⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-28 更新
The Missing Point in Vision Transformers for Universal Image Segmentation
Authors:Sajjad Shahabodini, Mobina Mansoori, Farnoush Bayatmakou, Jamshid Abouei, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Arash Mohammadi
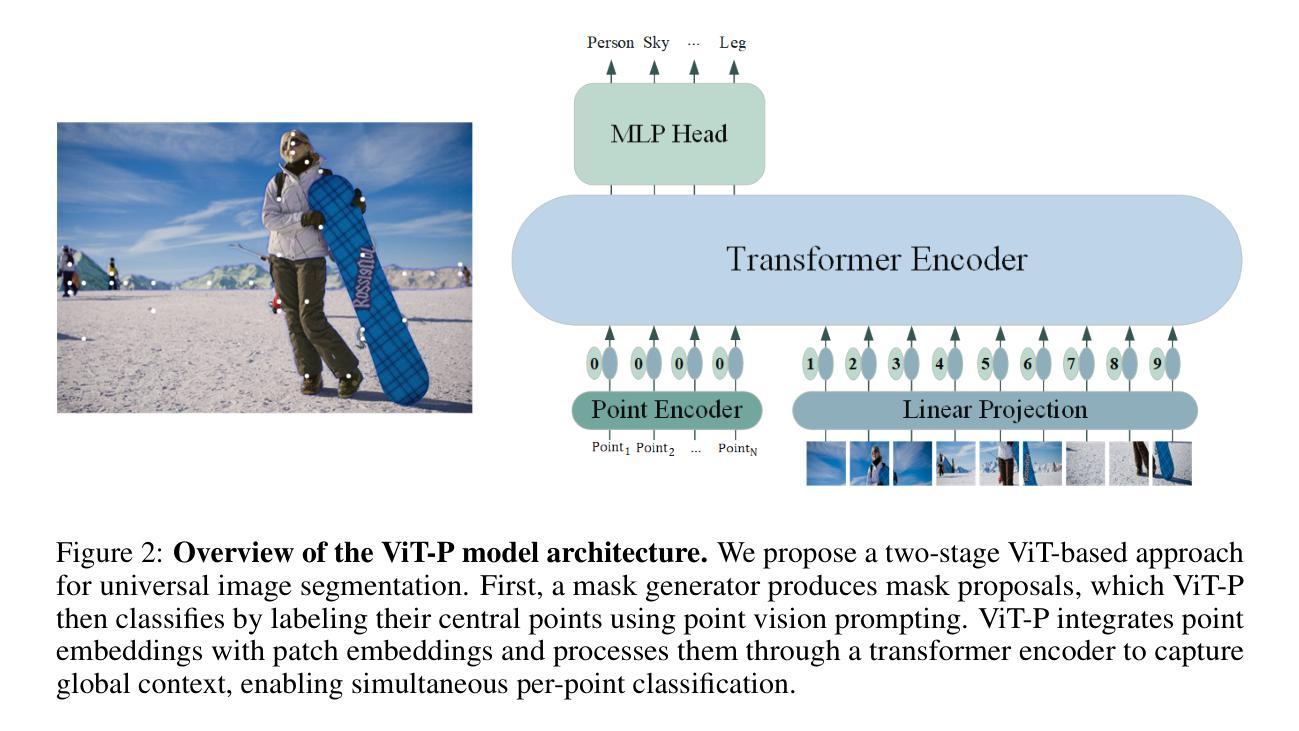
Image segmentation remains a challenging task in computer vision, demanding robust mask generation and precise classification. Recent mask-based approaches yield high-quality masks by capturing global context. However, accurately classifying these masks, especially in the presence of ambiguous boundaries and imbalanced class distributions, remains an open challenge. In this work, we introduce ViT-P, a novel two-stage segmentation framework that decouples mask generation from classification. The first stage employs a proposal generator to produce class-agnostic mask proposals, while the second stage utilizes a point-based classification model built on the Vision Transformer (ViT) to refine predictions by focusing on mask central points. ViT-P serves as a pre-training-free adapter, allowing the integration of various pre-trained vision transformers without modifying their architecture, ensuring adaptability to dense prediction tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that coarse and bounding box annotations can effectively enhance classification without requiring additional training on fine annotation datasets, reducing annotation costs while maintaining strong performance. Extensive experiments across COCO, ADE20K, and Cityscapes datasets validate the effectiveness of ViT-P, achieving state-of-the-art results with 54.0 PQ on ADE20K panoptic segmentation, 87.4 mIoU on Cityscapes semantic segmentation, and 63.6 mIoU on ADE20K semantic segmentation. The code and pretrained models are available at: https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P}{https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P.
图像分割仍是计算机视觉中的一项具有挑战性的任务,需要生成稳健的掩膜和精确的分类。最近的基于掩膜的方法通过捕捉全局上下文来生成高质量掩膜。然而,特别是在存在模糊边界和类别分布不平衡的情况下,对这些掩膜进行准确分类仍然是一个开放性问题。在这项工作中,我们引入了ViT-P,这是一种新型的两阶段分割框架,它将掩膜生成与分类解耦。第一阶段采用提案生成器生成类别无关的掩膜提案,而第二阶段则基于视觉变压器(ViT)的点分类模型对预测进行细化,专注于掩膜中心点。ViT-P作为一种无需预训练的适配器,可以集成各种预训练的视觉变压器而无需修改其架构,确保适应密集预测任务。此外,我们证明粗标注和边界框标注可以有效地增强分类,而无需在精细标注数据集上进行额外训练,从而在降低标注成本的同时保持强劲性能。在COCO、ADE20K和Cityscapes数据集上的大量实验验证了ViT-P的有效性,在ADE20K全景分割上实现了54.0 PQ的先进结果,Cityscapes语义分割上达到了87.4 mIoU,ADE20K语义分割上达到了63.6 mIoU。代码和预先训练的模型可在:https://github.com/sajjad-sh33/ViT-P上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ViT-P的新型两阶段图像分割框架,该框架将掩膜生成与分类阶段解耦。第一阶段生成类别无关的掩膜提案,第二阶段利用基于视觉Transformer(ViT)的点分类模型进行预测精细化。ViT-P可作为无需预训练的适配器,可整合各种预训练视觉Transformer,确保适应密集预测任务。此外,研究证明粗略和边界框注释能有效提高分类性能,同时降低精细标注数据集的训练成本。在COCO、ADE20K和Cityscapes数据集上的实验验证了ViT-P的有效性,取得了先进的结果。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-P是一个两阶段的图像分割框架,将掩膜生成与分类阶段分开,以提高性能和准确性。
- 第一阶段生成类别无关的掩膜提案,为后续的分类阶段提供基础。
- 第二阶段利用基于视觉Transformer(ViT)的点分类模型进行精细化预测。
- ViT-P可作为无需预训练的适配器,整合各种预训练视觉Transformer。
- 粗略和边界框注释能提高分类性能,同时降低标注成本。
- 在多个数据集上的实验验证了ViT-P的有效性,取得了显著成果。
点此查看论文截图

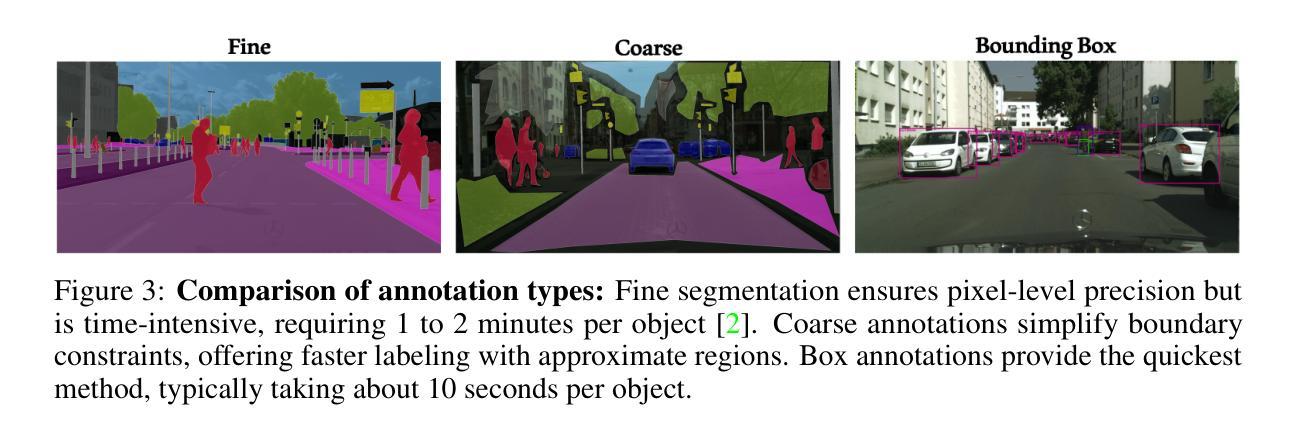
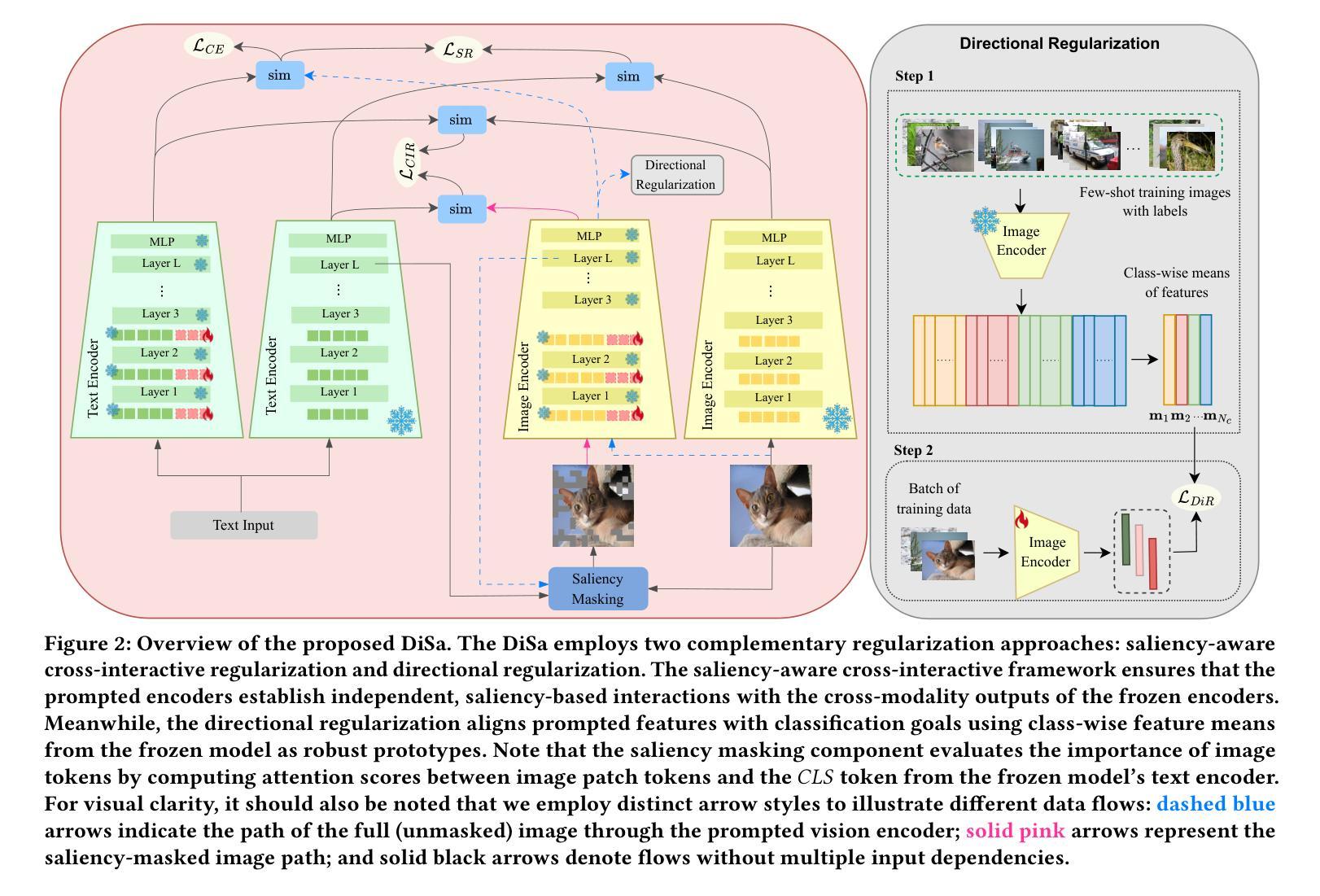
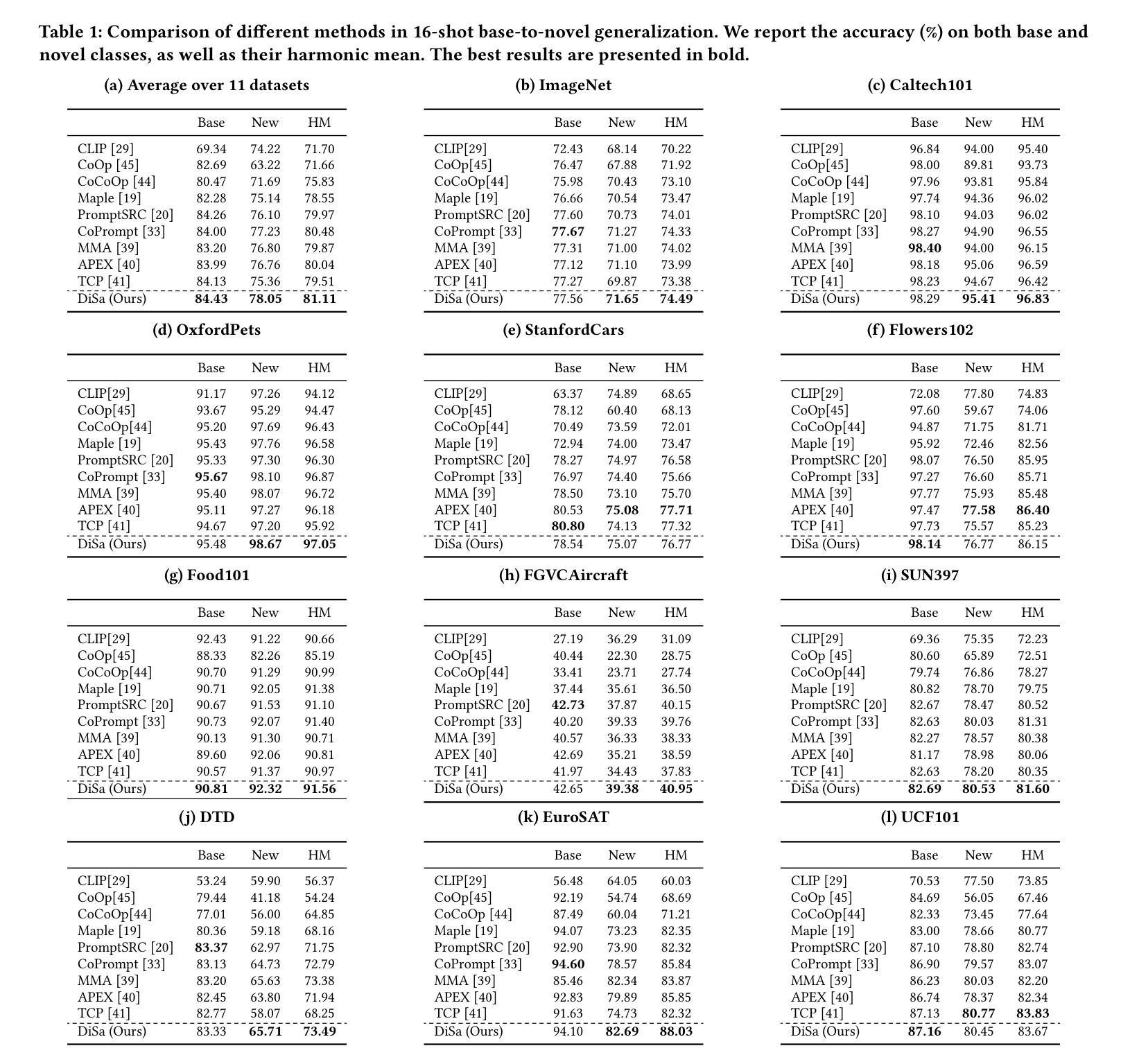
DiSa: Directional Saliency-Aware Prompt Learning for Generalizable Vision-Language Models
Authors:Niloufar Alipour Talemi, Hossein Kashiani, Hossein R. Nowdeh, Fatemeh Afghah
Prompt learning has emerged as a powerful paradigm for adapting vision-language models such as CLIP to downstream tasks. However, existing methods often overfit to seen data, leading to significant performance degradation when generalizing to novel classes or unseen domains. To address this limitation, we propose DiSa, a Directional Saliency-Aware Prompt Learning framework that integrates two complementary regularization strategies to enhance generalization. First, our Cross-Interactive Regularization (CIR) fosters cross-modal alignment by enabling cooperative learning between prompted and frozen encoders. Within CIR, a saliency-aware masking strategy guides the image encoder to prioritize semantically critical image regions, reducing reliance on less informative patches. Second, we introduce a directional regularization strategy that aligns visual embeddings with class-wise prototype features in a directional manner to prioritize consistency in feature orientation over strict proximity. This approach ensures robust generalization by leveraging stable prototype directions derived from class-mean statistics. Extensive evaluations on 11 diverse image classification benchmarks demonstrate that DiSa consistently outperforms state-of-the-art prompt learning methods across various settings, including base-to-novel generalization, cross-dataset transfer, domain generalization, and few-shot learning.
提示学习已经成为一种强大的范式,用于将诸如CLIP之类的视觉语言模型适应于下游任务。然而,现有方法往往会对已见数据进行过度拟合,导致在推广到新型类别或未见领域时性能显著下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了DiSa,一个面向方向的显著性感知提示学习框架,它集成了两种互补的正则化策略,以增强泛化能力。首先,我们的交叉交互正则化(CIR)通过促进提示和冻结编码器之间的合作学习,实现跨模态对齐。在CIR中,一种显著性感知掩码策略引导图像编码器优先处理语义上关键的图像区域,减少对于信息量较少的补丁的依赖。其次,我们引入了一种方向性正则化策略,以方向性方式将视觉嵌入与类原型特征对齐,优先保证特征方向的一致性,而非严格的接近程度。这种方法通过利用从类均值统计得出的稳定原型方向,确保了稳健的泛化。在11个不同的图像分类基准测试上的广泛评估表明,DiSa在各种设置下均一致优于最先进的提示学习方法,包括基础到新型的泛化、跨数据集转换、域泛化和小样本学习。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 31st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD 2025)
Summary
针对视觉语言模型(如CLIP)下游任务的适应性,提示学习已成为一种强大的范式。然而,现有方法常常对可见数据过度拟合,在推广到新型类别或未见领域时性能显著下降。为解决此局限性,我们提出DiSa,一种方向性显著性感知提示学习框架,它融合了两种互补的正则化策略以增强泛化能力。首先,我们的交互正则化(CIR)通过促进提示和冻结编码器之间的合作性学习来增强跨模态对齐。CIR内的显著性感知掩码策略引导图像编码器优先关注语义关键图像区域,减少了对信息较少区域的依赖。其次,我们引入了一种方向性正则化策略,以方向性方式将视觉嵌入与类原型特征对齐,以优先保证特征方向的连续性而非严格接近性。此方法通过利用从类均值统计得出的稳定原型方向,确保了稳健泛化。在11个不同的图像分类基准测试上的广泛评估表明,DiSa在多种设置下始终优于最新提示学习方法,包括基础到新型的泛化、跨数据集迁移、域泛化和小样本学习。
Key Takeaways
- 提示学习是适应视觉语言模型下游任务的有效范式。
- 现有提示学习方法存在过度拟合问题,限制了模型在新型类别或未见领域的性能。
- DiSa框架通过集成两种正则化策略来解决此问题,增强模型的泛化能力。
- Cross-Interactive Regularization (CIR) 促进跨模态对齐,通过显著性感知掩码策略引导图像编码器的关注重点。
- 引入的方向性正则化策略注重特征方向的连续性,通过利用类原型特征的稳定方向来提高模型泛化。
- DiSa在多种图像分类基准测试上表现优越,包括基础到新型的泛化、跨数据集迁移、域泛化和小样本学习。
点此查看论文截图
A Smart Healthcare System for Monkeypox Skin Lesion Detection and Tracking
Authors:Huda Alghoraibi, Nuha Alqurashi, Sarah Alotaibi, Renad Alkhudaydi, Bdoor Aldajani, Lubna Alqurashi, Jood Batweel, Maha A. Thafar
Monkeypox is a viral disease characterized by distinctive skin lesions and has been reported in many countries. The recent global outbreak has emphasized the urgent need for scalable, accessible, and accurate diagnostic solutions to support public health responses. In this study, we developed ITMAINN, an intelligent, AI-driven healthcare system specifically designed to detect Monkeypox from skin lesion images using advanced deep learning techniques. Our system consists of three main components. First, we trained and evaluated several pretrained models using transfer learning on publicly available skin lesion datasets to identify the most effective models. For binary classification (Monkeypox vs. non-Monkeypox), the Vision Transformer, MobileViT, Transformer-in-Transformer, and VGG16 achieved the highest performance, each with an accuracy and F1-score of 97.8%. For multiclass classification, which contains images of patients with Monkeypox and five other classes (chickenpox, measles, hand-foot-mouth disease, cowpox, and healthy), ResNetViT and ViT Hybrid models achieved 92% accuracy, with F1 scores of 92.24% and 92.19%, respectively. The best-performing and most lightweight model, MobileViT, was deployed within the mobile application. The second component is a cross-platform smartphone application that enables users to detect Monkeypox through image analysis, track symptoms, and receive recommendations for nearby healthcare centers based on their location. The third component is a real-time monitoring dashboard designed for health authorities to support them in tracking cases, analyzing symptom trends, guiding public health interventions, and taking proactive measures. This system is fundamental in developing responsive healthcare infrastructure within smart cities. Our solution, ITMAINN, is part of revolutionizing public health management.
天花的病毒性疾病特征在于具有显著特征的皮肤病变,已经出现在多个国家。最近的全球爆发强调了迫切需要对可扩展、可访问和准确的诊断解决方案的支持,以应对公共卫生挑战。在这项研究中,我们开发了ITMAINN系统,这是一个智能的AI驱动的医疗保健系统,专门用于利用先进的深度学习技术从皮肤病变图像中检测天花病毒。我们的系统由三个主要组成部分构成。首先,我们使用迁移学习在公开的皮肤病数据集上训练和评估了一些预训练模型,以确定最有效的模型。对于二元分类(天花与非天花),Vision Transformer、MobileViT、Transformer-in-Transformer和VGG16表现最佳,准确率和F1分数均达到97.8%。对于包含天花图像以及其他五种类别(水痘、麻疹、手足口、牛痘和正常)患者的多分类,ResNetViT和ViT混合模型准确率达到92%,F1分数分别为92.24%和92.19%。表现最佳且最轻量级模型MobileViT已部署在移动应用程序中。第二个组成部分是一个跨平台的智能手机应用程序,使用户能够通过图像分析检测天花病毒,跟踪症状,并根据其位置获得附近医疗保健中心的推荐。第三个组成部分是一个实时监视仪表板,专为卫生当局设计,以支持他们跟踪病例、分析症状趋势、指导公共卫生干预和采取积极措施。这一系统在智能城市建立响应迅速的卫生保健基础设施方面至关重要。我们的解决方案ITMAINN是公共卫生管理革命的一部分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 5 figures
摘要
本研究开发了一种名为ITMAINN的智能AI医疗系统,用于通过皮肤病变图像检测猴痘病毒。该系统包含三个主要组件,通过先进的深度学习技术实现对猴痘的二元分类和多分类。该系统训练并使用多个预训练模型在公开的皮肤病变数据集上进行迁移学习,以识别最有效的模型。对于二元分类(猴痘与非猴痘),其准确率达到了惊人的97.8%。对于包含猴痘和其他五种疾病(鸡痘、麻疹、手足口、牛痘和正常)的多类分类,其准确率也达到了92%。其中表现最佳且最轻量级模型MobileViT已被部署在手机应用程序中。此外,该系统还包括一个跨平台手机应用程序和用于追踪病例、分析症状趋势并支持公共卫生干预和采取预防措施的实时监视仪表板。ITMAINN系统是智能城市响应医疗基础设施发展的重要组成部分,对公共卫生管理革命具有重要意义。
关键见解
- ITMAINN系统是一种基于AI的智能医疗系统,可通过对皮肤病变图像的分析来检测猴痘病毒。
- 使用深度学习技术进行二元分类和多分类,以区分猴痘与其他皮肤疾病。
- 在二元分类中,多个模型(如Vision Transformer、MobileViT等)表现出高准确率(97.8%)。
- 在多类分类中,ResNetViT和ViT Hybrid模型达到92%的准确率和相应的F1分数。
- MobileViT模型因其高效性能被部署在手机应用程序中。
- 系统包括一个手机应用程序,用于图像分析、症状追踪和附近医疗中心的推荐。
点此查看论文截图

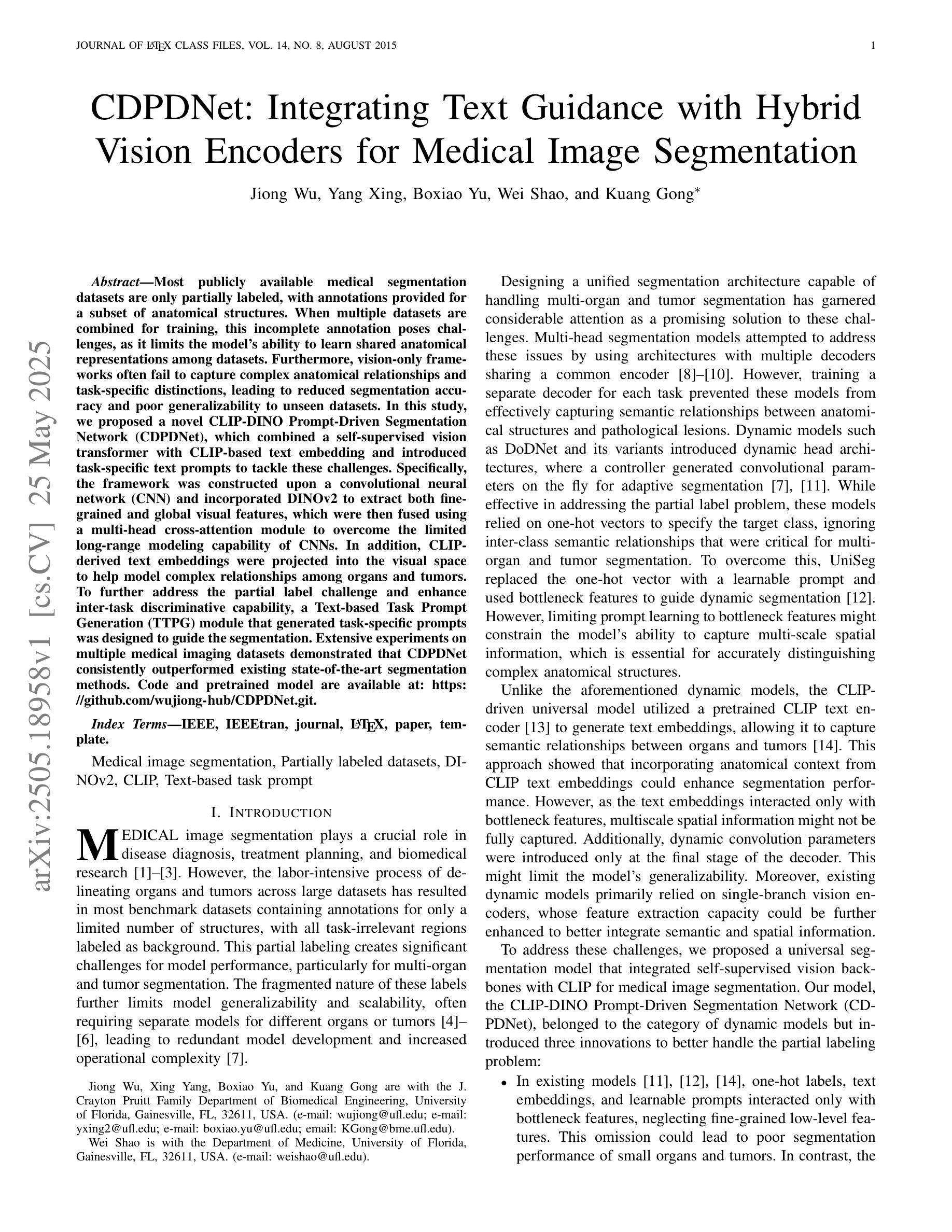
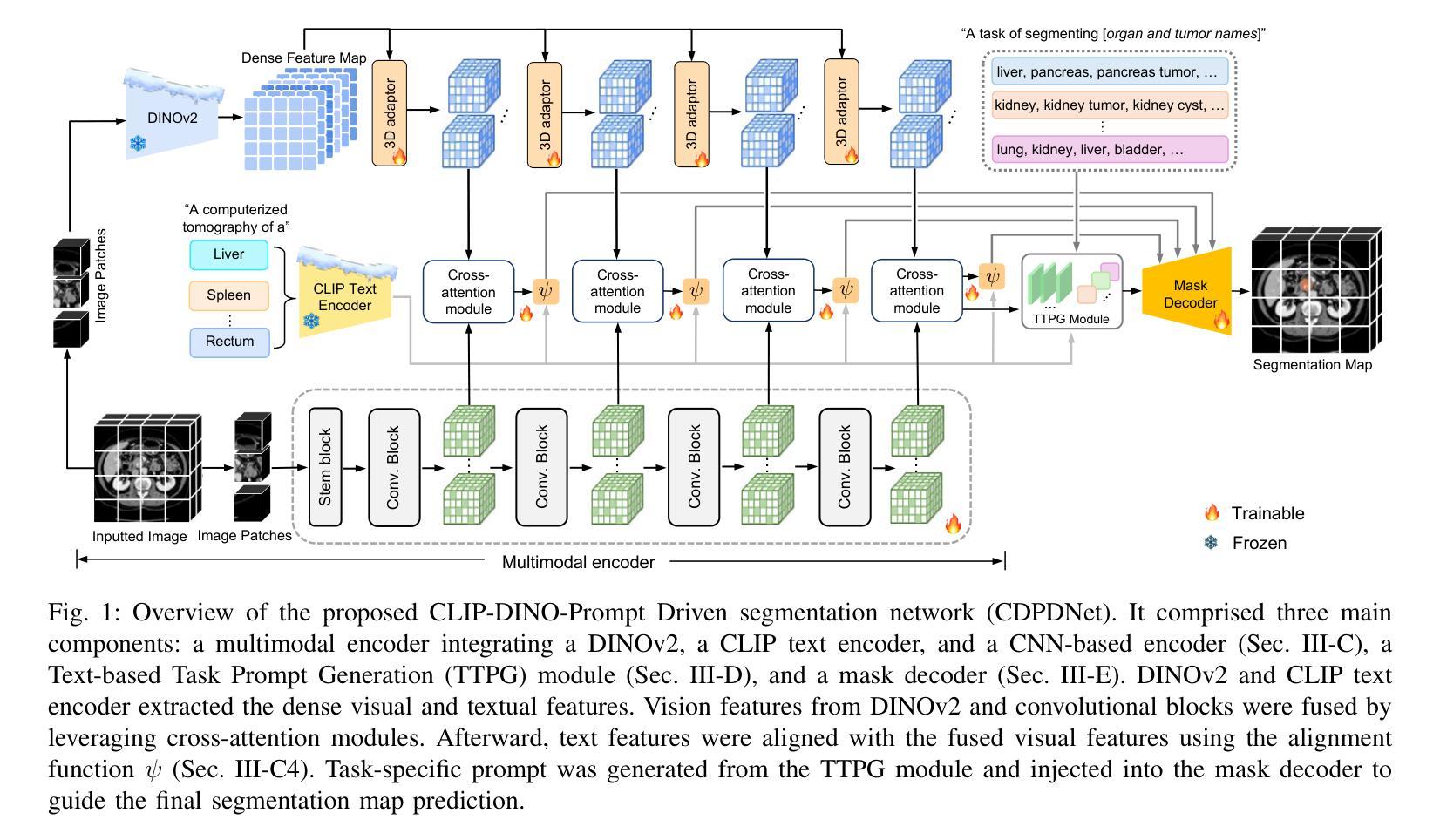
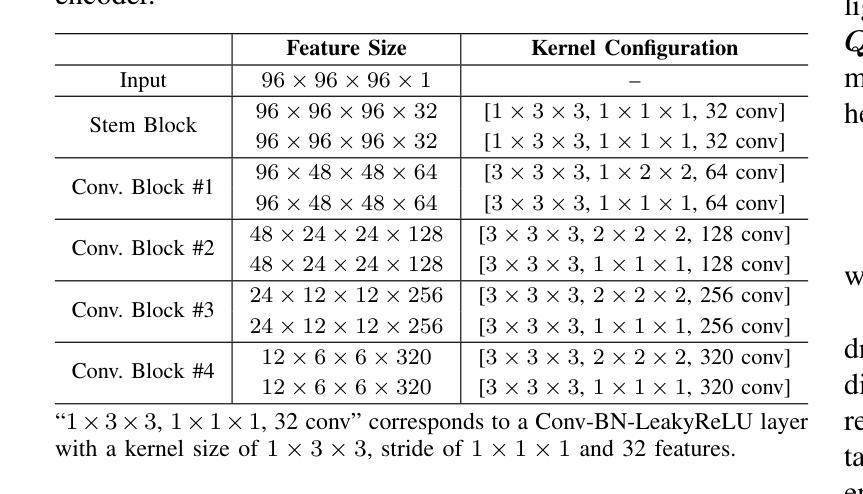
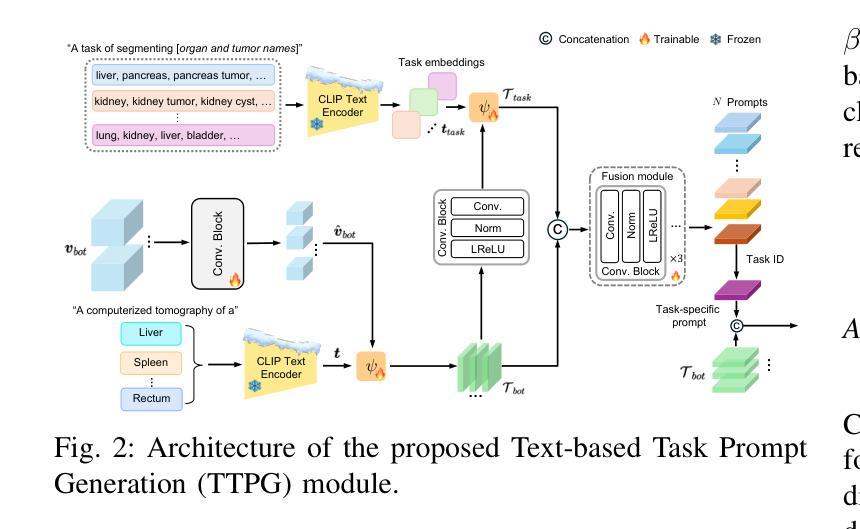
CDPDNet: Integrating Text Guidance with Hybrid Vision Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiong Wu, Yang Xing, Boxiao Yu, Wei Shao, Kuang Gong
Most publicly available medical segmentation datasets are only partially labeled, with annotations provided for a subset of anatomical structures. When multiple datasets are combined for training, this incomplete annotation poses challenges, as it limits the model’s ability to learn shared anatomical representations among datasets. Furthermore, vision-only frameworks often fail to capture complex anatomical relationships and task-specific distinctions, leading to reduced segmentation accuracy and poor generalizability to unseen datasets. In this study, we proposed a novel CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network (CDPDNet), which combined a self-supervised vision transformer with CLIP-based text embedding and introduced task-specific text prompts to tackle these challenges. Specifically, the framework was constructed upon a convolutional neural network (CNN) and incorporated DINOv2 to extract both fine-grained and global visual features, which were then fused using a multi-head cross-attention module to overcome the limited long-range modeling capability of CNNs. In addition, CLIP-derived text embeddings were projected into the visual space to help model complex relationships among organs and tumors. To further address the partial label challenge and enhance inter-task discriminative capability, a Text-based Task Prompt Generation (TTPG) module that generated task-specific prompts was designed to guide the segmentation. Extensive experiments on multiple medical imaging datasets demonstrated that CDPDNet consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art segmentation methods. Code and pretrained model are available at: https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git.
大部分公开可用的医学分割数据集仅部分标注,只为部分解剖结构提供注释。当多个数据集组合进行训练时,这种不完全的注释带来了挑战,因为它限制了模型在数据集之间学习共享解剖表征的能力。此外,仅依赖视觉的框架通常无法捕捉复杂的解剖关系和任务特定的区别,从而导致分割精度降低和未见数据集的泛化能力较差。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新颖的CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动分割网络(CDPDNet),它将自监督的视觉变压器与CLIP基于文本的嵌入相结合,并引入任务特定的文本提示来解决这些挑战。具体来说,该框架建立在卷积神经网络(CNN)之上,并融入了DINOv2来提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,然后使用多头交叉注意模块融合这些特征,以克服CNN有限的长期建模能力。此外,CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投射到视觉空间中,以帮助模型模拟器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。为了进一步解决部分标签挑战并增强任务间的判别能力,设计了一个基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块,该模块生成特定任务的提示来指导分割。在多个医学成像数据集上的广泛实验表明,CDPDNet持续优于现有的最先进的分割方法。代码和预训练模型可在https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动的分段网络(CDPDNet),结合了自监督视觉变压器和CLIP文本嵌入技术,解决了医学图像分割中的部分标注问题和复杂解剖关系捕捉问题。CDPDNet通过CNN和DINOv2提取精细和全局视觉特征,并采用多头交叉注意力模块融合特征,生成任务特定提示来指导分割,同时在多个医学成像数据集上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- CDPDNet解决了医学图像分割中数据集部分标注的问题,通过结合自监督视觉变压器和CLIP文本嵌入技术,提高了模型学习和泛化能力。
- CDPDNet结合CNN和DINOv2提取视觉特征,通过多头交叉注意力模块融合特征,提高了模型的长期建模能力。
- CLIP文本嵌入被引入到视觉空间,帮助模型捕捉复杂的器官和肿瘤关系。
- Text-based Task Prompt Generation(TTPG)模块生成任务特定提示,进一步解决了部分标签挑战,增强了任务间的判别能力。
- CDPDNet在多个医学成像数据集上的表现优于现有最先进的分割方法。
- CDPDNet的实现代码和预先训练的模型可在公开仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图
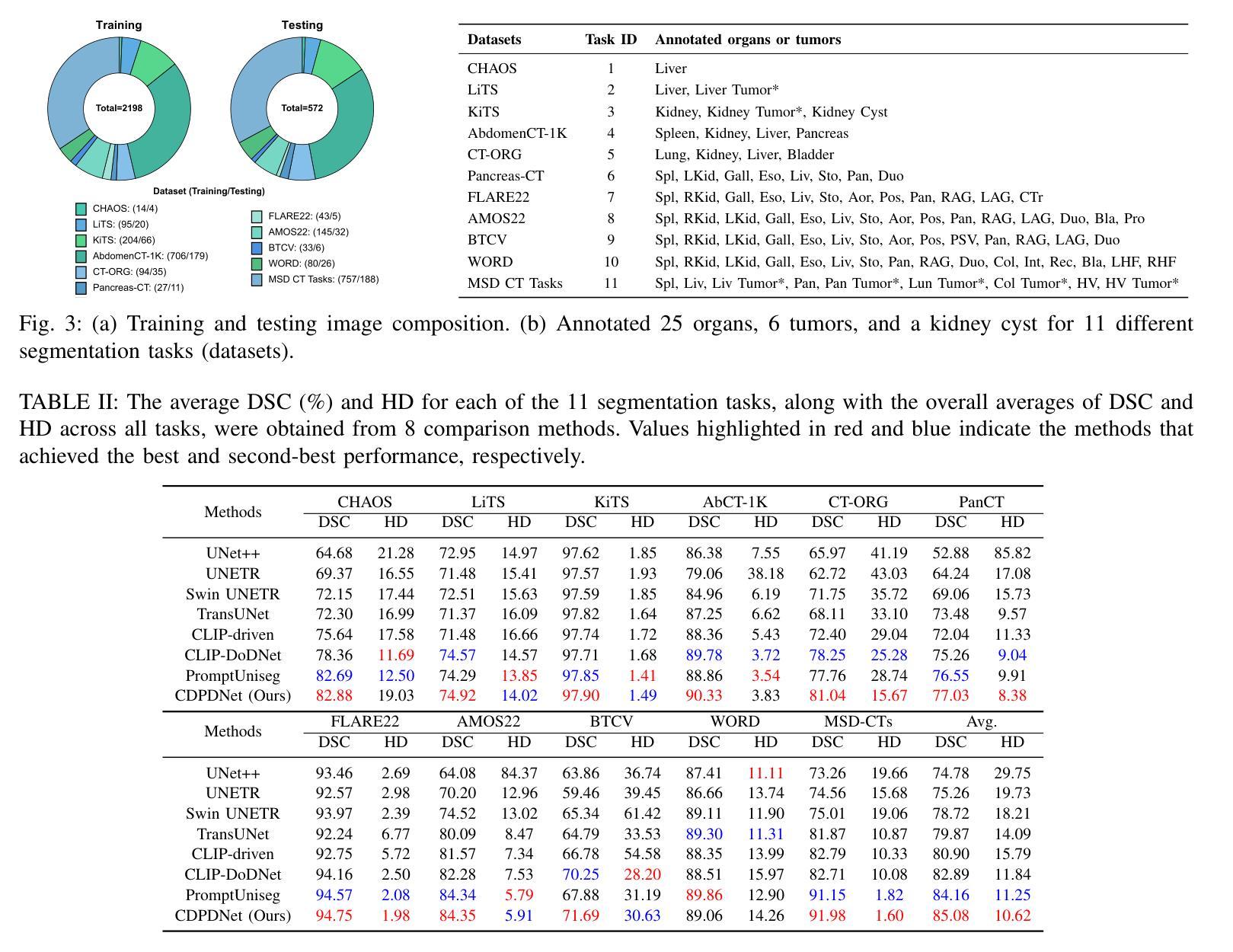
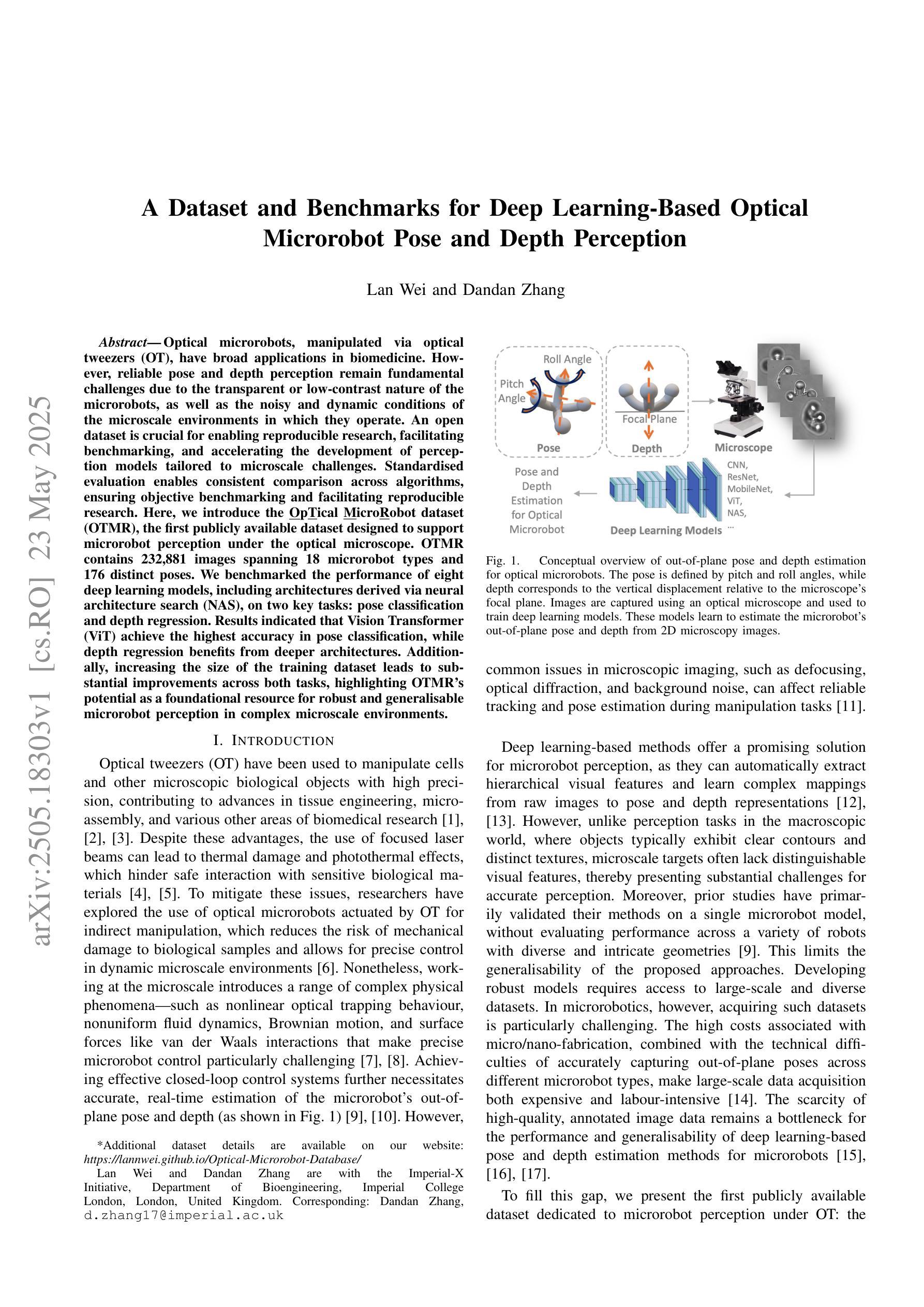
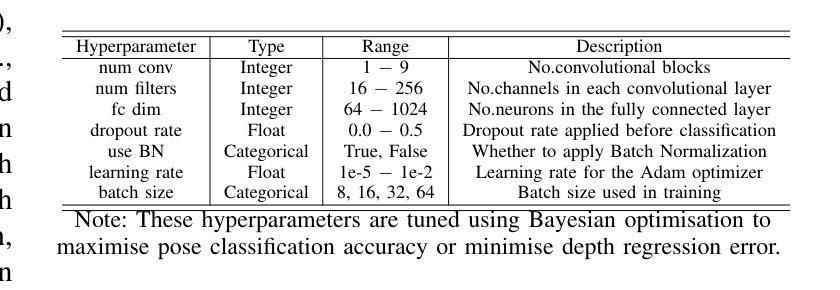
A Dataset and Benchmarks for Deep Learning-Based Optical Microrobot Pose and Depth Perception
Authors:Lan Wei, Dandan Zhang
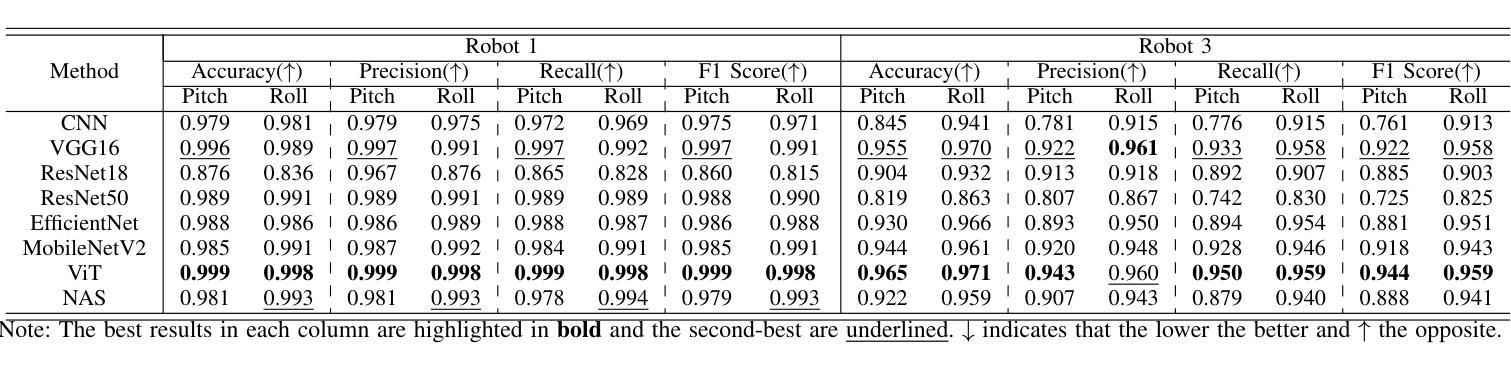
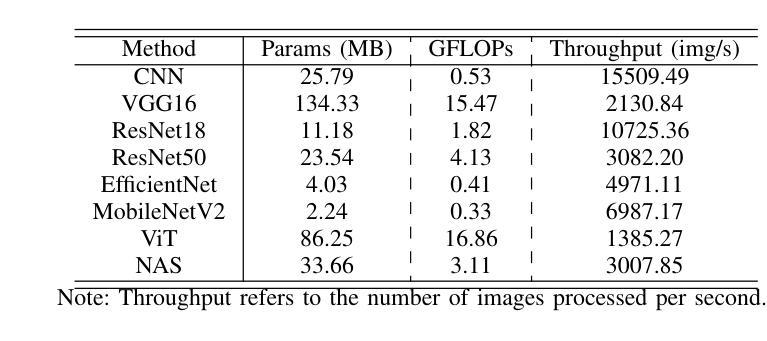
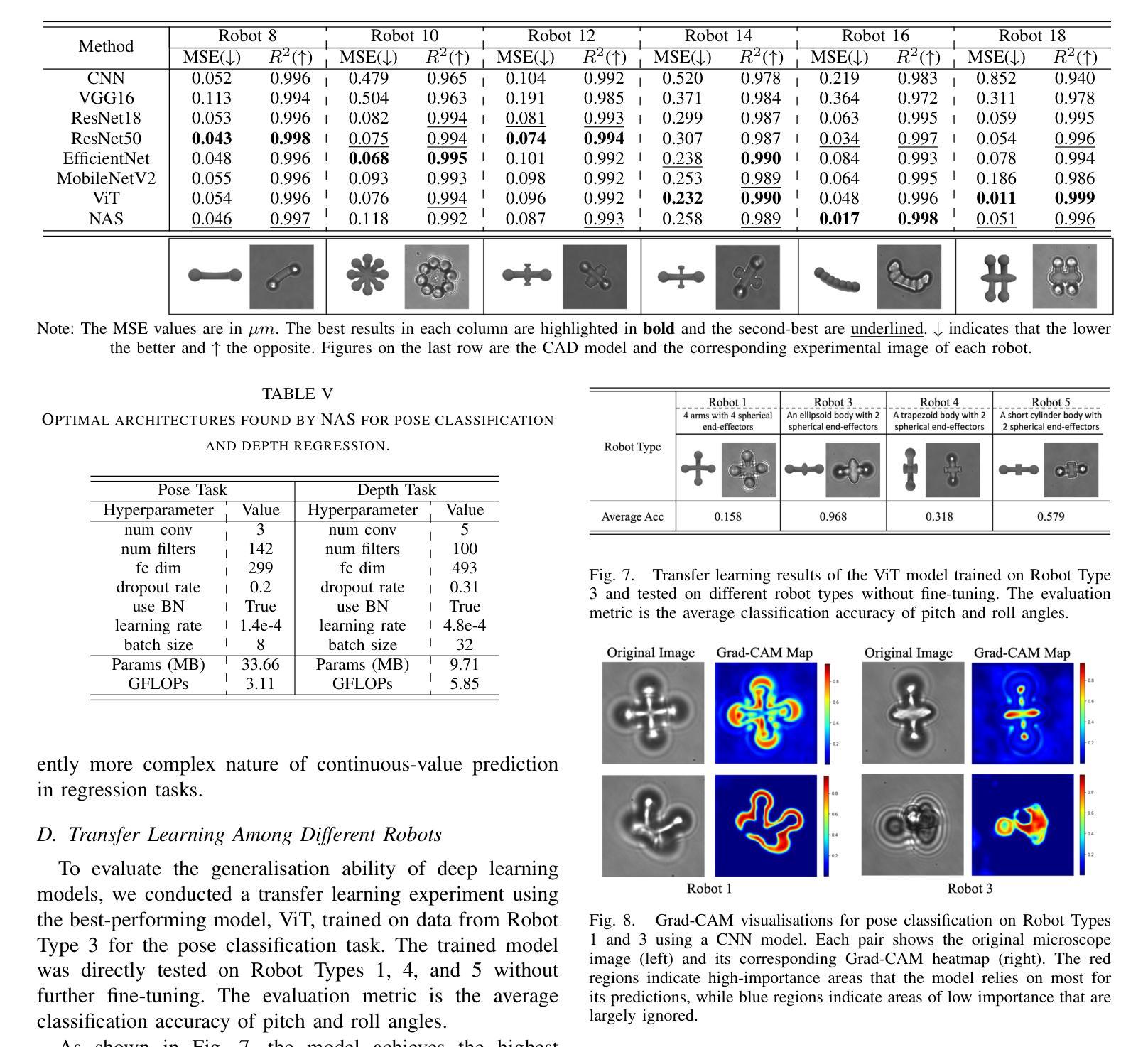
Optical microrobots, manipulated via optical tweezers (OT), have broad applications in biomedicine. However, reliable pose and depth perception remain fundamental challenges due to the transparent or low-contrast nature of the microrobots, as well as the noisy and dynamic conditions of the microscale environments in which they operate. An open dataset is crucial for enabling reproducible research, facilitating benchmarking, and accelerating the development of perception models tailored to microscale challenges. Standardised evaluation enables consistent comparison across algorithms, ensuring objective benchmarking and facilitating reproducible research. Here, we introduce the OpTical MicroRobot dataset (OTMR), the first publicly available dataset designed to support microrobot perception under the optical microscope. OTMR contains 232,881 images spanning 18 microrobot types and 176 distinct poses. We benchmarked the performance of eight deep learning models, including architectures derived via neural architecture search (NAS), on two key tasks: pose classification and depth regression. Results indicated that Vision Transformer (ViT) achieve the highest accuracy in pose classification, while depth regression benefits from deeper architectures. Additionally, increasing the size of the training dataset leads to substantial improvements across both tasks, highlighting OTMR’s potential as a foundational resource for robust and generalisable microrobot perception in complex microscale environments.
光学微机器人通过光学扳手(OT)进行操作,在生物医学领域有着广泛的应用。然而,由于微机器人的透明性或低对比度特性,以及它们所操作的微尺度环境的噪声和动态条件,可靠的姿态和深度感知仍然是一个基本挑战。对于促进可重复研究、推动基准测试并加速针对微尺度挑战的感知模型开发而言,开放数据集至关重要。标准化评估可以确保算法之间的一致比较,保证客观基准测试并促进可重复研究。在这里,我们介绍了OpTical MicroRobot数据集(OTMR),这是为了支持光学显微镜下微机器人感知而设计的第一个公开数据集。OTMR包含跨越18种微机器人类型和176种不同姿态的232881张图像。我们对八种深度学习模型进行了基准测试,包括通过神经网络架构搜索(NAS)派生出的架构,主要针对两项任务:姿态分类和深度回归。结果表明,在姿态分类方面,Vision Transformer(ViT)的准确度最高,而深度回归则受益于更深的架构。此外,增加训练数据集的大小对这两项任务都有实质性的改进,突显了OTMR作为在复杂微尺度环境中进行稳健和通用微机器人感知的基础资源的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 2025 International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS)
Summary
本文介绍了光学微机器人数据集(OTMR)的创建及其重要性。OTMR是首个支持光学显微镜下的微机器人感知的数据集,包含涵盖多种类型和姿态的大量图像。研究者在该数据集上评估了多个深度学习模型,发现Vision Transformer(ViT)在姿态分类任务上表现最佳,深度回归任务受益于更深的架构。此外,扩大训练数据集大小对两项任务都有显著改进,展示了OTMR在复杂微尺度环境中实现稳健和通用微机器人感知的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 光学微机器人领域面临姿态和深度感知的挑战,主要由于微机器人的透明性或低对比度以及微尺度环境的噪声和动态条件。
- 公开数据集对于推动可重复研究、基准测试以及加速针对微尺度挑战的感知模型开发至关重要。
- 介绍了首个支持光学显微镜下的微机器人感知的数据集——OpTical MicroRobot(OTMR)数据集。
- OTMR包含涵盖多种类型和姿态的大量图像,为微机器人感知研究提供了丰富资源。
- 研究评估了多个深度学习模型在OTMR上的表现,发现Vision Transformer(ViT)在姿态分类任务上表现最佳。
- 深度回归任务受益于更深的架构,表明深度神经网络在解决微机器人深度感知问题上的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

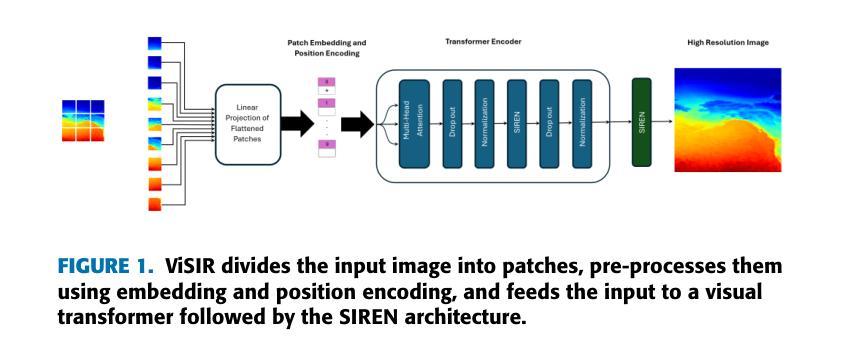
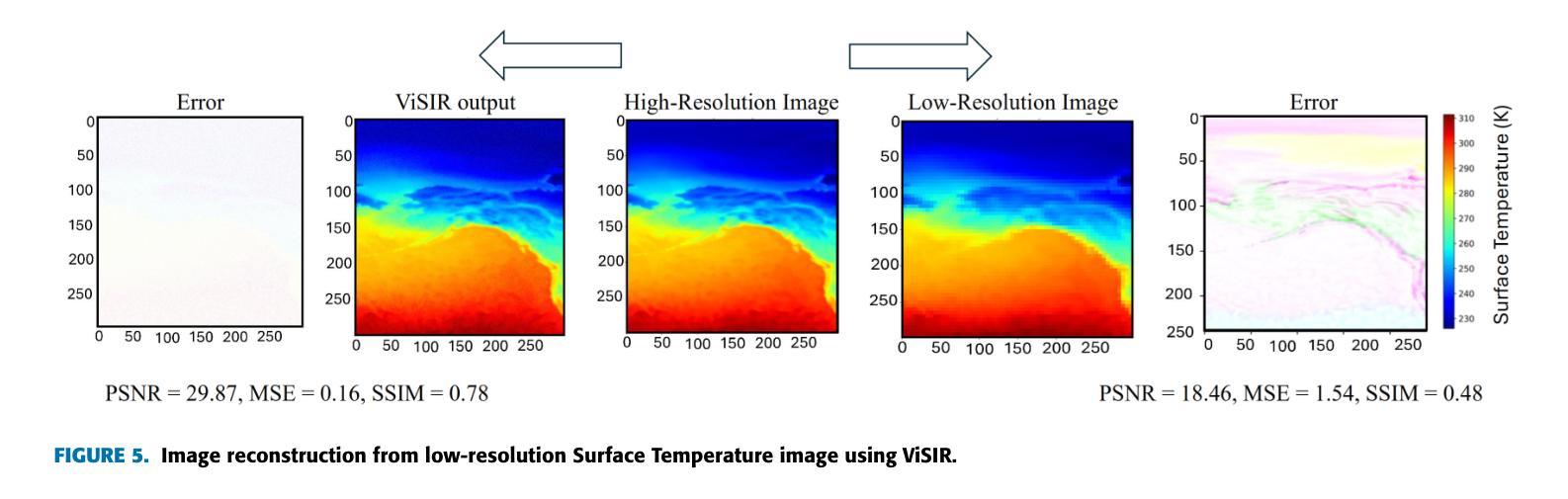
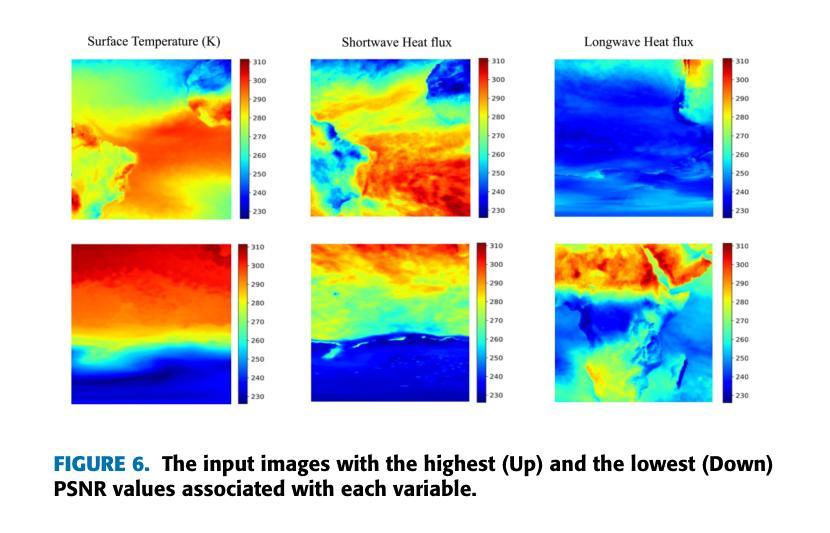
ViSIR: Vision Transformer Single Image Reconstruction Method for Earth System Models
Authors:Ehsan Zeraatkar, Salah Faroughi, Jelena Tešić
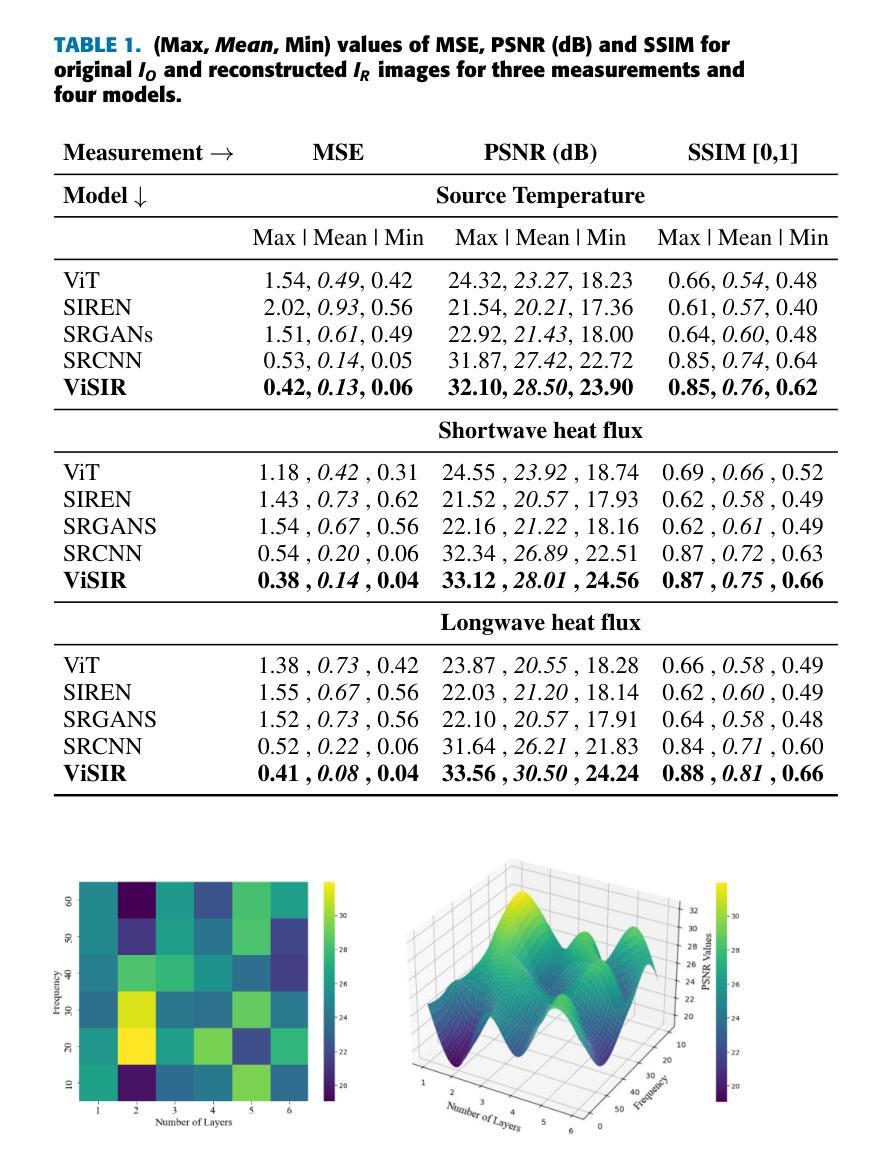
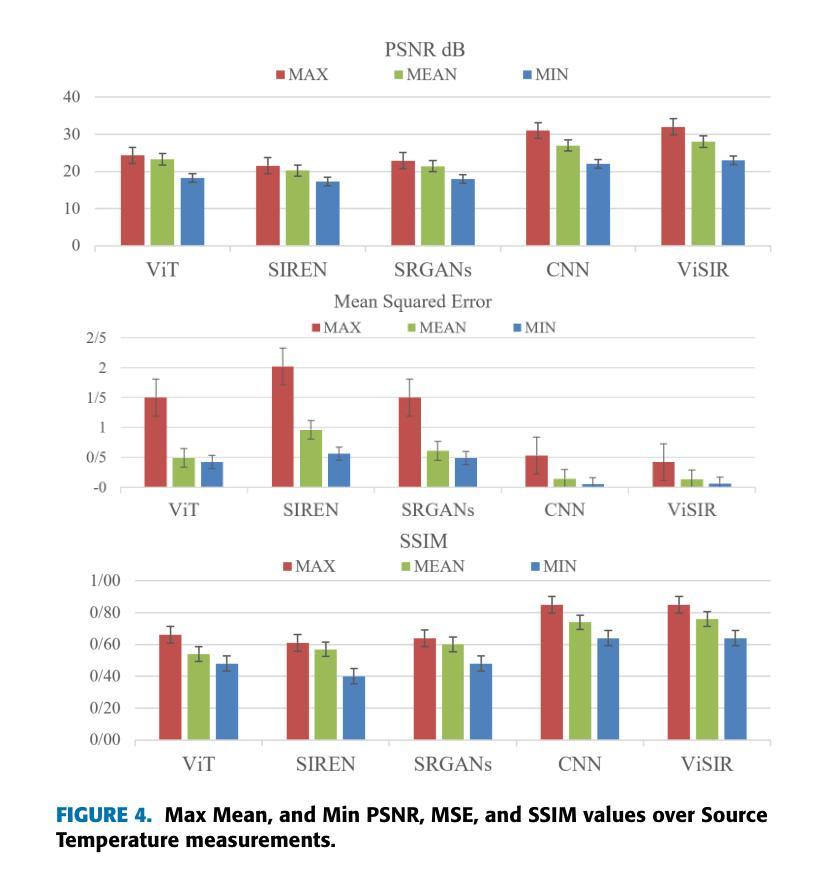
Purpose: Earth system models (ESMs) integrate the interactions of the atmosphere, ocean, land, ice, and biosphere to estimate the state of regional and global climate under a wide variety of conditions. The ESMs are highly complex; thus, deep neural network architectures are used to model the complexity and store the down-sampled data. This paper proposes the Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks (ViSIR) to improve the ESM data’s single image SR (SR) reconstruction task. Methods: ViSIR combines the SR capability of Vision Transformers (ViT) with the high-frequency detail preservation of the Sinusoidal Representation Network (SIREN) to address the spectral bias observed in SR tasks. Results: The ViSIR outperforms SRCNN by 2.16 db, ViT by 6.29 dB, SIREN by 8.34 dB, and SR-Generative Adversarial (SRGANs) by 7.93 dB PSNR on average for three different measurements. Conclusion: The proposed ViSIR is evaluated and compared with state-of-the-art methods. The results show that the proposed algorithm is outperforming other methods in terms of Mean Square Error(MSE), Peak-Signal-to-Noise-Ratio(PSNR), and Structural Similarity Index Measure(SSIM).
目的:地球系统模型(ESM)整合了大气、海洋、陆地、冰川和生物圈的相互作用,以在多种条件下估计区域和全球气候的状态。由于地球系统模型高度复杂,因此使用深度神经网络架构来对其进行建模并存储降采样数据。本文提出Vision Transformer正弦表示网络(ViSIR)来改善ESM数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。方法:ViSIR结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)的超分辨率能力和正弦表示网络(SIREN)的高频细节保留功能,以解决SR任务中观察到的频谱偏差问题。结果:ViSIR在三个不同测量指标上的性能平均优于SRCNN 2.16 dB、ViT 6.29 dB、SIREN 8.34 dB以及SR生成对抗网络(SRGANs)7.93 dB的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。结论:对提出的ViSIR进行了评估,并与最新方法进行了比较。结果表明,该算法在均方误差(MSE)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了地球系统模型(ESMs)的复杂性及其利用深度神经网络进行建模的方法。为改进ESM数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务,本文提出了结合Vision Transformer与Sinusoidal Representation Network(ViSIR)的方法。ViSIR结合了Vision Transformer的超分辨率能力与Sinusoidal Representation Network的高频细节保留功能,解决了SR任务中的光谱偏差问题。实验结果显示,ViSIR在多个测量指标上均优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 地球系统模型(ESMs)整合大气、海洋、陆地、冰和生物圈交互作用,以估算各种条件下的区域和全球气候状态。
- ESMs高度复杂,需要使用深度神经网络进行建模并处理下采样数据。
- 本文提出了Vision Transformer Sinusoidal Representation Networks(ViSIR)以改进ESM数据的单图像超分辨率(SR)重建任务。
- ViSIR结合了Vision Transformer(ViT)的超分辨率能力与Sinusoidal Representation Network(SIREN)的高频细节保留功能。
- ViSIR解决了SR任务中的光谱偏差问题。
- 实验结果显示,ViSIR在PSNR上平均优于其他方法,如SRCNN、ViT、SIREN和SRGANs。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Lung Ultrasound Severity Scoring Using Dedicated Feature Extractor
Authors:Jiaqi Guo, Yunan Wu, Evangelos Kaimakamis, Georgios Petmezas, Vasileios E. Papageorgiou, Nicos Maglaveras, Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
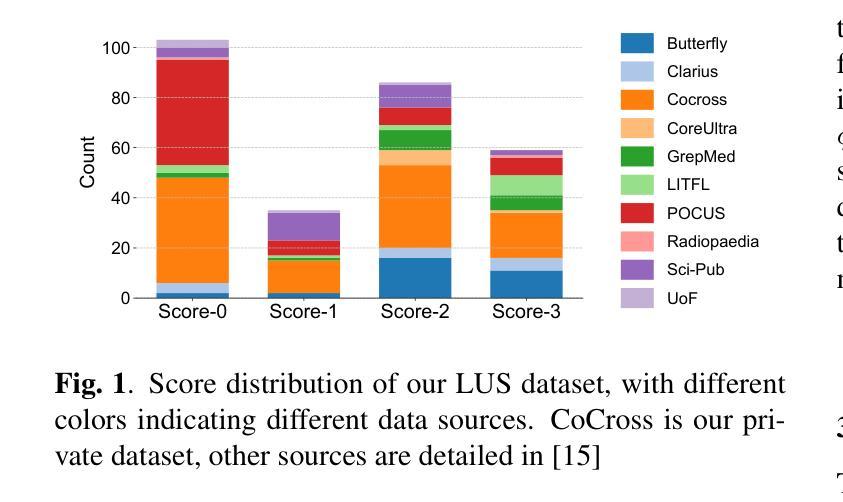
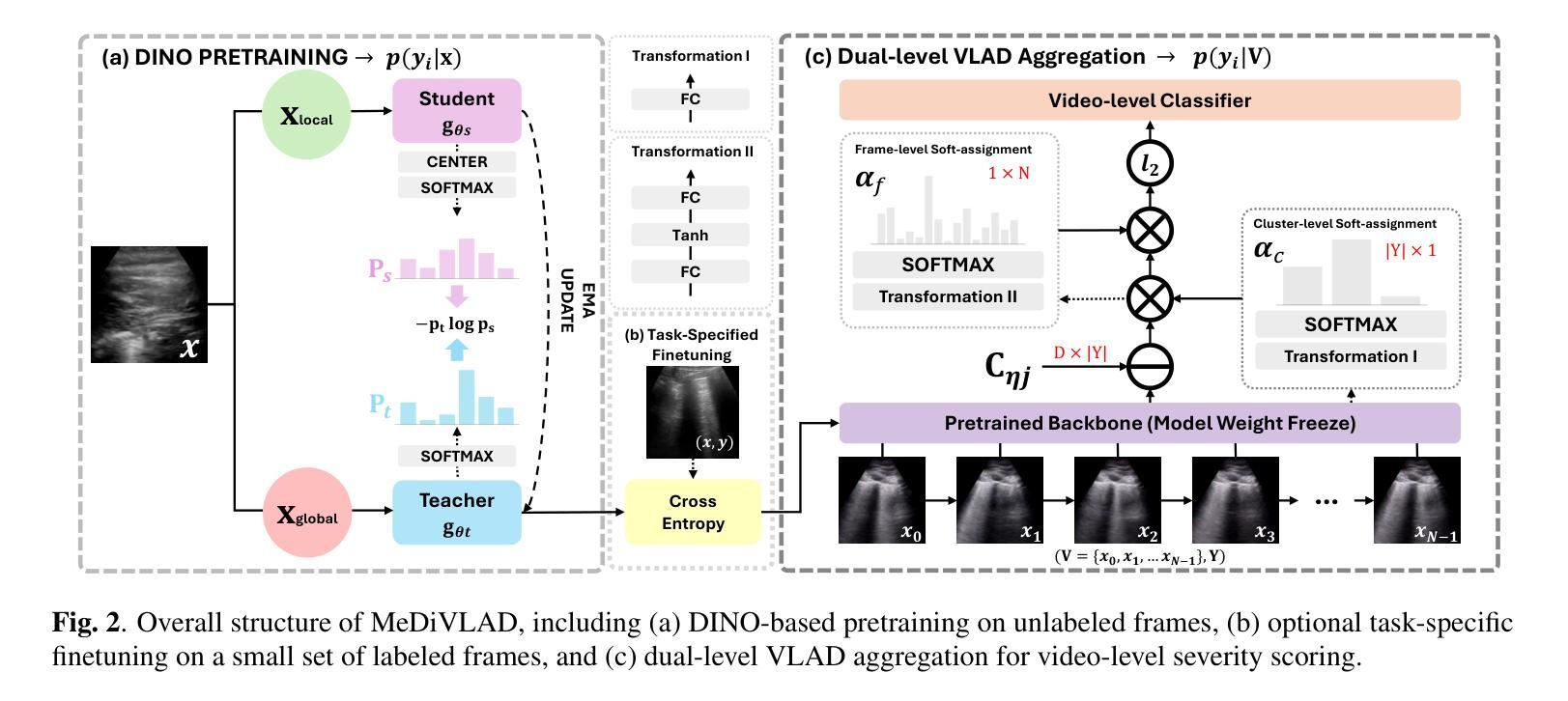
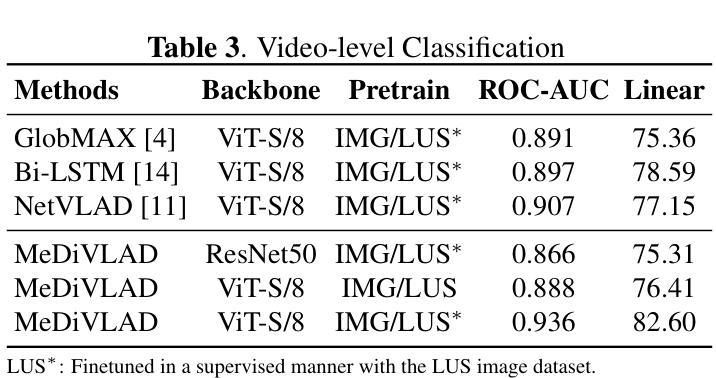
With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, ultrasound imaging has emerged as a promising technique for COVID-19 detection, due to its non-invasive nature, affordability, and portability. In response, researchers have focused on developing AI-based scoring systems to provide real-time diagnostic support. However, the limited size and lack of proper annotation in publicly available ultrasound datasets pose significant challenges for training a robust AI model. This paper proposes MeDiVLAD, a novel pipeline to address the above issue for multi-level lung-ultrasound (LUS) severity scoring. In particular, we leverage self-knowledge distillation to pretrain a vision transformer (ViT) without label and aggregate frame-level features via dual-level VLAD aggregation. We show that with minimal finetuning, MeDiVLAD outperforms conventional fully-supervised methods in both frame- and video-level scoring, while offering classification reasoning with exceptional quality. This superior performance enables key applications such as the automatic identification of critical lung pathology areas and provides a robust solution for broader medical video classification tasks.
随着COVID-19大流行的到来,由于其无创、负担得起和便携的特点,超声成像作为检测COVID-19的一种有前途的技术应运而生。因此,研究人员致力于开发基于人工智能的评分系统,以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集的大小有限且缺乏适当的注释,这给训练稳健的人工智能模型带来了重大挑战。本文针对上述问题提出了MeDiVLAD,这是一个用于多级肺超声(LUS)严重程度评分的新型管道。特别是,我们利用自我知识蒸馏对无需标签的视界转换器(ViT)进行预训练,并通过双级VLAD聚合技术聚合帧级特征。我们表明,通过最小的微调,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分方面都优于传统的全监督方法,同时提供出色的分类推理质量。这种卓越的性能能够实现关键应用,如自动识别关键的肺部病理区域,并为更广泛的医学视频分类任务提供稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ISBI 2025 (Selected for oral presentation); 2025/4/15 (v2): Corrected a notation error in Figure 2
Summary
随着COVID-19疫情的出现,超声成像在新冠病毒检测方面展现出巨大潜力。研究人员为此开发出基于AI的评分系统以提供实时诊断支持。然而,公开可用的超声数据集规模有限且缺乏适当标注,给训练稳健的AI模型带来挑战。本文提出MeDiVLAD,一个针对多层次肺部超声(LUS)严重程度评分问题的新型管道。我们利用自我知识蒸馏对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练,并通过双层次VLAD聚合来汇总帧级特征。结果表明,MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上均优于传统全监督方法,同时分类推理质量卓越。此卓越性能使得自动识别关键肺部病理区域成为可能,并为更广泛的医疗视频分类任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 超声成像在新冠病毒检测中具有潜力,因其非侵入性、经济性和便携性而受到关注。
- AI评分系统为实时诊断提供了支持,但公开可用的超声数据集存在局限性。
- MeDiVLAD是一个针对多层次肺部超声(LUS)严重程度评分的新型管道。
- 利用自我知识蒸馏对视觉转换器(ViT)进行预训练。
- 通过双层次VLAD聚合汇总帧级特征。
- MeDiVLAD在帧级和视频级评分上表现出卓越性能,优于传统全监督方法。
点此查看论文截图