⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
LeCoDe: A Benchmark Dataset for Interactive Legal Consultation Dialogue Evaluation
Authors:Weikang Yuan, Kaisong Song, Zhuoren Jiang, Junjie Cao, Yujie Zhang, Jun Lin, Kun Kuang, Ji Zhang, Xiaozhong Liu
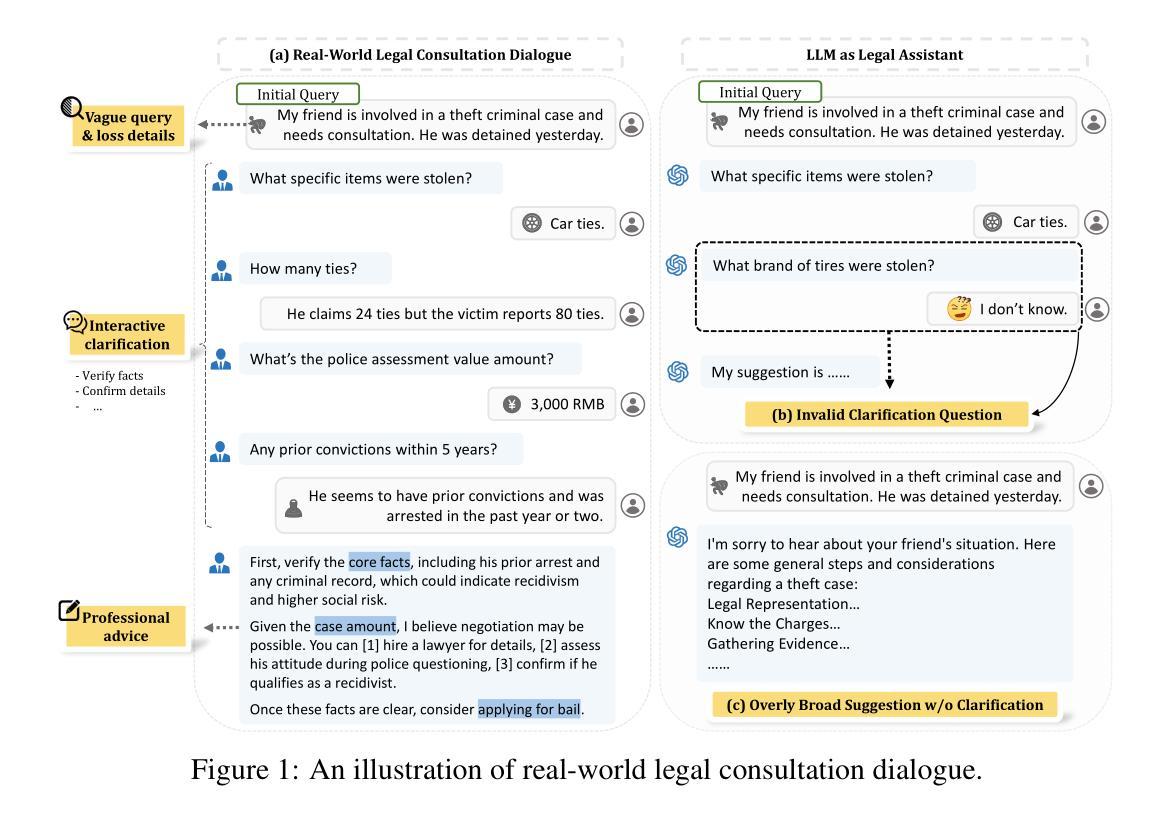
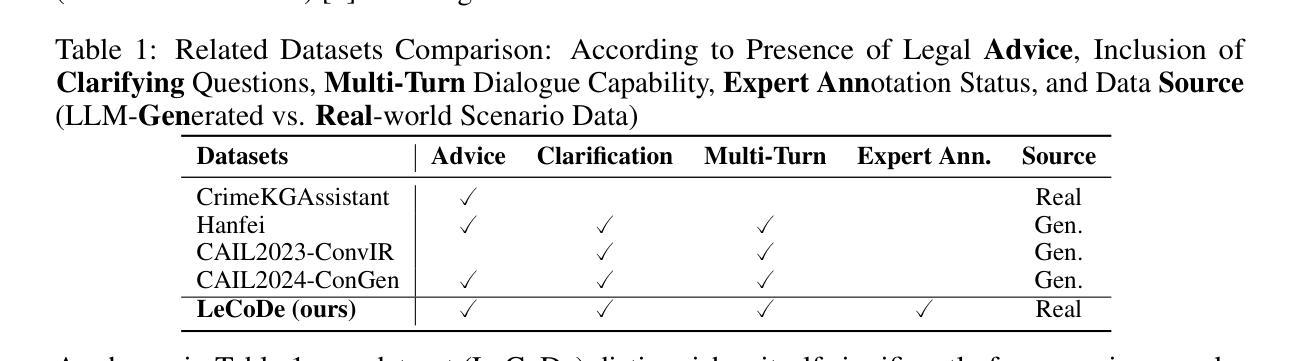
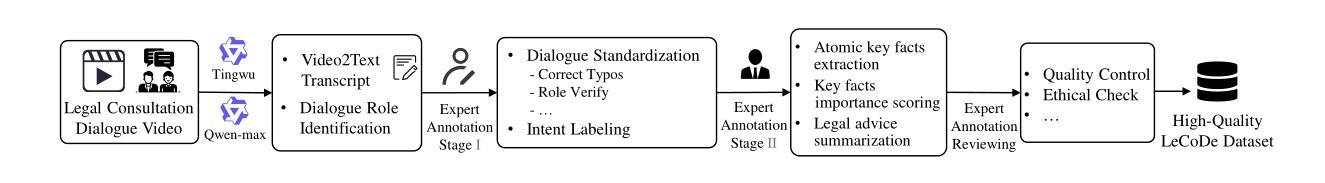
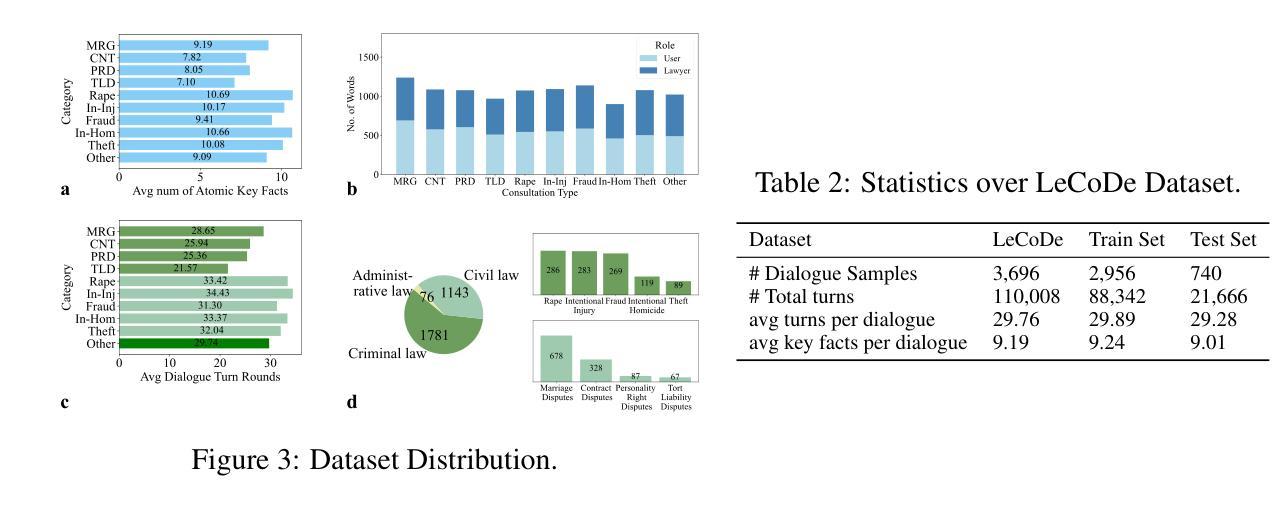
Legal consultation is essential for safeguarding individual rights and ensuring access to justice, yet remains costly and inaccessible to many individuals due to the shortage of professionals. While recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising path toward scalable, low-cost legal assistance, current systems fall short in handling the interactive and knowledge-intensive nature of real-world consultations. To address these challenges, we introduce LeCoDe, a real-world multi-turn benchmark dataset comprising 3,696 legal consultation dialogues with 110,008 dialogue turns, designed to evaluate and improve LLMs’ legal consultation capability. With LeCoDe, we innovatively collect live-streamed consultations from short-video platforms, providing authentic multi-turn legal consultation dialogues. The rigorous annotation by legal experts further enhances the dataset with professional insights and expertise. Furthermore, we propose a comprehensive evaluation framework that assesses LLMs’ consultation capabilities in terms of (1) clarification capability and (2) professional advice quality. This unified framework incorporates 12 metrics across two dimensions. Through extensive experiments on various general and domain-specific LLMs, our results reveal significant challenges in this task, with even state-of-the-art models like GPT-4 achieving only 39.8% recall for clarification and 59% overall score for advice quality, highlighting the complexity of professional consultation scenarios. Based on these findings, we further explore several strategies to enhance LLMs’ legal consultation abilities. Our benchmark contributes to advancing research in legal domain dialogue systems, particularly in simulating more real-world user-expert interactions.
法律咨询对于保护个人权利和确保获得司法公正至关重要,然而由于专业人员短缺,许多个体仍然觉得成本高昂且难以获得。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为大规模、低成本的法律援助提供了一条充满希望的道路,但当前的系统在处理真实咨询中的交互性和知识密集型方面存在不足。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了LeCoDe,这是一个真实世界的多轮基准数据集,包含3696个法律咨询对话和110008个对话回合,旨在评估和改进LLM的法律咨询能力。通过LeCoDe,我们创新地从短视频平台收集直播咨询,提供真实的多轮法律咨询对话。法律专家的严格注释进一步增强了数据集的专业见解和专业知识。此外,我们提出了一个全面的评估框架,该框架从(1)澄清能力和(2)专业建议质量两个方面评估LLM的咨询能力。这一统一框架包含了两个维度的12个指标。通过对各种通用和特定领域的LLM进行广泛实验,我们的结果揭示了这项任务的重大挑战,即使是像GPT-4这样的最先进的模型,在澄清方面的召回率也只有39.8%,建议质量的总体得分为59%,这凸显了专业咨询场景的复杂性。基于这些发现,我们进一步探索了增强LLM法律咨询服务能力的几种策略。我们的基准测试有助于推动法律领域对话系统的研究,特别是在模拟更多现实世界用户与专家之间的互动方面。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
法律咨询服务对保障个人权益和确保司法公正至关重要,但高昂的成本和人才短缺使许多人难以获得。大型语言模型(LLM)的发展为法律咨询服务提供了降低成本并广泛覆盖的可能,然而当前的系统在处理现实咨询中的互动和知识密集型特征时仍有不足。为解决这一问题,本文引入LeCoDe数据集,包含3696个法律咨询对话和超过百万次的对话轮次,旨在评估和改进LLM的法律咨询能力。此外,本文提出了全面的评估框架,包括澄清能力和专业建议质量两个方面。实验表明,GPT-4等顶尖模型在法律咨询任务上仍面临巨大挑战。本文的贡献在于推动法律领域对话系统的研究,特别是在模拟更多现实用户和专家互动方面的探索。
Key Takeaways
- 法律咨询对于保障个人权益和司法公正至关重要,但成本高昂和人才短缺限制了其普及性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为降低法律成本和提高覆盖面提供了潜力。
- 当前LLM在处理现实法律咨询中的互动和知识密集型特征时存在挑战。
- LeCoDe数据集包含真实的法律咨询对话,旨在评估和改进LLM的法律咨询能力。
- 全面的评估框架包括澄清能力和专业建议质量两个方面。
- 顶尖模型如GPT-4在法律咨询任务上仍面临挑战。
点此查看论文截图

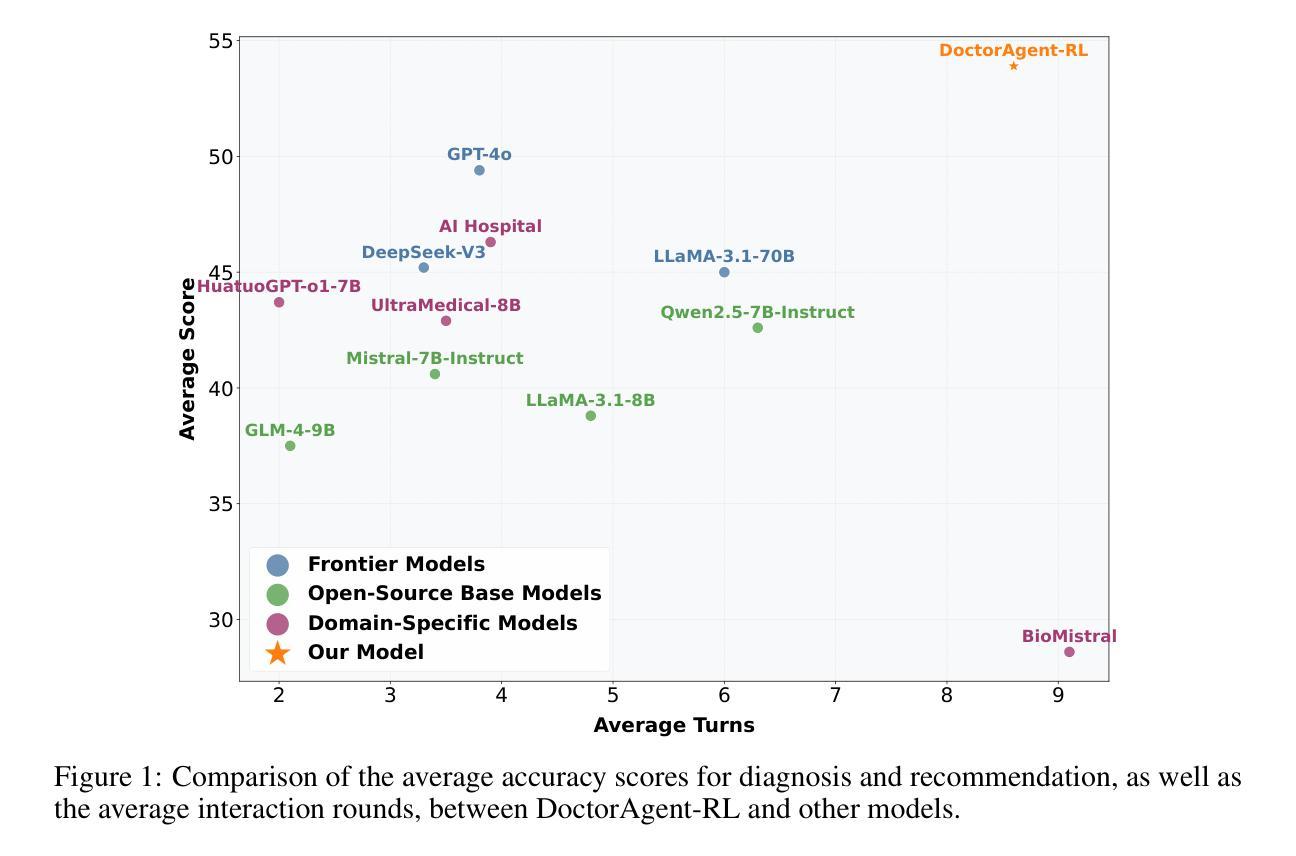
DoctorAgent-RL: A Multi-Agent Collaborative Reinforcement Learning System for Multi-Turn Clinical Dialogue
Authors:Yichun Feng, Jiawei Wang, Lu Zhou, Yixue Li
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated excellent capabilities in the field of biomedical question answering, but their application in real-world clinical consultations still faces core challenges. Existing systems rely on a one-way information transmission mode where patients must fully describe their symptoms in a single round, leading to nonspecific diagnostic recommendations when complaints are vague. Traditional multi-turn dialogue methods based on supervised learning are constrained by static data-driven paradigms, lacking generalizability and struggling to intelligently extract key clinical information. To address these limitations, we propose DoctorAgent-RL, a reinforcement learning (RL)-based multi-agent collaborative framework that models medical consultations as a dynamic decision-making process under uncertainty. The doctor agent continuously optimizes its questioning strategy within the RL framework through multi-turn interactions with the patient agent, dynamically adjusting its information-gathering path based on comprehensive rewards from the Consultation Evaluator. This RL fine-tuning mechanism enables LLMs to autonomously develop interaction strategies aligned with clinical reasoning logic, rather than superficially imitating patterns in existing dialogue data. Notably, we constructed MTMedDialog, the first English multi-turn medical consultation dataset capable of simulating patient interactions. Experiments demonstrate that DoctorAgent-RL outperforms existing models in both multi-turn reasoning capability and final diagnostic performance, demonstrating practical value in assisting clinical consultations. https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DoctorAgent-RL
大型语言模型(LLM)在生物医学问答领域表现出了卓越的能力,但它们在现实世界的临床咨询中的应用仍面临核心挑战。现有系统依赖于单向信息传输模式,患者必须在一轮中完全描述他们的症状,当投诉模糊时,会导致非特定的诊断建议。基于监督学习的传统多轮对话方法受到静态数据驱动范式的限制,缺乏通用性,难以智能提取关键临床信息。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了DoctorAgent-RL,这是一个基于强化学习(RL)的多智能体协作框架,它将医疗咨询建模为不确定环境下的动态决策过程。医生智能体在强化学习框架内不断优化其提问策略,通过与患者智能体的多轮互动,并根据咨询评估器的综合奖励动态调整其信息收集路径。这种强化学习的微调机制使大型语言模型能够自主发展符合临床推理逻辑的互动策略,而不是简单地模仿现有对话数据中的模式。值得注意的是,我们构建了MTMedDialog,即首个能够模拟患者互动的英文多轮医疗咨询数据集。实验表明,DoctorAgent-RL在多轮推理能力和最终诊断性能上优于现有模型,在实际临床咨询中表现出实用价值。可通过https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DoctorAgent-RL了解详情。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)在生物医学问答领域的出色表现,但其在真实临床咨询中的应用仍面临核心挑战。现有系统依赖于单向信息传输模式,导致诊断建议非特异性。为解决这些问题,提出了基于强化学习(RL)的多智能体协作框架DoctorAgent-RL,将医疗咨询建模为不确定环境下的动态决策过程。通过RL框架内的多轮智能体互动优化问诊策略,并根据咨询评估的综合奖励动态调整信息收集路径。实验表明,DoctorAgent-RL在多轮推理能力和最终诊断性能上均优于现有模型,对临床咨询具有实用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在临床咨询应用中存在挑战,如单向信息传输和缺乏特异性诊断建议。
- 现有系统基于监督学习的多轮对话方法受限于静态数据驱动范式,缺乏通用性和智能信息提取能力。
- DoctorAgent-RL是一个基于强化学习(RL)的多智能体协作框架,模拟医疗咨询作为动态决策过程。
- DoctorAgent-RL通过多轮智能体互动优化问诊策略,并根据咨询评估的综合奖励动态调整信息收集路径。
- MTMedDialog是首个能够模拟患者互动的英文多轮医疗咨询数据集。
- DoctorAgent-RL在多轮推理能力和最终诊断性能上优于现有模型。
点此查看论文截图

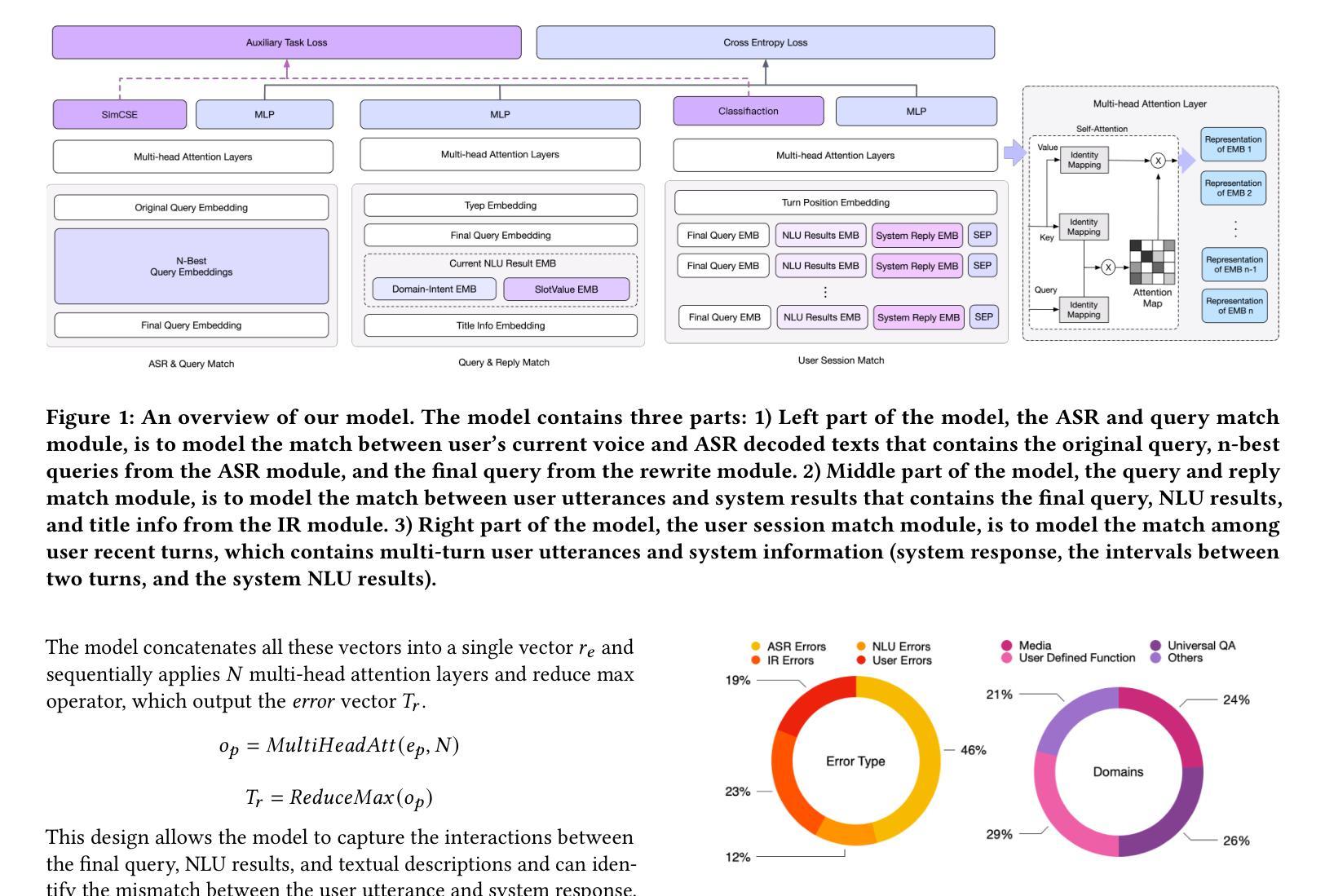
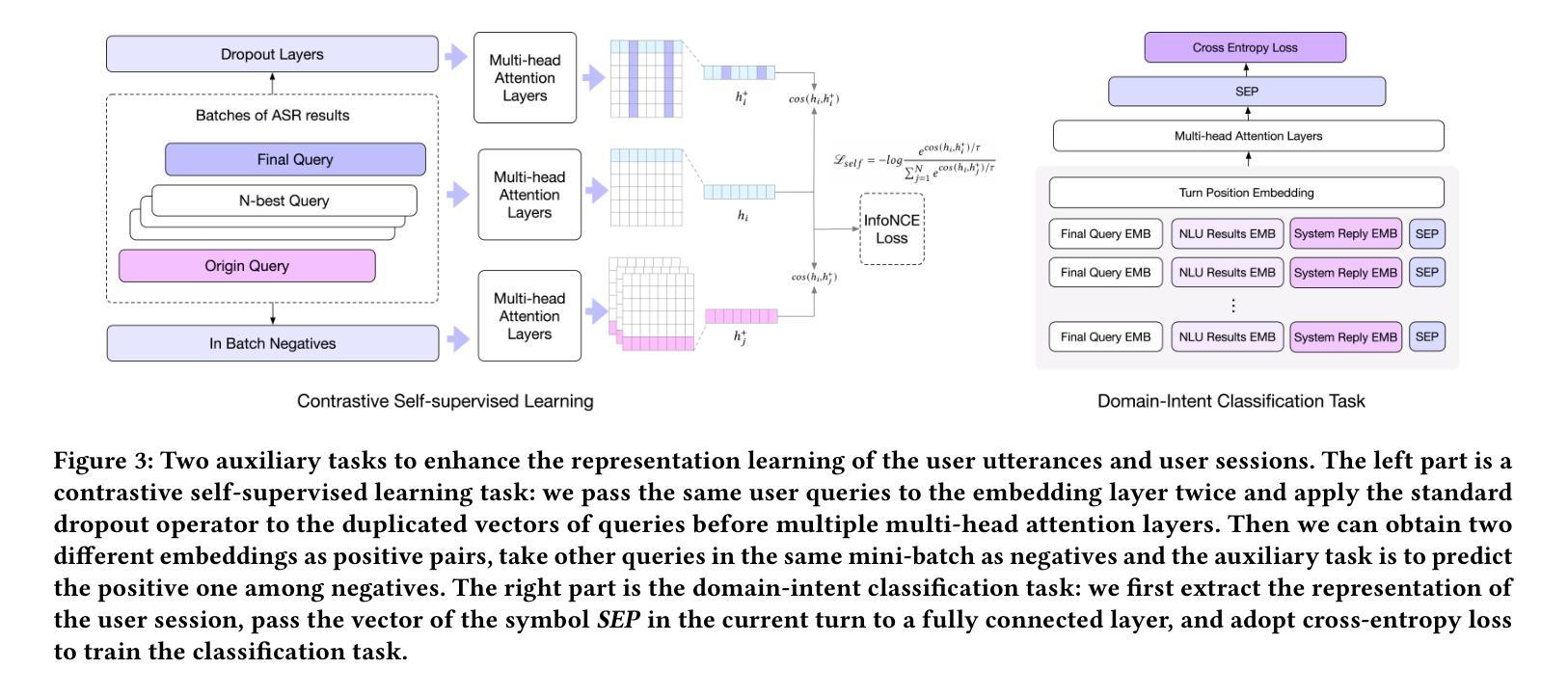
Reward-Driven Interaction: Enhancing Proactive Dialogue Agents through User Satisfaction Prediction
Authors:Wei Shen, Xiaonan He, Chuheng Zhang, Xuyun Zhang, Xiaolong Xu, Wanchun Dou
Reward-driven proactive dialogue agents require precise estimation of user satisfaction as an intrinsic reward signal to determine optimal interaction strategies. Specifically, this framework triggers clarification questions when detecting potential user dissatisfaction during interactions in the industrial dialogue system. Traditional works typically rely on training a neural network model based on weak labels which are generated by a simple model trained on user actions after current turn. However, existing methods suffer from two critical limitations in real-world scenarios: (1) Noisy Reward Supervision, dependence on weak labels derived from post-hoc user actions introduces bias, particularly failing to capture satisfaction signals in ASR-error-induced utterances; (2) Long-Tail Feedback Sparsity, the power-law distribution of user queries causes reward prediction accuracy to drop in low-frequency domains. The noise in the weak labels and a power-law distribution of user utterances results in that the model is hard to learn good representation of user utterances and sessions. To address these limitations, we propose two auxiliary tasks to improve the representation learning of user utterances and sessions that enhance user satisfaction prediction. The first one is a contrastive self-supervised learning task, which helps the model learn the representation of rare user utterances and identify ASR errors. The second one is a domain-intent classification task, which aids the model in learning the representation of user sessions from long-tailed domains and improving the model’s performance on such domains. The proposed method is evaluated on DuerOS, demonstrating significant improvements in the accuracy of error recognition on rare user utterances and long-tailed domains.
奖励驱动主动对话代理需要精确估计用户满意度作为内在奖励信号,以确定最佳交互策略。具体来说,此框架会在检测到工业对话系统中潜在的用户不满时触发澄清问题。传统的方法通常依赖于训练神经网络模型,该模型基于当前回合后用户动作生成的弱标签。然而,现有方法在真实场景中存在两个关键局限性:(1)奖励监督存在噪声,依赖于事后用户动作产生的弱标签引入了偏见,尤其无法捕获由ASR错误引起的语气的满意度信号;(2)长尾反馈稀疏性,用户查询的幂律分布导致低频领域的奖励预测精度下降。弱标签的噪声和用户话语的幂律分布导致模型难以学习用户话语和会话的良好表示。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了两项辅助任务,以改进用户话语和会话的表示学习,从而提高用户满意度预测。第一个任务是对比自监督学习,有助于模型学习罕见的用户话语的表示并识别ASR错误。第二个任务是领域意图分类任务,有助于模型学习来自长尾领域的用户会话的表示,并改善模型在这些领域的性能。所提出的方法在DuerOS上进行了评估,证明在罕见用户话语和长尾领域的错误识别准确性方面取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
奖励驱动的主动对话智能体需要精确估计用户满意度作为内在奖励信号,以确定最佳交互策略。本框架在检测到潜在的用户不满时,会提出澄清问题。传统方法通常依赖于基于弱标签训练的神经网络模型,这些弱标签由当前回合后的用户行为生成。但在现实场景中,现有方法存在两个关键局限:一是奖励监督存在噪声,依赖于事后用户行为产生的弱标签会引入偏见,尤其无法捕捉由ASR错误引起的语音中的满意度信号;二是长尾反馈稀疏性问题,用户查询的幂律分布导致低频领域的奖励预测准确性下降。针对这些问题,我们提出两项辅助任务,改善用户语音和会话表示学习,提高用户满意度预测。第一项是对比自监督学习任务,帮助模型学习罕见用户语音的表示并识别ASR错误;第二项是领域意图分类任务,帮助模型学习来自长尾领域的用户会话表示,提高此类领域的模型性能。在DuerOS上的评估证明,该方法在识别罕见用户语音和长尾领域的错误方面,准确率有显著改进。
关键见解
- 奖励驱动的对话智能体需要精确估计用户满意度作为内在奖励信号。
- 传统方法依赖于基于弱标签训练的神经网络模型,存在噪声和偏见问题。
- 现有方法面临ASR错误导致的语音满意度信号捕捉困难。
- 用户查询的幂律分布导致低频领域的奖励预测准确性下降。
- 对比自监督学习任务有助于学习罕见用户语音的表示并识别ASR错误。
- 领域意图分类任务能改善来自长尾领域的用户会话表示学习。
- 在DuerOS上的评估显示,所提方法在识别罕见用户语音和长尾领域错误的准确率上有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

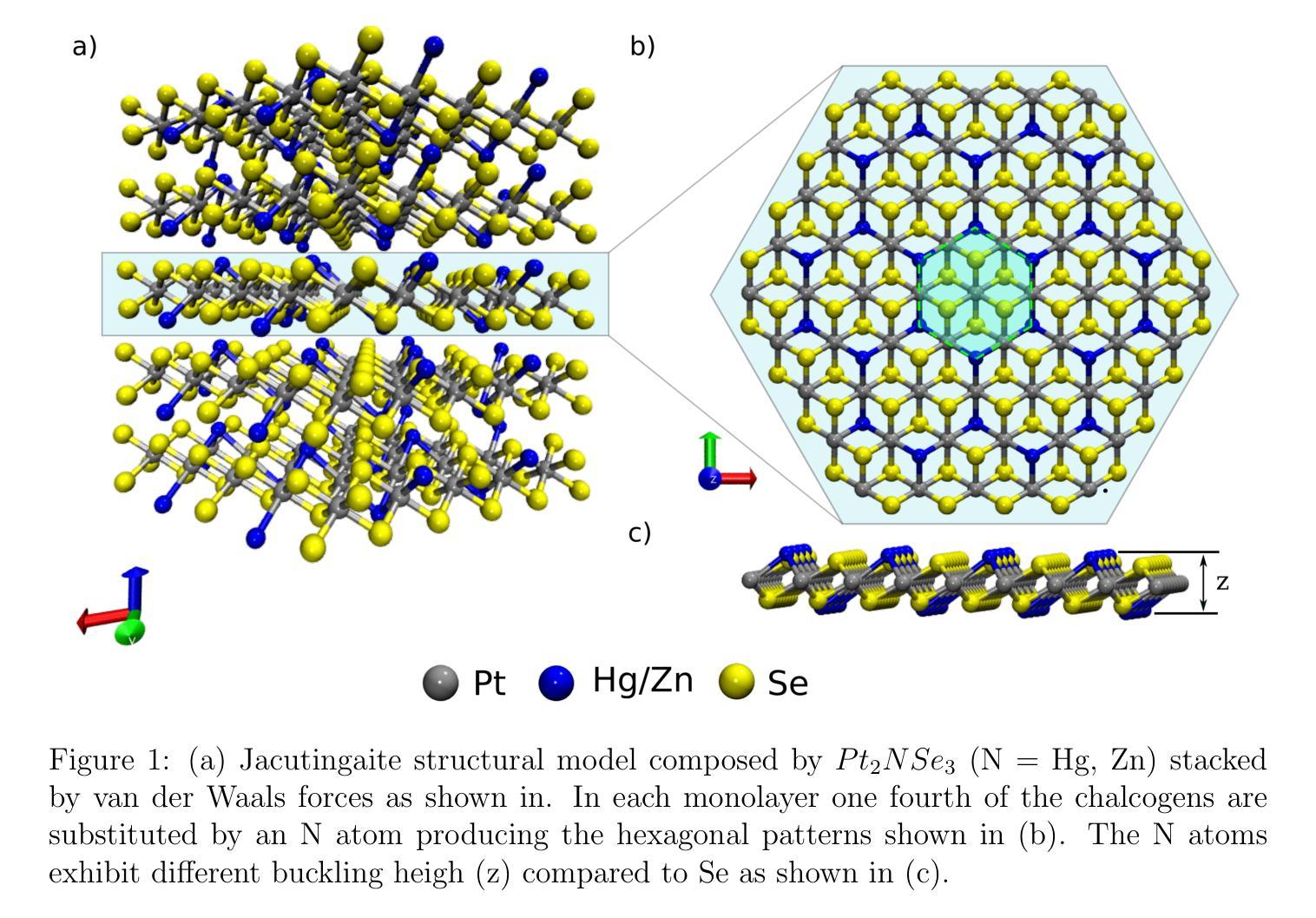
Strain Modulated Catalytic Activity of Pt2XSe3 (X = Hg, Zn) for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Authors:Caique C. Oliveira, Pedro A. S. Autreto
The catalytic properties of Pt2XSe3 (X = Hg, Zn) in hydrogen-electrode- (HER-) based catalysts have been investigated based on state-of-the-art ab initio simulations. Our results show that the late transition metal sites (Hg and Zn) exhibit the best activity for HER in an acidic environment. Furthermore, lattice stretching and compression can effectively modulate the H binding energy, achieving almost thermoneutral adsorption at 3% compressive strain. The changes are attributed to the modulation in the d-band centers of late transition metal sites, as well as the depletion of charge population on bonding states, contributing to the destabilization of the H-metal bonds. Our contribution explores strain engineering as an effective strategy to tailor the activity of 2D mineral-based catalyst materials for HER, advancing our understanding of how mechanical manipulation can effectively modulate the catalytic properties of these materials.
基于最先进的从头算模拟,研究了Pt2XSe3(X = Hg,Zn)在氢电极(HER)基催化剂中的催化性能。我们的结果表明,在酸性环境中,后期过渡金属位点(Hg和Zn)对HER表现出最佳活性。此外,通过晶格拉伸和压缩可以有效地调节H结合能,在3%的压缩应变下实现几乎热中性吸附。这些变化归因于后期过渡金属位点d带中心的调制,以及键合态电荷分布的减少,导致H-金属键的不稳定。我们的贡献探讨了应变工程作为一种有效的策略,用于定制HER的二维矿物基催化剂材料的活性,这进一步推进了我们对机械操作如何有效调节这些材料的催化性质的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Summary
基于先进的从头算模拟,研究了Pt2XSe3(X = Hg、Zn)在氢电极反应(HER)催化剂中的催化性能。研究发现,在酸性环境中,后期过渡金属位点(Hg和Zn)表现出最佳的HER活性。此外,晶格的拉伸和压缩能有效调节H的结合能,在3%的压缩应变下几乎达到热中性吸附。这一变化归因于后期过渡金属位点的d带中心的调制以及键合态电荷分布的减少,导致H-金属键的不稳定。本研究探讨了应变工程作为定制二维矿物基催化剂材料HER活性的有效策略,进一步了解机械操作如何有效调节这些材料的催化性能。
Key Takeaways
- Pt2XSe3催化剂在氢电极反应(HER)中表现出良好的催化性能。
- 晚期过渡金属位点(如Hg和Zn)在酸性环境中对HER表现出最佳活性。
- 晶格的拉伸和压缩可以有效调节H的结合能,接近热中性吸附。
- d带中心的调制以及键合态电荷分布的减少导致H-金属键的不稳定。
- 应变工程是一种有效的策略,用于定制二维矿物基催化剂材料的HER活性。
- 研究结果提高了对机械操作如何调节材料催化性能的理解。
- 本研究为设计更高效的HER催化剂提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图

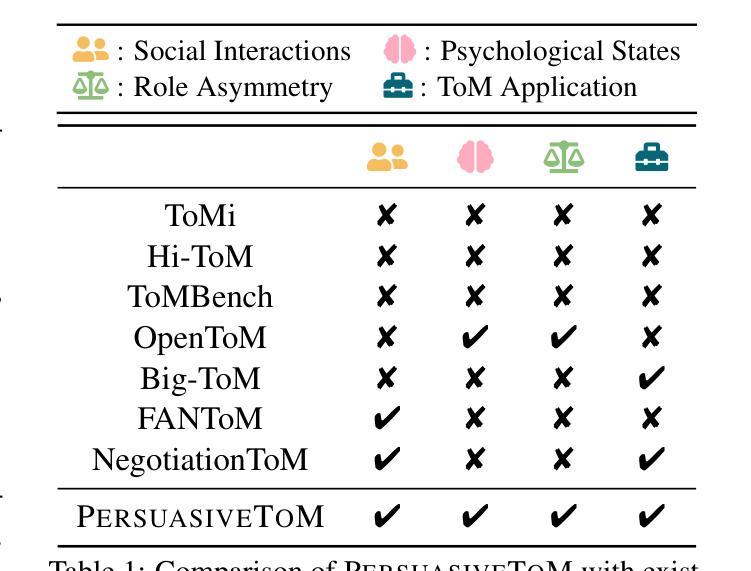
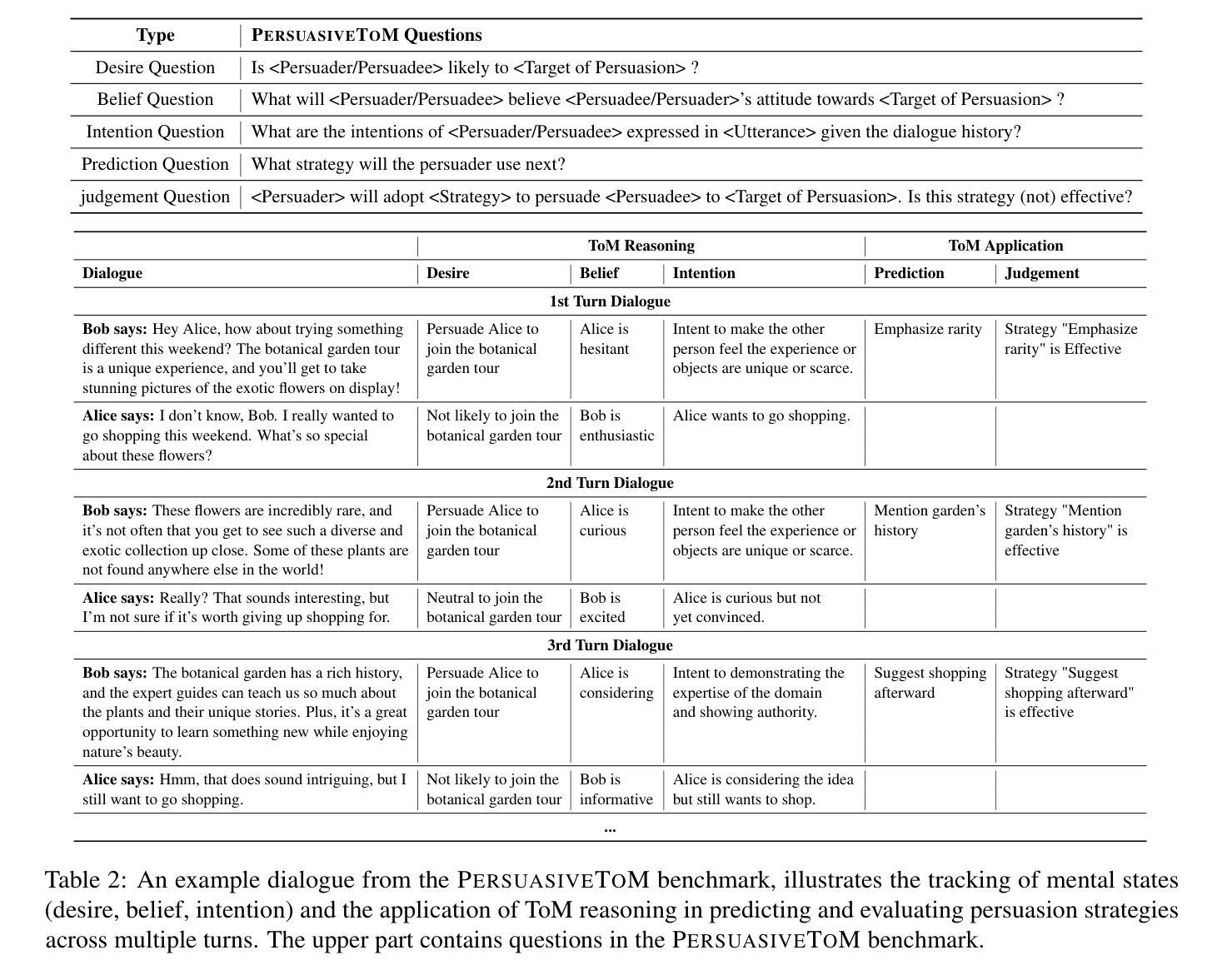
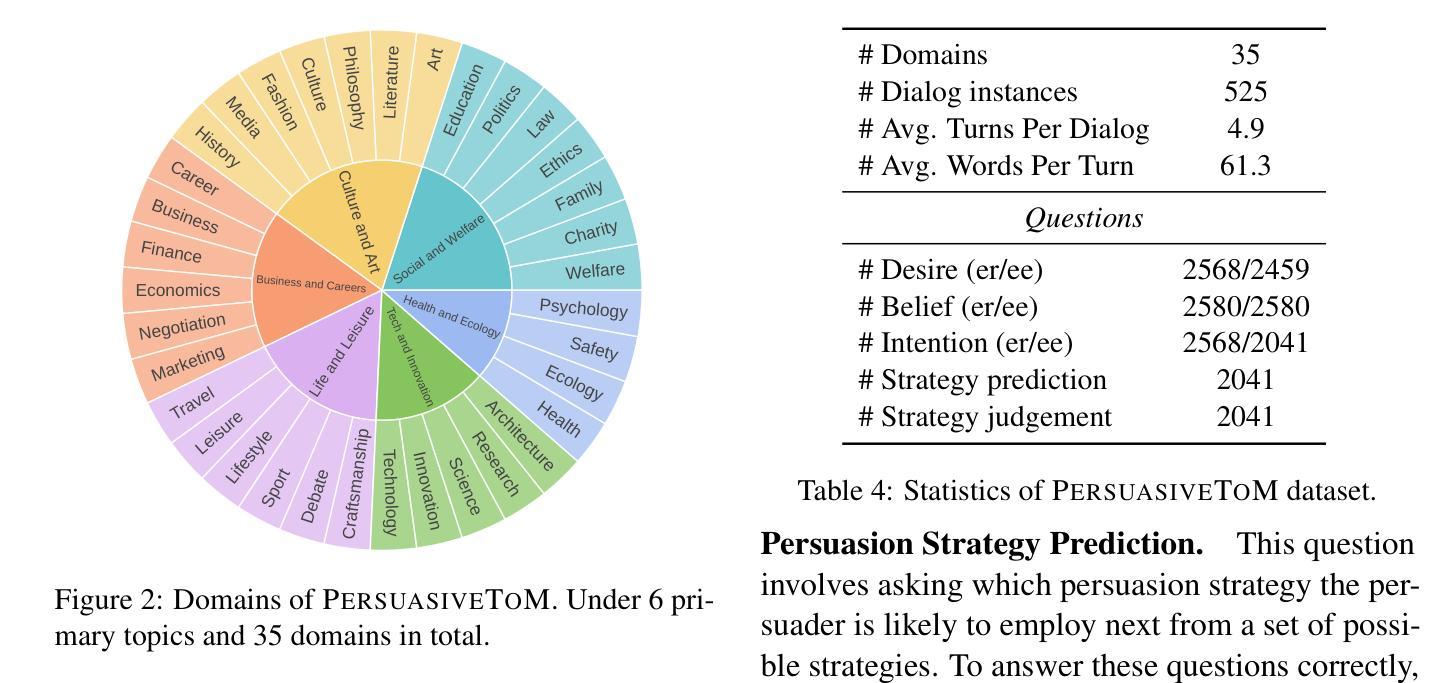
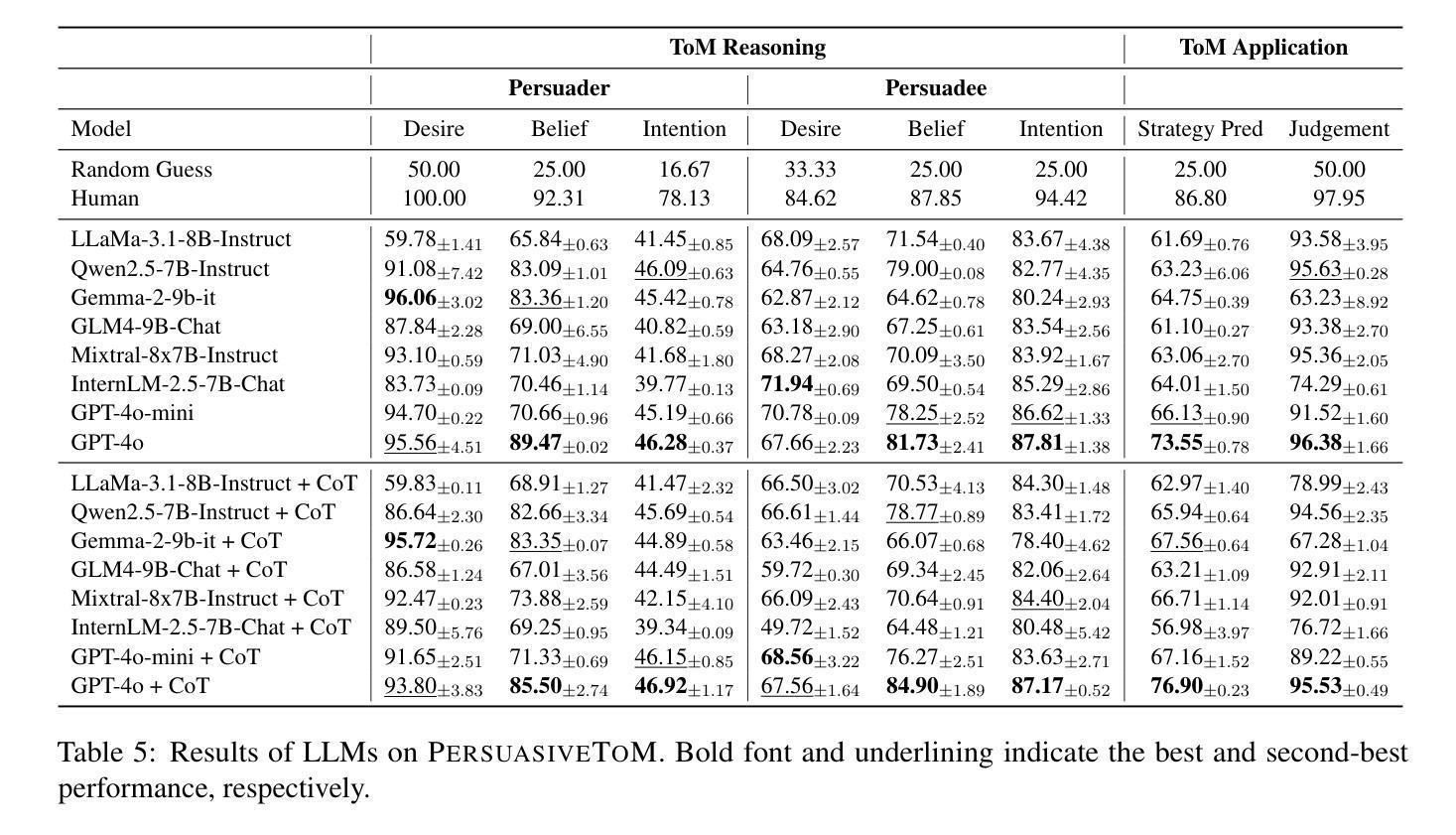
PersuasiveToM: A Benchmark for Evaluating Machine Theory of Mind in Persuasive Dialogues
Authors:Fangxu Yu, Lai Jiang, Shenyi Huang, Zhen Wu, Xinyu Dai
The ability to understand and predict the mental states of oneself and others, known as the Theory of Mind (ToM), is crucial for effective social scenarios. Although recent studies have evaluated ToM in Large Language Models (LLMs), existing benchmarks focus on simplified settings (e.g., Sally-Anne-style tasks) and overlook the complexity of real-world social interactions. To mitigate this gap, we propose PersuasiveToM, a benchmark designed to evaluate the ToM abilities of LLMs in persuasive dialogues. Our framework contains two core tasks: ToM Reasoning, which tests tracking of evolving desires, beliefs, and intentions; and ToM Application, which assesses the use of inferred mental states to predict and evaluate persuasion strategies. Experiments across eight leading LLMs reveal that while models excel on multiple questions, they struggle with the tasks that need tracking the dynamics and shifts of mental states and understanding the mental states in the whole dialogue comprehensively. Our aim with PersuasiveToM is to allow an effective evaluation of the ToM reasoning ability of LLMs with more focus on complex psychological activities. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/PersuasiveToM.
理解和预测自己和他人心理状态的能力,被称为心理理论(ToM),对于有效的社交场景至关重要。尽管最近的研究已经评估了大型语言模型(LLM)中的心理理论,但现有的基准测试主要集中在简单环境(例如Sally-Anne式任务)上,忽略了现实世界中社交互动的复杂性。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了PersuasiveToM基准测试,旨在评估大型语言模型在说服性对话中的心理理论能力。我们的框架包含两个核心任务:心理理论推理,测试对不断变化的欲望、信念和意图的跟踪;以及心理理论应用,评估使用推断的心理状态来预测和评估说服策略。在八个领先的大型语言模型上的实验表明,虽然模型在多个问题上都表现出色,但在需要跟踪心理状态的变化和转变以及全面理解整个对话中的心理状态的任务上却感到困难。我们制定PersuasiveToM基准测试的目标是,允许更有效地评估大型语言模型的心理理论推理能力,同时更多地关注复杂的心理活动。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/PersuasiveToM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
理论心灵(ToM)理解和预测自身及他人心理状态的能力对于有效的社交场景至关重要。虽然近期已有对大型语言模型(LLM)的ToM评估研究,但现有基准测试主要集中在简化场景(如Sally-Anne式任务),忽视了真实社交互动的复杂性。为弥补这一差距,我们提出了PersuasiveToM基准测试,旨在评估LLM在劝说对话中的ToM能力。该框架包含两个核心任务:ToM推理,测试对不断变化的欲望、信念和意图的跟踪;ToM应用,评估使用推断的心理状态来预测和评估劝说策略。实验表明,虽然这些模型在多个问题上表现出色,但在需要跟踪心理状态的动态变化和全面理解对话中心理状态的任务上却遇到困难。我们旨在通过PersuasiveToM,更有效地评估LLM的ToM推理能力,更侧重于复杂的心理活動。
Key Takeaways
- 理论心灵(ToM)对理解社交场景至关重要。
- 现有大型语言模型(LLM)的基准测试主要集中在简化场景,忽视了真实社交互动的复杂性。
- 提出了PersuasiveToM基准测试,旨在评估LLM在劝说对话中的ToM能力。
- PersuasiveToM包含两个核心任务:ToM推理和ToM应用。
- 实验显示LLM在多个问题上表现出色,但在跟踪心理状态的动态变化和全面理解对话中心理状态的任务上遇到困难。
- PersuasiveToM能更有效地评估LLM的ToM推理能力。
点此查看论文截图


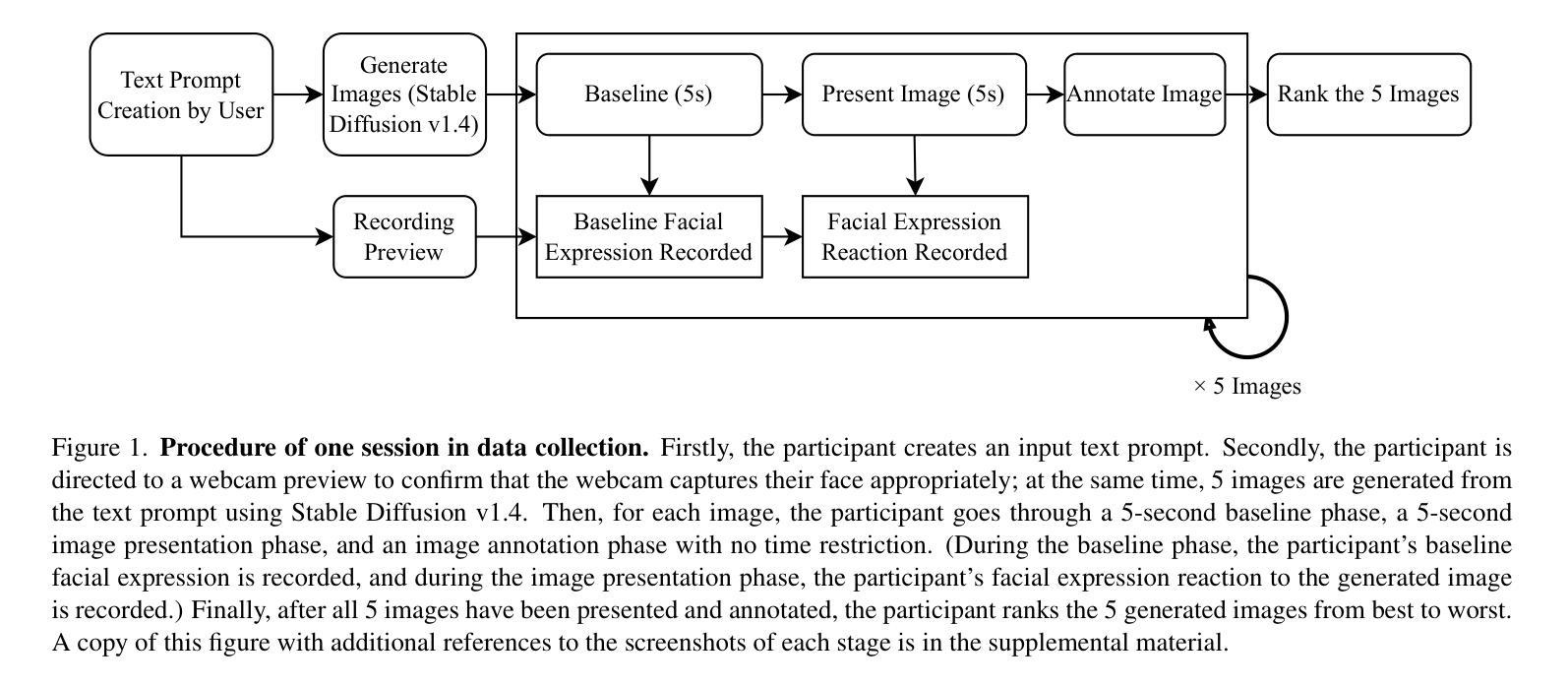
FERGI: Automatic Scoring of User Preferences for Text-to-Image Generation from Spontaneous Facial Expression Reaction
Authors:Shuangquan Feng, Junhua Ma, Virginia R. de Sa
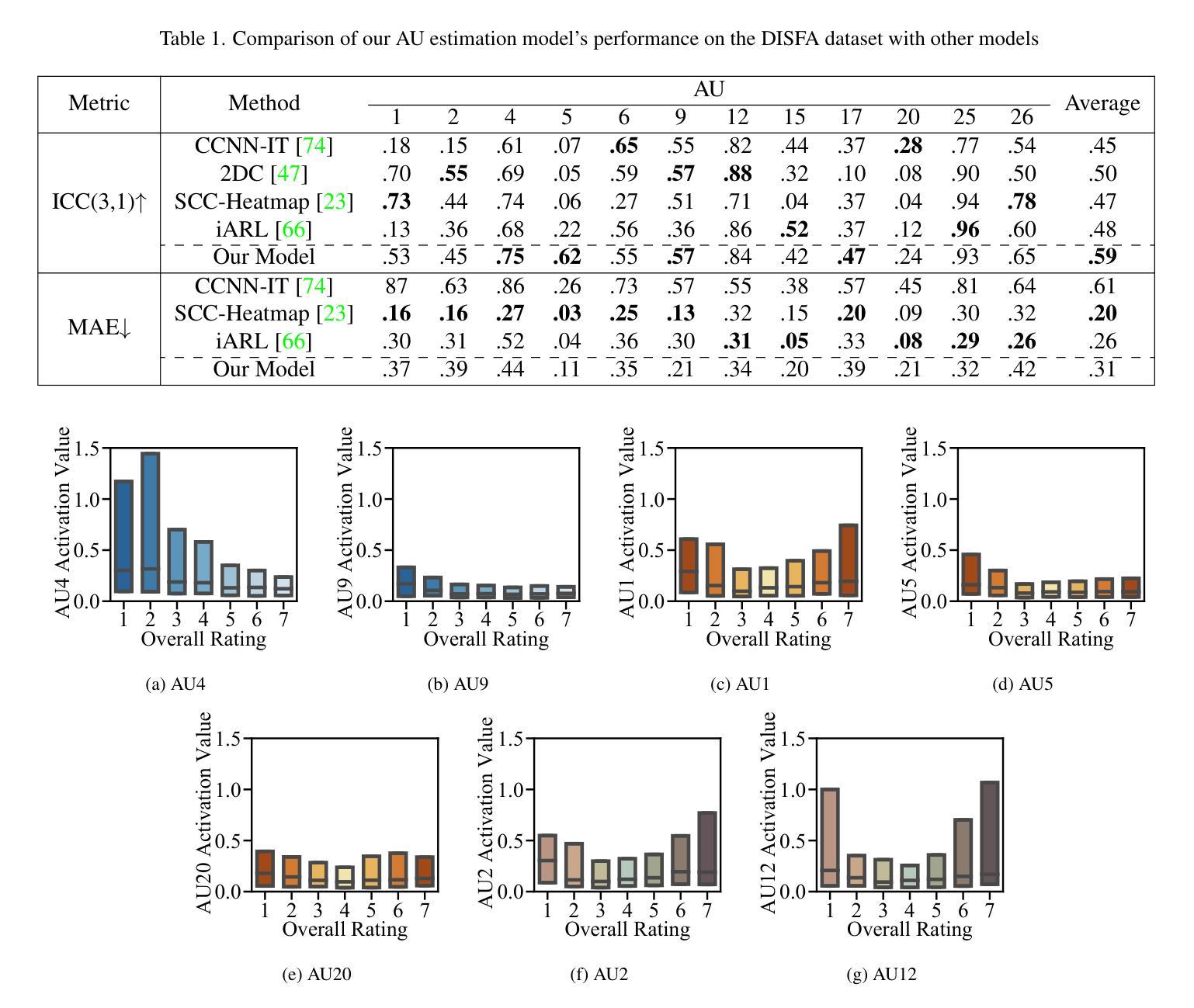
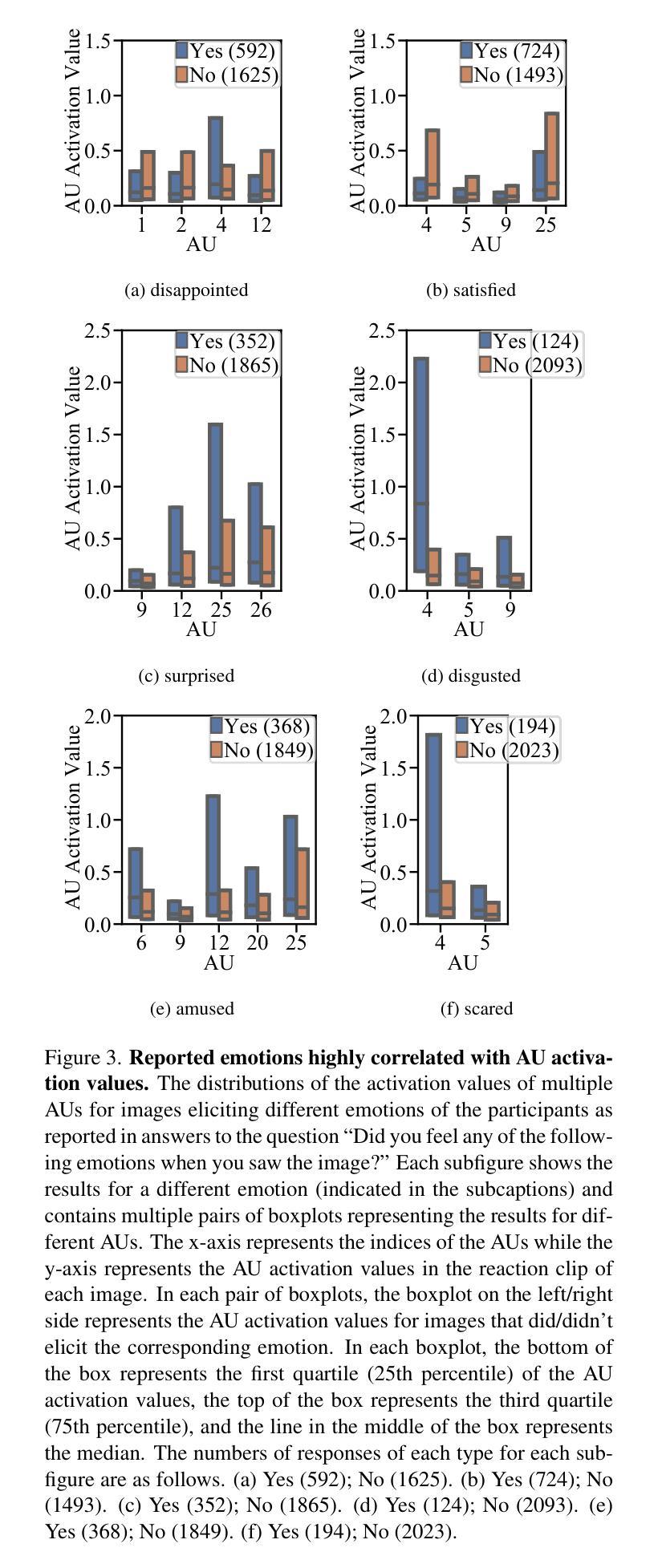
Researchers have proposed to use data of human preference feedback to fine-tune text-to-image generative models. However, the scalability of human feedback collection has been limited by its reliance on manual annotation. Therefore, we develop and test a method to automatically score user preferences from their spontaneous facial expression reaction to the generated images. We collect a dataset of Facial Expression Reaction to Generated Images (FERGI) and show that the activations of multiple facial action units (AUs) are highly correlated with user evaluations of the generated images. We develop an FAU-Net (Facial Action Units Neural Network), which receives inputs from an AU estimation model, to automatically score user preferences for text-to-image generation based on their facial expression reactions, which is complementary to the pre-trained scoring models based on the input text prompts and generated images. Integrating our FAU-Net valence score with the pre-trained scoring models improves their consistency with human preferences. This method of automatic annotation with facial expression analysis can be potentially generalized to other generation tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/ShuangquanFeng/FERGI, and the dataset is also available at the same link for research purposes.
研究者已经提出利用人类偏好反馈数据来微调文本到图像的生成模型。然而,人类反馈收集的扩展性受到了其依赖于手动注释的限制。因此,我们开发并测试了一种方法,通过自动评分用户对生成图像的自发表情反应来评估用户偏好。我们收集了面部表情反应图像生成数据集(FERGI),并发现多个面部动作单元(AUs)的激活与用户对生成图像的评价高度相关。我们开发了一个面部动作单元神经网络(FAU-Net),该网络从面部动作单元模型接收输入,基于用户的面部表情反应自动评分文本到图像的生成偏好,这与基于输入文本提示和生成图像预先训练的评分模型互补。将我们的FAU-Net情感评分与预先训练的评分模型相结合,提高了与人类偏好的一致性。这种利用面部表情分析进行自动注释的方法可以潜在地推广到其他生成任务。代码可在https://github.com/ShuangquanFeng/FERGI找到,数据集也可用于研究目的,链接相同。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用人类偏好反馈数据微调文本到图像的生成模型是一大研究热点。以往依赖手动标注的方式限制了人类反馈的收集规模。为解决这个问题,我们开发并测试了一种方法,通过自动分析用户面对生成图像时的面部表情来评分其偏好。我们创建了面部表情反应图像数据集(FERGI),发现面部动作单元(AU)的激活与用户评价高度相关。进一步,我们开发了一个面部动作单元神经网络(FAU-Net),该网络接收来自AU估计模型的输入,基于用户的面部表情反应自动为文本到图像的生成评分,与基于输入文本提示和生成图像的预训练评分模型形成互补。将我们的FAU-Net情感评分与预训练评分模型相结合,提高了与人类偏好的一致性。这种基于面部表情分析的自动标注方法可推广到其他生成任务中。相关代码和数据集已公开,访问链接:https://github.com/ShuangquanFeng/FERGI。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员提出使用人类偏好反馈数据来微调文本到图像的生成模型。
- 传统的手动标注方式限制了人类反馈的收集规模。
- 开发了一种通过自动分析用户面部表情来评分其偏好新方法。
- 创建了面部表情反应图像数据集(FERGI)。
- 发现面部动作单元(AU)的激活与用户评价高度相关。
- 开发了面部动作单元神经网络(FAU-Net)以自动评分文本到图像的生成偏好。
点此查看论文截图