⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
Multimodal LLM-Guided Semantic Correction in Text-to-Image Diffusion
Authors:Zheqi Lv, Junhao Chen, Qi Tian, Keting Yin, Shengyu Zhang, Fei Wu
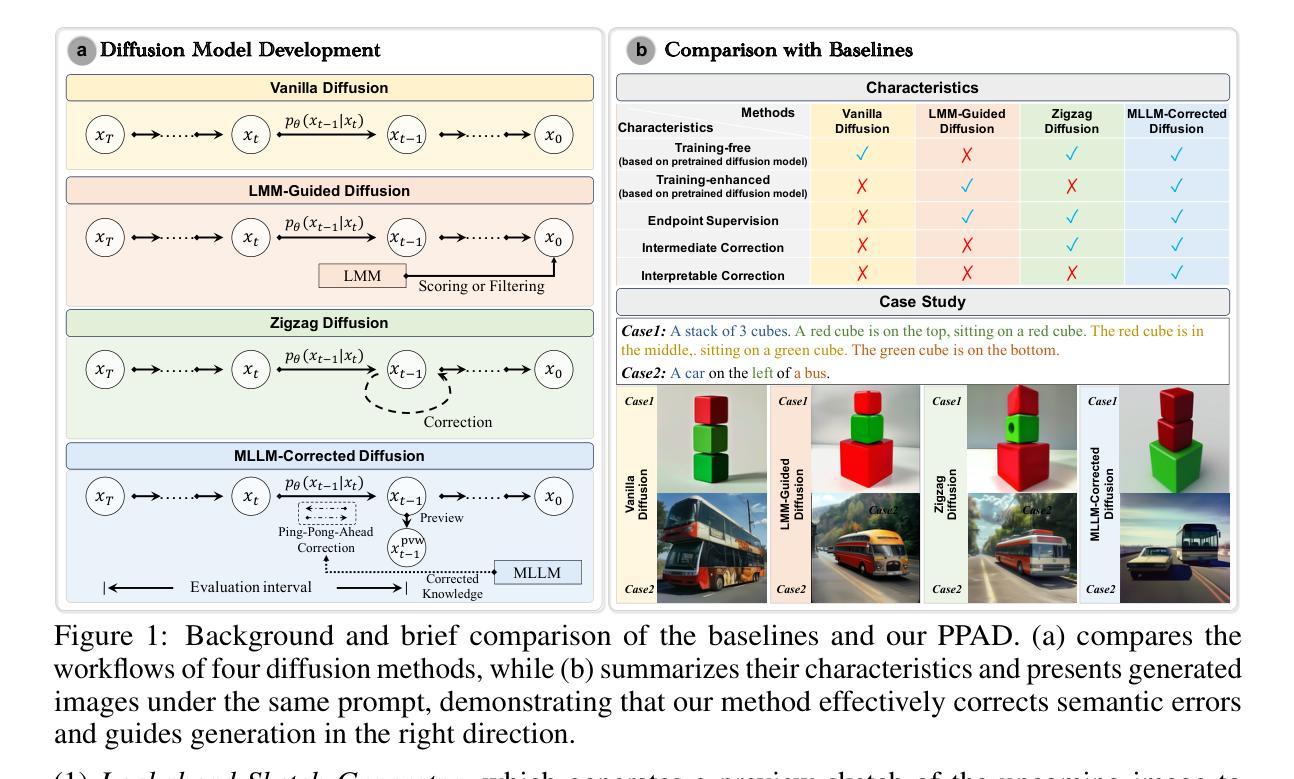
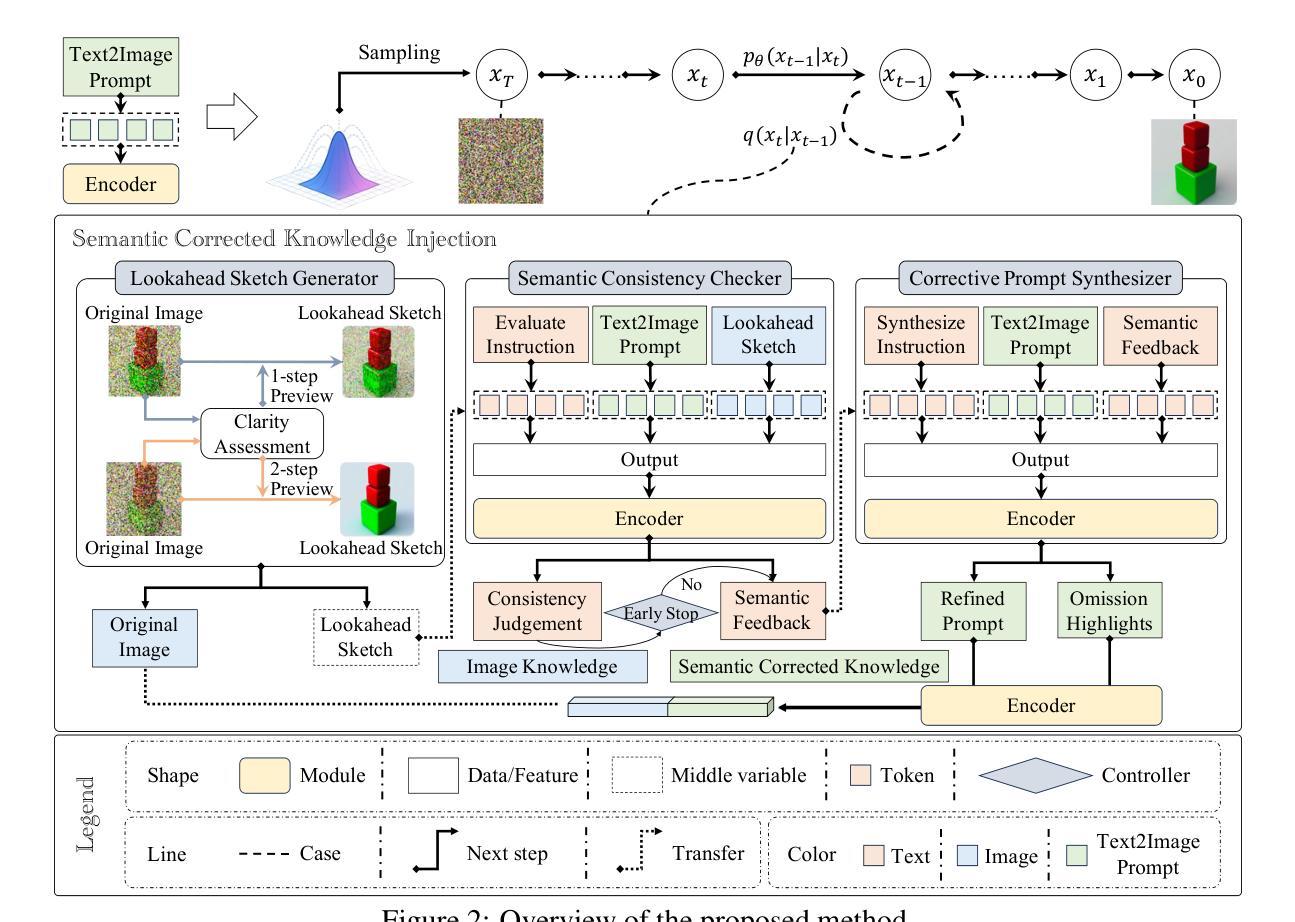
Diffusion models have become the mainstream architecture for text-to-image generation, achieving remarkable progress in visual quality and prompt controllability. However, current inference pipelines generally lack interpretable semantic supervision and correction mechanisms throughout the denoising process. Most existing approaches rely solely on post-hoc scoring of the final image, prompt filtering, or heuristic resampling strategies-making them ineffective in providing actionable guidance for correcting the generative trajectory. As a result, models often suffer from object confusion, spatial errors, inaccurate counts, and missing semantic elements, severely compromising prompt-image alignment and image quality. To tackle these challenges, we propose MLLM Semantic-Corrected Ping-Pong-Ahead Diffusion (PPAD), a novel framework that, for the first time, introduces a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) as a semantic observer during inference. PPAD performs real-time analysis on intermediate generations, identifies latent semantic inconsistencies, and translates feedback into controllable signals that actively guide the remaining denoising steps. The framework supports both inference-only and training-enhanced settings, and performs semantic correction at only extremely few diffusion steps, offering strong generality and scalability. Extensive experiments demonstrate PPAD’s significant improvements.
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构,在视觉质量和提示可控性方面取得了显著的进步。然而,当前的推理管道通常在整个去噪过程中缺乏可解释的语义监督和校正机制。大多数现有方法仅依赖于最终图像的后验评分、提示过滤或启发式重采样策略,无法为校正生成轨迹提供有效的指导。因此,模型经常遭受目标混淆、空间错误、计数不准确和丢失语义元素等问题的困扰,严重损害了提示与图像的对应和图像质量。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MLLM语义校正乒乓前扩散(PPAD)这一新颖框架,它首次在推理过程中引入了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为语义观察者。PPAD对中间生成物进行实时分析,识别潜在的语义不一致,并将反馈转化为可控信号,主动引导剩余的去噪步骤。该框架支持仅推理和训练增强两种设置,仅在极少数的扩散步骤中进行语义校正,表现出强大的通用性和可扩展性。大量实验证明了PPAD的显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构,取得了令人瞩目的视觉质量和提示可控性进步。然而,当前推理流程通常缺乏可解释的语义监督和修正机制。针对此问题,我们提出MLLM语义校正乒乓前扩散(PPAD)框架,首次引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为语义观察者进行实时分析。PPAD框架在中间生成阶段进行实时分析,识别潜在语义不一致,将反馈转化为可控信号,主动引导剩余的去噪步骤。该框架支持仅推理和训练增强设置,在极少扩散步骤中进行语义校正,表现出强大的通用性和可扩展性。实验证明PPAD的显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流架构。
- 当前推理流程缺乏语义监督和修正机制。
- 提出MLLM语义校正乒乓前扩散(PPAD)框架来解决上述问题。
- PPAD引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)作为语义观察者。
- PPAD框架在中间生成阶段进行实时分析,识别潜在语义不一致。
- PPAD将反馈转化为可控信号,主动引导剩余的去噪步骤。
点此查看论文截图

MT$^{3}$: Scaling MLLM-based Text Image Machine Translation via Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhaopeng Feng, Yupu Liang, Shaosheng Cao, Jiayuan Su, Jiahan Ren, Zhe Xu, Yao Hu, Wenxuan Huang, Jian Wu, Zuozhu Liu
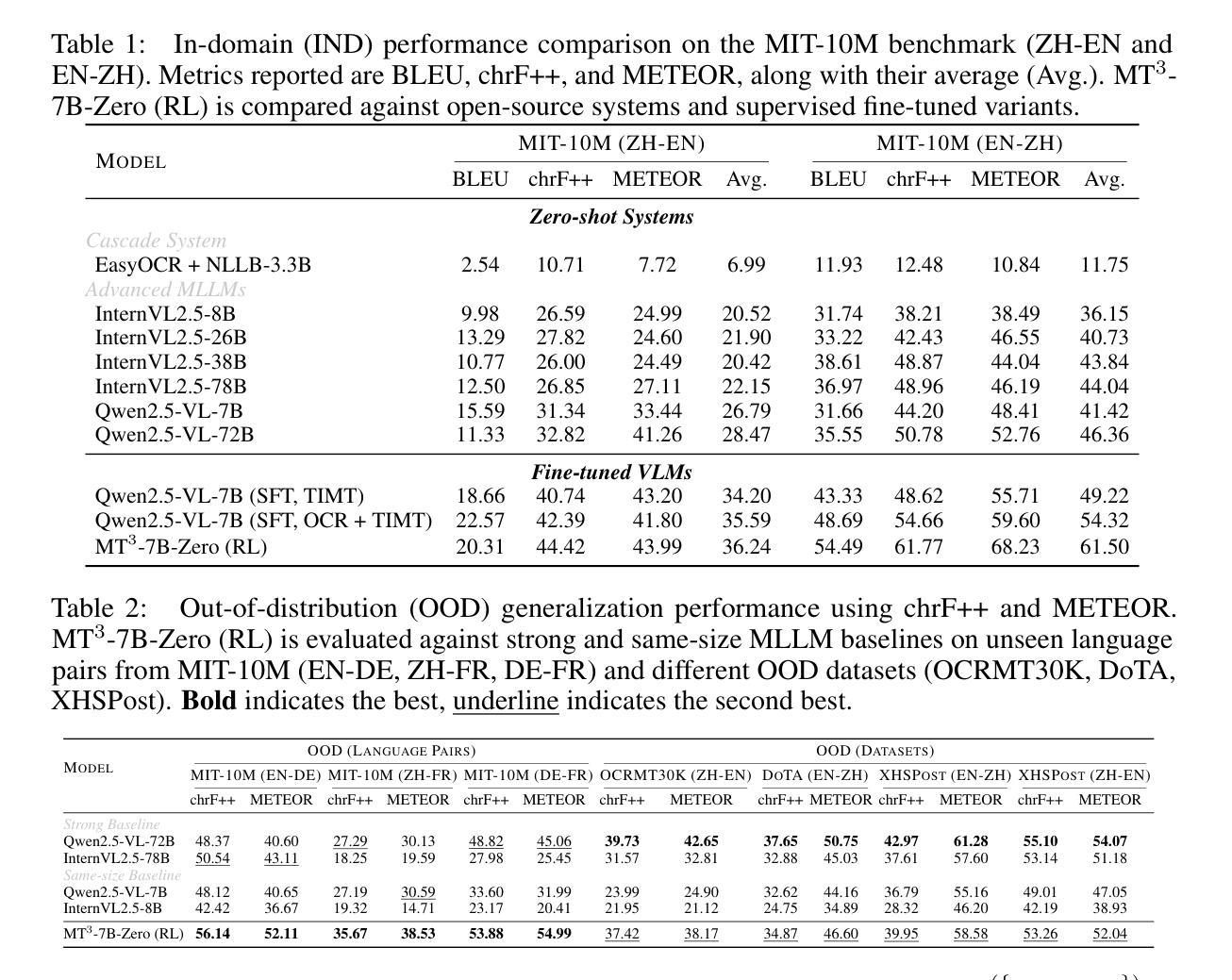
Text Image Machine Translation (TIMT)-the task of translating textual content embedded in images-is critical for applications in accessibility, cross-lingual information access, and real-world document understanding. However, TIMT remains a complex challenge due to the need for accurate optical character recognition (OCR), robust visual-text reasoning, and high-quality translation, often requiring cascading multi-stage pipelines. Recent advances in large-scale Reinforcement Learning (RL) have improved reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), but their application to end-to-end TIMT is still underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce MT$^{3}$, the first framework to apply Multi-Task RL to MLLMs for end-to-end TIMT. MT$^{3}$ adopts a multi-task optimization paradigm targeting three key sub-skills: text recognition, context-aware reasoning, and translation. It is trained using a novel multi-mixed reward mechanism that adapts rule-based RL strategies to TIMT’s intricacies, offering fine-grained, non-binary feedback across tasks. Furthermore, to facilitate the evaluation of TIMT in authentic cross-cultural and real-world social media contexts, we introduced XHSPost, the first social media TIMT benchmark. Our MT$^{3}$-7B-Zero achieves state-of-the-art results on the latest in-domain MIT-10M benchmark, outperforming strong baselines such as Qwen2.5-VL-72B and InternVL2.5-78B by notable margins across multiple metrics. Additionally, the model shows strong generalization to out-of-distribution language pairs and datasets. In-depth analyses reveal how multi-task synergy, reinforcement learning initialization, curriculum design, and reward formulation contribute to advancing MLLM-driven TIMT.
文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)——将嵌入图像中的文本内容进行翻译的任务——对于可访问性、跨语言信息访问和现实世界文档理解等应用至关重要。然而,由于需要准确的光学字符识别(OCR)、稳健的视觉文本推理和高品质翻译,通常需要使用级联的多阶段流水线,因此TIMT仍然是一个复杂的挑战。最近大规模强化学习(RL)的进展改善了大型语言模型(LLM)和多模态LLM(MLLM)中的推理能力,但其在端到端TIMT中的应用仍然被探索得很少。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了MT$^{3}$,这是第一个将多任务RL应用于MLLM进行端到端TIMT的框架。MT$^{3}$采用了一种多任务优化范式,针对三个关键子技能:文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译。它使用一种新型的多混合奖励机制进行训练,该机制适应了基于规则的RL策略到TIMT的复杂性,提供跨任务的精细粒度、非二元反馈。此外,为了促进在真实跨文化和现实世界社交媒体背景下对TIMT的评估,我们推出了XHSPost,这是第一个社交媒体TIMT基准测试。我们的MT$^{3}$-7B-Zero在最新的领域专项MIT-10M基准测试中取得了最新结果,相较于强基线Qwen2.5-VL-72B和InternVL2.5-78B等多指标有明显优势。此外,该模型在跨分布的语言对和数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。深入分析揭示了多任务协同、强化学习初始化、课程设计以及奖励公式等如何为MLLM驱动的TIMT做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)是访问性、跨语言信息访问、以及真实世界文档理解等应用中的关键任务。尽管需要准确的光学字符识别(OCR)、稳健的视觉文本推理和高品质翻译等复杂挑战,但大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLMs(MLLMs)中的增强学习(RL)最新进展已改善了推理能力。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了MT3,这是第一个将多任务RL应用于MLLMs进行端到端TIMT的框架。MT3采用针对三项关键技能的多任务优化范式:文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译。它使用一种新型的多混合奖励机制进行训练,该机制适应基于规则的RL策略,为TIMT的复杂性提供跨任务的精细粒度非二元反馈。此外,为了评估真实跨文化和真实世界社交媒体环境中的TIMT,我们推出了XHSPost,即首个社交媒体TIMT基准测试。我们的MT3-7B-Zero在最新的MIT-10M基准测试中取得了最新成果,明显优于强基线Qwen2.5-VL-72B和InternVL2.5-78B等多项指标。此外,该模型在跨语言对和数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。深入分析揭示了多任务协同、强化学习初始化、课程设计以及奖励公式等如何推动MLLM驱动的TIMT的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)在访问性、跨语言信息访问和真实世界文档理解等领域具有关键作用。
- TIMT面临准确光学字符识别(OCR)、稳健视觉文本推理和高品质翻译的复杂挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLMs(MLLMs)中的增强学习(RL)最新进展改善了推理能力。
- MT3框架首次将多任务RL应用于MLLMs进行端到端TIMT。
- MT3采用多任务优化范式,针对文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译三项关键技能。
- MT3使用新型多混合奖励机制进行训练,适应基于规则的RL策略,为TIMT的复杂性提供跨任务的反馈。
点此查看论文截图

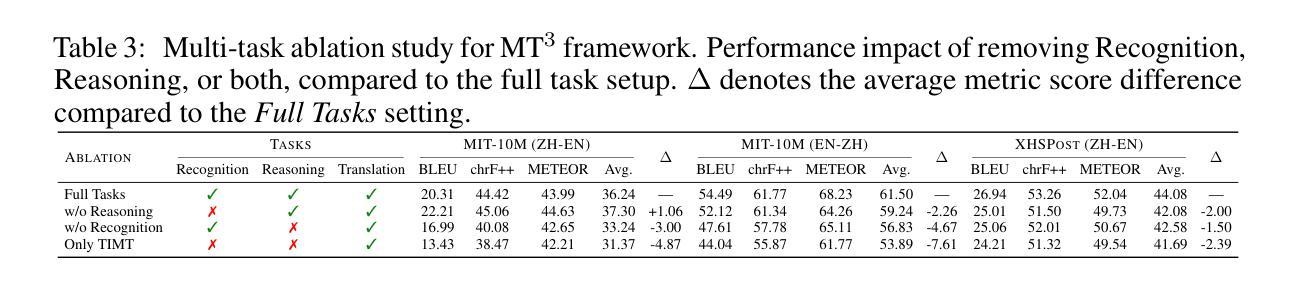
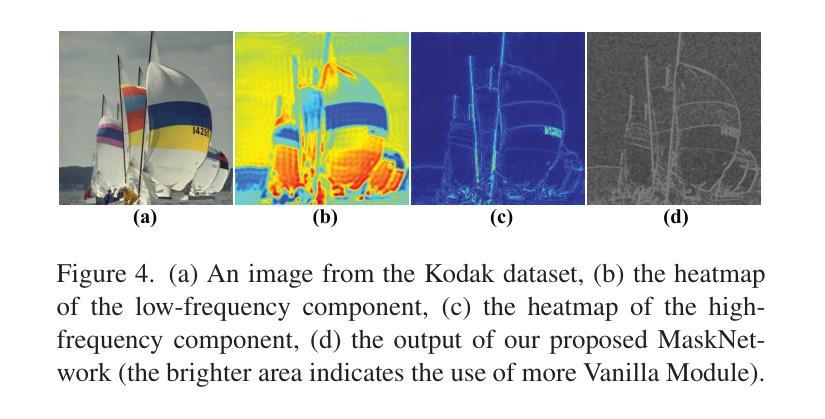
Rotation-Equivariant Self-Supervised Method in Image Denoising
Authors:Hanze Liu, Jiahong Fu, Qi Xie, Deyu Meng
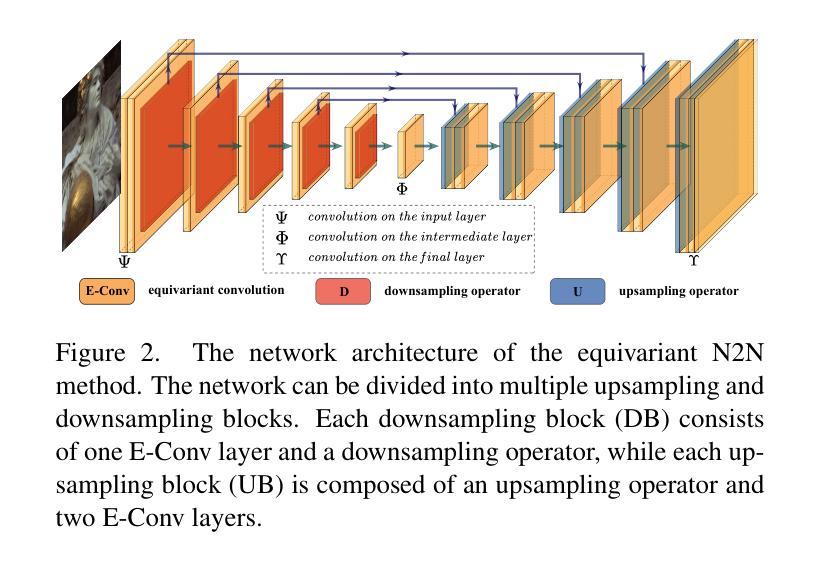
Self-supervised image denoising methods have garnered significant research attention in recent years, for this kind of method reduces the requirement of large training datasets. Compared to supervised methods, self-supervised methods rely more on the prior embedded in deep networks themselves. As a result, most of the self-supervised methods are designed with Convolution Neural Networks (CNNs) architectures, which well capture one of the most important image prior, translation equivariant prior. Inspired by the great success achieved by the introduction of translational equivariance, in this paper, we explore the way to further incorporate another important image prior. Specifically, we first apply high-accuracy rotation equivariant convolution to self-supervised image denoising. Through rigorous theoretical analysis, we have proved that simply replacing all the convolution layers with rotation equivariant convolution layers would modify the network into its rotation equivariant version. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that rotation equivariant image prior is introduced to self-supervised image denoising at the network architecture level with a comprehensive theoretical analysis of equivariance errors, which offers a new perspective to the field of self-supervised image denoising. Moreover, to further improve the performance, we design a new mask mechanism to fusion the output of rotation equivariant network and vanilla CNN-based network, and construct an adaptive rotation equivariant framework. Through extensive experiments on three typical methods, we have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method.
自监督图像去噪方法近年来引起了研究人员的广泛关注,因为这种方法降低了对大规模训练数据集的要求。与监督方法相比,自监督方法更依赖于嵌入到深度网络本身的先验知识。因此,大多数自监督方法都是基于卷积神经网络(CNN)架构设计的,很好地捕获了最重要的图像先验之一,即平移等价先验。受引入平移等价性巨大成功的启发,本文探索了将另一种重要的图像先验结合进来的方法。具体而言,我们首先将高精度旋转等价卷积应用于自监督图像去噪。通过严格的理论分析,我们已经证明,只需用旋转等价卷积层替换所有卷积层,就可以将网络修改为旋转等价版本。据我们所知,这是首次在网络架构层面将旋转等价的图像先验引入到自监督图像去噪中,并对等价性误差进行了全面的理论分析,这为自监督图像去噪领域提供了新的视角。此外,为了进一步提高性能,我们设计了一种新的掩码机制,融合了旋转等价网络与普通CNN基网络的输出,构建了一个自适应的旋转等价框架。通过对三种典型方法的广泛实验,我们验证了所提出方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文探索了将旋转等价图像先验引入自监督图像去噪的方法。通过理论分析和实验验证,证明了用旋转等价卷积替换所有卷积层可以使网络具有旋转等价性,从而提高去噪性能。同时,设计了一种新的融合机制,融合了旋转等价网络和普通CNN网络的输出,构建了一个自适应的旋转等价框架。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督图像去噪方法近年来受到广泛关注,因为它们减少了大规模训练数据集的需求。
- 与监督方法相比,自监督方法更依赖于深度网络中的先验知识。
- 大多数自监督方法使用CNN架构,捕捉图像中重要的平移等价先验。
- 本文首次将旋转等价图像先验引入到自监督图像去噪的网络架构中,并进行全面的理论分析。
- 用高精度的旋转等价卷积替换所有卷积层,可以使网络具有旋转等价性。
- 设计了一种新的融合机制,融合了旋转等价网络和CNN网络的输出,以提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

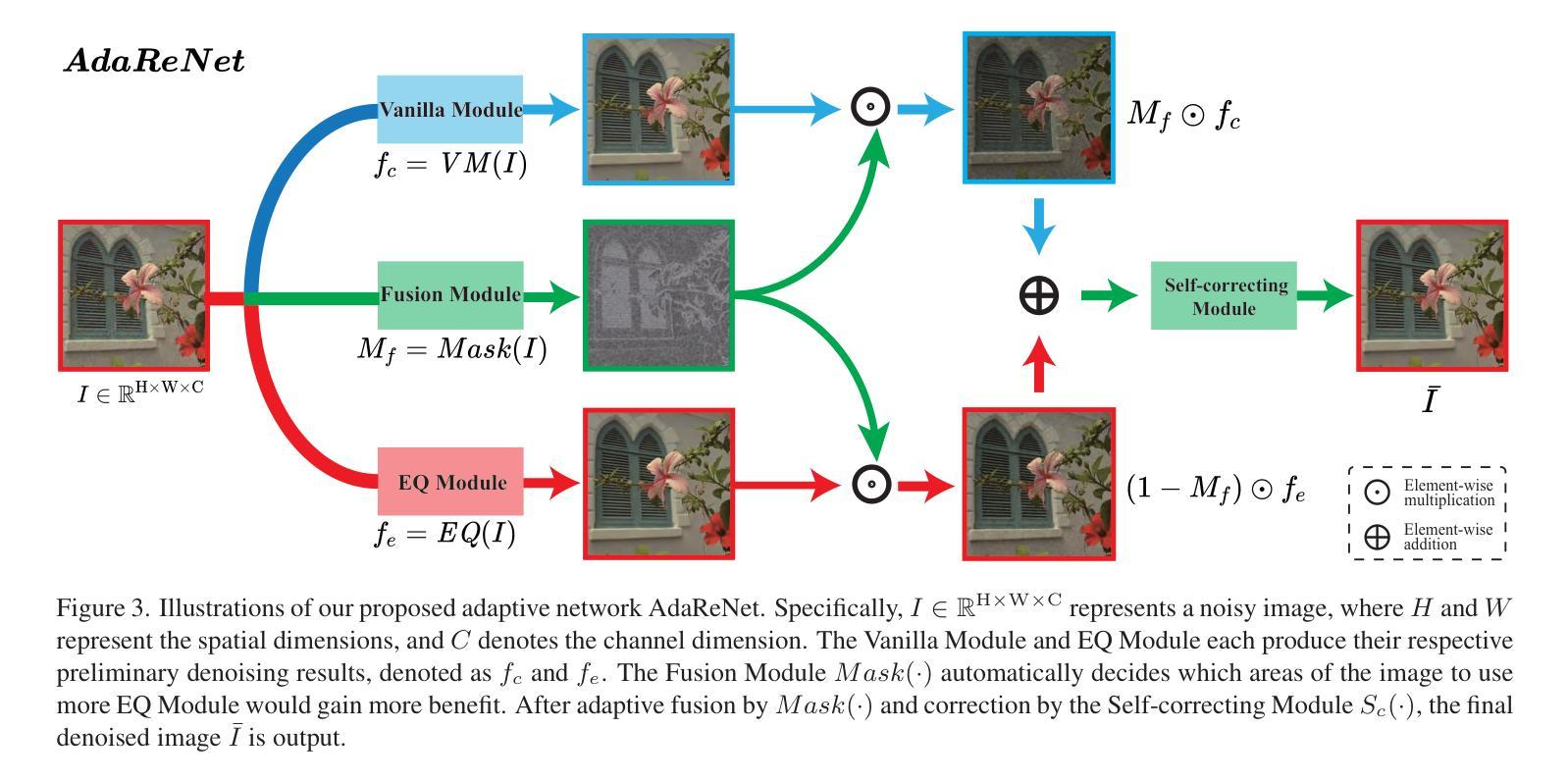

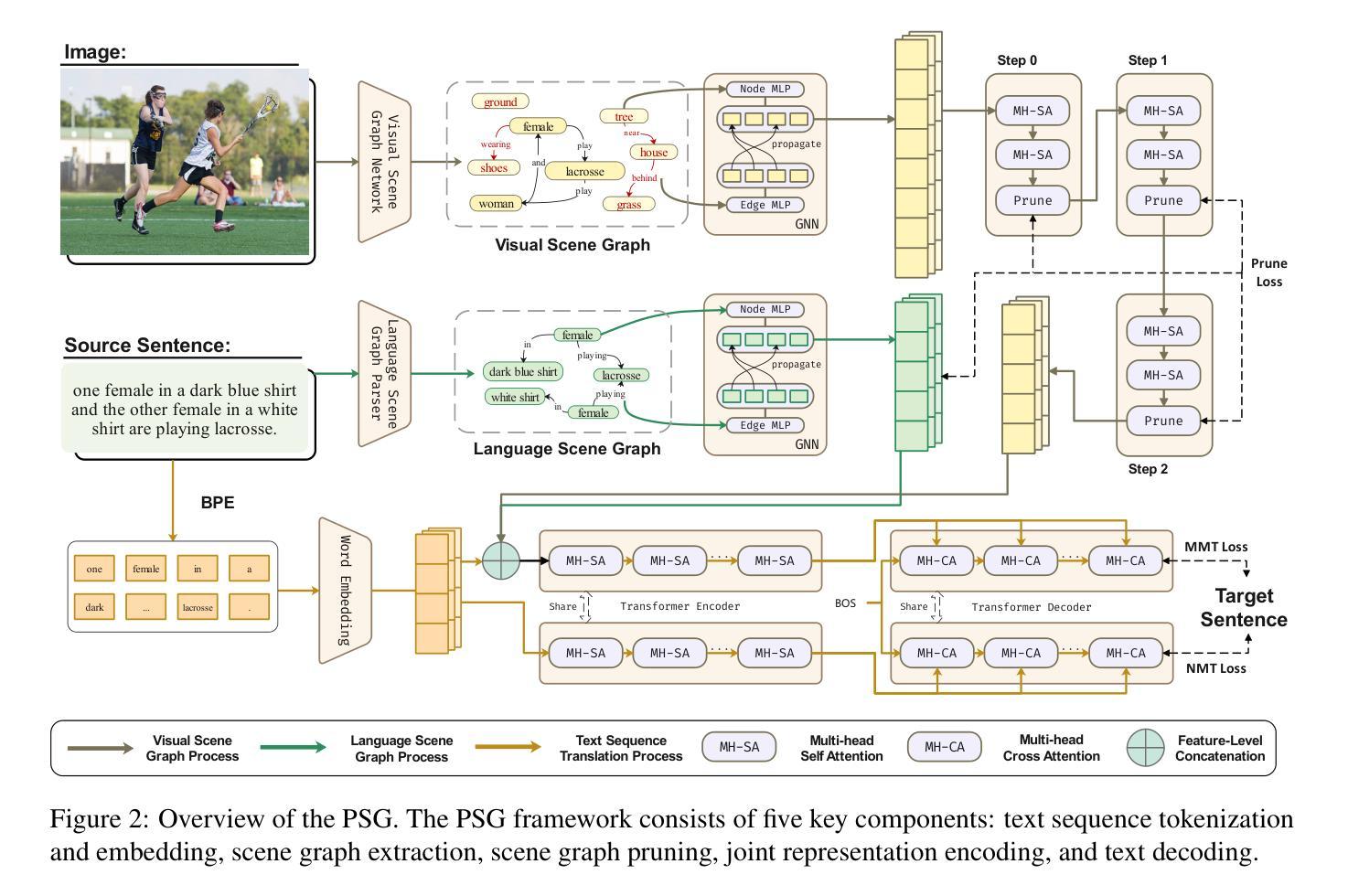
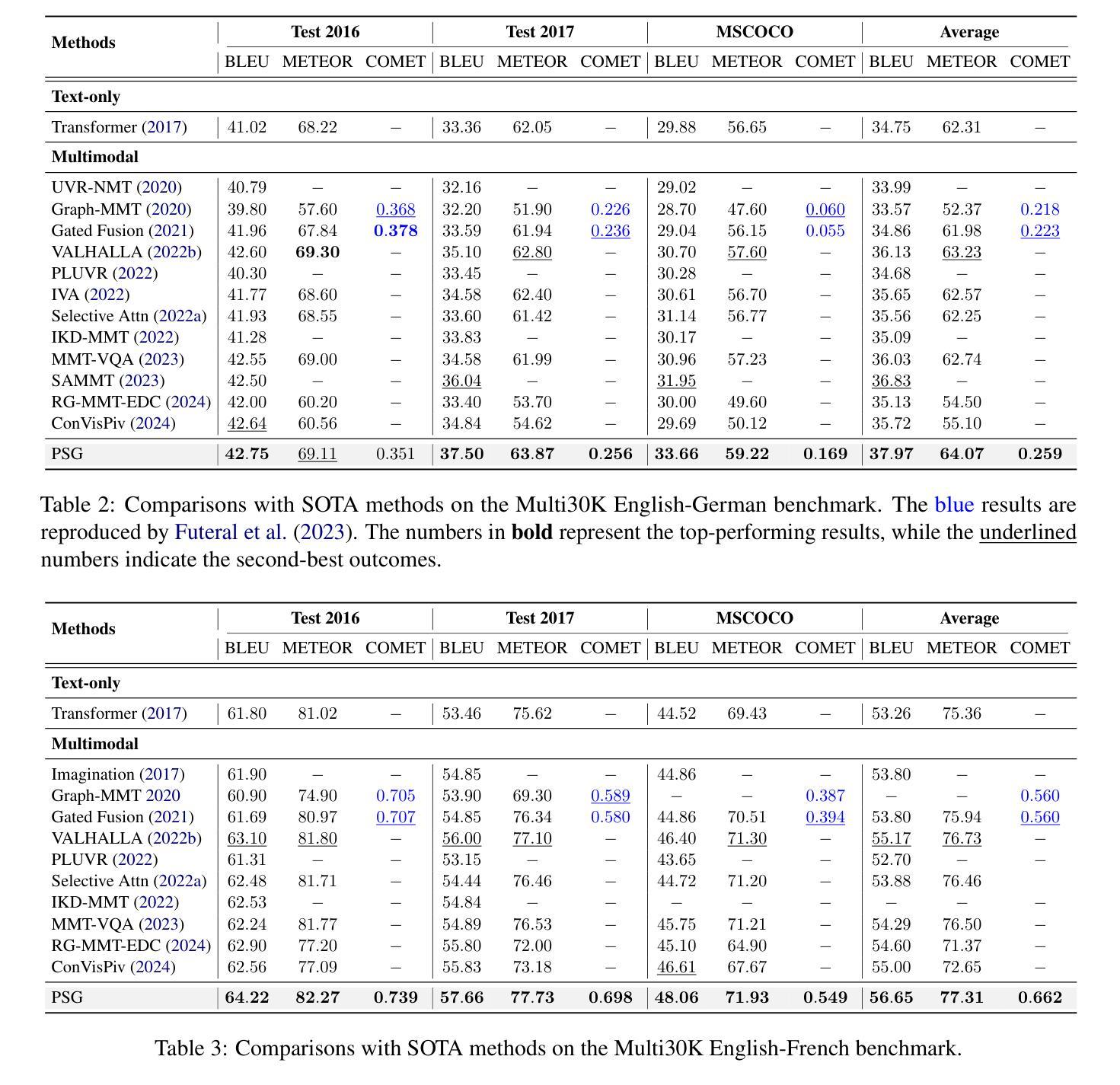
Multimodal Machine Translation with Visual Scene Graph Pruning
Authors:Chenyu Lu, Shiliang Sun, Jing Zhao, Nan Zhang, Tengfei Song, Hao Yang
Multimodal machine translation (MMT) seeks to address the challenges posed by linguistic polysemy and ambiguity in translation tasks by incorporating visual information. A key bottleneck in current MMT research is the effective utilization of visual data. Previous approaches have focused on extracting global or region-level image features and using attention or gating mechanisms for multimodal information fusion. However, these methods have not adequately tackled the issue of visual information redundancy in MMT, nor have they proposed effective solutions. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach–multimodal machine translation with visual Scene Graph Pruning (PSG), which leverages language scene graph information to guide the pruning of redundant nodes in visual scene graphs, thereby reducing noise in downstream translation tasks. Through extensive comparative experiments with state-of-the-art methods and ablation studies, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the PSG model. Our results also highlight the promising potential of visual information pruning in advancing the field of MMT.
多模态机器翻译(MMT)通过融入视觉信息来解决翻译任务中的语言多义性和模糊性所带来的挑战。当前MMT研究的关键瓶颈在于如何有效利用视觉数据。以往的研究主要集中在提取全局或区域级别的图像特征,并使用注意力或门控机制进行多模态信息融合。然而,这些方法并未充分应对MMT中视觉信息冗余的问题,也没有提出有效的解决方案。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法——基于视觉场景图裁剪(PSG)的多模态机器翻译,该方法利用语言场景图信息来指导视觉场景图中冗余节点的裁剪,从而减少对下游翻译任务中的噪声干扰。通过与最新方法的对比实验和消融研究,我们证明了PSG模型的有效性。我们的结果也突出了视觉信息裁剪在推动MMT领域发展的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:多模态机器翻译(MMT)通过结合视觉信息解决语言翻译中的语义多义性和歧义性挑战。当前研究瓶颈在于如何有效利用视觉数据。本文提出一种新方法——基于视觉场景图裁剪的多模态机器翻译(PSG),利用语言场景图信息引导裁剪视觉场景图中的冗余节点,减少下游翻译任务中的噪声。实验证明PSG模型的有效性,并展现出视觉信息裁剪在MMT领域的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态机器翻译(MMT)结合视觉信息解决翻译中的语言挑战。
- 当前MMT研究的瓶颈在于有效地利用视觉数据。
- 以往方法主要提取全局或区域级别的图像特征,使用注意力或门控机制进行多模态信息融合,但未能妥善处理视觉信息冗余问题。
- 本文提出基于视觉场景图裁剪的多模态机器翻译(PSG)新方法,利用语言场景图信息引导裁剪冗余节点,减少翻译任务中的噪声。
- 实验证明PSG模型的有效性。
- PSG模型在减少视觉信息冗余、提高翻译质量方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

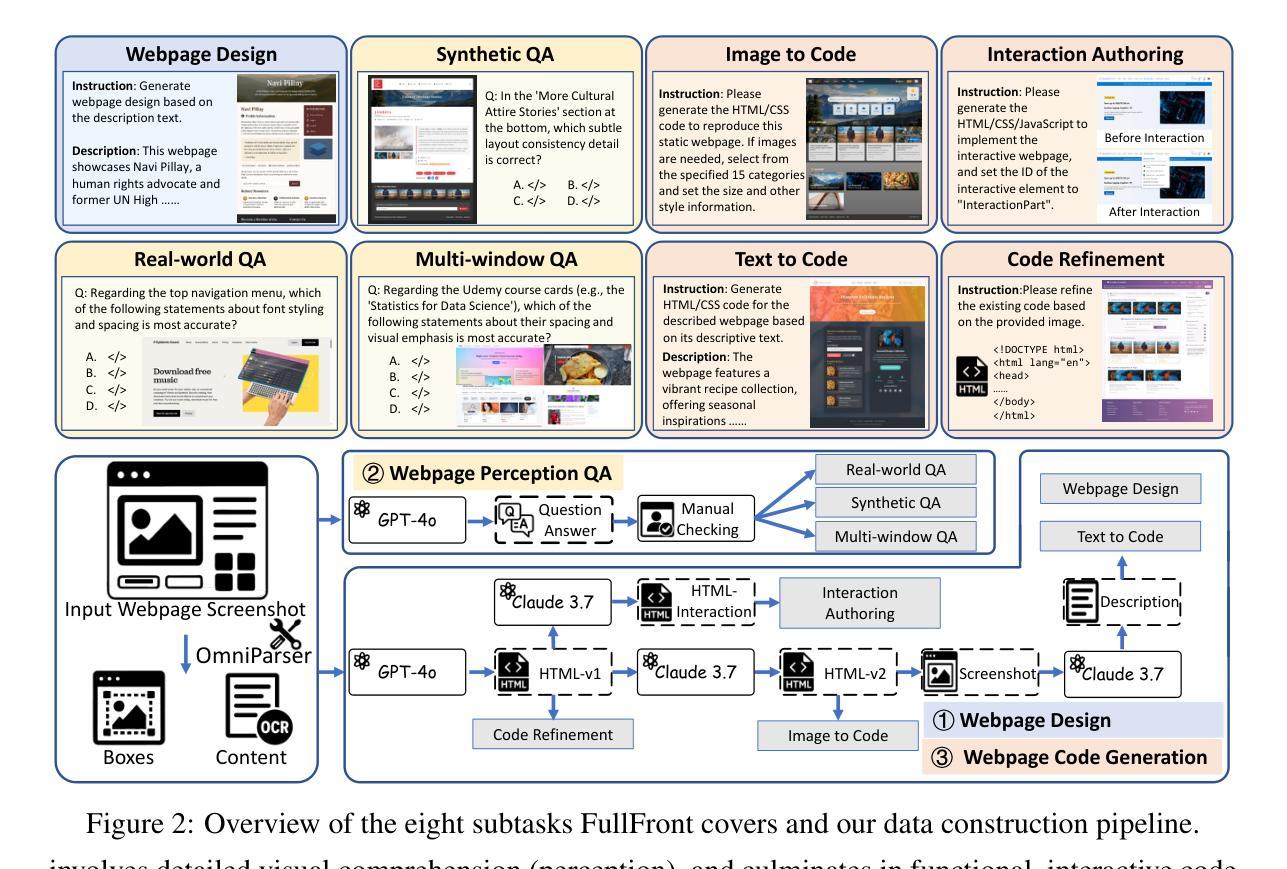
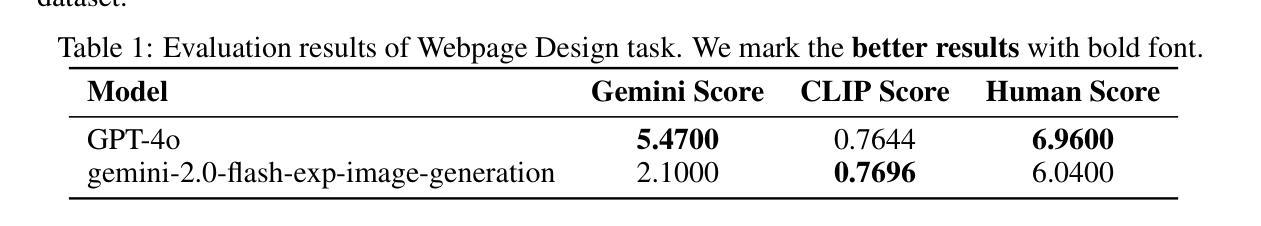
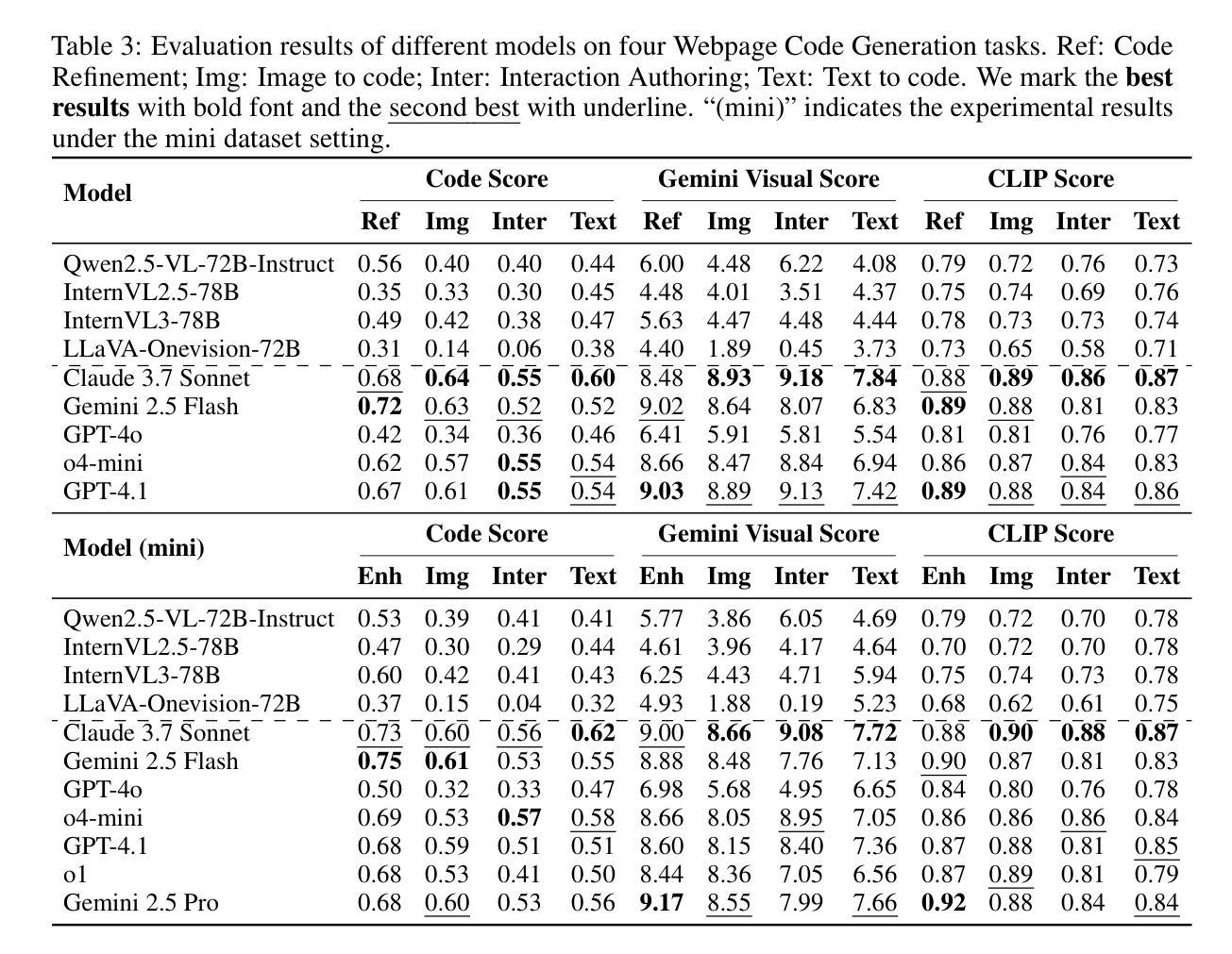
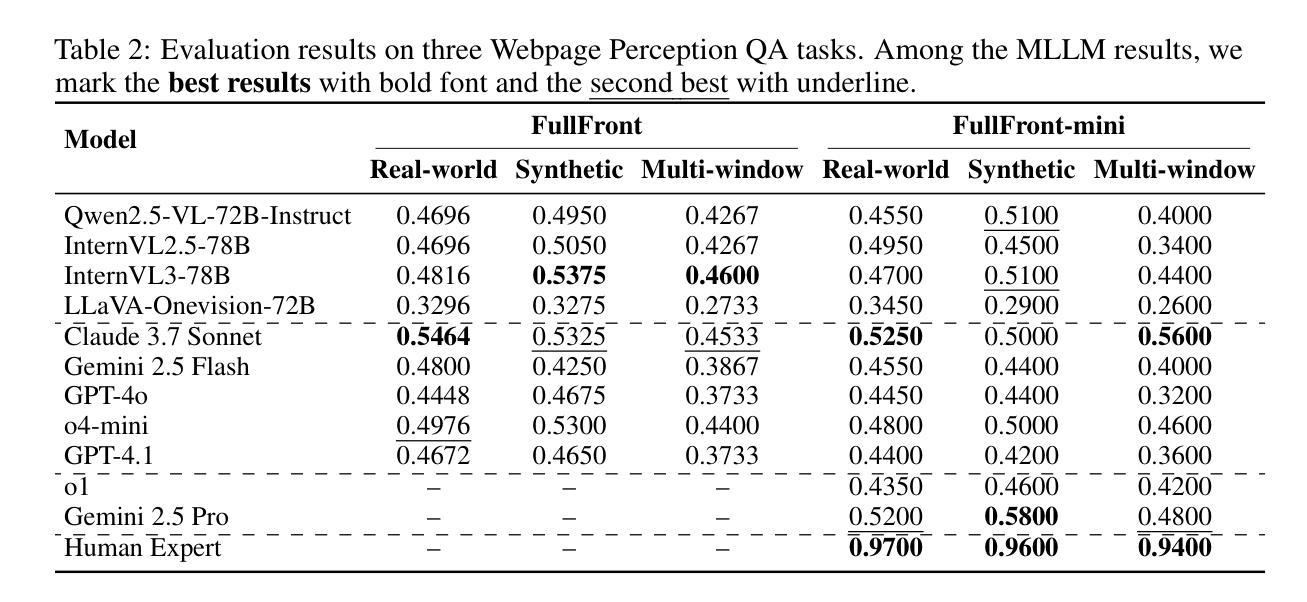
FullFront: Benchmarking MLLMs Across the Full Front-End Engineering Workflow
Authors:Haoyu Sun, Huichen Will Wang, Jiawei Gu, Linjie Li, Yu Cheng
Front-end engineering involves a complex workflow where engineers conceptualize designs, translate them into code, and iteratively refine the implementation. While recent benchmarks primarily focus on converting visual designs to code, we present FullFront, a benchmark designed to evaluate Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) \textbf{across the full front-end development pipeline}. FullFront assesses three fundamental tasks that map directly to the front-end engineering pipeline: Webpage Design (conceptualization phase), Webpage Perception QA (comprehension of visual organization and elements), and Webpage Code Generation (implementation phase). Unlike existing benchmarks that use either scraped websites with bloated code or oversimplified LLM-generated HTML, FullFront employs a novel, two-stage process to transform real-world webpages into clean, standardized HTML while maintaining diverse visual designs and avoiding copyright issues. Extensive testing of state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals significant limitations in page perception, code generation (particularly for image handling and layout), and interaction implementation. Our results quantitatively demonstrate performance disparities across models and tasks, and highlight a substantial gap between current MLLM capabilities and human expert performance in front-end engineering. The FullFront benchmark and code are available in https://github.com/Mikivishy/FullFront.
前端工程涉及复杂的流程,工程师需要构思设计,将它们翻译成代码,并迭代优化实现。虽然最近的基准测试主要关注将视觉设计转换为代码,但我们推出了FullFront,这是一个旨在评估全前端开发流程中的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的基准测试。FullFront评估三个直接与前端工程流程相对应的基本任务:网页设计(概念化阶段)、网页感知问答(对视觉组织和元素的理解)和网页代码生成(实现阶段)。与现有基准测试使用的要么是带有冗余代码的刮取网站,要么是过于简单的LLM生成的HTML不同,FullFront采用新颖的两阶段流程来将现实世界中的网页转换为干净、标准化的HTML,同时保持多样化的视觉设计,并避免版权问题。对最先进的MLLMs的广泛测试表明,在页面感知、代码生成(尤其是图像处理布局)和交互实现方面存在重大局限性。我们的结果定量地显示了模型和任务之间的性能差异,并突出了当前MLLM能力与前端工程领域人类专家性能之间的巨大差距。FullFront基准测试和代码可在https://github.com/Mikivishy/FullFront获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:前端工程涉及复杂的流程,包括工程师构思设计、将设计转化为代码并迭代优化实现。针对前端开发流程,提出了一种新的基准测试FullFront,用于评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在整个前端开发流程中的表现。FullFront包括三个基本任务:网页设计、网页感知质量评估和网页代码生成。它采用两阶段过程将真实网页转化为简洁、标准化的HTML,同时保持多样化的视觉设计并避免版权问题。测试显示,现有模型在网页感知、代码生成和交互实现方面存在显著局限性。
Key Takeaways:
- FullFront是一种针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在前端开发流程中的性能评估的基准测试。
- FullFront包括三个任务:网页设计、网页感知质量评估和网页代码生成,直接映射前端工程流程。
- FullFront采用两阶段过程将真实网页转化为简洁、标准化的HTML。
- 现有模型在网页感知、代码生成方面存在局限性,特别是在图像处理、布局和交互实现方面。
- FullFront测试揭示了不同模型和任务之间的性能差异。
- 当前MLLMs的能力与前端工程专家的人类性能之间存在显著差距。
点此查看论文截图


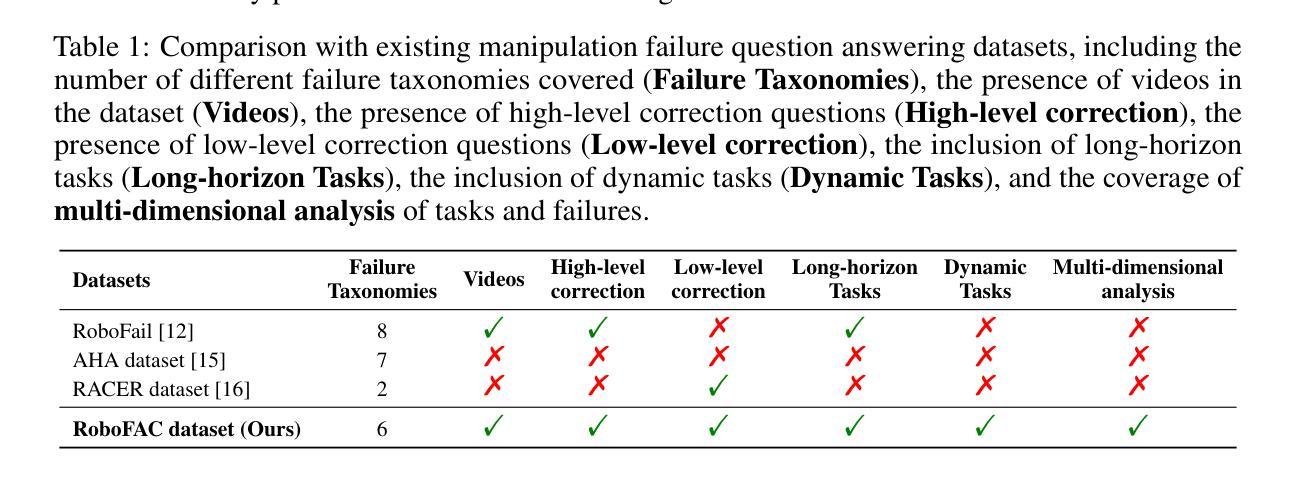
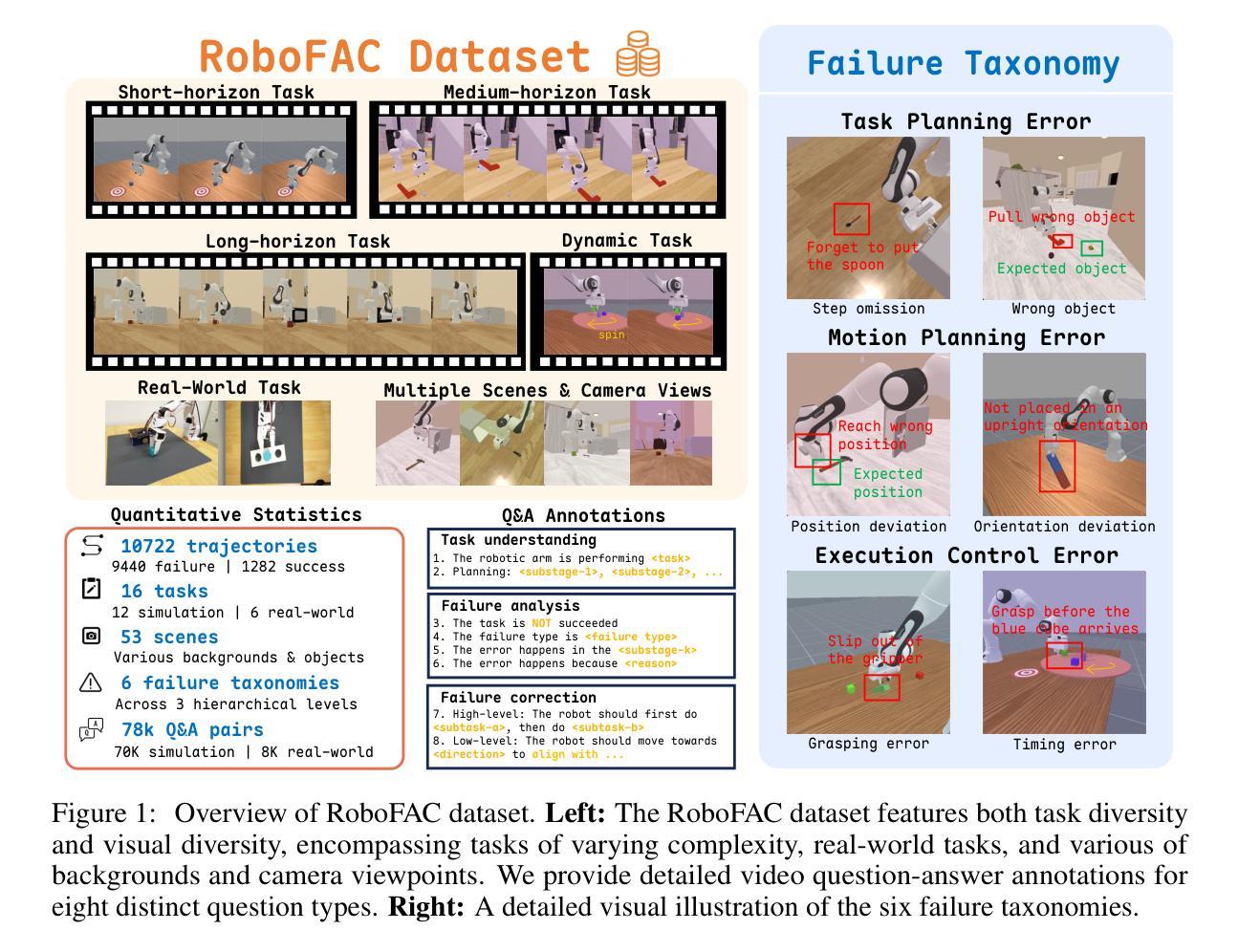
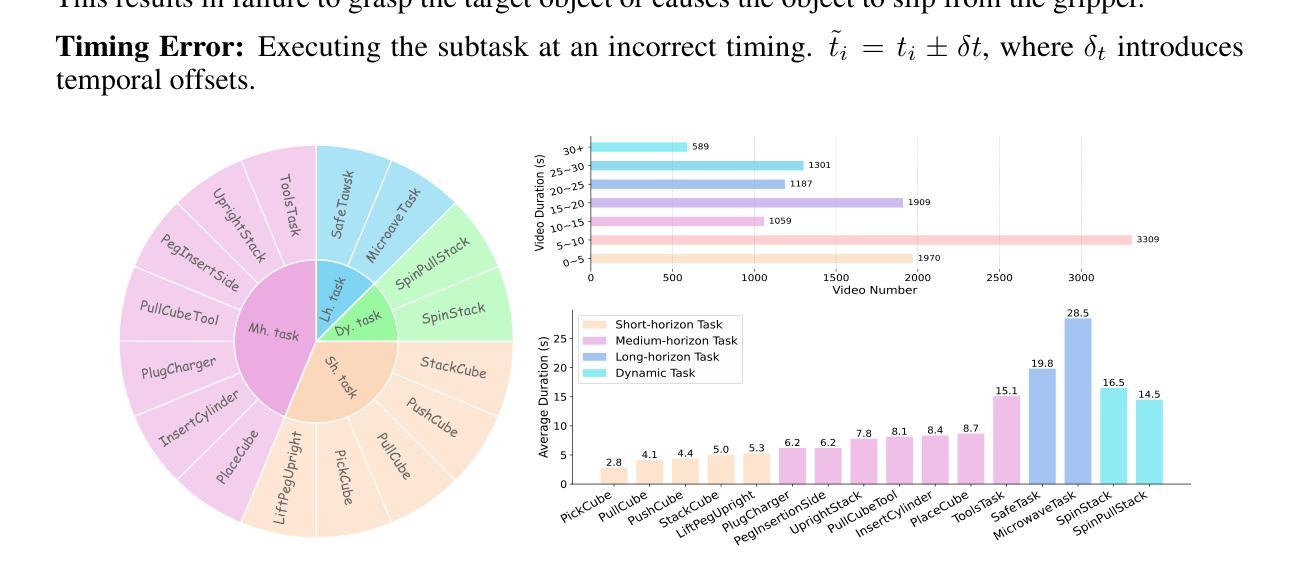
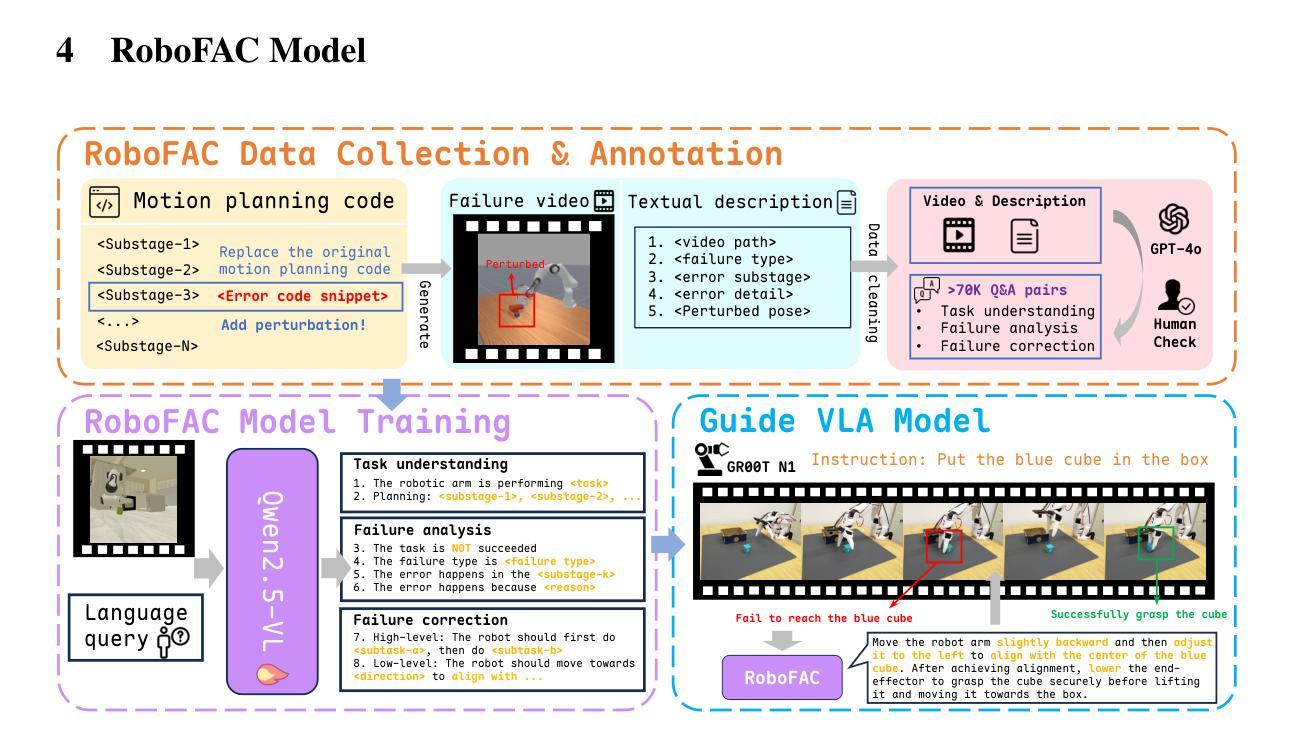
RoboFAC: A Comprehensive Framework for Robotic Failure Analysis and Correction
Authors:Weifeng Lu, Minghao Ye, Zewei Ye, Ruihan Tao, Shuo Yang, Bo Zhao
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently advanced robotic manipulation by translating natural-language instructions and image information into sequential control actions. However, these models often underperform in open-world scenarios, as they are predominantly trained on successful expert demonstrations and exhibit a limited capacity for failure recovery. In this work, we present a Robotic Failure Analysis and Correction (RoboFAC) framework to address this issue. Firstly, we construct RoboFAC dataset comprising 9,440 erroneous manipulation trajectories and 78,623 QA pairs across 16 diverse tasks and 53 scenes in both simulation and real-world environments. Leveraging our dataset, we develop RoboFAC model, which is capable of Task Understanding, Failure Analysis and Failure Correction. Experimental results demonstrate that the RoboFAC model outperforms GPT-4o by 34.1% on our evaluation benchmark. Furthermore, we integrate the RoboFAC model into a real-world VLA control pipeline as an external supervision providing correction instructions, yielding a 29.1% relative improvement on average on four real-world tasks. The results show that our RoboFAC framework effectively handles robotic failures and assists the VLA model in recovering from failures.
视觉语言动作(VLA)模型最近通过将自然语言指令和图像信息翻译成一系列控制动作,推动了机器人操作技术的发展。然而,这些模型在开放世界场景下通常表现不佳,因为它们主要基于成功的专家演示进行训练,并且在故障恢复方面能力有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个机器人故障分析与纠正(RoboFAC)框架来解决这个问题。首先,我们构建了RoboFAC数据集,其中包含9440个错误的操作轨迹和78623个问答对,涉及16项不同任务和53个场景,包括模拟和真实世界环境。利用我们的数据集,我们开发了RoboFAC模型,具备任务理解、故障分析和故障纠正的能力。实验结果表明,RoboFAC模型在我们的评估基准测试上比GPT-4o高出34.1%。此外,我们将RoboFAC模型集成到真实的VLA控制管道中,作为外部监督提供纠正指令,在四项真实任务上平均实现了29.1%的相对改进。结果表明,我们的RoboFAC框架有效地处理了机器人故障,并帮助VLA模型从故障中恢复。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文章介绍了VLA模型在机器人操作中的最新进展,该模型能够将自然语言指令和图像信息翻译成连续的控制动作。然而,该模型在开放世界场景下表现不佳,主要由于它主要基于成功的专家演示进行训练,对于错误恢复的能力有限。为解决这一问题,文章提出了一种名为RoboFAC的机器人故障分析与纠正框架。该框架构建了一个包含错误操作轨迹和问答对的大型数据集,并基于此数据集开发了一个能够进行任务理解、故障分析和故障纠正的RoboFAC模型。实验结果表明,RoboFAC模型在评估指标上优于GPT-4o达34.1%,并且将其集成到真实的VLA控制管道中,为机器人提供纠正指令,在四个真实任务上的平均表现提高了29.1%。这表明RoboFAC框架能够有效处理机器人故障并帮助VLA模型从故障中恢复。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型能够将自然语言指令和图像信息转化为连续控制动作,推动机器人操作的发展。
- VLA模型在开放世界场景下的表现有待提高,尤其在错误恢复方面存在局限。
- 提出了RoboFAC框架来解决VLA模型的缺陷,该框架包括一个大型数据集,包含错误操作轨迹和问答对。
- RoboFAC模型具备任务理解、故障分析和故障纠正的能力。
- 实验结果显示,RoboFAC模型在评估指标上显著优于GPT-4o。
- 将RoboFAC模型集成到真实VLA控制管道中,为机器人提供纠正指令,提高了机器人在真实任务中的表现。
点此查看论文截图