⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Fine-Grained Geometric Understanding in Large Multimodal Models
Authors:Kai Sun, Yushi Bai, Zhen Yang, Jiajie Zhang, Ji Qi, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
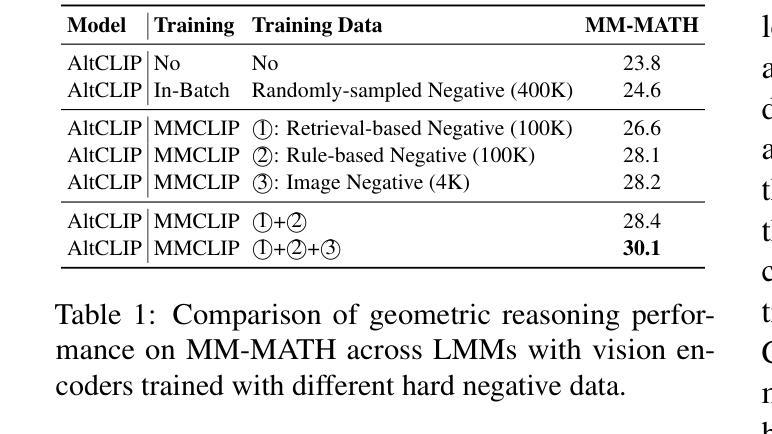
Benefiting from contrastively trained visual encoders on large-scale natural scene images, Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable performance across various visual perception tasks. However, the inherent limitations of contrastive learning upon summarized descriptions fundamentally restrict the capabilities of models in meticulous reasoning, particularly in crucial scenarios of geometric problem-solving. To enhance geometric understanding, we propose a novel hard negative contrastive learning framework for the vision encoder, which combines image-based contrastive learning using generation-based hard negatives created by perturbing diagram generation code, and text-based contrastive learning using rule-based negatives derived from modified geometric descriptions and retrieval-based negatives selected based on caption similarity. We train CLIP using our strong negative learning method, namely MMCLIP (Multimodal Math CLIP), and subsequently train an LMM for geometric problem-solving. Experiments show that our trained model, MMGeoLM, significantly outperforms other open-source models on three geometric reasoning benchmarks. Even with a size of 7B, it can rival powerful closed-source models like GPT-4o. We further study the impact of different negative sample construction methods and the number of negative samples on the geometric reasoning performance of LMM, yielding fruitful conclusions. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/THU-KEG/MMGeoLM.
受益于大规模自然场景图像上的对比训练视觉编码器,大型多模态模型(LMMs)在各种视觉感知任务中取得了显著的性能。然而,对比学习在总结描述上的固有局限性,从根本上限制了模型在精细推理方面的能力,特别是在解决几何问题的关键场景中应用时更加明显。为了增强对几何结构的理解,我们提出了一种新型的硬负对比学习框架,用于视觉编码器。该框架结合了基于图像对比学习使用生成式硬负样本,通过扰动图生成代码来创建这些样本;以及基于文本对比学习使用规则负样本,这些样本来源于修改后的几何描述和基于检索的负样本,根据描述相似性进行筛选。我们使用强大的负学习方法MMCLIP(多模态数学CLIP)训练CLIP模型,并进一步训练用于解决几何问题的LMM模型。实验表明,我们训练的MMGeoLM模型在三个几何推理基准测试中显著优于其他开源模型。即使规模达到7B,它也能与强大的闭源模型如GPT-4o相抗衡。我们还研究了不同负样本构建方法和负样本数量对LMM几何推理性能的影响,得出了有益的结论。代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/THU-KEG/MMGeoLM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模自然场景图像上的对比训练视觉编码器使大型多模态模型(LMMs)在各种视觉感知任务上取得了显著的性能。然而,对比学习在简洁描述上的固有局限性限制了模型在精细推理方面的能力,特别是在解决几何问题的关键场景中。为增强几何理解,我们提出了一种新型的硬负对比学习框架,该框架结合了基于图像和文本的对比学习。通过扰动图解生成代码生成基于生成的硬负样本,以及通过修改几何描述和基于检索的负样本选择,实现基于文本的对比学习。我们使用强大的负学习方法MMCLIP训练CLIP,随后训练用于解决几何问题的LMM。实验表明,我们训练的MMGeoLM模型在三个几何推理基准测试上显著优于其他开源模型,即使规模为7B,也能与强大的闭源模型GPT-4o相抗衡。
Key Takeaways
- Large Multimodal Models (LMMs)利用对比学习在视觉感知任务上取得显著性能。
- 对比学习在简洁描述上的局限性限制了模型在精细推理方面的能力。
- 为提高几何理解,提出了结合图像和文本对比学习的新型硬负对比学习框架。
- 通过扰动图解生成代码、修改几何描述和基于检索的负样本选择来实现基于生成的硬负样本和基于文本的对比学习。
- 使用MMCLIP的强负学习方法训练CLIP,随后训练用于解决几何问题的LMM。
- MMGeoLM模型在几何推理基准测试上表现优异,甚至能与强大闭源模型如GPT-4o相抗衡。
点此查看论文截图

A Contrastive Learning Foundation Model Based on Perfectly Aligned Sample Pairs for Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Hengtong Shen, Haiyan Gu, Haitao Li, Yi Yang, Agen qiu
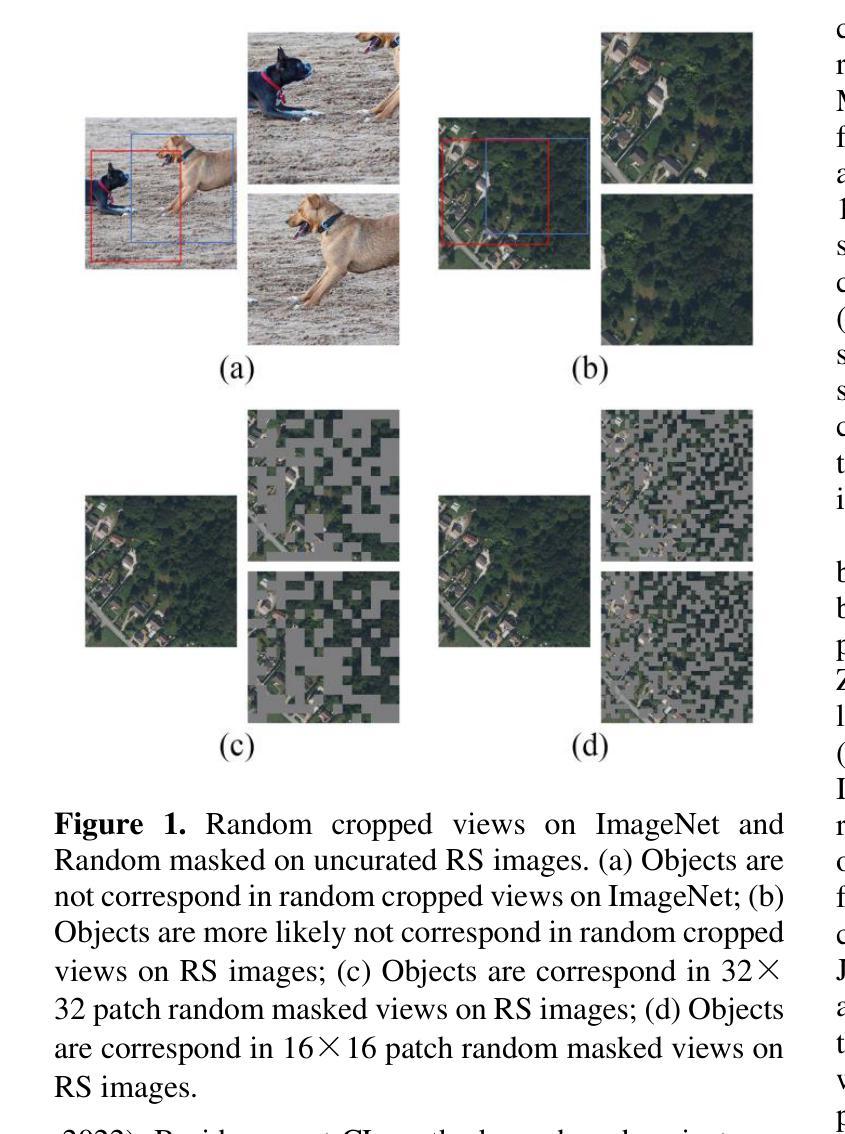
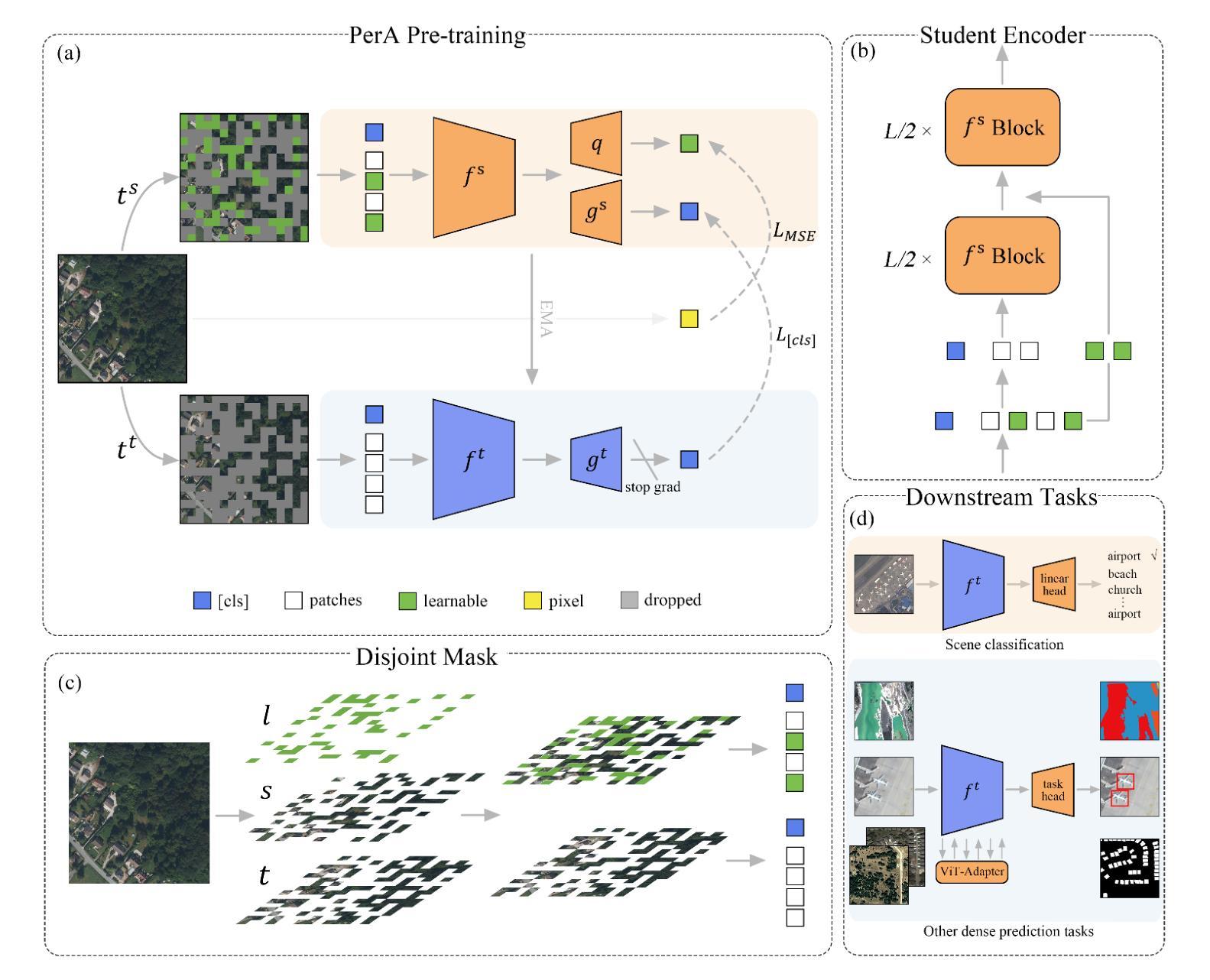
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) enables us to pre-train foundation models without costly labeled data. Among SSL methods, Contrastive Learning (CL) methods are better at obtaining accurate semantic representations in noise interference. However, due to the significant domain gap, while CL methods have achieved great success in many computer vision tasks, they still require specific adaptation for Remote Sensing (RS) images. To this end, we present a novel self-supervised method called PerA, which produces all-purpose RS features through semantically Perfectly Aligned sample pairs. Specifically, PerA obtains features from sampled views by applying spatially disjoint masks to augmented images rather than random cropping. With disjoint masks, we divide patches from different views into different parts that are semantically aligned but inconsistent in appearance. Our framework provides high-quality features by ensuring consistency between teacher and student and predicting learnable mask tokens. Compared to previous contrastive methods, our method demonstrates higher memory efficiency and can be trained with larger batches due to its sparse inputs. We also collect an unlabeled pre-training dataset, which contains about 5 million RS images. We conducted experiments on multiple downstream task datasets and achieved performance comparable to previous state-of-the-art methods with a limited model scale, which verified the superiority of our method. We hope this work will contribute to practical remote sensing interpretation works.
自监督学习(SSL)使我们能够在没有昂贵的标记数据的情况下预先训练基础模型。在SSL方法中,对比学习(CL)方法更擅长在噪声干扰中获得准确的语义表示。然而,由于领域差距较大,虽然对比学习方法在许多计算机视觉任务中取得了巨大成功,但它们仍然需要对遥感(RS)图像进行特定适配。为此,我们提出了一种新的自监督方法,称为PerA,它通过语义上完全对齐的样本对产生通用的遥感特征。具体来说,PerA通过对增强图像应用空间上不连续的面具来从采样视图中获取特征,而不是随机裁剪。通过不连续的面具,我们将来自不同视图的补丁分成语义上对齐但外观上不一致的部分。我们的框架通过确保教师和学生在预测可学习的掩码令牌时的一致性,从而提供高质量的特征。与之前的方法相比,我们的方法具有更高的内存效率,并且由于其稀疏输入,可以使用更大的批次进行训练。我们还收集了一个包含约5百万遥感图像的无标签预训练数据集。我们在多个下游任务数据集上进行了实验,在有限的模型规模下实现了与之前最先进的方法相当的性能,这验证了我们的方法的优越性。我们希望这项工作能为实际的遥感解释工作做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PerA的新型自监督学习方法,该方法通过语义上完美对齐的样本对生成通用遥感特征。通过在增强图像上应用空间不连续掩膜来获取特征,确保教师和学生之间的一致性,并预测可学习的掩码令牌。与之前的对比方法相比,该方法具有更高的内存效率,并且由于稀疏输入,可以训练更大的批次。在多个下游任务数据集上进行的实验验证了该方法的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) 用于预训练遥感模型的基石。
- 对比学习(CL)在噪声干扰下获得准确语义表示方面表现出优势。
- 对于遥感图像,对比学习方法需要特定适应,因为存在显著域差距。
- 提出了一种新型自监督方法PerA,通过语义完美对齐的样本对生成通用遥感特征。
- PerA使用空间不连续掩膜从样本视图中获取特征。
- PerA方法具有更高的内存效率和训练更大批次的能力。
点此查看论文截图


Domain and Task-Focused Example Selection for Data-Efficient Contrastive Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tyler Ward, Aaron Moseley, Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran
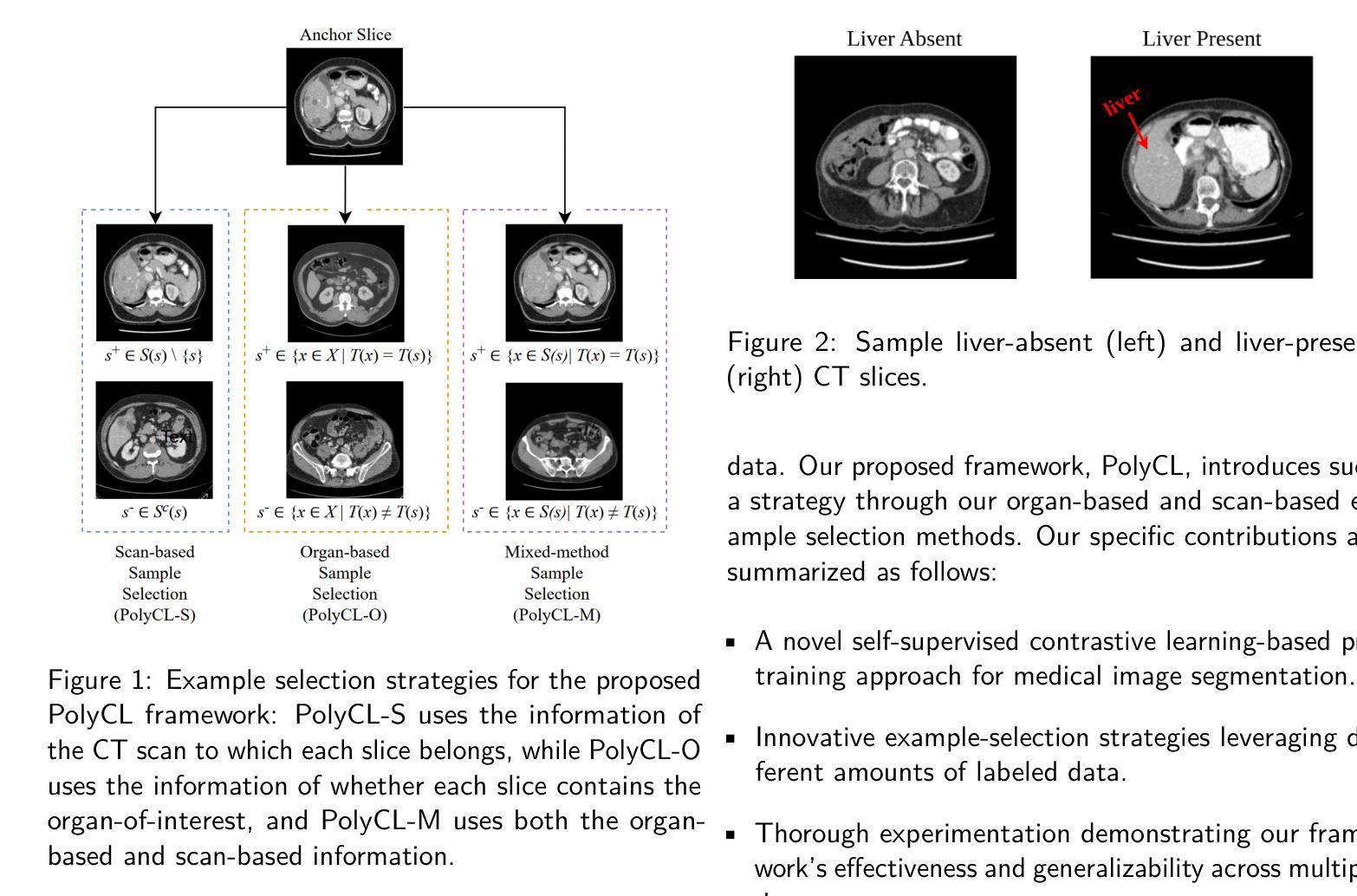
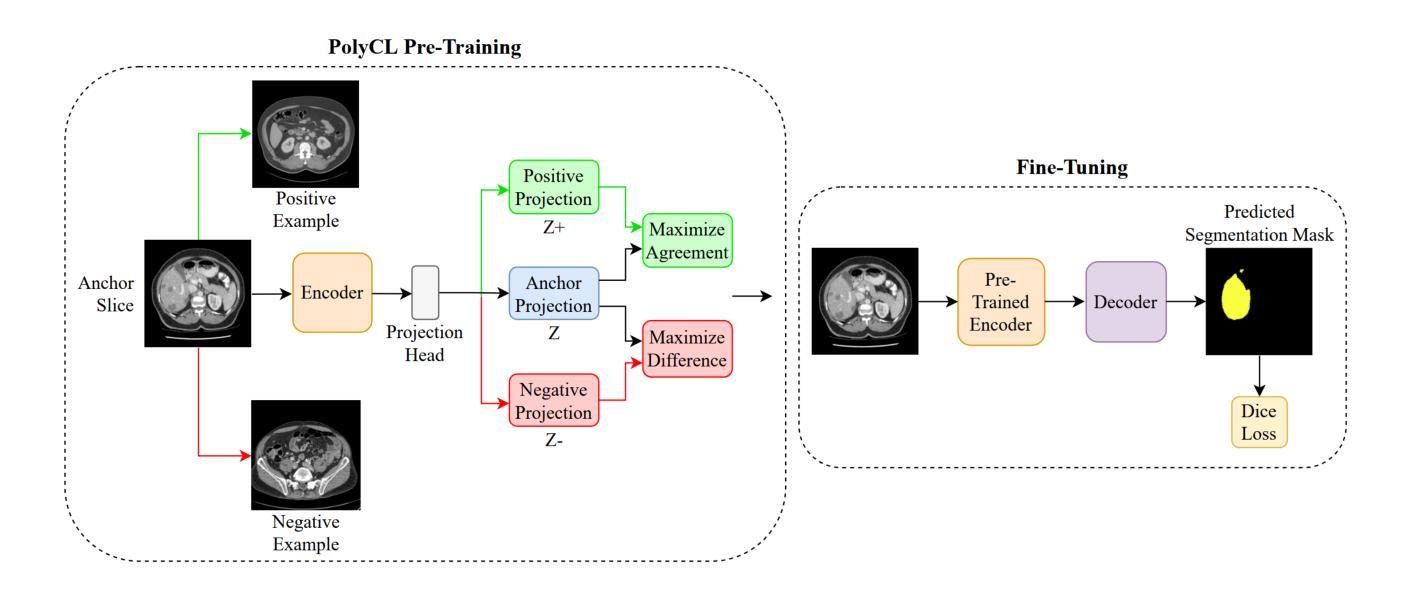
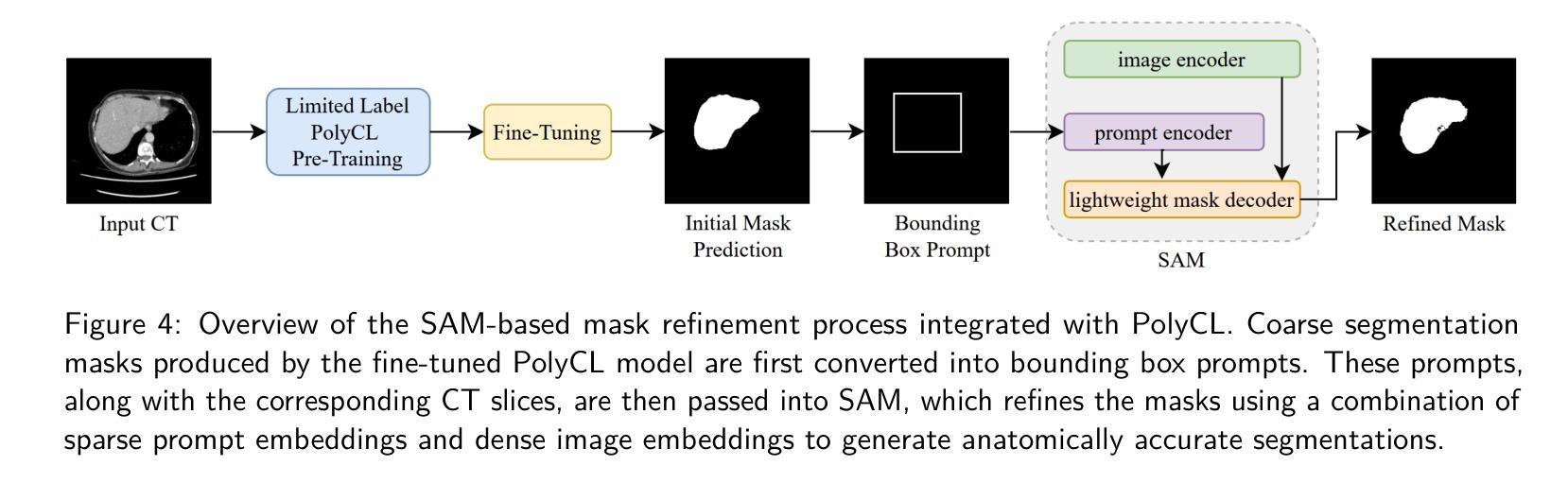
Segmentation is one of the most important tasks in the medical imaging pipeline as it influences a number of image-based decisions. To be effective, fully supervised segmentation approaches require large amounts of manually annotated training data. However, the pixel-level annotation process is expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone, hindering progress and making it challenging to perform effective segmentations. Therefore, models must learn efficiently from limited labeled data. Self-supervised learning (SSL), particularly contrastive learning via pre-training on unlabeled data and fine-tuning on limited annotations, can facilitate such limited labeled image segmentation. To this end, we propose a novel self-supervised contrastive learning framework for medical image segmentation, leveraging inherent relationships of different images, dubbed PolyCL. Without requiring any pixel-level annotations or unreasonable data augmentations, our PolyCL learns and transfers context-aware discriminant features useful for segmentation from an innovative surrogate, in a task-related manner. Additionally, we integrate the Segment Anything Model (SAM) into our framework in two novel ways: as a post-processing refinement module that improves the accuracy of predicted masks using bounding box prompts derived from coarse outputs, and as a propagation mechanism via SAM 2 that generates volumetric segmentations from a single annotated 2D slice. Experimental evaluations on three public computed tomography (CT) datasets demonstrate that PolyCL outperforms fully-supervised and self-supervised baselines in both low-data and cross-domain scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/tbwa233/PolyCL.
分割是医学影像处理流程中最重要的任务之一,因为它会影响许多基于图像的决定。为了有效进行分割,全监督分割方法需要大批量手动标注的训练数据。然而,像素级标注过程成本高昂、耗时且易出错,阻碍了进度,使得进行有效的分割具有挑战性。因此,模型必须有效地从有限的有标签数据中学习。自监督学习(SSL),特别是通过预训练无标签数据和微调有限标注进行对比学习,可以促进这种有限标注图像分割。为此,我们提出了一种用于医学图像分割的新型自监督对比学习框架,利用不同图像的内在关系,被称为PolyCL。我们的PolyCL不需要任何像素级标注或不合理的数据增强,而是以任务相关的方式,从一个创新代理中学习并转移有助于分割的上下文感知判别特征。此外,我们以两种新颖的方式将Segment Anything Model(SAM)集成到我们的框架中:作为一种后处理优化模块,利用来自粗略输出的边界框提示提高预测掩码的准确性;以及作为一种通过SAM 2的传播机制,从单个注释的2D切片生成体积分割。在三个公共计算机断层扫描(CT)数据集上的实验评估表明,PolyCL在低数据和跨域场景中均超越了全监督和自监督基准。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tbwa233/PolyCL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自监督对比学习框架的医疗图像分割方法PolyCL,它利用不同图像之间的内在关系,无需像素级标注,就能从创新代理中学习并转移上下文感知的判别特征用于分割任务。此外,PolyCL还将Segment Anything Model(SAM)作为后处理细化模块和传播机制集成到框架中,以提高预测掩码的准确性并生成体积分割。实验评估显示,PolyCL在低数据量和跨域场景中均优于全监督和自监督基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 分割是医疗成像流程中最重要的任务之一,影响基于图像的多个决策。
- 完全监督的分割方法需要大量手动标注的训练数据,但这一标注过程成本高、耗时长且容易出错。
- 自监督学习(SSL)特别是通过预训练无标签数据和微调有限标注的对比学习,有助于解决从有限标注数据中有效学习的问题。
- PolyCL是一种新型自监督对比学习框架,利用不同图像之间的内在关系进行医疗图像分割。
- PolyCL不需要像素级标注或无理性的数据增强,能从创新代理中学习上下文感知的判别特征,并以任务相关的方式应用于分割。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)被集成到PolyCL框架中,作为后处理细化模块和传播机制,提高预测掩码的准确性并生成体积分割。
点此查看论文截图