⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-27 更新
Reward Model Generalization for Compute-Aware Test-Time Reasoning
Authors:Zeen Song, Wenwen Qiang, Siyu Zhao, Changwen Zheng, Gang Hua
External test-time reasoning enhances large language models (LLMs) by decoupling generation and selection. At inference time, the model generates multiple reasoning paths, and an auxiliary process reward model (PRM) is used to score and select the best one. A central challenge in this setting is test-time compute optimality (TCO), i.e., how to maximize answer accuracy under a fixed inference budget. In this work, we establish a theoretical framework to analyze how the generalization error of the PRM affects compute efficiency and reasoning performance. Leveraging PAC-Bayes theory, we derive generalization bounds and show that a lower generalization error of PRM leads to fewer samples required to find correct answers. Motivated by this analysis, we propose Compute-Aware Tree Search (CATS), an actor-critic framework that dynamically controls search behavior. The actor outputs sampling hyperparameters based on reward distributions and sparsity statistics, while the critic estimates their utility to guide budget allocation. Experiments on the MATH and AIME benchmarks with various LLMs and PRMs demonstrate that CATS consistently outperforms other external TTS methods, validating our theoretical predictions.
外部测试时间推理通过解耦生成和选择来增强大型语言模型(LLM)。在推理阶段,模型生成多个推理路径,并使用辅助过程奖励模型(PRM)对它们进行评分和选择最佳路径。在此设置中的核心挑战是测试时间计算最优(TCO),即如何在固定推理预算下最大化答案的准确性。在这项工作中,我们建立了一个理论框架,分析PRM的泛化误差如何影响计算效率和推理性能。我们利用PAC-Bayes理论,推导出泛化边界,并表明PRM的较低泛化误差会导致找到正确答案所需样本数减少。受此分析启发,我们提出了计算感知树搜索(CATS),这是一种动态控制搜索行为的演员-评论家框架。演员根据奖励分布和稀疏性统计输出采样超参数,而评论家则估计它们的效用以指导预算分配。在MATH和AIME基准测试上对多种LLM和PRM进行的实验表明,CATS始终优于其他外部TTS方法,验证了我们的理论预测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
外部测试时间推理通过解耦生成和选择过程增强大型语言模型(LLM)。在推理阶段,模型生成多个推理路径,并使用辅助过程奖励模型(PRM)进行评分和选择最佳路径。本文主要分析测试时间计算最优性(TCO),即如何在固定推理预算下最大化答案的准确性。通过利用PAC-Bayes理论,本文得出泛化误差的界限,并证明PRM的泛化误差降低可以减少寻找正确答案所需的样本数量。基于分析,本文提出了计算感知树搜索(CATS)方法,这是一种动态控制搜索行为的演员-评论家框架。演员根据奖励分布和稀疏统计输出采样超参数,而评论家则估计它们的效用以指导预算分配。在MATH和AIME基准测试中,对各种LLM和PRM进行的实验表明,CATS持续优于其他外部测试时间推理方法,验证了本文的理论预测。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间推理通过解耦生成和选择过程增强大型语言模型(LLM)。
- 在测试时间计算最优性(TCO)下,需要最大化答案准确性同时受限于固定推理预算。
- 利用PAC-Bayes理论得出奖励模型(PRM)泛化误差的界限。
- PRM的泛化误差降低可以减少寻找正确答案所需的样本数量。
- 提出计算感知树搜索(CATS)方法,动态控制搜索行为基于奖励分布和预算分配的策略。
- 演员和评论家协同工作:演员输出采样超参数,评论家则评估其效用。
点此查看论文截图
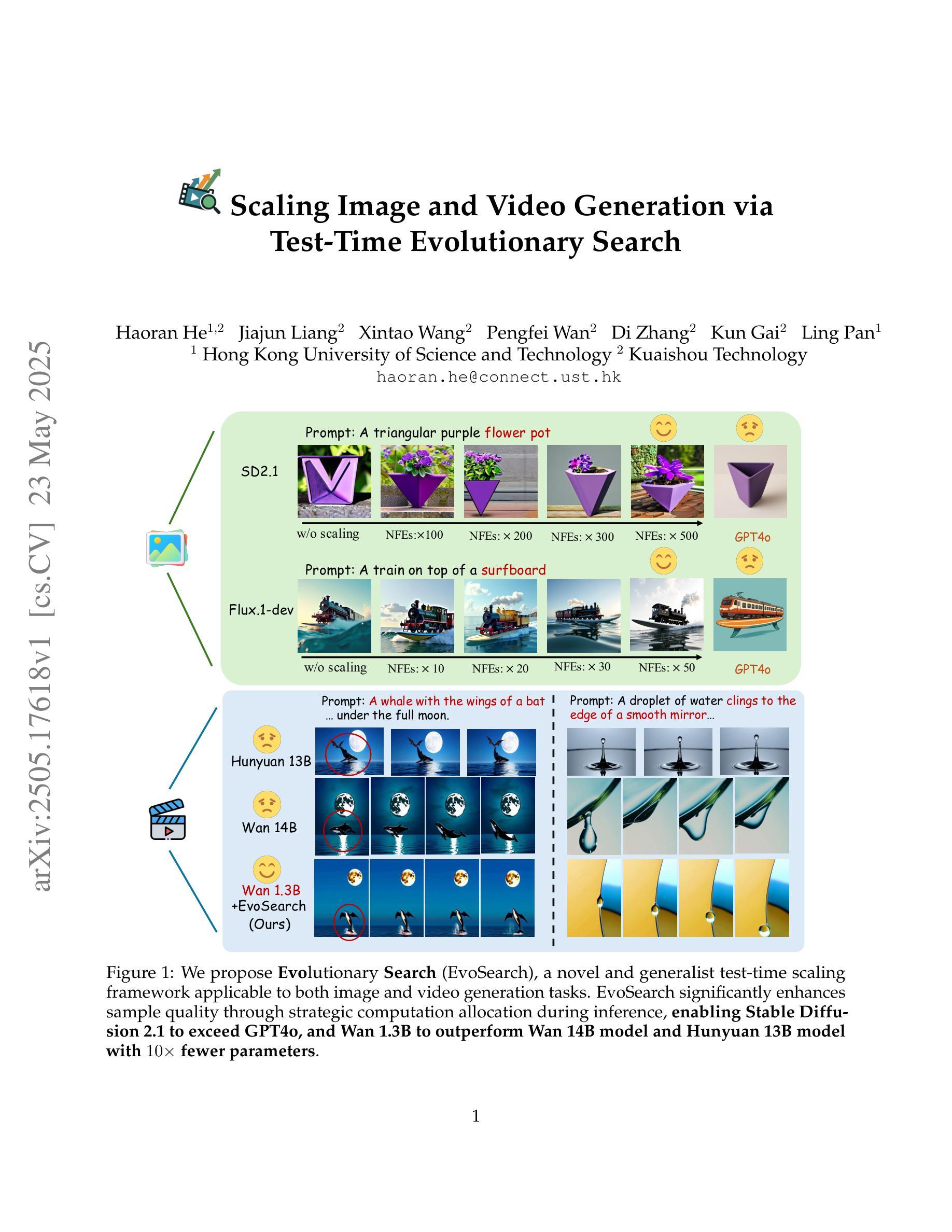
Scaling Image and Video Generation via Test-Time Evolutionary Search
Authors:Haoran He, Jiajun Liang, Xintao Wang, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang, Kun Gai, Ling Pan
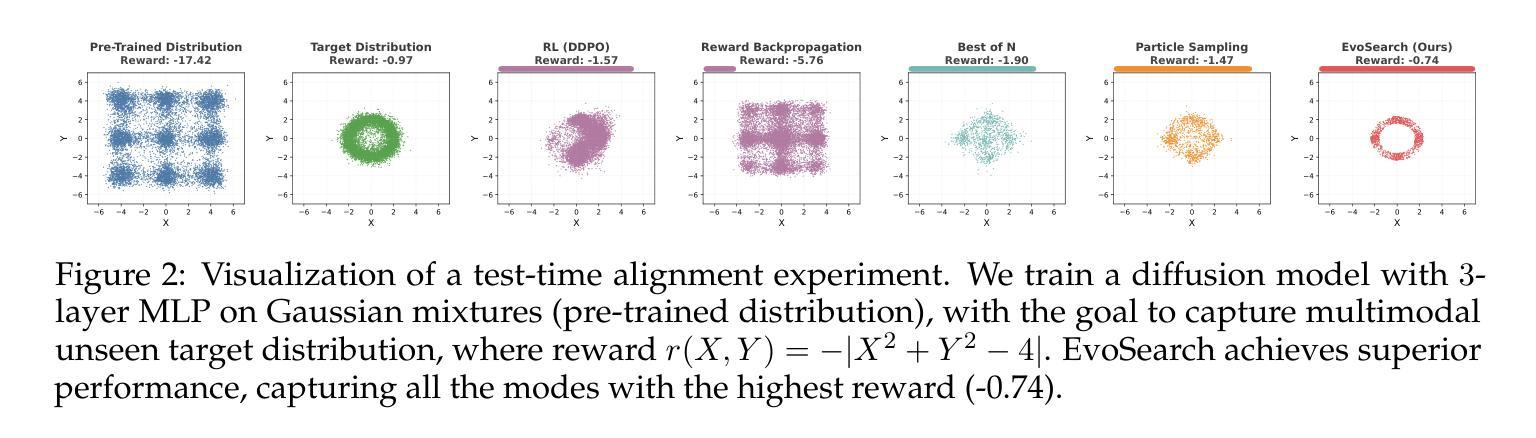
As the marginal cost of scaling computation (data and parameters) during model pre-training continues to increase substantially, test-time scaling (TTS) has emerged as a promising direction for improving generative model performance by allocating additional computation at inference time. While TTS has demonstrated significant success across multiple language tasks, there remains a notable gap in understanding the test-time scaling behaviors of image and video generative models (diffusion-based or flow-based models). Although recent works have initiated exploration into inference-time strategies for vision tasks, these approaches face critical limitations: being constrained to task-specific domains, exhibiting poor scalability, or falling into reward over-optimization that sacrifices sample diversity. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Evo}lutionary \textbf{Search} (EvoSearch), a novel, generalist, and efficient TTS method that effectively enhances the scalability of both image and video generation across diffusion and flow models, without requiring additional training or model expansion. EvoSearch reformulates test-time scaling for diffusion and flow models as an evolutionary search problem, leveraging principles from biological evolution to efficiently explore and refine the denoising trajectory. By incorporating carefully designed selection and mutation mechanisms tailored to the stochastic differential equation denoising process, EvoSearch iteratively generates higher-quality offspring while preserving population diversity. Through extensive evaluation across both diffusion and flow architectures for image and video generation tasks, we demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches, achieves higher diversity, and shows strong generalizability to unseen evaluation metrics. Our project is available at the website https://tinnerhrhe.github.io/evosearch.
随着模型预训练过程中计算(数据和参数)边际成本的持续大幅增加,测试时扩展(TTS)已成为一种有前景的方向,通过在推理时间分配额外的计算来提高生成模型的性能。虽然TTS在多语言任务中取得了显著的成功,但在图像和视频生成模型(基于扩散或基于流的模型)的测试时间扩展行为的理解方面仍存在明显差距。尽管近期的工作已经开始探索视觉任务的推理时间策略,但这些方法面临关键局限性:受限于特定任务领域、表现出较差的可扩展性,或者陷入奖励过度优化而牺牲样本多样性。在本文中,我们提出了进化搜索(EvoSearch)这一新型、通用、高效的TTS方法,它有效地提高了基于扩散和基于流的模型的图像和视频生成的可扩展性,无需额外的训练或模型扩展。EvoSearch将基于扩散和基于流的模型的测试时间扩展重新表述为进化搜索问题,利用生物进化的原理来有效地探索和细化去噪轨迹。通过融入精心设计的选择机制和针对随机微分方程去噪过程的突变机制,EvoSearch在保持种群多样性的同时,迭代生成更高质量的后代。通过对图像和视频生成任务的扩散和流架构的广泛评估,我们证明了我们的方法始终优于现有方法,实现了更高的多样性,并对未见评估指标表现出强大的泛化能力。我们的项目可在网站https://tinnerhrhe.github.io/evosearch上查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages. Project: https://tinnerhrhe.github.io/evosearch
Summary
文本介绍了随着模型预训练过程中计算量(数据和参数)边际成本的大幅增加,测试时缩放(TTS)已成为改进生成模型性能的有前途的方向。本文提出了一种新型的TTS方法——进化搜索(EvoSearch),该方法有效提高了图像和视频生成的扩散和流动模型的扩展性,无需额外的训练或模型扩展。进化搜索将测试时的缩放问题重新表述为一个进化搜索问题,利用生物进化的原理来有效地探索和优化去噪轨迹。通过广泛的评估和实验验证,进化搜索在图像和视频生成任务中的扩散和流动架构上表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时缩放(TTS)已成为改进生成模型性能的重要方向,特别是在模型预训练的计算成本大幅上升的背景下。
- 进化搜索(EvoSearch)是一种新型的TTS方法,适用于图像和视频生成模型(如扩散和流动模型)。
- EvoSearch通过将测试时的缩放问题重新表述为进化搜索问题来增强其效率和效果。
- EvoSearch利用生物进化的原理来有效地探索和优化去噪轨迹,从而生成更高质量的图像和视频。
- EvoSearch具有通用性,无需额外的训练或模型扩展即可提高模型的扩展性。
- 广泛的评估和实验验证表明,EvoSearch在图像和视频生成任务的扩散和流动架构上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图
CosyVoice 3: Towards In-the-wild Speech Generation via Scaling-up and Post-training
Authors:Zhihao Du, Changfeng Gao, Yuxuan Wang, Fan Yu, Tianyu Zhao, Hao Wang, Xiang Lv, Hui Wang, Xian Shi, Keyu An, Guanrou Yang, Yabin Li, Yanni Chen, Zhifu Gao, Qian Chen, Yue Gu, Mengzhe Chen, Yafeng Chen, Shiliang Zhang, Wen Wang, Jieping Ye
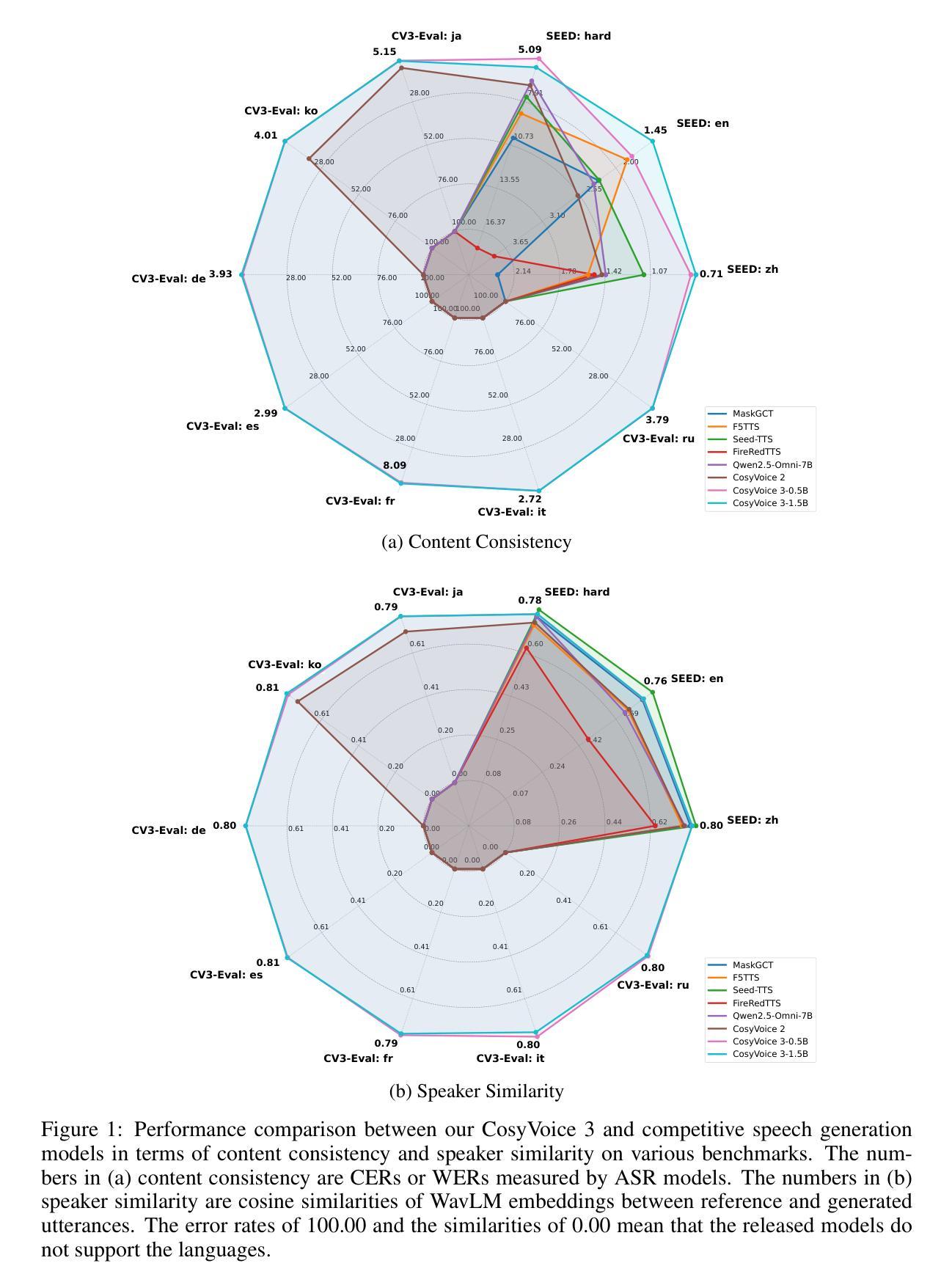
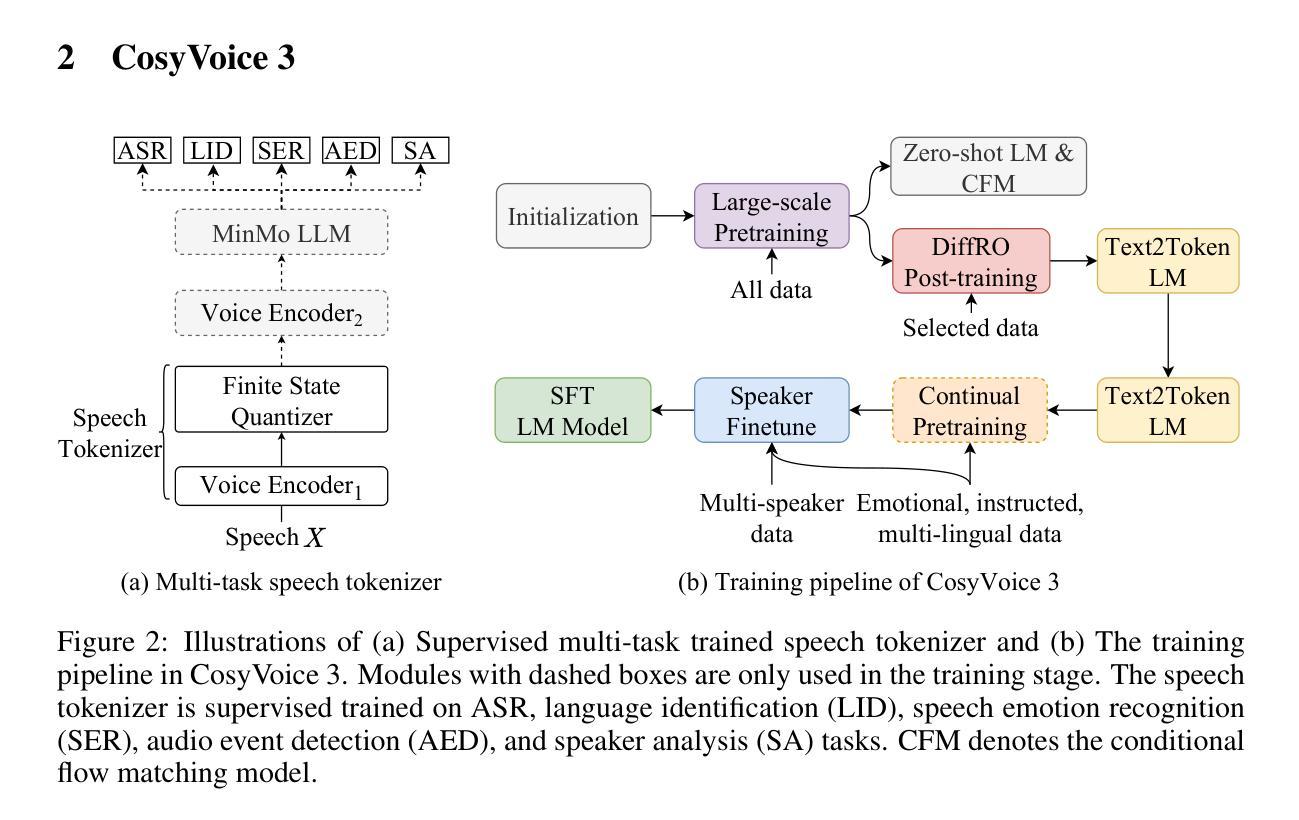
In our prior works, we introduced a scalable streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which integrates a large language model (LLM) and a chunk-aware flow matching (FM) model, and achieves low-latency bi-streaming speech synthesis and human-parity quality. Despite these advancements, CosyVoice 2 exhibits limitations in language coverage, domain diversity, data volume, text formats, and post-training techniques. In this paper, we present CosyVoice 3, an improved model designed for zero-shot multilingual speech synthesis in the wild, surpassing its predecessor in content consistency, speaker similarity, and prosody naturalness. Key features of CosyVoice 3 include: 1) A novel speech tokenizer to improve prosody naturalness, developed via supervised multi-task training, including automatic speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, language identification, audio event detection, and speaker analysis. 2) A new differentiable reward model for post-training applicable not only to CosyVoice 3 but also to other LLM-based speech synthesis models. 3) Dataset Size Scaling: Training data is expanded from ten thousand hours to one million hours, encompassing 9 languages and 18 Chinese dialects across various domains and text formats. 4) Model Size Scaling: Model parameters are increased from 0.5 billion to 1.5 billion, resulting in enhanced performance on our multilingual benchmark due to the larger model capacity. These advancements contribute significantly to the progress of speech synthesis in the wild. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3.
在我们之前的工作中,我们推出了一款可扩展的流式语音合成模型CosyVoice 2,它集成了一个大型语言模型(LLM)和基于分块的流匹配(FM)模型,实现了低延迟的双向流式语音合成和与人类相当的质量。尽管有了这些进步,CosyVoice 2在语言覆盖、领域多样性、数据量、文本格式和训练后技术方面仍存在局限性。在本文中,我们介绍了CosyVoice 3,这是一款改进后的模型,旨在实现野外零样本多语言语音合成,在内容一致性、演讲者相似性和语调自然性方面超越了其前身。CosyVoice 3的主要特点包括:1)一种新型语音标记器,通过监督多任务训练开发,旨在提高语调的自然性,包括自动语音识别、语音情感识别、语言识别、音频事件检测和说话人分析。2)一种新的可微奖励模型,适用于训练后的任务,不仅适用于CosyVoice 3,而且适用于其他基于LLM的语音合成模型。3)数据集大小缩放:训练数据从一万小时扩大到一百万小时,涵盖9种语言和18种中文方言,以及多种领域和文本格式。4)模型大小缩放:模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,由于模型容量更大,我们的多语种基准测试性能得到提升。这些进步为野外语音合成的进展做出了重大贡献。我们鼓励读者通过https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3聆听演示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, work in progress
摘要
本文介绍了新一代的语音合成模型CosyVoice 3,它在前代模型的基础上进行了多方面的改进。CosyVoice 3具有零次多语言语音合成的能力,并在内容一致性、发音人相似性和语调自然性方面超越了其前身。它的关键特性包括:1)采用新型语音分词器以提高语调自然性,该分词器通过包括语音识别、语音情感识别、语言识别、音频事件检测和发音人分析在内的监督多任务训练开发而成。2)提出一种新的可微奖励模型,适用于CosyVoice 3和其他基于LLM的语音合成模型进行后期训练。3)数据集大小扩展:训练数据从一万小时扩展到一百万小时,涵盖9种语言和18种中文方言,涉及多个领域和文本格式。4)模型大小扩展:模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,由于模型容量更大,其在我们的多语言基准测试上的表现得到提升。这些进步对野外语音合成的发展做出了重大贡献。
要点
- CosyVoice 3实现了零次多语言语音合成,增强了内容一致性、发音人相似性和语调自然性。
- 新型语音分词器通过监督多任务训练提高语调自然性,包括多种语音相关任务。
- 引入可微奖励模型,适用于后期训练,不仅适用于CosyVoice 3,还适用于其他LLM-based语音合成模型。
- 数据集规模从一万小时扩展到一百万小时,涵盖多种语言和中文方言,以及不同领域和文本格式。
- 模型参数从0.5亿增加到1.5亿,由于模型容量增大,多语言基准测试性能提升。
- 鼓励听众通过指定网址体验CosyVoice 3的演示效果。
点此查看论文截图

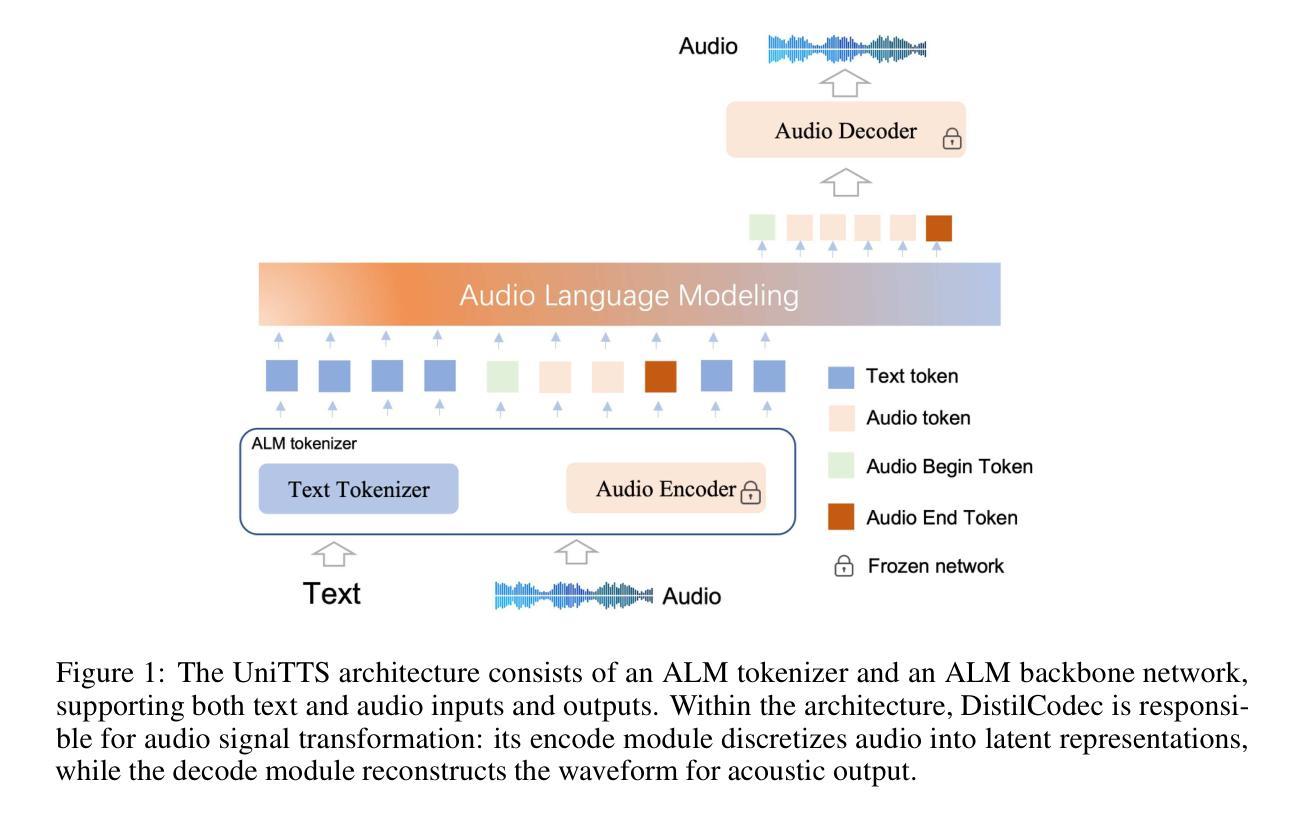
UniTTS: An end-to-end TTS system without decoupling of acoustic and semantic information
Authors:Rui Wang, Qianguo Sun, Tianrong Chen, Zhiyun Zeng, Junlong Wu, Jiaxing Zhang
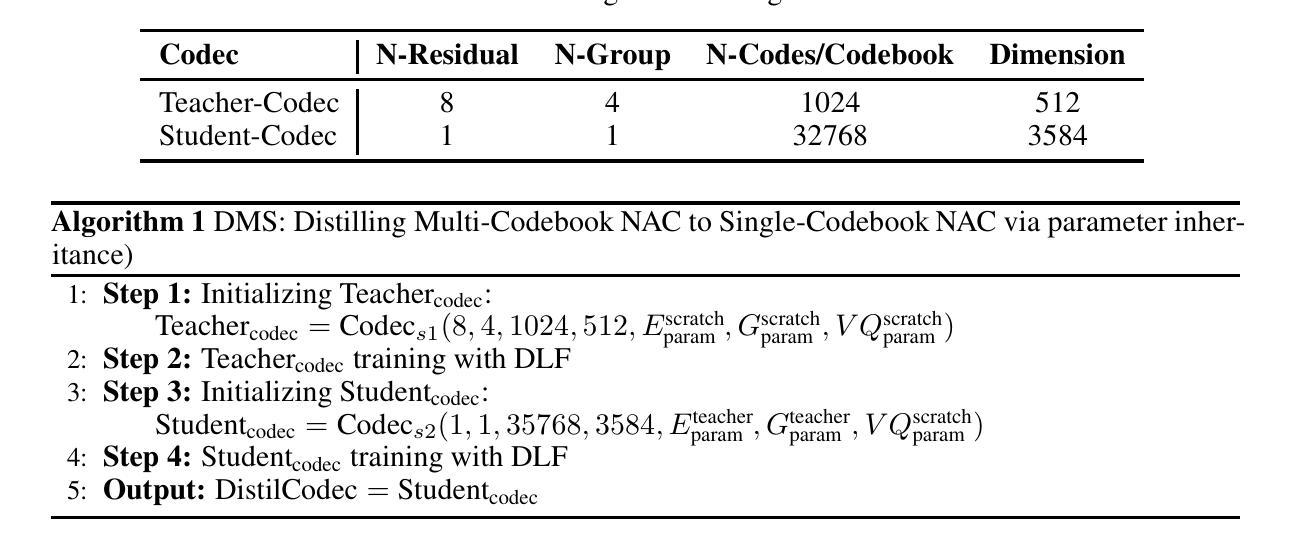
The emergence of multi-codebook neutral audio codecs such as Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) and Group Vector Quantization (GVQ) has significantly advanced Large-Language-Model (LLM) based Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems. These codecs are crucial in separating semantic and acoustic information while efficiently harnessing semantic priors. However, since semantic and acoustic information cannot be fully aligned, a significant drawback of these methods when applied to LLM-based TTS is that large language models may have limited access to comprehensive audio information. To address this limitation, we propose DistilCodec and UniTTS, which collectively offer the following advantages: 1) This method can distill a multi-codebook audio codec into a single-codebook audio codec with 32,768 codes while achieving a near 100% utilization. 2) As DistilCodec does not employ a semantic alignment scheme, a large amount of high-quality unlabeled audio (such as audiobooks with sound effects, songs, etc.) can be incorporated during training, further expanding data diversity and broadening its applicability. 3) Leveraging the comprehensive audio information modeling of DistilCodec, we integrated three key tasks into UniTTS’s pre-training framework: audio modality autoregression, text modality autoregression, and speech-text cross-modal autoregression. This allows UniTTS to accept interleaved text and speech/audio prompts while substantially preserving LLM’s text capabilities. 4) UniTTS employs a three-stage training process: Pre-Training, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Alignment. Source code and model checkpoints are publicly available at https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/UniTTS and https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/DistilCodec.
随着残差向量量化(RVQ)和组向量量化(GVQ)等多码本中性音频编码器的出现,基于大语言模型的文本到语音(TTS)系统得到了显著的提升。这些编码器和解码器在分离语义和听觉信息的同时,有效地利用语义先验,起到了关键作用。然而,由于语义和听觉信息无法完全对齐,这些方法在应用于基于大语言模型的TTS时存在明显的缺点,即大语言模型可能难以获取全面的音频信息。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了DistilCodec和UniTTS,它们共同具有以下优点:
- 该方法可以将多码本音频编码解码器蒸馏为单码本音频编码解码器,同时使用32768个码本,利用率接近100%。
- 由于DistilCodec没有采用语义对齐方案,因此在训练过程中可以融入大量高质量的无标签音频(如带有音效的有声读物、歌曲等),进一步扩大了数据多样性并拓宽了其应用范围。
- 利用DistilCodec的全面音频信息建模,我们将三个关键任务整合到UniTTS的预训练框架中:音频模态自回归、文本模态自回归和语音-文本跨模态自回归。这使得UniTTS能够接受交替的文本和语音/音频提示,同时保留大语言模型的文本功能。
- UniTTS采用三阶段训练过程:预训练、监督微调(SFT)和对齐。源代码和模型检查点已公开在https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/UniTTS和https://github.com/IDEA-Emdoor-Lab/DistilCodec。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多代码本中立音频编码技术如残差矢量量化(RVQ)和组矢量量化(GVQ)在基于大语言模型的文本转语音(TTS)系统中发挥了重要作用。然而,这些方法在应用于基于LLM的TTS系统时存在语义和声音信息无法完全对齐的局限性。为解决此问题,研究团队推出了DistilCodec与UniTTS解决方案。该方法能将多代码本音频编码提炼为单一代码本音频编码,并利用大量的高质量无标签音频数据,扩充数据多样性并增强其适用性。此外,UniTTS集成三个关键任务到预训练框架中,并采用了三阶段训练流程。源代码和模型检查点已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 多代码本中立音频编码技术提升了基于大语言模型的文本转语音(TTS)系统的性能。
- RVQ和GVQ等技术在分离语义和声音信息方面发挥了关键作用。
- 由于语义和声音信息无法完全对齐,现有的TTS系统存在局限性。
- DistilCodec能解决这一局限性,将多代码本音频编码提炼为单一代码本,提高利用率。
- DistilCodec能利用大量高质量无标签音频数据,增强数据多样性和适用性。
- UniTTS预训练框架集成了三个关键任务,包括音频模态自回归、文本模态自回归和语音-文本跨模态自回归。
点此查看论文截图

URSA: Understanding and Verifying Chain-of-thought Reasoning in Multimodal Mathematics
Authors:Ruilin Luo, Zhuofan Zheng, Yifan Wang, Xinzhe Ni, Zicheng Lin, Songtao Jiang, Yiyao Yu, Chufan Shi, Ruihang Chu, Jin Zeng, Yujiu Yang
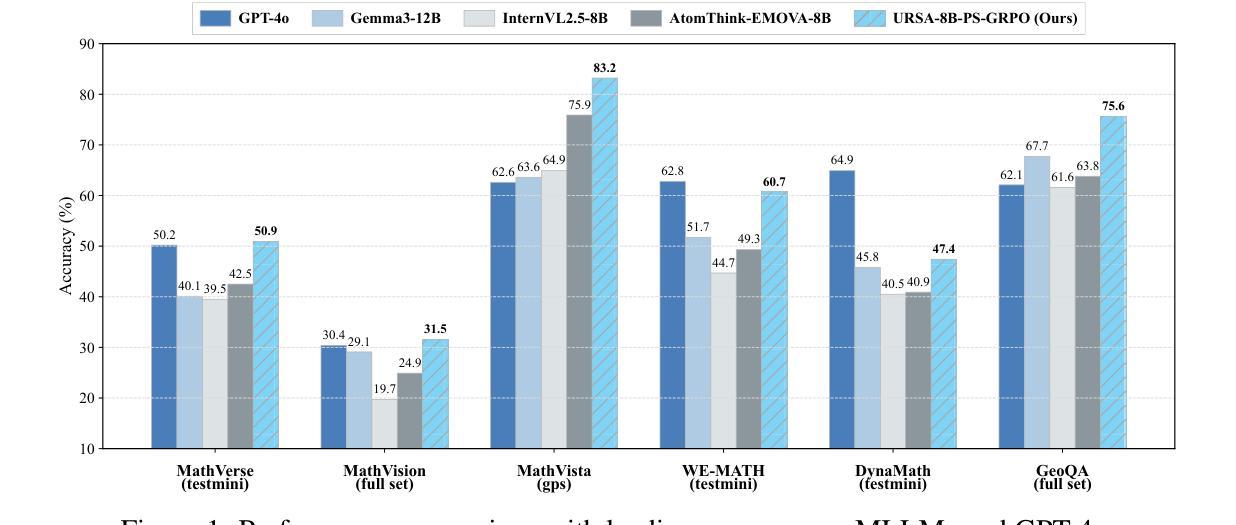
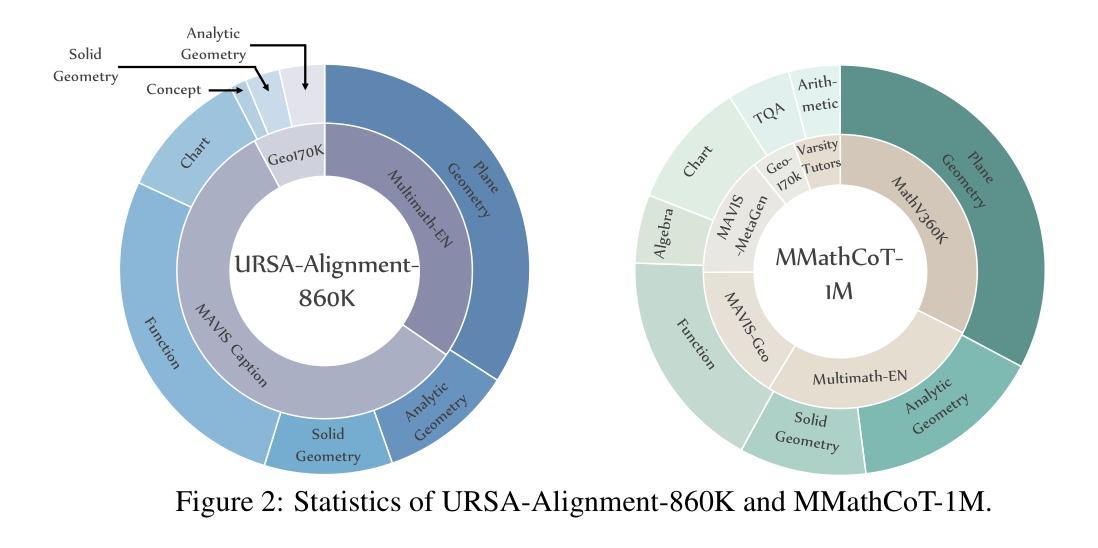
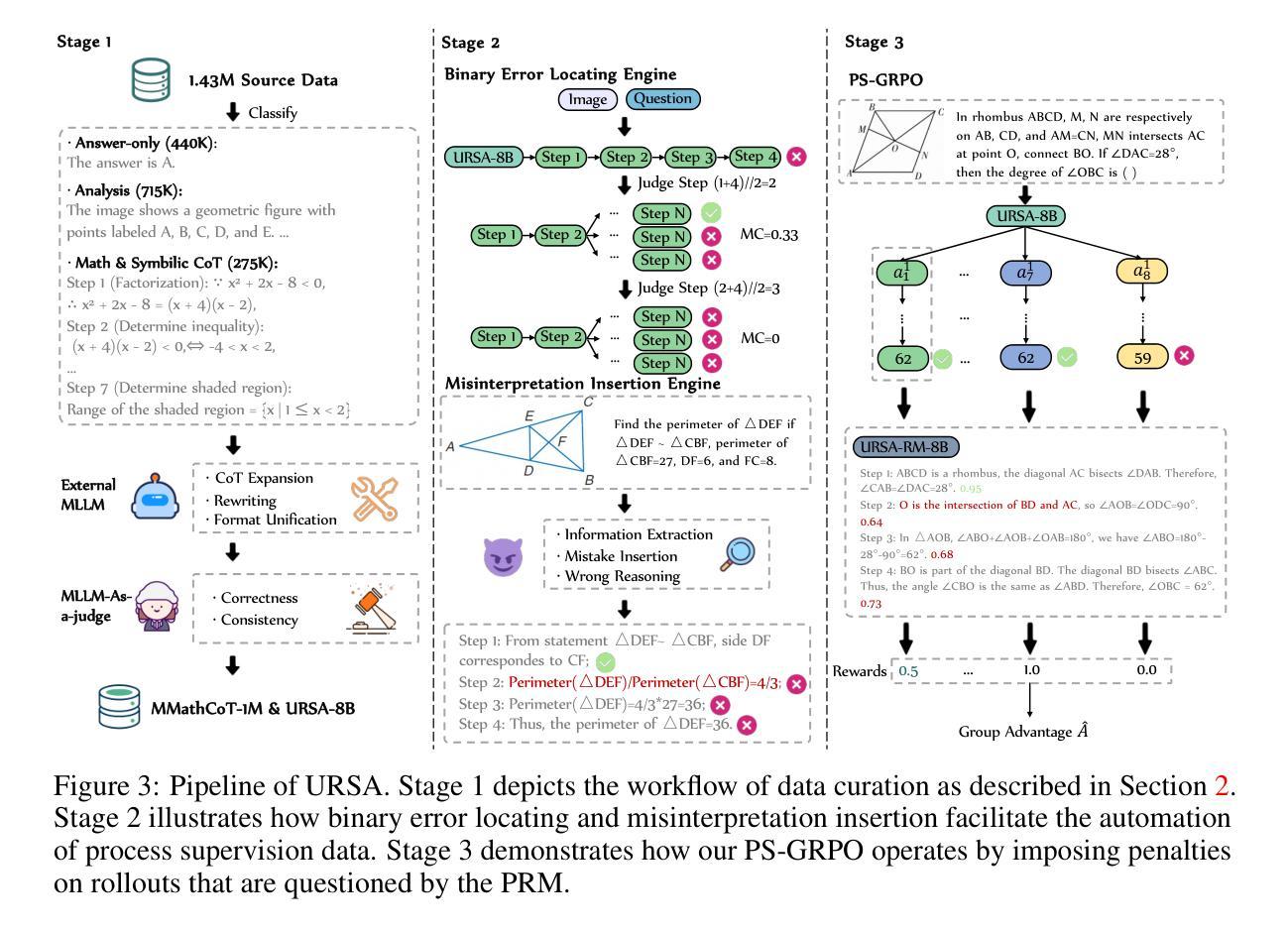
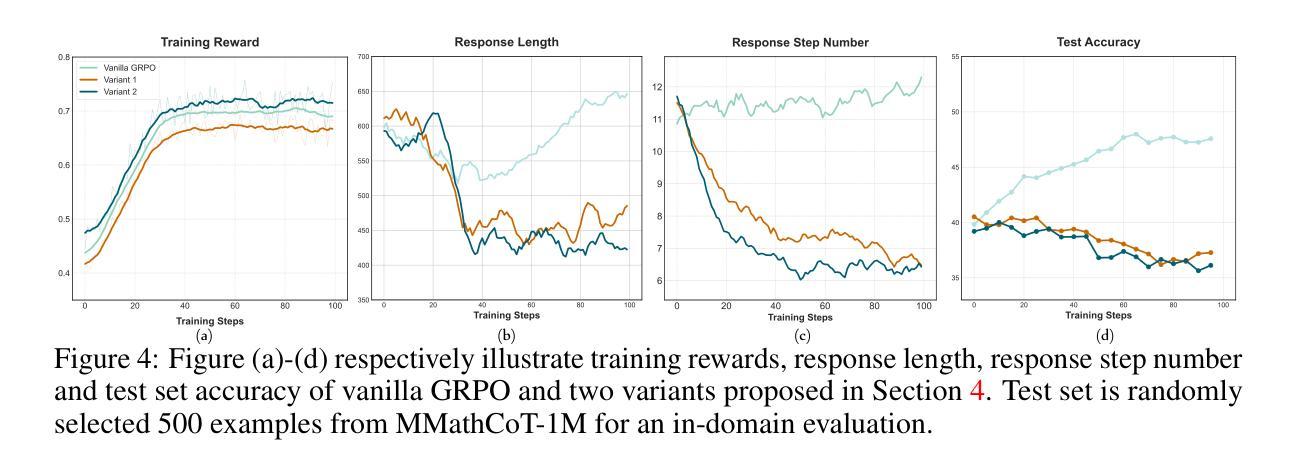
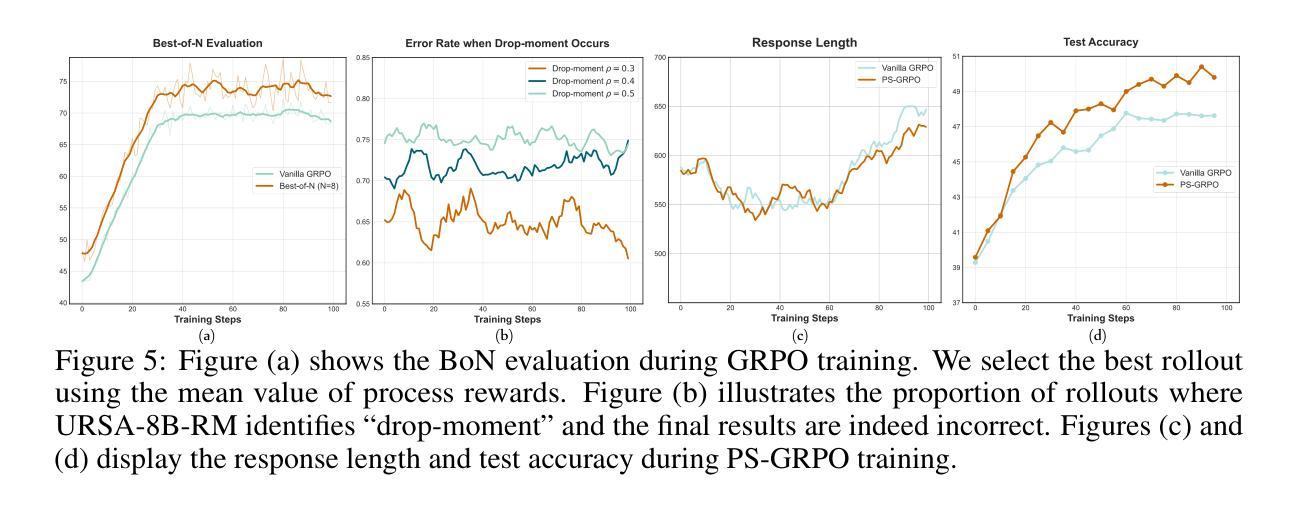
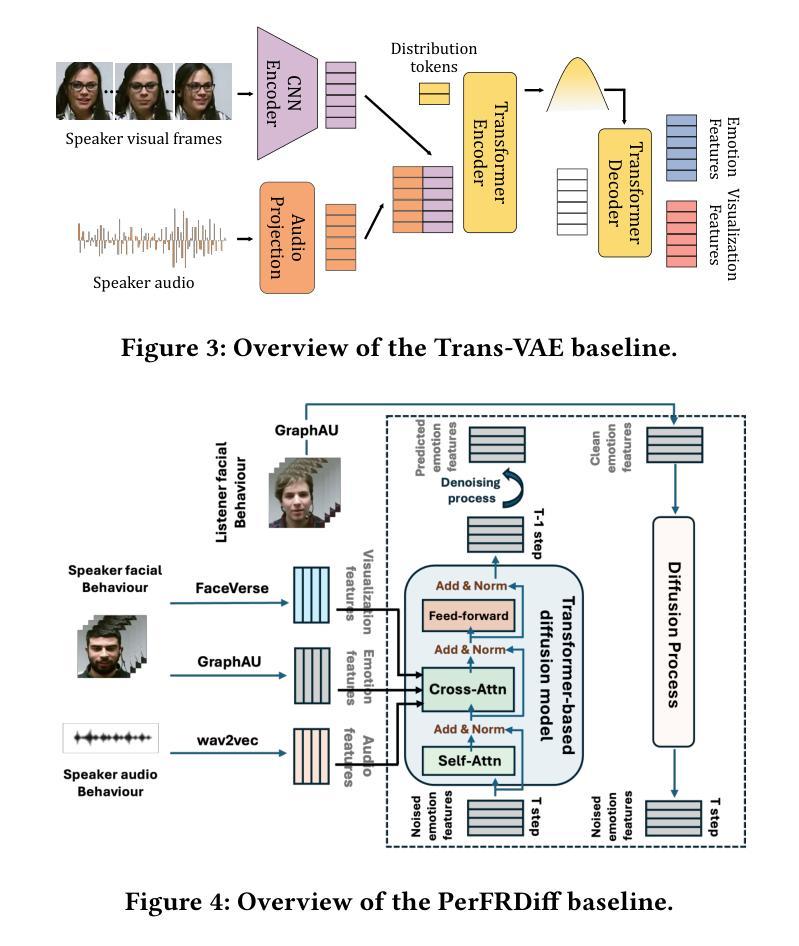
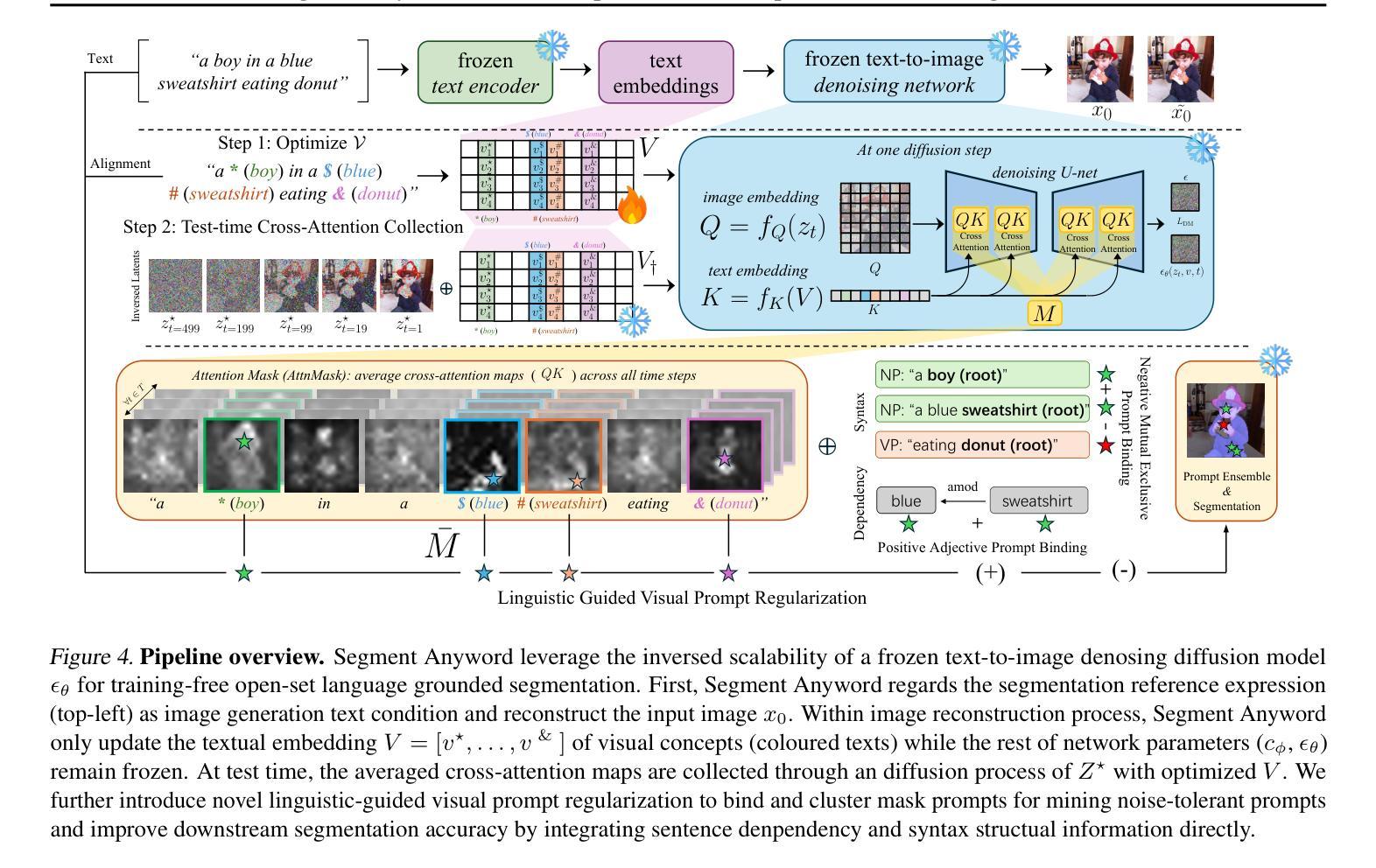
Process Reward Models (PRMs) have shown promise in enhancing the mathematical reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) through Test-Time Scaling (TTS). However, their integration into multimodal reasoning remains largely unexplored. In this work, we take the first step toward unlocking the potential of PRMs in multimodal mathematical reasoning. We identify three key challenges: (1) the scarcity of high-quality reasoning data constrains the capabilities of foundation Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which imposes further limitations on the upper bounds of TTS and reinforcement learning (RL); (2) a lack of automated methods for process labeling within multimodal contexts persists; (3) the employment of process rewards in unimodal RL faces issues like reward hacking, which may extend to multimodal scenarios. To address these issues, we introduce URSA, a three-stage Unfolding multimodal Process-Supervision Aided training framework. We first construct MMathCoT-1M, a high-quality large-scale multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning dataset, to build a stronger math reasoning foundation MLLM, URSA-8B. Subsequently, we go through an automatic process to synthesize process supervision data, which emphasizes both logical correctness and perceptual consistency. We introduce DualMath-1.1M to facilitate the training of URSA-8B-RM. Finally, we propose Process-Supervised Group-Relative-Policy-Optimization (PS-GRPO), pioneering a multimodal PRM-aided online RL method that outperforms vanilla GRPO. With PS-GRPO application, URSA-8B-PS-GRPO outperforms Gemma3-12B and GPT-4o by 8.4% and 2.7% on average across 6 benchmarks. Code, data and checkpoint can be found at https://github.com/URSA-MATH.
过程奖励模型(PRM)通过测试时间缩放(TTS)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)的数学推理能力方面显示出潜力。然而,它们在多模态推理中的集成仍然鲜有研究。在这项工作中,我们迈出了实现PRM在多模态数学推理中潜力的第一步。我们确定了三个关键挑战:(1)高质量推理数据的稀缺性限制了基础多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的能力,这给TTS和强化学习(RL)的上限带来了进一步的限制;(2)在多模态背景下,过程标签的自动化方法仍然缺乏;(3)在单模态RL中使用过程奖励面临着奖励操纵等问题,这些问题可能会扩展到多模态场景。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了URSA,这是一个三阶段展开的多模态过程监督辅助训练框架。首先,我们构建了MMathCoT-1M这一高质量的大规模多模态思维链(CoT)推理数据集,以建立更强大的数学推理基础MLLM,URSA-8B。随后,我们通过一个自动过程来合成过程监督数据,这一过程既强调逻辑的正确性又强调感知的一致性。我们引入了DualMath-1.1M来促进URSA-8B-RM的训练。最后,我们提出了过程监督组相对策略优化(PS-GRPO),开创了一种多模态PRM辅助的在线RL方法,该方法优于普通的GRPO。通过应用PS-GRPO,URSA-8B-PS-GRPO在6个基准测试上的平均表现优于Gemma3-12B和GPT-4o分别为8.4%和2.7%。相关代码、数据和检查点可访问https://github.com/URSA-MATH查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Update version. Project url: https://ursa-math.github.io
Summary
该文探讨了将过程奖励模型(PRM)应用于多模态数学推理中的潜力。针对当前存在的挑战,如高质量推理数据的稀缺性、多模态环境下过程标签的自动化方法的缺乏以及在单模态强化学习中使用过程奖励的潜在问题,文章提出了URSA这一训练框架,通过构建大规模多模态推理数据集MMathCoT-1M,引入过程监督数据合成方法,并开发了一种新的多模态PRM辅助在线强化学习方法PS-GRPO,提高了模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文章首次探索了将过程奖励模型(PRM)应用于多模态数学推理中的潜力。
- 文章指出了当前在集成PRM到多模态数学推理中的三个主要挑战。
- 为了解决这些挑战,文章提出了URSA训练框架,该框架包括构建大规模多模态推理数据集MMathCoT-1M,以及自动合成过程监督数据的方法。
- 文章创新地提出了PS-GRPO这一新的多模态PRM辅助在线强化学习方法,提高了模型的性能。
- 模型URSA-8B-PS-GRPO在六个基准测试上的表现超过了Gemma3-12B和GPT-4o。
- 该工作的代码、数据和检查点可以在https://github.com/URSA-MATH找到。
- 该研究强调了逻辑正确性感知一致性的重要性在合成过程监督数据中的。
点此查看论文截图