⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
KnowTrace: Bootstrapping Iterative Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Structured Knowledge Tracing
Authors:Rui Li, Quanyu Dai, Zeyu Zhang, Xu Chen, Zhenhua Dong, Ji-Rong Wen
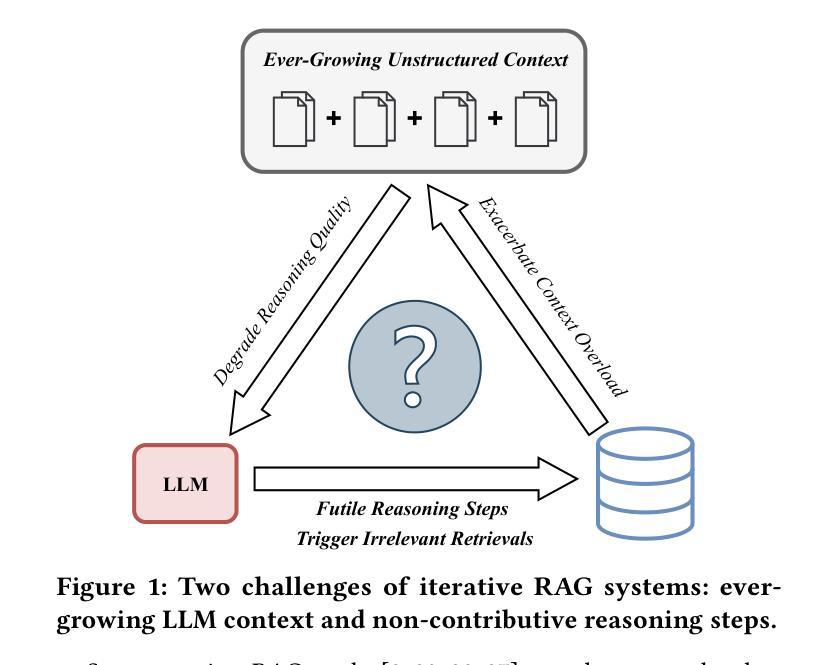
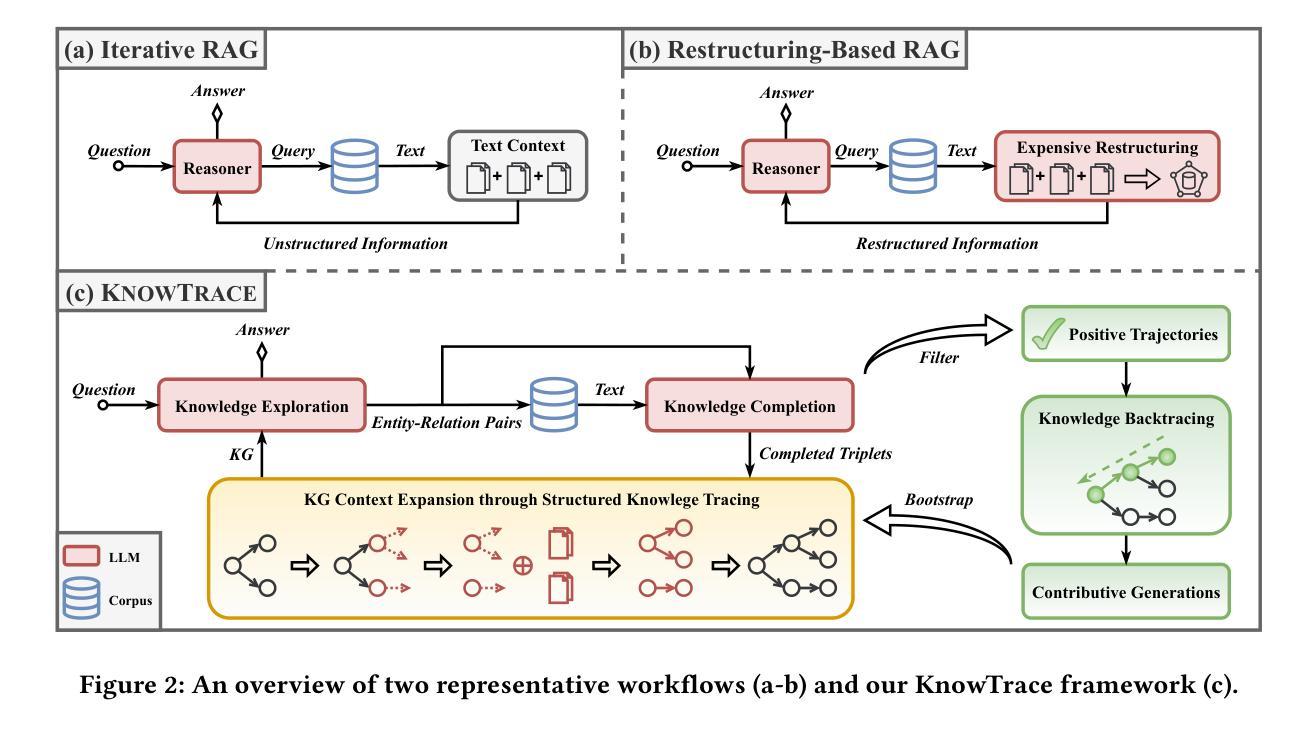
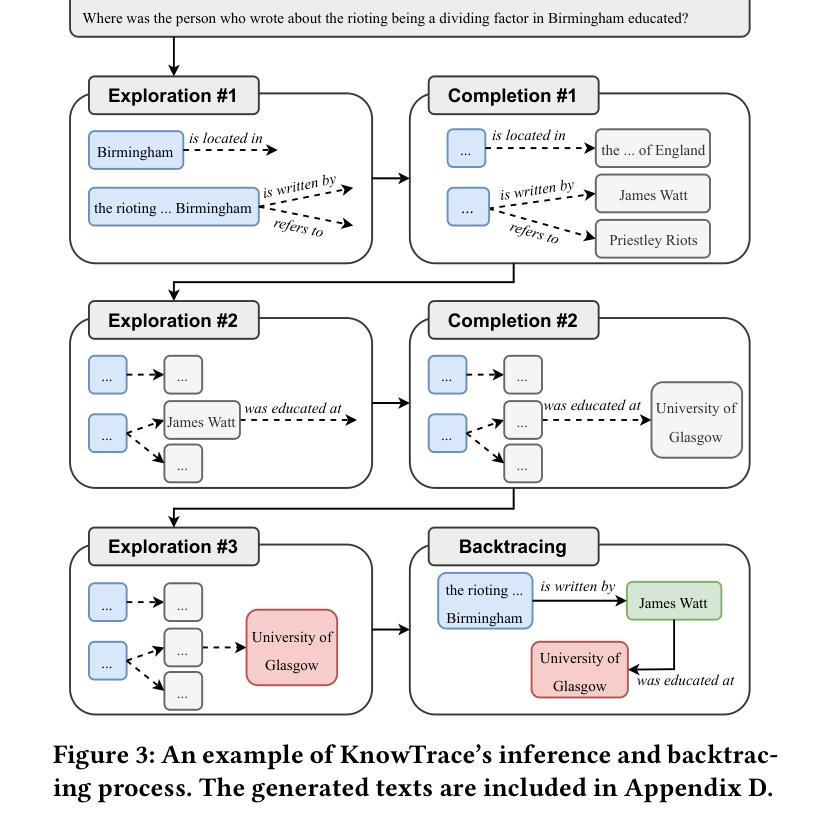
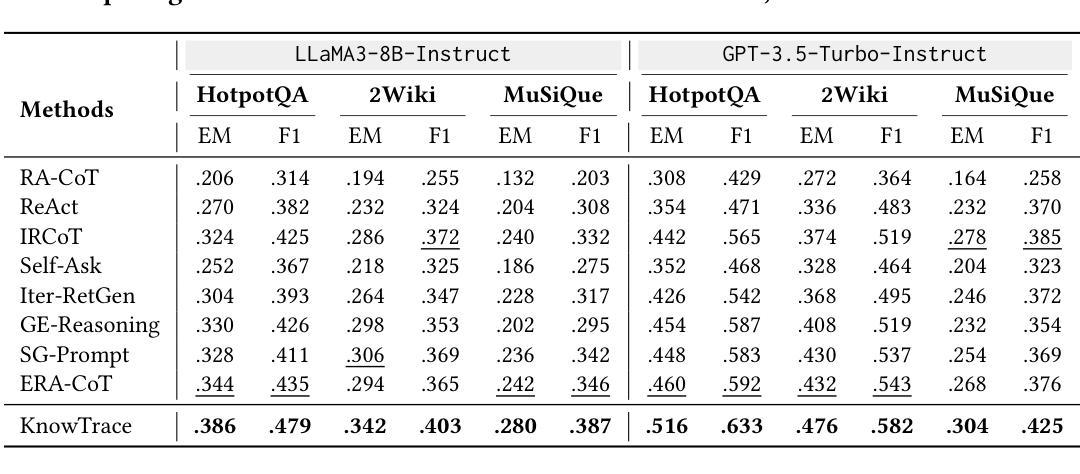
Recent advances in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) furnish large language models (LLMs) with iterative retrievals of relevant information to handle complex multi-hop questions. These methods typically alternate between LLM reasoning and retrieval to accumulate external information into the LLM’s context. However, the ever-growing context inherently imposes an increasing burden on the LLM to perceive connections among critical information pieces, with futile reasoning steps further exacerbating this overload issue. In this paper, we present KnowTrace, an elegant RAG framework to (1) mitigate the context overload and (2) bootstrap higher-quality multi-step reasoning. Instead of simply piling the retrieved contents, KnowTrace autonomously traces out desired knowledge triplets to organize a specific knowledge graph relevant to the input question. Such a structured workflow not only empowers the LLM with an intelligible context for inference, but also naturally inspires a reflective mechanism of knowledge backtracing to identify contributive LLM generations as process supervision data for self-bootstrapping. Extensive experiments show that KnowTrace consistently surpasses existing methods across three multi-hop question answering benchmarks, and the bootstrapped version further amplifies the gains.
最近,检索增强生成(RAG)技术的进展为大型语言模型(LLM)提供了相关的迭代检索信息,以处理复杂的多跳问题。这些方法通常在LLM推理和检索之间进行交替,以将外部信息累积到LLM的上下文中。然而,不断增长的上下文固有地对LLM感知关键信息片段之间的联系施加了越来越重的负担,徒劳的推理步骤进一步加剧了这一过载问题。在本文中,我们提出了KnowTrace,这是一个优雅的RAG框架,旨在(1)减轻上下文过载问题;(2)启动更高质量的多步推理。KnowTrace并没有简单地堆砌检索内容,而是自主地追踪所需的知识三元组,以组织出与输入问题相关的特定知识图谱。这种结构化的工作流程不仅为LLM提供了用于推断的可理解上下文,而且还自然地激发了知识回溯的反思机制,以识别作为过程监督数据的贡献LLM世代,以实现自我引导。大量实验表明,KnowTrace在三个多跳问题回答基准测试上始终超过现有方法,并且启动的版本进一步扩大了收益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD 2025
Summary
大型语言模型通过检索增强生成技术处理复杂多跳问题时,面临上下文信息过载的问题。本文提出KnowTrace框架,通过追踪所需知识三元组组织特定知识图谱,缓解上下文信息过载问题,并促进高质量多步推理。KnowTrace框架自主构建知识图谱,提供易于理解的上下文进行推理,并通过知识回溯机制自我提升。实验表明,KnowTrace在三个多跳问答基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理复杂多跳问题时,上下文信息过载是一个关键问题。
- KnowTrace框架通过追踪所需知识三元组来缓解上下文信息过载问题。
- KnowTrace能够自主构建与输入问题相关的特定知识图谱。
- KnowTrace框架提供了一种易于理解的上下文,增强了大型语言模型的推理能力。
- KnowTrace通过知识回溯机制,实现了大型语言模型的自我提升。
- 实验结果表明,KnowTrace在多个多跳问答测试中表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



RedAHD: Reduction-Based End-to-End Automatic Heuristic Design with Large Language Models
Authors:Nguyen Thach, Aida Riahifar, Nathan Huynh, Hau Chan
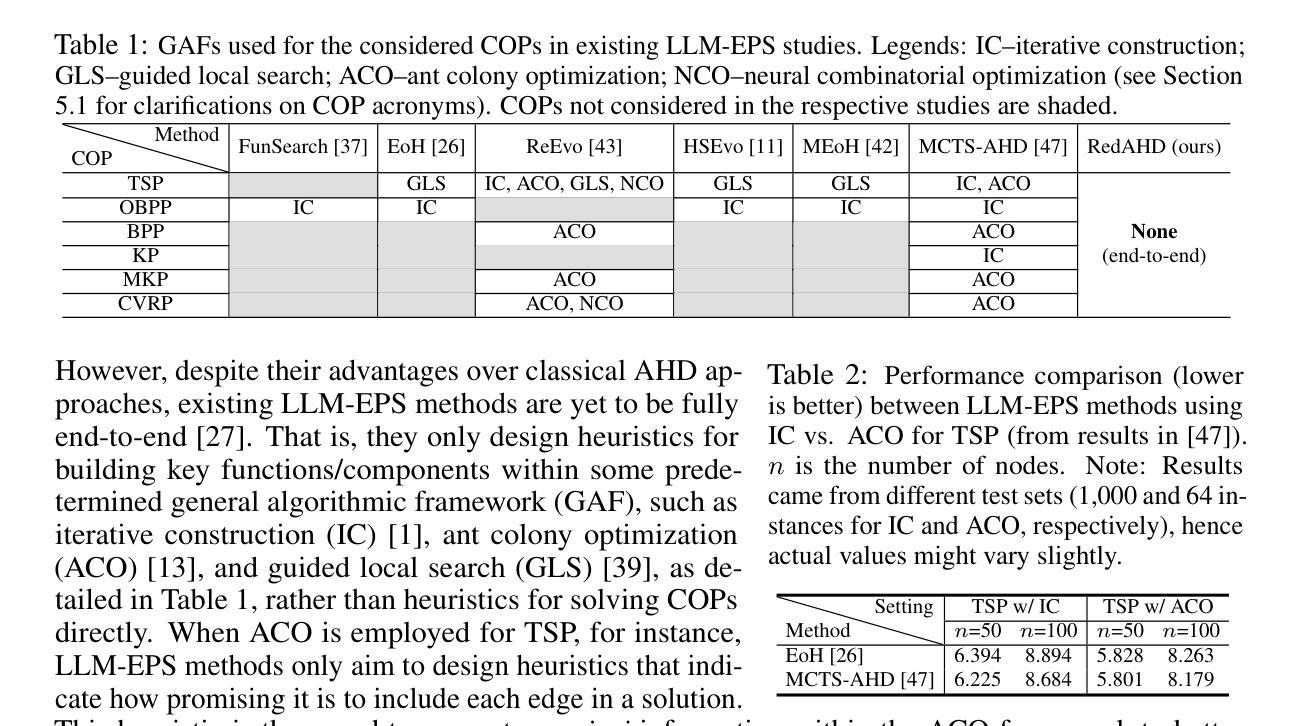
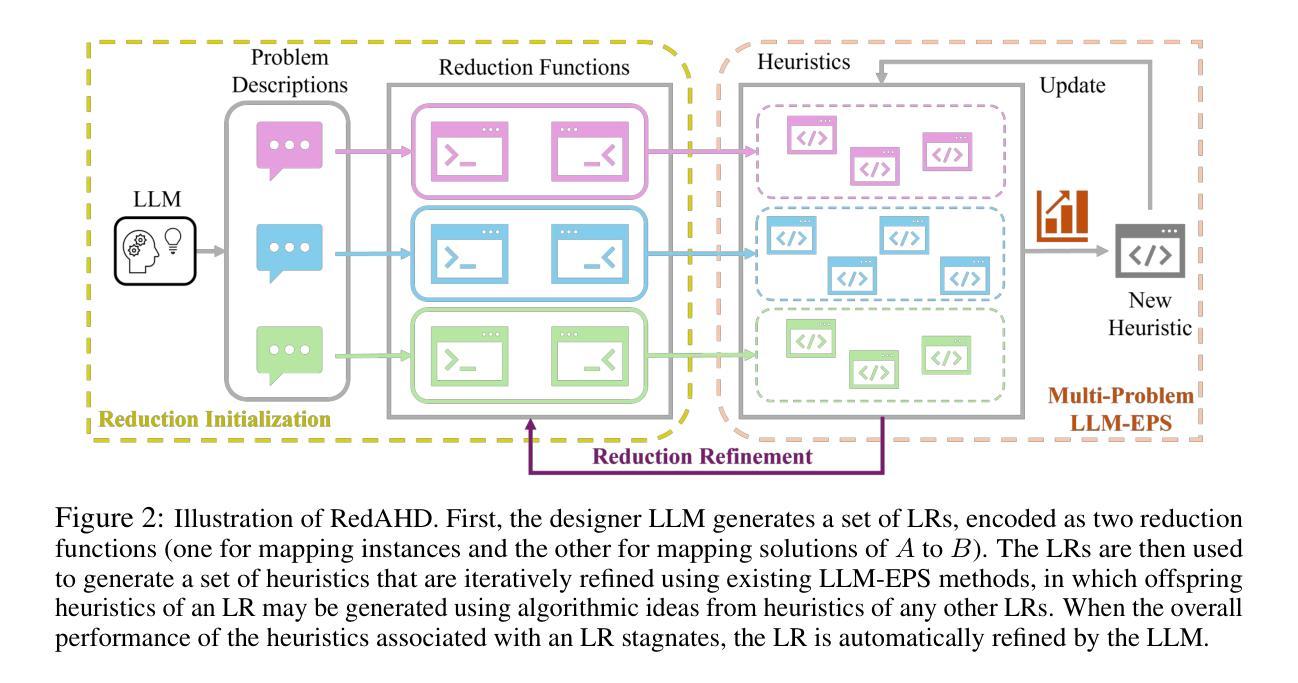
Solving NP-hard combinatorial optimization problems (COPs) (e.g., traveling salesman problems (TSPs) and capacitated vehicle routing problems (CVRPs)) in practice traditionally involves handcrafting heuristics or specifying a search space for finding effective heuristics. The main challenges from these approaches, however, are the sheer amount of domain knowledge and implementation efforts required from human experts. Recently, significant progress has been made to address these challenges, particularly by using large language models (LLMs) to design heuristics within some predetermined generalized algorithmic framework (GAF, e.g., ant colony optimization and guided local search) for building key functions/components (e.g., a priori information on how promising it is to include each edge in a solution for TSP and CVRP). Although existing methods leveraging this idea have shown to yield impressive optimization performance, they are not fully end-to-end and still require considerable manual interventions. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end framework, named RedAHD, that enables these LLM-based heuristic design methods to operate without the need of GAFs. More specifically, RedAHD employs LLMs to automate the process of reduction, i.e., transforming the COP at hand into similar COPs that are better-understood, from which LLM-based heuristic design methods can design effective heuristics for directly solving the transformed COPs and, in turn, indirectly solving the original COP. Our experimental results, evaluated on six COPs, show that RedAHD is capable of designing heuristics with competitive or improved results over the state-of-the-art methods with minimal human involvement.
解决NP难的组合优化问题(COPs)(例如旅行推销员问题(TSP)和容量车辆路径问题(CVRP))在实践中通常涉及手工制作启发式方法或指定一个搜索空间以找到有效的启发式方法。然而,这些方法面临的主要挑战是:需要大量领域知识和实现努力来自人类专家。最近,特别是在使用大型语言模型(LLM)在预定的通用算法框架(GAF,例如蚁群优化和引导局部搜索)内设计启发式方法来构建关键功能/组件方面取得了重大进展(例如,有关TSP和CVRP的解决方案中包含每条边的潜在前景的先验信息)。尽管现有的利用这一思想的方法已经显示出令人印象深刻的优化性能,但它们并不完全端到端,仍然需要大量的手动干预。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型端到端框架RedAHD,使这些基于LLM的启发式设计方法能够在不需要GAF的情况下进行操作。更具体地说,RedAHD采用LLM自动化缩减过程,即将手头的COP转换为更易于理解的相似COP,基于LLM的启发式设计方法可以直接为转换后的COP设计有效的启发式方法,从而间接解决原始的COP。我们在六种COP上进行的实验结果表明,RedAHD设计的启发式方法与最新技术相比具有竞争力或更佳的结果,并且几乎不需要人工参与。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
在解决NP难的组合优化问题(如旅行商问题和带容量约束的车辆路径问题)时,传统的方法通常需要人类专家手动设计启发式算法或在预定的通用算法框架内寻找有效的启发式算法。然而,这些方法需要大量的领域知识和实施努力。最近,通过使用大型语言模型(LLM)来设计启发式算法,已经取得了显著的进展。本文提出了一种新型端到端框架RedAHD,该框架使用LLM自动化减少组合优化问题的复杂性,从而无需通用算法框架即可设计启发式算法。实验结果表明,RedAHD能够在六个组合优化问题上设计具有竞争力的启发式算法,且只需最少的人工参与。
Key Takeaways
- 解决NP难的组合优化问题传统上需要手动设计启发式算法或寻找有效的启发式算法,这需要大量的领域知识和实施努力。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在解决这些挑战方面取得了显著进展,尤其是在设计启发式算法方面。
- 提出了一种新型端到端框架RedAHD,该框架使用LLM自动化减少问题的复杂性,从而无需通用算法框架即可设计启发式算法。
- RedAHD框架可以直接解决转换后的组合优化问题,从而间接解决原始问题。
- 实验结果表明,RedAHD能够在多个组合优化问题上设计具有竞争力的启发式算法。
- RedAHD设计的启发式算法在结果上可以与现有最先进的方法相竞争或有所改进。
点此查看论文截图

DreamPRM: Domain-Reweighted Process Reward Model for Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Qi Cao, Ruiyi Wang, Ruiyi Zhang, Sai Ashish Somayajula, Pengtao Xie
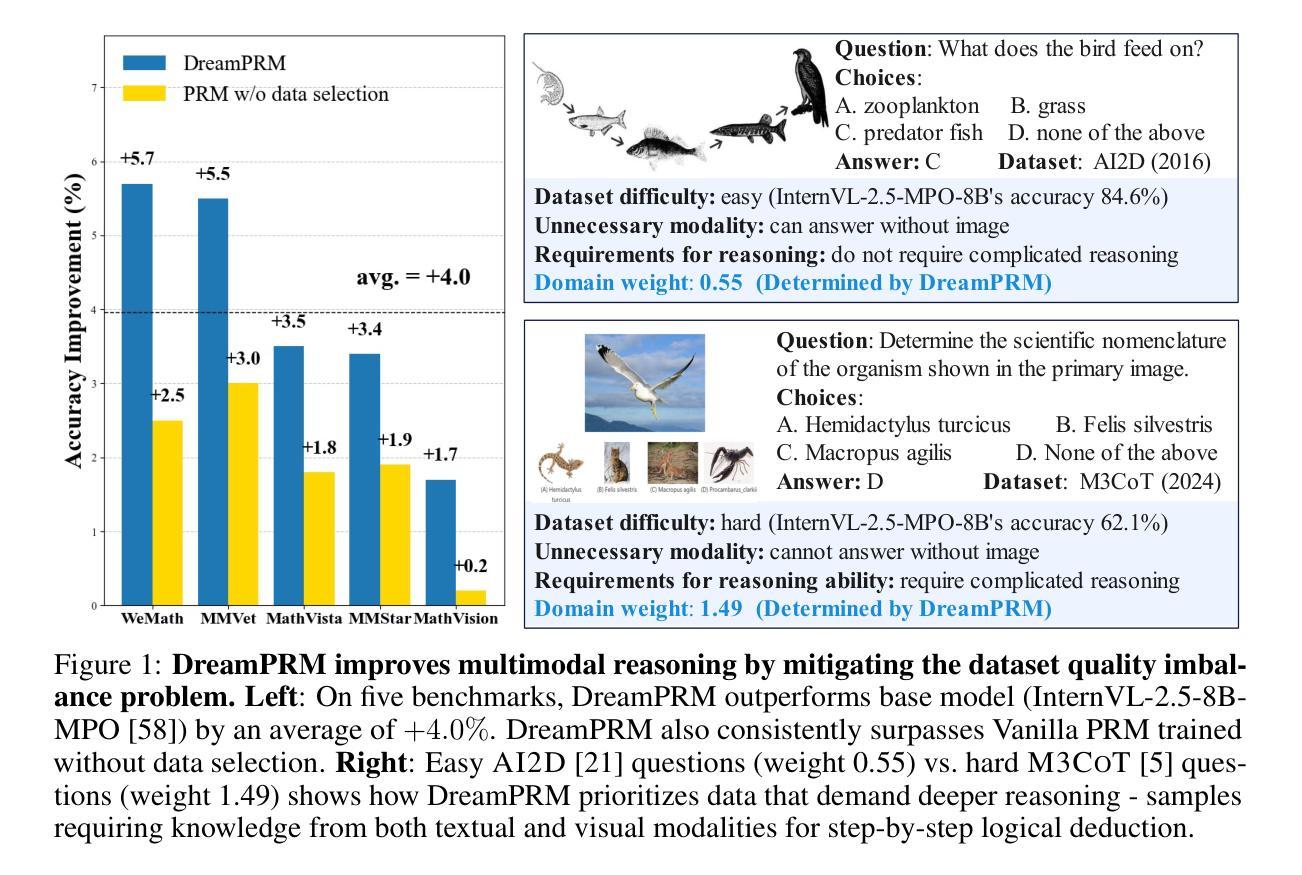
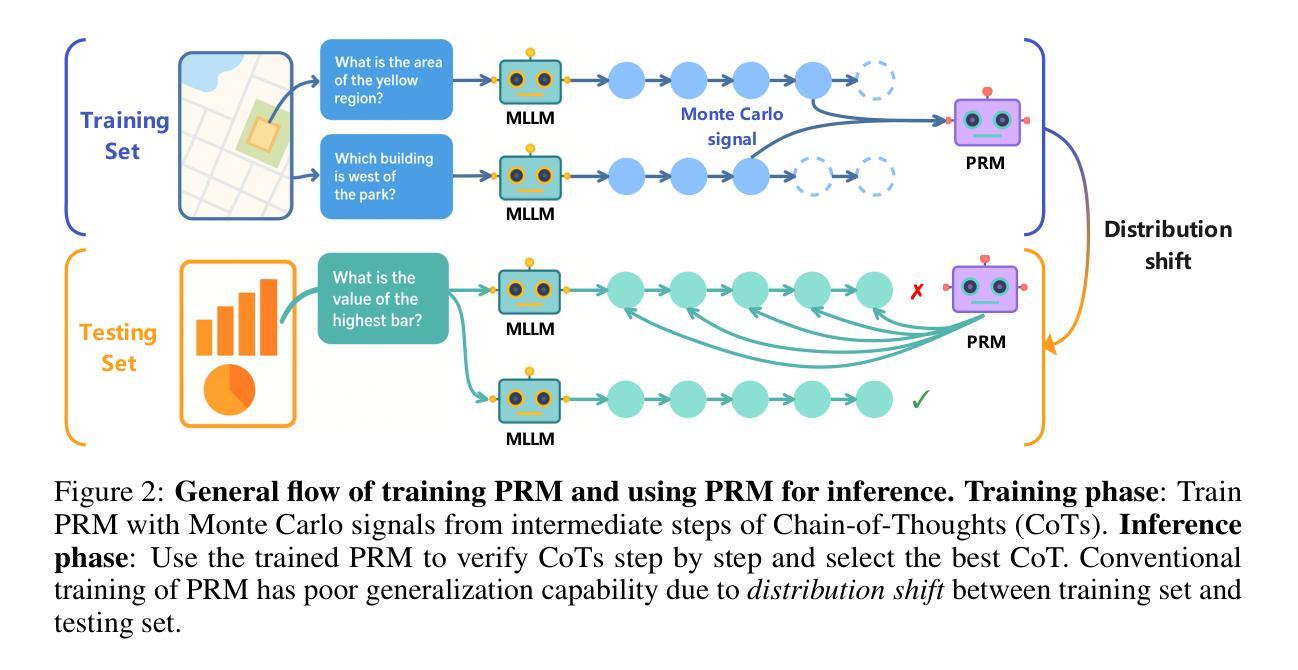
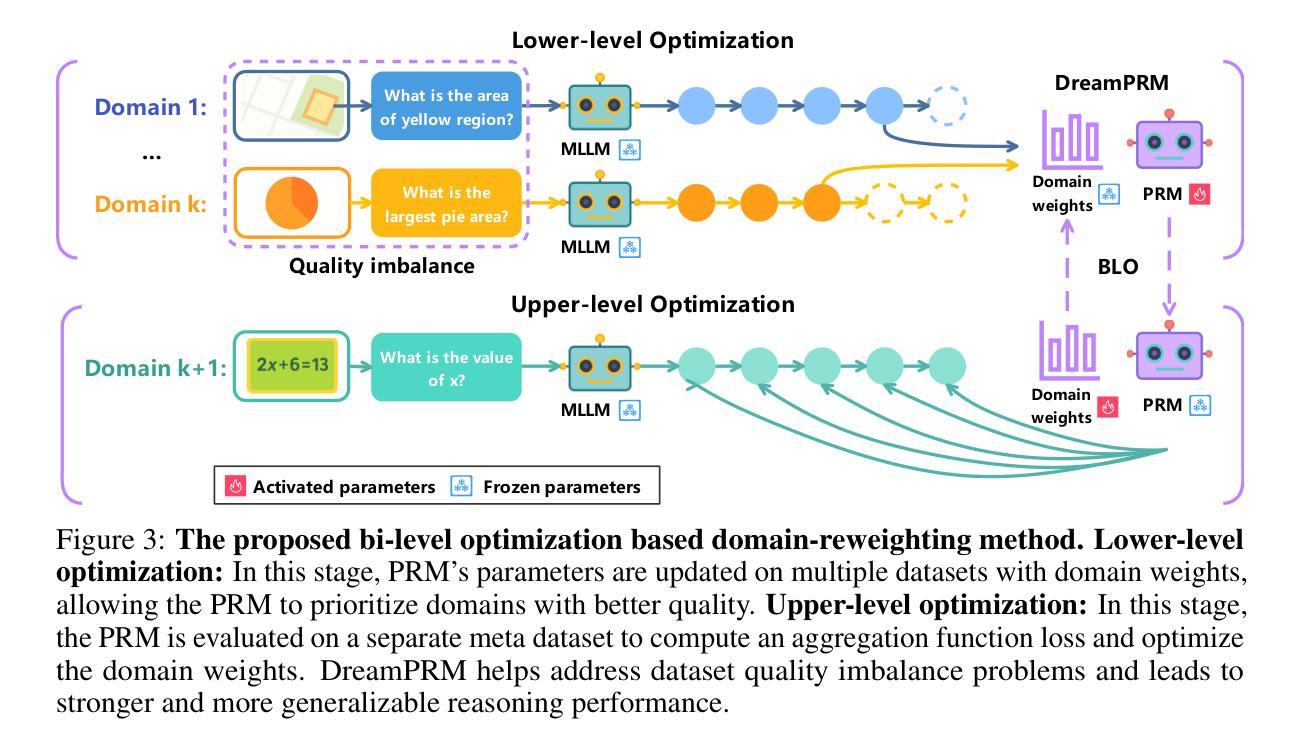
Reasoning has substantially improved the performance of large language models (LLMs) on complicated tasks. Central to the current reasoning studies, Process Reward Models (PRMs) offer a fine-grained evaluation of intermediate reasoning steps and guide the reasoning process. However, extending PRMs to multimodal large language models (MLLMs) introduces challenges. Since multimodal reasoning covers a wider range of tasks compared to text-only scenarios, the resulting distribution shift from the training to testing sets is more severe, leading to greater generalization difficulty. Training a reliable multimodal PRM, therefore, demands large and diverse datasets to ensure sufficient coverage. However, current multimodal reasoning datasets suffer from a marked quality imbalance, which degrades PRM performance and highlights the need for an effective data selection strategy. To address the issues, we introduce DreamPRM, a domain-reweighted training framework for multimodal PRMs which employs bi-level optimization. In the lower-level optimization, DreamPRM performs fine-tuning on multiple datasets with domain weights, allowing the PRM to prioritize high-quality reasoning signals and alleviating the impact of dataset quality imbalance. In the upper-level optimization, the PRM is evaluated on a separate meta-learning dataset; this feedback updates the domain weights through an aggregation loss function, thereby improving the generalization capability of trained PRM. Extensive experiments on multiple multimodal reasoning benchmarks covering both mathematical and general reasoning show that test-time scaling with DreamPRM consistently improves the performance of state-of-the-art MLLMs. Further comparisons reveal that DreamPRM’s domain-reweighting strategy surpasses other data selection methods and yields higher accuracy gains than existing test-time scaling approaches.
推理技术已显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的性能。当前的推理研究的核心,过程奖励模型(PRM)对中间推理步骤进行了精细评估,并引导了推理过程。然而,将PRM扩展到多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时面临挑战。由于多模态推理涵盖了与纯文本场景相比更广泛的范围的任务,从训练集到测试集的分布变化更加严重,导致更大的泛化难度。因此,训练可靠的多模态PRM需要大型且多样化的数据集以确保足够的覆盖范围。然而,当前的多模态推理数据集存在明显的质量不平衡问题,这降低了PRM的性能,并突出了对有效数据选择策略的需求。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了DreamPRM,这是一个多模态PRM的域加权训练框架,它采用双层优化。在下层优化中,DreamPRM在多个数据集上进行微调并使用域权重,使PRM能够优先考虑高质量推理信号,并减轻数据集质量不平衡的影响。在上层优化中,PRM在一个单独的元学习数据集上进行评估;此反馈通过聚合损失函数更新域权重,从而提高训练有素的PRM的泛化能力。在涵盖数学和一般推理的多个多模态推理基准测试上的大量实验表明,使用DreamPRM的测试时间缩放一致地提高了最先进的多模态语言模型性能。进一步的比较表明,DreamPRM的域重权策略优于其他数据选择方法,并产生了高于现有测试时间缩放方法的准确性增益。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的表现通过引入推理机制得到了显著提升。过程奖励模型(PRM)作为当前推理研究的中心,能对中间推理步骤进行精细评估并引导推理过程。然而,将PRM扩展到多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时面临挑战。多模态推理涵盖的任务范围更广,导致从训练集到测试集的分布转移更加严重,加大了泛化难度。因此,训练可靠的多模态PRM需要大规模、多样化的数据集以确保充分覆盖。然而,当前的多模态推理数据集存在明显质量不平衡问题,降低了PRM的性能,凸显出有效数据选择策略的必要性。为解决这些问题,我们提出了DreamPRM,一种多模态PRM的领域加权训练框架,采用两级优化。DreamPRM通过精细调整多个数据集上的领域权重来进行低级优化,使PRM能够优先获取高质量的推理信号,减轻数据集质量不平衡的影响。在高级优化中,PRM在单独的元学习数据集上进行评估,通过聚合损失函数更新领域权重,从而提高训练好的PRM的泛化能力。在多个涵盖数学和通用推理的多模态推理基准测试上的实验表明,使用DreamPRM的测试时间缩放一致地提高了最先进的多模态LLM的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 推理机制已显著提升了大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂任务上的表现。
- 过程奖励模型(PRM)能够精细评估中间推理步骤并引导推理过程。
- 将PRM扩展到多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时存在挑战,因为多模态推理涵盖更广泛的任务范围。
- 多模态推理数据集存在质量不平衡问题,需要有效数据选择策略。
- DreamPRM是一种多模态PRM的领域加权训练框架,采用两级优化来提高PRMs的性能和泛化能力。
- DreamPRM通过精细调整领域权重来应对数据集质量不平衡问题。
点此查看论文截图

FLAME-MoE: A Transparent End-to-End Research Platform for Mixture-of-Experts Language Models
Authors:Hao Kang, Zichun Yu, Chenyan Xiong
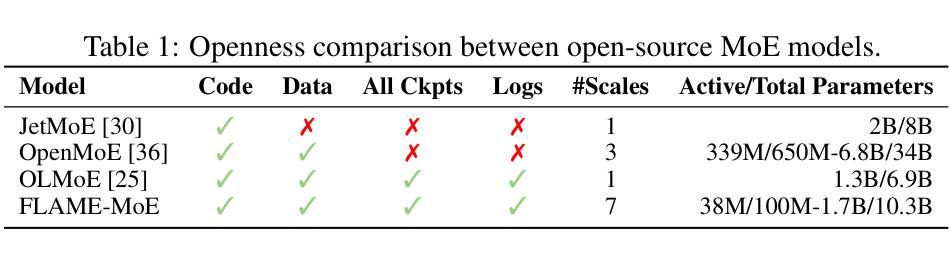
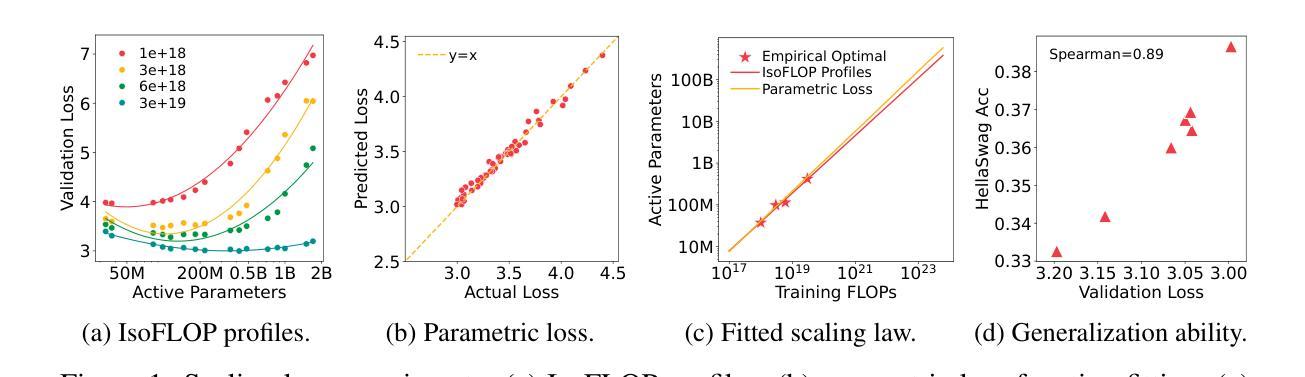
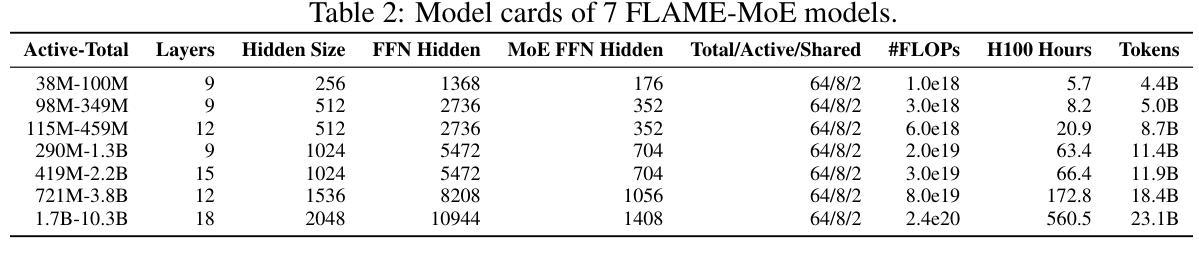
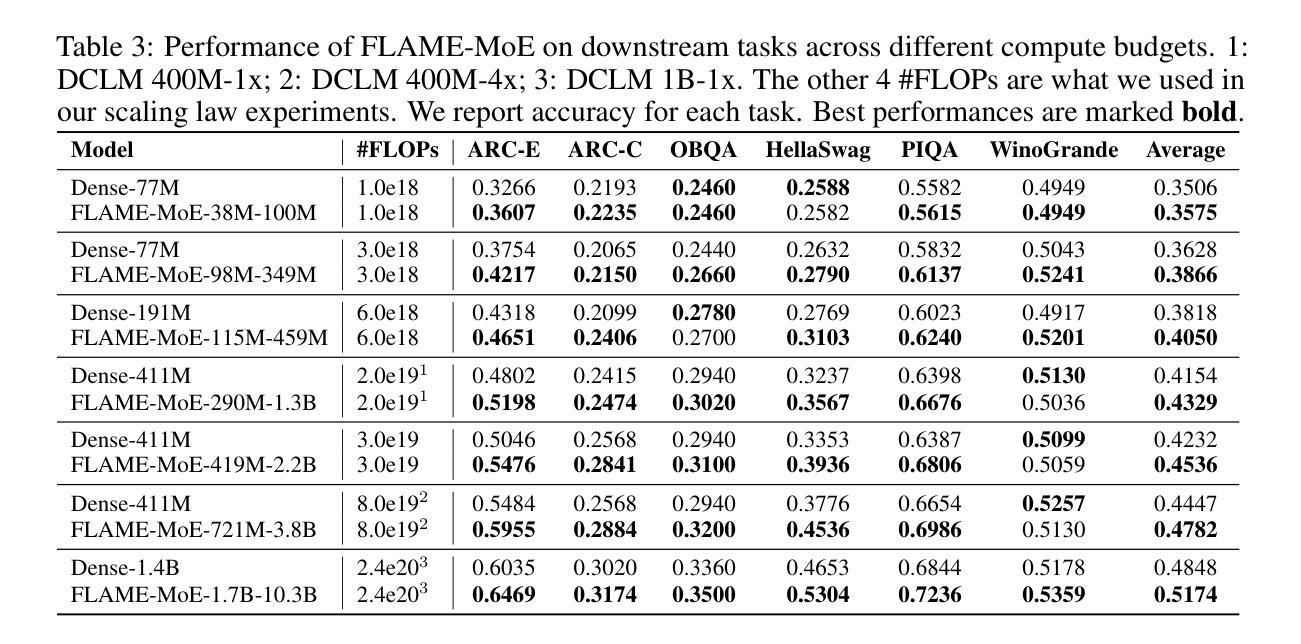
Recent large language models such as Gemini-1.5, DeepSeek-V3, and Llama-4 increasingly adopt Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures, which offer strong efficiency-performance trade-offs by activating only a fraction of the model per token. Yet academic researchers still lack a fully open, end-to-end MoE platform for investigating scaling, routing, and expert behavior. We release FLAME-MoE, a completely open-source research suite composed of seven decoder-only models, ranging from 38M to 1.7B active parameters, whose architecture–64 experts with top-8 gating and 2 shared experts–closely reflects modern production LLMs. All training data pipelines, scripts, logs, and checkpoints are publicly available to enable reproducible experimentation. Across six evaluation tasks, FLAME-MoE improves average accuracy by up to 3.4 points over dense baselines trained with identical FLOPs. Leveraging full training trace transparency, we present initial analyses showing that (i) experts increasingly specialize on distinct token subsets, (ii) co-activation matrices remain sparse, reflecting diverse expert usage, and (iii) routing behavior stabilizes early in training. All code, training logs, and model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/cmu-flame/FLAME-MoE.
最近的大型语言模型,如Gemini-1.5、DeepSeek-V3和Llama-4,越来越采用Mixture-of-Experts(MoE)架构。这种架构通过每令牌仅激活模型的一部分,实现了强大的效率性能权衡。然而,研究人员仍缺乏一个完全开放的端到端MoE平台来调查规模扩展、路由和专家行为。我们发布FLAME-MoE,这是一个完全开源的研究套件,包含七个仅解码器模型,活跃参数范围从38M到1.7B。其架构包括64个专家、前8个门控和2个共享专家,紧密地反映了现代生产大型语言模型。所有训练数据管道、脚本、日志和检查点都公开可用,以便进行可重复的实验。在六个评估任务中,FLAME-MoE在密集基准线上平均提高了高达3.4点的准确性,这是使用相同FLOPs进行训练的。利用完全的训练轨迹透明度,我们初步分析表明:(i)专家越来越擅长处理不同的令牌子集;(ii)协同激活矩阵保持稀疏,反映了专家的多样化使用;(iii)路由行为在训练早期趋于稳定。所有代码、训练日志和模型检查点均可在https://github.com/cmu-flame/FLAME-MoE获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF All code, training logs, and model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/cmu-flame/FLAME-MoE
Summary:
近期的大型语言模型如Gemini-1.5、DeepSeek-V3和Llama-4采用Mixture-of-Experts(MoE)架构,通过每令牌仅激活模型的一部分来实现高效的性能权衡。然而,研究人员仍缺乏一个完全开放的端到端MoE平台来探究规模扩展、路由和专家行为。为此,我们发布了完全开源的研究套件FLAME-MoE,包含7个解码器模型,活跃参数范围从3.8亿到17亿不等。其架构由现代生产型LLM借鉴,采用专家数量达64个,前八个进行门控选择,并共享两个专家。所有训练数据管道、脚本、日志和检查点都已公开,便于进行可重复的实验。在六个评估任务中,FLAME-MoE相较于使用相同浮点运算次数训练的密集基准模型,平均准确度提高了高达3.4个点。借助完整的训练轨迹透明度,我们初步分析表明专家越来越专注于特定的令牌子集,联合激活矩阵保持稀疏反映多样的专家使用状况,且路由行为在训练早期就稳定下来。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)开始采用Mixture-of-Experts(MoE)架构来提升效率和性能。
- 缺乏全面的MoE平台来深入研究其特点如规模扩展、路由和专家行为。
- 新推出的开源研究套件FLAME-MoE旨在解决上述问题,包含一系列解码器模型,并公开所有训练数据和脚本。
- FLAME-MoE在六个评估任务中的性能优于基准模型,平均准确度提高达3.4个点。
- 专家分析显示不同专家在不同令牌子集上的专业分工越来越明确。
- 联合激活矩阵保持稀疏反映了专家使用方式的多样性。
点此查看论文截图

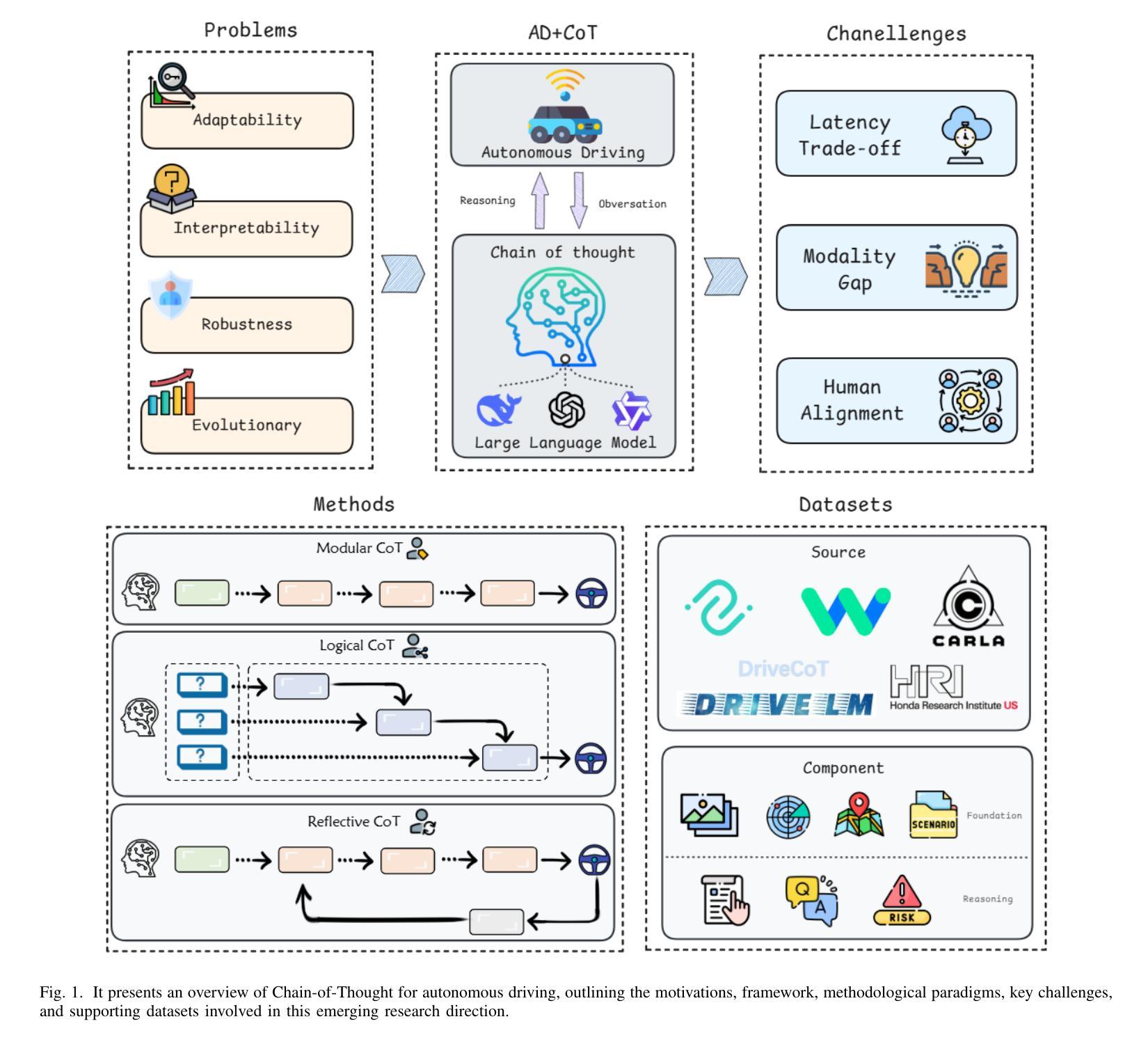
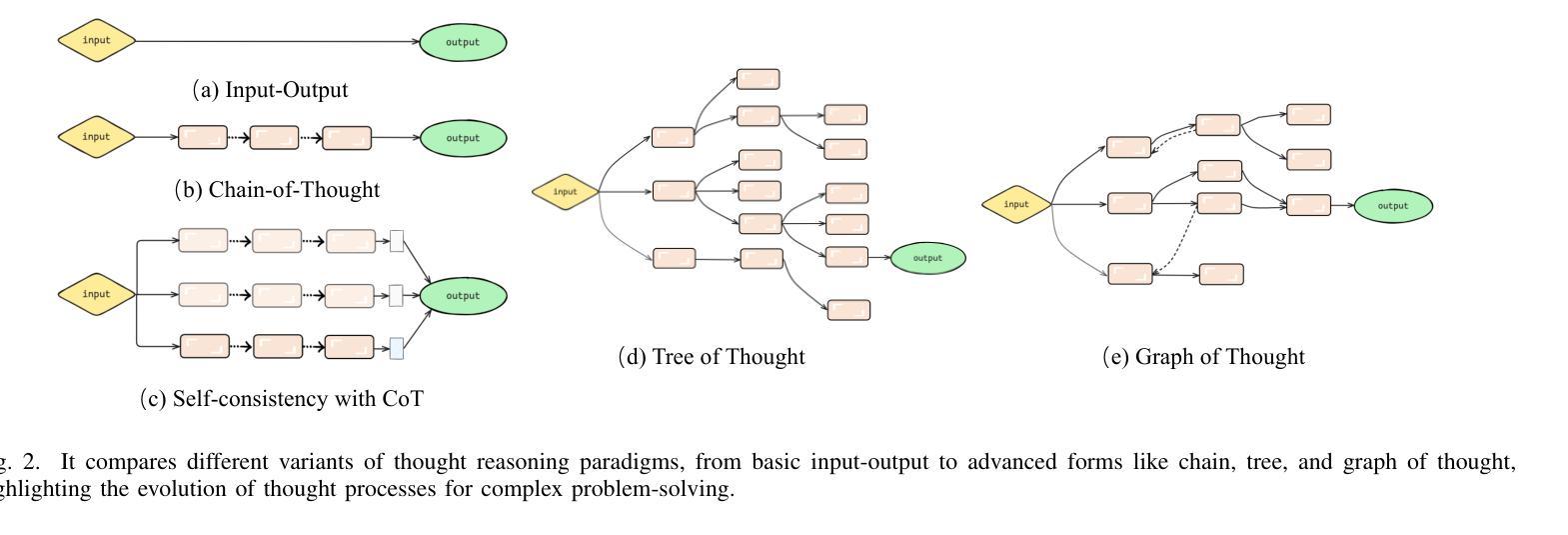
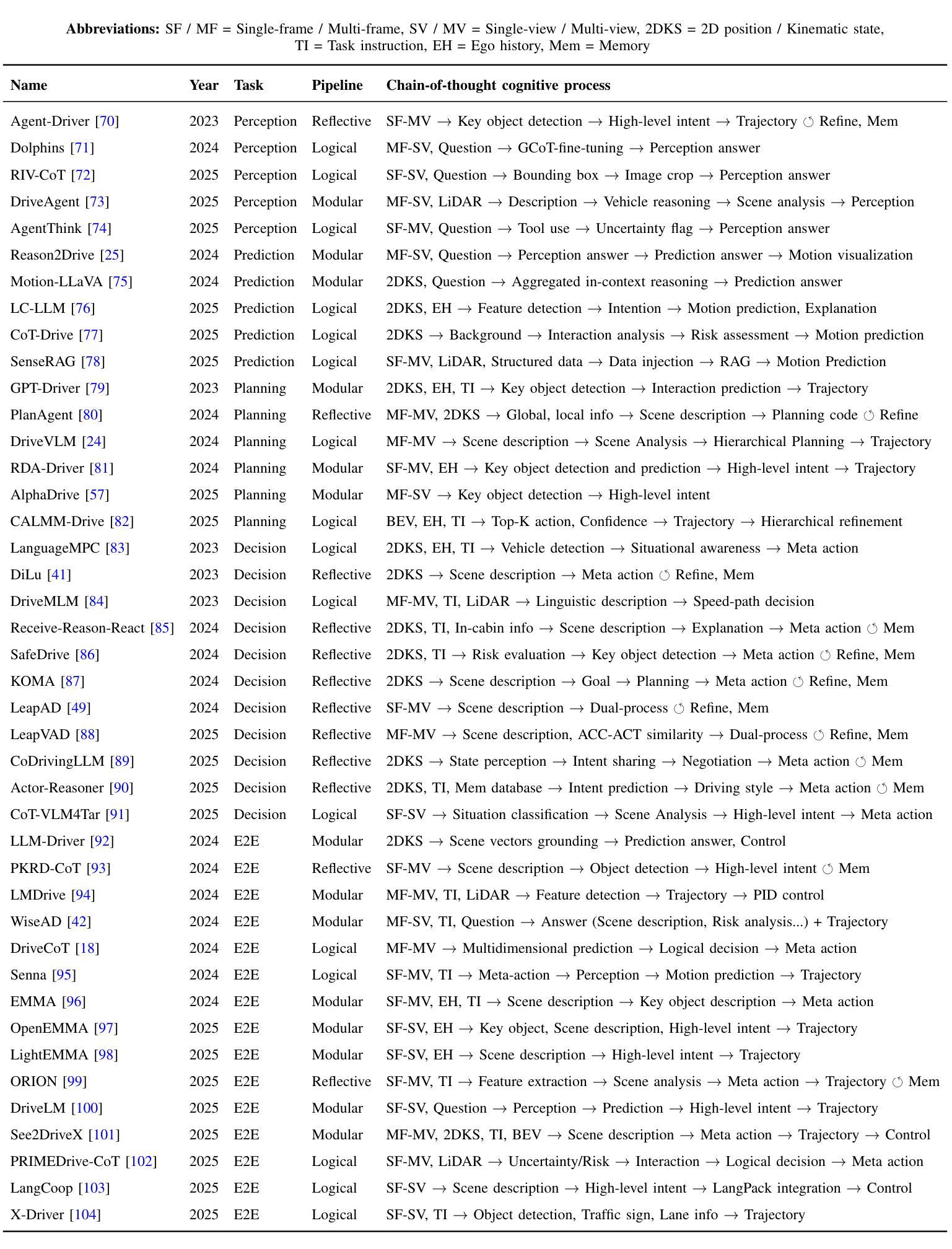
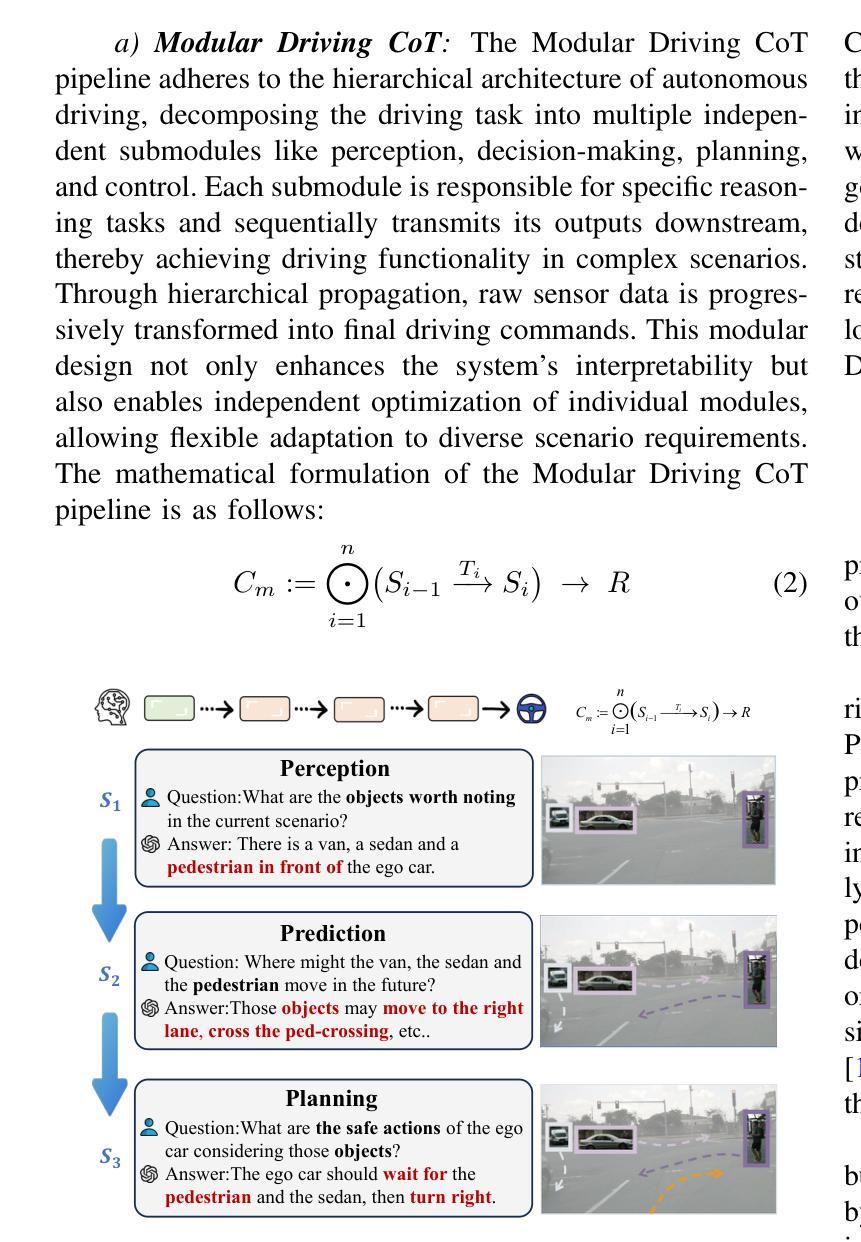
Chain-of-Thought for Autonomous Driving: A Comprehensive Survey and Future Prospects
Authors:Yixin Cui, Haotian Lin, Shuo Yang, Yixiao Wang, Yanjun Huang, Hong Chen
The rapid evolution of large language models in natural language processing has substantially elevated their semantic understanding and logical reasoning capabilities. Such proficiencies have been leveraged in autonomous driving systems, contributing to significant improvements in system performance. Models such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek-R1, leverage Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, an advanced cognitive method that simulates human thinking processes, demonstrating remarkable reasoning capabilities in complex tasks. By structuring complex driving scenarios within a systematic reasoning framework, this approach has emerged as a prominent research focus in autonomous driving, substantially improving the system’s ability to handle challenging cases. This paper investigates how CoT methods improve the reasoning abilities of autonomous driving models. Based on a comprehensive literature review, we present a systematic analysis of the motivations, methodologies, challenges, and future research directions of CoT in autonomous driving. Furthermore, we propose the insight of combining CoT with self-learning to facilitate self-evolution in driving systems. To ensure the relevance and timeliness of this study, we have compiled a dynamic repository of literature and open-source projects, diligently updated to incorporate forefront developments. The repository is publicly available at https://github.com/cuiyx1720/Awesome-CoT4AD.
自然语言处理中的大型语言模型迅速进化,极大地提升了其语义理解和逻辑推理能力。这种能力已被应用于自动驾驶系统,为系统性能带来了显著改进。诸如OpenAI o1和DeepSeek-R1等模型,采用思维链(CoT)推理,这是一种高级认知方法,模拟人类思维过程,在复杂任务中展现出卓越的推理能力。通过在一个系统的推理框架内构建复杂的驾驶场景,这种方法已成为自动驾驶的一个主要研究方向,极大地提高了系统处理挑战案例的能力。本文研究了CoT方法如何改善自动驾驶模型的推理能力。基于全面的文献综述,我们对CoT在自动驾驶中的动机、方法、挑战和未来研究方向进行了系统的分析。此外,我们提出了将CoT与自我学习相结合,以促进驾驶系统的自我进化的见解。为确保研究的时效性和时效性,我们精心收集和更新前沿文献和开源项目,并将其动态编入知识库,供公众访问。知识库可通过以下链接访问:https://github.com/cuiyx1720/Awesome-CoT4AD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 6 figures
Summary
大型语言模型在自然语言处理领域的快速发展显著提升了其语义理解和逻辑推理能力。这些能力已被应用于自动驾驶系统,极大地提升了系统性能。本文探讨了如何通过链式思维(Chain-of-Thought,CoT)方法提高自动驾驶模型的推理能力,展现了一种模拟人类思维过程的先进认知方法。通过系统分析CoT方法在自动驾驶中的动机、方法、挑战和未来研究方向,结合自我学习方法的融合,促进驾驶系统的自我进化。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型语义理解和逻辑推理能力的显著提升。
- 自动驾驶系统中应用大型语言模型,极大提升了系统性能。
- 链式思维(CoT)方法模拟人类思维过程,展现强大推理能力。
- CoT方法在自动驾驶中的动机、方法、挑战和未来研究方向的系统分析。
- CoT方法与自我学习方法的结合,促进驾驶系统的自我进化。
- 论文通过文献综述和开源项目动态更新,确保研究的时效性和相关性。
点此查看论文截图

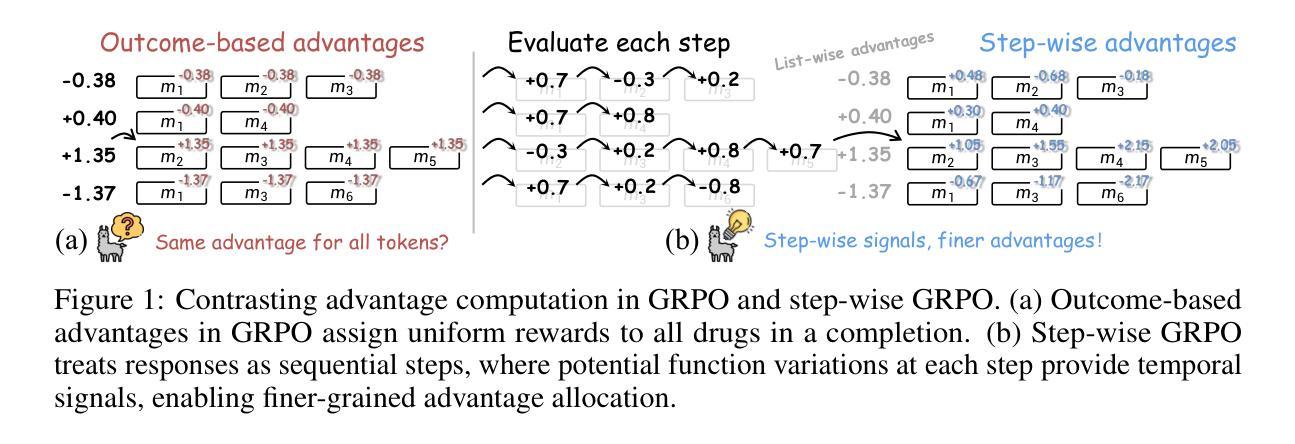
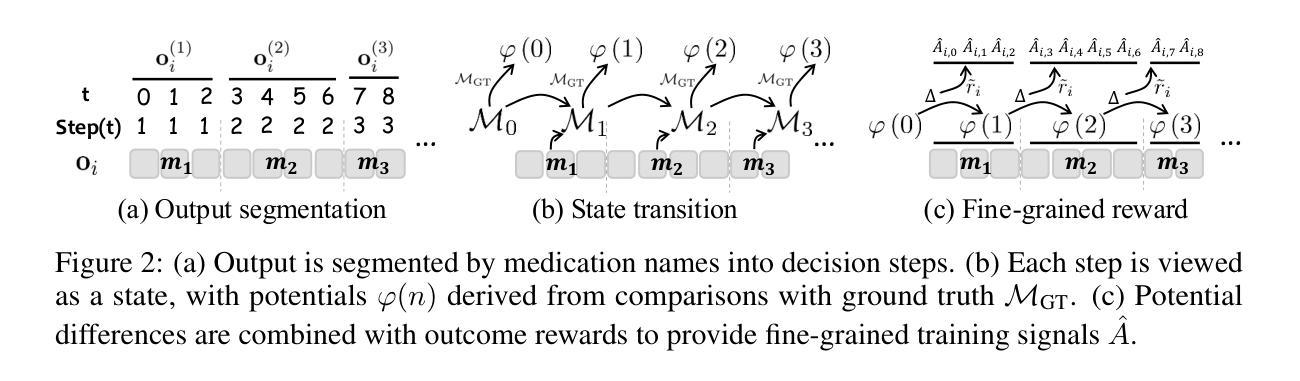
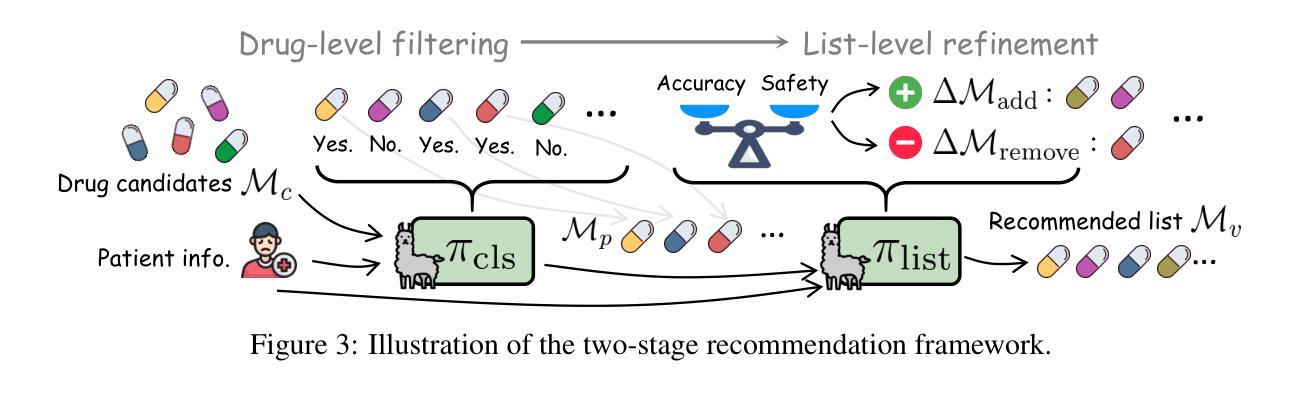
Fine-grained List-wise Alignment for Generative Medication Recommendation
Authors:Chenxiao Fan, Chongming Gao, Wentao Shi, Yaxin Gong, Zihao Zhao, Fuli Feng
Accurate and safe medication recommendations are critical for effective clinical decision-making, especially in multimorbidity cases. However, existing systems rely on point-wise prediction paradigms that overlook synergistic drug effects and potential adverse drug-drug interactions (DDIs). We propose FLAME, a fine-grained list-wise alignment framework for large language models (LLMs), enabling drug-by-drug generation of drug lists. FLAME formulates recommendation as a sequential decision process, where each step adds or removes a single drug. To provide fine-grained learning signals, we devise step-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with potential-based reward shaping, which explicitly models DDIs and optimizes the contribution of each drug to the overall prescription. Furthermore, FLAME enhances patient modeling by integrating structured clinical knowledge and collaborative information into the representation space of LLMs. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that FLAME achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering superior accuracy, controllable safety-accuracy trade-offs, and strong generalization across diverse clinical scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/cxfann/Flame.
准确且安全的用药推荐对于有效的临床决策至关重要,特别是在多病共存的情况下。然而,现有系统依赖于点对点预测范式,忽略了药物间的协同作用和潜在的药物相互作用(DDI)。我们提出了FLAME,一种用于大型语言模型(LLM)的精细粒度列表对齐框架,能够实现按药物逐个生成药物列表。FLAME将推荐表述为一个顺序决策过程,每一步都会增加或删除一种药物。为了提供精细化的学习信号,我们设计了基于步骤的组相对策略优化(GRPO)和基于潜力的奖励塑造,这明确地建模了药物相互作用,并优化了每个药物对整体处方的贡献。此外,FLAME通过整合结构化临床知识和协作信息到LLM的表示空间来增强患者建模。在基准数据集上的实验表明,FLAME达到了最先进的性能,具有出色的准确性、可控的安全性和准确性权衡以及在各种临床场景中的强大泛化能力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/cxfann/Flame找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
精准且安全的用药推荐对于有效的临床决策至关重要,特别是在多病共存的情况下。现有系统多采用点预测模式,忽略了药物间的协同作用和潜在的药品不良相互作用(DDI)。本研究提出FLAME模型,基于大型语言模型(LLM)的精细列表对齐框架,实现药物逐个生成的药物列表推荐。FLAME将推荐过程视为一个顺序决策过程,每一步添加或移除一种药物。通过采用精细化学习信号的分组相对策略优化(GRPO),结合基于潜能的奖励塑造技术,该模型明确模拟药物间的相互作用,优化每种药物对整体处方的贡献。此外,FLAME通过整合结构化临床知识和协作信息提升患者建模能力。在基准数据集上的实验显示,FLAME实现最新性能,表现出优越的准确性、可控的安全准确性和良好的跨多种临床场景的泛化能力。代码已公开于https://github.com/cxfann/Flame。
Key Takeaways
- 精准安全的用药推荐对临床决策至关重要。特别是在多病共存的情况下。
- 现有系统基于点预测模式,忽略了药物间的协同作用和潜在不良相互作用(DDI)。
- FLAME模型采用基于大型语言模型的精细列表对齐框架进行药物推荐。
- 推荐过程被视为顺序决策过程,每一步都涉及药物的添加或移除。
- 通过分组相对策略优化(GRPO)和基于潜能的奖励塑造技术提供精细化学习信号。
- 模型考虑了每种药物对整体处方的贡献以及药物间的相互作用模拟。
- FLAME结合了结构化临床知识和协作信息来提升患者建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

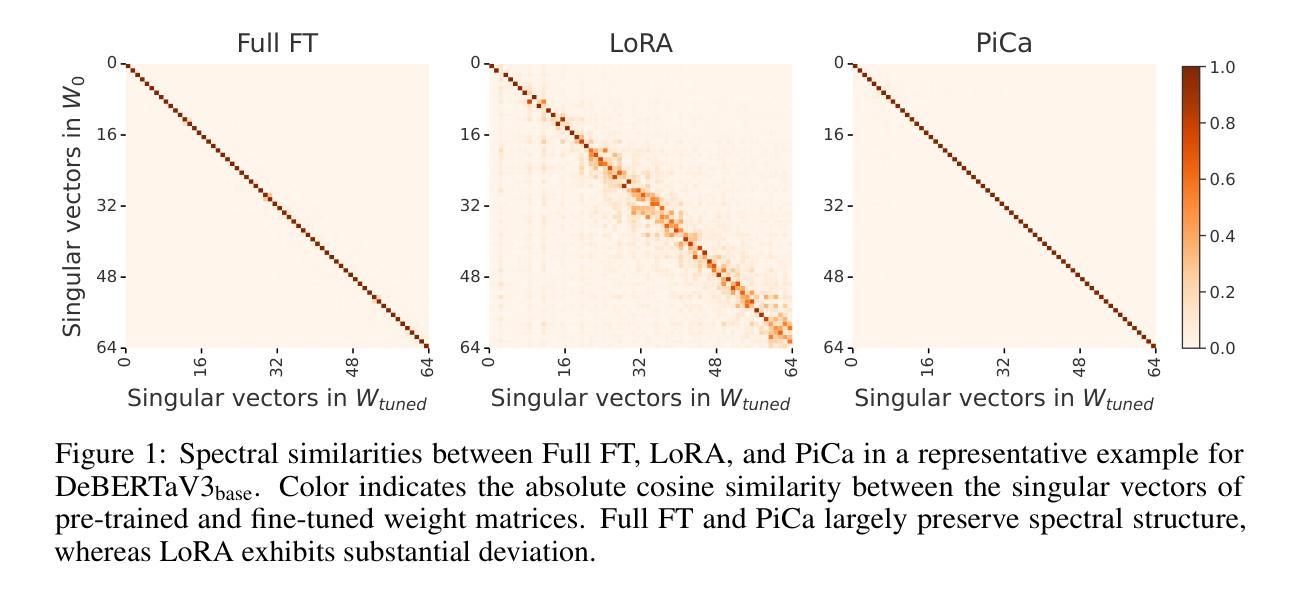
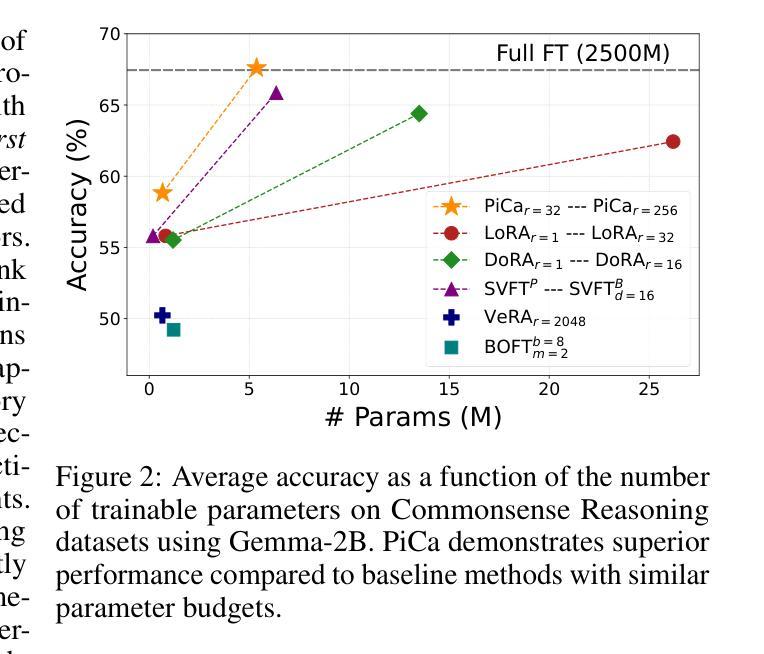
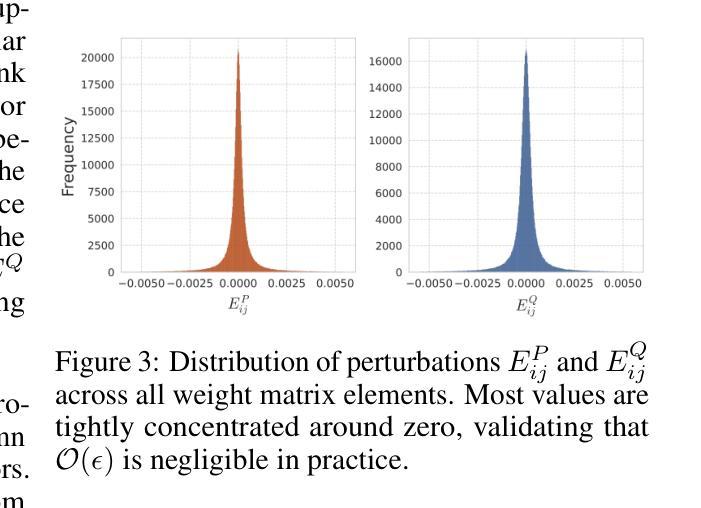
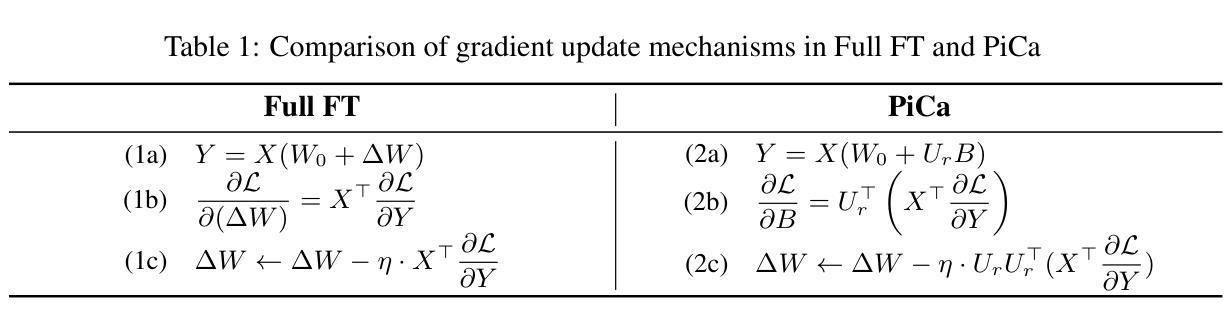
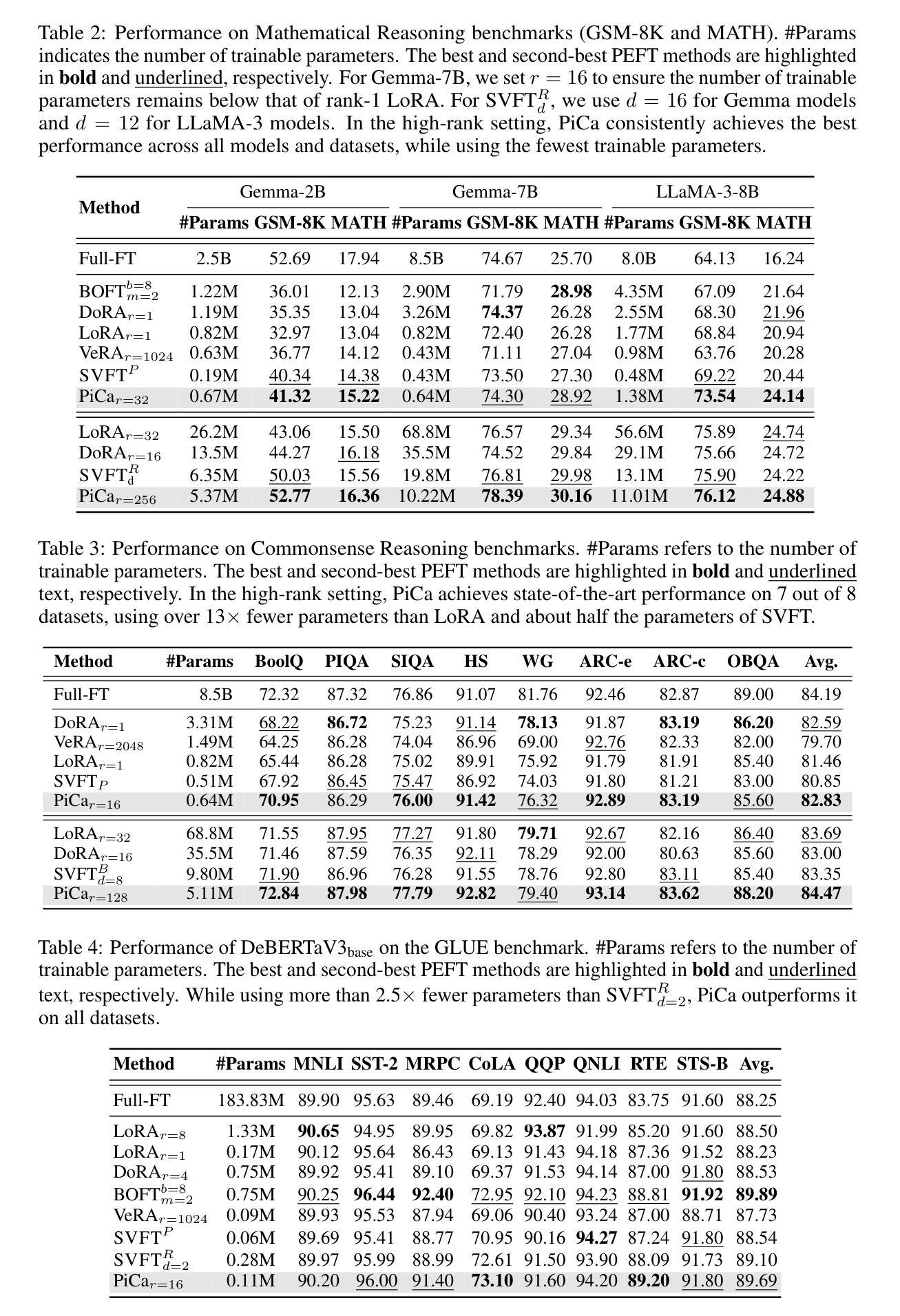
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning with Column Space Projection
Authors:Junseo Hwang, Wonguk Cho, Taesup Kim
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with minimal computational overhead is essential for efficiently adapting them to downstream tasks under resource constraints. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), facilitate this by updating only a small subset of parameters. However, recent studies show that LoRA diverges from full fine-tuning (Full FT) in its learning behavior, particularly in terms of spectral properties. Motivated by these findings, we propose PiCa, the first theoretically grounded PEFT method based on the spectral properties of fine-tuned weights. PiCa projects gradients onto the low-rank column subspace of pre-trained weights and exhibits learning patterns more closely aligned with Full FT. Furthermore, we show that combining PiCa with weight sharing drastically reduces the number of trainable parameters without compromising performance, enabling to achieve superior performance than LoRA using 13x fewer trainable parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate PiCa achieves the state-of-the-art performance compared to existing PEFT methods.
使用最小的计算开销微调大型语言模型(LLM),在资源约束条件下有效地将它们适应下游任务至关重要。参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,如低秩适应(LoRA),只能更新一小部分参数,从而促进了这一点。然而,最近的研究表明,LoRA在全微调(Full FT)的学习行为上存在差异,特别是在光谱特性方面。受这些发现的启发,我们提出了PiCa,这是基于微调权重的光谱特性的首个有理论基础的PEFT方法。PiCa将梯度投影到预训练权重的低秩列子空间上,并表现出与全FT更为一致的学习模式。此外,我们表明,将PiCa与权重共享相结合,可以大幅度减少可训练参数的数量,而且不会损害性能,能够实现以较少的可训练参数优于LoRA的性能。大量实验证明,PiCa相较于现有的PEFT方法达到了最先进的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对大型语言模型(LLM)的微调方法,特别是参数有效微调(PEFT)方法的重要性及其在资源受限条件下对其进行高效适应下游任务的应用。提出的PiCa方法基于fine-tuned权重的谱属性,是首个有理论基础的PEFT方法。PiCa通过将梯度投影到预训练权重的低秩列子空间来展现学习模式,与全微调(Full FT)更为接近。此外,结合权重共享,PiCa大幅减少了可训练参数数量,同时不妥协性能,以远优于LoRA的性能实现了仅使用13倍参数的训练。实验证明,PiCa相较于现有PEFT方法取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 参数有效微调(PEFT)方法在资源受限条件下对于大型语言模型(LLM)的适应至关重要。
- LoRA等PEFT方法在谱属性方面与全微调存在学习行为差异。
- PiCa是一种基于fine-tuned权重谱属性的PEFT方法,通过将梯度投影到预训练权重的低秩子空间来展现学习模式。
- PiCa与权重共享结合,大幅减少可训练参数数量,同时保持高性能。
- PiCa在实验中相较于其他PEFT方法取得了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

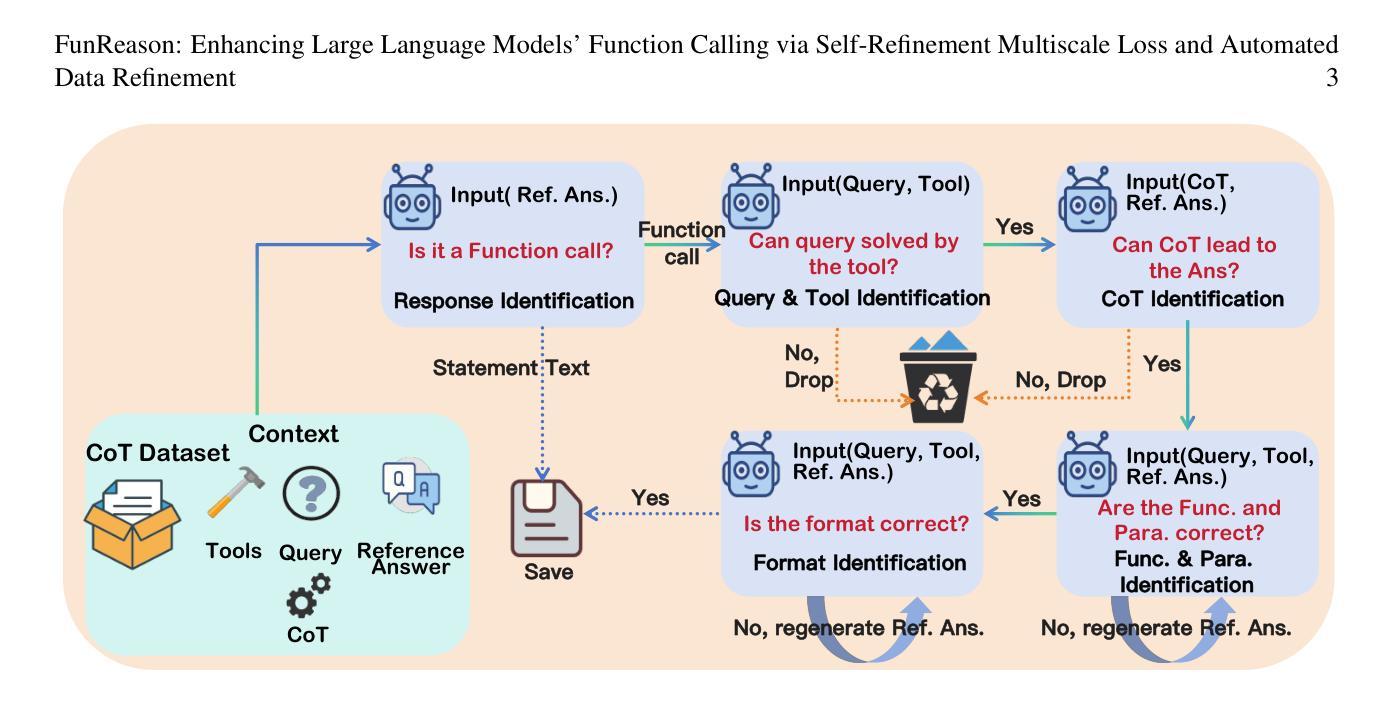
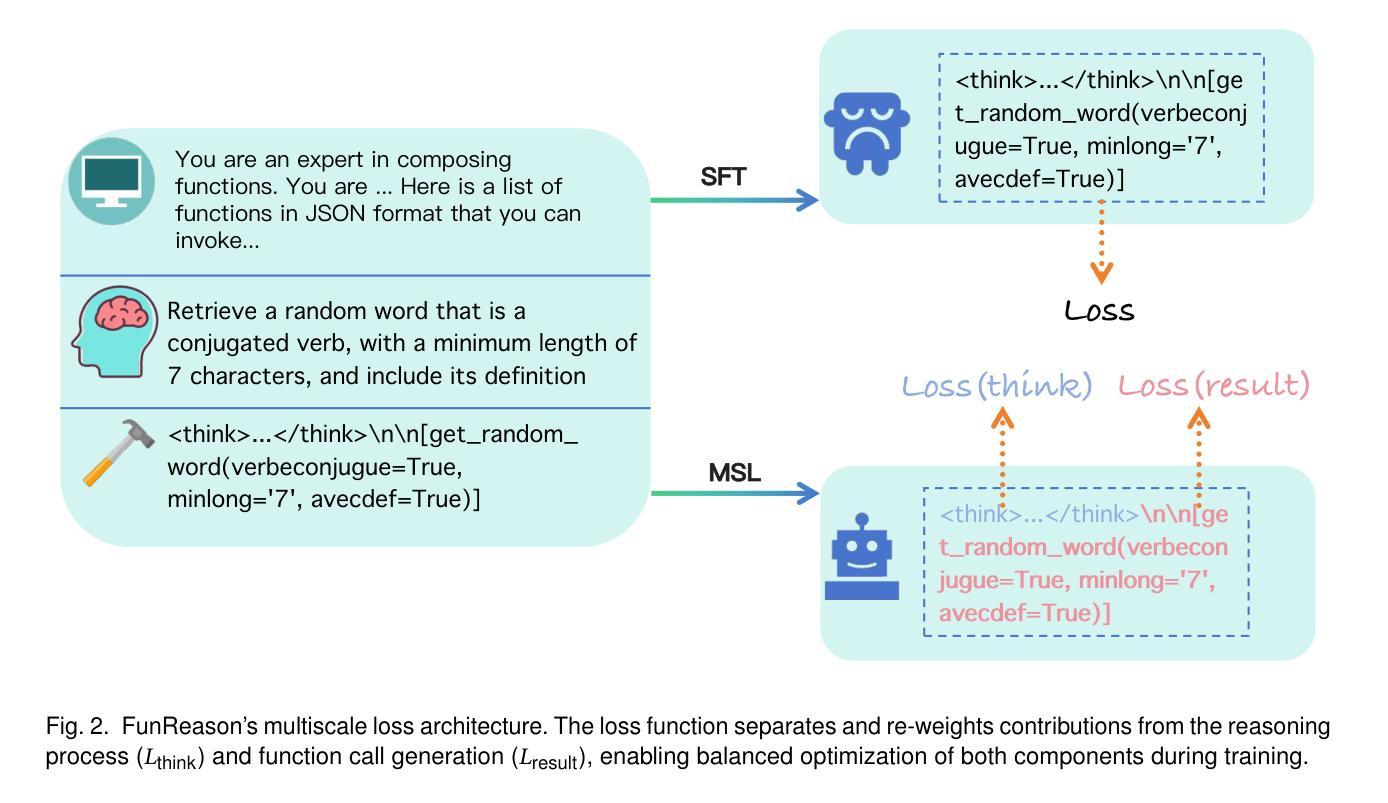
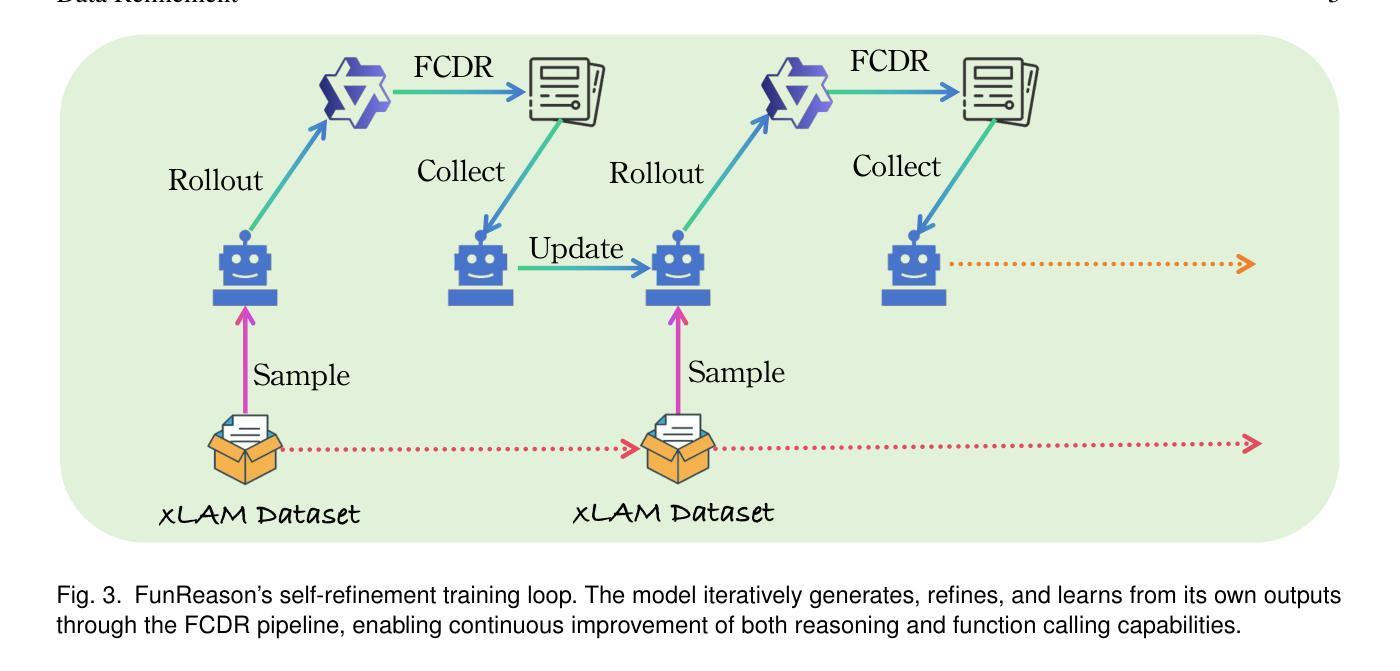
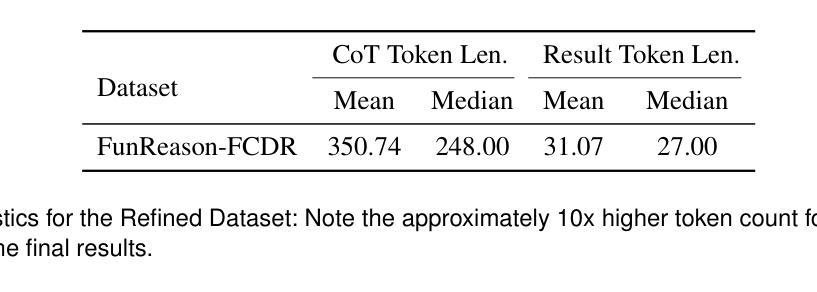
FunReason: Enhancing Large Language Models’ Function Calling via Self-Refinement Multiscale Loss and Automated Data Refinement
Authors:Bingguang Hao, Maolin Wang, Zengzhuang Xu, Cunyin Peng, Yicheng Chen, Xiangyu Zhao, Jinjie Gu, Chenyi Zhuang
The integration of large language models (LLMs) with function calling has emerged as a crucial capability for enhancing their practical utility in real-world applications. However, effectively combining reasoning processes with accurate function execution remains a significant challenge. Traditional training approaches often struggle to balance the detailed reasoning steps with the precision of function calls, leading to suboptimal performance. To address these limitations, we introduce FunReason, a novel framework that enhances LLMs’ function calling capabilities through an automated data refinement strategy and a Self-Refinement Multiscale Loss (SRML) approach. FunReason leverages LLMs’ natural reasoning abilities to generate high-quality training examples, focusing on query parseability, reasoning coherence, and function call precision. The SRML approach dynamically balances the contribution of reasoning processes and function call accuracy during training, addressing the inherent trade-off between these two critical aspects. FunReason achieves performance comparable to GPT-4o while effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning. FunReason provides a comprehensive solution for enhancing LLMs’ function calling capabilities by introducing a balanced training methodology and a data refinement pipeline. For code and dataset, please refer to our repository at GitHub https://github.com/BingguangHao/FunReason
大型语言模型(LLM)与函数调用的集成在增强其在实际应用中的实用性方面表现出了关键能力。然而,将推理过程与准确的函数执行有效地结合起来仍然是一个巨大的挑战。传统的训练方法往往很难平衡详细的推理步骤与函数调用的精确性,导致性能不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了FunReason这一新型框架。FunReason通过自动化数据细化策略和自细化多尺度损失(SRML)方法,增强LLM的函数调用能力。FunReason利用LLM的自然推理能力生成高质量的训练样本,专注于查询解析性、推理连贯性和函数调用精度。SRML方法动态平衡了推理过程和函数调用准确性在训练过程中的贡献,解决了这两者之间的固有权衡。FunReason的性能可与GPT-4o相媲美,同时有效减轻了微调过程中的灾难性遗忘。FunReason通过引入平衡的训练方法和数据细化流程,为增强LLM的函数调用能力提供了全面解决方案。有关代码和数据集,请参见我们在GitHub上的存储库:[https://github.com/BingguangHao/FunReason。(这里可能有些内容没有完全符合原意)](https://github.com/BingguangHao/FunReason%E3%80%82%EF%BC%88%E8%BF%99%E9%87%8C%E5%AF%BC%E8%83%BD%E6%9C%89%E4%BA%9B%E5%86%85%E5%AE%B9%E6%B2%A1%E6%9C%89%E5%AE%9A%E5%BC%BA%E7%BB%B4%E6%8C%AF)
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)与函数调用的融合对于提升其在现实世界应用中的实用性至关重要。然而,将推理过程与准确函数调用有效结合存在挑战。传统训练方法难以平衡推理步骤与函数调用精度,导致性能不佳。为解决此问题,FunReason框架通过自动化数据精炼策略和自适应多尺度损失(SRML)方法,提升LLM的函数调用能力。FunReason利用LLM的自然推理能力生成高质量训练样本,关注查询解析性、推理连贯性和函数调用精度。SRML方法动态平衡推理过程和函数调用准确性的贡献,解决两者之间的固有权衡。FunReason性能与GPT-4相当,同时有效缓解微调时的灾难性遗忘问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)与函数调用的结合对于提升模型实用性至关重要。
- 传统训练方法难以平衡推理与函数调用的准确性。
- FunReason框架通过自动化数据精炼策略提升LLM的函数调用能力。
- FunReason利用LLM的自然推理能力,关注查询解析性、推理连贯性和函数调用精度。
- SRML方法动态平衡推理和函数调用之间的贡献,解决两者之间的权衡问题。
- FunReason性能表现优异,与GPT-4相当。
- FunReason有效缓解微调过程中的灾难性遗忘问题。
点此查看论文截图

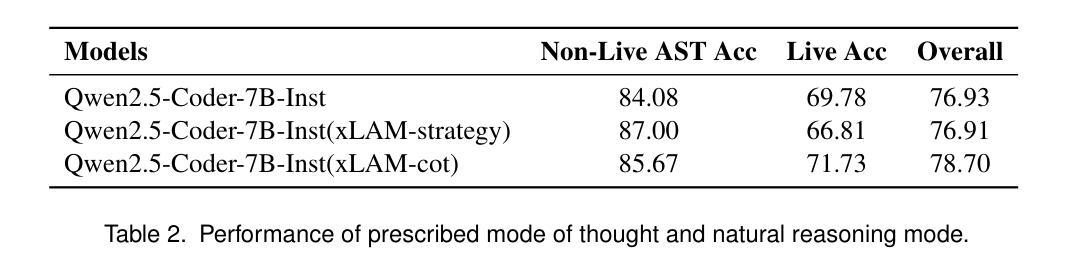
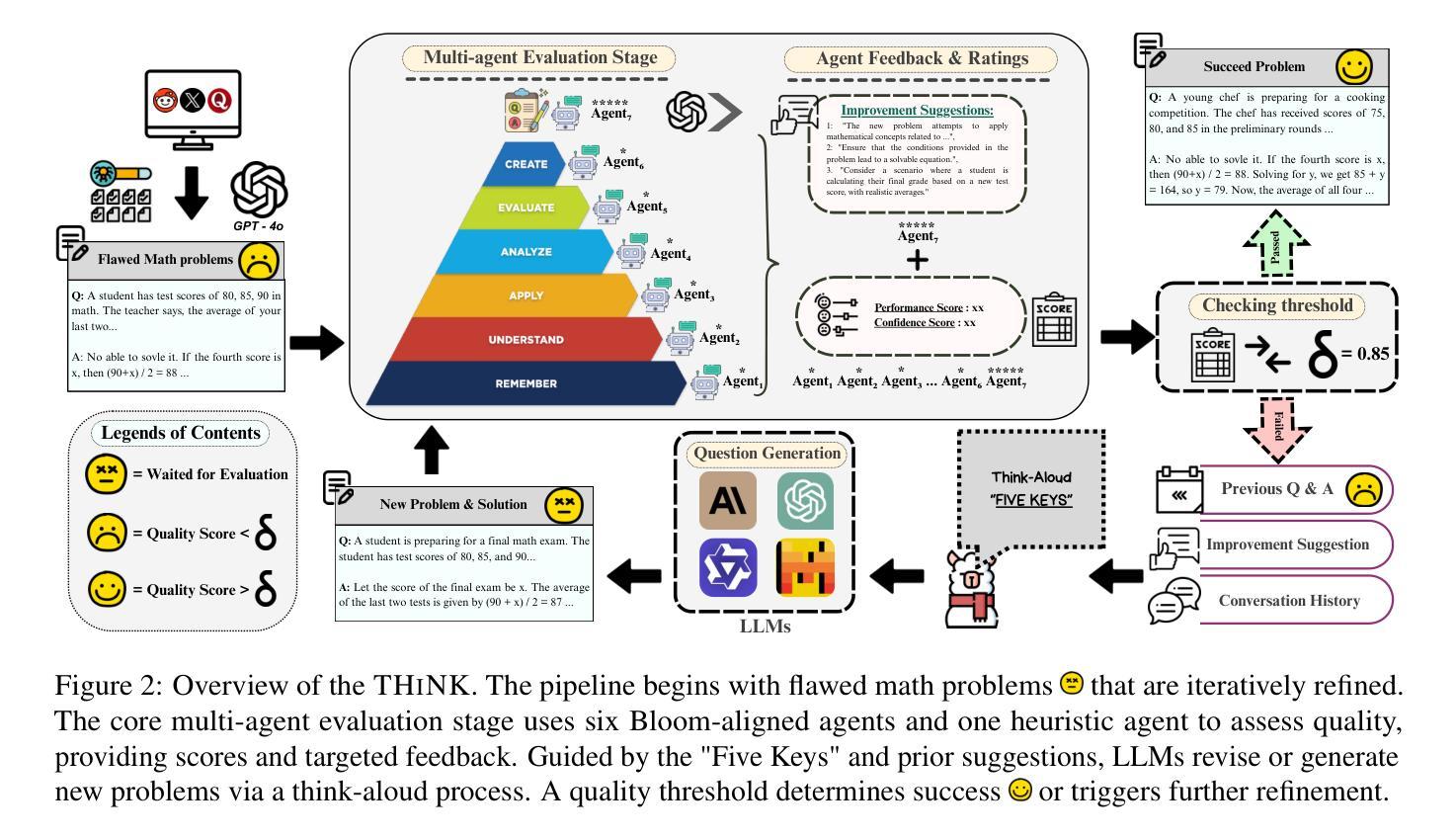
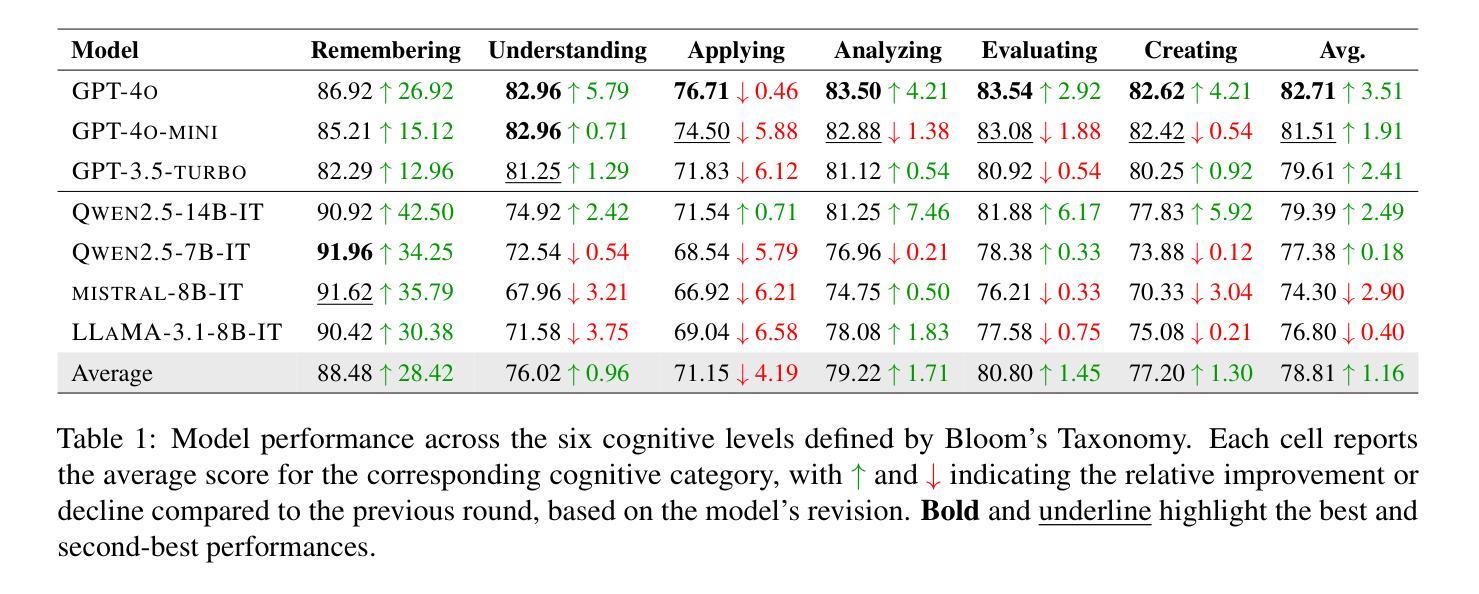
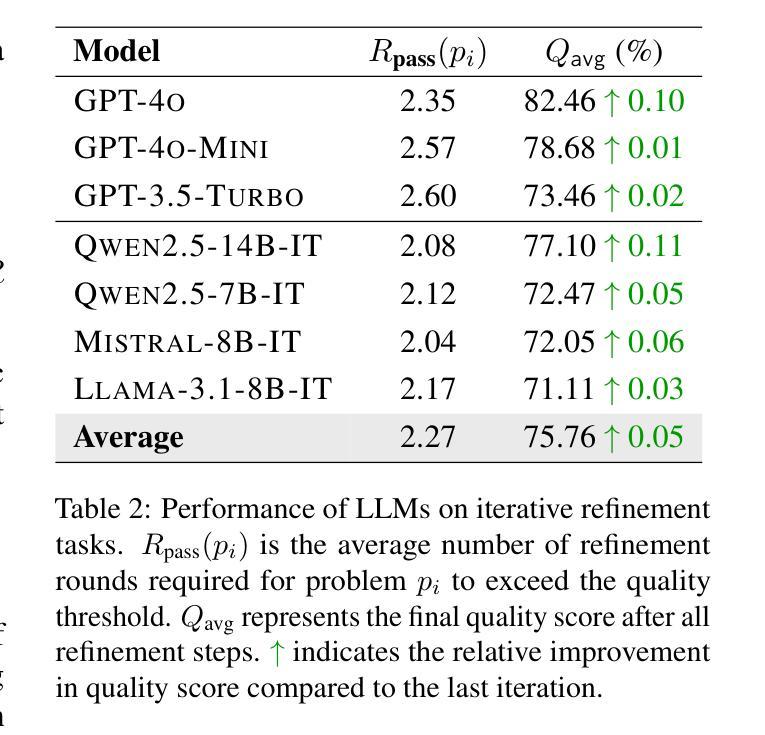
THiNK: Can Large Language Models Think-aloud?
Authors:Yongan Yu, Mengqian Wu, Yiran Lin, Nikki G. Lobczowski
Assessing higher-order thinking skills in large language models (LLMs) remains a fundamental challenge, especially in tasks that go beyond surface-level accuracy. In this work, we propose THiNK (Testing Higher-order Notion of Knowledge), a multi-agent, feedback-driven evaluation framework grounded in Bloom’s Taxonomy. THiNK frames reasoning assessment as an iterative task of problem generation, critique, and revision, encouraging LLMs to think-aloud through step-by-step reflection and refinement. This enables a systematic evaluation of both lower-order (e.g., remember, understand) and higher-order (e.g., evaluate, create) thinking skills. We apply THiNK to seven state-of-the-art LLMs and perform a detailed cognitive analysis of their outputs. Results reveal that while models reliably perform lower-order categories well, they struggle with applying knowledge in realistic contexts and exhibit limited abstraction. Structured feedback loops significantly improve reasoning performance, particularly in higher-order thinking. Qualitative evaluations further confirm that THiNK-guided outputs better align with domain logic and problem structure. The code of our framework provides a scalable methodology for probing and enhancing LLM reasoning, offering new directions for evaluation grounded in learning science, which is available at our GitHub repository.
评估大规模语言模型(LLM)的高级思维技能仍然是一个基本挑战,尤其是在超越表面层次准确性的任务中。在这项工作中,我们提出了THiNK(知识高阶认知测试),这是一个基于布鲁姆分类法的多主体、反馈驱动的评价框架。THiNK将推理评估视为问题生成、批判和修订的迭代任务,鼓励LLM通过逐步反思和完善进行“思考”,这对于测试知识很重要。这能够系统地评估低级(例如,记忆、理解)和高级(例如,评估、创造)思维技能。我们将THiNK应用于七个最先进的大型语言模型,并对其输出进行了详细的认知分析。结果表明,虽然模型在低级类别上表现可靠,但在现实语境中应用知识方面存在困难,表现出有限的抽象能力。结构化反馈循环显著提高了推理性能,尤其是在高级思维方面。定性评估进一步证实,THiNK指导的输出更符合领域逻辑和问题结构。我们的框架代码提供了一种可扩展的方法,用于探测和改进LLM推理能力,为基于学习科学的评估提供了新方向,可在我们的GitHub存储库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出THiNK框架,基于布隆认知领域分类评估大型语言模型(LLM)的高级思维技能。该框架为多智能体、反馈驱动型评价框架,通过问题生成、批判和修订的迭代任务来评估推理能力,鼓励LLM通过逐步反思和修正进行“思考”。THiNK框架能够系统地评估LLM的低阶思维技能(如记忆、理解)和高阶思维技能(如评估、创造)。实验结果表明,虽然LLM在低阶技能上表现良好,但在真实场景中应用知识方面存在困难,抽象能力有限。反馈环路能显著提高推理性能,特别是在高阶思维方面。定性评价进一步证实,THiNK引导的输出更符合领域逻辑和问题的结构。该框架代码提供了一种可靠的方法来探测和提升LLM的推理能力,并为基于学习科学的评估提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- THiNK框架用于评估LLM的高级思维技能,遵循布隆认知领域分类。
- 该框架是多智能体、反馈驱动型的评价框架,强调问题生成、批判和修订的迭代过程。
- LLM在低阶思维技能上表现良好,但在真实场景中应用知识和抽象能力方面存在局限。
- 反馈环路对提升LLM的推理性能有重要作用,特别是在高阶思维方面。
- THiNK引导的输出更符合领域逻辑和问题结构,表明其在定性评价中的有效性。
- THiNK框架代码提供了一可靠的方法来进行LLM推理能力的探测和提升。
点此查看论文截图


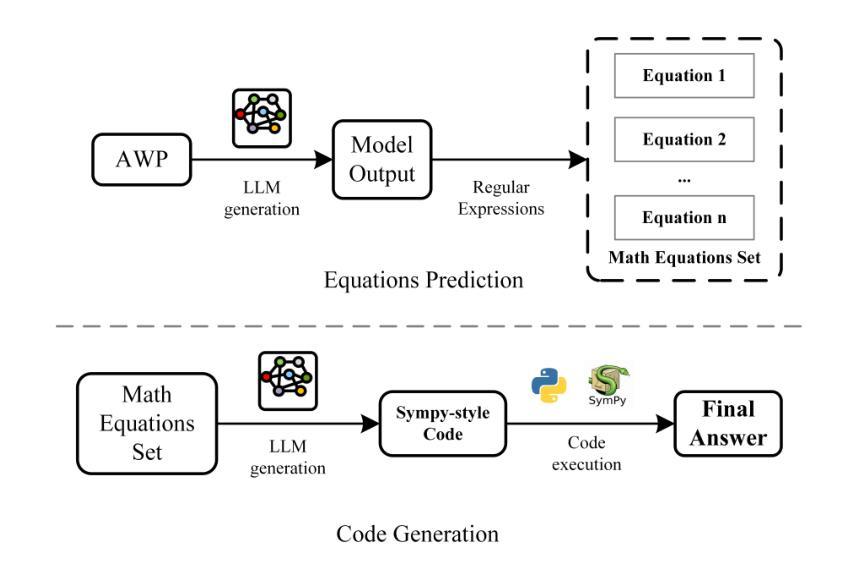
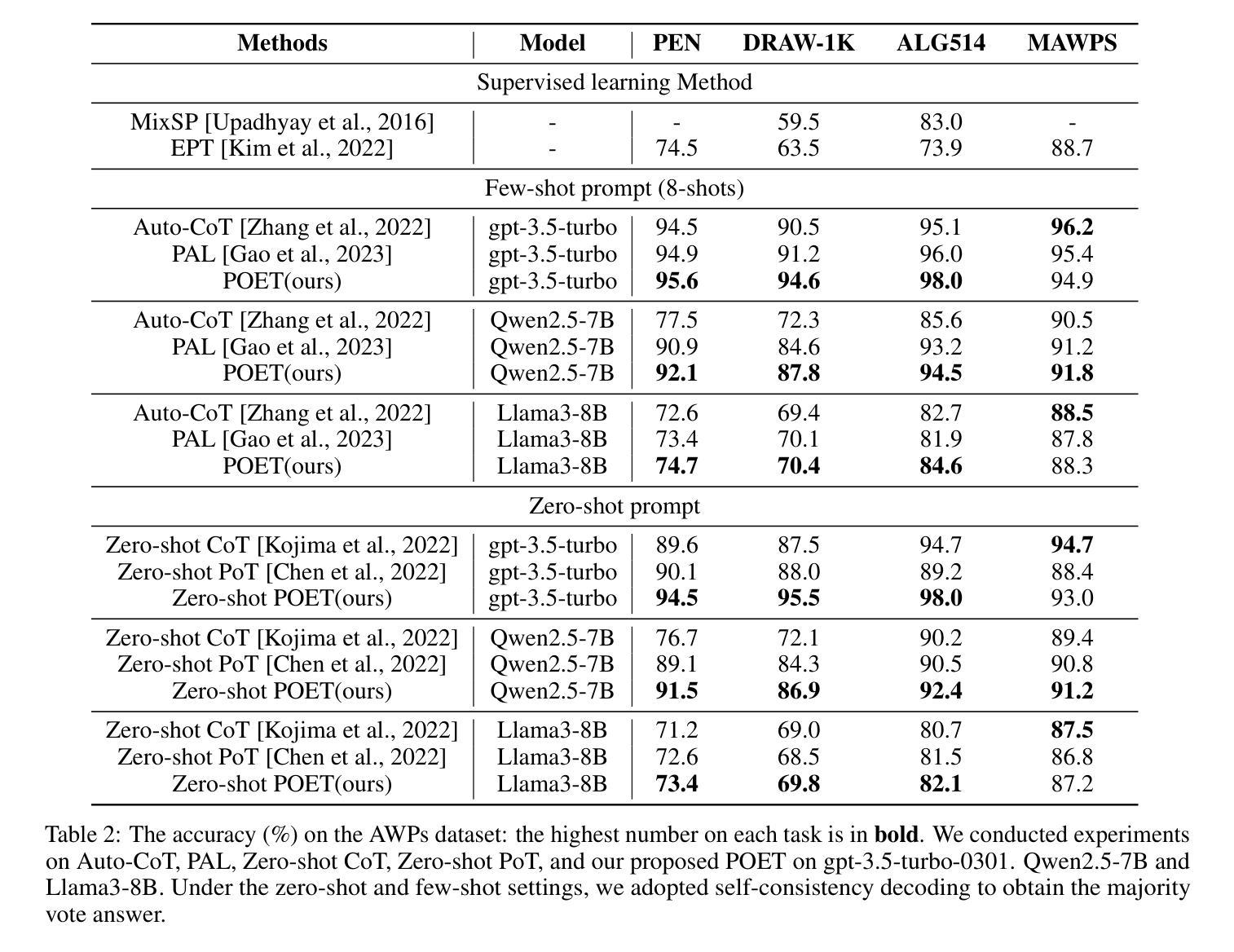
Program of Equations Thoughts to Solve Algebra Word Problems
Authors:Yunze Lin
Solving algebraic word problems (AWPs) has recently emerged as an important natural language processing task. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated powerful mathematical capabilities, and the Chain-of-Thought technique, which guides LLMs through step-by-step reasoning, has yielded impressive results. However, this reasoning ability is limited by the computational weaknesses of LLMs themselves, where calculation errors can accumulate, leading to incorrect final answers. To address this, we propose Program of Equations Thoughts (POET), which transforms the task of generating step-by-step reasoning answers into a two-stage task of predicting equations and generating code, offloading complex computations to a Python interpreter to avoid calculation errors in LLMs. Furthermore, we propose Zero-shot POET, which utilizes a manually designed template to enable LLMs to directly generate Python code for one-step solving. Our method achieves accuracies of 95.3% and 98.0% on the PEN and ALG514 datasets, respectively, setting a new state-of-the-art (SOTA). Zero-shot POET also achieves the SOTA result of 95.5% on the DRAW-1K dataset.
解决代数文字题(AWPs)是一项新近出现的自然语言处理重要任务。近来,大型语言模型(LLM)已展现出强大的数学能力,通过逐步推理的“思维链”技术也取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,这种推理能力受到LLM自身计算弱点的限制,计算错误会累积,导致最终答案错误。为解决这一问题,我们提出“方程式思维程序”(POET),将生成逐步推理答案的任务转变为预测方程式和生成代码的两阶段任务,将复杂计算卸载给Python解释器,避免在LLM中出现计算错误。此外,我们提出零样本POET,它利用手动设计的模板,使LLM能够直接生成一步解决的Python代码。我们的方法在PEN和ALG514数据集上分别达到了95.3%和98.0%的准确率,创造了新的最佳水平(SOTA)。零样本POET在DRAW-1K数据集上也达到了95.5%的SOTA结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
解决代数文字问题(AWPs)是自然语言处理领域的重要任务,近年来大语言模型(LLMs)展现了强大的数学能力,利用链式思维方法生成分步解答效果显著。然而,计算中的错误累积限制了这一能力。为此,本研究提出了公式化思维(POET)方法,将生成分步推理答案的任务转化为预测方程式和生成代码的两阶段任务,将复杂计算交给Python解释器执行,避免LLMs中的计算错误。此外,本研究还提出了零样本POET方法,利用手动设计的模板直接生成一步解决问题的Python代码。该方法在PEN和ALG514数据集上的准确率分别达到95.3%和98%,创造了新的最佳记录。零样本POET在DRAW-1K数据集上也取得了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 解决代数文字问题是自然语言处理的重要任务。
- 大语言模型展现出强大的数学能力,通过链式思维方法分步解答效果显著。
- 计算错误限制了语言模型的推理能力。
- 公式化思维(POET)方法通过将问题转化为预测方程式和生成代码的两阶段任务来避免计算错误。
- POET利用Python解释器执行复杂计算。
- 零样本POET方法利用手动设计的模板直接生成一步解决Python代码。
点此查看论文截图




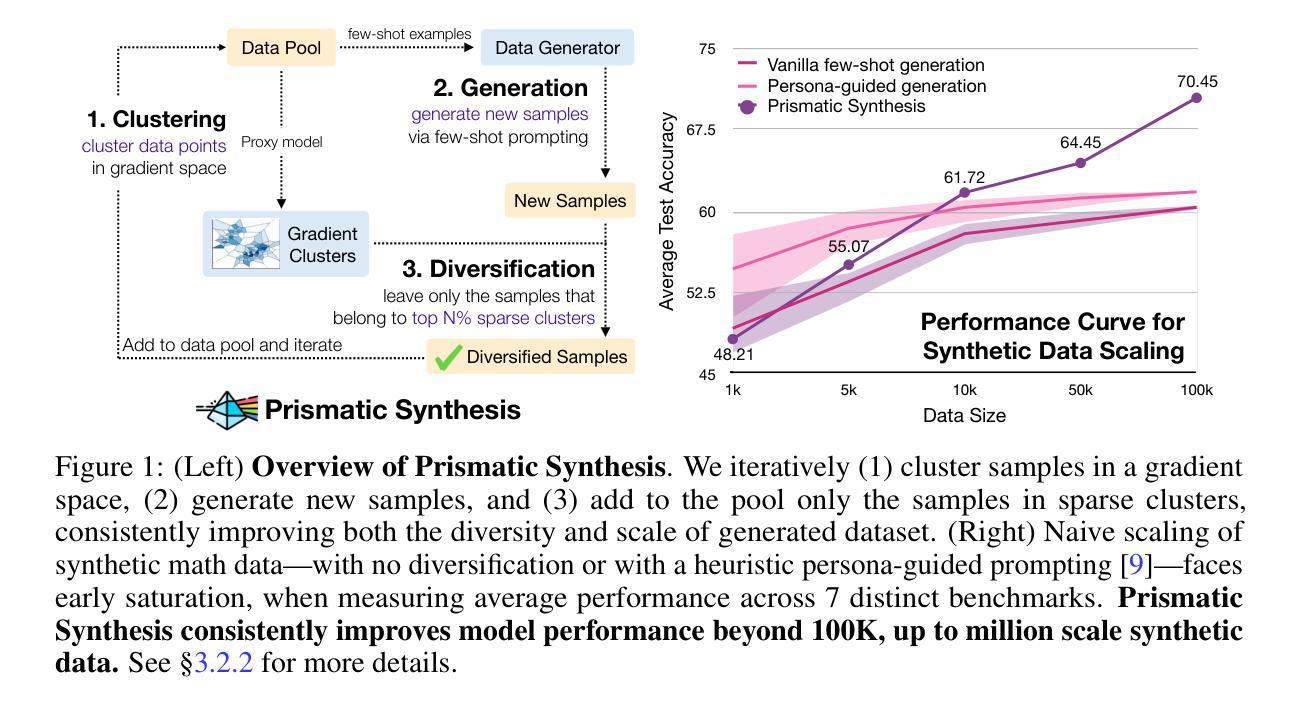
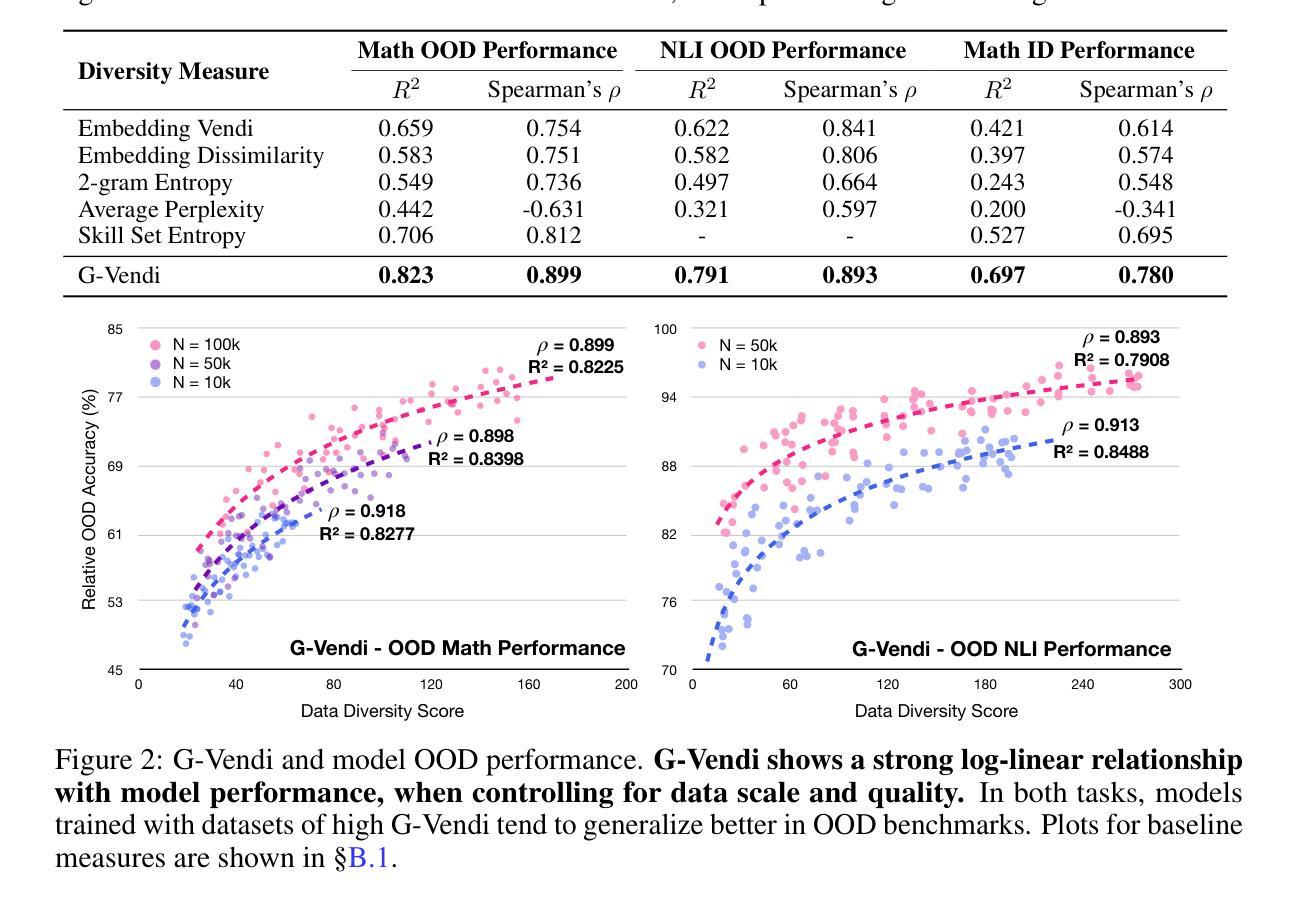
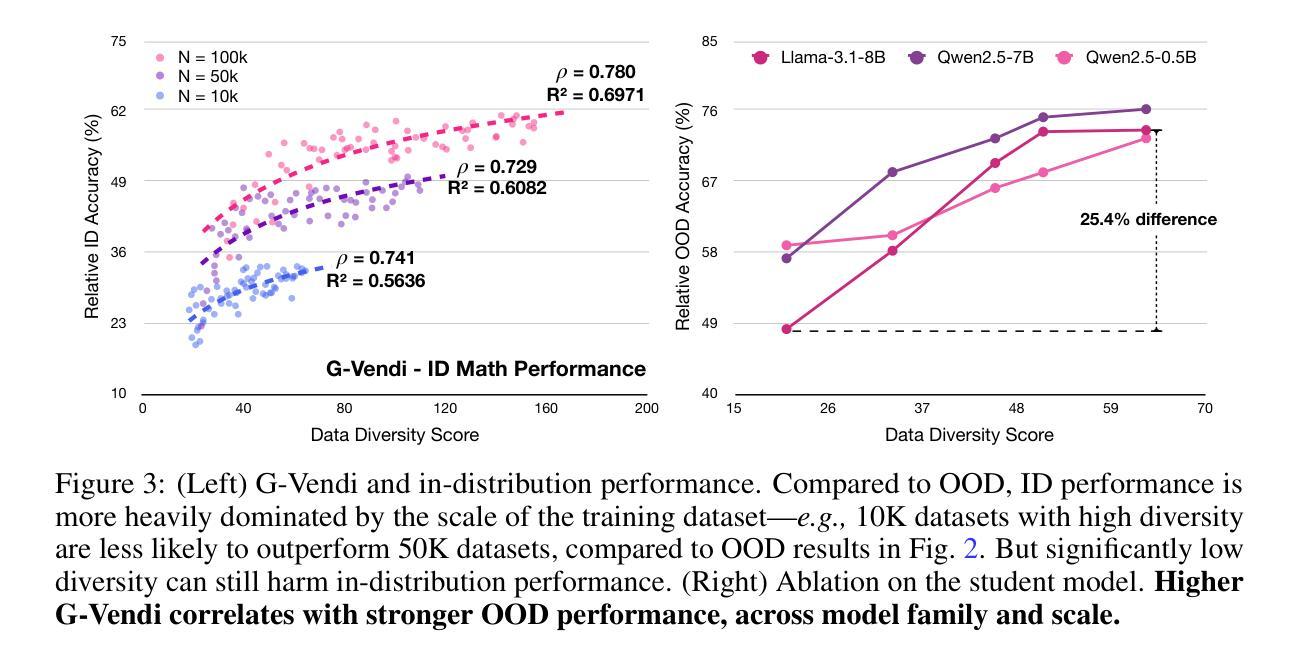
Prismatic Synthesis: Gradient-based Data Diversification Boosts Generalization in LLM Reasoning
Authors:Jaehun Jung, Seungju Han, Ximing Lu, Skyler Hallinan, David Acuna, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Mostafa Patwary, Mohammad Shoeybi, Bryan Catanzaro, Yejin Choi
Effective generalization in language models depends critically on the diversity of their training data. Yet existing diversity metrics often fall short of this goal, relying on surface-level heuristics that are decoupled from model behavior. This motivates us to ask: What kind of diversity in training data actually drives generalization in language models – and how can we measure and amplify it? Through large-scale empirical analyses spanning over 300 training runs, carefully controlled for data scale and quality, we show that data diversity can be a strong predictor of generalization in LLM reasoning – as measured by average model performance on unseen out-of-distribution benchmarks. We introduce G-Vendi, a metric that quantifies diversity via the entropy of model-induced gradients. Despite using a small off-the-shelf proxy model for gradients, G-Vendi consistently outperforms alternative measures, achieving strong correlation (Spearman’s $\rho \approx 0.9$) with out-of-distribution (OOD) performance on both natural language inference (NLI) and math reasoning tasks. Building on this insight, we present Prismatic Synthesis, a framework for generating diverse synthetic data by targeting underrepresented regions in gradient space. Experimental results show that Prismatic Synthesis consistently improves model performance as we scale synthetic data – not just on in-distribution test but across unseen, out-of-distribution benchmarks – significantly outperforming state-of-the-art models that rely on 20 times larger data generator than ours. For example, PrismMath-7B, our model distilled from a 32B LLM, outperforms R1-Distill-Qwen-7B – the same base model trained on proprietary data generated by 671B R1 – on 6 out of 7 challenging benchmarks.
训练数据的有效性在很大程度上取决于训练数据的多样性,但在自然语言模型的现实场景中,现有的多样性度量通常难以实现这一目标。它们依赖于与模型行为脱钩的表面启发式策略。这促使我们提出以下问题:训练数据中什么样的多样性实际上可以驱动语言模型的泛化——我们如何衡量并增强这种多样性?通过对超过300次训练运行的大规模实证分析,在严格控制数据规模和质量的条件下,我们发现数据多样性可以作为自然语言模型推理泛化的强大预测指标——这是通过模型在未见过的不符合分布基准测试上的平均性能来衡量的。我们引入了G-Vendi指标,它通过模型诱导梯度的熵来衡量多样性。尽管它使用现成的梯度代理模型规模较小,但G-Vendi始终优于其他度量标准,与未见分布(OOD)的性能具有很强的相关性(斯皮尔曼的ρ值约为0.9),无论是在自然语言推理(NLI)还是数学推理任务上。基于这一见解,我们提出了Prismatic合成框架,该框架旨在生成针对梯度空间中代表性不足区域的多样化合成数据。实验结果表明,随着合成数据的规模扩大,Prismatic合成始终提高了模型性能——不仅在内部测试集上表现良好,而且在未见的不符合分布基准测试中表现优异,显著优于依赖比我们大20倍的数据生成器的当前最先进模型。例如,PrismMath-7B(由我们的从规模为32B的自然语言模型蒸馏而成)在七个基准测试中取得了六个领先的结果,超越了以相同基础模型训练的R1-Distill-Qwen-7B(基于使用671B的R1生成的专有数据)。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
训练数据的多样性对于语言模型的泛化至关重要。现有多样性指标常常难以达到这一目标,依赖于与模型行为脱节的表面启发式方法。因此,我们提出以下问题:什么样的训练数据多样性实际上能驱动语言模型的泛化——我们如何衡量并增强这种多样性?通过涵盖超过300次训练运行的大规模实证分析,在严格控制数据规模和质量的情况下,我们发现数据多样性可以是语言模型推理泛化的有力预测指标——通过模型在未见过的分布外基准测试上的平均性能来衡量。我们引入了G-Vendi指标,该指标通过模型诱导梯度的熵来量化多样性。尽管使用了小型现成的梯度代理模型,但G-Vendi始终优于其他措施,与未见分布(OOD)的表现在自然语言推理(NLI)和数学推理任务上实现了强烈的相关性(Spearman’sρ≈0.9)。基于这一见解,我们提出了Prismatic合成框架,该框架通过针对梯度空间中的表示不足区域来生成多样化的合成数据。实验结果表明,随着合成数据的规模扩大,Prismatic合成持续提高了模型性能——不仅在内部测试上,而且在未见过的分布外基准测试上,显著优于依赖比我们大20倍数据生成器的最先进模型。例如,我们从规模为32B的大型语言模型中提炼出的PrismMath-7B模型,在六个基准测试中表现优于基于规模为671B的R1模型训练的R1-Distill-Qwen-7B模型。
关键见解
- 训练数据的多样性对语言模型的泛化至关重要。
- 现有多样性指标往往无法准确预测模型的泛化能力。
- 引入G-Vendi指标,通过模型诱导梯度的熵来量化数据多样性,与未见分布的任务表现呈现强烈相关性。
- 提出Prismatic合成框架,生成针对梯度空间中表示不足区域的多样化合成数据。
- Prismatic合成能提高模型性能,不仅在内部测试上,而且在未见过的分布外基准测试上。
- 实验显示,在多个基准测试中,使用Prismatic合成的较小规模模型表现优于使用更大规模数据生成的先进模型。
点此查看论文截图

Pangu Light: Weight Re-Initialization for Pruning and Accelerating LLMs
Authors:Hanting Chen, Jiarui Qin, Jialong Guo, Tao Yuan, Yichun Yin, Huiling Zhen, Yasheng Wang, Jinpeng Li, Xiaojun Meng, Meng Zhang, Rongju Ruan, Zheyuan Bai, Yehui Tang, Can Chen, Xinghao Chen, Fisher Yu, Ruiming Tang, Yunhe Wang
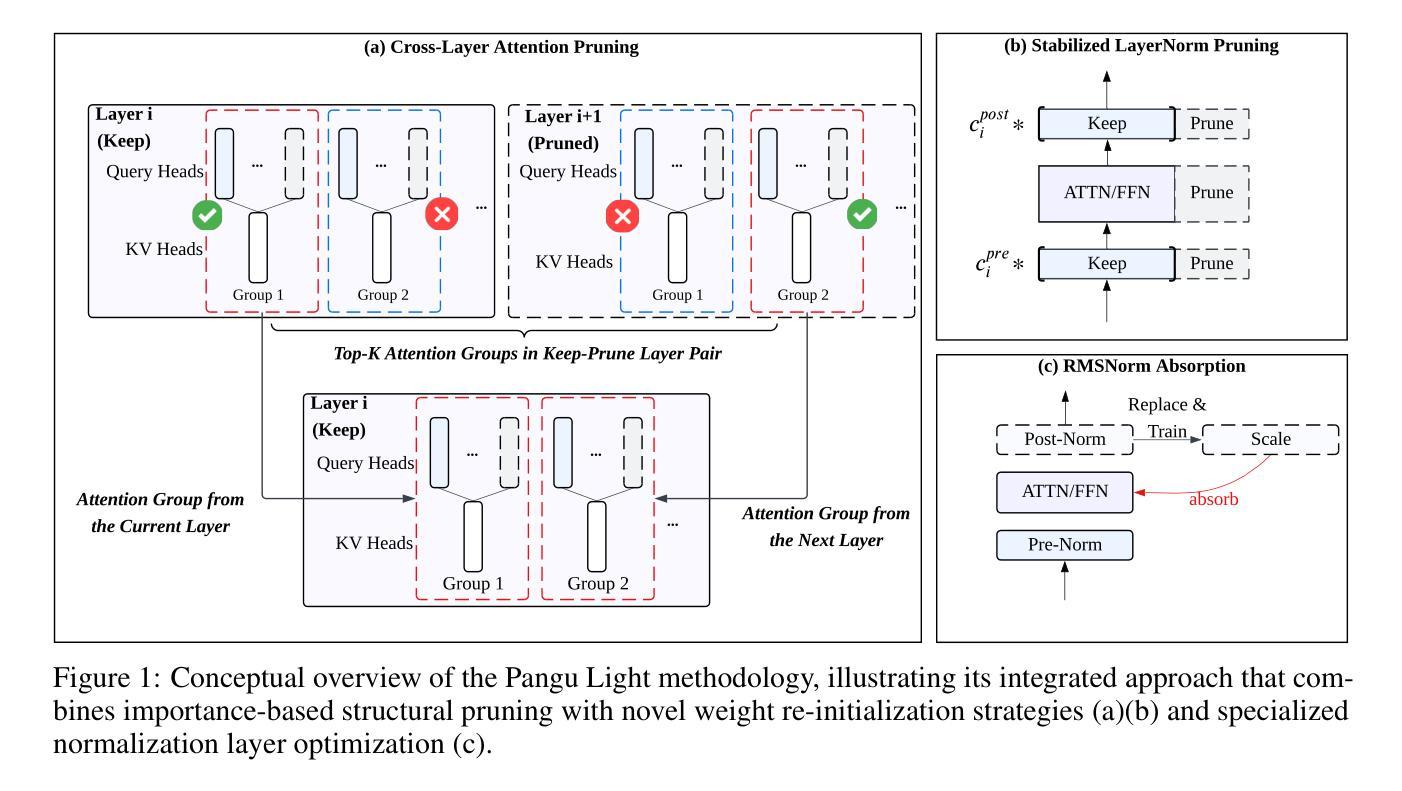
Large Language Models (LLMs) deliver state-of-the-art capabilities across numerous tasks, but their immense size and inference costs pose significant computational challenges for practical deployment. While structured pruning offers a promising avenue for model compression, existing methods often struggle with the detrimental effects of aggressive, simultaneous width and depth reductions, leading to substantial performance degradation. This paper argues that a critical, often overlooked, aspect in making such aggressive joint pruning viable is the strategic re-initialization and adjustment of remaining weights to improve the model post-pruning training accuracies. We introduce Pangu Light, a framework for LLM acceleration centered around structured pruning coupled with novel weight re-initialization techniques designed to address this ``missing piece’’. Our framework systematically targets multiple axes, including model width, depth, attention heads, and RMSNorm, with its effectiveness rooted in novel re-initialization methods like Cross-Layer Attention Pruning (CLAP) and Stabilized LayerNorm Pruning (SLNP) that mitigate performance drops by providing the network a better training starting point. Further enhancing efficiency, Pangu Light incorporates specialized optimizations such as absorbing Post-RMSNorm computations and tailors its strategies to Ascend NPU characteristics. The Pangu Light models consistently exhibit a superior accuracy-efficiency trade-off, outperforming prominent baseline pruning methods like Nemotron and established LLMs like Qwen3 series. For instance, on Ascend NPUs, Pangu Light-32B’s 81.6 average score and 2585 tokens/s throughput exceed Qwen3-32B’s 80.9 average score and 2225 tokens/s.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多个任务上提供了最先进的技术能力,但它们的庞大规模和推理成本为实际部署带来了重大的计算挑战。虽然结构化剪枝为模型压缩提供了有前景的途径,但现有方法往往难以应对激烈的同时宽度和深度缩减的负面影响,导致性能大幅下降。本文认为,在采取这种激烈的联合剪枝时,经常被忽视的一个关键方面是战略性地重新初始化和调整剩余权重,以提高模型剪枝后的训练精度。我们推出了“盘古光”框架,该框架以加速大型语言模型为中心,结合了结构化剪枝和新型权重重新初始化技术,旨在解决这一“缺失的部分”。我们的框架系统地针对多个轴进行优化,包括模型宽度、深度、注意力头和RMSNorm,其有效性源于新的重新初始化方法,如跨层注意力剪枝(CLAP)和稳定的层标准化剪枝(SLNP),这些方法通过为网络提供更好的训练起点来减轻性能下降。进一步提高效率,“盘古光”结合了专门优化,如吸收Post-RMSNorm计算,并针对Ascend NPU特性调整其策略。盘古光模型在准确性和效率之间表现出卓越的权衡,优于主流的基线剪枝方法,如Nemotron和现有的大型语言模型,如Qwen3系列。例如,在Ascend NPU上,Pangu Light-32B的平均得分81.6和吞吐量2585令牌/秒超过了Qwen3-32B的平均得分80.9和吞吐量2225令牌/秒。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多任务中展现出卓越的性能,但其庞大的规模和推理成本为实际应用带来了重大计算挑战。本文提出了一种名为Pangu Light的框架,它通过结合结构剪枝和权重再初始化技术,以加速LLM的运行。该框架针对模型的宽度、深度、注意力头和RMSNorm等多个方面进行优化,通过创新的再初始化方法如跨层注意力剪枝(CLAP)和稳定LayerNorm剪枝(SLNP)来减轻性能下降。同时,Pangu Light还结合了特殊优化,如吸收Post-RMSNorm计算,并针对Ascend NPU的特性定制策略。在Ascend NPUs上,Pangu Light模型在准确性和效率方面表现出卓越的性能,超越了Nemotron等基线剪枝方法和Qwen3系列LLM。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)面临计算挑战,其实践部署需要解决规模庞大和推理成本高昂的问题。
- Pangu Light框架旨在通过结合结构剪枝和权重再初始化技术来加速LLM。
- Pangu Light框架针对模型的多个方面进行优化,包括宽度、深度、注意力头和RMSNorm等。
- 通过创新的再初始化方法如CLAP和SLNP,Pangu Light减轻性能下降,提供更好的训练起点。
- Pangu Light结合了特殊优化,如吸收Post-RMSNorm计算,以提高效率。
- Pangu Light的策略根据Ascend NPU的特性定制,实现了卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

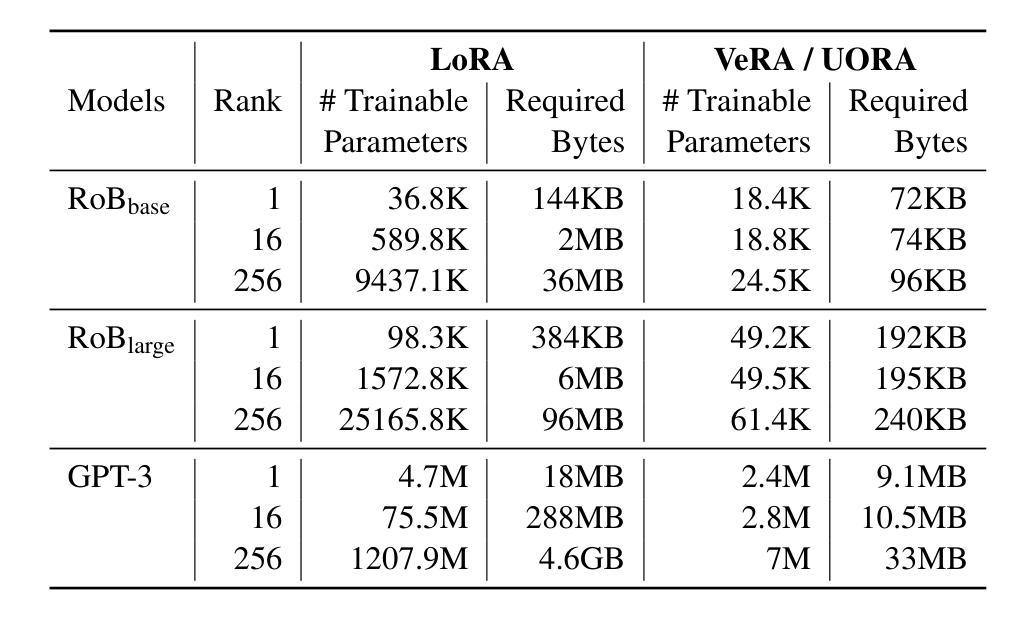
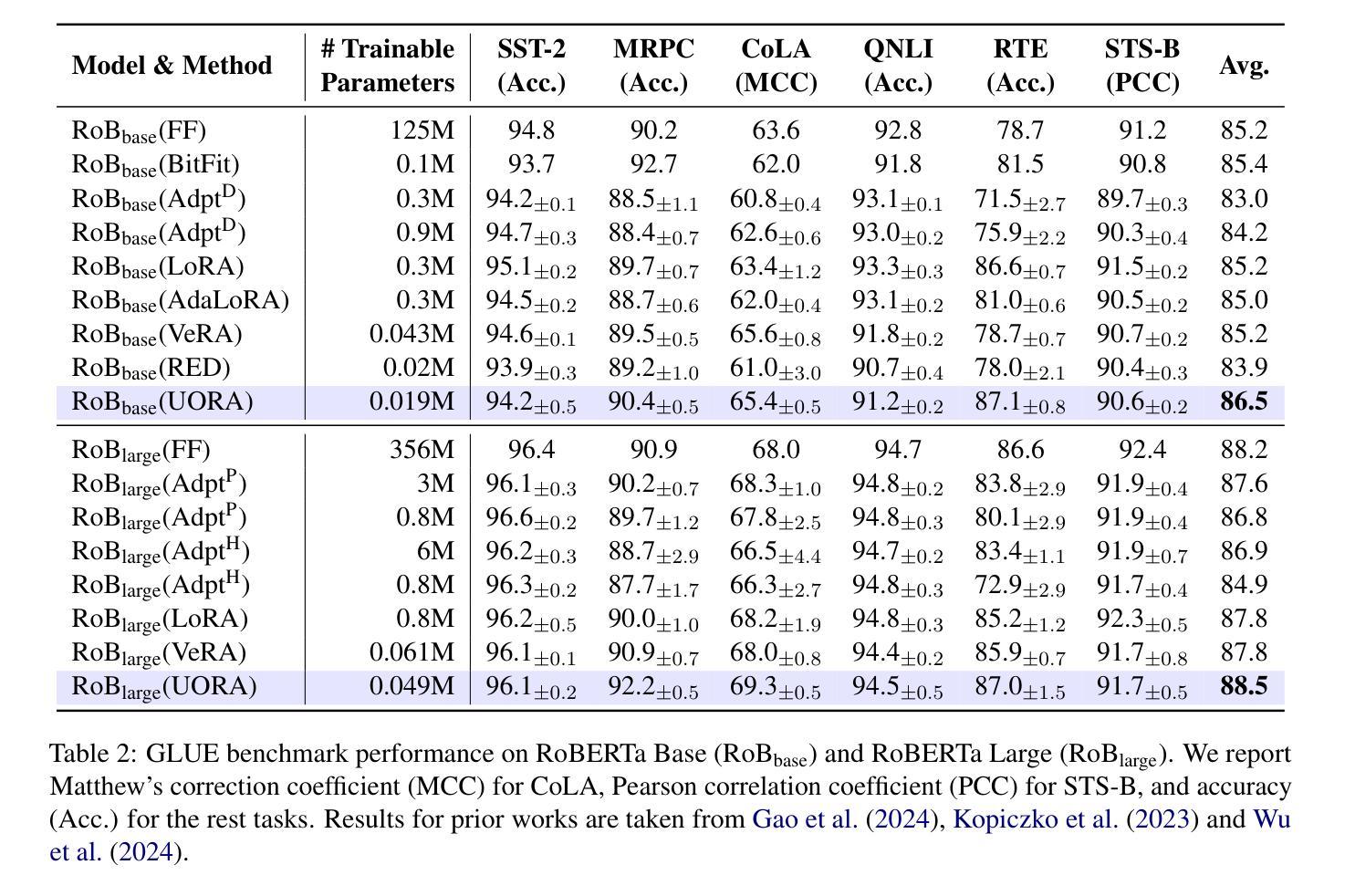
UORA: Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation in Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Models
Authors:Xueyan Zhang, Jinman Zhao, Zhifei Yang, Yibo Zhong, Shuhao Guan, Linbo Cao, Yining Wang
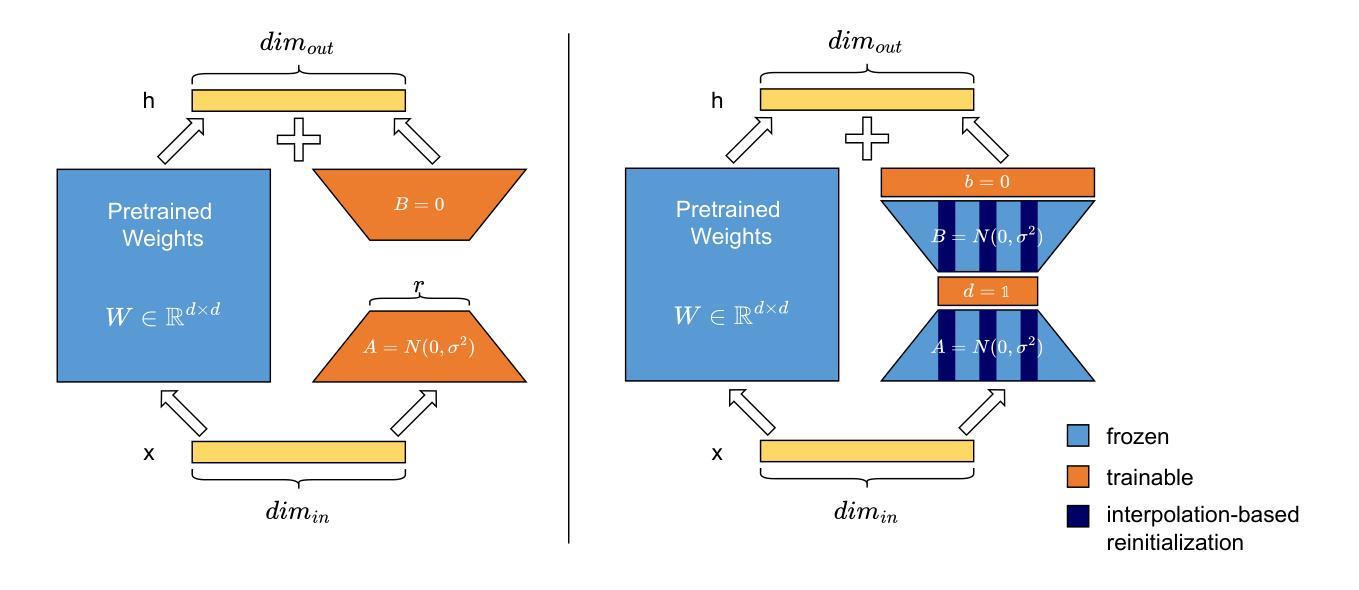
This paper introduces Uniform Orthogonal Reinitialization Adaptation (UORA), a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approach for Large Language Models (LLMs). UORA achieves state-of-the-art performance and parameter efficiency by leveraging a low-rank approximation method to reduce the number of trainable parameters. Unlike existing methods such as LoRA and VeRA, UORA employs an interpolation-based reparametrization mechanism that selectively reinitializes rows and columns in frozen projection matrices, guided by the vector magnitude heuristic. This results in substantially fewer trainable parameters compared to LoRA and outperforms VeRA in computation and storage efficiency. Comprehensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate UORA’s superiority in achieving competitive fine-tuning performance with negligible computational overhead. We demonstrate its performance on GLUE and E2E benchmarks and its effectiveness in instruction-tuning large language models and image classification models. Our contributions establish a new paradigm for scalable and resource-efficient fine-tuning of LLMs.
本文介绍了统一正交再初始化适配(UORA),这是一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)的新型参数高效微调(PEFT)方法。UORA利用低秩逼近方法减少训练参数的数量,实现了最先进的性能和参数效率。与现有的LoRA和VeRA方法不同,UORA采用基于插值的重新参数化机制,该机制根据向量幅度启发式选择性地重新初始化冻结投影矩阵的行和列。这导致与LoRA相比,训练参数大大减少,并且在计算和存储效率方面优于VeRA。在不同基准测试上的综合实验表明,UORA在竞争微调性能方面表现出卓越性能,计算开销微乎其微。我们在GLUE和E2E基准测试上展示了其性能,以及其在大规模语言模型和图像分类模型的指令调整中的有效性。我们的贡献为LLM的可扩展和资源高效的微调建立了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 2 figures, 15 tables
摘要
本文介绍了统一正交重初始化适应(UORA)方法,这是一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)的新型参数高效微调(PEFT)方法。UORA通过利用低秩逼近方法减少训练参数的数量,实现了最先进的性能和参数效率。与现有的LoRA和VeRA方法不同,UORA采用基于插值的重新参数化机制,该机制有选择地重新初始化冻结投影矩阵的行和列,由向量幅度启发式指导。这导致与LoRA相比大大减少了可训练参数的数量,并且在计算和存储效率方面优于VeRA。在多个基准测试上的综合实验表明,UORA在竞争微调性能方面表现出卓越性能,计算开销微乎其微。我们在GLUE和E2E基准测试上展示了其性能,并证明了其在指令微调大型语言模型和图像分类模型中的有效性。我们的贡献为可伸缩和资源高效的大型语言模型微调建立了新的范例。
关键见解
- UORA是一种针对大型语言模型的参数高效微调方法。
- UORA利用低秩逼近方法减少训练参数数量。
- UORA采用基于插值的重新参数化机制,有选择地重新初始化冻结投影矩阵。
- UORA在向量幅度启发式指导下进行工作,这影响了其重新参数化机制的选择。
- 与LoRA相比,UORA大幅减少了可训练参数的数量。
- UORA在计算和存储效率上优于VeRA。
点此查看论文截图

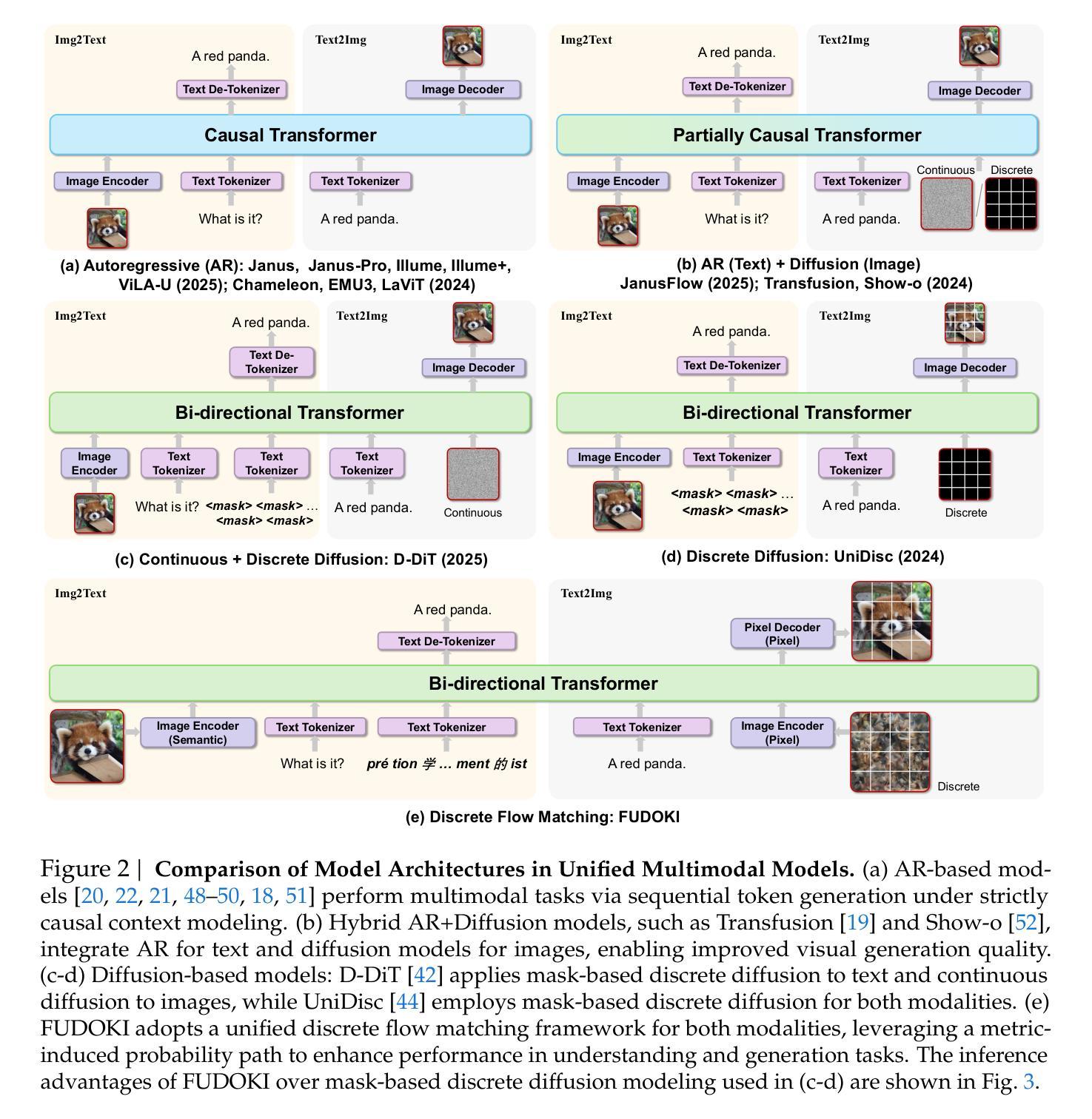
FUDOKI: Discrete Flow-based Unified Understanding and Generation via Kinetic-Optimal Velocities
Authors:Jin Wang, Yao Lai, Aoxue Li, Shifeng Zhang, Jiacheng Sun, Ning Kang, Chengyue Wu, Zhenguo Li, Ping Luo
The rapid progress of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed the emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) that unify visual understanding and image generation within a single framework. However, most existing MLLMs rely on autoregressive (AR) architectures, which impose inherent limitations on future development, such as the raster-scan order in image generation and restricted reasoning abilities in causal context modeling. In this work, we challenge the dominance of AR-based approaches by introducing FUDOKI, a unified multimodal model purely based on discrete flow matching, as an alternative to conventional AR paradigms. By leveraging metric-induced probability paths with kinetic optimal velocities, our framework goes beyond the previous masking-based corruption process, enabling iterative refinement with self-correction capability and richer bidirectional context integration during generation. To mitigate the high cost of training from scratch, we initialize FUDOKI from pre-trained AR-based MLLMs and adaptively transition to the discrete flow matching paradigm. Experimental results show that FUDOKI achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art AR-based MLLMs across both visual understanding and image generation tasks, highlighting its potential as a foundation for next-generation unified multimodal models. Furthermore, we show that applying test-time scaling techniques to FUDOKI yields significant performance gains, further underscoring its promise for future enhancement through reinforcement learning.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展催生了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的出现,这些模型在一个框架内统一了视觉理解和图像生成。然而,大多数现有的MLLM依赖于自回归(AR)架构,这对其未来发展造成了固有局限,例如图像生成中的扫描顺序和因果上下文建模中的有限推理能力。在这项工作中,我们通过对传统AR方法提出挑战,引入了一种基于离散流匹配的统一多模态模型FUDOKI作为替代方案。通过利用度量诱导概率路径和动力学最优速度,我们的框架超越了之前的基于掩码的腐蚀过程,实现了迭代细化、自我校正能力和生成过程中的更丰富双向上下文集成。为了降低从头开始训练的成本,我们从预训练的AR-based MLLM初始化FUDOKI,并逐步过渡到离散流匹配范式。实验结果表明,FUDOKI在视觉理解和图像生成任务上的性能与最先进的AR-based MLLM相当,凸显了其作为下一代统一多模态模型基础潜力。此外,我们对FUDOKI应用测试时缩放技术,实现了显著的性能提升,进一步证明其通过强化学习进行未来增强的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages, 12 figures
Summary:大型语言模型的快速发展推动了多模态大型语言模型的兴起,该模型在一个框架内融合了视觉理解和图像生成。然而,大多数现有模型依赖于自回归架构,存在图像生成顺序和因果上下文建模能力的局限性。本研究挑战了自回归方法的主导地位,提出了基于离散流匹配的统一多模态模型FUDOKI,超越了传统的基于遮蔽的腐蚀过程,具有自我修正能力和丰富的双向上下文集成功能。我们从预训练的基于自回归的多模态语言模型中初始化FUDOKI并逐步适应离散流匹配范式。实验结果表明,FUDOKI在视觉理解和图像生成任务上的性能与基于自回归的模型相当,显示出其作为下一代统一多模态模型基础的潜力。应用测试时缩放技术能显著提升其性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了视觉理解和图像生成在一个框架内。
- 现有MLLMs大多依赖自回归(AR)架构,存在局限性。
- FUDOKI是一个基于离散流匹配的非AR多模态模型,具有自我修正能力和丰富的上下文集成功能。
- FUDOKI通过利用预训练的AR模型进行初始化并逐步过渡到离散流匹配范式,降低训练成本。
- 实验显示FUDOKI在视觉理解和图像生成任务上表现优秀,具有成为下一代多模态模型基础的潜力。
- 测试时缩放技术能显著提升FUDOKI的性能。
点此查看论文截图


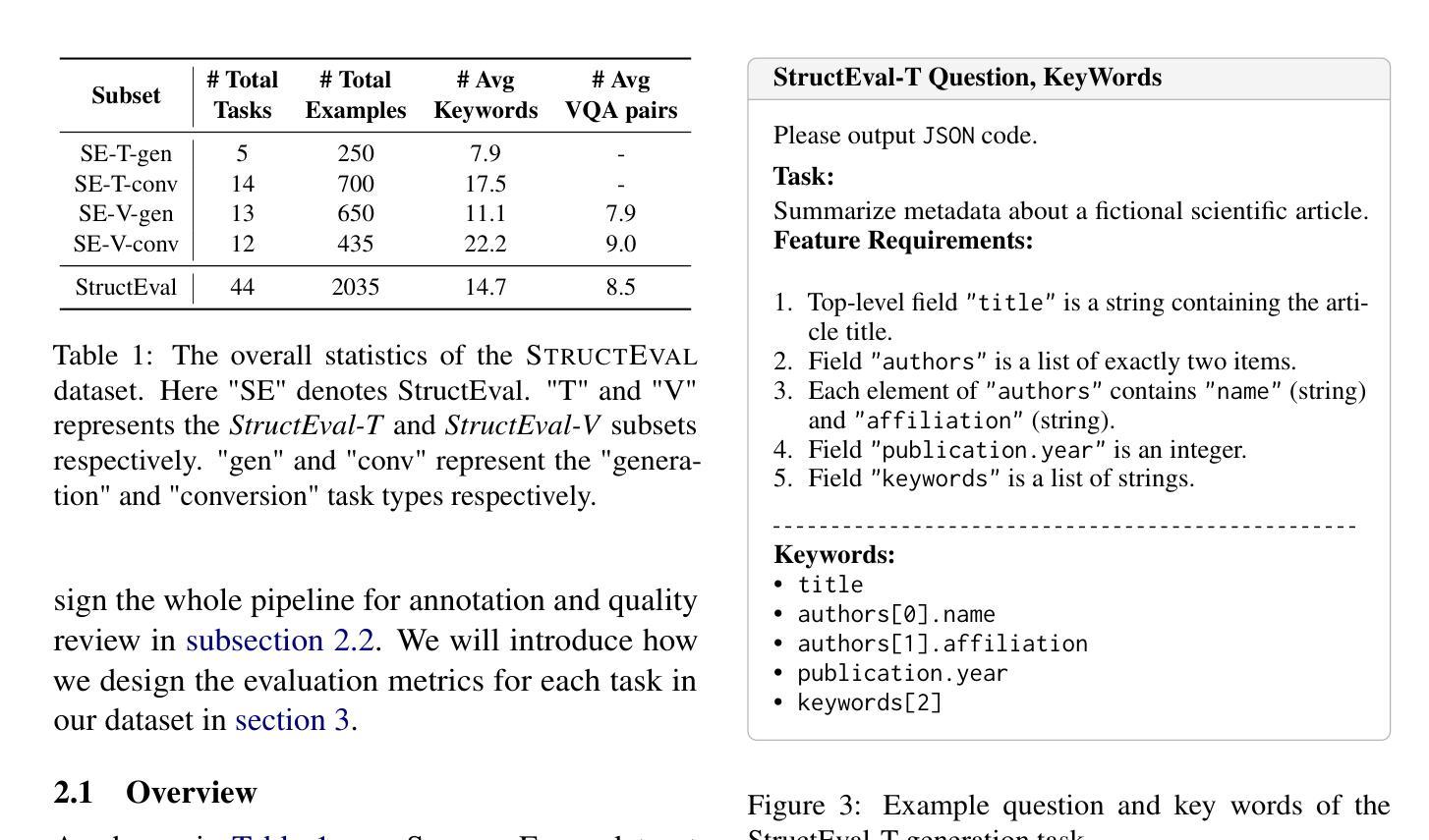
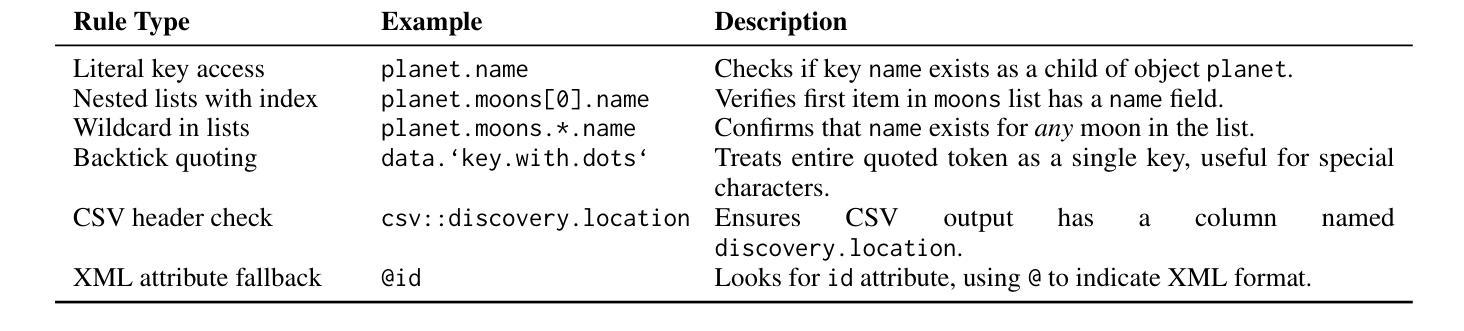
StructEval: Benchmarking LLMs’ Capabilities to Generate Structural Outputs
Authors:Jialin Yang, Dongfu Jiang, Lipeng He, Sherman Siu, Yuxuan Zhang, Disen Liao, Zhuofeng Li, Huaye Zeng, Yiming Jia, Haozhe Wang, Benjamin Schneider, Chi Ruan, Wentao Ma, Zhiheng Lyu, Yifei Wang, Yi Lu, Quy Duc Do, Ziyan Jiang, Ping Nie, Wenhu Chen
As Large Language Models (LLMs) become integral to software development workflows, their ability to generate structured outputs has become critically important. We introduce StructEval, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLMs’ capabilities in producing both non-renderable (JSON, YAML, CSV) and renderable (HTML, React, SVG) structured formats. Unlike prior benchmarks, StructEval systematically evaluates structural fidelity across diverse formats through two paradigms: 1) generation tasks, producing structured output from natural language prompts, and 2) conversion tasks, translating between structured formats. Our benchmark encompasses 18 formats and 44 types of task, with novel metrics for format adherence and structural correctness. Results reveal significant performance gaps, even state-of-the-art models like o1-mini achieve only 75.58 average score, with open-source alternatives lagging approximately 10 points behind. We find generation tasks more challenging than conversion tasks, and producing correct visual content more difficult than generating text-only structures.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在软件开发流程中不可或缺,它们生成结构化输出的能力变得至关重要。我们推出了StructEval,这是一个全面基准测试,旨在评估LLM生成非渲染(JSON、YAML、CSV)和可渲染(HTML、React、SVG)结构化格式的能力。与之前的基准测试不同,StructEval通过两种范式系统地评估了跨多种格式的结构保真度:1)生成任务,根据自然语言提示生成结构化输出;2)转换任务,在结构化格式之间进行翻译。我们的基准测试涵盖了18种格式和44种任务类型,包括新的格式遵循度和结构正确性的指标。结果表明,即使是最先进的模型,如o1-mini也仅达到75.58的平均分,开源替代方案大约落后10分。我们发现生成任务比转换任务更具挑战性,生成正确的视觉内容比生成纯文本结构更为困难。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 9 figures, 13 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成结构化输出方面的能力对于软件开发流程至关重要。本文介绍了StructEval,一个全面评估LLM生成多种非渲染(JSON、YAML、CSV)和可渲染(HTML、React、SVG)结构化格式能力的基准测试。StructEval通过生成任务和转换任务两个范式系统地评估了结构保真度。结果显示,即使是最新模型也存在显著性能差距,生成任务比转换任务更具挑战性,生成正确视觉内容比生成纯文本结构更为困难。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在软件开发生成结构化输出方面的能力日益关键。
- StructEval是一种新的基准测试,旨在评估LLM生成多种结构化格式的能力。
- StructEval包含生成任务和转换任务两大范式,涵盖18种格式和44种任务类型。
- 最新模型在StructEval上的表现存在显著性能差距。
- 生成任务比转换任务更具挑战性。
- 生成正确视觉内容比生成纯文本结构更为困难。
点此查看论文截图


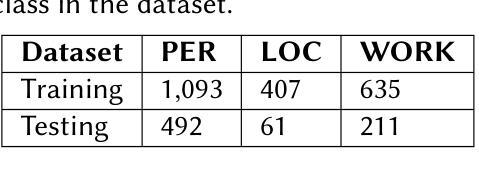
Named Entity Recognition in Historical Italian: The Case of Giacomo Leopardi’s Zibaldone
Authors:Cristian Santini, Laura Melosi, Emanuele Frontoni
The increased digitization of world’s textual heritage poses significant challenges for both computer science and literary studies. Overall, there is an urgent need of computational techniques able to adapt to the challenges of historical texts, such as orthographic and spelling variations, fragmentary structure and digitization errors. The rise of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized natural language processing, suggesting promising applications for Named Entity Recognition (NER) on historical documents. In spite of this, no thorough evaluation has been proposed for Italian texts. This research tries to fill the gap by proposing a new challenging dataset for entity extraction based on a corpus of 19th century scholarly notes, i.e. Giacomo Leopardi’s Zibaldone (1898), containing 2,899 references to people, locations and literary works. This dataset was used to carry out reproducible experiments with both domain-specific BERT-based models and state-of-the-art LLMs such as LLaMa3.1. Results show that instruction-tuned models encounter multiple difficulties handling historical humanistic texts, while fine-tuned NER models offer more robust performance even with challenging entity types such as bibliographic references.
随着世界文本遗产的数字化程度不断提高,这给计算机科学和文学研究都带来了重大挑战。总体而言,急需能够适应历史文本挑战的计算技术,例如正字法、拼写变化、片段结构和数字化错误等。大型语言模型(LLM)的崛起已经彻底改变了自然语言处理,为历史文献中的命名实体识别(NER)带来了充满希望的应用前景。尽管如此,尚未有针对意大利语文本的全面评估。本研究试图通过提出一个基于19世纪学术笔记的新数据集来填补这一空白,该数据集来自贾科莫·莱奥帕迪的《齐巴尔多内》(Zibaldone)(1898年),包含对人名、地名和文学作品的2899处引用。该数据集被用于进行可重复实验,采用基于BERT的特定领域模型和最新的大型语言模型LLaMa 3.1等先进的大型语言模型进行处理。结果表明,经过指令调优的模型在处理历史人文文本时遇到多重困难,而经过精细调整的NER模型即使在处理如参考文献等具有挑战性的实体类型时也能提供更稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着世界文本遗产的数字化进程加速,计算机科学与文学研究领域面临着诸多挑战。为适应历史文本的特殊性,如正字法、拼写变化、结构片段化和数字化错误等,急需发展计算技术。大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理领域的应用具有革命性意义,特别是在历史文献的命名实体识别(NER)方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,针对意大利文本的研究尚缺乏全面评估。本研究尝试以19世纪的学术笔记——贾科莫·列奥帕蒂的《吉巴尔多内》(1898)为基础,建立一个包含2899个关于人物、地点和文学作品引用的实体提取数据集,以填补这一空白。该数据集用于进行可重复实验,比较特定领域的BERT模型和最新的LLMs(如LLaMa 3.1)。结果显示,指令微调模型在处理历史人文文本时面临诸多困难,而精细调整的NER模型即使在处理具有挑战性的实体类型(如参考文献)时也能提供更稳健的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本遗产数字化对计算机科学和文学研究领域带来挑战。
- 历史文本的特殊性包括正字法、拼写变化、结构片段化和数字化错误等。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理领域具有显著潜力。
- 命名实体识别(NER)在历史文献中的应用是LLM的一个重要应用领域。
- 针对意大利文本的研究在LLM应用方面缺乏全面评估。
- 研究使用19世纪学术笔记建立了一个实体提取数据集。
- 实验结果显示,精细调整的NER模型在处理具有挑战性的实体类型时表现更稳健。
点此查看论文截图


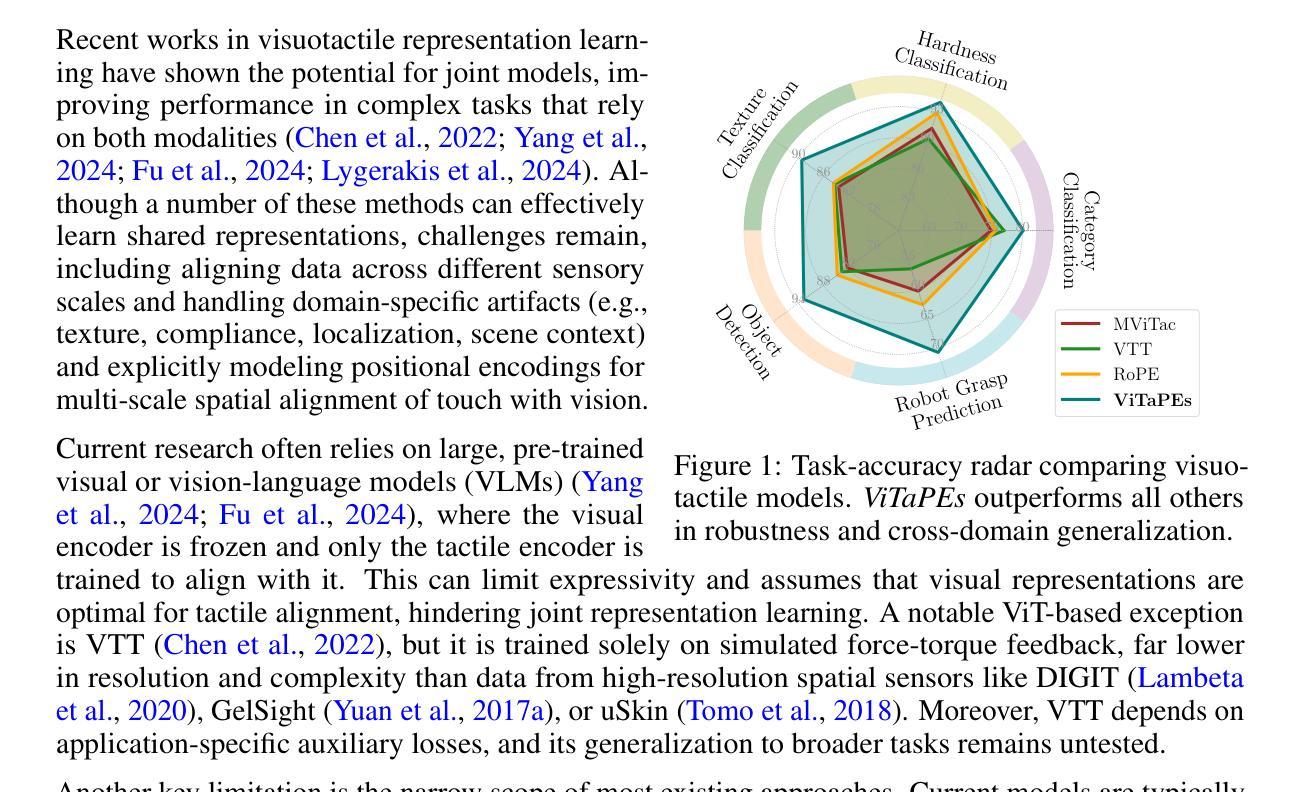
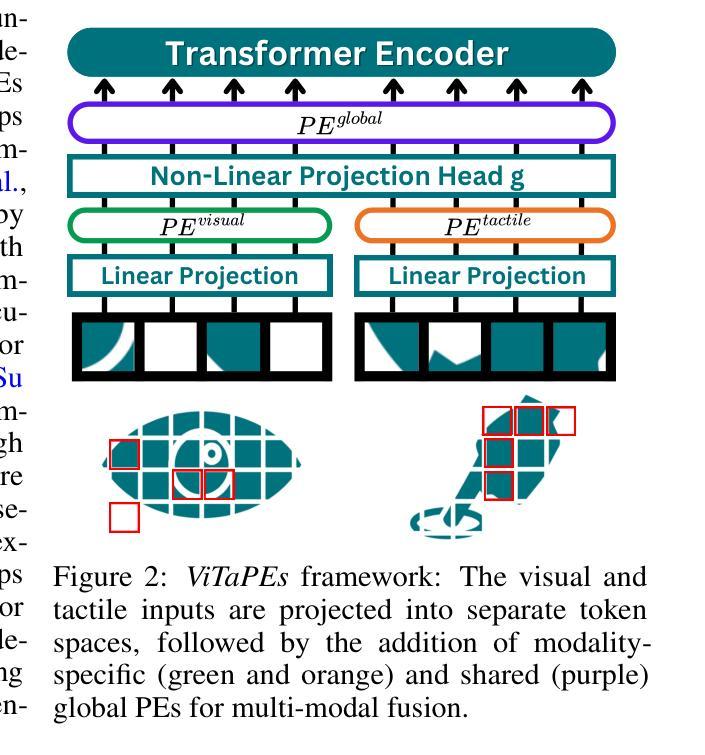
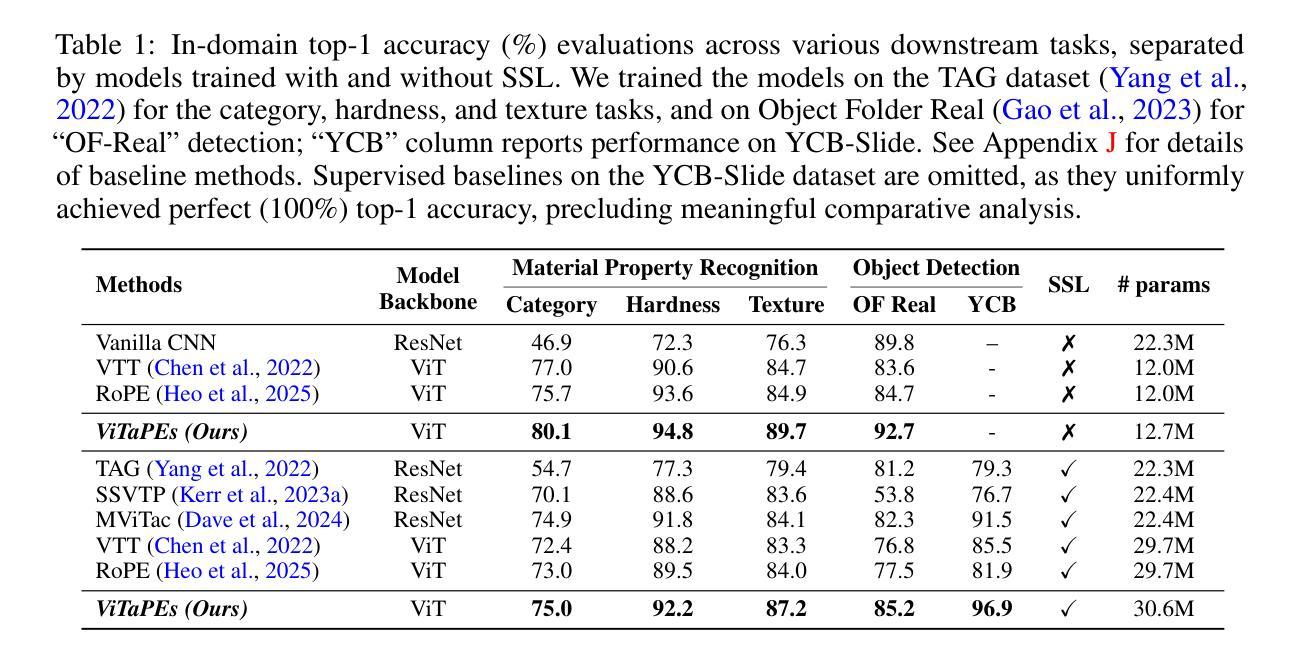
ViTaPEs: Visuotactile Position Encodings for Cross-Modal Alignment in Multimodal Transformers
Authors:Fotios Lygerakis, Ozan Özdenizci, Elmar Rückert
Tactile sensing provides local essential information that is complementary to visual perception, such as texture, compliance, and force. Despite recent advances in visuotactile representation learning, challenges remain in fusing these modalities and generalizing across tasks and environments without heavy reliance on pre-trained vision-language models. Moreover, existing methods do not study positional encodings, thereby overlooking the multi-scale spatial reasoning needed to capture fine-grained visuotactile correlations. We introduce ViTaPEs, a transformer-based framework that robustly integrates visual and tactile input data to learn task-agnostic representations for visuotactile perception. Our approach exploits a novel multi-scale positional encoding scheme to capture intra-modal structures, while simultaneously modeling cross-modal cues. Unlike prior work, we provide provable guarantees in visuotactile fusion, showing that our encodings are injective, rigid-motion-equivariant, and information-preserving, validating these properties empirically. Experiments on multiple large-scale real-world datasets show that ViTaPEs not only surpasses state-of-the-art baselines across various recognition tasks but also demonstrates zero-shot generalization to unseen, out-of-domain scenarios. We further demonstrate the transfer-learning strength of ViTaPEs in a robotic grasping task, where it outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in predicting grasp success. Project page: https://sites.google.com/view/vitapes
触觉感知提供了与视觉感知互补的局部重要信息,如纹理、弹性和力度。尽管视觉触觉表示学习方面最近取得了进展,但融合这些模式、跨任务和跨环境推广仍然面临挑战,而且不能过度依赖预训练的视觉语言模型。此外,现有方法并未研究位置编码,从而忽略了捕捉精细视觉触觉关联所需的多尺度空间推理。我们引入了ViTaPEs,这是一个基于transformer的框架,能够稳健地集成视觉和触觉输入数据,学习用于视觉触觉感知的任务通用表示。我们的方法利用了一种新型的多尺度位置编码方案,来捕捉内部模式结构,同时建模跨模式线索。与先前的工作不同,我们在视觉触觉融合方面提供了可证明的保证,表明我们的编码是注入的、刚性运动等变的、信息保持的,并通过实验验证了这些属性。在多个大规模现实世界数据集上的实验表明,ViTaPEs不仅在各种识别任务上超越了最新基线,而且还表现出对未见过的、超出领域范围的场景的零样本泛化能力。我们进一步展示了ViTaPEs在机器人抓取任务中的迁移学习优势,在预测抓取成功方面超越了最新基线。项目页面:https://sites.google.com/view/vitapes
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉和触觉感知的结合对于获取物体的纹理、弹性和力度等局部重要信息至关重要。然而,现有方法在融合这两种模态时仍面临挑战,缺乏跨任务和环境的通用性,且过度依赖预训练的视觉语言模型。本文提出了一种基于变压器的新框架ViTaPEs,该框架能够稳健地整合视觉和触觉输入数据,学习用于视觉触觉感知的任务无关表示。通过一种新的多尺度位置编码方案,ViTaPEs能够捕捉跨模态线索的模态内结构和跨模态线索。此外,本文为触觉视觉融合提供了可证明的理论保证,并在多个大规模现实数据集上的实验表明,ViTaPEs不仅超越了各种识别任务的最新基线,而且在未见过的、超出领域范围的场景中实现了零样本泛化。同时,在机器人抓取任务中,ViTaPEs的迁移学习能力也得到了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉和触觉感知结合对于获取物体局部重要信息至关重要。
- 现有方法在融合视觉和触觉模态时存在挑战,缺乏跨任务和环境的通用性。
- ViTaPEs框架能够稳健地整合视觉和触觉输入数据,学习任务无关表示。
- ViTaPEs采用新的多尺度位置编码方案,捕捉跨模态线索的模态内结构和跨模态信息。
- ViTaPEs为触觉视觉融合提供了可证明的理论保证。
- ViTaPEs在多个大规模现实数据集上表现超越最新基线,实现零样本泛化。
点此查看论文截图

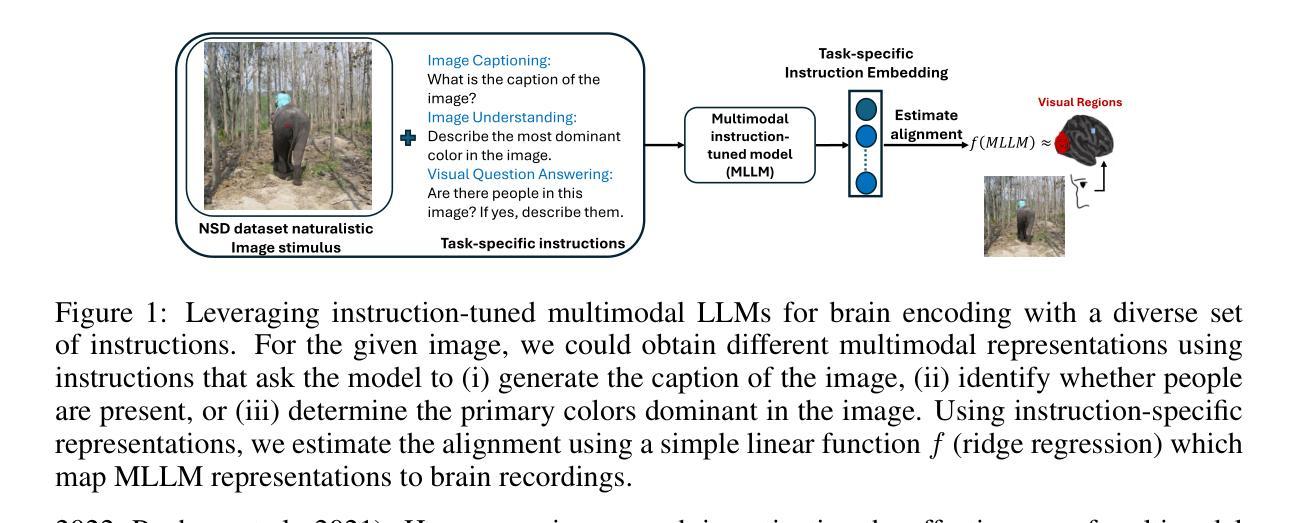
Correlating instruction-tuning (in multimodal models) with vision-language processing (in the brain)
Authors:Subba Reddy Oota, Akshett Jindal, Ishani Mondal, Khushbu Pahwa, Satya Sai Srinath Namburi, Manish Shrivastava, Maneesh Singh, Bapi S. Raju, Manish Gupta
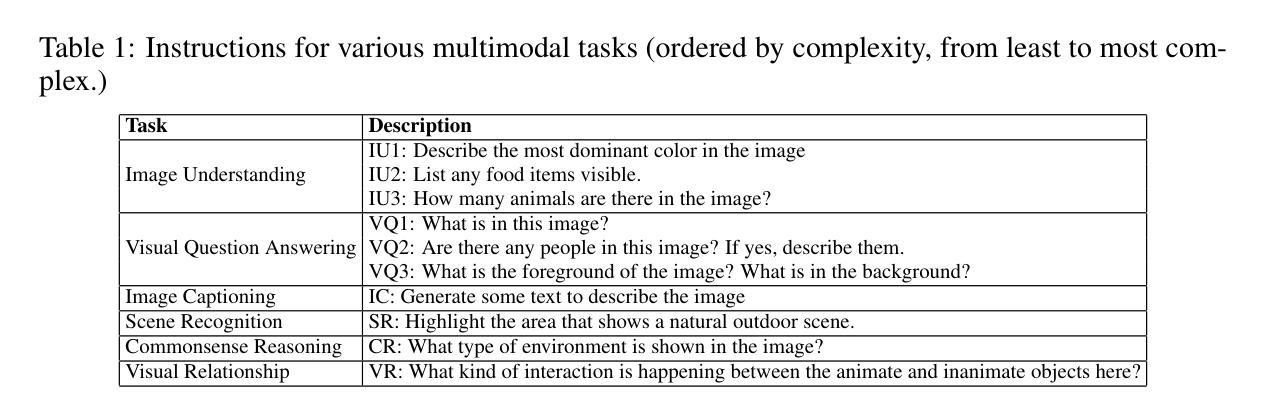
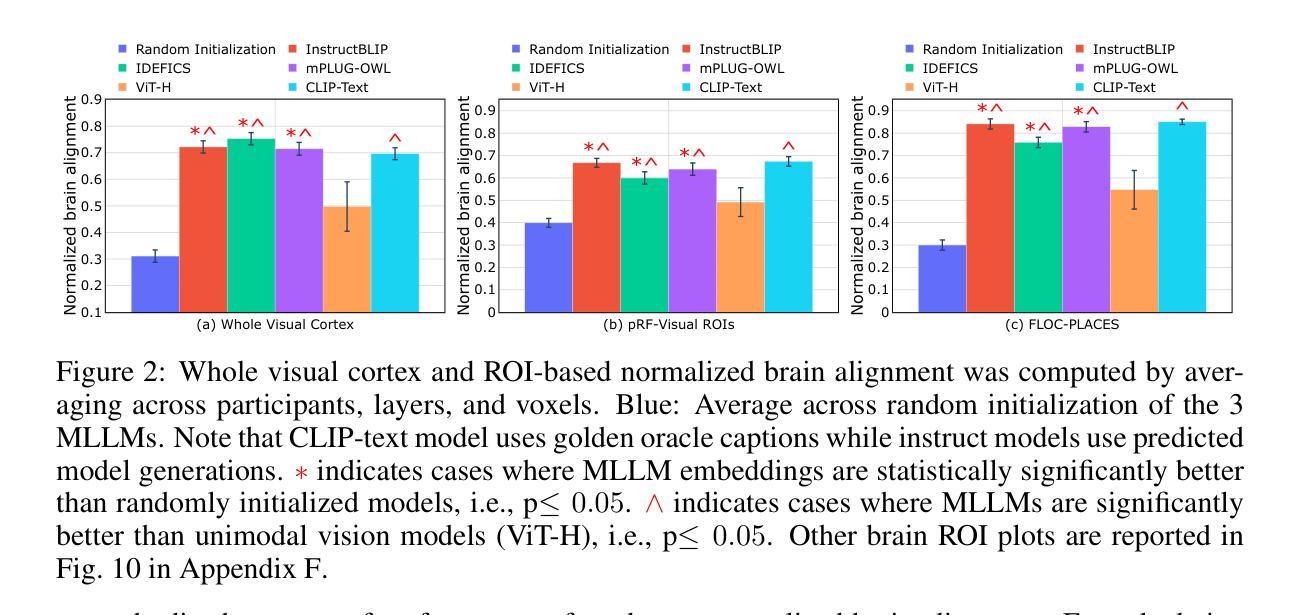
Transformer-based language models, though not explicitly trained to mimic brain recordings, have demonstrated surprising alignment with brain activity. Progress in these models-through increased size, instruction-tuning, and multimodality-has led to better representational alignment with neural data. Recently, a new class of instruction-tuned multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) have emerged, showing remarkable zero-shot capabilities in open-ended multimodal vision tasks. However, it is unknown whether MLLMs, when prompted with natural instructions, lead to better brain alignment and effectively capture instruction-specific representations. To address this, we first investigate brain alignment, i.e., measuring the degree of predictivity of neural visual activity using text output response embeddings from MLLMs as participants engage in watching natural scenes. Experiments with 10 different instructions show that MLLMs exhibit significantly better brain alignment than vision-only models and perform comparably to non-instruction-tuned multimodal models like CLIP. We also find that while these MLLMs are effective at generating high-quality responses suitable to the task-specific instructions, not all instructions are relevant for brain alignment. Further, by varying instructions, we make the MLLMs encode instruction-specific visual concepts related to the input image. This analysis shows that MLLMs effectively capture count-related and recognition-related concepts, demonstrating strong alignment with brain activity. Notably, the majority of the explained variance of the brain encoding models is shared between MLLM embeddings of image captioning and other instructions. These results suggest that enhancing MLLMs’ ability to capture task-specific information could lead to better differentiation between various types of instructions, and thereby improving their precision in predicting brain responses.
虽然基于Transformer的语言模型并未经过明确的训练来模仿脑电波记录,但它们已经表现出令人惊讶的与脑活动的对齐性。这些模型通过扩大规模、指令微调以及多模态融合的发展,使得它们在神经数据表征对齐方面表现更好。最近,新兴的一类经过指令微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在开放式的多模态视觉任务中表现出了引人注目的零样本能力。然而,当人们用自然语言指令来提示MLLMs时,它们是否能实现对大脑的更好对齐并有效捕获指令特定的表征仍是未知的。为了解决这个问题,我们首先研究大脑对齐问题,即测量参与者观看自然场景时,使用MLLMs产生的文本输出响应嵌入来提高神经视觉活动的预测性。用1:项不同指令进行的实验表明,MLLMs在大脑对齐方面显著优于仅用于视觉的模型,并且与未经指令调整的多模态模型(如CLIP)表现相当。我们还发现,虽然这些MLLMs在生成适合特定任务指令的高质量响应方面非常有效,但并非所有指令都与大脑对齐相关。此外,通过改变指令,我们让MLLMs对输入图像进行编码,涉及特定指令的视觉概念。这一分析表明,MLLMs能够有效地捕获计数相关和识别相关的概念,表现出与脑活动的强烈对齐性。值得注意的是,大脑编码模型的大部分解释方差存在于MLLM的图像描述和其他指令的嵌入之间。这些结果表明,提高MLLMs捕获特定任务信息的能力可能会使它们能够更好地区分不同类型的指令,从而提高它们在预测大脑反应方面的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages, 22 figures, The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR-2025, Singapore. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=xkgfLXZ4e0
摘要
基于Transformer的语言模型虽未经过模仿脑记录的明确训练,但已显示出与脑活动惊人的对齐程度。这些模型的进步——通过规模扩大、指令微调和多模态——导致了与神经数据的代表性对齐能力的提高。最近,一类新的指令微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的出现,在开放的多模态视觉任务中显示出惊人的零镜头能力。然而,尚不清楚当MLLMs接收到自然指令时,是否会对脑对齐产生更好的影响,并有效地捕获指令特定的表示。本研究首先调查了脑对齐,即使用MLLMs的文本输出响应嵌入来测量参与者观看自然场景时神经视觉活动的预测程度。实验显示,与仅关注视觉的模型相比,MLLMs在脑对齐方面表现出显著的优势,并且与非指令调整的多模态模型如CLIP的表现相当。我们还发现,虽然这些MLLMs在生成适合特定任务指令的高质量响应方面非常有效,但并不是所有指令都与脑对齐相关。此外,通过改变指令,我们使MLLMs编码与输入图像相关的指令特定视觉概念。分析显示,MLLMs有效地捕获了计数相关和识别相关的概念,显示出与脑活动的强烈对齐。特别是,大脑编码模型的大部分解释方差都存在于MLLM的图像描述和其他指令嵌入之间。这些结果表明,提高MLLMs捕获特定任务信息的能力可能会导致不同类型指令之间的更好区分,从而改善它们在预测大脑反应方面的精确度。
关键见解
- 基于Transformer的语言模型与脑活动显示出惊人的对齐程度。
- 指令微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在脑对齐方面表现出显著优势。
- MLLMs在生成适合特定任务指令的高质量响应方面非常有效。
- 并非所有指令都与脑对齐相关。
- MLLMs能够通过编码指令特定的视觉概念来响应输入图像。
- MLLMs有效地捕获计数和识别相关的概念,与脑活动对齐。
点此查看论文截图

Automated CAD Modeling Sequence Generation from Text Descriptions via Transformer-Based Large Language Models
Authors:Jianxing Liao, Junyan Xu, Yatao Sun, Maowen Tang, Sicheng He, Jingxian Liao, Shui Yu, Yun Li, Hongguan Xiao
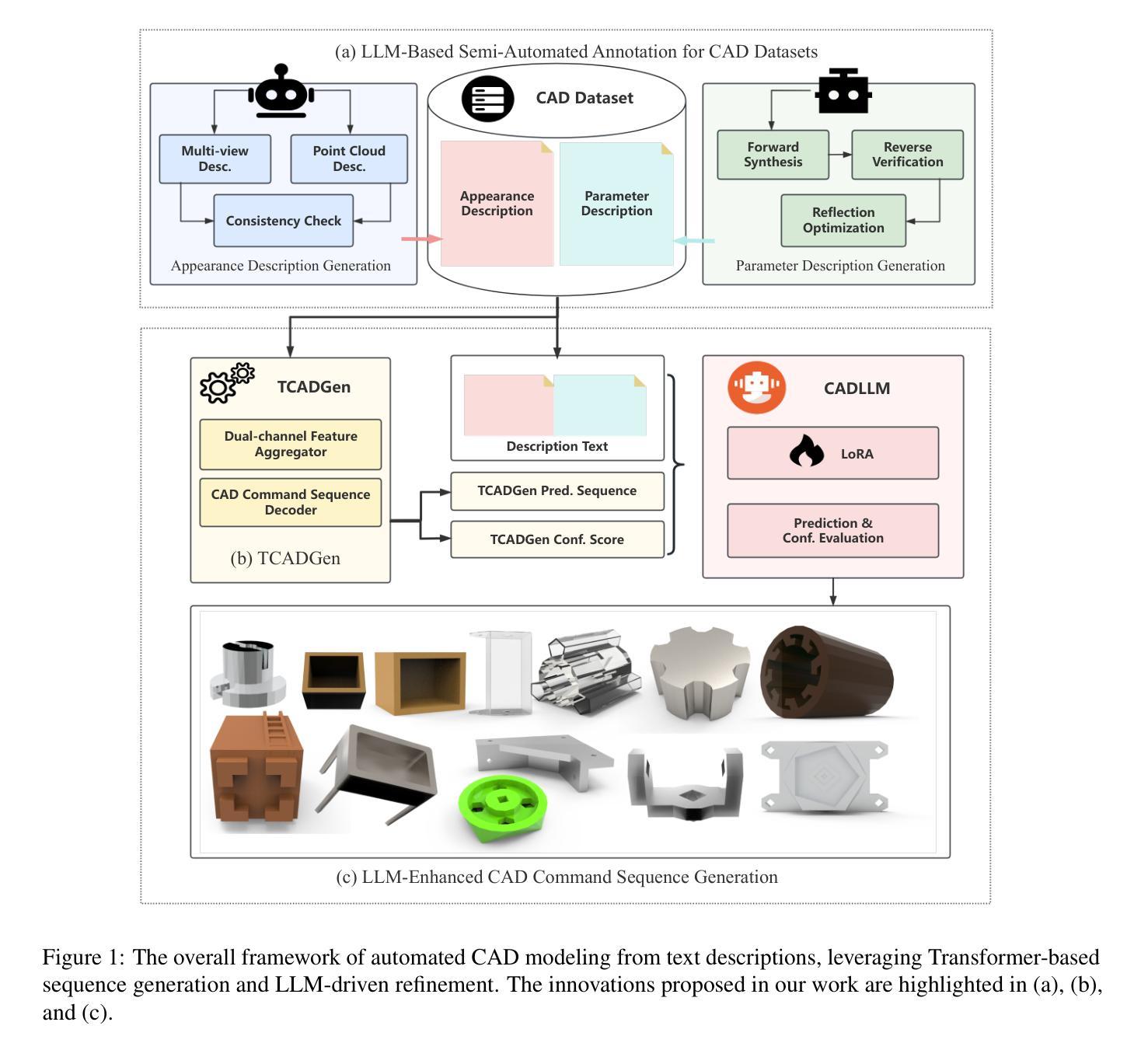
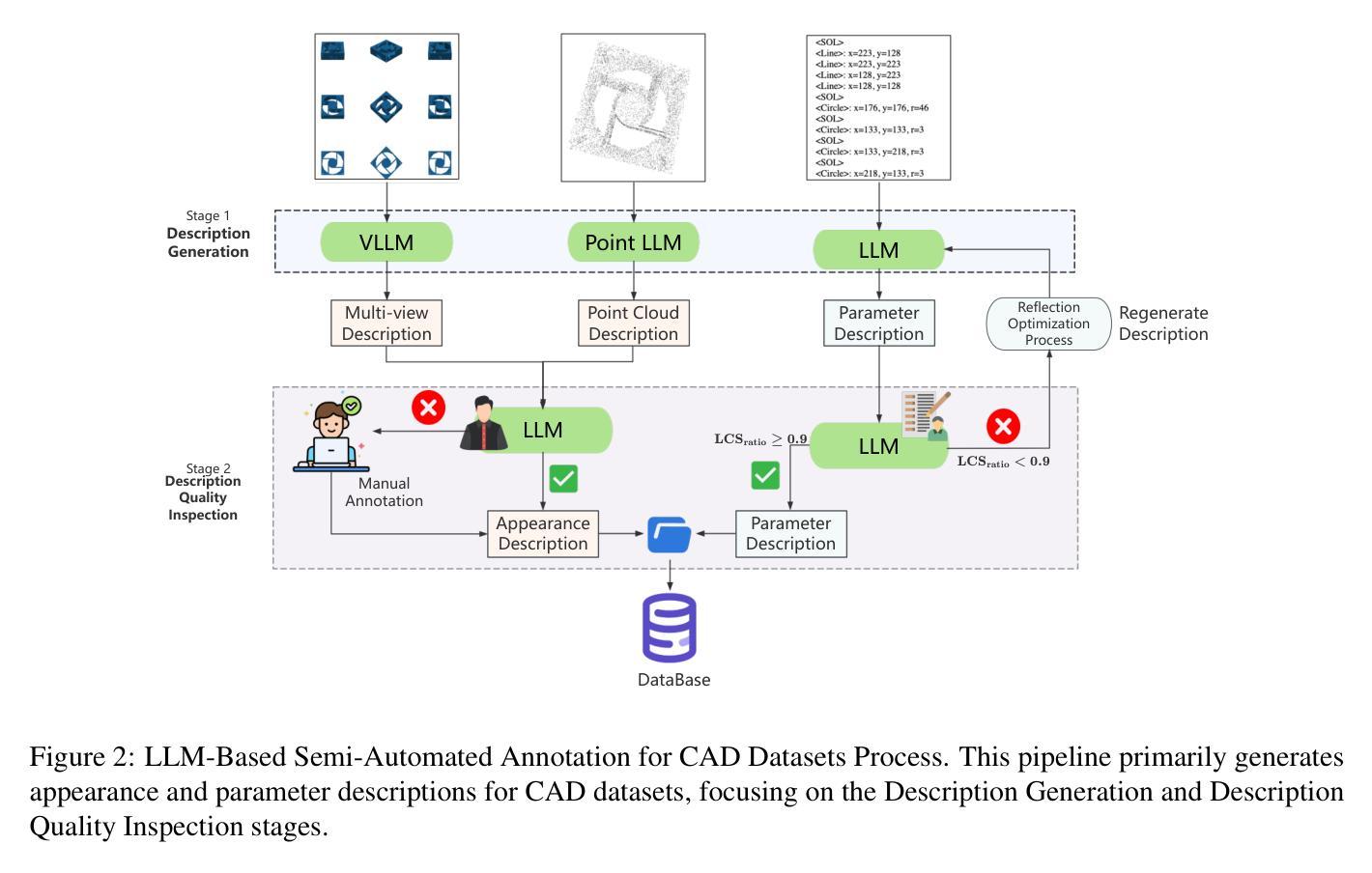
Designing complex computer-aided design (CAD) models is often time-consuming due to challenges such as computational inefficiency and the difficulty of generating precise models. We propose a novel language-guided framework for industrial design automation to address these issues, integrating large language models (LLMs) with computer-automated design (CAutoD).Through this framework, CAD models are automatically generated from parameters and appearance descriptions, supporting the automation of design tasks during the detailed CAD design phase. Our approach introduces three key innovations: (1) a semi-automated data annotation pipeline that leverages LLMs and vision-language large models (VLLMs) to generate high-quality parameters and appearance descriptions; (2) a Transformer-based CAD generator (TCADGen) that predicts modeling sequences via dual-channel feature aggregation; (3) an enhanced CAD modeling generation model, called CADLLM, that is designed to refine the generated sequences by incorporating the confidence scores from TCADGen. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms traditional methods in both accuracy and efficiency, providing a powerful tool for automating industrial workflows and generating complex CAD models from textual prompts. The code is available at https://jianxliao.github.io/cadllm-page/
设计复杂的计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型通常很耗时,因为存在计算效率低下和难以生成精确模型等挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种用于工业自动化设计的新型语言引导框架,该框架将大型语言模型(LLM)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD)相结合。通过此框架,CAD模型可以根据参数和外观描述自动生成,支持详细CAD设计阶段的设计任务自动化。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:(1)一种半自动数据注释管道,利用LLM和视觉语言大型模型(VLLM)生成高质量参数和外观描述;(2)基于Transformer的CAD生成器(TCADGen),通过双通道特征聚合来预测建模序列;(3)增强型CAD建模生成模型,即CADLLM,旨在通过结合TCADGen的信心分数来优化生成的序列。实验结果表明,该方法在准确性和效率方面都优于传统方法,为自动化工业工作流程和根据文本提示生成复杂的CAD模型提供了强大的工具。代码可在[https://jianxliao.github.io/cadllm-page/]找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
一个全新的语言引导工业设计自动化框架被提出,该框架整合了大语言模型(LLMs)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD)。通过这一框架,可以从参数和外观描述自动生成CAD模型,支持详细设计阶段的自动化设计任务。此框架包含三个主要创新点:半自动数据标注管道、基于Transformer的CAD生成器(TCADGen)和增强的CAD建模生成模型CADLLM。实验结果显示,该方法在准确性和效率上均优于传统方法,为自动化工业流程和从文本提示生成复杂CAD模型提供了强大工具。
Key Takeaways
- 整合大语言模型(LLMs)与计算机自动化设计(CAutoD),形成新的设计自动化框架。
- 通过该框架,可以从参数和外观描述自动生成CAD模型。
- 采用半自动数据标注管道,利用LLMs和视觉语言大型模型(VLLMs)生成高质量参数和外观描述。
- 利用基于Transformer的CAD生成器(TCADGen)通过双通道特征聚合预测建模序列。
- 推出增强的CAD建模生成模型CADLLM,结合TCADGen的信心分数优化生成序列。
- 实验结果证明,该框架在准确性和效率上均优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

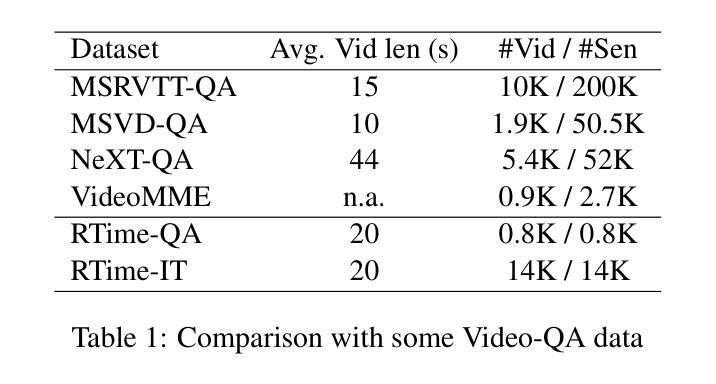
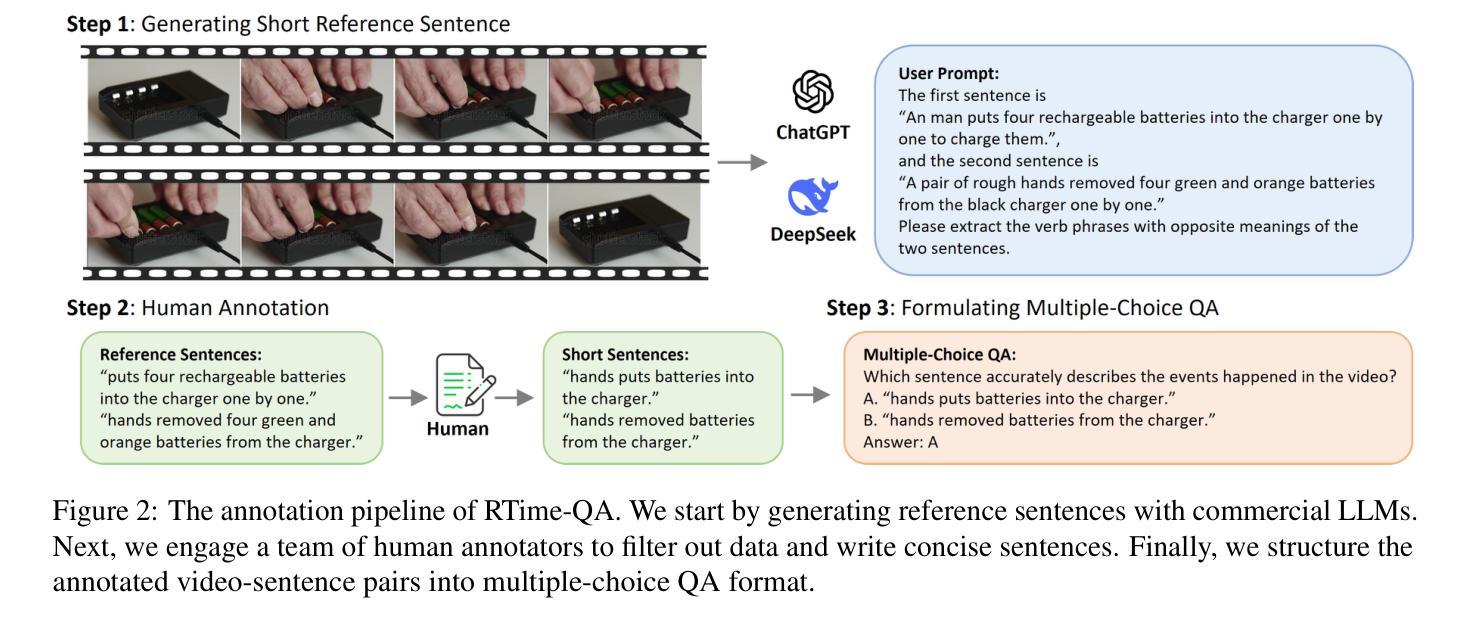
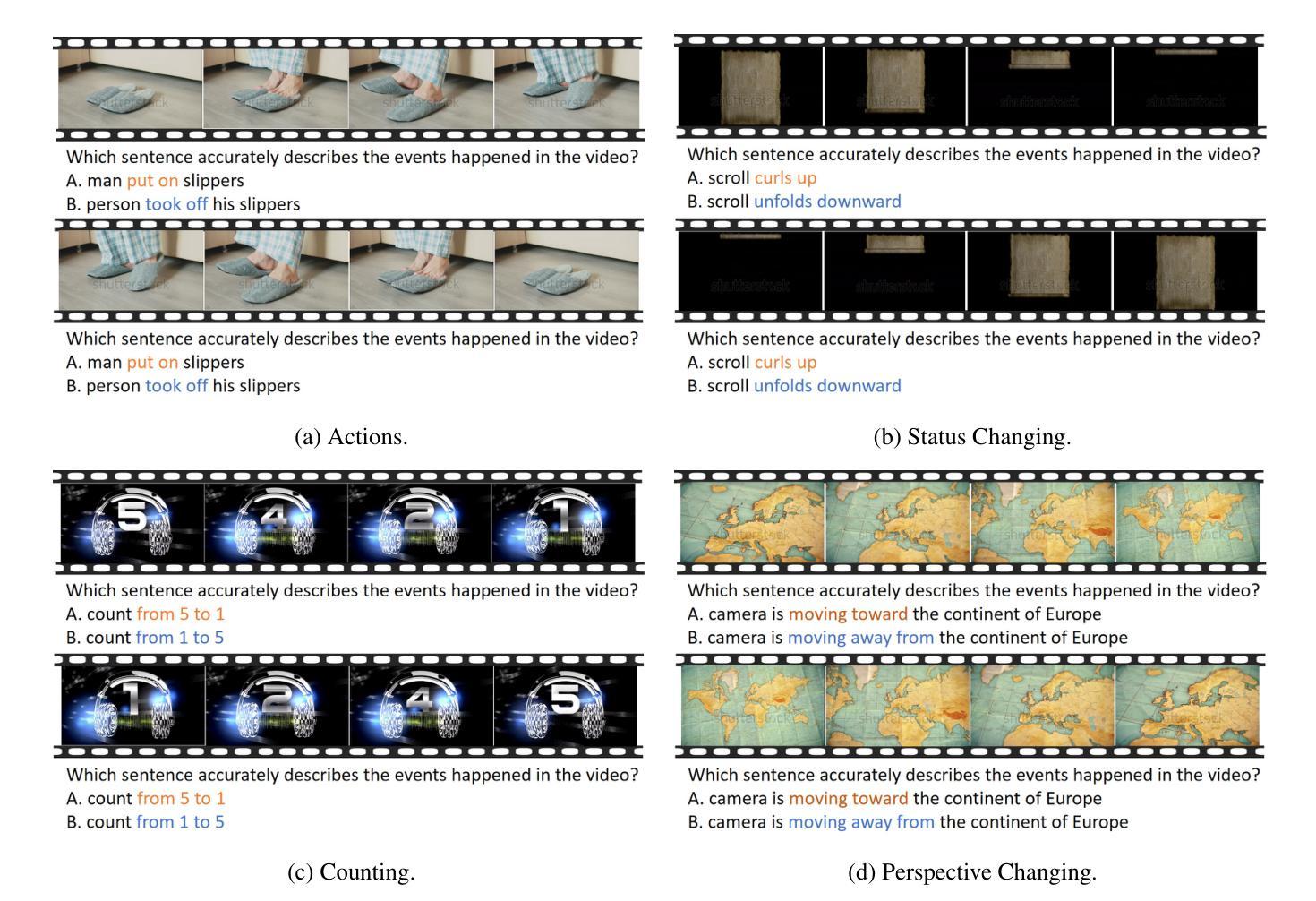
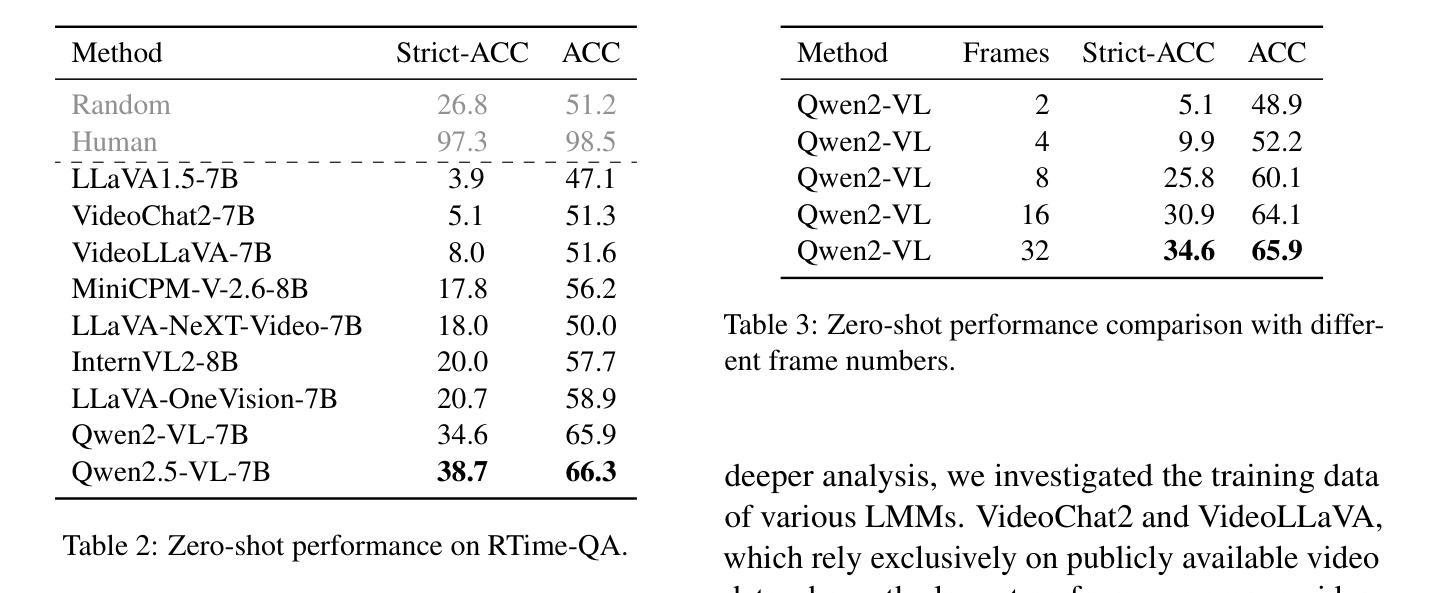
RTime-QA: A Benchmark for Atomic Temporal Event Understanding in Large Multi-modal Models
Authors:Yuqi Liu, Qin Jin, Tianyuan Qu, Xuan Liu, Yang Du, Bei Yu, Jiaya Jia
Understanding accurate atomic temporal event is essential for video comprehension. However, current video-language benchmarks often fall short to evaluate Large Multi-modal Models’ (LMMs) temporal event understanding capabilities, as they can be effectively addressed using image-language models. In this paper, we introduce RTime-QA, a novel benchmark specifically designed to assess the atomic temporal event understanding ability of LMMs. RTime-QA comprises 822 high-quality, carefully-curated video-text questions, each meticulously annotated by human experts. Each question features a video depicting an atomic temporal event, paired with both correct answers and temporal negative descriptions, specifically designed to evaluate temporal understanding. To advance LMMs’ temporal event understanding ability, we further introduce RTime-IT, a 14k instruction-tuning dataset that employs a similar annotation process as RTime-QA. Extensive experimental analysis demonstrates that RTime-QA presents a significant challenge for LMMs: the state-of-the-art model Qwen2-VL achieves only 34.6 on strict-ACC metric, substantially lagging behind human performance. Furthermore, our experiments reveal that RTime-IT effectively enhance LMMs’ capacity in temporal understanding. By fine-tuning on RTime-IT, our Qwen2-VL achieves 65.9 on RTime-QA.
理解准确的原子时序事件对视频理解至关重要。然而,现有的视频语言基准测试通常难以评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)的时序事件理解能力,因为使用图像语言模型可以有效地解决这些问题。在本文中,我们介绍了RTime-QA,这是一个专门设计用于评估LMMs的原子时序事件理解能力的新型基准测试。RTime-QA包含822个高质量、精心策划的视频文本问题,每个问题都由人类专家精心标注。每个问题都有一个描述原子时序事件的视频,配有正确答案和专门设计用于评估时间理解的临时负面描述。为了提升LMMs的时序事件理解能力,我们还引入了RTime-IT,这是一个拥有1.4万条指令的微调数据集,采用与RTime-QA类似的注释流程。广泛的实验分析表明,RTime-QA对LMMs构成了一项重大挑战:最先进的模型Qwen2-VL在严格准确性指标上仅达到34.6,远远落后于人类表现。此外,我们的实验表明,RTime-IT确实提高了LMMs在时序理解方面的能力。通过在RTime-IT上进行微调,我们的Qwen2-VL在RTime-QA上达到了65.9。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
为评估大型多模态模型(LMMs)对原子时态事件的理解能力,本文引入了RTime-QA基准测试。该基准测试包含822个高质量、精心策划的视频文本问题,每个问题均由人类专家精心标注。此外,为提升LMMs的时态事件理解能力,还推出了RTime-IT指令调整数据集。实验表明,RTime-QA对LMMs构成重大挑战,而在RTime-IT上进行微调后,模型性能有所提升。
Key Takeaways:
- RTime-QA基准测试专为评估LMMs对原子时态事件的理解能力而设计。
- RTime-QA包含822个高质量、精心策划的视频文本问题,每个问题都有专家标注。
- RTime-QA中的问题旨在评价模型对时态事件的理解,包括正确答案是和特意设计的时态负描述。
- 推出RTime-IT数据集,用于提升LMMs的时态事件理解能力,采用与RTime-QA相似的标注过程。
- 实验显示,RTime-QA对LMMs构成挑战,现有最佳模型在严格准确率指标上的表现仅为34.6%。
- RTime-IT能有效提升LMMs的时空理解能力,经过RTime-IT微调后,模型性能提升至65.9%。
点此查看论文截图