⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
REACT 2025: the Third Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation Challenge
Authors:Siyang Song, Micol Spitale, Xiangyu Kong, Hengde Zhu, Cheng Luo, Cristina Palmero, German Barquero, Sergio Escalera, Michel Valstar, Mohamed Daoudi, Tobias Baur, Fabien Ringeval, Andrew Howes, Elisabeth Andre, Hatice Gunes
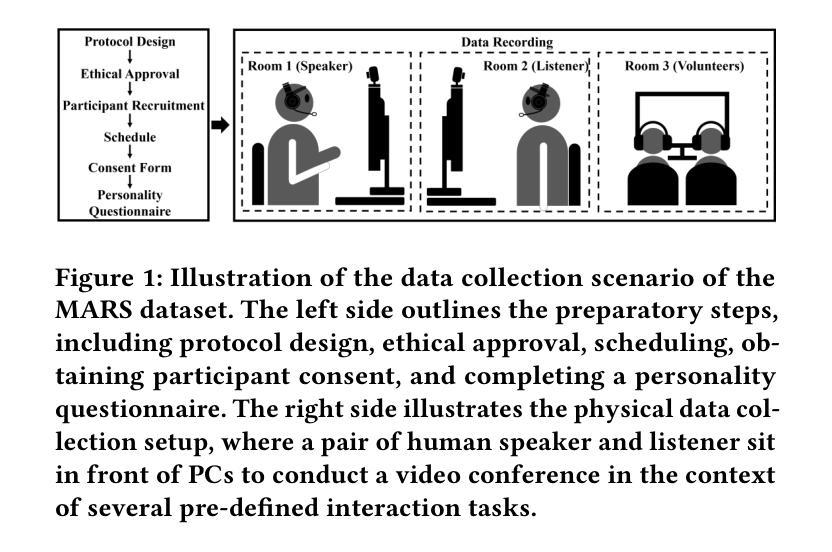
In dyadic interactions, a broad spectrum of human facial reactions might be appropriate for responding to each human speaker behaviour. Following the successful organisation of the REACT 2023 and REACT 2024 challenges, we are proposing the REACT 2025 challenge encouraging the development and benchmarking of Machine Learning (ML) models that can be used to generate multiple appropriate, diverse, realistic and synchronised human-style facial reactions expressed by human listeners in response to an input stimulus (i.e., audio-visual behaviours expressed by their corresponding speakers). As a key of the challenge, we provide challenge participants with the first natural and large-scale multi-modal MAFRG dataset (called MARS) recording 137 human-human dyadic interactions containing a total of 2856 interaction sessions covering five different topics. In addition, this paper also presents the challenge guidelines and the performance of our baselines on the two proposed sub-challenges: Offline MAFRG and Online MAFRG, respectively. The challenge baseline code is publicly available at https://github.com/reactmultimodalchallenge/baseline_react2025
在双人互动中,人类对面部反应的广泛反应可能适用于每种人类说话者行为。继REACT 2023和REACT 2024挑战的成功组织之后,我们正在推出REACT 2025挑战,鼓励开发和评估机器学习(ML)模型,这些模型可用于生成多种恰当、多样化、逼真且同步的人类风格的面部反应,这些反应由人类听众对输入刺激作出回应(即对应发言者的视听行为)。作为该挑战的关键,我们为挑战参与者提供了首个自然且大规模的多模式MAFRG数据集(称为MARS),记录了137个人与人之间的双人互动,共包含涵盖五个不同话题的2856个互动会话。此外,本文还介绍了挑战准则以及我们在两个提出的子挑战:离线MAFRG和在线MAFRG上的基线性能。挑战基线代码公开可用:https://github.com/reactmultimodalchallenge/baseline_react2025
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸表情识别领域不断发展,随着REACT 2025挑战的提出,鼓励开发并评估机器学习模型来生成多种适当、多样、真实且同步的人脸表情反应。该挑战提供了首个自然大规模多模态MAFRG数据集MARS,包含多种话题的137个人与人之间的二元互动记录。同时公开了挑战基准代码。
Key Takeaways
- REACT 2025挑战旨在鼓励开发并评估机器学习模型,用于生成多种适当的人脸表情反应。
- 该挑战的核心是提供首个自然大规模多模态MAFRG数据集MARS。
- MARS数据集包含五种不同话题的二元互动记录。
- 数据集记录了人类听众对于输入刺激(如音频视觉行为)产生的面部表情反应。
- 该挑战包含两个子挑战:Offline MAFRG和Online MAFRG。
- 公开了挑战的基准代码以供参与者参考和使用。
点此查看论文截图

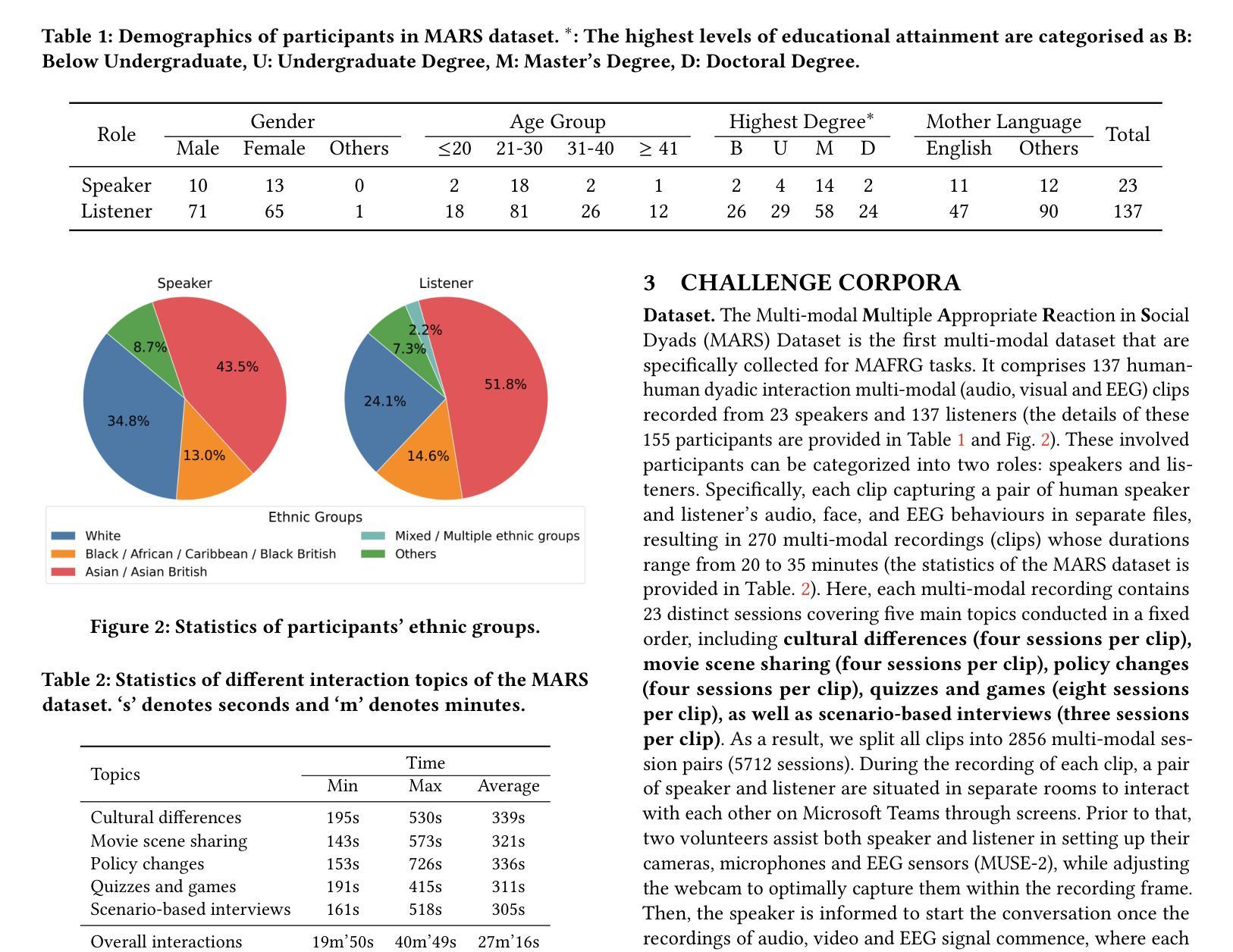
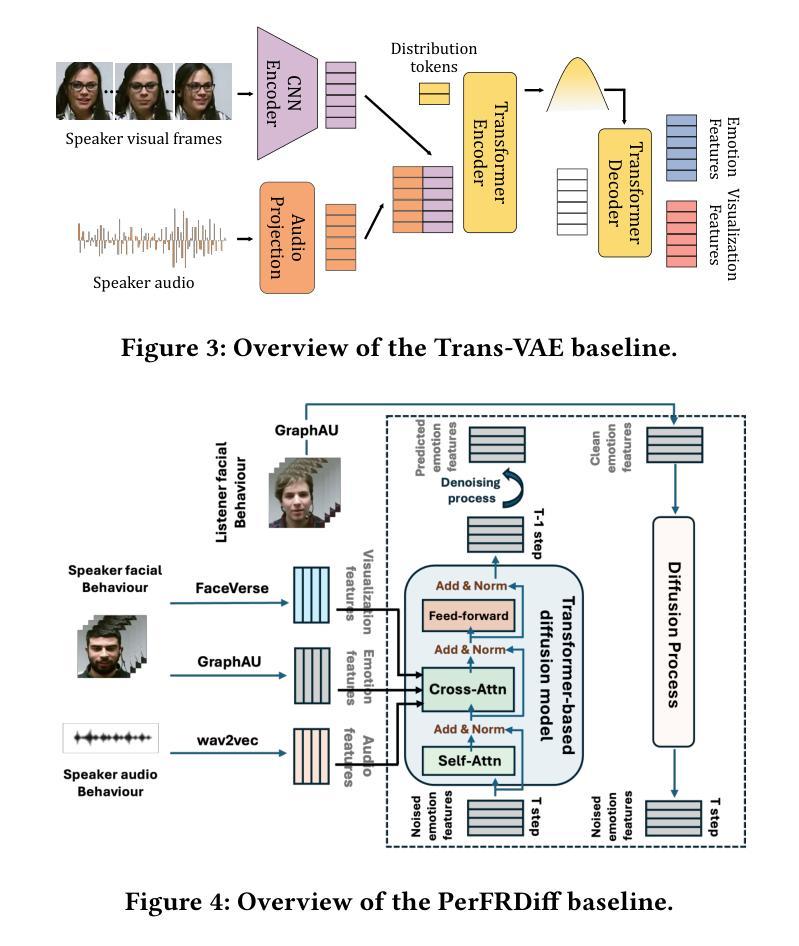
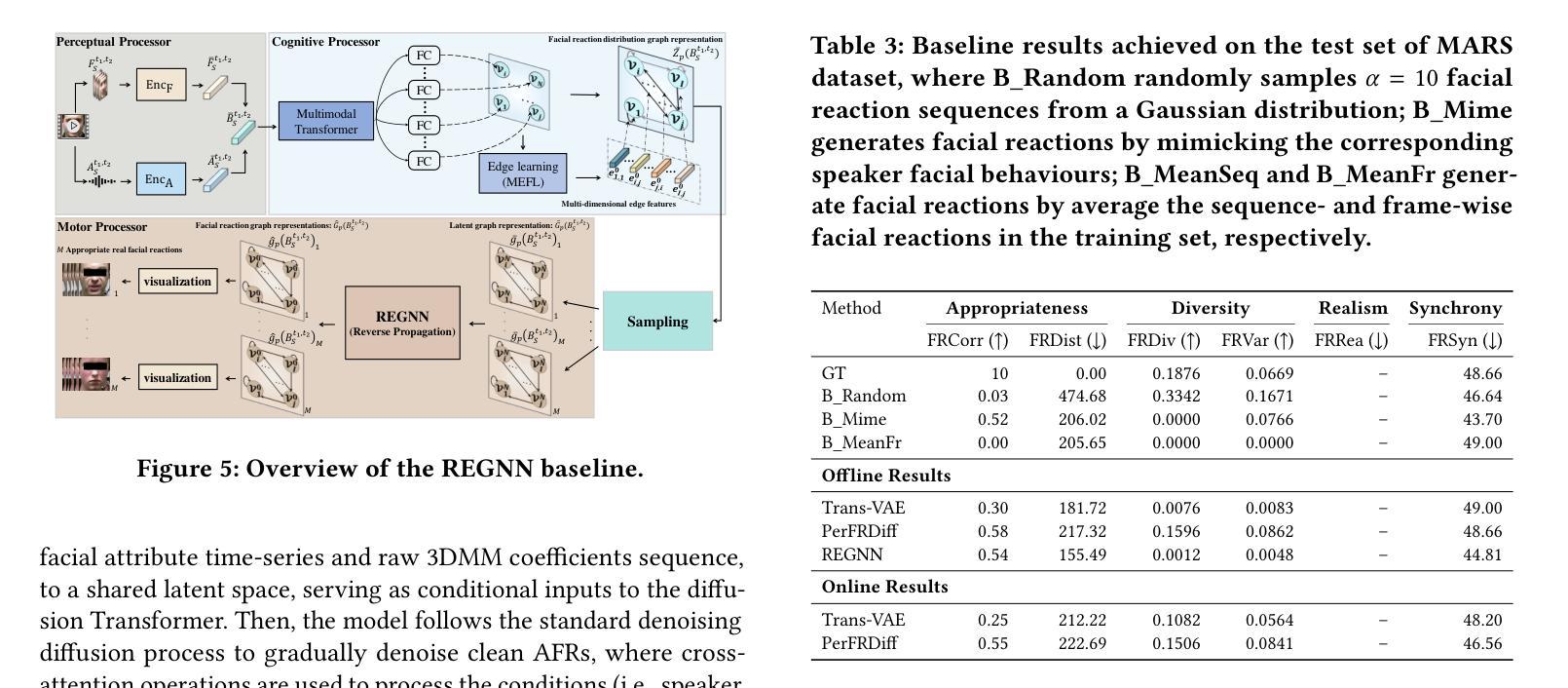
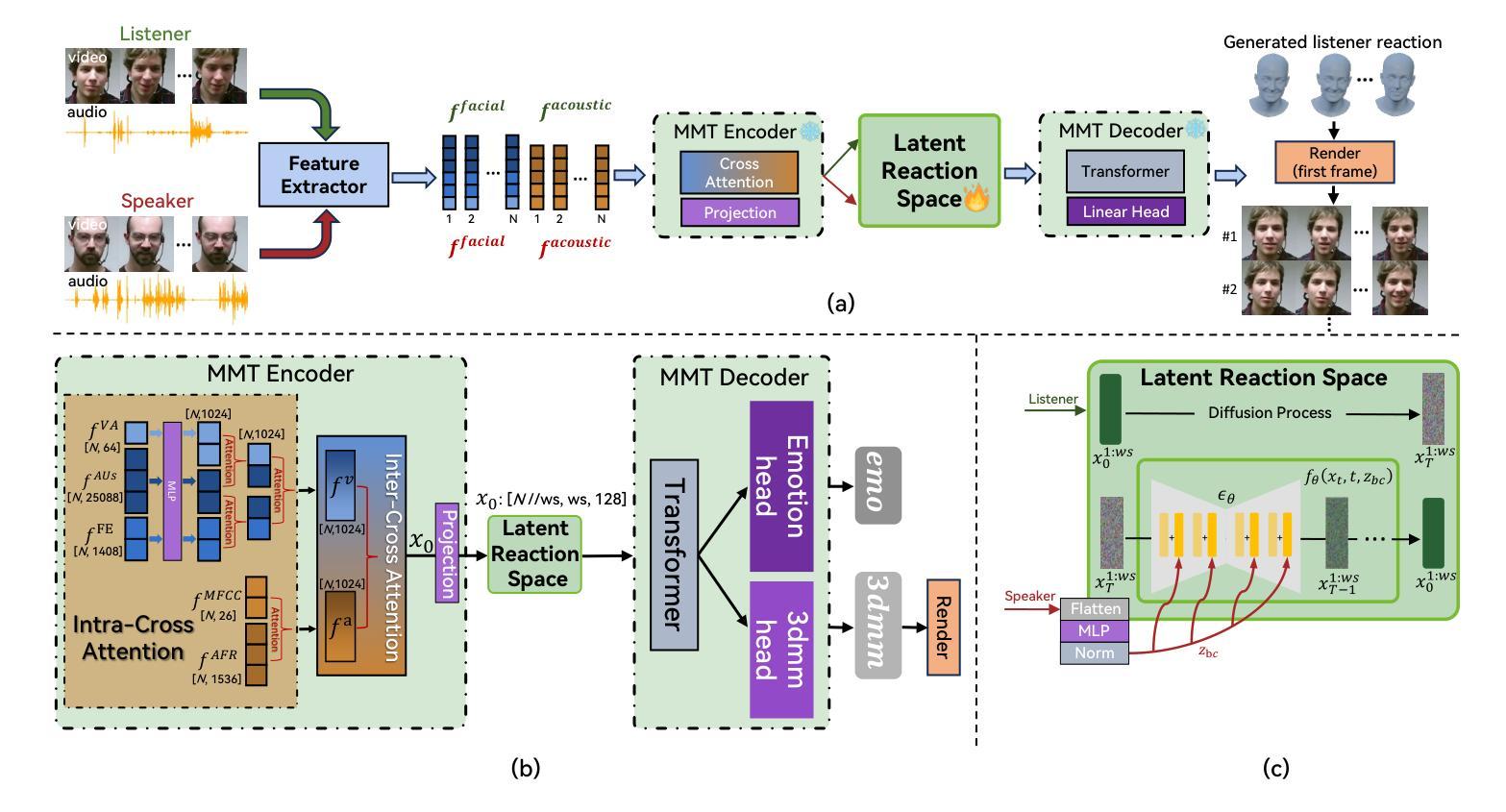
ReactDiff: Latent Diffusion for Facial Reaction Generation
Authors:Jiaming Li, Sheng Wang, Xin Wang, Yitao Zhu, Honglin Xiong, Zixu Zhuang, Qian Wang
Given the audio-visual clip of the speaker, facial reaction generation aims to predict the listener’s facial reactions. The challenge lies in capturing the relevance between video and audio while balancing appropriateness, realism, and diversity. While prior works have mostly focused on uni-modal inputs or simplified reaction mappings, recent approaches such as PerFRDiff have explored multi-modal inputs and the one-to-many nature of appropriate reaction mappings. In this work, we propose the Facial Reaction Diffusion (ReactDiff) framework that uniquely integrates a Multi-Modality Transformer with conditional diffusion in the latent space for enhanced reaction generation. Unlike existing methods, ReactDiff leverages intra- and inter-class attention for fine-grained multi-modal interaction, while the latent diffusion process between the encoder and decoder enables diverse yet contextually appropriate outputs. Experimental results demonstrate that ReactDiff significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving a facial reaction correlation of 0.26 and diversity score of 0.094 while maintaining competitive realism. The code is open-sourced at \href{https://github.com/Hunan-Tiger/ReactDiff}{github}.
基于说话人的视听剪辑,面部表情生成旨在预测听众的面部表情反应。挑战在于在平衡适当性、现实性和多样性的同时,捕捉视频和音频之间的相关性。虽然早期的工作主要集中在单模态输入或简化的反应映射上,但最近的方法,如PerFRDiff,已经探索了多模态输入和适当的反应映射的一对多性质。在这项工作中,我们提出了面部反应扩散(ReactDiff)框架,该框架独特地结合了多模态变压器和有条件潜伏空间扩散,以增强反应生成。与现有方法不同,ReactDiff利用类内和类间注意力进行精细粒度的多模态交互,而编码器和解码器之间的潜在扩散过程则产生了多样但上下文恰当的输出。实验结果表明,ReactDiff在面部反应相关性方面显著优于现有方法,达到0.26的面部反应相关性和0.094的多样性得分,同时保持竞争力强的现实性。代码已开源,可在github(https://github.com/Hunan-Tiger/ReactDiff)上查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Neural Networks
Summary
本文介绍了面部反应生成技术的新进展。研究提出了一种名为Facial Reaction Diffusion(ReactDiff)的新框架,结合多模态变压器和潜在空间的条件扩散,以改进反应生成。该框架利用细粒度的多模态交互和编码器与解码器之间的潜在扩散过程,实现多样化的上下文相关输出。实验结果证明,ReactDiff在面部反应相关性和多样性方面显著优于现有方法,同时在现实性方面保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标是基于音频视觉剪辑预测听众的面部反应,挑战在于捕捉视频和音频之间的相关性,同时平衡适当性、现实性和多样性。
- 现有方法主要关注单模态输入或简化的反应映射,而新方法如PerFRDiff已探索多模态输入和适当的反应映射的一对多性质。
- ReactDiff框架独特地整合了多模态变压器和潜在空间的条件扩散,用于改进反应生成。
- ReactDiff利用细粒度的多模态交互,通过类内和类间注意力实现更好的性能。
- 编码器与解码器之间的潜在扩散过程使输出更加多样化和上下文相关。
- 实验结果表明,ReactDiff在面部反应相关性和多样性方面显著优于现有方法,同时保持现实性竞争力。
点此查看论文截图