⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
Zero-Shot Pseudo Labels Generation Using SAM and CLIP for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Nagito Saito, Shintaro Ito, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki
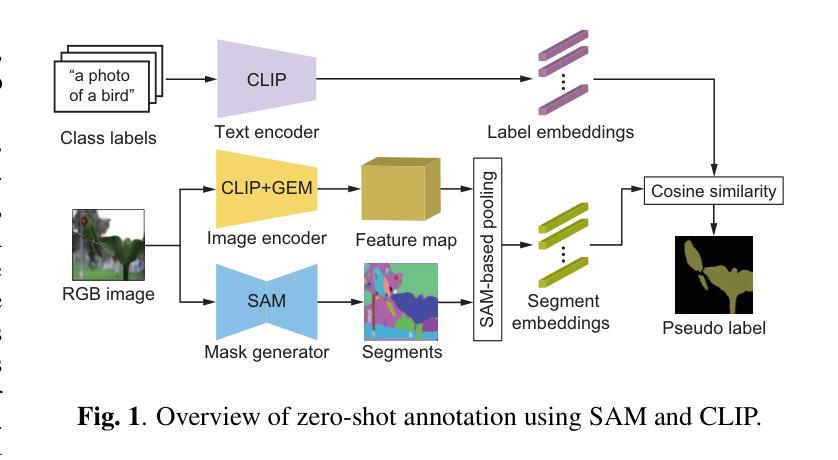
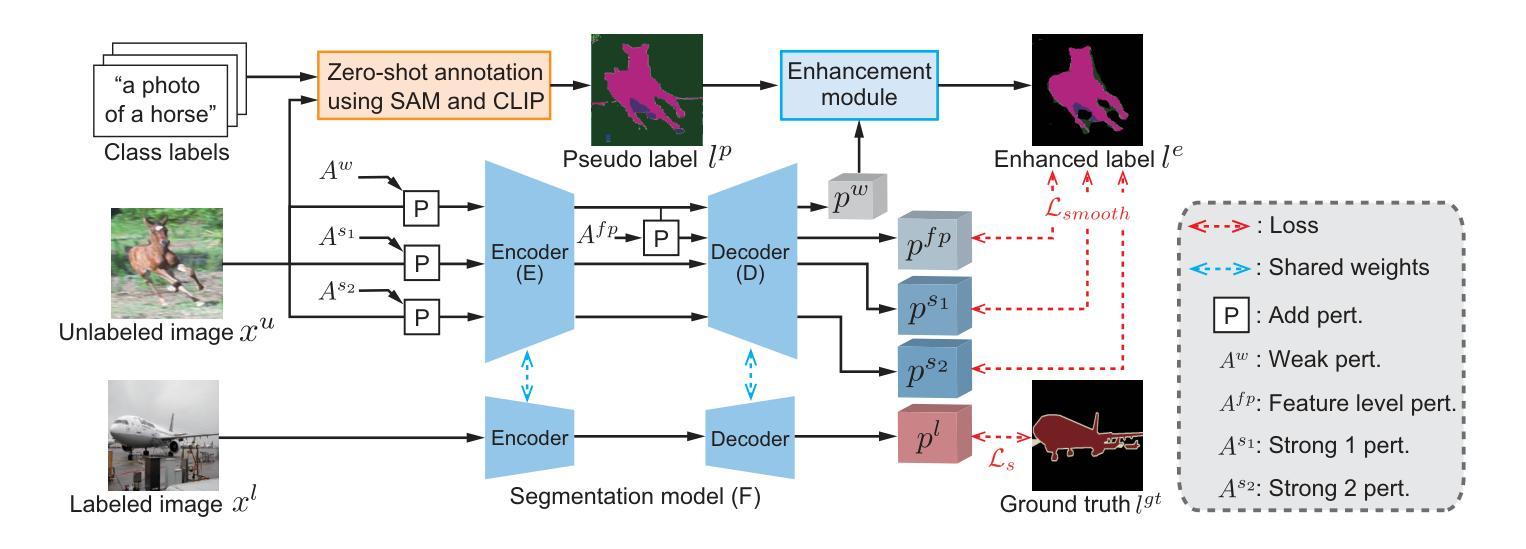
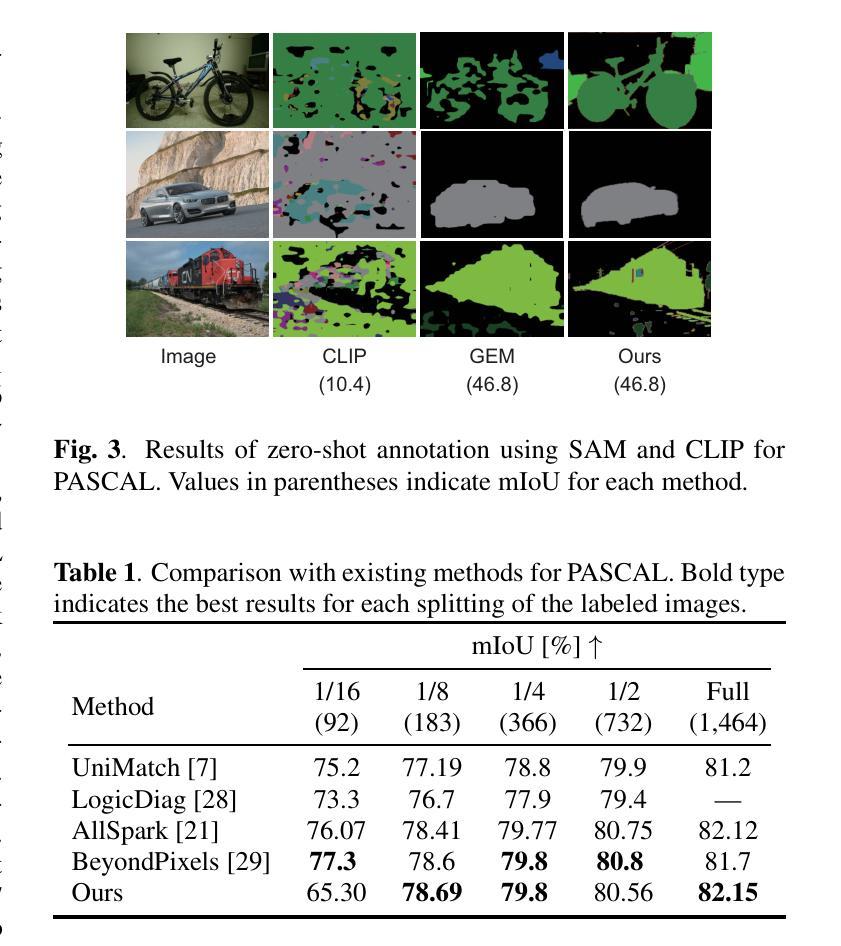
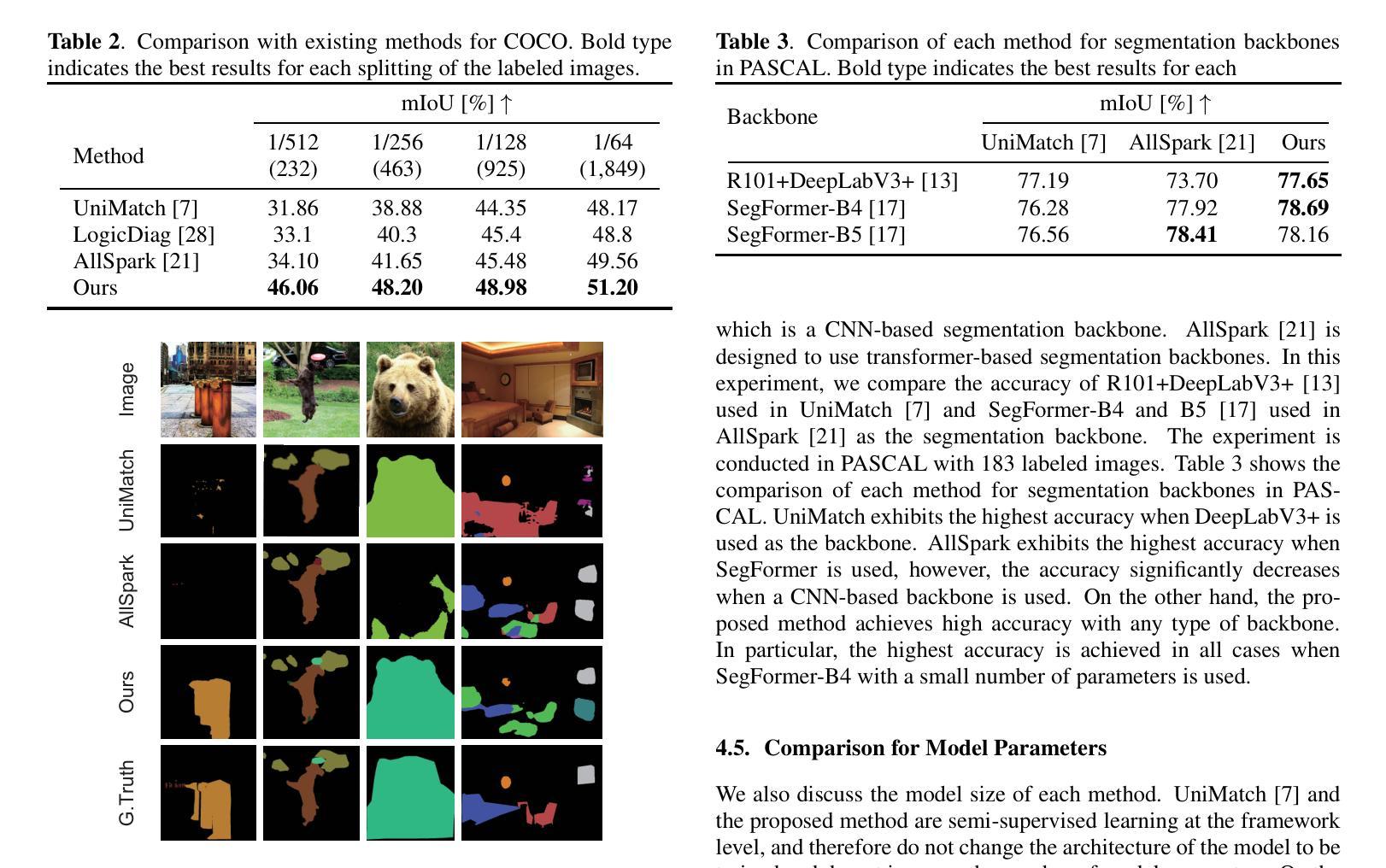
Semantic segmentation is a fundamental task in medical image analysis and autonomous driving and has a problem with the high cost of annotating the labels required in training. To address this problem, semantic segmentation methods based on semi-supervised learning with a small number of labeled data have been proposed. For example, one approach is to train a semantic segmentation model using images with annotated labels and pseudo labels. In this approach, the accuracy of the semantic segmentation model depends on the quality of the pseudo labels, and the quality of the pseudo labels depends on the performance of the model to be trained and the amount of data with annotated labels. In this paper, we generate pseudo labels using zero-shot annotation with the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP), improve the accuracy of the pseudo labels using the Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach (UniMatch), and use them as enhanced labels to train a semantic segmentation model. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through the experiments using the public datasets: PASCAL and MS COCO.
语义分割是医学图像分析和自动驾驶中的一项基本任务,存在训练时标注标签成本高昂的问题。为了解决这一问题,已经提出了基于半监督学习的小量标注数据的语义分割方法。例如,一种方法是使用带有标注标签和伪标签的图像来训练语义分割模型。在此方法中,语义分割模型的准确性取决于伪标签的质量,而伪标签的质量又取决于待训练模型的性能以及带有标注标签的数据量。在本文中,我们使用零样本标注、借助Segment Anything Model(SAM)和Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP)来生成伪标签,采用Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach(UniMatch)提高伪标签的准确性,然后将其作为增强标签来训练语义分割模型。通过PASCAL和MS COCO公开数据集的实验,验证了所提方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP 2025
Summary:
针对医疗图像分析和自动驾驶中的语义分割任务中标注成本高昂的问题,提出了基于半监督学习的语义分割方法。本文通过使用Segment Anything Model(SAM)和Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP)生成零样本标注的伪标签,并采用Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach(UniMatch)提高伪标签质量,将其作为增强标签训练语义分割模型。在PASCAL和MS COCO公开数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 语义分割是医疗图像分析和自动驾驶中的基础任务,但标注成本高昂是其主要问题。
- 提出了基于半监督学习的语义分割方法,使用少量标注数据和伪标签进行训练。
- 伪标签的质量取决于待训练模型的表现和标注数据的数量。
- 利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)和Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining(CLIP)生成伪标签。
- 采用Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach(UniMatch)提高伪标签的准确性。
- 将这些增强标签用于训练语义分割模型,提高模型精度。
点此查看论文截图

IGL-DT: Iterative Global-Local Feature Learning with Dual-Teacher Semantic Segmentation Framework under Limited Annotation Scheme
Authors:Dinh Dai Quan Tran, Hoang-Thien Nguyen, Thanh-Huy Nguyen, Gia-Van To, Tien-Huy Nguyen, Quan Nguyen
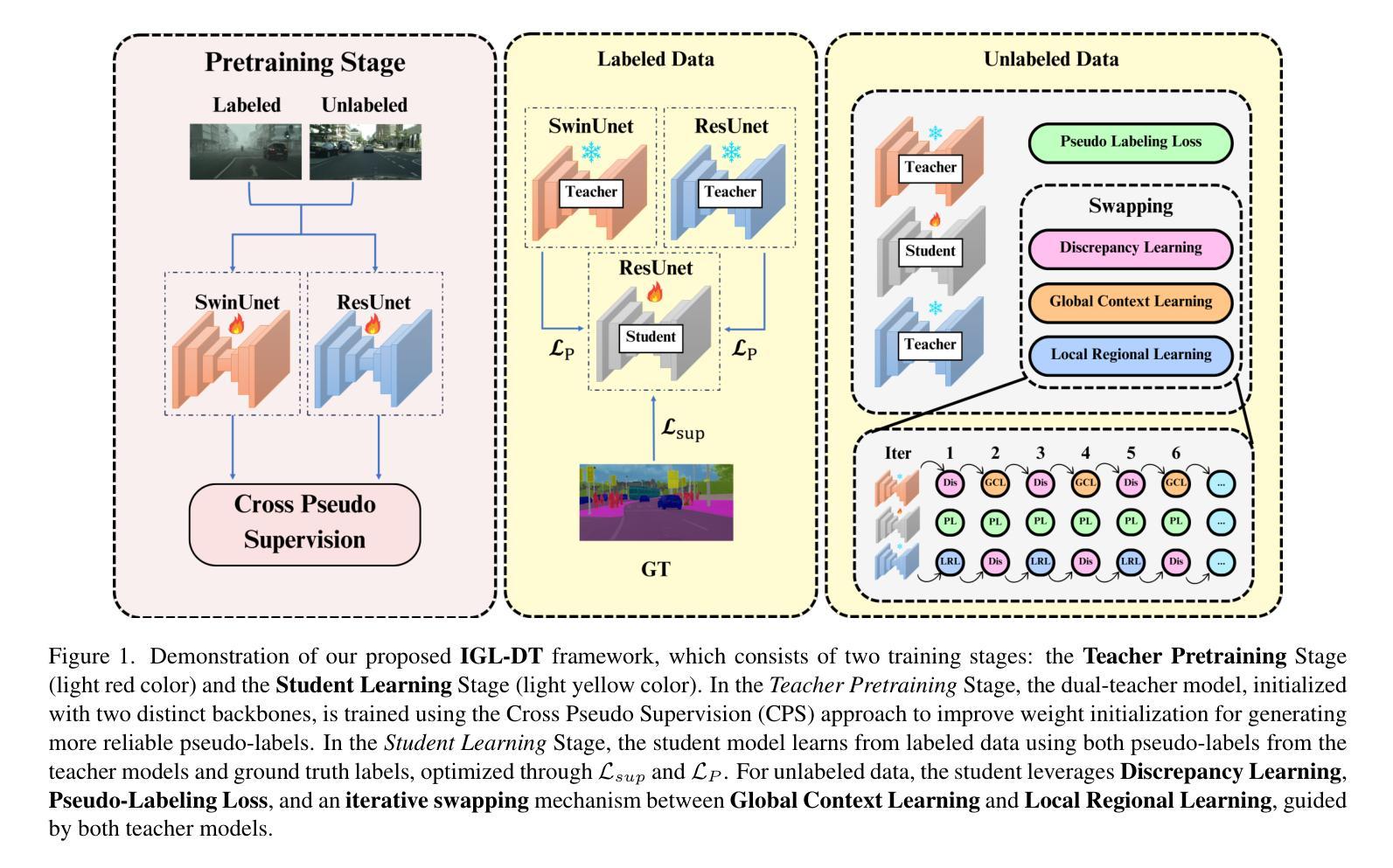
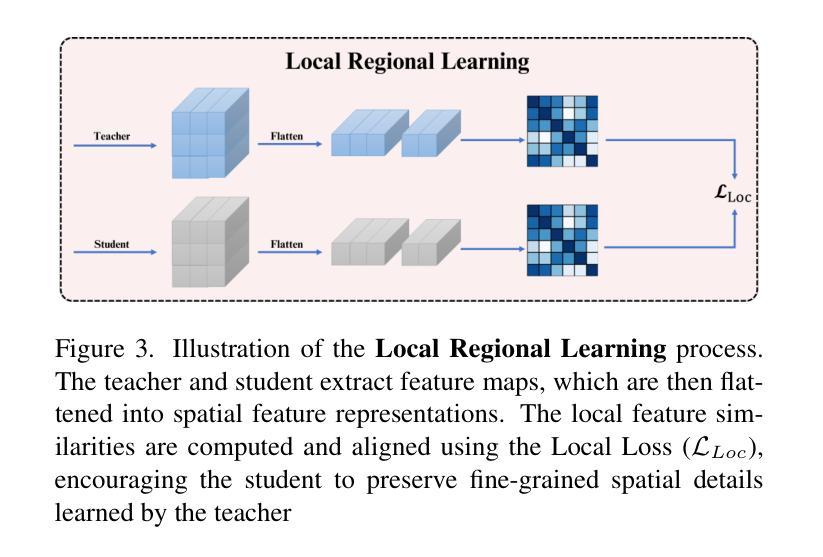
Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (SSSS) aims to improve segmentation accuracy by leveraging a small set of labeled images alongside a larger pool of unlabeled data. Recent advances primarily focus on pseudo-labeling, consistency regularization, and co-training strategies. However, existing methods struggle to balance global semantic representation with fine-grained local feature extraction. To address this challenge, we propose a novel tri-branch semi-supervised segmentation framework incorporating a dual-teacher strategy, named IGL-DT. Our approach employs SwinUnet for high-level semantic guidance through Global Context Learning and ResUnet for detailed feature refinement via Local Regional Learning. Additionally, a Discrepancy Learning mechanism mitigates over-reliance on a single teacher, promoting adaptive feature learning. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior segmentation performance across various data regimes.
半监督语义分割(SSSS)旨在利用少量标记图像和大量未标记数据来提高分割精度。最近的进展主要集中在伪标签、一致性正则化和协同训练策略上。然而,现有方法在平衡全局语义表示和精细局部特征提取方面存在困难。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的三分支半监督分割框架,采用双教师策略,名为IGL-DT。我们的方法采用SwinUnet进行高级语义指导的全局上下文学习,以及ResUnet进行细节特征精修的局部区域学习。此外,差异学习机制减轻了对单一教师的过度依赖,促进了自适应特征学习。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进的方法,在各种数据环境下实现优越的分割性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
SSSSS方法旨在通过少量有标签图像和大量无标签数据的结合来提高分割精度。为应对全局语义表示与精细局部特征提取的平衡挑战,提出了一种新型的三分支半监督分割框架IGL-DT,采用双教师策略。通过全局上下文学习使用SwinUnet进行高级语义指导,通过局部区域学习使用ResUnet进行详细的特征细化。差异学习机制减轻了方法对单一教师的过度依赖,促进了自适应特征学习。在基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于最新技术,在各种数据条件下实现了出色的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- SSSS方法利用少量有标签图像和大量无标签数据提高分割精度。
- 当前方法面临全局语义与局部特征提取的平衡挑战。
- 提出的IGL-DT框架采用双教师策略应对这一挑战。
- SwinUnet用于高级语义指导的全局上下文学习。
- ResUnet用于详细的特征细化局部区域学习。
- 差异学习机制促进自适应特征学习,减轻对单一教师的依赖。
- 在基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法在多种数据条件下实现了优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

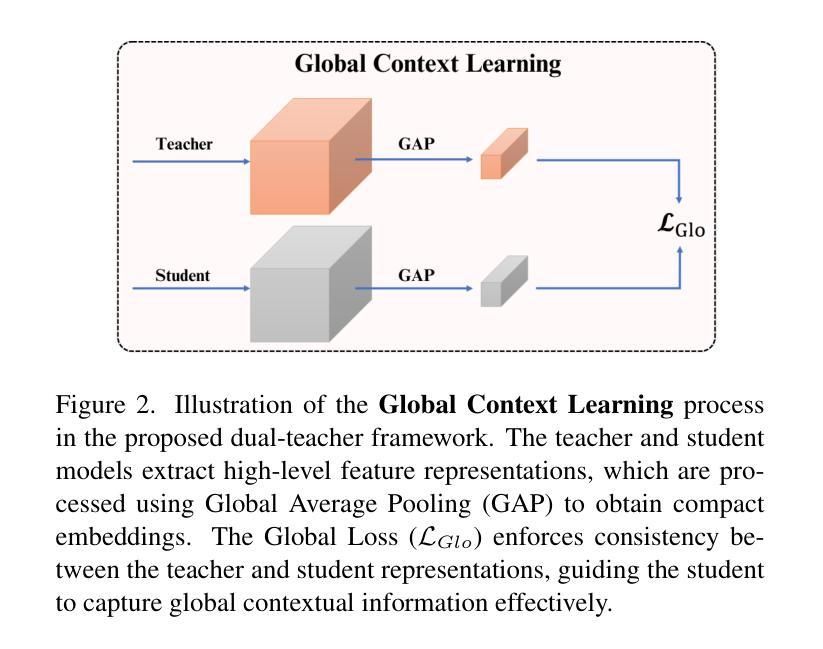
PointOBB-v3: Expanding Performance Boundaries of Single Point-Supervised Oriented Object Detection
Authors:Peiyuan Zhang, Junwei Luo, Xue Yang, Yi Yu, Qingyun Li, Yue Zhou, Xiaosong Jia, Xudong Lu, Jingdong Chen, Xiang Li, Junchi Yan, Yansheng Li
With the growing demand for oriented object detection (OOD), recent studies on point-supervised OOD have attracted significant interest. In this paper, we propose PointOBB-v3, a stronger single point-supervised OOD framework. Compared to existing methods, it generates pseudo rotated boxes without additional priors and incorporates support for the end-to-end paradigm. PointOBB-v3 functions by integrating three unique image views: the original view, a resized view, and a rotated/flipped (rot/flp) view. Based on the views, a scale augmentation module and an angle acquisition module are constructed. In the first module, a Scale-Sensitive Consistency (SSC) loss and a Scale-Sensitive Feature Fusion (SSFF) module are introduced to improve the model’s ability to estimate object scale. To achieve precise angle predictions, the second module employs symmetry-based self-supervised learning. Additionally, we introduce an end-to-end version that eliminates the pseudo-label generation process by integrating a detector branch and introduces an Instance-Aware Weighting (IAW) strategy to focus on high-quality predictions. We conducted extensive experiments on the DIOR-R, DOTA-v1.0/v1.5/v2.0, FAIR1M, STAR, and RSAR datasets. Across all these datasets, our method achieves an average improvement in accuracy of 3.56% in comparison to previous state-of-the-art methods. The code will be available at https://github.com/ZpyWHU/PointOBB-v3.
随着面向对象检测(OOD)需求的不断增长,关于点监督OOD的最近研究引起了极大的兴趣。本文提出了PointOBB-v3,这是一种更强的单点监督OOD框架。与现有方法相比,它能够在没有额外先验知识的情况下生成伪旋转框,并支持端到端的范式。PointOBB-v3通过集成三种独特的图像视图来发挥作用:原始视图、调整大小后的视图以及旋转/翻转(旋转/翻转)视图。基于这些视图,构建了尺度增强模块和角度获取模块。在第一个模块中,引入了尺度敏感一致性(SSC)损失和尺度敏感特征融合(SSFF)模块,以提高模型对目标尺度的估计能力。为了实现精确的角度预测,第二个模块采用了基于对称性的自监督学习。此外,我们还引入了端到端的版本,通过集成检测器分支来消除伪标签生成过程,并引入了实例感知加权(IAW)策略,以关注高质量预测。我们在DIOR-R、DOTA-v1.0/v1.5/v2.0、FAIR1M、STAR和RSAR数据集上进行了大量实验。与以前的最先进方法相比,我们的方法在所有这些数据集上的平均准确率提高了3.56%。代码将在https://github.com/ZpyWHU/PointOBB-v3上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 7 figures, 11 tables
Summary
该文提出PointOBB-v3,一种强大的单点监督导向物体检测框架。它集成了三种独特的图像视图,通过规模增强模块和角度获取模块提高模型性能。实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上的准确度平均提高了3.56%。
Key Takeaways
- PointOBB-v3是一种新的单点监督导向物体检测框架,适用于日益增长的有向物体检测需求。
- 该框架通过整合三种图像视图(原始视图、调整大小视图和旋转/翻转视图)来提高性能。
- 规模增强模块和角度获取模块被构建以提高模型的物体尺度估计和精确角度预测能力。
- PointOBB-v3通过引入端对端版本消除了伪标签生成过程,并引入了实例感知加权策略来关注高质量预测。
- 实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上的准确度显著提高,平均提高了3.56%。
- 模型的代码将在[网址]公开。
点此查看论文截图

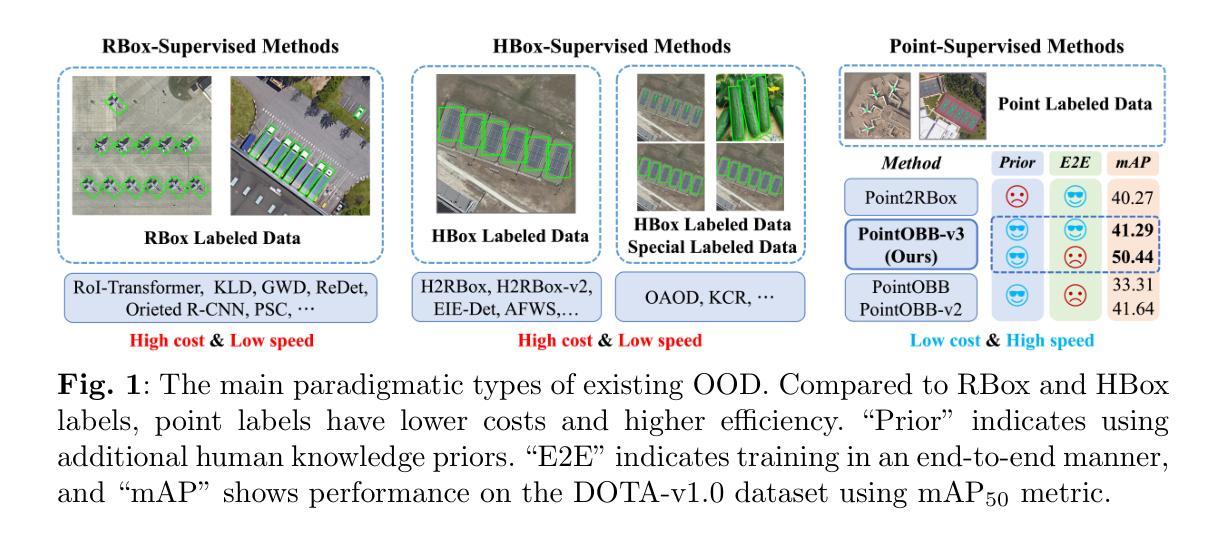
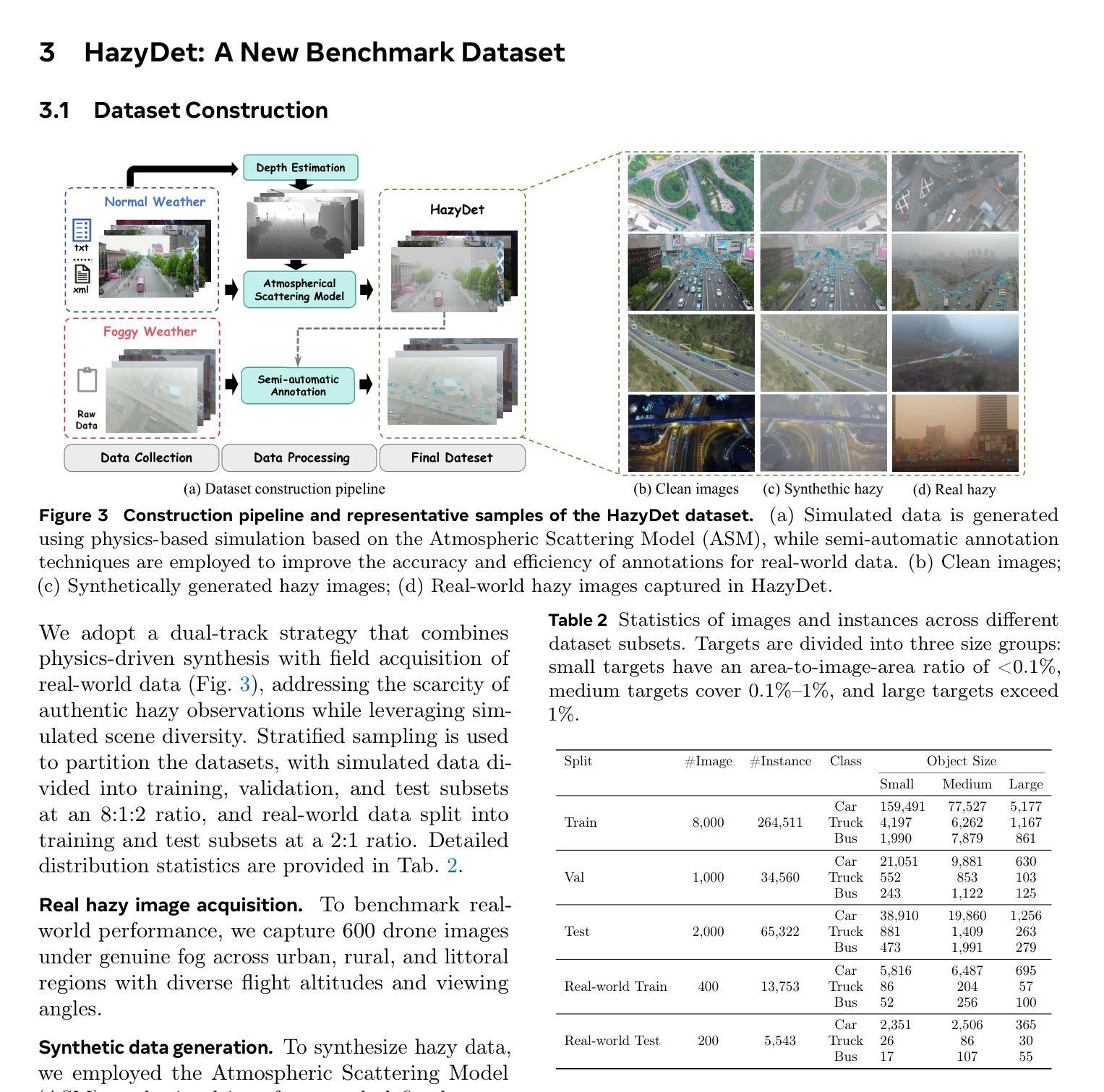
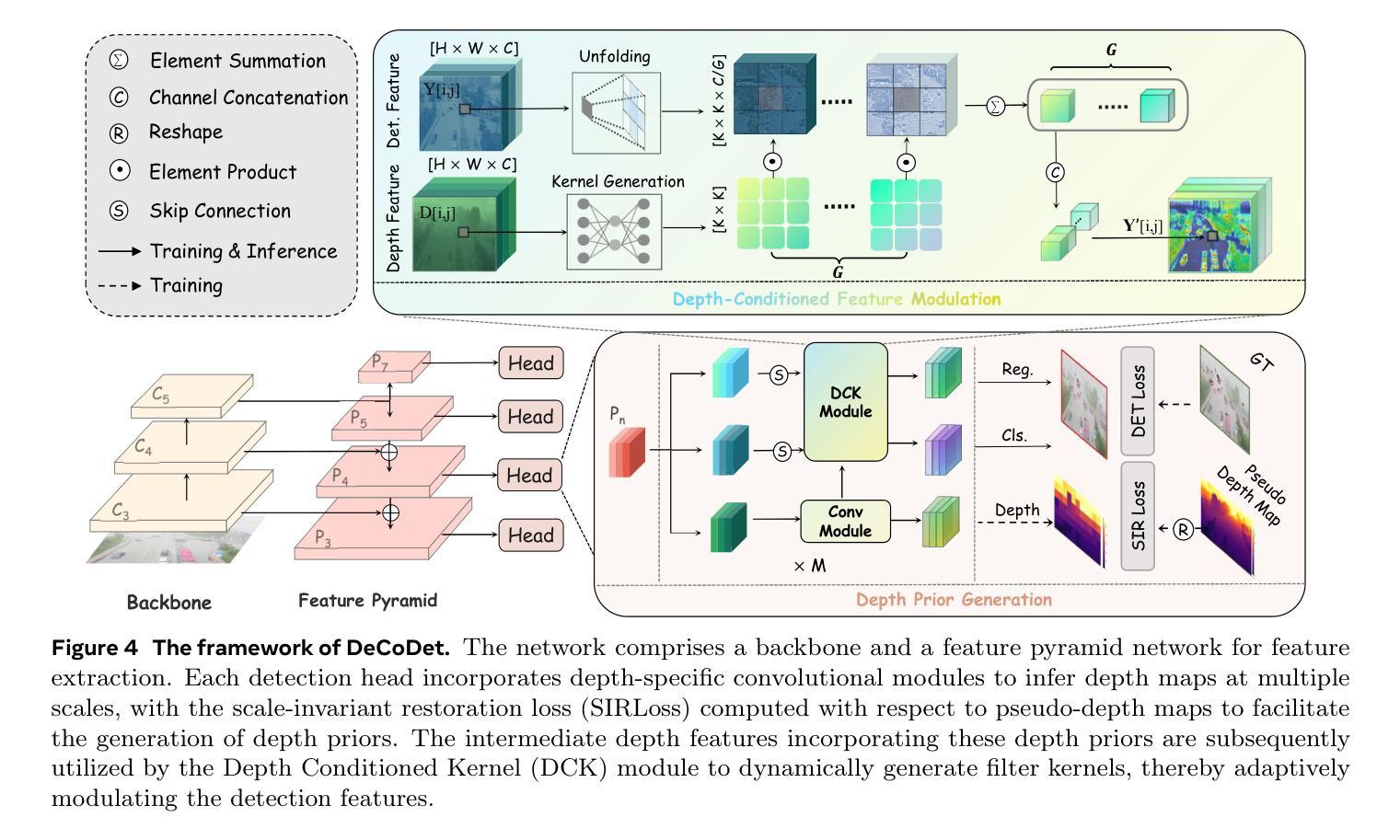
HazyDet: Open-Source Benchmark for Drone-View Object Detection with Depth-Cues in Hazy Scenes
Authors:Changfeng Feng, Zhenyuan Chen, Xiang Li, Chunping Wang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Yimian Dai, Qiang Fu
Object detection from aerial platforms under adverse atmospheric conditions, particularly haze, is paramount for robust drone autonomy. Yet, this domain remains largely underexplored, primarily hindered by the absence of specialized benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we present \textit{HazyDet}, the first, large-scale benchmark specifically designed for drone-view object detection in hazy conditions. Comprising 383,000 real-world instances derived from both naturally hazy captures and synthetically hazed scenes augmented from clear images, HazyDet provides a challenging and realistic testbed for advancing detection algorithms. To address the severe visual degradation induced by haze, we propose the Depth-Conditioned Detector (DeCoDet), a novel architecture that integrates a Depth-Conditioned Kernel to dynamically modulate feature representations based on depth cues. The practical efficacy and robustness of DeCoDet are further enhanced by its training with a Progressive Domain Fine-Tuning (PDFT) strategy to navigate synthetic-to-real domain shifts, and a Scale-Invariant Refurbishment Loss (SIRLoss) to ensure resilient learning from potentially noisy depth annotations. Comprehensive empirical validation on HazyDet substantiates the superiority of our unified DeCoDet framework, which achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing the closest competitor by a notable +1.5% mAP on challenging real-world hazy test scenarios. Our dataset and toolkit are available at https://github.com/GrokCV/HazyDet.
从高空平台在恶劣大气条件下,尤其是雾霾中的目标检测,对于实现稳健的无人机自主性至关重要。然而,这个领域仍然在很大程度上被忽视,其主要原因是缺乏专门的基准测试集。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了首个专门用于雾霾条件下无人机视角目标检测的基准测试集——HazyDet。HazyDet包含从自然雾霾捕捉和通过合成手段从清晰图像中增强模糊场景所衍生的真实世界实例,总计达三十八点三万例,提供了一个富有挑战性和现实意义的测试环境来推动检测算法的发展。为了解决雾霾引起的严重视觉退化问题,我们提出了深度条件检测器(DeCoDet),这是一种新型架构,它集成了深度条件核来根据深度线索动态调整特征表示。通过采用渐进域微调(PDFT)策略训练DeCoDet来应对合成域到真实域的转移,并采用尺度不变翻新损失(SIRLoss)来确保从潜在的噪声深度标注中进行恢复学习。在HazyDet上进行的综合实证研究证实了我们统一的DeCoDet框架的优越性,它实现了最先进的性能表现,在具有挑战性的真实世界雾霾测试场景中比最接近的竞争对手高出+1.5%的mAP。我们的数据集和工具箱可以在https://github.com/GrokCV/HazyDet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We have updated our method, resulting in a large improvement in detection performance
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对无人机在雾霾环境下物体检测的大型基准测试集HazyDet。该数据集通过自然雾霾捕捉和从清晰图像合成雾霾场景增强得到,为改进检测算法提供了具有挑战性和现实性的测试平台。为解决雾霾引起的严重视觉退化问题,提出了Depth-Conditioned Detector(DeCoDet)架构,通过深度线索动态调制特征表示。此外,采用渐进域微调策略和尺度不变修复损失来增强模型的实用性和稳健性。在HazyDet上的综合实证验证证实了DeCoDet框架的优越性,其在具有挑战性的真实雾霾测试场景中实现了超过最接近竞争对手的+1.5%的mAP提升。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一个新的基准测试集HazyDet,专门针对无人机在雾霾环境中的物体检测。
- HazyDet数据集由自然雾霾捕捉和从清晰图像合成的雾霾场景增强得到,为检测算法提供了现实性和挑战性的测试平台。
- 提出了一种新的架构Depth-Conditioned Detector(DeCoDet),利用深度线索动态调制特征表示以解决雾霾引起的视觉退化问题。
- DeCoDet采用渐进域微调策略和尺度不变修复损失来增强模型的实用性和稳健性。
- DeCoDet框架在HazyDet上的表现超过了其他方法,实现了更高的检测精度。
- DeCoDet在具有挑战性的真实雾霾测试场景中达到了显著的+1.5%的mAP提升。
点此查看论文截图

SpecDETR: A Transformer-based Hyperspectral Point Object Detection Network
Authors:Zhaoxu Li, Wei An, Gaowei Guo, Longguang Wang, Yingqian Wang, Zaiping Lin
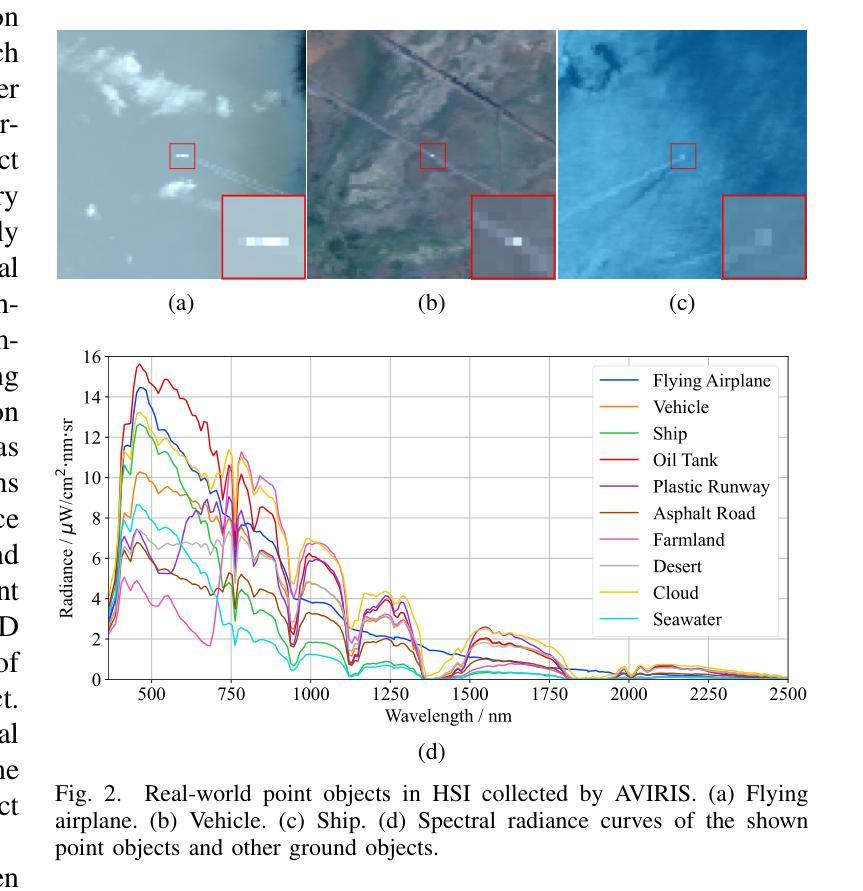
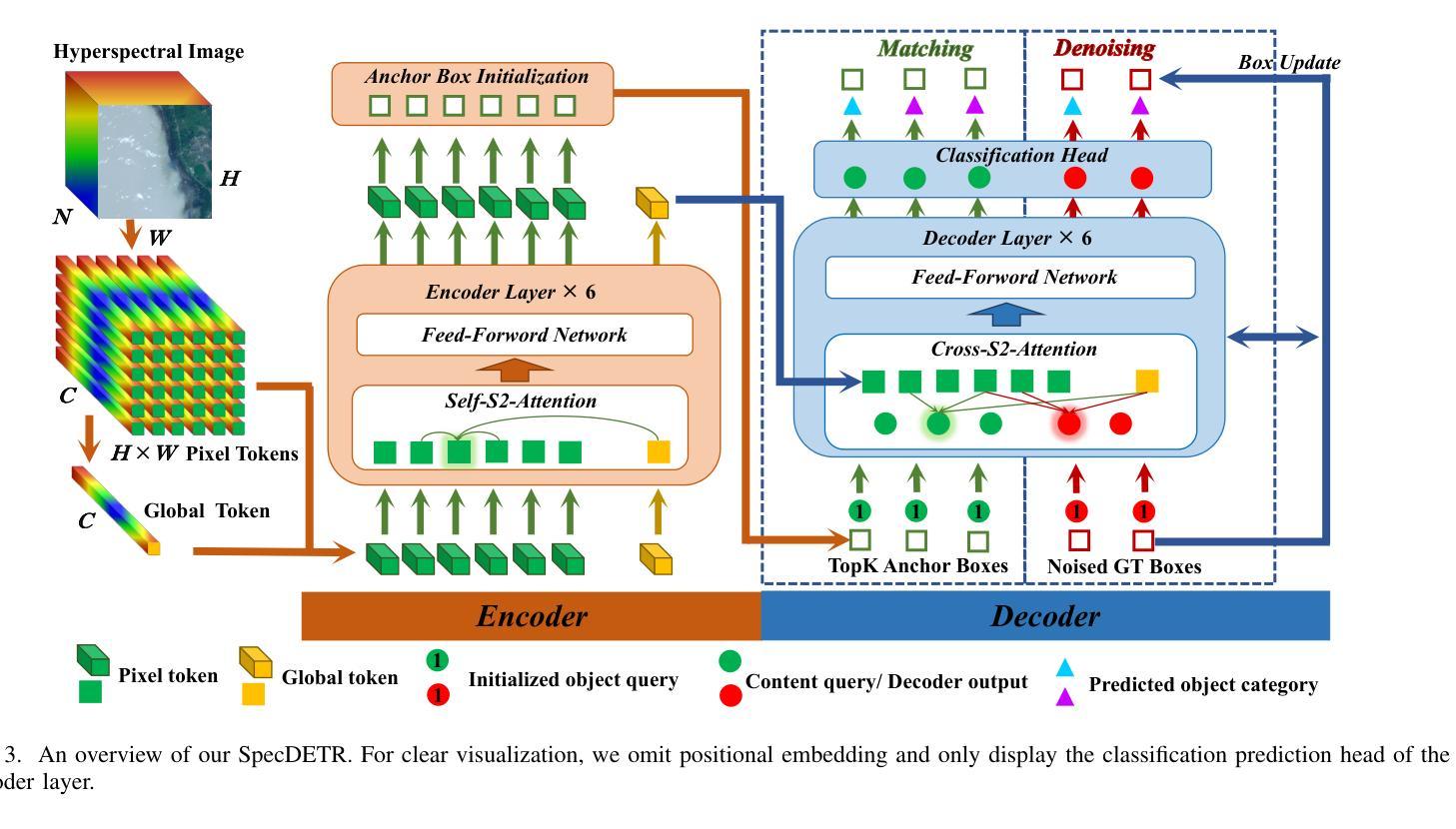
Hyperspectral target detection (HTD) aims to identify specific materials based on spectral information in hyperspectral imagery and can detect extremely small-sized objects, some of which occupy a smaller than one-pixel area. However, existing HTD methods are developed based on per-pixel binary classification, neglecting the three-dimensional cube structure of hyperspectral images (HSIs) that integrates both spatial and spectral dimensions. The synergistic existence of spatial and spectral features in HSIs enable objects to simultaneously exhibit both, yet the per-pixel HTD framework limits the joint expression of these features. In this paper, we rethink HTD from the perspective of spatial-spectral synergistic representation and propose hyperspectral point object detection as an innovative task framework. We introduce SpecDETR, the first specialized network for hyperspectral multi-class point object detection, which eliminates dependence on pre-trained backbone networks commonly required by vision-based object detectors. SpecDETR uses a multi-layer Transformer encoder with self-excited subpixel-scale attention modules to directly extract deep spatial-spectral joint features from hyperspectral cubes. We develop a simulated hyperspectral point object detection benchmark termed SPOD, and for the first time, evaluate and compare the performance of visual object detection networks and HTD methods on hyperspectral point object detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed SpecDETR outperforms SOTA visual object detection networks and HTD methods. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ZhaoxuLi123/SpecDETR.
超光谱目标检测(HTD)旨在基于超光谱图像中的光谱信息识别特定材料,并能够检测极小尺寸的对象,其中一些对象的面积小于一个像素。然而,现有的HTD方法主要基于像素级的二元分类开发,忽略了超光谱图像(HSI)的三维立方体结构,该结构融合了空间和光谱两个维度。HSI中空间和光谱特征的协同存在使得对象可以同时表现出这两种特征,但基于像素的HTD框架限制了这些特征的联合表达。在本文中,我们从空间光谱协同表示的角度重新思考HTD,并提出超光谱点对象检测作为创新的任务框架。我们引入了SpecDETR,这是第一个用于超光谱多类点对象检测的专用网络,它消除了对视觉对象检测器通常所需的预训练主干网络的依赖。SpecDETR使用多层Transformer编码器以及自激励子像素尺度注意力模块,直接从超光谱立方体中提取深度空间光谱联合特征。我们开发了一个名为SPOD的模拟超光谱点对象检测基准,首次对视觉对象检测网络和HTD方法在超光谱点对象检测上的性能进行了评估和比较。大量实验表明,我们提出的SpecDETR优于最新的视觉对象检测网络和HTD方法。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/ZhaoxuLi123/SpecDETR找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
光谱目标检测旨在利用高光谱图像中的光谱信息识别特定材料,并能检测到小于单像素区域的小尺寸物体。然而,现有的光谱目标检测方法大多基于像素级的二分类,忽略了高光谱图像的三维立方体结构,该结构融合了空间和光谱维度。本文从新角度重新审视光谱目标检测,提出高光谱点目标检测作为任务框架。并引入SpecDETR网络,该网络无需依赖预先训练的骨架网络即可进行高光谱多类点目标检测。SpecDETR使用多层Transformer编码器以及带有自激励子像素尺度注意力模块的结构,直接提取高光谱立方体中的深空间-光谱联合特征。此外,还构建了模拟的高光谱点目标检测基准数据集SPOD并进行评测比较。实验证明,SpecDETR优于其他前沿的视觉目标检测网络以及光谱目标检测方法。相关代码和数据集可通过https://github.com/ZhaoxuLi123/SpecDETR获取。
Key Takeaways:
- 高光谱目标检测(HTD)能够识别特定材料和小尺寸物体。
- 现有HTD方法主要基于像素级二分类,忽略了高光谱图像的三维立方体结构(空间与光谱维度)。
- 本文提出从空间-光谱协同表示角度重新思考HTD,并引入高光谱点目标检测作为新的任务框架。
- 提出了首个针对高光谱多类点目标检测的专用网络SpecDETR,无需依赖预先训练的骨架网络。
- SpecDETR使用带有自激励子像素尺度注意力模块的多层Transformer编码器,直接从高光谱立方体中提取特征。
- 建立了模拟的高光谱点目标检测基准数据集SPOD,并进行了性能评估和比较。
点此查看论文截图

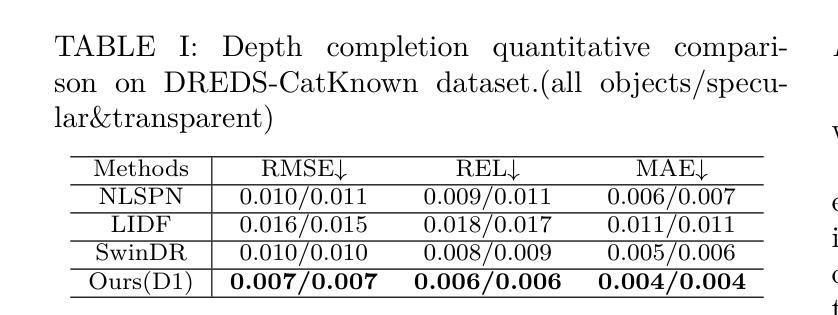
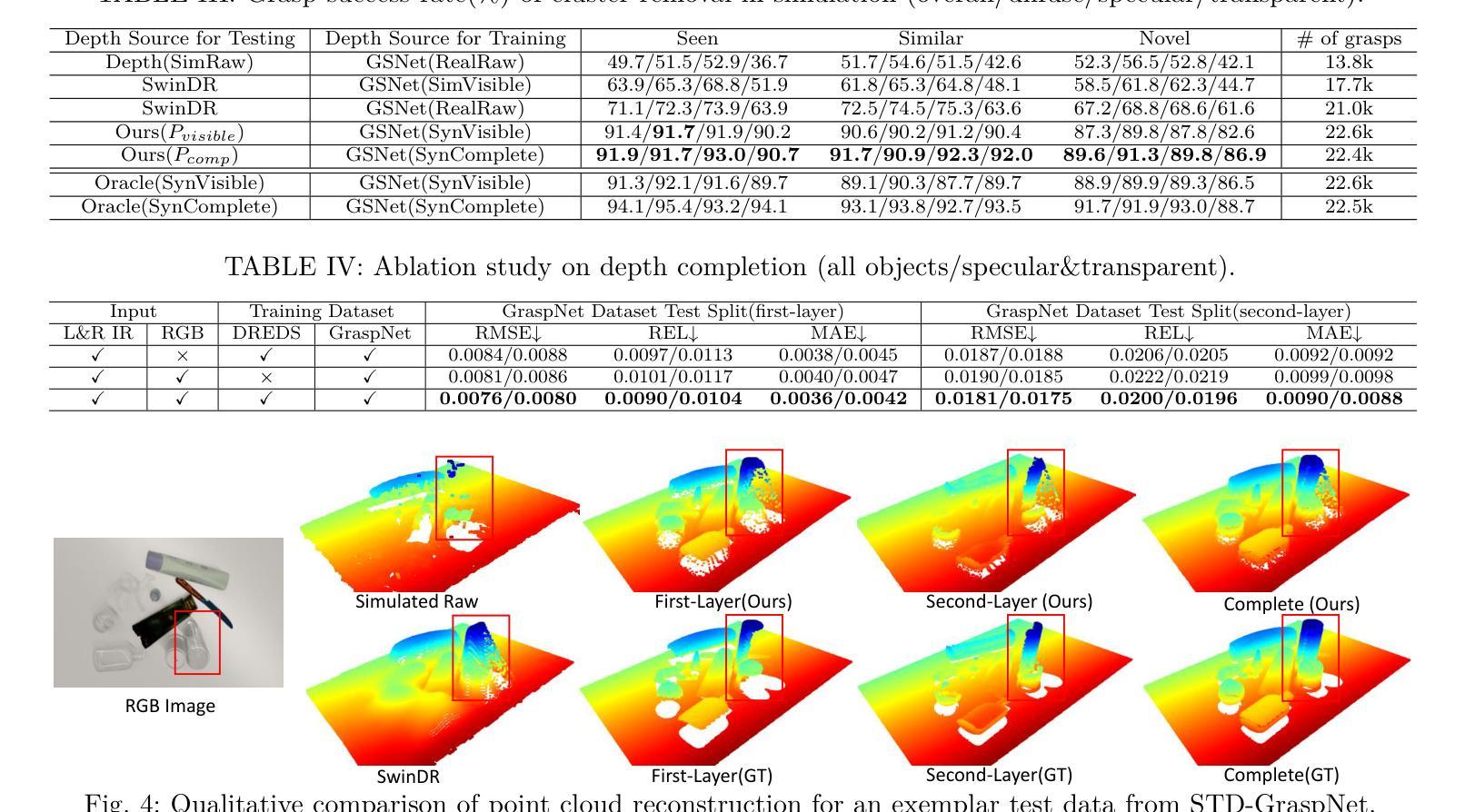
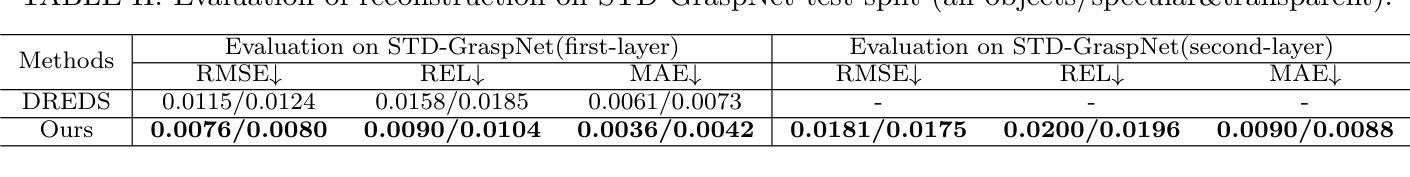
ASGrasp: Generalizable Transparent Object Reconstruction and 6-DoF Grasp Detection from RGB-D Active Stereo Camera
Authors:Jun Shi, Yong A, Yixiang Jin, Dingzhe Li, Haoyu Niu, Zhezhu Jin, He Wang
In this paper, we tackle the problem of grasping transparent and specular objects. This issue holds importance, yet it remains unsolved within the field of robotics due to failure of recover their accurate geometry by depth cameras. For the first time, we propose ASGrasp, a 6-DoF grasp detection network that uses an RGB-D active stereo camera. ASGrasp utilizes a two-layer learning-based stereo network for the purpose of transparent object reconstruction, enabling material-agnostic object grasping in cluttered environments. In contrast to existing RGB-D based grasp detection methods, which heavily depend on depth restoration networks and the quality of depth maps generated by depth cameras, our system distinguishes itself by its ability to directly utilize raw IR and RGB images for transparent object geometry reconstruction. We create an extensive synthetic dataset through domain randomization, which is based on GraspNet-1Billion. Our experiments demonstrate that ASGrasp can achieve over 90% success rate for generalizable transparent object grasping in both simulation and the real via seamless sim-to-real transfer. Our method significantly outperforms SOTA networks and even surpasses the performance upper bound set by perfect visible point cloud inputs.Project page: https://pku-epic.github.io/ASGrasp
在这篇论文中,我们解决了抓取透明和镜面物体的问题。这个问题非常重要,然而,由于深度相机无法恢复其准确几何结构,它在机器人领域仍然是一个未解决的问题。首次提出ASGrasp,一个使用RGB-D主动立体相机的6自由度抓取检测网络。ASGrasp利用两层基于学习的立体网络进行透明物体重建,实现在杂乱环境中材质无关的对象抓取。与现有的RGB-D基抓取检测方法不同,这些方法严重依赖于深度恢复网络和深度相机生成的深度图质量,我们的系统通过直接利用原始红外和RGB图像进行透明物体几何重建来区分自己。我们通过基于GraspNet-1Billion的领域随机化创建了一个大规模合成数据集。我们的实验表明,在模拟和实际环境中,ASGrasp都可以实现超过90%的通用透明物体抓取成功率,通过无缝仿真到实际转换。我们的方法显著优于SOTA网络,甚至超过了由完美的可见点云输入设定的性能上限。项目页面:https://pku-epic.github.io/ASGrasp
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2024
Summary
本文将解决的问题是抓取透明和光泽物体的难题。此问题在机器人领域中仍未解决,主要由于深度相机无法准确恢复其几何结构。本文首次提出ASGrasp,一个使用RGB-D主动立体相机的6自由度抓取检测网络。该网络通过两层学习基础的立体网络重构透明物体,从而在杂乱环境中实现材料无关的对象抓取。不同于现有的依赖于深度恢复网络和深度相机生成的深度图质量的RGB-D抓取检测方法,我们的系统通过直接利用原始红外和RGB图像进行透明物体几何重构来区分自身能力。通过基于GraspNet-1Billion的域随机化,我们创建了一个大规模的综合数据集。实验表明,无论是在仿真还是现实中通过无缝仿真到现实的转换,ASGrasp都能达到超过90%的通用透明物体抓取成功率。该方法显著优于当前最先进的技术,甚至超过了完美可见点云输入所设定的性能上限。有关项目页面可访问:链接。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决了透明和光泽物体的抓取问题,这是机器人领域的一个难题。
- 提出了一种新的方法,使用RGB-D主动立体相机的6自由度抓取检测网络进行抓取操作。
- 利用两层学习基础的立体网络进行透明物体的重建,增强了在杂乱环境中的材料无关对象抓取能力。
- 与现有方法不同,该网络直接利用原始红外和RGB图像进行透明物体几何重构,不受深度相机生成深度图质量的限制。
点此查看论文截图