⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
MT$^{3}$: Scaling MLLM-based Text Image Machine Translation via Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Zhaopeng Feng, Yupu Liang, Shaosheng Cao, Jiayuan Su, Jiahan Ren, Zhe Xu, Yao Hu, Wenxuan Huang, Jian Wu, Zuozhu Liu
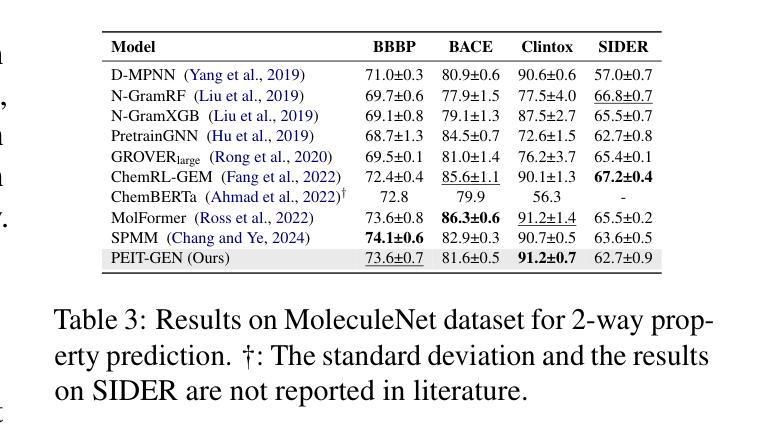
Text Image Machine Translation (TIMT)-the task of translating textual content embedded in images-is critical for applications in accessibility, cross-lingual information access, and real-world document understanding. However, TIMT remains a complex challenge due to the need for accurate optical character recognition (OCR), robust visual-text reasoning, and high-quality translation, often requiring cascading multi-stage pipelines. Recent advances in large-scale Reinforcement Learning (RL) have improved reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), but their application to end-to-end TIMT is still underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce MT$^{3}$, the first framework to apply Multi-Task RL to MLLMs for end-to-end TIMT. MT$^{3}$ adopts a multi-task optimization paradigm targeting three key sub-skills: text recognition, context-aware reasoning, and translation. It is trained using a novel multi-mixed reward mechanism that adapts rule-based RL strategies to TIMT’s intricacies, offering fine-grained, non-binary feedback across tasks. Furthermore, to facilitate the evaluation of TIMT in authentic cross-cultural and real-world social media contexts, we introduced XHSPost, the first social media TIMT benchmark. Our MT$^{3}$-7B-Zero achieves state-of-the-art results on the latest in-domain MIT-10M benchmark, outperforming strong baselines such as Qwen2.5-VL-72B and InternVL2.5-78B by notable margins across multiple metrics. Additionally, the model shows strong generalization to out-of-distribution language pairs and datasets. In-depth analyses reveal how multi-task synergy, reinforcement learning initialization, curriculum design, and reward formulation contribute to advancing MLLM-driven TIMT.
文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)——将嵌入图像中的文本内容进行翻译的任务——对于应用程序的可访问性、跨语言信息访问和现实世界文档理解至关重要。然而,由于需要准确的光学字符识别(OCR)、稳健的视觉文本推理和高质量的翻译,且通常需要级联的多阶段管道,TIMT仍然是一个复杂的挑战。最近大规模强化学习(RL)的进步提高了大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLM(MLLMs)中的推理能力,但其在端到端的TIMT中的应用仍然被探索得不够。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了MT$^{3}$,这是第一个将多任务RL应用于MLLMs进行端到端TIMT的框架。MT$^{3}$采用了一种多任务优化范式,针对三个关键子技能:文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译。它使用一种新型的多混合奖励机制进行训练,该机制将基于规则的RL策略适应到TIMT的复杂性中,提供跨任务的精细粒度非二元反馈。此外,为了促进在真实跨文化和现实世界社交媒体背景下对TIMT的评估,我们引入了XHSPost,这是第一个社交媒体TIMT基准测试。我们的MT$^{3}$-7B-Zero在最新的域内MIT-10M基准测试上取得了最新技术成果,显著优于Qwen2.5-VL-72B和InternVL2.5-78B等强基线,跨越多个指标。此外,该模型在跨分布的语言对和数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。深入分析揭示了多任务协同、强化学习初始化、课程设计以及奖励制定如何推动MLLM驱动的TIMT的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
摘要
文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)是访问性、跨语言信息访问和现实世界文档理解等应用中的关键任务。然而,TIMT仍然是一个复杂的挑战,需要准确的光学字符识别(OCR)、稳健的视觉文本推理和高质量翻译,通常需要级联的多阶段管道。最近大规模强化学习(RL)的进步提高了大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLMs(MLLMs)中的推理能力,但其在端到端TIMT中的应用仍然探索不足。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了MT3,这是第一个将多任务RL应用于MLLMs的端到端TIMT框架。MT3采用多任务优化范式,针对文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译三个关键子技能。它使用一种新型的多混合奖励机制进行训练,该机制根据规则化的RL策略适应TIMT的复杂性,提供跨任务的精细粒度非二进制反馈。此外,为了评估TIMT在真实跨文化和社交媒体环境下的表现,我们推出了XHSPost,这是第一个社交媒体TIMT基准测试。我们的MT3-7B-Zero在最新的MIT-10M基准测试中取得了最新技术成果,显著优于Qwen2.5-VL-72B和InternVL2.5-78B等强大基线模型,并且在多个指标上都实现了可观的差距。此外,该模型在跨语言对和数据集上表现出强大的泛化能力。深入分析揭示了多任务协同、强化学习初始化、课程设计以及奖励制定如何推动MLLM驱动的TIMT的发展。
要点掌握
- 文本图像机器翻译(TIMT)在访问性、跨语言信息访问和现实世界文档理解等领域具有关键作用。
- TIMT是一个复杂的挑战,需要OCR、视觉文本推理和高质量翻译等技术。
- MT$^{3}$框架采用多任务强化学习(RL)应用于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),实现端到端TIMT。
- MT$^{3}$针对文本识别、上下文感知推理和翻译三个关键子技能进行多任务优化。
- 使用多混合奖励机制训练MT$^{3}$,以适应TIMT的复杂性并提供精细的反馈。
- 推出了XHSPost社交媒体TIMT基准测试,用于评估TIMT在真实环境下的表现。
点此查看论文截图

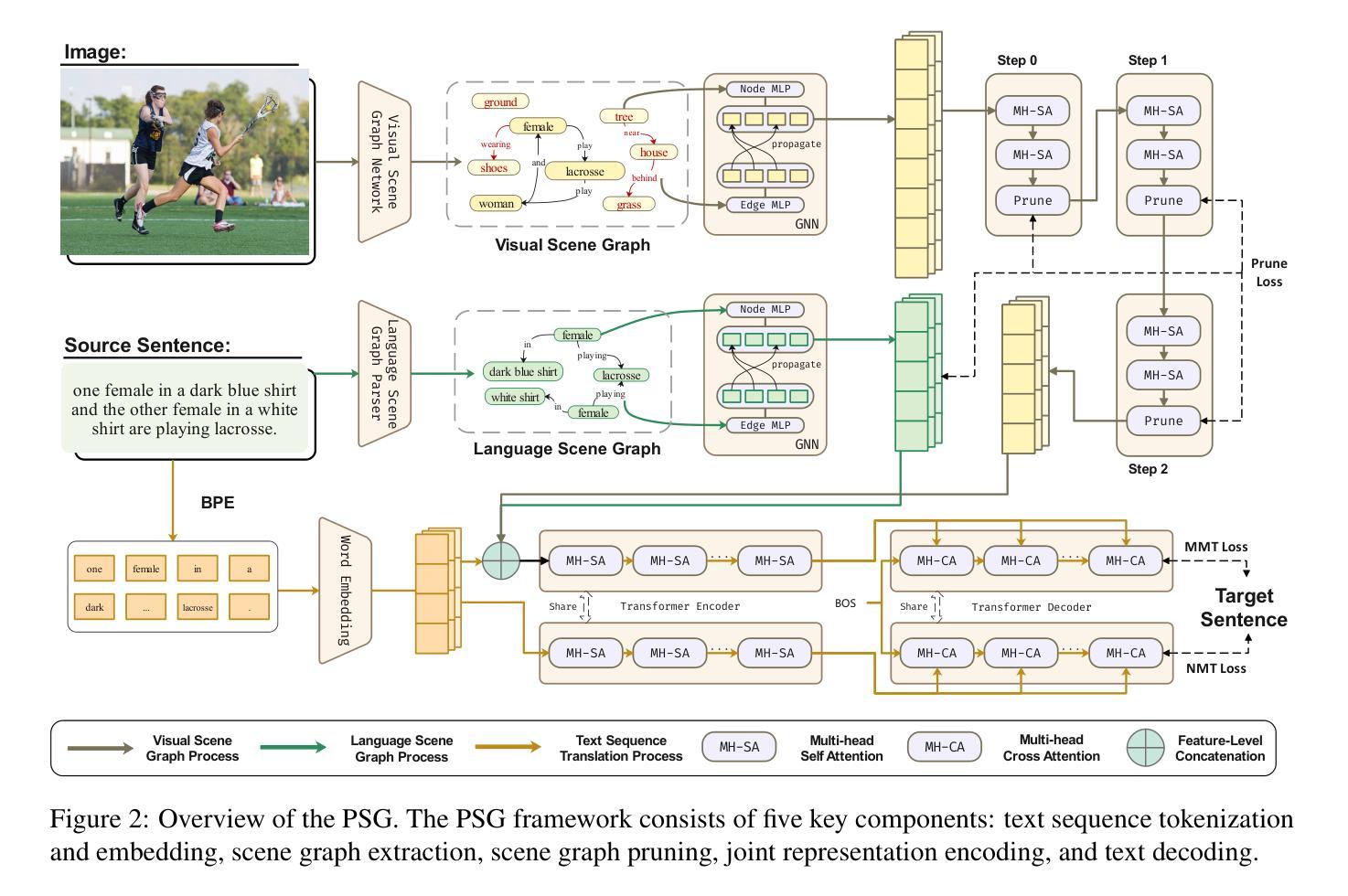
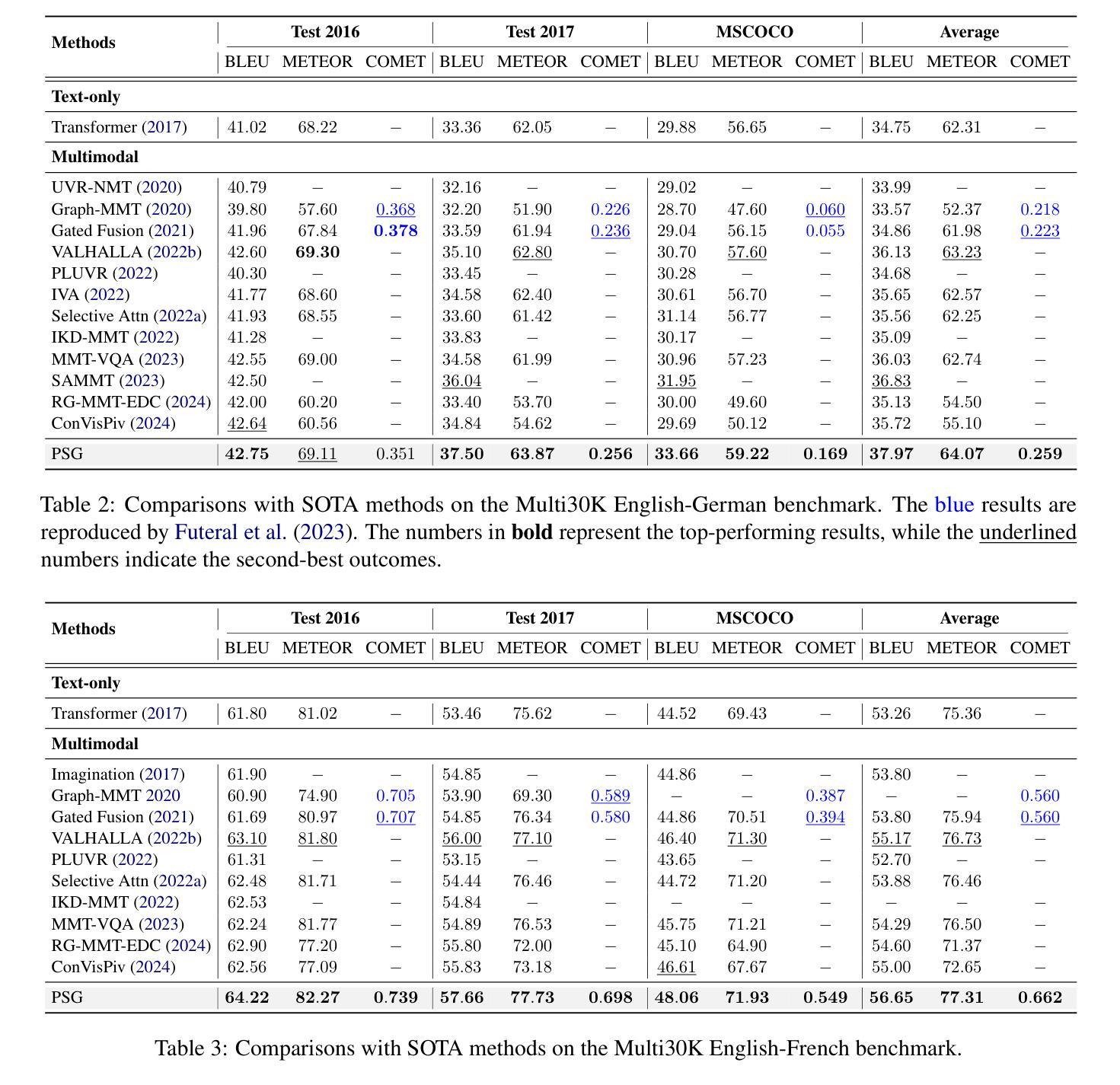
Multimodal Machine Translation with Visual Scene Graph Pruning
Authors:Chenyu Lu, Shiliang Sun, Jing Zhao, Nan Zhang, Tengfei Song, Hao Yang
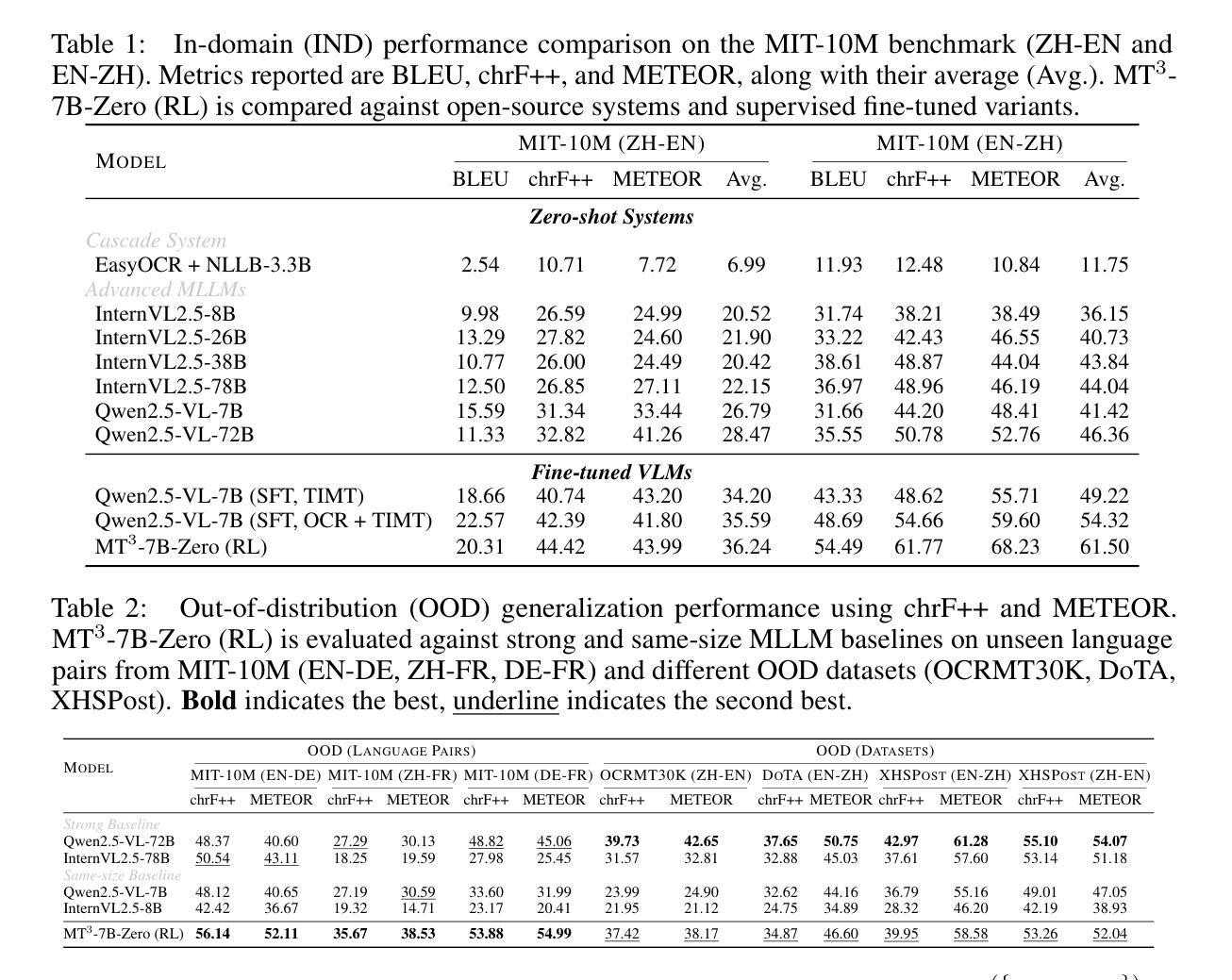
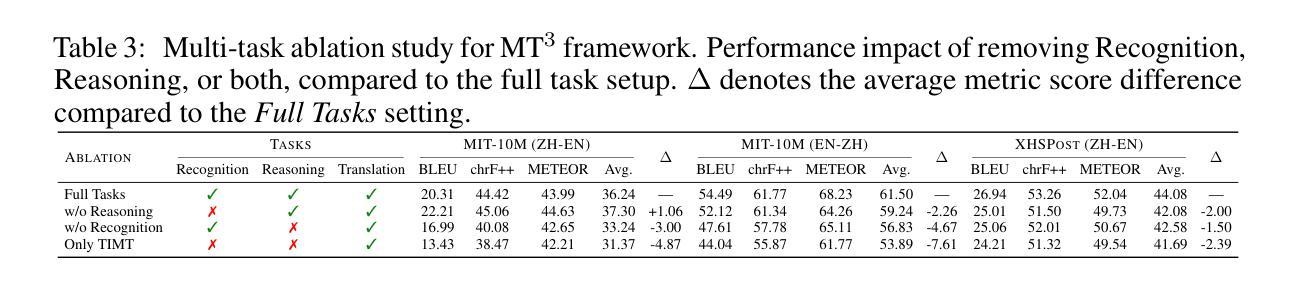
Multimodal machine translation (MMT) seeks to address the challenges posed by linguistic polysemy and ambiguity in translation tasks by incorporating visual information. A key bottleneck in current MMT research is the effective utilization of visual data. Previous approaches have focused on extracting global or region-level image features and using attention or gating mechanisms for multimodal information fusion. However, these methods have not adequately tackled the issue of visual information redundancy in MMT, nor have they proposed effective solutions. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach–multimodal machine translation with visual Scene Graph Pruning (PSG), which leverages language scene graph information to guide the pruning of redundant nodes in visual scene graphs, thereby reducing noise in downstream translation tasks. Through extensive comparative experiments with state-of-the-art methods and ablation studies, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the PSG model. Our results also highlight the promising potential of visual information pruning in advancing the field of MMT.
多模态机器翻译(MMT)旨在通过融入视觉信息来解决翻译任务中的语言多义性和模糊性所带来的挑战。当前MMT研究的一个关键瓶颈是如何有效地利用视觉数据。之前的方法主要集中在提取全局或区域级别的图像特征,并使用注意力或门控机制进行多模态信息融合。然而,这些方法尚未有效解决MMT中视觉信息冗余的问题,也未提出有效的解决方案。在本文中,我们引入了一种新方法——利用视觉场景图修剪(PSG)的多模态机器翻译,该方法利用语言场景图信息来引导视觉场景图中冗余节点的修剪,从而减少对下游翻译任务中的噪声。通过与最新方法和消融研究的广泛对比实验,我们证明了PSG模型的有效性。我们的结果也突出了视觉信息修剪在推动MMT领域发展方面的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态机器翻译(MMT)面临的挑战及解决方案。当前MMT研究的瓶颈在于如何利用视觉数据。为解决视觉信息冗余问题,本文提出了一种新的方法——基于视觉场景图裁剪的多模态机器翻译(PSG)。该方法利用语言场景图信息来引导裁剪视觉场景图中的冗余节点,从而减少下游翻译任务中的噪声。实验结果表明,PSG模型有效且有望推动MMT领域的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态机器翻译(MMT)通过融入视觉信息来解决翻译任务中的语言歧义和多义问题。
- 当前MMT研究的关键挑战在于如何有效利用视觉数据。
- 现有方法主要关注全局或区域级图像特征的提取,以及注意力或门控机制进行多模态信息融合。
- 视觉信息冗余是MMT中的一个重要问题,现有方法未能妥善解决。
- 本文提出了一种基于视觉场景图裁剪的多模态机器翻译(PSG)新方法。
- PSG方法利用语言场景图信息来引导裁剪视觉场景图中的冗余节点,减少下游翻译任务的噪声。
点此查看论文截图

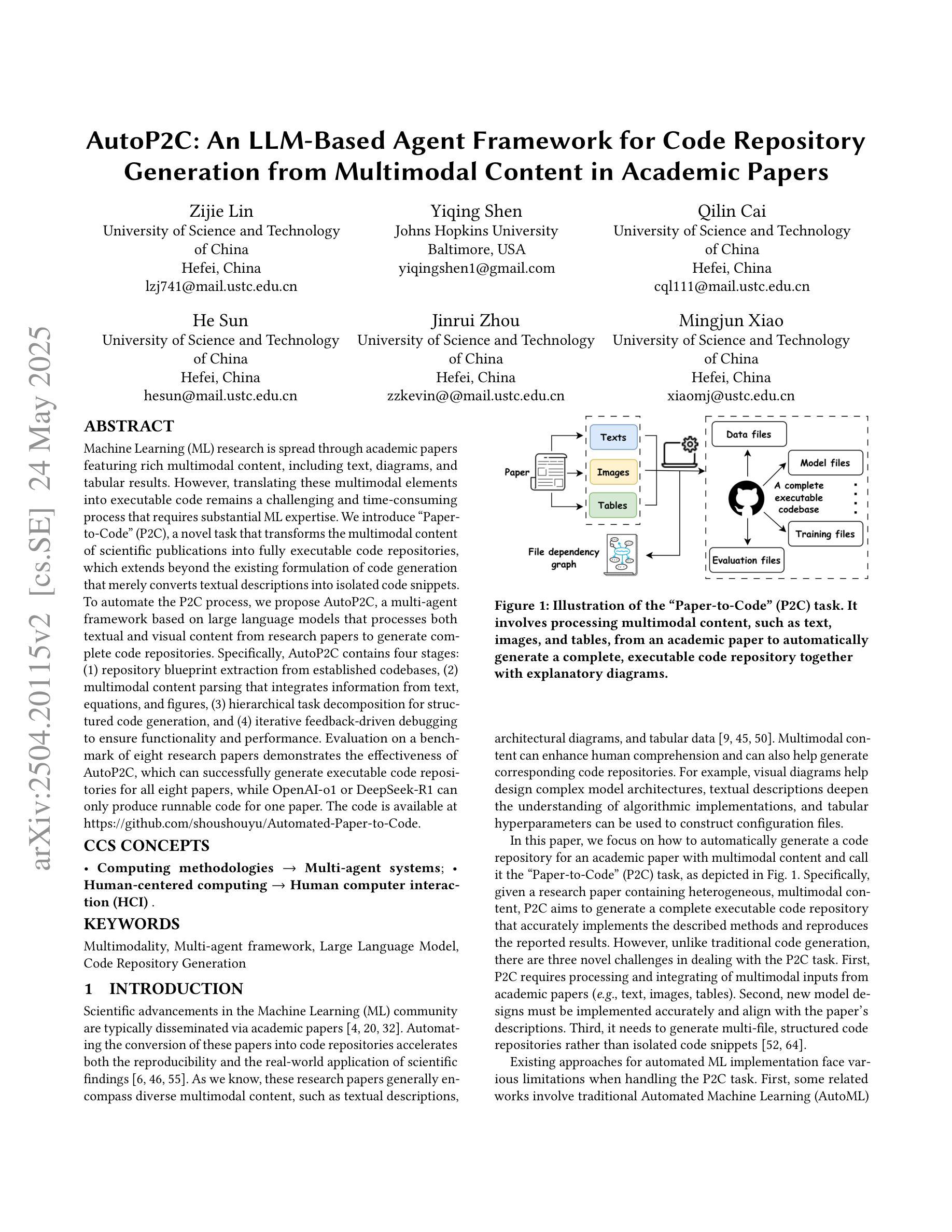
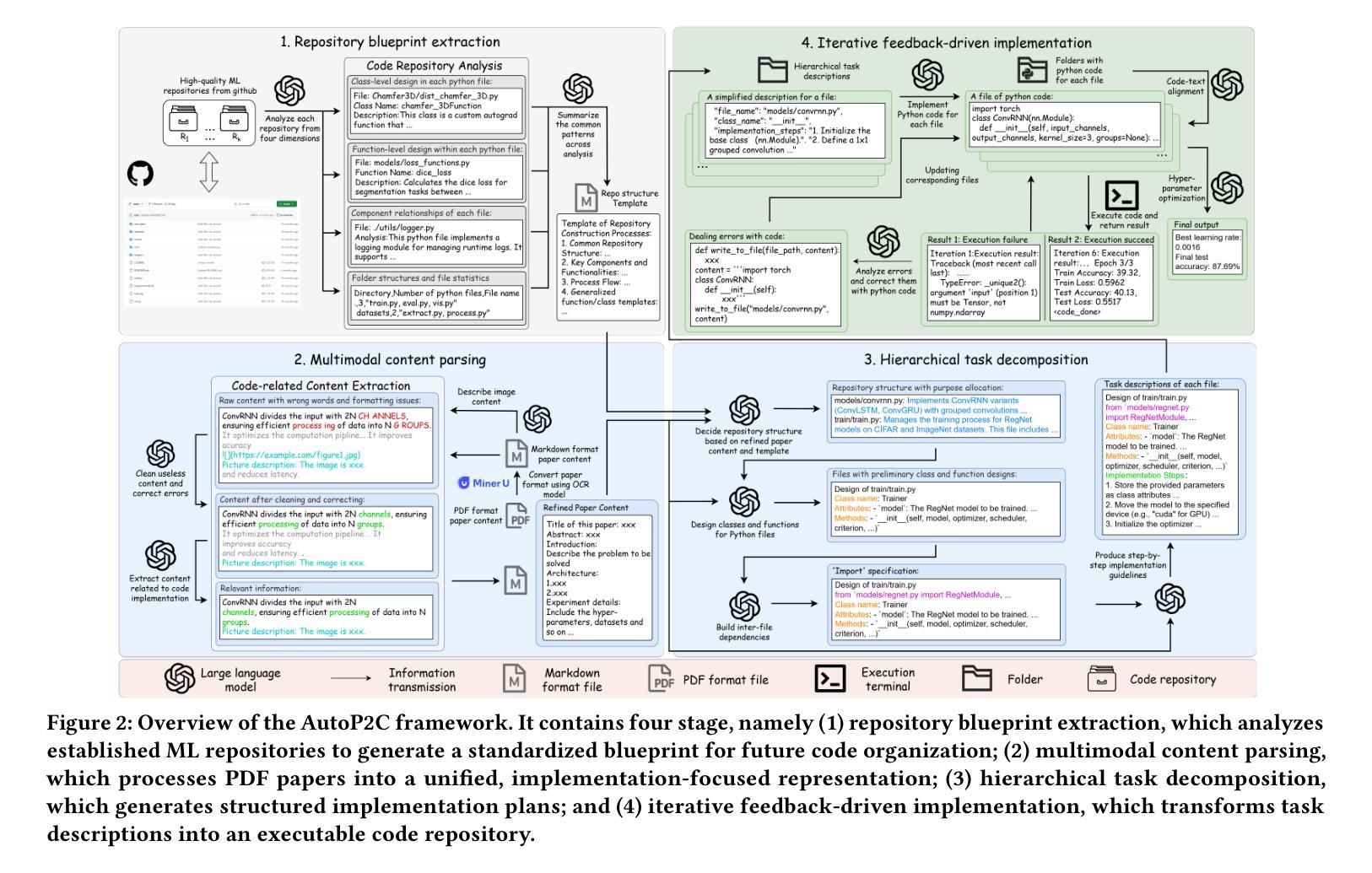
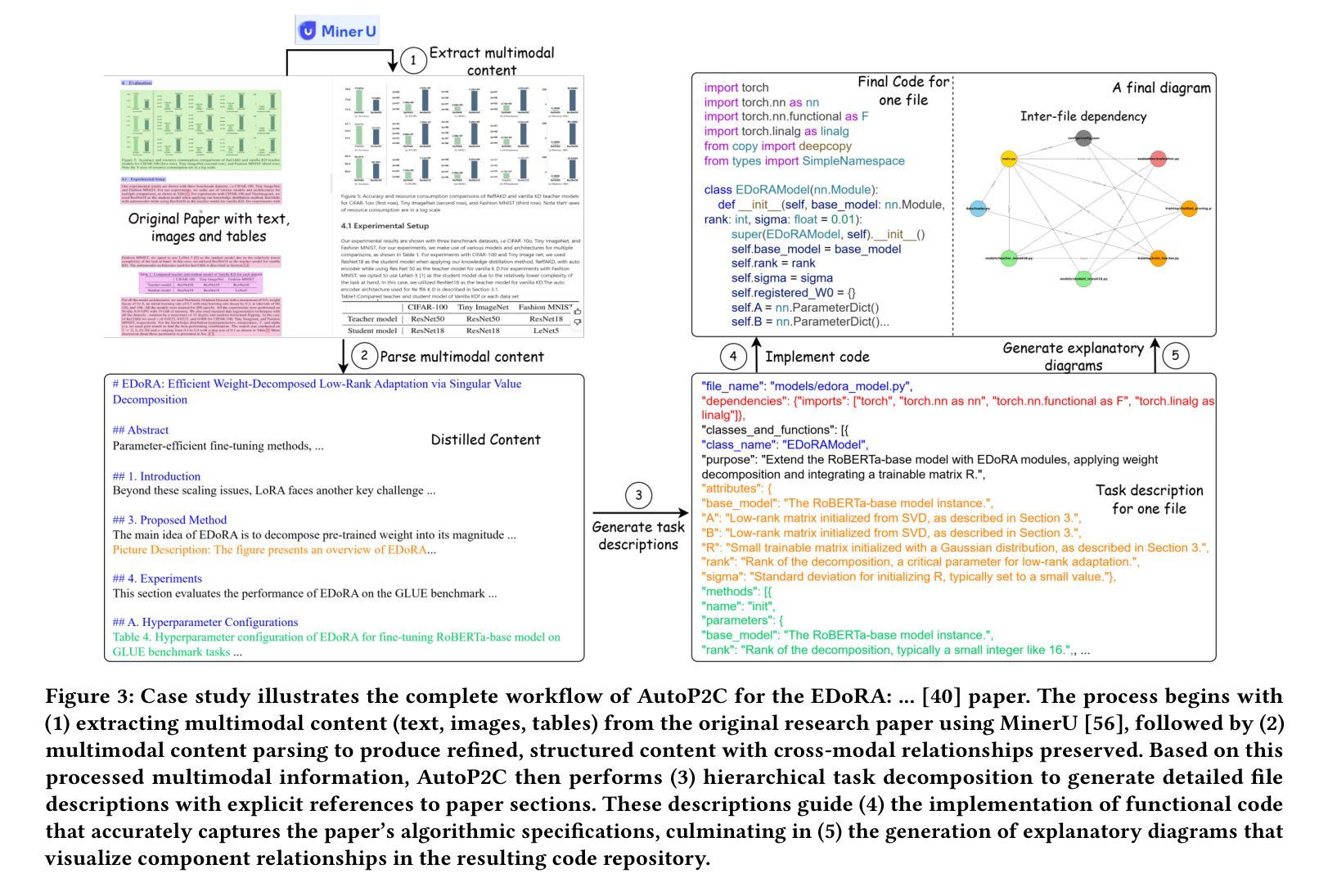
AutoP2C: An LLM-Based Agent Framework for Code Repository Generation from Multimodal Content in Academic Papers
Authors:Zijie Lin, Yiqing Shen, Qilin Cai, He Sun, Jinrui Zhou, Mingjun Xiao
Machine Learning (ML) research is spread through academic papers featuring rich multimodal content, including text, diagrams, and tabular results. However, translating these multimodal elements into executable code remains a challenging and time-consuming process that requires substantial ML expertise. We introduce ``Paper-to-Code’’ (P2C), a novel task that transforms the multimodal content of scientific publications into fully executable code repositories, which extends beyond the existing formulation of code generation that merely converts textual descriptions into isolated code snippets. To automate the P2C process, we propose AutoP2C, a multi-agent framework based on large language models that processes both textual and visual content from research papers to generate complete code repositories. Specifically, AutoP2C contains four stages: (1) repository blueprint extraction from established codebases, (2) multimodal content parsing that integrates information from text, equations, and figures, (3) hierarchical task decomposition for structured code generation, and (4) iterative feedback-driven debugging to ensure functionality and performance. Evaluation on a benchmark of eight research papers demonstrates the effectiveness of AutoP2C, which can successfully generate executable code repositories for all eight papers, while OpenAI-o1 or DeepSeek-R1 can only produce runnable code for one paper. The code is available at https://github.com/shoushouyu/Automated-Paper-to-Code.
机器学习(ML)研究通过包含丰富多模式内容的学术论文进行传播,这些内容包括文本、图表和表格结果。然而,将这些多模式元素翻译成可执行代码仍然是一个具有挑战性和耗时的过程,需要大量的ML专业知识。我们引入了“论文到代码”(P2C)这一新任务,它将学术出版物中的多模式内容转化为可执行的代码仓库,这超出了现有代码生成方法的范围,后者仅将文本描述转换为孤立的代码片段。为了自动化P2C过程,我们提出了基于大型语言模型的多代理框架AutoP2C,该框架处理研究论文中的文本和视觉内容,以生成完整的代码仓库。具体来说,AutoP2C包含四个阶段:(1)从已建立的代码库中提取仓库蓝图,(2)解析多模式内容,整合文本、方程和图表的资料,(3)进行分层任务分解以实现结构化代码生成,(4)通过迭代反馈驱动的调试确保功能和性能。在包含八篇论文的基准测试上的评估证明了AutoP2C的有效性,它成功地为所有八篇论文生成了可执行代码仓库,而OpenAI-o1或DeepSeek-R1只能为一篇论文生成可运行的代码。代码可在https://github.com/shoushouyu/Automated-Paper-to-Code找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项将学术论文中的多媒体内容转化为可执行代码的新任务——“论文到代码”(P2C)。为此任务,提出了一种基于大型语言模型的多智能体框架AutoP2C。该框架包含四个阶段:从现有代码库中提取存储库蓝图、解析文本、方程式和图表中的多媒体内容、进行结构化代码生成以及确保功能和性能的迭代反馈驱动调试。评估表明,AutoP2C在八篇论文的基准测试上表现出色,能够成功生成所有论文的可执行代码存储库,而其他工具如OpenAI-o1或DeepSeek-R1仅能生成一篇论文的可执行代码。
Key Takeaways
- Machine Learning (ML) 论文富含多种模式内容(文本、图表等),转化为可执行代码是困难的且耗时的。需要深厚的技术背景以及充足的技能支持完成转换。为此提出了一个新的任务 —— “论文到代码”(P2C)。
- AutoP2C 是一个基于大型语言模型的多智能体框架,旨在自动化 P2C 过程。它包含四个主要阶段:提取存储库蓝图、解析多媒体内容、结构化代码生成以及反馈驱动的调试。
- AutoP2C 成功生成了八篇论文的可执行代码存储库,相较于其他工具如 OpenAI-o1 或 DeepSeek-R1 在性能方面展现优势。它不仅可以从文本描述生成代码片段,而且可以处理整个存储库的生成和管理。这提高了代码的生成效率和功能性。这项研究成果可在 https://github.com/shoushouyu/Automated-Paper-to-Code 获得使用。
点此查看论文截图
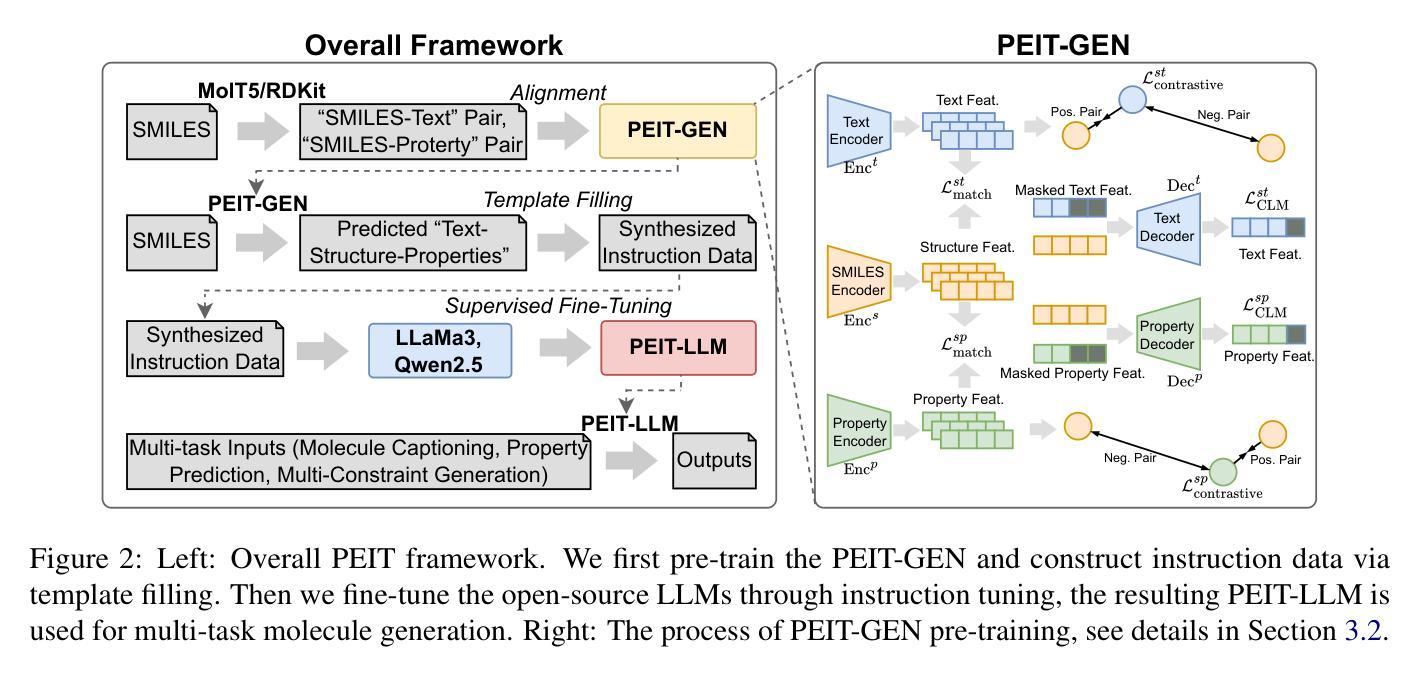
Property Enhanced Instruction Tuning for Multi-task Molecule Generation with Large Language Models
Authors:Xuan Lin, Long Chen, Yile Wang, Xiangxiang Zeng, Philip S. Yu
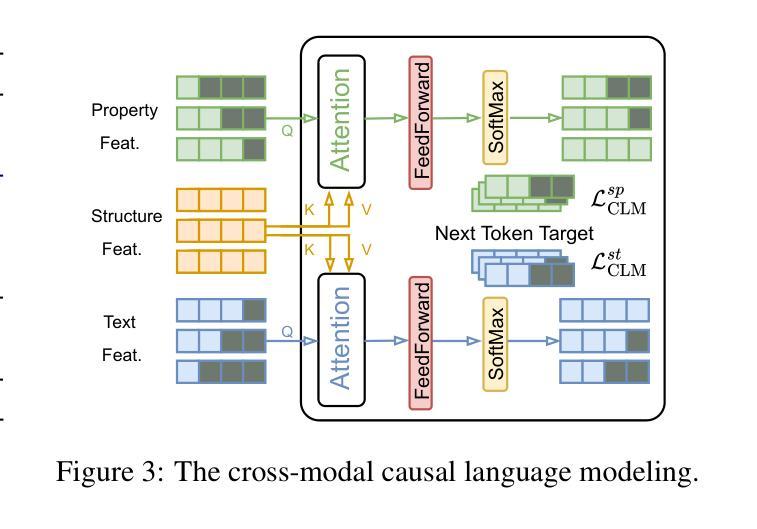
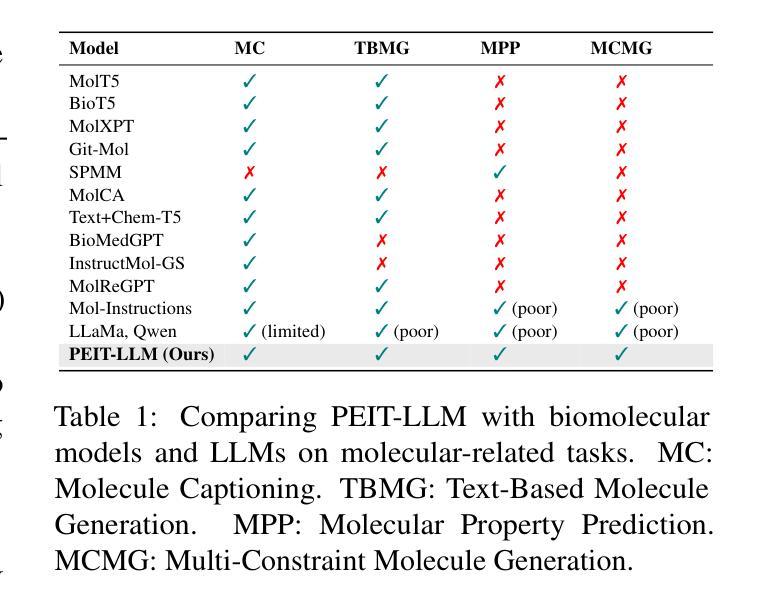
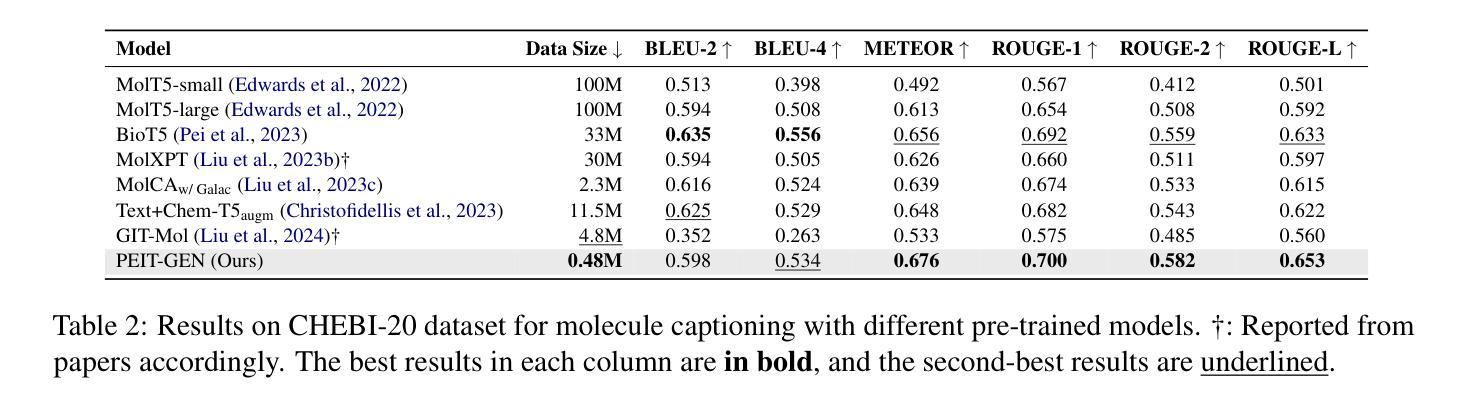
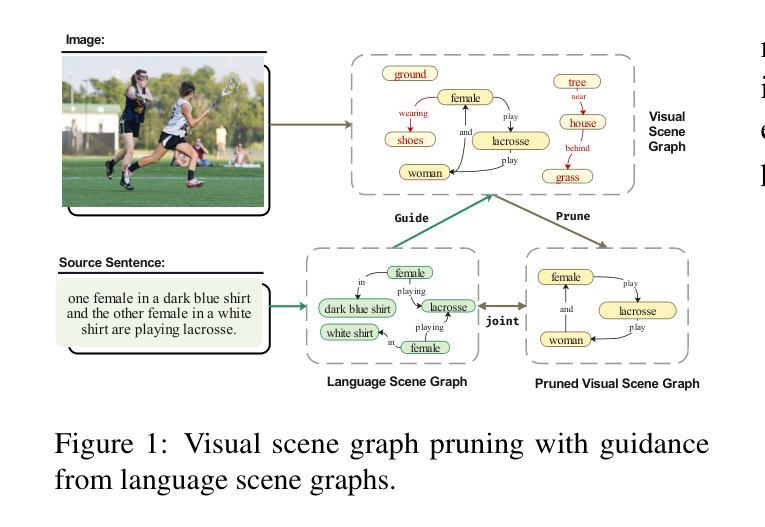
Large language models (LLMs) are widely applied in various natural language processing tasks such as question answering and machine translation. However, due to the lack of labeled data and the difficulty of manual annotation for biochemical properties, the performance for molecule generation tasks is still limited, especially for tasks involving multi-properties constraints. In this work, we present a two-step framework PEIT (Property Enhanced Instruction Tuning) to improve LLMs for molecular-related tasks. In the first step, we use textual descriptions, SMILES, and biochemical properties as multimodal inputs to pre-train a model called PEIT-GEN, by aligning multi-modal representations to synthesize instruction data. In the second step, we fine-tune existing open-source LLMs with the synthesized data, the resulting PEIT-LLM can handle molecule captioning, text-based molecule generation, molecular property prediction, and our newly proposed multi-constraint molecule generation tasks. Experimental results show that our pre-trained PEIT-GEN outperforms MolT5 and BioT5 in molecule captioning, demonstrating modalities align well between textual descriptions, structures, and biochemical properties. Furthermore, PEIT-LLM shows promising improvements in multi-task molecule generation, proving the scalability of the PEIT framework for various molecular tasks. We release the code, constructed instruction data, and model checkpoints in https://github.com/chenlong164/PEIT.
大型语言模型(LLM)在问答和机器翻译等多种自然语言处理任务中得到了广泛应用。然而,由于缺乏标签数据和生物化学属性手动标注的困难,分子生成任务的性能仍然有限,尤其是对于涉及多属性约束的任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个两步框架PEIT(属性增强指令调整)来提高LLM在分子相关任务上的性能。首先,我们使用文本描述、SMILES和生物化学属性作为多模式输入,通过对齐多模式表示来合成指令数据,以预训练一个名为PEIT-GEN的模型。在第二步中,我们使用合成数据对现有的开源LLM进行微调。结果得到的PEIT-LLM可以处理分子描述、文本分子生成、分子属性预测以及我们新提出的多约束分子生成任务。实验结果表明,我们预训练的PEIT-GEN在分子描述方面优于MolT5和BioT5,证明了文本描述、结构和生物化学属性之间的模态对齐良好。此外,PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面显示出有希望的改进,证明了PEIT框架在各种分子任务中的可扩展性。我们在https://github.com/chenlong164/PEIT上发布了代码、构建指令数据和模型检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PEIT的两步框架,用于改进大型语言模型(LLMs)在分子相关任务上的性能。首先,使用文本描述、SMILES和生物化学性质作为多模式输入进行模型预训练;然后,使用合成数据进行现有开源LLMs的微调。实验结果表明,预训练的PEIT-GEN在分子描述方面优于MolT5和BioT5,且PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面显示出显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在分子生成任务上由于缺乏标注数据和手动标注困难,性能受到限制。
- PEIT框架分为两步:第一步是预训练PEIT-GEN模型,使用多模式输入(文本描述、SMILES和生物化学性质);第二步是使用合成数据微调现有开源LLMs。
- PEIT-GEN模型通过对齐多模式表示来合成指令数据,能处理分子描述、文本基础的分子生成、分子属性预测以及新提出的多约束分子生成任务。
- 实验结果表明,PEIT-GEN在分子描述方面优于MolT5和BioT5。
- PEIT框架对多种分子任务具有可扩展性,PEIT-LLM在多任务分子生成方面显示出显著改进。
- 代码、构建指令数据和模型检查点已公开在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图