⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
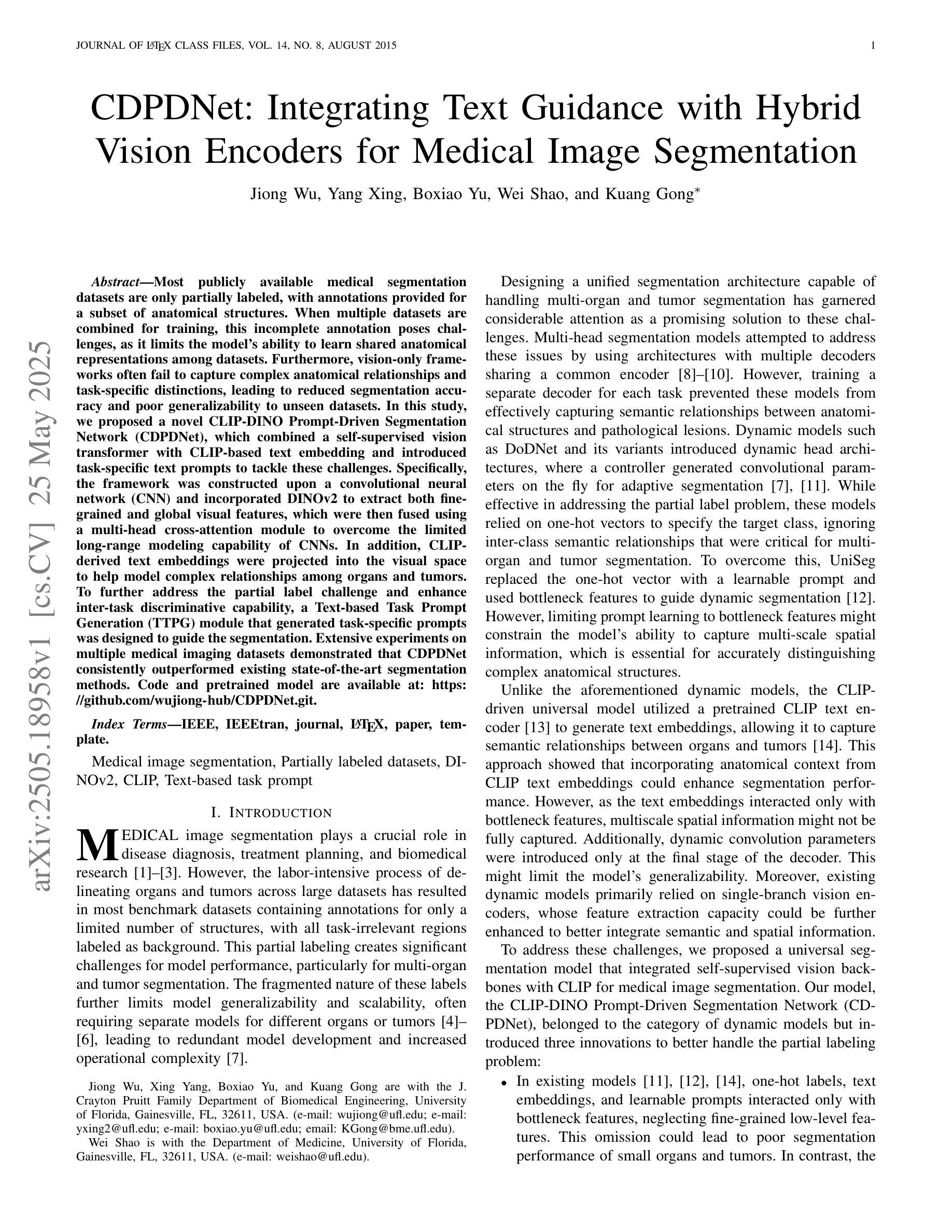
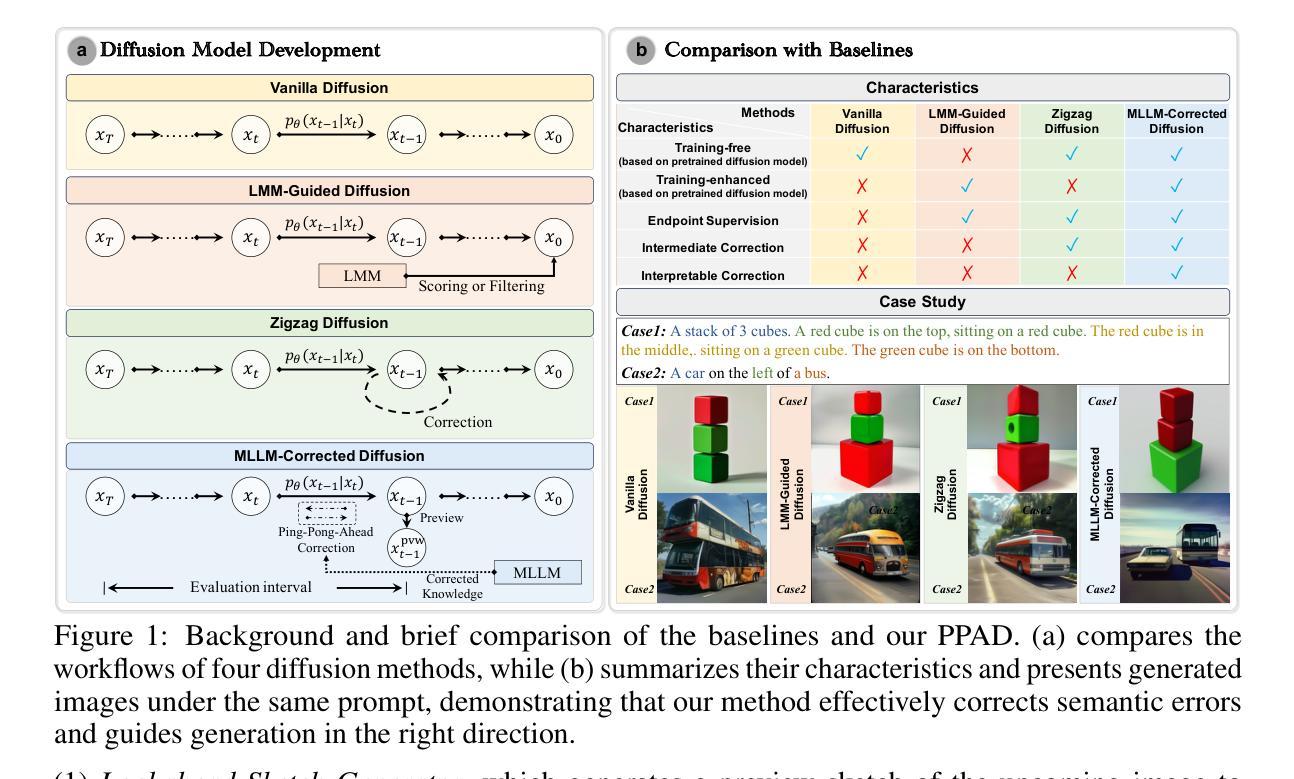
Multimodal LLM-Guided Semantic Correction in Text-to-Image Diffusion
Authors:Zheqi Lv, Junhao Chen, Qi Tian, Keting Yin, Shengyu Zhang, Fei Wu
Diffusion models have become the mainstream architecture for text-to-image generation, achieving remarkable progress in visual quality and prompt controllability. However, current inference pipelines generally lack interpretable semantic supervision and correction mechanisms throughout the denoising process. Most existing approaches rely solely on post-hoc scoring of the final image, prompt filtering, or heuristic resampling strategies-making them ineffective in providing actionable guidance for correcting the generative trajectory. As a result, models often suffer from object confusion, spatial errors, inaccurate counts, and missing semantic elements, severely compromising prompt-image alignment and image quality. To tackle these challenges, we propose MLLM Semantic-Corrected Ping-Pong-Ahead Diffusion (PPAD), a novel framework that, for the first time, introduces a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) as a semantic observer during inference. PPAD performs real-time analysis on intermediate generations, identifies latent semantic inconsistencies, and translates feedback into controllable signals that actively guide the remaining denoising steps. The framework supports both inference-only and training-enhanced settings, and performs semantic correction at only extremely few diffusion steps, offering strong generality and scalability. Extensive experiments demonstrate PPAD’s significant improvements.
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构,在视觉质量和提示可控性方面取得了显著的进步。然而,当前的推理管道通常在去噪过程中缺乏可解释的语义监督和校正机制。大多数现有方法仅依赖于最终图像的后验评分、提示过滤或启发式重采样策略,这使得它们无法为纠正生成轨迹提供有效的指导。因此,模型经常遭受目标混淆、空间错误、计数不准确和缺失语义元素等问题的影响,严重损害了提示-图像对齐和图像质量。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MLLM语义校正乒乓前向扩散(PPAD)这一新框架,它首次在推理过程中引入了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为语义观察者。PPAD对中间生成物进行实时分析,识别潜在的语义不一致,并将反馈转化为可控信号,主动引导剩余的去噪步骤。该框架支持仅推理和训练增强的设置,并在极少的扩散步骤中进行语义校正,表现出强大的通用性和可扩展性。大量实验证明了PPAD的显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构,其在视觉质量和提示可控性方面取得了显著进展。然而,当前推理管道普遍缺乏可解释的语义监督和校正机制贯穿去噪过程。针对模型对象混淆、空间误差、计数不准确和缺少语义元素等问题,我们提出了MLLM语义校正乒乓前向扩散(PPAD)新框架。该框架首次引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为推理过程中的语义观察者,实时分析中间生成内容,识别潜在语义不一致性,并将反馈转化为可控信号,主动引导剩余的去噪步骤。该框架支持仅推理和训练增强设置,在极少扩散步骤中进行语义校正,表现出强大的通用性和可扩展性。实验证明PPAD的改进非常显著。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构。
- 当前扩散模型在推理过程中缺乏语义监督和校正机制。
- 模型常面临对象混淆、空间误差、计数不准确和缺少语义元素等问题。
- PPAD框架通过引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为语义观察者来解决这些问题。
- PPAD能实时分析中间生成内容,识别语义不一致性,并转化为可控信号引导去噪步骤。
- PPAD框架支持仅推理和训练增强两种设置,可在极少步骤中进行语义校正。
点此查看论文截图

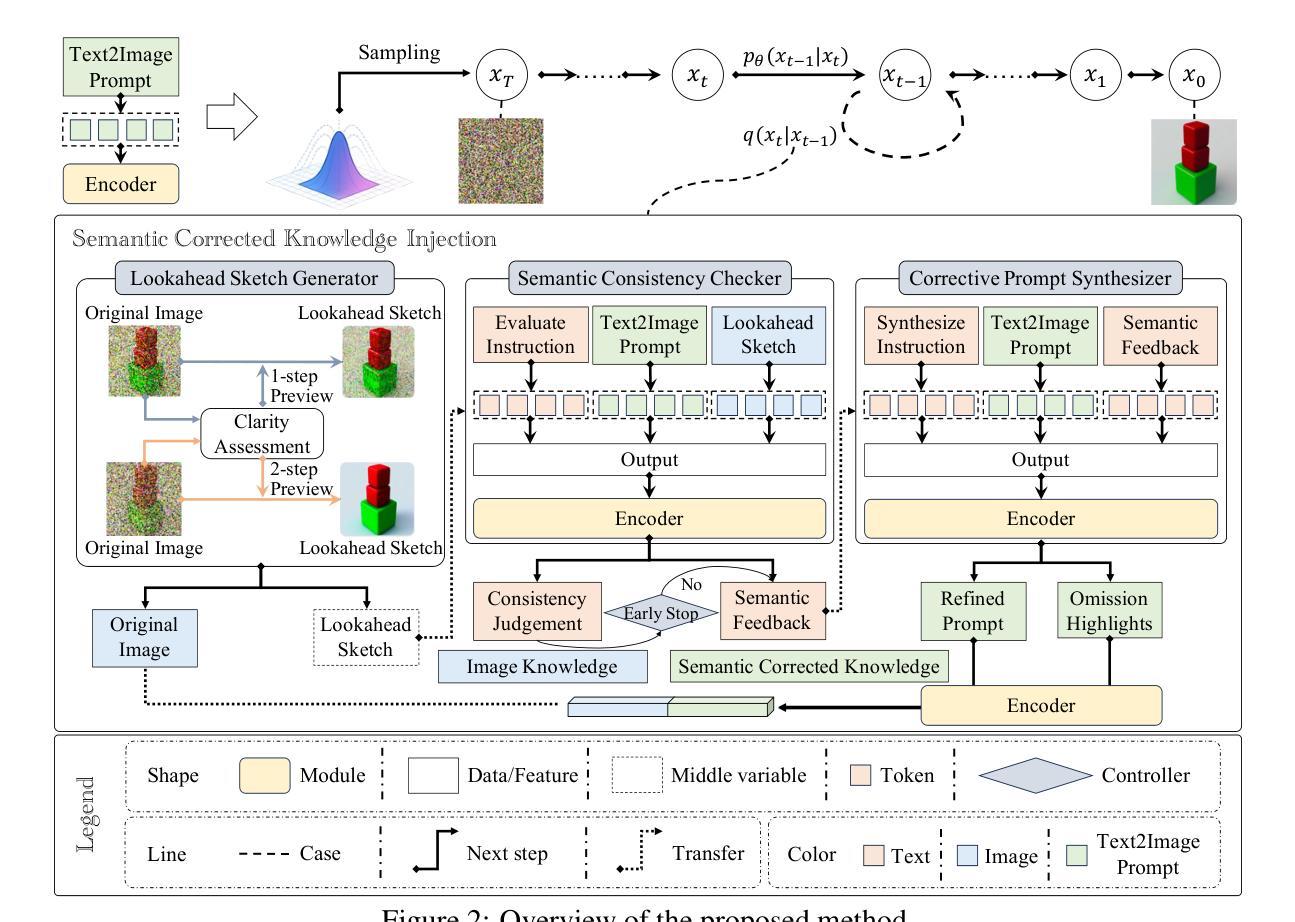
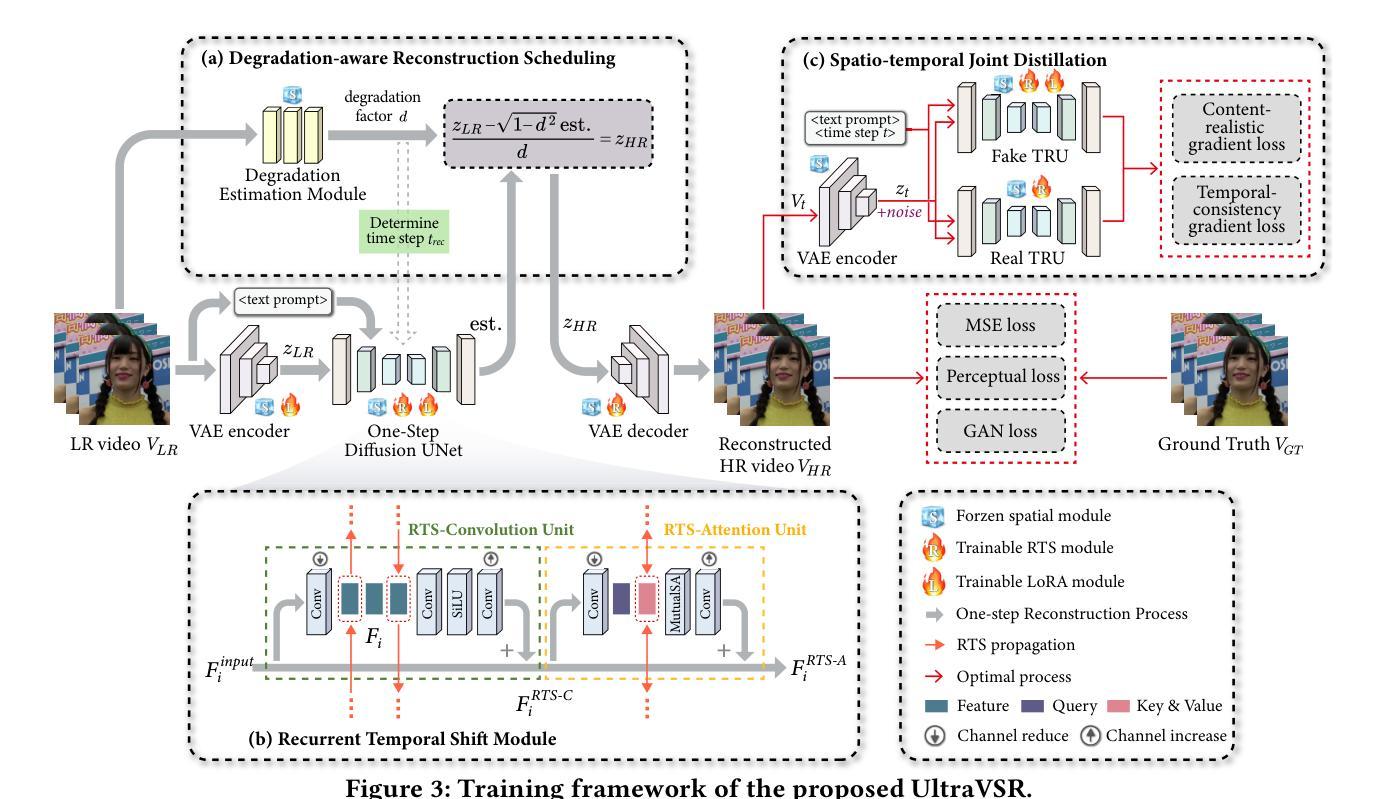
UltraVSR: Achieving Ultra-Realistic Video Super-Resolution with Efficient One-Step Diffusion Space
Authors:Yong Liu, Jinshan Pan, Yinchuan Li, Qingji Dong, Chao Zhu, Yu Guo, Fei Wang
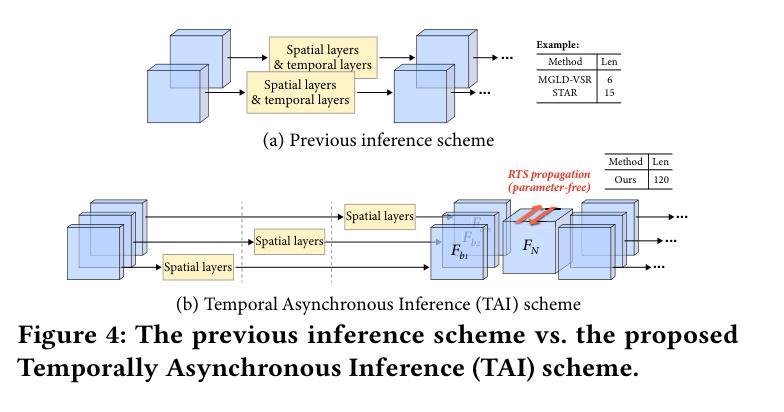
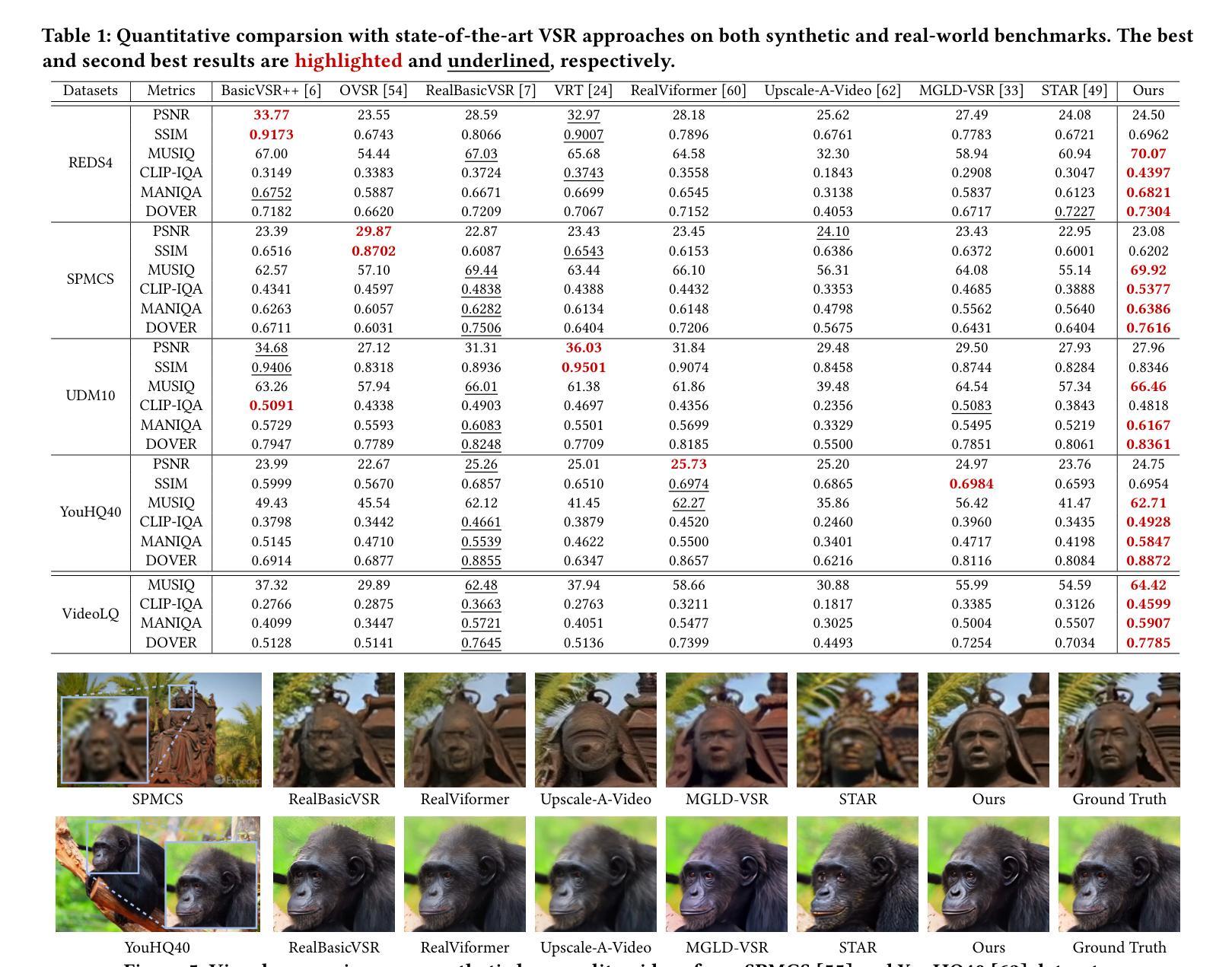
Diffusion models have shown great potential in generating realistic image detail. However, adapting these models to video super-resolution (VSR) remains challenging due to their inherent stochasticity and lack of temporal modeling. In this paper, we propose UltraVSR, a novel framework that enables ultra-realistic and temporal-coherent VSR through an efficient one-step diffusion space. A central component of UltraVSR is the Degradation-aware Restoration Schedule (DRS), which estimates a degradation factor from the low-resolution input and transforms iterative denoising process into a single-step reconstruction from from low-resolution to high-resolution videos. This design eliminates randomness from diffusion noise and significantly speeds up inference. To ensure temporal consistency, we propose a lightweight yet effective Recurrent Temporal Shift (RTS) module, composed of an RTS-convolution unit and an RTS-attention unit. By partially shifting feature components along the temporal dimension, these two units collaboratively facilitate effective feature propagation, fusion, and alignment across neighboring frames, without relying on explicit temporal layers. The RTS module is integrated into a pretrained text-to-image diffusion model and is further enhanced through Spatio-temporal Joint Distillation (SJD), which improves temporal coherence while preserving realistic details. Additionally, we introduce a Temporally Asynchronous Inference (TAI) strategy to capture long-range temporal dependencies under limited memory constraints. Extensive experiments show that UltraVSR achieves state-of-the-art performance, both qualitatively and quantitatively, in a single sampling step.
扩散模型在生成逼真的图像细节方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,由于这些模型固有的随机性和缺乏时间建模,将这些模型适应于视频超分辨率(VSR)仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了UltraVSR,这是一种新型框架,能够通过高效的一次性扩散空间实现超逼真和时间连贯的视频超分辨率。UltraVSR的核心组件是退化感知恢复计划(DRS),它根据低分辨率输入估计退化因子,并将迭代去噪过程转变为从低分辨率到高分辨率视频的一次性重建。这种设计消除了扩散噪声的随机性,并显著加快了推理速度。为了确保时间连贯性,我们提出了一个轻量级但有效的循环时间移位(RTS)模块,它由RTS卷积单元和RTS注意力单元组成。这两个单元通过沿时间维度部分移动特征分量,协同实现有效特征传播、融合和对齐相邻帧,无需依赖显式的时间层。RTS模块被集成到预训练的文本到图像扩散模型中,并通过时空联合蒸馏(SJD)得到进一步改进,这提高了时间连贯性,同时保留了逼真的细节。此外,我们引入了一种时间上异步推理(TAI)策略,以在有限的内存约束下捕获长期时间依赖性。大量实验表明,UltraVSR在单次采样步骤中实现了定性和定量上的先进性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review, 10 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为UltraVSR的新型框架,用于通过高效的一步扩散空间实现超逼真且时间连贯的视频超分辨率(VSR)。该框架通过引入降质感知恢复调度(DRS)消除扩散噪声的随机性,并加速推理。此外,它还提出一种轻量级的循环时间移位(RTS)模块,通过部分沿时间维度移动特征组件,实现跨相邻帧的有效特征传播、融合和对齐。结合时空联合蒸馏(SJD)技术,UltraVSR在不依赖明确时间层的情况下,提升了时间连贯性并保持真实细节。实验表明,UltraVSR在单步采样中实现了先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- UltraVSR框架成功将扩散模型应用于视频超分辨率,生成超逼真且时间连贯的视频。
- 通过降质感知恢复调度(DRS),实现了从低分辨率到高分辨率视频的单一步骤重建,消除了扩散模型的随机性并加速了推理过程。
- 循环时间移位(RTS)模块确保时间连贯性,通过特征传播、融合和对齐提升性能。
- 时空联合蒸馏(SJD)技术提高了时间连贯性的同时,保留了真实细节。
- UltraVSR通过引入异步推理策略(TAI),在有限内存约束下捕获长程时间依赖性。
- 实验证明,UltraVSR在单步采样中实现了先进性能,无论是定性还是定量评估。
- UltraVSR框架对于视频超分辨率任务具有潜在的实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

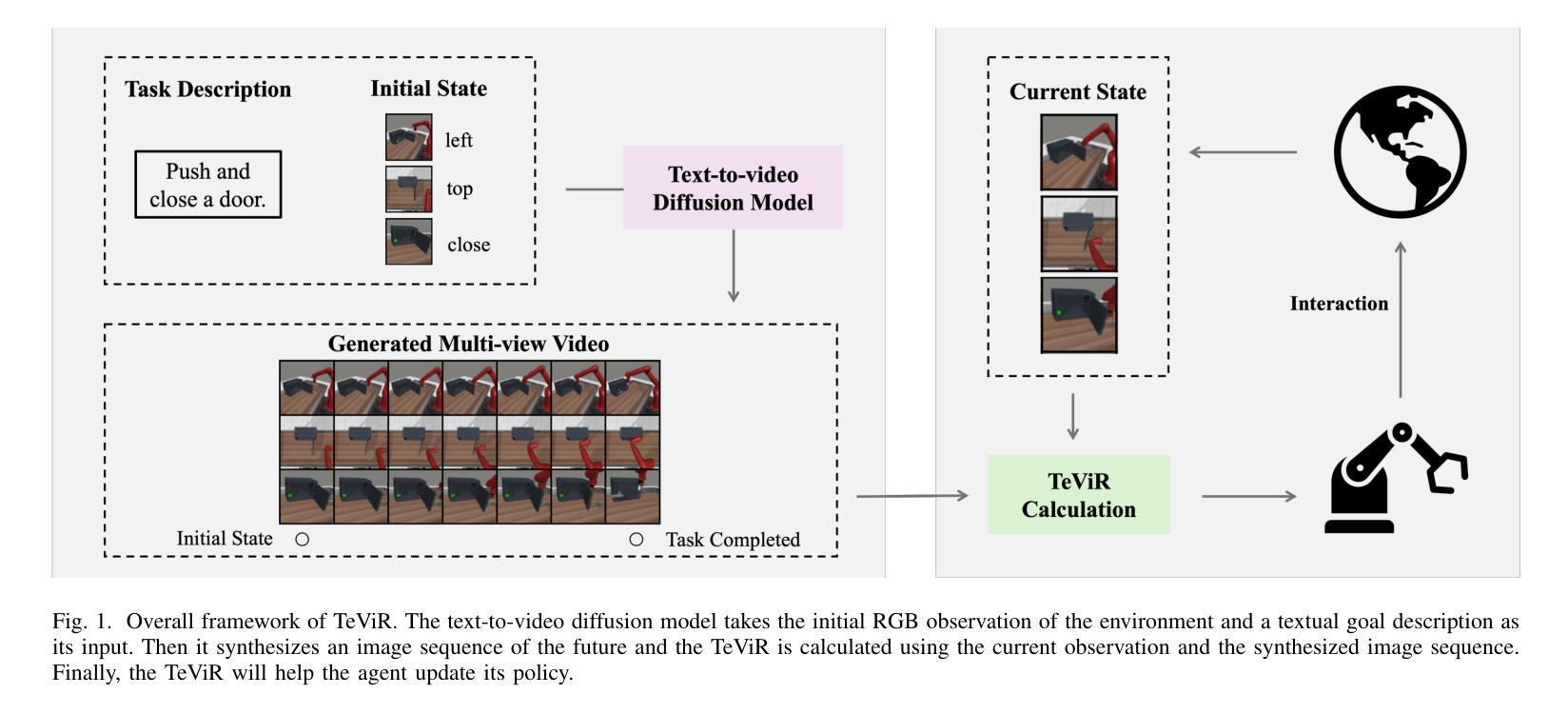
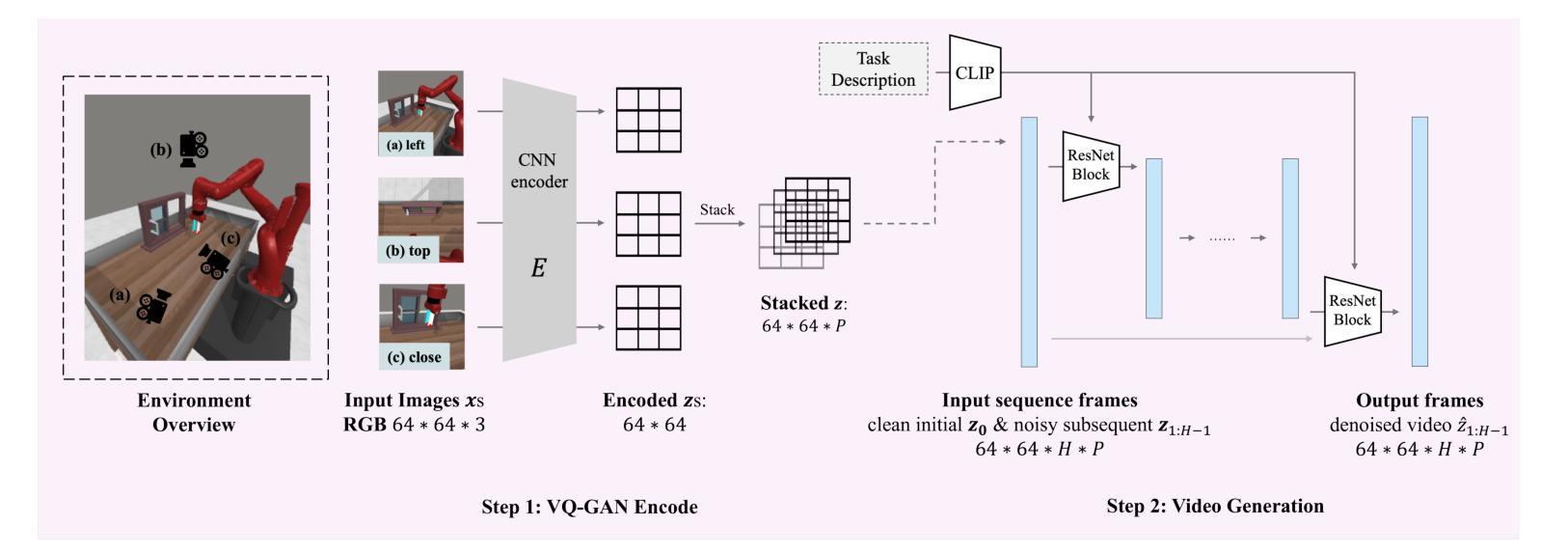
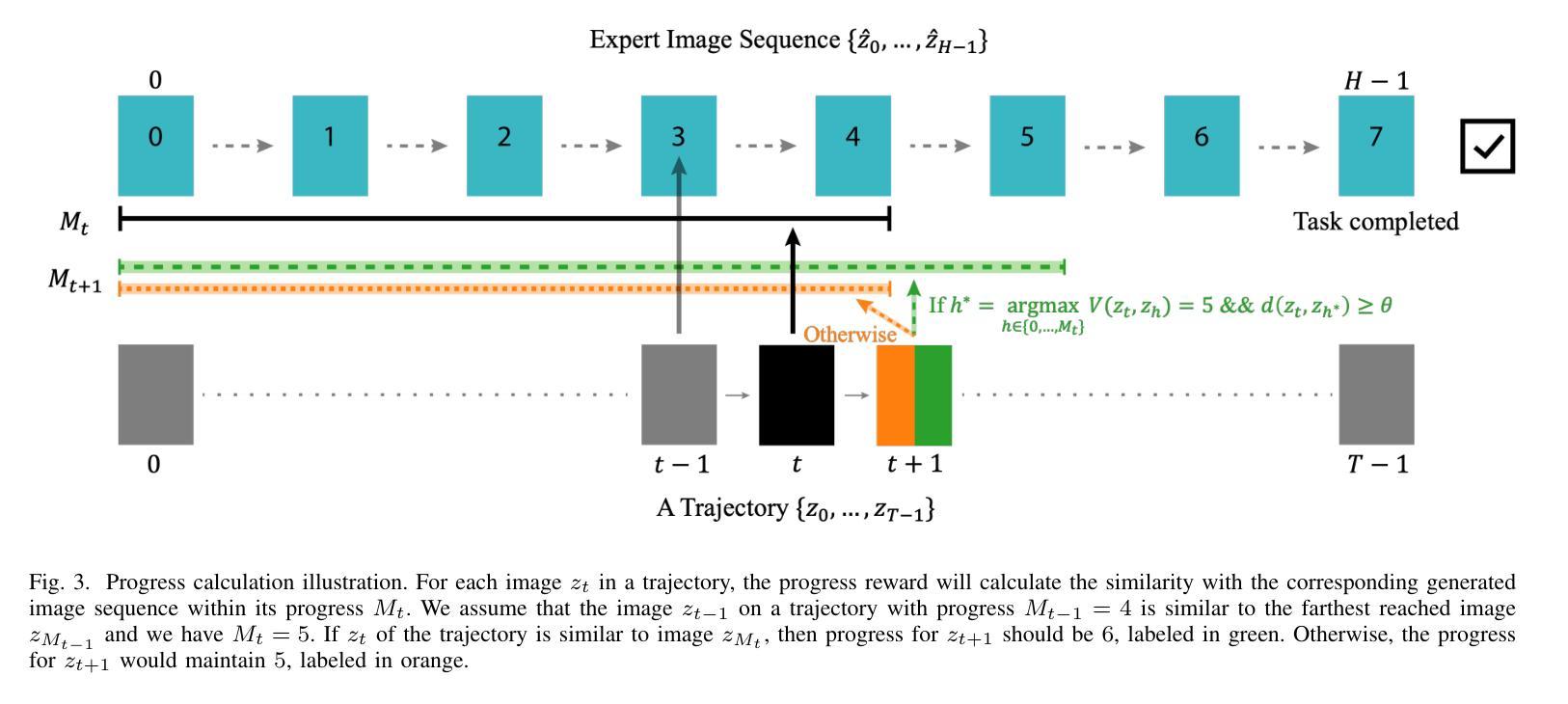
TeViR: Text-to-Video Reward with Diffusion Models for Efficient Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Yuhui Chen, Haoran Li, Zhennan Jiang, Haowei Wen, Dongbin Zhao
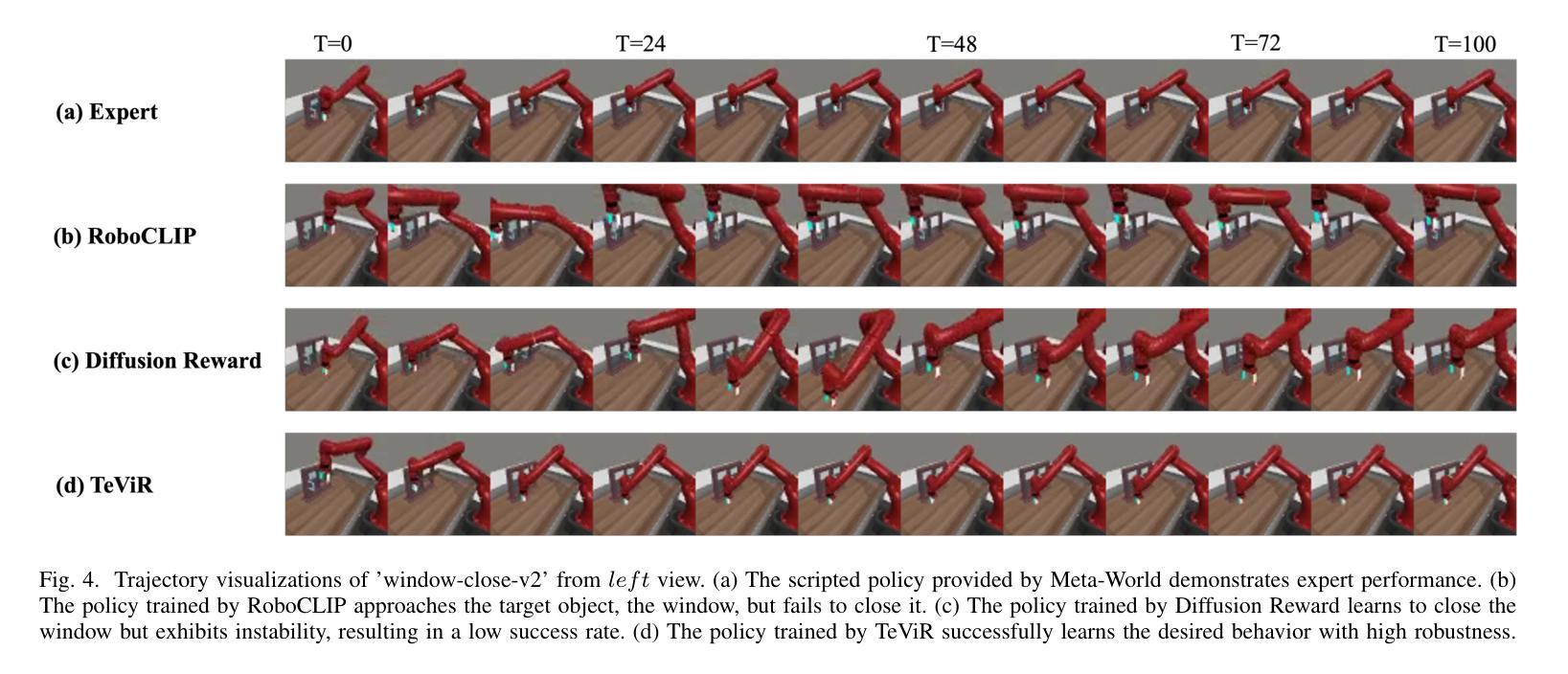
Developing scalable and generalizable reward engineering for reinforcement learning (RL) is crucial for creating general-purpose agents, especially in the challenging domain of robotic manipulation. While recent advances in reward engineering with Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promise, their sparse reward nature significantly limits sample efficiency. This paper introduces TeViR, a novel method that leverages a pre-trained text-to-video diffusion model to generate dense rewards by comparing the predicted image sequence with current observations. Experimental results across 11 complex robotic tasks demonstrate that TeViR outperforms traditional methods leveraging sparse rewards and other state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, achieving better sample efficiency and performance without ground truth environmental rewards. TeViR’s ability to efficiently guide agents in complex environments highlights its potential to advance reinforcement learning applications in robotic manipulation.
开发可扩展且可通用的强化学习(RL)奖励工程对于创建通用智能体至关重要,特别是在机器人操作这一挑战性领域。虽然最近使用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的奖励工程进展显示出了一定的前景,但其稀疏奖励的特性极大地限制了样本效率。本文介绍了一种新方法TeViR,它利用预训练的文本到视频扩散模型来生成密集奖励,通过比较预测的图像序列与当前观察结果来实现。在跨越11个复杂机器人任务的实验中,TeViR的表现优于利用稀疏奖励的传统方法以及其他最新技术方法,能够在没有真实环境奖励的情况下实现更好的样本效率和性能。TeViR在复杂环境中有效引导智能体的能力凸显了其推动机器人在强化学习应用方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练的文本到视频扩散模型TeViR,通过对比预测图像序列与当前观测值生成密集奖励,提高了样本效率和性能。在11项复杂的机器人任务中,TeViR表现优于传统稀疏奖励方法和其它先进方法,无需环境真实奖励即可指导智能体在复杂环境中高效运行,为机器人操纵领域的强化学习应用带来潜在进步。
Key Takeaways
- TeViR利用预训练的文本到视频扩散模型生成密集奖励,解决了传统奖励工程中的样本效率问题。
- TeViR通过对比预测图像序列与当前观测值来工作,这在机器人操纵领域具有广泛应用。
- 在11项复杂的机器人任务中,TeViR表现优于其它方法和传统稀疏奖励方法。
- TeViR能够在没有环境真实奖励的情况下指导智能体运行,增强了其在复杂环境中的适应性。
- TeViR的引入有助于推动强化学习在机器人操纵领域的应用进步。
- 该方法充分利用了扩散模型的潜力,展示了其在生成密集奖励方面的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

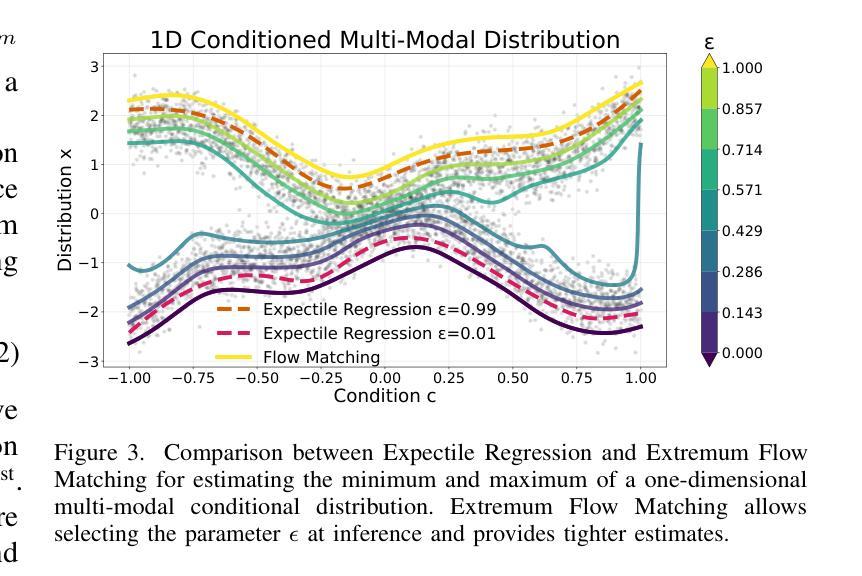
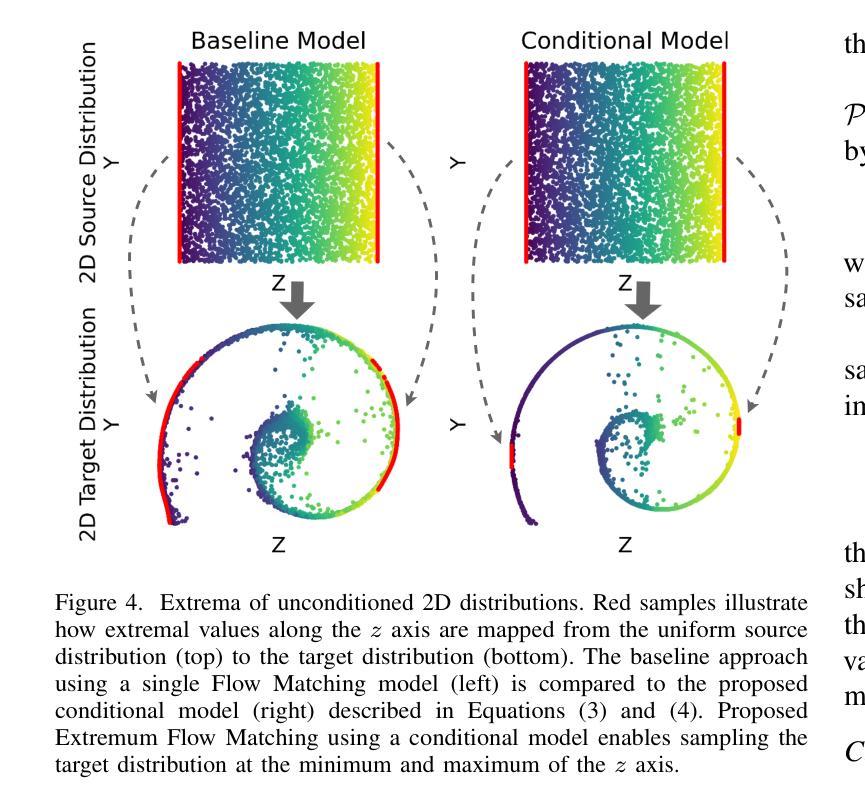
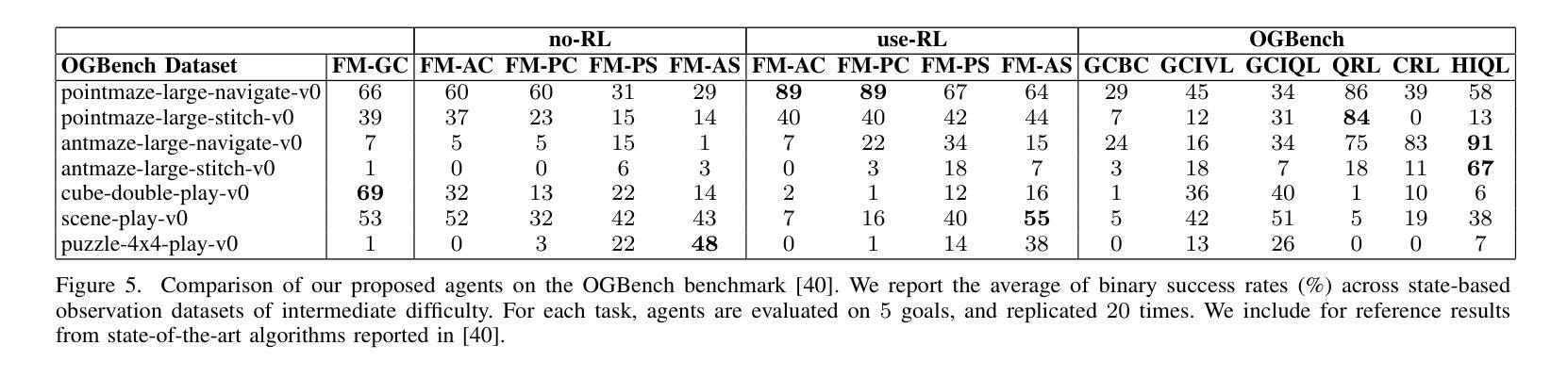
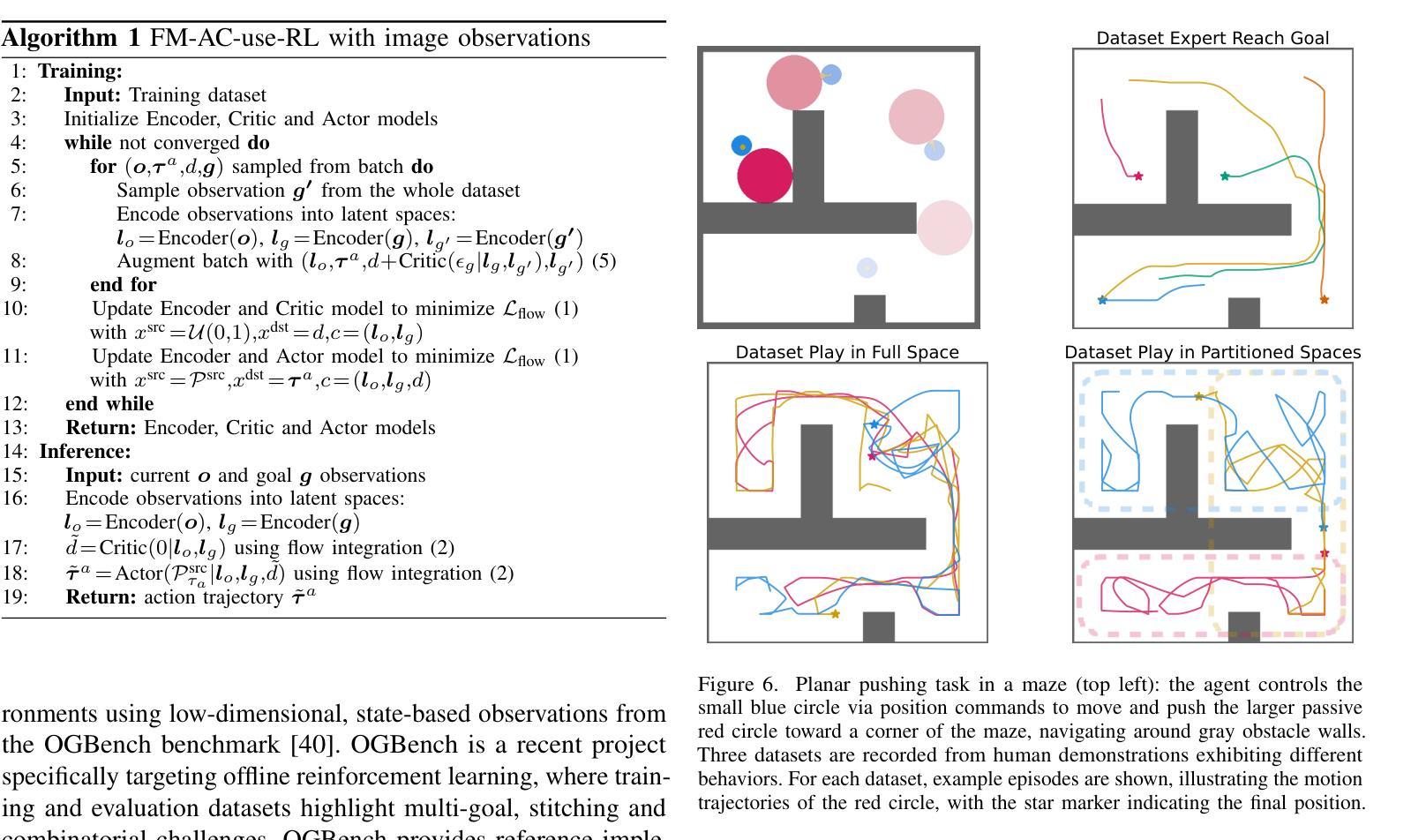
Extremum Flow Matching for Offline Goal Conditioned Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Quentin Rouxel, Clemente Donoso, Fei Chen, Serena Ivaldi, Jean-Baptiste Mouret
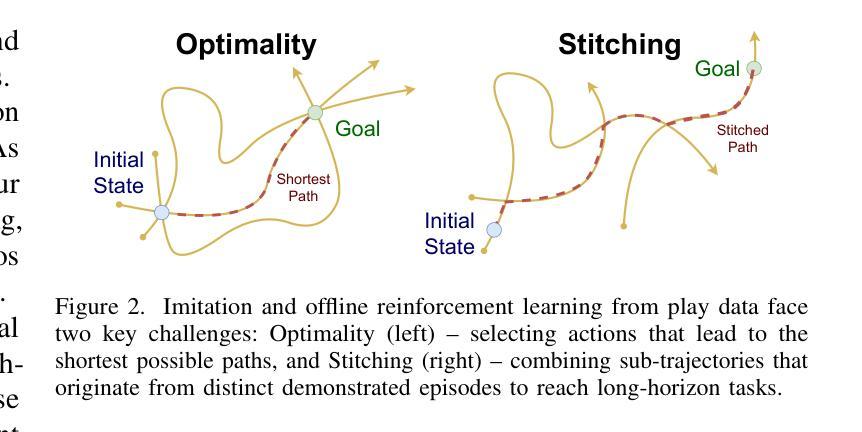
Imitation learning is a promising approach for enabling generalist capabilities in humanoid robots, but its scaling is fundamentally constrained by the scarcity of high-quality expert demonstrations. This limitation can be mitigated by leveraging suboptimal, open-ended play data, often easier to collect and offering greater diversity. This work builds upon recent advances in generative modeling, specifically Flow Matching, an alternative to Diffusion models. We introduce a method for estimating the extremum of the learned distribution by leveraging the unique properties of Flow Matching, namely, deterministic transport and support for arbitrary source distributions. We apply this method to develop several goal-conditioned imitation and reinforcement learning algorithms based on Flow Matching, where policies are conditioned on both current and goal observations. We explore and compare different architectural configurations by combining core components, such as critic, planner, actor, or world model, in various ways. We evaluated our agents on the OGBench benchmark and analyzed how different demonstration behaviors during data collection affect performance in a 2D non-prehensile pushing task. Furthermore, we validated our approach on real hardware by deploying it on the Talos humanoid robot to perform complex manipulation tasks based on high-dimensional image observations, featuring a sequence of pick-and-place and articulated object manipulation in a realistic kitchen environment. Experimental videos and code are available at: https://hucebot.github.io/extremum_flow_matching_website/
模仿学习是在人形机器人中实现通用能力的一种有前途的方法,但其扩展从根本上受到高质量专家演示稀缺性的限制。通过利用次优、开放式的游戏数据,可以缓解这种限制,这些数据通常更容易收集并且具有更大的多样性。这项工作建立在生成建模的最新进展之上,特别是流匹配(Flow Matching)技术,它是扩散模型的一种替代方案。我们介绍了一种利用流匹配独特属性来估计所学分布极值的方法,即确定性传输和对任意源分布的支持。我们应用这种方法,基于流匹配开发了几种目标条件模仿和强化学习算法,这些算法的策略既取决于当前观察也取决于目标观察。我们通过组合核心组件(如评论家、规划师、演员或世界模型)的不同方式,探索和比较了不同的架构配置。我们在OGBench基准测试上评估了我们的代理,并分析了在数据收集过程中不同演示行为对二维非抓取推动任务性能的影响。此外,我们通过将方法部署在Talos人形机器人上执行基于高维图像观察的复杂操作任务来验证我们的方法,包括一系列拿起放下和在现实厨房环境中操作关节物体。实验视频和代码可通过以下网址获得:[https://hucebot.github.io/extremum_flow_matching_website/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用生成建模的最新进展,特别是替代扩散模型的流量匹配技术,通过利用其独特属性(如确定性传输和任意源分布支持),估计学习分布极值的方法。研究开发了基于流量匹配的多种目标导向模仿和强化学习算法,策略基于当前和目标观察结果。在OGBench基准测试上评估了代理,并分析了数据收集过程中不同演示行为对二维非抓取推动任务性能的影响。此外,在Talos人形机器人上验证了方法的有效性,以执行基于高维图像观察的复杂操纵任务。详情可见:https://hucebot.github.io/extremum_flow_matching_website/。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用流量匹配技术,一种生成建模的替代方法,来估计学习分布的极值。
- 方法利用流量匹配的独特属性,包括确定性传输和任意源分布支持。
- 开发基于流量匹配的模仿和强化学习算法,这些算法基于当前和目标观察结果。
- 在OGBench基准测试上评估了算法性能。
- 研究分析了演示行为在数据收集过程中对任务性能的影响。
- 在Talos人形机器人上验证了方法的有效性,展示了执行复杂操纵任务的能力。
点此查看论文截图


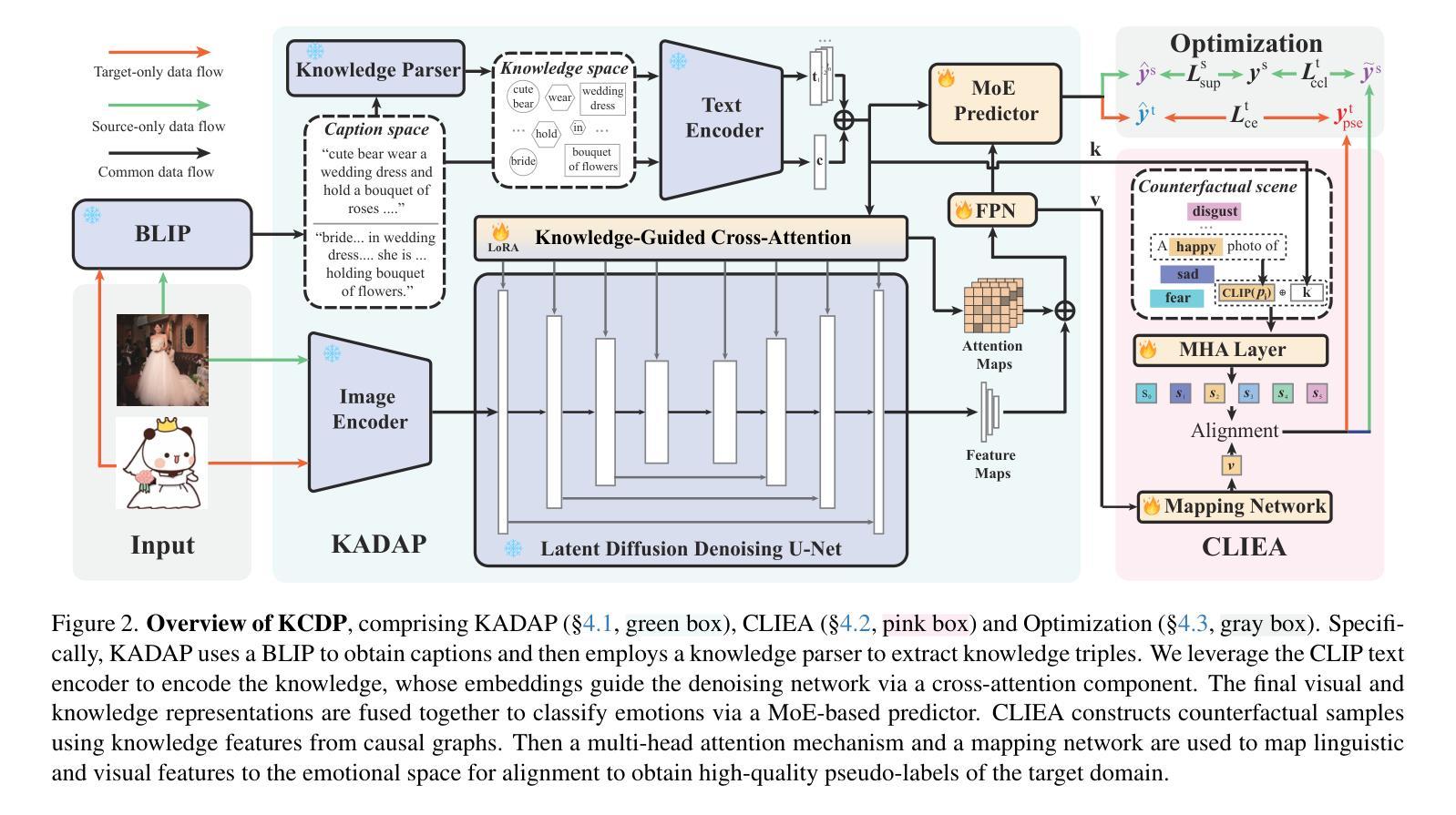
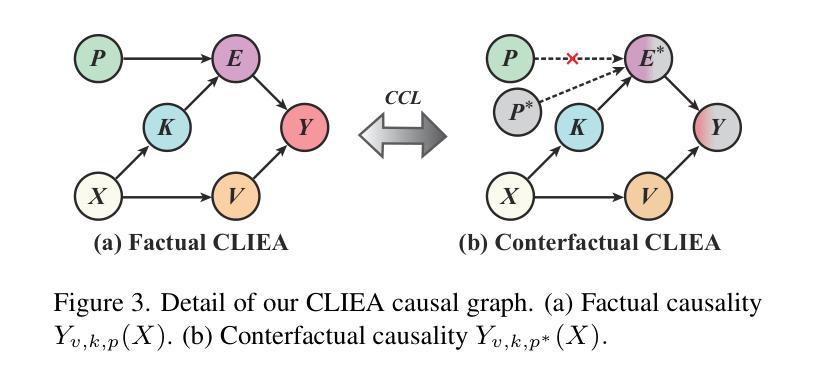
Knowledge-Aligned Counterfactual-Enhancement Diffusion Perception for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Visual Emotion Recognition
Authors:Wen Yin, Yong Wang, Guiduo Duan, Dongyang Zhang, Xin Hu, Yuan-Fang Li, Tao He
Visual Emotion Recognition (VER) is a critical yet challenging task aimed at inferring emotional states of individuals based on visual cues. However, existing works focus on single domains, e.g., realistic images or stickers, limiting VER models’ cross-domain generalizability. To fill this gap, we introduce an Unsupervised Cross-Domain Visual Emotion Recognition (UCDVER) task, which aims to generalize visual emotion recognition from the source domain (e.g., realistic images) to the low-resource target domain (e.g., stickers) in an unsupervised manner. Compared to the conventional unsupervised domain adaptation problems, UCDVER presents two key challenges: a significant emotional expression variability and an affective distribution shift. To mitigate these issues, we propose the Knowledge-aligned Counterfactual-enhancement Diffusion Perception (KCDP) framework. Specifically, KCDP leverages a VLM to align emotional representations in a shared knowledge space and guides diffusion models for improved visual affective perception. Furthermore, a Counterfactual-Enhanced Language-image Emotional Alignment (CLIEA) method generates high-quality pseudo-labels for the target domain. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model surpasses SOTA models in both perceptibility and generalization, e.g., gaining 12% improvements over the SOTA VER model TGCA-PVT. The project page is at https://yinwen2019.github.io/ucdver.
视觉情感识别(VER)是一项至关重要但具有挑战性的任务,旨在基于视觉线索推断个体的情感状态。然而,现有工作主要集中在单一领域,例如真实图像或贴纸,这限制了VER模型跨领域的泛化能力。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了无监督跨域视觉情感识别(UCDVER)任务,旨在以无监督的方式将从源域(例如真实图像)学到的视觉情感识别能力推广到资源有限的目标域(例如贴纸)。与传统的无监督域适应问题相比,UCDVER面临两个关键挑战:情感表达的显著可变性和情感分布偏移。为了缓解这些问题,我们提出了知识对齐的逆向增强扩散感知(KCDP)框架。具体来说,KCDP利用VLM对齐共享知识空间中的情感表示,并指导扩散模型以改进视觉情感感知。此外,逆向增强语言-图像情感对齐(CLIEA)方法为目标域生成高质量伪标签。大量实验表明,我们的模型在感知和泛化方面都超越了最先进模型,例如比最先进的VER模型TGCA-PVT提高了12%。项目页面位于https://yinwen2019.github.io/ucdver。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了视觉情绪识别(VER)的重要性及其面临的挑战,如跨域泛化能力有限。为此,文章提出了无监督跨域视觉情绪识别(UCDVER)任务,旨在从源域(如真实图像)向低资源目标域(如贴纸)进行无监督的视觉情感识别泛化。文章还介绍了知识对齐的因果增强扩散感知(KCDP)框架和对抗性语言图像情感对齐(CLIEA)方法,以提高感知和泛化性能。实验证明,该模型在感知和泛化方面都超过了最先进的VER模型。
Key Takeaways
- VER(视觉情绪识别)是一项重要且具有挑战性的任务,旨在基于视觉线索推断个体的情绪状态。
- 现有研究主要集中在单一领域,限制了VER模型的跨域泛化能力。
- UCDVER(无监督跨域视觉情绪识别)任务旨在从源域向低资源的目标域进行无监督的视觉情感识别泛化。
- UCDVER面临两个关键挑战:情绪表达的显著可变性和情感分布转移。
- KCDP(知识对齐的因果增强扩散感知)框架用于解决这些问题,通过利用VLM对齐情感表示,并引导扩散模型提高视觉情感感知。
- CLIEA(对抗性语言图像情感对齐)方法用于生成高质量的目标域伪标签。
点此查看论文截图

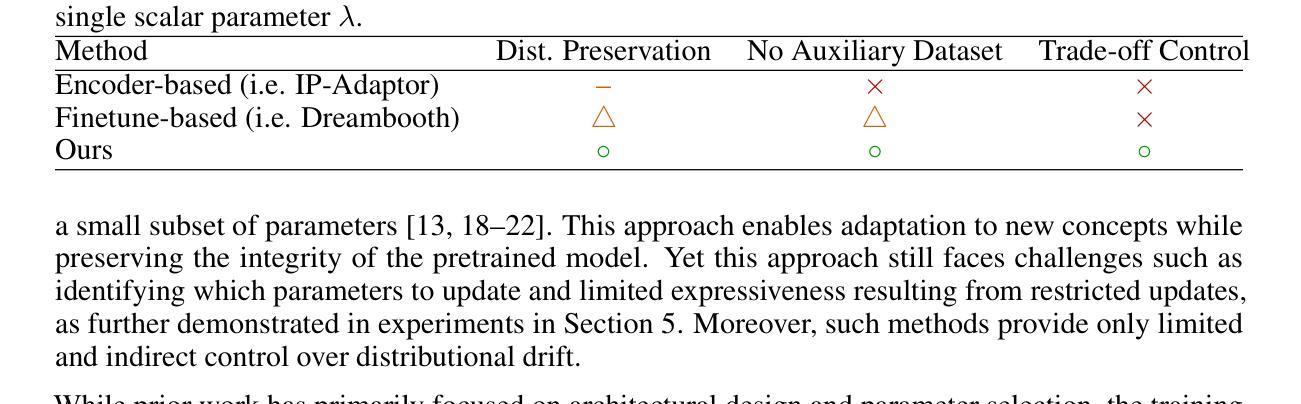
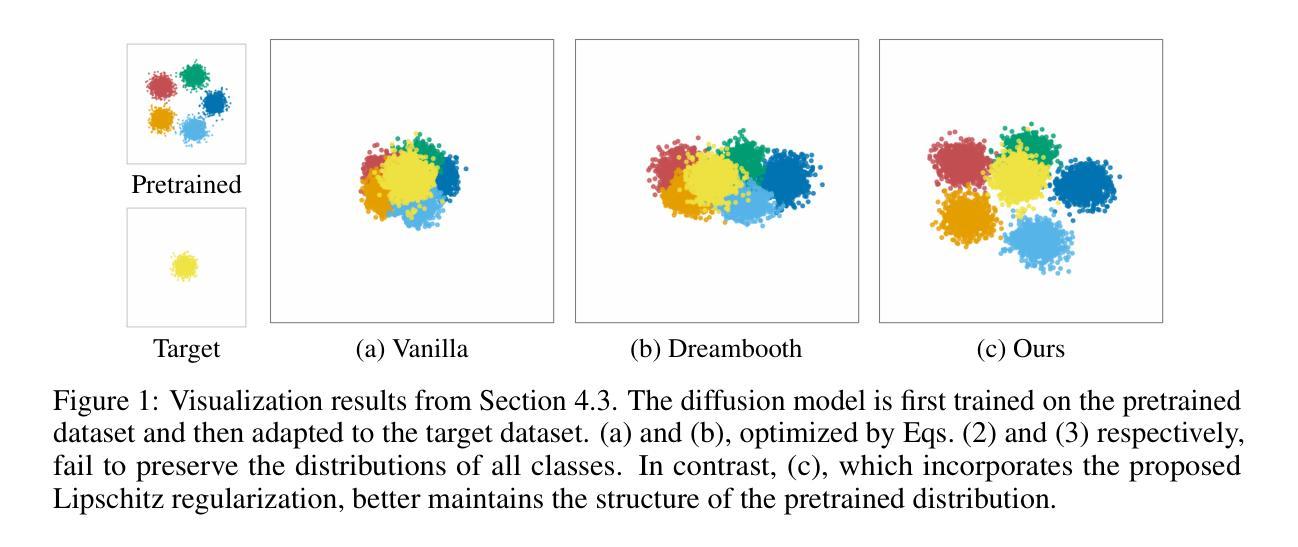
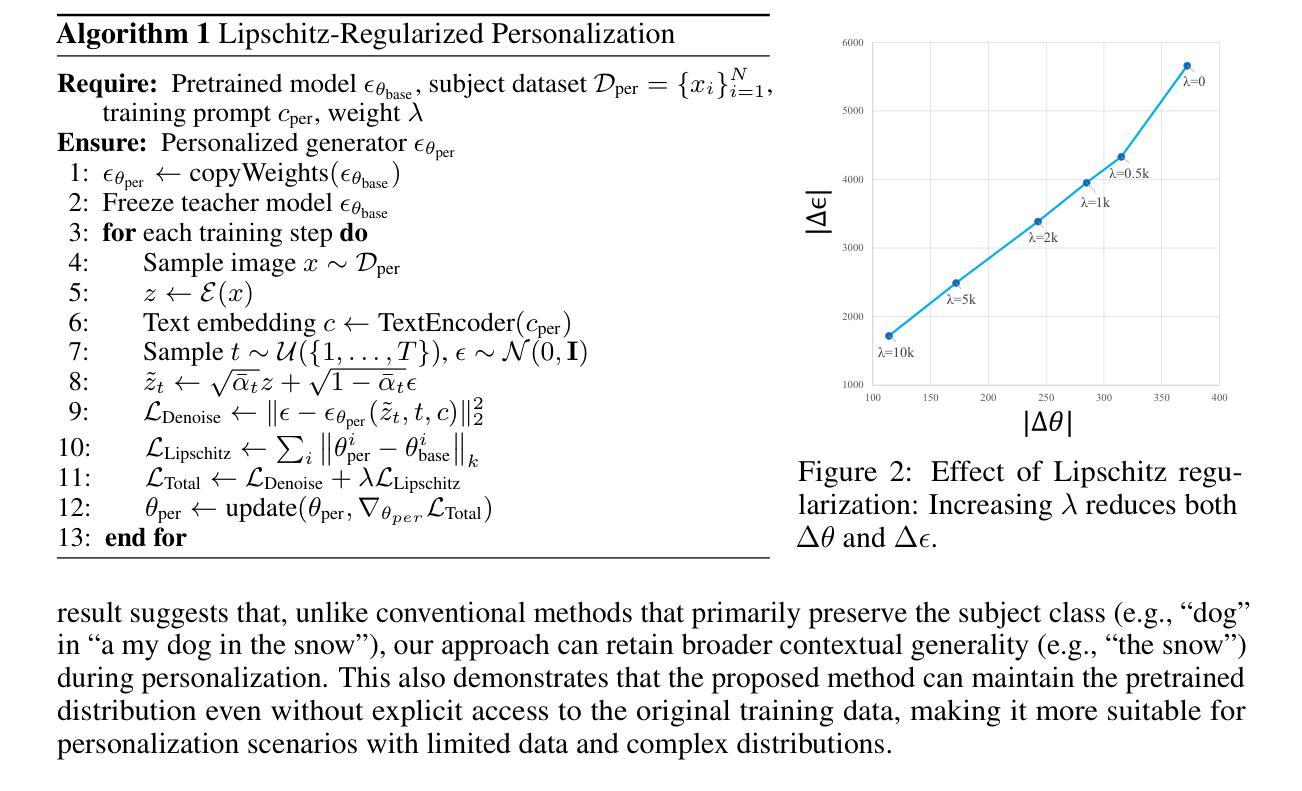
Regularized Personalization of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models without Distributional Drift
Authors:Gihoon Kim, Hyungjin Park, Taesup Kim
Personalization using text-to-image diffusion models involves adapting a pretrained model to novel subjects with only a few image examples. This task presents a fundamental challenge, as the model must not only learn the new subject effectively but also preserve its ability to generate diverse and coherent outputs across a wide range of prompts. In other words, successful personalization requires integrating new concepts without forgetting previously learned generative capabilities. Forgetting denotes unintended distributional drift, where the model’s output distribution deviates from that of the original pretrained model. In this paper, we provide an analysis of this issue and identify a mismatch between standard training objectives and the goals of personalization. To address this, we propose a new training objective based on a Lipschitz-bounded formulation that explicitly constrains deviation from the pretrained distribution. Our method provides improved control over distributional drift and performs well even in data-scarce scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing personalization methods, achieving higher CLIP-T, CLIP-I, and DINO scores.
使用文本到图像扩散模型进行个性化涉及仅使用少量图像示例来适应预训练模型以应对新主题。此任务呈现了一个基本挑战,因为模型不仅需要有效地学习新主题,而且还要保持其在广泛提示中生成多样化和连贯输出的能力。换句话说,成功的个性化要求整合新概念而不会忘记先前学习的生成能力。遗忘表示意外的分布漂移,即模型输出分布偏离原始预训练模型的分布。在本文中,我们对此问题进行了分析,并确定了标准培训目标与个性化目标之间的不匹配。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于Lipschitz界定的新培训目标,该目标显式约束了与预训练分布的偏差。我们的方法在控制分布漂移方面提供了更好的控制,即使在数据稀缺的情况下也能表现良好。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于现有的个性化方法,实现了更高的CLIP-T、CLIP-I和DINO分数。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了利用文本到图像扩散模型进行个性化任务时面临的挑战。在只有少量图像示例的情况下,模型需要适应新主题,同时保持生成多样化和连贯性输出的能力。本文分析了这个问题,并指出标准训练目标与个性化目标之间的不匹配。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于Lipschitz约束的新训练目标,该目标显式约束模型输出分布与预训练分布的偏差。该方法在数据稀缺的场景下表现良好,实验结果表明,我们的方法在一致性、图像理解和得分方面均优于现有个性化方法。
要点
- 文本到图像扩散模型的个性化任务面临挑战,需要在适应新主题的同时保持生成多样化输出的能力。
- 本文分析了标准训练目标与个性化目标之间的不匹配问题。
- 提出了一种基于Lipschitz约束的新训练目标,以控制模型输出分布与预训练分布之间的偏差。
- 新方法能有效适应数据稀缺的场景。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在CLIP-T、CLIP-I和DINO评分方面均优于现有个性化方法。
- 个人化过程需整合新概念的同时保留已学能力,避免遗忘(分布漂移)。
点此查看论文截图

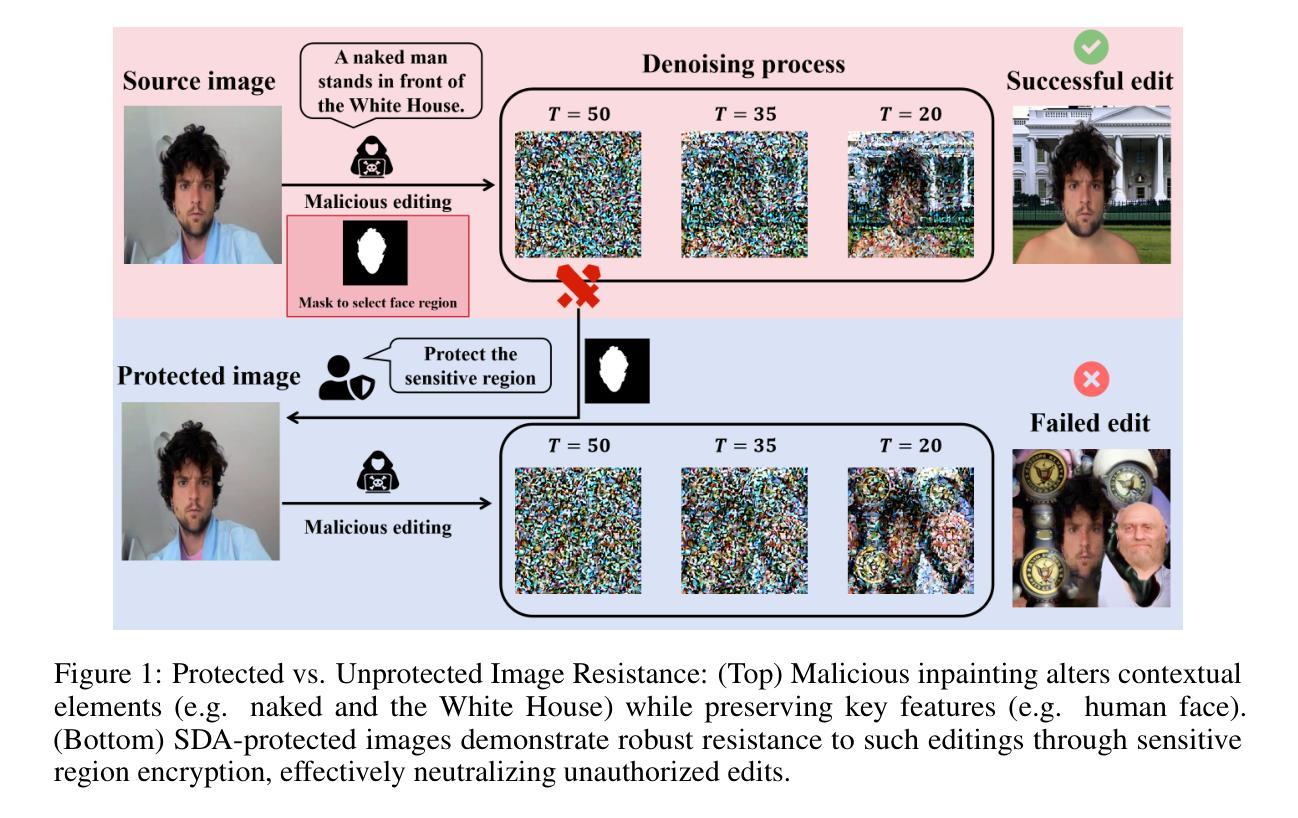
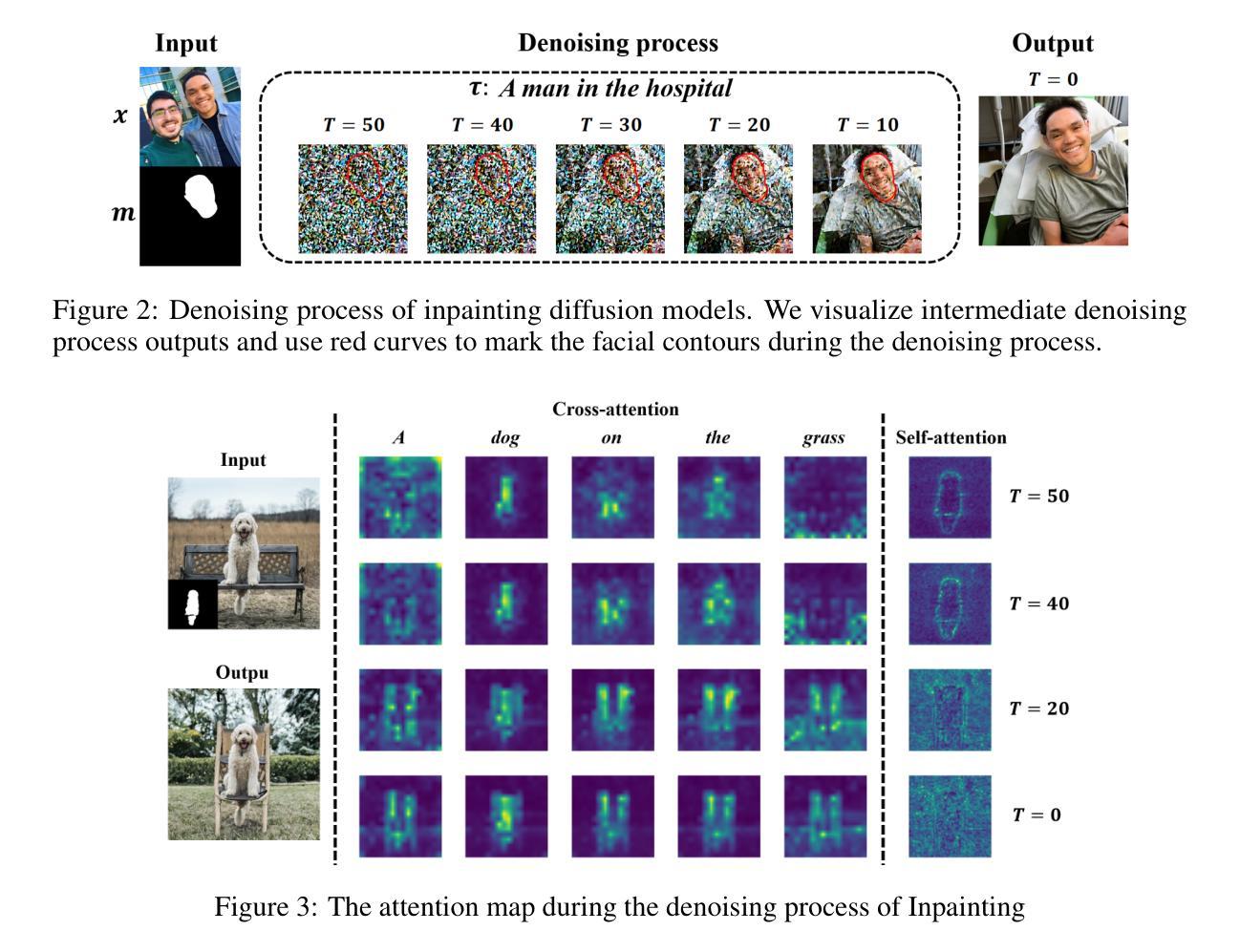
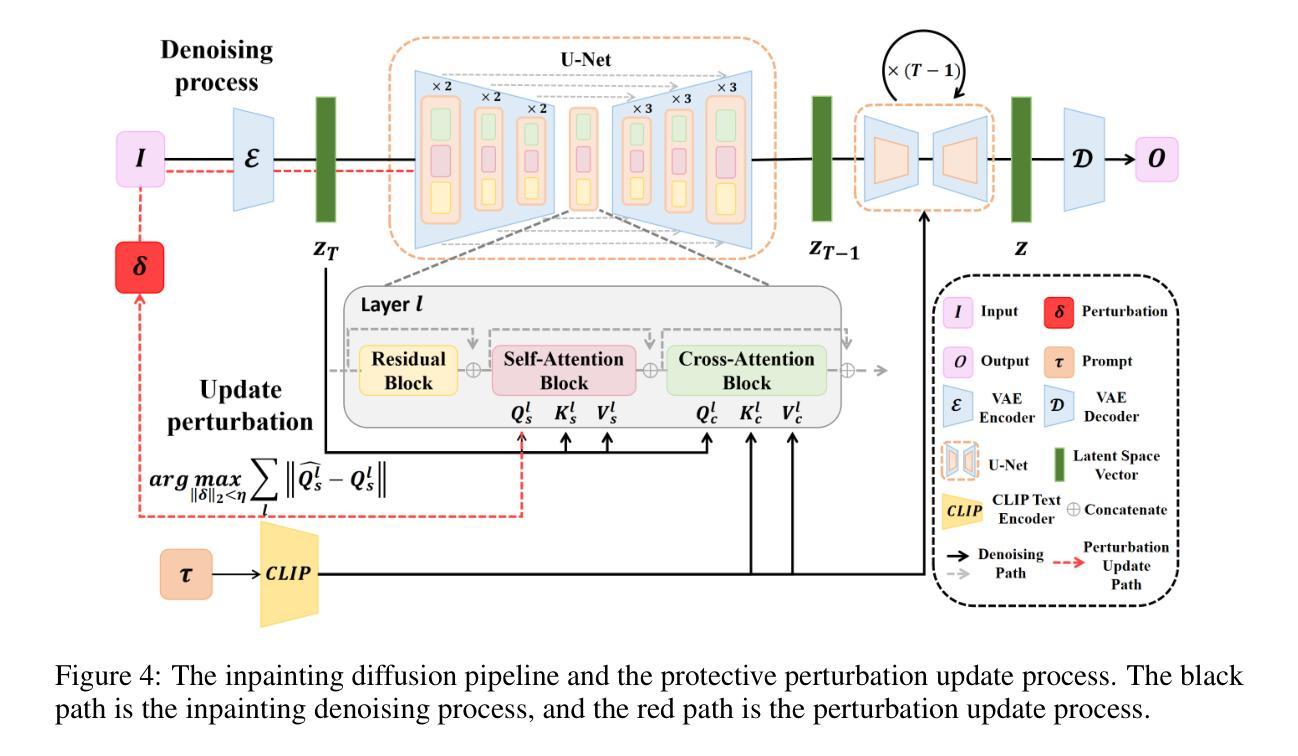
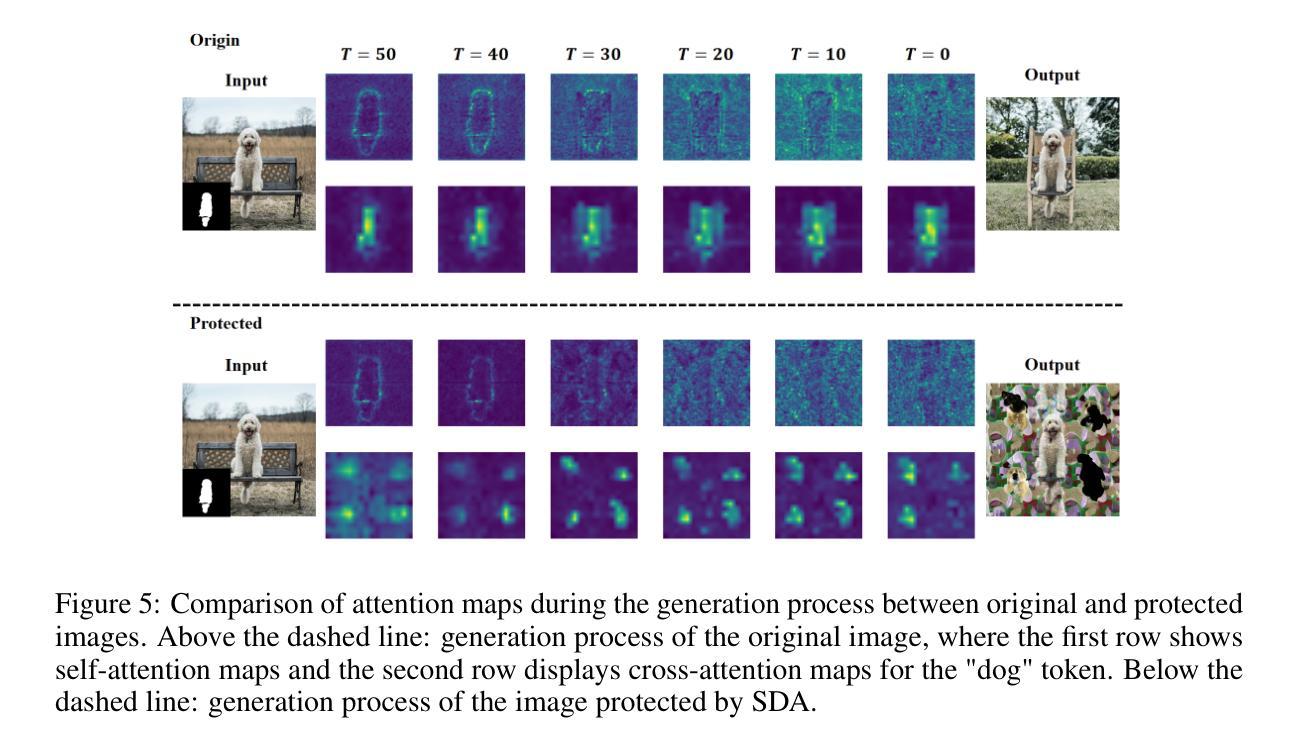
Structure Disruption: Subverting Malicious Diffusion-Based Inpainting via Self-Attention Query Perturbation
Authors:Yuhao He, Jinyu Tian, Haiwei Wu, Jianqing Li
The rapid advancement of diffusion models has enhanced their image inpainting and editing capabilities but also introduced significant societal risks. Adversaries can exploit user images from social media to generate misleading or harmful content. While adversarial perturbations can disrupt inpainting, global perturbation-based methods fail in mask-guided editing tasks due to spatial constraints. To address these challenges, we propose Structure Disruption Attack (SDA), a powerful protection framework for safeguarding sensitive image regions against inpainting-based editing. Building upon the contour-focused nature of self-attention mechanisms of diffusion models, SDA optimizes perturbations by disrupting queries in self-attention during the initial denoising step to destroy the contour generation process. This targeted interference directly disrupts the structural generation capability of diffusion models, effectively preventing them from producing coherent images. We validate our motivation through visualization techniques and extensive experiments on public datasets, demonstrating that SDA achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) protection performance while maintaining strong robustness.
扩散模型的快速发展增强了其图像补全和编辑功能,但同时也带来了重大的社会风险。对手可能会利用社交媒体上的用户图像生成误导性或有害内容。虽然对抗性扰动可以破坏图像补全,但基于全局扰动的方法在掩膜引导编辑任务中会因空间约束而失败。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了结构破坏攻击(SDA),这是一个强大的保护框架,用于保护敏感图像区域免受基于补全的编辑攻击。SDA建立在扩散模型的自注意机制轮廓重点的基础上,通过优化初始去噪步骤中自注意查询的扰动来破坏轮廓生成过程,从而破坏目标干扰。这种有针对性的干扰直接破坏了扩散模型的结构生成能力,有效地防止其生成连贯的图像。我们通过可视化技术和公开数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的动机,证明SDA在保护性能方面达到了最新水平,同时保持了强大的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型的快速发展提升了图像补全和编辑能力,但也带来了一定的社会风险。对手可能会利用社交媒体中的用户图像生成误导性或有害内容。为应对挑战,我们提出了结构破坏攻击(SDA)这一保护框架,保护敏感图像区域免受基于补全的编辑攻击。SDA通过干扰去噪步骤中的自注意力查询来破坏轮廓生成过程,优化干扰,实现对扩散模型结构生成能力的直接破坏,有效防止其生成连贯图像。通过可视化技术和公开数据集上的大量实验验证,SDA达到了业界最佳的防护性能,同时保持了强大的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的快速发展带来了图像补全和编辑能力的提升,但也存在社会风险。
- 对手可能利用社交媒体用户图像生成误导或有害内容。
- 结构破坏攻击(SDA)是一种保护框架,旨在保护敏感图像区域免受基于补全的编辑攻击。
- SDA通过干扰扩散模型的自注意力机制来破坏轮廓生成过程。
- SDA能有效防止扩散模型生成连贯图像。
- 通过可视化和公开数据集实验验证,SDA达到业界最佳防护性能。
点此查看论文截图

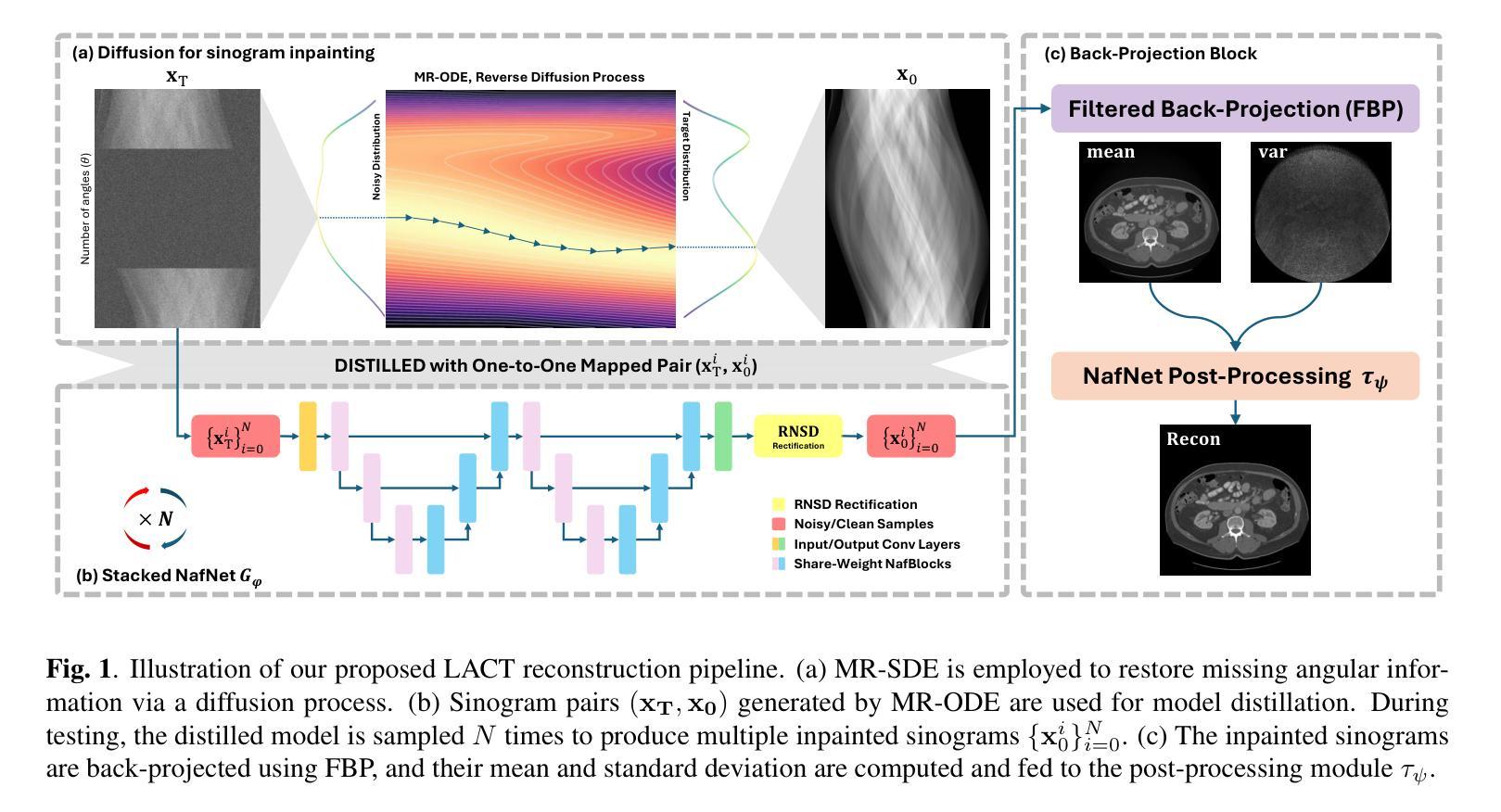
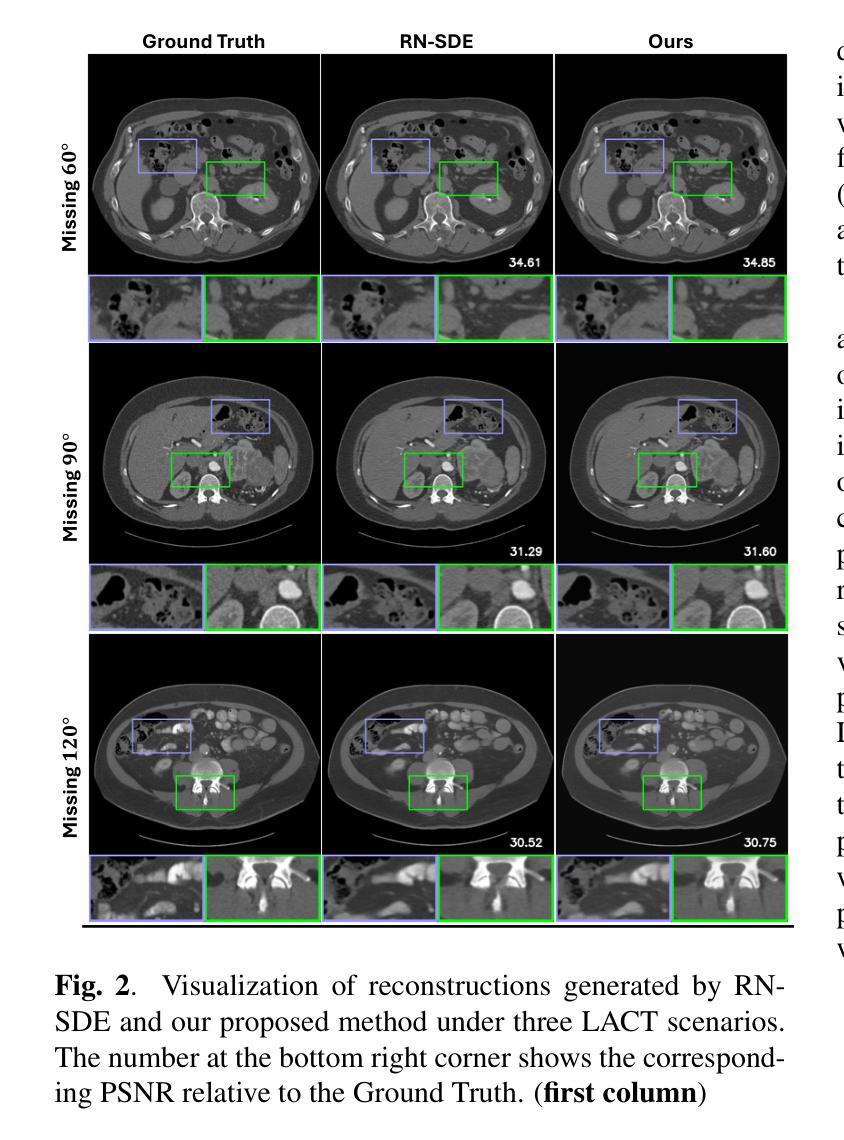
Advancing Limited-Angle CT Reconstruction Through Diffusion-Based Sinogram Completion
Authors:Jiaqi Guo, Santiago Lopez-Tapia, Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
Limited Angle Computed Tomography (LACT) often faces significant challenges due to missing angular information. Unlike previous methods that operate in the image domain, we propose a new method that focuses on sinogram inpainting. We leverage MR-SDEs, a variant of diffusion models that characterize the diffusion process with mean-reverting stochastic differential equations, to fill in missing angular data at the projection level. Furthermore, by combining distillation with constraining the output of the model using the pseudo-inverse of the inpainting matrix, the diffusion process is accelerated and done in a step, enabling efficient and accurate sinogram completion. A subsequent post-processing module back-projects the inpainted sinogram into the image domain and further refines the reconstruction, effectively suppressing artifacts while preserving critical structural details. Quantitative experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both perceptual and fidelity quality, offering a promising solution for LACT reconstruction in scientific and clinical applications.
有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)经常由于缺少角度信息而面临重大挑战。不同于之前在图像域操作的方法,我们提出了一种新方法,专注于辛格拉姆补全。我们利用MR-SDEs(一种用均值回归随机微分方程描述扩散过程的扩散模型的变体)在投影层面填充缺失的角度数据。此外,通过结合蒸馏技术并用补全矩阵的伪逆约束模型的输出,扩散过程得到加速并一次性完成,实现了高效准确的辛格拉姆补全。随后的后处理模块将补全的辛格拉姆反向投影到图像域,并进一步改进重建效果,有效地抑制伪影的同时保留关键的结构细节。定量实验结果表明,所提方法在实现感知和保真度质量方面均达到最新水平,为科学研究和临床应用中的LACT重建提供了有前景的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (Oral)
Summary
本文提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法,专注于处理Limited Angle Computed Tomography(LACT)中的缺失角度信息问题。该方法在投影层面使用MR-SDEs进行填充缺失的角数据,并采用蒸馏技术和伪逆补全矩阵进行输出约束以加速扩散过程。完成后的处理模块能够将补全的sinogram转回图像域,对重建图像进行进一步的优化和细节修复。实验结果证明了该方法在感知和保真质量方面达到了最新水平,为科学研究和临床应用中的LACT重建提供了前景。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的处理Limited Angle Computed Tomography(LACT)缺失角度信息的方法。
- 采用MR-SDEs扩散模型进行sinogram补全。
- 结合蒸馏技术和伪逆补全矩阵输出约束来加速扩散过程。
- 通过后处理模块将补全的sinogram转回图像域进行优化和细节修复。
- 实验结果证明了该方法在感知和保真质量方面的最新水平表现。
- 该方法具有高效性和准确性,为科学研究和临床应用中的LACT重建提供了前景。
点此查看论文截图

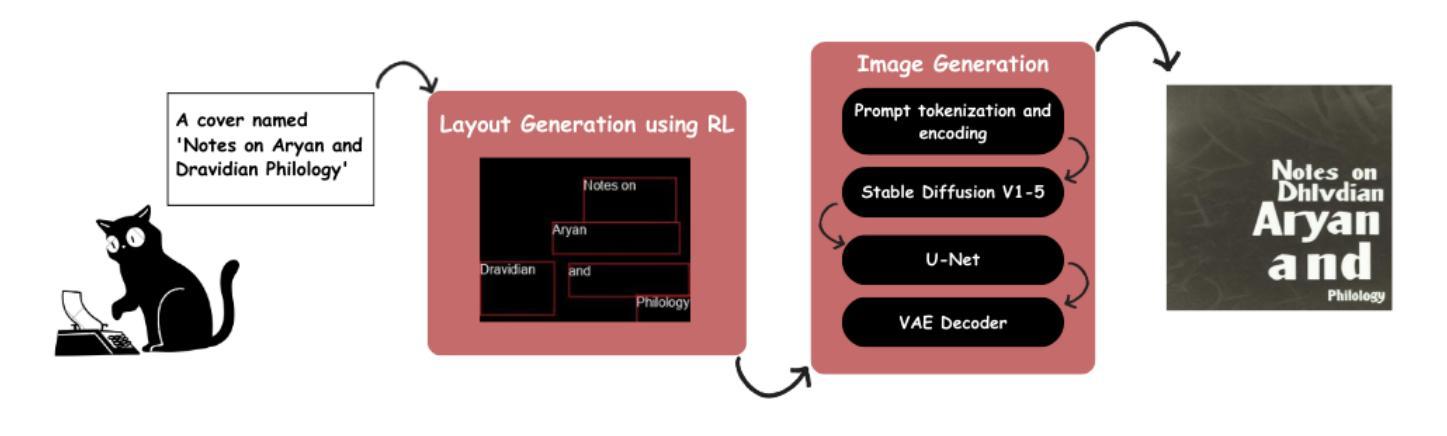
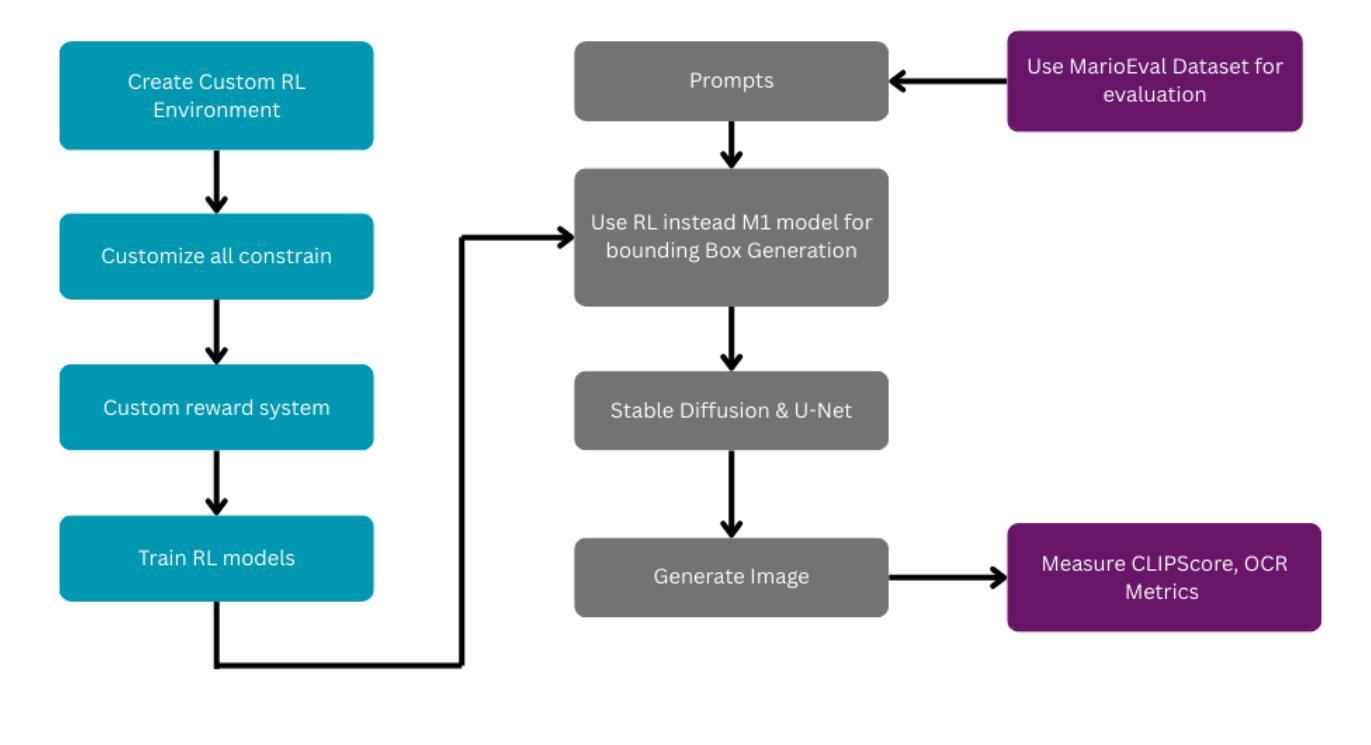
TextDiffuser-RL: Efficient and Robust Text Layout Optimization for High-Fidelity Text-to-Image Synthesis
Authors:Kazi Mahathir Rahman, Showrin Rahman, Sharmin Sultana Srishty
Text-embedded image generation plays a critical role in industries such as graphic design, advertising, and digital content creation. Text-to-Image generation methods leveraging diffusion models, such as TextDiffuser-2, have demonstrated promising results in producing images with embedded text. TextDiffuser-2 effectively generates bounding box layouts that guide the rendering of visual text, achieving high fidelity and coherence. However, existing approaches often rely on resource-intensive processes and are limited in their ability to run efficiently on both CPU and GPU platforms. To address these challenges, we propose a novel two-stage pipeline that integrates reinforcement learning (RL) for rapid and optimized text layout generation with a diffusion-based image synthesis model. Our RL-based approach significantly accelerates the bounding box prediction step while reducing overlaps, allowing the system to run efficiently on both CPUs and GPUs. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our framework maintains or surpasses TextDiffuser-2’s quality in text placement and image synthesis, with markedly faster runtime and increased flexibility. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our framework maintains or surpasses TextDiffuser-2’s quality in text placement and image synthesis, with markedly faster runtime and increased flexibility. Our approach has been evaluated on the MARIOEval benchmark, achieving OCR and CLIPScore metrics close to state-of-the-art models, while being 97.64% more faster and requiring only 2MB of memory to run.
文本嵌入图像生成在图形设计、广告和数字内容创建等行业扮演着至关重要的角色。利用扩散模型进行文本到图像生成的方法,如TextDiffuser-2,已展现出在生成嵌入文本的图像方面的巨大潜力。TextDiffuser-2通过生成有效的边界框布局来指导视觉文本的渲染,达到高保真度和连贯性。然而,现有方法往往依赖于资源密集型过程,并且在CPU和GPU平台上的运行效率有限。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型的两阶段管道,它集成了强化学习(RL)进行快速优化的文本布局生成和基于扩散的图像合成模型。我们的基于RL的方法显著加速了边界框预测步骤,同时减少了重叠,使系统能够在CPU和GPU上高效运行。广泛的评估表明,我们的框架在文本放置和图像合成方面保持或超越了TextDiffuser-2的质量,运行时明显更快,灵活性增强。我们的方法在MARIOEval基准测试上进行了评估,实现了接近最新模型的OCR和CLIPScore指标,同时运行速度提高了97.64%,并且只需2MB的内存即可运行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 26 figures. Submitted to arXiv for dissemination. Intended for future submission to a Generative AI conference
Summary
文本嵌入图像生成在图形设计、广告和数字化内容创作等行业扮演着关键角色。利用扩散模型的文本到图像生成方法,如TextDiffuser-2,已展现出生成嵌入文本图像时的潜力。为应对现有方法资源消耗大、CPU和GPU平台运行效率有限等挑战,我们提出了一种结合强化学习(RL)的两阶段流程,用于加速文本布局生成,并与基于扩散的图像合成模型相结合。该方法显著加速了边界框预测步骤,减少了重叠,使系统能在CPU和GPU上高效运行。评估显示,我们的框架在文本放置和图像合成方面保持或超越了TextDiffuser-2的质量,运行时显著加快,灵活性增强。在MARIOEval基准测试上,我们的方法接近最新模型的OCR和CLIPScore指标,同时运行速度快97.64%,仅需要2MB内存。
Key Takeaways
- 文本嵌入图像生成在多个行业具有关键作用。
- TextDiffuser-2利用扩散模型生成嵌入文本图像时表现出良好性能。
- 现有方法存在资源消耗大和在CPU及GPU平台运行效率有限的挑战。
- 提出了一种结合强化学习(RL)的两阶段流程来优化文本布局生成和图像合成。
- RL方法显著加速了边界框预测,减少了重叠,提高了运行效率。
- 评估显示,新框架在质量上保持或超越了TextDiffuser-2,运行时更快,灵活性增强。
点此查看论文截图

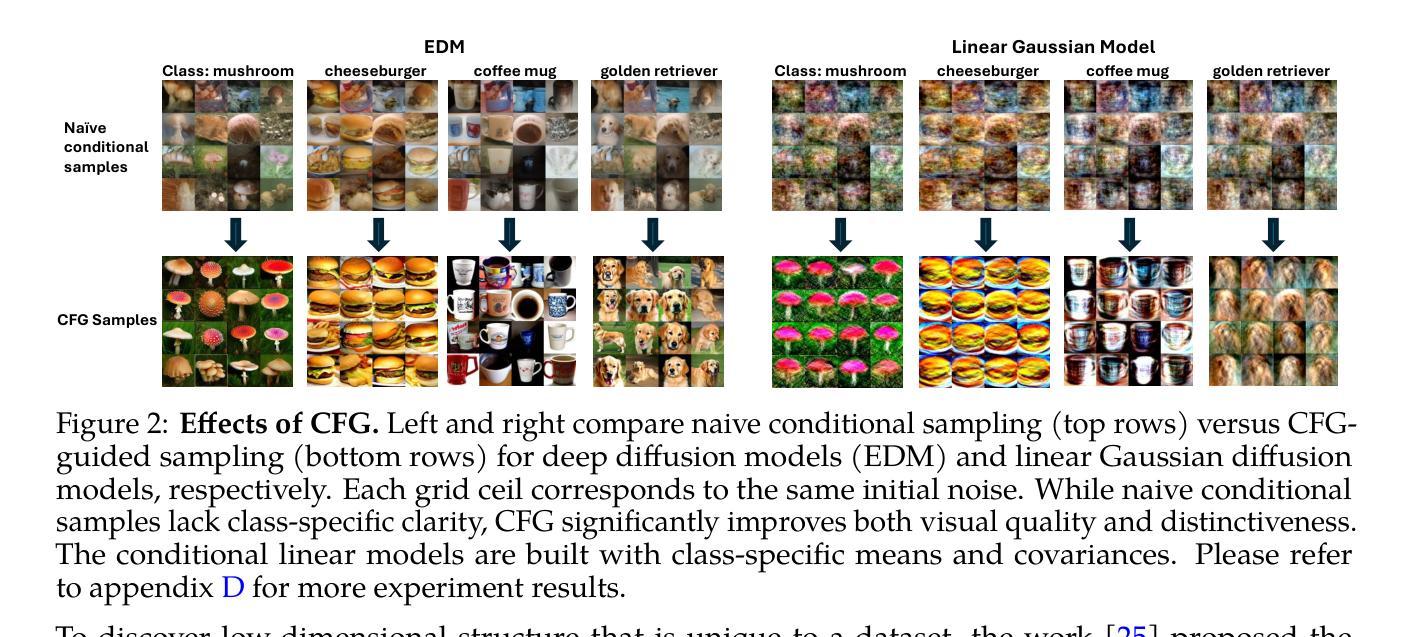
Towards Understanding the Mechanisms of Classifier-Free Guidance
Authors:Xiang Li, Rongrong Wang, Qing Qu
Classifier-free guidance (CFG) is a core technique powering state-of-the-art image generation systems, yet its underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this work, we begin by analyzing CFG in a simplified linear diffusion model, where we show its behavior closely resembles that observed in the nonlinear case. Our analysis reveals that linear CFG improves generation quality via three distinct components: (i) a mean-shift term that approximately steers samples in the direction of class means, (ii) a positive Contrastive Principal Components (CPC) term that amplifies class-specific features, and (iii) a negative CPC term that suppresses generic features prevalent in unconditional data. We then verify that these insights in real-world, nonlinear diffusion models: over a broad range of noise levels, linear CFG resembles the behavior of its nonlinear counterpart. Although the two eventually diverge at low noise levels, we discuss how the insights from the linear analysis still shed light on the CFG’s mechanism in the nonlinear regime.
无分类器引导(CFG)是驱动当前图像生成系统核心技术的重要组成部分,但其底层机制仍知之甚少。在这项工作中,我们首先在一个简化的线性扩散模型中分析CFG,该模型的行为与在非线性情况下观察到的行为非常相似。我们的分析表明,线性CFG通过三个不同部分提高了生成质量:(i)均值偏移项,它大致将样本引导到类别均值的方向;(ii)正向对比主成分(CPC)项,它放大了类别特定的特征;(iii)负CPC项,它抑制了无条件数据中普遍存在的通用特征。然后,我们在现实世界的非线性扩散模型中验证了这些见解:在广泛的噪声水平下,线性CFG的行为与其非线性对应物相似。尽管两者在低噪声水平下最终会分道扬镳,但我们讨论了线性分析中的见解如何仍然为非线性状态下的CFG机制提供启示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了分类器免费指导(CFG)在简化线性扩散模型中的应用行为,并揭示了其通过三种不同机制提高生成质量:平均偏移项引导样本朝向类别均值方向,正向对比主成分(CPC)项放大类别特定特征,以及负向CPC项抑制无条件数据中的通用特征。在现实世界中的非线性扩散模型中,验证了这些见解在广泛噪声水平下的适用性。尽管两者在低噪声水平下最终会发散,但本文讨论如何从线性分析中揭示CFG机制在非线性质地中的应用。
Key Takeaways
- 分类器免费指导(CFG)是提高图像生成系统性能的核心技术。
- 在简化线性扩散模型中,CFG的行为与在非线性模型中的行为类似。
- CFG通过三种机制提高生成质量:平均偏移项、正向对比主成分(CPC)项和负向CPC项。
- 平均偏移项引导样本朝向类别均值方向。
- 正向CPC项放大类别特定特征,而负向CPC项抑制无条件数据中的通用特征。
- 在现实世界的非线性扩散模型中,CFG的见解在广泛噪声水平下有效。
点此查看论文截图

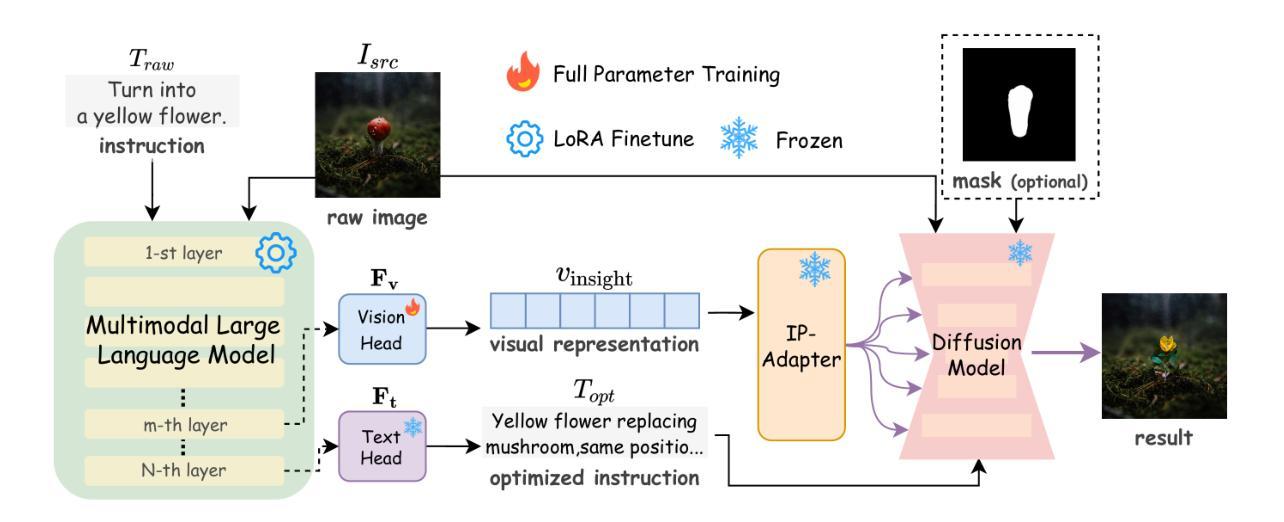
MIND-Edit: MLLM Insight-Driven Editing via Language-Vision Projection
Authors:Shuyu Wang, Weiqi Li, Qian Wang, Shijie Zhao, Jian Zhang
Recent advances in AI-generated content (AIGC) have significantly accelerated image editing techniques, driving increasing demand for diverse and fine-grained edits. Despite these advances, existing image editing methods still face challenges in achieving high precision and semantic accuracy in complex scenarios. Recent studies address this issue by incorporating multimodal large language models (MLLMs) into image editing pipelines. However, current MLLM-based methods mainly rely on interpreting textual instructions, leaving the intrinsic visual understanding of large models largely unexplored, thus resulting in insufficient alignment between textual semantics and visual outcomes. To overcome these limitations, we propose MIND-Edit, an end-to-end image-editing framework integrating pretrained diffusion model with MLLM. MIND-Edit introduces two complementary strategies: (1) a text instruction optimization strategy that clarifies ambiguous user instructions based on semantic reasoning from the MLLM, and (2) an MLLM insight-driven editing strategy that explicitly leverages the intrinsic visual understanding capability of the MLLM to infer editing intent and guide the diffusion process via generated visual embeddings. Furthermore, we propose a joint training approach to effectively integrate both strategies, allowing them to reinforce each other for more accurate instruction interpretation and visually coherent edits aligned with user intent. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MIND-Edit outperforms state-of-the-art image editing methods in both quantitative metrics and visual quality, particularly under complex and challenging scenarios.
近期人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的进步极大地加速了图像编辑技术,推动了对于多样化和精细化的编辑需求的增长。尽管有这些进步,现有的图像编辑方法仍然面临在复杂场景中实现高精度和语义准确性的挑战。最近的研究通过把多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)融入图像编辑流程来解决这个问题。然而,当前的基于MLLM的方法主要依赖于解读文本指令,使得大型模型的内在视觉理解在很大程度上被忽略,因此导致文本语义和视觉结果之间的对齐不足。为了克服这些局限,我们提出了MIND-Edit,这是一个端到端的图像编辑框架,它整合了预训练的扩散模型和MLLM。MIND-Edit引入了两种互补的策略:1)一种文本指令优化策略,它基于MLLM的语义推理来澄清模糊的用户指令;2)一种MLLM洞察驱动的编辑策略,它明确利用MLLM的内在视觉理解能力来推断编辑意图,并通过生成的视觉嵌入来指导扩散过程。此外,我们提出了一种联合训练方法,有效地整合了这两种策略,使它们在相互强化中实现了更精确的指令解读和与用户意图相一致的视觉连贯编辑。大量实验表明,MIND-Edit在定量指标和视觉质量上超越了最先进的图像编辑方法,特别是在复杂和挑战性的场景中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着人工智能生成内容(AIGC)的进展,图像编辑技术得到加速发展,对多样化、精细化的编辑需求不断增长。现有图像编辑方法面临复杂场景下高精度和语义准确度的挑战。最新研究通过结合多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来解决这一问题。然而,当前MLLM方法主要依赖文本指令解读,对大型模型的内在视觉理解探索不足,导致文本语义与视觉结果对齐不足。为此,我们提出MIND-Edit,一个结合预训练扩散模型与MLLM的端到端图像编辑框架。MIND-Edit引入两种互补策略:一是基于MLLM语义推理的文本指令优化策略,澄清模糊的用户指令;二是利用MLLM内在视觉理解能力的编辑策略,通过生成的视觉嵌入物来推断编辑意图并引导扩散过程。我们通过联合训练方法来有效整合这两种策略,使它们在指令解读和视觉编辑方面相互强化,实现更符合用户意图的准确编辑。
Key Takeaways
- AI-generated content (AIGC) 的进步推动了图像编辑技术的快速发展,对编辑的多样性和精细度提出了更高要求。
- 现有图像编辑方法在复杂场景下实现高精度和语义准确度方面存在挑战。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)被引入图像编辑流程以解决上述问题。
- 当前MLLM方法主要依赖文本指令解读,缺乏内在视觉理解的探索。
- MIND-Edit框架结合预训练扩散模型与MLLM,旨在解决上述挑战。
- MIND-Edit引入文本指令优化策略和基于MLLM视觉理解的编辑策略。
- 通过联合训练方法整合两种策略,实现更准确、视觉连贯的编辑。
点此查看论文截图


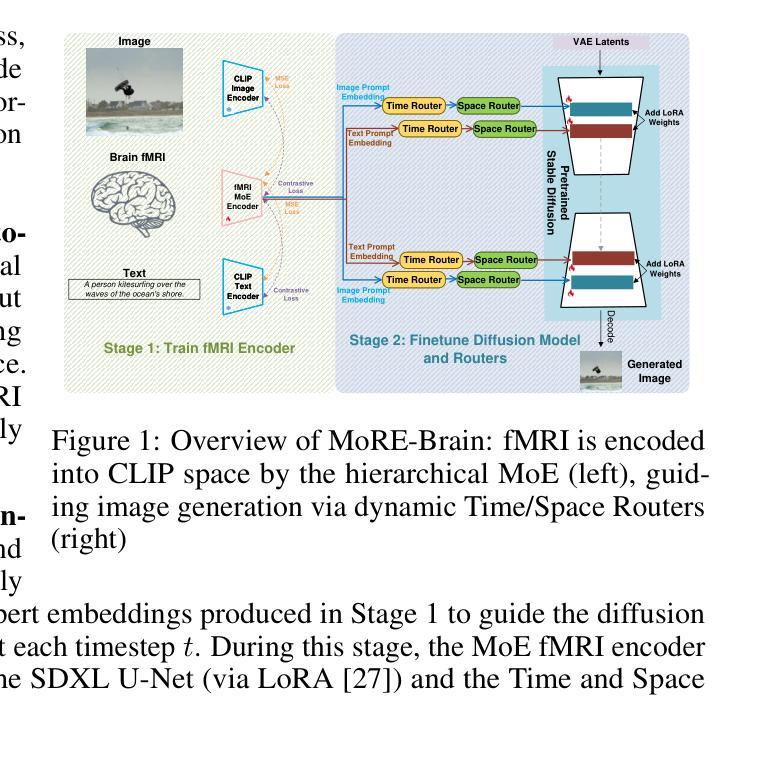
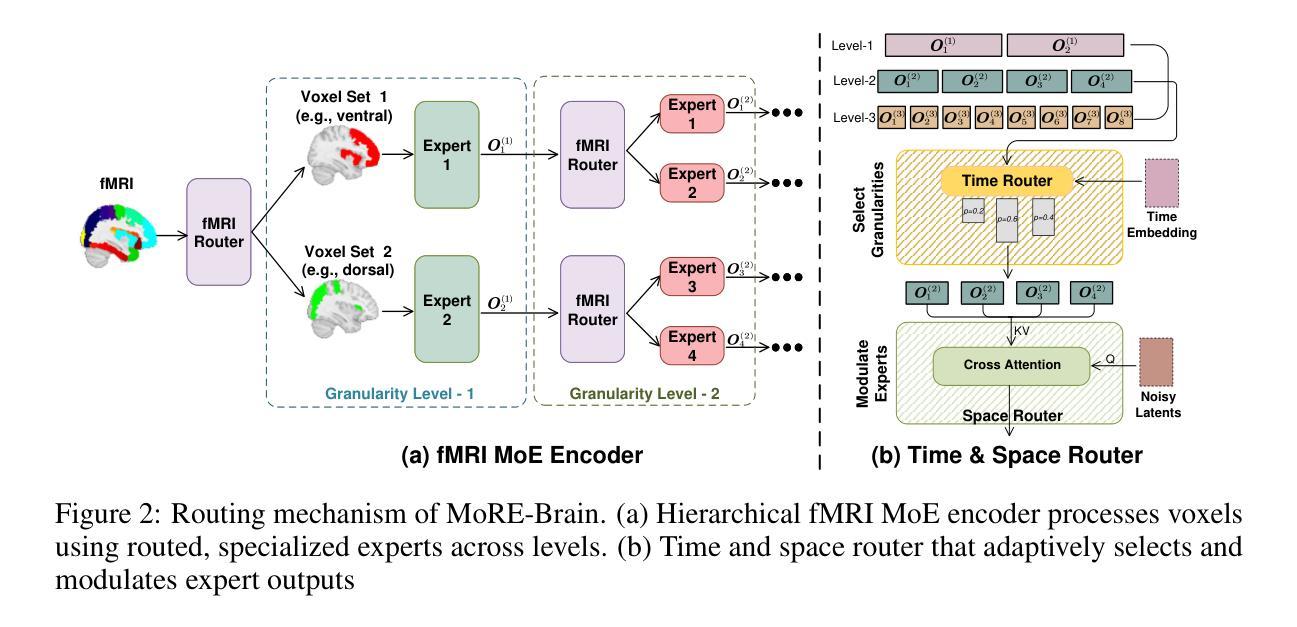
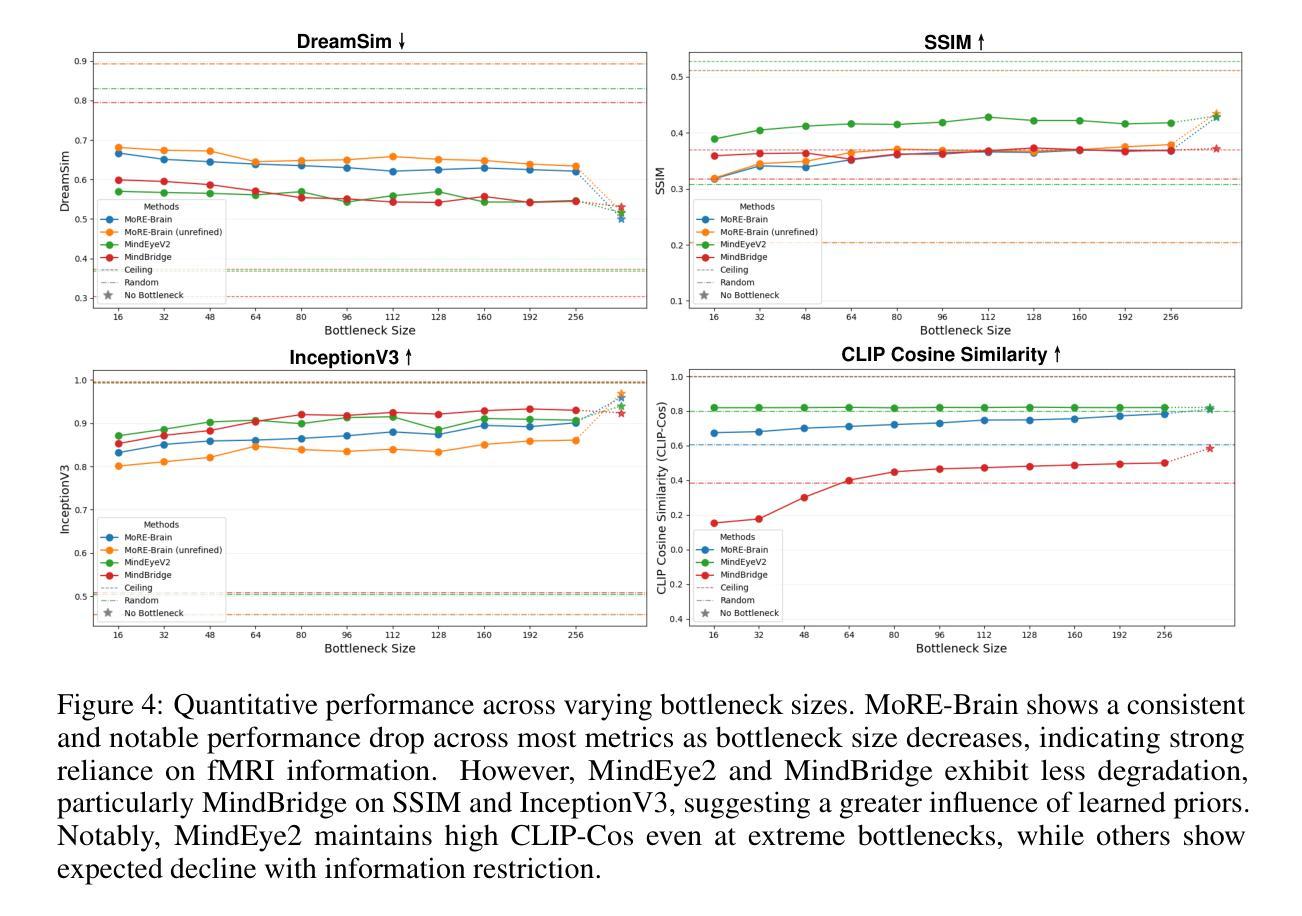
MoRE-Brain: Routed Mixture of Experts for Interpretable and Generalizable Cross-Subject fMRI Visual Decoding
Authors:Yuxiang Wei, Yanteng Zhang, Xi Xiao, Tianyang Wang, Xiao Wang, Vince D. Calhoun
Decoding visual experiences from fMRI offers a powerful avenue to understand human perception and develop advanced brain-computer interfaces. However, current progress often prioritizes maximizing reconstruction fidelity while overlooking interpretability, an essential aspect for deriving neuroscientific insight. To address this gap, we propose MoRE-Brain, a neuro-inspired framework designed for high-fidelity, adaptable, and interpretable visual reconstruction. MoRE-Brain uniquely employs a hierarchical Mixture-of-Experts architecture where distinct experts process fMRI signals from functionally related voxel groups, mimicking specialized brain networks. The experts are first trained to encode fMRI into the frozen CLIP space. A finetuned diffusion model then synthesizes images, guided by expert outputs through a novel dual-stage routing mechanism that dynamically weighs expert contributions across the diffusion process. MoRE-Brain offers three main advancements: First, it introduces a novel Mixture-of-Experts architecture grounded in brain network principles for neuro-decoding. Second, it achieves efficient cross-subject generalization by sharing core expert networks while adapting only subject-specific routers. Third, it provides enhanced mechanistic insight, as the explicit routing reveals precisely how different modeled brain regions shape the semantic and spatial attributes of the reconstructed image. Extensive experiments validate MoRE-Brain’s high reconstruction fidelity, with bottleneck analyses further demonstrating its effective utilization of fMRI signals, distinguishing genuine neural decoding from over-reliance on generative priors. Consequently, MoRE-Brain marks a substantial advance towards more generalizable and interpretable fMRI-based visual decoding. Code will be publicly available soon: https://github.com/yuxiangwei0808/MoRE-Brain.
从功能磁共振成像(fMRI)中解码视觉经验为我们理解人类感知并开发先进的脑机接口提供了强大的途径。然而,目前的进展往往优先最大化重建保真度,却忽视了可解释性这一对于获取神经科学洞察力的必要方面。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了MoRE-Brain,这是一个神经启发的框架,旨在实现高保真、可适应和可解释的视觉重建。MoRE-Brain独特地采用了一种层次化的混合专家架构,其中不同的专家处理来自功能相关体素组的fMRI信号,模仿专门的脑网络。专家首先被训练将fMRI编码到固定的CLIP空间中。然后,一个经过微调的分步模型在专家输出的引导下通过一种新型的双阶段路由机制合成图像,该机制在扩散过程中动态权衡专家的贡献。MoRE-Brain提供了三个主要进展:首先,它引入了一种基于脑网络原理的新型混合专家架构来进行神经解码。其次,它通过共享核心专家网络并仅调整特定主题的路由器,实现了跨主题的有效泛化。第三,它提供了增强的机械洞察力,因为明确的路由揭示了不同的模拟脑区域如何塑造重建图像的语义和空间属性。大量实验验证了MoRE-Brain的高重建保真度,瓶颈分析进一步证明了它有效利用fMRI信号的能力,区分了真正的神经解码和对生成优先级的依赖。因此,MoRE-Brain标志着朝着更通用和可解释的基于fMRI的视觉解码取得了重大进展。代码将在近期公开发布于:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了解码功能磁共振成像(fMRI)视觉体验的新方法,为解决当前研究中过于强调重建保真度而忽视解释性的问题,提出了一种名为MoRE-Brain的神经启发框架。该框架具有高精度、可适应和可解释的特点,采用层次化的混合专家架构处理fMRI信号,并通过训练专家对fMRI进行编码,再借助微调后的扩散模型合成图像。MoRE-Brain具有三大优势:引入基于脑网络原理的混合专家架构、实现跨主体高效泛化以及提供增强机制洞察力。代码即将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉体验的解码提供了理解人类感知和研发先进脑机接口的强大途径。
- 当前研究中过于重视重建保真度而忽视了解释性,这是神经科学洞察的关键方面。
- MoRE-Brain框架具有高精度、可适应和可解释的特点,解决了上述问题。
- MoRE-Brain采用混合专家架构处理fMRI信号,模仿专门化的脑网络。
- 该框架通过训练专家对fMRI进行编码,并通过扩散模型合成图像,提供一种新的解码方法。
- MoRE-Brain实现跨主体泛化,通过共享核心专家网络并仅调整主体特定路由器来实现高效性能。
点此查看论文截图


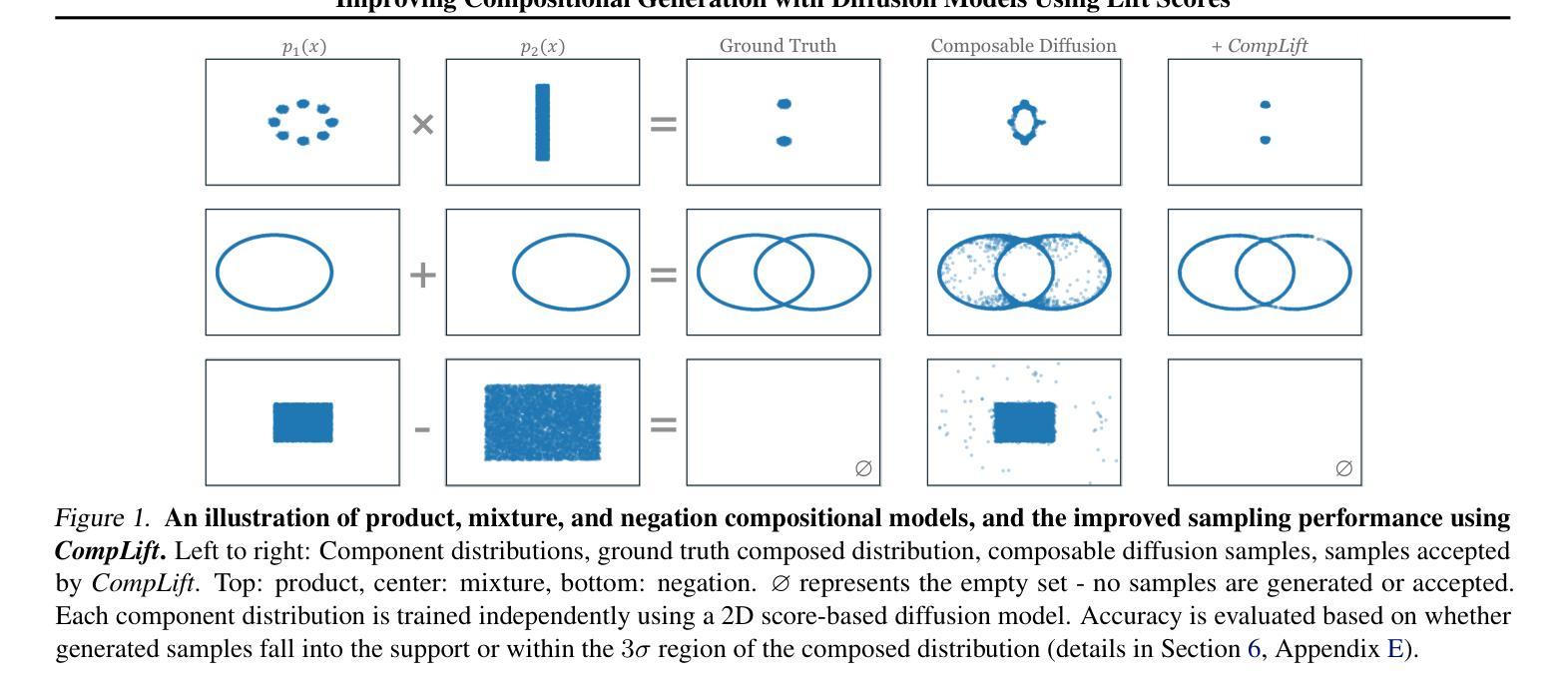
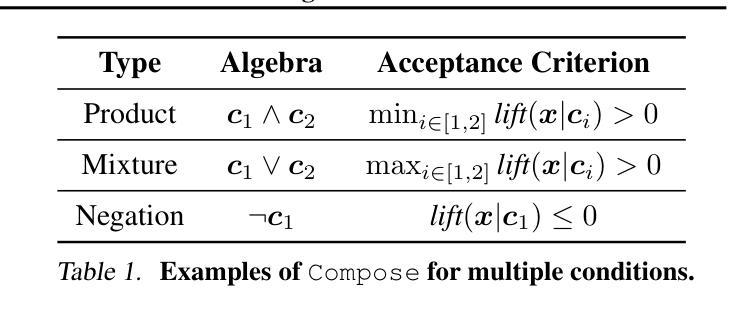
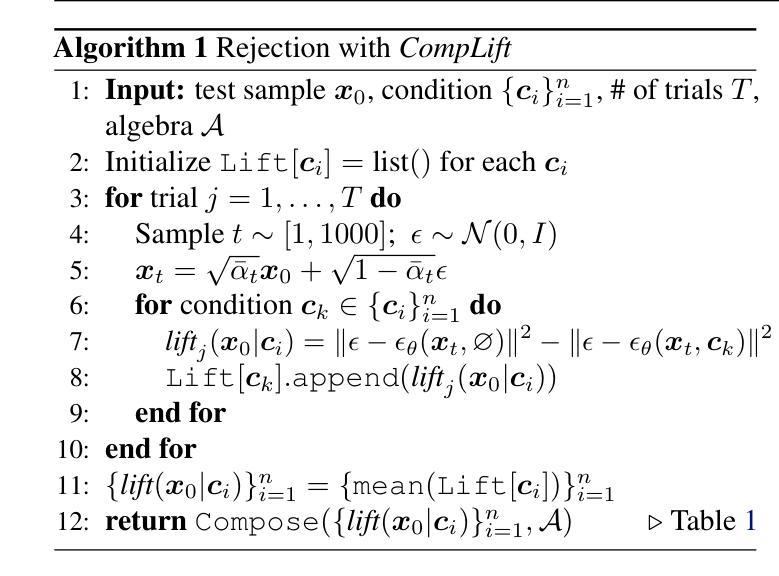
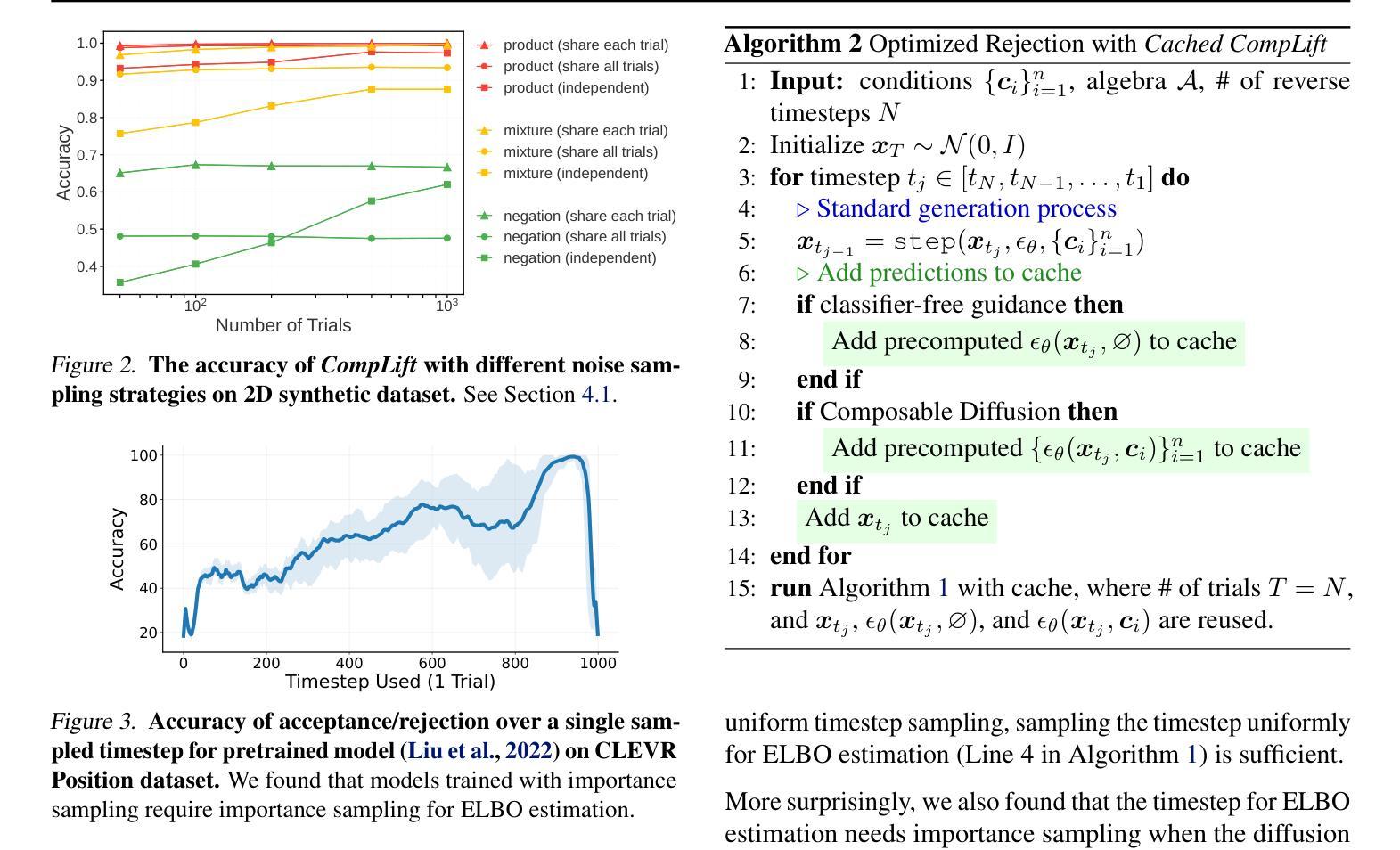
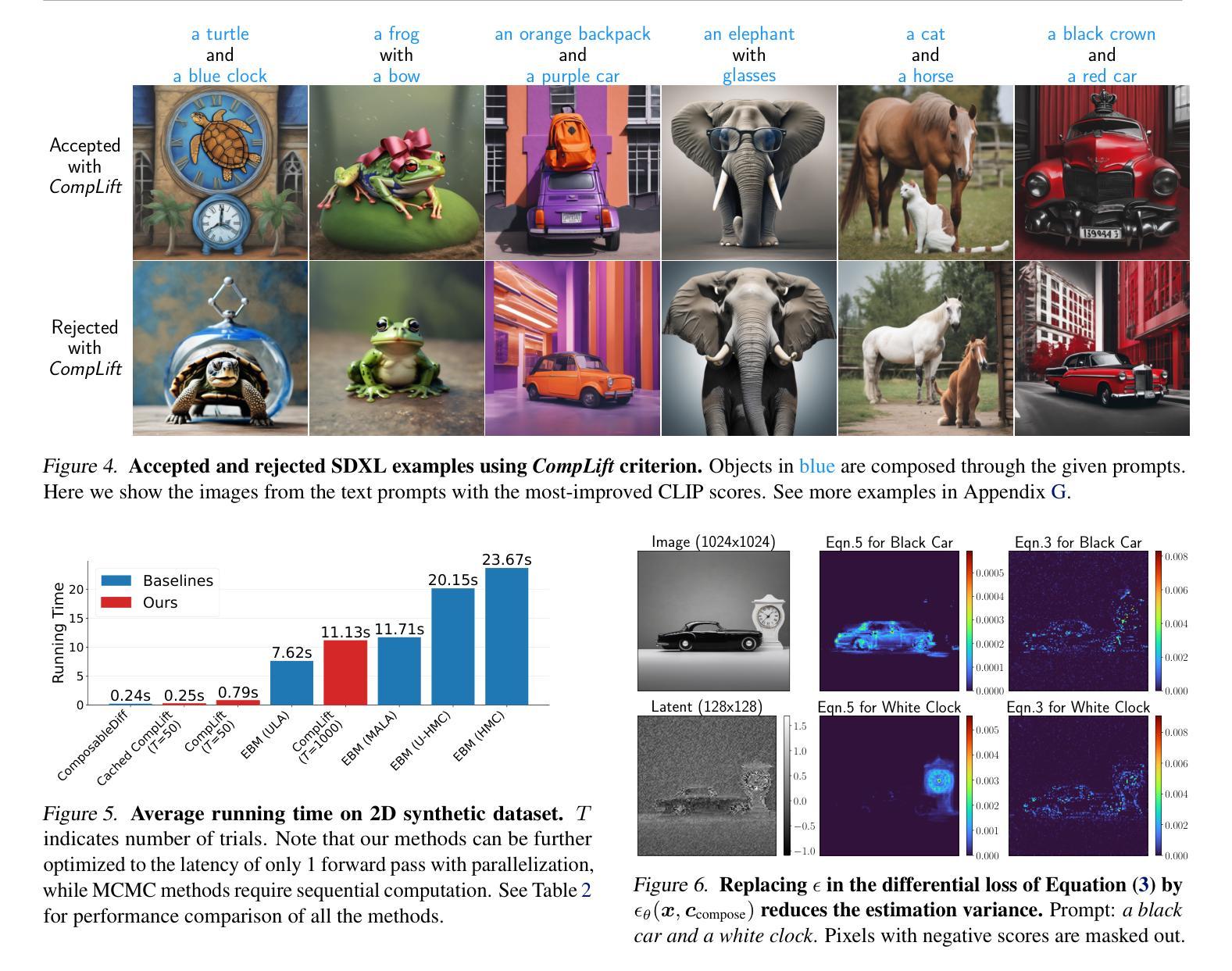
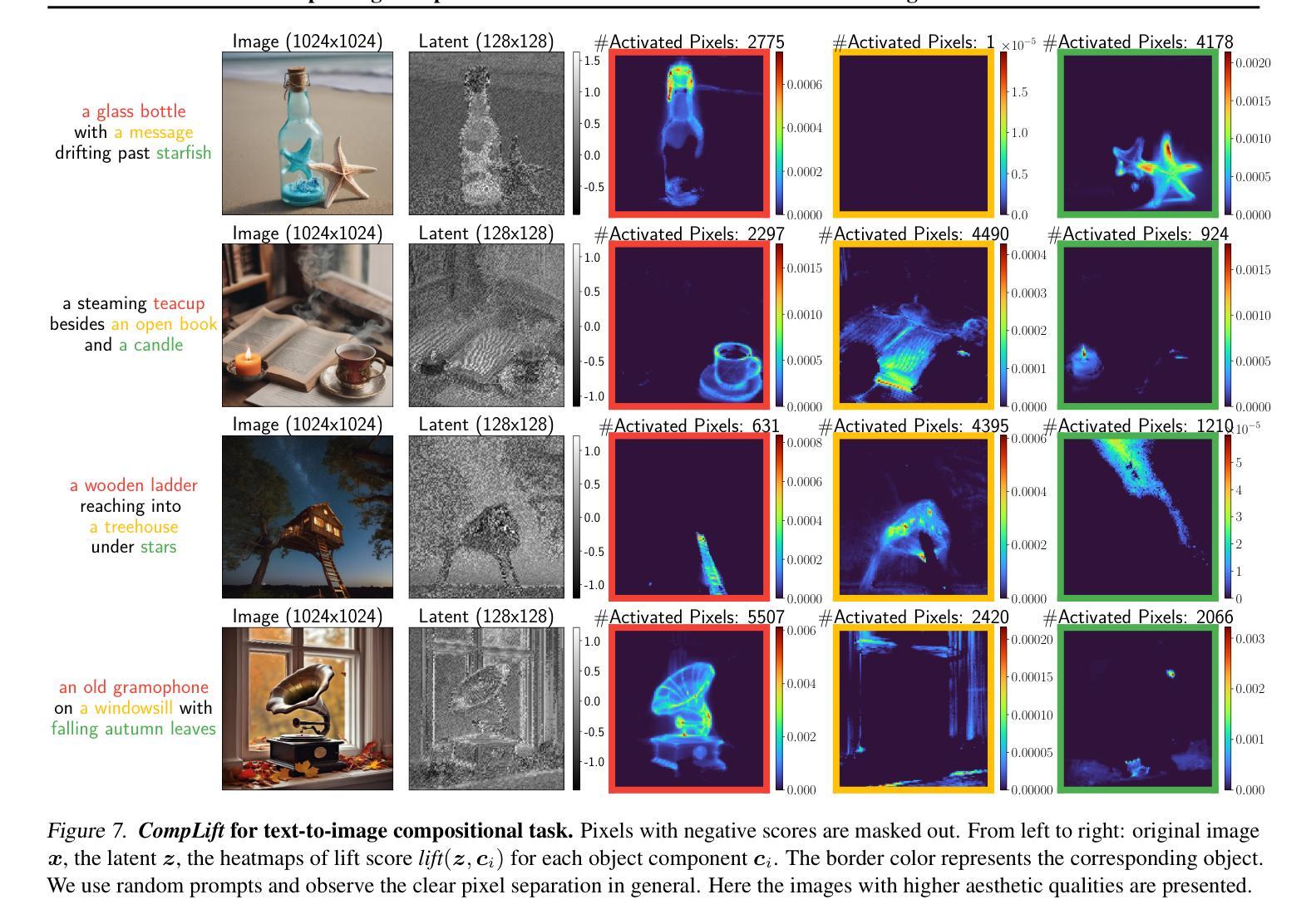
Improving Compositional Generation with Diffusion Models Using Lift Scores
Authors:Chenning Yu, Sicun Gao
We introduce a novel resampling criterion using lift scores, for improving compositional generation in diffusion models. By leveraging the lift scores, we evaluate whether generated samples align with each single condition and then compose the results to determine whether the composed prompt is satisfied. Our key insight is that lift scores can be efficiently approximated using only the original diffusion model, requiring no additional training or external modules. We develop an optimized variant that achieves relatively lower computational overhead during inference while maintaining effectiveness. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that lift scores significantly improved the condition alignment for compositional generation across 2D synthetic data, CLEVR position tasks, and text-to-image synthesis. Our code is available at http://rainorangelemon.github.io/complift.
我们引入了一种新的重采样准则,利用提升分数来提高扩散模型中的组合生成。通过利用提升分数,我们评估生成的样本是否符合单个条件,然后将结果组合起来,以确定组合提示是否满足要求。我们的关键见解是,仅使用原始的扩散模型就可以有效地近似提升分数,而无需进行额外的训练或外部模块。我们开发了一个优化版本,在推理过程中实现了较低的计算开销,同时保持了有效性。通过大量实验,我们证明提升分数在2D合成数据、CLEVR位置任务和文本到图像合成中的组合生成条件对齐方面有了显著改进。我们的代码可在http://rainorangelemon.github.io/complift上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种使用提升分数(lift scores)的新型重采样标准,用于改进扩散模型中的组合生成。该标准能够评估生成的样本是否符合单个条件,并将结果组合起来判断组合提示是否满足要求。关键之处在于,只需使用原始扩散模型即可有效估算提升分数,无需额外的训练或外部模块。实验表明,提升分数能显著提高组合生成的条件对齐性,适用于二维合成数据、CLEVR位置任务和文本到图像合成等领域。相关代码可在http://rainorangelemon.github.io/complift获取。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的重采样标准——提升分数(lift scores),用于改进扩散模型中的组合生成。
- 提升分数能够评估生成的样本是否符合单个条件,进而判断组合提示是否满足要求。
- 该方法无需额外的训练或外部模块,仅使用原始扩散模型即可估算提升分数。
- 实验表明提升分数在二维合成数据、CLEVR位置任务和文本到图像合成等方面能够显著提高条件对齐性。
- 所提出的方法具有较低的计算开销,同时保持了有效性。
- 该方法的实现代码已公开可用。
- 该方法对于提升扩散模型的性能,特别是在复杂的数据生成任务中具有潜在的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

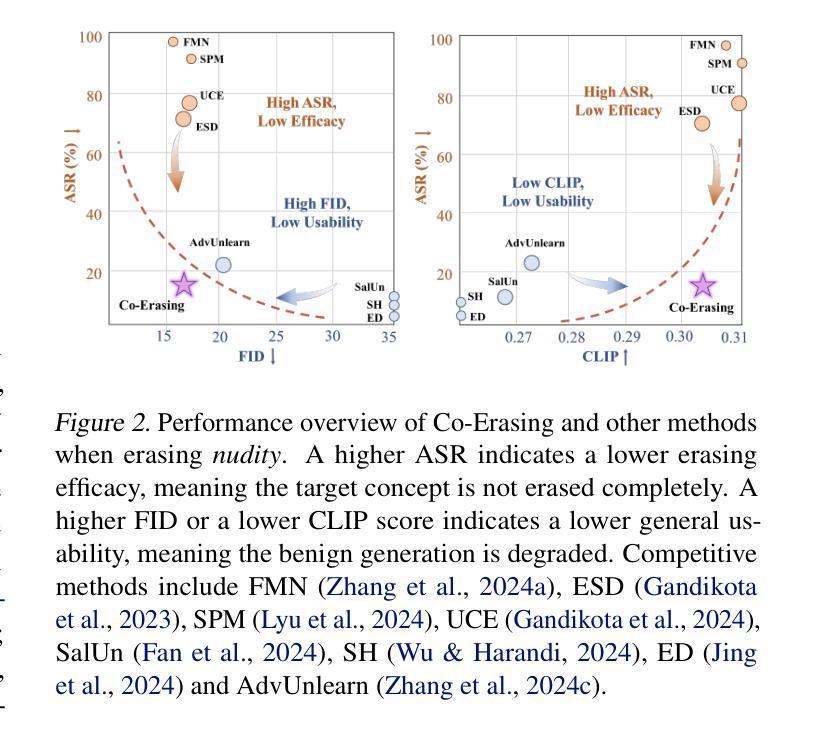
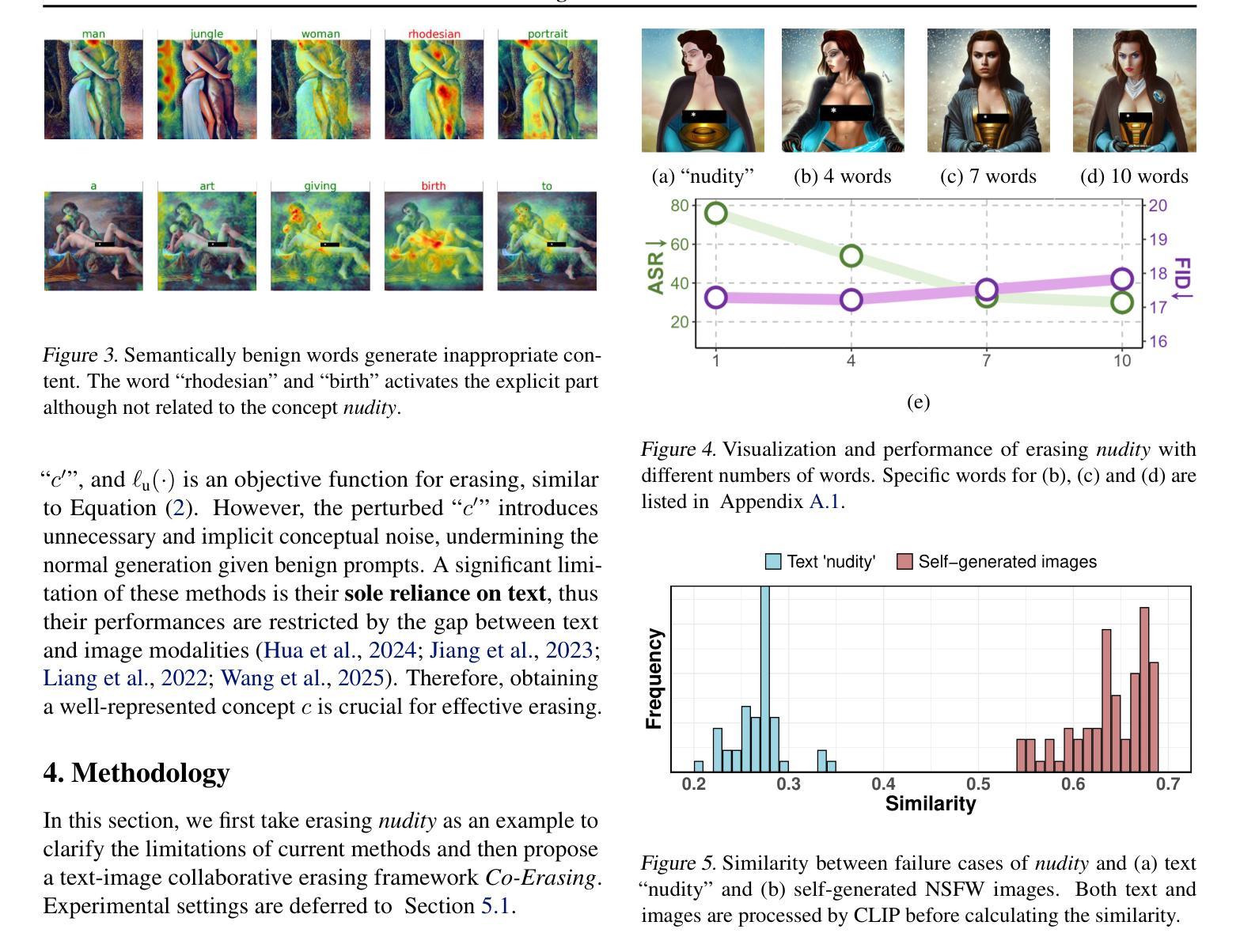
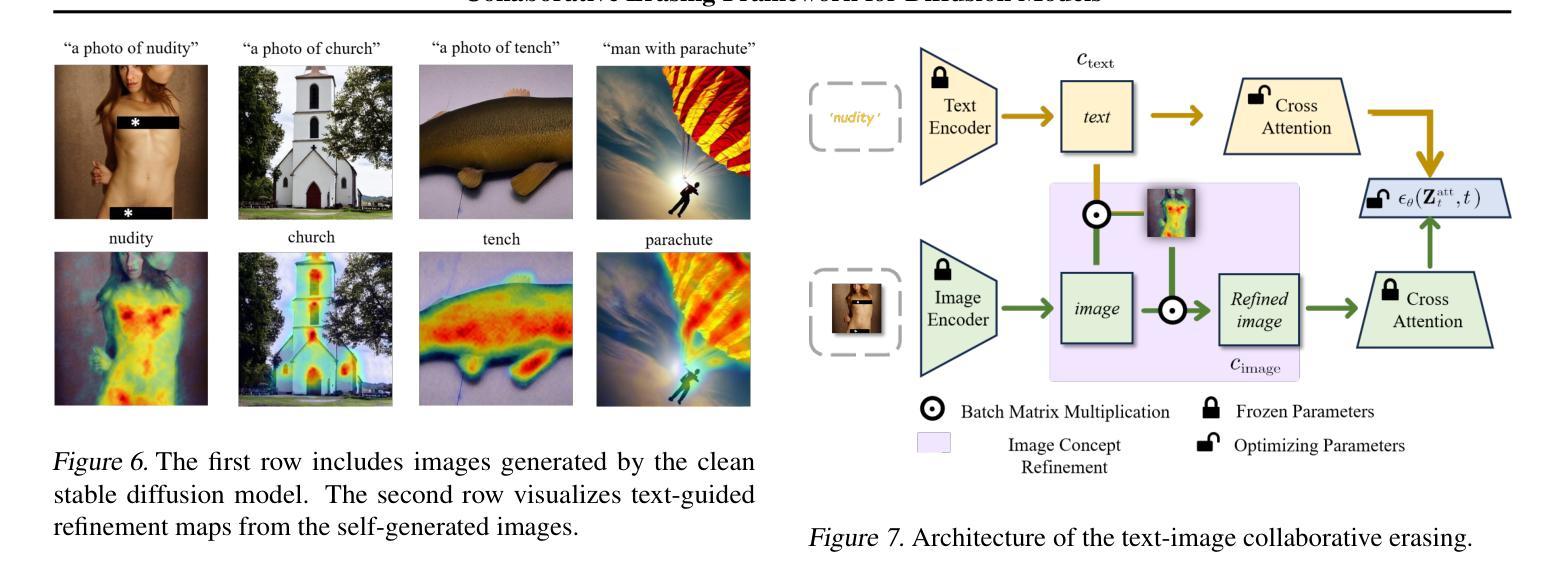
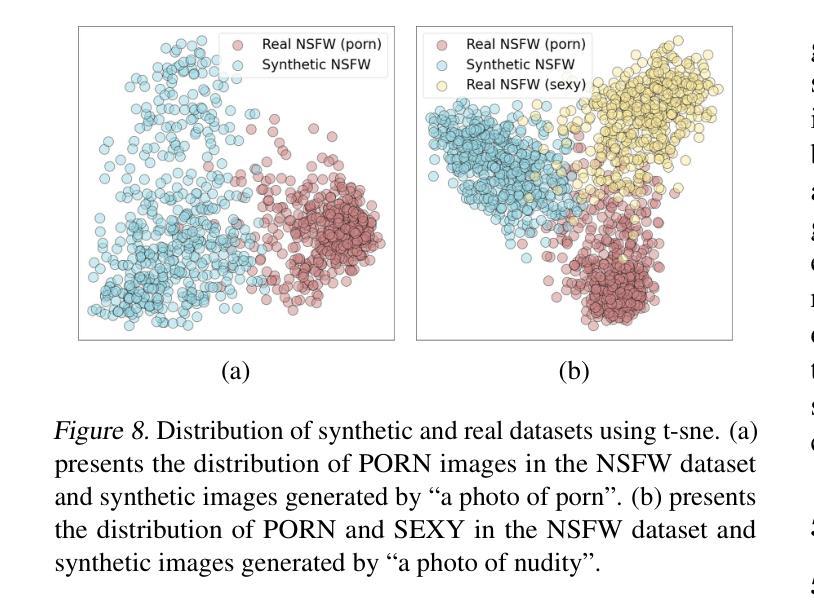
One Image is Worth a Thousand Words: A Usability Preservable Text-Image Collaborative Erasing Framework
Authors:Feiran Li, Qianqian Xu, Shilong Bao, Zhiyong Yang, Xiaochun Cao, Qingming Huang
Concept erasing has recently emerged as an effective paradigm to prevent text-to-image diffusion models from generating visually undesirable or even harmful content. However, current removal methods heavily rely on manually crafted text prompts, making it challenging to achieve a high erasure (efficacy) while minimizing the impact on other benign concepts (usability). In this paper, we attribute the limitations to the inherent gap between the text and image modalities, which makes it hard to transfer the intricately entangled concept knowledge from text prompts to the image generation process. To address this, we propose a novel solution by directly integrating visual supervision into the erasure process, introducing the first text-image Collaborative Concept Erasing (Co-Erasing) framework. Specifically, Co-Erasing describes the concept jointly by text prompts and the corresponding undesirable images induced by the prompts, and then reduces the generating probability of the target concept through negative guidance. This approach effectively bypasses the knowledge gap between text and image, significantly enhancing erasure efficacy. Additionally, we design a text-guided image concept refinement strategy that directs the model to focus on visual features most relevant to the specified text concept, minimizing disruption to other benign concepts. Finally, comprehensive experiments suggest that Co-Erasing outperforms state-of-the-art erasure approaches significantly with a better trade-off between efficacy and usability. Codes are available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/Co-Erasing.
概念擦除作为一种有效的范式,旨在防止文本到图像的扩散模型生成视觉不良甚至有害的内容。然而,当前的擦除方法严重依赖于手动构建的文本提示,这使得在减少对其他良性概念(可用性)影响的同时实现高擦除率(有效性)具有挑战性。本文认为这些局限性源于文本和图像模态之间的固有差距,这使得从文本提示将复杂纠缠的概念知识转移到图像生成过程变得困难。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种通过直接在擦除过程中引入视觉监督的解决方法,提出了首个文本图像协同概念擦除(Co-Erasing)框架。具体来说,Co-Erasing通过文本提示和由提示诱导的相应不良图像共同描述概念,然后通过负引导降低目标概念的产生概率。这种方法有效地绕过了文本和图像之间的知识差距,大大提高了擦除效果。此外,我们还设计了一种文本引导的图像概念细化策略,引导模型关注与指定文本概念最相关的视觉特征,尽量减少对其他良性概念的干扰。最后,综合实验表明,Co-Erasing在效果和可用性之间取得了更好的平衡,显著优于最先进的擦除方法。代码可从https://github.com/Ferry-Li/Co-Erasing获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepeted to ICML 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型文本-图像协同概念擦除(Co-Erasing)框架,通过直接整合视觉监督到擦除过程中,以有效防止文本到图像扩散模型生成不良内容。该框架通过联合文本提示和对应的不良图像描述概念,然后通过负引导降低目标概念的产生概率,从而显著提高了擦除效果。此外,还设计了一种文本引导的图像概念优化策略,使模型更关注与指定文本概念相关的视觉特征,最小化对其他良性概念的干扰。实验表明,Co-Erasing在擦除效果和可用性之间的权衡上显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 当前文本擦除方法存在挑战,需要在实现高擦除效果的同时最小化对其他良性概念的影响。
- 提出了一种新型文本-图像协同概念擦除框架(Co-Erasing),通过直接整合视觉监督到擦除过程中来解决挑战。
- Co-Erasing通过联合文本提示和不良图像描述概念来有效减少目标概念的生成概率。
- Co-Erasing设计了文本引导的图像概念优化策略,专注于与指定文本概念相关的视觉特征,减少对其他良性概念的干扰。
- 实验证明,Co-Erasing在擦除效果和可用性之间的权衡上显著优于现有方法。
- Co-Erasing框架的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

Inference-Time Scaling for Flow Models via Stochastic Generation and Rollover Budget Forcing
Authors:Jaihoon Kim, Taehoon Yoon, Jisung Hwang, Minhyuk Sung
We propose an inference-time scaling approach for pretrained flow models. Recently, inference-time scaling has gained significant attention in LLMs and diffusion models, improving sample quality or better aligning outputs with user preferences by leveraging additional computation. For diffusion models, particle sampling has allowed more efficient scaling due to the stochasticity at intermediate denoising steps. On the contrary, while flow models have gained popularity as an alternative to diffusion models–offering faster generation and high-quality outputs in state-of-the-art image and video generative models–efficient inference-time scaling methods used for diffusion models cannot be directly applied due to their deterministic generative process. To enable efficient inference-time scaling for flow models, we propose three key ideas: 1) SDE-based generation, enabling particle sampling in flow models, 2) Interpolant conversion, broadening the search space and enhancing sample diversity, and 3) Rollover Budget Forcing (RBF), an adaptive allocation of computational resources across timesteps to maximize budget utilization. Our experiments show that SDE-based generation, particularly variance-preserving (VP) interpolant-based generation, improves the performance of particle sampling methods for inference-time scaling in flow models. Additionally, we demonstrate that RBF with VP-SDE achieves the best performance, outperforming all previous inference-time scaling approaches.
我们为预训练的流模型提出了一种推理时间尺度方法。最近,推理时间尺度在大型语言模型和扩散模型中引起了广泛关注,通过利用额外的计算来提高样本质量或更好地使输出与用户偏好对齐。对于扩散模型,由于中间去噪步骤的随机性,粒子采样允许更有效的尺度扩展。相反,虽然流模型作为扩散模型的替代品而广受欢迎,提供了更快的生成速度和高质量输出,在先进的图像和视频生成模型中表现出色,但用于扩散模型的有效推理时间尺度方法不能直接应用于流模型,因为它们具有确定的生成过程。为了实现流模型的推理时间尺度的高效扩展,我们提出了三个关键想法:1)基于SDE的生成,使流模型能够进行粒子采样;2)插值转换,扩大搜索空间并增强样本多样性;3)滚动预算强制(RBF),自适应地在时间步长之间分配计算资源,以最大化预算利用。我们的实验表明,基于SDE的生成,特别是基于方差保持(VP)插值的生成,改进了流模型中推理时间尺度的粒子采样的性能。此外,我们还证明了VP-SDE与RBF相结合的方法取得了最佳性能,优于所有先前的推理时间尺度方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://flow-inference-time-scaling.github.io/
Summary
针对预训练的流程模型,我们提出了一种推理时间缩放方法。通过引入基于SDE的生成方法、插值转换和滚存预算强制(RBF)等技术,实现了流程模型的推理时间高效缩放。实验表明,VP插值基生成和RBF技术能够显著提高粒子采样方法在流程模型推理时间缩放中的性能,并优于以前的推理时间缩放方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了针对预训练流程模型的推理时间缩放方法。
- 利用SDE(随机微分方程)基础生成方法,使流程模型能够实现粒子采样。
- 通过插值转换技术拓宽搜索空间,提高样本多样性。
- 介绍了一种名为滚存预算强制(RBF)的技术,可自适应分配计算资源以最大化预算利用。
- VP插值基生成与RBF技术结合使用在流程模型推理时间缩放中表现出最佳性能。
- 该方法显著提高了流程模型的粒子采样方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

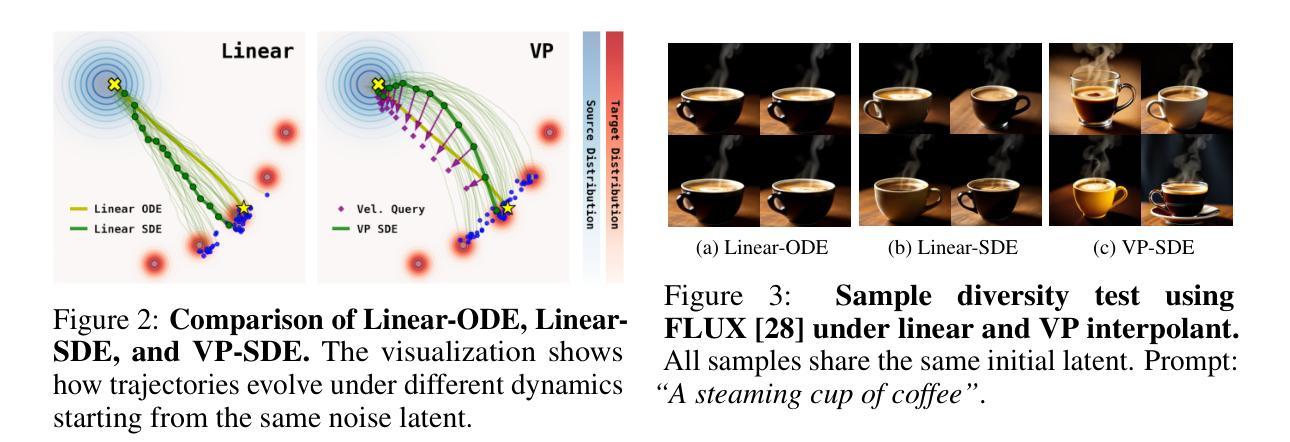
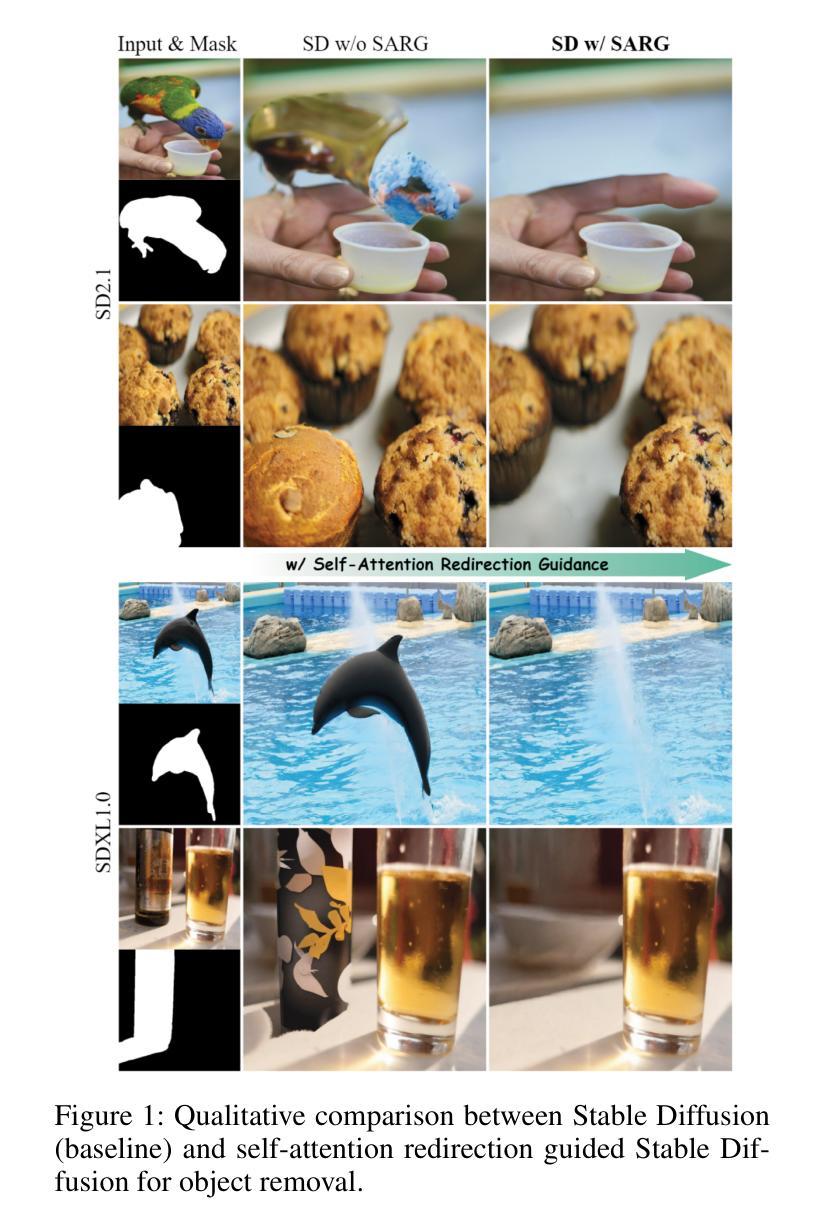
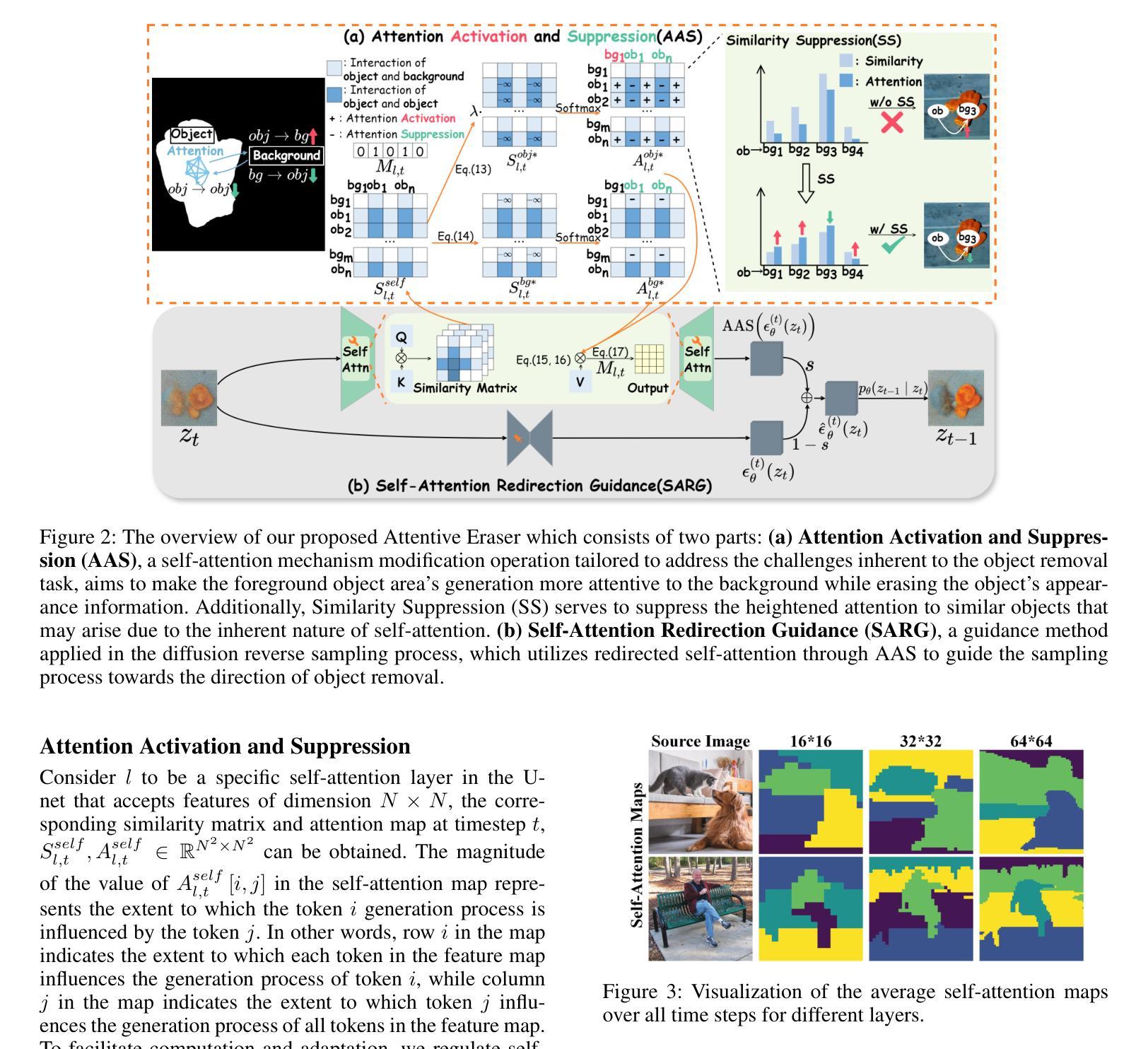
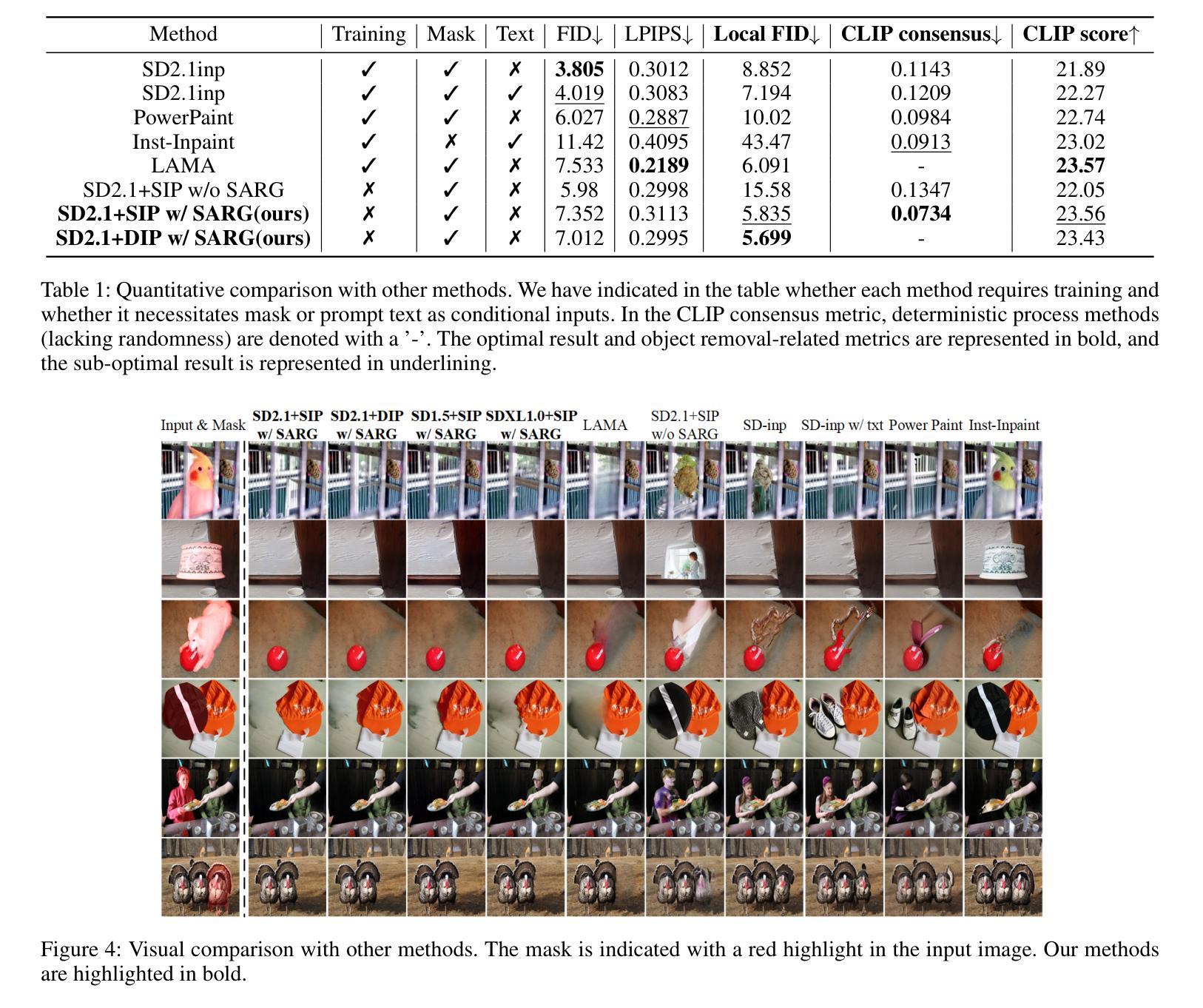
Attentive Eraser: Unleashing Diffusion Model’s Object Removal Potential via Self-Attention Redirection Guidance
Authors:Wenhao Sun, Benlei Cui, Xue-Mei Dong, Jingqun Tang, Yi Liu
Recently, diffusion models have emerged as promising newcomers in the field of generative models, shining brightly in image generation. However, when employed for object removal tasks, they still encounter issues such as generating random artifacts and the incapacity to repaint foreground object areas with appropriate content after removal. To tackle these problems, we propose Attentive Eraser, a tuning-free method to empower pre-trained diffusion models for stable and effective object removal. Firstly, in light of the observation that the self-attention maps influence the structure and shape details of the generated images, we propose Attention Activation and Suppression (ASS), which re-engineers the self-attention mechanism within the pre-trained diffusion models based on the given mask, thereby prioritizing the background over the foreground object during the reverse generation process. Moreover, we introduce Self-Attention Redirection Guidance (SARG), which utilizes the self-attention redirected by ASS to guide the generation process, effectively removing foreground objects within the mask while simultaneously generating content that is both plausible and coherent. Experiments demonstrate the stability and effectiveness of Attentive Eraser in object removal across a variety of pre-trained diffusion models, outperforming even training-based methods. Furthermore, Attentive Eraser can be implemented in various diffusion model architectures and checkpoints, enabling excellent scalability. Code is available at https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser.
近期,扩散模型作为生成模型领域的新晋热门,在图像生成方面表现出色。然而,当应用于目标移除任务时,它们仍然面临一些问题,例如产生随机伪影以及在移除后无法重新绘制前景对象区域以填充适当内容。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了“注意力擦除器”(Attentive Eraser),这是一种无需调整的方法,可增强预训练的扩散模型,以实现稳定有效的目标移除。首先,基于观察到自注意力图影响生成图像的结构和形状细节,我们提出了注意力激活和抑制(ASS),该方法根据给定的掩膜重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自注意力机制,从而在反向生成过程中优先处理背景而非前景目标。此外,我们引入了自注意力重定向指导(SARG),它利用ASS引导的自注意力来指导生成过程,从而在掩膜内有效地移除前景对象,同时生成既合理又连贯的内容。实验表明,Attentive Eraser在不同预训练的扩散模型中的目标移除表现稳定且有效,甚至超越了基于训练的方法。此外,Attentive Eraser可在各种扩散模型架构和检查点中实现,展现出卓越的可扩展性。代码可访问https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025(Oral)
Summary
扩散模型在新兴的生成模型领域展现出潜力,尤其在图像生成方面。但在对象移除任务中仍存在问题,如生成随机伪影和在移除前景对象后无法重新绘制适当内容。为此,提出无需调整的“Attentive Eraser”方法,使预训练的扩散模型能够进行稳定有效的对象移除。通过重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自我关注机制,优先处理背景而非前景对象,同时引入自我关注重定向指导(SARG),有效移除前景对象并生成合理连贯的内容。该方法在多种预训练扩散模型中表现稳定有效,超越基于训练的方法。此外,Attentive Eraser可在各种扩散模型架构和检查点实施,具有良好的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成模型领域有潜力,尤其在图像生成方面。
- 在对象移除任务中,扩散模型面临生成随机伪影和无法重新绘制内容的问题。
- 提出“Attentive Eraser”方法,使预训练的扩散模型能进行稳定有效的对象移除。
- 通过重新设计自我关注机制,优先处理背景,引入Attention Activation and Suppression(ASS)。
- 引入Self-Attention Redirection Guidance(SARG),有效移除前景对象并生成合理内容。
- Attentive Eraser在多种预训练扩散模型中表现优异,超越基于训练的方法。
点此查看论文截图


Diff-Def: Diffusion-Generated Deformation Fields for Conditional Atlases
Authors:Sophie Starck, Vasiliki Sideri-Lampretsa, Bernhard Kainz, Martin J. Menten, Tamara T. Mueller, Daniel Rueckert
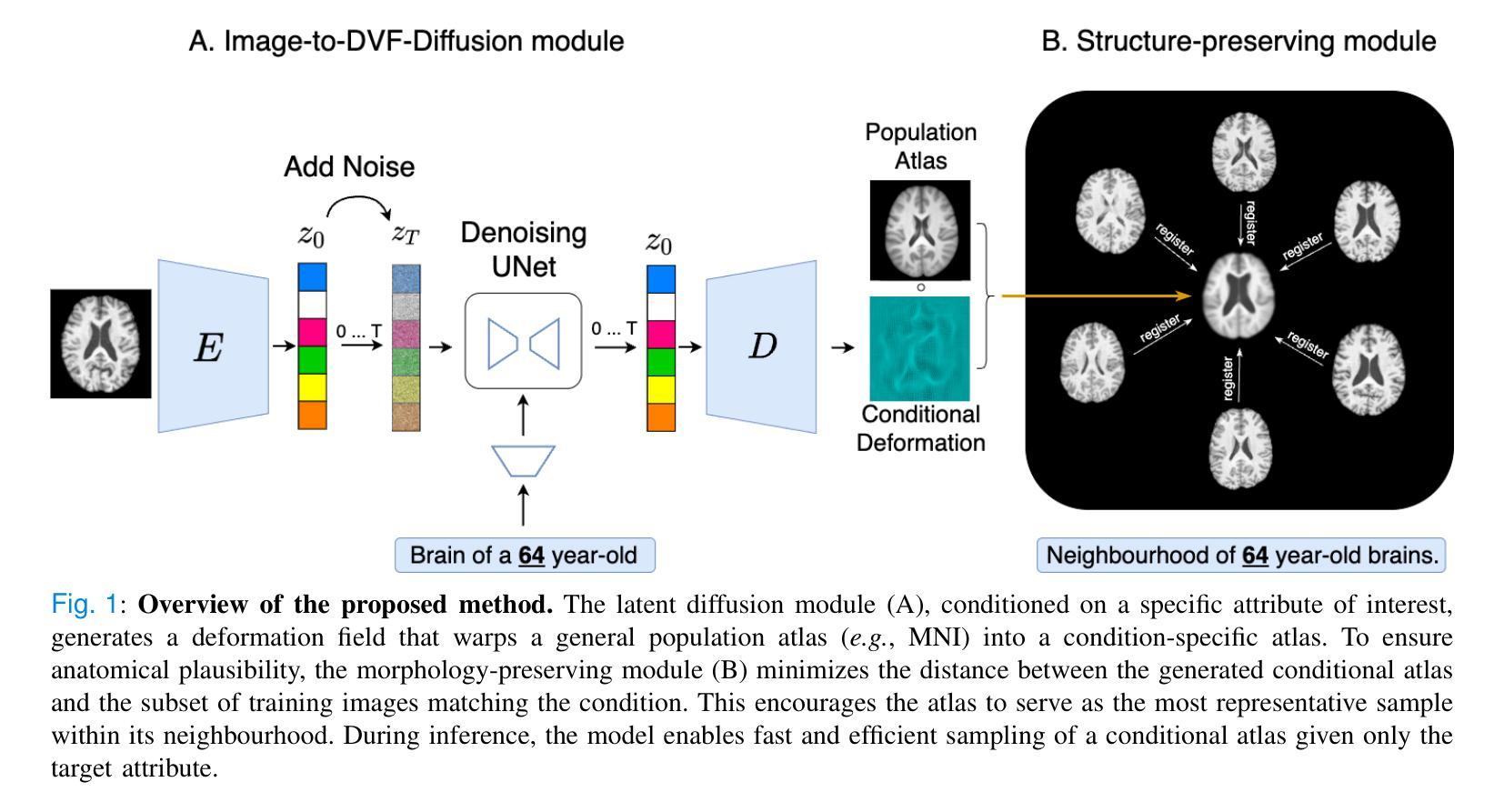
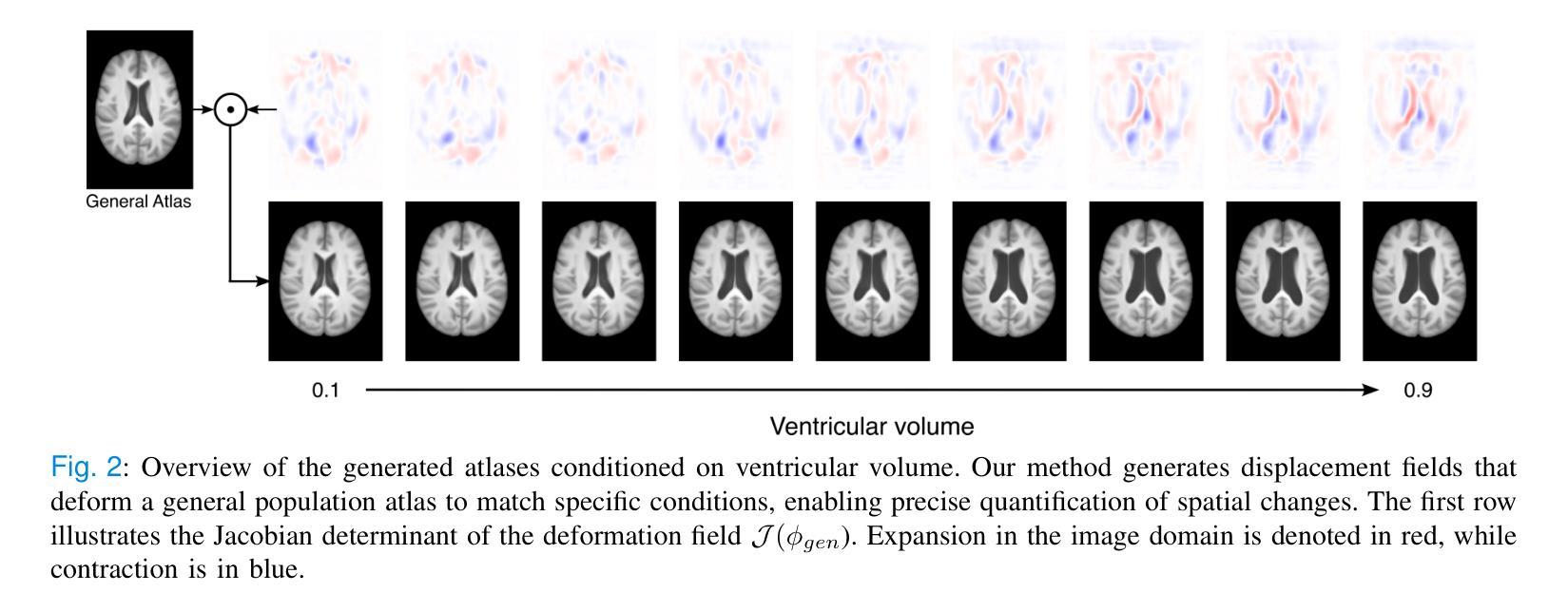
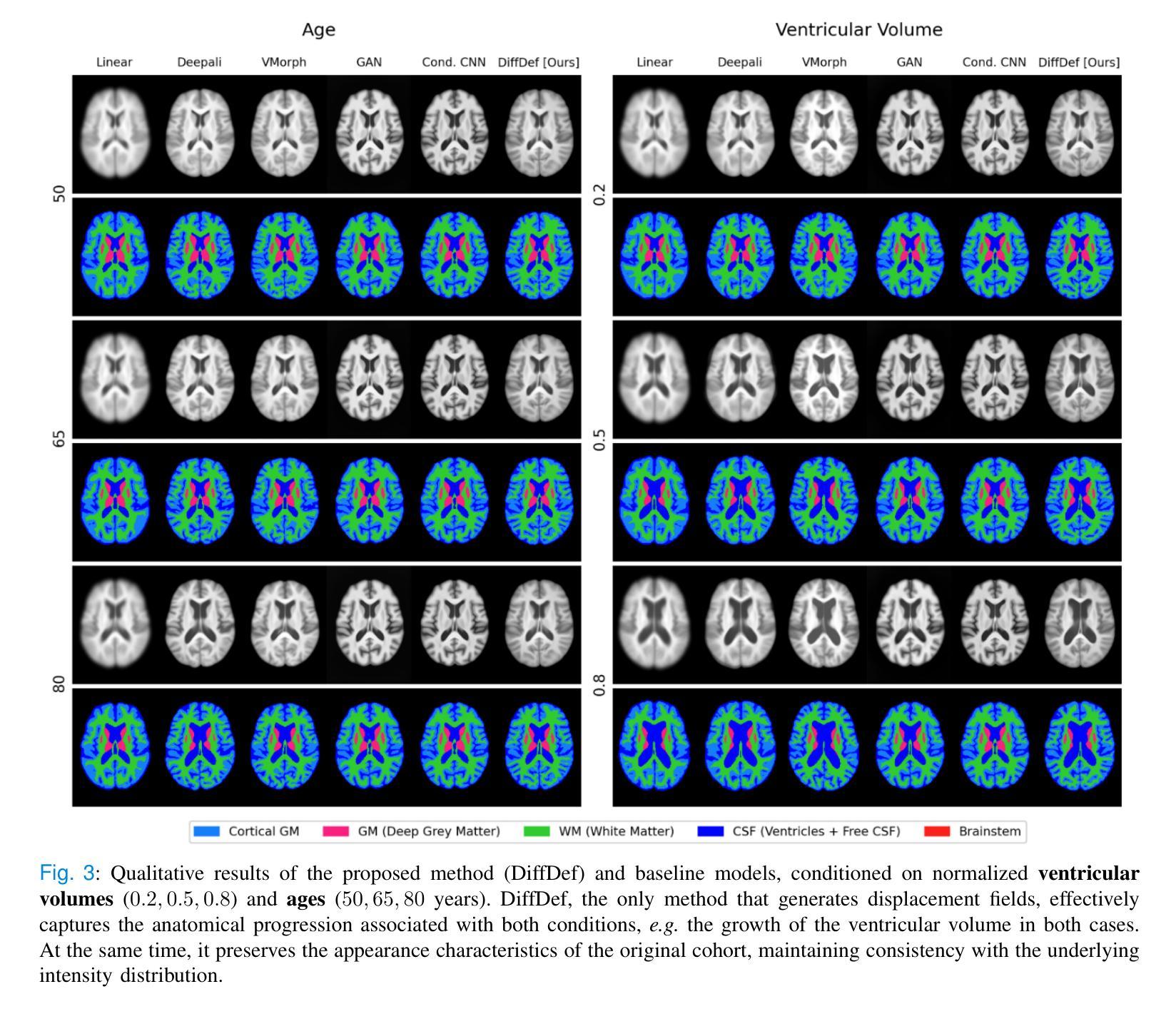
Anatomical atlases are widely used for population studies and analysis. Conditional atlases target a specific sub-population defined via certain conditions, such as demographics or pathologies, and allow for the investigation of fine-grained anatomical differences like morphological changes associated with ageing or disease. Existing approaches use either registration-based methods that are often unable to handle large anatomical variations or generative adversarial models, which are challenging to train since they can suffer from training instabilities. Instead of generating atlases directly in as intensities, we propose using latent diffusion models to generate deformation fields, which transform a general population atlas into one representing a specific sub-population. Our approach ensures structural integrity, enhances interpretability and avoids hallucinations that may arise during direct image synthesis by generating this deformation field and regularising it using a neighbourhood of images. We compare our method to several state-of-the-art atlas generation methods using brain MR images from the UK Biobank. Our method generates highly realistic atlases with smooth transformations and high anatomical fidelity, outperforming existing baselines. We demonstrate the quality of these atlases through comprehensive evaluations, including quantitative metrics for anatomical accuracy, perceptual similarity, and qualitative analyses displaying the consistency and realism of the generated atlases.
解剖图谱在人群研究和分析中得到了广泛应用。条件图谱针对通过某些条件(如人口统计学或病理学)定义的特定亚群体,并允许调查与衰老或疾病相关的形态学变化的细微解剖差异。现有方法使用基于注册的方法,这些方法通常无法处理大的解剖变异,或者使用生成对抗模型,由于训练不稳定性的挑战,这些模型的训练是一个挑战。我们并不直接在强度上生成图谱,而是建议使用潜在扩散模型来生成变形场,该变形场将一个通用人群图谱转变为代表特定亚人群的图谱。我们的方法确保了结构完整性,提高了可解释性,并且通过生成这种变形场并使用图像邻域进行正则化,避免了在直接图像合成过程中可能出现的幻觉。我们使用英国生物银行的大脑MRI图像,将我们的方法与几种最先进的图谱生成方法进行比较。我们的方法生成了高度逼真的图谱,具有平滑的变换和高度的解剖保真度,超过了现有的基线。我们通过包括解剖准确性的定量指标、感知相似性以及显示生成图谱的一致性和现实性的定性分析在内的全面评估,证明了这些图谱的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于潜在扩散模型的方法,用于生成表示特定亚人群的海图变形场。该方法通过将通用人群海图转化为特定亚人群海图,确保了结构完整性,提高了可解释性,避免了直接图像合成中可能出现的幻觉。通过对比使用英国生物银行大脑MRI图像的其他先进海图生成方法,本研究的方法生成的海图具有高度真实性和平滑转换以及高解剖学保真度,优于现有基线。通过综合评估证明了这些海图的质量,包括定量评估解剖精度、感知相似性以及定性分析显示生成海图的一致性和逼真性。
Key Takeaways
- 条件性图谱可以针对具有特定条件的亚人群进行精细的解剖学差异研究,如年龄增长或疾病相关的形态变化。
- 现有方法包括基于注册的方法和基于生成对抗模型的方法,分别存在处理大解剖变异和训练不稳定的问题。
- 本研究采用潜在扩散模型生成变形场,以转化通用人群图谱为特定亚人群图谱,增强了结构完整性、可解释性并避免了图像合成中的幻觉问题。
- 方法在UK Biobank的脑部MRI图像上进行了验证,生成的海图具有高度真实性和平滑转换以及高解剖学保真度。
- 评估包括定量评估解剖精度、感知相似性以及定性分析显示生成图谱的一致性和逼真性。
- 与其他先进方法相比,该方法表现优越。
点此查看论文截图