⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
Iterative Self-Incentivization Empowers Large Language Models as Agentic Searchers
Authors:Zhengliang Shi, Lingyong Yan, Dawei Yin, Suzan Verberne, Maarten de Rijke, Zhaochun Ren
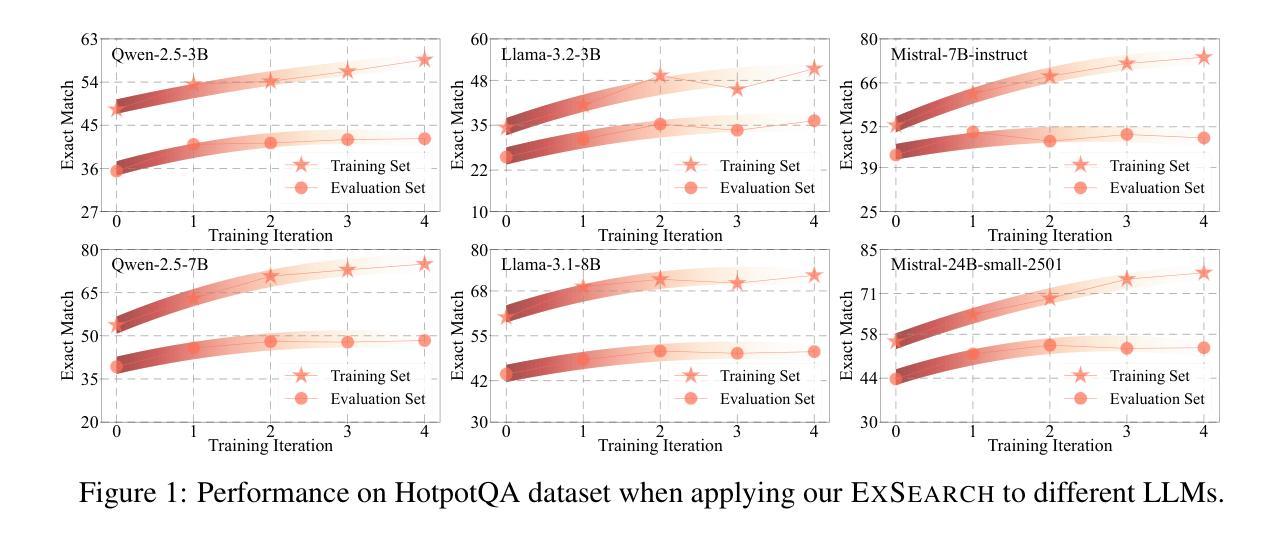
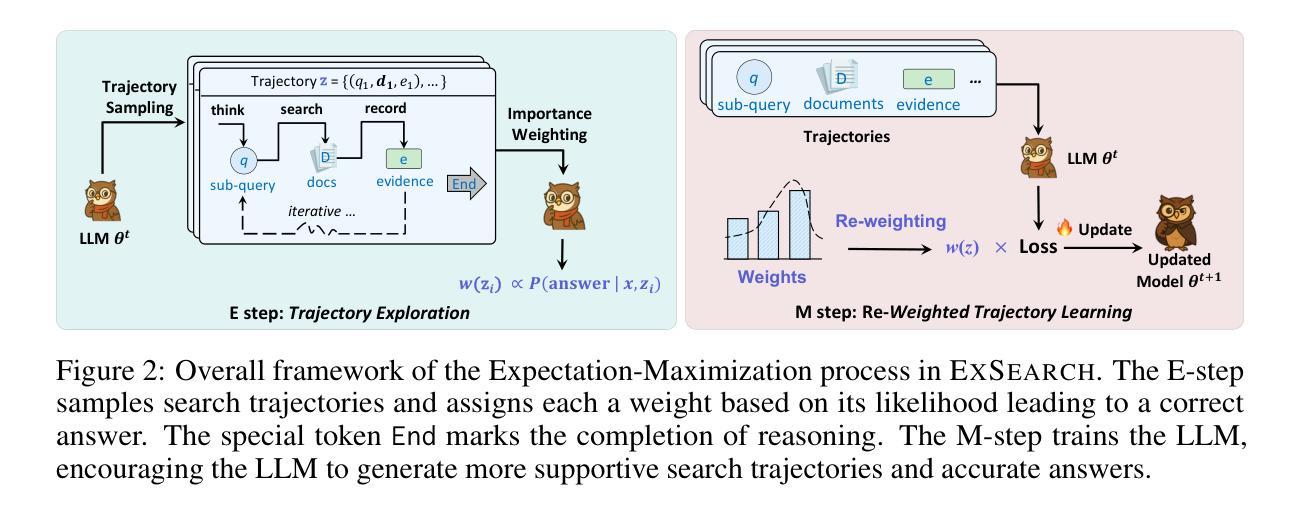
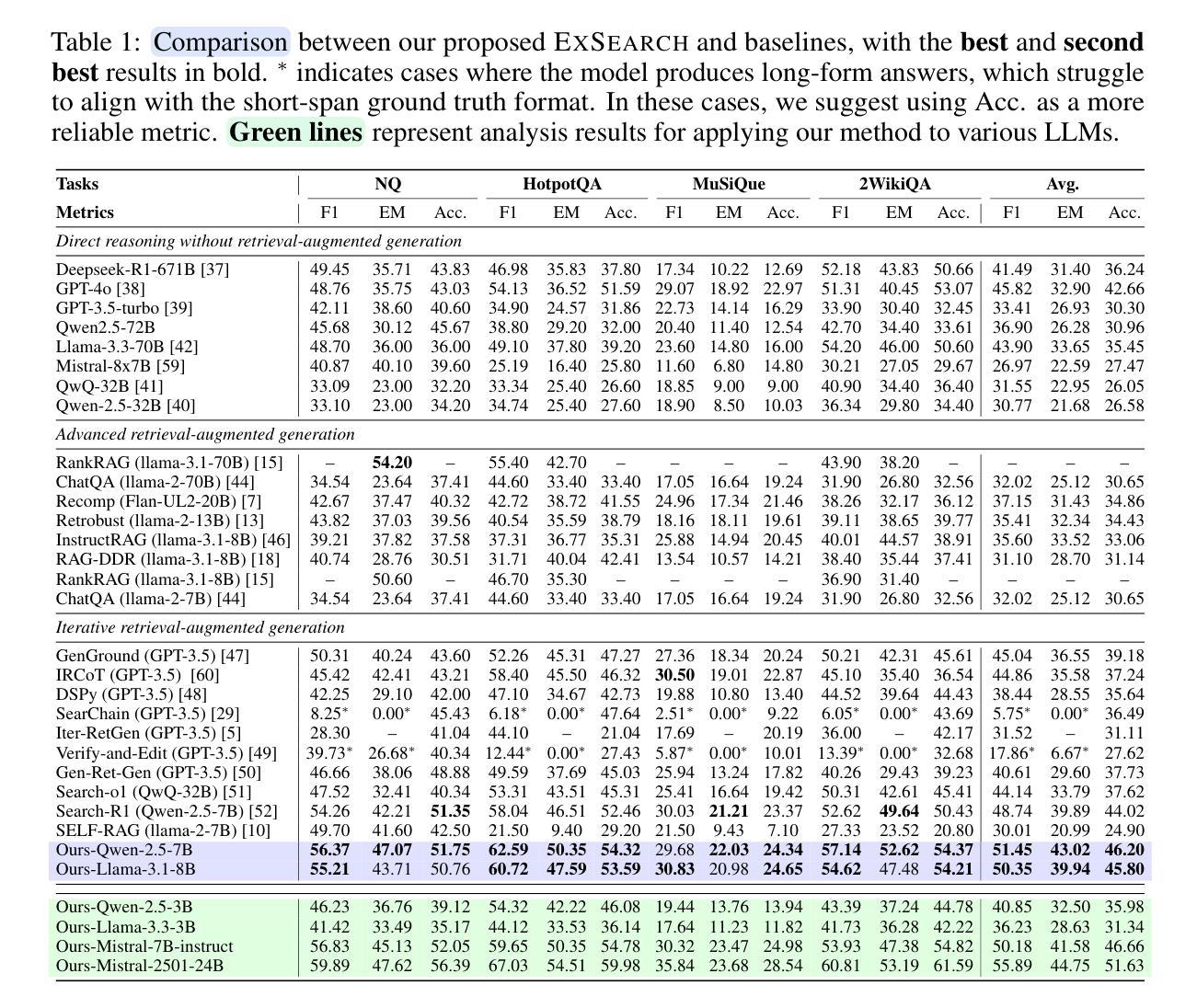
Large language models (LLMs) have been widely integrated into information retrieval to advance traditional techniques. However, effectively enabling LLMs to seek accurate knowledge in complex tasks remains a challenge due to the complexity of multi-hop queries as well as the irrelevant retrieved content. To address these limitations, we propose EXSEARCH, an agentic search framework, where the LLM learns to retrieve useful information as the reasoning unfolds through a self-incentivized process. At each step, the LLM decides what to retrieve (thinking), triggers an external retriever (search), and extracts fine-grained evidence (recording) to support next-step reasoning. To enable LLM with this capability, EXSEARCH adopts a Generalized Expectation-Maximization algorithm. In the E-step, the LLM generates multiple search trajectories and assigns an importance weight to each; the M-step trains the LLM on them with a re-weighted loss function. This creates a self-incentivized loop, where the LLM iteratively learns from its own generated data, progressively improving itself for search. We further theoretically analyze this training process, establishing convergence guarantees. Extensive experiments on four knowledge-intensive benchmarks show that EXSEARCH substantially outperforms baselines, e.g., +7.8% improvement on exact match score. Motivated by these promising results, we introduce EXSEARCH-Zoo, an extension that extends our method to broader scenarios, to facilitate future work.
大规模语言模型(LLM)已经广泛应用于信息检索,以推动传统技术的发展。然而,由于多跳查询的复杂性和检索内容的无关性,有效地使LLM在复杂任务中寻找准确知识仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了EXSEARCH,一个智能搜索框架,LLM在此框架中学习检索与推理过程中展开的有用信息,这通过自我激励的过程实现。在每个步骤中,LLM决定要检索什么(思考),触发外部检索器(搜索),并提取精细的证据(记录)以支持下一步的推理。为了实现LLM的这一能力,EXSEARCH采用了广义期望最大化算法。在E步中,LLM生成多个搜索轨迹并为每个轨迹分配重要性权重;在M步中,使用加权损失函数对LLM进行训练。这创建了一个自我激励的循环,LLM从中不断自我生成的数据中学习,逐步改进自身的搜索能力。我们进一步从理论上分析了这一训练过程,建立了收敛性保证。在四个知识密集型基准测试上的大量实验表明,EXSEARCH显著优于基线方法,例如在精确匹配得分上有+7.8%的改进。受这些令人鼓舞的结果的驱动,我们将EXSEARCH-Zoo作为我们方法的扩展介绍给更广泛的场景,以促进未来的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Working in process
Summary
大型语言模型在信息检索领域的应用虽广泛,但在复杂任务中准确寻找知识仍存在挑战,如多跳查询的复杂性和检索内容的无关性。为解决这些问题,我们提出EXSEARCH,一种代理搜索框架,让语言模型在推理过程中学习检索有用信息,形成自我激励循环。EXSEARCH采用广义期望最大化算法,在E步生成多个搜索轨迹并赋予权重,M步用加权损失函数训练模型。此过程理论上有收敛保障,在四个知识密集型基准测试上的实验显示,EXSEARCH大幅优于基线方法,如精确匹配得分提高7.8%。我们基于此成果推出EXSEARCH-Zoo,以应对更广泛场景。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在信息检索中面临多跳查询复杂性和检索内容无关性的挑战。
- EXSEARCH是一种代理搜索框架,通过自我激励循环使语言模型在推理过程中学习检索信息。
- EXSEARCH采用广义期望最大化算法,包括生成搜索轨迹和加权损失函数训练模型两个主要步骤。
- EXSEARCH有理论收敛保障。
- 在四个知识密集型基准测试上,EXSEARCH显著优于基线方法。
- EXSEARCH-Zoo是EXSEARCH的扩展,旨在应对更广泛的场景。
点此查看论文截图

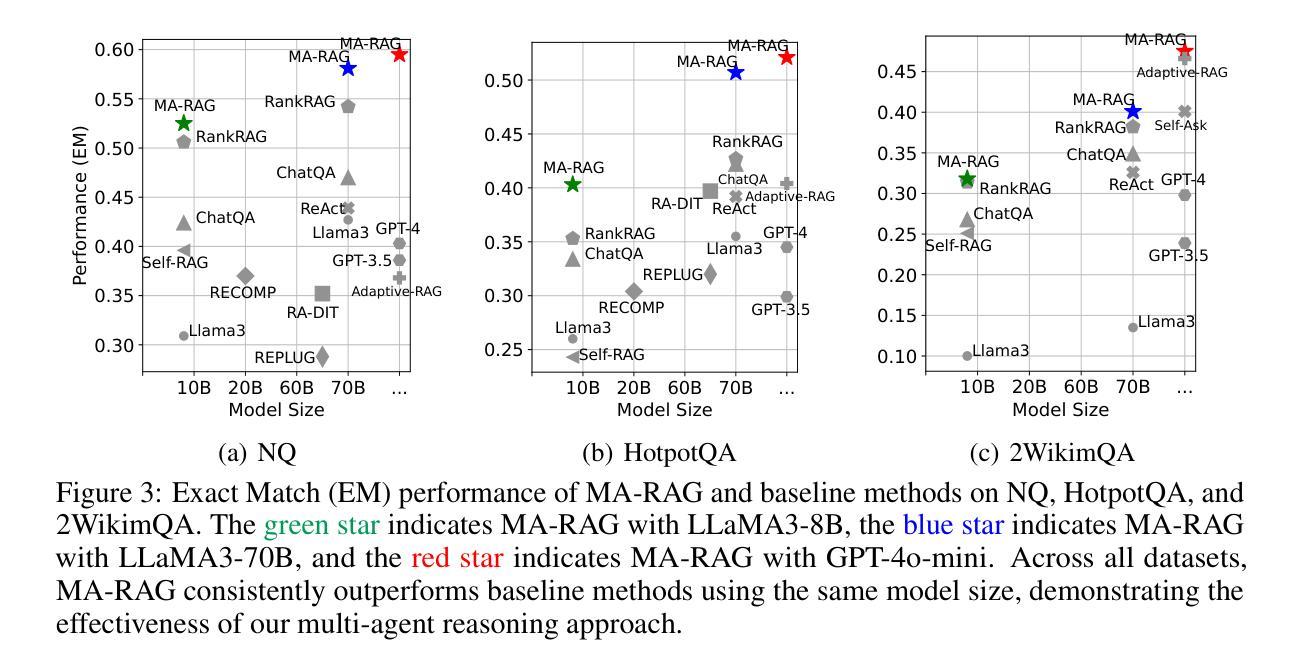
MA-RAG: Multi-Agent Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Collaborative Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Thang Nguyen, Peter Chin, Yu-Wing Tai
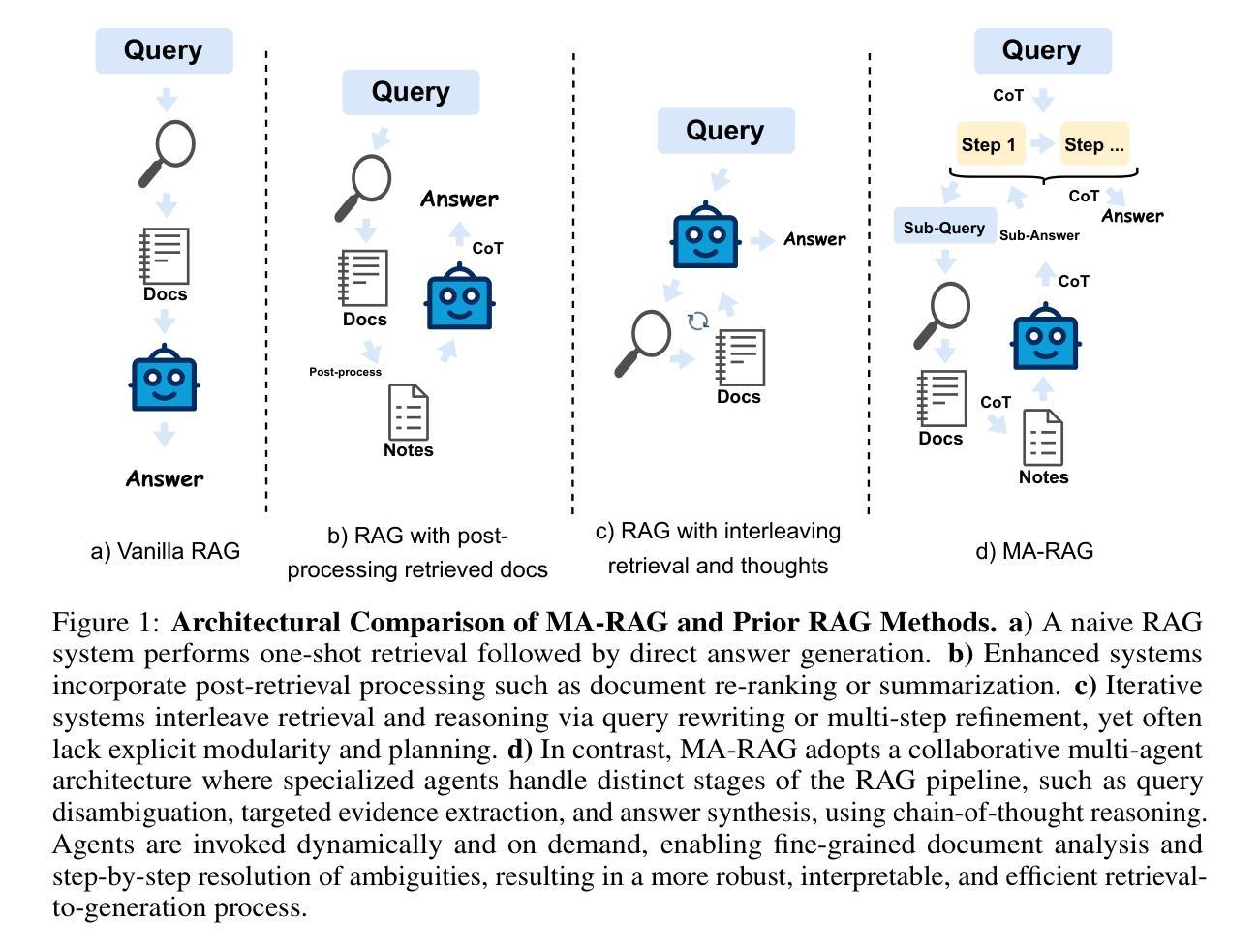
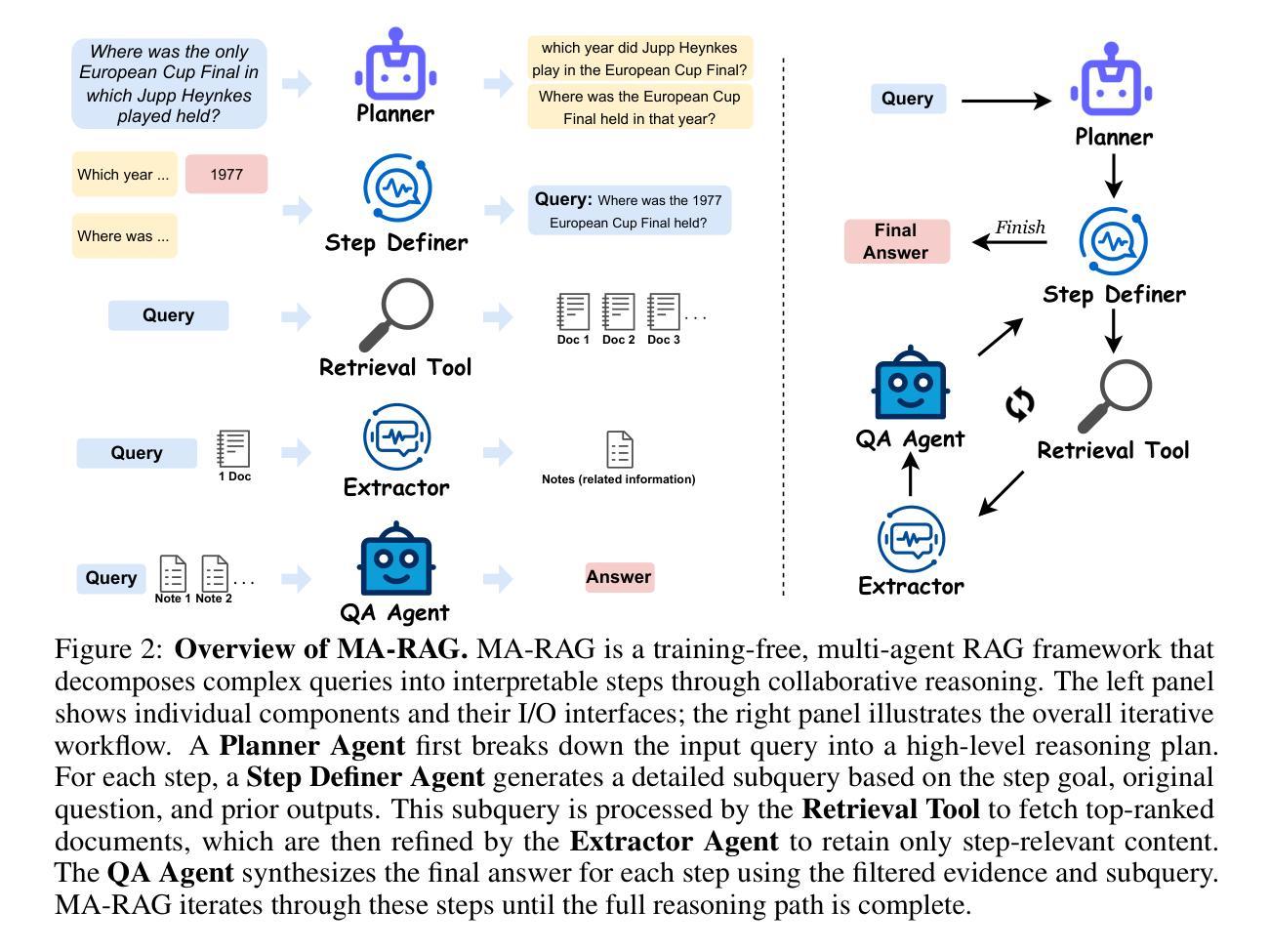
We present MA-RAG, a Multi-Agent framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that addresses the inherent ambiguities and reasoning challenges in complex information-seeking tasks. Unlike conventional RAG methods that rely on either end-to-end fine-tuning or isolated component enhancements, MA-RAG orchestrates a collaborative set of specialized AI agents: Planner, Step Definer, Extractor, and QA Agents, to tackle each stage of the RAG pipeline with task-aware reasoning. Ambiguities may arise from underspecified queries, sparse or indirect evidence in retrieved documents, or the need to integrate information scattered across multiple sources. MA-RAG mitigates these challenges by decomposing the problem into subtasks, such as query disambiguation, evidence extraction, and answer synthesis, and dispatching them to dedicated agents equipped with chain-of-thought prompting. These agents communicate intermediate reasoning and progressively refine the retrieval and synthesis process. Our design allows fine-grained control over information flow without any model fine-tuning. Crucially, agents are invoked on demand, enabling a dynamic and efficient workflow that avoids unnecessary computation. This modular and reasoning-driven architecture enables MA-RAG to deliver robust, interpretable results. Experiments on multi-hop and ambiguous QA benchmarks demonstrate that MA-RAG outperforms state-of-the-art training-free baselines and rivals fine-tuned systems, validating the effectiveness of collaborative agent-based reasoning in RAG.
我们提出MA-RAG,这是一个用于增强检索生成(RAG)的多代理框架,旨在解决复杂信息检索任务中固有的模糊性和推理挑战。不同于传统的RAG方法,它们依赖于端到端的微调或孤立的组件增强,MA-RAG协同工作一组专业的AI代理:计划代理、步骤定义代理、提取代理和问答代理,以任务感知推理解决RAG管道的每个阶段。模糊性可能来自未指定的查询、检索到的文档中的稀疏或间接证据,或需要整合来自多个来源的信息。MA-RAG通过将问题分解为子任务(如查询消歧、证据提取和答案合成),并派遣它们到配备思维链提示的专用代理来缓解这些挑战。这些代理沟通中间推理并逐步改进检索和合成过程。我们的设计允许对信息流进行精细控制,无需任何模型微调。最重要的是,代理是按需调用的,这避免了不必要计算的同时,实现了动态高效的工作流程。这种模块化和以推理驱动的结构使得MA-RAG能够提供更稳健、可解释的结果。在多跳和模糊问答基准测试上的实验表明,MA-RAG优于最新的无训练基准线并可与微调系统相媲美,这验证了基于代理的协作推理在RAG中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MA-RAG是一个多代理框架,用于增强检索生成(RAG),解决复杂信息检索任务中的固有模糊性和推理挑战。它通过分解问题,并调度专业代理处理每个阶段的任务感知推理,从而解决了常规RAG方法的问题。实验证明,MA-RAG在多跳和模糊问答基准测试中表现出色,验证了基于协作代理的推理在RAG中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MA-RAG是一个多代理框架,用于解决复杂信息检索任务中的模糊性和推理挑战。
- 它通过分解问题为子任务,如查询去模糊、证据提取和答案合成,并派遣专业代理处理。
- MA-RAG采用链式思维提示,代理之间进行沟通,逐步优化检索和合成过程。
- 该设计允许对信息流进行精细控制,无需模型微调。
- 代理按需调用,实现动态高效的工作流,避免不必要的计算。
- MA-RAG在多人跳和模糊问答基准测试中表现出色,证明其在RAG中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

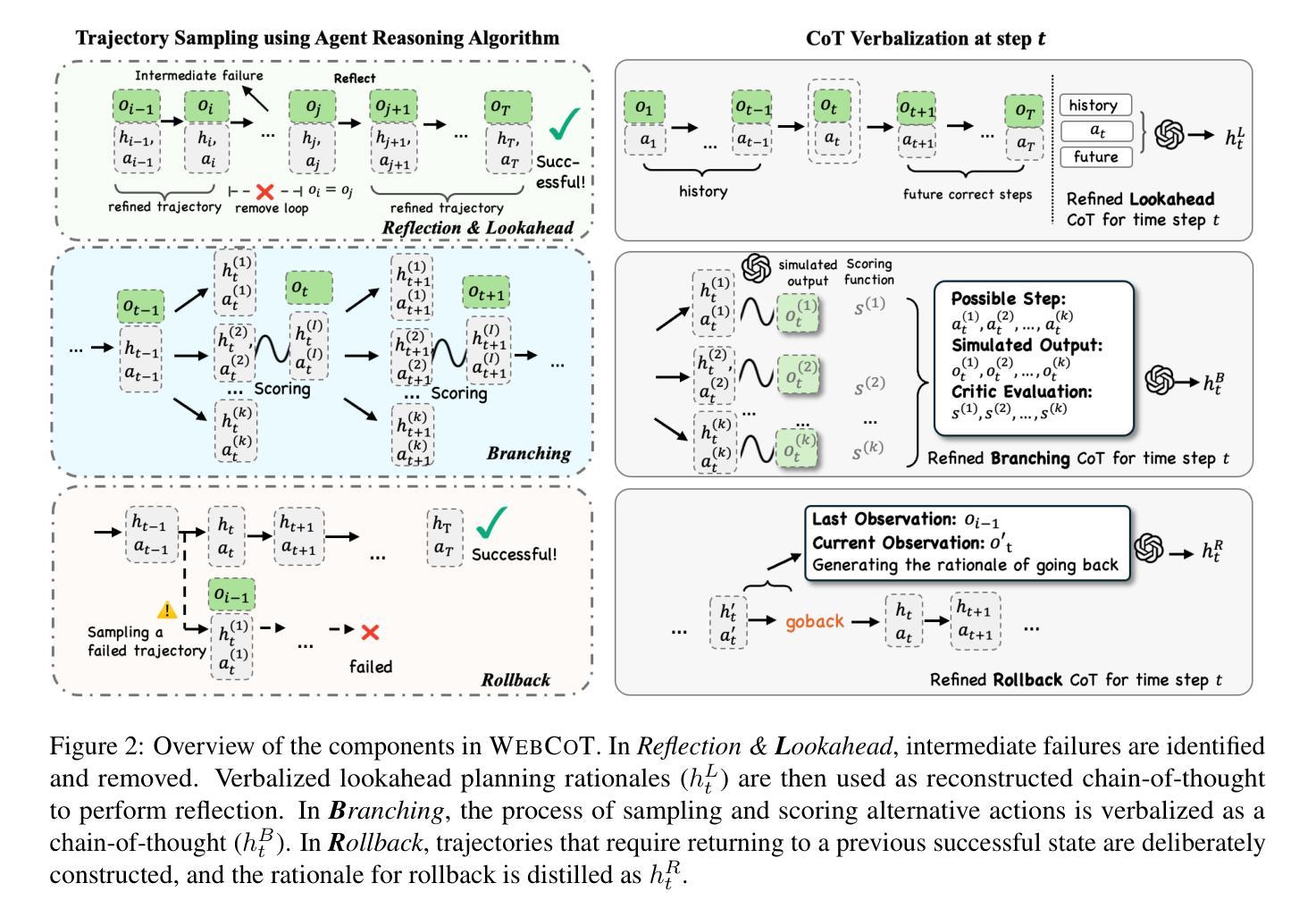
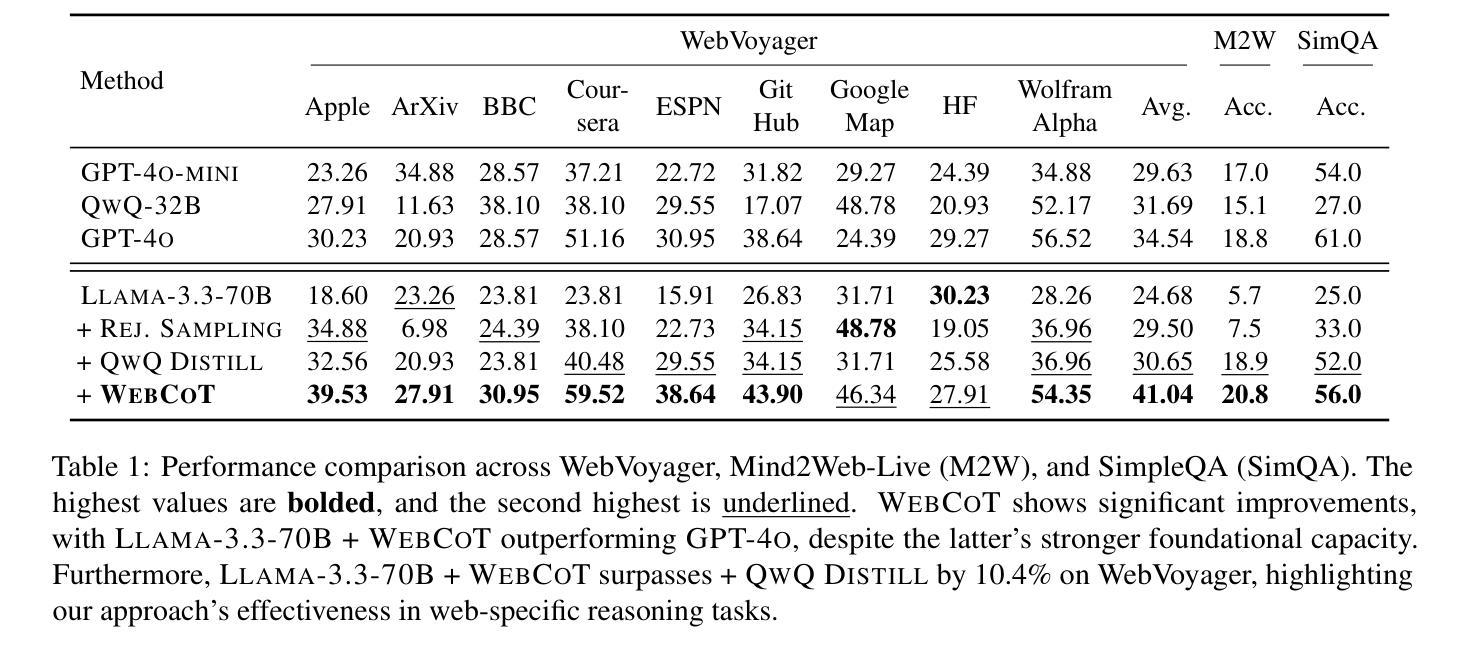
WebCoT: Enhancing Web Agent Reasoning by Reconstructing Chain-of-Thought in Reflection, Branching, and Rollback
Authors:Minda Hu, Tianqing Fang, Jianshu Zhang, Junyu Ma, Zhisong Zhang, Jingyan Zhou, Hongming Zhang, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu, Irwin King
Web agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise for next-generation AI, but their limited reasoning in uncertain, dynamic web environments hinders robust deployment. In this paper, we identify key reasoning skills essential for effective web agents, i.e., reflection & lookahead, branching, and rollback, and curate trajectory data that exemplifies these abilities by reconstructing the agent’s (inference-time) reasoning algorithms into chain-of-thought rationales. We conduct experiments in the agent self-improving benchmark, OpenWebVoyager, and demonstrate that distilling salient reasoning patterns into the backbone LLM via simple fine-tuning can substantially enhance its performance. Our approach yields significant improvements across multiple benchmarks, including WebVoyager, Mind2web-live, and SimpleQA (web search), highlighting the potential of targeted reasoning skill enhancement for web agents.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Web代理对下一代人工智能显示出潜力,但它们在不确定、动态网络环境中有限的推理能力阻碍了其稳健部署。在本文中,我们确定了对于有效Web代理至关重要的关键推理技能,即反思与前瞻性、分支和回滚,并通过重建代理(推理时间)的推理算法来提炼体现这些能力的轨迹数据,形成一系列思考理由。我们在代理自我改进基准测试OpenWebVoyager中进行了实验,并证明通过简单微调将显著的推理模式蒸馏到主干LLM中,可以极大地提高其性能。我们的方法在多基准测试中产生了显著改进,包括WebVoyager、Mind2web-live和SimpleQA(网络搜索),突出了针对Web代理进行针对性推理技能增强的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages
Summary
基于大型语言模型的网络代理展现出下一代人工智能的潜力,但在不确定的动态网络环境中其推理能力有限,阻碍了其稳健部署。本文识别出网络代理有效的关键推理技能,包括反思与前瞻、分支和回滚,并通过重建代理(推理时间)的推理算法来诠释这些能力的轨迹数据。在自我改进基准测试OpenWebVoyager中进行了实验,证明了通过简单微调将重要的推理模式蒸馏到基本的大型语言模型中,可以极大地提高其性能。该方法在多个基准测试中取得了显著改进,包括WebVoyager、Mind2web-live和SimpleQA(网络搜索),突显了针对网络代理进行有针对性的推理技能增强的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 网络代理在不确定的动态网络环境中存在推理能力限制。
- 本文识别了网络代理有效的关键推理技能,包括反思与前瞻、分支和回滚。
- 通过重建代理的推理算法轨迹数据,展示了这些能力的具体表现。
- 在自我改进基准测试OpenWebVoyager中进行了实验验证。
- 简单微调将重要的推理模式蒸馏到基础的大型语言模型中,可以显著提高代理性能。
- 该方法在多个基准测试中取得了显著改进,突显了增强网络代理推理技能的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

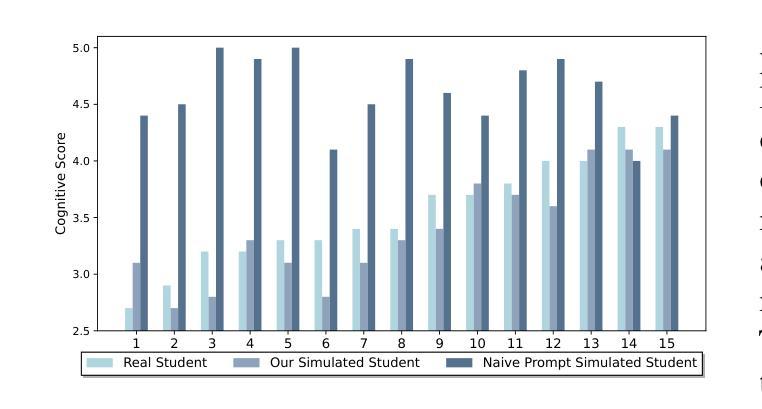
Embracing Imperfection: Simulating Students with Diverse Cognitive Levels Using LLM-based Agents
Authors:Tao Wu, Jingyuan Chen, Wang Lin, Mengze Li, Yumeng Zhu, Ang Li, Kun Kuang, Fei Wu
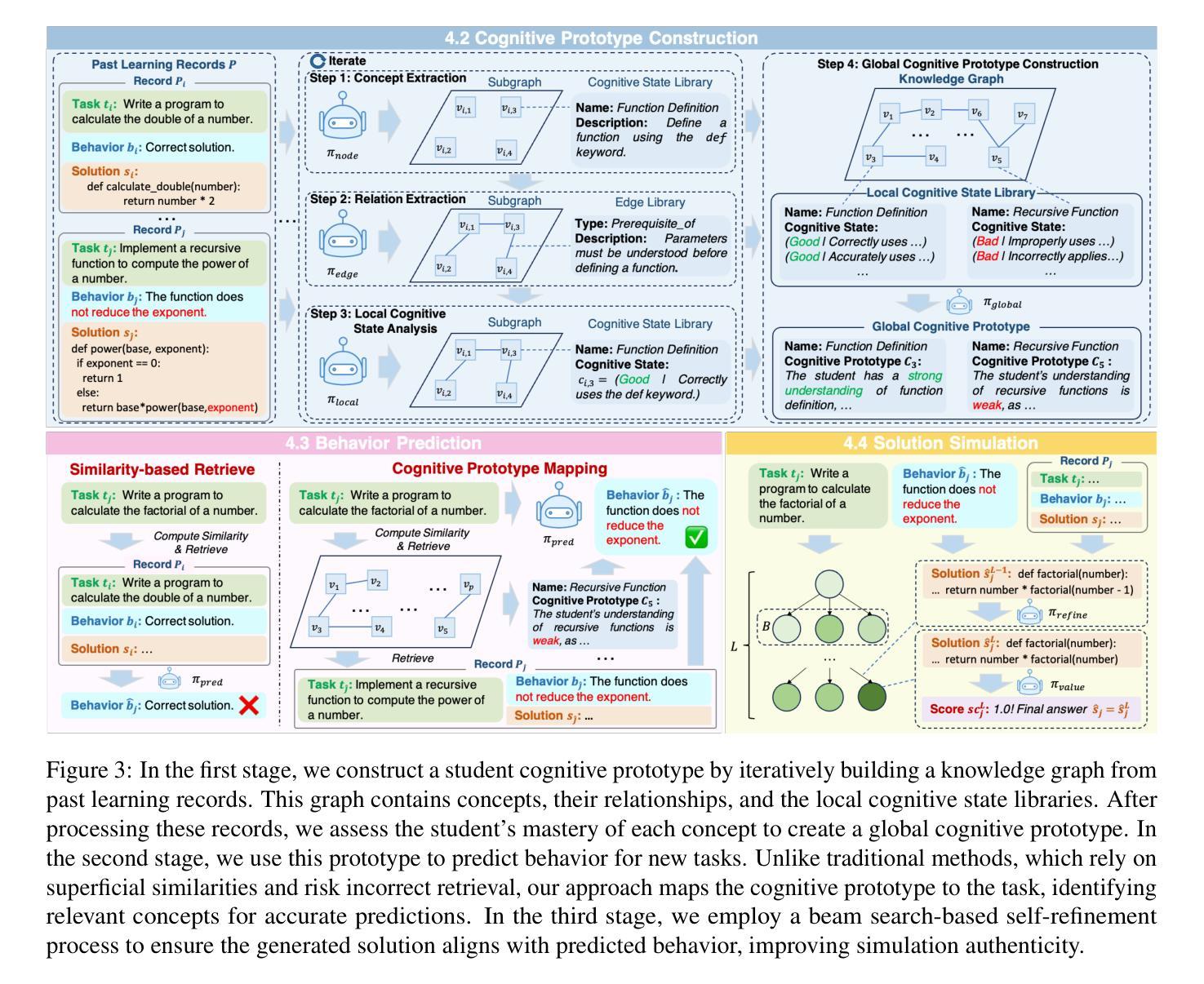
Large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing education, with LLM-based agents playing a key role in simulating student behavior. A major challenge in student simulation is modeling the diverse learning patterns of students at various cognitive levels. However, current LLMs, typically trained as ``helpful assistants’’, target at generating perfect responses. As a result, they struggle to simulate students with diverse cognitive abilities, as they often produce overly advanced answers, missing the natural imperfections that characterize student learning and resulting in unrealistic simulations. To address this issue, we propose a training-free framework for student simulation. We begin by constructing a cognitive prototype for each student using a knowledge graph, which captures their understanding of concepts from past learning records. This prototype is then mapped to new tasks to predict student performance. Next, we simulate student solutions based on these predictions and iteratively refine them using a beam search method to better replicate realistic mistakes. To validate our approach, we construct the \texttt{Student_100} dataset, consisting of $100$ students working on Python programming and $5,000$ learning records. Experimental results show that our method consistently outperforms baseline models, achieving $100%$ improvement in simulation accuracy.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在推动教育的革新,基于LLM的代理在学生行为模拟中扮演着关键角色。学生模拟面临的一个主要挑战是模拟学生在各种认知水平的各种学习模式。然而,当前的大型语言模型通常被训练成“有用的助手”,旨在生成完美的回应。因此,他们在模拟具有不同认知能力的学生时遇到了困难,因为这些模型往往产生过于高级的答案,忽略了学生在学习过程中表现出的自然缺陷,导致模拟结果不真实。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种无需训练的用于学生模拟的框架。我们首先使用知识图谱为每个学生构建认知原型,该图谱捕捉了他们对过去学习内容的理解。然后,我们将这个原型映射到新的任务来预测学生的表现。接下来,我们基于这些预测来模拟学生的解决方案,并使用一种贪心搜索方法来迭代地改进模拟结果,以更好地重现真实的错误。为了验证我们的方法,我们构建了
Student_100数据集,包含100名学习Python编程的学生和5000条学习记录。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于基线模型,在模拟精度上提高了100%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)正在改变教育方式,LLM驱动的代理在模拟学生行为方面发挥关键作用。当前LLM主要面临挑战是模拟不同认知层次的学生学习模式时存在缺陷,通常生成过于完美的答案,无法反映学生学习中的自然缺陷,导致模拟不真实。本研究提出了一种无需训练的模拟学生行为框架,通过构建知识图谱中的学生认知原型,预测学生表现,并模拟学生答案。通过迭代优化,该框架能更好地复制真实错误。实验结果显示,该方法在模拟准确性上明显优于基线模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正在教育领域中发挥作用,尤其是在模拟学生行为方面。
- 当前LLM在模拟不同认知层次的学生时存在挑战,倾向于生成过于完美的答案。
- 研究提出了一种无需训练的模拟学生行为框架,通过构建知识图谱中的学生认知原型来预测学生表现。
- 该框架能够模拟学生的答案,并迭代优化以更好地复制真实错误。
- 为了验证方法的有效性,构建了包含100名学生和5000条学习记录的Student_100数据集。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在模拟准确性上显著优于基线模型。
点此查看论文截图


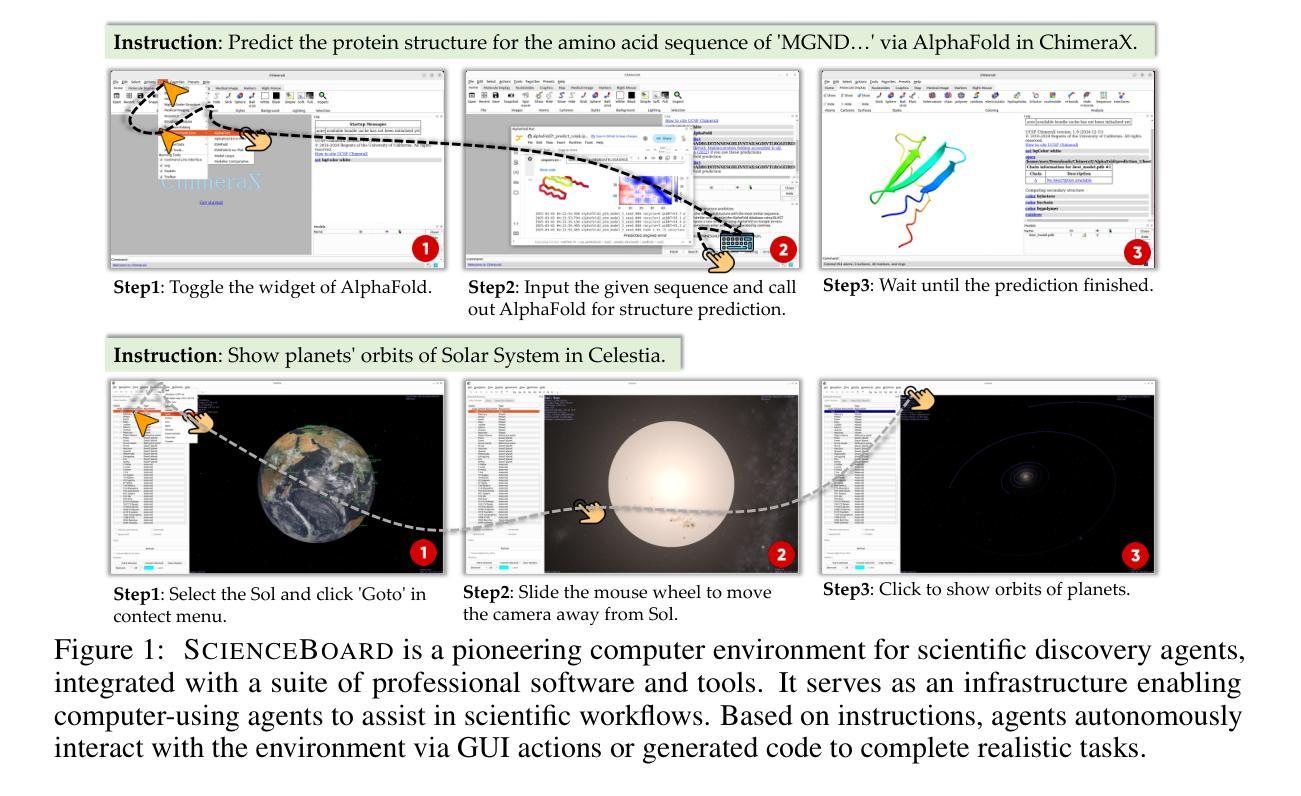
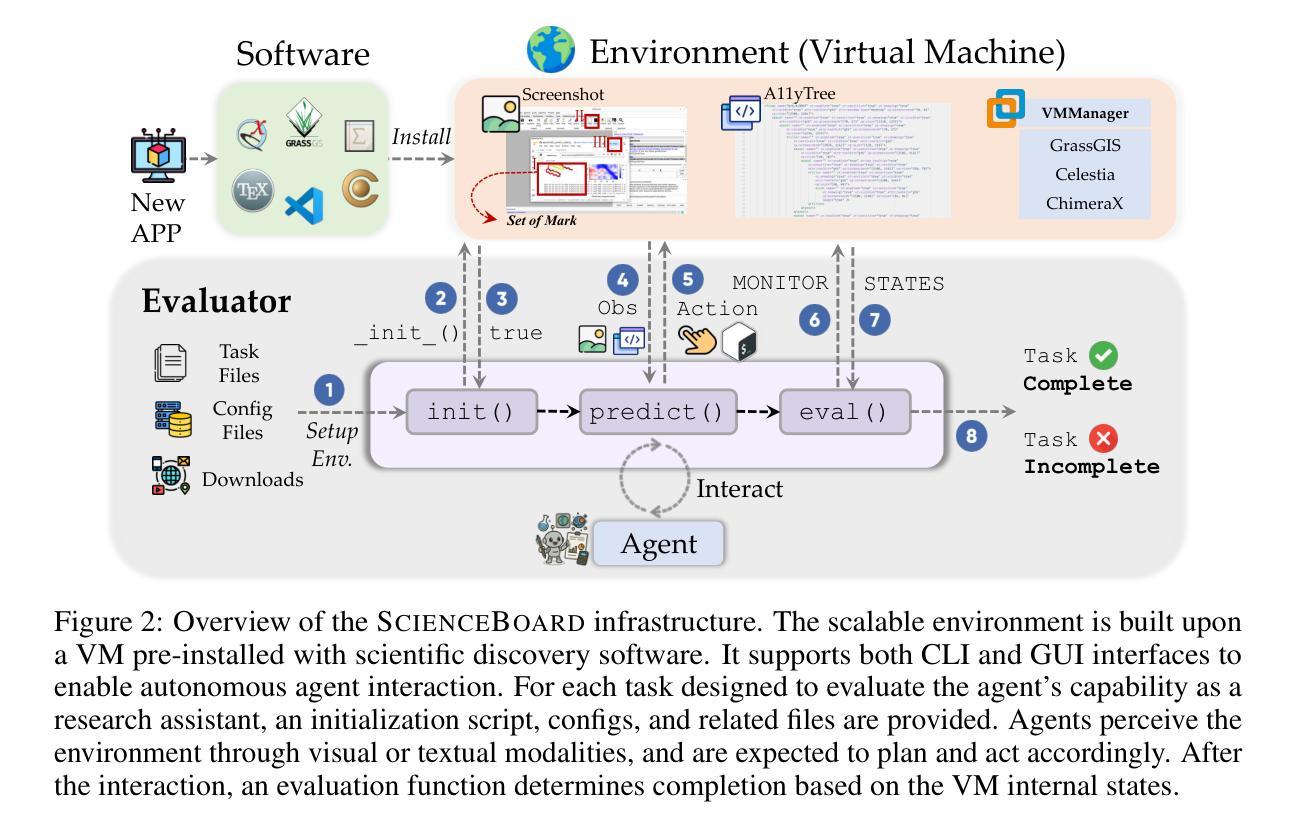
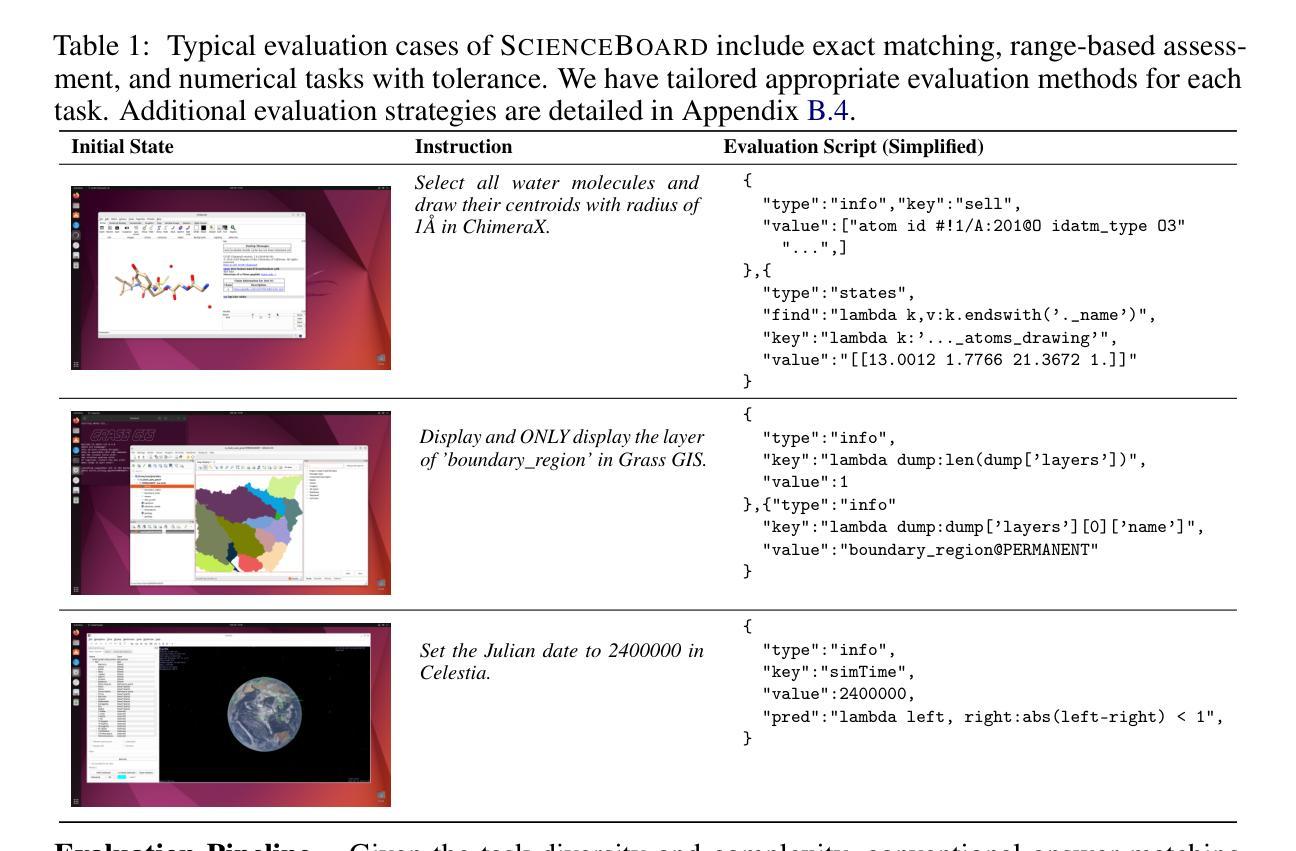
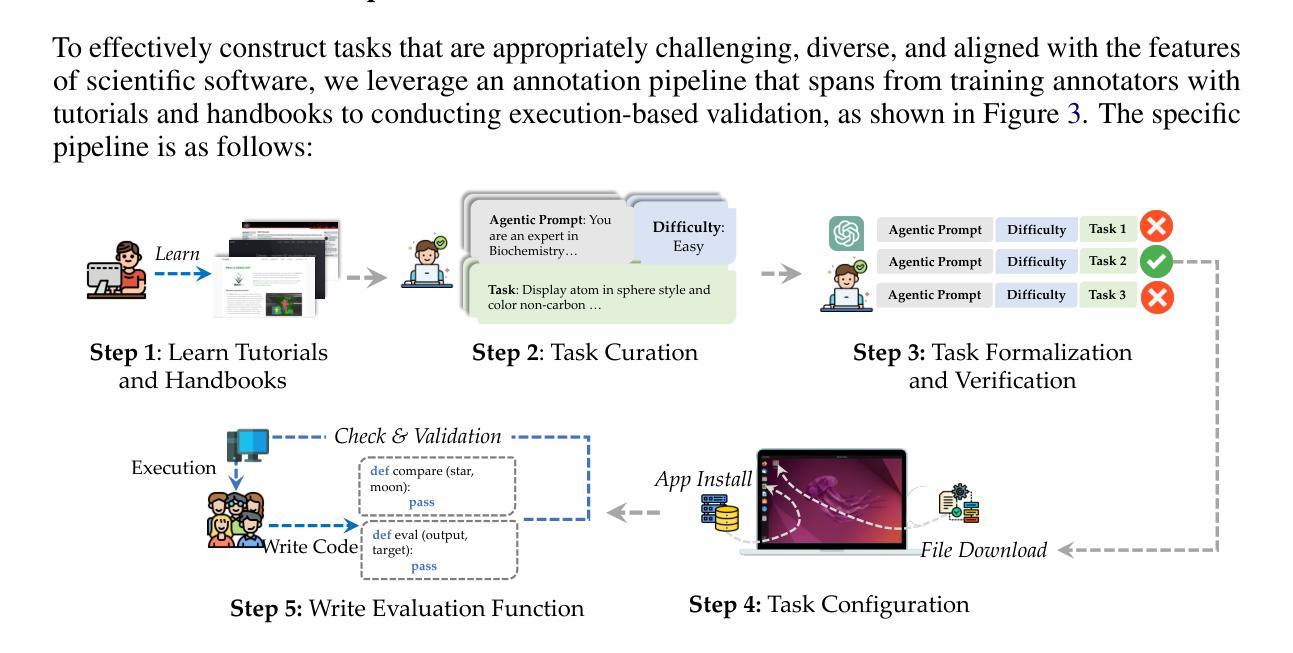
ScienceBoard: Evaluating Multimodal Autonomous Agents in Realistic Scientific Workflows
Authors:Qiushi Sun, Zhoumianze Liu, Chang Ma, Zichen Ding, Fangzhi Xu, Zhangyue Yin, Haiteng Zhao, Zhenyu Wu, Kanzhi Cheng, Zhaoyang Liu, Jianing Wang, Qintong Li, Xiangru Tang, Tianbao Xie, Xiachong Feng, Xiang Li, Ben Kao, Wenhai Wang, Biqing Qi, Lingpeng Kong, Zhiyong Wu
Large Language Models (LLMs) have extended their impact beyond Natural Language Processing, substantially fostering the development of interdisciplinary research. Recently, various LLM-based agents have been developed to assist scientific discovery progress across multiple aspects and domains. Among these, computer-using agents, capable of interacting with operating systems as humans do, are paving the way to automated scientific problem-solving and addressing routines in researchers’ workflows. Recognizing the transformative potential of these agents, we introduce ScienceBoard, which encompasses two complementary contributions: (i) a realistic, multi-domain environment featuring dynamic and visually rich scientific workflows with integrated professional software, where agents can autonomously interact via different interfaces to accelerate complex research tasks and experiments; and (ii) a challenging benchmark of 169 high-quality, rigorously validated real-world tasks curated by humans, spanning scientific-discovery workflows in domains such as biochemistry, astronomy, and geoinformatics. Extensive evaluations of agents with state-of-the-art backbones (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude 3.7, UI-TARS) show that, despite some promising results, they still fall short of reliably assisting scientists in complex workflows, achieving only a 15% overall success rate. In-depth analysis further provides valuable insights for addressing current agent limitations and more effective design principles, paving the way to build more capable agents for scientific discovery. Our code, environment, and benchmark are at https://qiushisun.github.io/ScienceBoard-Home/.
大型语言模型(LLMs)已经将其影响力扩展到了自然语言处理领域之外,极大地促进了跨学科研究的发展。最近,已经开发了各种基于LLM的代理,以协助多个方面和领域的科学发现进展。其中,能够与人类一样与操作系统交互的计算机使用代理正在为自动化科学问题解决和研究人员工作流程中的例行公事铺平道路。我们认识到了这些代理的变革潜力,因此推出了ScienceBoard,它包括两个互补的贡献:首先,一个现实的多领域环境,拥有动态且视觉丰富的科学工作流程以及集成专业软件,代理可以自主通过不同的接口进行交互,以加速复杂的科研任务和实验;其次,一个由人类策划的包含169个高质量、经过严格验证的现实世界任务的挑战性基准测试,这些任务涵盖了生物化学、天文学和地理信息科学等领域的科学发现工作流程。对具有最新技术后援(如GPT-4o、Claude 3.7、UI-TARS)的代理进行全面评估表明,尽管有一些令人鼓舞的结果,但它们仍然无法可靠地协助科学家进行复杂的工作流程,总体成功率仅为15%。深入分析还提供了有关解决当前代理局限性以及更有效设计原则的有价值见解,为构建更具能力的科学发现代理铺平了道路。我们的代码、环境和基准测试位于https://qiushisun.github.io/ScienceBoard-Home/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF work in progress
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)已超越自然语言处理领域,极大地促进了跨学科研究的发展。基于LLM的科研助理型智能体在多个领域和方面推动了科学发现的进步。其中,能像人一样与操作系统交互的计算机使用智能体,为自动化解决科学问题和应对研究者工作流程中的常规任务开辟了道路。为应对这一变革潜力,我们推出了ScienceBoard,包含两个互补的组成部分:(一)一个现实、跨领域的环境,拥有动态、视觉丰富的科研工作流程及集成专业软件,智能体能在此环境中通过不同接口自主交互,以加速复杂的科研任务和实验;(二)一个包含人类精心挑选的169个高质量、经过严格验证的现实任务的挑战基准测试,涵盖生物化学、天文学和地理信息科学等领域的科学发现流程。对智能体的广泛评估表明,尽管取得了一些令人鼓舞的结果,但它们仍无法可靠地协助科学家完成复杂的工作流程,整体成功率仅为15%。我们的代码、环境和基准测试位于https://qiushisun.github.io/ScienceBoard-Home/。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)已对跨学科研究产生深远影响。
- 基于LLM的科研助理型智能体在多个领域推动了科学发现进步。
- 计算机使用智能体能自主与操作系统交互,助力自动化解决科学问题。
- ScienceBoard包含现实跨领域环境与挑战基准测试。
- 智能体在复杂科研工作流程中的整体成功率仅为15%,仍有提升空间。
- 对智能体的深入评估提供了有价值的见解,以应对当前智能体的局限性。
点此查看论文截图

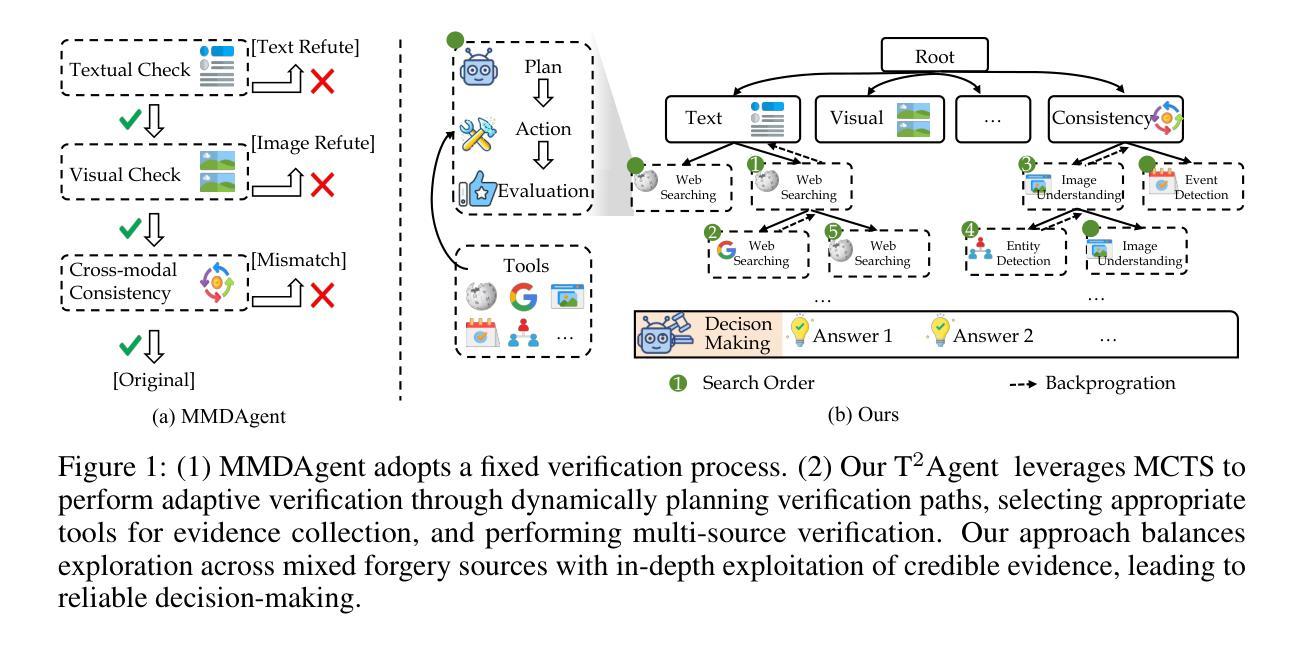
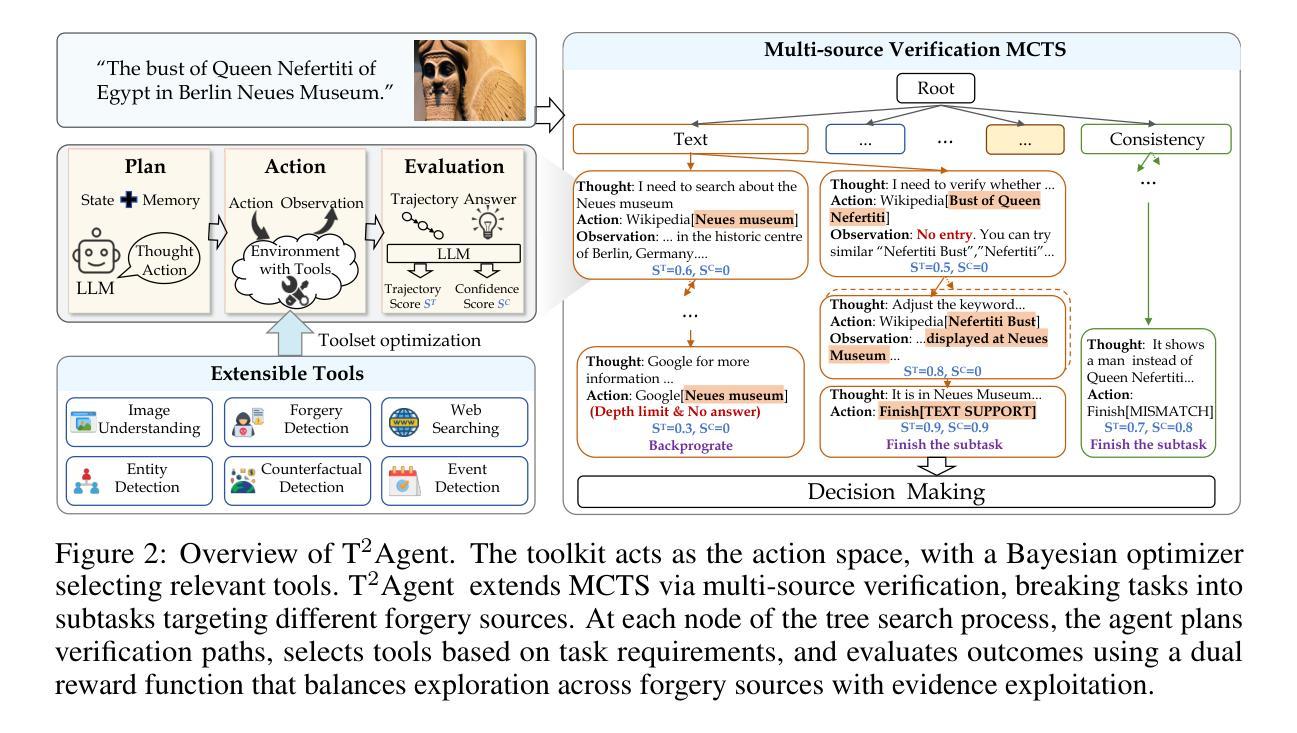
T^2Agent A Tool-augmented Multimodal Misinformation Detection Agent with Monte Carlo Tree Search
Authors:Xing Cui, Yueying Zou, Zekun Li, Peipei Li, Xinyuan Xu, Xuannan Liu, Huaibo Huang, Ran He
Real-world multimodal misinformation often arises from mixed forgery sources, requiring dynamic reasoning and adaptive verification. However, existing methods mainly rely on static pipelines and limited tool usage, limiting their ability to handle such complexity and diversity. To address this challenge, we propose T2Agent, a novel misinformation detection agent that incorporates an extensible toolkit with Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). The toolkit consists of modular tools such as web search, forgery detection, and consistency analysis. Each tool is described using standardized templates, enabling seamless integration and future expansion. To avoid inefficiency from using all tools simultaneously, a Bayesian optimization-based selector is proposed to identify a task-relevant subset. This subset then serves as the action space for MCTS to dynamically collect evidence and perform multi-source verification. To better align MCTS with the multi-source nature of misinformation detection, T2Agent extends traditional MCTS with multi-source verification, which decomposes the task into coordinated subtasks targeting different forgery sources. A dual reward mechanism containing a reasoning trajectory score and a confidence score is further proposed to encourage a balance between exploration across mixed forgery sources and exploitation for more reliable evidence. We conduct ablation studies to confirm the effectiveness of the tree search mechanism and tool usage. Extensive experiments further show that T2Agent consistently outperforms existing baselines on challenging mixed-source multimodal misinformation benchmarks, demonstrating its strong potential as a training-free approach for enhancing detection accuracy. The code will be released.
现实世界中的多模态错误信息往往源于混合的伪造源,这需要动态推理和自适应验证。然而,现有方法主要依赖于静态管道和有限的工具使用,这限制了它们处理这种复杂性和多样性的能力。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了T2Agent,这是一种新型的错误信息检测代理,它结合了可扩展的工具包和蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)。该工具包由模块化工具组成,如网络搜索、伪造检测、一致性分析等。每个工具都使用标准模板进行描述,以实现无缝集成和未来扩展。为了避免同时使用所有工具所带来的低效性,我们提出了一种基于贝叶斯优化的选择器来识别与任务相关的子集。然后,这个子集作为行动空间,为MCTS动态收集证据和进行多源验证提供支撑。为了更好地将MCTS与错误信息的多源性质相结合,T2Agent对传统的MCTS进行了扩展,实现多源验证,将任务分解为针对不同伪造源协调的子任务。进一步提出了一种包含推理轨迹得分和置信得分的双重奖励机制,以鼓励在混合伪造源之间进行探索与利用更可靠的证据之间保持平衡。我们通过消融研究证实了树搜索机制和工具使用的有效性。大量实验进一步表明,T2Agent在具有挑战性的混合源多模态错误信息基准测试上始终优于现有基线,显示出其作为无训练方法提高检测精度的强大潜力。代码将被发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为T2Agent的新型信息检测智能体,针对现实世界中由混合伪造源引发的多模式错误信息挑战。通过采用可拓展的工具包和蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),实现了高效的多源验证和动态推理。该工具包包括网页搜索、伪造检测和一致性分析等模块化工具,并使用标准化模板进行描述,确保无缝集成和未来扩展性。为了避免同时使用的所有工具的低效性,提出了基于贝叶斯优化的选择器来确定与任务相关的工具子集,作为MCTS的行动空间。此外,对MCTS进行了针对多源信息检测任务的扩展,将任务分解为针对不同伪造源协调的子任务。通过双重奖励机制平衡探索不同伪造源和可靠证据的开发。实验表明,T2Agent在混合源多模式错误信息检测基准测试中表现优异,具有强大的潜力成为一种无需训练即可提高检测准确性的方法。
Key Takeaways
- T2Agent提出一种新型信息检测智能体用于处理多模态误导信息。
- 采用包含多种模块化工具的工具体系结构应对复杂性和多样性。
- 利用蒙特卡洛树搜索进行动态证据收集和任务分解。
- 提出基于贝叶斯优化的选择器以提高效率。
- 通过双重奖励机制平衡探索与开发。
点此查看论文截图

RFTF: Reinforcement Fine-tuning for Embodied Agents with Temporal Feedback
Authors:Junyang Shu, Zhiwei Lin, Yongtao Wang
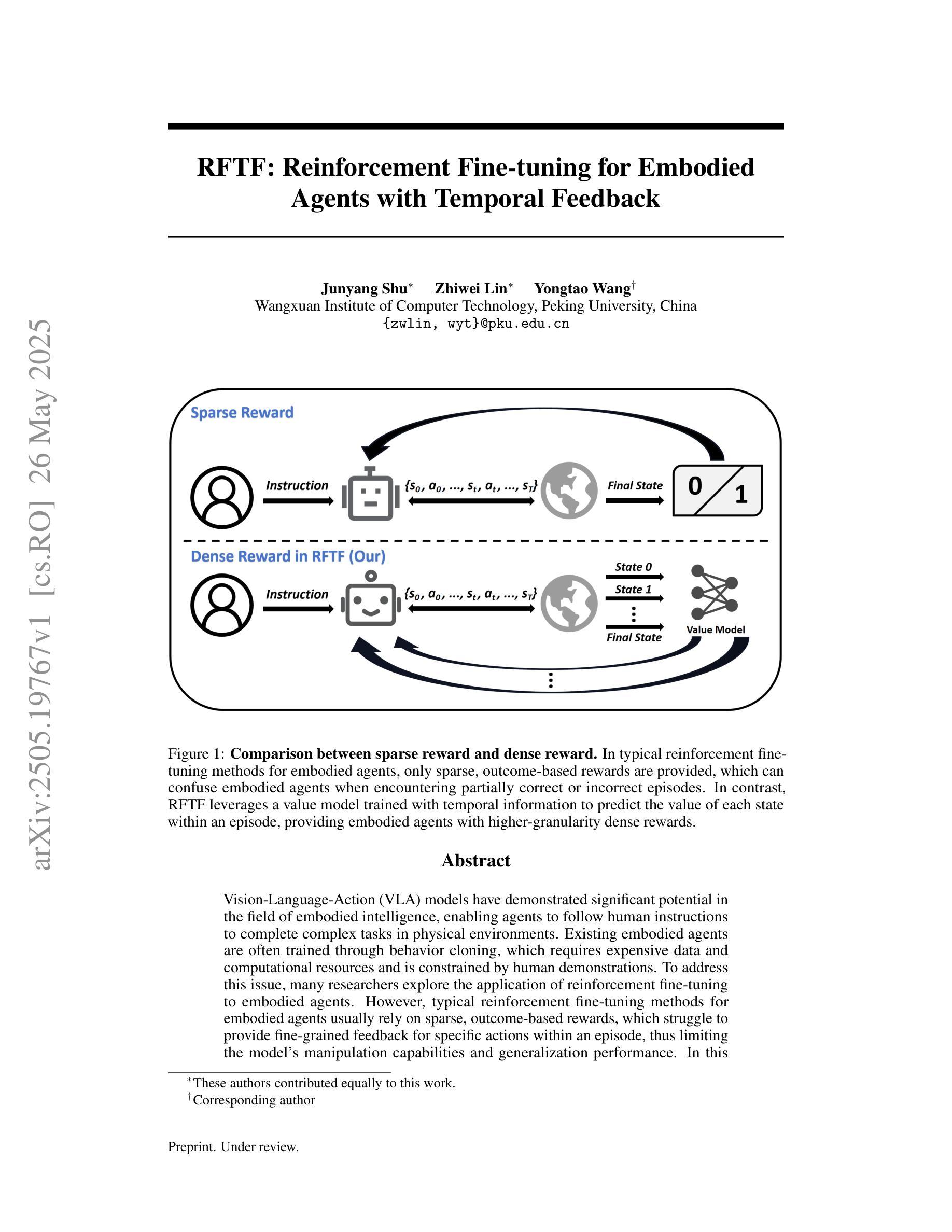
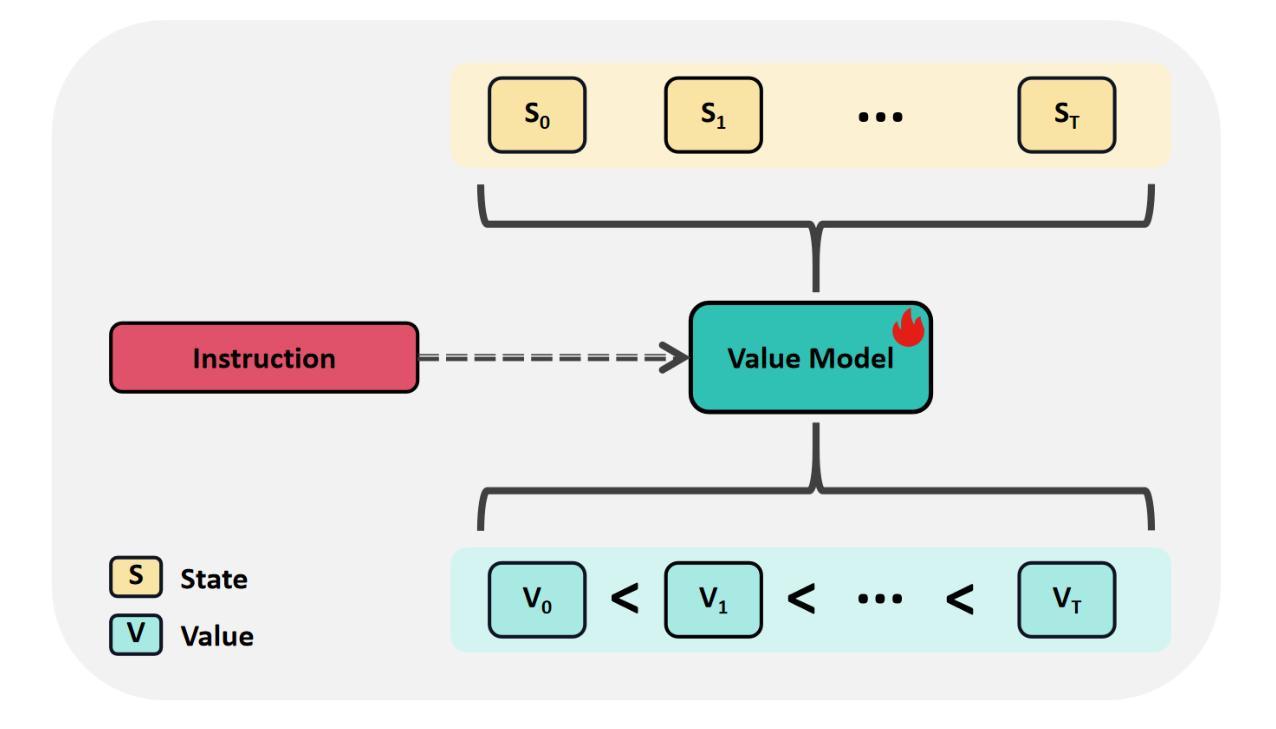
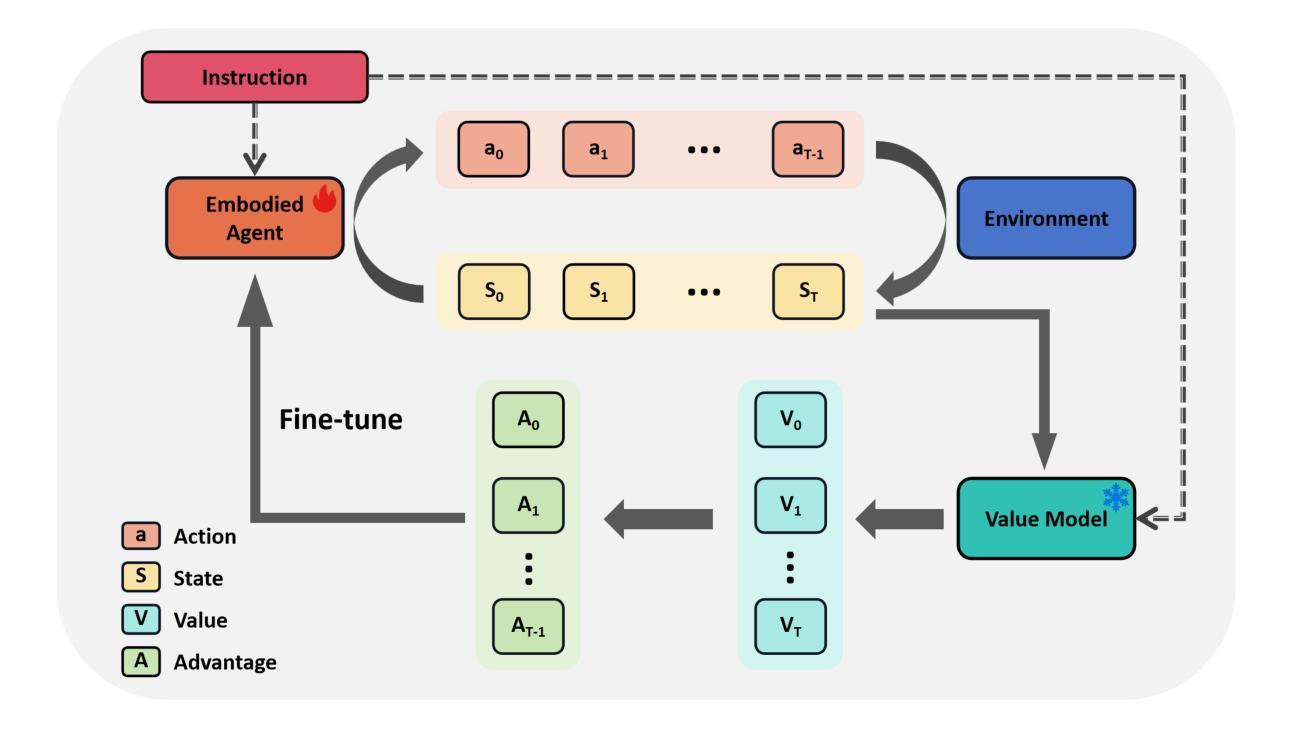
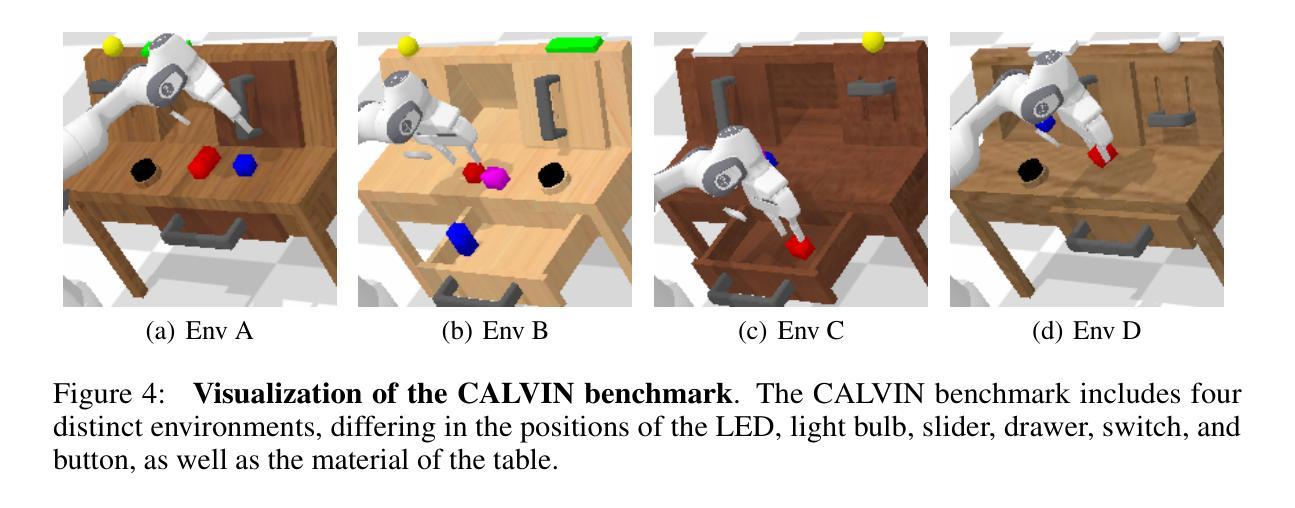
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated significant potential in the field of embodied intelligence, enabling agents to follow human instructions to complete complex tasks in physical environments. Existing embodied agents are often trained through behavior cloning, which requires expensive data and computational resources and is constrained by human demonstrations. To address this issue, many researchers explore the application of reinforcement fine-tuning to embodied agents. However, typical reinforcement fine-tuning methods for embodied agents usually rely on sparse, outcome-based rewards, which struggle to provide fine-grained feedback for specific actions within an episode, thus limiting the model’s manipulation capabilities and generalization performance. In this paper, we propose RFTF, a novel reinforcement fine-tuning method that leverages a value model to generate dense rewards in embodied scenarios. Specifically, our value model is trained using temporal information, eliminating the need for costly robot action labels. In addition, RFTF incorporates a range of techniques, such as GAE and sample balance to enhance the effectiveness of the fine-tuning process. By addressing the sparse reward problem in reinforcement fine-tuning, our method significantly improves the performance of embodied agents, delivering superior generalization and adaptation capabilities across diverse embodied tasks. Experimental results show that embodied agents fine-tuned with RFTF achieve new state-of-the-art performance on the challenging CALVIN ABC-D with an average success length of 4.296. Moreover, RFTF enables rapid adaptation to new environments. After fine-tuning in the D environment of CALVIN for a few episodes, RFTF achieved an average success length of 4.301 in this new environment.
视觉语言动作(VLA)模型在智能体领域表现出了巨大的潜力,使智能体能够遵循人类的指令在物理环境中完成复杂的任务。现有的智能体通常通过行为克隆进行训练,这需要大量的数据和计算资源,并受到人类演示的限制。为了解决这一问题,许多研究者探索将强化微调应用于智能体。然而,典型的智能体强化微调方法通常依赖于稀疏的结果型奖励,这很难为单次行动提供精细的反馈,从而限制了模型的操控能力和泛化性能。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的强化微调方法RFTF,它利用价值模型在智能场景中生成密集奖励。具体来说,我们的价值模型使用时序信息进行训练,无需昂贵的机器人动作标签。此外,RFTF还采用了一系列技术,如GAE和样本平衡,以增强微调过程的有效性。通过解决强化微调中的稀疏奖励问题,我们的方法显著提高了智能体的性能,在多种智能任务上展现了卓越的泛化和适应能力。实验结果表明,使用RFTF进行微调的智能体在具有挑战性的CALVIN ABC-D任务上达到了最新的最先进的性能,平均成功长度为4.296。此外,RFTF能够迅速适应新环境。在CALVIN的D环境中进行几轮微调后,RFTF在这个新环境中的平均成功长度达到了4.301。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在体智能领域,现有的体代理人通常通过行为克隆进行训练,这需要大量的数据和计算资源,并受限于人类演示。为解决此问题,研究者尝试应用强化精细调整方法。然而,传统强化精细调整方法通常依赖于稀疏的结果型奖励,难以在单集内为特定行动提供精细反馈,从而限制了模型的操控能力和泛化性能。本文提出一种新型强化精细调整方法RFTF,利用值模型在体场景中生成密集奖励。值模型通过时间信息训练,无需昂贵的机器人动作标签。此外,RFTF结合多种技术增强精细调整过程的有效性。实验结果显示,使用RFTF精细调整的体代理在具有挑战性的CALVIN ABC-D上取得最新最先进的性能,平均成功长度为4.296,且在新环境下能快速适应。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型在体智能领域有巨大潜力,能让代理遵循人类指令完成物理环境中的复杂任务。
- 当前体代理人主要通过行为克隆训练,这要求大量数据和计算资源,并受限于人类演示。
- 强化精细调整是解决此问题的一种方法,但传统方法依赖稀疏的结果型奖励,难以提供具体行动的精细反馈。
- 本文提出RFTF方法,利用值模型生成密集奖励,通过时间信息训练值模型,减少机器人动作标签成本。
- RFTF结合多种技术提升精细调整效果,如GAE和样本平衡。
- 实验显示,使用RFTF的体代理在CALVIN ABC-D任务上取得卓越性能,平均成功长度达4.296。
点此查看论文截图
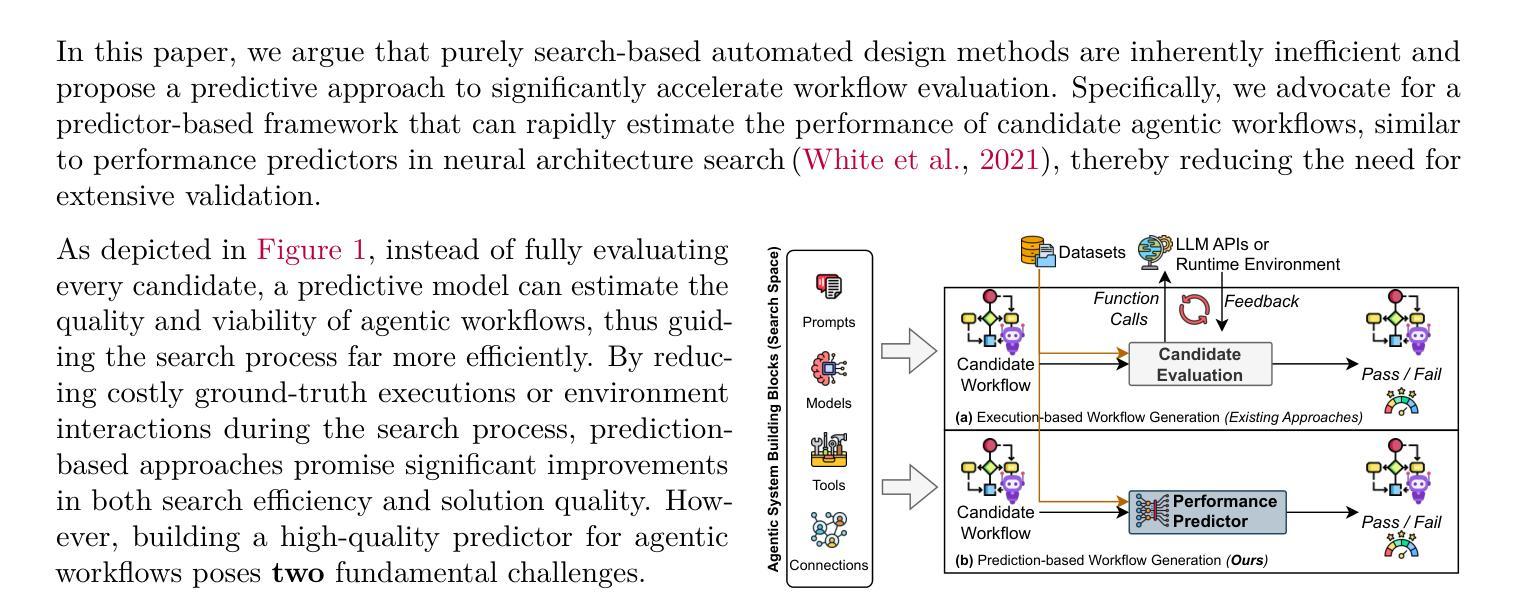
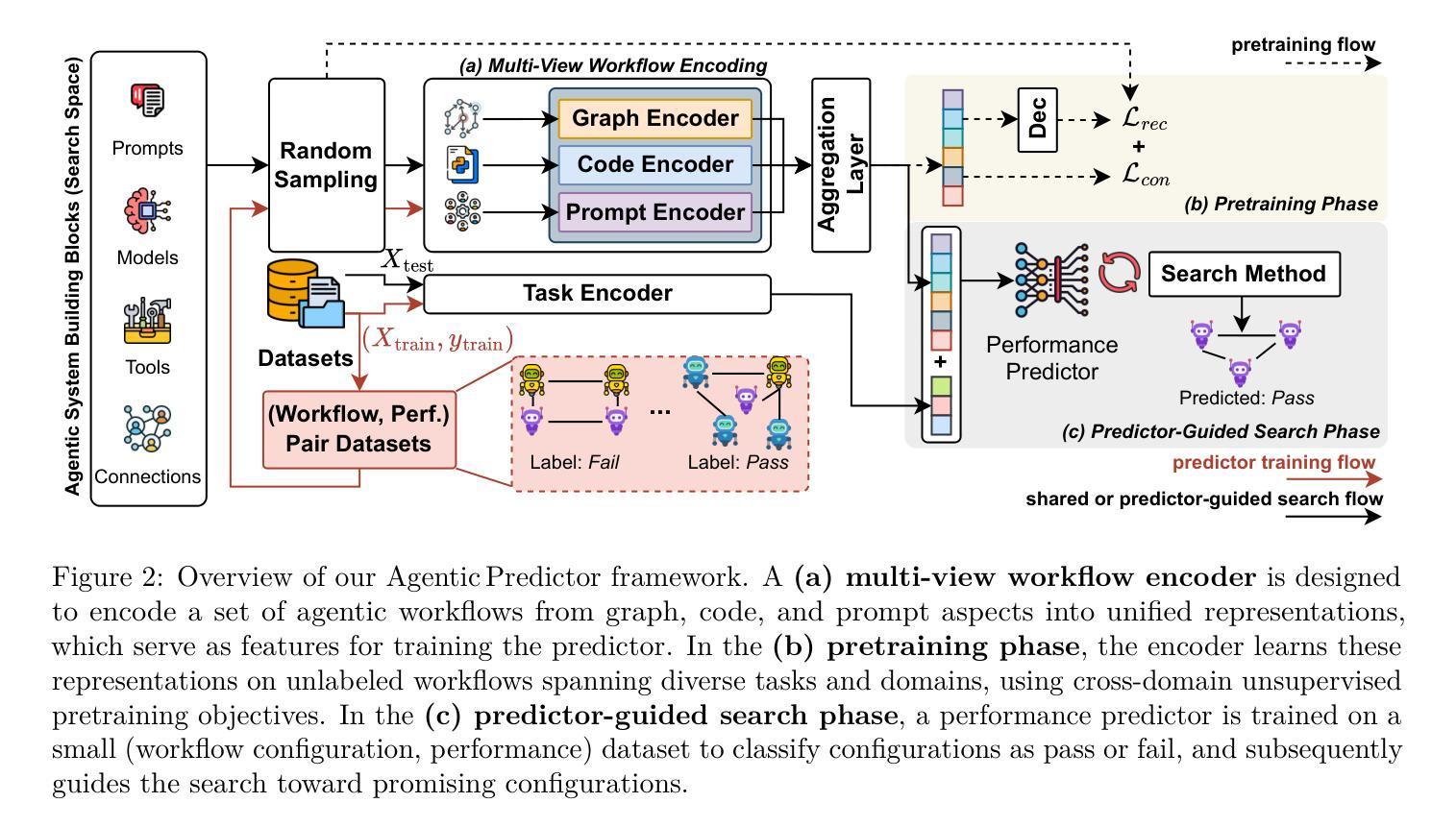
Agentic Predictor: Performance Prediction for Agentic Workflows via Multi-View Encoding
Authors:Patara Trirat, Wonyong Jeong, Sung Ju Hwang
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, but optimizing LLM-based agentic systems remains challenging due to the vast search space of agent configurations, prompting strategies, and communication patterns. Existing approaches often rely on heuristic-based tuning or exhaustive evaluation, which can be computationally expensive and suboptimal. This paper proposes Agentic Predictor, a lightweight predictor for efficient agentic workflow evaluation. Agentic Predictor is equipped with a multi-view workflow encoding technique that leverages multi-view representation learning of agentic systems by incorporating code architecture, textual prompts, and interaction graph features. To achieve high predictive accuracy while significantly reducing the number of required workflow evaluations for training a predictor, Agentic Predictor employs cross-domain unsupervised pretraining. By learning to approximate task success rates, Agentic Predictor enables fast and accurate selection of optimal agentic workflow configurations for a given task, significantly reducing the need for expensive trial-and-error evaluations. Experiments on a carefully curated benchmark spanning three domains show that our predictor outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both predictive accuracy and workflow utility, highlighting the potential of performance predictors in streamlining the design of LLM-based agentic workflows.
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中表现出了显著的能力,但由于代理配置、提示策略和通信模式的庞大搜索空间,优化基于LLM的代理系统仍然是一个挑战。现有方法常常依赖于基于启发式的方法或全面评估,这可能会计算量大且不够理想。本文提出了Agentic Predictor,这是一种用于高效代理工作流程评估的轻量级预测器。Agentic Predictor配备了一种多视角工作流程编码技术,该技术通过结合代码架构、文本提示和交互图特征,利用代理系统的多视角表示学习。为了实现高预测精度,同时大大减少训练预测器所需的工作流程评估次数,Agentic Predictor采用了跨域无监督预训练。通过学习近似任务成功率,Agentic Predictor能够快速准确地为给定任务选择最佳代理工作流程配置,大大降低了昂贵的试错评估的需求。在精心策划的涵盖三个领域的基准测试上的实验表明,我们的预测器在预测精度和流程实用性方面都优于最新方法,突显了性能预测器在简化基于LLM的代理工作流程设计方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code will be available at https://github.com/DeepAuto-AI/agentic-predictor
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中展现出卓越的能力,但优化LLM为基础的智能体系统仍然面临挑战。现有方法往往依赖启发式调整或全面评估,计算成本高且可能不够理想。本文提出Agentic Predictor,一种用于高效智能体工作流评估的轻量级预测器。Agentic Predictor具备多视角工作流编码技术,通过结合代码架构、文本提示和交互图特征,进行智能体系统的多视角表示学习。为在训练预测器时实现高预测精度并大大减少所需的工作流评估次数,Agentic Predictor采用跨域无监督预训练。通过学习估算任务成功率,Agentic Predictor可以快速准确地为目标任务选择最佳智能体工作流配置,大大减少昂贵的试错评估的需求。在跨越三个领域的精心挑选的基准测试上进行的实验表明,我们的预测器在预测精度和工作流实用性方面均优于最新方法,突显了性能预测器在简化LLM为基础的智能体系统设计方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多种任务中表现出色,但优化LLM为基础的智能体系统具有挑战。
- 现有方法如启发式调整和全面评估存在计算成本高和不够理想的问题。
- Agentic Predictor是一种轻量级预测器,能高效评估智能体工作流。
- Agentic Predictor采用多视角编码技术和跨域无监督预训练,提高预测精度并减少评估次数。
- Agentic Predictor能估算任务成功率,为任务选择最佳智能体工作流配置。
- 在多个领域的实验表明,Agentic Predictor在预测精度和工作流实用性上优于其他最新方法。
点此查看论文截图



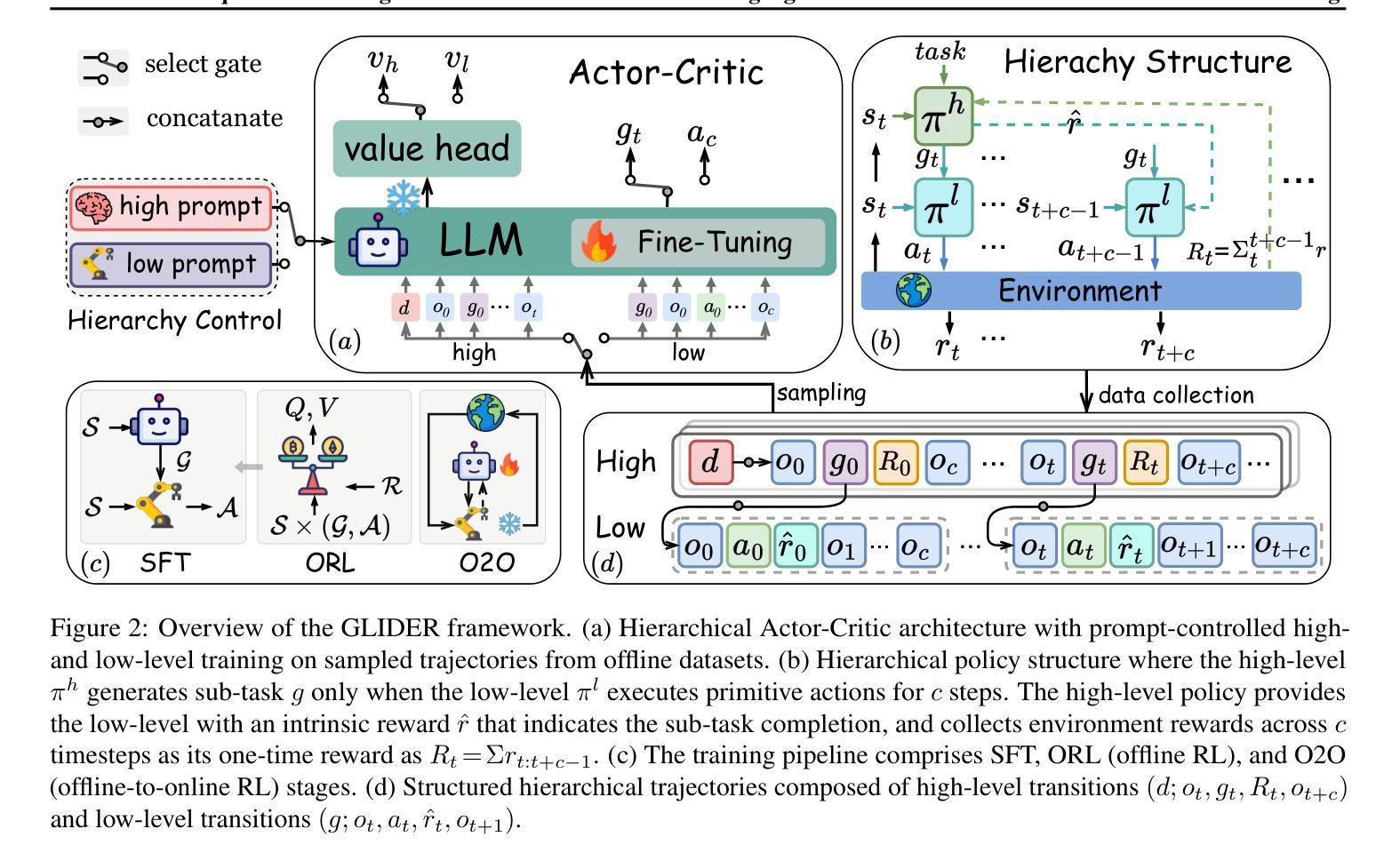
Divide and Conquer: Grounding LLMs as Efficient Decision-Making Agents via Offline Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zican Hu, Wei Liu, Xiaoye Qu, Xiangyu Yue, Chunlin Chen, Zhi Wang, Yu Cheng
While showing sophisticated reasoning abilities, large language models (LLMs) still struggle with long-horizon decision-making tasks due to deficient exploration and long-term credit assignment, especially in sparse-reward scenarios. Inspired by the divide-and-conquer principle, we propose an innovative framework GLIDER (Grounding Language Models as EffIcient Decision-Making Agents via Offline HiErarchical Reinforcement Learning) that introduces a parameter-efficient and generally applicable hierarchy to LLM policies. We develop a scheme where the low-level controller is supervised with abstract, step-by-step plans that are learned and instructed by the high-level policy. This design decomposes complicated problems into a series of coherent chain-of-thought reasoning sub-tasks, providing flexible temporal abstraction to significantly enhance exploration and learning for long-horizon tasks. Furthermore, GLIDER facilitates fast online adaptation to non-stationary environments owing to the strong transferability of its task-agnostic low-level skills. Experiments on ScienceWorld and ALFWorld benchmarks show that GLIDER achieves consistent performance gains, along with enhanced generalization capabilities.
在展现出复杂推理能力的同时,大型语言模型(LLM)仍然面临着长期决策任务的挑战,这主要是因为缺乏探索和长期信用分配,特别是在稀疏奖励场景中。受“分而治之”原则的启发,我们提出了一种创新框架GLIDER(通过离线分层强化学习将Grounding Language模型作为高效决策代理I)。它引入了对LLM策略具有通用适用性的参数高效的分层结构。我们开发了一种方案,其中低级控制器受到抽象、逐步计划的监督,这些计划是由高级策略学习和指导的。这种设计将复杂的问题分解为一系列连贯的链式思维推理子任务,提供了灵活的时序抽象,显著增强了长期任务的探索和学习能力。此外,由于非特定任务的低级技能具有强大的迁移能力,GLIDER能够快速适应非静态环境。在ScienceWorld和ALFWorld基准测试上的实验表明,GLIDER实现了性能的一致性提升,并增强了泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025, 21 pages
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在处理长期决策任务时面临探索和长期信用分配的问题,尤其在稀疏奖励场景中表现更为突出。本文提出一种基于分而治之原则的创新框架GLIDER,为LLM策略引入参数高效且普遍适用的层次结构。GLIDER设计低层次控制器,通过高层次策略的指导和学习,以抽象、分步计划进行监督。这分解了复杂问题,提供灵活的时间抽象,显著增强了长期任务的探索和学习能力。此外,GLIDER还便于对非稳定环境的快速在线适应。在ScienceWorld和ALFWorld基准测试上,GLIDER实现了性能上的持续提升,并增强了泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在处理长期决策任务时存在探索和长期信用分配的问题。
- GLIDER框架引入参数高效且普遍适用的层次结构来解决LLM的策略问题。
- GLIDER设计低层次控制器,通过高层次策略的指导和学习,以抽象、分步计划进行监督。
- GLIDER将复杂问题分解为一系列连贯的子任务,提供灵活的时间抽象,增强长期任务的探索和学习能力。
- GLIDER框架有助于快速适应非稳定环境。
- 在ScienceWorld和ALFWorld测试中,GLIDER实现了性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

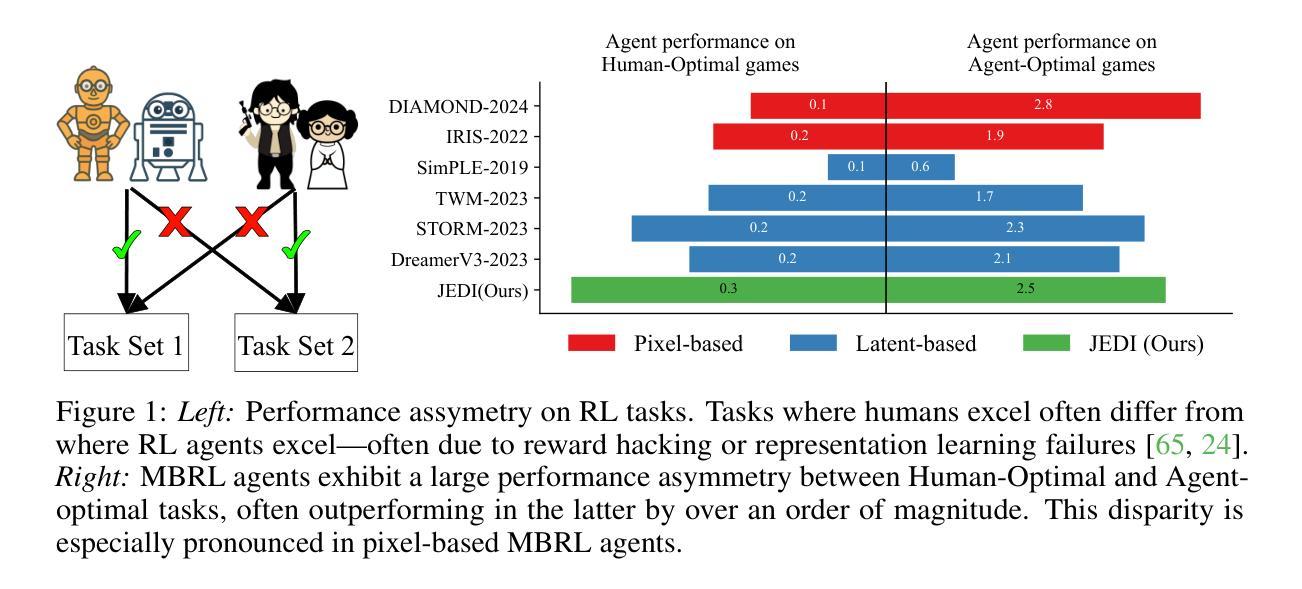
JEDI: Latent End-to-end Diffusion Mitigates Agent-Human Performance Asymmetry in Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Jing Yu Lim, Zarif Ikram, Samson Yu, Haozhe Ma, Tze-Yun Leong, Dianbo Liu
Recent advances in model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) have achieved super-human level performance on the Atari100k benchmark, driven by reinforcement learning agents trained on powerful diffusion world models. However, we identify that the current aggregates mask a major performance asymmetry: MBRL agents dramatically outperform humans in some tasks despite drastically underperforming in others, with the former inflating the aggregate metrics. This is especially pronounced in pixel-based agents trained with diffusion world models. In this work, we address the pronounced asymmetry observed in pixel-based agents as an initial attempt to reverse the worrying upward trend observed in them. We address the problematic aggregates by delineating all tasks as Agent-Optimal or Human-Optimal and advocate for equal importance on metrics from both sets. Next, we hypothesize this pronounced asymmetry is due to the lack of temporally-structured latent space trained with the World Model objective in pixel-based methods. Lastly, to address this issue, we propose Joint Embedding DIffusion (JEDI), a novel latent diffusion world model trained end-to-end with the self-consistency objective. JEDI outperforms SOTA models in human-optimal tasks while staying competitive across the Atari100k benchmark, and runs 3 times faster with 43% lower memory than the latest pixel-based diffusion baseline. Overall, our work rethinks what it truly means to cross human-level performance in Atari100k.
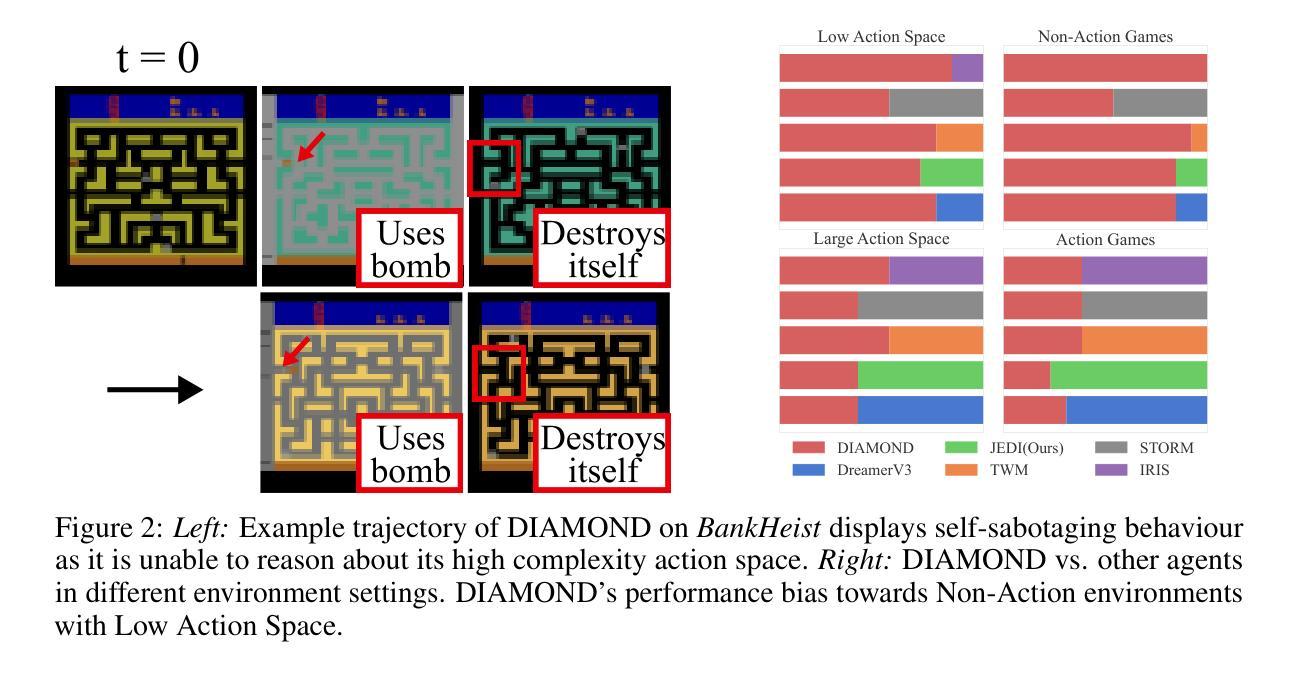
近期基于模型的强化学习(MBRL)的进展已经在Atari100k基准测试上达到了超人类水平的性能,其驱动因素是经过强大的扩散世界模型训练的强化学习智能体。然而,我们发现当前的汇总数据掩盖了主要的性能不对称:在某些任务中,MBRL智能体的表现远远超过了人类,尽管在其他任务中其表现远不如人类,而前者往往会抬高汇总指标。这在基于像素的代理训练中尤为明显,这些代理是使用扩散世界模型进行训练的。在这项工作中,我们关注在基于像素的代理中观察到的明显不对称现象,作为初步尝试来扭转这种令人担忧的上升趋势。我们通过将任务划分为以智能体为中心的最优任务或以人类为中心的最优任务来解决存在问题的汇总数据问题,并主张对两组指标给予同等重视。接下来,我们假设这种明显的不对称性是由于基于像素的方法在缺乏与世界模型目标结构化的时间结构潜在空间训练所导致的。最后,为了解决这个问题,我们提出了联合嵌入扩散(JEDI),这是一种新型潜在扩散世界模型,通过端到端的自一致性目标进行训练。JEDI在人类最优任务中超越了最新技术水平的模型,同时在Atari100k基准测试中保持竞争力,并且与最新的基于像素的扩散基准相比,运行速度快三倍,内存降低了43%。总的来说,我们的工作重新思考了在Atari100k基准测试中达到超越人类水平性能的真正含义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文探讨了基于模型的强化学习(MBRL)在Atari100k基准测试上的性能问题。尽管MBRL在某些任务上表现超常,但在其他任务上却远远落后于人类。文章提出对像素级代理中观察到的明显不对称性进行初步解决,通过提出联合嵌入扩散(JEDI)模型来改善人类最优任务中的性能,同时在整个Atari100k基准测试中保持竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- MBRL在某些任务上的表现远超人类,但在其他任务上却远远落后,导致整体性能指标存在偏差。
- 现有聚合指标掩盖了性能不对称的问题,特别是在像素级代理上训练的扩散世界模型中表现更为突出。
- 文章提出了一种解决像素级代理中明显不对称性的方法,即通过提出联合嵌入扩散(JEDI)模型来改善人类最优任务中的性能。
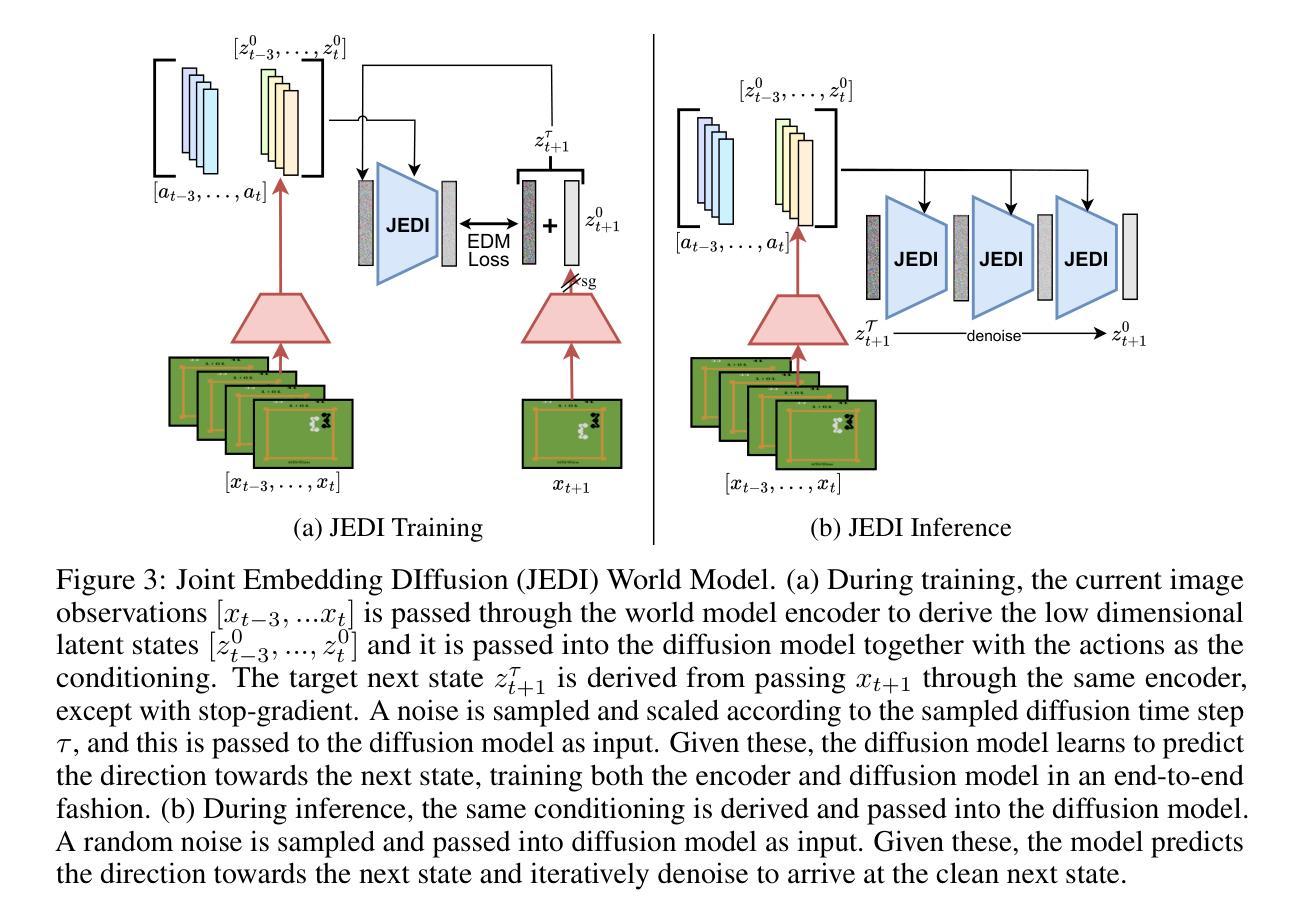
- JEDI模型通过端到端训练和自一致性目标来训练潜伏扩散世界模型,显著提高了性能。
- JEDI模型在保持竞争力的同时,运行速度比最新的像素级扩散基线快三倍,同时内存占用减少43%。
- 文章重新审视了在Atari100k基准测试中达到人类水平的真正含义。强调既要关注任务的代理最优指标,也要关注人类最优指标的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

O$^2$-Searcher: A Searching-based Agent Model for Open-Domain Open-Ended Question Answering
Authors:Jianbiao Mei, Tao Hu, Daocheng Fu, Licheng Wen, Xuemeng Yang, Rong Wu, Pinlong Cai, Xinyu Cai, Xing Gao, Yu Yang, Chengjun Xie, Botian Shi, Yong Liu, Yu Qiao
Large Language Models (LLMs), despite their advancements, are fundamentally limited by their static parametric knowledge, hindering performance on tasks requiring open-domain up-to-date information. While enabling LLMs to interact with external knowledge environments is a promising solution, current efforts primarily address closed-end problems. Open-ended questions, which characterized by lacking a standard answer or providing non-unique and diverse answers, remain underexplored. To bridge this gap, we present O$^2$-Searcher, a novel search agent leveraging reinforcement learning to effectively tackle both open-ended and closed-ended questions in the open domain. O$^2$-Searcher leverages an efficient, locally simulated search environment for dynamic knowledge acquisition, effectively decoupling the external world knowledge from model’s sophisticated reasoning processes. It employs a unified training mechanism with meticulously designed reward functions, enabling the agent to identify problem types and adapt different answer generation strategies. Furthermore, to evaluate performance on complex open-ended tasks, we construct O$^2$-QA, a high-quality benchmark featuring 300 manually curated, multi-domain open-ended questions with associated web page caches. Extensive experiments show that O$^2$-Searcher, using only a 3B model, significantly surpasses leading LLM agents on O$^2$-QA. It also achieves SOTA results on various closed-ended QA benchmarks against similarly-sized models, while performing on par with much larger ones.
尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)取得了进展,但它们仍然受到静态参数知识的根本限制,这阻碍了它们在需要开放领域最新信息的任务上的表现。虽然让LLMs与外部环境进行交互是一个有前景的解决方案,但目前的努力主要集中于解决封闭式问题。开放式问题(其特点是缺乏标准答案或提供非唯一和多样化的答案)仍然被探索得很少。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了O$^2$-Searcher,这是一个新型搜索代理,利用强化学习有效地解决开放式和封闭式问题。O$^2$-Searcher利用高效、局部模拟的搜索环境进行动态知识获取,有效地将外部世界知识与模型的复杂推理过程解耦。它采用统一的训练机制和精心设计的奖励函数,使代理能够识别问题类型并采用不同的答案生成策略。此外,为了评估在复杂开放式任务上的性能,我们构建了O$^2$-QA,这是一个高质量基准测试,包含300个手动整理的多领域开放式问题及其相关网页缓存。大量实验表明,仅使用3B模型的O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上显著超越了领先的大型语言模型代理。它在各种封闭式问答基准测试上也取得了最新结果,同时与更大的模型表现相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 9 figures
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在应对需要开放领域即时信息的任务上存在局限,尽管有所进展,但其静态参数知识仍是根本限制。为解决这一问题,我们提出了O$^2$-Searcher,一个利用强化学习有效应对开放和封闭问题的新型搜索代理。它通过高效的本地模拟搜索环境实现动态知识获取,将外部世界知识与模型的复杂推理过程分离。此外,我们构建了O$^2$-QA基准测试,以评估在复杂开放任务上的性能。实验表明,O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上的表现显著优于领先的大型语言模型代理,同时在各种封闭问答基准测试中实现了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs受限于静态参数知识,难以处理需要开放领域即时信息的任务。
- O$^2$-Searcher是一个新型搜索代理,利用强化学习应对开放和封闭问题。
- O$^2$-Searcher通过本地模拟搜索环境实现动态知识获取,分离外部世界知识与模型推理过程。
- O$^2$-Searcher使用统一的训练机制和精心设计的奖励函数,能识别问题类型并适应不同的答案生成策略。
- O$^2$-QA基准测试用于评估在复杂开放任务上的性能。
- O$^2$-Searcher在O$^2$-QA上的表现优于其他LLM代理,同时在封闭问答基准测试中实现最佳结果。
点此查看论文截图

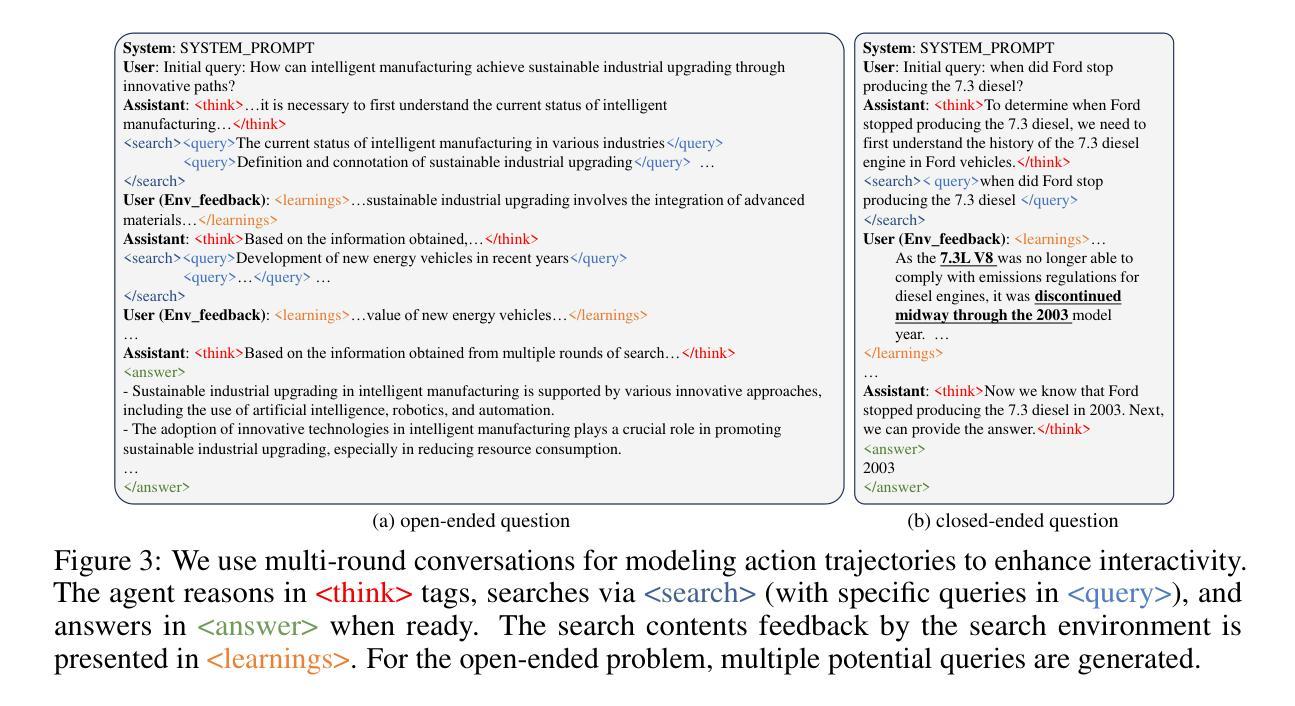
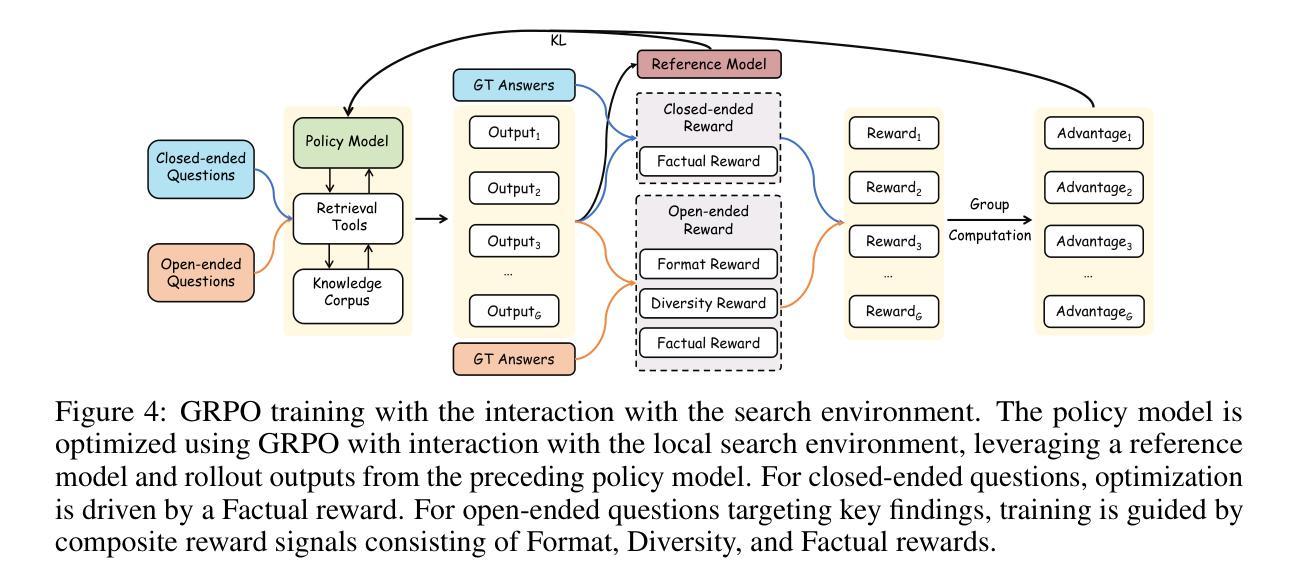
Mobile-Bench-v2: A More Realistic and Comprehensive Benchmark for VLM-based Mobile Agents
Authors:Weikai Xu, Zhizheng Jiang, Yuxuan Liu, Pengzhi Gao, Wei Liu, Jian Luan, Yuanchun Li, Yunxin Liu, Bin Wang, Bo An
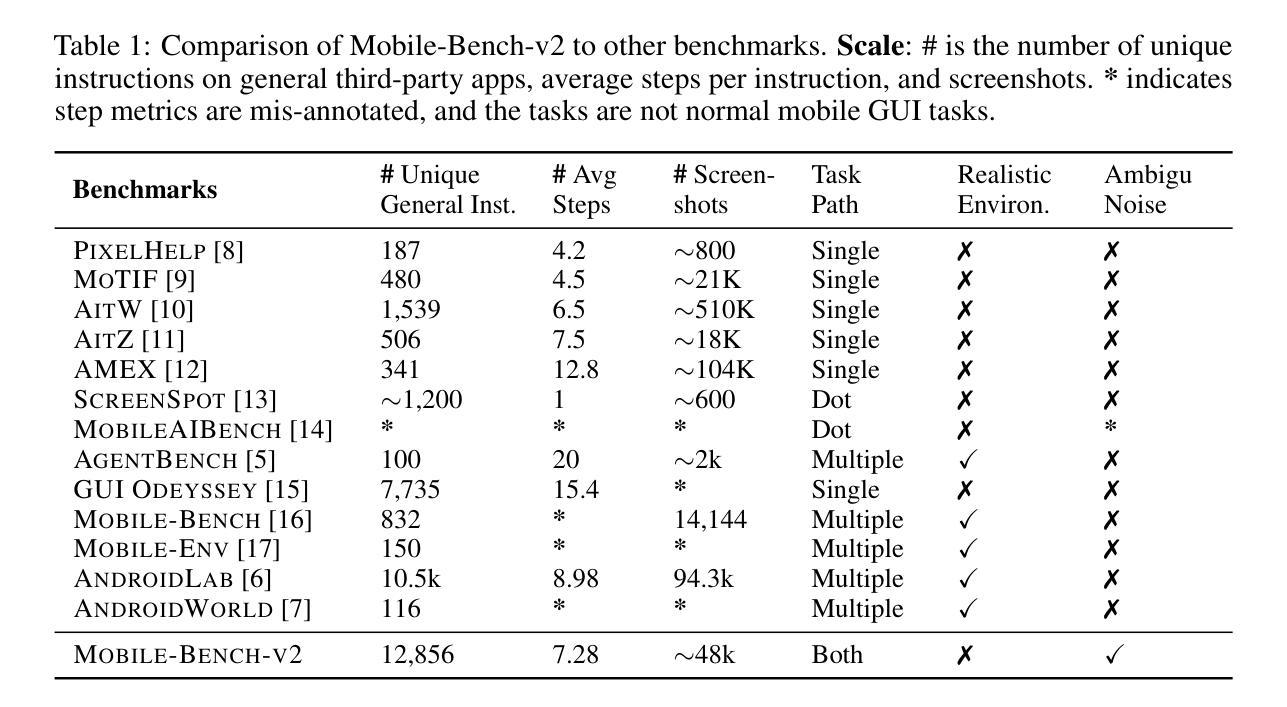
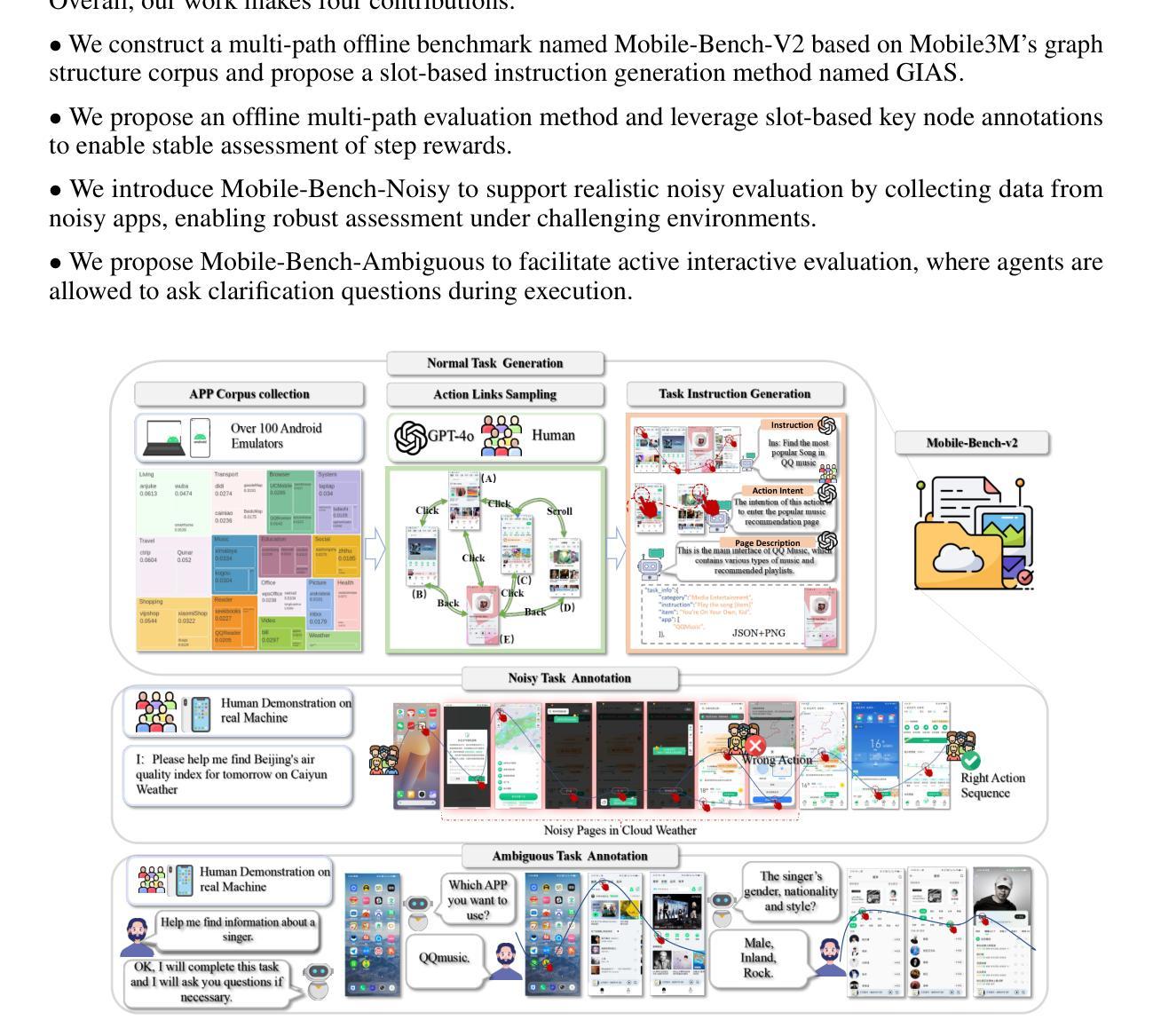
VLM-based mobile agents are increasingly popular due to their capabilities to interact with smartphone GUIs and XML-structured texts and to complete daily tasks. However, existing online benchmarks struggle with obtaining stable reward signals due to dynamic environmental changes. Offline benchmarks evaluate the agents through single-path trajectories, which stands in contrast to the inherently multi-solution characteristics of GUI tasks. Additionally, both types of benchmarks fail to assess whether mobile agents can handle noise or engage in proactive interactions due to a lack of noisy apps or overly full instructions during the evaluation process. To address these limitations, we use a slot-based instruction generation method to construct a more realistic and comprehensive benchmark named Mobile-Bench-v2. Mobile-Bench-v2 includes a common task split, with offline multi-path evaluation to assess the agent’s ability to obtain step rewards during task execution. It contains a noisy split based on pop-ups and ads apps, and a contaminated split named AITZ-Noise to formulate a real noisy environment. Furthermore, an ambiguous instruction split with preset Q&A interactions is released to evaluate the agent’s proactive interaction capabilities. We conduct evaluations on these splits using the single-agent framework AppAgent-v1, the multi-agent framework Mobile-Agent-v2, as well as other mobile agents such as UI-Tars and OS-Atlas. Code and data are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/xwk123/MobileBench-v2.
基于VLM的移动智能体因其能够与智能手机GUI和XML结构文本进行交互并完成日常任务而越来越受欢迎。然而,现有的在线基准测试因动态环境变化而无法获得稳定的奖励信号。离线基准测试通过单一路径轨迹评估智能体,这与GUI任务固有的多解决方案特性形成鲜明对比。此外,两种类型的基准测试都未能评估移动智能体是否能够处理噪声或进行主动交互,因为在评估过程中缺乏噪声应用程序或过于完整的指令。为了解决这些局限性,我们使用基于插槽的指令生成方法来构建更真实、更全面的名为Mobile-Bench-v2的基准测试。Mobile-Bench-v2包括任务分割,具有离线多路径评估,以评估智能体在执行任务过程中获得阶段性奖励的能力。它包含基于弹出窗口和广告应用程序的噪声分割,以及名为AITZ-Noise的污染分割,以形成真实噪声环境。此外,还发布了一个带有预设问答互动的模糊指令分割,以评估智能体的主动交互能力。我们使用单智能体框架AppAgent-v1、多智能体框架Mobile-Agent-v2以及其他移动智能体如UI-Tars和OS-Atlas对这些分割进行了评估。代码和数据可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/xwk123/MobileBench-v2上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
基于VLM的移动代理因能与智能手机GUI和XML结构文本交互并完成日常任务而日益普及。然而,现有线上评估标准在动态环境变化中难以获得稳定的奖励信号。线下评估标准则通过单一路径轨迹来评估代理,这与GUI任务本质上多解的特点相悖。为解决这些局限,采用基于插槽的指令生成方法构建了一个更真实、全面的MobileBench-v2评估标准。它包括通用任务分割、离线多路径评估以评估代理在执行任务过程中获得阶段性奖励的能力。还包括基于弹窗和广告应用的噪声分割以及用于形成真实噪声环境的AITZ噪声分割。此外,还发布了带有预设问答互动的模糊指令分割,以评估代理的主动互动能力。我们使用了AppAgent-v1单代理框架、Mobile-Agent-v2多代理框架以及其他移动代理如UI-Tars和OS-Atlas进行了评估。相关代码和数据可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/xwk123/MobileBench-v2获取。
关键见解
- VLM移动代理具有与智能手机GUI和XML文本交互的能力,可完成日常任务,因此越来越受欢迎。
- 现有线上和线下评估标准存在局限性,无法稳定评估动态环境中的奖励信号或反映GUI任务的多解特性。
- MobileBench-v2通过更现实的评估标准解决了这些限制,包括多路径评估、噪声分割以模拟真实噪声环境,以及模糊指令分割以评估代理的主动互动能力。
- MobileBench-v2包括通用任务分割,旨在全面评估代理在完成任务过程中的能力,包括获得阶段性奖励的能力。
- MobileBench-v2评估和测试框架可用于多种移动代理,如AppAgent-v1、Mobile-Agent-v2、UI-Tars和OS-Atlas等。
- MobileBench-v2的代码和数据可在指定网站获取,便于研究人员使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

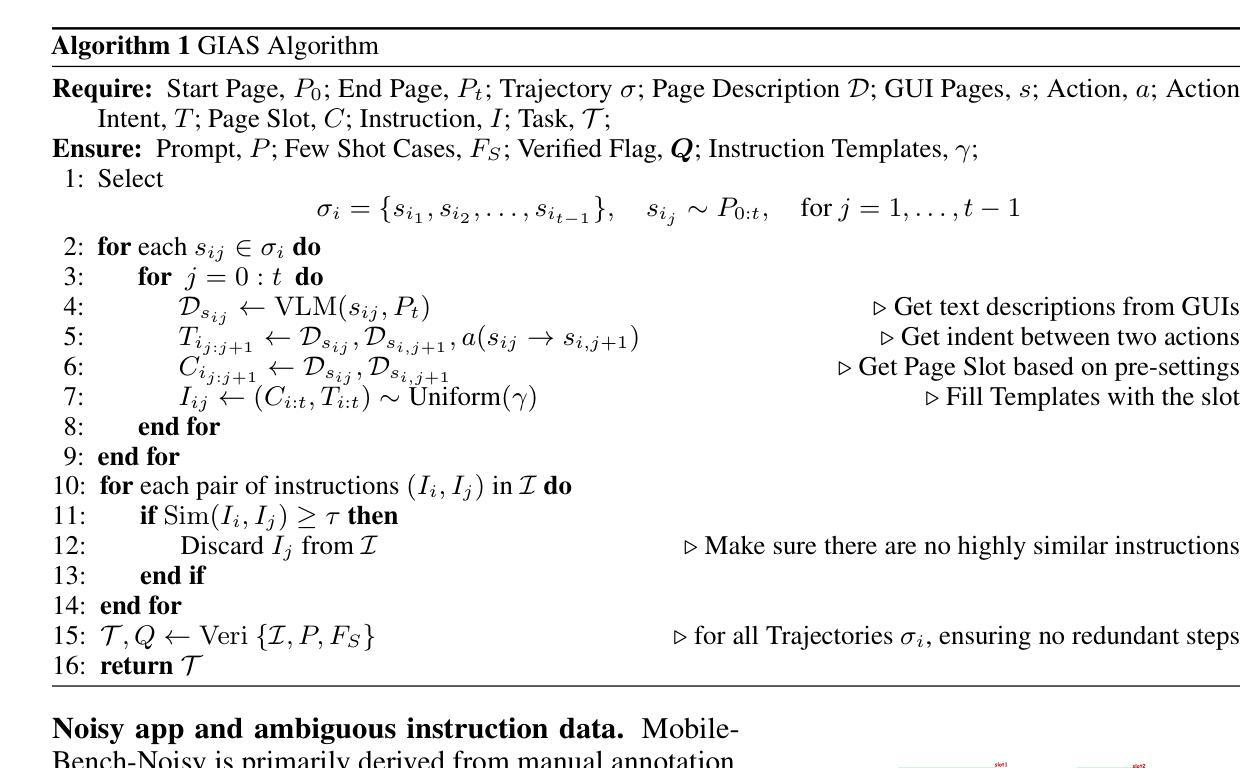
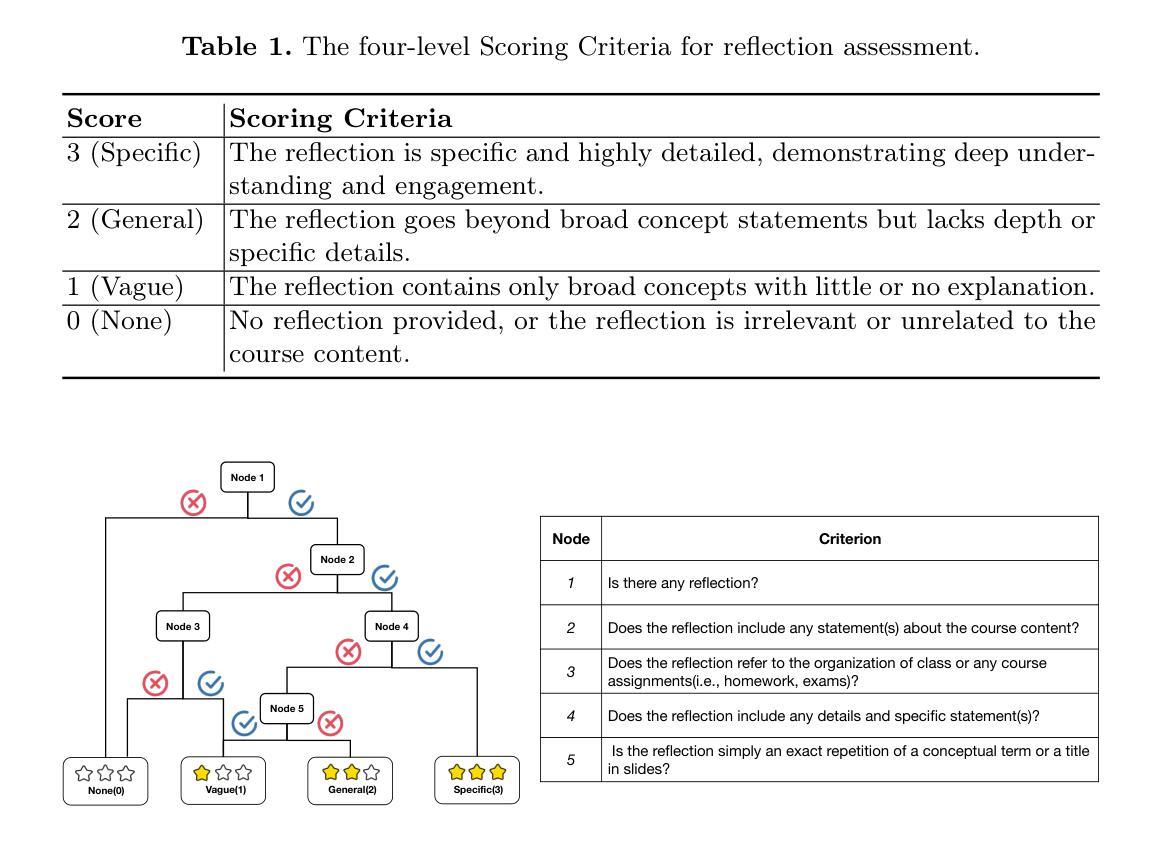
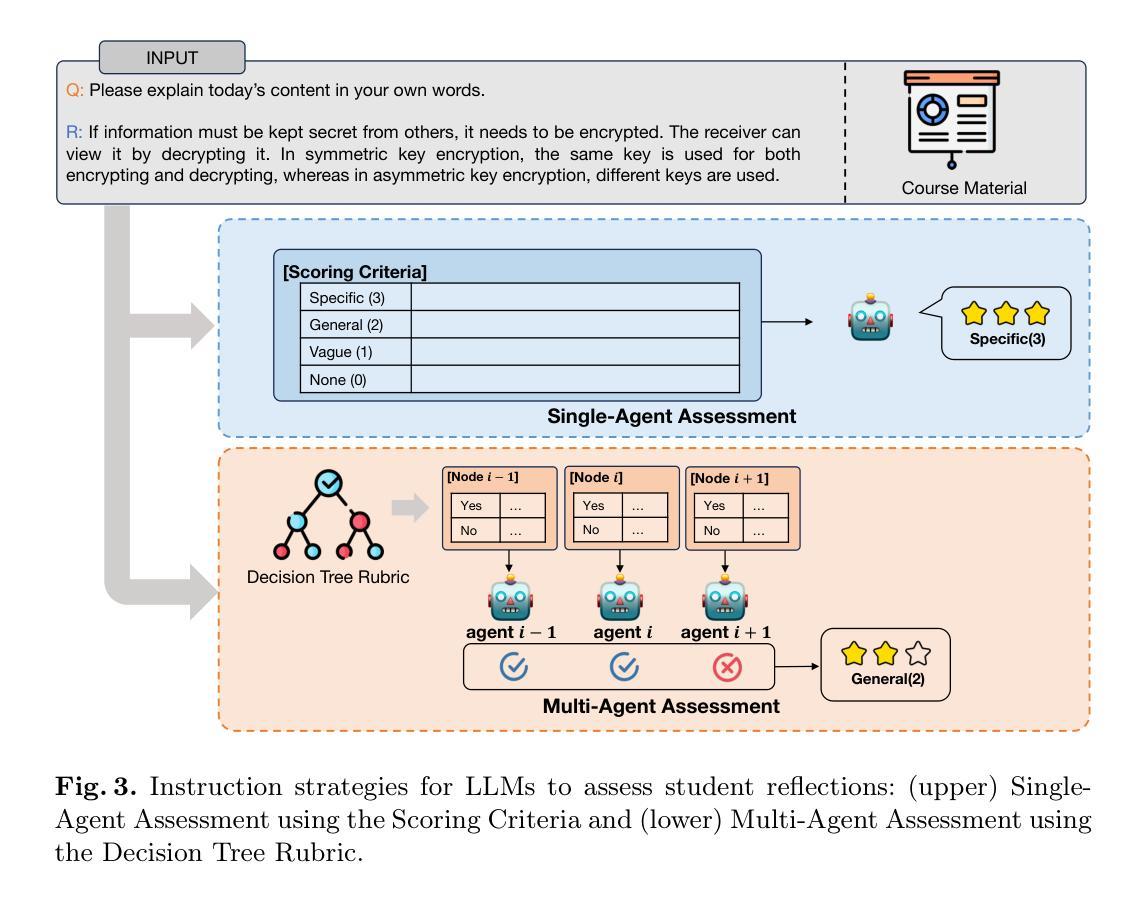
Single-Agent vs. Multi-Agent LLM Strategies for Automated Student Reflection Assessment
Authors:Gen Li, Li Chen, Cheng Tang, Valdemar Švábenský, Daisuke Deguchi, Takayoshi Yamashita, Atsushi Shimada
We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated assessment of open-text student reflections and prediction of academic performance. Traditional methods for evaluating reflections are time-consuming and may not scale effectively in educational settings. In this work, we employ LLMs to transform student reflections into quantitative scores using two assessment strategies (single-agent and multi-agent) and two prompting techniques (zero-shot and few-shot). Our experiments, conducted on a dataset of 5,278 reflections from 377 students over three academic terms, demonstrate that the single-agent with few-shot strategy achieves the highest match rate with human evaluations. Furthermore, models utilizing LLM-assessed reflection scores outperform baselines in both at-risk student identification and grade prediction tasks. These findings suggest that LLMs can effectively automate reflection assessment, reduce educators’ workload, and enable timely support for students who may need additional assistance. Our work emphasizes the potential of integrating advanced generative AI technologies into educational practices to enhance student engagement and academic success.
我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)在自动评估学生开放性反思和预测学业表现方面的应用。传统的反思评估方法耗时且可能无法在教育环境中有效地扩展。在这项工作中,我们采用LLM,使用两种评估策略(单智能体和多智能体)和两种提示技术(零样本和少量样本),将学生反思转化为量化分数。我们在包含来自377名学生在三个学术学期内的5,278篇反思的数据集上进行的实验表明,采用少量样本的单智能体策略与人类评估的匹配率最高。此外,使用LLM评估的反思分数的模型在处于风险的学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现都优于基线。这些结果表明,LLM可以有效地自动进行反思评估,减少教育工作者的工作量,并为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的支持。我们的工作强调了将先进的生成式人工智能技术与教育实践相结合,以提高学生参与度和学业成功的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Proceedings of the 29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD 2025)
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动评估学生开放文本反思和预测学业表现方面的应用。传统评估方法耗时且难以在教育环境中有效扩展。本研究使用LLMs将学生的反思转化为量化分数,采用两种评估策略和两种提示技术。实验表明,使用少数样本的单智能体策略与人工评价的匹配率最高。此外,使用LLM评估的反思分数模型在高风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中的表现优于基线模型。这显示LLMs可有效地自动进行反思评估,减轻教育者的工作量,并及时为可能需要额外帮助的学生提供支持。本研究强调了将高级生成式AI技术融入教育实践以提高学生参与度和学业成功的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)被用于自动评估学生的开放文本反思。
- 传统评估方法在教育环境中存在耗时且难以有效扩展的问题。
- 采用两种评估策略和两种提示技术进行处理,即单智能体和多智能体策略,以及零样本和少数样本提示技术。
- 实验结果显示,使用少数样本的单智能体策略与人工评价的匹配率最高。
- LLMs在反思评估中的表现优于基线模型,尤其是在高风险学生识别和成绩预测任务中。
- LLMs的自动评估可以有效减轻教育者的工作量,并为需要额外帮助的学生提供及时的反馈与支持。
点此查看论文截图


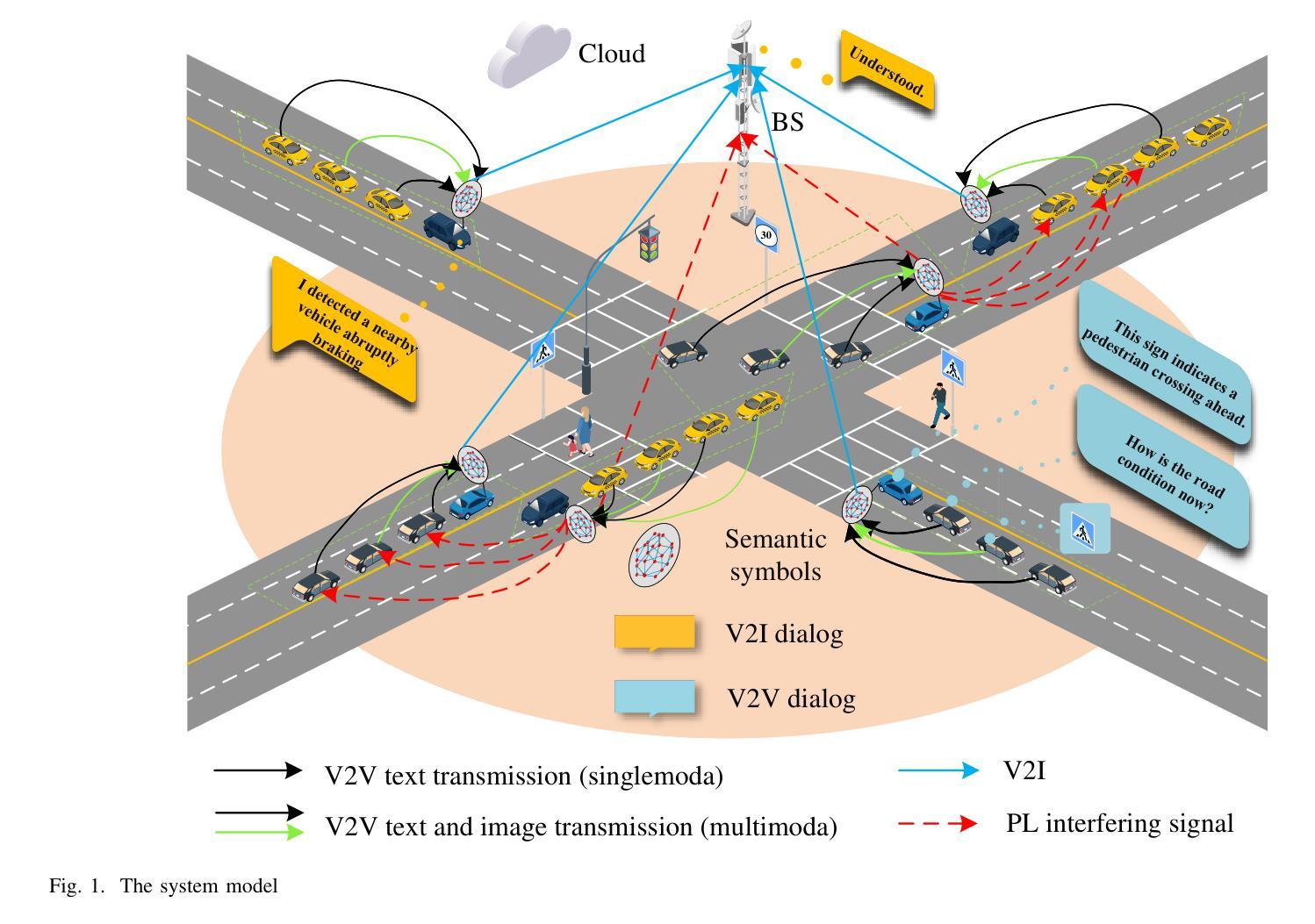
Semantic-Aware Resource Management for C-V2X Platooning via Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Wenjun Zhang, Qiong Wu, Pingyi Fan, Kezhi Wang, Nan Cheng, Wen Chen, Khaled B. Letaief
Semantic communication transmits the extracted features of information rather than raw data, significantly reducing redundancy, which is crucial for addressing spectrum and energy challenges in 6G networks. In this paper, we introduce semantic communication into a cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X)- based autonomous vehicle platoon system for the first time, aiming to achieve efficient management of communication resources in a dynamic environment. Firstly, we construct a mathematical model for semantic communication in platoon systems, in which the DeepSC model and MU-DeepSC model are used to semantically encode and decode unimodal and multi-modal data, respectively. Then, we propose the quality of experience (QoE) metric based on semantic similarity and semantic rate. Meanwhile, we consider the success rate of semantic information transmission (SRS) metric to ensure the fairness of channel resource allocation. Next, the optimization problem is posed with the aim of maximizing the QoE in vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) links while improving SRS. To solve this mixed integer nonlinear programming problem (MINLP) and adapt to time-varying channel conditions, the paper proposes a distributed semantic-aware multi-modal resource allocation (SAMRA) algorithm based on multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), referred to as SAMRAMARL. The algorithm can dynamically allocate channels and power and determine semantic symbol length based on the contextual importance of the transmitted information, ensuring efficient resource utilization. Finally, extensive simulations have demonstrated that SAMRAMARL outperforms existing methods, achieving significant gains in QoE, SRS, and communication delay in C-V2X platooning scenarios.
语义通信传输的是信息的特征提取而非原始数据,这大大降低了冗余性,对于应对6G网络中的频谱和能源挑战至关重要。在本文中,我们首次将语义通信引入基于蜂窝状车辆对一切(C-V2X)的自动驾驶车队系统,旨在实现动态环境中通信资源的高效管理。首先,我们构建了车队系统中语义通信的数学模型,其中DeepSC模型和MU-DeepSC模型分别用于单模态和多模态数据的语义编码和解码。其次,我们提出了基于语义相似性和语义速率的用户体验(QoE)指标。同时,我们考虑语义信息传输成功率(SRS)指标,以确保信道资源分配的公平性。接下来,以解决混合整数非线性规划(MINLP)问题并适应时变信道条件为目标,本文提出了一种基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的分布式语义感知多模态资源分配(SAMRA)算法,即SAMRAMARL算法。该算法可根据传输信息上下文的重要性动态分配信道和功率,并确定语义符号长度,确保资源的高效利用。最后,大量的模拟结果表明,SAMRAMARL算法在QoE、SRS和C-V2X车队场景中的通信延迟方面均优于现有方法,取得了显著的收益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been submitted to IEEE Journal. The source code has been released at:https://github.com/qiongwu86/Semantic-Aware-Resource-Management-for-C-V2X-Platooning-via-Multi-Agent-Reinforcement-Learning
Summary
本文主要介绍了语义通信在解决6G网络的频谱和能源挑战方面的优势,并将其首次引入基于蜂窝车联网(C-V2X)的自动驾驶车队系统。文章构建了语义通信的数学模型,并提出了基于语义相似性和语义速率的用户体验(QoE)指标。同时,为确保信道资源分配的公平性,考虑了语义信息传输成功率(SRS)指标。文章旨在解决一个混合整数非线性规划(MINLP)问题,提出了一种基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的分布式语义感知多模态资源分配(SAMRA)算法,可根据传输信息的重要性动态分配信道和功率,并确定语义符号长度。模拟结果表明,SAMRA算法在C-V2X车队场景中提高了QoE、SRS并降低了通信延迟。
Key Takeaways
- 语义通信能减少冗余信息,有助于解决6G网络的频谱和能源挑战。
- 文章首次将语义通信引入蜂窝车联网(C-V2X)的自动驾驶车队系统,旨在提高通信资源的管理效率。
- 构建了语义通信的数学模型,并使用DeepSC模型和MU-DeepSC模型进行单模态和多模态数据的语义编码和解码。
- 提出了基于语义相似性和语义速率的用户体验(QoE)指标以及语义信息传输成功率(SRS)指标。
- 解决了一个混合整数非线性规划(MINLP)问题,旨在最大化车辆间(V2V)链接的QoE并改善SRS。
- 提出了一种基于多智能体强化学习(MARL)的分布式语义感知多模态资源分配(SAMRA)算法,可根据信息的重要性动态分配资源和确定语义符号长度。
点此查看论文截图