⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
ErpGS: Equirectangular Image Rendering enhanced with 3D Gaussian Regularization
Authors:Shintaro Ito, Natsuki Takama, Koichi Ito, Hwann-Tzong Chen, Takafumi Aoki
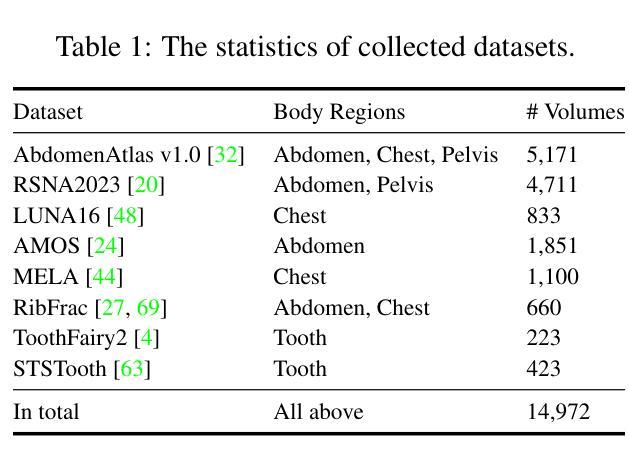
The use of multi-view images acquired by a 360-degree camera can reconstruct a 3D space with a wide area. There are 3D reconstruction methods from equirectangular images based on NeRF and 3DGS, as well as Novel View Synthesis (NVS) methods. On the other hand, it is necessary to overcome the large distortion caused by the projection model of a 360-degree camera when equirectangular images are used. In 3DGS-based methods, the large distortion of the 360-degree camera model generates extremely large 3D Gaussians, resulting in poor rendering accuracy. We propose ErpGS, which is Omnidirectional GS based on 3DGS to realize NVS addressing the problems. ErpGS introduce some rendering accuracy improvement techniques: geometric regularization, scale regularization, and distortion-aware weights and a mask to suppress the effects of obstacles in equirectangular images. Through experiments on public datasets, we demonstrate that ErpGS can render novel view images more accurately than conventional methods.
使用360度相机获取的多视角图像可以重建一个大面积的3D空间。有基于NeRF和3DGS的等距图像3D重建方法,以及新型视图合成(NVS)方法。另一方面,在使用等距图像时,需要克服由360度相机投影模型造成的大畸变。在基于3DGS的方法中,360度相机模型的大畸变会产生非常大的3D高斯,导致渲染精度较低。我们提出了基于3DGS的全方位GS(ErpGS),以实现NVS并解决这些问题。ErpGS引入了一些提高渲染精度的技术:几何正则化、尺度正则化,以及考虑畸变的权重和掩膜,以抑制等距图像中障碍物的影响。在公共数据集上的实验表明,ErpGS可以比传统方法更准确地进行新型视图图像的渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP2025
Summary
基于NeRF和3DGS的等距图像三维重建方法,利用全景相机采集的多视角图像可以重建出大面积的三维空间。然而,使用全景相机投影模型时会产生较大的失真问题,特别是在基于3DGS的方法中,会导致渲染精度降低。本文提出了一种基于Omnidirectional GS(ErpGS)的解决方案,旨在解决NVS中的这些问题。ErpGS引入了几项提高渲染精度的技术,包括几何正则化、尺度正则化以及考虑失真的权重和掩码,以抑制等距图像中障碍物的影响。实验表明,与传统方法相比,ErpGS可以更准确地渲染新型视图图像。
Key Takeaways
- 使用全景相机采集的多视角图像可以重建大面积的三维空间。
- 基于NeRF和3DGS的等距图像三维重建方法存在失真问题。
- 基于Omnidirectional GS的ErpGS方法旨在解决NVS中的失真问题。
- ErpGS引入了几项技术提高渲染精度,包括几何正则化、尺度正则化和考虑失真的权重与掩码。
- ErpGS能有效抑制等距图像中的障碍物影响。
- 实验表明,与传统方法相比,ErpGS能更准确地渲染新型视图图像。
点此查看论文截图

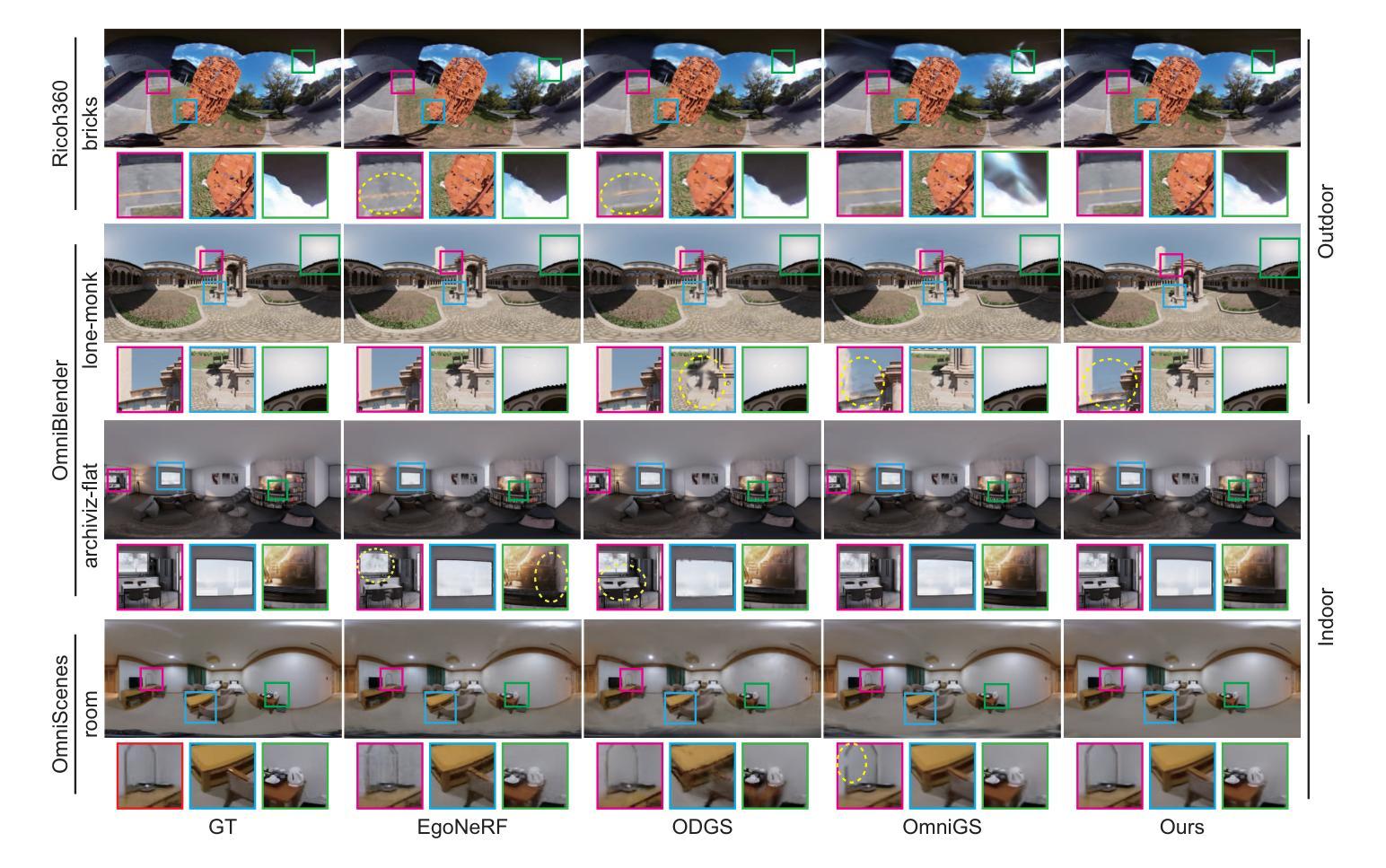

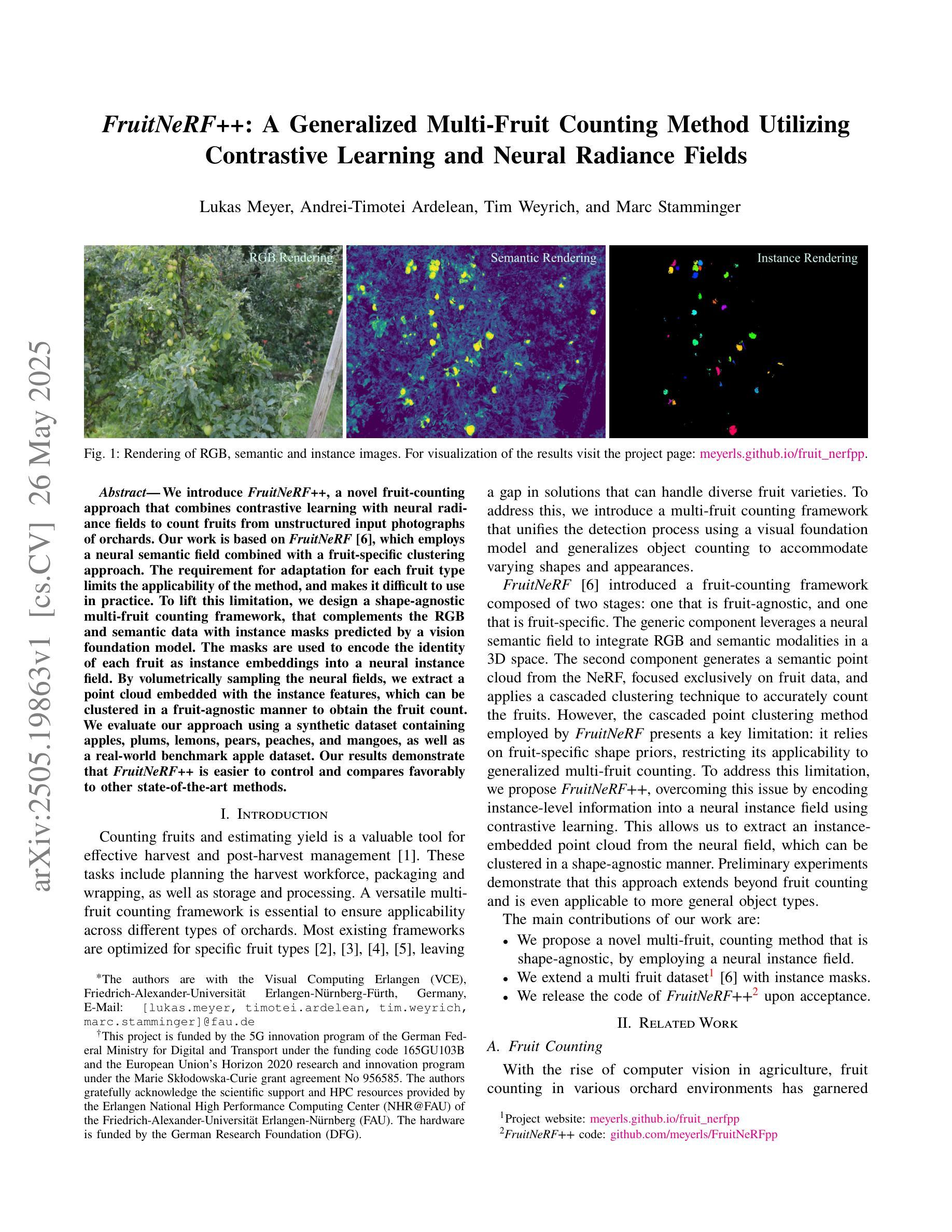
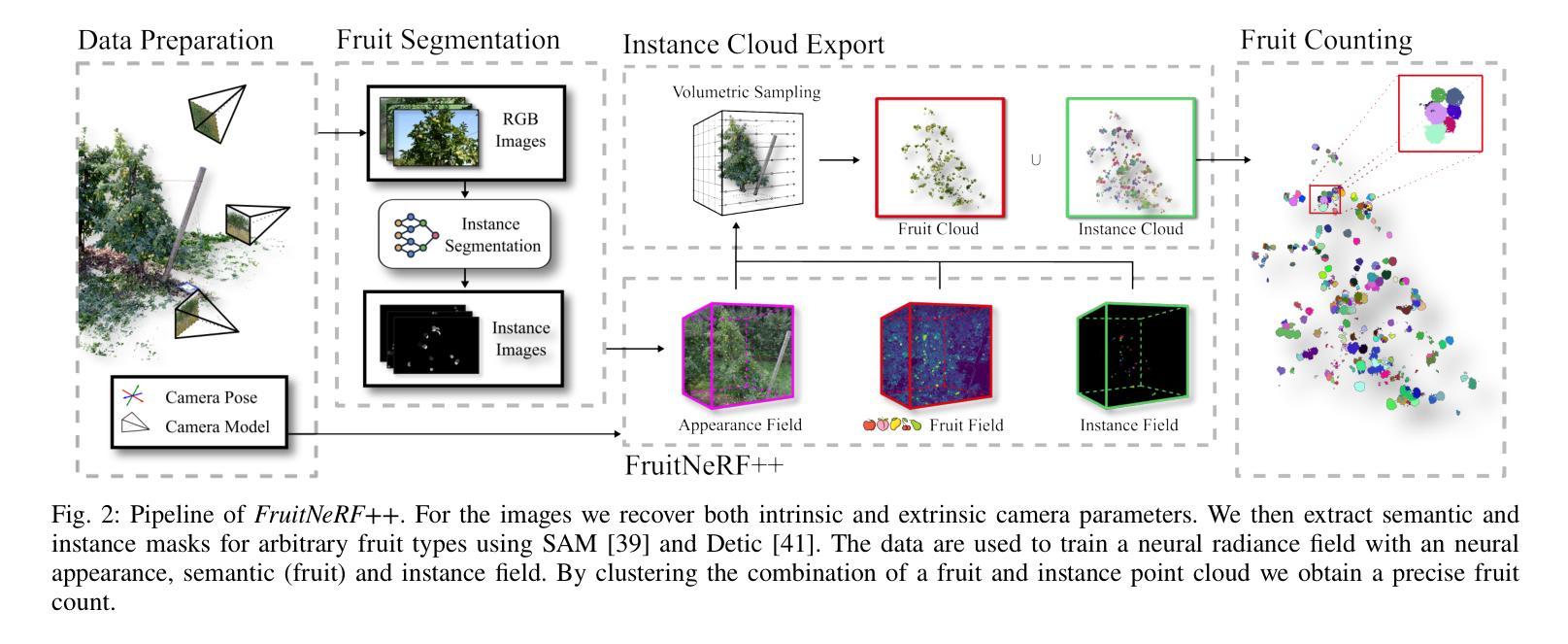
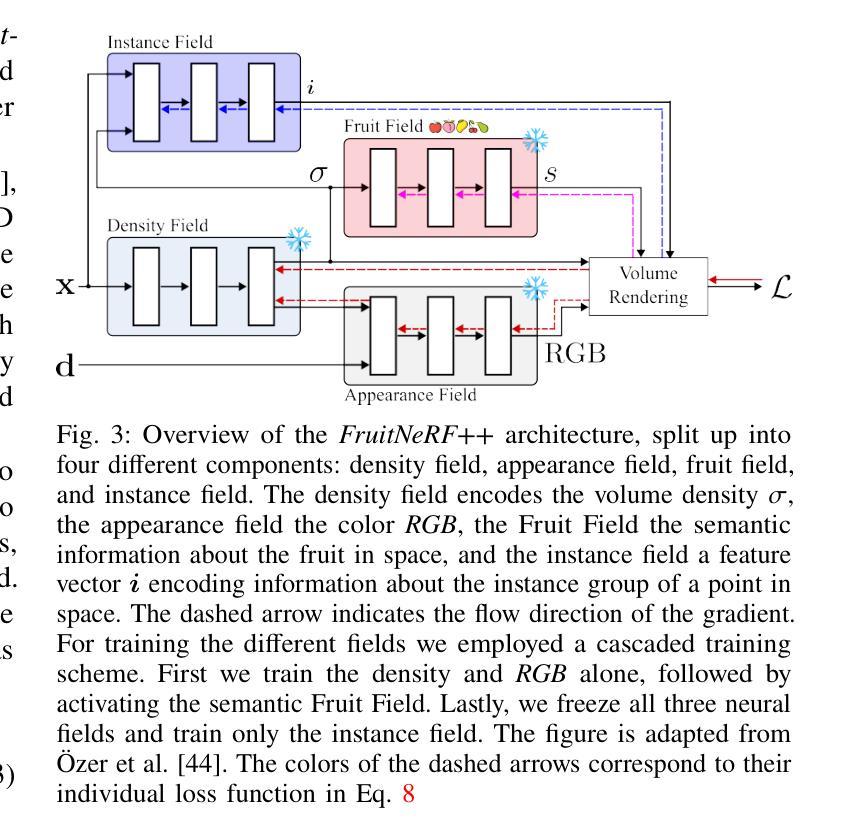
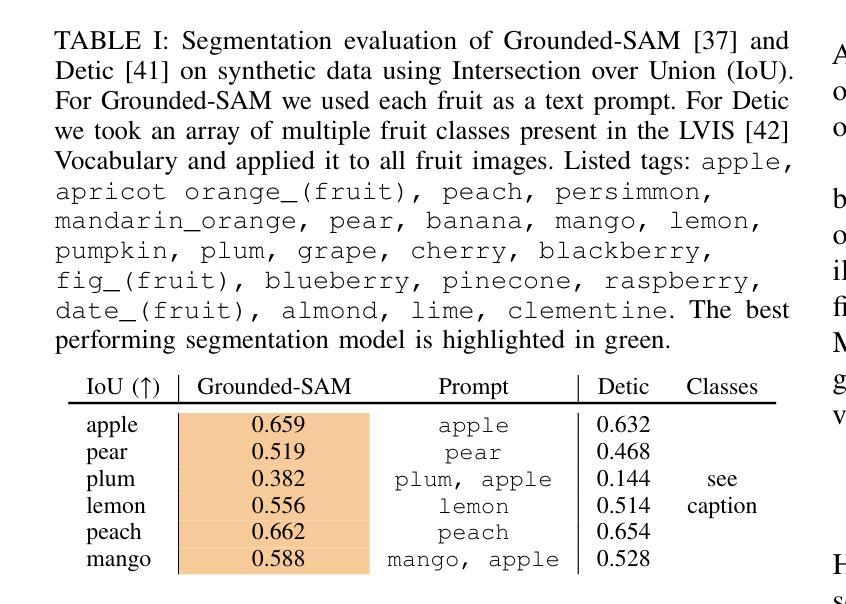
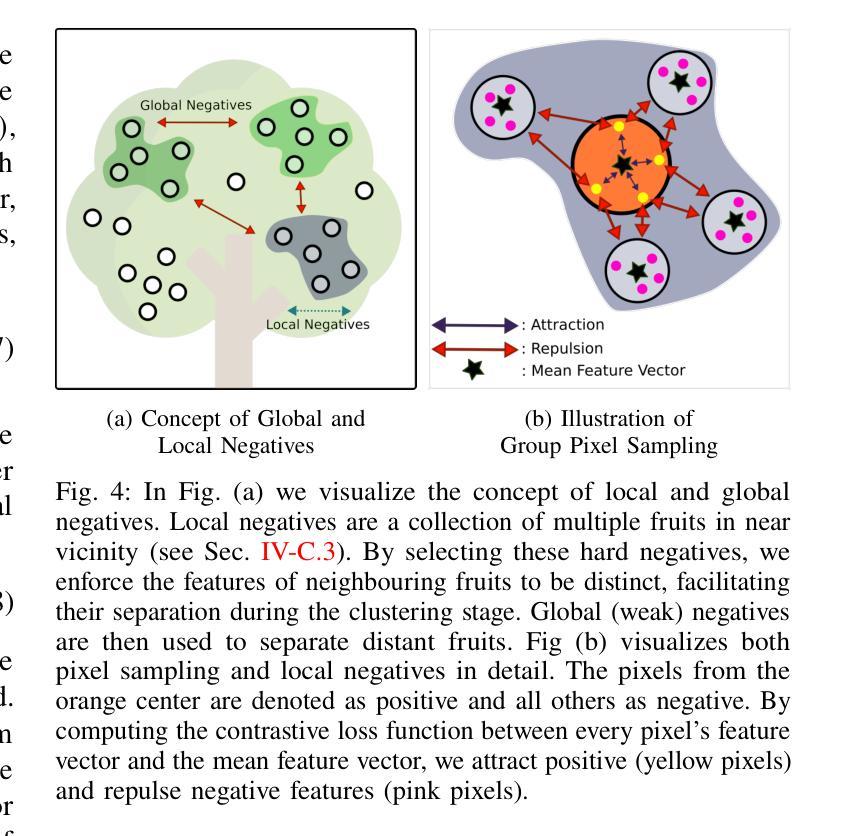
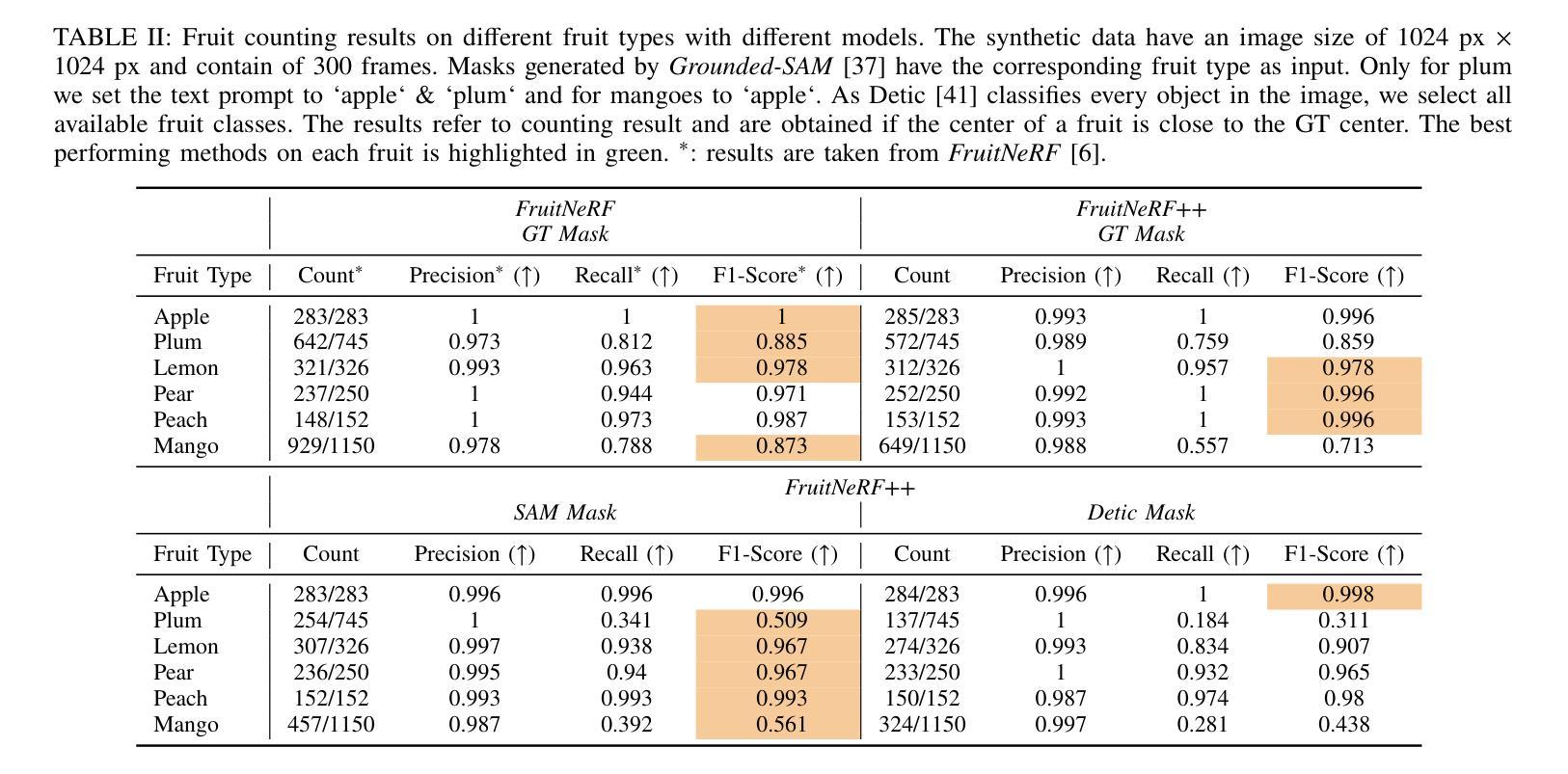
FruitNeRF++: A Generalized Multi-Fruit Counting Method Utilizing Contrastive Learning and Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Lukas Meyer, Andrei-Timotei Ardelean, Tim Weyrich, Marc Stamminger
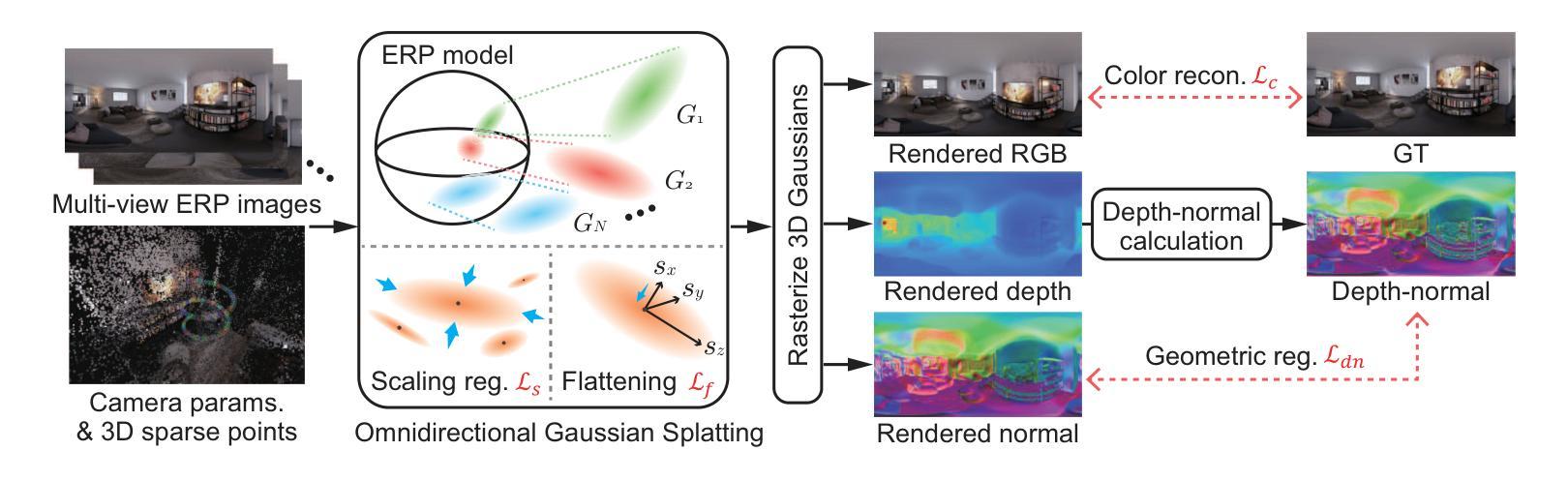
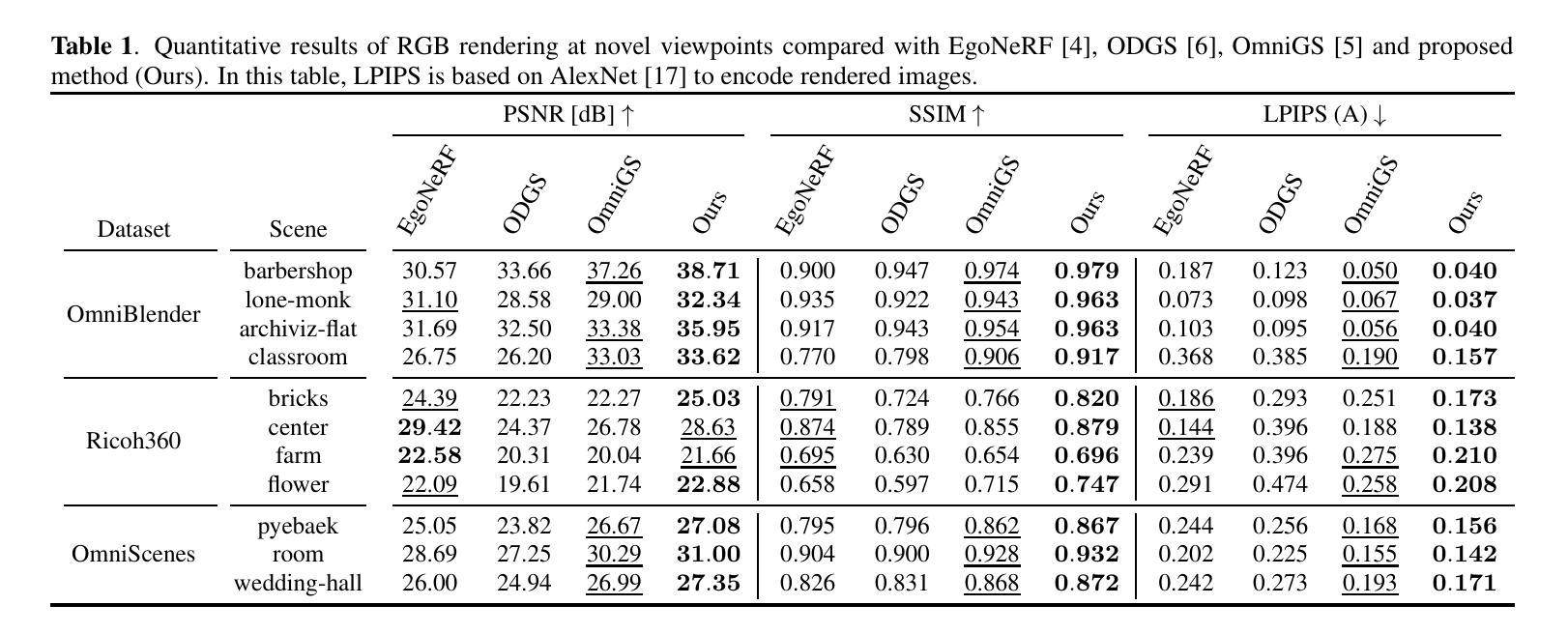
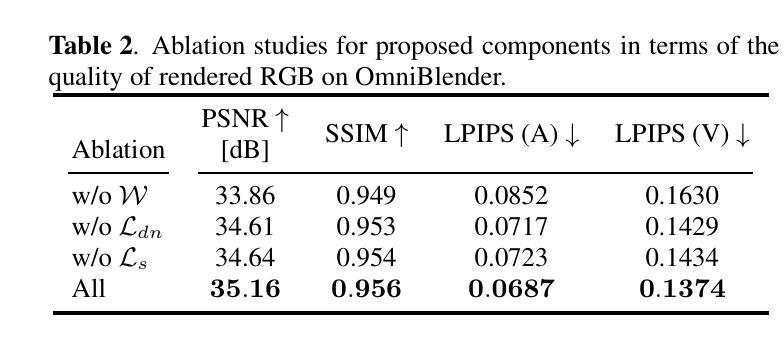
We introduce FruitNeRF++, a novel fruit-counting approach that combines contrastive learning with neural radiance fields to count fruits from unstructured input photographs of orchards. Our work is based on FruitNeRF, which employs a neural semantic field combined with a fruit-specific clustering approach. The requirement for adaptation for each fruit type limits the applicability of the method, and makes it difficult to use in practice. To lift this limitation, we design a shape-agnostic multi-fruit counting framework, that complements the RGB and semantic data with instance masks predicted by a vision foundation model. The masks are used to encode the identity of each fruit as instance embeddings into a neural instance field. By volumetrically sampling the neural fields, we extract a point cloud embedded with the instance features, which can be clustered in a fruit-agnostic manner to obtain the fruit count. We evaluate our approach using a synthetic dataset containing apples, plums, lemons, pears, peaches, and mangoes, as well as a real-world benchmark apple dataset. Our results demonstrate that FruitNeRF++ is easier to control and compares favorably to other state-of-the-art methods.
我们介绍了FruitNeRF++,这是一种结合对比学习和神经辐射场的新型水果计数方法,可从果园的非结构化输入照片中计算水果数量。我们的工作基于FruitNeRF,它采用神经语义场与水果特定聚类方法相结合。针对每种水果类型都需要进行适应的要求限制了该方法的应用,并使其在实践中难以使用。为了消除这一限制,我们设计了一个与形状无关的多水果计数框架,该框架用由视觉基础模型预测的实例掩模来补充RGB和语义数据。掩模用于将每个水果的身份编码为实例嵌入到神经实例场中。通过体积采样神经场,我们提取嵌入实例特征的点云,可以以与水果无关的方式对这些点云进行聚类,从而获得水果计数。我们使用包含苹果、李子、柠檬、梨、桃子和芒果的合成数据集以及现实世界苹果基准数据集来评估我们的方法。结果表明,FruitNeRF++更易于控制,并与其他最先进的方法相比具有优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF for project website, see https://meyerls.github.io/fruit_nerfpp
Summary
FruitNeRF++是一种结合对比学习和神经辐射场的新型水果计数方法,可从果园的无结构输入照片中计数水果。与基于FruitNeRF的方法相比,该方法设计了一个形状无关的多水果计数框架,通过视觉基础模型预测的实例掩膜来补充RGB和语义数据。通过体积采样神经场,提取嵌入实例特征的点云,以果实无关的方式进行聚类,从而获得果实计数。
Key Takeaways
- FruitNeRF++结合了对比学习和神经辐射场技术,用于从果园照片中计数水果。
- 该方法基于FruitNeRF,但解决了其针对每种果实类型需要适应的问题。
- 通过设计形状无关的多水果计数框架,使用实例掩膜编码每种水果的身份为实例嵌入,进入神经实例场。
- 使用体积采样神经场来提取嵌入实例特征的点云,以进行果实无关的聚类。
- 方法在合成数据集(包含多种水果)和真实世界苹果数据集上进行了评估。
- FruitNeRF++易于控制,并与其他最先进的方法相比表现良好。
点此查看论文截图
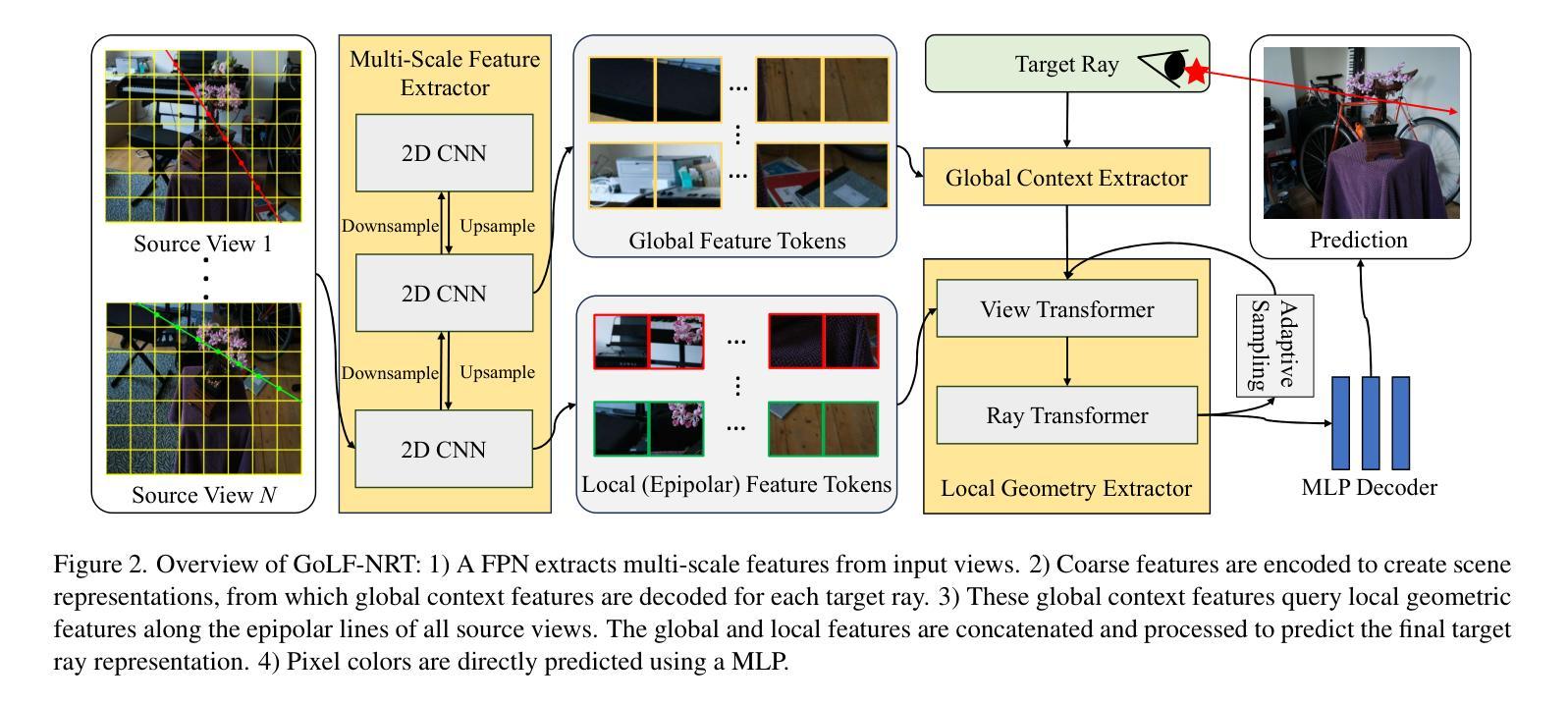
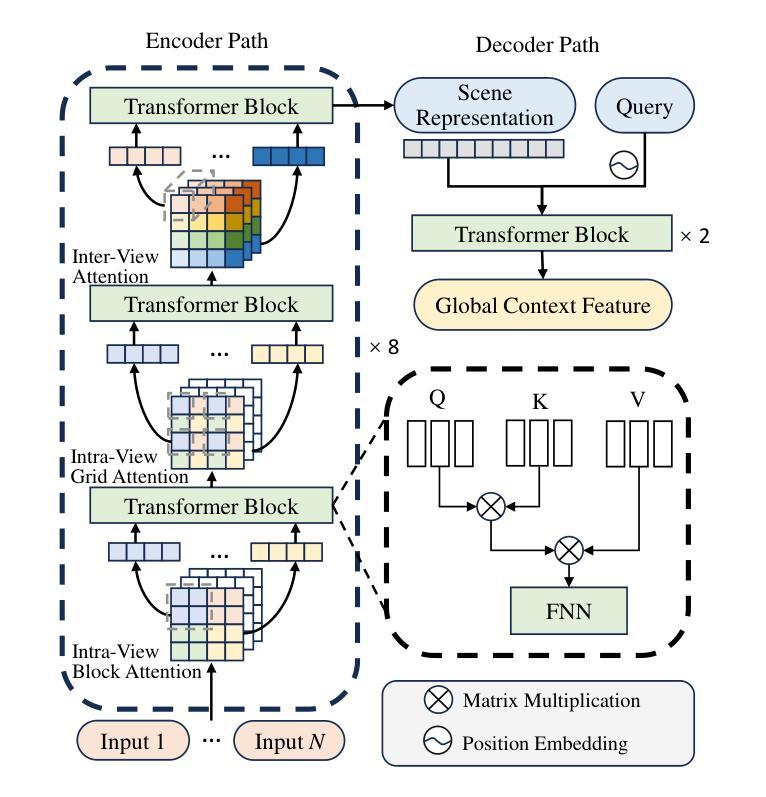
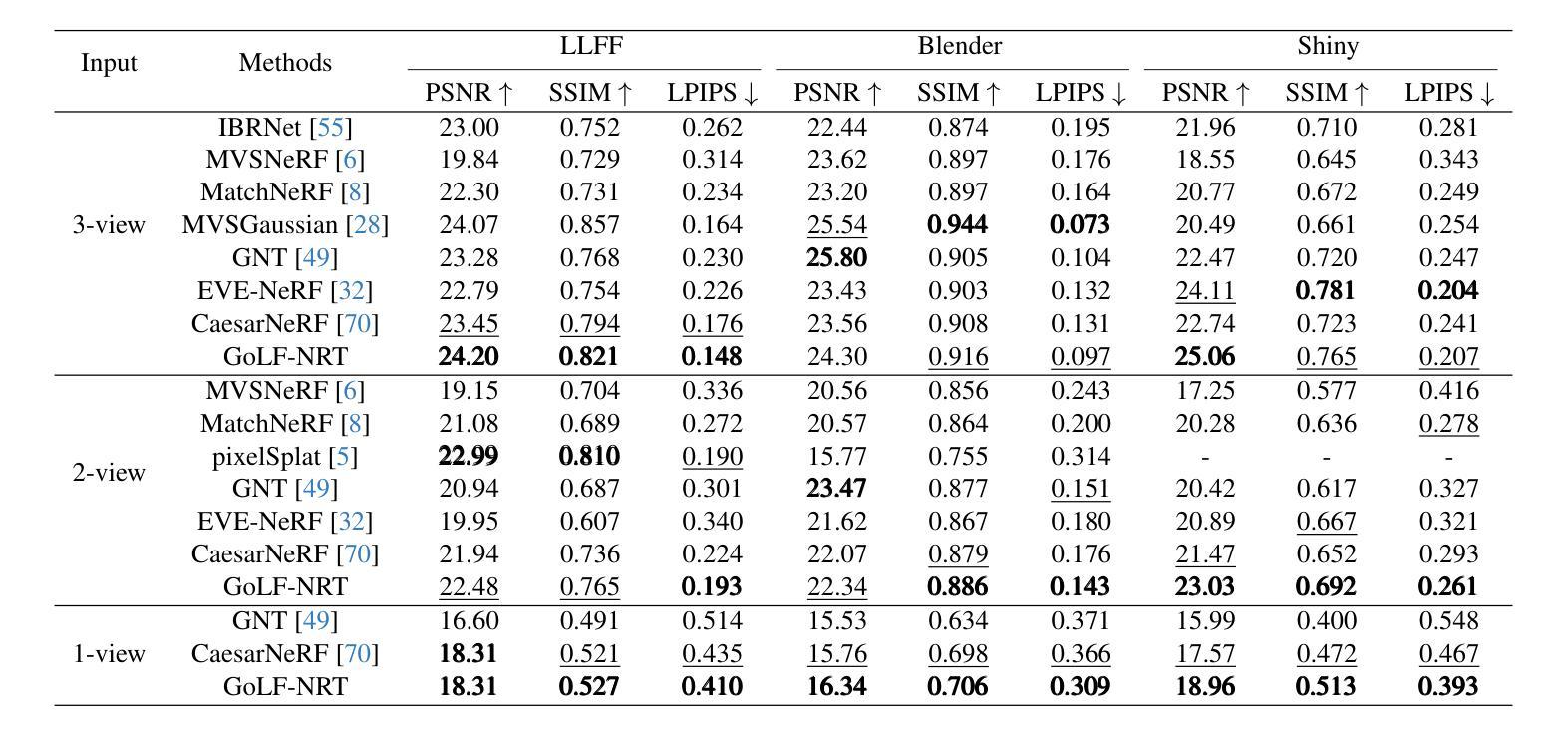
GoLF-NRT: Integrating Global Context and Local Geometry for Few-Shot View Synthesis
Authors:You Wang, Li Fang, Hao Zhu, Fei Hu, Long Ye, Zhan Ma
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have transformed novel view synthesis by modeling scene-specific volumetric representations directly from images. While generalizable NeRF models can generate novel views across unknown scenes by learning latent ray representations, their performance heavily depends on a large number of multi-view observations. However, with limited input views, these methods experience significant degradation in rendering quality. To address this limitation, we propose GoLF-NRT: a Global and Local feature Fusion-based Neural Rendering Transformer. GoLF-NRT enhances generalizable neural rendering from few input views by leveraging a 3D transformer with efficient sparse attention to capture global scene context. In parallel, it integrates local geometric features extracted along the epipolar line, enabling high-quality scene reconstruction from as few as 1 to 3 input views. Furthermore, we introduce an adaptive sampling strategy based on attention weights and kernel regression, improving the accuracy of transformer-based neural rendering. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that GoLF-NRT achieves state-of-the-art performance across varying numbers of input views, highlighting the effectiveness and superiority of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GoLF-NRT.
神经辐射场(NeRF)通过直接从图像建模场景特定的体积表示,从而实现了新颖视图合成的变革。虽然通用NeRF模型可以通过学习潜在射线表示来生成未知场景的新颖视图,但其性能严重依赖于大量多视图观察。然而,在输入视图有限的情况下,这些方法在渲染质量方面会出现显著下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了基于全局和局部特征融合的神经渲染变压器GoLF-NRT。GoLF-NRT通过利用带有高效稀疏注意力的3D变压器,增强从少数输入视图进行通用神经渲染的能力,以捕获场景的全局上下文。同时,它结合了沿极线提取的局部几何特征,从而能够从仅1到3个输入视图实现高质量的场景重建。此外,我们引入了一种基于注意力权重和核回归的自适应采样策略,提高了基于变压器的神经渲染的准确性。在公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,GoLF-NRT在不同数量的输入视图上实现了最先进的性能,凸显了我们方法的有效性和优越性。代码可在https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GoLF-NRT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
总结
NeRF技术已经实现了从图像直接建模场景体积表示的新视角合成。尽管通用NeRF模型可以通过学习潜在射线表示来生成未知场景的新视角,但其性能高度依赖于大量的多视角观察。然而,在输入视角有限的情况下,这些方法在渲染质量上会出现显著下降。为解决这一问题,提出了基于全局和局部特征融合的神经渲染转换器GoLF-NRT。GoLF-NRT通过利用具有高效稀疏注意力的3D变压器,增强了从少量输入视角进行通用神经渲染的能力,捕捉全局场景上下文。同时,它融合了沿极线提取的局部几何特征,使得即使仅从1到3个输入视角也能实现高质量的场景重建。此外,基于注意力权重和核回归的自适应采样策略,提高了基于变压器的神经渲染的准确性。在公开数据集上的广泛实验表明,GoLF-NRT在多种输入视角数量下实现了最先进的性能,凸显了该方法的有效性和优越性。相关代码可在“链接”中找到。
关键见解
- NeRF实现了从图像直接建模场景体积表示的新视角合成。
- 通用NeRF模型依赖于多视角观察,在输入视角有限时性能下降。
- GoLF-NRT基于全局和局部特征融合,增强了从少量输入视角进行神经渲染的能力。
- GoLF-NRT利用3D变压器捕捉全局场景上下文,并结合局部几何特征实现高质量场景重建。
- GoLF-NRT引入自适应采样策略,提高了基于神经渲染的准确性。
- GoLF-NRT在多种公开数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

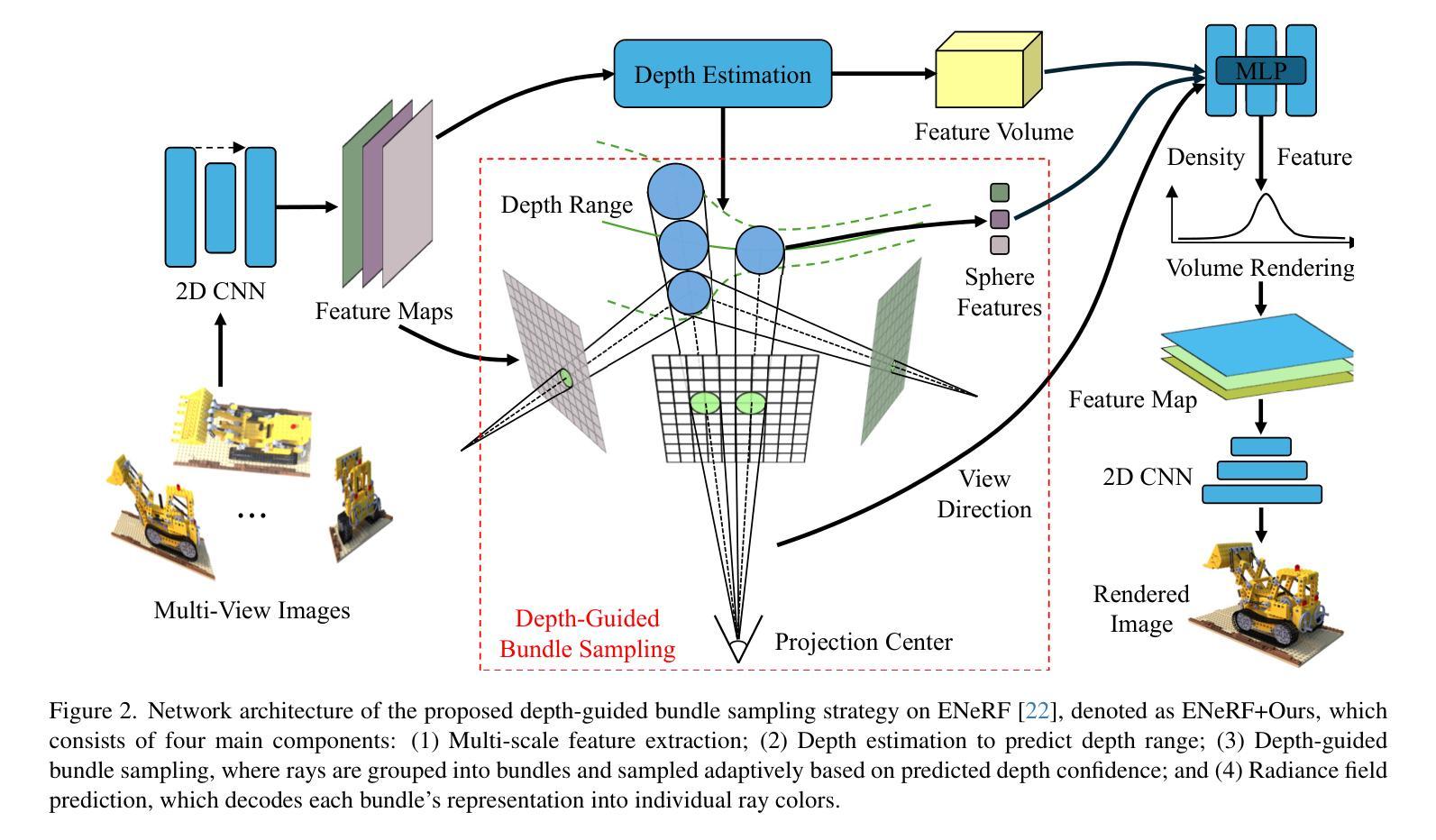
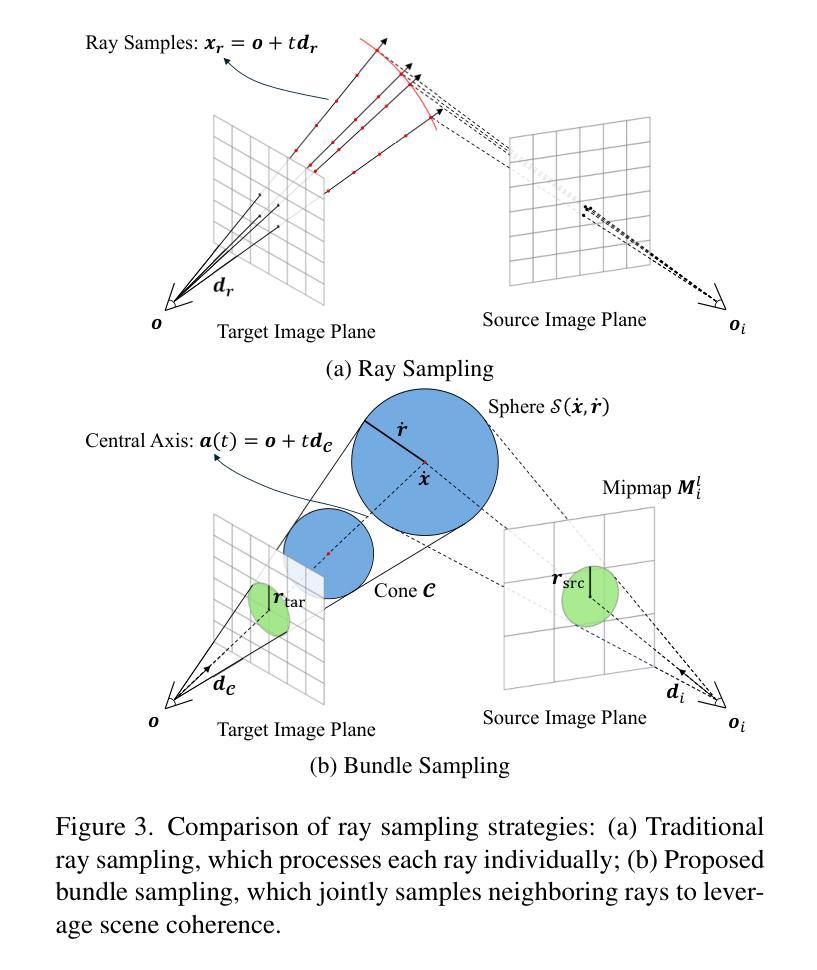
Depth-Guided Bundle Sampling for Efficient Generalizable Neural Radiance Field Reconstruction
Authors:Li Fang, Hao Zhu, Longlong Chen, Fei Hu, Long Ye, Zhan Ma
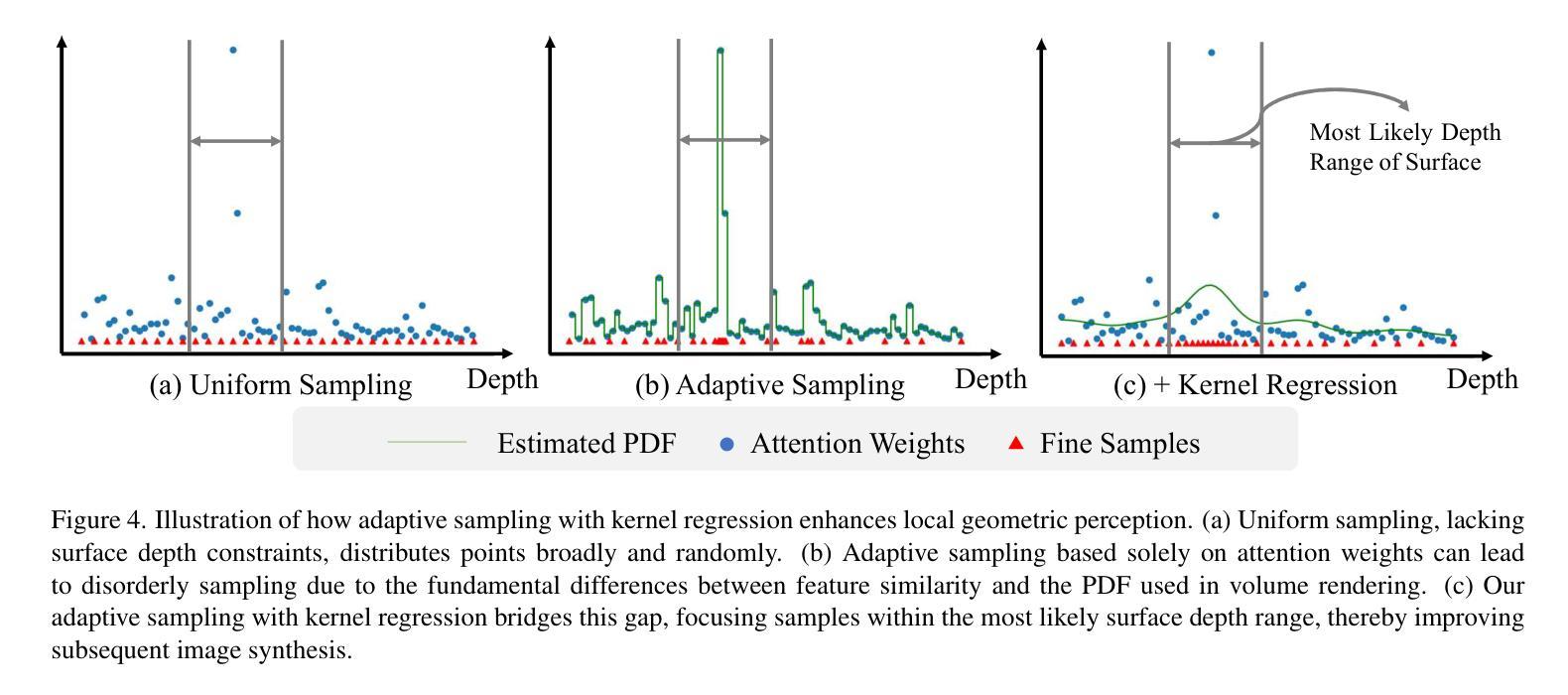
Recent advancements in generalizable novel view synthesis have achieved impressive quality through interpolation between nearby views. However, rendering high-resolution images remains computationally intensive due to the need for dense sampling of all rays. Recognizing that natural scenes are typically piecewise smooth and sampling all rays is often redundant, we propose a novel depth-guided bundle sampling strategy to accelerate rendering. By grouping adjacent rays into a bundle and sampling them collectively, a shared representation is generated for decoding all rays within the bundle. To further optimize efficiency, our adaptive sampling strategy dynamically allocates samples based on depth confidence, concentrating more samples in complex regions while reducing them in smoother areas. When applied to ENeRF, our method achieves up to a 1.27 dB PSNR improvement and a 47% increase in FPS on the DTU dataset. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art rendering quality and up to 2x faster rendering compared to existing generalizable methods. Code is available at https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GDB-NeRF.
最近,在可泛化的新型视角合成方面取得了进展,通过邻近视角的插值达到了令人印象深刻的品质。然而,由于需要对所有光线进行密集采样,渲染高分辨率图像在计算上仍然很密集。我们认识到自然场景通常是分段平滑的,并且采样所有光线通常是冗余的,因此我们提出了一种加速渲染的新型深度引导捆绑采样策略。通过将相邻的光线分组为束并集体采样它们,为束内的所有光线生成共享表示来进行解码。为了进一步优化效率,我们的自适应采样策略根据深度置信动态分配样本,在复杂区域集中更多样本,同时在平滑区域减少样本。当应用于ENeRF时,我们的方法在DTU数据集上实现了高达1.27 dB的PSNR改进和47%的FPS提升。在合成和真实世界数据集上的大量实验证明了其最先进的渲染质量和与现有可泛化方法相比最多快2倍的渲染速度。代码可在https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GDB-NeRF找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
近期在通用化新型视角合成技术上的进展已取得了令人印象深刻的插值效果。然而,由于需要对所有光线进行密集采样,渲染高分辨率图像的计算仍然很密集。考虑到自然场景通常是分段平滑的,并且对所有光线进行采样往往是冗余的,我们提出了一种新型的深度引导捆绑采样策略来加速渲染。通过将相邻光线分组为捆绑包并集体采样,为捆绑包内的所有光线生成共享表示。为了进一步优化效率,我们的自适应采样策略根据深度置信动态分配样本,在复杂区域集中更多样本,同时在平滑区域减少样本。应用于ENeRF时,我们的方法在DTU数据集上实现了高达1.27 dB的PSNR改进和47%的FPS提升。在合成和真实世界数据集上的广泛实验证明了其最先进的渲染质量和与现有通用方法相比高达2倍的快速渲染能力。代码已发布在[GitHub链接]。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了深度引导捆绑采样策略来加速渲染过程。
- 通过将相邻光线分组为捆绑并集体采样,减少了计算复杂性。
- 自适应采样策略根据场景复杂性动态分配样本。
- 方法在DTU数据集上实现了PSNR和FPS的双重提升。
- 在合成和真实世界数据集上的实验证明了其优越性能。
- 与现有方法相比,该方法提供了高达2倍的快速渲染能力。
点此查看论文截图
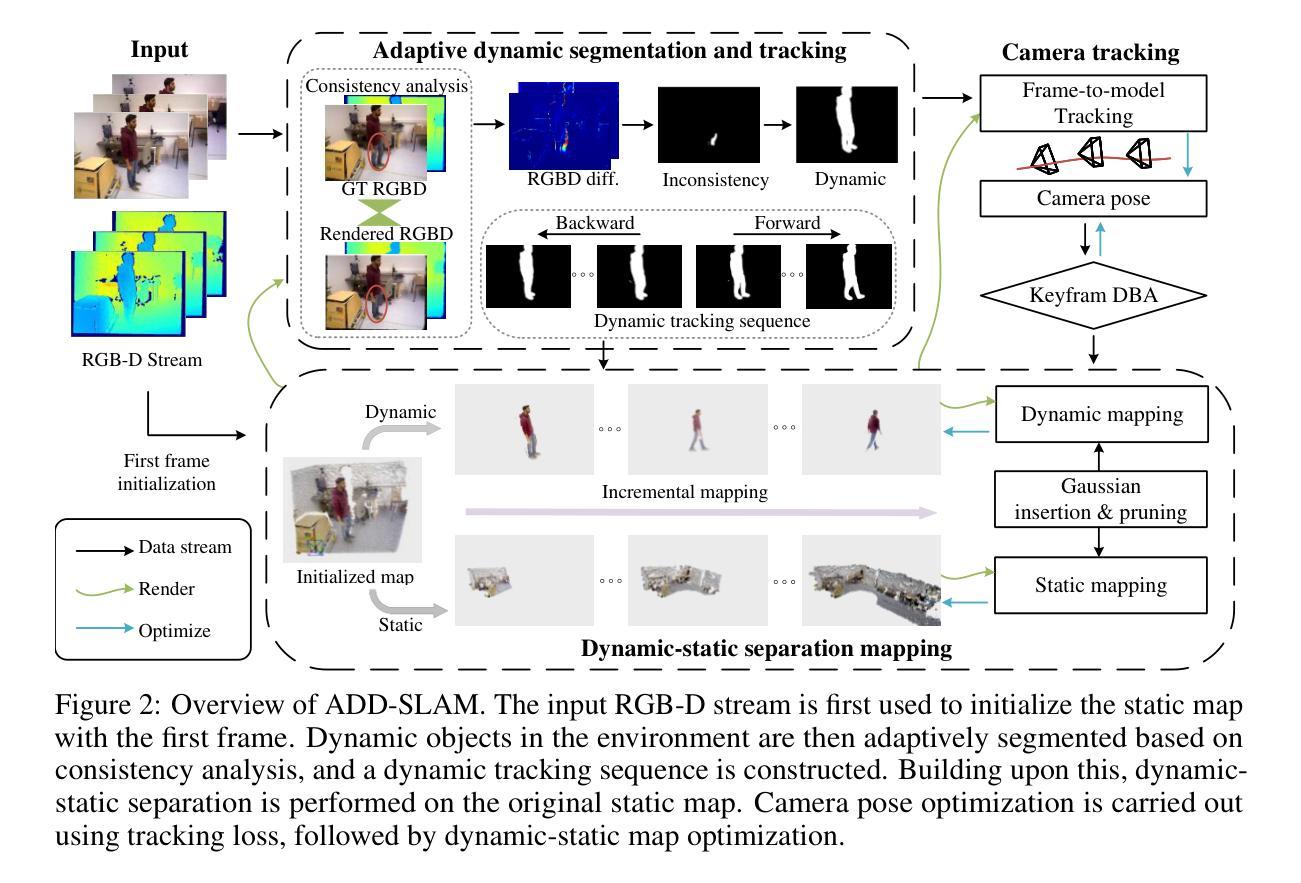
ADD-SLAM: Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Wenhua Wu, Chenpeng Su, Siting Zhu, Tianchen Deng, Zhe Liu, Hesheng Wang
Recent advancements in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods have demonstrated exceptional localization precision and remarkable dense mapping performance. However, dynamic objects introduce critical challenges by disrupting scene consistency, leading to tracking drift and mapping artifacts. Existing methods that employ semantic segmentation or object detection for dynamic identification and filtering typically rely on predefined categorical priors, while discarding dynamic scene information crucial for robotic applications such as dynamic obstacle avoidance and environmental interaction. To overcome these challenges, we propose ADD-SLAM: an Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM framework based on Gaussian splitting. We design an adaptive dynamic identification mechanism grounded in scene consistency analysis, comparing geometric and textural discrepancies between real-time observations and historical maps. Ours requires no predefined semantic category priors and adaptively discovers scene dynamics. Precise dynamic object recognition effectively mitigates interference from moving targets during localization. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic-static separation mapping strategy that constructs a temporal Gaussian model to achieve online incremental dynamic modeling. Experiments conducted on multiple dynamic datasets demonstrate our method’s flexible and accurate dynamic segmentation capabilities, along with state-of-the-art performance in both localization and mapping.
最近,神经辐射场(NeRF)和基于3D高斯的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法的进展,已经展现了出色的定位精度和显著的密集映射性能。然而,动态物体通过破坏场景一致性,引入了关键挑战,导致跟踪漂移和映射伪影。现有方法采用语义分割或目标检测进行动态识别和过滤,通常依赖于预设的类别先验知识,同时丢弃了对于机器人应用至关重要的动态场景信息,如动态避障和环境交互。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了ADD-SLAM:一种基于高斯分裂的自适应动态密集SLAM框架。我们设计了一种基于场景一致性分析的自适应动态识别机制,通过比较实时观察与历史地图之间的几何和纹理差异。我们的方法不需要预设的语义类别先验知识,并能自适应地发现场景动态。精确的动态目标识别有效地减轻了移动目标在定位过程中的干扰。此外,我们提出了一种动静分离映射策略,建立了一个临时高斯模型,以实现在线增量动态建模。在多个动态数据集上进行的实验证明了我们方法在动态分割方面的灵活性和准确性,以及在定位和映射方面的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于NeRF和3D高斯SLAM方法的最新进展,动态物体对场景一致性的干扰造成了定位漂移和映射伪影的问题。为此,本文提出了基于高斯分裂的ADD-SLAM自适应动态密集SLAM框架,设计了一种基于场景一致性分析的动态识别机制,并采用了动态静态分离映射策略,实现了在线增量动态建模。实验证明,该方法具有灵活准确的动态分割能力和先进的定位和映射性能。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3D高斯SLAM的最新进展在定位和密集映射方面表现出色。
- 动态物体干扰场景一致性,导致跟踪漂移和映射伪影。
- 现有方法使用语义分割或对象检测来识别动态物体,依赖于预定义的类别先验信息。
- ADD-SLAM框架通过自适应动态识别机制克服这些挑战,无需预定义的语义类别先验信息。
- 动态识别机制基于场景一致性分析,比较实时观察和历史地图之间的几何和纹理差异。
- 动态物体识别的精确性有效减轻了移动目标对定位的影响。
点此查看论文截图


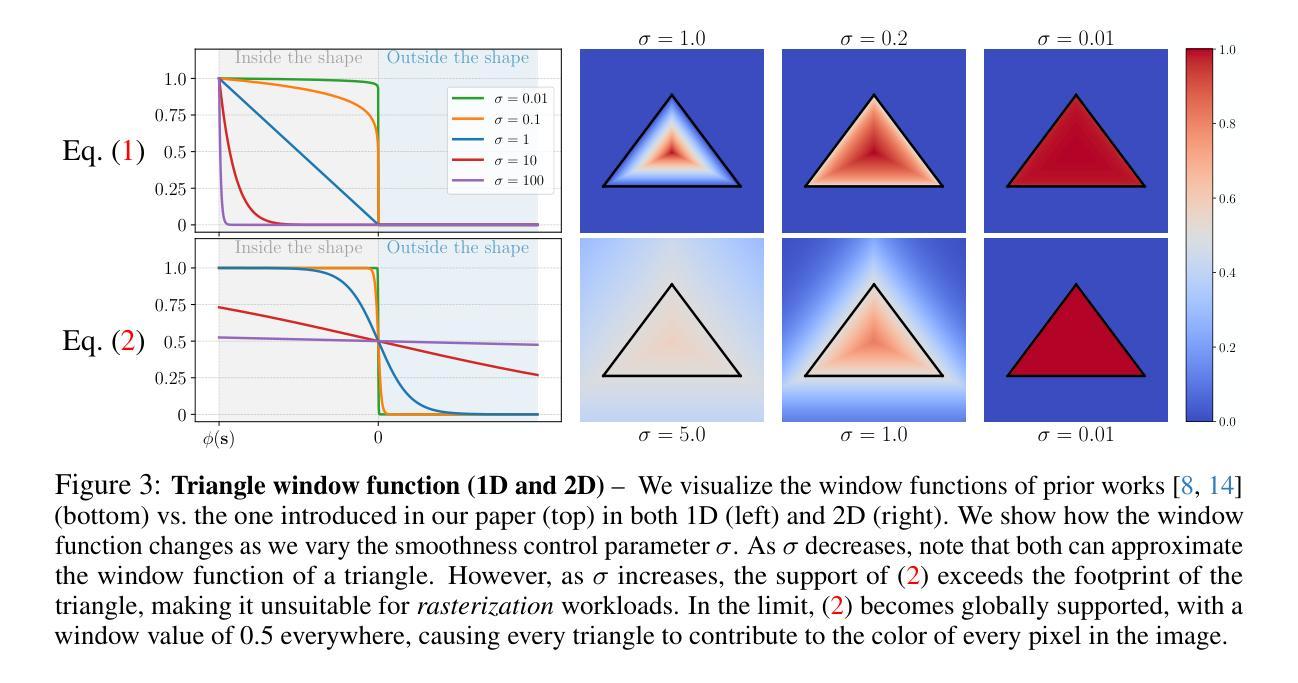
Triangle Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
Authors:Jan Held, Renaud Vandeghen, Adrien Deliege, Abdullah Hamdi, Silvio Giancola, Anthony Cioppa, Andrea Vedaldi, Bernard Ghanem, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Marc Van Droogenbroeck
The field of computer graphics was revolutionized by models such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, displacing triangles as the dominant representation for photogrammetry. In this paper, we argue for a triangle comeback. We develop a differentiable renderer that directly optimizes triangles via end-to-end gradients. We achieve this by rendering each triangle as differentiable splats, combining the efficiency of triangles with the adaptive density of representations based on independent primitives. Compared to popular 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting methods, our approach achieves higher visual fidelity, faster convergence, and increased rendering throughput. On the Mip-NeRF360 dataset, our method outperforms concurrent non-volumetric primitives in visual fidelity and achieves higher perceptual quality than the state-of-the-art Zip-NeRF on indoor scenes. Triangles are simple, compatible with standard graphics stacks and GPU hardware, and highly efficient: for the \textit{Garden} scene, we achieve over 2,400 FPS at 1280x720 resolution using an off-the-shelf mesh renderer. These results highlight the efficiency and effectiveness of triangle-based representations for high-quality novel view synthesis. Triangles bring us closer to mesh-based optimization by combining classical computer graphics with modern differentiable rendering frameworks. The project page is https://trianglesplatting.github.io/
神经网络辐射场和三维高斯拼贴等技术彻底改变了计算机图形学领域,取代了三角测量作为摄影测量的主要表现形式。在本文中,我们主张三角测量的复兴。我们开发了一种可微分渲染器,该渲染器通过端到端梯度直接优化三角测量。我们通过将每个三角形渲染为可微分的拼贴来实现这一点,结合了三角形的高效性和基于独立原始数据的自适应密度表示。与流行的二维和三维高斯拼贴方法相比,我们的方法实现了更高的视觉保真度、更快的收敛速度和增加的渲染吞吐量。在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,我们的方法在视觉保真度上超越了并发非体积原始数据,并在室内场景上达到了最先进的Zip-NeRF的感知质量。三角形简单、兼容标准图形堆栈和GPU硬件,并且高效:对于“花园”场景,我们使用现成的网格渲染器在1280x720分辨率下实现了超过2400帧每秒。这些结果突出了基于三角形的表示法在高质量新颖视图合成中的效率和有效性。通过结合经典计算机图形和现代可微分渲染框架,三角形使我们离基于网格的优化更近了一步。项目页面为https://trianglesplatting.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures, 10 tables
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)等模型在计算机图形学领域引发了革命性的变革,本文通过开发一种可微分渲染器让三角形成为主流的光测学表示方式。通过直接将三角形优化为可微分的splat,结合三角形的效率和基于独立原始数据的自适应密度表示,我们的方法在视觉保真度、收敛速度和渲染吞吐量方面取得了显著的成果。三角形简单、兼容标准图形堆栈和GPU硬件,并且高效。
Key Takeaways
- 本文主张三角形的回归,开发了一种可微分渲染器,直接优化三角形。
- 通过将三角形渲染为可微分的splat,实现了三角形和自适应密度表示的融合。
- 与流行的2D和3D高斯Splatting方法相比,该方法在视觉保真度、收敛速度和渲染吞吐量方面表现更优秀。
- 在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,该方法在视觉保真度上超越了并发非体积原始方法,并在室内场景上实现了比Zip-NeRF更高的感知质量。
- 三角形表示方法具有高效性,对于“花园”场景,使用现成的网格渲染器在1280x720分辨率下实现了超过2400 FPS的帧率。
- 三角形结合经典计算机图形和现代化可微分渲染框架,带来网格优化的可能性。
点此查看论文截图



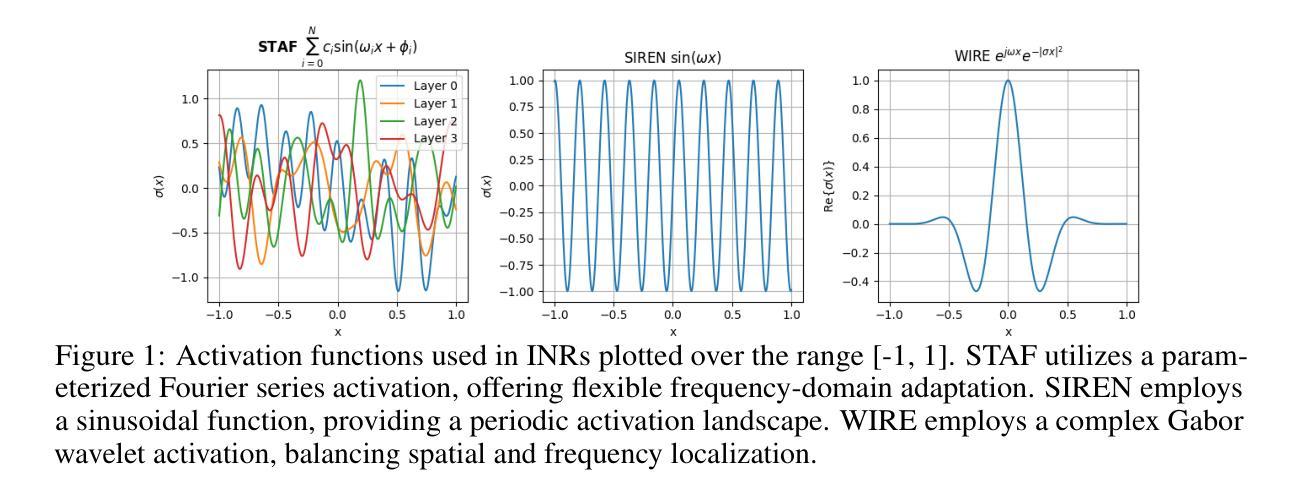
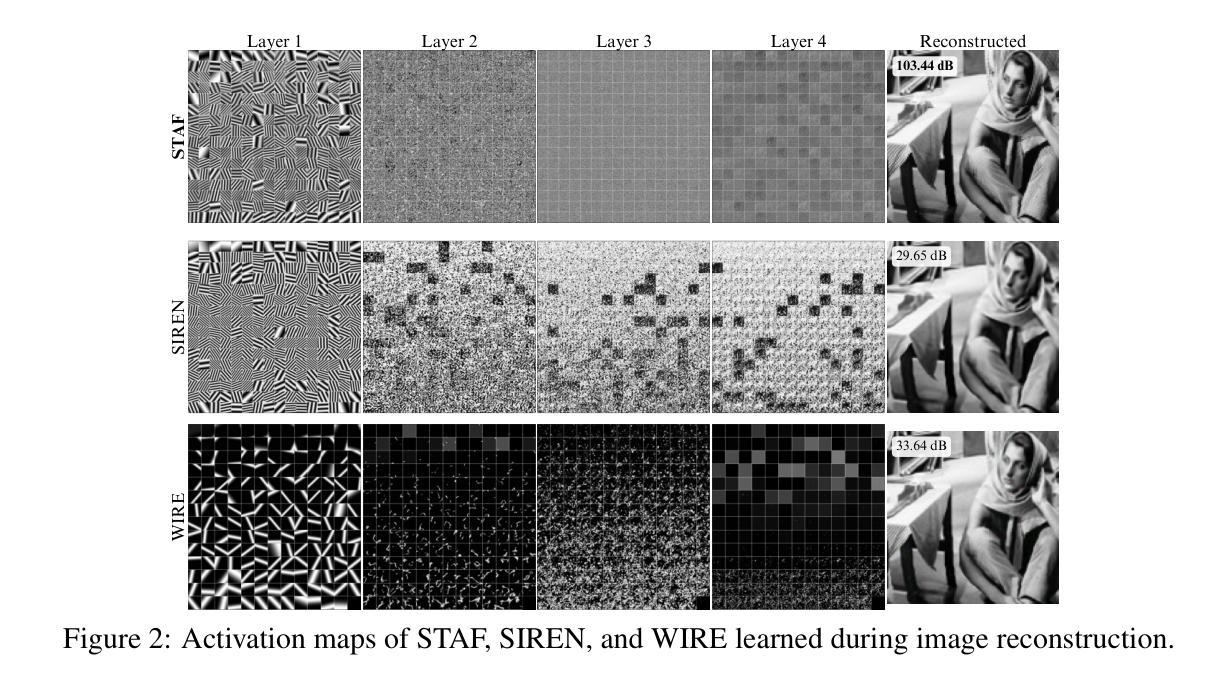
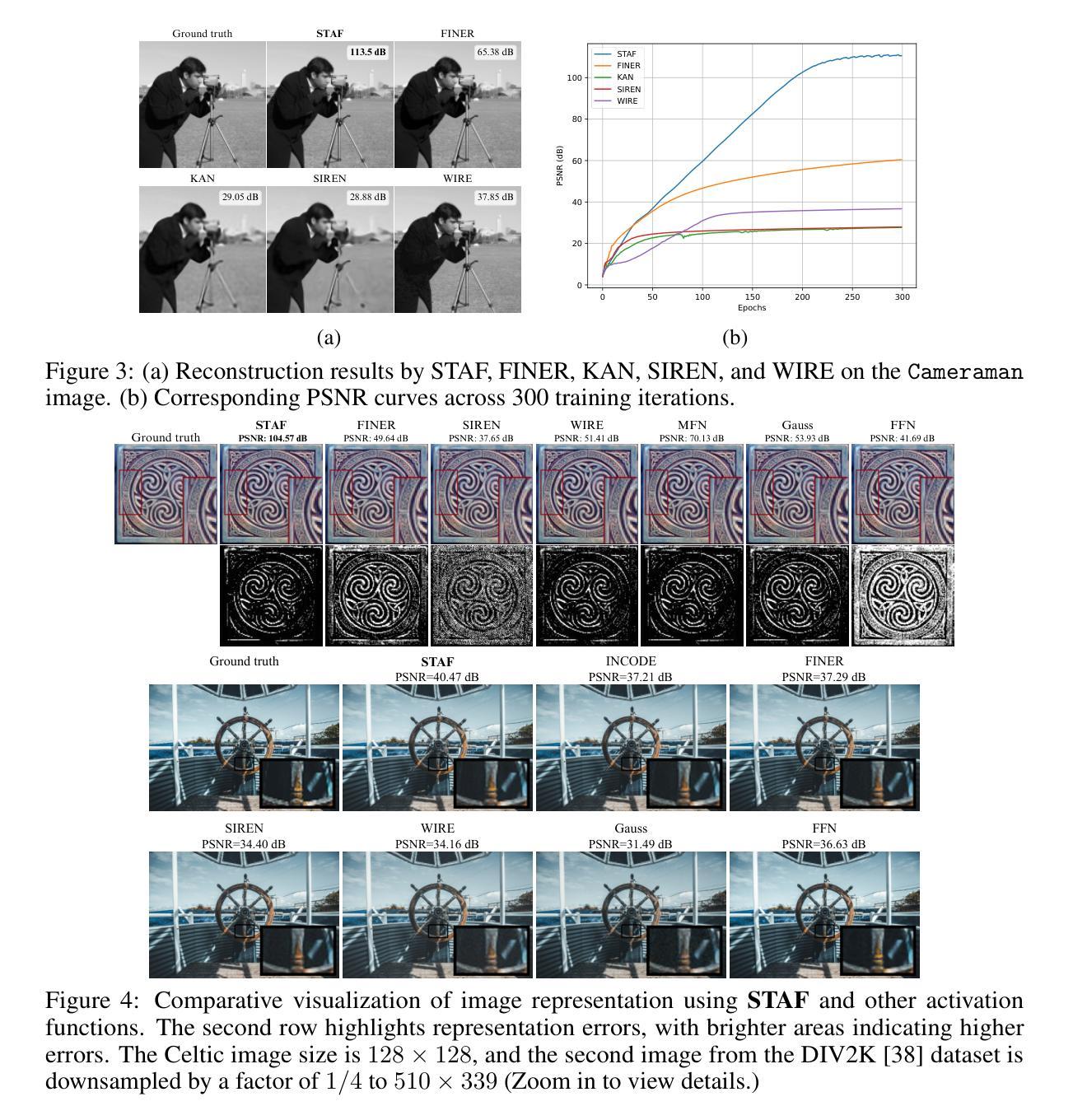
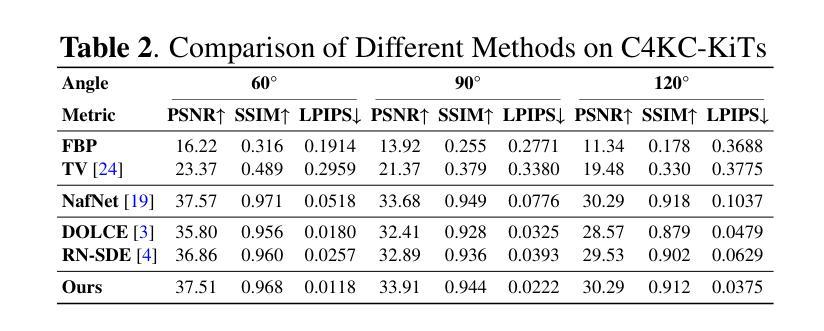
STAF: Sinusoidal Trainable Activation Functions for Implicit Neural Representation
Authors:Alireza Morsali, MohammadJavad Vaez, Mohammadhossein Soltani, Amirhossein Kazerouni, Babak Taati, Morteza Mohammad-Noori
Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have emerged as a powerful framework for modeling continuous signals. The spectral bias of ReLU-based networks is a well-established limitation, restricting their ability to capture fine-grained details in target signals. While previous works have attempted to mitigate this issue through frequency-based encodings or architectural modifications, these approaches often introduce additional complexity and do not fully address the underlying challenge of learning high-frequency components efficiently. We introduce Sinusoidal Trainable Activation Functions (STAF), designed to directly tackle this limitation by enabling networks to adaptively learn and represent complex signals with higher precision and efficiency. STAF inherently modulates its frequency components, allowing for self-adaptive spectral learning. This capability significantly improves convergence speed and expressivity, making STAF highly effective for both signal representations and inverse problems. Through extensive evaluations across a range of tasks, including signal representation (shape, image, audio) and inverse problems (super-resolution, denoising), as well as neural radiance fields (NeRF), we demonstrate that STAF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy and reconstruction fidelity. These results establish STAF as a robust solution to spectral bias and the capacity–convergence tradeoff, with broad applicability in computer vision and graphics. Our codebase is publicly accessible at https://github.com/AlirezaMorsali/STAF.
隐式神经网络表示(INR)已经成为连续信号建模的强大框架。ReLU网络的谱偏置是一个公认的局限性,限制了它们捕捉目标信号中的精细细节的能力。虽然以前的工作试图通过基于频率的编码或架构修改来解决这个问题,但这些方法通常引入了额外的复杂性,并没有完全解决高效学习高频成分的基本挑战。我们引入了可训练正弦激活函数(STAF),旨在通过使网络能够自适应地学习和表示具有更高精度和效率的复杂信号来直接解决这一局限性。STAF固有地调制其频率成分,从而实现自适应谱学习。这种能力显著提高了收敛速度和表现力,使STAF在信号表示和反向问题中都高度有效。通过广泛的任务评估,包括信号表示(形状、图像、音频)和反向问题(超分辨率、去噪),以及神经辐射场(NeRF),我们证明了STAF在精度和重建保真度方面始终优于最先进的方法。这些结果证明了STAF是解决谱偏置和容量收敛权衡的稳健解决方案,在计算机视觉和图形中具有广泛的应用性。我们的代码库可在https://github.com/AlirezaMorsali/STAF公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
提出一种新的可训练激活函数——正弦式可训练激活函数(STAF),旨在解决ReLU基网络在捕捉精细信号时的频谱偏差问题。STAF通过自适应学习并代表复杂信号,提高了网络的精度和效率,特别适用于信号表示和逆问题。在多种任务上,包括信号表示(形状、图像、音频)和逆问题(超分辨率、去噪)以及神经辐射场(NeRF),STAF表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了正弦式可训练激活函数(STAF),旨在解决ReLU基网络捕捉精细信号时的频谱偏差问题。
- STAF能够自适应学习和表示复杂信号,提高网络的精度和效率。
- STAF具有内在的频率组件调制能力,可实现自适应谱学习。
- STAF在信号表示和逆问题中表现出显著的优势,如形状、图像、音频等任务上的表现优秀。
- 在神经辐射场(NeRF)相关任务中,STAF也表现出卓越性能。
- 广泛的实验评估证明STAF在准确性和重建保真度方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图