⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
Fann or Flop: A Multigenre, Multiera Benchmark for Arabic Poetry Understanding in LLMs
Authors:Wafa Alghallabi, Ritesh Thawkar, Sara Ghaboura, Ketan More, Omkar Thawakar, Hisham Cholakkal, Salman Khan, Rao Muhammad Anwer
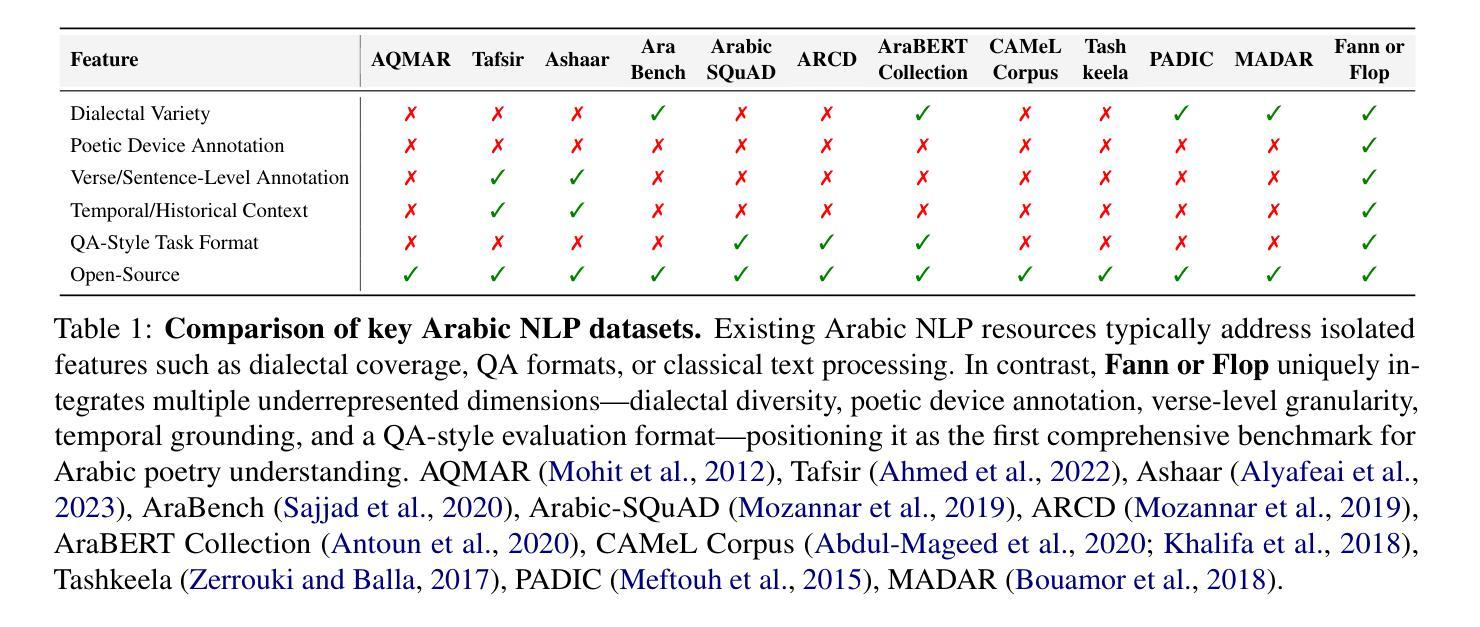
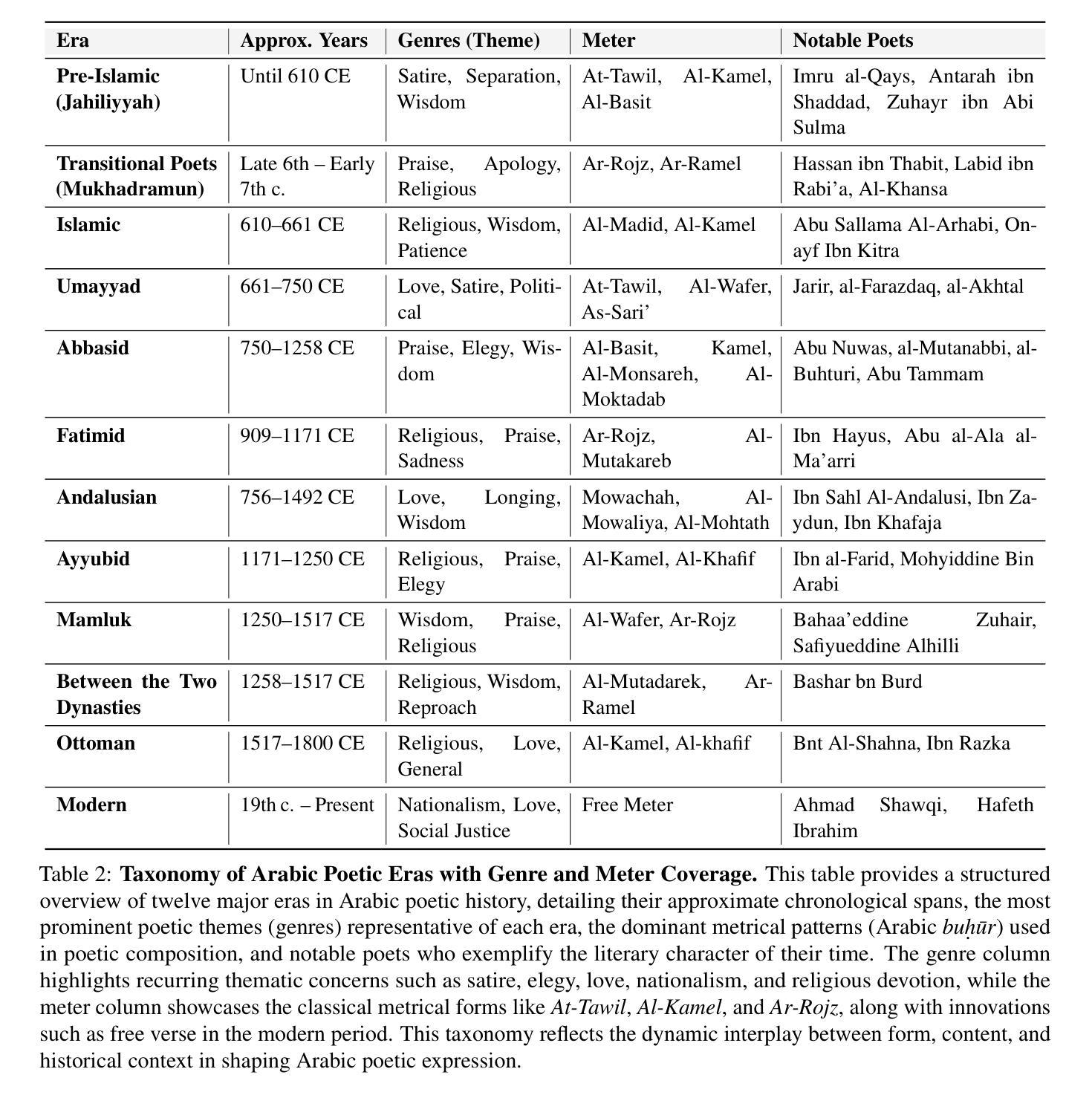
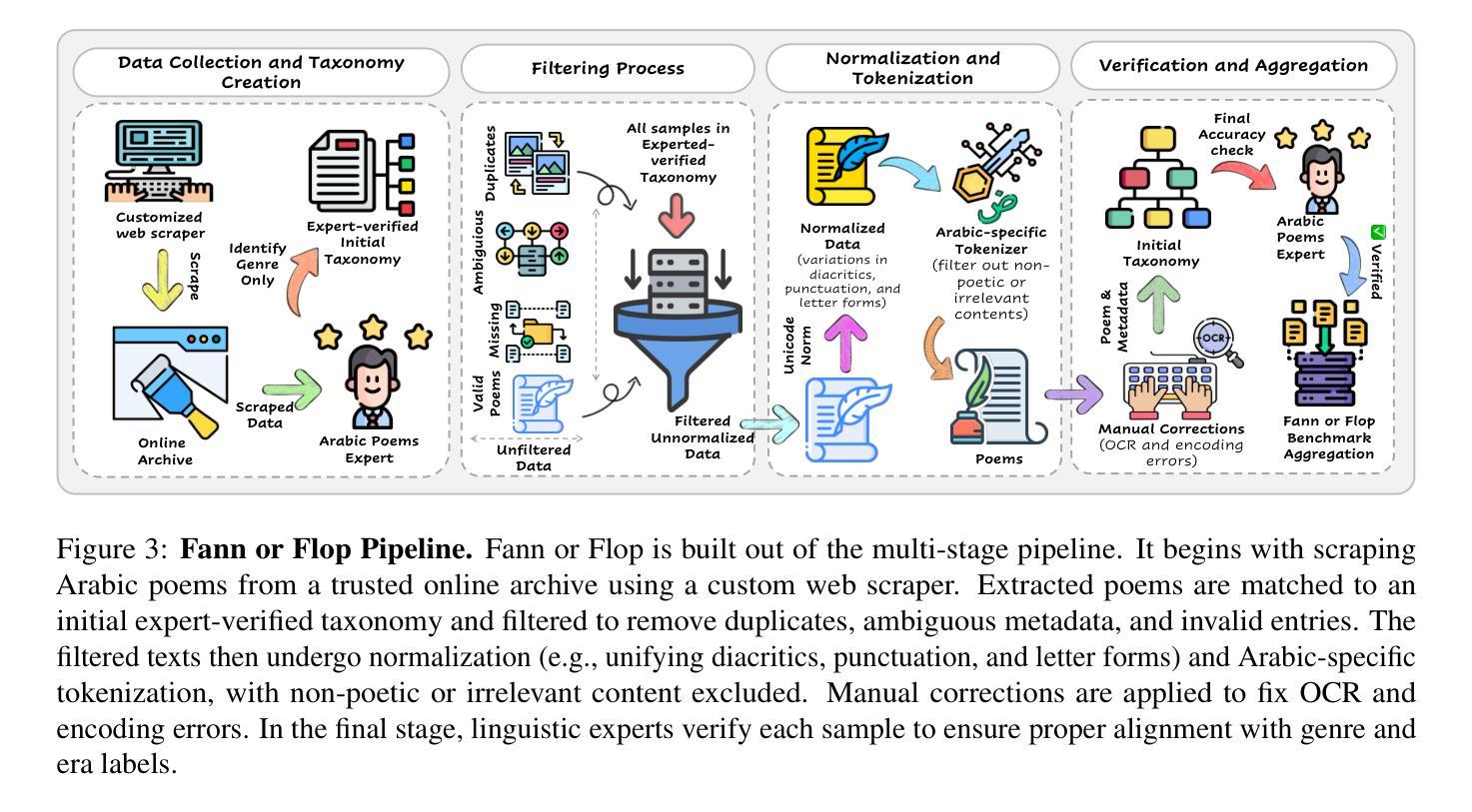
Arabic poetry stands as one of the most sophisticated and culturally embedded forms of expression in the Arabic language, known for its layered meanings, stylistic diversity, and deep historical continuity. Although large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance across languages and tasks, their ability to understand Arabic poetry remains largely unexplored. In this work, we introduce Fann or Flop, the first benchmark designed to assess the comprehension of Arabic poetry by LLMs in twelve historical eras, covering 21 core poetic genres and a variety of metrical forms, from classical structures to contemporary free verse. The benchmark comprises a curated corpus of poems with explanations that assess semantic understanding, metaphor interpretation, prosodic awareness, and cultural context. We argue that poetic comprehension offers a strong indicator for testing how good the LLM is in understanding classical Arabic through the Arabic poetry. Unlike surface-level tasks, this domain demands deeper interpretive reasoning and cultural sensitivity. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs shows that most models struggle with poetic understanding despite strong results on standard Arabic benchmarks. We release Fann or Flop along with the evaluation suite as an open-source resource to enable rigorous evaluation and advancement for Arabic language models. Code is available at: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/FannOrFlop.
阿拉伯诗歌是阿拉伯语中最精致、最富有文化特色的表达形式之一,以其多层次的含义、风格多样性和深厚的历史连续性而闻名。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)已在多种语言和任务中表现出强大的性能,但它们对阿拉伯诗歌的理解能力仍在很大程度上未被探索。在这项工作中,我们推出了
Fann or Flop',这是第一个旨在评估LLM对阿拉伯诗歌理解能力的基准测试,涵盖了十二个历史时期的诗歌,涉及21个核心诗歌流派和各种韵律形式,从古典结构到当代自由诗。该基准测试包括诗歌解释,评估语义理解、隐喻解释、韵律意识和文化背景。我们认为,诗歌理解是测试LLM对古典阿拉伯语理解能力的有力指标。与表层任务不同,这个领域需要更深层次的解释推理和文化敏感性。我们对最先进的LLM的评估表明,尽管在标准阿拉伯语基准测试中结果强劲,但大多数模型在诗歌理解方面仍存在困难。我们已将Fann or Flop’及其评估套件作为开源资源发布,以促进阿拉伯语言模型的严格评估和进步。代码可在:https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/FannOrFlop获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Github:https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/FannOrFlop, Dataset:https://huggingface.co/datasets/omkarthawakar/FannOrFlop
Summary
阿拉伯语诗歌是阿拉伯语表达形式中最精致、最富有文化内涵的一种,以其多层含义、风格多样和深厚的历史连续性而著称。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在其他语言和任务中表现出强大的性能,但它们在理解阿拉伯语诗歌方面的能力仍然很少被探索。在这项工作中,我们推出了Fann or Flop',这是第一个旨在评估LLM对阿拉伯语诗歌理解能力的基准测试,涵盖了十二个历史时期的21种核心诗歌体裁和多种韵律形式,从古典结构到当代自由诗。该基准测试包括诗歌的解释,旨在评估语义理解、隐喻解释、韵律意识和文化背景。我们认为,诗歌理解是测试LLM对古典阿拉伯语理解能力的有力指标。不同于表层任务,这个领域需要更深层次的解释推理和文化敏感性。我们对最先进的LLM的评估表明,大多数模型在诗歌理解方面遇到困难,尽管在标准阿拉伯语基准测试中表现良好。我们公开推出了Fann or Flop’及其评估套件作为开源资源,以促进阿拉伯语言模型的严格评估和进步。
Key Takeaways
- 阿拉伯语诗歌是一种表达丰富、历史深厚的语言艺术形式,具有多层含义、风格多样等特点。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在理解阿拉伯语诗歌方面的能力尚未得到充分探索。
- `Fann or Flop’是首个旨在评估LLM对阿拉伯语诗歌理解能力的基准测试。
- 该基准测试涵盖了多个历史时期、诗歌体裁和韵律形式,以全面评估模型对阿拉伯语诗歌的理解。
- 诗歌理解需要深厚的解释推理和文化敏感性,不同于简单的表层任务。
- 现有LLM在诗歌理解方面存在困难,尽管它们在标准阿拉伯语基准测试中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图


Lost in the Haystack: Smaller Needles are More Difficult for LLMs to Find
Authors:Owen Bianchi, Mathew J. Koretsky, Maya Willey, Chelsea X. Alvarado, Tanay Nayak, Adi Asija, Nicole Kuznetsov, Mike A. Nalls, Faraz Faghri, Daniel Khashabi
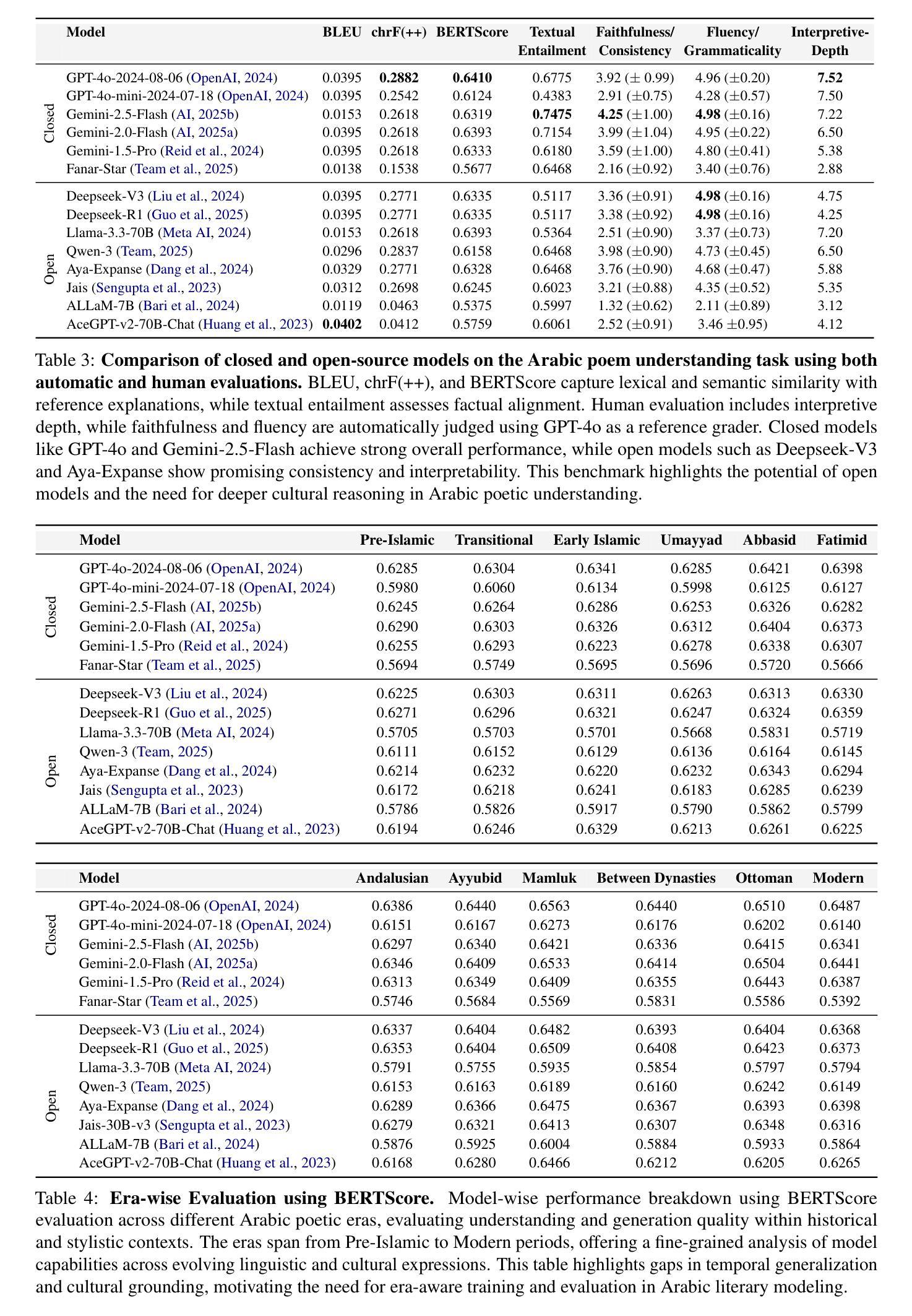
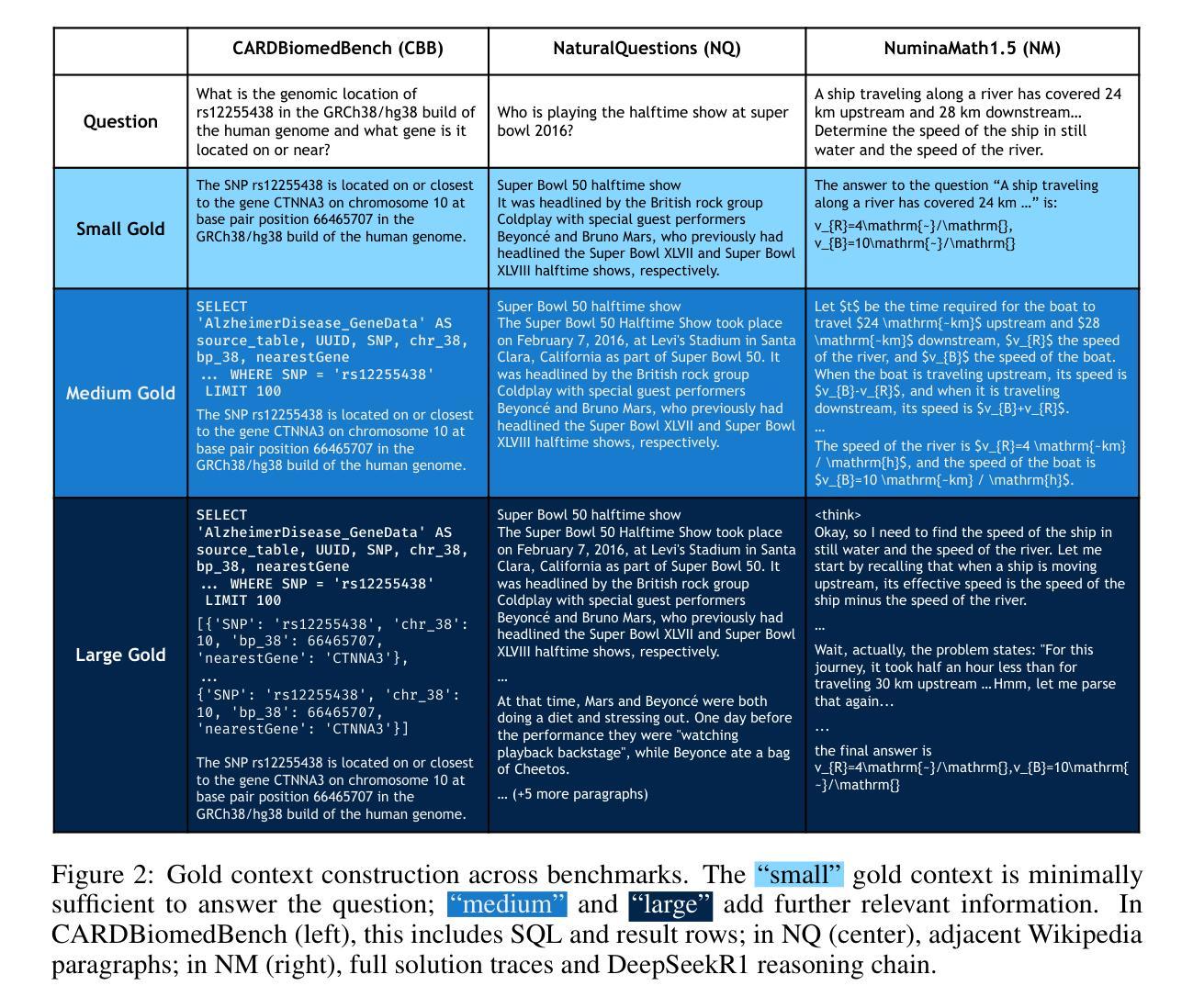
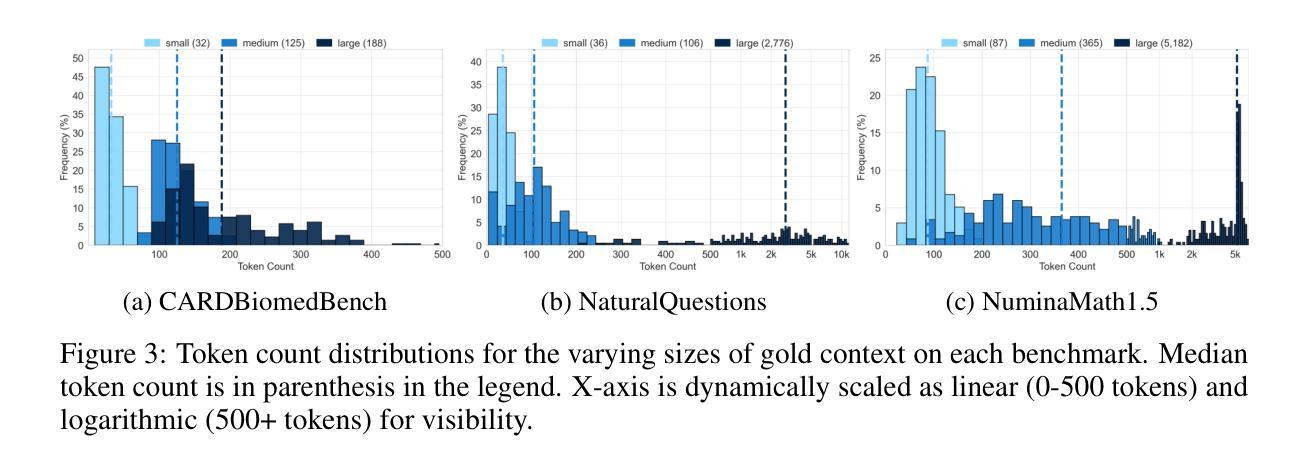
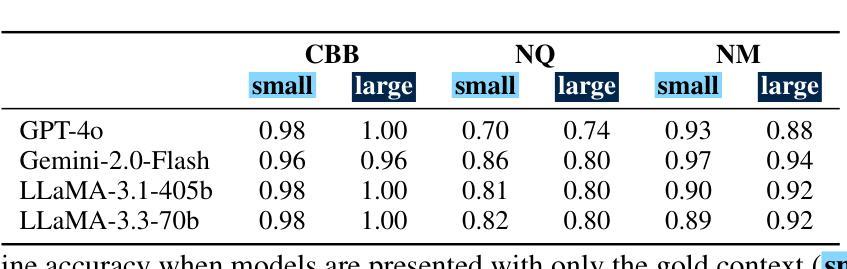
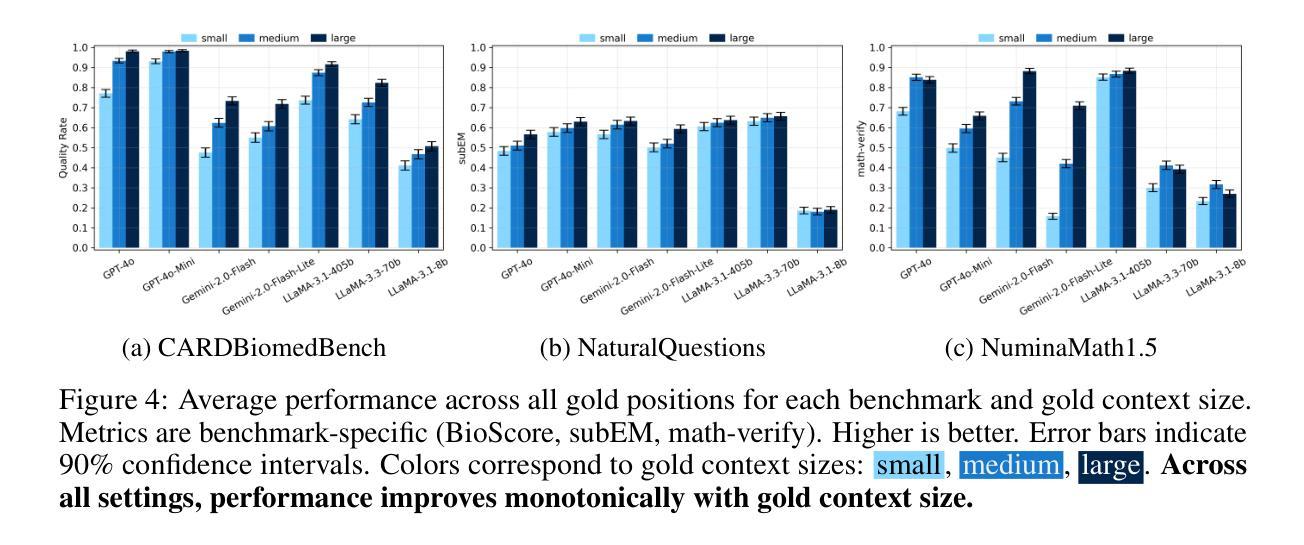
Large language models (LLMs) face significant challenges with needle-in-a-haystack tasks, where relevant information (“the needle”) must be drawn from a large pool of irrelevant context (“the haystack”). Previous studies have highlighted positional bias and distractor quantity as critical factors affecting model performance, yet the influence of gold context size has received little attention. We address this gap by systematically studying how variations in gold context length impact LLM performance on long-context question answering tasks. Our experiments reveal that LLM performance drops sharply when the gold context is shorter, i.e., smaller gold contexts consistently degrade model performance and amplify positional sensitivity, posing a major challenge for agentic systems that must integrate scattered, fine-grained information of varying lengths. This pattern holds across three diverse domains (general knowledge, biomedical reasoning, and mathematical reasoning) and seven state-of-the-art LLMs of various sizes and architectures. Our work provides clear insights to guide the design of robust, context-aware LLM-driven systems.
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理“海底捞针”任务时面临重大挑战,即从大量无关上下文信息(“大海”)中找出相关信息(“针”)。以往的研究已经强调了位置偏差和干扰项数量是影响模型性能的关键因素,但黄金上下文大小对模型的影响却被忽视。我们通过系统地研究黄金上下文长度变化对大型语言模型在长上下文问答任务性能的影响来填补这一空白。实验表明,当黄金上下文较短时,大型语言模型的性能急剧下降,即较小的黄金上下文始终会降低模型性能并加剧位置敏感性,这对必须整合分散、精细的变长信息的智能系统提出了重大挑战。这一模式在三个不同领域(通用知识、生物医学推理和数学推理)和七个不同大小和架构的先进大型语言模型中均适用。我们的研究提供了清晰的见解,为设计稳健的、具有上下文感知的大型语言模型驱动系统提供了指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理“众里寻针”的任务时面临挑战,即需要从大量无关内容中找出相关信息。虽然前人研究已指出位置偏差和干扰项数量是影响模型性能的关键因素,但黄金上下文规模的影响却鲜有研究。本研究通过系统地研究黄金上下文长度变化对长上下文问答任务中LLM性能的影响,填补了这一空白。实验表明,黄金上下文较短时,LLM性能急剧下降,即较小的黄金上下文会一致地降低模型性能并加剧位置敏感性,这对于必须整合各种长度分散、精细信息的代理系统是一个巨大挑战。这一模式在三个不同领域(通用知识、生物医学推理和数学推理)和七种不同规模和架构的先进LLM中均得到验证。本研究为设计稳健、上下文感知的LLM驱动系统提供了明确见解。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理需要从大量无关内容中找出相关信息(“众里寻针”任务)时面临挑战。
- 黄金上下文长度对LLM性能有重要影响。
- 较短的黄金上下文会导致LLM性能急剧下降。
- 较小的黄金上下文会降低模型性能并加剧位置敏感性。
- 这一现象在通用知识、生物医学推理和数学推理等多个领域都存在。
- 不同规模和架构的先进LLM都受到了这一挑战。
点此查看论文截图

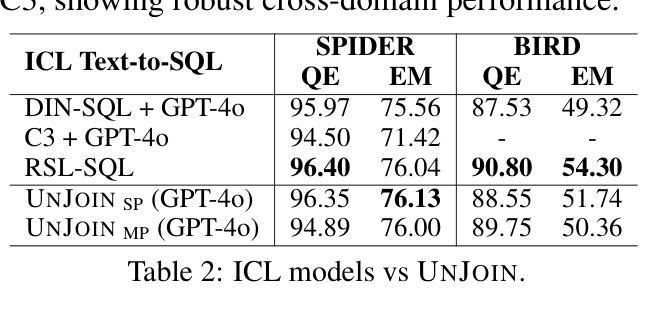
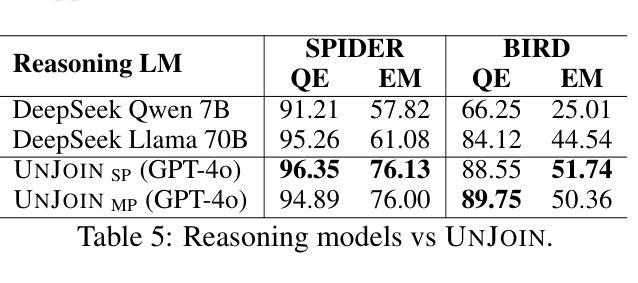
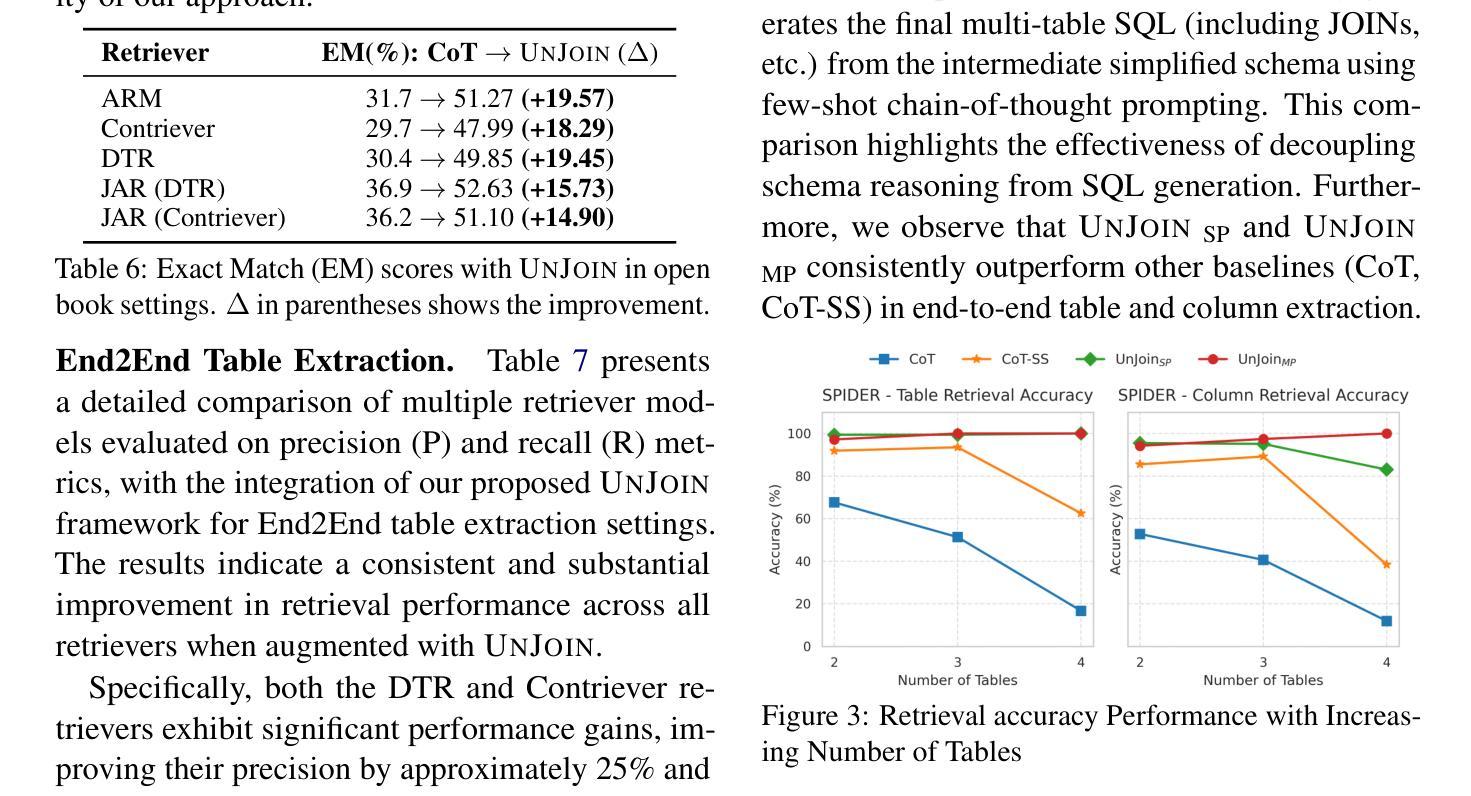
UNJOIN: Enhancing Multi-Table Text-to-SQL Generation via Schema Simplification
Authors:Poojah Ganesan, Rajat Aayush Jha, Dan Roth, Vivek Gupta
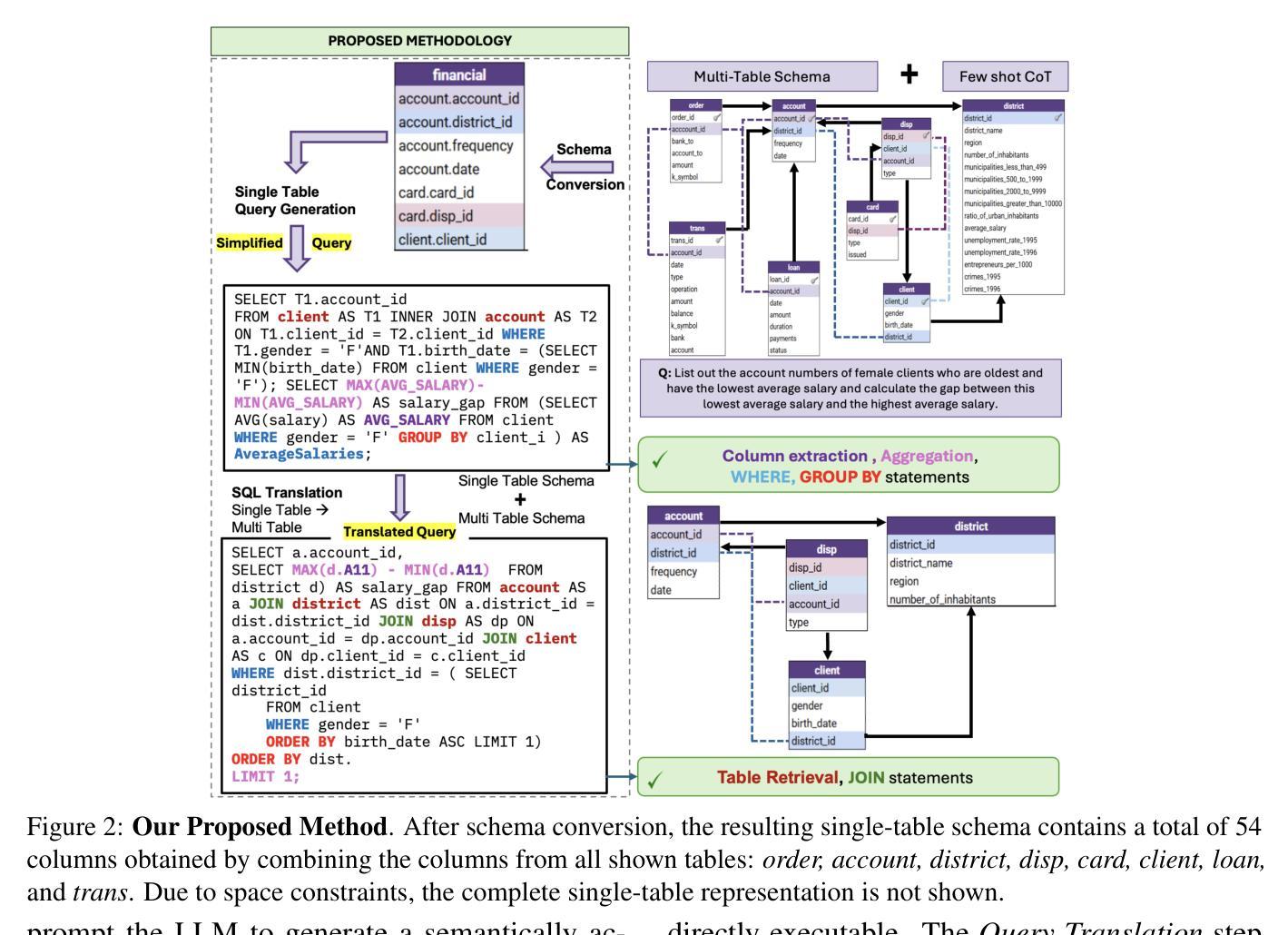
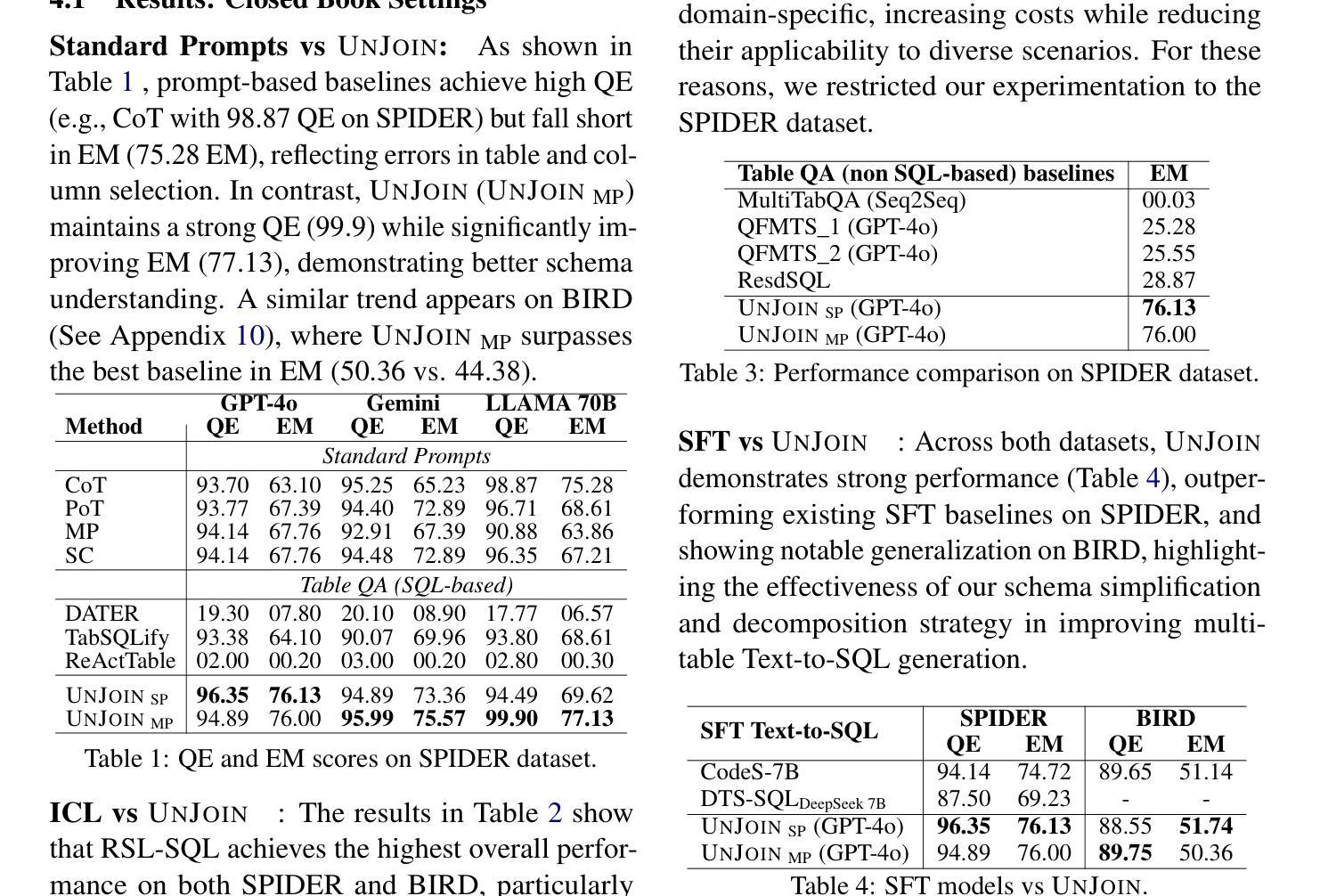
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have greatly improved Text-to-SQL performance for single-table queries. But, it remains challenging in multi-table databases due to complex schema and relational operations. Existing methods often struggle with retrieving the right tables and columns, generating accurate JOINs and UNIONs, and generalizing across diverse schemas. To address these issues, we introduce UNJOIN, a two-stage framework that decouples the retrieval of schema elements from SQL logic generation. In the first stage, we merge the column names of all tables in the database into a single-table representation by prefixing each column with its table name. This allows the model to focus purely on accurate retrieval without being distracted by the need to write complex SQL logic. In the second stage, the SQL query is generated on this simplified schema and mapped back to the original schema by reconstructing JOINs, UNIONs, and relational logic. Evaluations on SPIDER and BIRD datasets show that UNJOIN matches or exceeds the state-of-the-art baselines. UNJOIN uses only schema information, which does not require data access or fine-tuning, making it scalable and adaptable across databases.
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展极大地提高了单表查询的文本到SQL性能。然而,在多表数据库上仍然面临挑战,这主要是由于复杂的架构和关系操作。现有方法往往难以正确检索表和数据列,生成准确的JOINs和UNIONs,并且在多种架构之间进行归纳时遇到困难。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了UNJOIN,这是一个两阶段的框架,它将架构元素的检索与SQL逻辑生成分开。在第一阶段,我们通过为每列添加表名前缀的方式,将数据库中的所有表名合并为一个单一表表示形式。这允许模型专注于准确检索,而不受需要编写复杂的SQL逻辑所干扰。在第二阶段,在此简化的架构上生成SQL查询,并通过重新构建JOINs、UNIONs和关系逻辑将其映射回原始架构。在SPIDER和BIRD数据集上的评估表明,UNJOIN达到了或超过了最新基准测试水平。UNJOIN仅使用架构信息,无需数据访问或微调,使其可跨数据库进行扩展和适应。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)在面向单表查询的文本转SQL任务中取得了显著进步,但在多表数据库方面仍面临挑战。为解决现有方法在检索正确的表和列、生成准确的JOIN和UNION以及跨不同模式进行泛化方面的困难,提出了一种名为UNJOIN的两阶段框架。该框架通过将数据库中的所有表名列名合并为一个单一表表示,使模型能够专注于准确的检索,而不会受到需要编写复杂的SQL逻辑的影响。在简化模式上生成SQL查询,然后通过重建JOIN、UNION和关系逻辑将其映射回原始模式。在SPIDER和BIRD数据集上的评估显示,UNJOIN达到或超过了现有最新基线。由于仅使用模式信息且无需数据访问或微调,使其具有良好的可扩展性和适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在面向单表查询的文本转SQL任务上有所突破,但在多表数据库方面仍面临挑战。
- 现有方法在处理多表数据库时面临困难,如准确检索表和列、生成复杂的JOIN和UNION操作以及在多种模式之间进行泛化。
- UNJOIN框架被引入以解决这些问题,它通过两个阶段来实现:首先将所有表的列名合并为一个单一表示,使模型专注于准确检索;然后在简化模式上生成SQL查询并映射回原始模式。
- UNJOIN通过将复杂问题分解为两个阶段处理来提高模型的性能。
- UNJOIN在SPIDER和BIRD数据集上的评估表现良好,达到或超过了现有最新基线。
- UNJOIN仅使用模式信息,无需数据访问或微调,具有良好的可扩展性和适应性。
点此查看论文截图

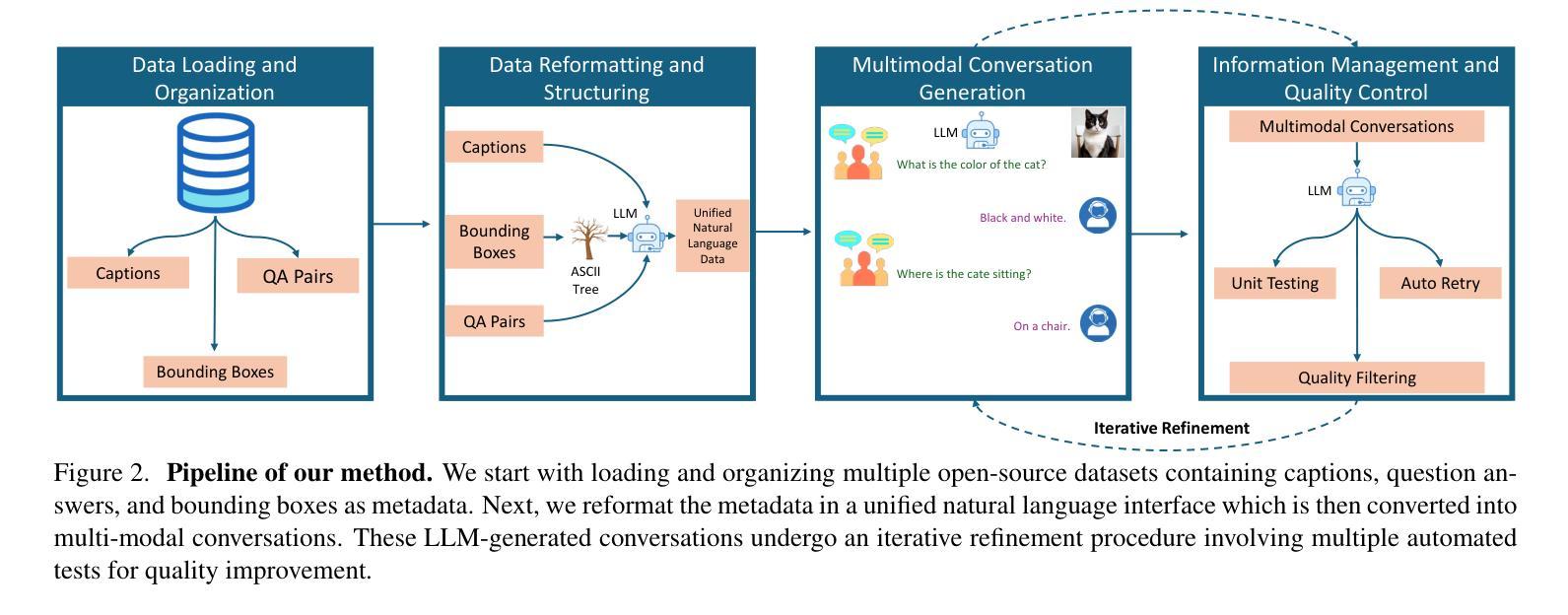
Instructify: Demystifying Metadata to Visual Instruction Tuning Data Conversion
Authors:Jacob Hansen, Wei Lin, Junmo Kang, Muhammad Jehanzeb Mirza, Hongyin Luo, Rogerio Feris, Alan Ritter, James Glass, Leonid Karlinsky
Visual Instruction Tuning (VisIT) data, commonly available as human-assistant conversations with images interleaved in the human turns, are currently the most widespread vehicle for aligning strong LLMs to understand visual inputs, converting them to strong LMMs. While many VisIT datasets are available, most are constructed using ad-hoc techniques developed independently by different groups. They are often poorly documented, lack reproducible code, and rely on paid, closed-source model APIs such as GPT-4, Gemini, or Claude to convert image metadata (labels) into VisIT instructions. This leads to high costs and makes it challenging to scale, enhance quality, or generate VisIT data for new datasets. In this work, we address these challenges and propose an open and unified recipe and approach,~\textbf{\method}, for converting available metadata to VisIT instructions using open LLMs. Our multi-stage \method features an efficient framework for metadata grouping, quality control, data and prompt organization, and conversation sampling. We show that our approach can reproduce or enhance the data quality of available VisIT datasets when applied to the same image data and metadata sources, improving GPT-4 generated VisIT instructions by ~3% on average and up to 12% on individual benchmarks using open models, such as Gemma 2 27B and LLaMa 3.1 70B. Additionally, our approach enables effective performance scaling - both in quantity and quality - by enhancing the resulting LMM performance across a wide range of benchmarks. We also analyze the impact of various factors, including conversation format, base model selection, and resampling strategies. Our code, which supports the reproduction of equal or higher-quality VisIT datasets and facilities future metadata-to-VisIT data conversion for niche domains, is released at https://github.com/jacob-hansen/Instructify.
视觉指令调整(VisIT)数据通常作为人类辅助对话中出现的人机交替图像呈现,是目前将强大的LLM对齐以理解视觉输入并将其转换为强大的LMM的最广泛工具。虽然有许多可用的VisIT数据集,但大多数是使用不同小组独立开发的特定技术构建的。它们通常文档不足,缺乏可重复使用的代码,并依赖于付费的、封闭源代码的模型API(如GPT-4、双子座或Claude)将图像元数据(标签)转换为VisIT指令。这导致了高昂的成本,并使得扩展、提高质量或为新数据集生成VisIT数据变得具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们应对这些挑战,并提出一种开放和统一的配方和方法——\method,使用开放的LLM将可用的元数据转换为VisIT指令。我们的多阶段\method方法具有高效的元数据分组、质量控制、数据和提示组织以及对话采样框架。我们表明,当应用于相同的图像数据和元数据源时,我们的方法可以复制或提高现有VisIT数据集的数据质量,在使用开放模型的情况下,GPT-4生成的VisIT指令平均提高约3%,个别基准测试最高可提高12%。此外,我们的方法通过提高所得LMM在广泛基准测试中的性能,实现了性能和质量的有效扩展。我们还分析了对话格式、基础模型选择和重新采样策略等各种因素的影响。我们的代码支持复制同等或更高质量的VisIT数据集,并为专业领域提供未来元数据到VisIT数据的转换,现已发布在https://github.com/jacob-hansen/Instructify。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强大的LLM模型理解和接受视觉输入的能力,可通过VisIT数据对其进行优化提升。然而,现有VisIT数据集多由不同团队独立开发构建,存在文档缺失、缺乏可复现代码、依赖收费闭源模型API等问题。本文提出一种开源统一的方案——方法(具体方案在文本中阐述),利用开源LLM将现有元数据转换为VisIT指令。该方法包含多个阶段,包括元数据分组、质量控制、数据和提示组织以及对话采样等。应用此方法可以改善现有VisIT数据集的质量,使用开源模型时,在相同图像数据和元数据来源上平均提高GPT-4生成的VisIT指令约3%,个别基准测试上最高可提高达12%。此外,此方法能有效提升性能规模,在多种基准测试中提高结果LLM的性能。同时,本文还分析了对话形式、基础模型选择和重采样策略等因素的影响,并公开了支持复现或更高质量VisIT数据集的工具和代码,以便未来进行元数据到VisIT数据的转换,以适应小众领域的需求。
Key Takeaways
- VisIT数据是优化LLM理解和处理视觉输入能力的主要手段。
- 当前VisIT数据集存在文档缺失、缺乏可复现代码、依赖收费闭源模型等问题。
- 提出一种开源统一的方案(具体细节在文中阐述)将现有元数据转换为VisIT指令。
- 此方法可以改善现有VisIT数据集质量,平均提高GPT-4生成的VisIT指令约3%,最高可达12%。
- 该方法可以提升性能规模,提高LLM在各种基准测试中的性能。
- 对话形式、基础模型选择和重采样策略等因素对该方法有影响。
点此查看论文截图


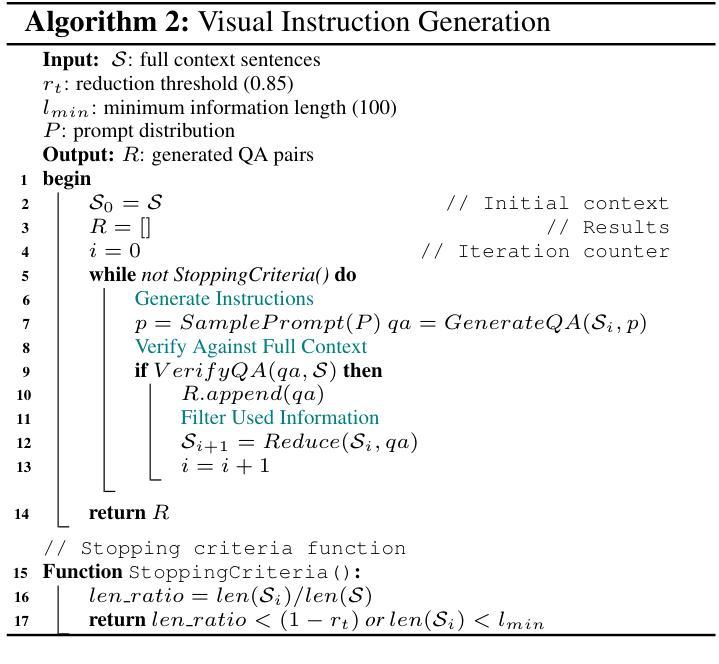
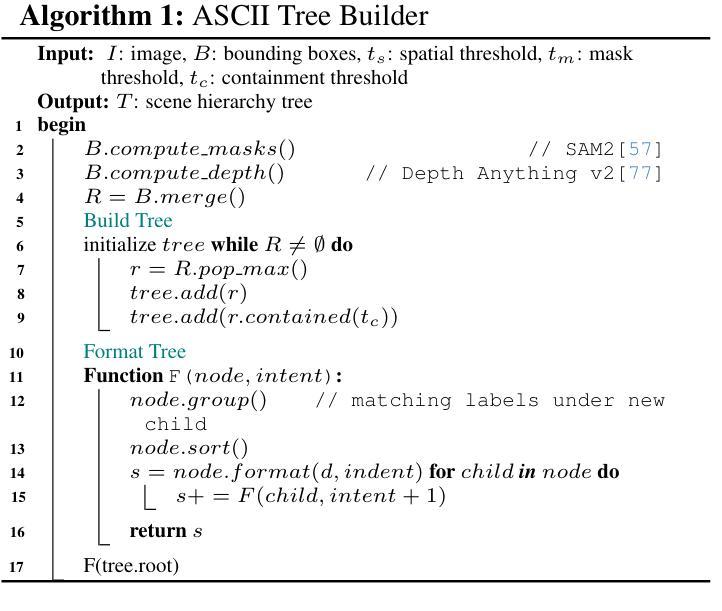
ManuSearch: Democratizing Deep Search in Large Language Models with a Transparent and Open Multi-Agent Framework
Authors:Lisheng Huang, Yichen Liu, Jinhao Jiang, Rongxiang Zhang, Jiahao Yan, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao
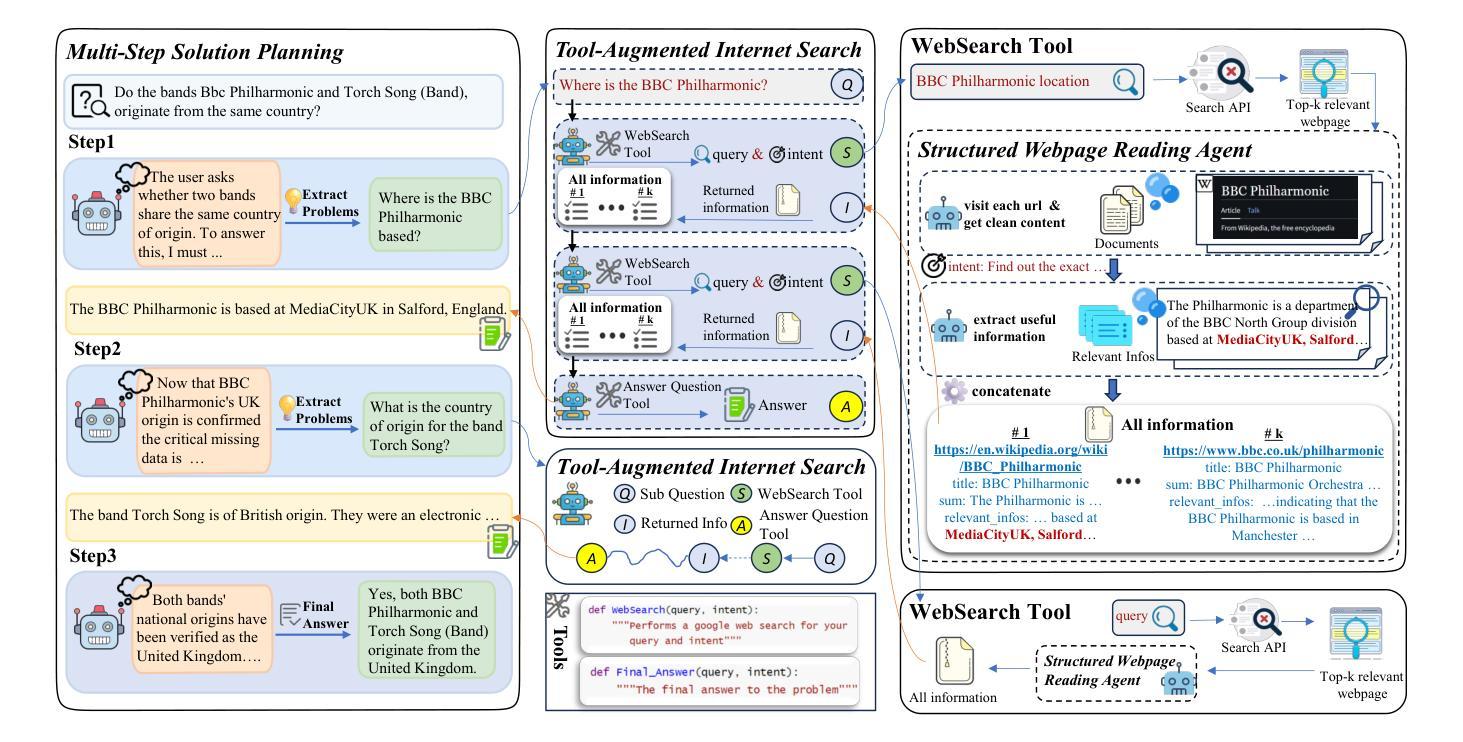
Recent advances in web-augmented large language models (LLMs) have exhibited strong performance in complex reasoning tasks, yet these capabilities are mostly locked in proprietary systems with opaque architectures. In this work, we propose \textbf{ManuSearch}, a transparent and modular multi-agent framework designed to democratize deep search for LLMs. ManuSearch decomposes the search and reasoning process into three collaborative agents: (1) a solution planning agent that iteratively formulates sub-queries, (2) an Internet search agent that retrieves relevant documents via real-time web search, and (3) a structured webpage reading agent that extracts key evidence from raw web content. To rigorously evaluate deep reasoning abilities, we introduce \textbf{ORION}, a challenging benchmark focused on open-web reasoning over long-tail entities, covering both English and Chinese. Experimental results show that ManuSearch substantially outperforms prior open-source baselines and even surpasses leading closed-source systems. Our work paves the way for reproducible, extensible research in open deep search systems. We release the data and code in https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ManuSearch
近期网络增强型大语言模型(LLM)的进步在复杂推理任务中表现出了强劲的性能,但这些能力大多被锁定在架构不透明的专有系统中。在这项工作中,我们提出了ManuSearch,这是一个透明且模块化的多智能体框架,旨在实现LLM的深度搜索民主化。ManuSearch将搜索和推理过程分解为三个协作的智能体:(1)解决方案规划智能体,它迭代地制定子查询;(2)互联网搜索智能体,它通过实时网页搜索检索相关文档;(3)结构化网页阅读智能体,它从原始网页内容中提取关键证据。为了严格评估深度推理能力,我们推出了ORION,这是一个专注于长尾实体上的开放网页推理的挑战性基准测试,涵盖英文和中文。实验结果表明,ManuSearch显著优于先前的开源基准测试,甚至超越了领先的专有系统。我们的工作为开放深度搜索系统中的可重复和可扩展研究铺平了道路。我们在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/ManuSearch公开了数据和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF LLM, Complex Search Benchmark
Summary
新一代网络增强大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂推理任务中展现出强大性能,但多数功能仅限于专有系统且架构不透明。本研究提出透明模块化多智能体框架ManuSearch,旨在实现LLM深度搜索的民主化。ManuSearch将搜索和推理过程分解为三个协作智能体:解决方案规划智能体、互联网搜索智能体和结构化网页阅读智能体。为严格评估深度推理能力,我们引入面向长尾实体的开放网络推理基准测试ORION,涵盖英文和中文。实验结果显示,ManuSearch显著优于先前开源基准线,甚至超越领先闭源系统。我们的研究为开放深度搜索系统的可复制和可扩展研究铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在复杂推理任务中具有强大性能,但功能局限于专有系统且架构不透明。
- ManuSearch是一个透明模块化多智能体框架,旨在实现LLM深度搜索的民主化。
- ManuSearch包括三个协作智能体:解决方案规划、互联网搜索和结构化网页阅读智能体。
- 为评估深度推理能力,引入了面向长尾实体的开放网络推理基准测试ORION。
- ManuSearch在实验中显著优于先前开源基准线,甚至超越领先闭源系统。
- 本研究为开放深度搜索系统的可复制和可扩展研究提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图

How Can I Publish My LLM Benchmark Without Giving the True Answers Away?
Authors:Takashi Ishida, Thanawat Lodkaew, Ikko Yamane
Publishing a large language model (LLM) benchmark on the Internet risks contaminating future LLMs: the benchmark may be unintentionally (or intentionally) used to train or select a model. A common mitigation is to keep the benchmark private and let participants submit their models or predictions to the organizers. However, this strategy will require trust in a single organization and still permits test-set overfitting through repeated queries. To overcome this issue, we propose a way to publish benchmarks without completely disclosing the ground-truth answers to the questions, while still maintaining the ability to openly evaluate LLMs. Our main idea is to inject randomness to the answers by preparing several logically correct answers, and only include one of them as the solution in the benchmark. This reduces the best possible accuracy, i.e., Bayes accuracy, of the benchmark. Not only is this helpful to keep us from disclosing the ground truth, but this approach also offers a test for detecting data contamination. In principle, even fully capable models should not surpass the Bayes accuracy. If a model surpasses this ceiling despite this expectation, this is a strong signal of data contamination. We present experimental evidence that our method can detect data contamination accurately on a wide range of benchmarks, models, and training methodologies.
在互联网上发布大型语言模型(LLM)的基准测试存在污染未来LLM的风险:基准测试可能被无意(或故意)用于训练或选择模型。常见的缓解方法是保持基准测试私有,让参与者向组织者提交他们的模型或预测。然而,这种策略需要信任单一组织,并且仍然允许通过重复查询来进行测试集过拟合。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种发布基准测试的方法,该方法无需完全公开问题的真实答案,同时仍能够公开评估LLM。我们的主要想法是通过准备多个逻辑正确的答案并随机注入答案,而只在基准测试中包括其中之一作为解决方案。这降低了基准测试的最佳可能准确度,即贝叶斯准确度。这不仅有助于我们避免公开真实答案,而且这种方法还提供了一种检测数据污染的方法。原则上,即使是非常完善的模型也不应超过贝叶斯准确度。如果一个模型超越了这一上限,尽管有这样的预期,这也是数据污染的一个强烈信号。我们提供的实验证据表明,我们的方法可以在广泛的基准测试、模型和训练方法论中准确地检测数据污染。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文讨论了在互联网上发布大型语言模型(LLM)基准测试的风险,可能会污染未来的LLM。为解决这个问题,提出了一种在基准测试中注入随机性的方法,通过准备多个逻辑正确的答案,只将其中一个作为基准测试中的解决方案。此方法不仅有助于不透露真实答案,还提供了一种检测数据污染的方法。实验证据表明,该方法能准确地在广泛的基准测试、模型和培训方法上检测数据污染。
Key Takeaways
- 发布LLM基准测试存在污染未来模型的风险。
- 一种常见策略是保持基准测试私密,让参与者提交模型或预测给组织者,但需信任单一组织并仍面临重复查询导致测试集过拟合的问题。
- 提出一种在基准测试中注入随机性的方法,通过准备多个逻辑正确答案为解决方案来公开评估LLM。
- 该方法降低基准测试的最佳准确度(即贝叶斯准确度),有助于不透露真实答案。
- 该方法提供检测数据污染的方法,理论上完全成熟的模型不应超过贝叶斯准确度。
- 若模型超过此上限,则为数据污染强烈信号。
点此查看论文截图


Deep Video Discovery: Agentic Search with Tool Use for Long-form Video Understanding
Authors:Xiaoyi Zhang, Zhaoyang Jia, Zongyu Guo, Jiahao Li, Bin Li, Houqiang Li, Yan Lu
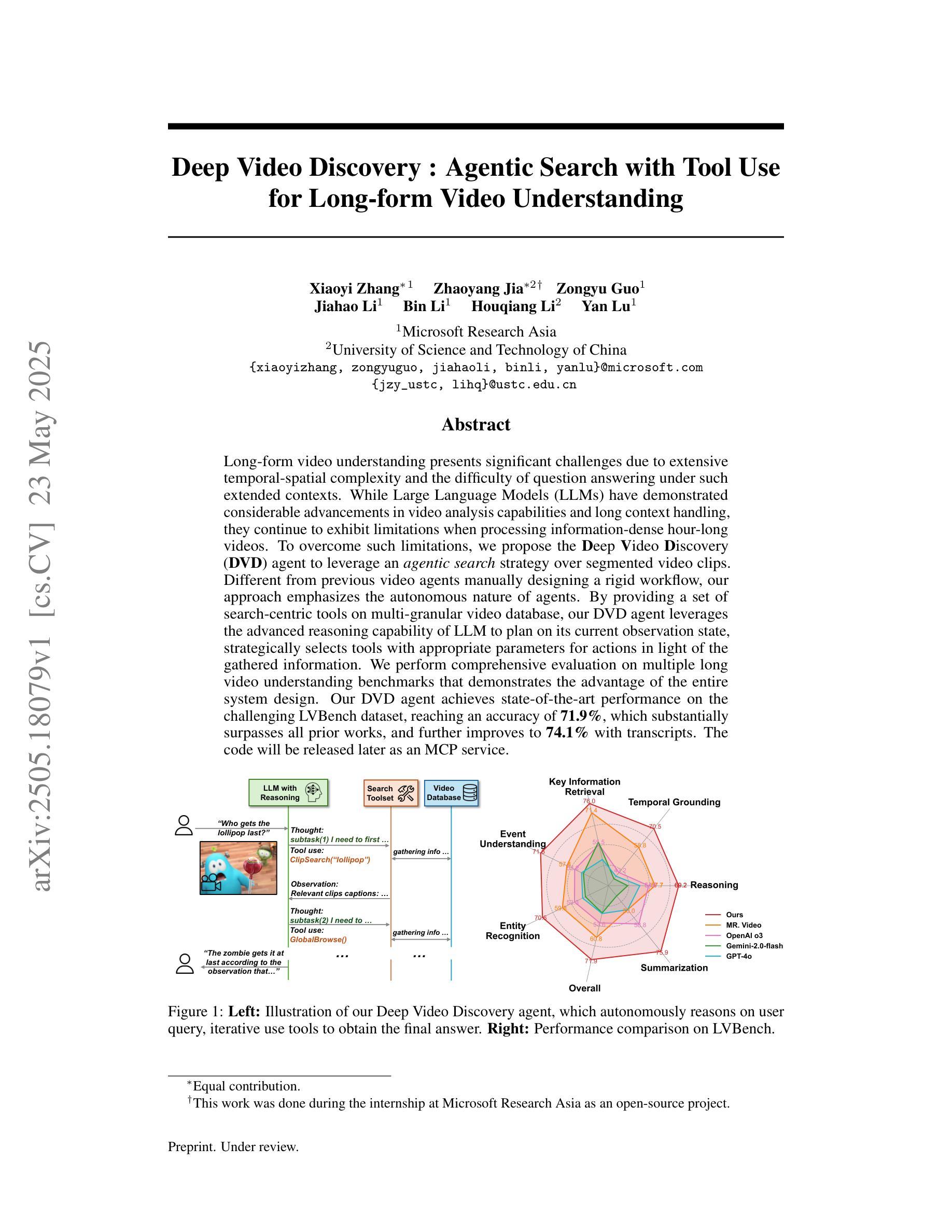
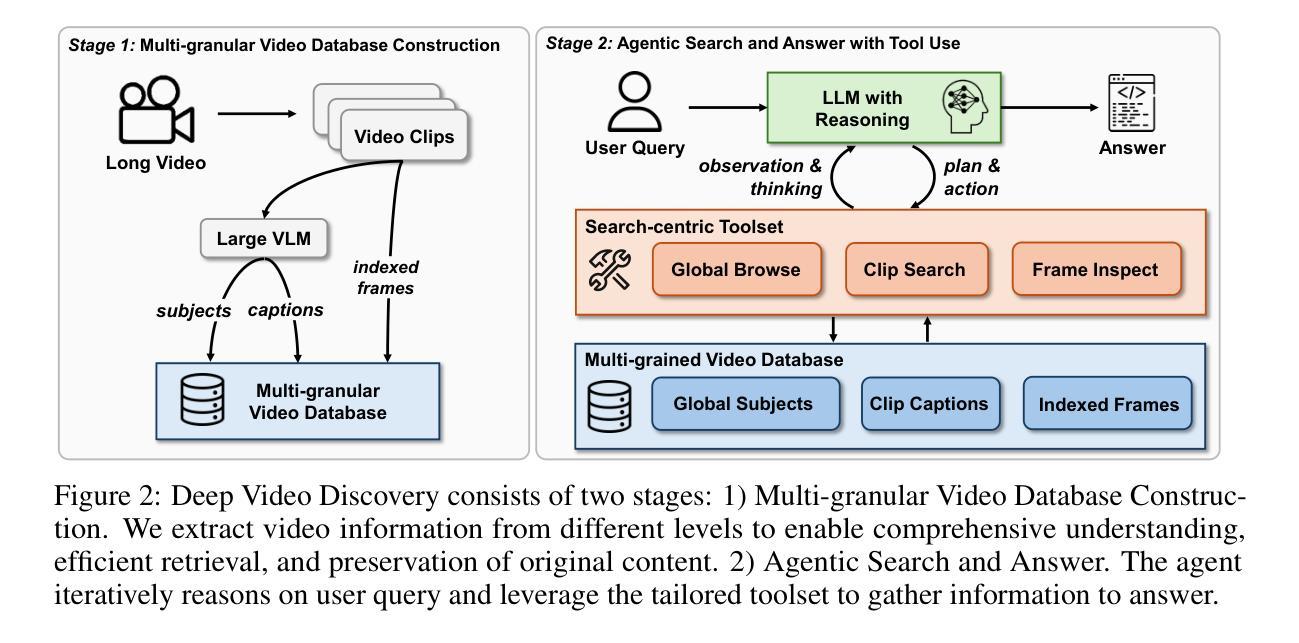
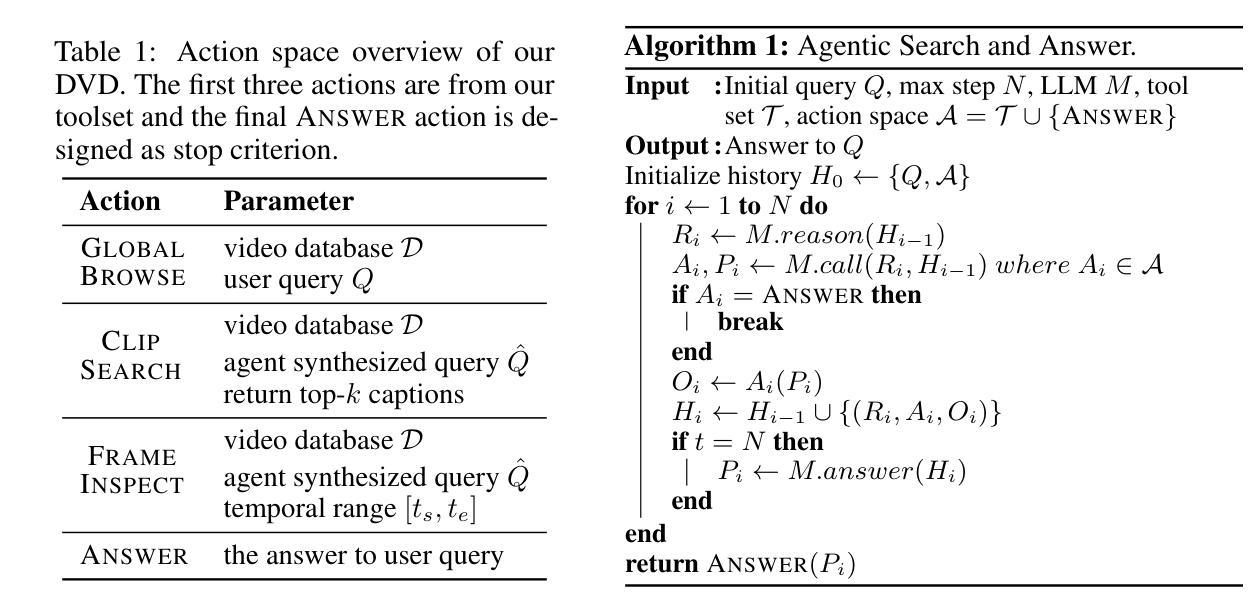
Long-form video understanding presents significant challenges due to extensive temporal-spatial complexity and the difficulty of question answering under such extended contexts. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated considerable advancements in video analysis capabilities and long context handling, they continue to exhibit limitations when processing information-dense hour-long videos. To overcome such limitations, we propose the Deep Video Discovery agent to leverage an agentic search strategy over segmented video clips. Different from previous video agents manually designing a rigid workflow, our approach emphasizes the autonomous nature of agents. By providing a set of search-centric tools on multi-granular video database, our DVD agent leverages the advanced reasoning capability of LLM to plan on its current observation state, strategically selects tools, formulates appropriate parameters for actions, and iteratively refines its internal reasoning in light of the gathered information. We perform comprehensive evaluation on multiple long video understanding benchmarks that demonstrates the advantage of the entire system design. Our DVD agent achieves SOTA performance, significantly surpassing prior works by a large margin on the challenging LVBench dataset. Comprehensive ablation studies and in-depth tool analyses are also provided, yielding insights to further advance intelligent agents tailored for long-form video understanding tasks. The code will be released later.
长视频理解面临着巨大的挑战,这主要是由于其庞大的时空复杂性和在这种扩展背景下进行问答的难度。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在视频分析能力和长文本处理能力方面取得了显著的进步,但在处理信息密集、时长为一小时的视频时,它们仍然表现出一些局限性。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了深度视频发现代理(DVD agent),采用基于分割视频片段的代理搜索策略。不同于以前的手动设计刚性工作流程的视频代理,我们的方法强调了代理的自主性。通过在多粒度视频数据库上提供一系列以搜索为中心的工具,DVD代理利用LLM的高级推理能力来规划其当前观察状态,策略性地选择工具,为行动制定适当参数,并根据收集的信息迭代优化其内部推理。我们在多个长视频理解基准测试上对系统进行了全面评估,证明了整个系统设计的优势。我们的DVD代理实现了最先进的性能,在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上大大超越了以前的工作。我们还提供了全面的消融研究和深入的工具分析,以推动针对长视频理解任务的智能代理的进一步发展。代码将在稍后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
长视频理解面临巨大的挑战,包括时空复杂度和长上下文下的问题回答难度。大型语言模型在处理信息密集型长视频时展现出优势但仍有限制。为此,我们提出Deep Video Discovery智能体解决方案,通过灵活的代理搜索策略,针对分段视频片段采用自主学习。与以往手动设计工作流程的视频代理不同,我们的方法强调代理的自主性。通过提供多粒度视频数据库上的搜索中心工具集,DVD智能体利用LLM的高级推理能力来规划当前观察状态,灵活选择工具,制定适当的行动参数,并根据收集到的信息迭代优化内部推理。我们在多个长视频理解基准测试集上进行了全面评估,证明了系统设计的优势。DVD智能体达到了先进性能水平,在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上大幅度超越了先前作品。同时提供了全面的消融研究和深入的工具分析,为针对长视频理解任务进一步开发智能体提供了见解。代码将随后发布。
Key Takeaways
- 长视频理解存在时空复杂性和长上下文问题回答的难点。
- 大型语言模型在处理信息密集型长视频时展现出优势,但仍存在限制。
- 提出的Deep Video Discovery智能体采用灵活的代理搜索策略,针对分段视频片段进行自主学习。
- DVD智能体的设计强调代理的自主性,能自主规划观察状态、选择工具、制定行动参数并优化内部推理。
- 在多个长视频理解基准测试集上全面评估,DVD智能体达到先进性能水平。
- 在具有挑战性的LVBench数据集上,DVD智能体大幅度超越了先前作品。
点此查看论文截图
Extended Inductive Reasoning for Personalized Preference Inference from Behavioral Signals
Authors:Jia-Nan Li, Jian Guan, Wei Wu, Rui Yan
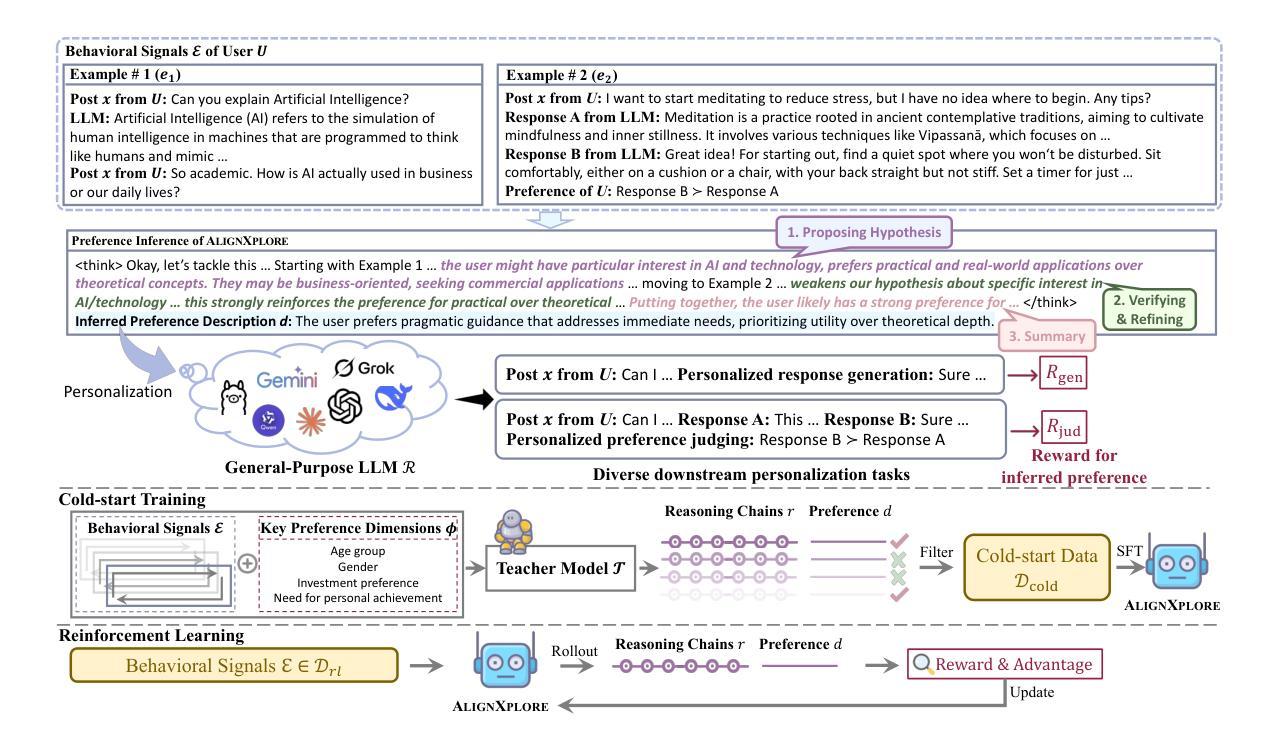
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant success in complex reasoning tasks such as math and coding. In contrast to these tasks where deductive reasoning predominates, inductive reasoning\textemdash the ability to derive general rules from incomplete evidence, remains underexplored. This paper investigates extended inductive reasoning in LLMs through the lens of personalized preference inference, a critical challenge in LLM alignment where current approaches struggle to capture diverse user preferences. The task demands strong inductive reasoning capabilities as user preferences are typically embedded implicitly across various interaction forms, requiring models to synthesize consistent preference patterns from scattered signals. We propose \textsc{AlignXplore}, a model that leverages extended reasoning chains to enable systematic preference inference from behavioral signals in users’ interaction histories. We develop \textsc{AlignXplore} by combining cold-start training based on synthetic data with subsequent online reinforcement learning. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that \textsc{AlignXplore} achieves substantial improvements over the backbone model by an average of 11.05% on in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks, while maintaining strong generalization ability across different input formats and downstream models. Further analyses establish best practices for preference inference learning through systematic comparison of reward modeling strategies, while revealing the emergence of human-like inductive reasoning patterns during training.
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂的推理任务(如数学和编程)中取得了显著的成功。然而,与这些以演绎推理为主的任务相比,关于归纳推理——从不完整证据中推导一般规则的能力——的研究仍然不足。本文通过个性化偏好推断的视角研究了LLM中的扩展归纳推理,这是LLM对齐中的一个关键挑战,因为当前的方法很难捕捉多样化的用户偏好。该任务需要强大的归纳推理能力,因为用户偏好通常隐含在各种交互形式中,需要模型从散乱的信号中综合出一致的偏好模式。\emph{我们提出了一个名为\emph{AlignXplore}的模型,该模型利用扩展的推理链,从用户交互历史的行为信号中进行系统的偏好推断。我们通过结合基于合成数据的冷启动训练与随后的在线强化学习来开发\emph{AlignXplore}。通过广泛的实验,我们证明了\emph{AlignXplore}在域内和域外基准测试上平均比基础模型提高了11.05%,同时在不同输入格式和下游模型中保持了强大的泛化能力。进一步的分析通过系统地比较奖励建模策略,建立了偏好推断学习的最佳实践,同时揭示了训练过程中人类式归纳推理模式的出现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂的推理任务(如数学和编程)中取得了显著的成功。然而,与以演绎推理为主的这些任务相比,关于归纳推理——从不完整证据中推导一般规则的能力——的研究仍然不足。本文通过个性化偏好推理的角度探索了LLM中的扩展归纳推理,这是LLM对齐中的一个关键挑战,因为现有的方法很难捕捉用户多样化的偏好。任务要求模型具备强大的归纳推理能力,因为用户偏好通常隐含在各种交互形式中,需要模型从散乱的信号中合成一致偏好模式。本文提出了一个名为AlignXplore的模型,它通过利用扩展推理链来实现从用户交互历史的行为信号中进行系统的偏好推理。我们结合基于合成数据的冷启动训练与随后的在线强化学习来开发AlignXplore。通过广泛的实验,我们证明了AlignXplore相较于基准模型在域内和域外基准测试上平均提高了11.05%的效果,同时在不同输入格式和下游模型中保持了强大的泛化能力。进一步的分析建立了偏好推理学习的最佳实践,通过奖励建模策略的系统比较,揭示了训练过程中人类归纳推理模式的出现。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在复杂推理任务中表现出显著成功,但在归纳推理方面研究不足。
- 个性化偏好推理是LLM对齐的关键挑战,现有方法难以捕捉用户多样化的偏好。
- 归纳推理在LLM中很重要,因为用户偏好通常隐含在各种交互形式中。
- 提出了AlignXplore模型,结合冷启动训练和在线强化学习,实现系统偏好推理。
- AlignXplore在域内和域外基准测试上较基准模型有显著提高,泛化能力强。
- 最佳实践表明,奖励建模策略对偏好推理学习至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

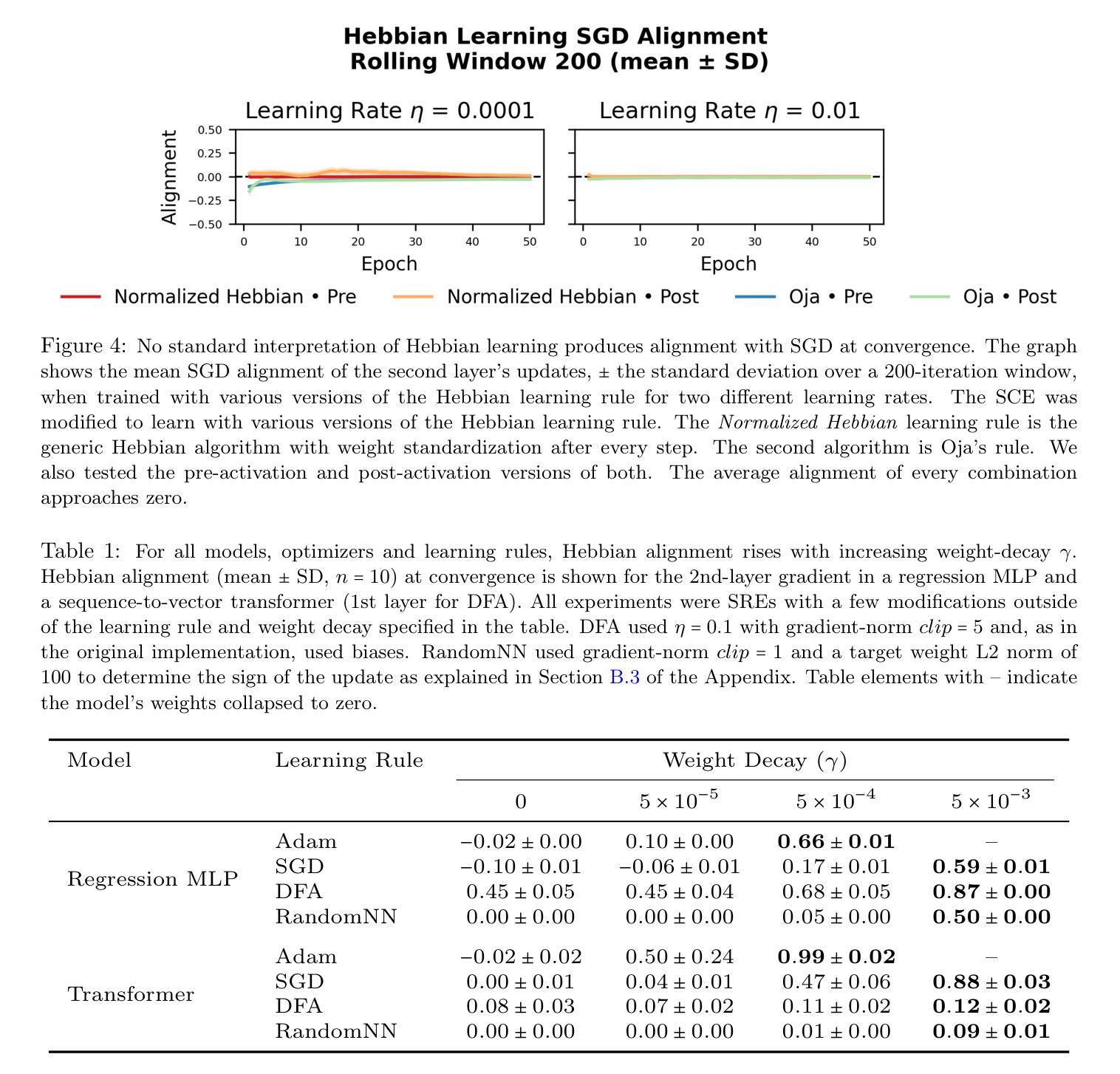
Emergence of Hebbian Dynamics in Regularized Non-Local Learners
Authors:David Koplow, Tomaso Poggio, Liu Ziyin
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) has emerged as a remarkably effective learning algorithm, underpinning nearly all state-of-the-art machine learning models, from large language models to autonomous vehicles. Despite its practical success, SGD appears fundamentally distinct from biological learning mechanisms. It is widely believed that the biological brain can not implement gradient descent because it is nonlocal, and we have found little (if any) experimental evidence for it. In contrast, the brain is widely thought to learn via local Hebbian learning principles, which have been seen as incompatible with gradient descent. In this paper, we establish a theoretical and empirical connection between the learning signals of neural networks trained using SGD with weight decay and those trained with Hebbian learning near convergence. We show that SGD with regularization can appear to learn according to a Hebbian rule, and SGD with injected noise according to an anti-Hebbian rule. We also provide empirical evidence that Hebbian learning properties can emerge in a network with weight decay from virtually any learning rule–even random ones. These results may bridge a long-standing gap between artificial and biological learning, revealing Hebbian properties as an epiphenomenon of deeper optimization principles and cautioning against interpreting their presence in neural data as evidence against more complex hetero-synaptic mechanisms.
随机梯度下降(SGD)作为一种极其有效的学习算法,已经成为几乎所有最先进的机器学习模型的基础,从大型语言模型到自动驾驶汽车。尽管SGD在实践中取得了成功,但它似乎与生物学习机制存在根本区别。普遍认为生物大脑无法实施梯度下降,因为它是非局部的,我们几乎没有(如果有的话)实验证据可以证明这一点。相反,人们普遍认为大脑通过局部的赫布学习原理来学习,这与梯度下降被认为是不相容的。在本文中,我们在理论上和实证上建立了使用带有权重衰减的SGD训练的神经网络的学习信号与在收敛附近使用赫布学习训练的学习信号之间的联系。我们表明,带有正则化的SGD似乎可以根据赫布规则来学习,而带有注入噪声的SGD则根据反赫布规则来学习。我们还提供实证证据表明,在带有权重衰减的网络中,赫布学习特性可以从几乎任何学习规则中出现,甚至是随机规则。这些结果可能填补了人工智能和生物学习之间的长期鸿沟,揭示赫布属性是更深层次优化原则的副产品,并警告人们不要将神经数据中的赫布属性解释为反对更复杂的异突触机制的证据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随机梯度下降(SGD)已成为一种非常有效的学习算法,几乎支撑了所有最先进的机器学习模型。尽管SGD与生物学习机制存在根本差异,但本文建立了SGD学习与Hebbian学习之间的理论联系和实证联系。我们展示了带有正则化的SGD似乎遵循Hebbian规则,而带有注入噪声的SGD则遵循anti-Hebbian规则。此外,实证证据表明,具有权重衰减的网络可以从几乎任何学习规则中展现出Hebbian学习属性,揭示了Hebbian属性是更深层次优化原则的副产品。
Key Takeaways:
- 随机梯度下降(SGD)是机器学习领域的主要学习算法,广泛应用于各种先进模型。
- SGD与生物学习机制存在根本差异,但本文探讨了它们之间的理论联系。
- 带有正则化的SGD表现出的学习与Hebbian学习规则相似。
- 带有注入噪声的SGD表现出与anti-Hebbian规则相似的特性。
- Hebbian学习属性可以在网络权重衰减过程中从各种学习规则中显现。
- 这些发现揭示了Hebbian属性可能是更深层次优化原则的副产品。
点此查看论文截图

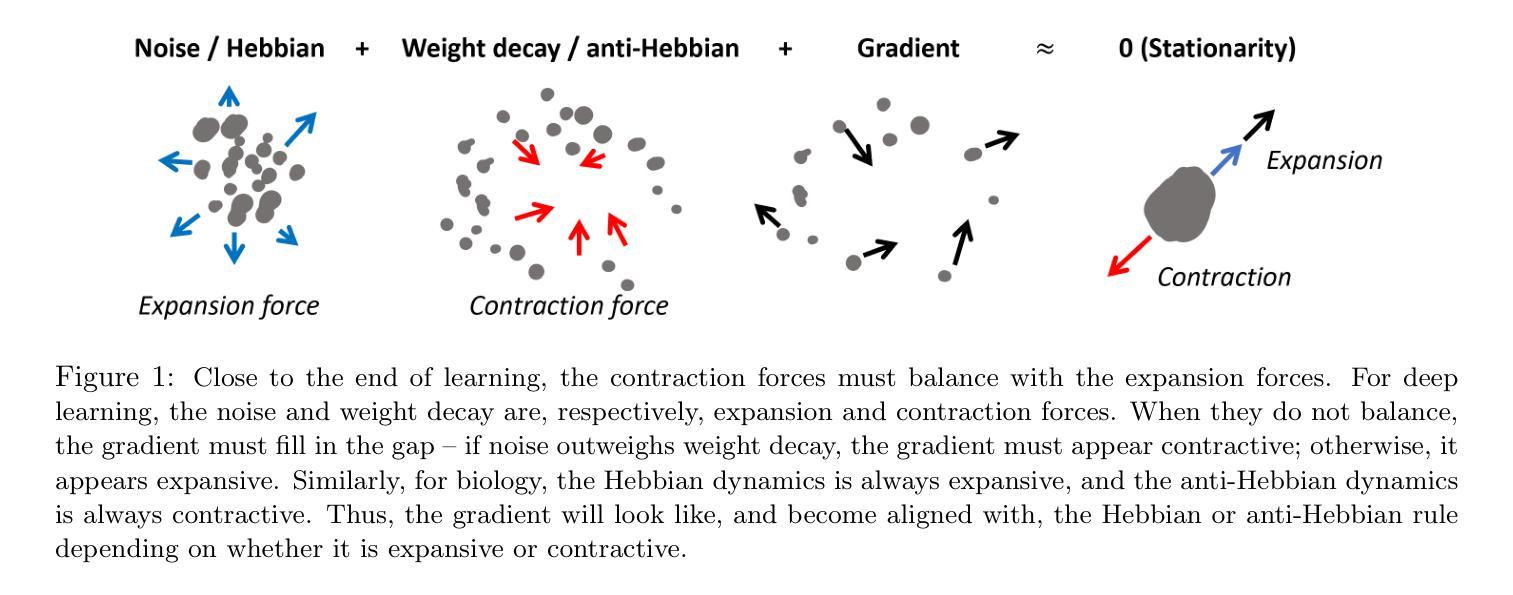
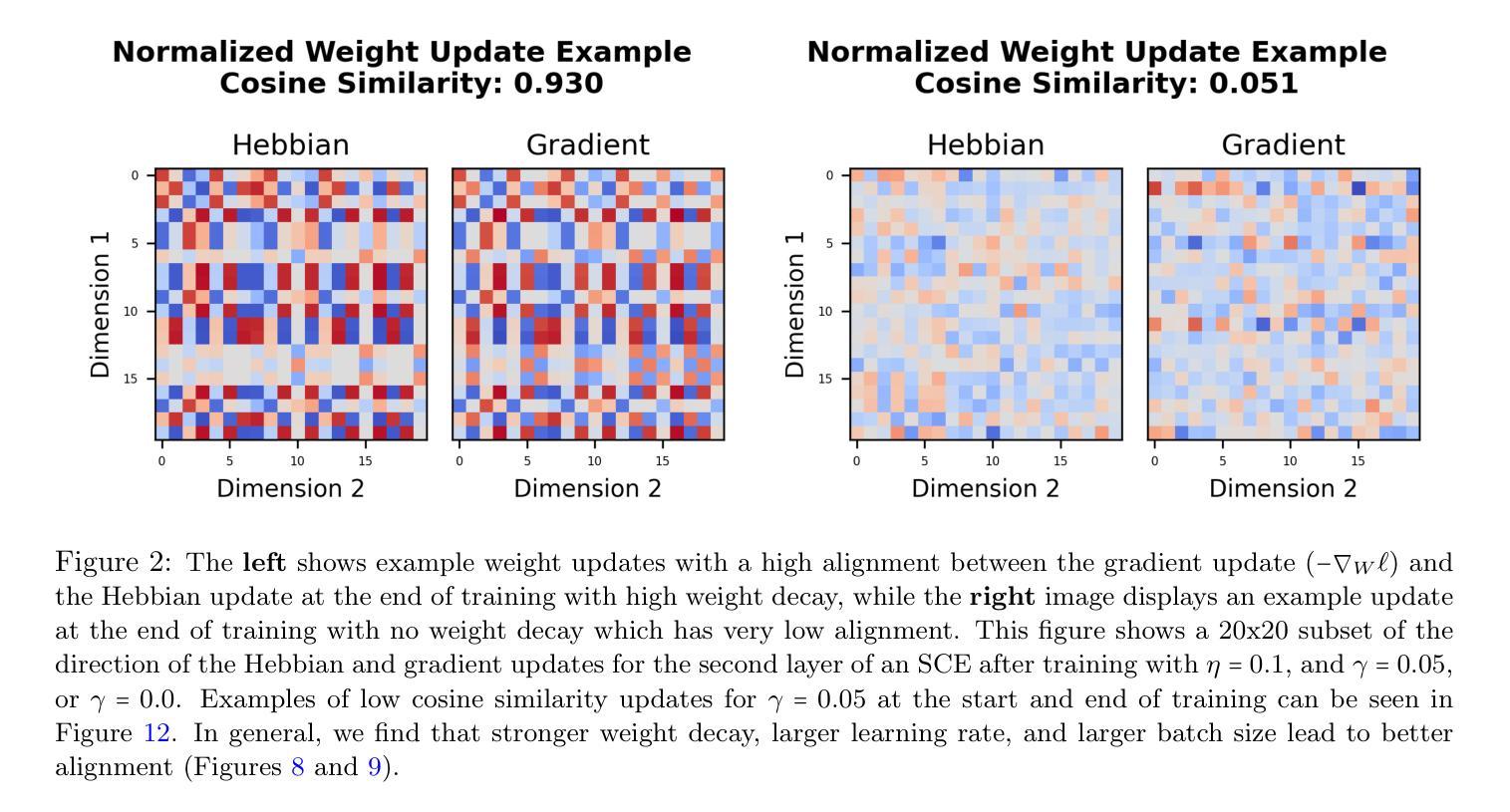
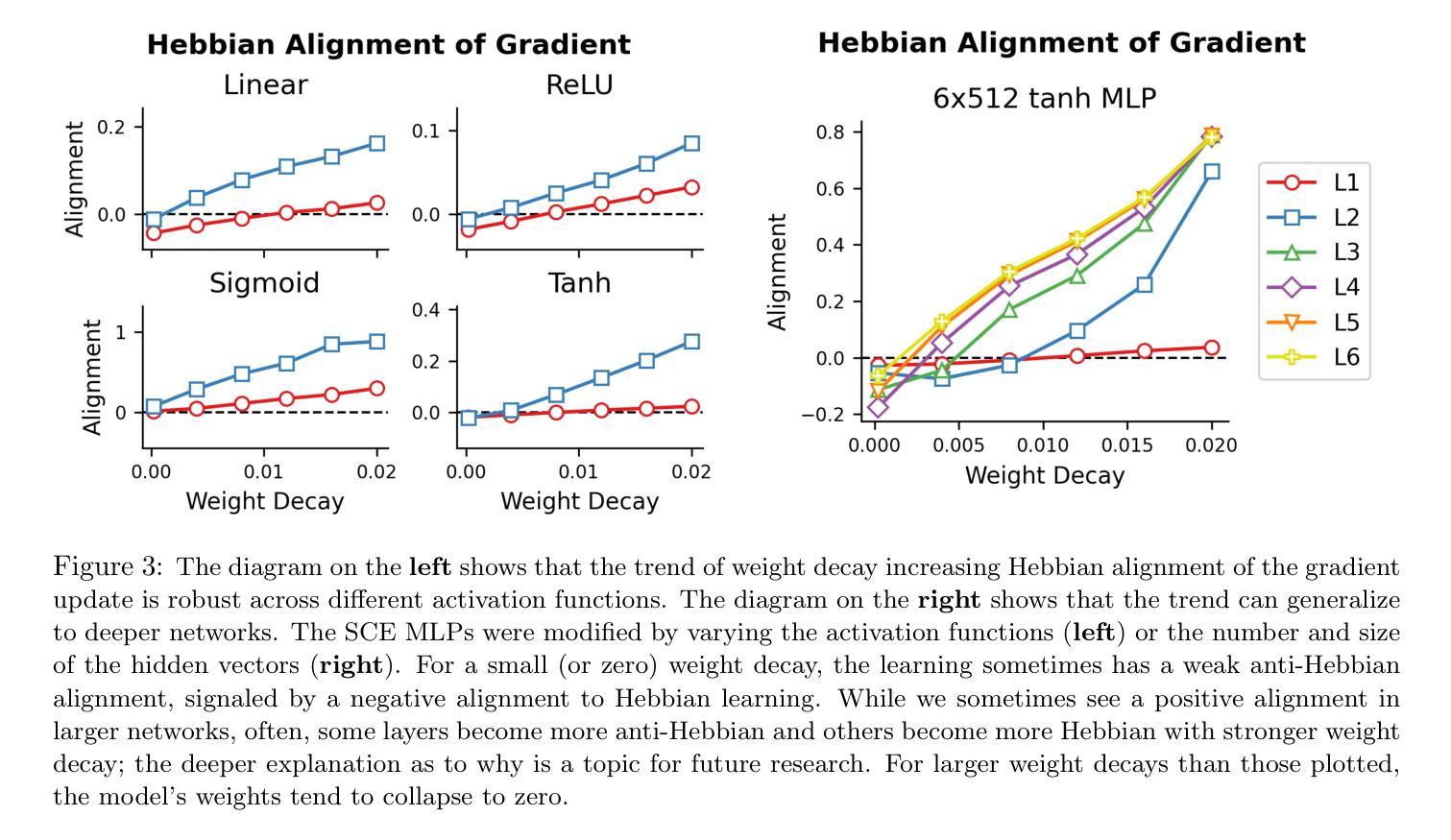
Reward Model Generalization for Compute-Aware Test-Time Reasoning
Authors:Zeen Song, Wenwen Qiang, Siyu Zhao, Changwen Zheng, Gang Hua
External test-time reasoning enhances large language models (LLMs) by decoupling generation and selection. At inference time, the model generates multiple reasoning paths, and an auxiliary process reward model (PRM) is used to score and select the best one. A central challenge in this setting is test-time compute optimality (TCO), i.e., how to maximize answer accuracy under a fixed inference budget. In this work, we establish a theoretical framework to analyze how the generalization error of the PRM affects compute efficiency and reasoning performance. Leveraging PAC-Bayes theory, we derive generalization bounds and show that a lower generalization error of PRM leads to fewer samples required to find correct answers. Motivated by this analysis, we propose Compute-Aware Tree Search (CATS), an actor-critic framework that dynamically controls search behavior. The actor outputs sampling hyperparameters based on reward distributions and sparsity statistics, while the critic estimates their utility to guide budget allocation. Experiments on the MATH and AIME benchmarks with various LLMs and PRMs demonstrate that CATS consistently outperforms other external TTS methods, validating our theoretical predictions.
外部测试时间推理通过解耦生成和选择来增强大型语言模型(LLM)。在推理阶段,模型生成多个推理路径,并使用辅助过程奖励模型(PRM)来评分和选择最佳路径。在这种情况下,核心挑战在于测试时间计算最优化(TCO),即如何在固定的推理预算下最大化答案的准确性。在这项工作中,我们建立了一个理论框架来分析PRM的泛化误差如何影响计算效率和推理性能。我们利用PAC-Bayes理论,推导出泛化边界,并证明PRM的较低泛化误差会导致寻找正确答案所需样本减少。受此分析启发,我们提出了计算感知树搜索(CATS),这是一种动态控制搜索行为的演员评论家框架。演员根据奖励分布和稀疏统计输出采样超参数,而评论家则估计它们的效用以指导预算分配。在MATH和AIME基准测试上对多种LLM和PRM进行的实验表明,CATS始终优于其他外部TTS方法,验证了我们的理论预测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过解耦生成和选择过程实现测试时的推理增强。在推理阶段,模型生成多个推理路径,并使用辅助奖励模型(PRM)进行评分和选择最佳路径。本文建立了一个理论框架,分析PRM的泛化误差对计算效率和推理性能的影响。利用PAC-Bayes理论,我们推导了泛化边界,表明PRM的泛化误差降低可以减少寻找正确答案所需的样本数量。受这一分析的启发,我们提出了计算感知树搜索(CATS),这是一种动态控制搜索行为的演员评论家框架。演员根据奖励分布和稀疏性统计输出采样超参数,而评论家则估计它们的效用,以指导预算分配。在MATH和AIME基准测试上的实验表明,CATS在各种LLM和PRM上的表现始终优于其他外部测试时间推理方法,验证了我们的理论预测。
Key Takeaways
- 外部测试时间推理通过解耦生成和选择过程增强大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 在推理阶段,模型使用辅助奖励模型(PRM)进行评分和选择最佳推理路径。
- 本文建立了理论框架分析PRM泛化误差对计算效率和推理性能的影响。
- 利用PAC-Bayes理论推导泛化边界,显示降低PRM的泛化误差可以减少寻找正确答案所需的样本数量。
- 提出计算感知树搜索(CATS)方法,动态控制搜索行为,包含演员和评论家的框架设计。
- 演员基于奖励分布和稀疏性统计输出采样超参数,评论家则估计这些超参数的效用以指导预算分配。
点此查看论文截图
Assessing the performance of 8 AI chatbots in bibliographic reference retrieval: Grok and DeepSeek outperform ChatGPT, but none are fully accurate
Authors:Álvaro Cabezas-Clavijo, Pavel Sidorenko-Bautista
This study analyzes the performance of eight generative artificial intelligence chatbots – ChatGPT, Claude, Copilot, DeepSeek, Gemini, Grok, Le Chat, and Perplexity – in their free versions, in the task of generating academic bibliographic references within the university context. A total of 400 references were evaluated across the five major areas of knowledge (Health, Engineering, Experimental Sciences, Social Sciences, and Humanities), based on a standardized prompt. Each reference was assessed according to five key components (authorship, year, title, source, and location), along with document type, publication age, and error count. The results show that only 26.5% of the references were fully correct, 33.8% partially correct, and 39.8% were either erroneous or entirely fabricated. Grok and DeepSeek stood out as the only chatbots that did not generate false references, while Copilot, Perplexity, and Claude exhibited the highest hallucination rates. Furthermore, the chatbots showed a greater tendency to generate book references over journal articles, although the latter had a significantly higher fabrication rate. A high degree of overlap was also detected among the sources provided by several models, particularly between DeepSeek, Grok, Gemini, and ChatGPT. These findings reveal structural limitations in current AI models, highlight the risks of uncritical use by students, and underscore the need to strengthen information and critical literacy regarding the use of AI tools in higher education.
本研究分析了八个生成式人工智能聊天机器人——ChatGPT、Claude、Copilot、DeepSeek、Gemini、Grok、Le Chat和Perplexity——在其免费版本中的表现,在生成大学背景下的学术参考文献的任务中。共评估了五大领域(健康、工程、实验科学、社会科学和人文科学)的参考文献共计400篇,基于标准化提示进行评估。每一条参考文献根据五个关键组成部分(作者、年份、标题、来源和位置),以及文档类型、出版年代和错误数量进行评估。结果显示,仅有26.5%的参考文献完全正确,33.8%部分正确,而错误或完全虚构的参考文献占到了39.8%。Grok和DeepSeek是唯一一个没有生成错误参考文献的聊天机器人,而Copilot、Perplexity和Claude展现出最高的虚构报告率。此外,聊天机器人更倾向于生成书籍参考文献而非期刊文章,尽管后者的虚构率显著更高。我们还发现了多个模型提供的来源之间存在大量重叠,尤其是DeepSeek、Grok、Gemini和ChatGPT之间。这些发现揭示了当前人工智能模型的结构局限性,凸显了学生无批判性使用的风险,并强调了加强关于高等教育中使用人工智能工具的信息和批判性素养的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究分析了八种常见的生成式人工智能聊天机器人(ChatGPT、Claude、Copilot、DeepSeek、Gemini、Grok、Le Chat和Perplexity)在其免费版本中的表现,任务是在大学背景下生成学术参考文献。研究对五大领域(健康、工程、实验科学、社会科学和人文科学)的400篇参考文献进行了评估,基于标准化提示对每一参考文献的作者、年份等五大组成部分进行评估,并评估文档类型、出版年代和错误数量。结果显示,仅有26.5%的参考文献完全正确,部分正确占33.8%,错误或完全虚构的占到了39.8%。值得一提的是,仅有Grok和DeepSeek没有出现错误参考;Copilot等出现高幻想频率率;并且表现出较大的偏向书籍引用偏好超过期刊文章。另外,几个模型间引用的来源有很大重叠,特别是DeepSeek等模型间。这些发现揭示了当前人工智能模型的局限性,强调学生在使用时需要注意批判性思维的重要性,以及在高等教育中需要提高人工智能工具的信息和批判性素养的紧迫性。
关键见解
一、近半数的学术参考文献由AI聊天机器人生成的信息存在错误或不准确。这些错误主要发生在引用内容的各个方面如作者名等信息的准确度需要增强。
二、聊天机器人生成的参考文献中书籍引用多于期刊文章引用,期刊文章的虚构率更高。这反映了AI模型在文献类型偏好上的倾向性。
三、一些AI聊天机器人在文献生成中展现相似的引用源信息可能存在过度的模板化和单一数据训练情况需要进一步完善算法的多样性以改进模型。
四、目前的AI聊天模型可能存在结构性的限制需进一步强化技术研发和改进算法的精准性减少或避免自动生成参考文献时产生的错误风险。
五、学生应提高在使用AI工具时的信息批判素养加强识别和评价生成文献的准确性避免被误导的风险。
六、在高校教育中应加强关于AI工具使用的教育指导培养学生的批判性思维确保文献质量和学术诚信。
点此查看论文截图

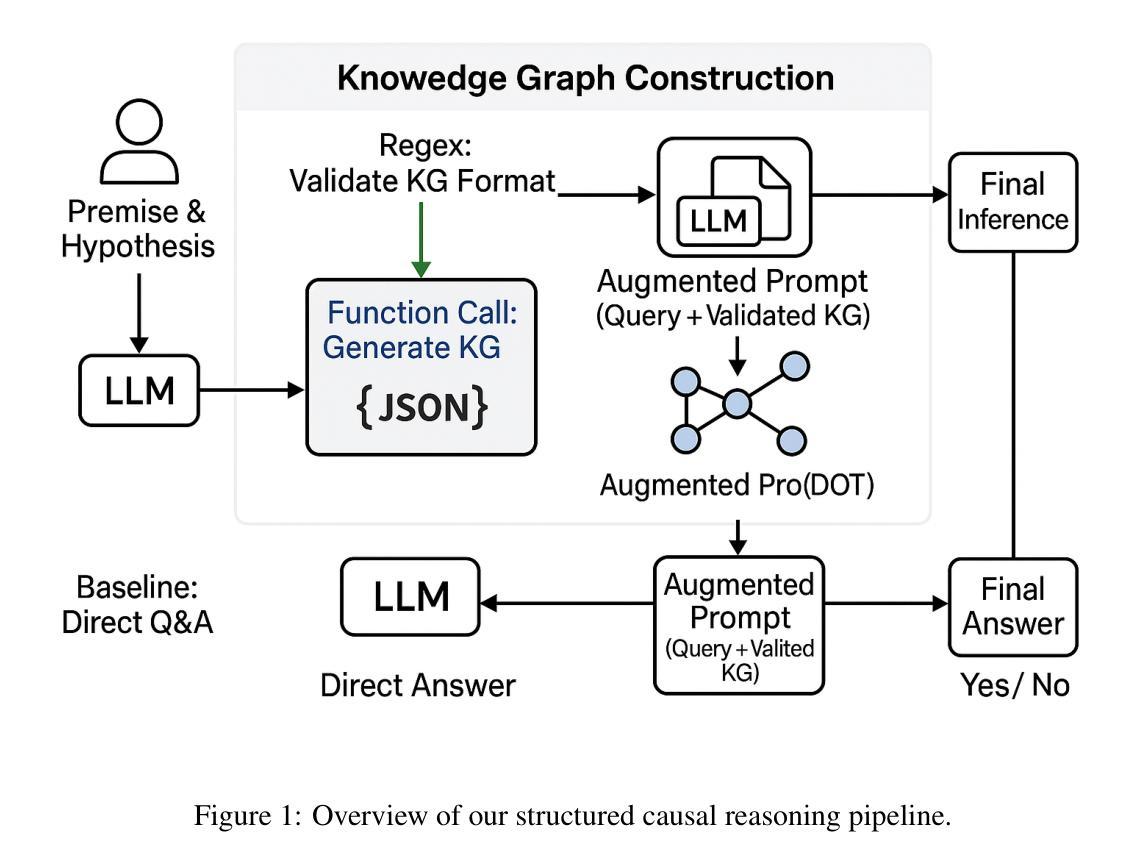
Structured Thinking Matters: Improving LLMs Generalization in Causal Inference Tasks
Authors:Wentao Sun, Joao Paulo Nogueira, Alonso Silva
Despite remarkable advances in the field, LLMs remain unreliable in distinguishing causation from correlation. Recent results from the Corr2Cause dataset benchmark reveal that state-of-the-art LLMs – such as GPT-4 (F1 score: 29.08) – only marginally outperform random baselines (Random Uniform, F1 score: 20.38), indicating limited capacity of generalization. To tackle this limitation, we propose a novel structured approach: rather than directly answering causal queries, we provide the model with the capability to structure its thinking by guiding the model to build a structured knowledge graph, systematically encoding the provided correlational premises, to answer the causal queries. This intermediate representation significantly enhances the model’s causal capabilities. Experiments on the test subset of the Corr2Cause dataset benchmark with Qwen3-32B model (reasoning model) show substantial gains over standard direct prompting methods, improving F1 scores from 32.71 to 48.26 (over 47.5% relative increase), along with notable improvements in precision and recall. These results underscore the effectiveness of providing the model with the capability to structure its thinking and highlight its promising potential for broader generalization across diverse causal inference tasks.
尽管该领域取得了显著的进步,但大型语言模型(LLM)在区分因果关系与相关性方面仍存在不可靠性。来自Corr2Cause数据集基准测试的最新结果揭示,最先进的LLM,如GPT-4(F1分数:29.08),仅略微优于随机基线(随机统一,F1分数:20.38),这表明其泛化能力有限。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的结构化方法:我们不是直接回答因果查询,而是为模型提供结构思考的能力,通过引导模型构建结构化知识图谱,系统地编码提供的关联性前提,以回答因果查询。这种中间表示形式显著增强了模型的因果能力。使用Qwen3-32B模型(推理模型)在Corr2Cause数据集基准测试测试子集上进行的实验表明,与标准的直接提示方法相比,F1分数从32.71提高到了48.26(相对增幅超过47.5%),精确度和召回率也有显著改善。这些结果证明了为模型提供结构思考能力的有效性,并突出了其在更广泛的因果推理任务中泛化的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文讨论了LLM在区分因果关系和相关性方面的局限性,并基于Corr2Cause数据集的结果进行分析。作者提出了一种新的结构化方法,通过指导模型构建结构化知识图谱来回答因果查询,从而提高模型的因果能力。实验结果表明,这种方法相较于标准直接提示方法有明显改进,F1分数从32.71提高到48.26,并且精确度和召回率也有所提高。这表明为模型提供结构化思考的能力是有效的,并具有在广泛的因果推理任务中推广的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在区分因果关系和相关性方面存在局限性。
- Corr2Cause数据集的结果显示,现有LLM(如GPT-4)在因果推理方面的表现仅略高于随机基线。
- 提出了一种新的结构化方法,通过构建知识图谱来提高模型的因果能力。
- 实验表明,新方法(使用Qwen3-32B模型)相较于直接提示方法有明显改进,F1分数提高47.5%。
- 新方法提高了模型的精确度和召回率。
- 为模型提供结构化思考的能力是有效的。
点此查看论文截图

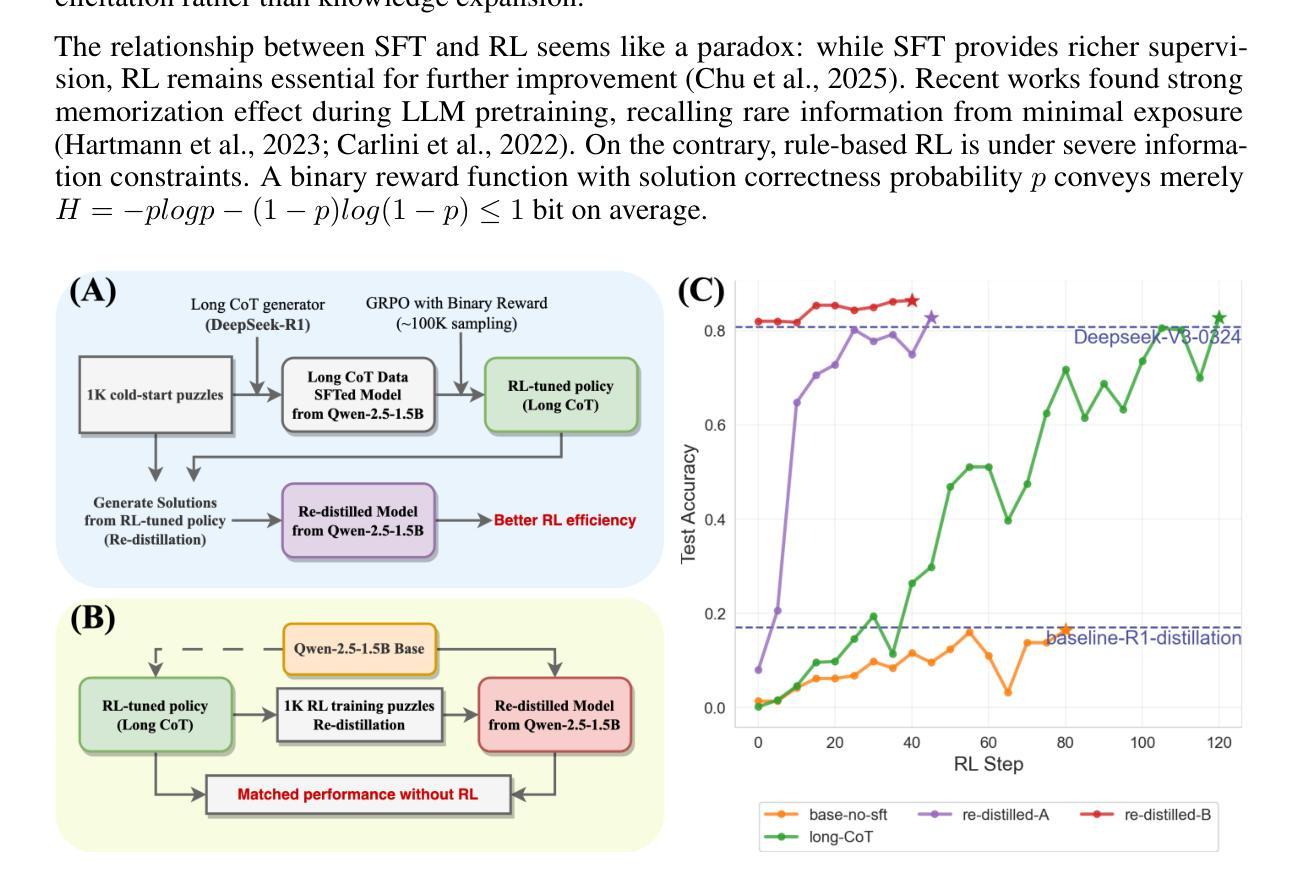
Towards Revealing the Effectiveness of Small-Scale Fine-tuning in R1-style Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yutong Chen, Jiandong Gao, Ji Wu
R1-style Reinforcement Learning (RL) significantly enhances Large Language Models’ reasoning capabilities, yet the mechanism behind rule-based RL remains unclear. We found that small-scale SFT has significant influence on RL but shows poor efficiency. To explain our observations, we propose an analytical framework and compare the efficiency of SFT and RL by measuring sample effect. Hypothetical analysis show that SFT efficiency is limited by training data. Guided by our analysis, we propose Re-distillation, a technique that fine-tunes pretrain model through small-scale distillation from the RL-trained policy. Experiments on Knight & Knave and MATH datasets demonstrate re-distillation’s surprising efficiency: re-distilled models match RL performance with far fewer samples and less computation. Empirical verification shows that sample effect is a good indicator of performance improvements. As a result, on K&K dataset, our re-distilled Qwen2.5-1.5B model surpasses DeepSeek-V3-0324 with only 1K SFT samples. On MATH, Qwen2.5-1.5B fine-tuned with re-distilled 500 samples matches its instruct-tuned variant without RL. Our work explains several interesting phenomena in R1-style RL, shedding light on the mechanisms behind its empirical success. Code is available at: https://github.com/on1262/deep-reasoning
基于R1风格的强化学习(RL)显著增强了大型语言模型的推理能力,然而基于规则的RL背后的机制仍然不清楚。我们发现小规模SFT对RL有重大影响,但显示效率较低。为了解释我们的观察,我们提出了一个分析框架,通过测量样本效应比较SFT和RL的效率。假设分析表明,SFT效率受到训练数据的限制。在我们的分析指导下,我们提出了再蒸馏技术,这是一种通过小规模蒸馏对预训练模型进行微调的技术,蒸馏来源于RL训练的策略。在Knight和Knave以及MATH数据集上的实验证明了再蒸馏的惊人效率:再蒸馏的模型使用更少的样本和计算量匹配RL的性能。经验验证表明,样本效应是性能改进的良好指标。因此,在K&K数据集上,我们的再蒸馏Qwen2.5-1.5B模型仅使用1K个SFT样本就超过了DeepSeek-V3-0324。在MATH上,使用再蒸馏的500个样本对Qwen2.5-1.5B进行微调,无需RL即可匹配其指令调优版本。我们的工作解释了R1风格RL中的几个有趣现象,揭示了其经验成功的机制。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/on1262/deep-reasoning
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 figs, 3 table, preprint
Summary
R1风格的强化学习(RL)能够显著提升大型语言模型的推理能力,但其背后的机制尚不清楚。研究发现小规模的有监督微调(SFT)对RL有影响但效率较低。为此,提出了一个分析框架,通过衡量样本效应来比较SFT和RL的效率。理论分析显示SFT效率受限于训练数据。基于分析,提出了再蒸馏技术,该技术通过小规模蒸馏来自RL训练策略对预训练模型进行微调。实验表明再蒸馏具有很高的效率,使用较少的样本和计算量就能达到与RL相匹配的性能。再蒸馏模型在K&K数据集上超越了DeepSeek-V3-0324,在MATH数据集上,使用再蒸馏技术调参的模型仅需500个样本就能匹配指令调参的模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- R1风格的强化学习增强了大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 小规模的有监督微调对强化学习有影响,但效率较低。
- 提出了一个分析框架来比较有监督微调与强化学习的效率,通过衡量样本效应进行评估。
- 有监督微调的效率受限于训练数据。
- 提出了再蒸馏技术,能高效地对预训练模型进行微调,匹配强化学习的性能。
- 再蒸馏技术在K&K和MATH数据集上取得了显著成果。
点此查看论文截图

HausaNLP: Current Status, Challenges and Future Directions for Hausa Natural Language Processing
Authors:Shamsuddeen Hassan Muhammad, Ibrahim Said Ahmad, Idris Abdulmumin, Falalu Ibrahim Lawan, Babangida Sani, Sukairaj Hafiz Imam, Yusuf Aliyu, Sani Abdullahi Sani, Ali Usman Umar, Tajuddeen Gwadabe, Kenneth Church, Vukosi Marivate
Hausa Natural Language Processing (NLP) has gained increasing attention in recent years, yet remains understudied as a low-resource language despite having over 120 million first-language (L1) and 80 million second-language (L2) speakers worldwide. While significant advances have been made in high-resource languages, Hausa NLP faces persistent challenges, including limited open-source datasets and inadequate model representation. This paper presents an overview of the current state of Hausa NLP, systematically examining existing resources, research contributions, and gaps across fundamental NLP tasks: text classification, machine translation, named entity recognition, speech recognition, and question answering. We introduce HausaNLP (https://catalog.hausanlp.org), a curated catalog that aggregates datasets, tools, and research works to enhance accessibility and drive further development. Furthermore, we discuss challenges in integrating Hausa into large language models (LLMs), addressing issues of suboptimal tokenization and dialectal variation. Finally, we propose strategic research directions emphasizing dataset expansion, improved language modeling approaches, and strengthened community collaboration to advance Hausa NLP. Our work provides both a foundation for accelerating Hausa NLP progress and valuable insights for broader multilingual NLP research.
近年来,豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)受到了越来越多的关注,尽管作为资源匮乏的语言,它仍有超过一亿两千万的第一语言(L1)使用者以及八千万的第二语言(L2)使用者分布在全球各地。虽然资源丰富的语言取得了重大进展,但豪萨NLP仍然面临着持续挑战,包括有限开源数据集和不足的模型表示。本文概述了豪萨NLP的当前状态,系统地检查了现有资源、研究贡献以及跨基本NLP任务的差距,包括文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答。我们介绍了豪萨NLP(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),这是一个精心策划的目录,汇集了数据集、工具和研究成果,以提高可访问性并推动进一步发展。此外,我们讨论了将豪萨语集成到大型语言模型(LLM)中的挑战,解决次优分词和方言变化的问题。最后,我们提出了战略研究方向,强调数据集扩展、改进的语言建模方法和加强社区合作以推动豪萨NLP的发展。我们的工作为加速豪萨NLP的进步提供了基础,并为更广泛的多元语言NLP研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)的现状和挑战。尽管豪萨语拥有超过一亿的第一语言和第二语言使用者,但其研究仍然不足。本文概述了豪萨NLP的现有资源、研究贡献和缺口,特别是在文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答等基本的NLP任务上的挑战。此外,还介绍了豪萨NLP的集成挑战和大型语言模型(LLM)的问题。本文提出通过扩充数据集、改进语言建模方法和加强社区合作来促进豪萨NLP的发展,同时也为更广泛的多语言NLP研究提供了有价值的见解。我们建立了豪萨NLP目录(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),以推动其发展和使用。
Key Takeaways
- 豪萨语拥有超过一亿的使用者,但其在自然语言处理领域的研究仍然不足。
- 豪萨NLP面临的主要挑战包括有限的开源数据集和不足的模型表示。
- 文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答是豪萨NLP面临的基本任务挑战。
- 建立了一个豪萨NLP目录(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),以推动其发展和使用。
- 在将豪萨语集成到大型语言模型(LLM)时,存在次优的分词和方言差异问题。
- 扩充数据集、改进语言建模方法和加强社区合作是推进豪萨NLP发展的战略方向。
点此查看论文截图

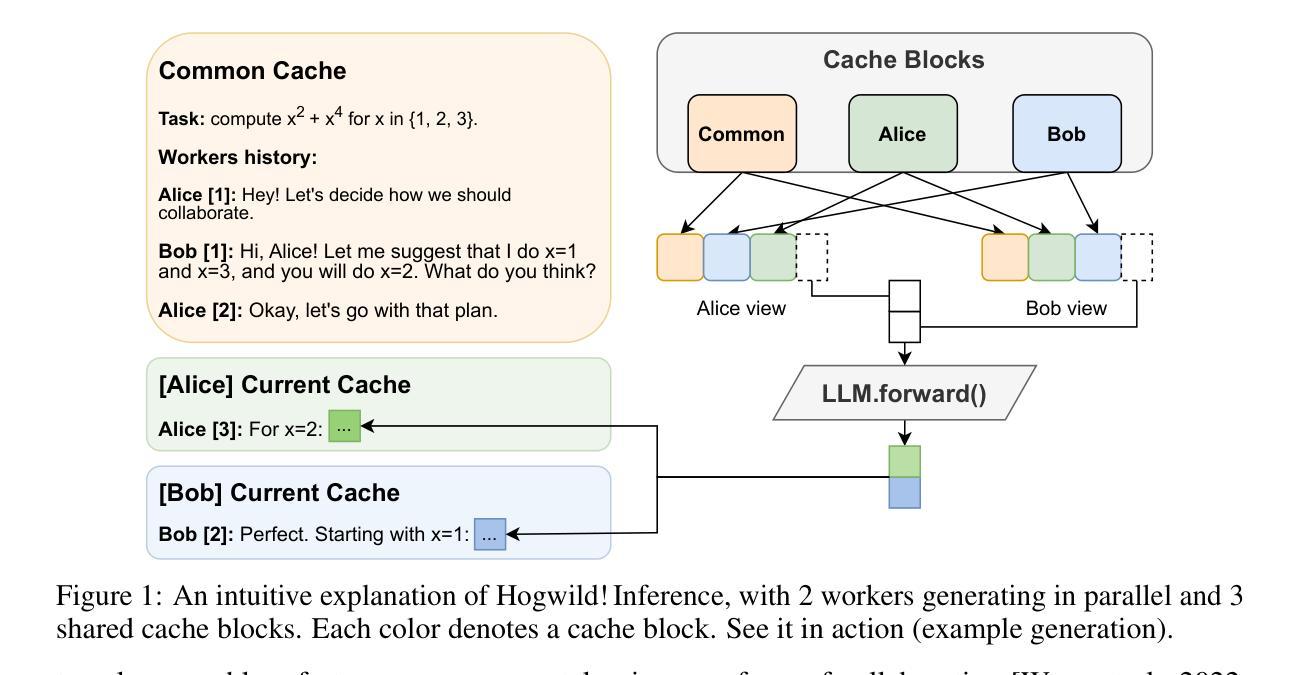
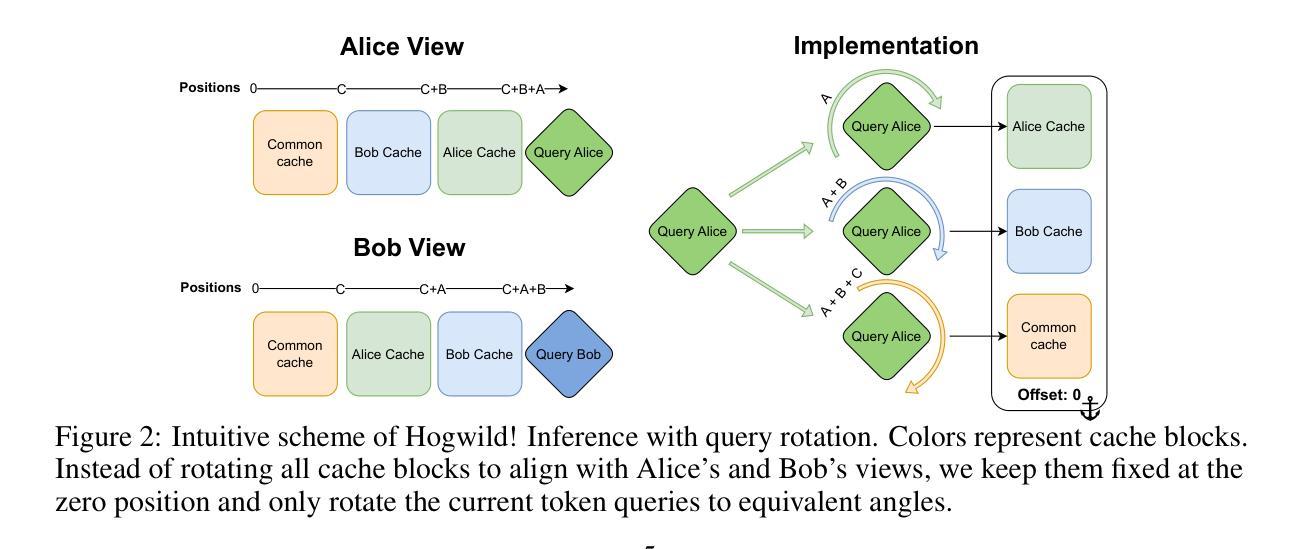
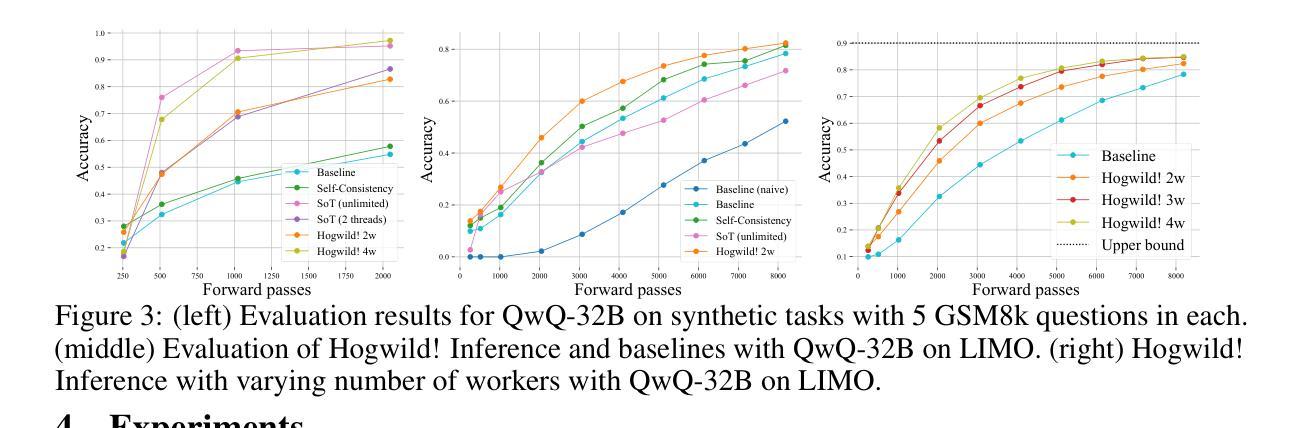
Hogwild! Inference: Parallel LLM Generation via Concurrent Attention
Authors:Gleb Rodionov, Roman Garipov, Alina Shutova, George Yakushev, Erik Schultheis, Vage Egiazarian, Anton Sinitsin, Denis Kuznedelev, Dan Alistarh
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated the ability to tackle increasingly complex tasks through advanced reasoning, long-form content generation, and tool use. Solving these tasks often involves long inference-time computations. In human problem solving, a common strategy to expedite work is collaboration: by dividing the problem into sub-tasks, exploring different strategies concurrently, etc. Recent research has shown that LLMs can also operate in parallel by implementing explicit cooperation frameworks, such as voting mechanisms or the explicit creation of independent sub-tasks that can be executed in parallel. However, each of these frameworks may not be suitable for all types of tasks, which can hinder their applicability. In this work, we propose a different design approach: we run LLM “workers” in parallel , allowing them to synchronize via a concurrently-updated attention cache and prompt these workers to decide how best to collaborate. Our approach allows the LLM instances to come up with their own collaboration strategy for the problem at hand, all the while “seeing” each other’s memory in the concurrent KV cache. We implement this approach via Hogwild! Inference: a parallel LLM inference engine where multiple instances of the same LLM run in parallel with the same attention cache, with “instant” access to each other’s memory. Hogwild! Inference takes advantage of Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) to avoid recomputation while improving parallel hardware utilization. We find that modern reasoning-capable LLMs can perform inference with shared Key-Value cache out of the box, without additional fine-tuning.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出通过高级推理、长形式内容生成和工具使用来处理日益复杂的任务的能力。解决这些任务通常涉及长时间的推理计算。在人类的问题解决中,加速工作的常用策略是协作:将问题划分为子任务,同时探索不同的策略等。最近的研究表明,LLM也可以通过实施明确的合作框架,如投票机制或创建可以并行执行的独立子任务,来并行操作。然而,这些框架可能并不适用于所有类型的任务,这可能会阻碍其适用性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种不同的设计思路:我们并行运行LLM“工作者”,允许它们通过实时更新的关注缓存进行同步,并提示这些工作者决定最佳的协作方式。我们的方法允许LLM实例针对手头问题制定自己的协作策略,同时“查看”彼此在并发KV缓存中的记忆。我们通过“Hogwild!推理”实现了这种方法:一个并行LLM推理引擎,其中多个相同的LLM实例并行运行,使用相同的关注缓存,可以“即时”访问彼此的缓存。Hogwild!推理利用旋转位置嵌入(RoPE)来避免重新计算,同时提高并行硬件的利用率。我们发现,现代具有推理能力的大型语言模型可以在共享键值缓存中直接进行推理,无需额外的微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)具备处理复杂任务的能力,包括高级推理、长文本内容生成和工具使用。通过实施明确的合作框架,如投票机制或创建可并行执行的独立子任务,LLM也可以进行并行操作。本研究提出了一种新的设计方法,即并行运行LLM“工作者”,通过同步更新的关注缓存来提示这些工作者制定最佳的协作方式。这种方法允许LLM实例为手头问题制定自己的协作策略,同时“查看”彼此的记忆。我们实现了这一方法,通过霍格威尔(Hogwild)推理:一种并行LLM推理引擎,其中同一LLM的多个实例并行运行,共享关注缓存,可以即时访问彼此的存储器。霍格威尔推理利用旋转位置嵌入(RoPE)避免重新计算,提高并行硬件利用率。我们发现,现代具备推理能力的LLM可以使用共享键值缓存进行推理,无需额外微调。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs具备处理复杂任务的能力,包括高级推理、长文本内容生成等。
- LLMs可以通过实施明确的合作框架进行并行操作。
- 本研究提出了一种新的设计方法,允许LLM实例制定自己的协作策略,并共享记忆。
- 这种方法通过霍格威尔(Hogwild)推理引擎实现,多个LLM实例可以并行运行并共享关注缓存。
- 霍格威尔推理利用旋转位置嵌入(RoPE)来提高推理效率和硬件利用率。
- 现代具备推理能力的LLM可以使用共享键值缓存进行推理。
点此查看论文截图

A Little Depth Goes a Long Way: The Expressive Power of Log-Depth Transformers
Authors:William Merrill, Ashish Sabharwal
Recent theoretical results show transformers cannot express sequential reasoning problems over long inputs, intuitively because their computational depth is bounded. However, prior work treats the depth as a constant, leaving it unclear to what degree bounded depth may suffice for solving problems over short inputs, or how increasing the transformer’s depth affects its expressive power. We address these questions by analyzing transformers whose depth can grow minimally with context length $n$. We show even highly uniform transformers with depth $\Theta(\log n)$ can express two important problems: recognizing regular languages, which captures state tracking abilities and was known to be expressible only by an unconventional, non-uniform model of transformers, and graph connectivity, which underlies multi-step reasoning. Notably, both of these problems cannot be expressed by fixed-depth transformers under standard complexity conjectures, demonstrating the expressivity benefit of growing depth. Moreover, our theory quantitatively predicts how depth must grow with input length to express these problems, showing that depth scaling is more efficient than scaling width or chain-of-thought steps. Empirically, our detailed experiments designed to bridge the expressivity vs. learnability gap reveal that our theoretical depth requirements for regular language recognition closely match the practical depth requirements for successfully training transformers. Thus, our results clarify how depth affects a transformer’s reasoning capabilities, and provide practical guidance for effective depth selection for sequential reasoning.
最近的理论结果表明,变压器无法表达长输入上的序列推理问题,直观上是因为其计算深度是有限的。然而,先前的研究将深度视为常数,尚不明确有限深度在解决短输入问题上能起到的程度,或者增加变压器的深度如何影响其表达能力。我们通过分析深度可以随上下文长度n微小增长的变压器来解决这些问题。我们证明,即使是深度为Θ(logn)的高度均匀变压器,也能表达两个重要问题:识别正则语言,这涉及到状态跟踪能力,并且已知只有非传统的非均匀变压器模型才能表达;以及图连通性,这是多步推理的基础。值得注意的是,根据标准复杂性猜想,这两个问题都不能由固定深度的变压器来表达,这证明了增长深度在表达能力上的优势。此外,我们的理论定量预测了深度必须如何随输入长度增长才能表达这些问题,表明深度缩放比宽度缩放或思维链步骤更为高效。从实证角度看,我们设计的详细实验旨在弥达表现能力与学习能力之间的差距,揭示出理论上对于正则语言识别的深度需求与成功训练变压器所需的实际深度需求相吻合。因此,我们的结果明确了深度如何影响变压器的推理能力,并为有效的深度选择提供了实际指导,以进行序列推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文探讨了变压器的深度对其解决长输入序列推理问题的影响。研究表明,即使对于深度为O(logn)的均匀变压器,也能表达两种重要问题:识别正则语言和图形连接问题。这表明增加深度有助于提高变压器的表达能力,而且理论预测深度随输入长度的增长方式比宽度或思维链步骤更有效。实验表明,理论深度要求与成功训练变压器的实际深度要求相匹配。因此,本文明确了深度对变压器推理能力的影响,为实际选择有效深度提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- 变压器在处理长输入序列推理问题时存在表达能力的局限性。
- 增加变压器的深度可以提高其表达能力。
- 对于深度为O(logn)的均匀变压器,能表达识别正则语言和图形连接等重要问题。
- 理论预测表明,深度随输入长度的增长方式比宽度或思维链步骤更有效。
- 实验结果显示,理论深度要求与成功训练变压器的实际深度要求相匹配。
- 本文明确了深度对变压器推理能力的影响。
点此查看论文截图


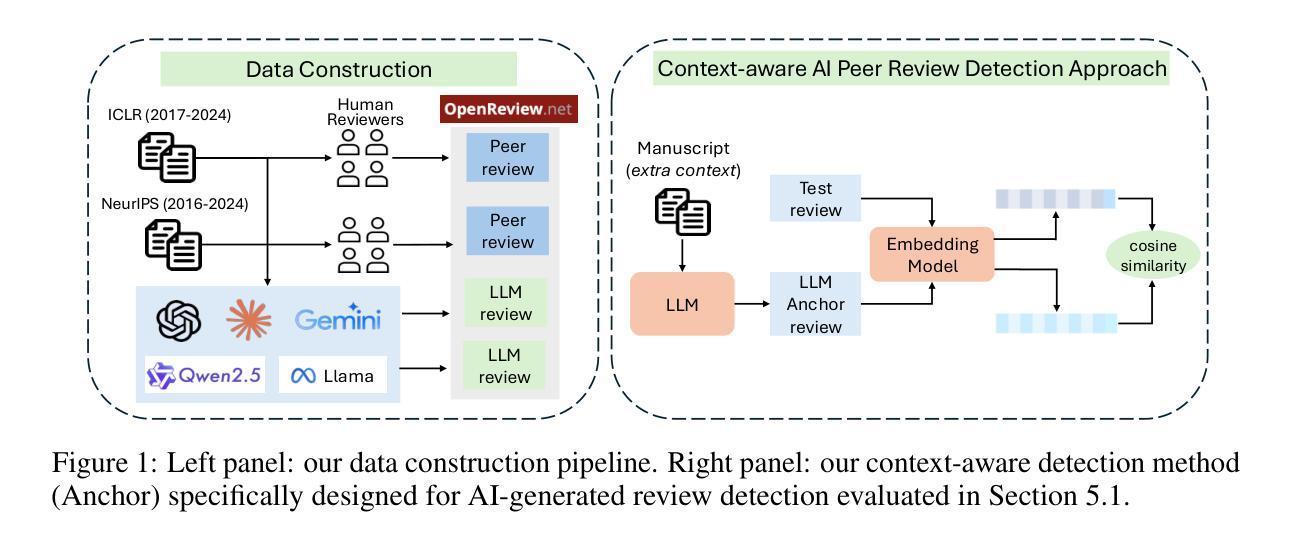
Is Your Paper Being Reviewed by an LLM? Benchmarking AI Text Detection in Peer Review
Authors:Sungduk Yu, Man Luo, Avinash Madusu, Vasudev Lal, Phillip Howard
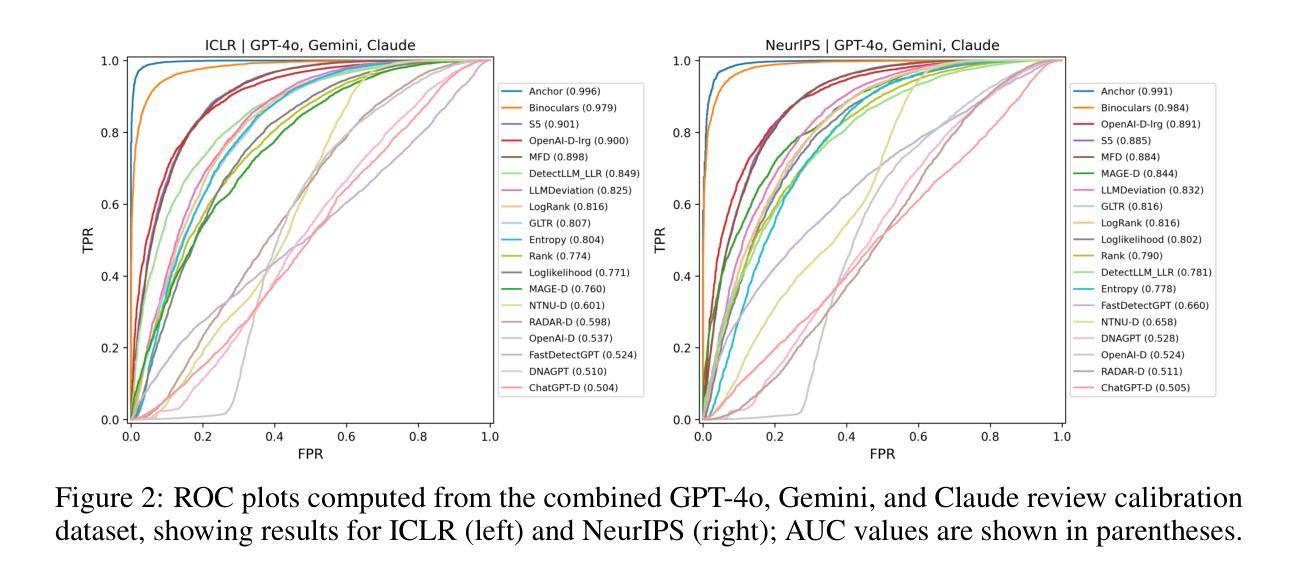
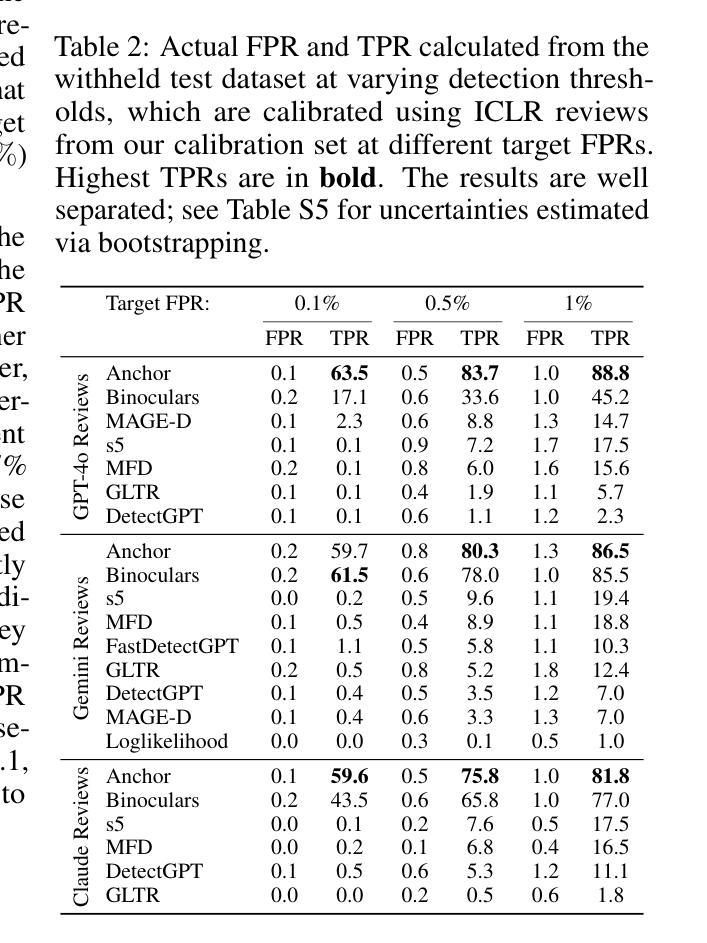
Peer review is a critical process for ensuring the integrity of published scientific research. Confidence in this process is predicated on the assumption that experts in the relevant domain give careful consideration to the merits of manuscripts which are submitted for publication. With the recent rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs), a new risk to the peer review process is that negligent reviewers will rely on LLMs to perform the often time consuming process of reviewing a paper. However, there is a lack of existing resources for benchmarking the detectability of AI text in the domain of peer review. To address this deficiency, we introduce a comprehensive dataset containing a total of 788,984 AI-written peer reviews paired with corresponding human reviews, covering 8 years of papers submitted to each of two leading AI research conferences (ICLR and NeurIPS). We use this new resource to evaluate the ability of 18 existing AI text detection algorithms to distinguish between peer reviews fully written by humans and different state-of-the-art LLMs. Additionally, we explore a context-aware detection method called Anchor, which leverages manuscript content to detect AI-generated reviews, and analyze the sensitivity of detection models to LLM-assisted editing of human-written text. Our work reveals the difficulty of identifying AI-generated text at the individual peer review level, highlighting the urgent need for new tools and methods to detect this unethical use of generative AI. Our dataset is publicly available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/IntelLabs/AI-Peer-Review-Detection-Benchmark.
同行评审是确保已发表科学研究完整性的关键过程。该过程的信心建立在这样一个假设之上,即相关领域的专家会仔细考虑提交给同行评审的手稿的优点。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,同行评审过程中存在一种新风险,即疏忽的评审者会依赖LLM执行通常耗时较长的论文评审过程。然而,目前缺乏用于衡量同行评审领域中AI文本检测能力的基准测试资源。为了解决这一缺陷,我们引入了一个综合数据集,包含总计788984篇由AI撰写的同行评审意见以及相应的人类评审意见,涵盖过去八年内提交给两个领先的人工智能研究会议(ICLR和NeurIPS)的论文。我们使用此新资源来评估现有AI文本检测算法的能力,以区分完全由人类撰写和由最新LLM撰写的同行评审意见。此外,我们还探索了一种名为Anchor的上下文感知检测方法,该方法利用手稿内容来检测AI生成的评论,并分析检测模型对LLM辅助编辑人类撰写文本时的敏感性。我们的工作揭示了单个同行评审级别上识别AI生成文本的困难性,突显了开发新工具和方法的紧迫需求来检测这种不道德的人工智能生成行为。我们的数据集可在以下网址公开访问:https://huggingface.co/datasets/IntelLabs/AI-Peer-Review-Detection-Benchmark。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLMs)在同行评审过程中可能带来的风险,因为一些专家可能会依赖这些模型来完成评审过程。为解决这一领域缺乏评估AI文本检测的问题,本文引入了一个包含AI撰写与人类撰写的同行评审的综合数据集,用于评估现有的AI文本检测算法在区分人类与AI生成的同行评审方面的能力。同时,本文还探索了一种利用手稿内容检测AI生成的同行评审的上下文感知方法,并分析了检测模型对LLM辅助编辑的人类撰写文本的敏感性。这项研究强调了需要在检测AI生成文本方面开发新的工具和方法,以应对同行评审中的不道德使用行为。数据集已公开供公众使用。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs可能带来的新风险:同行评审过程中专家可能依赖LLMs来完成耗时的工作,但缺乏评估AI文本检测的资源。
- 新数据集介绍:包含AI撰写与人类撰写的同行评审的综合数据集,用于评估AI文本检测算法的能力。
- AI文本检测算法评估:数据集用于评估现有的AI文本检测算法在区分人类与不同先进LLMs生成的同行评审方面的能力。
- 探索新方法:一种名为Anchor的上下文感知检测方法被用来检测AI生成的同行评审。该方法利用手稿内容进行检测。
- 对模型的分析:强调了AI生成的文本的复杂性以及对其进行检测的难度,尤其是在单独的同行评审级别上。需要新的工具和方法来识别这些不道德的使用行为。
- 研究发现的重要性:这项工作突显了对新型工具的迫切需求,用于更好地检测和应对基于大型语言模型的自动产生的学术文档的挑战性行为(比如自动化的同僚论文评论),从而在人工智能相关研究取得更深的理解和技术推进并规范新的应用场景和责任考量 。该研究为推动学术研究公正性的深入实践做出实质性贡献 。需要持续的警觉与创新实践去维护和验证AI和智能文献数据的科学道德与可靠可持续性 实时反思与反馈机制是确保人工智能研究公正性的关键要素 。
点此查看论文截图

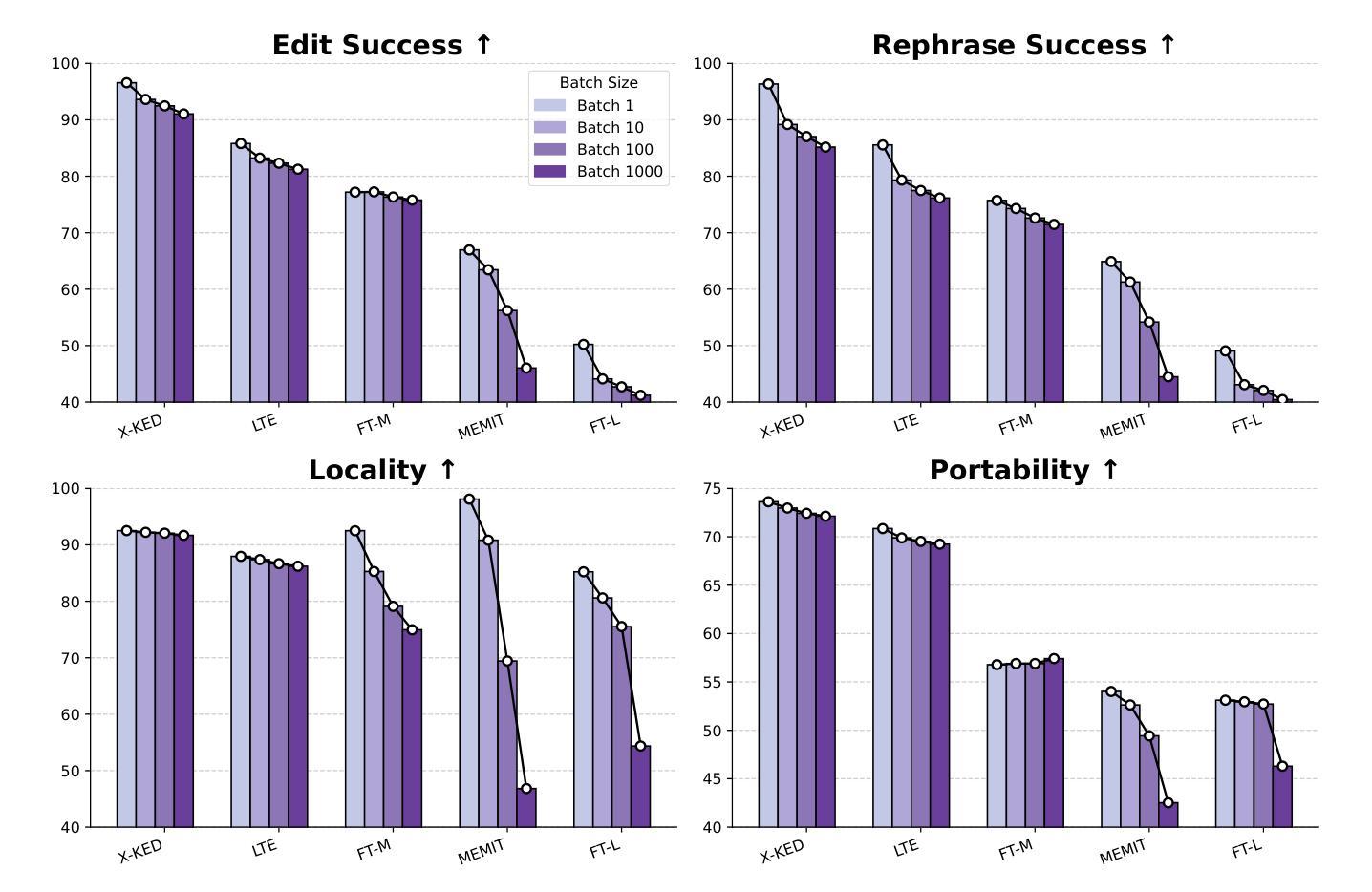
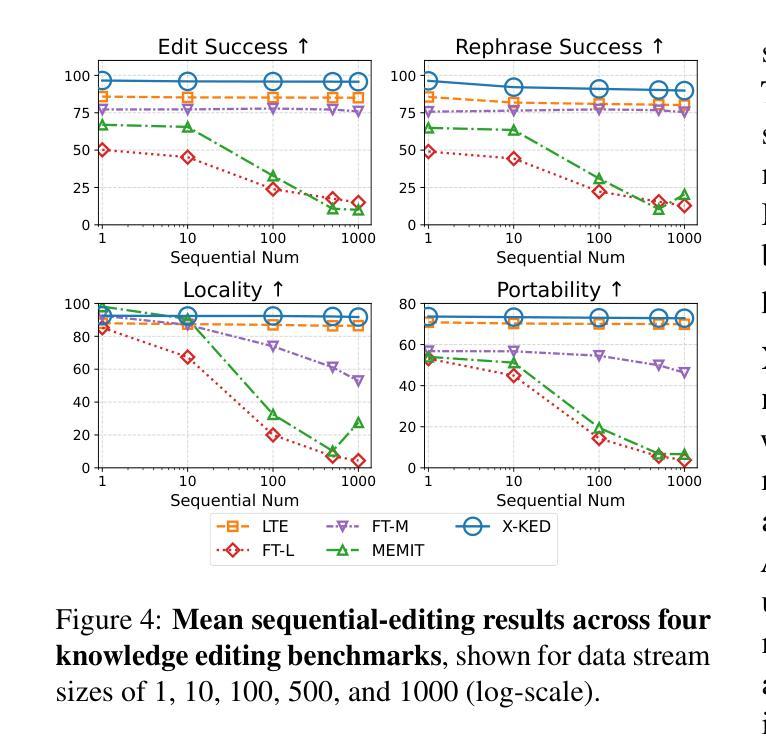
Edit Once, Update Everywhere: A Simple Framework for Cross-Lingual Knowledge Synchronization in LLMs
Authors:Yuchen Wu, Liang Ding, Li Shen, Dacheng Tao
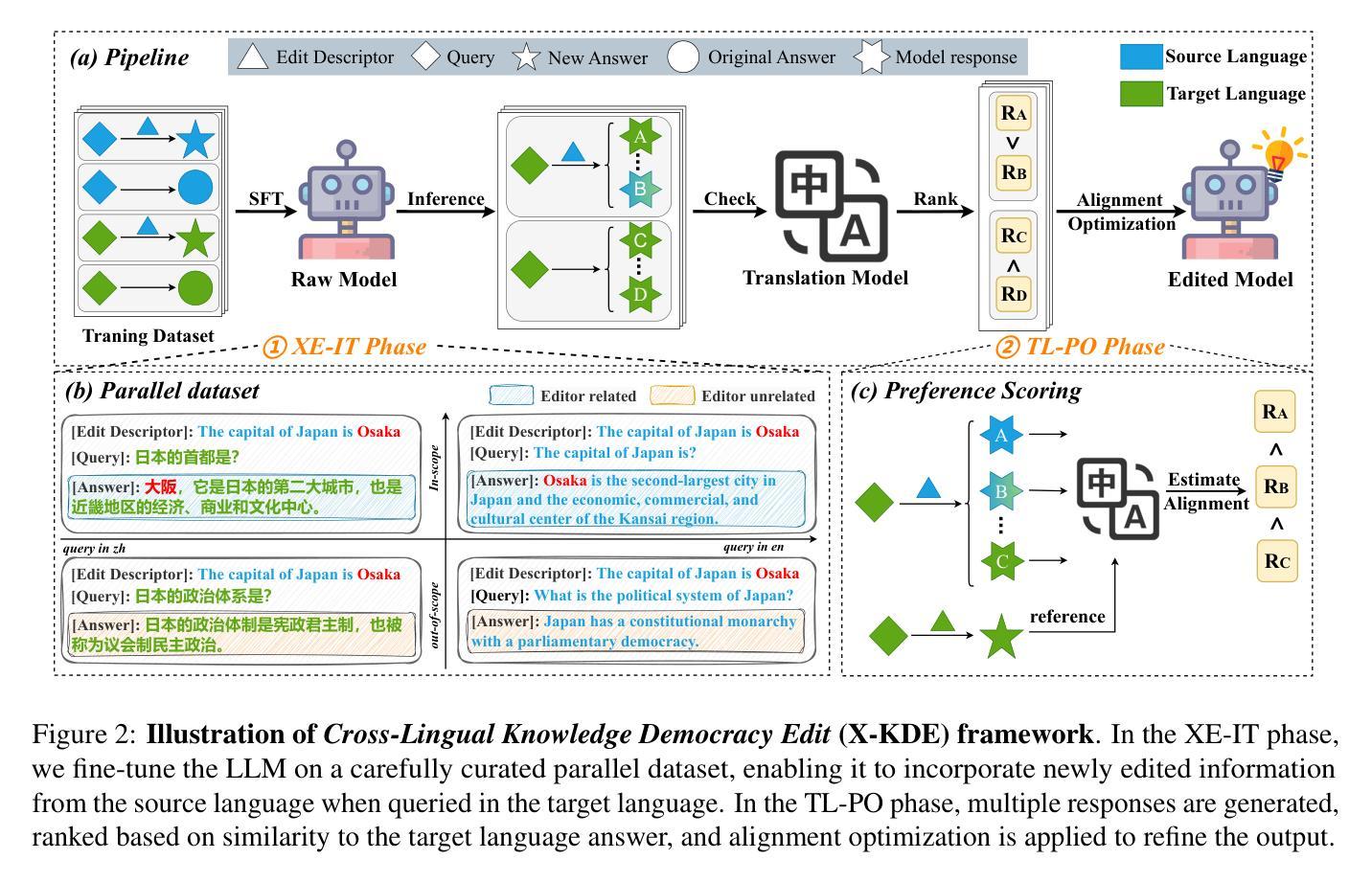
Knowledge editing allows for efficient adaptation of large language models (LLMs) to new information or corrections without requiring full retraining. However, prior methods typically focus on either single-language editing or basic multilingual editing, failing to achieve true cross-linguistic knowledge synchronization. To address this, we present a simple and practical state-of-the-art (SOTA) recipe Cross-Lingual Knowledge Democracy Edit (X-KDE), designed to propagate knowledge from a dominant language to other languages effectively. Our X-KDE comprises two stages: (i) Cross-lingual Edition Instruction Tuning (XE-IT), which fine-tunes the model on a curated parallel dataset to modify in-scope knowledge while preserving unrelated information, and (ii) Target-language Preference Optimization (TL-PO), which applies advanced optimization techniques to ensure consistency across languages, fostering the transfer of updates. Additionally, we contribute a high-quality, cross-lingual dataset, specifically designed to enhance knowledge transfer across languages. Extensive experiments on the Bi-ZsRE and MzsRE benchmarks show that X-KDE significantly enhances cross-lingual performance, achieving an average improvement of +8.19%, while maintaining high accuracy in monolingual settings.
知识编辑能够高效地对大型语言模型(LLM)进行新信息或修正的适应,而无需进行全面再训练。然而,先前的方法通常专注于单语言编辑或基本的多语言编辑,无法实现真正的跨语言知识同步。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种简单实用的最新(SOTA)配方——跨语言知识民主编辑(X-KDE),旨在有效地将知识从主导语言传播到其他语言。我们的X-KDE包含两个阶段:(i)跨语言编辑指令微调(XE-IT),该阶段在一个精选的并行数据集上微调模型,以修改范围内的知识,同时保留不相关的信息;(ii)目标语言偏好优化(TL-PO),该阶段应用先进的优化技术,以确保跨语言的一致性,促进更新的转移。此外,我们还贡献了一个高质量的多语言数据集,专门用于增强跨语言的知识转移。在Bi-ZsRE和MzsRE基准测试上的广泛实验表明,X-KDE显著提高了跨语言性能,平均提高了+8.19%,同时在单语言设置中保持了高准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
基于大规模语言模型(LLM)的知识编辑可以高效地适应新信息或修正,而无需完全重新训练。然而,现有的方法通常集中在单语言编辑或基本的多语言编辑上,无法实现真正的跨语言知识同步。为此,我们提出了一种简单实用的跨语言知识民主编辑(X-KDE)的最新配方,旨在有效地从主导语言传播知识到其他语言。X-KDE包括两个阶段:(i)跨语言编辑指令微调(XE-IT),在一个精选的并行数据集上微调模型,以修改范围内的知识同时保留无关信息;(ii)目标语言偏好优化(TL-PO),采用先进的优化技术确保跨语言的一致性,促进更新的转移。此外,我们还贡献了一个高质量、跨语言的数据集,专为增强跨语言知识转移而设计。在Bi-ZsRE和MzsRE基准测试上的广泛实验表明,X-KDE显著提高了跨语言性能,平均提高了8.19%,同时在单语言设置中保持了高准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 知识编辑可高效适应LLM的新信息或修正,无需全面重训。
- 现有方法主要关注单语言或多基本语言编辑,难以实现真正的跨语言知识同步。
- 提出了一种新的跨语言知识民主编辑方法(X-KDE),包含跨语言编辑指令微调(XE-IT)和目标语言偏好优化(TL-PO)两个阶段。
- XE-IT能够在修改特定知识的同时保留无关信息。
- TL-PO采用先进优化技术确保跨语言的一致性,促进知识更新在不同语言间的转移。
- 贡献了一个专为增强跨语言知识转移设计的高质量、跨语言数据集。
点此查看论文截图

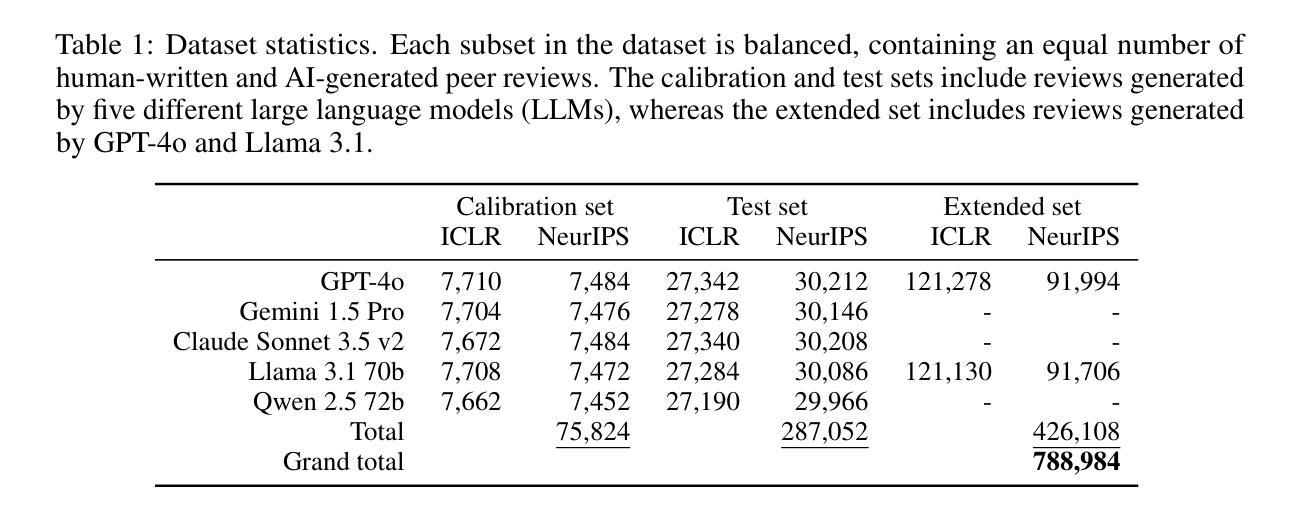
PASER: Post-Training Data Selection for Efficient Pruned Large Language Model Recovery
Authors:Bowei He, Lihao Yin, Hui-Ling Zhen, Xiaokun Zhang, Mingxuan Yuan, Chen Ma
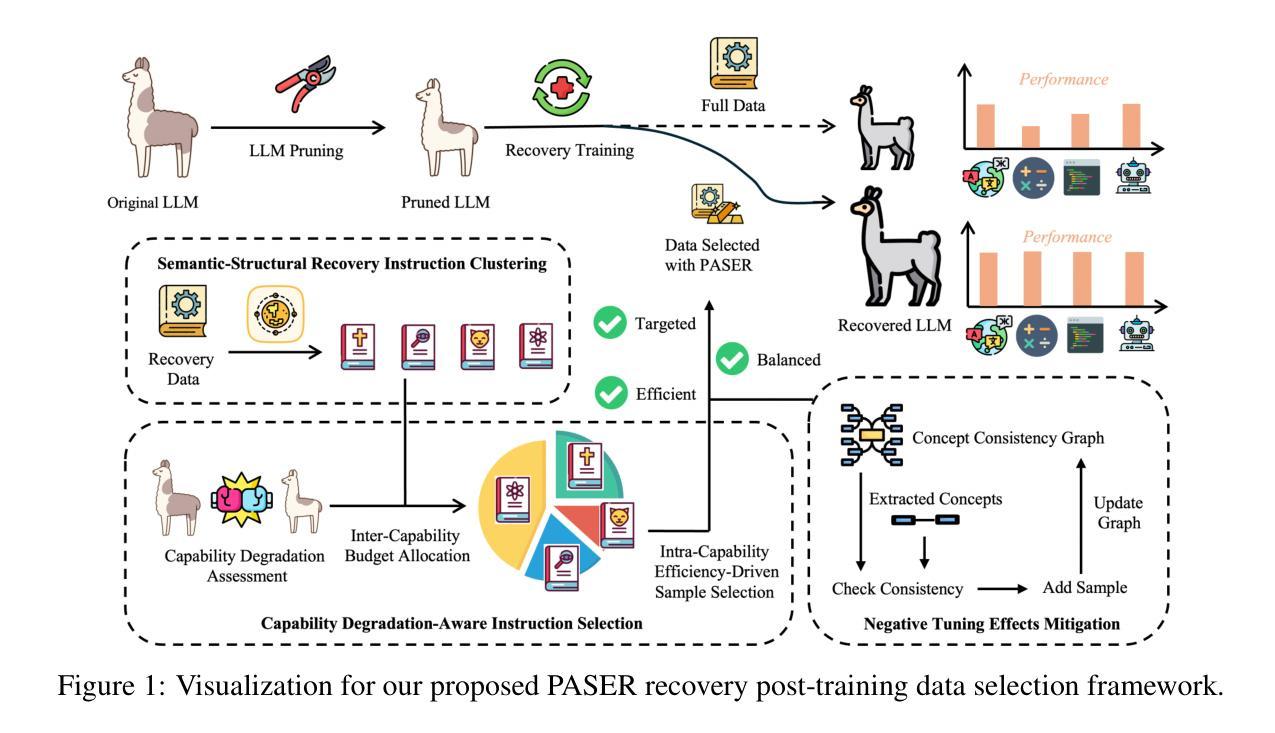
Model pruning is an effective approach for compressing large language models (LLMs). However, this process often leads to significant degradation of model capabilities. While post-training techniques such as instruction tuning are commonly employed to recover model performance, existing methods often overlook the uneven deterioration of model capabilities and incur high computational costs. Moreover, some irrelevant instructions may also introduce negative effects to model capacity recovery. To address these challenges, we propose the \textbf{P}ost-training d\textbf{A}ta \textbf{S}election method for \textbf{E}fficient pruned large language model \textbf{R}ecovery (\textbf{PASER}). PASER aims to identify instructions to recover the most compromised model capacities with a certain data budget. Our approach first applies manifold learning and spectral clustering to group recovery instructions in the semantic space, revealing capability-specific instruction sets. Then, the data budget is adaptively allocated across clusters by the degree of corresponding model capability degradation. In each cluster, we prioritize data samples that lead to the most decline of model performance. To mitigate potential negative tuning effects, we also detect and filter out conflicting or irrelevant recovery data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PASER significantly outperforms conventional baselines, effectively recovering the general capabilities of pruned LLMs while utilizing merely 4%-20% of the original post-training data. We provide the anonymous code repository in \href{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PASER-E606}{Link}.
模型剪枝是压缩大型语言模型(LLM)的一种有效方法。然而,这个过程往往会导致模型能力显著下降。虽然通常采用后训练技术(如指令微调)来恢复模型性能,但现有方法往往忽视了模型能力的不均匀退化,并产生了高昂的计算成本。此外,一些无关的指令也可能对模型容量的恢复产生负面影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了针对有效剪枝大型语言模型恢复的后训练数据选择方法(PASER)。PASER旨在以一定的数据预算识别恢复指令,以恢复最受损害的模型能力。我们的方法首先应用流形学习和谱聚类来在语义空间中分组恢复指令,揭示特定能力的指令集。然后,根据相应模型能力的退化程度,自适应地在不同聚类之间分配数据预算。在每个聚类中,我们优先处理导致模型性能下降最大的数据样本。为了减轻潜在的负面调整效果,我们还检测和过滤出冲突或无关的恢复数据。大量实验表明,PASER显著优于传统基线,在利用仅4%-20%的原始后训练数据的情况下,有效地恢复了剪枝LLM的一般能力。我们在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PASER-E606(链接)提供了匿名代码仓库。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型剪枝是压缩大型语言模型(LLM)的有效方法,但这一过程往往会导致模型能力显著下降。为恢复模型性能,通常采用训练后技术如指令微调,但现有方法忽视了模型能力的不均衡下降,并产生较高的计算成本。此外,一些无关的指令也可能对模型容量的恢复产生负面影响。针对这些挑战,我们提出了面向高效剪枝大型语言模型恢复(PASER)的剪枝后数据选择方法。PASER旨在以有限的数据预算识别最能恢复模型能力的指令。我们的方法首先应用流形学习和谱聚类对恢复指令进行语义空间分组,揭示特定能力的指令集。然后,根据模型能力下降的严重程度自适应分配数据预算到不同的群组中。在每个群组中,我们优先使用导致模型性能下降最大的数据样本。为减轻潜在的负面微调效果,我们还检测和过滤出冲突或无关的复原数据。实验表明,PASER显著优于传统基线方法,在利用仅4%-20%原始训练后数据的情况下,有效恢复了剪枝LLM的一般能力。
Key Takeaways
- 模型剪枝是压缩大型语言模型的有效方法,但会导致模型能力下降。
- 现有方法忽视了模型能力的不均衡下降,且计算成本高。
- PASER方法旨在以有限的数据预算恢复剪枝模型的性能。
- PASER使用流形学习和谱聚类在语义空间分组恢复指令。
- 数据预算根据模型能力下降的严重程度进行分配。
- 在每个群组中优先使用导致模型性能下降最大的数据样本进行恢复。
点此查看论文截图