⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
Deep Spectral Prior
Authors:Yanqi Cheng, Tieyong Zeng, Pietro Lio, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb, Angelica I Aviles-Rivero
We introduce Deep Spectral Prior (DSP), a new formulation of Deep Image Prior (DIP) that redefines image reconstruction as a frequency-domain alignment problem. Unlike traditional DIP, which relies on pixel-wise loss and early stopping to mitigate overfitting, DSP directly matches Fourier coefficients between the network output and observed measurements. This shift introduces an explicit inductive bias towards spectral coherence, aligning with the known frequency structure of images and the spectral bias of convolutional neural networks. We provide a rigorous theoretical framework demonstrating that DSP acts as an implicit spectral regulariser, suppressing high-frequency noise by design and eliminating the need for early stopping. Our analysis spans four core dimensions establishing smooth convergence dynamics, local stability, and favourable bias-variance tradeoffs. We further show that DSP naturally projects reconstructions onto a frequency-consistent manifold, enhancing interpretability and robustness. These theoretical guarantees are supported by empirical results across denoising, inpainting, and super-resolution tasks, where DSP consistently outperforms classical DIP and other unsupervised baselines.
我们引入了深度谱先验(DSP),这是深度图像先验(DIP)的一种新形式,它将图像重建重新定义为一个频域对齐问题。不同于传统的DIP,它依赖于像素级的损失和早期停止来缓解过拟合,DSP直接匹配网络输出和观测测量之间的傅里叶系数。这种转变引入了对频谱一致性的明确归纳偏置,与已知的图像频率结构和卷积神经网络的频谱偏置相对应。我们提供了一个严格的理论框架,证明DSP充当隐式谱正则化器,通过设计抑制高频噪声,不需要早期停止。我们的分析涵盖了四个核心维度,建立了平稳的收敛动力学、局部稳定性和有利的偏见-方差权衡。我们进一步表明,DSP自然地将重建投影到频率一致的流形上,增强了可解释性和稳健性。这些理论保证在降噪、修复和超分辨率任务上的经验结果中得到了支持,在这些任务中,DSP始终优于经典的DIP和其他无监督基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Deep Spectral Prior(DSP)是一种新的Deep Image Prior(DIP)表述方式,它将图像重建定义为频域对齐问题。与传统的DIP不同,DSP直接匹配网络输出和观测值之间的傅里叶系数,引入了对频谱一致性的显性诱导偏见。DSP的理论框架证明其能够作为一种隐式频谱正则化器,通过设计抑制高频噪声,并消除对早期停止的需要。此外,DSP在理论上保证了平滑的收敛动力学、局部稳定性以及有利的偏差-方差权衡。实证分析显示,DSP在降噪、修复和超分辨率任务上表现优异,且相较于传统的DIP和其他无监督基准测试具有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- DSP是DIP的新表述方式,将图像重建定义为频域对齐问题。
- DSP直接匹配网络输出和观测值之间的傅里叶系数,引入频谱一致性偏见。
- DSP作为一种隐式频谱正则化器,能够抑制高频噪声,无需早期停止。
- DSP具有理论保证,包括平滑收敛动力学、局部稳定性和偏差-方差权衡。
- DSP能提高图像重建的可解释性和稳健性,通过频率一致性将重建投影到流形上。
- DSP在降噪、修复和超分辨率任务上的表现优于传统DIP和其他无监督方法。
- DSP的引入为图像重建问题提供了新的视角和解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

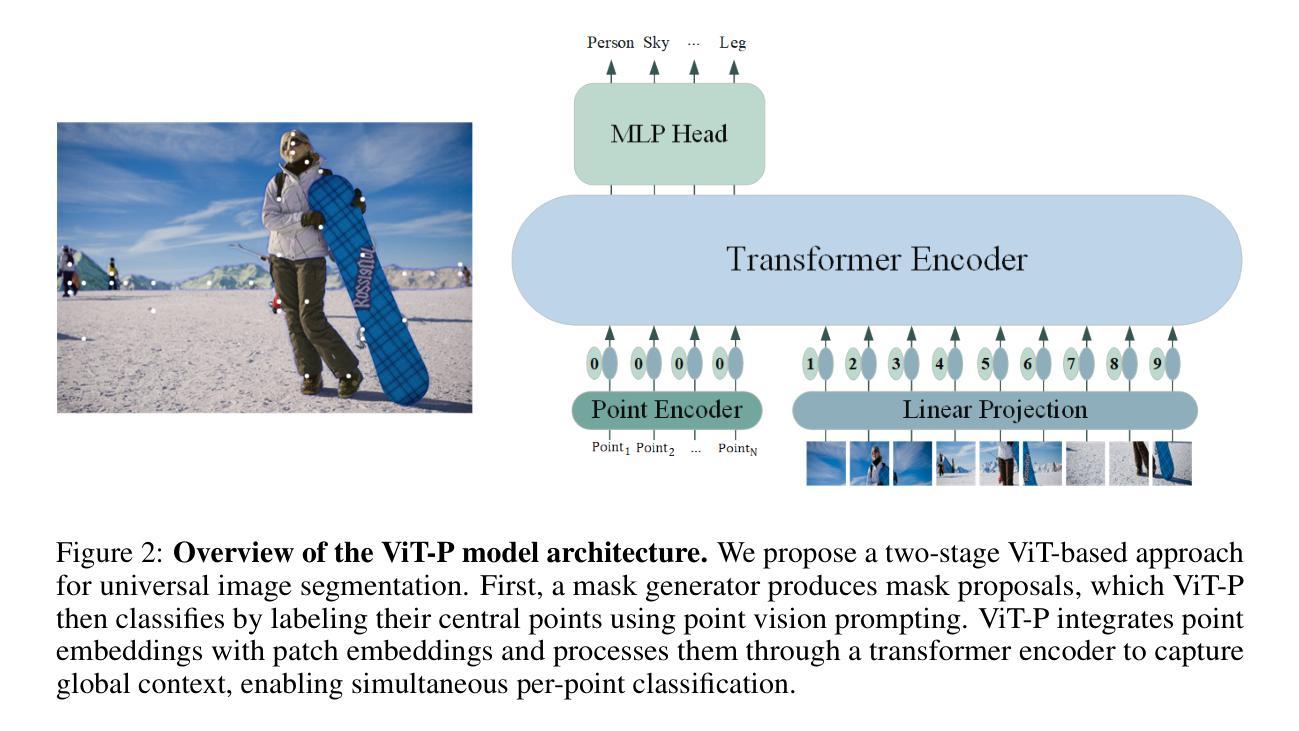
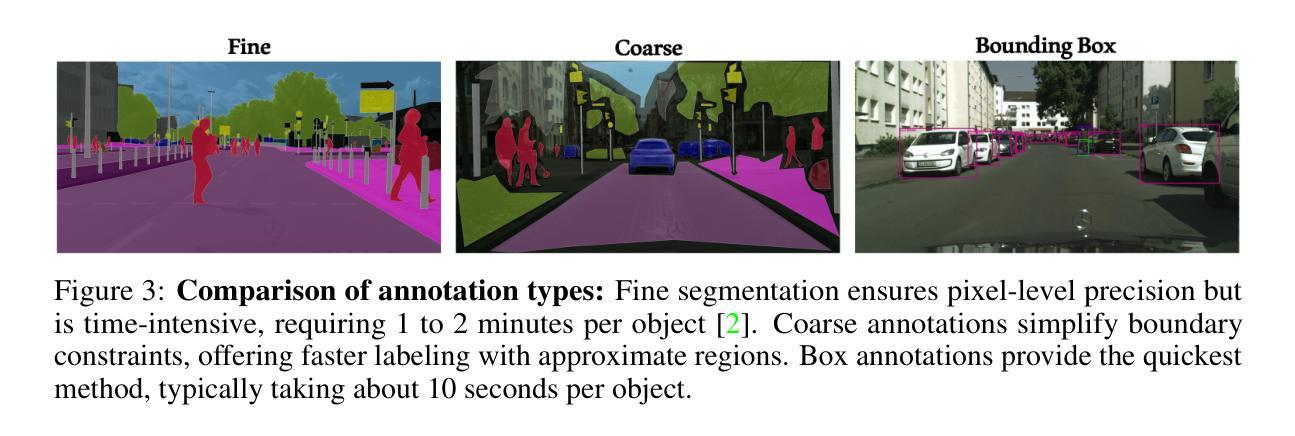
The Missing Point in Vision Transformers for Universal Image Segmentation
Authors:Sajjad Shahabodini, Mobina Mansoori, Farnoush Bayatmakou, Jamshid Abouei, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Arash Mohammadi
Image segmentation remains a challenging task in computer vision, demanding robust mask generation and precise classification. Recent mask-based approaches yield high-quality masks by capturing global context. However, accurately classifying these masks, especially in the presence of ambiguous boundaries and imbalanced class distributions, remains an open challenge. In this work, we introduce ViT-P, a novel two-stage segmentation framework that decouples mask generation from classification. The first stage employs a proposal generator to produce class-agnostic mask proposals, while the second stage utilizes a point-based classification model built on the Vision Transformer (ViT) to refine predictions by focusing on mask central points. ViT-P serves as a pre-training-free adapter, allowing the integration of various pre-trained vision transformers without modifying their architecture, ensuring adaptability to dense prediction tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that coarse and bounding box annotations can effectively enhance classification without requiring additional training on fine annotation datasets, reducing annotation costs while maintaining strong performance. Extensive experiments across COCO, ADE20K, and Cityscapes datasets validate the effectiveness of ViT-P, achieving state-of-the-art results with 54.0 PQ on ADE20K panoptic segmentation, 87.4 mIoU on Cityscapes semantic segmentation, and 63.6 mIoU on ADE20K semantic segmentation. The code and pretrained models are available at: https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P}{https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P.
图像分割仍是计算机视觉中的一项具有挑战性的任务,需要生成稳健的掩膜和精确的分类。最近的基于掩膜的方法通过捕捉全局上下文来生成高质量掩膜。然而,在这些掩膜上进行准确分类仍然是一个开放性的挑战,特别是在存在边界模糊和类别分布不平衡的情况下。在这项工作中,我们引入了ViT-P,这是一种新型的两阶段分割框架,它将掩膜生成与分类解耦。第一阶段采用提案生成器来产生类无关的掩膜提案,而第二阶段则基于视觉转换器(ViT)采用点分类模型,通过关注掩膜中心点来优化预测。ViT-P作为一种无需预训练的适配器,可以集成各种预训练的视觉转换器而无需修改其架构,确保适应密集预测任务。此外,我们证明粗标注和边界框标注可以有效地增强分类,而无需在精细标注数据集上进行额外的训练,从而在降低标注成本的同时保持强大的性能。在COCO、ADE20K和Cityscapes数据集上的大量实验验证了ViT-P的有效性,其在ADE20K全景分割上实现了54.0 PQ的最新结果,Cityscapes语义分割上实现了87.4 mIoU,ADE20K语义分割上实现了63.6 mIoU。代码和预先训练的模型可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ViT-P的新型两阶段图像分割框架,它解决了图像分割中的掩膜生成和分类挑战。第一阶段生成类别无关的掩膜提案,第二阶段使用基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的点分类模型进行预测精细化。ViT-P适用于多种预训练视觉变压器,无需预训练,且能利用粗标注和边界框标注提高分类性能。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,ViT-P达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-P是一种两阶段图像分割框架,用于解决图像分割中的掩膜生成和分类挑战。
- 第一阶段生成类别无关的掩膜提案。
- 第二阶段使用基于Vision Transformer的点分类模型进行预测精细化。
- ViT-P无需预训练,并能适应多种预训练视觉变压器。
- 利用粗标注和边界框标注能提高分类性能,降低标注成本。
- ViT-P在多个数据集上实现了先进水平的结果。
点此查看论文截图

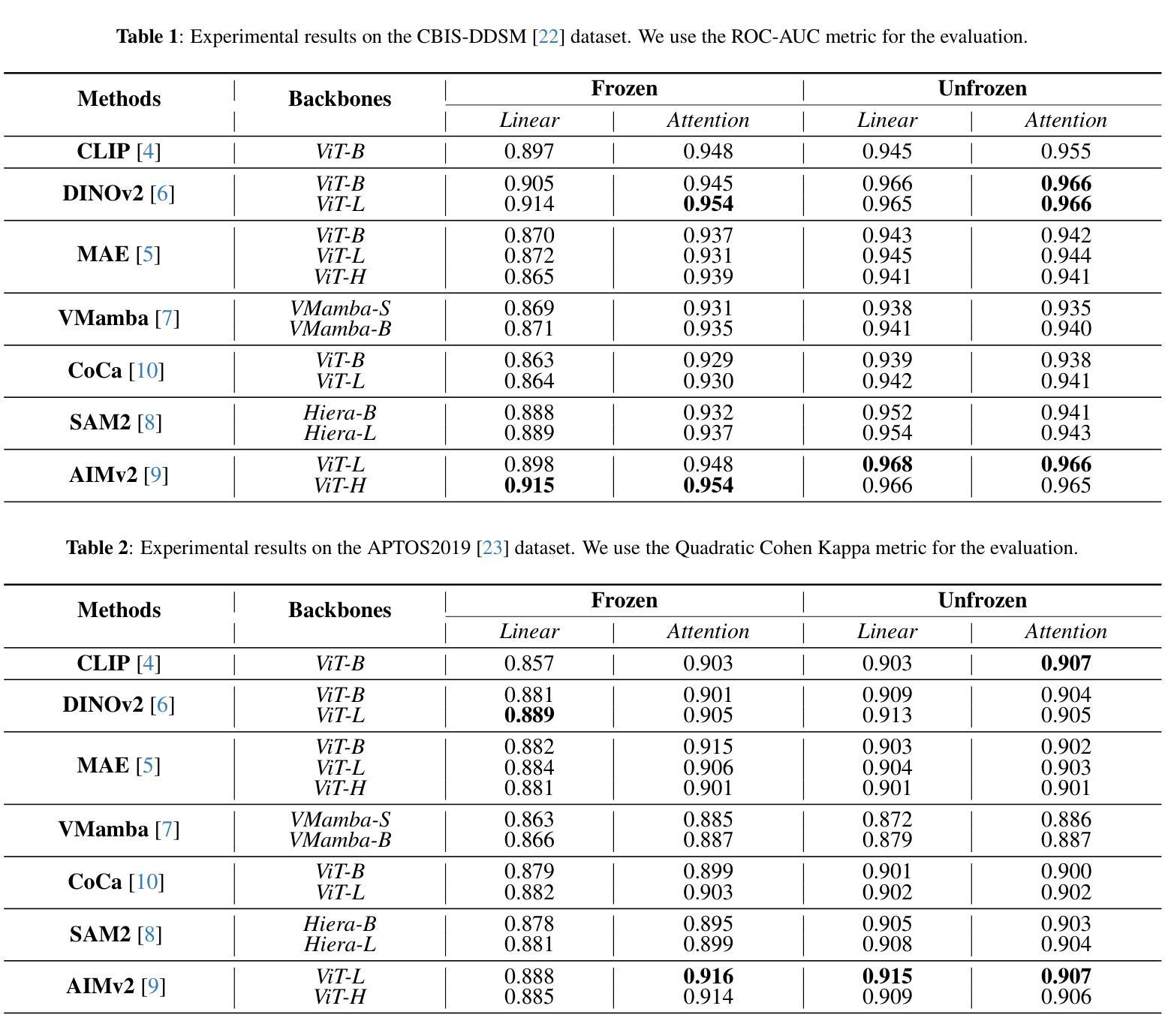
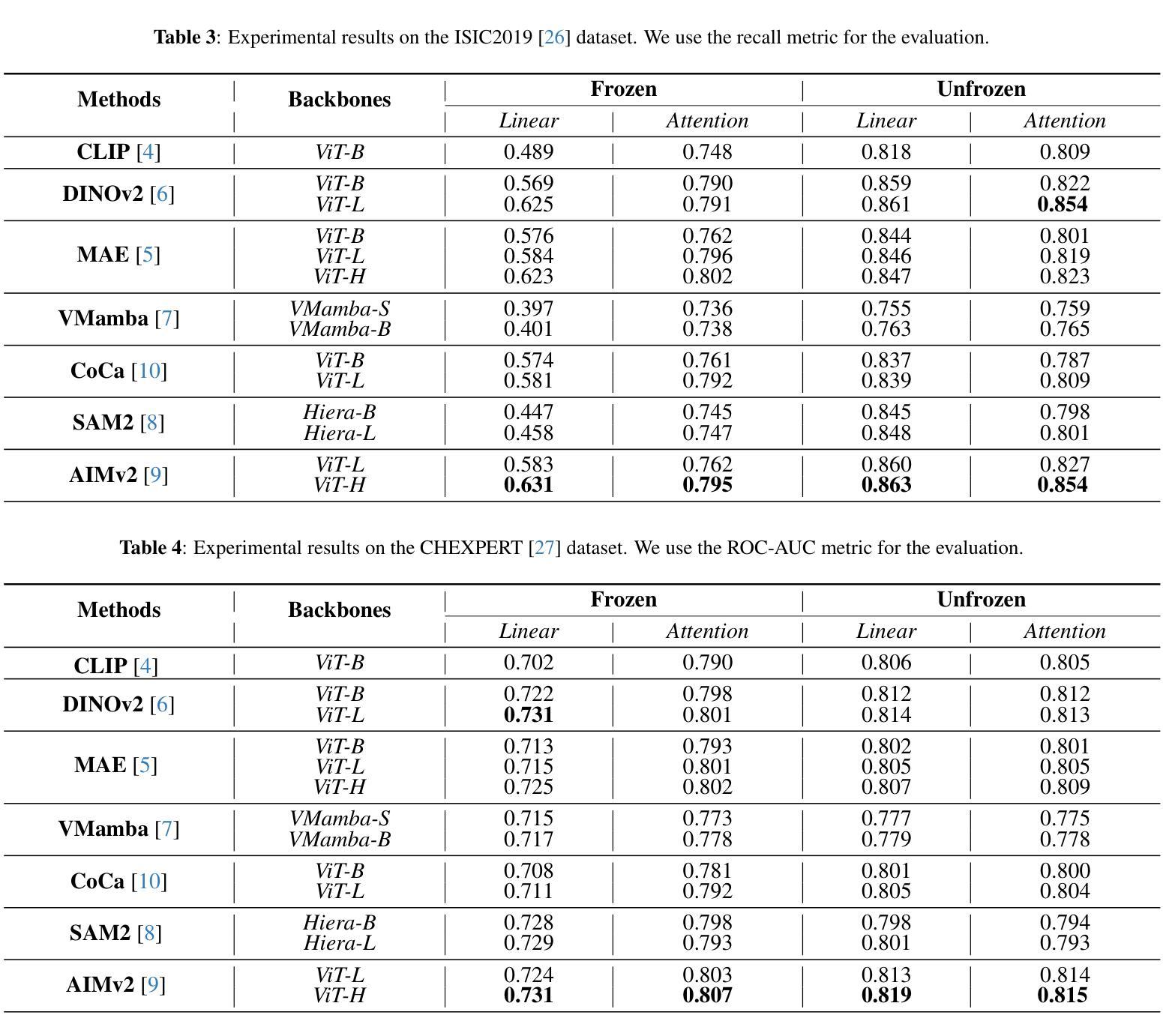
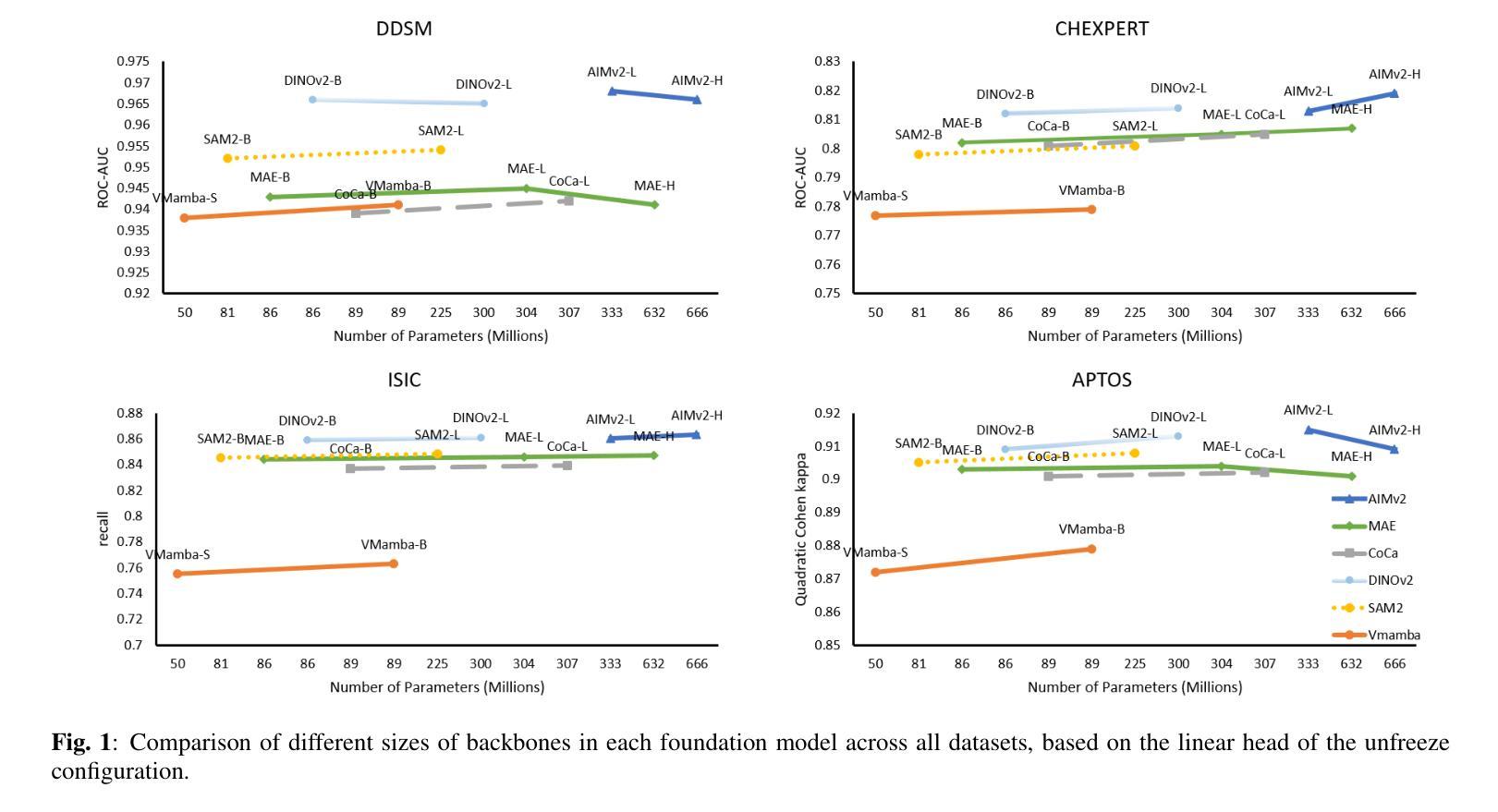
Advancements in Medical Image Classification through Fine-Tuning Natural Domain Foundation Models
Authors:Mobina Mansoori, Sajjad Shahabodini, Farnoush Bayatmakou, Jamshid Abouei, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Arash Mohammadi
Using massive datasets, foundation models are large-scale, pre-trained models that perform a wide range of tasks. These models have shown consistently improved results with the introduction of new methods. It is crucial to analyze how these trends impact the medical field and determine whether these advancements can drive meaningful change. This study investigates the application of recent state-of-the-art foundation models, DINOv2, MAE, VMamba, CoCa, SAM2, and AIMv2, for medical image classification. We explore their effectiveness on datasets including CBIS-DDSM for mammography, ISIC2019 for skin lesions, APTOS2019 for diabetic retinopathy, and CHEXPERT for chest radiographs. By fine-tuning these models and evaluating their configurations, we aim to understand the potential of these advancements in medical image classification. The results indicate that these advanced models significantly enhance classification outcomes, demonstrating robust performance despite limited labeled data. Based on our results, AIMv2, DINOv2, and SAM2 models outperformed others, demonstrating that progress in natural domain training has positively impacted the medical domain and improved classification outcomes. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/Medical-Transfer-Learning.
利用大规模数据集,基础模型是大型预训练模型,可以执行各种任务。随着新方法的引入,这些模型的结果持续得到改进。分析这些趋势如何影响医疗领域,以及这些进步是否能带来有意义的变化至关重要。本研究调查了最新最先进的基础模型(DINOv2、MAE、VMamba、CoCa、SAM2和AIMv2)在医学图像分类中的应用。我们在CBIS-DDSM乳腺癌筛查数据集、ISIC2019皮肤病变数据集、APTOS2019糖尿病视网膜病变数据集和CHEXPERT胸部X射线数据集上探索了它们的有效性。通过微调这些模型并评估其配置,我们旨在了解这些进步在医学图像分类中的潜力。结果表明,这些先进模型显著提高了分类效果,在有限标记数据的情况下表现出稳健的性能。根据我们的结果,AIMv2、DINOv2和SAM2模型表现最佳,这表明自然域训练的进展对医学领域产生了积极影响,提高了分类效果。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/Medical-Transfer-Learning。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究调查了最新先进的基金会模型在医学图像分类中的应用,包括DINOv2、MAE、VMamba、CoCa、SAM2和AIMv2等。在医学图像分类数据集上进行精细调整并评估配置后,这些模型展现出显著的分类效果,特别是在有限标记数据的情况下。AIMv2、DINOv2和SAM2表现最佳,表明自然域训练的进展对医学领域产生了积极影响,并提高了分类结果。
Key Takeaways
- 基金会模型是使用大规模数据集进行预训练的大型模型,能够执行各种任务,并随着新方法的引入而持续提高结果。
- 该研究调查了最新先进的基金会模型在医学图像分类中的应用,涉及多个数据集,包括CBIS-DDSM、ISIC2019、APTOS2019和CHEXPERT。
- 这些模型在医学图像分类方面展现出显著的效果,特别是在有限标记数据的情况下。
- AIMv2、DINOv2和SAM2等模型表现最佳,表明它们在医学图像分类方面具有更高的潜力。
- 研究结果表明,自然域训练的进展对医学领域产生了积极影响,并提高了分类结果。
- 公开可用的代码为医学迁移学习提供了有用的资源和参考。
点此查看论文截图

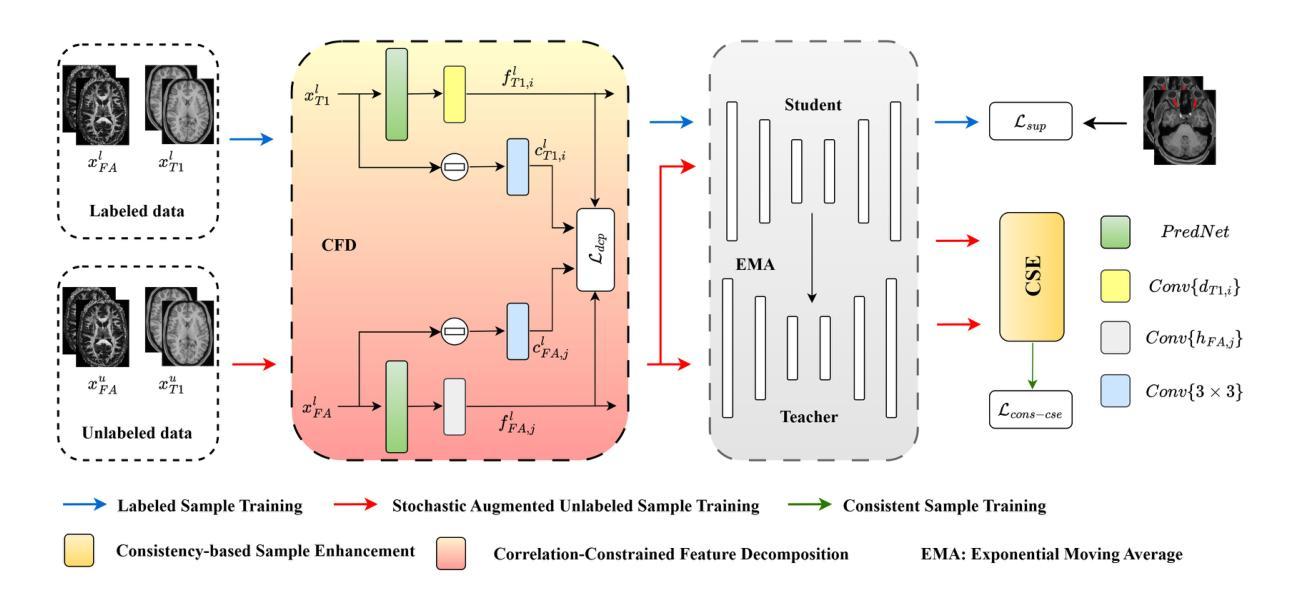
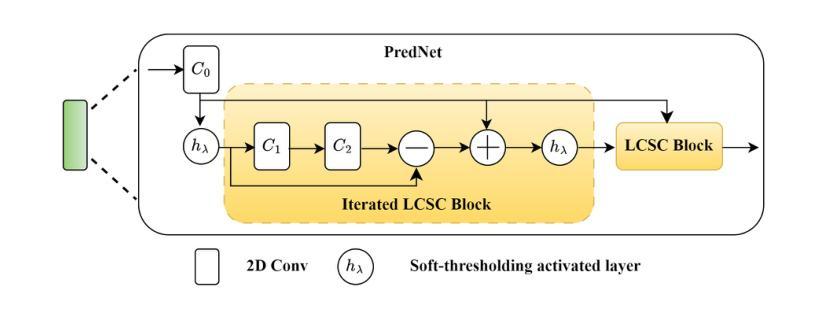
Cross-Sequence Semi-Supervised Learning for Multi-Parametric MRI-Based Visual Pathway Delineation
Authors:Alou Diakite, Cheng Li, Lei Xie, Yuanjing Feng, Ruoyou Wu, Jianzhong He, Hairong Zheng, Shanshan Wang
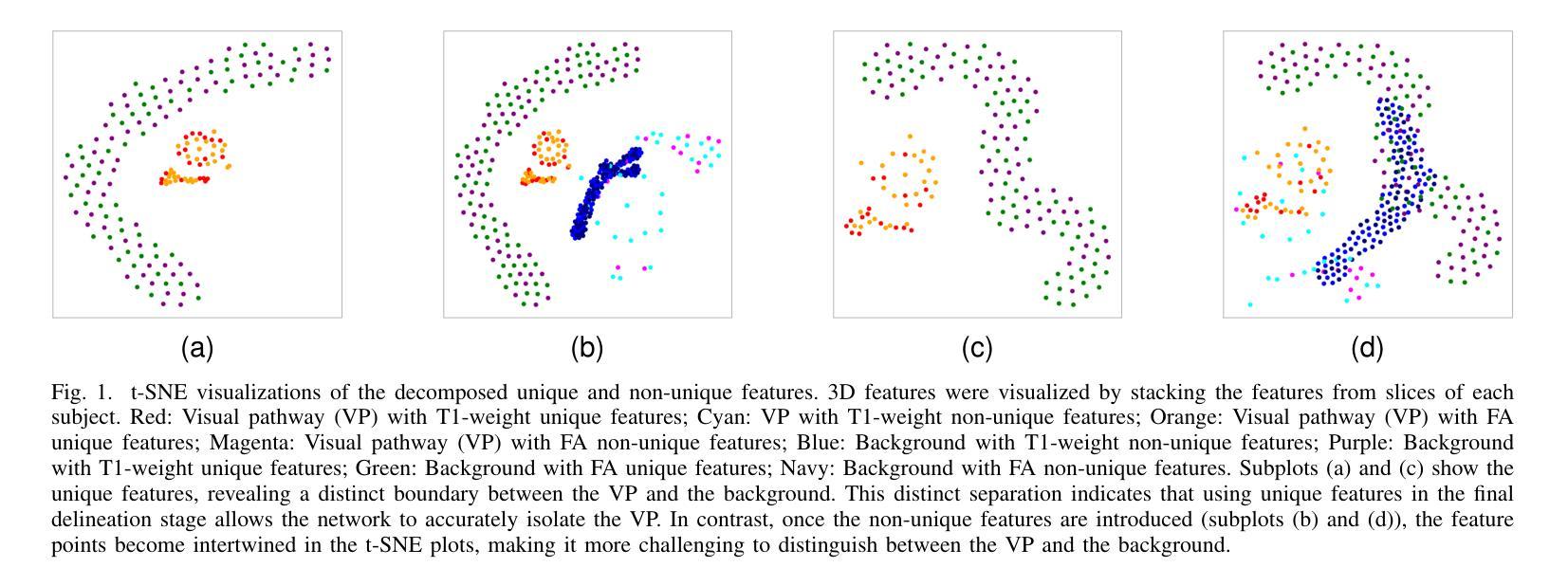
Accurately delineating the visual pathway (VP) is crucial for understanding the human visual system and diagnosing related disorders. Exploring multi-parametric MR imaging data has been identified as an important way to delineate VP. However, due to the complex cross-sequence relationships, existing methods cannot effectively model the complementary information from different MRI sequences. In addition, these existing methods heavily rely on large training data with labels, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming to obtain. In this work, we propose a novel semi-supervised multi-parametric feature decomposition framework for VP delineation. Specifically, a correlation-constrained feature decomposition (CFD) is designed to handle the complex cross-sequence relationships by capturing the unique characteristics of each MRI sequence and easing the multi-parametric information fusion process. Furthermore, a consistency-based sample enhancement (CSE) module is developed to address the limited labeled data issue, by generating and promoting meaningful edge information from unlabeled data. We validate our framework using two public datasets, and one in-house Multi-Shell Diffusion MRI (MDM) dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our approach in terms of delineation performance when compared to seven state-of-the-art approaches.
准确地描绘视觉通路(VP)对于理解人类视觉系统和诊断相关疾病至关重要。探索多参数MR成像数据已被确定为描绘VP的重要方式。然而,由于复杂的跨序列关系,现有方法无法有效地对来自不同MRI序列的互补信息进行建模。此外,这些方法严重依赖于带有标签的大量训练数据,而这些数据的获取既耗费人力又耗时。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的半监督多参数特征分解框架,用于VP描绘。具体来说,设计了一种相关性约束特征分解(CFD),通过捕捉每个MRI序列的独特特征来处理复杂的跨序列关系,并简化多参数信息融合过程。此外,开发了一个基于一致性的样本增强(CSE)模块,以解决标签数据有限的问题,通过从未标记的数据生成并促进有意义的边缘信息。我们使用两个公共数据集和一个内部的多壳扩散MRI(MDM)数据集验证了我们的框架。实验结果表明,与七种最新方法相比,我们的方法在描绘性能方面具有优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学视觉路径(VP)的精确描绘对于理解人类视觉系统和诊断相关疾病至关重要。多参数MR成像数据是描绘VP的重要方法,但现有方法难以有效建模不同MRI序列的互补信息。本文提出一种新型半监督多参数特征分解框架,包括用于处理复杂跨序列关系的关联约束特征分解(CFD),并开发一致性样本增强(CSE)模块解决标注数据有限问题。实验结果证明该方法在对比七个最新方法时具有优越的描述性能。
Key Takeaways
- 准确描绘视觉路径(VP)对理解人类视觉系统和诊断相关疾病至关重要。
- 多参数MR成像数据是描绘VP的重要方法。
- 现有方法难以有效建模不同MRI序列的互补信息,且需要大量标注数据进行训练。
- 提出一种新型半监督多参数特征分解框架,包括关联约束特征分解(CFD)和一致性样本增强(CSE)模块。
- CFD能够捕捉每个MRI序列的独特特征,并简化多参数信息融合过程。
- CSE模块通过从无标签数据中生成并推广边缘信息,解决了标注数据有限的问题。
点此查看论文截图


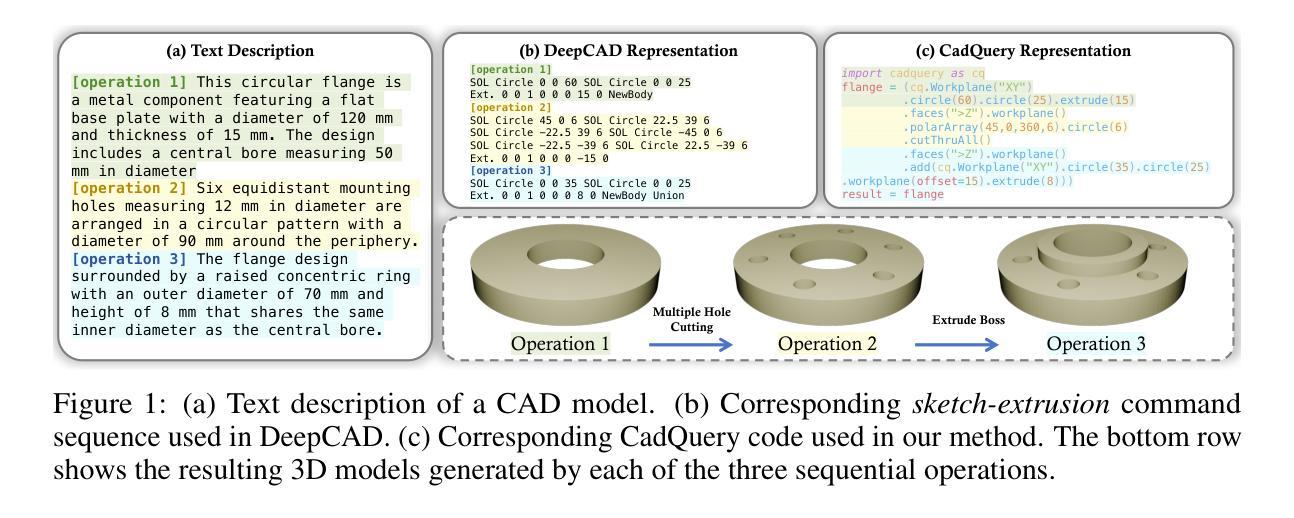
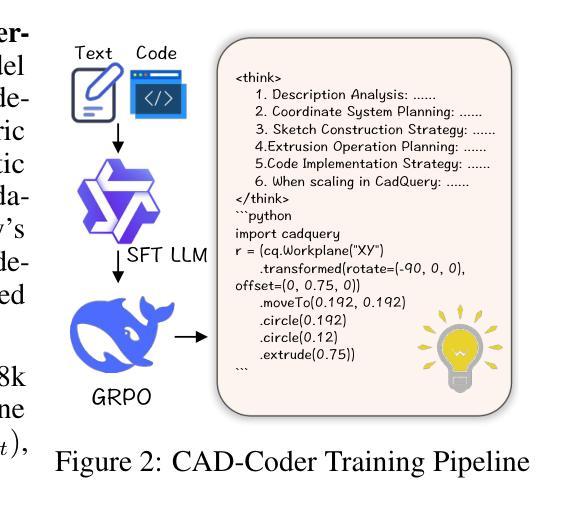
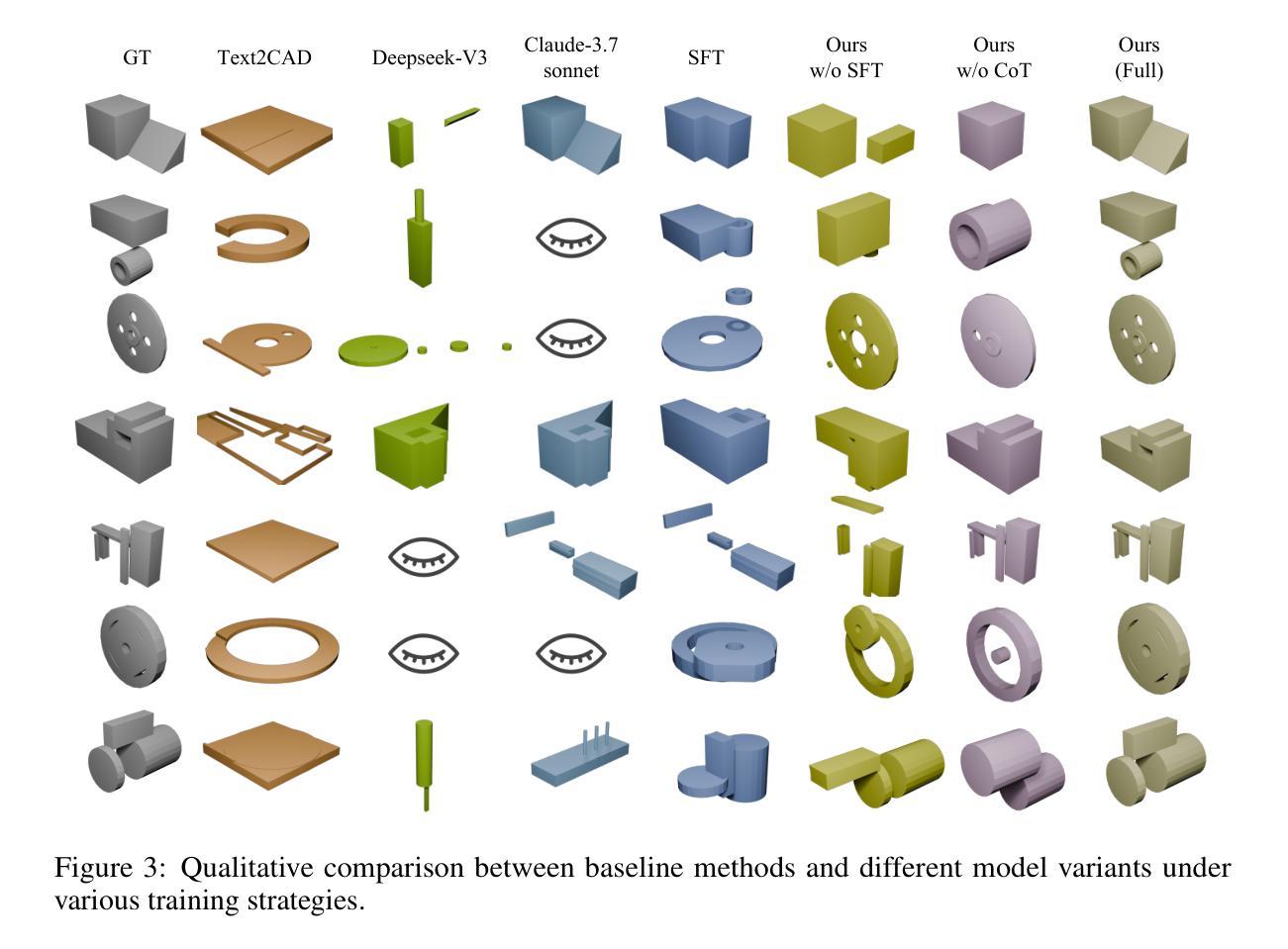
CAD-Coder: Text-to-CAD Generation with Chain-of-Thought and Geometric Reward
Authors:Yandong Guan, Xilin Wang, Xingxi Ming, Jing Zhang, Dong Xu, Qian Yu
In this work, we introduce CAD-Coder, a novel framework that reformulates text-to-CAD as the generation of CadQuery scripts - a Python-based, parametric CAD language. This representation enables direct geometric validation, a richer modeling vocabulary, and seamless integration with existing LLMs. To further enhance code validity and geometric fidelity, we propose a two-stage learning pipeline: (1) supervised fine-tuning on paired text-CadQuery data, and (2) reinforcement learning with Group Reward Policy Optimization (GRPO), guided by a CAD-specific reward comprising both a geometric reward (Chamfer Distance) and a format reward. We also introduce a chain-of-thought (CoT) planning process to improve model reasoning, and construct a large-scale, high-quality dataset of 110K text-CadQuery-3D model triplets and 1.5K CoT samples via an automated pipeline. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CAD-Coder enables LLMs to generate diverse, valid, and complex CAD models directly from natural language, advancing the state of the art of text-to-CAD generation and geometric reasoning.
在这项工作中,我们介绍了CAD-Coder这一新型框架,它将文本到CAD(计算机辅助设计)的问题重新定义为CadQuery脚本的生成问题。CadQuery是一种基于Python的参数化CAD语言。这种表示方法能够实现直接的几何验证、更丰富的建模词汇和无缝集成现有的大型语言模型。为了进一步提高代码的有效性和几何保真度,我们提出了一个两阶段的学习流程,包括:(1)在配对文本-CadQuery数据上进行监督微调;(2)采用集团奖励政策优化(GRPO)进行强化学习,以CAD特定奖励为指导,该奖励包括几何奖励(Chamfer距离)和格式奖励。我们还引入了思维链(CoT)规划过程来改善模型推理能力,并通过自动化流程构建了一个大规模、高质量的包含11万份文本-CadQuery-3D模型三元组和1500份CoT样本的数据集。大量实验表明,CAD-Coder使大型语言模型能够直接从自然语言生成多样、有效和复杂的CAD模型,推动了文本到CAD生成和几何推理的最新技术进展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CAD-Coder框架能将文本转化为CAD设计,通过生成CadQuery脚本实现。该框架支持直接几何验证、丰富的建模词汇,并能无缝集成现有的大型语言模型。为提高代码的有效性和几何精度,研究提出了包含监督微调与强化学习的两阶段学习管道,并引入了CAD特定奖励策略。同时,通过思考链规划过程提高模型推理能力,并构建大规模高质量数据集。实验表明,CAD-Coder能促使语言模型直接从自然语言生成多样、有效且复杂的CAD模型,推动文本到CAD生成和几何推理领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- CAD-Coder是一个将文本转化为CAD设计的全新框架,通过生成CadQuery脚本实现。
- 该框架支持直接几何验证、丰富的建模词汇,并能无缝集成现有的大型语言模型。
- 研究提出两阶段学习管道,包括监督微调和强化学习,以提高代码的有效性和几何精度。
- 引入了CAD特定奖励策略,结合几何奖励和格式奖励。
- 通过思考链规划过程提高模型推理能力。
- 构建了一个大规模、高质量的数据集,包含110K文本-CadQuery-3D模型三元组和1.5K思考链样本。
点此查看论文截图

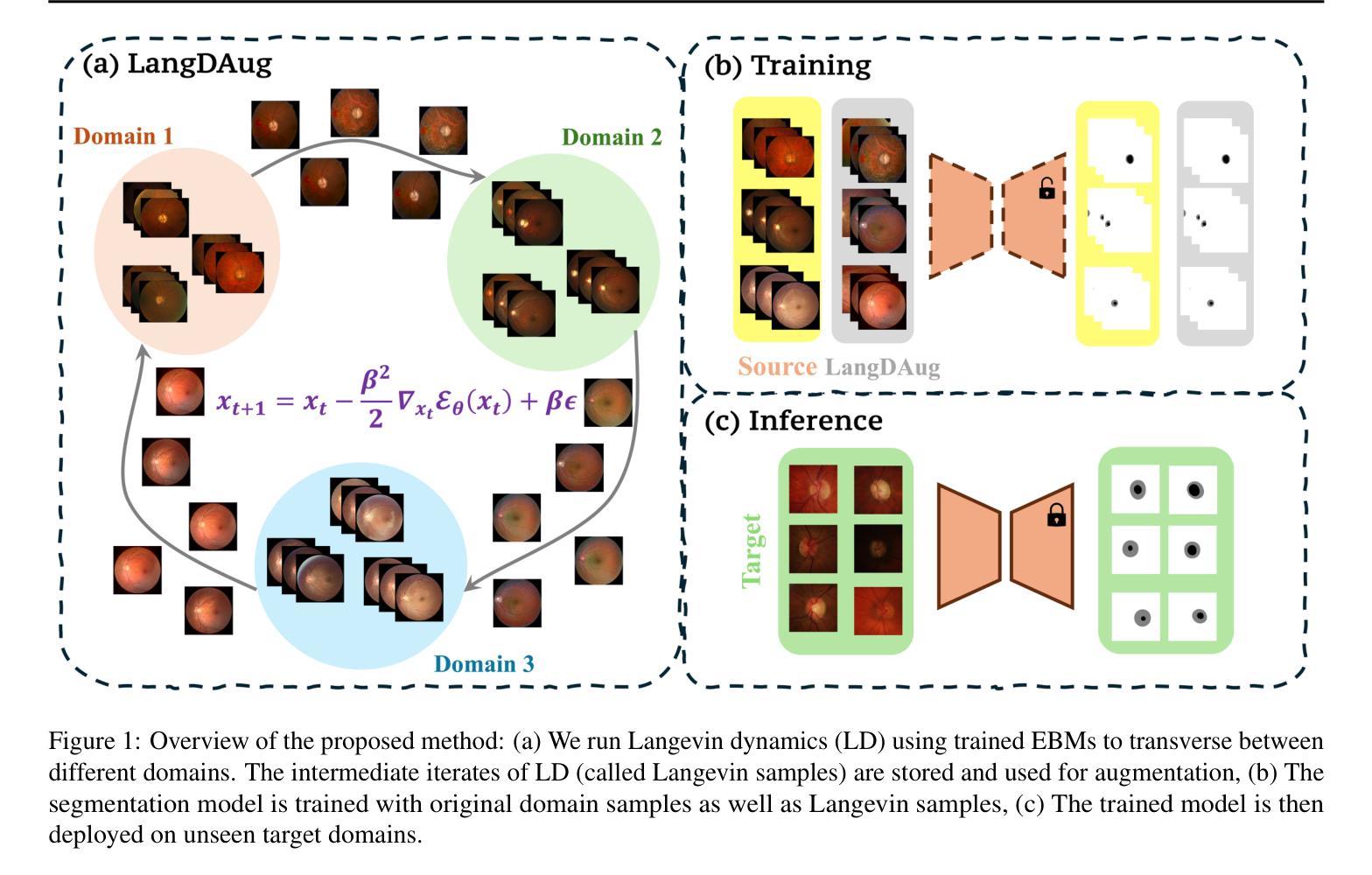
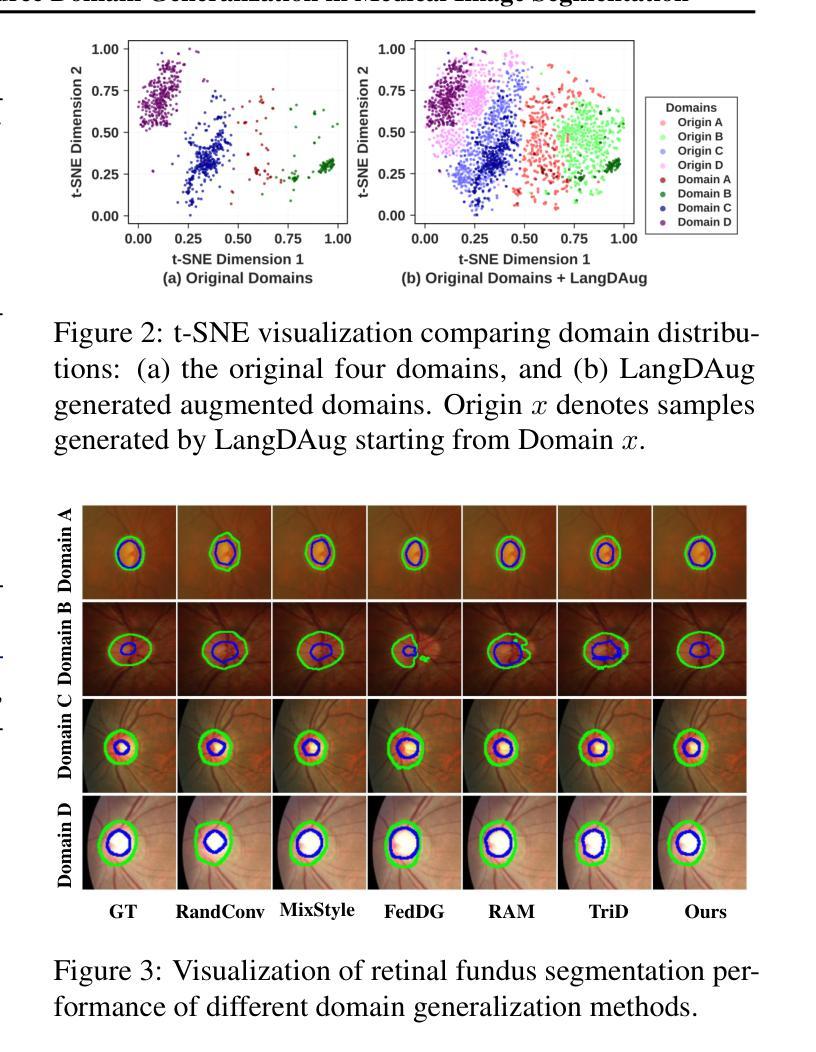
LangDAug: Langevin Data Augmentation for Multi-Source Domain Generalization in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Piyush Tiwary, Kinjawl Bhattacharyya, Prathosh A. P
Medical image segmentation models often struggle to generalize across different domains due to various reasons. Domain Generalization (DG) methods overcome this either through representation learning or data augmentation (DAug). While representation learning methods seek domain-invariant features, they often rely on ad-hoc techniques and lack formal guarantees. DAug methods, which enrich model representations through synthetic samples, have shown comparable or superior performance to representation learning approaches. We propose LangDAug, a novel $\textbf{Lang}$evin $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{Aug}$mentation for multi-source domain generalization in 2D medical image segmentation. LangDAug leverages Energy-Based Models (EBMs) trained via contrastive divergence to traverse between source domains, generating intermediate samples through Langevin dynamics. Theoretical analysis shows that LangDAug induces a regularization effect, and for GLMs, it upper-bounds the Rademacher complexity by the intrinsic dimensionality of the data manifold. Through extensive experiments on Fundus segmentation and 2D MRI prostate segmentation benchmarks, we show that LangDAug outperforms state-of-the-art domain generalization methods and effectively complements existing domain-randomization approaches. The codebase for our method is available at https://github.com/backpropagator/LangDAug.
医学图像分割模型由于各种原因,往往难以在不同领域进行推广。领域泛化(DG)方法通过表示学习或数据增强(DAug)来克服这一问题。表示学习方法虽然寻找领域不变的特征,但它们往往依赖于特殊技巧,缺乏正式保证。数据增强方法通过合成样本丰富模型表示,其性能与表示学习方法相当或更优。我们提出了LangDAug,这是一种新型的针对二维医学图像分割的多源域泛化朗维数据增强方法。LangDAug利用通过对比散度训练的能量模型(EBMs),在源域之间进行遍历,通过朗维动力学生成中间样本。理论分析表明,LangDAug产生正则化效应,对于广义线性模型(GLMs),它通过数据流形的固有维度上限Rademacher复杂性。在眼底分割和二维MRI前列腺分割基准测试的大量实验中,我们证明了LangDAug优于最新的领域泛化方法,并能有效地补充现有的领域随机化方法。我们的方法的代码库可在https://github.com/backpropagator/LangDAug找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨医学图像分割模型在不同领域中的泛化问题,提出一种名为LangDAug的新型数据增强方法,用于多源领域泛化。该方法基于能量基模型(EBMs)和Langevin动态,通过对比分歧在源领域之间遍历,生成中间样本。理论分析显示,LangDAug具有正则化效果,且对于广义线性模型(GLMs),它能通过数据流的内在维度上限Rademacher复杂性。在基金分割和二维磁共振成像前列腺分割基准测试上的实验表明,LangDAug优于最新的领域泛化方法,并能有效地补充现有的领域随机化方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割模型在不同领域的泛化是一个挑战。
- Domain Generalization (DG)方法通过表示学习或数据增强(DAug)来克服这一问题。
- LangDAug是一种新型的数据增强方法,用于多源领域泛化在医学图像分割中。
- LangDAug利用能量基模型(EBMs)和Langevin动态生成中间样本。
- 理论分析显示LangDAug具有正则化效果,并能限制Rademacher复杂性。
- 实验表明,LangDAug在基金分割和二维磁共振成像前列腺分割基准测试上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

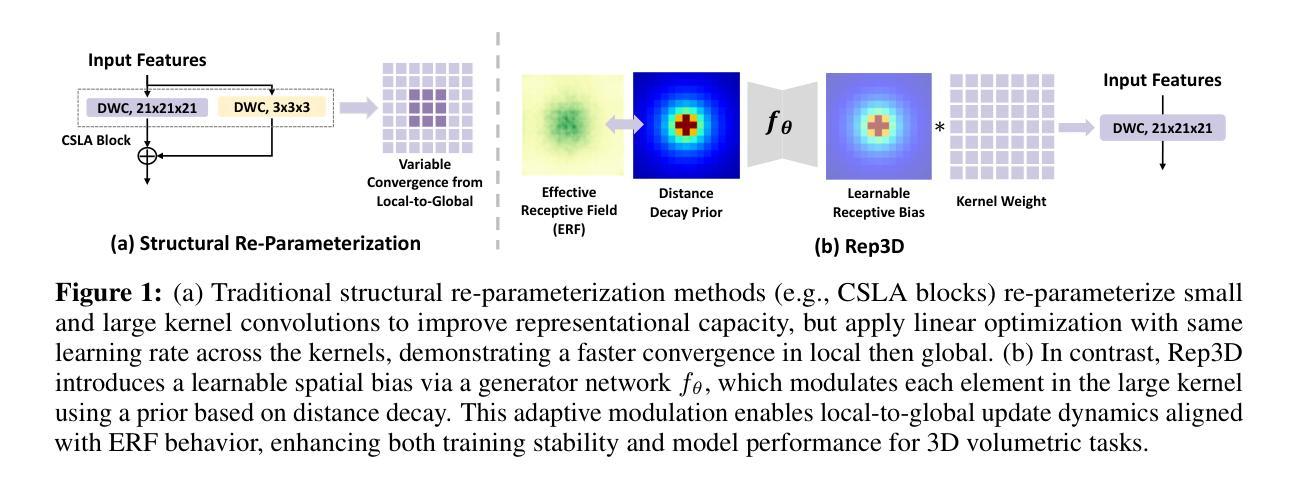
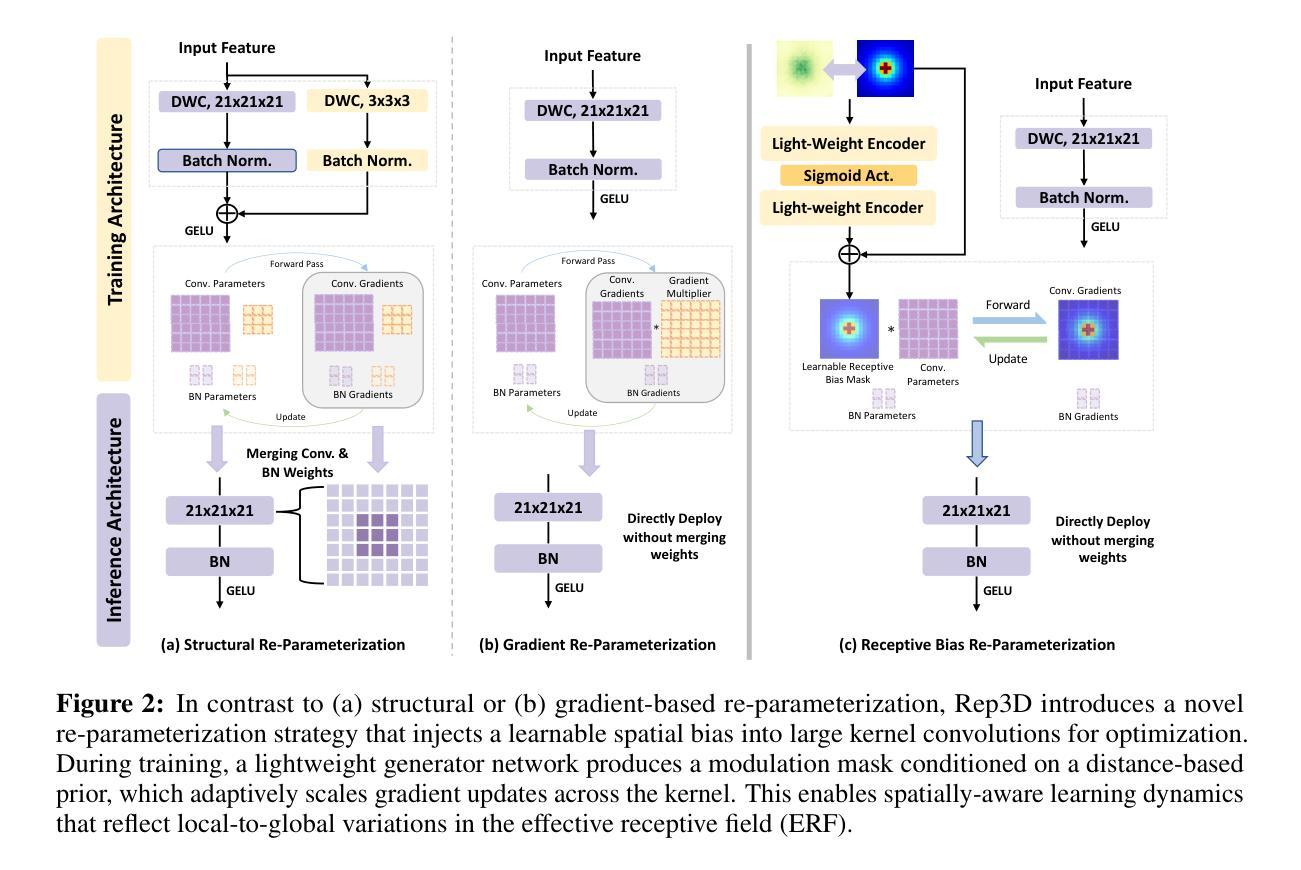
Rep3D: Re-parameterize Large 3D Kernels with Low-Rank Receptive Modeling for Medical Imaging
Authors:Ho Hin Lee, Quan Liu, Shunxing Bao, Yuankai Huo, Bennett A. Landman
In contrast to vision transformers, which model long-range dependencies through global self-attention, large kernel convolutions provide a more efficient and scalable alternative, particularly in high-resolution 3D volumetric settings. However, naively increasing kernel size often leads to optimization instability and degradation in performance. Motivated by the spatial bias observed in effective receptive fields (ERFs), we hypothesize that different kernel elements converge at variable rates during training. To support this, we derive a theoretical connection between element-wise gradients and first-order optimization, showing that structurally re-parameterized convolution blocks inherently induce spatially varying learning rates. Building on this insight, we introduce Rep3D, a 3D convolutional framework that incorporates a learnable spatial prior into large kernel training. A lightweight two-stage modulation network generates a receptive-biased scaling mask, adaptively re-weighting kernel updates and enabling local-to-global convergence behavior. Rep3D adopts a plain encoder design with large depthwise convolutions, avoiding the architectural complexity of multi-branch compositions. We evaluate Rep3D on five challenging 3D segmentation benchmarks and demonstrate consistent improvements over state-of-the-art baselines, including transformer-based and fixed-prior re-parameterization methods. By unifying spatial inductive bias with optimization-aware learning, Rep3D offers an interpretable, and scalable solution for 3D medical image analysis. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/leeh43/Rep3D.
与通过全局自注意力机制建模长程依赖关系的视觉变压器相比,大内核卷积提供了一种更高效且可扩展的替代方案,特别是在高分辨率的3D体积环境中。然而,盲目地增加内核大小往往会导致优化不稳定和性能下降。受有效感受野(ERFs)中观察到的空间偏置的启发,我们假设在训练过程中,不同的内核元素会以不同的速率收敛。为了支持这一点,我们推导出元素级梯度与一阶优化之间的理论联系,表明结构上重新参数化的卷积块固有地会诱导空间上变化的学习速率。基于这一见解,我们引入了Rep3D,这是一个融入可学习空间先验知识的大型内核训练中的3D卷积框架。一个轻量级的两阶段调制网络生成一个感受野偏向的缩放掩码,自适应地重新加权内核更新,并实现了从局部到全局的收敛行为。Rep3D采用简单的编码器设计,使用大型深度卷积,避免了多分支组合的架构复杂性。我们在五个具有挑战性的3D分割基准上对Rep3D进行了评估,证明了其相较于包括基于转换器和固定先验重参数化方法在内的最新基线具有持续的可改进性。通过将空间归纳偏见与优化感知学习相结合,Rep3D为3D医学图像分析提供了可解释且可扩展的解决方案。源代码可在https://github.com/leeh43/Rep3D获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
本文探讨了不同于模型长期依赖关系的视觉变压器,大内核卷积在高分辨率三维体积设置中的高效性和可扩展性替代方案。但单纯增加内核大小会导致优化不稳定和性能下降。研究提出一个理论联系元素梯度与一阶优化之间的观点,显示出重新参数化的卷积块固有地引发空间变化学习率。基于此,引入Rep3D框架,该框架将可学习的空间先验知识融入大内核训练中。通过生成具有感受野偏好的缩放掩膜,自适应地重新加权内核更新,实现局部到全局的收敛行为。在五个挑战性的三维分割基准测试中评估了Rep3D,证明了其在最新基准上的持续改进,包括基于转换器和固定先验重新参数化方法。Rep3D通过将空间归纳偏置与具有意识的学习统一起来,为三维医学图像分析提供了一种可解释和可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 大内核卷积在高分辨率三维医学图像分析中提供了高效和可扩展的替代方案。
- 单纯增加内核大小可能导致优化不稳定和性能下降。
- 提出了元素梯度与一阶优化之间的理论联系,揭示了空间变化学习率的内在机制。
- 引入了Rep3D框架,该框架结合了大内核训练中的可学习空间先验知识。
- 通过生成具有感受野偏好的缩放掩膜,自适应地重新加权内核更新。
- Rep3D在多个基准测试中表现出对最新技术的持续改进。
点此查看论文截图

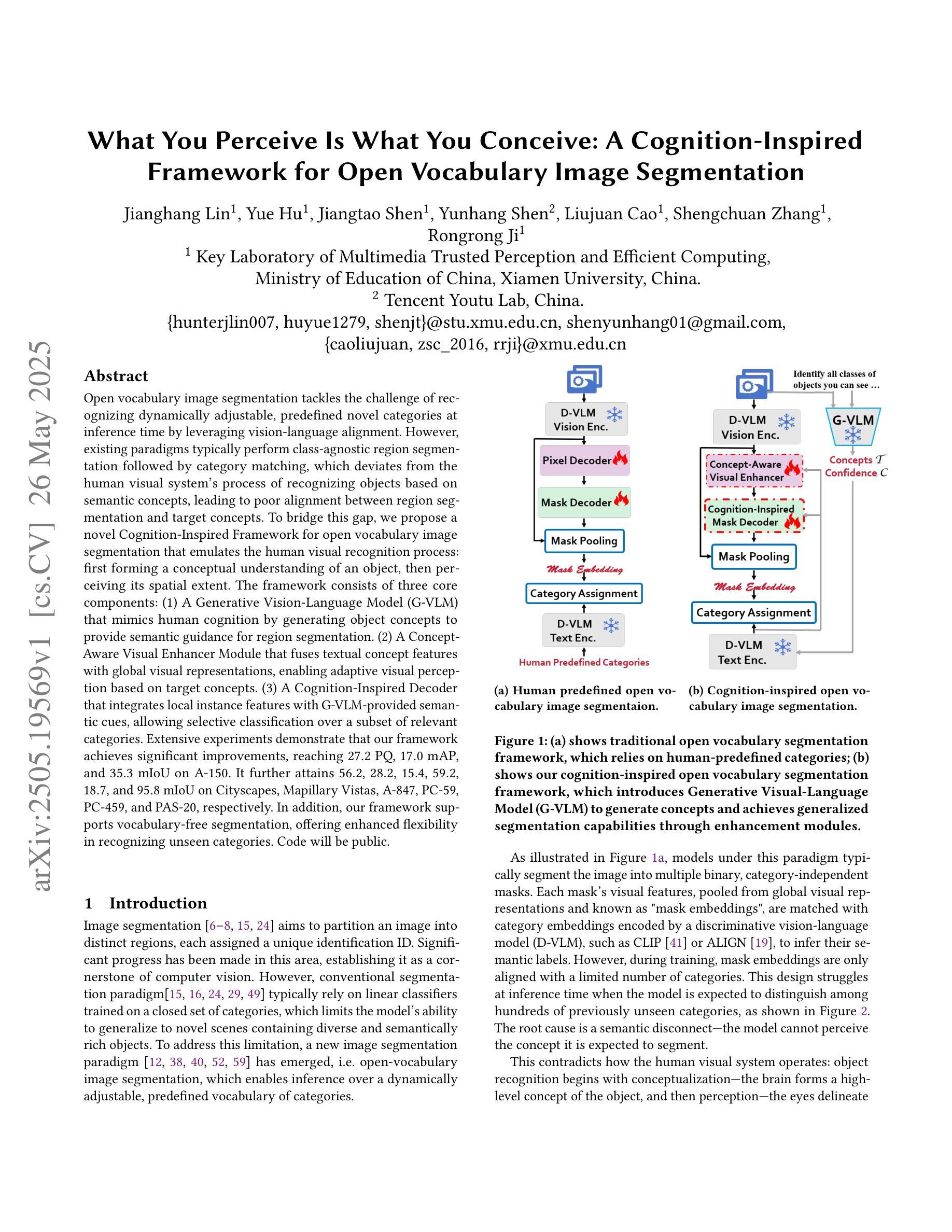
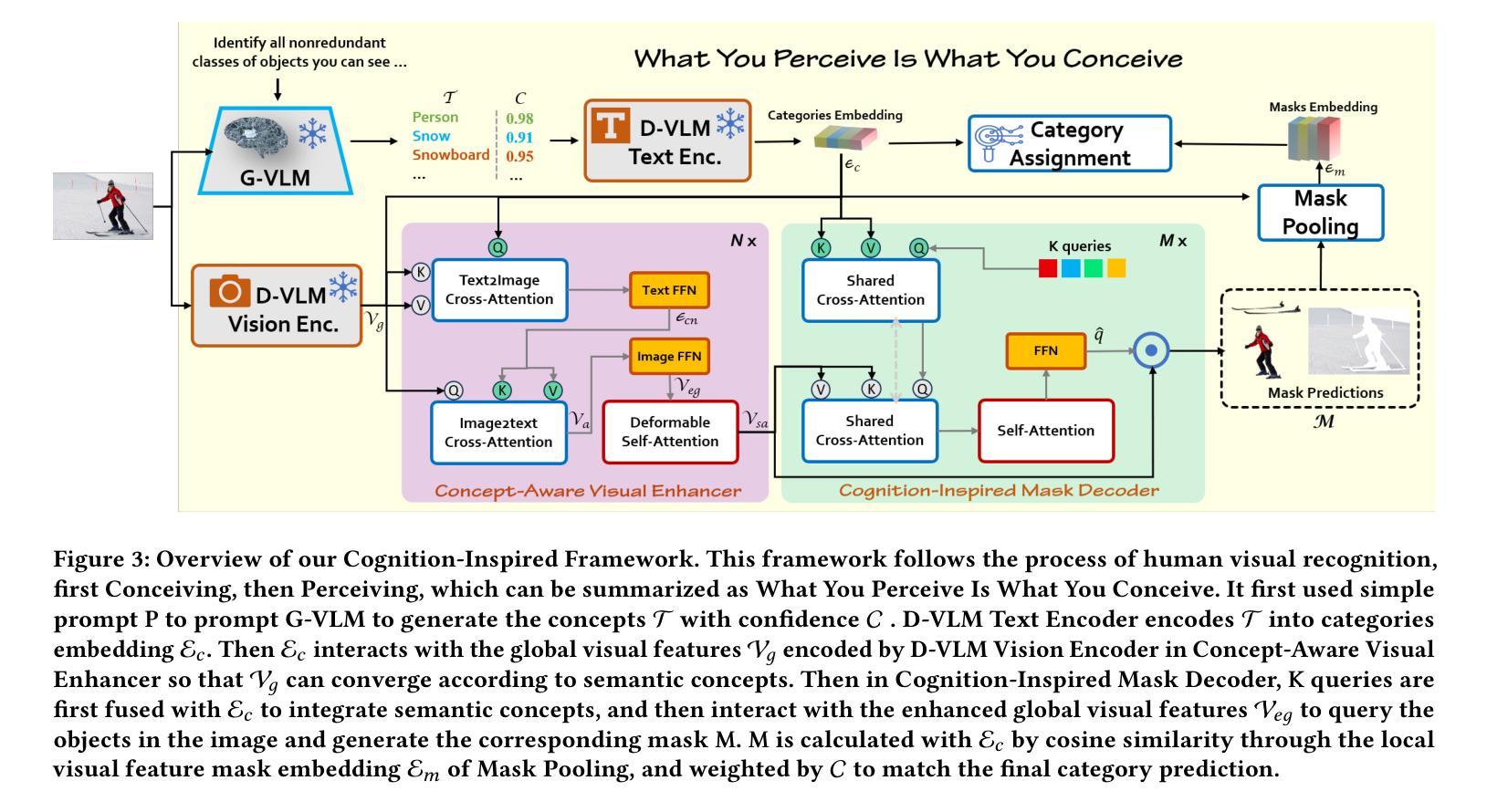
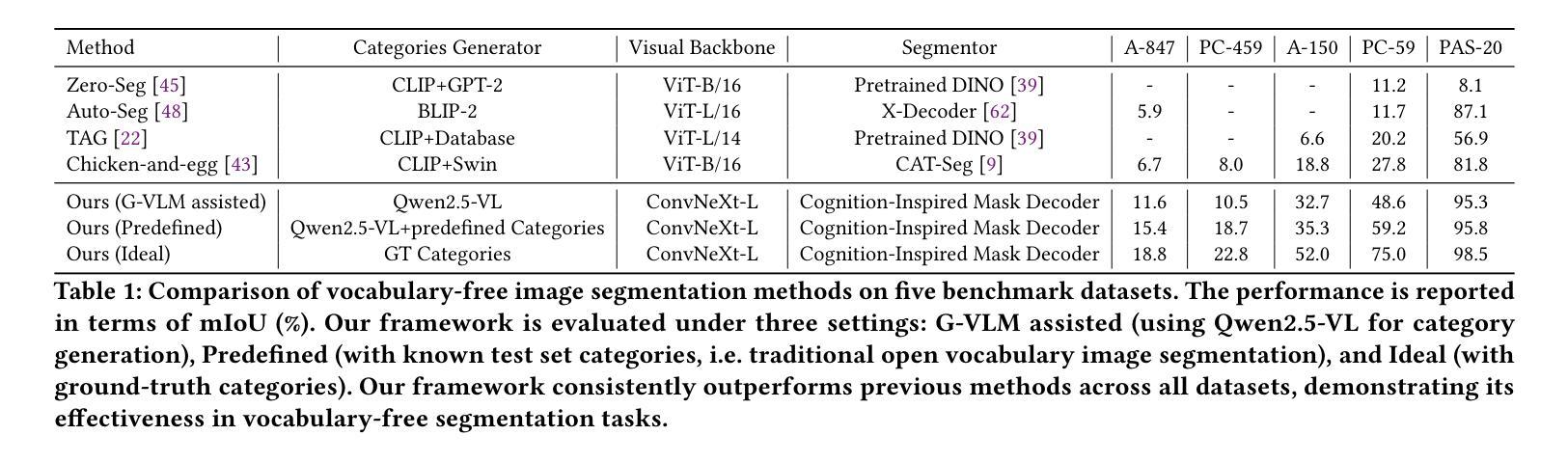
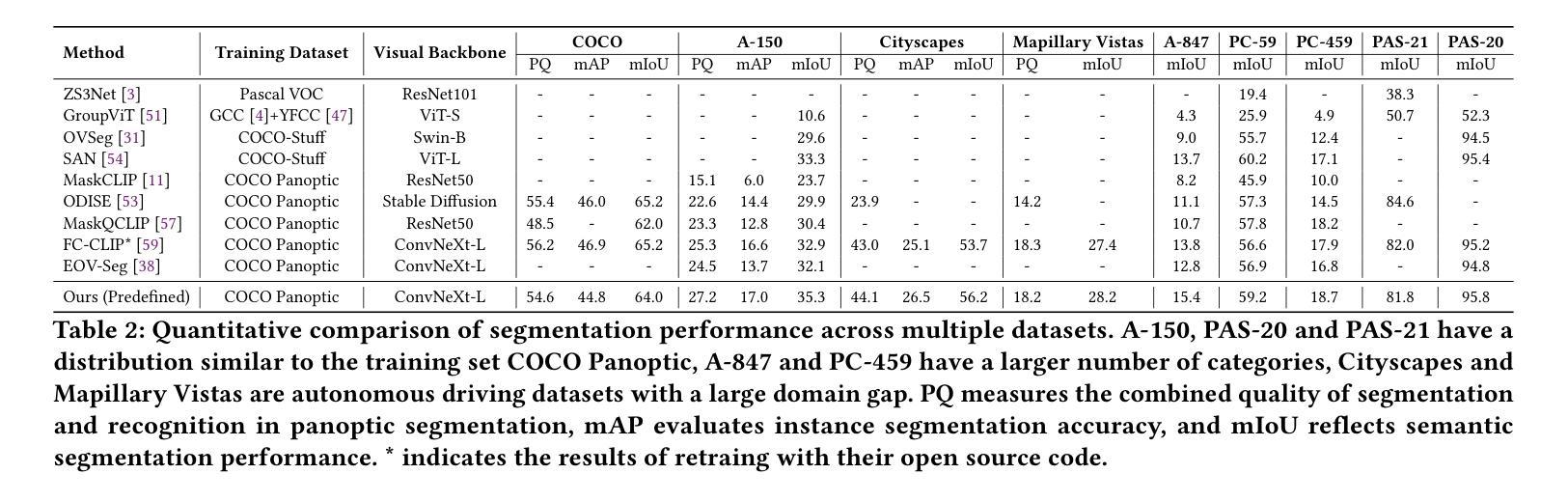
What You Perceive Is What You Conceive: A Cognition-Inspired Framework for Open Vocabulary Image Segmentation
Authors:Jianghang Lin, Yue Hu, Jiangtao Shen, Yunhang Shen, Liujuan Cao, Shengchuan Zhang, Rongrong Ji
Open vocabulary image segmentation tackles the challenge of recognizing dynamically adjustable, predefined novel categories at inference time by leveraging vision-language alignment. However, existing paradigms typically perform class-agnostic region segmentation followed by category matching, which deviates from the human visual system’s process of recognizing objects based on semantic concepts, leading to poor alignment between region segmentation and target concepts. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel Cognition-Inspired Framework for open vocabulary image segmentation that emulates the human visual recognition process: first forming a conceptual understanding of an object, then perceiving its spatial extent. The framework consists of three core components: (1) A Generative Vision-Language Model (G-VLM) that mimics human cognition by generating object concepts to provide semantic guidance for region segmentation. (2) A Concept-Aware Visual Enhancer Module that fuses textual concept features with global visual representations, enabling adaptive visual perception based on target concepts. (3) A Cognition-Inspired Decoder that integrates local instance features with G-VLM-provided semantic cues, allowing selective classification over a subset of relevant categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves significant improvements, reaching $27.2$ PQ, $17.0$ mAP, and $35.3$ mIoU on A-150. It further attains $56.2$, $28.2$, $15.4$, $59.2$, $18.7$, and $95.8$ mIoU on Cityscapes, Mapillary Vistas, A-847, PC-59, PC-459, and PAS-20, respectively. In addition, our framework supports vocabulary-free segmentation, offering enhanced flexibility in recognizing unseen categories. Code will be public.
开放词汇图像分割通过利用视觉语言对齐来解决在推理时识别动态可调整、预先定义的新类别的挑战。然而,现有的范式通常执行类别无关的区域分割,然后进行类别匹配,这偏离了人类视觉系统基于语义概念识别物体的过程,导致区域分割与目标概念之间的对齐不佳。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一种模拟人类视觉识别过程的开放词汇图像分割的认知启发框架:首先形成对物体的概念理解,然后感知其空间范围。该框架由三个核心组件构成:(1)生成式视觉语言模型(G-VLM),通过生成对象概念来模拟人类认知,为区域分割提供语义指导。(2)概念感知视觉增强模块,将文本概念特征与全局视觉表示相融合,实现基于目标概念的自适应视觉感知。(3)认知启发解码器,它融合了局部实例特征与G-VLM提供的语义线索,允许在相关类别子集上进行选择性分类。大量实验表明,我们的框架实现了显著改进,在A-150上达到了27.2 PQ、17.0 mAP和35.3 mIoU。此外,它在Cityscapes、Mapillary Vistas、A-847、PC-59、PC-459和PAS-20上分别达到了56.2、28.2、15.4、59.2、18.7和95.8 mIoU。我们的框架还支持无词汇分割,为识别未见类别提供了更高的灵活性。代码将公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种认知启发框架,用于开放词汇图像分割,该框架模拟人类视觉识别过程。该框架包括生成式视觉语言模型、概念感知视觉增强器模块和认知启发解码器三个核心组件。实验结果证明了该框架在多个数据集上的显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇图像分割通过利用视觉语言对齐来识别动态可调整、预定义的未知类别。
- 现有方法通常进行类别无关的区域分割,然后进行类别匹配,这与人识别物体基于语义概念的视觉系统过程不符,导致区域分割与目标概念之间的对齐不佳。
- 提出的认知启发框架模拟人类视觉识别过程,包括生成物体概念、感知物体空间范围的步骤。
- 框架包括三个核心组件:生成式视觉语言模型、概念感知视觉增强器模块和认知启发解码器。这些组件通过融合文本概念特征和全局视觉表示,实现基于目标概念的自适应视觉感知,并整合局部实例特征与语义线索进行选择性分类。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在多个数据集上取得了显著改进,包括A-150、Cityscapes、Mapillary Vistas等。
- 该框架支持词汇无关的分割,提高了识别未见类别的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图
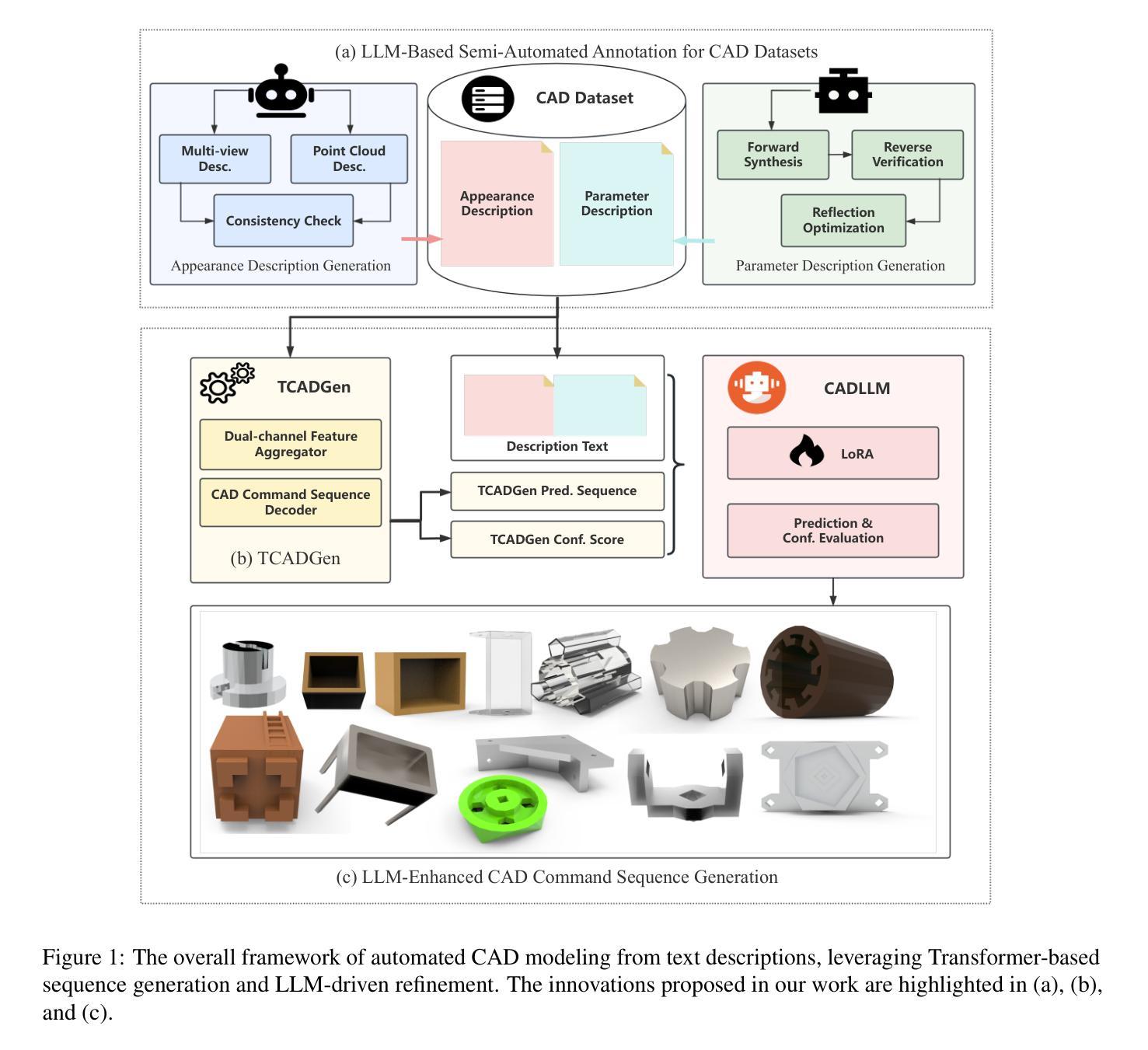
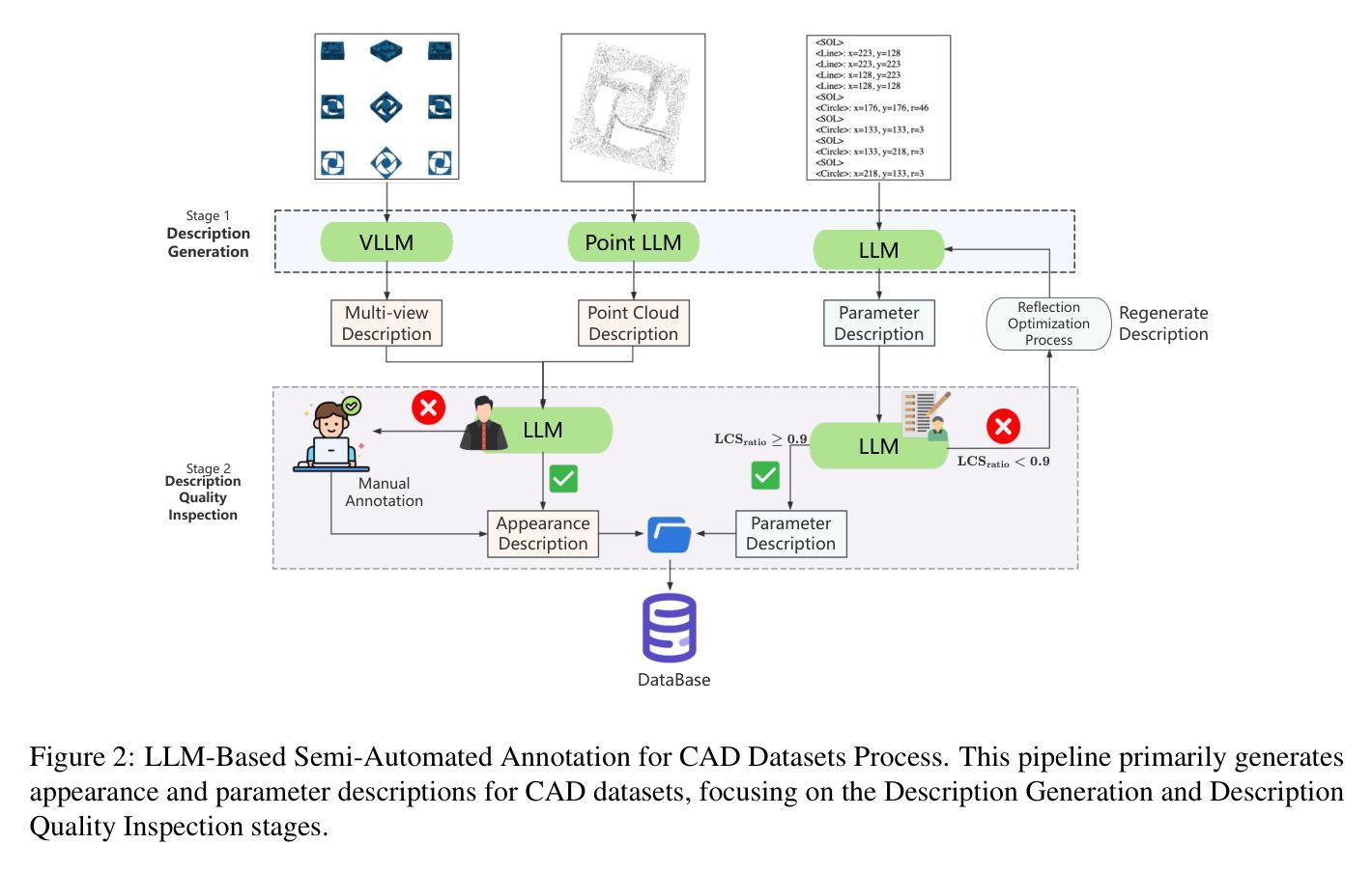
Automated CAD Modeling Sequence Generation from Text Descriptions via Transformer-Based Large Language Models
Authors:Jianxing Liao, Junyan Xu, Yatao Sun, Maowen Tang, Sicheng He, Jingxian Liao, Shui Yu, Yun Li, Hongguan Xiao
Designing complex computer-aided design (CAD) models is often time-consuming due to challenges such as computational inefficiency and the difficulty of generating precise models. We propose a novel language-guided framework for industrial design automation to address these issues, integrating large language models (LLMs) with computer-automated design (CAutoD).Through this framework, CAD models are automatically generated from parameters and appearance descriptions, supporting the automation of design tasks during the detailed CAD design phase. Our approach introduces three key innovations: (1) a semi-automated data annotation pipeline that leverages LLMs and vision-language large models (VLLMs) to generate high-quality parameters and appearance descriptions; (2) a Transformer-based CAD generator (TCADGen) that predicts modeling sequences via dual-channel feature aggregation; (3) an enhanced CAD modeling generation model, called CADLLM, that is designed to refine the generated sequences by incorporating the confidence scores from TCADGen. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms traditional methods in both accuracy and efficiency, providing a powerful tool for automating industrial workflows and generating complex CAD models from textual prompts. The code is available at https://jianxliao.github.io/cadllm-page/
设计复杂的计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型通常很耗时,因为存在计算效率低下和难以生成精确模型等挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于工业自动化设计的新型语言引导框架,该框架将大型语言模型(LLM)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD)相结合。通过此框架,CAD模型可以根据参数和外观描述自动生成,支持详细CAD设计阶段的自动化设计任务。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:(1)一种半自动数据注释管道,利用LLM和视觉语言大型模型(VLLM)生成高质量参数和外观描述;(2)基于Transformer的CAD生成器(TCADGen),通过双通道特征聚合预测建模序列;(3)一种增强的CAD建模生成模型,称为CADLLM,旨在通过结合TCADGen的信心分数来优化生成的序列。实验结果表明,该方法在准确性和效率方面都优于传统方法,为自动化工业工作流程和根据文本提示生成复杂的CAD模型提供了强大的工具。相关代码可在[https://jianxliao.github.io/cadllm-page/]找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新型的语言引导工业设计自动化框架,它结合了大型语言模型(LLMs)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD)。该框架能够自动从参数和外观描述生成CAD模型,支持详细设计阶段的设计任务自动化。其三大创新点包括:半自动数据标注管道、基于Transformer的CAD生成器(TCADGen)以及增强的CAD建模生成模型CADLLM。实验结果证明,该方法在准确性和效率上均优于传统方法,为自动化工业流程和从文本提示生成复杂CAD模型提供了强大工具。
Key Takeaways
- 该框架整合了大型语言模型(LLMs)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD),提高了设计效率和精度。
- 采用半自动数据标注管道,利用LLMs和视觉语言大型模型(VLLMs)生成高质量参数和外观描述。
- TCADGen基于Transformer的CAD生成器能通过双通道特征聚合预测建模序列。
- CADLLM模型用于优化生成的序列,通过结合TCADGen的信心分数来完善CAD建模生成。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在准确度和效率方面均优于传统方法。
- 该框架为自动化工业流程提供了有力支持,能够从文本提示生成复杂的CAD模型。
点此查看论文截图

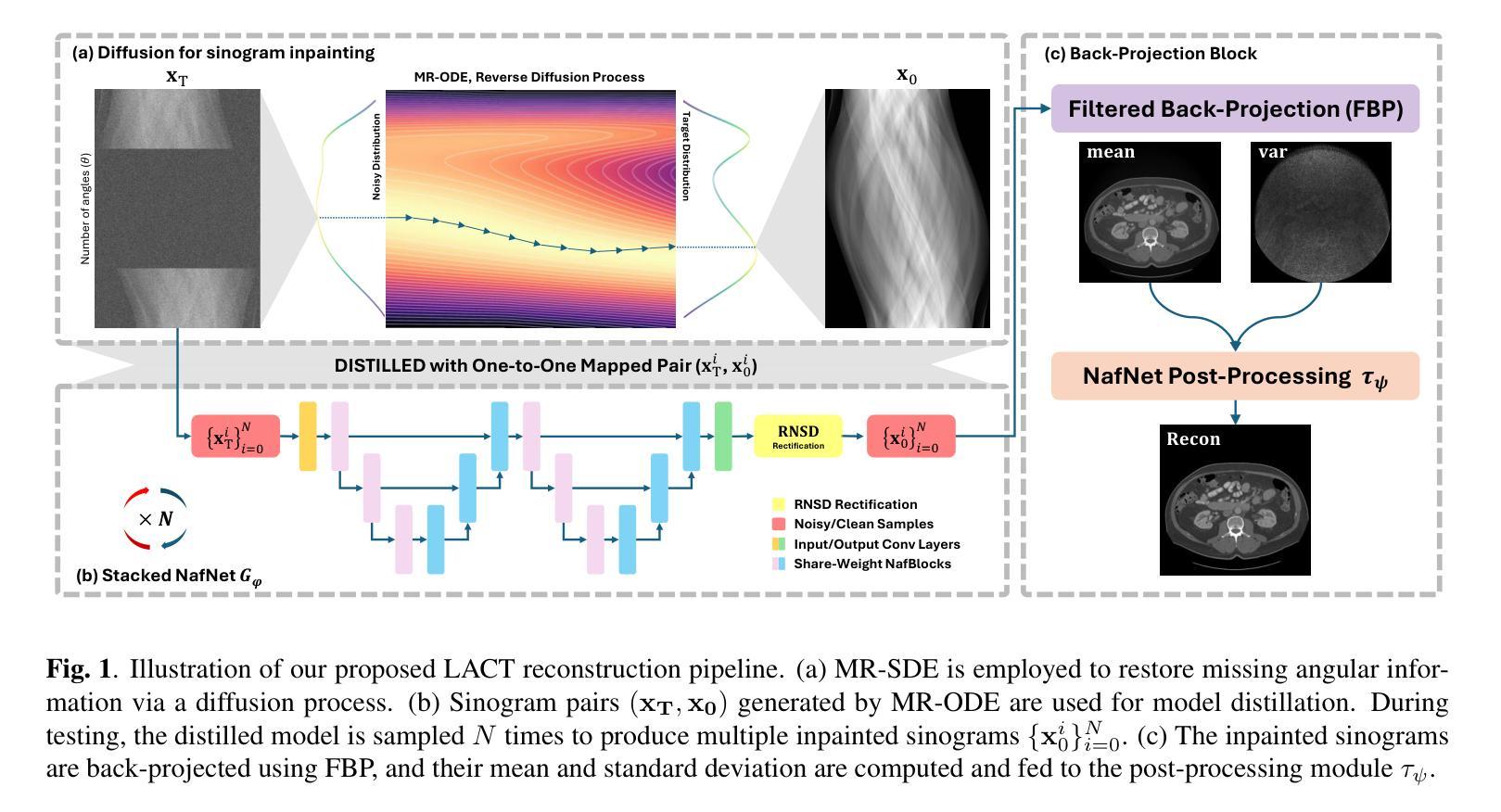
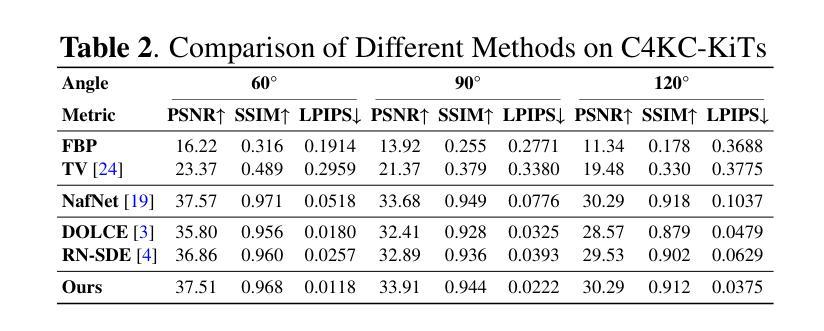
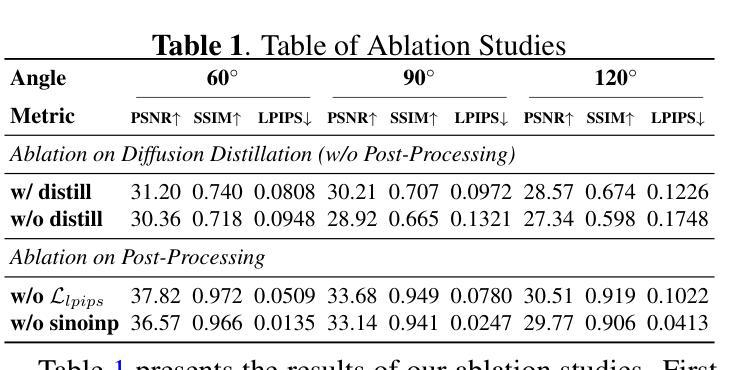
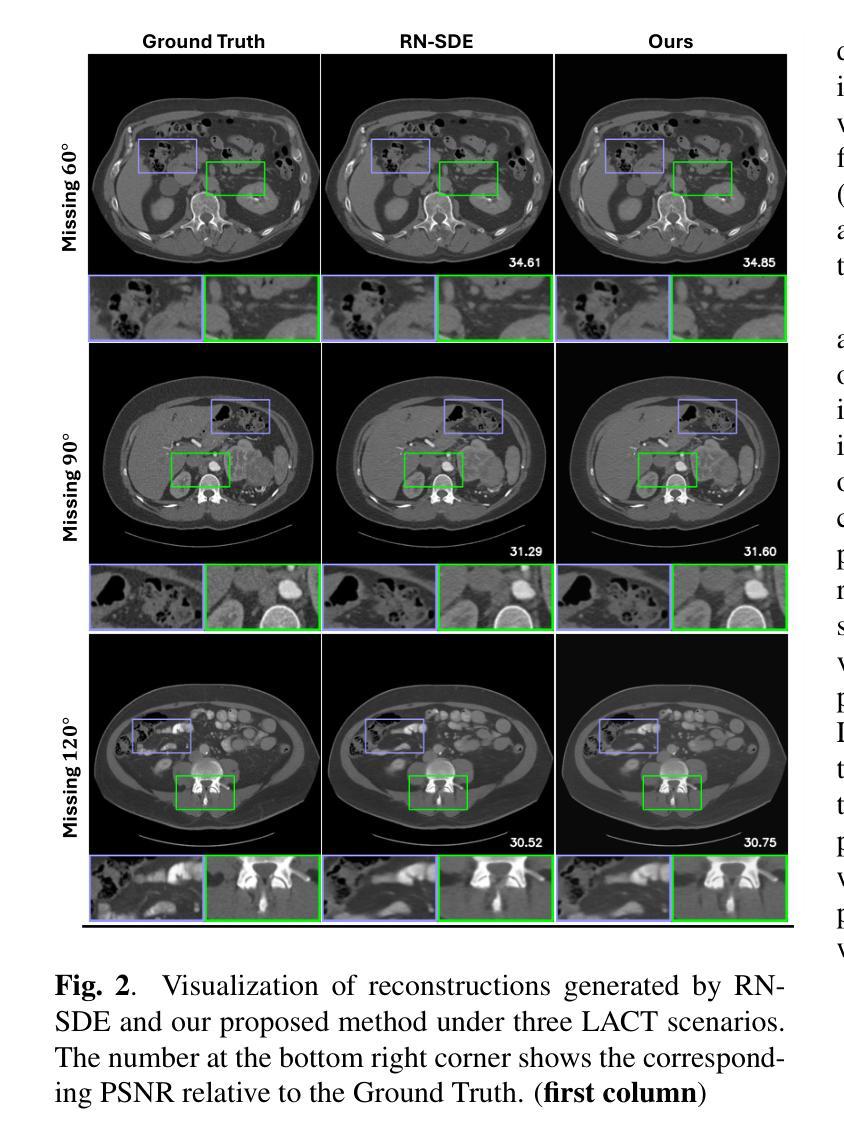
Advancing Limited-Angle CT Reconstruction Through Diffusion-Based Sinogram Completion
Authors:Jiaqi Guo, Santiago Lopez-Tapia, Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
Limited Angle Computed Tomography (LACT) often faces significant challenges due to missing angular information. Unlike previous methods that operate in the image domain, we propose a new method that focuses on sinogram inpainting. We leverage MR-SDEs, a variant of diffusion models that characterize the diffusion process with mean-reverting stochastic differential equations, to fill in missing angular data at the projection level. Furthermore, by combining distillation with constraining the output of the model using the pseudo-inverse of the inpainting matrix, the diffusion process is accelerated and done in a step, enabling efficient and accurate sinogram completion. A subsequent post-processing module back-projects the inpainted sinogram into the image domain and further refines the reconstruction, effectively suppressing artifacts while preserving critical structural details. Quantitative experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both perceptual and fidelity quality, offering a promising solution for LACT reconstruction in scientific and clinical applications.
有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)由于缺少角度信息而面临重大挑战。不同于之前在图像域操作的方法,我们提出了一种新方法,该方法主要关注sinogram的填充。我们利用MR-SDEs(一种用平均回归随机微分方程描述扩散过程的扩散模型的变体)在投影层面填充缺失的角度数据。此外,通过结合蒸馏技术并使用填充矩阵的伪逆约束模型的输出,可以加速扩散过程并在一步内完成,从而实现高效且准确的sinogram完成。随后的后处理模块将填充的sinogram反向投影到图像域,并进一步优化重建结果,有效地抑制伪影的同时保留关键的结构细节。定量实验结果表明,所提出的方法在感知和保真质量方面都达到了最新技术水平,为科学和临床应用中LACT重建提供了有前景的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (Oral)
Summary
本文提出了一种基于MR-SDEs扩散模型的新方法,专注于辛格拉姆插值,以填充有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)中的缺失角度数据。结合蒸馏技术和使用补全矩阵的伪逆约束模型输出,加速了扩散过程,实现了高效且准确的辛格拉姆补全。后处理模块将补全的辛格拉姆投影回图像域,进一步改进重建效果,有效抑制伪影同时保留关键结构细节。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的基于MR-SDEs扩散模型的方法,专注于辛格拉姆插值以解决LACT中的缺失角度信息问题。
- 在投影级别填充缺失的角度数据,结合蒸馏技术加速扩散过程。
- 使用约束模型输出来提高辛格拉姆补全的准确性。
- 后处理模块能够将补全的辛格拉姆投影回图像域,有效抑制伪影并保留关键结构细节。
- 定量实验结果表明,该方法在感知和保真质量方面达到最新水平,为科学和临床应用中的LACT重建提供了有前途的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

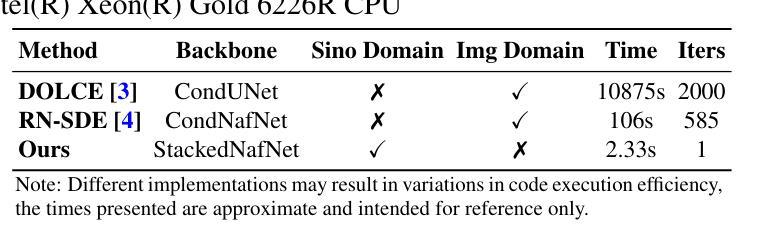
PolyPose: Localizing Deformable Anatomy in 3D from Sparse 2D X-ray Images using Polyrigid Transforms
Authors:Vivek Gopalakrishnan, Neel Dey, Polina Golland
Determining the 3D pose of a patient from a limited set of 2D X-ray images is a critical task in interventional settings. While preoperative volumetric imaging (e.g., CT and MRI) provides precise 3D localization and visualization of anatomical targets, these modalities cannot be acquired during procedures, where fast 2D imaging (X-ray) is used instead. To integrate volumetric guidance into intraoperative procedures, we present PolyPose, a simple and robust method for deformable 2D/3D registration. PolyPose parameterizes complex 3D deformation fields as a composition of rigid transforms, leveraging the biological constraint that individual bones do not bend in typical motion. Unlike existing methods that either assume no inter-joint movement or fail outright in this under-determined setting, our polyrigid formulation enforces anatomically plausible priors that respect the piecewise rigid nature of human movement. This approach eliminates the need for expensive deformation regularizers that require patient- and procedure-specific hyperparameter optimization. Across extensive experiments on diverse datasets from orthopedic surgery and radiotherapy, we show that this strong inductive bias enables PolyPose to successfully align the patient’s preoperative volume to as few as two X-ray images, thereby providing crucial 3D guidance in challenging sparse-view and limited-angle settings where current registration methods fail.
在介入环境中,从有限的2D X射线图像集中确定患者的3D姿势是一项关键任务。虽然术前体积成像(例如CT和MRI)可以提供精确的3D定位和解剖目标的可视化,但这些模式不能在手术过程中获取,此时使用的是快速的2D成像(X射线)。为了将体积引导集成到术中程序中,我们提出了PolyPose,这是一种简单而稳健的可变形2D/3D注册方法。PolyPose将复杂的3D变形场参数化为刚体变换的组合,利用个体骨骼在典型运动中的弯曲约束。与现有的方法不同,这些方法要么假设关节之间没有运动,要么在这个未知设定的环境下彻底失败,我们的多刚体公式强制采用符合人体解剖结构的先验知识,尊重人体的分段刚性运动特性。这种方法消除了昂贵的变形正则化器,这些正则化器需要进行患者和手术特定的超参数优化。在骨科手术和放射治疗等不同数据集的大量实验中,我们证明了这种强大的归纳偏见使PolyPose能够将患者的术前体积成功对齐到仅两张X射线图像上,从而在具有挑战性的稀疏视图和有限角度设置下为当前的注册方法提供关键的3D指导,而这些情况下当前注册方法往往会失败。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PolyPose是一种简单而稳健的变形2D/3D注册方法,适用于介入手术中的体积引导。它通过参数化复杂的3D变形场为刚性变换的组合,利用个体骨骼在典型运动中的刚性约束,解决了在有限2D X射线图像下患者3D姿态确定的关键问题。该方法在多样化的数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证,在当前的注册方法难以应对的挑战性稀疏视图和有限角度设置下,该方法能够成功地将患者的术前体积与仅两张X射线图像对齐,从而为手术提供关键的3D指导。
Key Takeaways
- PolyPose方法旨在解决在介入手术中通过有限的2D X射线图像确定患者3D姿态的难题。
- 它利用参数化的复杂3D变形场来实现变形过程的模拟。
- 该方法采用刚性变换的组合来表示变形场,符合人体骨骼在典型运动中的刚性约束。
- PolyPose通过引入解剖结构先验知识来约束人体分段刚性的运动特性,解决了现有方法的局限性。
- 该方法无需昂贵的变形正则化器,避免了针对特定患者和程序的超参数优化需求。
- 在骨科手术和放射治疗等不同数据集上的广泛实验验证了PolyPose的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
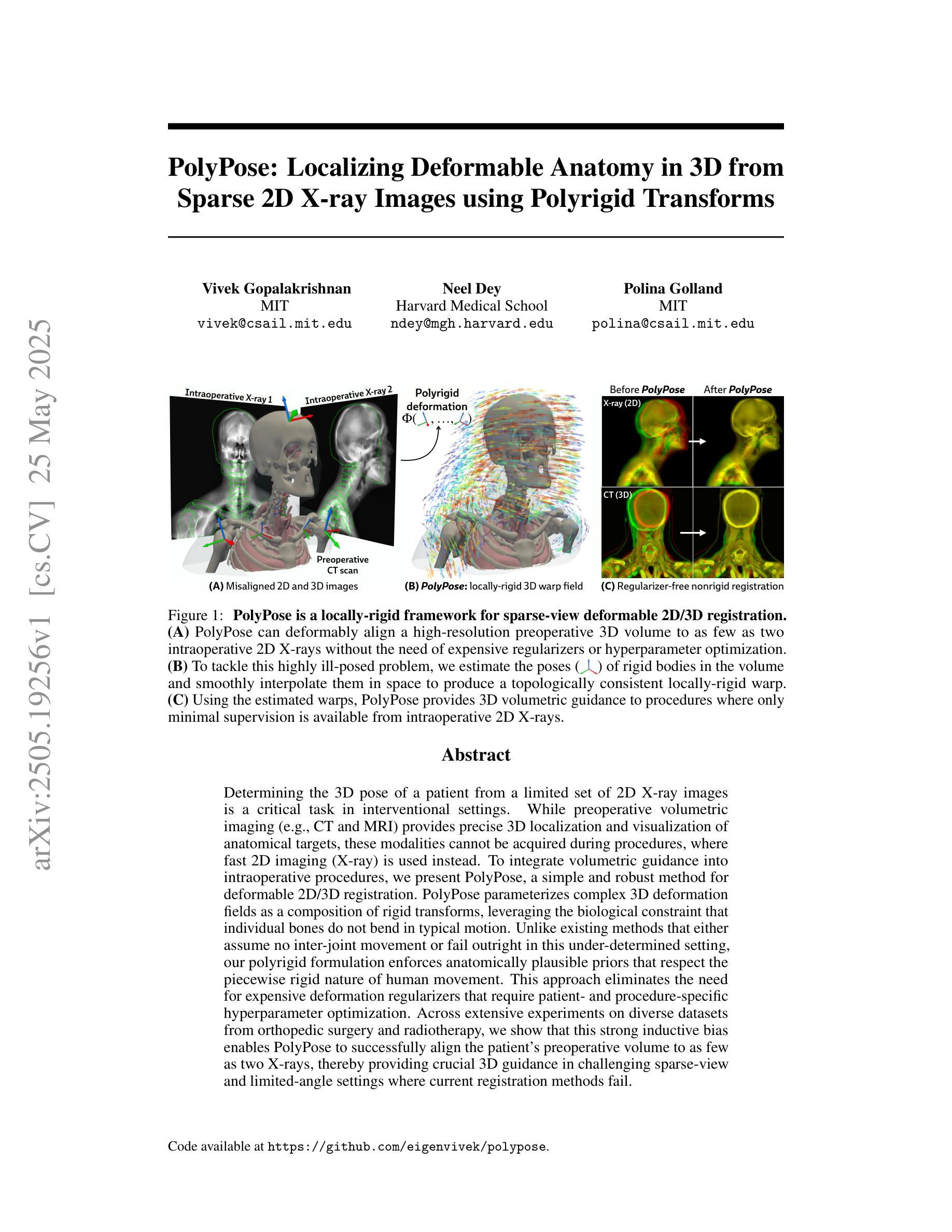
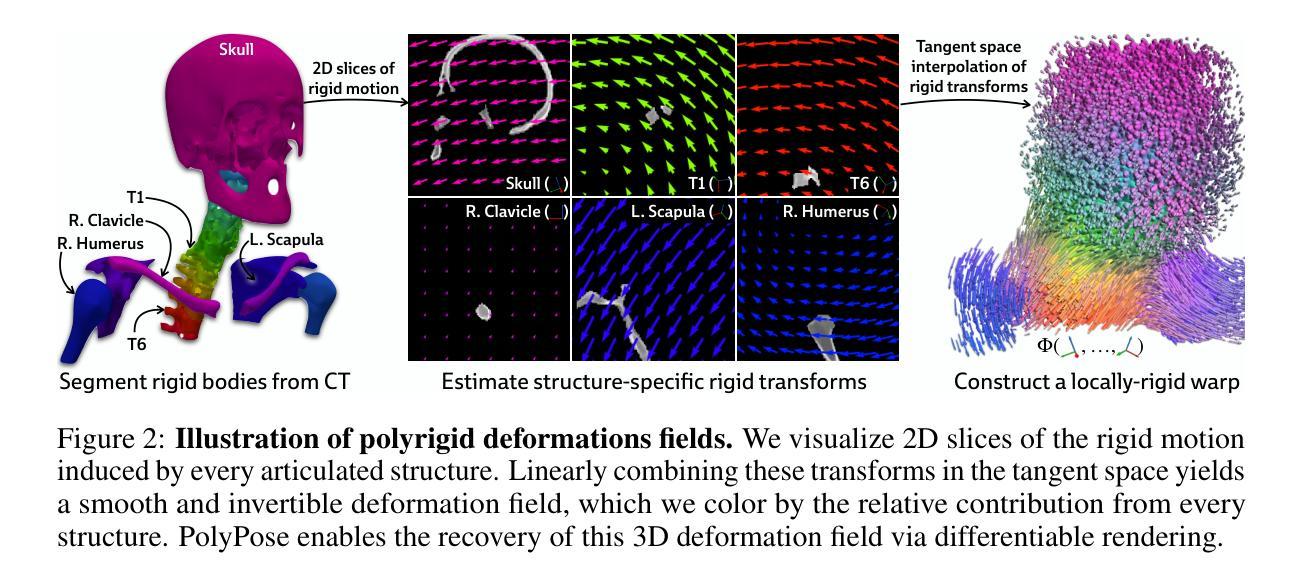
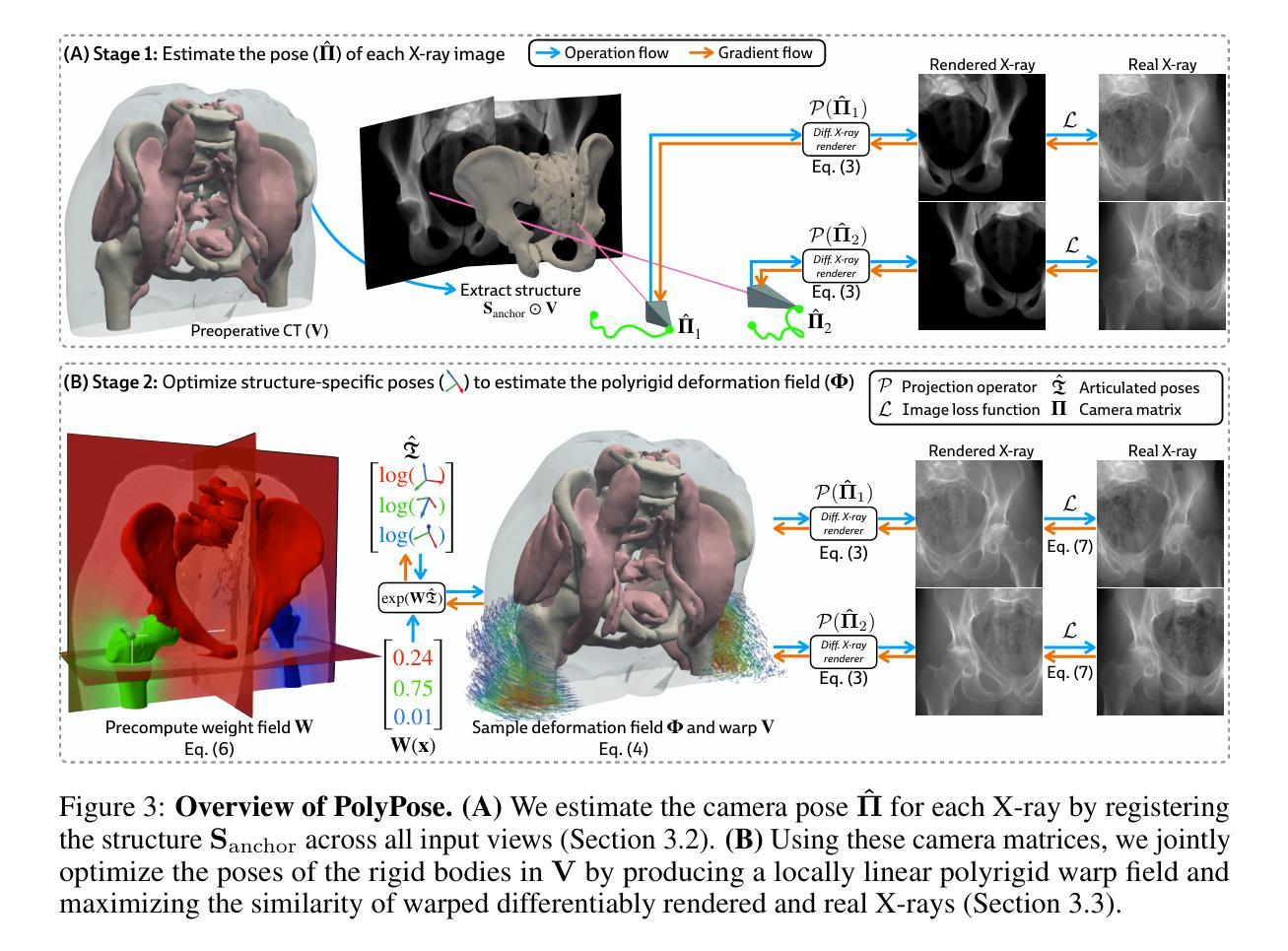
MedITok: A Unified Tokenizer for Medical Image Synthesis and Interpretation
Authors:Chenglong Ma, Yuanfeng Ji, Jin Ye, Zilong Li, Chenhui Wang, Junzhi Ning, Wei Li, Lihao Liu, Qiushan Guo, Tianbin Li, Junjun He, Hongming Shan
Advanced autoregressive models have reshaped multimodal AI. However, their transformative potential in medical imaging remains largely untapped due to the absence of a unified visual tokenizer – one capable of capturing fine-grained visual structures for faithful image reconstruction and realistic image synthesis, as well as rich semantics for accurate diagnosis and image interpretation. To this end, we present MedITok, the first unified tokenizer tailored for medical images, encoding both low-level structural details and high-level clinical semantics within a unified latent space. To balance these competing objectives, we introduce a novel two-stage training framework: a visual representation alignment stage that cold-starts the tokenizer reconstruction learning with a visual semantic constraint, followed by a textual semantic representation alignment stage that infuses detailed clinical semantics into the latent space. Trained on the meticulously collected large-scale dataset with over 30 million medical images and 2 million image-caption pairs, MedITok achieves state-of-the-art performance on more than 30 datasets across 9 imaging modalities and 4 different tasks. By providing a unified token space for autoregressive modeling, MedITok supports a wide range of tasks in clinical diagnostics and generative healthcare applications. Model and code will be made publicly available at: https://github.com/Masaaki-75/meditok.
先进的自回归模型已经重塑了多模态人工智能。然而,由于缺少统一的视觉分词器——一个能够捕捉精细粒度的视觉结构以实现忠实的图像重建和逼真的图像合成,以及丰富的语义以进行准确的诊断和图像解释的视觉分词器,其在医学成像中的变革潜力在很大程度上尚未被开发出来。为此,我们推出了MedITok,它是针对医学图像的首个统一分词器,在一个统一的潜在空间内编码低级别的结构细节和高级别的临床语义。为了平衡这些相互竞争的目标,我们引入了一种新型的两阶段训练框架:视觉表示对齐阶段,用视觉语义约束冷启动分词器重建学习,然后是文本语义表示对齐阶段,将详细的临床语义注入潜在空间。MedITok是在精心收集的大规模数据集上训练的,包含超过3000万张医学图像和200万张图像-字幕对。它在超过30个数据集、9种成像模态和4个不同任务上达到了最先进的性能。通过为自回归模型提供统一的标记空间,MedITok支持临床诊断和生成医疗应用的广泛任务。模型和代码将在https://github.com/Masaaki-75/meditok上公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
先进的自回归模型已经重塑了多模态人工智能,但在医学成像领域的应用潜力尚未得到充分发掘。为此,我们提出了MedITok,这是一款针对医学图像设计的统一分词器,可在统一的潜在空间中编码低级别的结构细节和高级别的临床语义。通过引入两阶段训练框架,实现视觉表示对齐和文本语义表示对齐,使MedITok在超过30个数据集、9种成像模态和4个不同任务上取得了最新技术水平的性能。MedITok为自回归模型提供了一个统一的令牌空间,支持临床诊断和生成医疗应用中的多种任务。
Key Takeaways
- MedITok是首个针对医学图像设计的统一分词器。
- 它能在统一的潜在空间中编码低级别的结构细节和高级别的临床语义。
- 通过两阶段训练框架实现视觉和文本语义表示的对齐。
- MedITok在多个数据集、不同成像模态和任务上取得了最新技术水平的性能。
- MedITok支持自回归模型在临床医学领域的应用,包括临床诊断和生成医疗应用。
- 该模型在大型数据集上进行训练,包含超过3000万张医学图像和200万张图像-字幕对。
点此查看论文截图

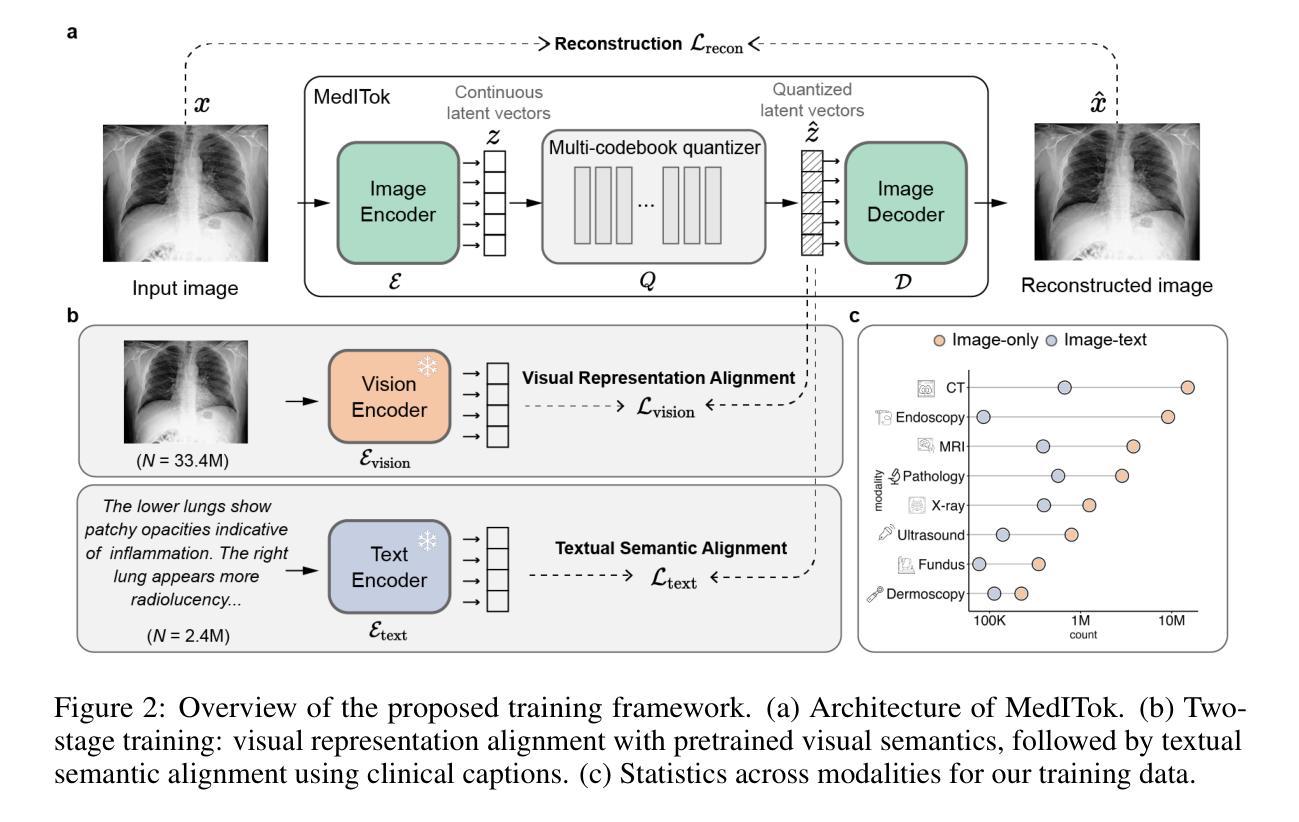
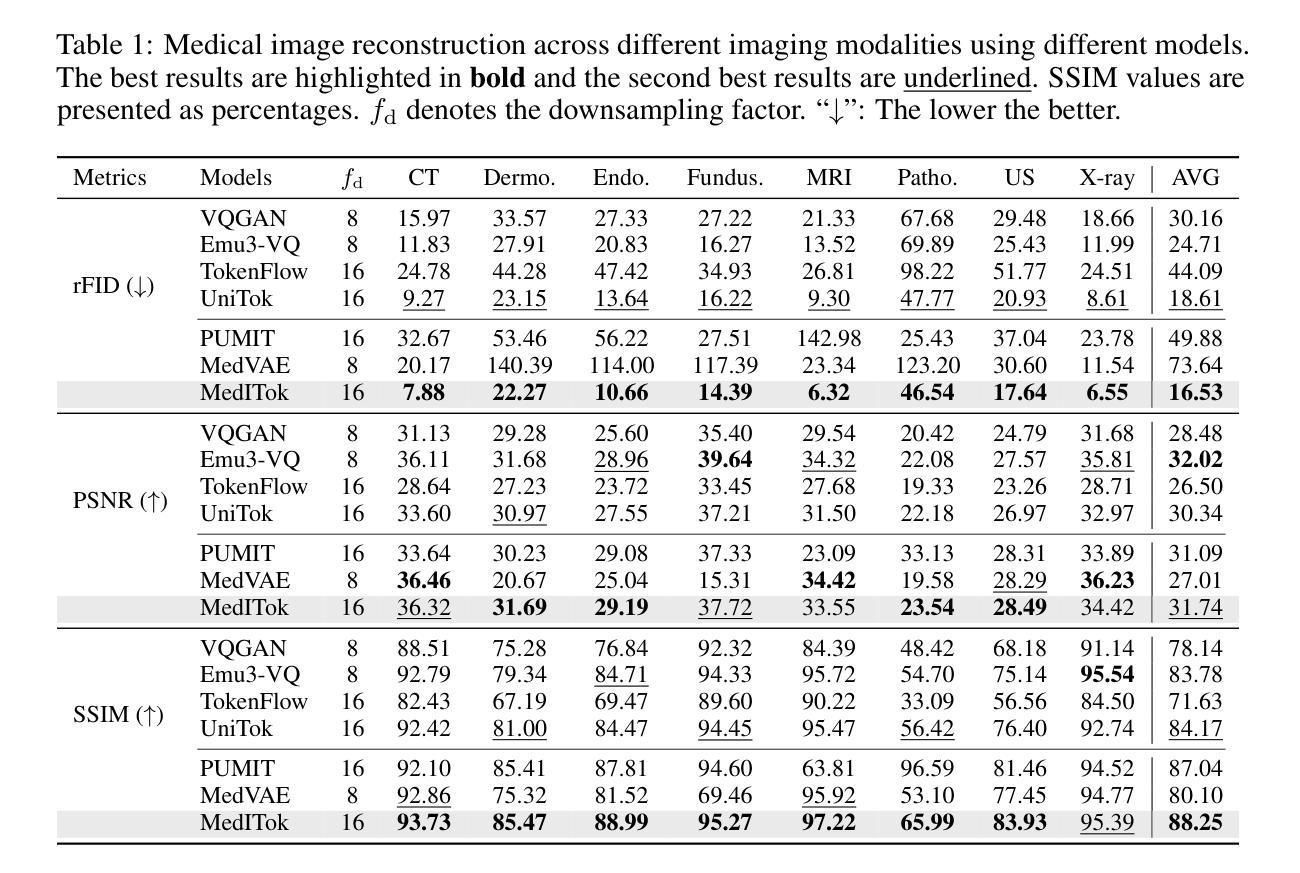
Domain and Task-Focused Example Selection for Data-Efficient Contrastive Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tyler Ward, Aaron Moseley, Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran
Segmentation is one of the most important tasks in the medical imaging pipeline as it influences a number of image-based decisions. To be effective, fully supervised segmentation approaches require large amounts of manually annotated training data. However, the pixel-level annotation process is expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone, hindering progress and making it challenging to perform effective segmentations. Therefore, models must learn efficiently from limited labeled data. Self-supervised learning (SSL), particularly contrastive learning via pre-training on unlabeled data and fine-tuning on limited annotations, can facilitate such limited labeled image segmentation. To this end, we propose a novel self-supervised contrastive learning framework for medical image segmentation, leveraging inherent relationships of different images, dubbed PolyCL. Without requiring any pixel-level annotations or unreasonable data augmentations, our PolyCL learns and transfers context-aware discriminant features useful for segmentation from an innovative surrogate, in a task-related manner. Additionally, we integrate the Segment Anything Model (SAM) into our framework in two novel ways: as a post-processing refinement module that improves the accuracy of predicted masks using bounding box prompts derived from coarse outputs, and as a propagation mechanism via SAM 2 that generates volumetric segmentations from a single annotated 2D slice. Experimental evaluations on three public computed tomography (CT) datasets demonstrate that PolyCL outperforms fully-supervised and self-supervised baselines in both low-data and cross-domain scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/tbwa233/PolyCL.
分割是医学影像处理流程中最重要的任务之一,因为它会影响许多基于影像的决策。为了取得良好效果,全监督分割方法需要大量手动标注的训练数据。然而,像素级标注过程成本高昂、耗时且易出错,阻碍了进度,使得进行有效分割变得具有挑战性。因此,模型必须高效地从小规模标记数据中学习。自监督学习(SSL)尤其是通过预训练无标签数据和微调有限标注数据的对比学习,可以促进这种有限标注图像分割。为此,我们提出了一种用于医学图像分割的新型自监督对比学习框架,利用不同图像之间的内在关系,称为PolyCL。我们的PolyCL不需要任何像素级标注或不合理的数据增强,而是以一种与任务相关的方式,从一个创新替代物中学习并转移有助于分割的上下文感知判别特征。此外,我们以两种新颖的方式将“分割任何事物模型”(SAM)集成到我们的框架中:作为后处理优化模块,利用来自粗略输出的边界框提示提高预测掩码的准确性;以及作为通过SAM 2的传播机制,从单个注释的2D切片生成体积分割。在三个公共计算机断层扫描(CT)数据集上的实验评估表明,PolyCL在低数据量和跨域场景中均优于全监督和自监督基线。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tbwa233/PolyCL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学图像分割是医学成像流程中最重要的任务之一,因为它影响许多基于图像的决定。然而,完全监督的分割方法需要大量手动注释的训练数据才能有效。但像素级注释过程既昂贵又耗时,还容易出错,这使得从有限标记数据中有效学习变得具有挑战性。自监督学习(SSL),特别是通过预训练无标签数据和微调有限注释进行对比学习,可以促进有限的标记图像分割。为此,我们提出了一种新型的自我监督对比学习框架,用于医学图像分割,该框架利用不同图像之间的内在关系,被称为PolyCL。PolyCL不需要任何像素级注释或不合理的数据增强,以任务相关的方式从创新的替代物中学习并转移上下文感知的判别特征,这些特征对于分割很有用。此外,我们以两种新颖的方式将Segment Anything Model(SAM)集成到我们的框架中:作为后处理细化模块,利用来自粗略输出的边界框提示提高预测掩码的准确性;作为SAM 2的传播机制,从单个注释的2D切片生成体积分割。在三个公共计算机断层扫描(CT)数据集上的实验评估表明,PolyCL在低数据和跨域场景中均优于完全监督和自监督的基线。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tbwa233/PolyCL上找到。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割是医学成像中的重要环节,对多种基于图像的决定产生影响。
- 完全监督的分割方法需要大量手动标注的训练数据,但这一过程既耗时又昂贵。
- 自监督学习(SSL)和对比学习在有限的标记数据上促进医学图像分割。
- PolyCL框架利用无标签数据的预训练和有限注释的微调,无需像素级注释或不合理的数据增强。
- PolyCL框架通过学习任务相关的方式从替代物中学习上下文感知的判别特征。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)以两种方式集成到PolyCL框架中:作为后处理细化模块和提高预测掩码准确性的传播机制。
点此查看论文截图

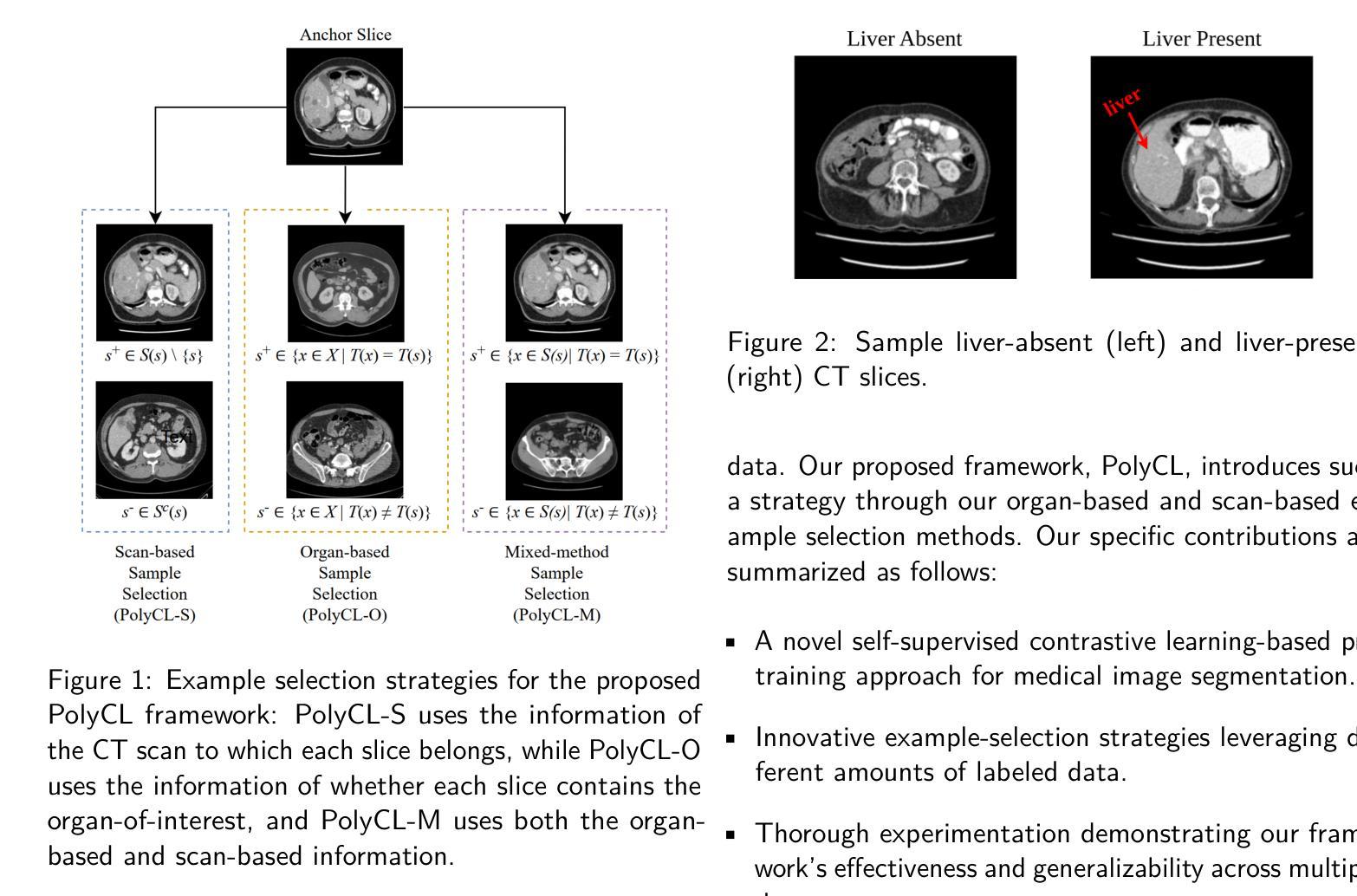
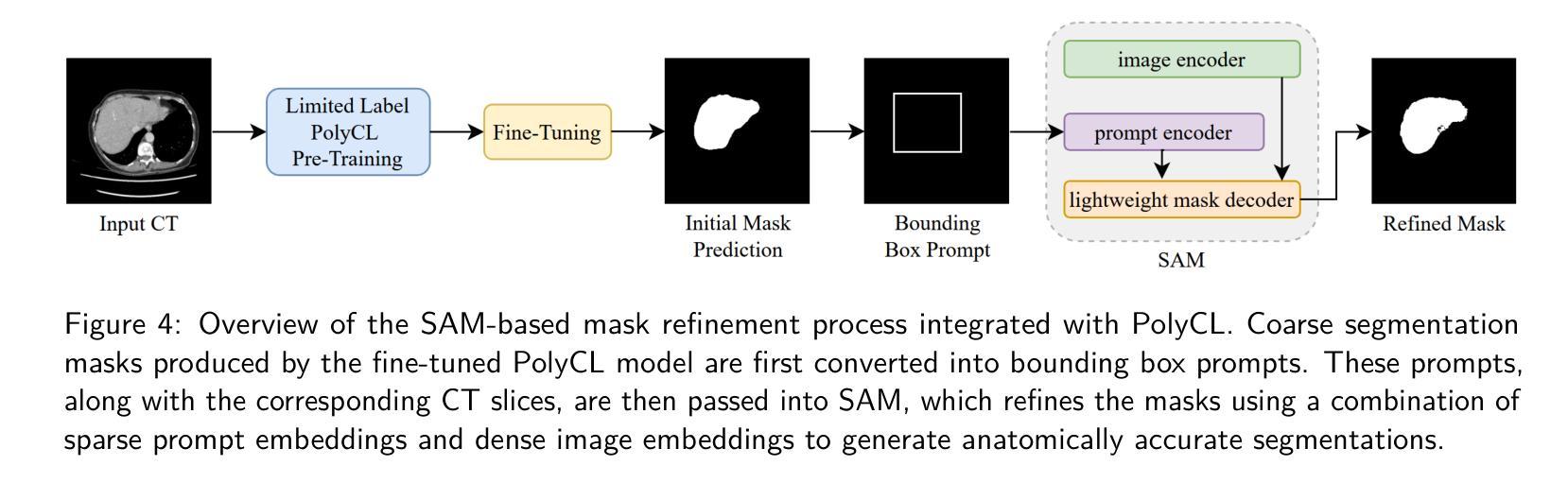
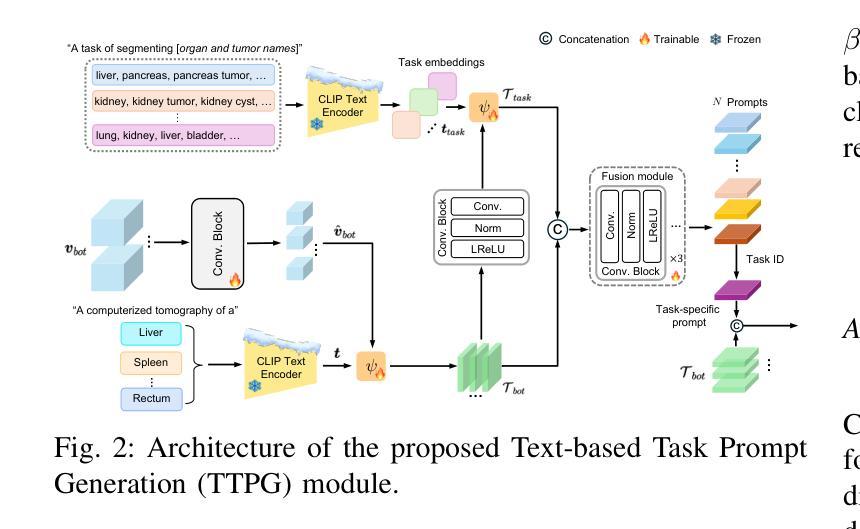
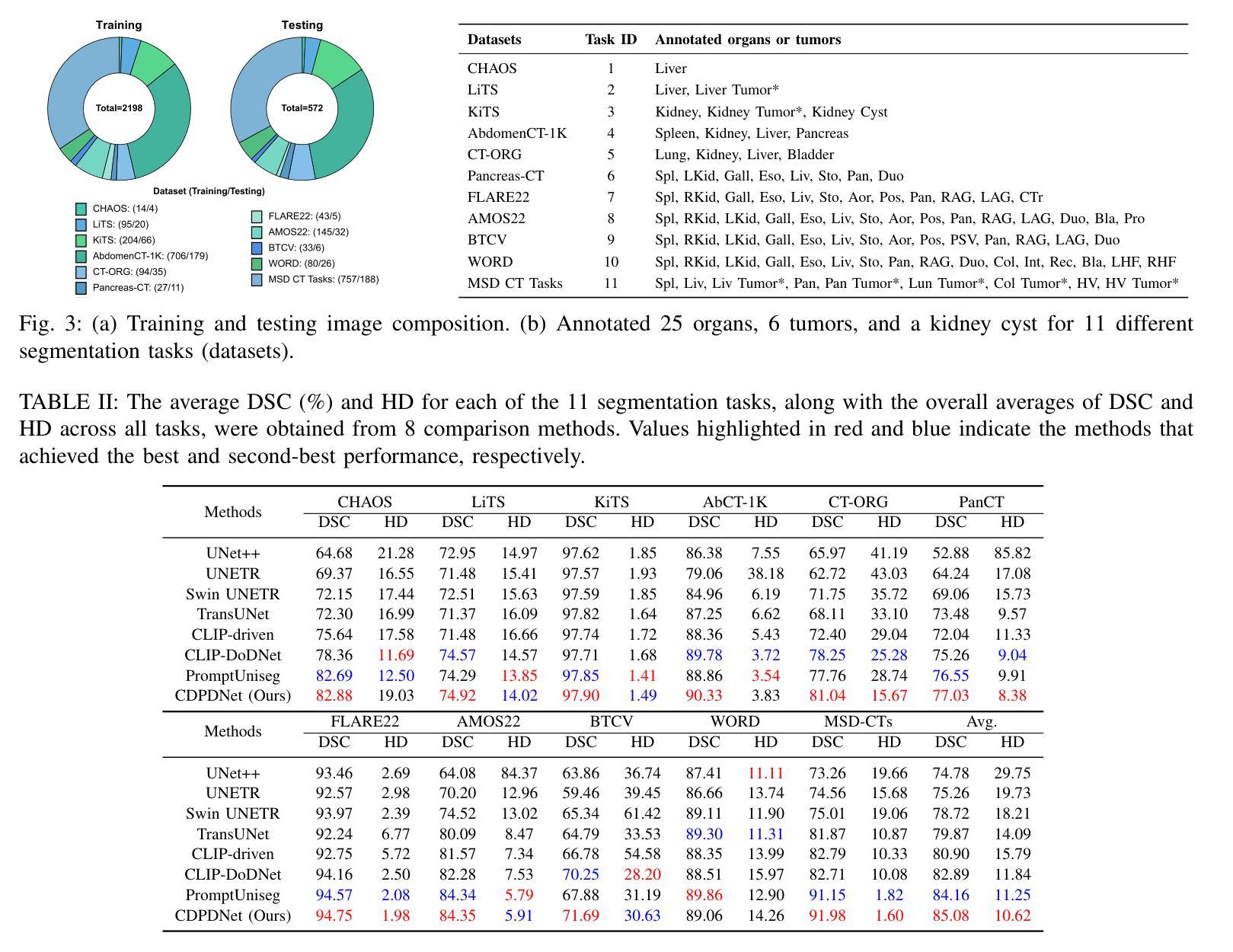
CDPDNet: Integrating Text Guidance with Hybrid Vision Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiong Wu, Yang Xing, Boxiao Yu, Wei Shao, Kuang Gong
Most publicly available medical segmentation datasets are only partially labeled, with annotations provided for a subset of anatomical structures. When multiple datasets are combined for training, this incomplete annotation poses challenges, as it limits the model’s ability to learn shared anatomical representations among datasets. Furthermore, vision-only frameworks often fail to capture complex anatomical relationships and task-specific distinctions, leading to reduced segmentation accuracy and poor generalizability to unseen datasets. In this study, we proposed a novel CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network (CDPDNet), which combined a self-supervised vision transformer with CLIP-based text embedding and introduced task-specific text prompts to tackle these challenges. Specifically, the framework was constructed upon a convolutional neural network (CNN) and incorporated DINOv2 to extract both fine-grained and global visual features, which were then fused using a multi-head cross-attention module to overcome the limited long-range modeling capability of CNNs. In addition, CLIP-derived text embeddings were projected into the visual space to help model complex relationships among organs and tumors. To further address the partial label challenge and enhance inter-task discriminative capability, a Text-based Task Prompt Generation (TTPG) module that generated task-specific prompts was designed to guide the segmentation. Extensive experiments on multiple medical imaging datasets demonstrated that CDPDNet consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art segmentation methods. Code and pretrained model are available at: https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git.
大部分公开可用的医学分割数据集仅部分标注,只为部分解剖结构提供注释。当多个数据集组合进行训练时,这种不完全的注释带来了挑战,因为它限制了模型在数据集之间学习共享解剖表征的能力。此外,仅依赖视觉的框架通常无法捕捉复杂的解剖关系和任务特定的区别,从而导致分割精度降低,并且难以推广到未见过的数据集。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新颖的CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network(CDPDNet),它将自我监督的视觉变压器与CLIP基于文本的嵌入相结合,并引入任务特定的文本提示来解决这些挑战。具体来说,该框架建立在卷积神经网络(CNN)之上,并融合了DINOv2以提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,然后使用多头交叉注意模块融合这些特征,以克服CNN有限的长期建模能力。此外,CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投射到视觉空间中,以帮助建模器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。为了进一步解决部分标签挑战并增强任务间的辨别能力,设计了一个基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块,以生成特定任务的提示来指导分割。在多个医学影像数据集上的广泛实验表明,CDPDNet始终优于现有的最先进的分割方法。代码和预先训练的模型可在[https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动分割网络(CDPDNet),通过结合自监督视觉变换器、CLIP基础文本嵌入和特定任务文本提示,解决医学图像分割中面临的部分标注和复杂解剖关系的问题。实验证明,CDPDNet在多个医学成像数据集上的表现均优于现有先进分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- CDPDNet结合自监督视觉变换器和CLIP基础文本嵌入,解决医学图像分割中的部分标注问题。
- 通过引入特定任务文本提示,CDPDNet能够捕捉复杂的解剖关系,提高分割精度。
- CDPDNet采用卷积神经网络(CNN)和DINOv2提取精细颗粒和全局视觉特征,然后通过多头交叉注意力模块融合这些特征,以克服CNN的长期建模能力限制。
- CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投射到视觉空间,以帮助模型模拟器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。
- 为应对部分标签挑战和提高任务间的辨别能力,设计了基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块。
- 在多个医学成像数据集上的广泛实验证明,CDPDNet的性能优于其他先进的分割方法。
- 代码和预先训练的模型可在https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git上获取。
点此查看论文截图
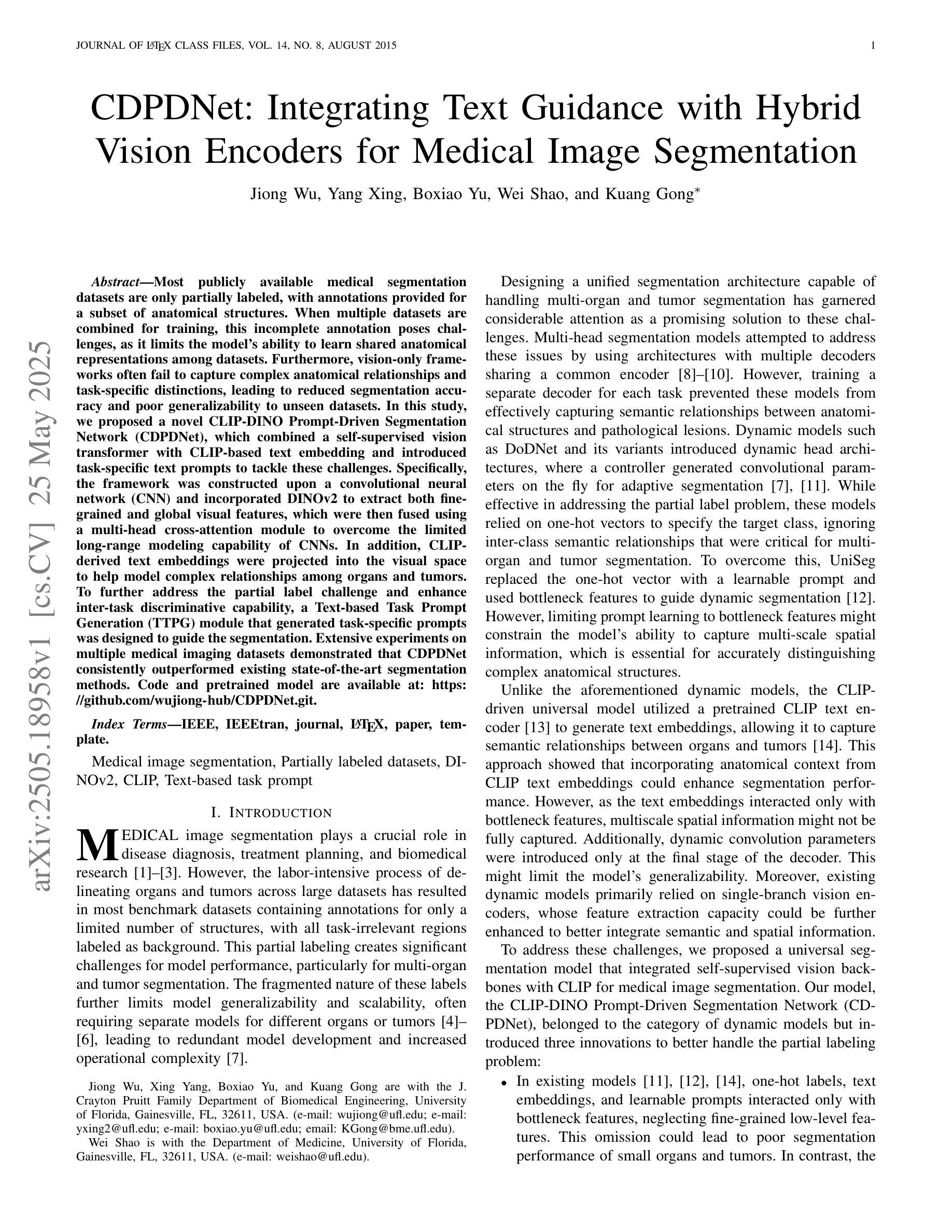
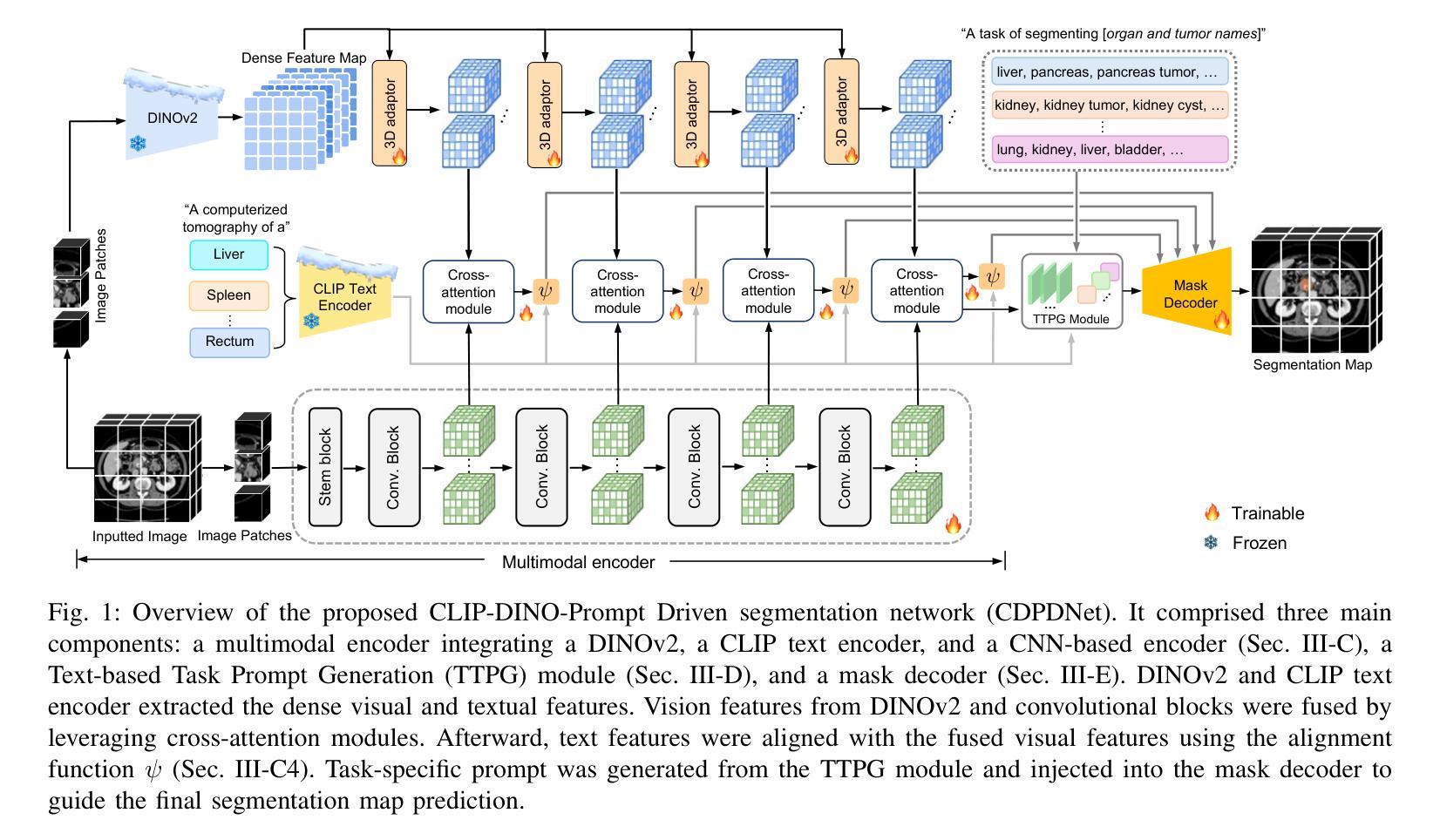
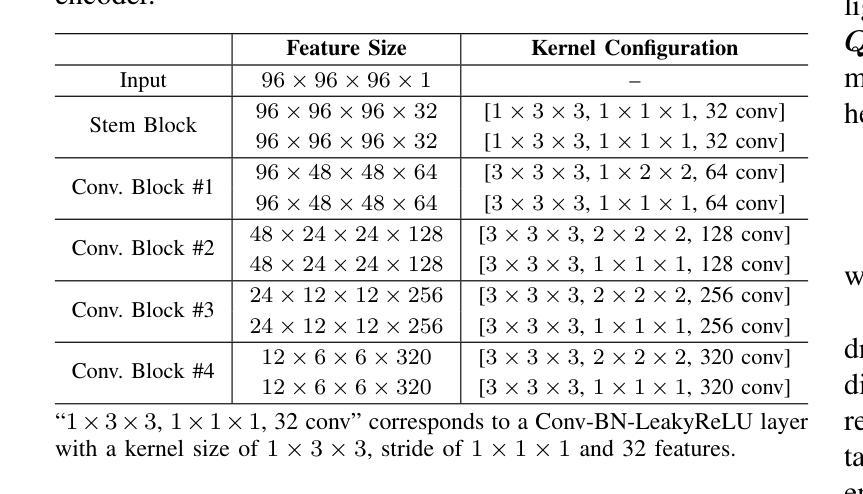
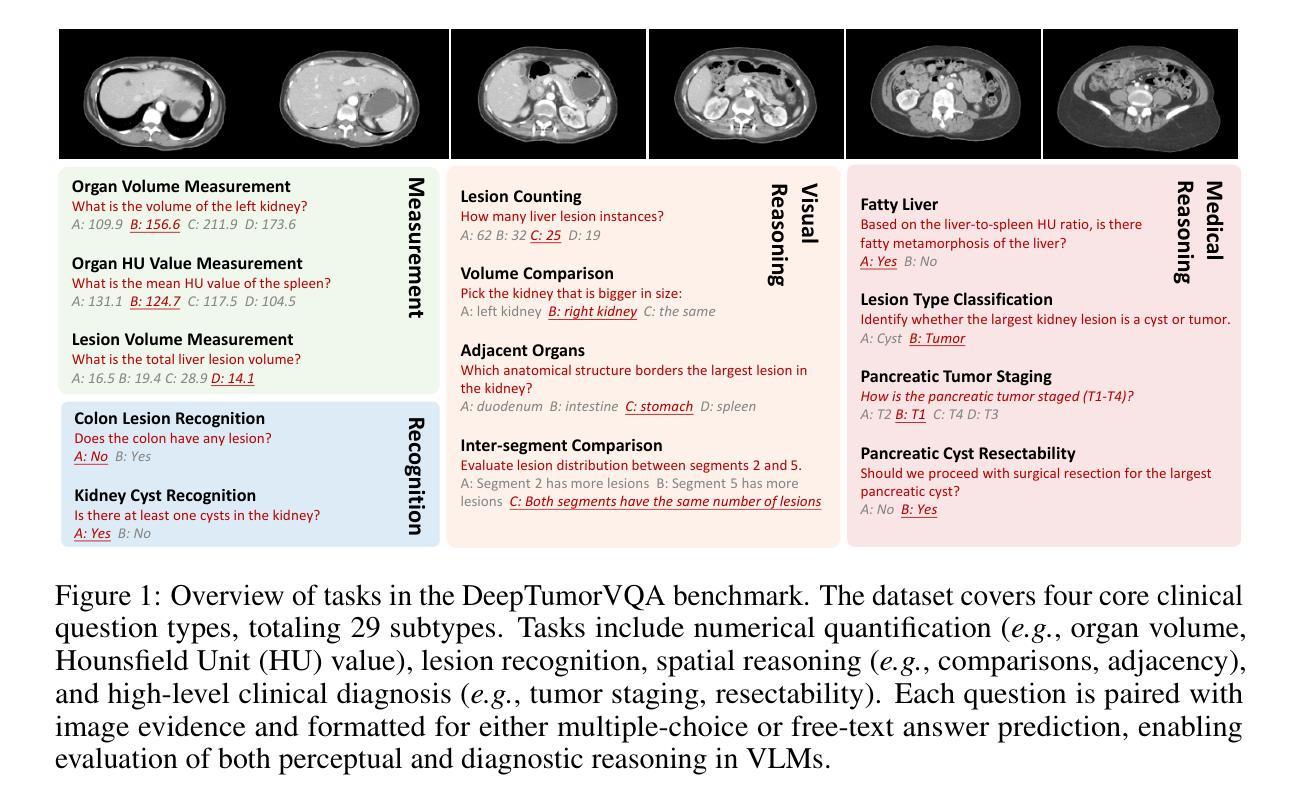
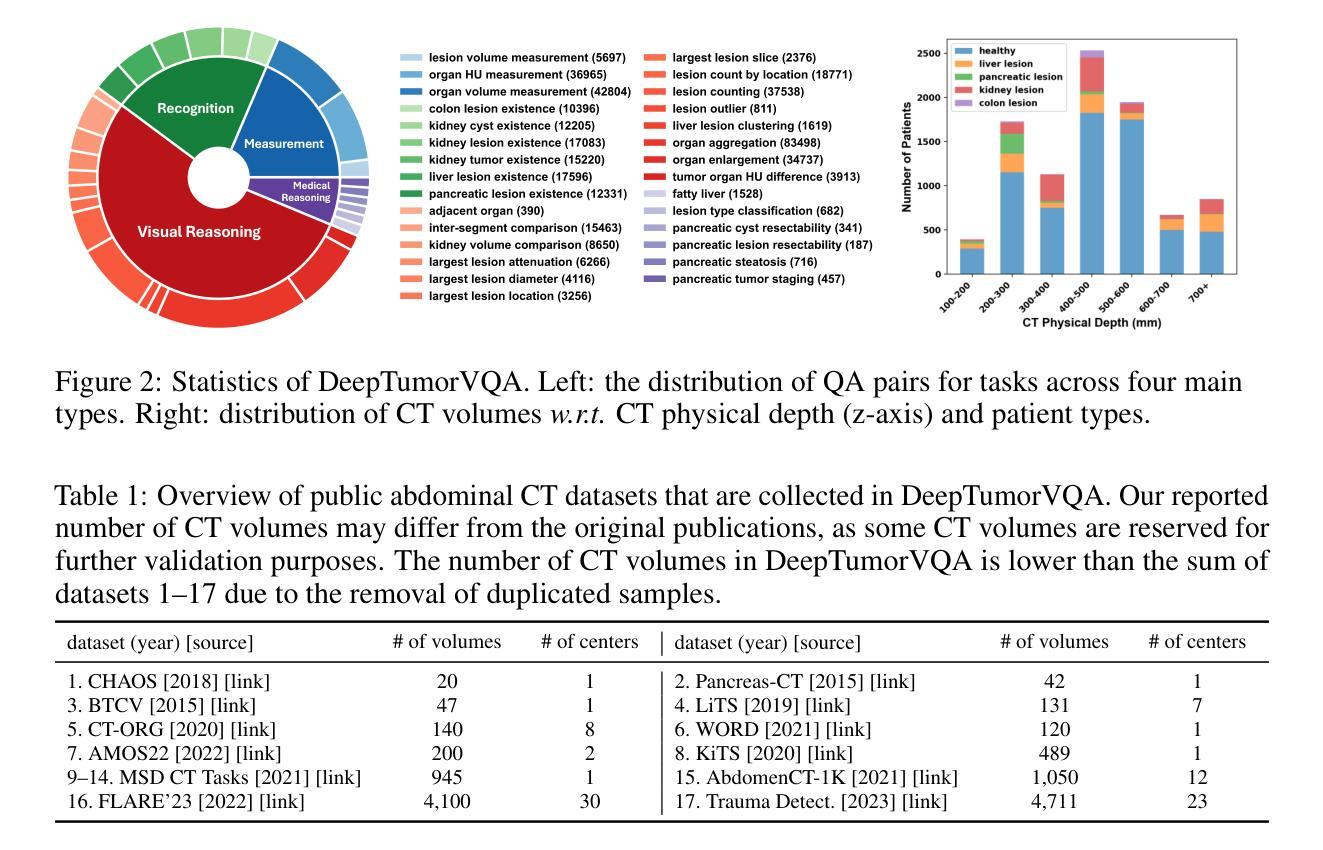
Are Vision Language Models Ready for Clinical Diagnosis? A 3D Medical Benchmark for Tumor-centric Visual Question Answering
Authors:Yixiong Chen, Wenjie Xiao, Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Xinze Zhou, Sezgin Er, Ibrahim Ethem Hamamci, Zongwei Zhou, Alan Yuille
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promise in various 2D visual tasks, yet their readiness for 3D clinical diagnosis remains unclear due to stringent demands for recognition precision, reasoning ability, and domain knowledge. To systematically evaluate these dimensions, we present DeepTumorVQA, a diagnostic visual question answering (VQA) benchmark targeting abdominal tumors in CT scans. It comprises 9,262 CT volumes (3.7M slices) from 17 public datasets, with 395K expert-level questions spanning four categories: Recognition, Measurement, Visual Reasoning, and Medical Reasoning. DeepTumorVQA introduces unique challenges, including small tumor detection and clinical reasoning across 3D anatomy. Benchmarking four advanced VLMs (RadFM, M3D, Merlin, CT-CHAT), we find current models perform adequately on measurement tasks but struggle with lesion recognition and reasoning, and are still not meeting clinical needs. Two key insights emerge: (1) large-scale multimodal pretraining plays a crucial role in DeepTumorVQA testing performance, making RadFM stand out among all VLMs. (2) Our dataset exposes critical differences in VLM components, where proper image preprocessing and design of vision modules significantly affect 3D perception. To facilitate medical multimodal research, we have released DeepTumorVQA as a rigorous benchmark: https://github.com/Schuture/DeepTumorVQA.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在各种2D视觉任务中显示出巨大的潜力,但由于对识别精度、推理能力和领域知识的严格需求,它们是否准备好用于3D临床诊断仍然不明确。为了系统地评估这些方面,我们推出了DeepTumorVQA,这是一个针对腹部肿瘤CT扫描的诊断视觉问答(VQA)基准测试。它包含来自17个公共数据集的9,262个CT体积(370万切片),涵盖四个类别的专家级问题,共39.5万个:识别、测量、视觉推理和医学推理。DeepTumorVQA带来了独特的挑战,包括在三维解剖结构中的小肿瘤检测和临床推理。对四个先进的VLM(RadFM、M3D、Merlin、CT-CHAT)进行基准测试后,我们发现当前模型在测量任务上表现良好,但在病灶识别和推理方面遇到困难,仍不能满足临床需求。出现了两个关键见解:(1)大规模多模式预训练在DeepTumorVQA测试性能中起着至关重要的作用,使RadFM在所有VLM中脱颖而出。(2)我们的数据集暴露了VLM组件之间的关键差异,其中适当的图像预处理和视觉模块的设计对3D感知有重大影响。为了促进医学多模式研究,我们已经将DeepTumorVQA作为严格的基准测试发布:https://github.com/Schuture/DeepTumorVQA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025 datasets&benchmarks track submission
Summary
本文介绍了针对腹部肿瘤在CT扫描中的诊断视觉问答(VQA)基准测试DeepTumorVQA。该基准测试包含来自17个公共数据集的9262个CT体积(370万切片),以及涵盖识别、测量、视觉推理和医学推理四个类别的39.5万专家级问题。评估了四种先进的VLM模型,发现当前模型在测量任务上表现良好,但在病灶识别和推理方面存在困难,尚不能满足临床需求。大规模多模式预训练在DeepTumorVQA测试中起着关键作用。
Key Takeaways
- DeepTumorVQA是一个针对腹部肿瘤CT扫描的诊断视觉问答(VQA)基准测试,涵盖了多种任务类型,包括识别、测量、视觉推理和医学推理。
- 当前VLM模型在测量任务上表现良好,但在病灶识别和推理方面存在困难,难以满足临床需求。
- 大规模多模式预训练对DeepTumorVQA测试性能至关重要。
- DeepTumorVQA数据集揭示了VLM组件的关键差异,适当的图像预处理和视觉模块的设计对3D感知有重大影响。
- DeepTumorVQA已作为严格的基准测试发布,以推动医疗多模式研究。
- 通过比较不同的VLM模型,发现RadFM在DeepTumorVQA测试中表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

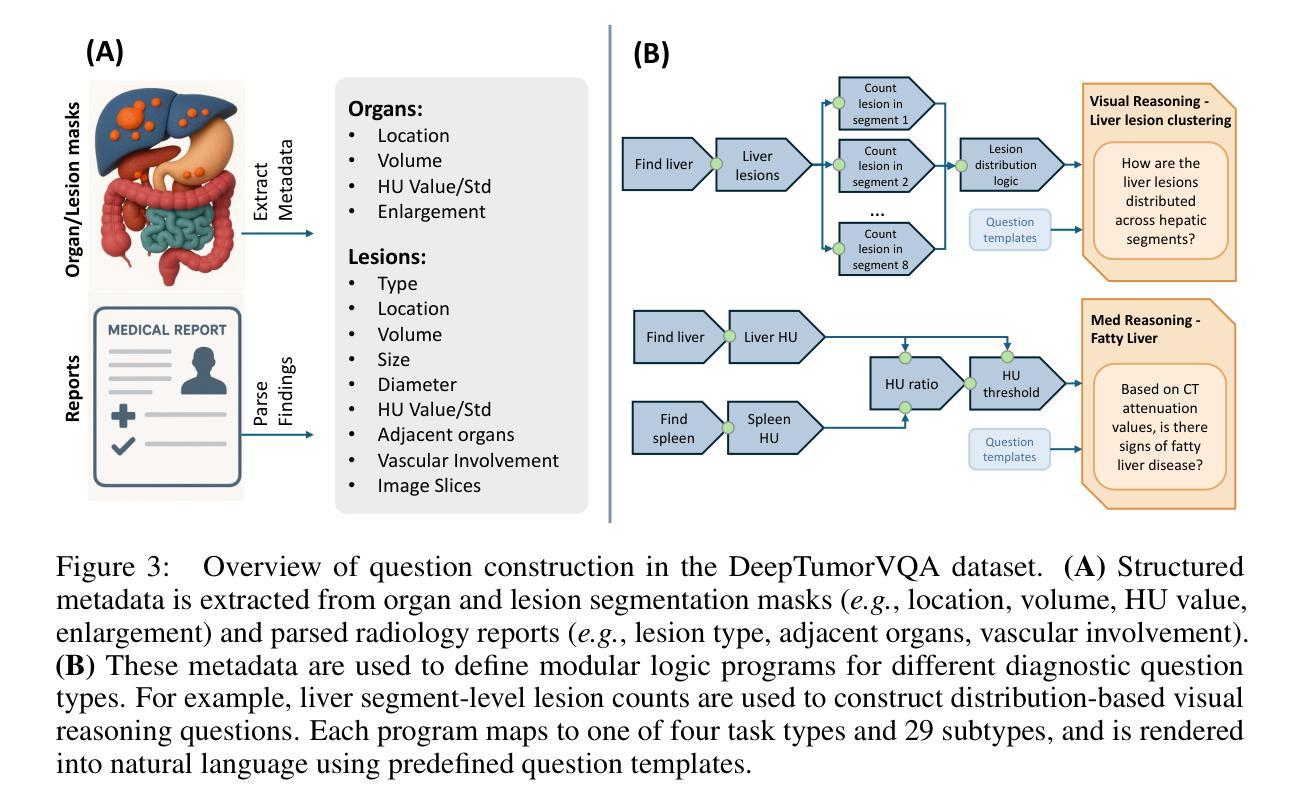
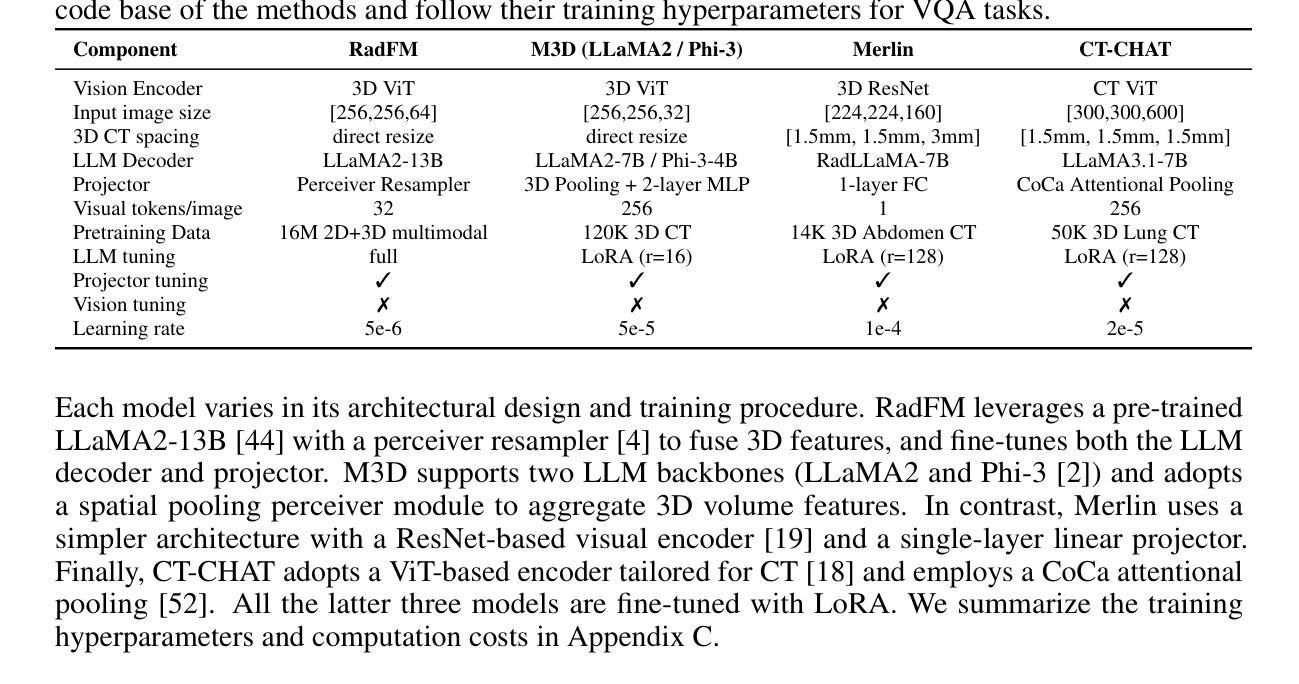
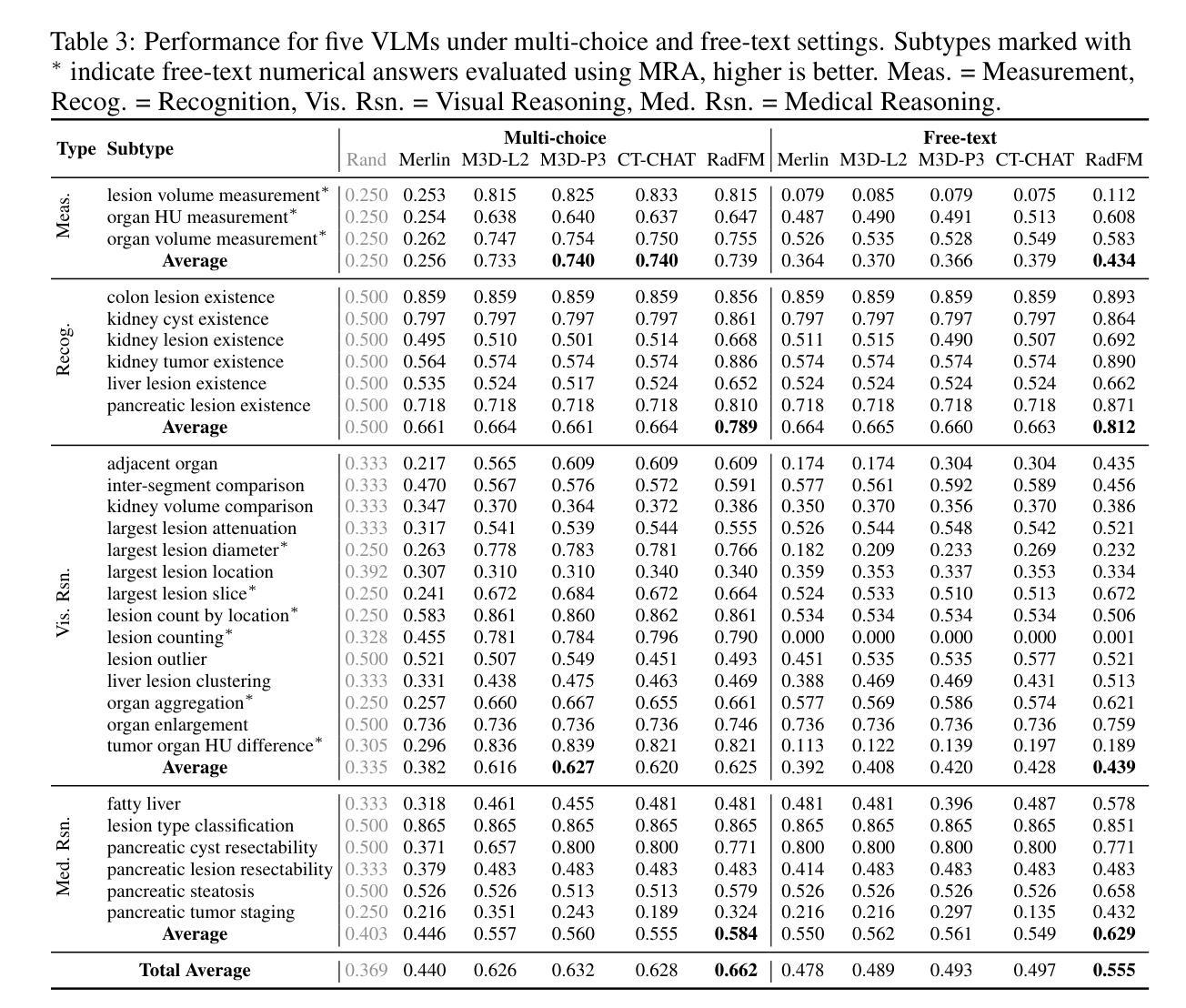
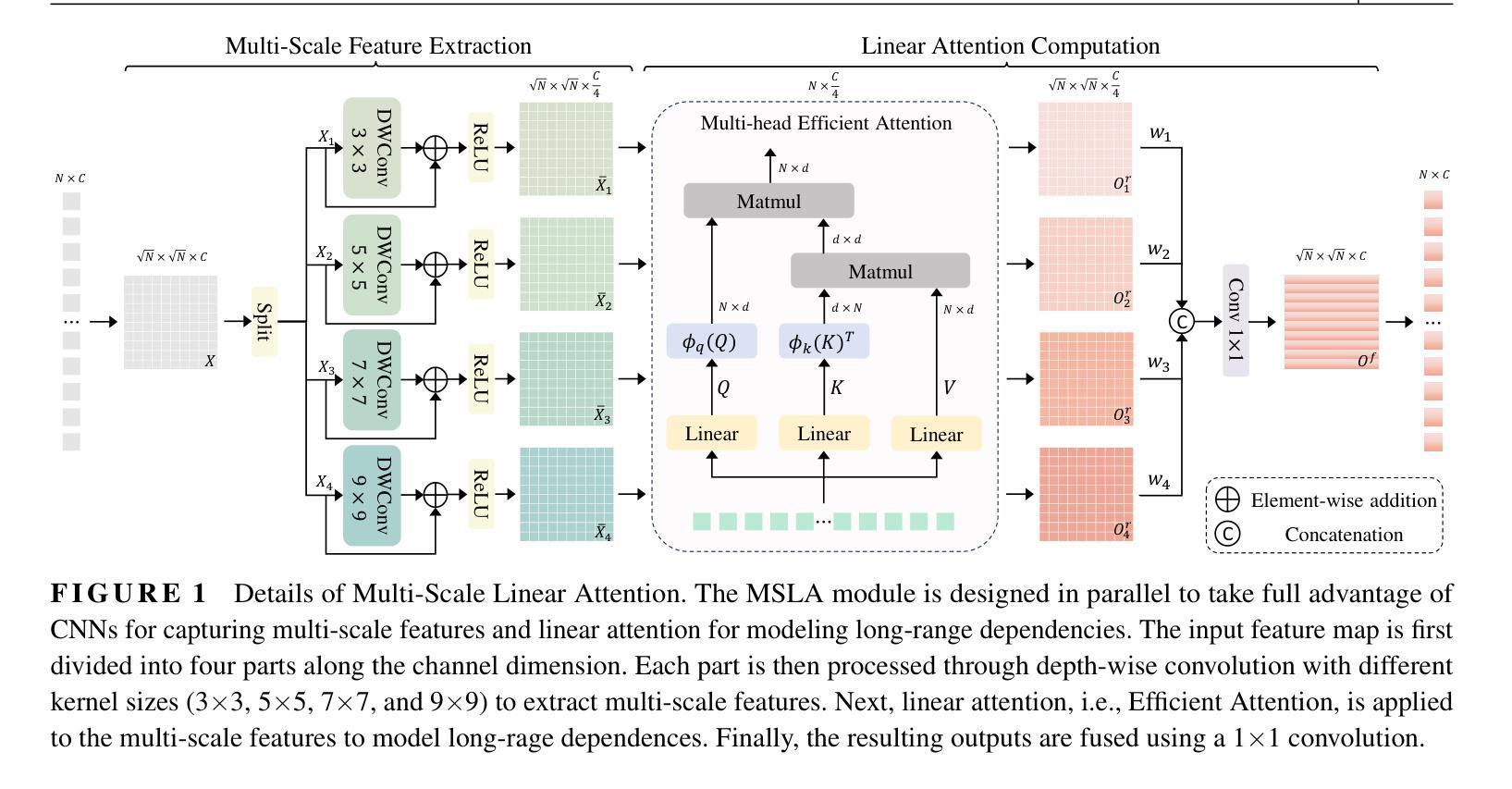
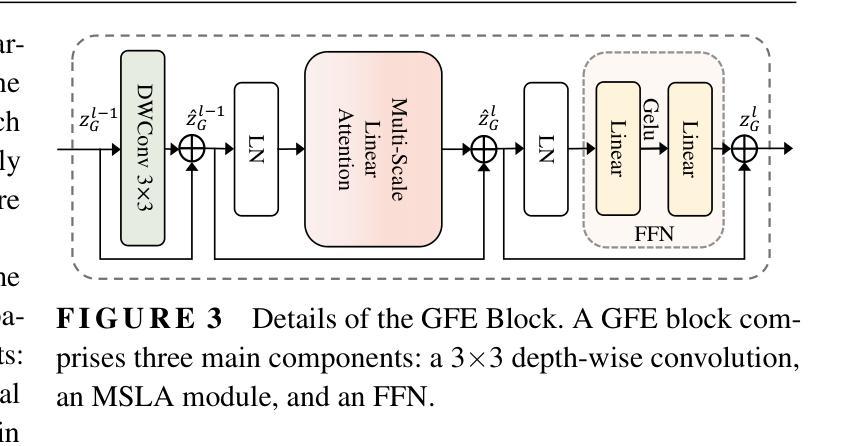
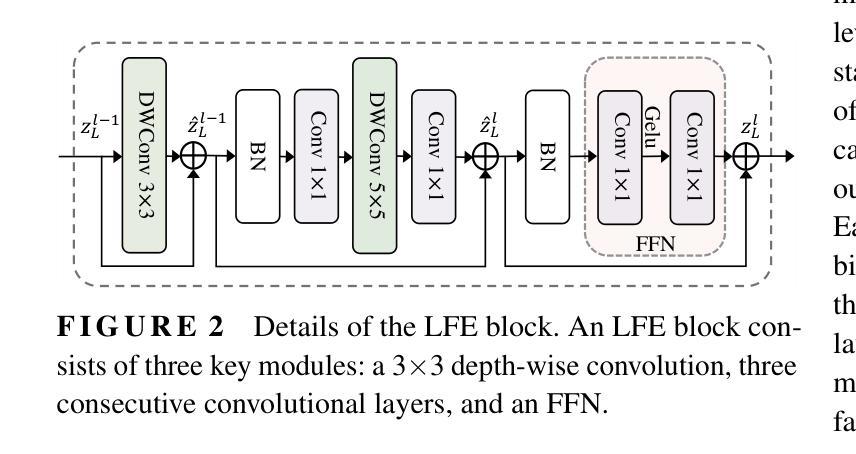
MSLAU-Net: A Hybird CNN-Transformer Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Libin Lan, Yanxin Li, Xiaojuan Liu, Juan Zhou, Jianxun Zhang, Nannan Huang, Yudong Zhang
Both CNN-based and Transformer-based methods have achieved remarkable success in medical image segmentation tasks. However, CNN-based methods struggle to effectively capture global contextual information due to the inherent limitations of convolution operations. Meanwhile, Transformer-based methods suffer from insufficient local feature modeling and face challenges related to the high computational complexity caused by the self-attention mechanism. To address these limitations, we propose a novel hybrid CNN-Transformer architecture, named MSLAU-Net, which integrates the strengths of both paradigms. The proposed MSLAU-Net incorporates two key ideas. First, it introduces Multi-Scale Linear Attention, designed to efficiently extract multi-scale features from medical images while modeling long-range dependencies with low computational complexity. Second, it adopts a top-down feature aggregation mechanism, which performs multi-level feature aggregation and restores spatial resolution using a lightweight structure. Extensive experiments conducted on benchmark datasets covering three imaging modalities demonstrate that the proposed MSLAU-Net outperforms other state-of-the-art methods on nearly all evaluation metrics, validating the superiority, effectiveness, and robustness of our approach. Our code is available at https://github.com/Monsoon49/MSLAU-Net.
基于CNN的方法和基于Transformer的方法在医学图像分割任务中都取得了显著的成功。然而,由于卷积操作固有的局限性,基于CNN的方法在有效地捕获全局上下文信息方面存在困难。同时,基于Transformer的方法在局部特征建模方面不足,并且面临由自注意力机制引起的高计算复杂度的挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的混合CNN-Transformer架构,名为MSLAU-Net,它结合了两种范式的好处。所提出的MSLAU-Net包含两个关键思想。首先,它引入了多尺度线性注意力,旨在从医学图像中有效地提取多尺度特征,同时以低计算复杂度对长距离依赖关系进行建模。其次,它采用自上而下的特征聚合机制,进行多级特征聚合,并使用轻量级结构恢复空间分辨率。在涵盖三种成像模式的基准数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,所提出的MSLAU-Net几乎在所有评估指标上都优于其他最先进的方法,验证了我们的方法的优越性、有效性和稳健性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Monsoon49/MSLAU-Net。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 7 figures, 7 tables
Summary
医学图像分割任务中,CNN和Transformer方法均有显著成效,但各有不足。为结合两者优势,提出名为MSLAU-Net的混合CNN-Transformer架构。它引入多尺度线性注意力机制,实现高效多尺度特征提取和长距离依赖建模,同时采用自上而下的特征聚合机制,实现多层级特征聚合和空间分辨率恢复。在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,MSLAU-Net在各项评估指标上均超越其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- CNN和Transformer方法在医学图像分割任务中均取得显著成效,但存在局限性。
- CNN方法难以有效捕捉全局上下文信息,而Transformer方法则面临局部特征建模不足和计算复杂度高的挑战。
- 提出名为MSLAU-Net的混合CNN-Transformer架构,结合两者优势。
- MSLAU-Net引入多尺度线性注意力机制,实现多尺度特征提取和长距离依赖建模。
- MSLAU-Net采用自上而下的特征聚合机制,实现多层级特征聚合和空间分辨率恢复。
- 在多个基准数据集上的实验表明,MSLAU-Net在医学图像分割任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
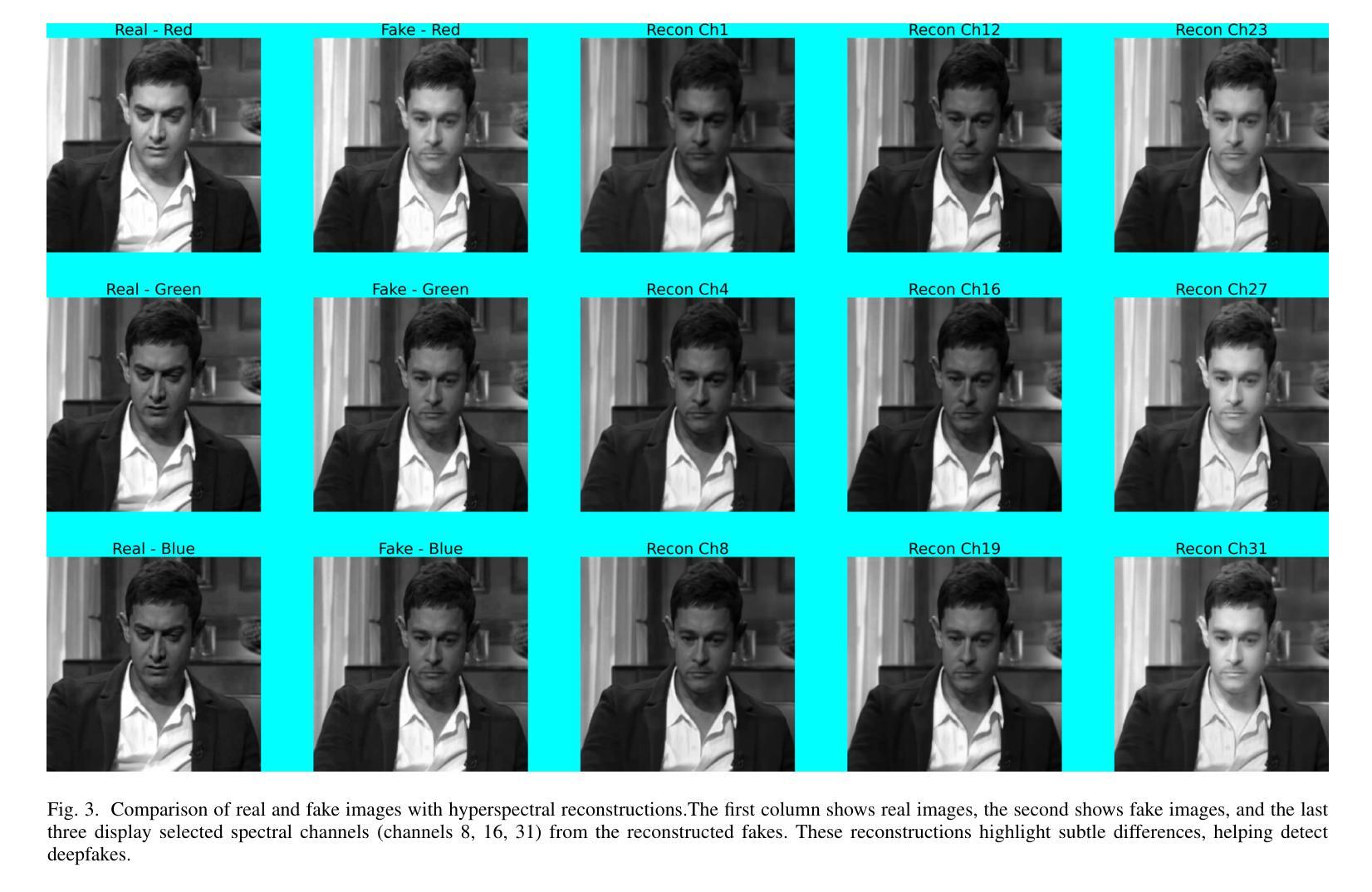
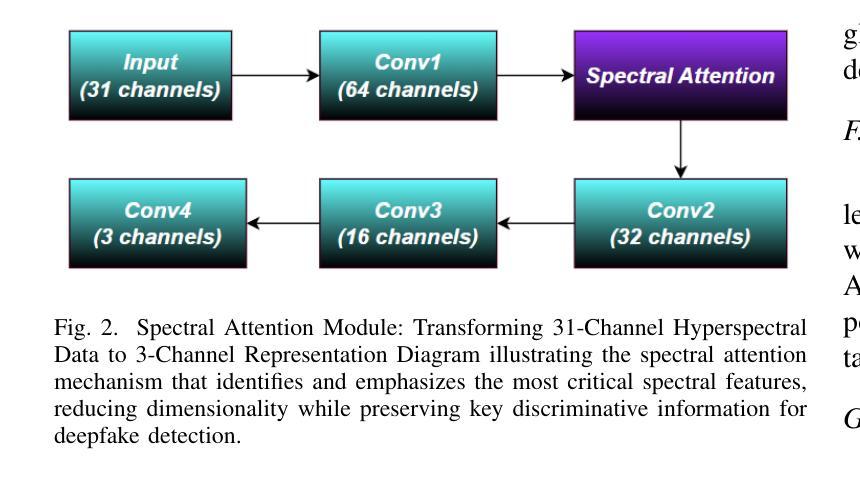
HyperFake: Hyperspectral Reconstruction and Attention-Guided Analysis for Advanced Deepfake Detection
Authors:Pavan C Shekar, Pawan Soni, Vivek Kanhangad
Deepfakes pose a significant threat to digital media security, with current detection methods struggling to generalize across different manipulation techniques and datasets. While recent approaches combine CNN-based architectures with Vision Transformers or leverage multi-modal learning, they remain limited by the inherent constraints of RGB data. We introduce HyperFake, a novel deepfake detection pipeline that reconstructs 31-channel hyperspectral data from standard RGB videos, revealing hidden manipulation traces invisible to conventional methods. Using an improved MST++ architecture, HyperFake enhances hyperspectral reconstruction, while a spectral attention mechanism selects the most critical spectral features for deepfake detection. The refined spectral data is then processed by an EfficientNet-based classifier optimized for spectral analysis, enabling more accurate and generalizable detection across different deepfake styles and datasets, all without the need for expensive hyperspectral cameras. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach to leverage hyperspectral imaging reconstruction for deepfake detection, opening new possibilities for detecting increasingly sophisticated manipulations.
深度伪造技术对数字媒体安全构成了重大威胁,现有的检测方法在应对不同的操作技术和数据集时,泛化能力有限。虽然最近的方法结合了基于CNN的架构与视觉变压器,或者利用多模态学习,但它们仍然受到RGB数据固有约束的限制。我们引入了HyperFake,这是一种新型深度伪造检测流程,它能够从标准RGB视频中重建31通道的超高光谱数据,揭示传统方法无法察觉的隐藏操作痕迹。使用改进的MST++架构,HyperFake增强了超高光谱重建,同时光谱注意机制选择了对深度伪造检测最关键的光谱特征。然后,经过细化的光谱数据由针对光谱分析优化的EfficientNet分类器进行处理,能够在不同的深度伪造风格和数据集上实现更准确、更通用的检测,而且无需昂贵的超高光谱相机。据我们所知,这是首次利用超高光谱成像重建进行深度伪造检测的方法,为检测日益复杂的操作开辟了新途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures, 1 table. Preliminary results on FaceForensics++ dataset. First approach to use hyperspectral reconstruction for deepfake detection
Summary
深度伪造技术对数字媒体安全构成重大威胁,当前检测手段在应对不同伪造技术和数据集时存在泛化困难的问题。本文提出HyperFake,一种新型深度伪造检测流程,通过重建31通道的超高光谱数据,揭示传统方法无法察觉的操纵痕迹。利用改进后的MST++架构和光谱注意力机制,HyperFake提高了超高光谱数据的重建能力,并选择最关键的光谱特征进行深度伪造检测。经过优化的EfficientNet分类器对光谱数据进行分析,提高了在不同深度伪造方式和数据集上的检测准确性和泛化能力,且无需昂贵的超高光谱相机。这是首次尝试利用超高光谱成像重建技术进行深度伪造检测,为检测日益复杂的操纵提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度伪造技术威胁数字媒体安全,现有检测手段泛化能力不足。
- HyperFake利用超高光谱数据重建技术揭示隐藏操纵痕迹。
- HyperFake采用改进MST++架构和光谱注意力机制提高检测性能。
- EfficientNet分类器优化用于光谱分析,提高检测准确性和泛化能力。
- HyperFake无需昂贵的超高光谱相机即可实现检测。
- 这是首次尝试将超高光谱成像重建技术应用于深度伪造检测。
点此查看论文截图



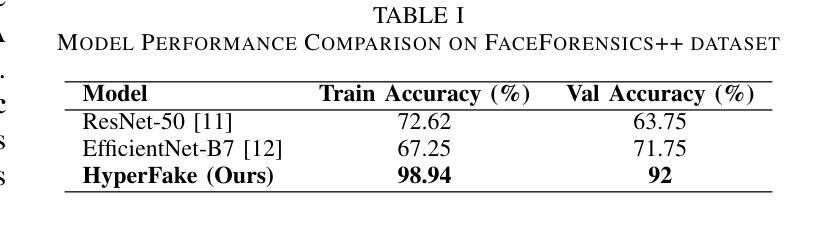
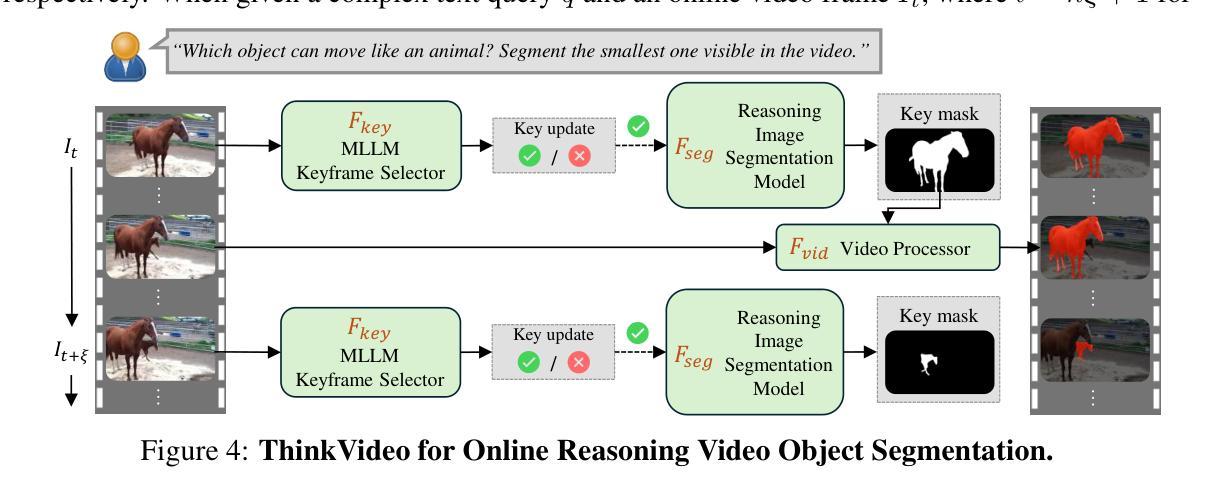
ThinkVideo: High-Quality Reasoning Video Segmentation with Chain of Thoughts
Authors:Shiu-hong Kao, Yu-Wing Tai, Chi-Keung Tang
Reasoning Video Object Segmentation is a challenging task, which generates a mask sequence from an input video and an implicit, complex text query. Existing works probe into the problem by finetuning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) for segmentation-based output, while still falling short in difficult cases on videos given temporally-sensitive queries, primarily due to the failure to integrate temporal and spatial information. In this paper, we propose ThinkVideo, a novel framework which leverages the zero-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) capability of MLLM to address these challenges. Specifically, ThinkVideo utilizes the CoT prompts to extract object selectivities associated with particular keyframes, then bridging the reasoning image segmentation model and SAM2 video processor to output mask sequences. The ThinkVideo framework is training-free and compatible with closed-source MLLMs, which can be applied to Reasoning Video Instance Segmentation. We further extend the framework for online video streams, where the CoT is used to update the object of interest when a better target starts to emerge and becomes visible. We conduct extensive experiments on video object segmentation with explicit and implicit queries. The results show that ThinkVideo significantly outperforms previous works in both cases, qualitatively and quantitatively.
视频对象推理分割是一项具有挑战性的任务,它根据输入的视频和隐含的复杂文本查询生成一个掩膜序列。现有工作通过微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来进行基于分割的输出,但在处理视频时仍存在时间敏感查询困难的问题,主要是因为时空信息的融合失败。针对这些问题,本文提出了ThinkVideo框架,它利用多模态大型语言模型的零样本思维链(CoT)能力来解决这些挑战。具体来说,ThinkVideo利用CoT提示来提取与特定关键帧关联的对象选择性,然后通过连接推理图像分割模型和SAM2视频处理器来输出掩膜序列。ThinkVideo框架无需训练且与开源MLLM兼容,可应用于视频实例推理分割。我们进一步将框架扩展到在线视频流中,其中使用CoT在出现更好的目标并开始可见时进行更新感兴趣的对象。我们对带有明确和隐含查询的视频对象分割进行了大量实验。结果表明,无论是在定性还是定量上,ThinkVideo都显著优于以前的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~skao/thinkvideo.html
Summary
医学视频对象分割是一项挑战任务,需从输入视频和复杂文本查询中生成掩膜序列。现有工作通过微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)进行分割输出,但在对具有时间敏感查询的视频上表现不足。本文提出ThinkVideo框架,利用MLLM的零样本思维链(CoT)能力解决挑战,提取与特定关键帧关联的对象选择性,再连接推理图像分割模型和SAM2视频处理器以输出掩膜序列。ThinkVideo框架无需训练且兼容闭源MLLM,可应用于推理视频实例分割。此外,我们扩展了框架以处理在线视频流,使用CoT在更好的目标出现时进行更新。实验表明,ThinkVideo在显性和隐性查询的视频对象分割上均显著优于以前的工作。
Key Takeaways
- 医学视频对象分割是一项挑战任务,需要从输入视频和复杂文本查询生成掩膜序列。
- 现有工作虽然尝试通过微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)解决该问题,但在处理具有时间敏感查询的视频时仍有困难。
- ThinkVideo框架利用MLLM的零样本思维链(CoT)能力来解决挑战。
- ThinkVideo框架可以提取与特定关键帧关联的对象选择性,连接推理图像分割模型和SAM2视频处理器来输出掩膜序列。
- ThinkVideo框架无需训练,且兼容多种闭源MLLM。
- 该框架可应用于推理视频实例分割。
点此查看论文截图

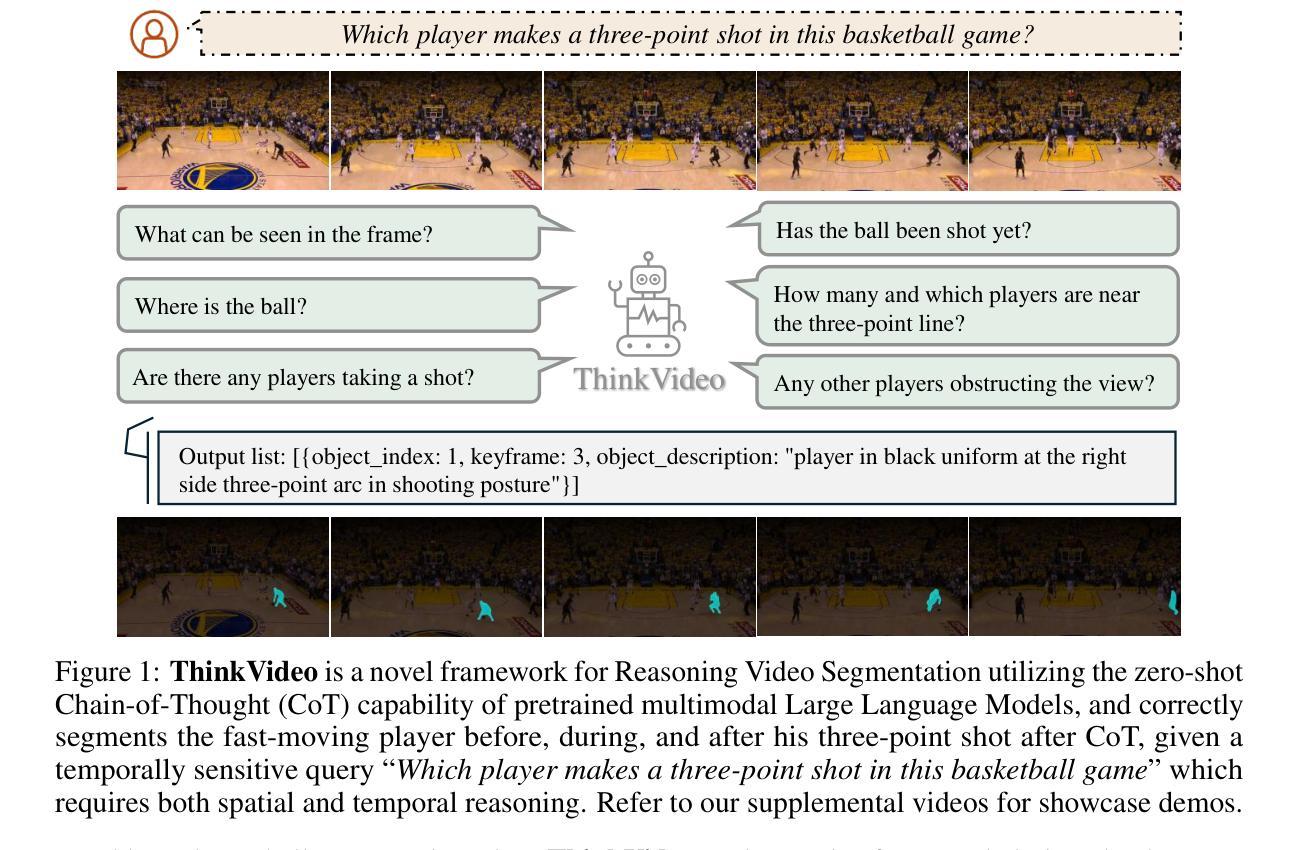
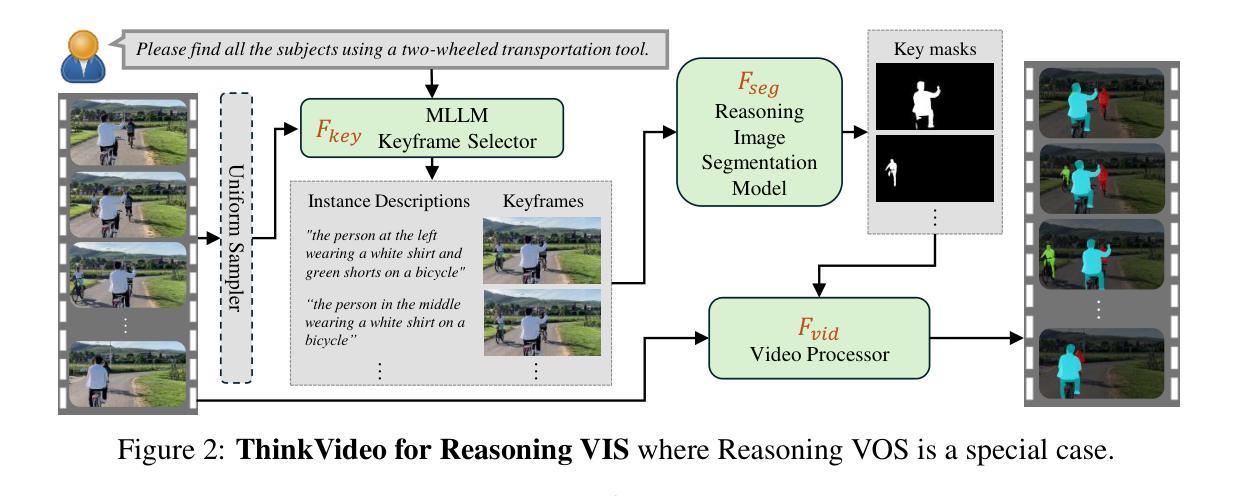
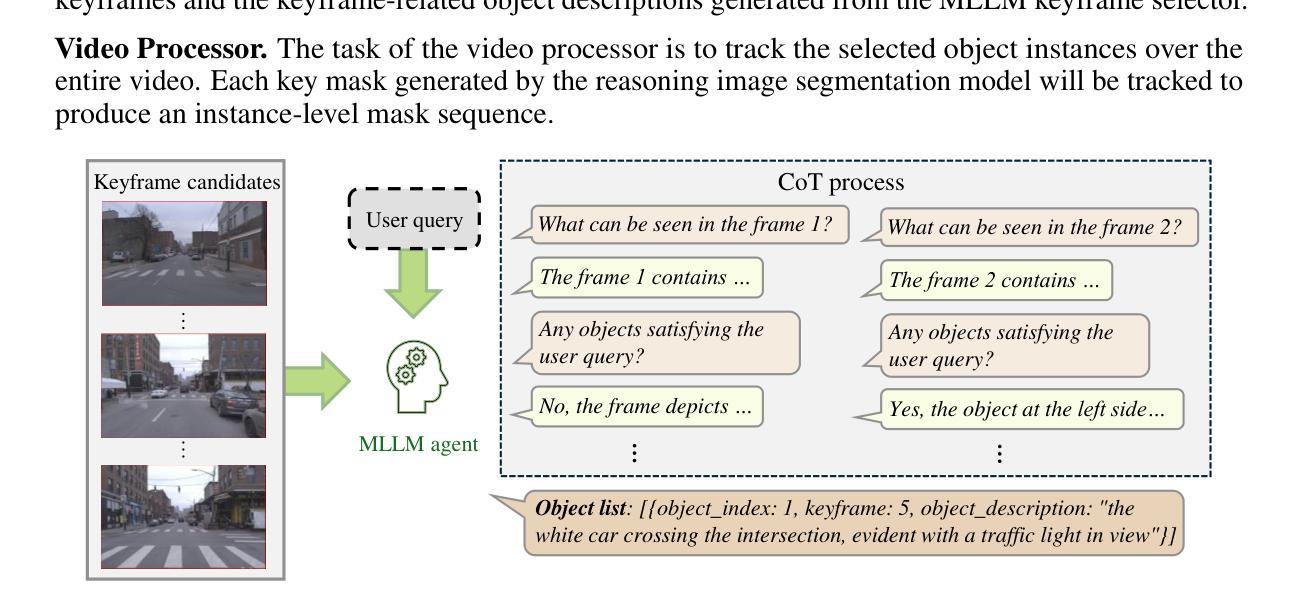
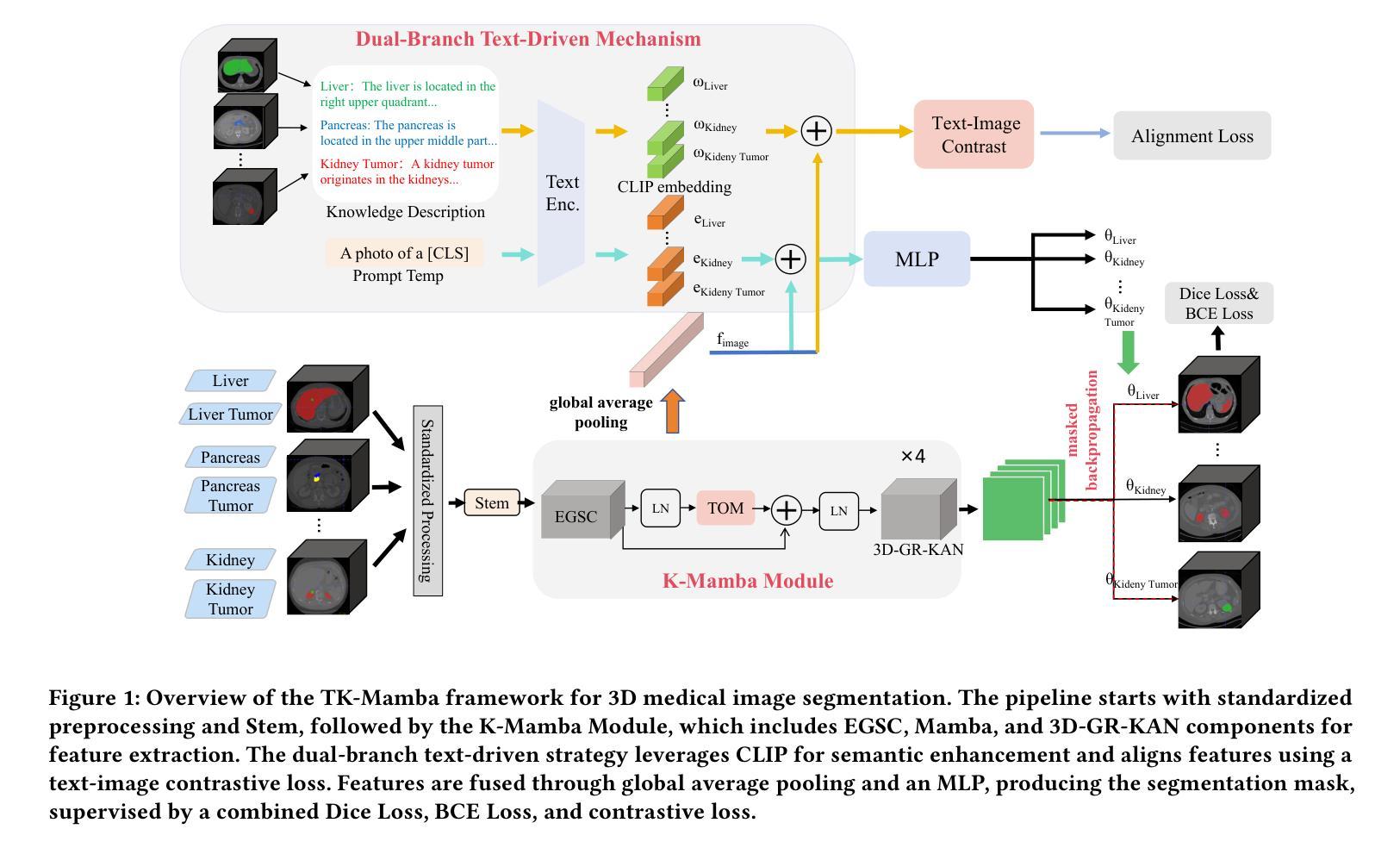
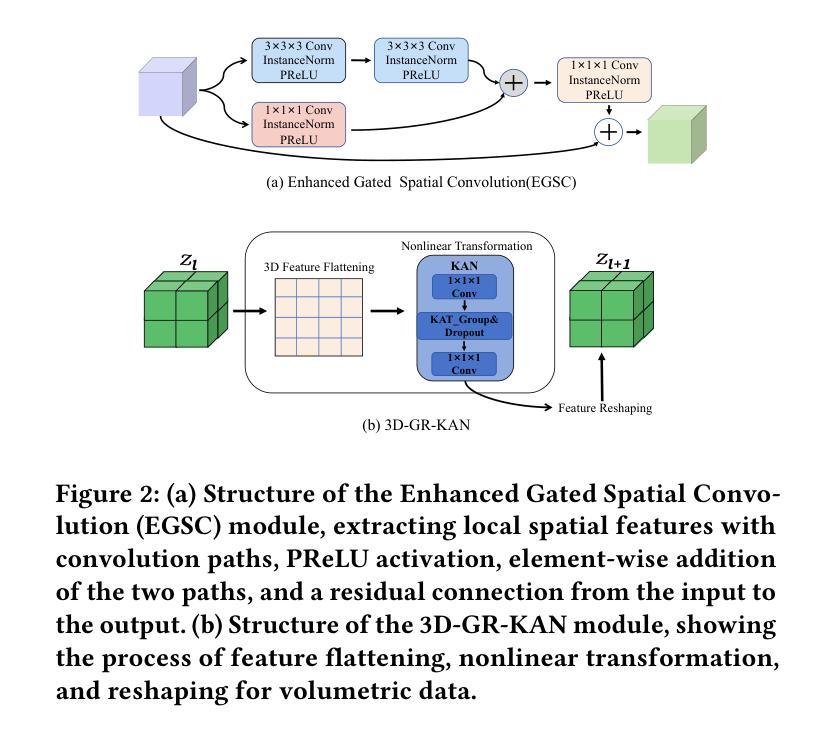
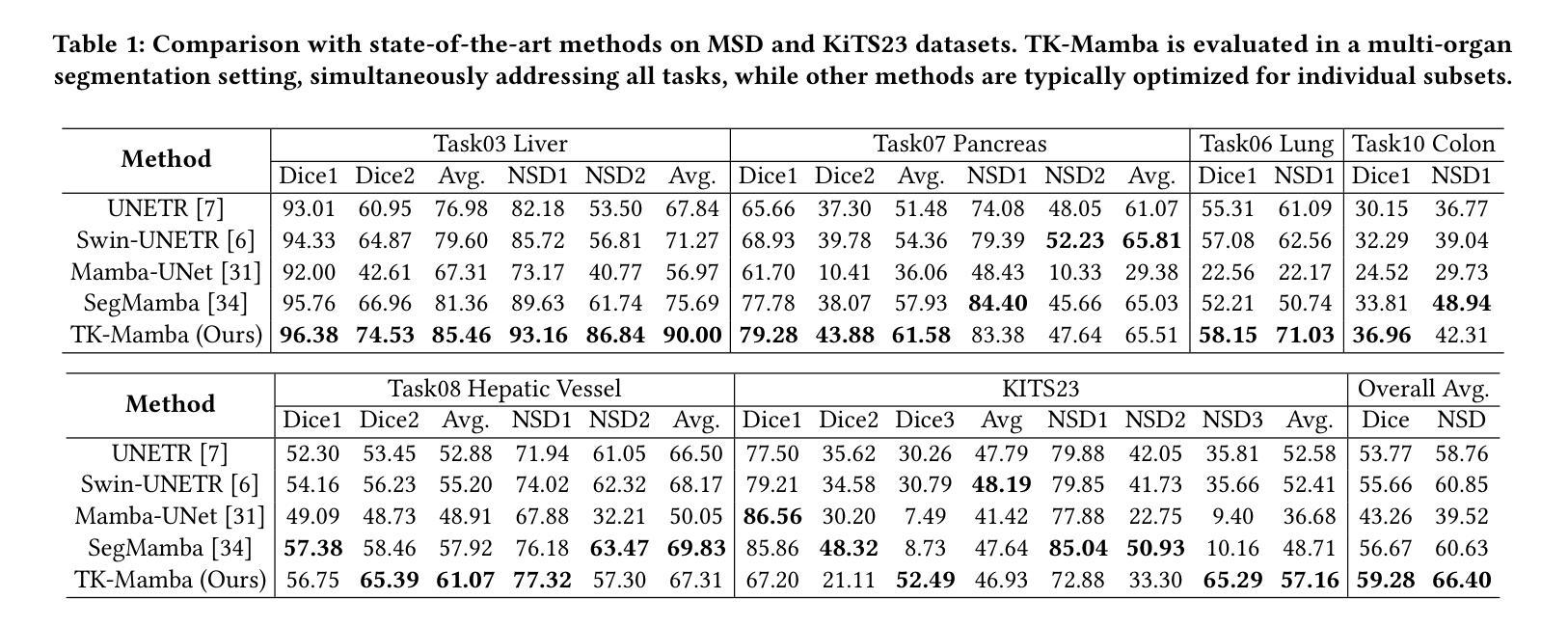
TK-Mamba: Marrying KAN with Mamba for Text-Driven 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Haoyu Yang, Yuxiang Cai, Jintao Chen, Xuhong Zhang, Wenhui Lei, Xiaoming Shi, Jianwei Yin, Yankai Jiang
3D medical image segmentation is vital for clinical diagnosis and treatment but is challenged by high-dimensional data and complex spatial dependencies. Traditional single-modality networks, such as CNNs and Transformers, are often limited by computational inefficiency and constrained contextual modeling in 3D settings. We introduce a novel multimodal framework that leverages Mamba and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) as an efficient backbone for long-sequence modeling. Our approach features three key innovations: First, an EGSC (Enhanced Gated Spatial Convolution) module captures spatial information when unfolding 3D images into 1D sequences. Second, we extend Group-Rational KAN (GR-KAN), a Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks variant with rational basis functions, into 3D-Group-Rational KAN (3D-GR-KAN) for 3D medical imaging - its first application in this domain - enabling superior feature representation tailored to volumetric data. Third, a dual-branch text-driven strategy leverages CLIP’s text embeddings: one branch swaps one-hot labels for semantic vectors to preserve inter-organ semantic relationships, while the other aligns images with detailed organ descriptions to enhance semantic alignment. Experiments on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) and KiTS23 datasets show our method achieving state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing approaches in accuracy and efficiency. This work highlights the power of combining advanced sequence modeling, extended network architectures, and vision-language synergy to push forward 3D medical image segmentation, delivering a scalable solution for clinical use. The source code is openly available at https://github.com/yhy-whu/TK-Mamba.
三维医学图像分割对临床诊断和治疗至关重要,但面临着高维数据和复杂空间依赖性的挑战。传统的单一模式网络,如卷积神经网络和Transformer,在三维环境中往往受到计算效率低下和上下文建模受限的限制。我们引入了一种新型的多模式框架,该框架利用Mamba和Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)作为长序列建模的有效骨干。我们的方法有三个关键创新点:首先,EGSC(增强门控空间卷积)模块在将三维图像展开成一维序列时捕获空间信息。其次,我们将基于有理基函数的Kolmogorov-Arnold网络变体Group-Rational KAN(GR-KAN)扩展到用于三维医学影像的3D-Group-Rational KAN(3D-GR-KAN),这是该领域中的首次应用,能够实现针对体积数据的优越特征表示。第三,双分支文本驱动策略利用CLIP的文本嵌入:一个分支用语义向量替换单热标签以保留器官间的语义关系,而另一个分支则将图像与详细的器官描述对齐,以增强语义对齐。在Medical Segmentation Decathlon(MSD)和KiTS23数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能,在准确性和效率上超越了现有方法。这项工作强调了结合先进序列建模、扩展网络架构和视觉语言协同作用推动三维医学图像分割的力量,为临床使用提供了可扩展的解决方案。源代码公开在https://github.com/yhy-whu/TK-Mamba。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于三维医学图像分割的多模态框架,该框架结合了Mamba和Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN),并引入了三个关键创新点:EGSC模块、3D-GR-KAN网络和双分支文本驱动策略。该框架在医学分割挑战赛(MSD)和KiTS23数据集上的实验结果表明,其性能达到了最新水平,超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 三维医学图像分割在临床诊断和治疗中至关重要,面临高维数据和复杂空间依赖性的挑战。
- 传统单模态网络(如CNN和Transformer)在处理三维数据时存在计算效率低下和上下文建模受限的问题。
- 引入了一种多模态框架,结合Mamba和Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN),为长序列建模提供了高效的后端。
- 框架的三个关键创新点包括:EGSC模块、3D-GR-KAN网络和双分支文本驱动策略。
- EGSC模块在将三维图像展开成一维序列时能够捕捉空间信息。
- 首次将Group-Rational KAN(GR-KAN)扩展到三维领域的3D-GR-KAN,实现了对体积数据的优化特征表示。
点此查看论文截图

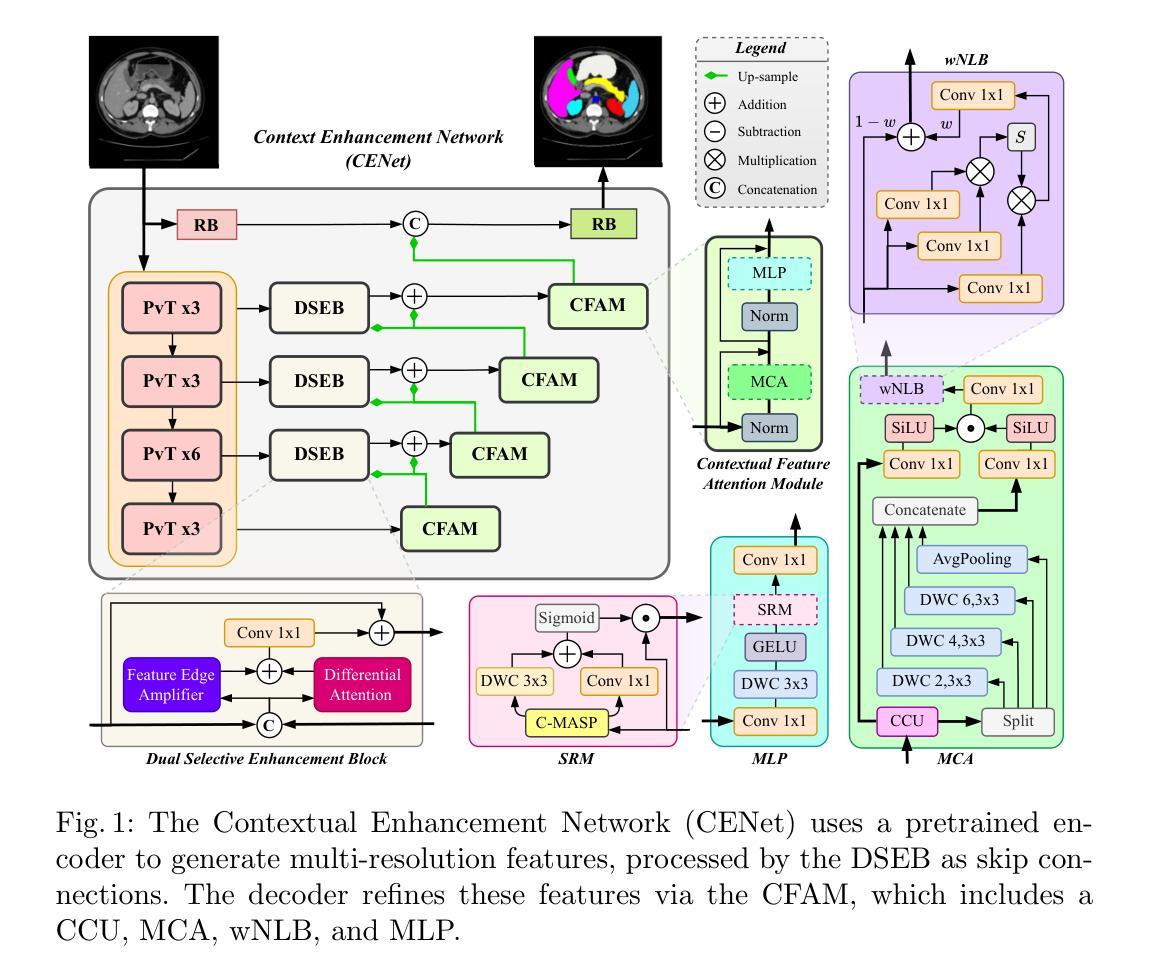
CENet: Context Enhancement Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Afshin Bozorgpour, Sina Ghorbani Kolahi, Reza Azad, Ilker Hacihaliloglu, Dorit Merhof
Medical image segmentation, particularly in multi-domain scenarios, requires precise preservation of anatomical structures across diverse representations. While deep learning has advanced this field, existing models often struggle with accurate boundary representation, variability in organ morphology, and information loss during downsampling, limiting their accuracy and robustness. To address these challenges, we propose the Context Enhancement Network (CENet), a novel segmentation framework featuring two key innovations. First, the Dual Selective Enhancement Block (DSEB) integrated into skip connections enhances boundary details and improves the detection of smaller organs in a context-aware manner. Second, the Context Feature Attention Module (CFAM) in the decoder employs a multi-scale design to maintain spatial integrity, reduce feature redundancy, and mitigate overly enhanced representations. Extensive evaluations on both radiology and dermoscopic datasets demonstrate that CENet outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in multi-organ segmentation and boundary detail preservation, offering a robust and accurate solution for complex medical image analysis tasks. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/xmindflow/cenet.
医学图像分割,特别是在多领域场景中,需要在各种表示法中精确保留解剖结构。虽然深度学习已经推动了该领域的发展,但现有模型在准确表示边界、器官形态的变异以及下采样过程中的信息丢失方面仍存在挑战,这限制了其准确性和稳健性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Context Enhancement Network (CENet),这是一种新的分割框架,具有两个关键的创新点。首先,集成到跳过连接中的Dual Selective Enhancement Block (DSEB)可以增强边界细节,并以上下文感知的方式提高对小器官的检测。其次,解码器中的Context Feature Attention Module (CFAM)采用多尺度设计,以维持空间完整性、减少特征冗余,并减轻过度增强的表示。在放射学和皮肤科数据集上的广泛评估表明,CENet在多器官分割和边界细节保留方面优于最新(SOTA)方法,为复杂的医学图像分析任务提供了稳健且准确的解决方案。代码公开在https://github.com/xmindflow/cenet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Provisionally accepted at MICCAI-2025
摘要
针对医学图像分割在多领域场景中对解剖结构精确保留的需求,文章提出了一种新的分割框架Context Enhancement Network(CENet)。该框架具有两大创新点:一是通过集成Dual Selective Enhancement Block(DSEB)到skip连接以增强边界细节和检测较小器官的能力;二是Context Feature Attention Module(CFAM)采用多尺度设计以维持空间完整性、减少特征冗余并减轻过度增强表示。在放射和皮肤镜数据集上的广泛评估表明,CENet在多器官分割和边界细节保留方面优于现有先进技术,为复杂医学图像分析任务提供了稳健且准确的解决方案。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割在多领域场景中需要精确保留解剖结构。
- 现有模型在边界表示、器官形态变异及下采样中的信息损失方面存在挑战。
- CENet通过DSEB增强边界细节,提高小器官检测能力。
- CFAM采用多尺度设计来维持空间完整性,减少特征冗余。
- CENet在放射和皮肤镜数据集上的表现优于现有先进技术。
- CENet对于复杂医学图像分析任务提供了稳健且准确的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图