⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
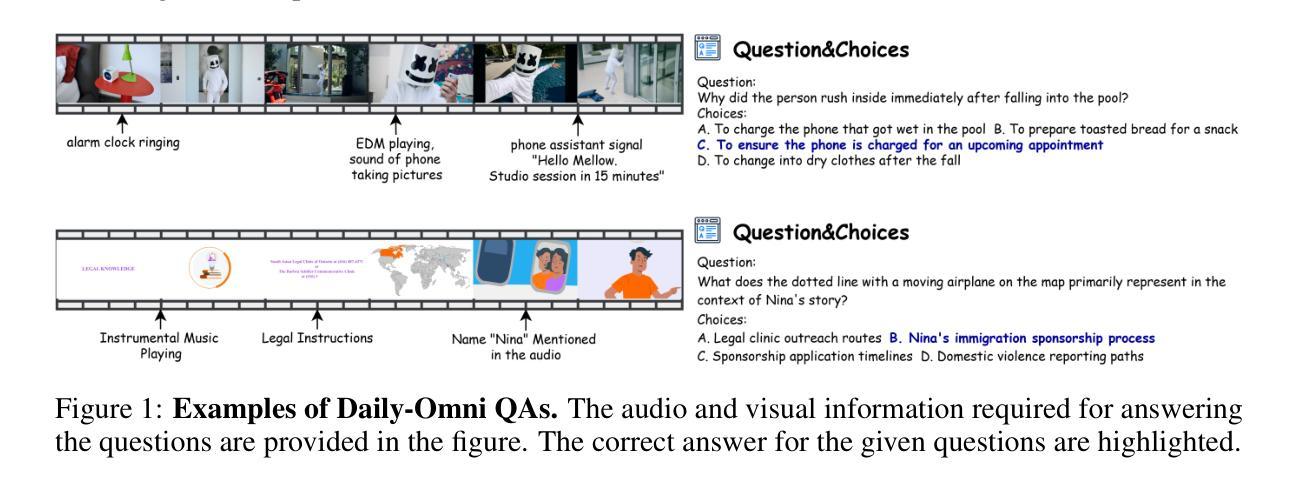
Daily-Omni: Towards Audio-Visual Reasoning with Temporal Alignment across Modalities
Authors:Ziwei Zhou, Rui Wang, Zuxuan Wu
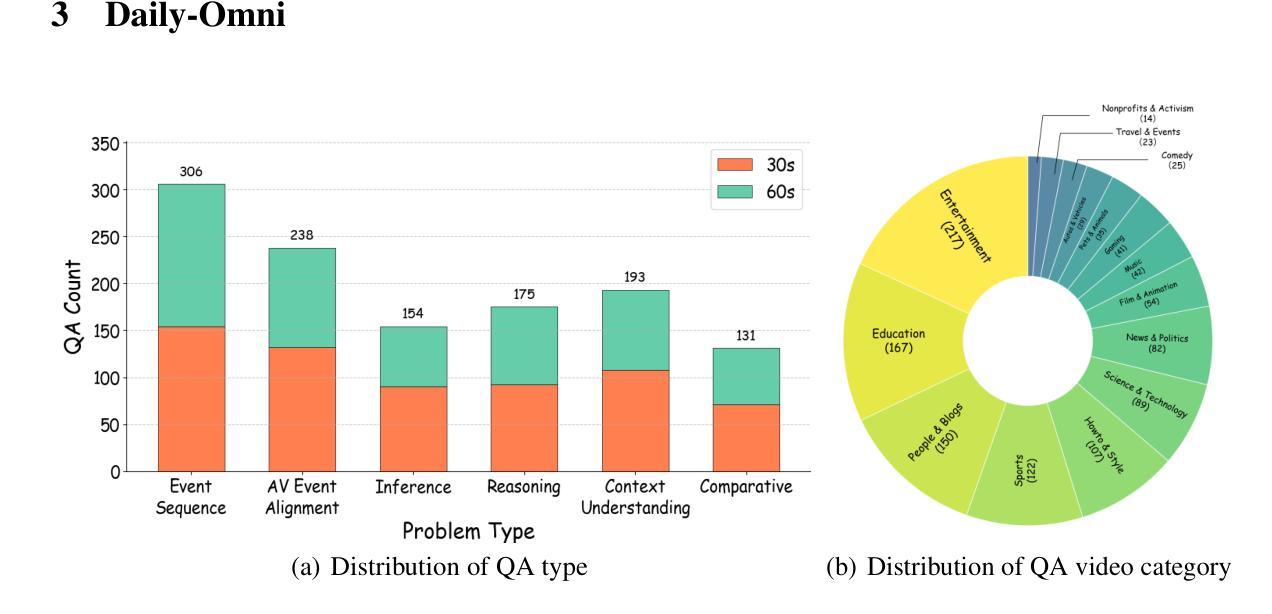
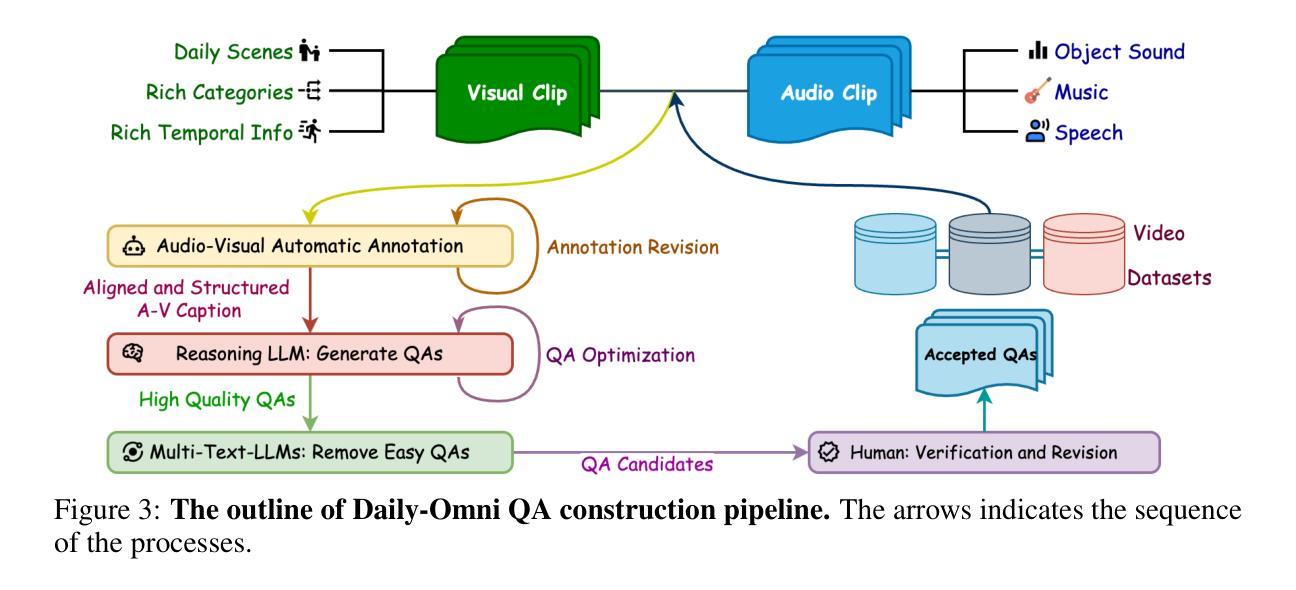
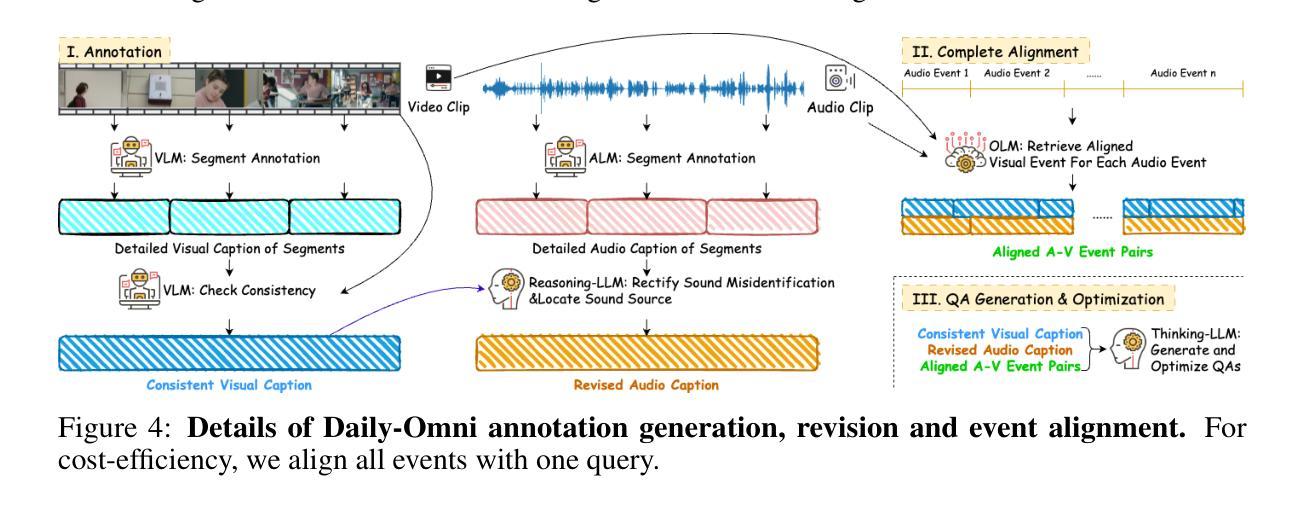
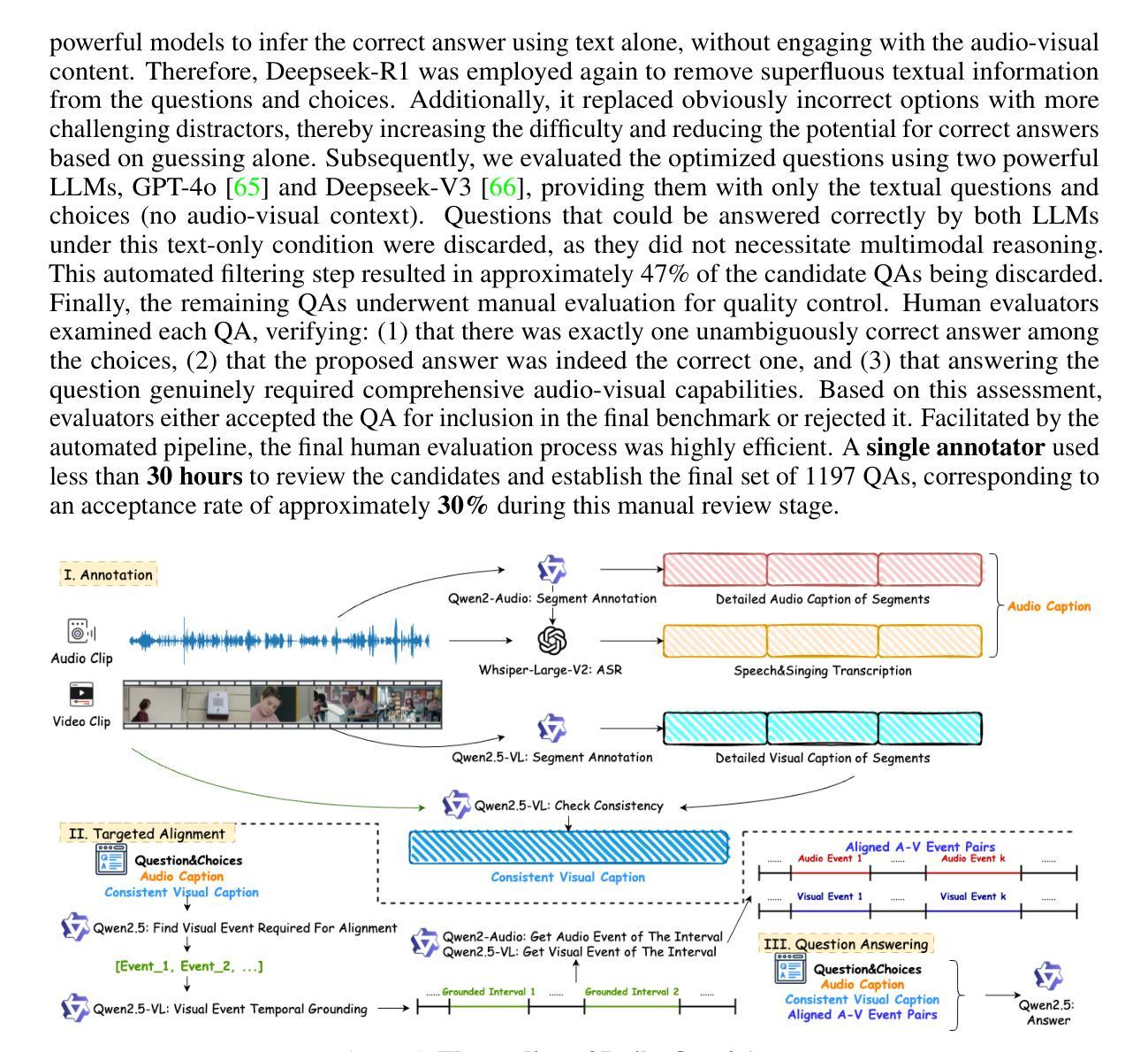
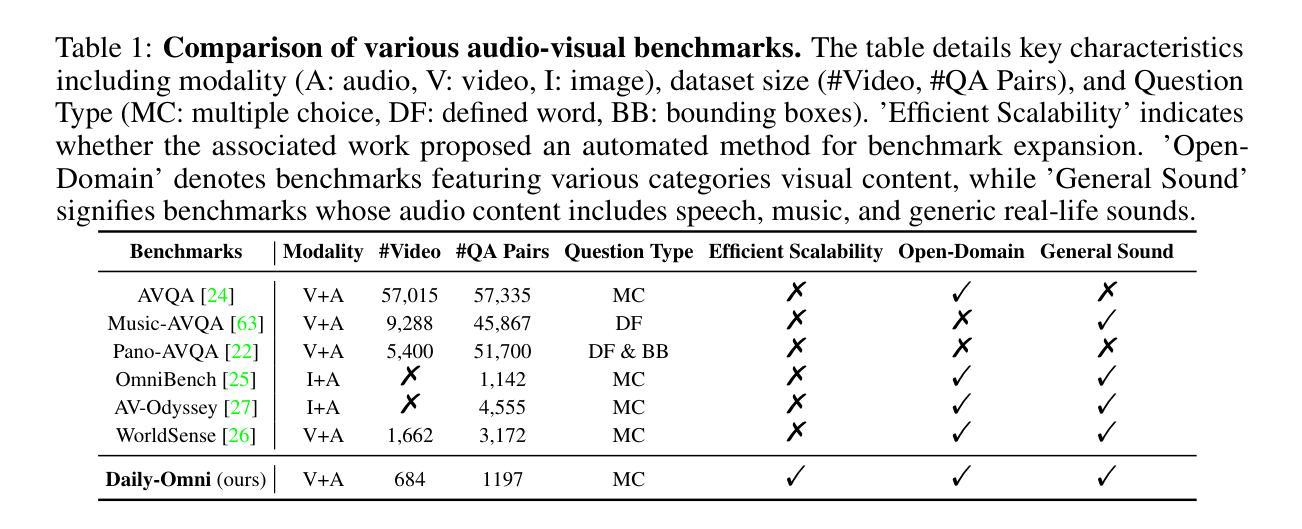
Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve promising performance on visual and audio benchmarks independently. However, the ability of these models to process cross-modal information synchronously remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce: 1) Daily-Omni, an Audio-Visual Questioning and Answering benchmark comprising 684 videos of daily life scenarios from diverse sources, rich in both audio and visual information, and featuring 1197 multiple-choice QA pairs across 6 major tasks; 2) Daily-Omni QA Generation Pipeline, which includes automatic annotation, QA generation and QA optimization, significantly improves efficiency for human evaluation and scalability of the benchmark; 3) Daily-Omni-Agent, a training-free agent utilizing open-source Visual Language Model (VLM), Audio Language Model (ALM) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) model to establish a baseline for this benchmark. The results show that current MLLMs still struggle significantly with tasks requiring audio-visual integration, but combining VLMs and ALMs with simple temporal alignment techniques can achieve substantially better performance. Codes and benchmark are available at \href{https://github.com/Lliar-liar/Daily-Omni}{https://github.com/Lliar-liar/Daily-Omni}.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉和音频基准测试上独立地取得了有前景的表现。然而,这些模型处理跨模态信息同步的能力仍然很大程度上未被探索。在本文中,我们介绍了以下内容:1)Daily-Omni,一个包含音频视觉问答的基准测试,它由来自不同源的684个日常生活场景的视频组成,这些视频富含音频和视觉信息,涵盖了6大类任务的1197个多项选择问答对;2)Daily-Omni问答生成管道,包括自动标注、问答生成和问答优化,它极大地提高了人类评估和基准测试的可扩展性的效率;3)无需训练的Daily-Omni-Agent,它利用开源的视觉语言模型(VLM)、音频语言模型(ALM)和自动语音识别(ASR)模型来建立这个基准测试的基线。结果表明,当前的多模态大型语言模型在处理需要视听整合的任务时仍存在较大的困难,但通过结合VLM和ALM以及简单的时序对齐技术,可以取得显著更好的性能。代码和基准测试可在https://github.com/Lliar-liar/Daily-Omni处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对视听信息的问答基准测试——Daily-Omni。该基准测试包含富含视听信息的684个日常生活场景视频,涵盖6项主要任务,并提供了自动标注、问答生成和问答优化的生成管道,提高了人类评估和基准测试的扩展性。此外,还介绍了无需训练的Daily-Omni-Agent,它通过利用视觉语言模型、音频语言模型和语音识别模型,为基准测试建立了基线。结果表明,当前的多模态大型语言模型在需要视听整合的任务上仍有显著挑战,但通过结合视觉语言模型和音频语言模型,并使用简单的时序对齐技术,可以取得更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Daily-Omni是一个视听问答基准测试,包含丰富的日常生活场景视频和多元选择问答对。
- Daily-Omni引入了高效的QA生成管道,包括自动标注、问答生成和问答优化。
- Daily-Omni-Agent是一个无需训练的模型,结合了视觉语言模型、音频语言模型和语音识别模型。
- 当前多模态大型语言模型在视听整合任务上存在挑战。
- 结合视觉语言模型和音频语言模型,并使用简单的时序对齐技术,可以显著提高模型性能。
- 论文提供了相关代码和基准测试链接,便于公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

CosyVoice 3: Towards In-the-wild Speech Generation via Scaling-up and Post-training
Authors:Zhihao Du, Changfeng Gao, Yuxuan Wang, Fan Yu, Tianyu Zhao, Hao Wang, Xiang Lv, Hui Wang, Xian Shi, Keyu An, Guanrou Yang, Yabin Li, Yanni Chen, Zhifu Gao, Qian Chen, Yue Gu, Mengzhe Chen, Yafeng Chen, Shiliang Zhang, Wen Wang, Jieping Ye
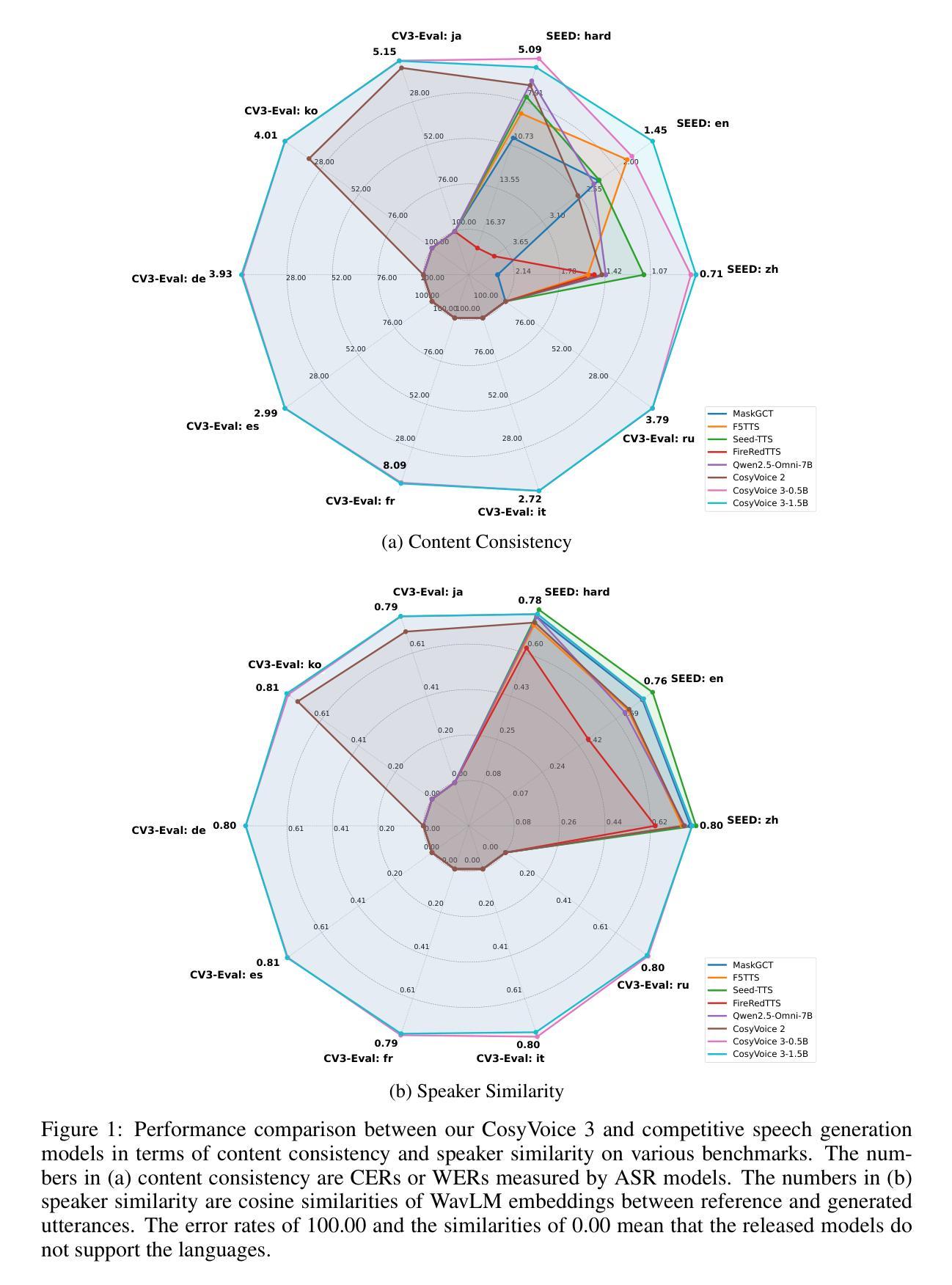
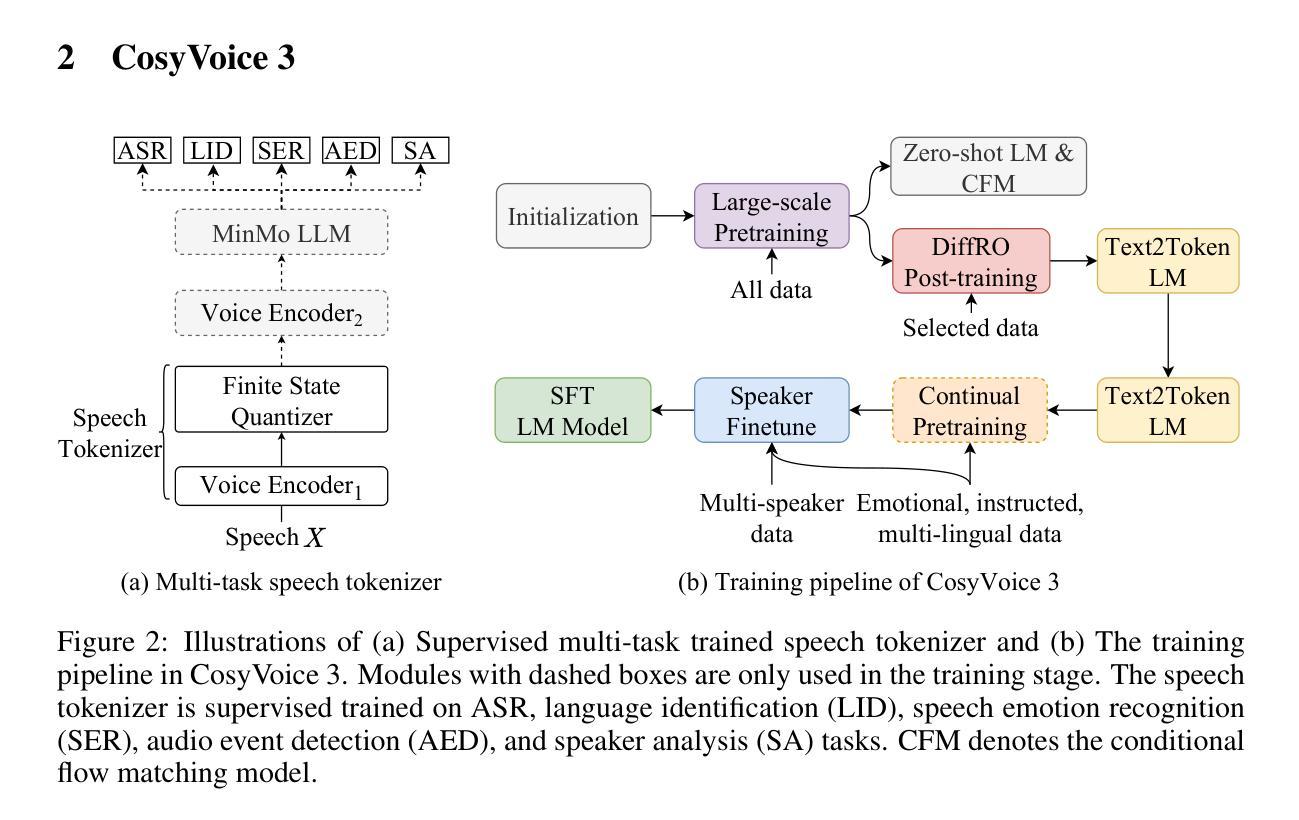
In our prior works, we introduced a scalable streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which integrates a large language model (LLM) and a chunk-aware flow matching (FM) model, and achieves low-latency bi-streaming speech synthesis and human-parity quality. Despite these advancements, CosyVoice 2 exhibits limitations in language coverage, domain diversity, data volume, text formats, and post-training techniques. In this paper, we present CosyVoice 3, an improved model designed for zero-shot multilingual speech synthesis in the wild, surpassing its predecessor in content consistency, speaker similarity, and prosody naturalness. Key features of CosyVoice 3 include: 1) A novel speech tokenizer to improve prosody naturalness, developed via supervised multi-task training, including automatic speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, language identification, audio event detection, and speaker analysis. 2) A new differentiable reward model for post-training applicable not only to CosyVoice 3 but also to other LLM-based speech synthesis models. 3) Dataset Size Scaling: Training data is expanded from ten thousand hours to one million hours, encompassing 9 languages and 18 Chinese dialects across various domains and text formats. 4) Model Size Scaling: Model parameters are increased from 0.5 billion to 1.5 billion, resulting in enhanced performance on our multilingual benchmark due to the larger model capacity. These advancements contribute significantly to the progress of speech synthesis in the wild. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3.
在我们之前的工作中,我们推出了一款可扩展的流式语音合成模型CosyVoice 2,它集成了一个大型语言模型(LLM)和基于片段感知的流匹配(FM)模型,实现了低延迟的双向流式语音合成和接近真人水平的语音质量。尽管取得了这些进展,但在语言覆盖、领域多样性、数据量、文本格式和训练后技术方面,CosyVoice 2仍存在一定局限性。在本文中,我们介绍了CosyVoice 3,这是一款针对野外零样本多语种语音合成的改进模型,在内容一致性、说话人相似性和语调自然度方面超越了其前身。CosyVoice 3的主要特点包括:1)一种新型语音标记器,通过监督多任务训练开发,旨在提高语调的自然度,包括自动语音识别、语音情感识别、语言识别、音频事件检测和说话人分析。2)一种新的可微奖励模型,适用于训练后的场景,不仅适用于CosyVoice 3,也适用于其他基于LLM的语音合成模型。3)数据集大小扩展:训练数据从一万小时扩展到一百万小时,涵盖9种语言和18种中文方言,涉及各种领域和文本格式。4)模型大小扩展:模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,由于模型容量更大,我们的多语种基准测试性能有所提高。这些进步为野外语音合成的进展做出了重大贡献。我们鼓励读者在https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3上试听演示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, work in progress
摘要
本文介绍了CosyVoice 3模型,该模型是对先前工作的改进,用于零样本多语种野外语音合成。相较于前代产品,CosyVoice 3在内容一致性、发音人相似性和语调自然度上有所超越。关键特性包括:1)通过监督多任务训练开发的新型语音标记器,以提高语调的自然性;2)适用于CosyVoice 3和其他基于LLM的语音合成模型的新型可微奖励模型;3)数据集大小扩展:训练数据从一万小时扩展到一百万小时,涵盖9种语言和18种中文方言,涉及各种领域和文本格式;4)模型大小扩展:模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,由于模型容量更大,我们的多语种基准测试性能增强。这些进展对野外语音合成的进步具有重要意义。
关键见解
- CosyVoice 3模型是对CosyVoice 2的改进,用于零样本多语种野外语音合成。
- CosyVoice 3在内容一致性、发音人相似性和语调自然度上有所超越。
- 新型语音标记器通过监督多任务训练提高语调自然性。
- 引入新型可微奖励模型,适用于CosyVoice 3和其他LLM语音合成模型的后期训练。
- 训练数据集从十万小时扩展到百万小时,涵盖多种语言和中文方言,以及多种领域和文本格式。
- 模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,提升了多语种性能。
- 鼓励听众通过网站链接体验Demo。
点此查看论文截图

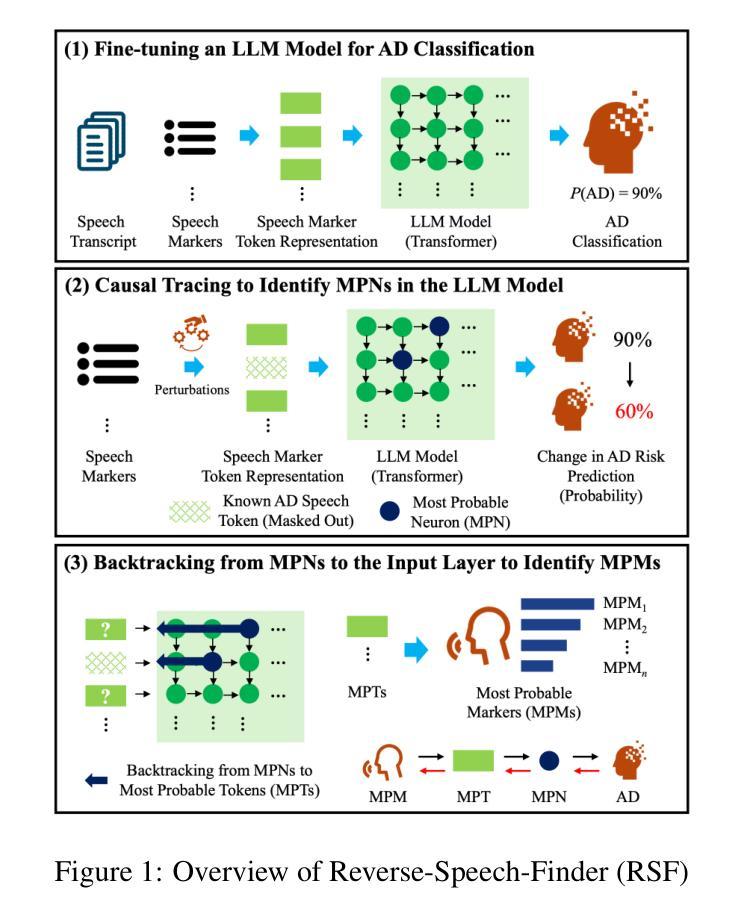
Reverse-Speech-Finder: A Neural Network Backtracking Architecture for Generating Alzheimer’s Disease Speech Samples and Improving Diagnosis Performance
Authors:Victor OK Li, Yang Han, Jacqueline CK Lam, Lawrence YL Cheung
This study introduces Reverse-Speech-Finder (RSF), a groundbreaking neural network backtracking architecture designed to enhance Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) diagnosis through speech analysis. Leveraging the power of pre-trained large language models, RSF identifies and utilizes the most probable AD-specific speech markers, addressing both the scarcity of real AD speech samples and the challenge of limited interpretability in existing models. RSF’s unique approach consists of three core innovations: Firstly, it exploits the observation that speech markers most probable of predicting AD, defined as the most probable speech-markers (MPMs), must have the highest probability of activating those neurons (in the neural network) with the highest probability of predicting AD, defined as the most probable neurons (MPNs). Secondly, it utilizes a speech token representation at the input layer, allowing backtracking from MPNs to identify the most probable speech-tokens (MPTs) of AD. Lastly, it develops an innovative backtracking method to track backwards from the MPNs to the input layer, identifying the MPTs and the corresponding MPMs, and ingeniously uncovering novel speech markers for AD detection. Experimental results demonstrate RSF’s superiority over traditional methods such as SHAP and Integrated Gradients, achieving a 3.5% improvement in accuracy and a 3.2% boost in F1-score. By generating speech data that encapsulates novel markers, RSF not only mitigates the limitations of real data scarcity but also significantly enhances the robustness and accuracy of AD diagnostic models. These findings underscore RSF’s potential as a transformative tool in speech-based AD detection, offering new insights into AD-related linguistic deficits and paving the way for more effective non-invasive early intervention strategies.
本研究介绍了Reverse-Speech-Finder(RSF),这是一种突破性的神经网络回溯架构,旨在通过语音分析提高阿尔茨海默病(AD)的诊断能力。RSF利用预训练的大型语言模型的威力,识别和利用最可能的AD特异性语音标记,解决真实AD语音样本稀缺和现有模型解释性有限的挑战。RSF的独特方法包括三个核心创新:首先,它利用了一个观察结果,即最可能预测AD的语音标记(定义为MPM),在神经网络中必须激活那些最可能预测AD的神经元(定义为MPN)。其次,它在输入层使用语音标记表示,允许从MPN回溯来识别AD的最可能语音标记(MPTs)。最后,它开发了一种创新的回溯方法,从MPN回溯到输入层,识别MPTs和相应的MPMs,并巧妙地发现了用于检测AD的新型语音标记。实验结果表明,RSF优于SHAP和集成梯度等传统方法,在准确率上提高了3.5%,F1分数提高了3.2%。通过生成包含新型标记的语音数据,RSF不仅缓解了真实数据稀缺的限制,还显著提高了AD诊断模型的稳健性和准确性。这些发现突显了RSF在基于语音的AD检测中的潜力,为AD相关的语言缺陷提供了新的见解,并为更有效的非侵入性早期干预策略铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该研究提出一种名为Reverse-Speech-Finder(RSF)的突破性神经网络回溯架构,通过语音分析提高阿尔茨海默病(AD)诊断的准确性。RSF利用预训练的大型语言模型的强大功能,识别和利用最可能的AD特异性语音标记物,解决真实AD语音样本缺乏和现有模型解释性有限的问题。RSF的独特方法包括三个核心创新点:首先,它利用最可能的语音标记物(MPMs)必须激活那些最可能预测AD的神经元(在神经网络中定义为最可能的神经元MPNs)的观点。其次,它在输入层使用语音标记表示,允许从MPNs回溯以识别AD的最可能的语音标记符(MPTs)。最后,它开发了一种创新的回溯方法,从MPNs回溯到输入层,识别MPTs和相应的MPMs,并巧妙地揭示用于AD检测的新语音标记物。实验结果表明,RSF优于传统方法如SHAP和集成梯度法,准确率提高了3.5%,F1得分提高了3.2%。通过生成包含新型标记的语音数据,RSF不仅缓解了真实数据稀缺的限制,而且大大提高了AD诊断模型的稳健性和准确性。这些发现突显了RSF在基于语音的AD检测中的潜力,为AD相关的语言缺陷提供了新的见解,并为更有效的非侵入性早期干预策略铺平了道路。
关键见解
- RSF是一个基于神经网络的回溯架构,旨在通过语音分析提高阿尔茨海默病(AD)的诊断。
- 利用预训练的大型语言模型来识别和利用最可能的AD特异性语音标记物。
- RSF的核心创新包括:利用最可能的语音标记物和神经元之间的关系,使用语音标记表示在输入层,以及开发一种创新的回溯方法来识别AD的新型语音标记物。
- 实验结果表明RSF在AD检测方面优于传统方法,准确率和F1得分均有显著提高。
- RSF不仅缓解了真实数据稀缺的问题,还提高了AD诊断模型的稳健性和准确性。
- RSF的潜力在于为AD相关的语言缺陷提供新的见解,并可能为更有效的非侵入性早期干预策略提供指导。
点此查看论文截图

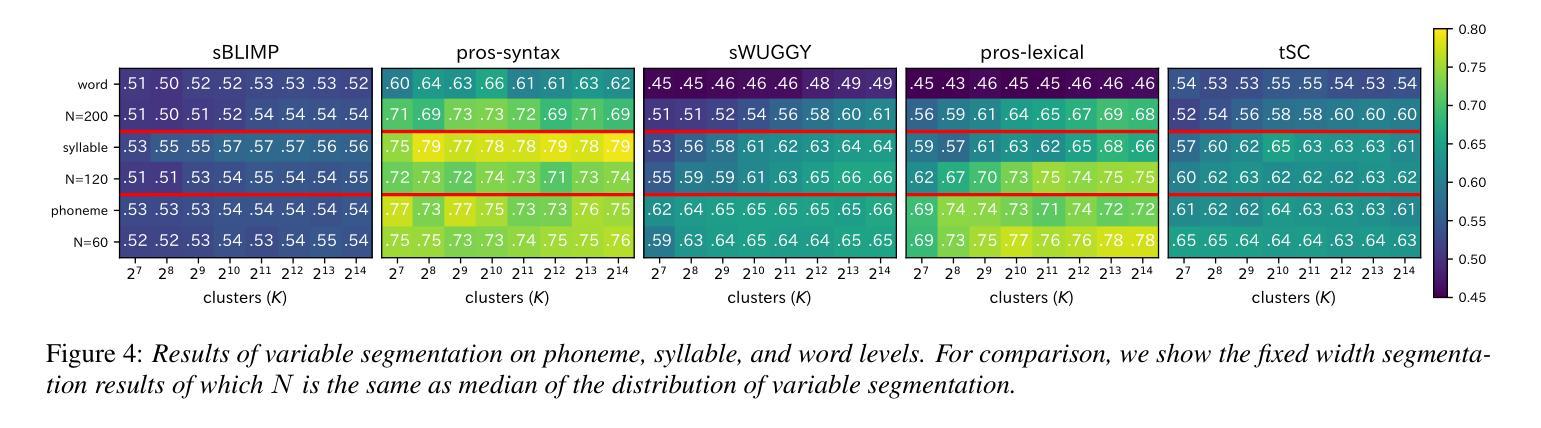
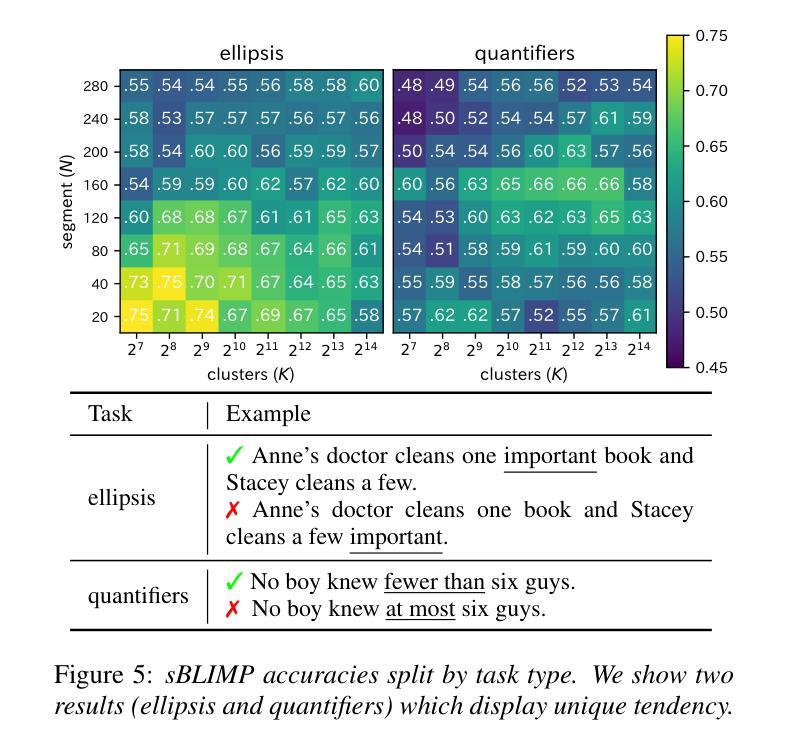
Exploring the Effect of Segmentation and Vocabulary Size on Speech Tokenization for Speech Language Models
Authors:Shunsuke Kando, Yusuke Miyao, Shinnosuke Takamichi
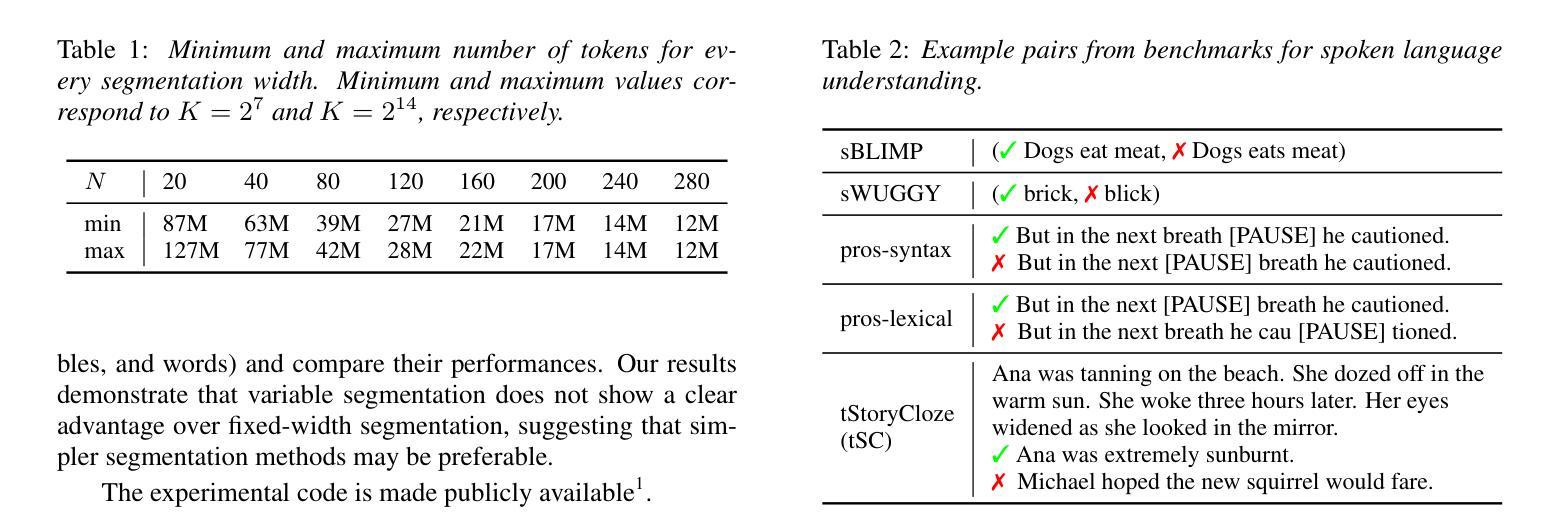
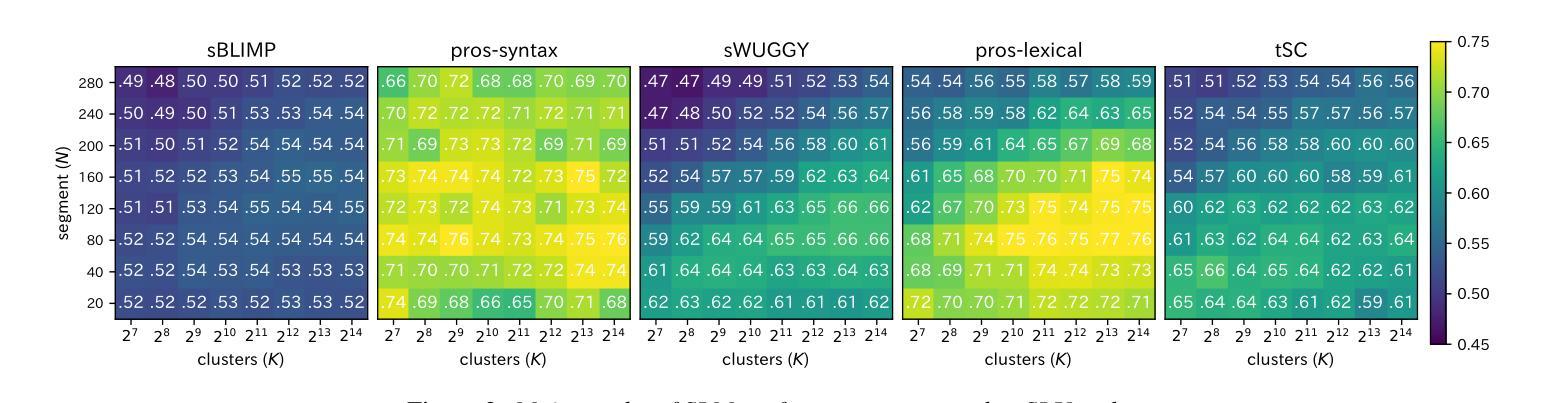
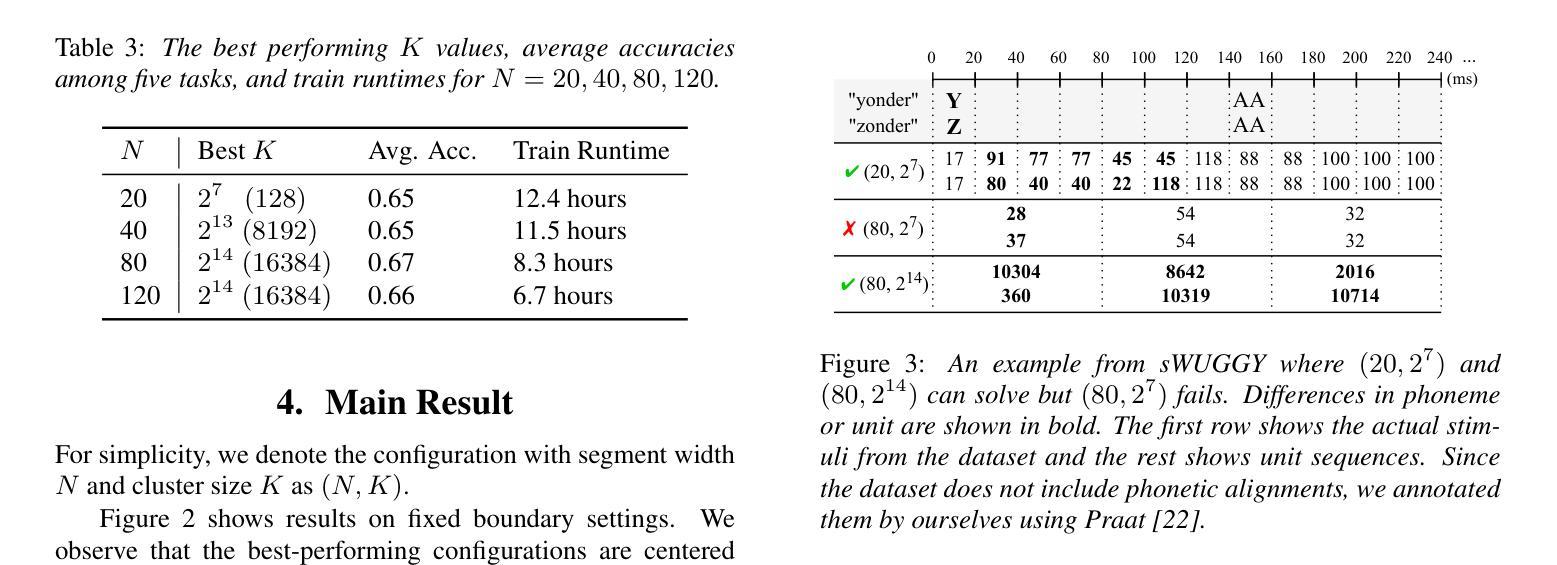
The purpose of speech tokenization is to transform a speech signal into a sequence of discrete representations, serving as the foundation for speech language models (SLMs). While speech tokenization has many options, their effect on the performance of SLMs remains unclear. This paper investigates two key aspects of speech tokenization: the segmentation width and the cluster size of discrete units. First, we segment speech signals into fixed/variable widths and pooled representations. We then train K-means models in multiple cluster sizes. Through the evaluation on zero-shot spoken language understanding benchmarks, we find the positive effect of moderately coarse segmentation and bigger cluster size. Notably, among the best-performing models, the most efficient one achieves a 50% reduction in training data and a 70% decrease in training runtime. Our analysis highlights the importance of combining multiple tokens to enhance fine-grained spoken language understanding.
语音切词的目的是将语音信号转换为一系列离散表示,作为语音语言模型(SLM)的基础。虽然语音切词有很多选择,但它们对SLM性能的影响仍不明确。本文研究了语音切词的两个方面:分段宽度和离散单元簇的大小。首先,我们将语音信号分段为固定/可变宽度和汇总表示。然后,我们在多个簇大小上训练K-means模型。通过对零样本口语理解基准测试进行评估,我们发现适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小产生了积极的影响。值得注意的是,在表现最佳的模型中,最有效的方法实现了训练数据减少50%,训练运行时间减少70%。我们的分析强调了结合多个令牌以增强精细粒度口语理解的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech2025
总结
语音标记化的目的是将语音信号转化为一系列离散表示,作为语音语言模型(SLM)的基础。本文研究了语音标记化的两个关键方面:分段宽度和离散单元簇的大小。实验通过固定或可变宽度的分段以及池化表示,训练了不同簇大小的K-means模型。在零样本口语理解基准测试上,本文发现适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小具有积极影响。最高效的模型甚至实现了训练数据减少50%,训练时间减少70%。分析表明,结合多个标记有助于提高精细口语的理解能力。
要点
- 语音标记化是将语音信号转化为离散表示序列的过程,是语音语言模型的基础。
- 语音标记化的两个关键方面为分段宽度和离散单元簇的大小。
- 通过固定或可变宽度的分段以及池化表示,训练了K-means模型。
- 适度粗糙的分段和较大的簇大小对语音语言模型的性能有积极影响。
- 最高效的模型实现了训练数据和时间的显著减少。
- 结合多个标记有助于提高精细口语理解能力。
点此查看论文截图

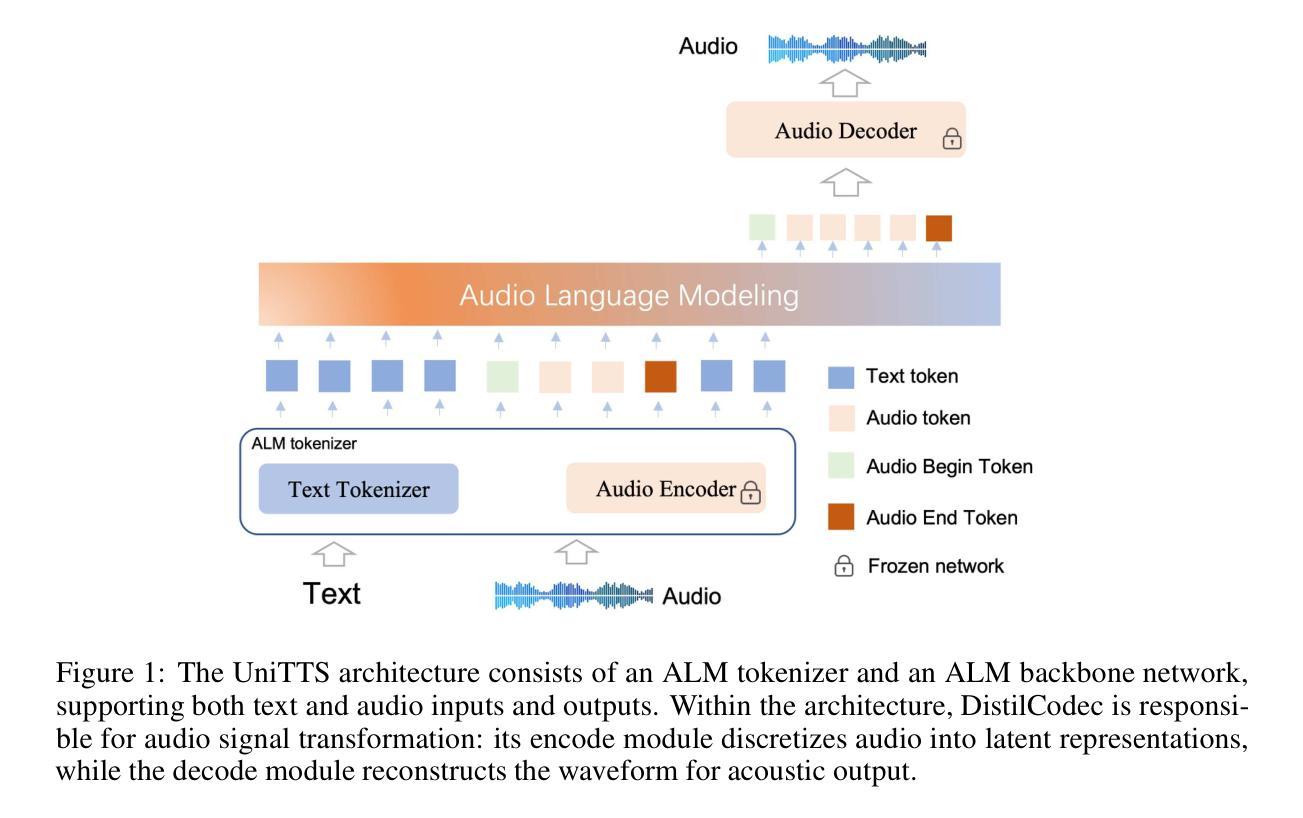
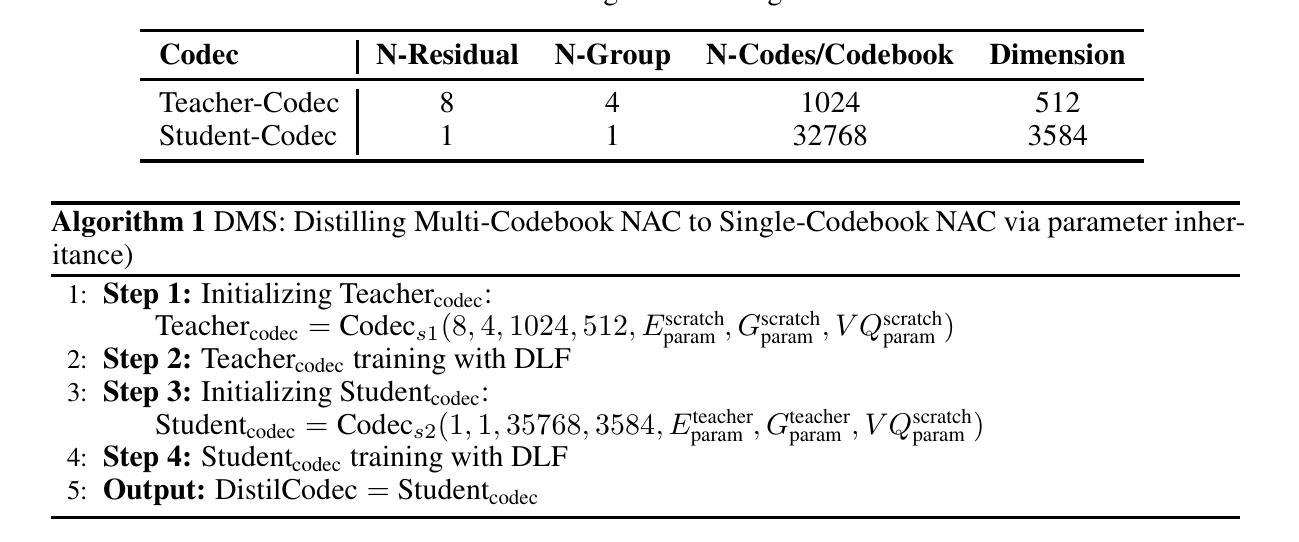
UniTTS: An end-to-end TTS system without decoupling of acoustic and semantic information
Authors:Rui Wang, Qianguo Sun, Tianrong Chen, Zhiyun Zeng, Junlong Wu, Jiaxing Zhang
The emergence of multi-codebook neutral audio codecs such as Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) and Group Vector Quantization (GVQ) has significantly advanced Large-Language-Model (LLM) based Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems. These codecs are crucial in separating semantic and acoustic information while efficiently harnessing semantic priors. However, since semantic and acoustic information cannot be fully aligned, a significant drawback of these methods when applied to LLM-based TTS is that large language models may have limited access to comprehensive audio information. To address this limitation, we propose DistilCodec and UniTTS, which collectively offer the following advantages: 1) This method can distill a multi-codebook audio codec into a single-codebook audio codec with 32,768 codes while achieving a near 100% utilization. 2) As DistilCodec does not employ a semantic alignment scheme, a large amount of high-quality unlabeled audio (such as audiobooks with sound effects, songs, etc.) can be incorporated during training, further expanding data diversity and broadening its applicability. 3) Leveraging the comprehensive audio information modeling of DistilCodec, we integrated three key tasks into UniTTS’s pre-training framework: audio modality autoregression, text modality autoregression, and speech-text cross-modal autoregression. This allows UniTTS to accept interleaved text and speech/audio prompts while substantially preserving LLM’s text capabilities. 4) UniTTS employs a three-stage training process: Pre-Training, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Alignment. Source code and model checkpoints are publicly available at https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/UniTTS and https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/DistilCodec.
随着多码本中性音频编解码器(如残差矢量量化(RVQ)和组矢量量化(GVQ))的出现,显著推动了基于大型语言模型(LLM)的文本转语音(TTS)系统的发展。这些编解码器在分离语义和声音信息的同时,有效地利用语义先验知识方面发挥着关键作用。然而,由于语义和声音信息无法完全对齐,这些方法应用于基于LLM的TTS时的一个重大缺点是大型语言模型可能无法获得全面的音频信息。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了DistilCodec和UniTTS,它们共同具有以下优点:1)此方法可以将多码本音频编解码器蒸馏为单码本音频编解码器,同时拥有32768个码本,且利用率接近100%。2)由于DistilCodec没有采用语义对齐方案,因此可以在训练过程中融入大量高质量的无标签音频(如带有音效的有声读物、歌曲等),进一步扩大了数据多样性和拓宽了其适用性。3)利用DistilCodec的全面音频信息建模,我们将三个关键任务整合到UniTTS的预训练框架中:音频模态自回归、文本模态自回归和语音-文本跨模态自回归。这允许UniTTS在接受交织的文本和语音/音频提示时,同时保留LLM的文本功能。4)UniTTS采用三阶段训练过程:预训练、监督微调(SFT)和对齐。源代码和模型检查点可在https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/UniTTS和https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/DistilCodec上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多代码本中立音频编码器的出现,如残差矢量量化(RVQ)和组矢量量化(GVQ),已经显著推进了基于大语言模型(LLM)的文本到语音(TTS)系统的发展。然而,这些方法在应用于LLM-based TTS时存在语义和音频信息无法完全对齐的局限性。为解决此问题,提出了DistilCodec和UniTTS,它们能够:将多代码本音频编码器转化为单代码本音频编码器,实现近100%的利用率;利用无需语义对齐的方法,纳入大量高质量未标注音频,提高数据多样性和适用性;整合三个关键任务到UniTTS的预训练框架中,接受交替的文本和语音/音频提示,同时保留LLM的文本能力;采用三阶段训练过程。
Key Takeaways
- 多代码本中立音频编码器的出现已经显著推动了基于大语言模型的文本到语音系统的发展。
- 语义和音频信息的不完全对齐是当前方法的一个重大挑战。
- DistilCodec方法能够将多代码本音频编码器转化为单代码本音频编码器,并实现近100%的利用率。
- 由于不需要语义对齐,DistilCodec可以纳入大量未标注的音频数据。
- UniTTS整合了三个关键任务到其预训练框架中,以提高系统的功能性和灵活性。
- UniTTS采用了包括预训练、监督微调和对齐在内的三阶段训练过程。
- 源代码和模型检查点已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

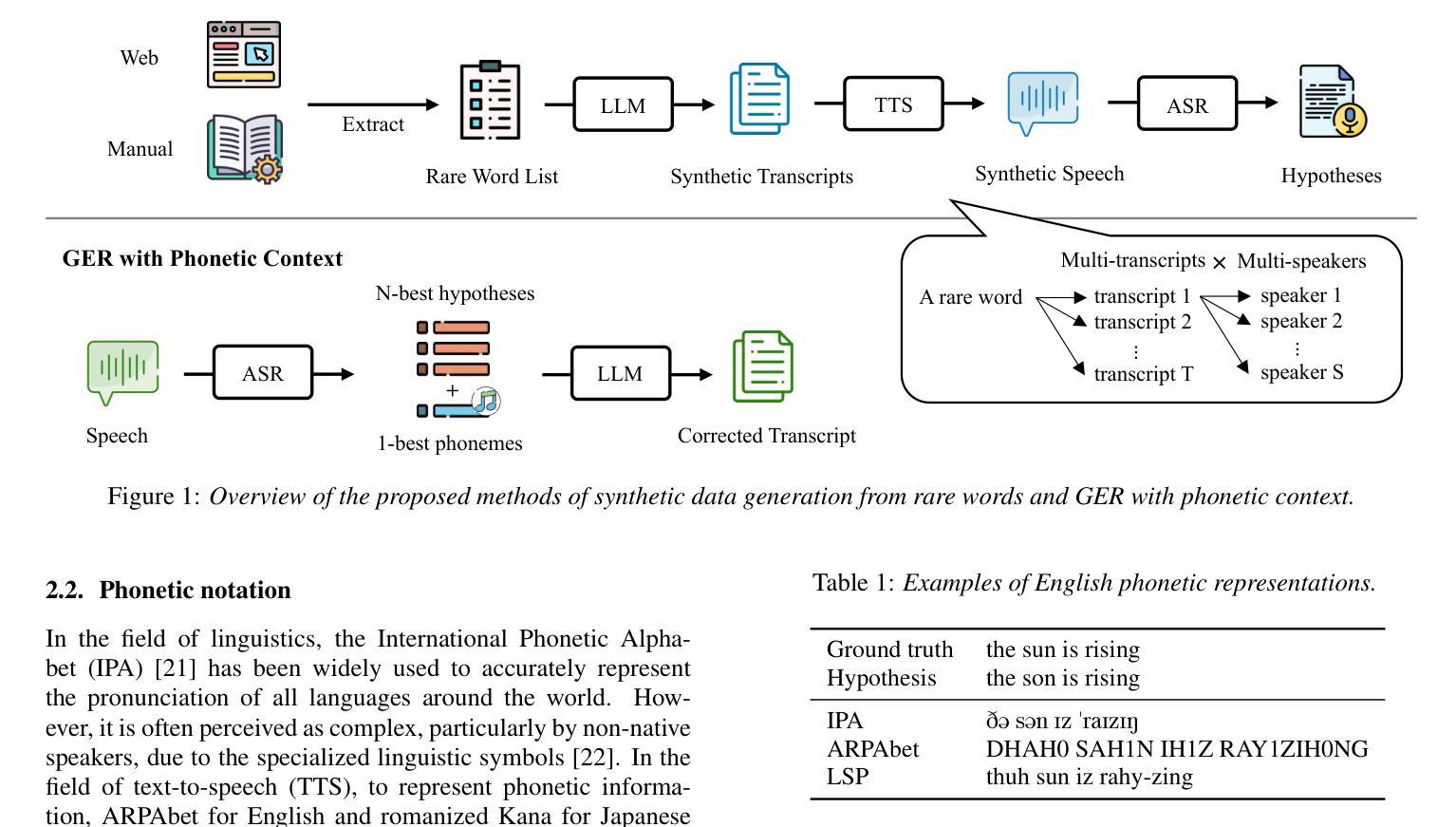
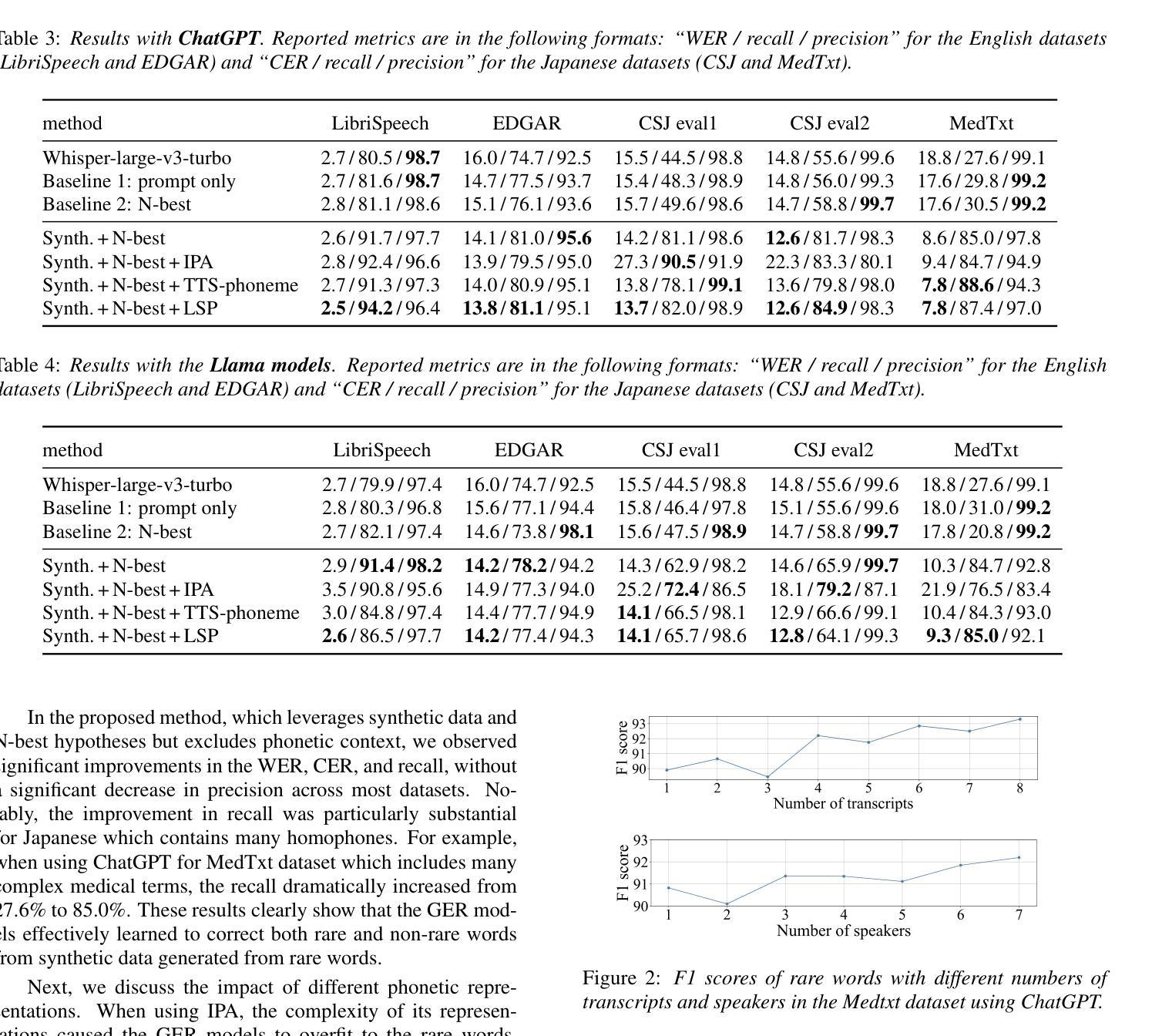
LLM-based Generative Error Correction for Rare Words with Synthetic Data and Phonetic Context
Authors:Natsuo Yamashita, Masaaki Yamamoto, Hiroaki Kokubo, Yohei Kawaguchi
Generative error correction (GER) with large language models (LLMs) has emerged as an effective post-processing approach to improve automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance. However, it often struggles with rare or domain-specific words due to limited training data. Furthermore, existing LLM-based GER approaches primarily rely on textual information, neglecting phonetic cues, which leads to over-correction. To address these issues, we propose a novel LLM-based GER approach that targets rare words and incorporates phonetic information. First, we generate synthetic data to contain rare words for fine-tuning the GER model. Second, we integrate ASR’s N-best hypotheses along with phonetic context to mitigate over-correction. Experimental results show that our method not only improves the correction of rare words but also reduces the WER and CER across both English and Japanese datasets.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的生成式错误校正(GER)已成为提高自动语音识别(ASR)性能的有效后处理的方法。然而,由于训练数据的有限,它通常在处理稀有词或特定领域的词时面临挑战。此外,现有的基于LLM的GER方法主要依赖文本信息,忽略了语音线索,从而导致过度校正。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的基于LLM的GER方法,该方法针对稀有词并融入了语音信息。首先,我们生成合成数据,其中包含稀有词,以微调GER模型。其次,我们结合ASR的N-best假设和语音环境,以减轻过度校正。实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅提高了稀有词的校正率,而且降低了英语和日语数据集的词错误率和字符错误率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by INTERSPEECH 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的生成式错误更正(GER)是提升自动语音识别(ASR)性能的有效后处理方法。然而,它因训练数据有限而难以应对稀有词或特定领域的词汇。此外,现有的LLM-based GER方法主要依赖文本信息,忽略了语音线索,导致过度修正。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种针对稀有词并融入语音信息的新型LLM-based GER方法。首先,我们生成合成数据以包含稀有词,对GER模型进行微调。其次,我们结合ASR的N-best假设和语音环境来减轻过度修正的问题。实验结果表明,我们的方法不仅提高了稀有词的修正效果,还降低了英语和日语数据集的词错误率和字符错误率。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式错误更正(GER)是提升自动语音识别(ASR)性能的有效后处理方法。
- LLM-based GER方法面临稀有词和特定领域词汇的识别挑战。
- 现有LLM-based GER方法主要依赖文本信息,导致过度修正。
- 提出了一种新型LLM-based GER方法,该方法针对稀有词并融入语音信息。
- 通过生成合成数据对GER模型进行微调,以包含稀有词。
- 结合ASR的N-best假设和语音环境来减轻过度修正问题。
点此查看论文截图

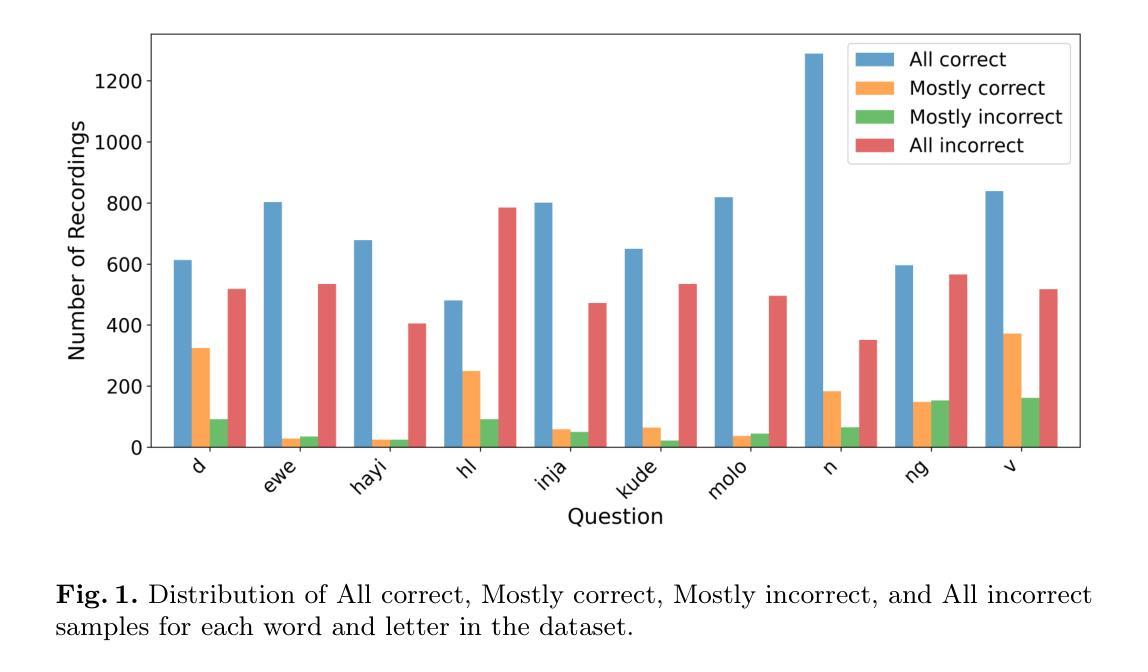
An End-to-End Approach for Child Reading Assessment in the Xhosa Language
Authors:Sergio Chevtchenko, Nikhil Navas, Rafaella Vale, Franco Ubaudi, Sipumelele Lucwaba, Cally Ardington, Soheil Afshar, Mark Antoniou, Saeed Afshar
Child literacy is a strong predictor of life outcomes at the subsequent stages of an individual’s life. This points to a need for targeted interventions in vulnerable low and middle income populations to help bridge the gap between literacy levels in these regions and high income ones. In this effort, reading assessments provide an important tool to measure the effectiveness of these programs and AI can be a reliable and economical tool to support educators with this task. Developing accurate automatic reading assessment systems for child speech in low-resource languages poses significant challenges due to limited data and the unique acoustic properties of children’s voices. This study focuses on Xhosa, a language spoken in South Africa, to advance child speech recognition capabilities. We present a novel dataset composed of child speech samples in Xhosa. The dataset is available upon request and contains ten words and letters, which are part of the Early Grade Reading Assessment (EGRA) system. Each recording is labeled with an online and cost-effective approach by multiple markers and a subsample is validated by an independent EGRA reviewer. This dataset is evaluated with three fine-tuned state-of-the-art end-to-end models: wav2vec 2.0, HuBERT, and Whisper. The results indicate that the performance of these models can be significantly influenced by the amount and balancing of the available training data, which is fundamental for cost-effective large dataset collection. Furthermore, our experiments indicate that the wav2vec 2.0 performance is improved by training on multiple classes at a time, even when the number of available samples is constrained.
儿童识字能力是个人后续生命阶段生活成果的重要预测指标。这指出了针对脆弱的中低收入群体进行针对性干预的必要性,以帮助缩小这些地区识字水平与高收入地区之间的差距。在此类工作中,阅读评估是衡量这些项目效果的重要工具,人工智能可以作为支持教育工作者完成这项任务的可靠且经济的工具。对于低资源语言中的儿童语音,开发准确的自动阅读评估系统面临着重大挑战,因为数据有限且儿童的声音具有独特的声学特性。本研究以南非使用的语言之一——科萨语为例,旨在提高儿童语音识别能力。我们展示了一个由儿童科萨语语音样本组成的新数据集。该数据集可在收到请求后获得,包含十个单词和字母,这些单词和字母是早期阅读能力评估(EGRA)系统的一部分。每个录音都通过多个标记者采用在线和低成本的方式进行标记,部分录音还经过独立的EGRA审核人员进行验证。该数据集经过三种最新端到端模型的微调后进行了评估:wav2vec 2.0、HuBERT和Whisper。结果表明,这些模型的性能可能会受到可用训练数据的数量和平衡性的显著影响,这对于低成本大规模数据集的收集至关重要。此外,我们的实验表明,即使在可用样本数量受限的情况下,通过一次性训练多个类别也可以提高wav2vec 2.0的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted on AIED 2025 containing 14 pages, 6 figures and 4 tables
Summary
本文探讨儿童阅读能力对其未来生活阶段的影响,并指出对低收入和中收入群体的脆弱人群进行有针对性的干预是必要的。阅读评估是评估这些项目效果的重要工具,而人工智能可以可靠且经济地支持教育者完成这项任务。本研究关注南非使用的语言——科萨语,以推进儿童语音识别能力。研究团队推出了一份新型数据集,包含科萨语儿童语音样本。该数据集由在线和成本效益方法进行标注,部分数据经过独立早期阅读能力评估系统审核员验证。使用wav2vec 2.0、HuBERT和Whisper三种先进端对端模型进行评估的结果表明,可用训练数据的数量和平衡度会对模型性能产生显著影响,这对于低成本大规模数据集的收集至关重要。此外,实验显示,即使在可用样本数量有限的情况下,通过同时训练多个类别也能提高wav2vec 2.0的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 儿童阅读能力是预测其未来生活阶段的重要因素,需要关注对低收入和中收入脆弱群体的有针对性的干预措施。
- 阅读评估是评估阅读推广项目效果的重要工具,人工智能可以支持教育者进行这项任务。
- 本研究关注科萨语的儿童语音识别能力发展,推出新型数据集。
- 数据集通过在线和成本效益方法进行标注,部分数据经过独立审核员验证。
- wav2vec 2.0、HuBERT和Whisper三种模型被用于评估儿童语音样本。
- 可用训练数据的数量和平衡度对模型性能有显著影响,强调低成本大规模数据集收集的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

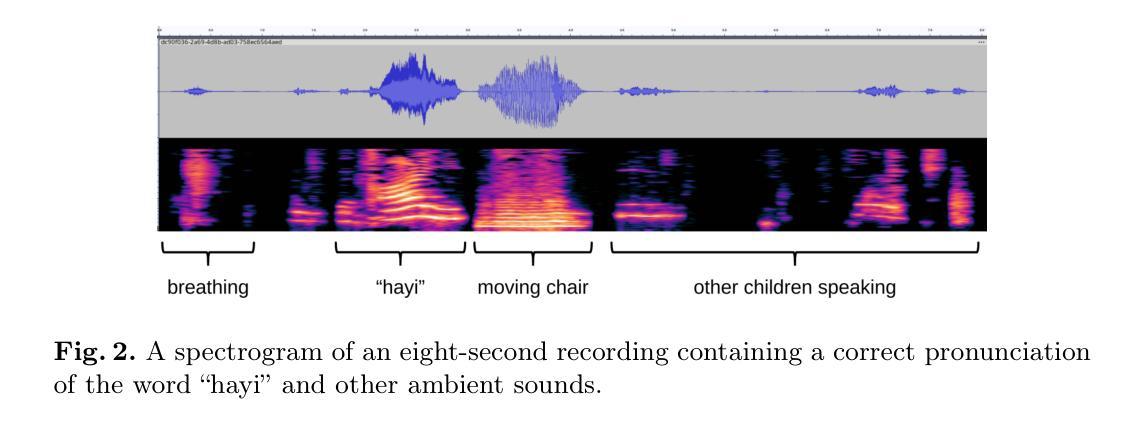
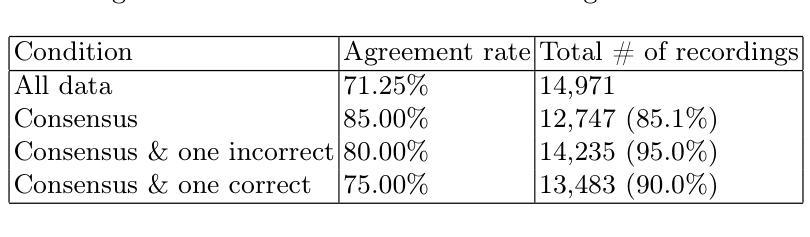
Active Speech Enhancement: Active Speech Denoising Decliping and Deveraberation
Authors:Ofir Yaish, Yehuda Mishaly, Eliya Nachmani
We introduce a new paradigm for active sound modification: Active Speech Enhancement (ASE). While Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) algorithms focus on suppressing external interference, ASE goes further by actively shaping the speech signal – both attenuating unwanted noise components and amplifying speech-relevant frequencies – to improve intelligibility and perceptual quality. To enable this, we propose a novel Transformer-Mamba-based architecture, along with a task-specific loss function designed to jointly optimize interference suppression and signal enrichment. Our method outperforms existing baselines across multiple speech processing tasks – including denoising, dereverberation, and declipping – demonstrating the effectiveness of active, targeted modulation in challenging acoustic environments.
我们介绍了一种主动声音修改的新范式:主动语音增强(ASE)。而主动降噪(ANC)算法主要侧重于抑制外部干扰,ASE更进一步地通过主动塑造语音信号来改善语音的清晰度和感知质量,即衰减不需要的噪声成分并放大语音相关的频率。为此,我们提出了一种基于Transformer-Mamba的新型架构,以及一种针对特定任务的损失函数,旨在联合优化干扰抑制和信号增强。我们的方法在多个语音处理任务上的表现优于现有基线,包括去噪、去混响和去削波,证明了在具有挑战性的声学环境中进行主动、针对性调制的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
主动声音修改领域出现了一种新的范式:主动语音增强(ASE)。与传统的主动降噪(ANC)算法侧重于抑制外部干扰不同,ASE能够积极塑造语音信号,既减少不需要的噪声成分,又放大语音相关的频率,从而提高可理解性和感知质量。为实现这一点,我们提出了一种基于Transformer-Mamba的新型架构,以及专为优化干扰抑制和信号增强而设计的特定任务损失函数。我们的方法在多个语音处理任务上的表现优于现有基线,包括去噪、消除回声和去剪辑,证明了在具有挑战性的声学环境中进行主动、针对性调制的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了主动语音增强(ASE)这一新的声音修改范式。
- 与主动降噪(ANC)算法不同,ASE能够积极塑造语音信号。
- ASE能够同时减少不需要的噪声成分并放大语音相关的频率,提高语音的可理解性和感知质量。
- 提出了一种基于Transformer-Mamba的新型架构来实现ASE。
- 特定任务损失函数的设计能够联合优化干扰抑制和信号增强。
- 在多个语音处理任务上,包括去噪、消除回声和去剪辑,该方法表现优于现有基线。
点此查看论文截图

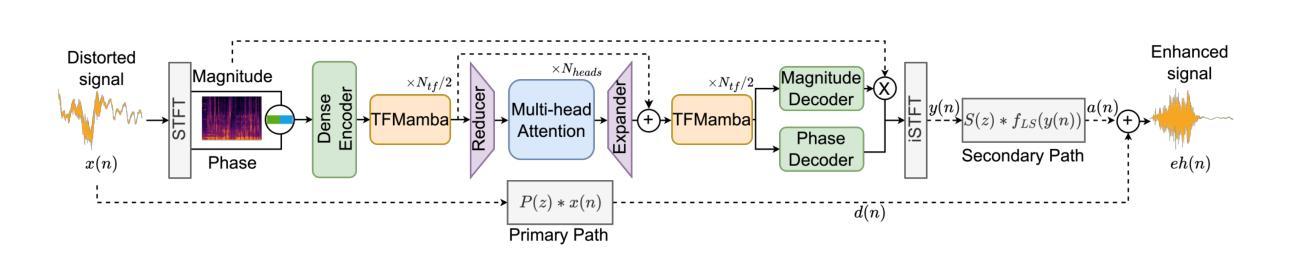
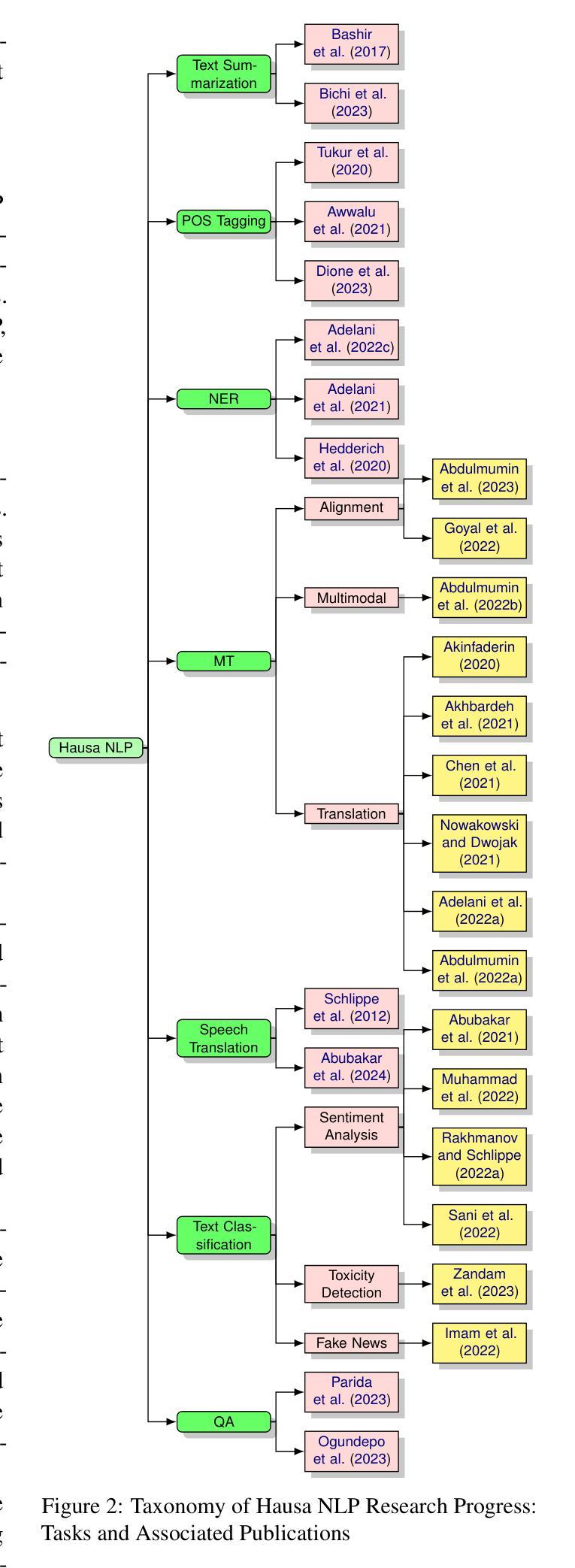
HausaNLP: Current Status, Challenges and Future Directions for Hausa Natural Language Processing
Authors:Shamsuddeen Hassan Muhammad, Ibrahim Said Ahmad, Idris Abdulmumin, Falalu Ibrahim Lawan, Babangida Sani, Sukairaj Hafiz Imam, Yusuf Aliyu, Sani Abdullahi Sani, Ali Usman Umar, Tajuddeen Gwadabe, Kenneth Church, Vukosi Marivate
Hausa Natural Language Processing (NLP) has gained increasing attention in recent years, yet remains understudied as a low-resource language despite having over 120 million first-language (L1) and 80 million second-language (L2) speakers worldwide. While significant advances have been made in high-resource languages, Hausa NLP faces persistent challenges, including limited open-source datasets and inadequate model representation. This paper presents an overview of the current state of Hausa NLP, systematically examining existing resources, research contributions, and gaps across fundamental NLP tasks: text classification, machine translation, named entity recognition, speech recognition, and question answering. We introduce HausaNLP (https://catalog.hausanlp.org), a curated catalog that aggregates datasets, tools, and research works to enhance accessibility and drive further development. Furthermore, we discuss challenges in integrating Hausa into large language models (LLMs), addressing issues of suboptimal tokenization and dialectal variation. Finally, we propose strategic research directions emphasizing dataset expansion, improved language modeling approaches, and strengthened community collaboration to advance Hausa NLP. Our work provides both a foundation for accelerating Hausa NLP progress and valuable insights for broader multilingual NLP research.
近年来,豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)受到了越来越多的关注,尽管全球有超过1.2亿的第一语言(L1)和8千万的第二语言(L2)使用者,但它作为一个资源贫乏的语言仍然没有得到充分研究。尽管在高资源语言方面取得了重大进展,但豪萨NLP仍然面临持续挑战,包括有限的开源数据集和不足的模型表示。本文概述了豪萨NLP的当前状态,系统地检查了基本NLP任务的现有资源、研究贡献和差距,包括文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答。我们介绍了豪萨NLP(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),这是一个聚合数据集、工具和研究工作的精选目录,旨在增强可访问性并推动进一步发展。此外,我们讨论了将豪萨语集成到大型语言模型(LLM)中的挑战,解决次优分词和方言变化的问题。最后,我们提出了战略研究方向,强调扩大数据集、改进语言建模方法和加强社区合作,以推动豪萨NLP的发展。我们的工作为加速豪萨NLP的进步提供了基础,并为更广泛的多语言NLP研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)的现状。尽管豪萨语有超一亿的第一语言和第二语言使用者,但作为低资源语言,其研究仍然不足。本文系统回顾了豪萨NLP的现有资源、研究贡献和空白领域,如文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别、语音识别和问答等。此外,文章还介绍了豪萨NLP面临的挑战,如有限开放数据集和模型表示不足的问题。为增强可访问性和推动进一步发展,本文推出了豪萨NLP目录(https://catalog.hausanlp.org)。本文最后提出了战略性的研究方向,强调数据集扩展、改进的语言建模方法和加强社区协作,以推动豪萨NLP的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 豪萨自然语言处理(NLP)尽管有大量的使用者,但研究仍然不足。
- 该领域面临有限开放数据集和模型表示不足的挑战。
- 存在多个基础NLP任务,包括文本分类、机器翻译、命名实体识别等。
- 推出了豪萨NLP目录(https://catalog.hausanlp.org),以推动该领域的发展。
- 集成豪萨语到大型语言模型(LLM)中面临一些问题,如次优的分词和方言变化。
- 需要扩展数据集、改进语言建模方法和加强社区协作来推动豪萨NLP的进步。
点此查看论文截图

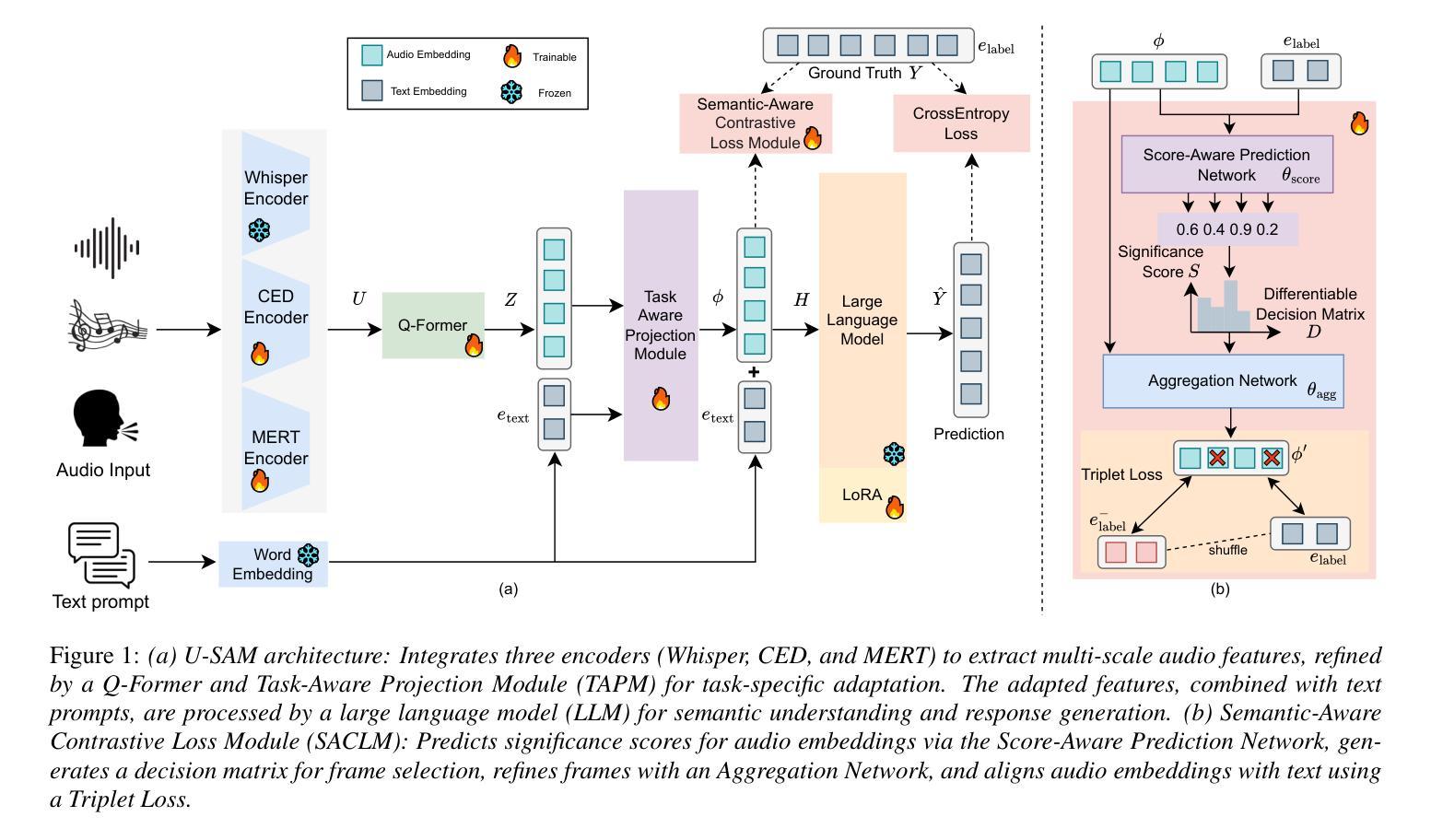
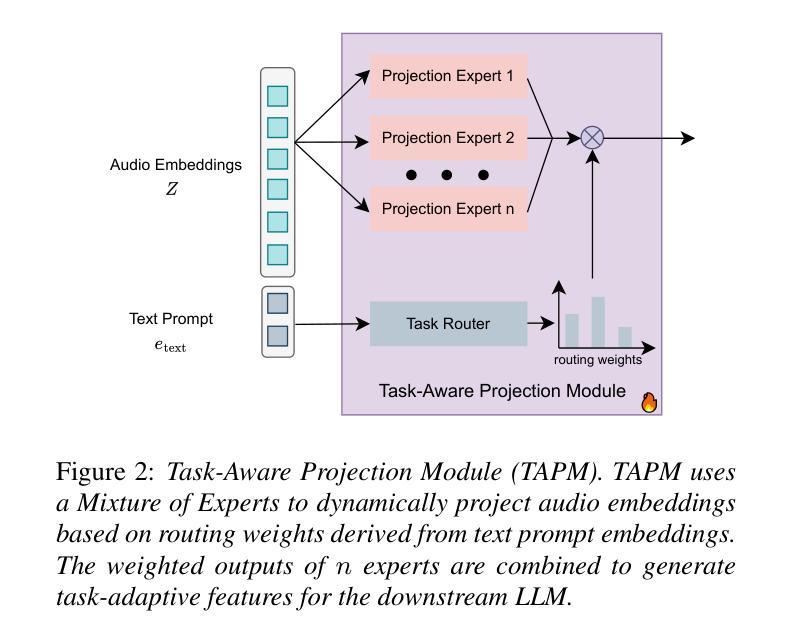
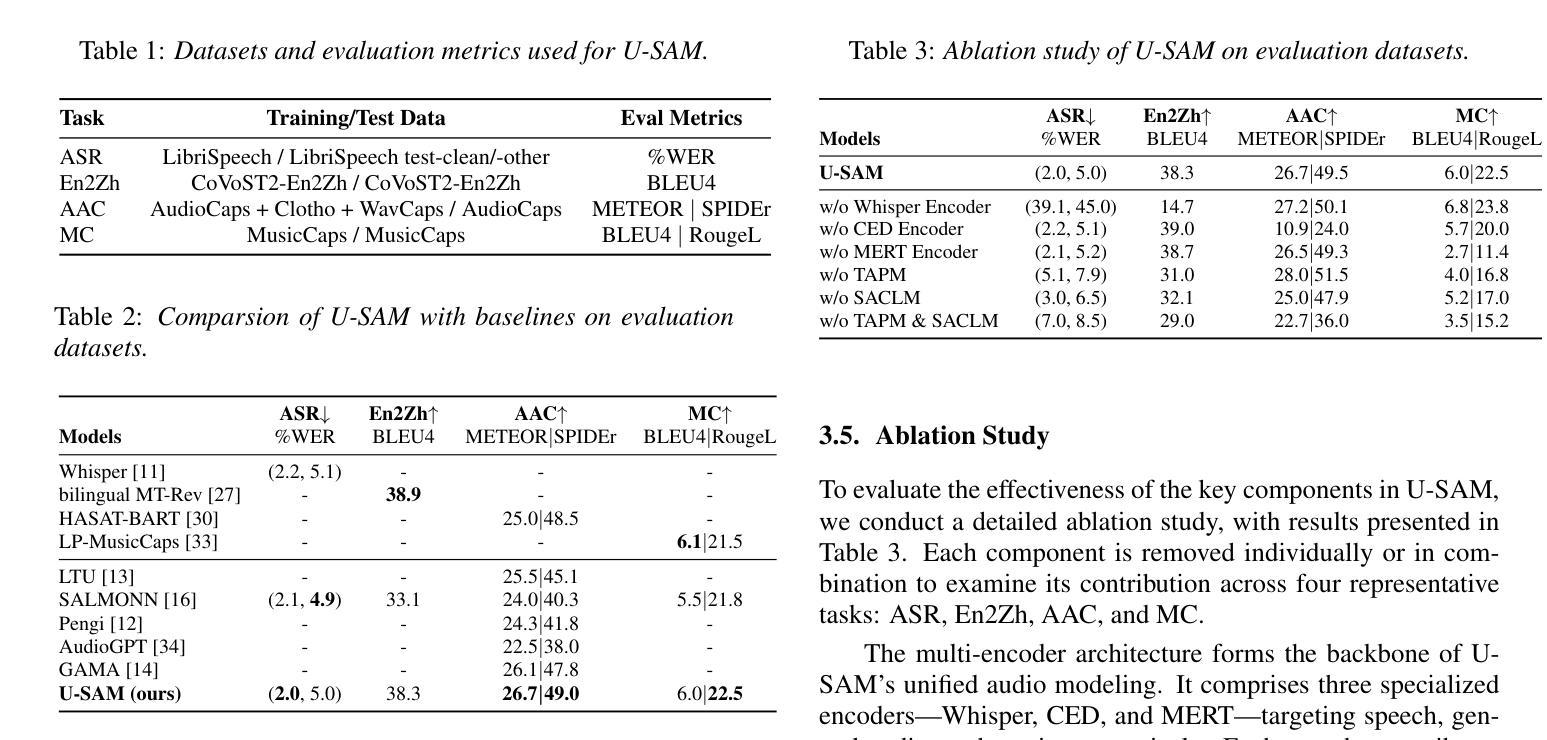
U-SAM: An audio language Model for Unified Speech, Audio, and Music Understanding
Authors:Ziqian Wang, Xianjun Xia, Xinfa Zhu, Lei Xie
The text generation paradigm for audio tasks has opened new possibilities for unified audio understanding. However, existing models face significant challenges in achieving a comprehensive understanding across diverse audio types, such as speech, general audio events, and music. Furthermore, their exclusive reliance on cross-entropy loss for alignment often falls short, as it treats all tokens equally and fails to account for redundant audio features, leading to weaker cross-modal alignment. To deal with the above challenges, this paper introduces U-SAM, an advanced audio language model that integrates specialized encoders for speech, audio, and music with a pre-trained large language model (LLM). U-SAM employs a Mixture of Experts (MoE) projector for task-aware feature fusion, dynamically routing and integrating the domain-specific encoder outputs. Additionally, U-SAM incorporates a Semantic-Aware Contrastive Loss Module, which explicitly identifies redundant audio features under language supervision and rectifies their semantic and spectral representations to enhance cross-modal alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that U-SAM consistently outperforms both specialized models and existing audio language models across multiple benchmarks. Moreover, it exhibits emergent capabilities on unseen tasks, showcasing its generalization potential. Code is available (https://github.com/Honee-W/U-SAM/).
音频任务文本生成范式为统一音频理解开启了新的可能性。然而,现有模型在实现不同类型音频的全面理解方面面临重大挑战,如语音、通用音频事件和音乐。此外,它们对交叉熵损失的过度依赖往往难以达到预期效果,因为这种方法将所有标记一视同仁,忽视了冗余的音频特征,导致跨模态对齐较弱。为了应对上述挑战,本文介绍了U-SAM,这是一种先进的音频语言模型,它集成了针对语音、音频和音乐的专用编码器以及预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。U-SAM采用混合专家(MoE)投影仪进行任务感知特征融合,动态路由并集成领域特定编码器的输出。此外,U-SAM还包含语义感知对比损失模块,该模块在语言监督下明确识别冗余音频特征,并纠正其语义和光谱表示,以增强跨模态对齐。大量实验表明,U-SAM在多个基准测试中始终优于专业模型和现有音频语言模型。此外,它在未见过的任务上展现出新兴能力,展示了其泛化潜力。代码可用(https://github.com/Honee-W/U-SAM/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种先进的音频语言模型U-SAM,它针对音频任务中的文本生成范式挑战进行了改进。U-SAM通过集成专业化的语音、音频和音乐编码器,并结合预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)来解决跨多种音频类型的全面理解问题。它采用混合专家(MoE)投影器进行任务感知特征融合,并动态路由和集成特定领域的编码器输出。此外,U-SAM还引入了一个语义感知对比损失模块,该模块在语言的监督下明确识别冗余音频特征,并纠正其语义和光谱表示,以提高跨模态对齐。实验表明,U-SAM在多个基准测试中持续优于专业模型和现有音频语言模型。它还具有在未见任务上的新兴能力,显示出其通用性潜力。
Key Takeaways
- U-SAM是一种先进的音频语言模型,解决了现有模型在多样音频类型理解上的挑战。
- U-SAM集成了专业化的语音、音频和音乐编码器,结合预训练的大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 采用混合专家(MoE)投影器实现任务感知特征融合和动态路由集成。
- U-SAM引入了语义感知对比损失模块,以提高跨模态对齐效果。
- 冗余音频特征在语言的监督下被识别和纠正。
- U-SAM在多个基准测试中表现优异,优于专业模型和现有音频语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

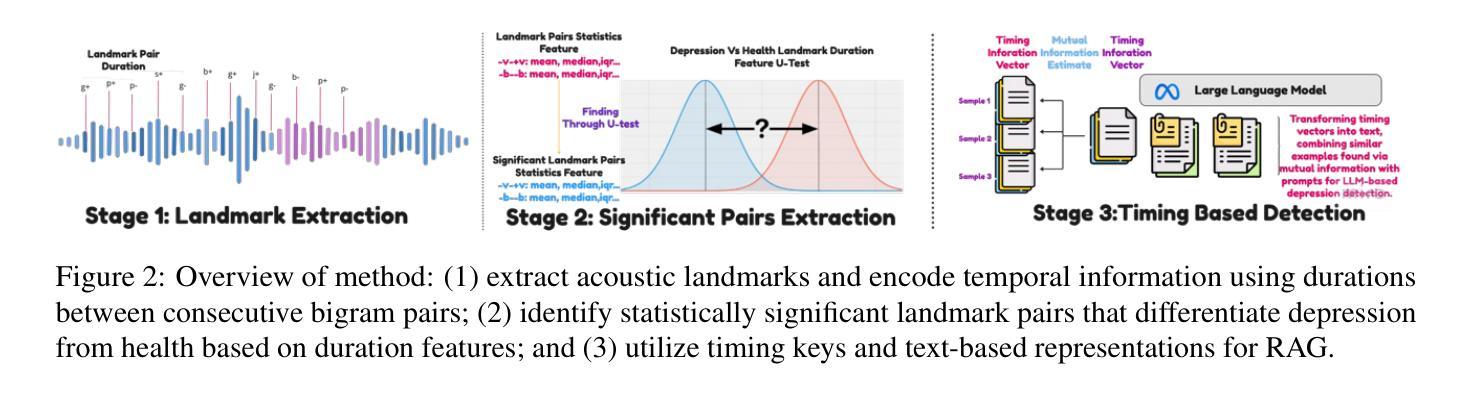
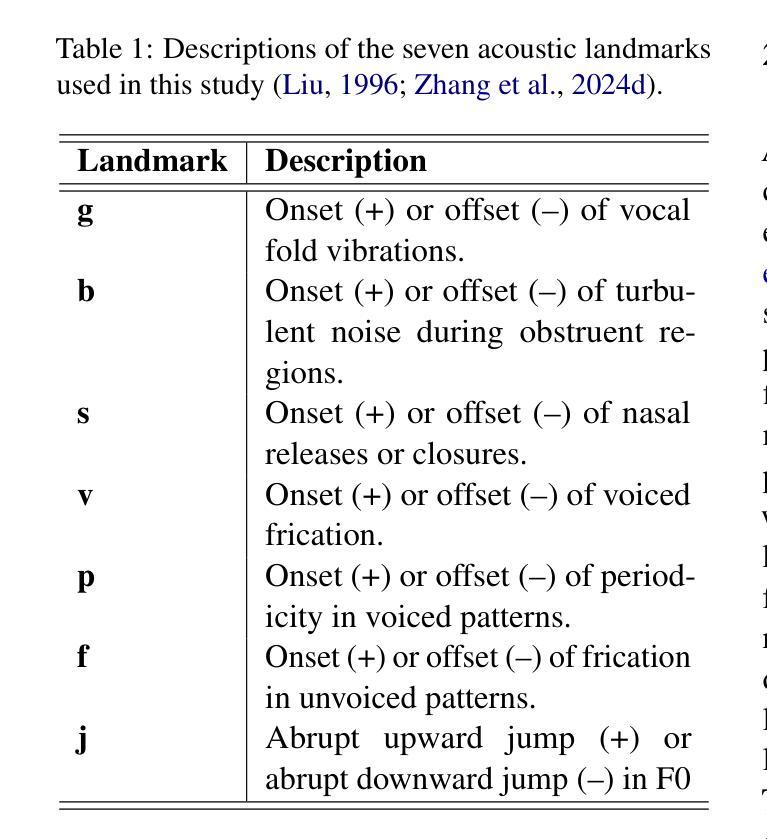
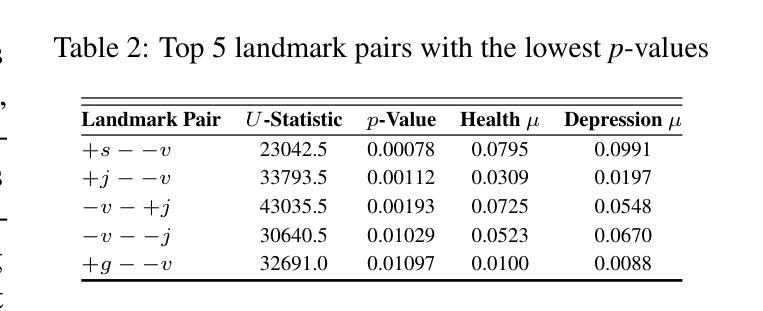
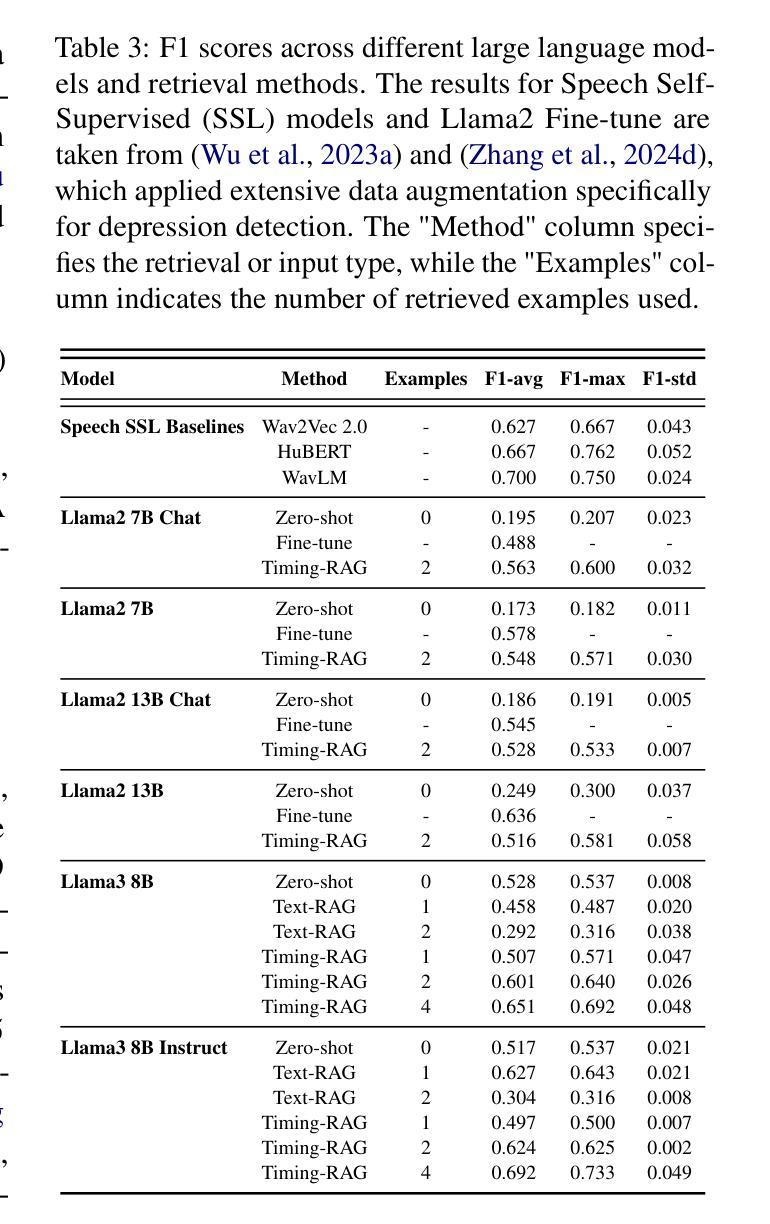
SpeechT-RAG: Reliable Depression Detection in LLMs with Retrieval-Augmented Generation Using Speech Timing Information
Authors:Xiangyu Zhang, Hexin Liu, Qiquan Zhang, Beena Ahmed, Julien Epps
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been increasingly adopted for health-related tasks, yet their performance in depression detection remains limited when relying solely on text input. While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) typically enhances LLM capabilities, our experiments indicate that traditional text-based RAG systems struggle to significantly improve depression detection accuracy. This challenge stems partly from the rich depression-relevant information encoded in acoustic speech patterns information that current text-only approaches fail to capture effectively. To address this limitation, we conduct a systematic analysis of temporal speech patterns, comparing healthy individuals with those experiencing depression. Based on our findings, we introduce Speech Timing-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation, SpeechT-RAG, a novel system that leverages speech timing features for both accurate depression detection and reliable confidence estimation. This integrated approach not only outperforms traditional text-based RAG systems in detection accuracy but also enhances uncertainty quantification through a confidence scoring mechanism that naturally extends from the same temporal features. Our unified framework achieves comparable results to fine-tuned LLMs without additional training while simultaneously addressing the fundamental requirements for both accuracy and trustworthiness in mental health assessment.
大型语言模型(LLM)在健康相关任务中的应用越来越广泛,但在仅依赖文本输入的情况下,它们在抑郁症检测方面的表现仍然有限。虽然检索增强生成(RAG)通常可以增强LLM的能力,但我们的实验表明,传统的基于文本的RAG系统在提高抑郁症检测准确性方面存在困难。这一挑战部分源于编码在语音模式信息中的丰富抑郁症相关信息,而当前仅使用文本的方法无法有效地捕获这些信息。为了解决这个问题,我们对时间性语音模式进行了系统分析,比较了健康个体和抑郁症患者的差异。基于我们的发现,我们引入了基于语音时序的检索增强生成(SpeechT-RAG),这是一个新型系统,利用语音时序特征进行准确的抑郁症检测和可靠的可信估计。这种综合方法不仅优于传统的基于文本的RAG系统在检测准确性方面,而且还通过置信度评分机制增强了不确定性量化,该机制自然地扩展了相同的时序特征。我们的统一框架在不进行额外训练的情况下实现了与微调LLM相当的结果,同时解决了心理健康评估中对准确性和可信度的基本要求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在健康相关任务中的应用日益广泛,但在仅依赖文本输入进行抑郁症检测时,其性能表现仍有限。尽管检索增强生成(RAG)技术通常能提升LLM的能力,但实验表明,传统的文本型RAG系统在提高抑郁症检测准确性方面效果并不显著。这一挑战部分源于语音模式中的丰富抑郁症相关信息,这是当前仅依赖文本的做无法有效捕获的。为解决这一局限,我们对抑郁症患者与健康人的语音时间模式进行了系统分析。基于我们的发现,引入了基于语音时序特征的检索增强生成系统SpeechT-RAG。该系统不仅利用语音时序特征进行准确的抑郁症检测,还通过信心评分机制实现可靠的不确定性量化,自然地扩展了相同的时序特征的应用。我们的统一框架在不经过额外训练的情况下实现了与精细调整的LLM相当的结果,同时满足精神健康评估对准确性和可靠性的基本要求。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在抑郁症检测方面的性能受限于仅使用文本输入。
- 传统的文本型检索增强生成(RAG)系统在提高抑郁症检测准确性方面效果有限。
- 语音模式中的抑郁症相关信息丰富,当前仅依赖文本的模型无法有效捕获。
- 对抑郁症患者与健康人的语音时间模式进行了系统分析。
- 引入了基于语音时序特征的检索增强生成系统SpeechT-RAG,用于准确检测抑郁症并进行信心评分。
- SpeechT-RAG系统不仅提高了检测准确性,还通过信心评分机制实现了不确定性量化。
点此查看论文截图

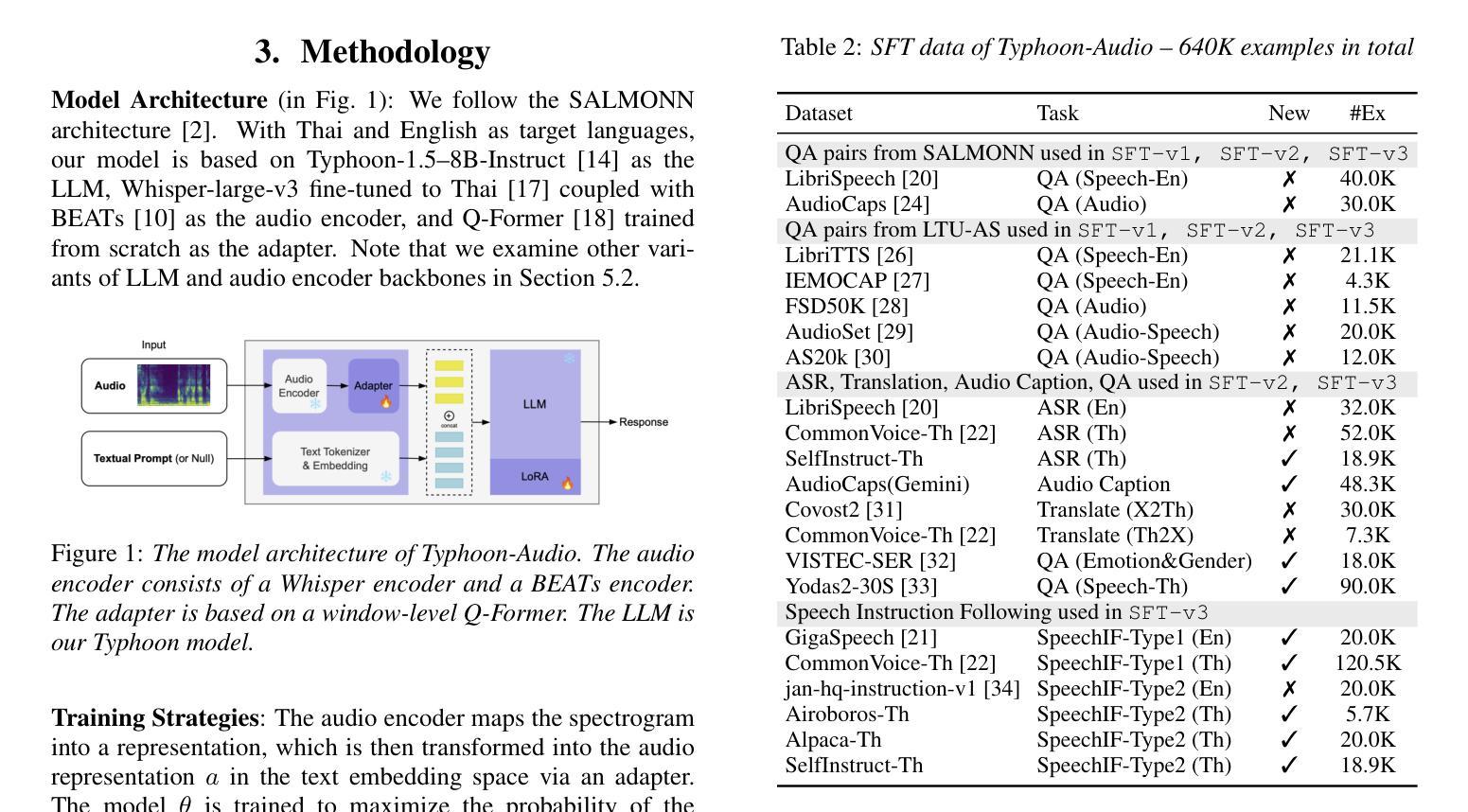
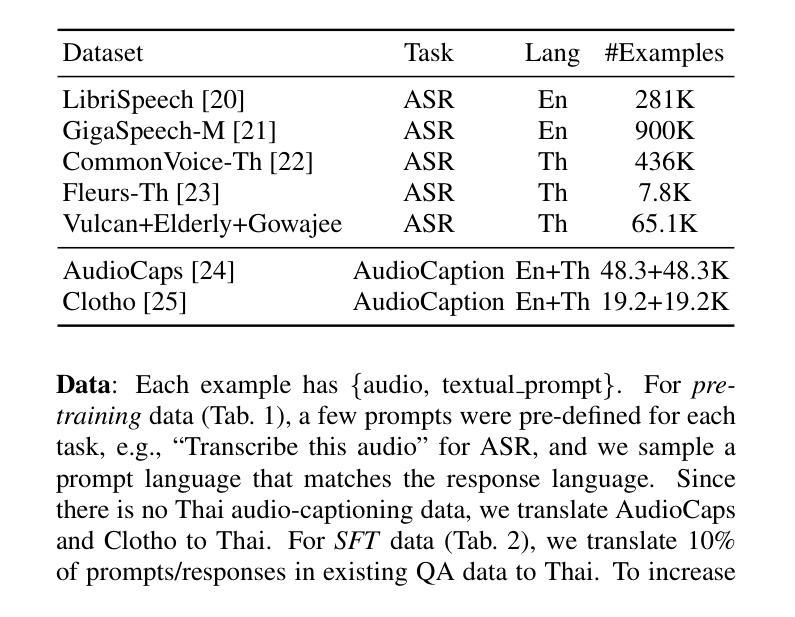
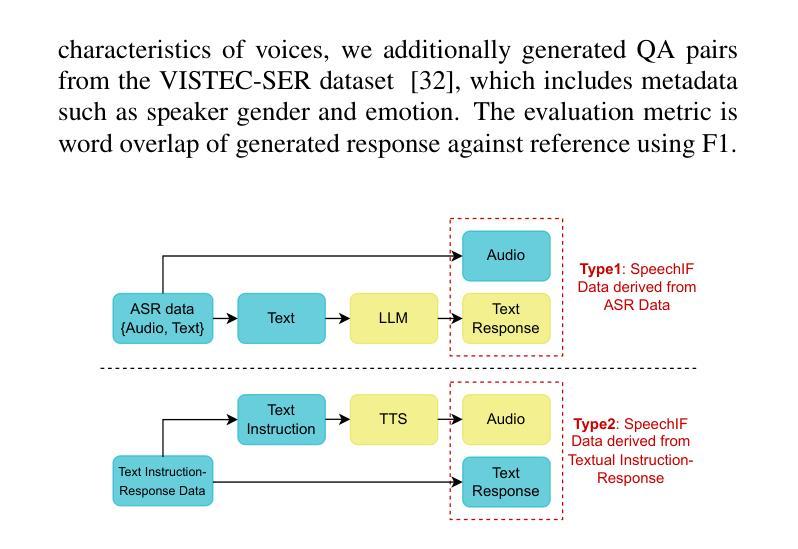
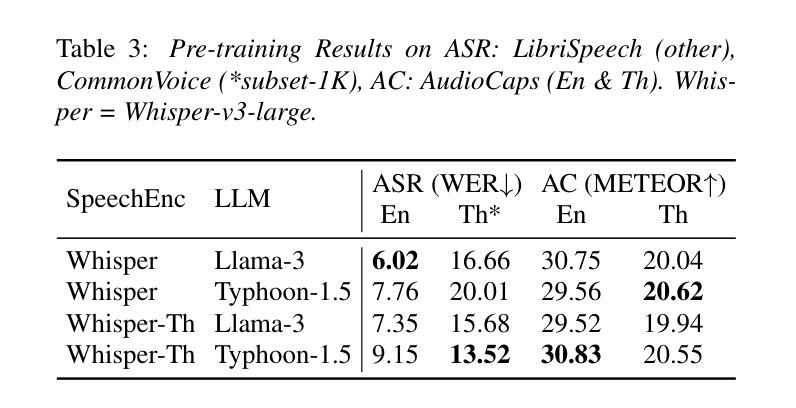
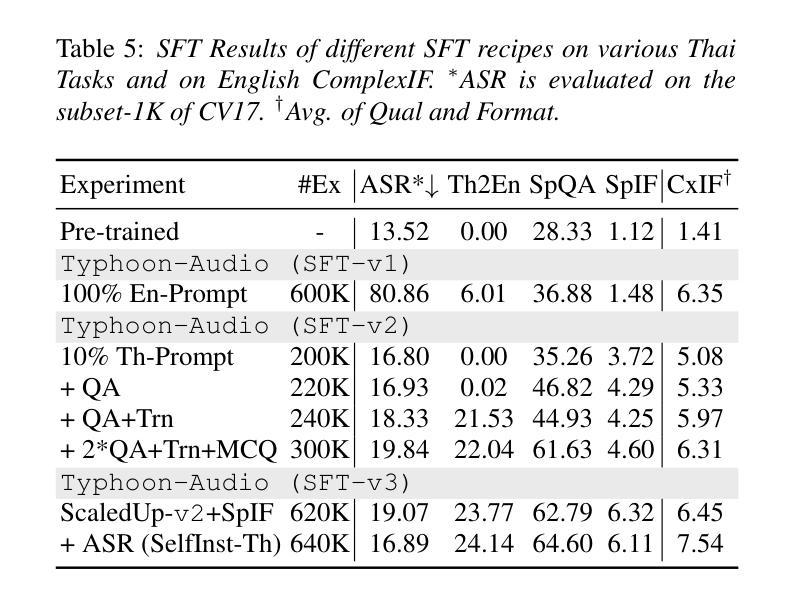
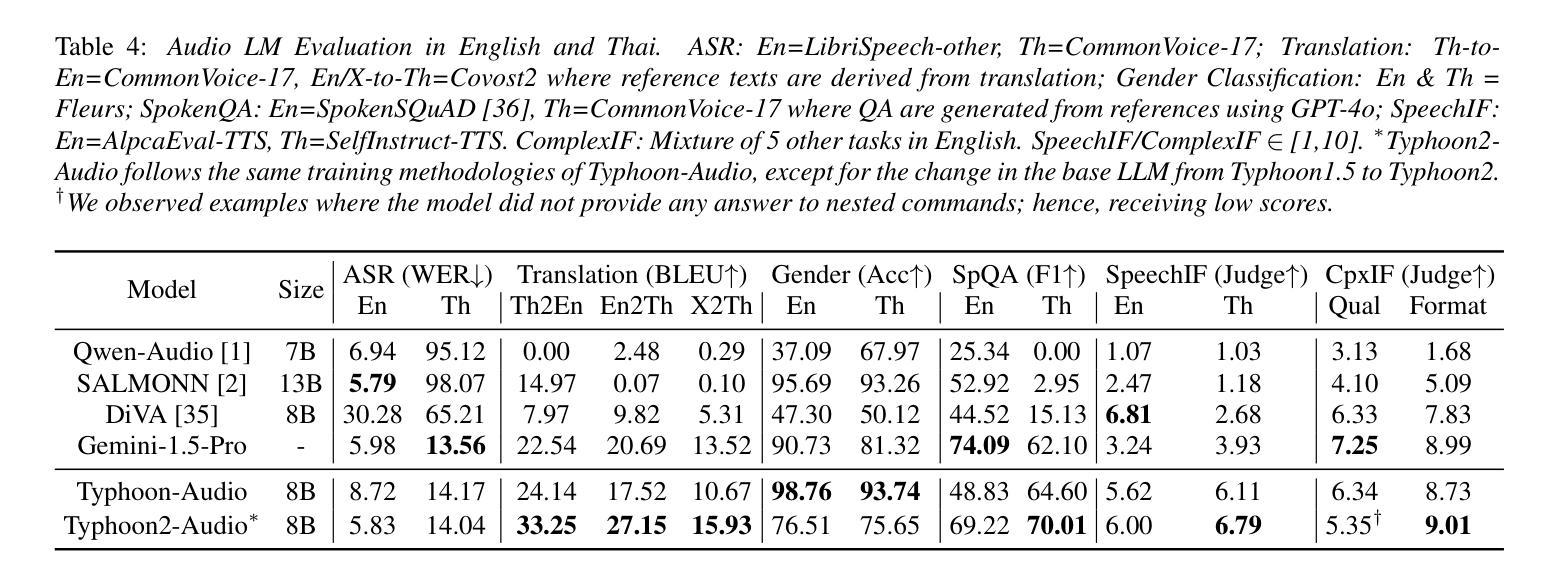
Enhancing Low-Resource Language and Instruction Following Capabilities of Audio Language Models
Authors:Potsawee Manakul, Guangzhi Sun, Warit Sirichotedumrong, Kasima Tharnpipitchai, Kunat Pipatanakul
Audio language models process audio inputs using textual prompts for tasks like speech recognition and audio captioning. Although built on multilingual pre-trained components, most are trained primarily on English, limiting their usability for other languages. This paper evaluates audio language models on Thai, a low-resource language, and finds that they lack emergent cross-lingual abilities despite their multilingual foundations. To address this, we explore data mixtures that optimize audio language models for both a target language and English while integrating audio comprehension and speech instruction-following into a unified model. Our experiments provide insights into improving instruction-following in low-resource languages by balancing language-specific and multilingual training data. The proposed model, Typhoon-Audio, significantly outperforms existing open-source models and achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art Gemini-1.5-Pro in both English and Thai.
音频语言模型使用文本提示来处理音频输入,用于语音识别和音频字幕等任务。尽管这些模型建立在多语言预训练组件之上,但大多数主要使用英语进行训练,从而限制了它们在其他语言中的可用性。本文评估了音频语言模型在泰语(一种资源匮乏的语言)中的应用,发现尽管它们具有多语言基础,但缺乏跨语言的应急能力。为了解决这一问题,我们探索了优化目标语言和英语音频语言模型的数据混合,同时将音频理解和语音指令遵循集成到一个统一模型中。我们的实验通过平衡语言特定和多语言训练数据,为改进低资源语言中的指令遵循提供了见解。所提出的Typhoon-Audio模型显著优于现有开源模型,在英语和泰语方面的性能与最先进的Gemini-1.5-Pro相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文探讨了音频语言模型在处理泰语等低资源语言时的表现。尽管这些模型基于多语言预训练组件,但大多数主要训练于英语,对于其他语言的可用性有限。本研究评估了音频语言模型在泰语中的表现,并发现它们缺乏跨语言的综合能力。为了改善这一情况,研究探索了同时针对目标语言和英语进行优化的数据混合方法,将音频理解和语音指令跟随集成到一个统一模型中。实验结果显示,通过平衡语言特定和多语言训练数据,可以改善低资源语言中的指令跟随能力。提出的Typhoon-Audio模型在泰语和英语上的表现均优于现有开源模型,达到了与Gemini-1.5-Pro相当的水平。
Key Takeaways
- 音频语言模型主要用于处理语音任务,如语音识别和音频描述等。
- 尽管大多数音频语言模型基于多语言预训练组件,但它们主要训练于英语,对其他语言的可用性受限。
- 在泰语等低资源语言中,音频语言模型缺乏跨语言的综合能力。
- 通过优化数据混合方法,可以同时针对目标语言和英语改善音频语言模型的表现。
- 将音频理解和语音指令跟随集成到一个统一模型中有助于提高模型的性能。
- 实验表明,平衡语言特定和多语言训练数据能改善低资源语言中的指令跟随能力。
点此查看论文截图