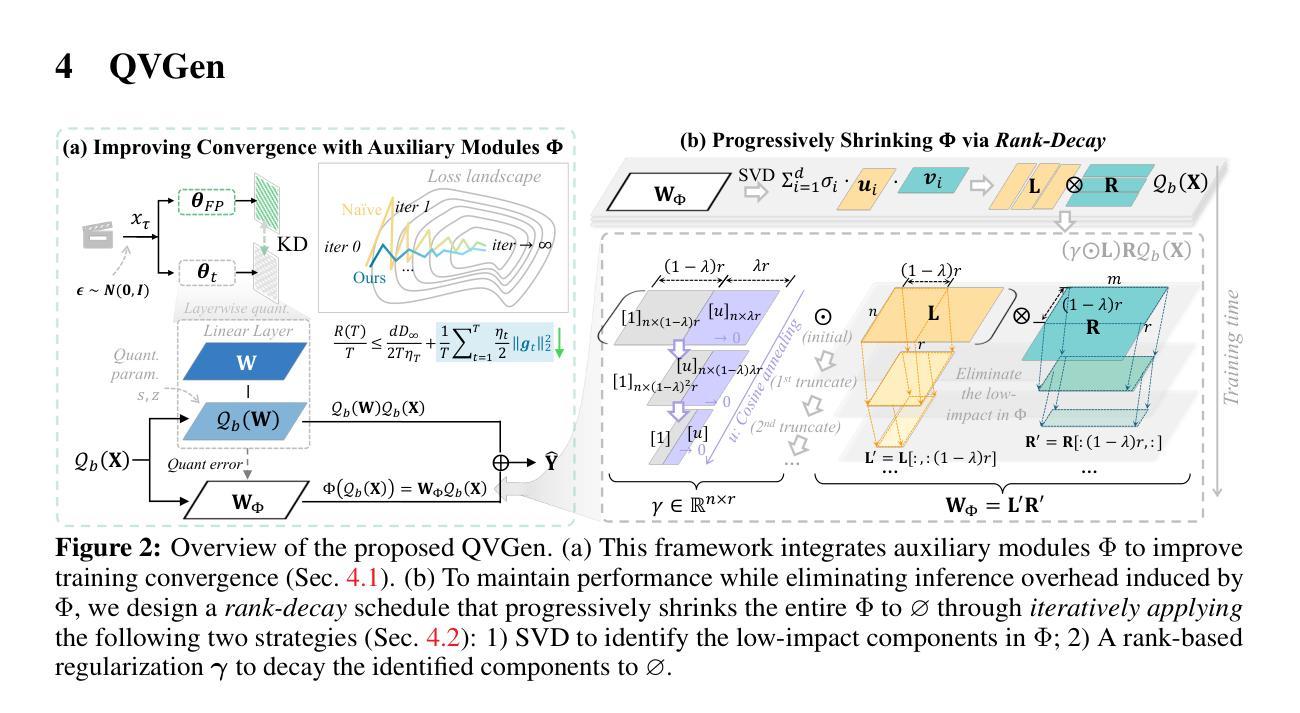
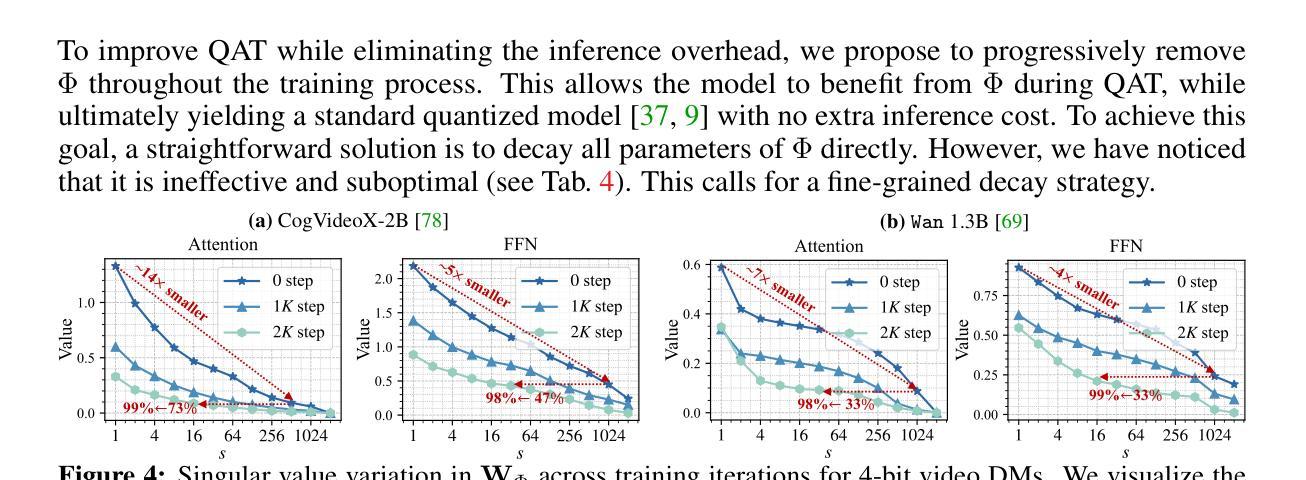
QVGen: Pushing the Limit of Quantized Video Generative Models
Authors:Yushi Huang, Ruihao Gong, Jing Liu, Yifu Ding, Chengtao Lv, Haotong Qin, Jun Zhang
Video diffusion models (DMs) have enabled high-quality video synthesis. Yet, their substantial computational and memory demands pose serious challenges to real-world deployment, even on high-end GPUs. As a commonly adopted solution, quantization has proven notable success in reducing cost for image DMs, while its direct application to video DMs remains ineffective. In this paper, we present QVGen, a novel quantization-aware training (QAT) framework tailored for high-performance and inference-efficient video DMs under extremely low-bit quantization (e.g., 4-bit or below). We begin with a theoretical analysis demonstrating that reducing the gradient norm is essential to facilitate convergence for QAT. To this end, we introduce auxiliary modules ($\Phi$) to mitigate large quantization errors, leading to significantly enhanced convergence. To eliminate the inference overhead of $\Phi$, we propose a rank-decay strategy that progressively eliminates $\Phi$. Specifically, we repeatedly employ singular value decomposition (SVD) and a proposed rank-based regularization $\mathbf{\gamma}$ to identify and decay low-contributing components. This strategy retains performance while zeroing out inference overhead. Extensive experiments across $4$ state-of-the-art (SOTA) video DMs, with parameter sizes ranging from $1.3$B $\sim14$B, show that QVGen is the first to reach full-precision comparable quality under 4-bit settings. Moreover, it significantly outperforms existing methods. For instance, our 3-bit CogVideoX-2B achieves improvements of $+25.28$ in Dynamic Degree and $+8.43$ in Scene Consistency on VBench.
视频扩散模型(DMs)已经能够实现高质量的视频合成。然而,其巨大的计算和内存需求对现实世界的应用部署,即使在高端GPU上,也构成了严重的挑战。作为一种常用的解决方案,量化在降低图像DM的成本方面已经取得了显著的成效,而将其直接应用于视频DM仍然无效。在本文中,我们介绍了QVGen,这是一个专为极端低比特量化(例如4位及以下)下高性能和推理效率高的视频DM定制的量化感知训练(QAT)框架。我们从理论分析开始,证明降低梯度范数是促进QAT收敛的关键。为此,我们引入了辅助模块(Φ)来减轻大量的量化误差,从而显著增强了收敛性。为了消除Φ的推理开销,我们提出了一种排名衰减策略,该策略逐步消除Φ。具体来说,我们反复使用奇异值分解(SVD)和提出的基于排名的正则化γ来识别和衰减低贡献成分。此策略在保持性能的同时消除了推理开销。在4种最先进的视频DMs上的广泛实验,参数大小从1.3B到14B,表明QVGen首次在4位设置下达到全精度可比质量。而且,它显著优于现有方法。例如,我们的3位CogVideoX-2B在VBench上的动态度提高了+25.28,场景一致性提高了+8.43。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code will be released upon acceptance
摘要
视频扩散模型(DMs)可实现高质量视频合成,但其巨大的计算和内存需求对现实世界的部署构成了严峻挑战,即使在高端GPU上也是如此。量化作为一种常用的解决方案,在降低图像DM的成本方面取得了显著的成效,而直接应用于视频DM则效果不佳。本文提出了QVGen,这是一个针对高性能和推理效率的视频DM量身定制的量化感知训练(QAT)框架,适用于极低比特量化(例如4位及以下)。本文首先进行理论分析,证明降低梯度范数是促进QAT收敛的关键。为此,我们引入了辅助模块(Φ)来缓解量化误差,从而显著提高了收敛性。为了消除Φ的推理开销,我们提出了一种等级衰减策略,该策略逐步消除了Φ。具体来说,我们反复使用奇异值分解(SVD)和提出的基于等级的规则γ来识别和衰减低贡献成分。此策略在保持性能的同时消除了推理开销。在参数规模从1.3B到14B的4种最先进视频DM上进行的广泛实验表明,QVGen在四比特设置下首次达到全精度可比质量,并显著优于现有方法。例如,我们的3位CogVideoX-2B在VBench上的动态度和场景一致性分别提高了+25.28和+8.43。
关键见解
- 视频扩散模型(DMs)可实现高质量视频合成,但部署挑战在于其高计算和内存需求。
- 量化作为一种降低图像DM成本的解决方案已经取得了成功,但直接应用于视频DM效果不佳。
- QVGen是一个针对视频DM的量化感知训练(QAT)框架,旨在提高高性能和推理效率,适用于极低比特量化。
- QVGen通过引入辅助模块和等级衰减策略来提高QAT的收敛性和性能。
- 辅助模块用于缓解量化误差,而等级衰减策略逐步消除推理开销。
- QVGen在多种视频DM上实现了全精度可比质量,特别是在4位设置下。
点此查看论文截图


AnimeDL-2M: Million-Scale AI-Generated Anime Image Detection and Localization in Diffusion Era
Authors:Chenyang Zhu, Xing Zhang, Yuyang Sun, Ching-Chun Chang, Isao Echizen
Recent advances in image generation, particularly diffusion models, have significantly lowered the barrier for creating sophisticated forgeries, making image manipulation detection and localization (IMDL) increasingly challenging. While prior work in IMDL has focused largely on natural images, the anime domain remains underexplored-despite its growing vulnerability to AI-generated forgeries. Misrepresentations of AI-generated images as hand-drawn artwork, copyright violations, and inappropriate content modifications pose serious threats to the anime community and industry. To address this gap, we propose AnimeDL-2M, the first large-scale benchmark for anime IMDL with comprehensive annotations. It comprises over two million images including real, partially manipulated, and fully AI-generated samples. Experiments indicate that models trained on existing IMDL datasets of natural images perform poorly when applied to anime images, highlighting a clear domain gap between anime and natural images. To better handle IMDL tasks in anime domain, we further propose AniXplore, a novel model tailored to the visual characteristics of anime imagery. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that AniXplore achieves superior performance compared to existing methods. Dataset and code can be found in https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/.
近期图像生成领域的进展,特别是扩散模型,大大降低了创建复杂伪造作品的门槛,使得图像操纵检测与定位(IMDL)越来越具有挑战性。尽管先前在IMDL方面的工作主要集中在自然图像上,但动漫领域仍然鲜有研究——尽管它越来越容易受到AI生成的伪造作品的威胁。将AI生成的图像误表示为手绘艺术品、版权侵犯以及不当内容修改对动漫社区和行业构成严重威胁。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了AnimeDL-2M,这是首个用于动漫IMDL的大规模基准测试,包含全面的注释。它包含超过两百万张图像,包括真实、部分操纵和完全AI生成的样本。实验表明,在自然图像IMDL数据集上训练的模型在应用于动漫图像时表现不佳,这凸显了动漫和自然图像之间的明显领域差距。为了更好地处理动漫领域的IMDL任务,我们进一步提出了AniXplore,这是一个针对动漫图像视觉特征量身定制的新型模型。广泛评估表明,与现有方法相比,AniXplore实现了卓越的性能。数据集和代码可在https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8+2 pages; update figure 3,4,5 as adding real images into detection task tests
Summary
最新进展的图像生成技术,特别是扩散模型,大大降低了创建复杂伪造作品的门槛,使得图像操纵检测与定位(IMDL)越来越具挑战性。尽管IMDL先前的工作主要集中在自然图像上,但动漫领域仍然被忽视,尽管该领域面临AI生成伪造作品的日益增长的脆弱性。我们提出了AnimeDL-2M,这是首个大规模动漫IMDL基准测试集,带有全面注释,包含超过两百万张图像,包括真实、部分操纵和完全AI生成的样本。实验表明,在动漫图像上应用训练有素的自然图像IMDL数据集表现不佳,突显出动漫和自然图像之间的明显领域差距。为了更好地处理动漫领域的IMDL任务,我们进一步提出了AniXplore模型,该模型针对动漫图像的视觉特性量身定制。广泛的评估表明,与现有方法相比,AniXplore实现了卓越的性能。数据集和代码可在https://flytweety.github.io/AnimeDL2M/找到。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的发展使得图像生成变得更加容易,从而增加了创建复杂伪造作品的难度。
- 图像操纵检测与定位(IMDL)面临新的挑战,因为动漫领域对AI生成伪造作品的脆弱性日益增加。
- 当前IMDL数据集主要集中在自然图像上,而动漫领域的数据集仍然缺乏。
- 动漫图像与自然图像之间存在明显的领域差距。
- 训练有素的自然图像IMDL数据集在动漫图像上的表现不佳。
- 提出了首个针对动漫IMDL的大规模基准测试集AnimeDL-2M,包含全面注释和超过两百万张图像。
点此查看论文截图


REG: Rectified Gradient Guidance for Conditional Diffusion Models
Authors:Zhengqi Gao, Kaiwen Zha, Tianyuan Zhang, Zihui Xue, Duane S. Boning
Guidance techniques are simple yet effective for improving conditional generation in diffusion models. Albeit their empirical success, the practical implementation of guidance diverges significantly from its theoretical motivation. In this paper, we reconcile this discrepancy by replacing the scaled marginal distribution target, which we prove theoretically invalid, with a valid scaled joint distribution objective. Additionally, we show that the established guidance implementations are approximations to the intractable optimal solution under no future foresight constraint. Building on these theoretical insights, we propose rectified gradient guidance (REG), a versatile enhancement designed to boost the performance of existing guidance methods. Experiments on 1D and 2D demonstrate that REG provides a better approximation to the optimal solution than prior guidance techniques, validating the proposed theoretical framework. Extensive experiments on class-conditional ImageNet and text-to-image generation tasks show that incorporating REG consistently improves FID and Inception/CLIP scores across various settings compared to its absence.
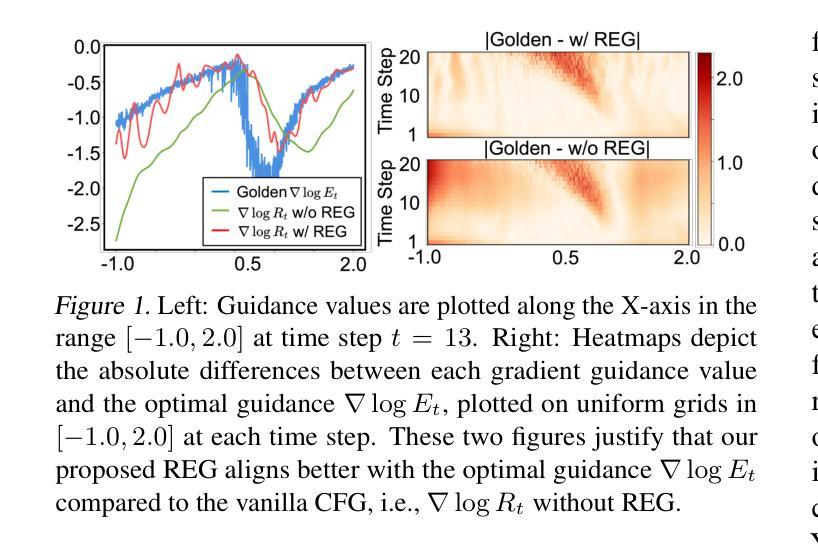
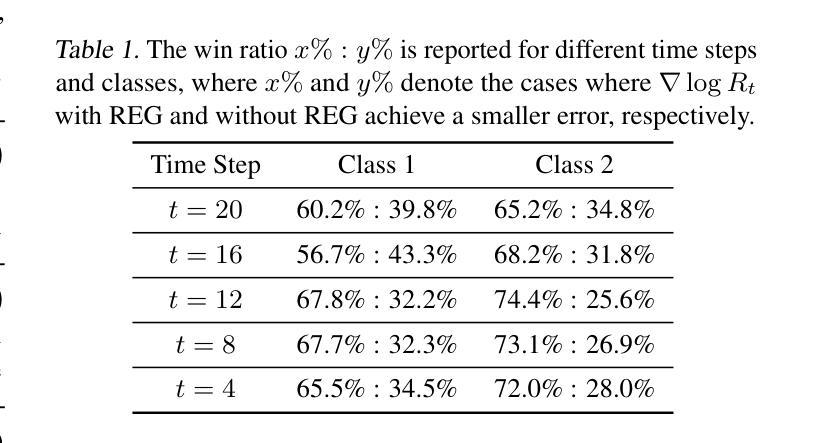
指导技术在扩散模型中用于改善条件生成简单而有效。尽管它们在经验上取得了成功,但指导的实际实施与其理论动机存在很大差异。在本文中,我们通过用有效的缩放联合分布目标替换理论上无效的可缩放边际分布目标来解决这一差异。此外,我们证明现有的指导实现是在没有未来预测约束下不可行最优解的近似解。基于这些理论见解,我们提出了修正梯度指导(REG),这是一种通用增强设计,旨在提高现有指导方法的性能。在一维和二维实验表明,相对于之前的指导技术,REG更好地接近最优解,验证了所提出理论框架的正确性。在类条件ImageNet和文本到图像生成任务的广泛实验表明,在各种设置中融入REG与缺少REG相比,FID和Inception/CLIP分数均有所提高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 10 figures; accepted by ICML’25
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型中指导技术的改进对条件生成的影响。针对现有指导技术实施与理论动机的偏差,本文进行了调和。通过替换理论上无效的比例边际分布目标,采用有效的比例联合分布目标,并证明现有指导实现是在无未来预见约束下对最优解的近似。在此基础上,本文提出了矫正梯度指导(REG)这一通用增强技术,旨在提升现有指导方法的性能。实验证明,REG相较于先前的指导技术,在逼近最优解方面表现更佳。在类条件ImageNet和文本到图像生成任务上的实验显示,引入REG在不同设置下始终提高了FID和Inception/CLIP得分。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中的指导技术对于改进条件生成至关重要。
- 现有指导技术的实施与理论动机存在偏差。
- 通过采用有效的比例联合分布目标替换理论上无效的比例边际分布目标,解决了这一偏差。
- 现有指导实现是对于无未来预见约束下最优解的近似。
- 提出矫正梯度指导(REG)技术,旨在增强现有指导方法的性能。
- REG在逼近最优解方面表现优于先前的指导技术。
点此查看论文截图

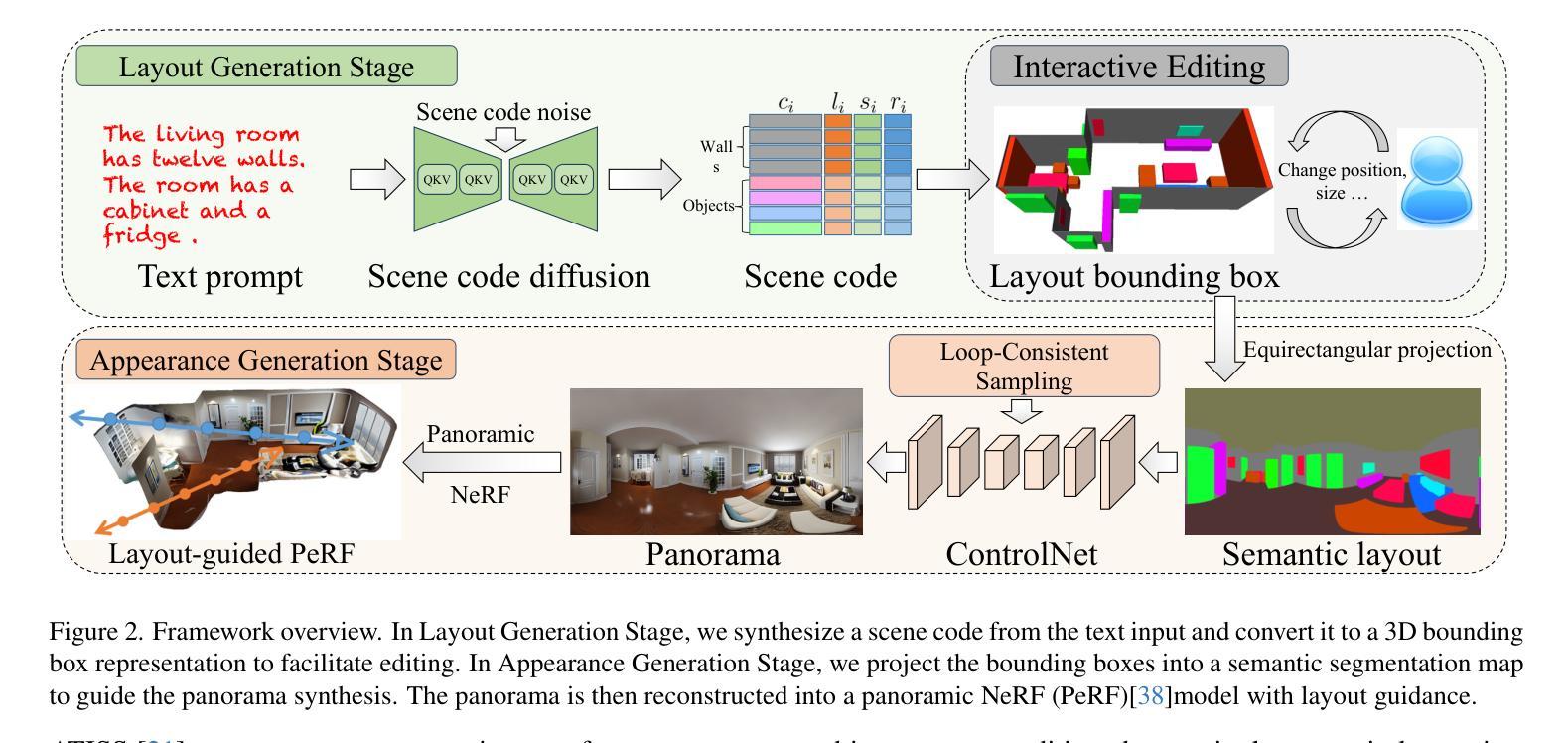
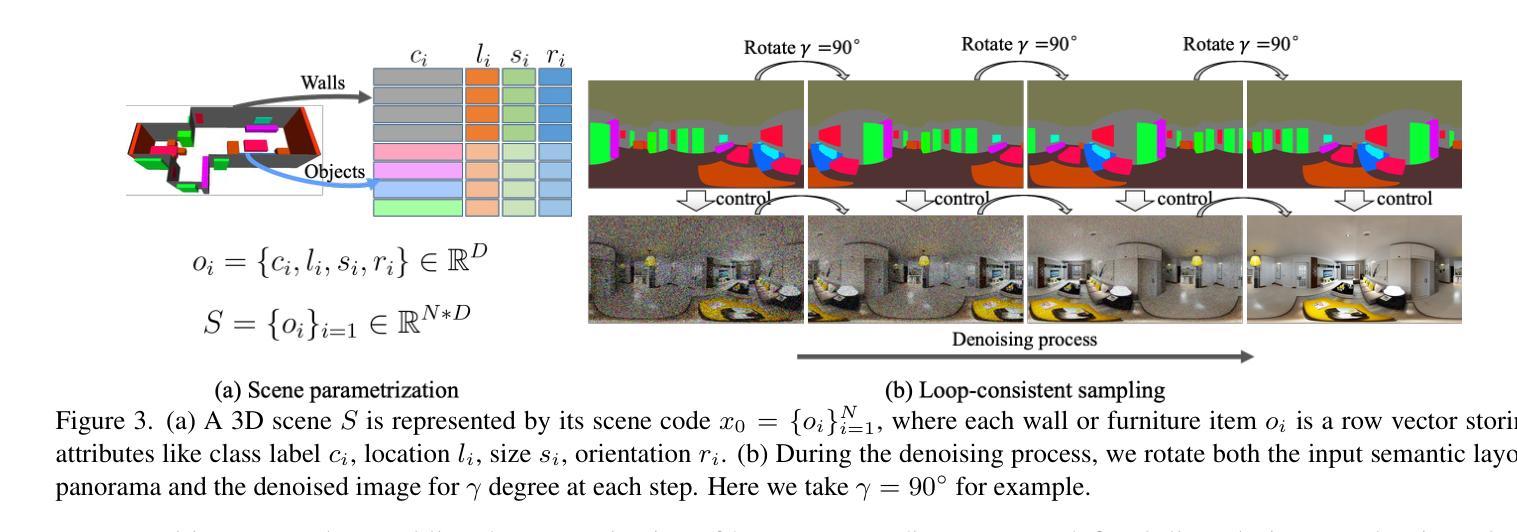
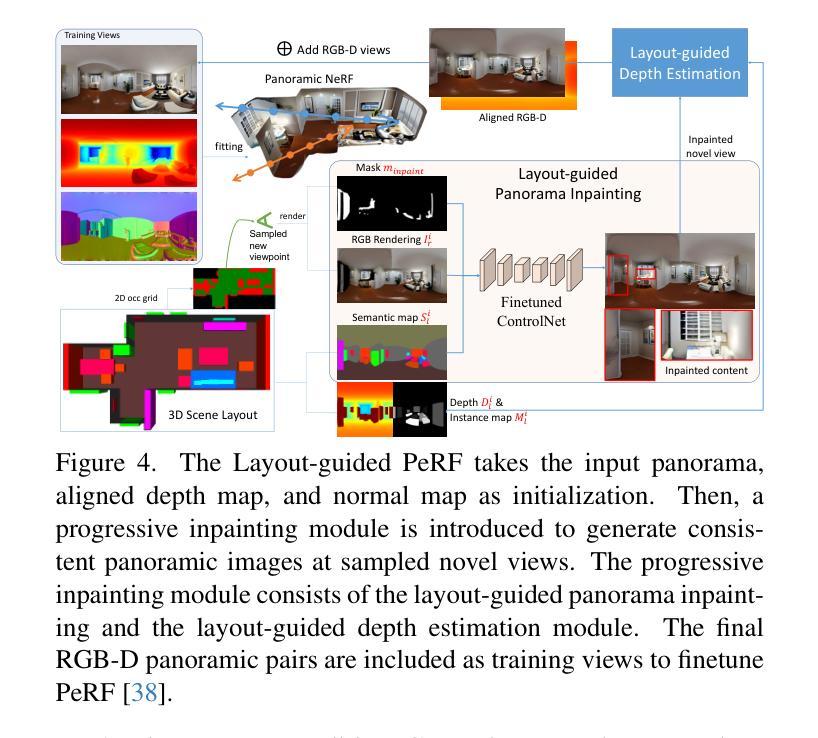
Ctrl-Room: Controllable Text-to-3D Room Meshes Generation with Layout Constraints
Authors:Chuan Fang, Yuan Dong, Kunming Luo, Xiaotao Hu, Rakesh Shrestha, Ping Tan
Text-driven 3D indoor scene generation is useful for gaming, the film industry, and AR/VR applications. However, existing methods cannot faithfully capture the room layout, nor do they allow flexible editing of individual objects in the room. To address these problems, we present Ctrl-Room, which can generate convincing 3D rooms with designer-style layouts and high-fidelity textures from just a text prompt. Moreover, Ctrl-Room enables versatile interactive editing operations such as resizing or moving individual furniture items. Our key insight is to separate the modeling of layouts and appearance. Our proposed method consists of two stages: a Layout Generation Stage and an Appearance Generation Stage. The Layout Generation Stage trains a text-conditional diffusion model to learn the layout distribution with our holistic scene code parameterization. Next, the Appearance Generation Stage employs a fine-tuned ControlNet to produce a vivid panoramic image of the room guided by the 3D scene layout and text prompt. We thus achieve a high-quality 3D room generation with convincing layouts and lively textures. Benefiting from the scene code parameterization, we can easily edit the generated room model through our mask-guided editing module, without expensive edit-specific training. Extensive experiments on the Structured3D dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms existing methods in producing more reasonable, view-consistent, and editable 3D rooms from natural language prompts.
文本驱动的3D室内场景生成在游戏、电影产业和AR/VR应用中非常有用。然而,现有方法无法真实地捕捉房间布局,也不允许对房间中的单个物体进行灵活的编辑。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Ctrl-Room,它仅通过文本提示就能生成具有设计师风格的布局和高保真纹理的令人信服的3D房间。此外,Ctrl-Room还启用了多样化的交互编辑操作,如调整大小或移动单个家具物品。我们的关键见解是分离布局和外观的建模。我们提出的方法分为两个阶段:布局生成阶段和外观生成阶段。布局生成阶段训练了一个文本条件扩散模型,以学习我们的整体场景代码参数化的布局分布。接下来,外观生成阶段采用经过微调的控制网(ControlNet)生成受3D场景布局和文本提示引导的房间生动全景图像。因此,我们实现了具有令人信服的布局和生动纹理的高质量3D房间生成。得益于场景代码参数化,我们可以轻松通过我们的遮罩引导编辑模块编辑生成的房间模型,而无需进行昂贵的特定编辑训练。在Structured3D数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在根据自然语言提示生成更合理、视角一致且可编辑的3D房间方面优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本驱动的3D室内场景生成技术为游戏、影视、AR/VR等领域带来了便捷。现有方法难以真实还原房间布局,也无法灵活编辑室内物件。本研究提出Ctrl-Room技术,仅通过文本提示即可生成具有设计感布局和高保真纹理的3D房间,并实现个体家具的缩放和移动等交互式编辑操作。核心在于布局与外观的建模分离,包括布局生成阶段和外观生成阶段。在Structured3D数据集上的实验表明,Ctrl-Room技术较现有方法更优,能生成更合理、视角一致、可编辑的3D房间。
Key Takeaways
- Ctrl-Room技术通过文本驱动生成3D室内场景,应用于游戏、影视、AR/VR领域。
- 现有方法难以真实还原房间布局,且缺乏灵活的编辑功能。
- Ctrl-Room技术分为布局生成阶段和外观生成阶段,实现布局与外观的建模分离。
- 采用全景图像生成技术,根据3D场景布局和文本提示生成生动逼真的纹理。
- 通过场景代码参数化,实现轻松编辑生成的房间模型。
- Ctrl-Room技术通过mask-guided编辑模块,无需特定培训即可进行编辑。
点此查看论文截图