⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
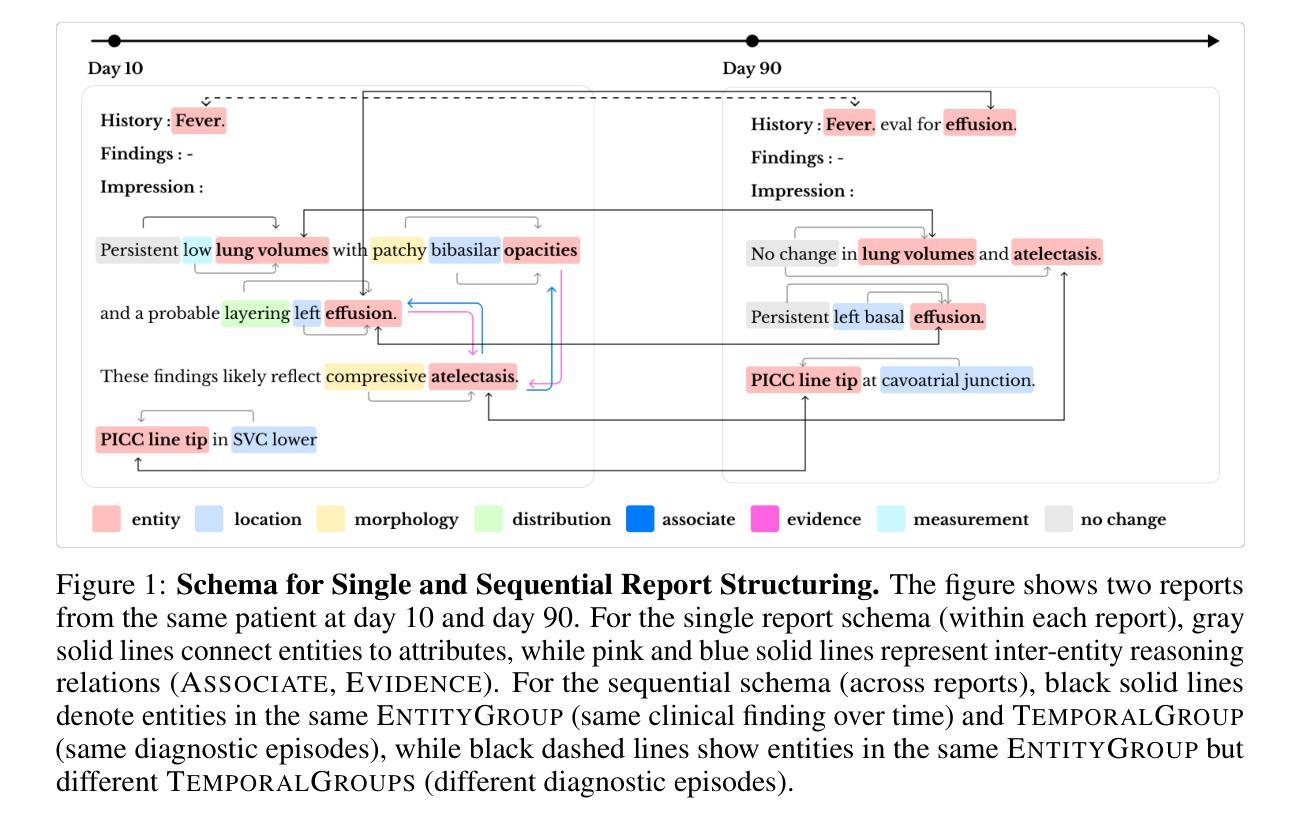
Lunguage: A Benchmark for Structured and Sequential Chest X-ray Interpretation
Authors:Jong Hak Moon, Geon Choi, Paloma Rabaey, Min Gwan Kim, Hyuk Gi Hong, Jung-Oh Lee, Hangyul Yoon, Eun Woo Doe, Jiyoun Kim, Harshita Sharma, Daniel C. Castro, Javier Alvarez-Valle, Edward Choi
Radiology reports convey detailed clinical observations and capture diagnostic reasoning that evolves over time. However, existing evaluation methods are limited to single-report settings and rely on coarse metrics that fail to capture fine-grained clinical semantics and temporal dependencies. We introduce LUNGUAGE,a benchmark dataset for structured radiology report generation that supports both single-report evaluation and longitudinal patient-level assessment across multiple studies. It contains 1,473 annotated chest X-ray reports, each reviewed by experts, and 80 of them contain longitudinal annotations to capture disease progression and inter-study intervals, also reviewed by experts. Using this benchmark, we develop a two-stage framework that transforms generated reports into fine-grained, schema-aligned structured representations, enabling longitudinal interpretation. We also propose LUNGUAGESCORE, an interpretable metric that compares structured outputs at the entity, relation, and attribute level while modeling temporal consistency across patient timelines. These contributions establish the first benchmark dataset, structuring framework, and evaluation metric for sequential radiology reporting, with empirical results demonstrating that LUNGUAGESCORE effectively supports structured report evaluation. The code is available at: https://github.com/SuperSupermoon/Lunguage
放射学报告传达详细的临床观察,并捕捉随时间演变的诊断推理。然而,现有的评估方法仅限于单一报告设置,并依赖于粗糙的指标,无法捕捉精细的临床语义和时间依赖关系。我们介绍了LUNGUAGE,这是一个用于结构化放射学报告生成的基准数据集,支持单报告评估和多研究中的纵向患者水平评估。它包含1473份经过专家审查的胸部X射线报告注释,其中80份包含纵向注释,以捕捉疾病进展和研究间间隔,也经过专家审查。使用这个基准数据集,我们开发了一个两阶段框架,将生成的报告转换为精细的、与模式对齐的结构化表示形式,以实现纵向解释。我们还提出了LUNGUAGESCORE这一可解释的指标,该指标可以在实体、关系和属性层面比较结构化输出,同时建模患者时间线上的时间一致性。这些贡献建立了首个基准数据集、结构化框架和顺序放射学报告的评估指标,实证结果表明LUNGUAGESCORE有效地支持结构化报告评估。代码可用在:https://github.com/SuperSupermoon/Lunguage 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了LUNGUAGE数据集,该数据集用于结构化放射学报告生成的评价,支持单报告评价和跨多研究的纵向病人级评估。该数据集包含经过专家审核的胸部X射线报告,其中部分报告包含疾病进展和跨研究时间间隔的纵向注释。文章还提出了一种两阶段框架和LUNGUAGESCORE评价指标,用于对生成的报告进行精细结构化表示,并在实体、关系和属性级别进行比较,同时建立患者时间线的时序一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告包含详细的临床观察和诊断推理,但现有的评估方法仅限于单报告设置,并依赖于无法捕获细微临床语义和时序依赖性的粗略指标。
- 引入LUNGUAGE数据集,该数据集包含经过专家审核的胸部X射线报告,并支持单报告评价和跨研究的纵向病人级评估。
- 数据集中部分报告包含描述疾病进展和跨研究时间间隔的纵向注释,这些注释经过专家审核。
- 提出一种两阶段框架,将生成的报告转化为精细的结构化表示,以支持纵向解释。
- 引入LUNGUAGESCORE评价指标,该指标在实体、关系和属性级别比较结构化输出,并建模患者时间线的时序一致性。
- 这是首个针对序列放射学报告的结构化数据集、构建框架和评价指标。
点此查看论文截图

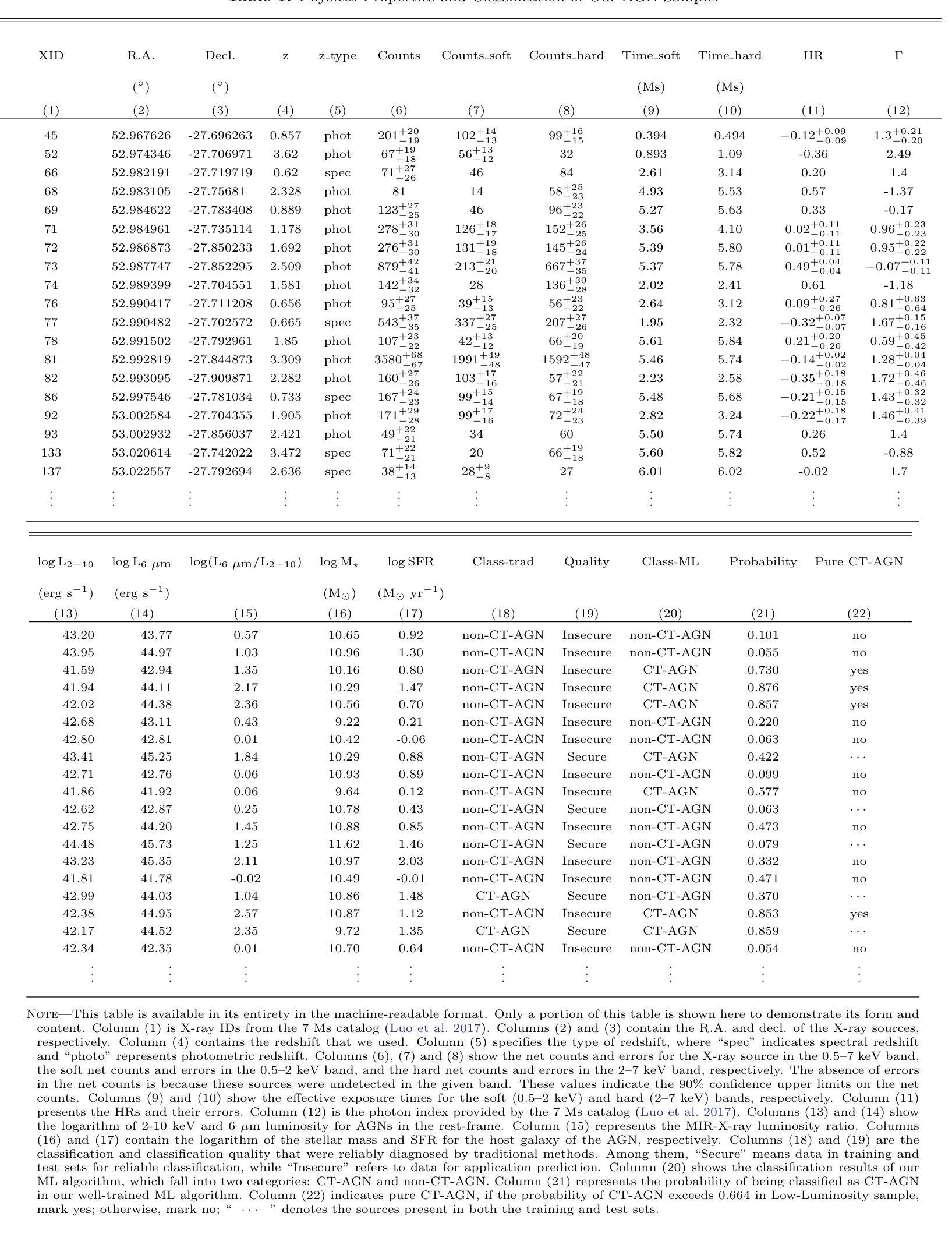
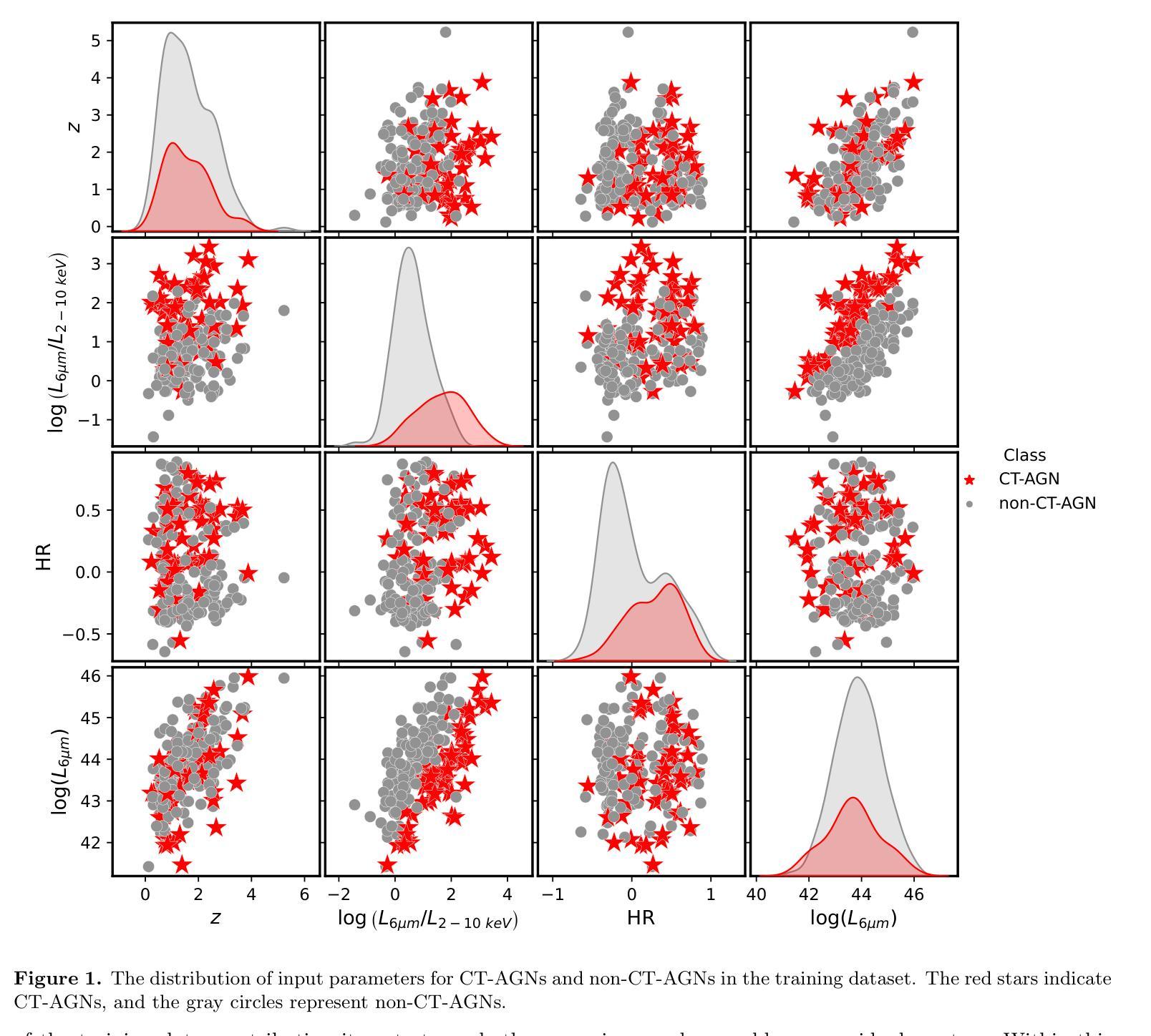
Identifying Compton-thick AGNs with Machine learning algorithm in Chandra Deep Field-South
Authors:Rui Zhang, Xiaotong Guo, Qiusheng Gu, Guanwen Fang, Jun Xu, Hai-Cheng Feng, Yongyun Chen, Rui Li, Nan Ding, Hongtao Wang
Compton-thick active galactic nuclei (CT-AGNs), which are defined by column density $\mathrm{N_H} \geqslant 1.5 \times 10^{24} \ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$, emit feeble X-ray radiation, even undetectable by X-ray instruments. Despite this, the X-ray emissions from CT-AGNs are believed to be a substantial contributor to the cosmic X-ray background (CXB). According to synthesis models of AGNs, CT-AGNs are expected to make up a significant fraction of the AGN population, likely around 30% or more. However, only $\sim$11% of AGNs have been identified as CT-AGNs in the Chandra Deep Field-South (CDFS). To identify hitherto unknown CT-AGNs in the field, we used a Random Forest algorithm for identifying them. First, we build a secure classified subset of 210 AGNs to train and evaluate our algorithm. Our algorithm achieved an accuracy rate of 90% on the test set after training. Then, we applied our algorithm to an additional subset of 254 AGNs, successfully identifying 67 CT-AGNs within this group. This result significantly increased the fraction of CT-AGNs in the CDFS, which is closer to the theoretical predictions of the CXB. Finally, we compared the properties of host galaxies between CT-AGNs and non-CT-AGNs and found that the host galaxies of CT-AGNs exhibit higher levels of star formation activity.
康普顿厚活动星系核(CT-AGNs),以其列密度$\mathrm{N_H} \geqslant 1.5 \times 10^{24} \ \mathrm{cm}^{-2}$为特征,发出微弱的X射线辐射,甚至无法被X射线仪器探测到。尽管如此,CT-AGNs的X射线发射被认为是宇宙X射线背景(CXB)的重要组成部分。根据活动星系核的合成模型,CT-AGNs预计占活动星系核人口的很大一部分,可能达到30%或更多。然而,在钱德拉南深场(CDFS)中,只有约11%的活动星系核被识别为CT-AGNs。为了识别领域中的未知CT-AGNs,我们采用了随机森林算法进行识别。首先,我们建立了一个包含210个安全分类的活动星系核子集来训练和评估我们的算法。我们的算法在测试集上达到了90%的准确率。然后,我们将算法应用于额外的254个活动星系核子集,成功识别出其中的67个CT-AGNs。这一结果显著增加了CDFS中CT-AGNs的比例,更接近CXB的理论预测。最后,我们比较了CT-AGNs和非CT-AGNs宿主星系的属性,发现CT-AGNs的宿主星系表现出更高的恒星形成活性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 6 figures, 2 Tables. Accepted for publication in ApJ
Summary
本文介绍了高柱密度活动星系核(CT-AGNs)的X-ray辐射特性及其对宇宙X-ray背景(CXB)的贡献。虽然CT-AGNs的X-ray辐射微弱,甚至无法被X-ray仪器探测到,但它们被认为是CXB的重要组成部分。通过运用随机森林算法,成功识别出更多的CT-AGNs,并发现其宿主星系具有较高的恒星形成活性。
Key Takeaways
- CT-AGNs的X-ray辐射特性微弱,但仍然对宇宙X-ray背景(CXB)有显著贡献。
- 合成模型预测CT-AGNs在AGN总体中占相当大的比例,可能达到或超过30%。
- 通过随机森林算法,提高了对CT-AGNs的识别率,准确率达到了90%。
- 在CDFS中成功识别出的CT-AGNs数量增加,更接近理论预测。
- 与非CT-AGNs相比,CT-AGNs的宿主星系表现出更高的恒星形成活性。
- 训练集和测试集的选择对算法的性能至关重要。需要选择适当的子集来训练和评估算法以确保准确性。
点此查看论文截图

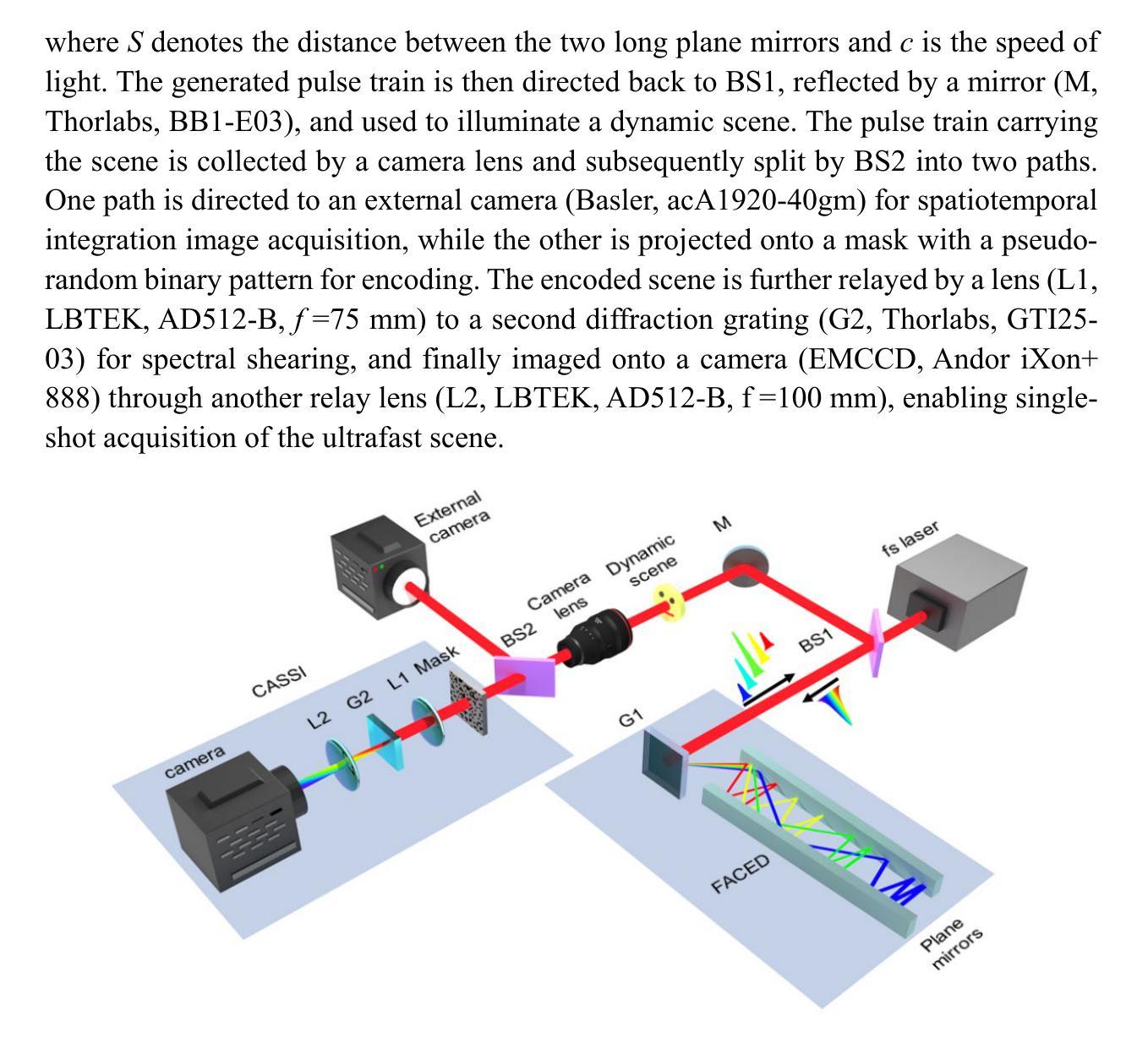
All-optical discrete illumination-based compressed ultrafast photography
Authors:Long Cheng, Dalong Qi, Jiali Yao, Ning Xu, Chengyu Zhou, Wenzhang Lin, Yu He, Zhen Pan, Yunhua Yao, Lianzhong Deng, Yuecheng Shen, Zhenrong Sun, Shian Zhang
Snapshot ultrafast optical imaging (SUOI) plays a vital role in capturing complex transient events in real time, with significant implications for both fundamental science and practical applications. As an outstanding talent in SUOI, compressed ultrafast photography (CUP) has demonstrated remarkable frame rate reaching trillions of frames per second and hundreds of sequence depth. Nevertheless, as CUP relies on streak cameras, the system’s imaging fidelity suffers from an inevitable limitation induced by the charge coupling artifacts in a streak camera. Moreover, although advanced image reconstruction algorithms have improved the recovered scenes, its high compression ratio still causes a compromise in image quality. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach termed all-optical discrete illumination compressed ultrafast photography (AOD-CUP), which employs a free-space angular-chirp-enhanced delay (FACED) technique to temporally stretch femtosecond pulses and achieves discrete illumination for dynamic scenes. With its distinctive system architecture, AOD-CUP features adjustable frame numbers and flexible inter-frame intervals ranging from picoseconds to nanoseconds, thereby achieving high-fidelity ultrafast imaging in a snapshot. Experimental results demonstrate the system’s superior dynamic spatial resolution and its capability to visualize ultrafast phenomena with complex spatial details, such as stress wave propagation in LiF crystals and air plasma channel formation. These results highlight the potential of AOD-CUP for high-fidelity, real-time ultrafast imaging, which provides an unprecedented tool for advancing the frontiers of ultrafast science.
快照超高速光学成像(SUOI)在实时捕捉复杂的瞬态事件方面起着至关重要的作用,对基础科学和实际应用都有重要意义。作为SUOI领域的杰出人才,压缩超高速摄影(CUP)已经实现了高达每秒数万亿帧的帧率以及数百序列深度。然而,由于CUP依赖于条纹相机,系统的成像保真度受到条纹相机中电荷耦合伪影引起的不可避免的限制。尽管先进的图像重建算法提高了恢复的场景质量,但其较高的压缩比仍然会导致图像质量的妥协。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为全光学离散照明压缩超高速摄影(AOD-CUP),该方法采用自由空间角啁啾增强延迟(FACED)技术来延长飞秒脉冲的时间,并为动态场景实现离散照明。凭借独特的系统架构,AOD-CUP具有可调整的帧数和灵活的帧间间隔,范围从皮秒到纳秒,从而在一次快照中实现高保真超高速成像。实验结果证明了系统出色的动态空间分辨率以及其在可视化具有复杂空间细节的超快现象方面的能力,如LiF晶体中的应力波传播和空气等离子体通道的形成。这些结果突显了AOD-CUP在高保真、实时超高速成像方面的潜力,为超快科学的前沿发展提供了前所未有的工具。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
快照超高速光学成像(SUOI)在实时捕捉复杂瞬态事件方面发挥着至关重要的作用,对基础科学和实际应用都具有重要意义。压缩超高速摄影(CUP)作为SUOI的杰出人才,帧率高达每秒数万亿帧,序列深度达数百个。然而,由于CUP依赖于条纹相机,系统成像保真度受到条纹相机中电荷耦合伪影的固有限制的影响。尽管先进的图像重建算法改善了恢复的场景,但其高压缩比仍然会影响图像质量。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为全光学离散照明压缩超高速摄影(AOD-CUP)的新方法,该方法采用自由空间角啁��ーム增强延迟(FACED)技术,对飞秒脉冲进行时间拉伸,实现动态场景的离散照明。凭借独特系统架构,AOD-CUP具有可调帧数和灵活的帧间间隔,范围从皮秒到纳秒,从而实现高保真超高速快照成像。实验结果证明了系统出色的动态空间分辨率和可视化复杂空间细节的超高现象的能力,如LiF晶体中的应力波传播和空气等离子体通道的形成。这些结果突显了AOD-CUP在高保真、实时超高速成像方面的潜力,为超高速科学领域的发展提供了前所未有的工具。
要点
- SUOI在捕捉复杂瞬态事件方面至关重要,对科学和应用都有重要意义。
- CUP作为SUOI的杰出代表,具有极高的帧率和序列深度。
3.条纹相机带来的电荷耦合伪影限制了CUP的成像质量。 - 提出AOD-CUP新方法,采用FACED技术实现离散照明和灵活帧间间隔。
- AOD-CUP具有可调帧数,可实现高动态空间分辨率的超高速成像。
- 实验结果证明AOD-CUP在可视化复杂空间细节的超高现象方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图

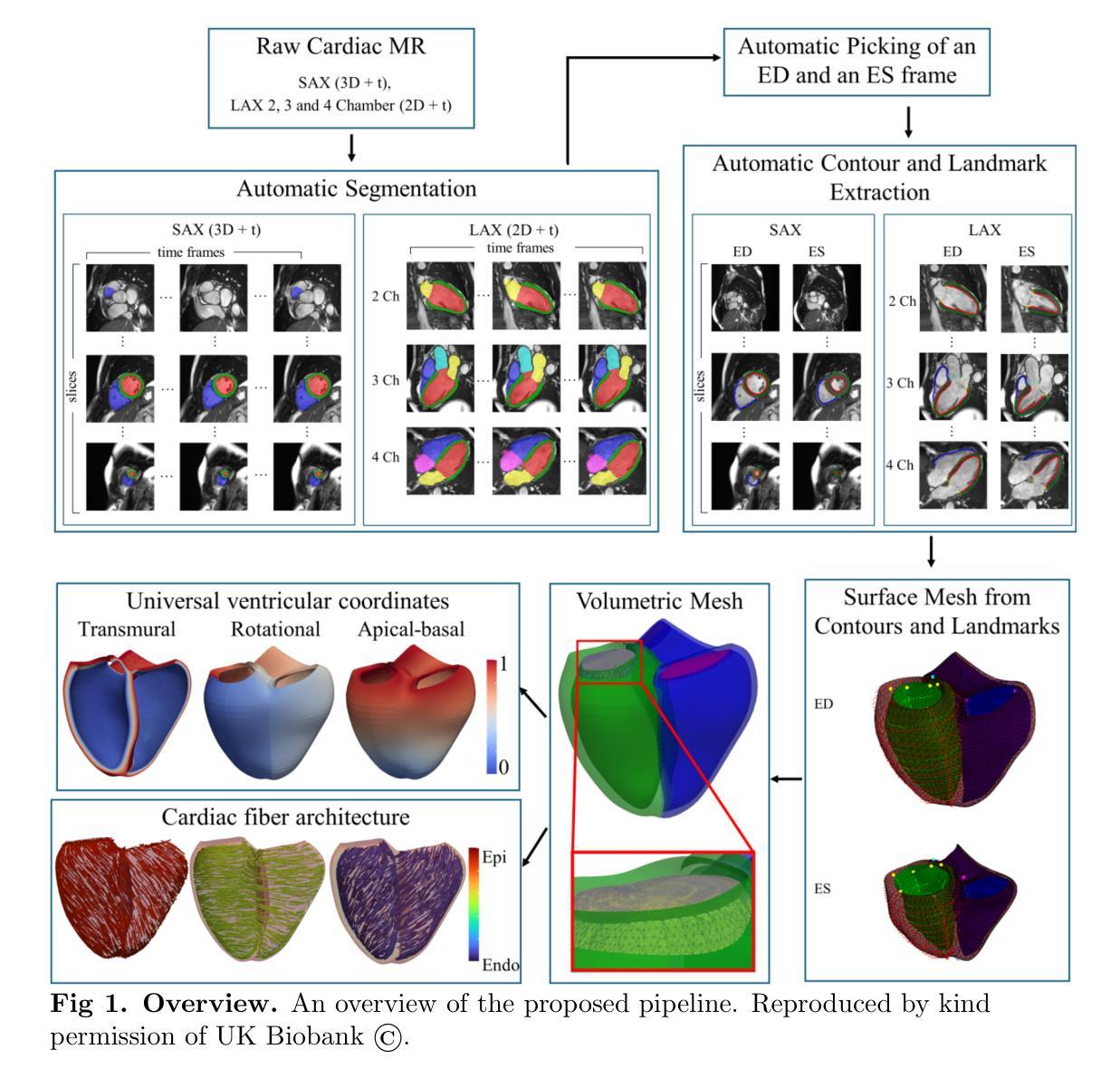
Cardiac Digital Twins at Scale from MRI: Open Tools and Representative Models from ~55000 UK Biobank Participants
Authors:Devran Ugurlu, Shuang Qian, Elliot Fairweather, Charlene Mauger, Bram Ruijsink, Laura Dal Toso, Yu Deng, Marina Strocchi, Reza Razavi, Alistair Young, Pablo Lamata, Steven Niederer, Martin Bishop
A cardiac digital twin is a virtual replica of a patient’s heart for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, risk assessment, and treatment planning of cardiovascular diseases. This requires an anatomically accurate patient-specific 3D structural representation of the heart, suitable for electro-mechanical simulations or study of disease mechanisms. However, generation of cardiac digital twins at scale is demanding and there are no public repositories of models across demographic groups. We describe an automatic open-source pipeline for creating patient-specific left and right ventricular meshes from cardiovascular magnetic resonance images, its application to a large cohort of ~55000 participants from UK Biobank, and the construction of the most comprehensive cohort of adult heart models to date, comprising 1423 representative meshes across sex (male, female), body mass index (range: 16 - 42 kg/m$^2$) and age (range: 49 - 80 years). Our code is available at https://github.com/cdttk/biv-volumetric-meshing/tree/plos2025 , and pre-trained networks, representative volumetric meshes with fibers and UVCs will be made available soon.
心脏数字孪生体是指患者心脏的虚拟副本,用于心血管疾病的筛查、诊断、预后评估、风险评估和治疗计划。这需要患者心脏的具体解剖结构的三维结构表示,适用于机电模拟或疾病机理研究。然而,大规模生成心脏数字孪生体是有挑战性的,并且目前没有跨人口群体的模型公共仓库。我们描述了一个自动开源管道,用于从心血管磁共振图像创建患者特定的左心室和右心室网格,将其应用于来自英国生物银行的约55000名参与者的研究,并构建了迄今为止最全面的成人心脏模型队列,包括按性别(男性、女性)、体重指数(范围:16-42 kg/m²)和年龄(范围:49-80岁)划分的代表性网格共1423个。我们的代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/cdttk/biv-volumetric-meshing/tree/plos2025,并且预训练网络和具有代表性的体积网格(带有纤维和紫外线杀菌剂)将很快提供使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这是一项关于心脏数字双胞胎的研究,该研究利用心血管磁共振图像创建患者特定的左心室和右心室网格,并应用于大规模的UK Biobank参与者群体,构建了迄今为止最全面的成人心脏模型。该研究提供了自动开源管道,并创建了包含性别、体重指数和年龄等跨人口特征的模型库。这些模型可用于心血管疾病筛查、诊断、预后评估和治疗计划。其代码和资源库公开,方便研究者获取和应用。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏数字双胞胎是一种虚拟患者心脏复制品,主要用于心血管疾病的筛查、诊断、预后评估和治疗计划。
- 需要解剖学准确的患者特定心脏三维结构表示,适用于机电模拟或疾病机理研究。
- 自动开源管道被开发出来,用于从心血管磁共振图像创建患者特定的左心室和右心室网格。
- 该管道成功应用于大规模的UK Biobank参与者群体,创建了迄今为止最全面的成人心脏模型。
- 模型考虑了性别、体重指数和年龄等多种因素,使其成为跨人口特征的模型库。这对于各种类型的心血管疾病研究具有重要价值。
点此查看论文截图

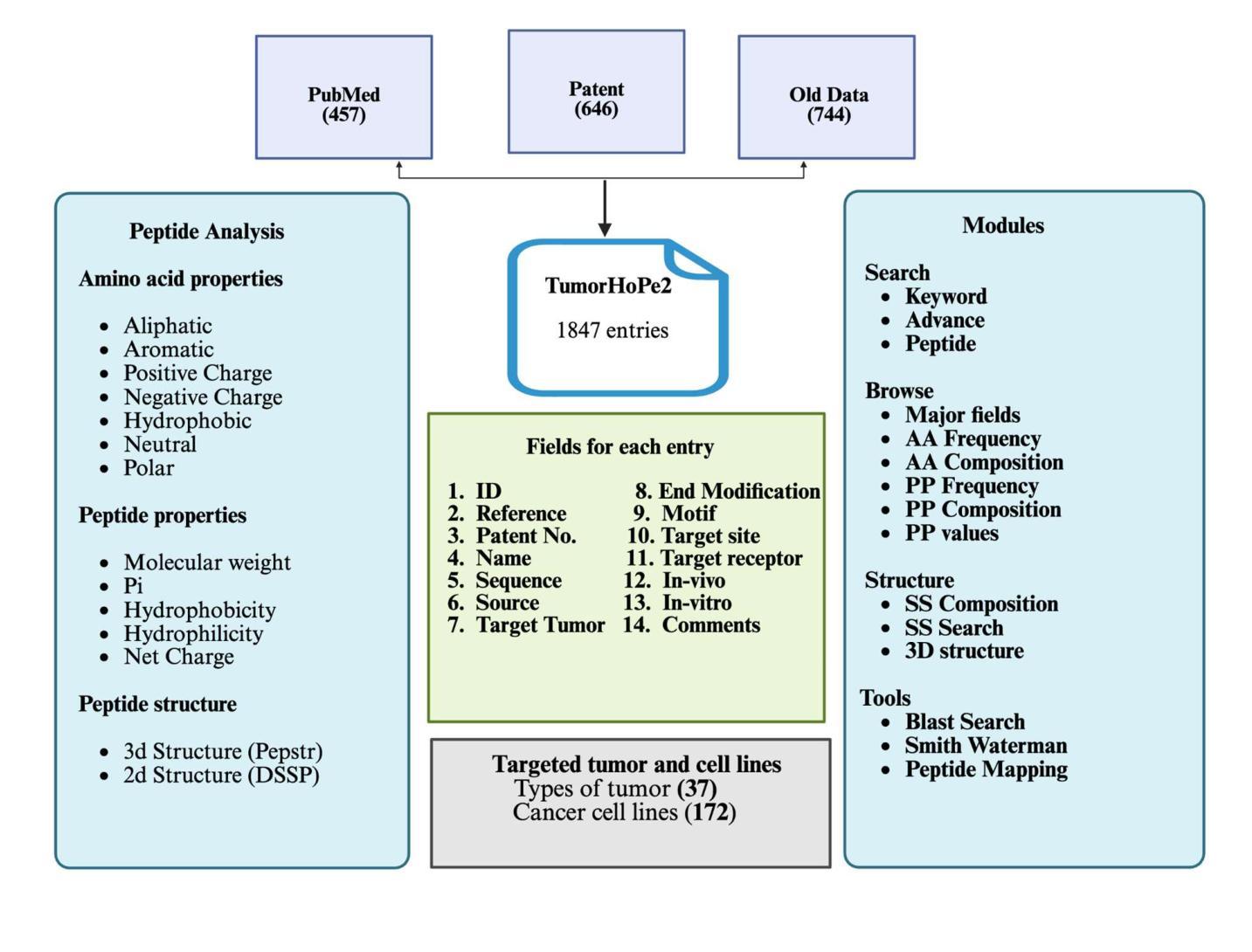
TumorHoPe2: An updated database for Tumor Homing Peptides
Authors:Diksha Kashyap, Devanshi Gupta, Naman Kumar Mehta, Gajendra P. S. Raghava
Addressing the growing need for organized data on tumor homing peptides (THPs), we present TumorHoPe2, a manually curated database offering extensive details on experimentally validated THPs. This represents a significant update to TumorHoPe, originally developed by our group in 2012. TumorHoPe2 now contains 1847 entries, representing 1297 unique tumor homing peptides, a substantial expansion from the 744 entries in its predecessor. For each peptide, the database provides critical information, including sequence, terminal or chemical modifications, corresponding cancer cell lines, and specific tumor types targeted. The database compiles data from two primary sources: phage display libraries, which are commonly used to identify peptide ligands targeting tumor-specific markers, and synthetic peptides, which are chemically modified to enhance properties such as stability, binding affinity, and specificity. Our dataset includes 594 chemically modified peptides, with 255 having N-terminal and 195 C-terminal modifications. These THPs have been validated against 172 cancer cell lines and demonstrate specificity for 37 distinct tumor types. To maximize utility for the research community, TumorHoPe2 is equipped with intuitive tools for data searching, filtering, and analysis, alongside a RESTful API for efficient programmatic access and integration into bioinformatics pipelines. It is freely available at https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/tumorhope2/
为了应对肿瘤归巢肽(THPs)有序数据不断增长的需求,我们推出了TumorHoPe2,这是一个手动整理数据库,提供了经过实验验证的THPs的详细信息。这是对2012年由我们团队开发的TumorHoPe的重大更新。TumorHoPe2目前包含1847个条目,代表有1297个独特的肿瘤归巢肽,较前一代的744个条目有了实质性的扩展。对于每个肽,数据库提供了关键信息,包括序列、末端或化学修饰、相应的癌细胞株以及特定的靶向肿瘤类型。数据库整理了两种主要来源的数据:常用于识别针对肿瘤特异性标记物的肽配体的噬菌体展示库,以及通过化学修饰增强稳定性、结合亲和力和特异性的合成肽。我们的数据集包含594个化学修饰的肽,其中255个具有N端修饰和195个具有C端修饰。这些THPs已经通过针对172种癌细胞株的验证,显示出对37种不同肿瘤类型的特异性。为了最大化对研究群体的效用,TumorHoPe2配备了用于数据搜索、过滤和分析的直观工具,以及用于高效编程访问和整合到生物信息学流程的RESTful API。它可在https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/tumorhope2/免费访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
肿瘤HoPe数据库的新版本——TumorHoPe2现已推出,包含经过实验验证的肿瘤归巢肽(THP)的详细信息。此数据库包含大量关于肿瘤归巢肽的信息,包括序列、终端或化学修饰、相应的癌细胞株以及特定肿瘤类型等。相比之前的版本,新数据库扩充了内容,并提供了更直观的工具进行数据搜索、筛选和分析。
Key Takeaways
- TumorHoPe2是TumorHoPe数据库的升级版,包含更多关于肿瘤归巢肽(THP)的信息。
- 数据库包含1847个条目,代表1297个独特的肿瘤归巢肽。
- 数据库数据主要来自噬菌体展示库和合成肽两种来源。
- 数据库中包含594个经过化学修饰的肽,其中255个具有N末端和195个具有C末端修饰。
- 这些THPs已针对172种癌细胞株进行验证,并显示出对37种不同肿瘤的特异性。
- TumorHoPe2提供了直观的工具进行数据搜索、筛选和分析。
点此查看论文截图

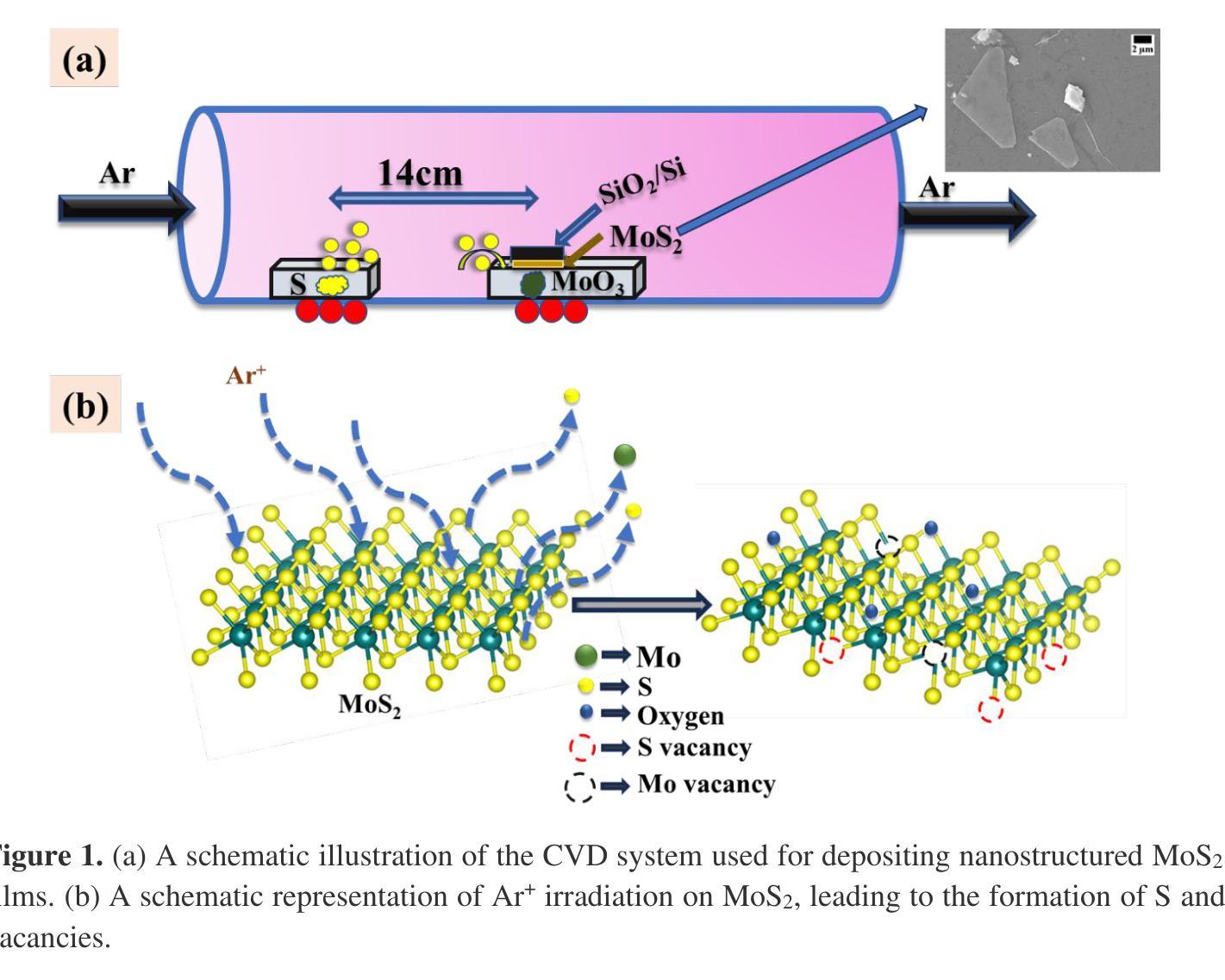
Highly Enhanced robust room temperature ferromagnetism in CVD-grown nano-dimensional MoS2 flakes by modifying edges and defect engineering
Authors:Sharmistha Dey, Nahid Chaudhary, Ulrich Kentsch, Rajendra Singh, Pankaj Srivastava, Santanu Ghosh
The alterations in the magnetic properties and electronic structure of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown nano-dimensional molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) after low energy ion irradiation are thoroughly investigated. The formation of pure hexagonal 2-H phase has been identified by Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The pristine samples are irradiated by Argon (Ar) ions with low energy at different fluences. A comprehensive analysis of Raman spectroscopy data manifests the formation of lattice defects like S-vacancies across the samples after irradiation. Triangular-flake formation in the pristine sample is confirmed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images. After increasing irradiation fluences the big flakes commenced to fragment into smaller ones enhancing the number of edge-terminated structures. The electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA) analysis verifies the absence of any magnetic impurity. Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study confirm the formation of S-vacancies after irradiation. The pristine sample exhibits diamagnetic behavior at room temperature. The saturation magnetization value increases with increasing the ion irradiation fluences, and the sample irradiated with 1e15 ions/cm2 demonstrates the highest magnetization value of 4.18 emu/g. The impact of edge-terminated structure and point defects like S-vacancies to induce room-temperature ferromagnetism (RTFM) is thoroughly examined.
采用化学气相沉积(CVD)生长的纳米级二硫化钼(MoS2)在低能量离子辐射后的磁性和电子结构变化得到了深入研究。通过拉曼光谱和X射线衍射(XRD)确定了纯六角形2-H相的形成。原始样品受到不同流强的氩(Ar)离子低能量辐射。拉曼光谱数据的综合分析表明,辐射后在样品中形成了晶格缺陷,如硫空位。场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)图像证实了原始样品中三角形片状结构的形成。随着辐射流强的增加,大片状结构开始碎裂成较小的片状结构,增加了边缘终止结构的数量。电子探针微分析仪(EPMA)分析验证了无磁性杂质的存在。卢瑟福背散射光谱仪(RBS)和X射线光电子光谱仪(XPS)的研究证实了硫空位在辐射后的形成。原始样品在室温下表现出抗磁性行为。随着离子辐射流强的增加,饱和磁化强度值增加,辐照离子数为1e15离子/cm2的样品表现出最高的磁化强度值为4.18emu/g。边缘终止结构和硫空位等点缺陷对诱导室温铁磁性(RTFM)的影响得到了彻底检查。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
化学气相沉积法制备的纳米级二硫化钼在受到低能量离子辐射后,其磁性和电子结构发生变化。研究通过拉曼光谱和X射线衍射确认形成了纯净的六角形2-H相,并发现离子辐射后产生了硫空位等晶格缺陷。随着辐射剂量的增加,大晶片开始碎裂成更小的晶片,增加了边缘终止结构数量。电子探针微分析仪分析确认无磁性杂质。硫空位形成的原因通过卢瑟福背散射光谱和X射线光电子光谱研究得到证实。样品的饱和磁化强度随着离子辐射剂量的增加而增加,受到离子辐射后的样品显示出最高的磁化强度为每克样品产生4.18emu的磁化强度。文中详细研究了边缘终止结构和硫空位等点缺陷对室温铁磁性的影响。
Key Takeaways
- CVD生长的纳米级二硫化钼在经过低能量离子辐射后,磁性和电子结构发生变化。
- 确认了纯净的六角形2-H相的形成。
- 拉曼光谱分析表明离子辐射后产生了硫空位等晶格缺陷。
- 随着辐射剂量的增加,大晶片碎裂成更小的晶片,边缘终止结构数量增加。
- 无磁性杂质的存在得到电子探针微分析仪的验证。
- 研究确认了硫空位在离子辐射后的形成机制。
点此查看论文截图

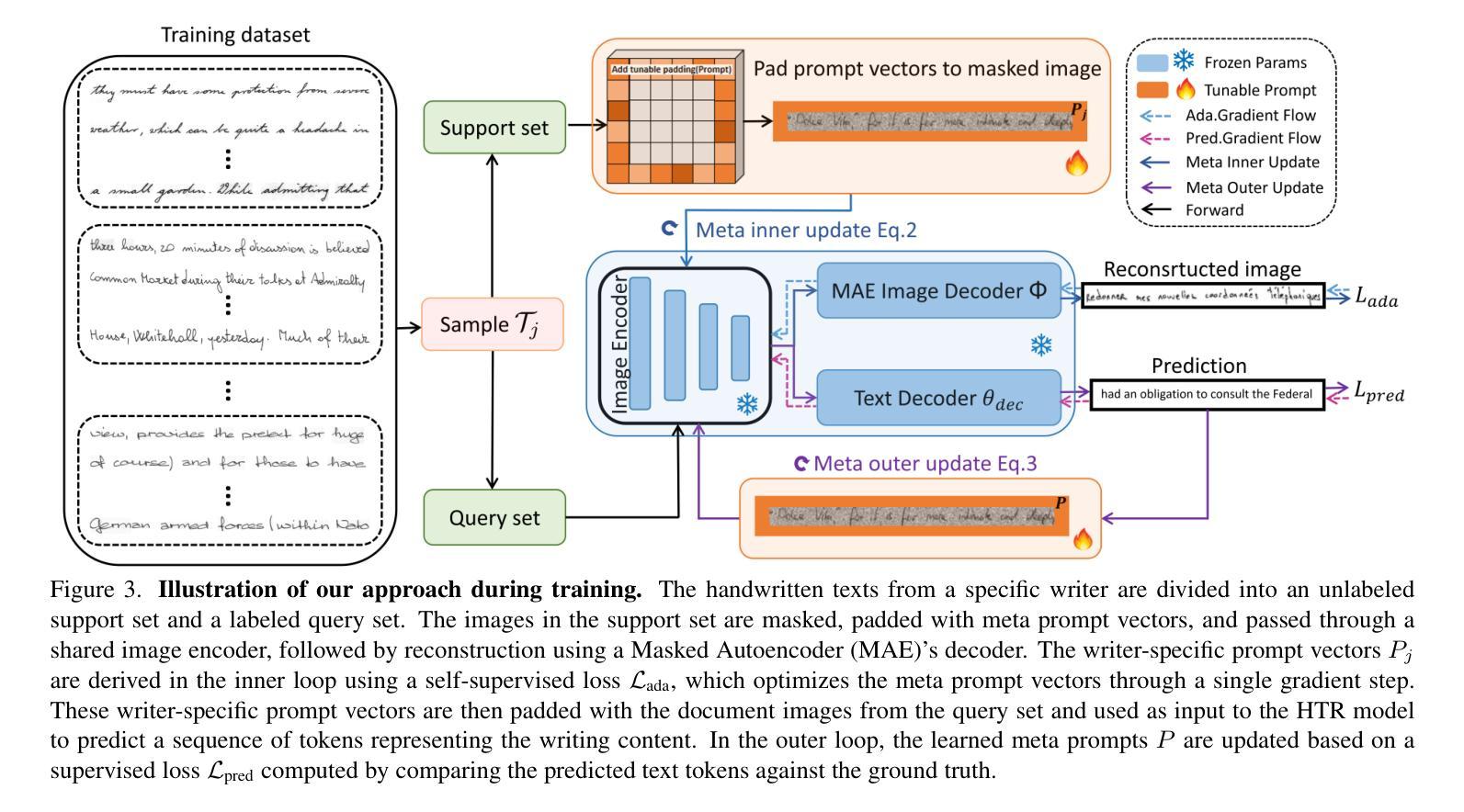
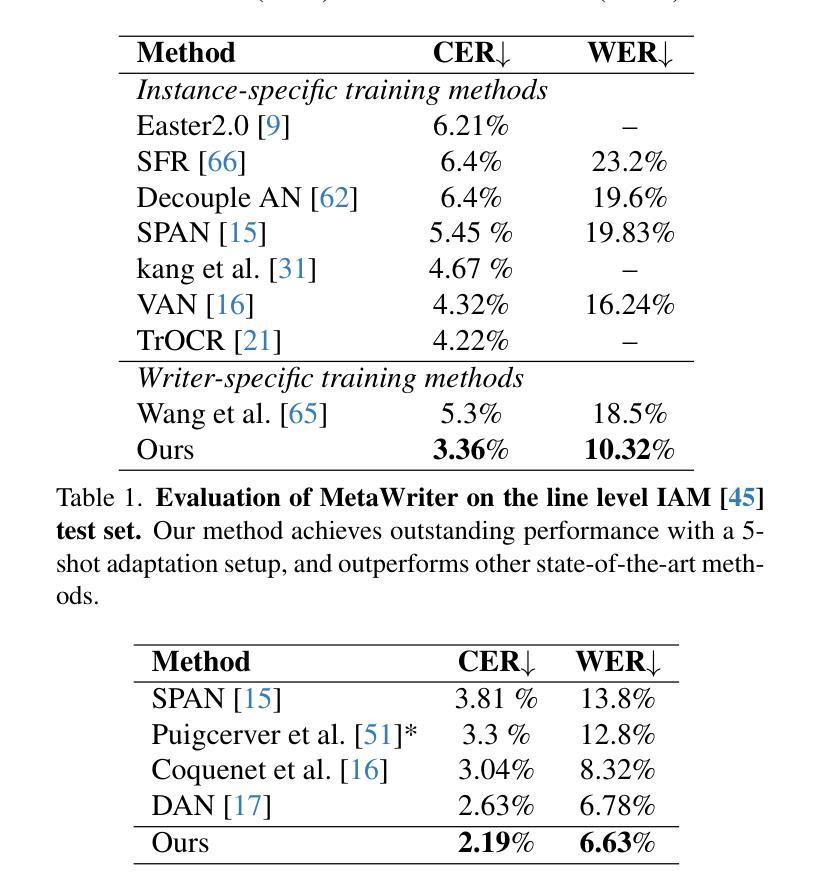
MetaWriter: Personalized Handwritten Text Recognition Using Meta-Learned Prompt Tuning
Authors:Wenhao Gu, Li Gu, Ching Yee Suen, Yang Wang
Recent advancements in handwritten text recognition (HTR) have enabled the effective conversion of handwritten text to digital formats. However, achieving robust recognition across diverse writing styles remains challenging. Traditional HTR methods lack writer-specific personalization at test time due to limitations in model architecture and training strategies. Existing attempts to bridge this gap, through gradient-based meta-learning, still require labeled examples and suffer from parameter-inefficient fine-tuning, leading to substantial computational and memory overhead. To overcome these challenges, we propose an efficient framework that formulates personalization as prompt tuning, incorporating an auxiliary image reconstruction task with a self-supervised loss to guide prompt adaptation with unlabeled test-time examples. To ensure self-supervised loss effectively minimizes text recognition error, we leverage meta-learning to learn the optimal initialization of the prompts. As a result, our method allows the model to efficiently capture unique writing styles by updating less than 1% of its parameters and eliminating the need for time-intensive annotation processes. We validate our approach on the RIMES and IAM Handwriting Database benchmarks, where it consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods while using 20x fewer parameters. We believe this represents a significant advancement in personalized handwritten text recognition, paving the way for more reliable and practical deployment in resource-constrained scenarios.
手写文本识别(HTR)的最新进展已经实现了手写文本向数字格式的有效转换。然而,实现在各种书写风格中的稳健识别仍然具有挑战性。传统HTR方法由于在模型架构和训练策略上的局限性,在测试时缺乏针对特定作者的个性化。现有的一些尝试通过梯度基础的元学习(Meta-Learning)来弥补这一差距,但依旧需要标注样本,并且在精细调整参数时效率低下,导致计算与内存负担巨大。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了一个高效的框架,将个性化表述为提示调整(Prompt Tuning),并结合一个辅助图像重建任务与自我监督损失来指导无标签测试样本的提示适应。为了确保自我监督损失能有效地最小化文本识别错误,我们利用元学习来学习提示的最优初始化。因此,我们的方法允许模型通过更新不到1%的参数来有效地捕捉独特的书写风格,并且无需耗时的人工标注过程。我们在RIMES和IAM手写数据库基准测试上验证了我们的方法,它始终优于之前的最先进方法,同时使用的参数少了20倍。我们相信这代表了个性化手写文本识别的重大进展,为资源受限的场景中更可靠、更实际的部署铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
手写文本识别(HTR)技术的最新进展实现了手写文本向数字格式的有效转换,但实现跨不同书写风格的稳健识别仍然具有挑战性。针对传统HTR方法缺乏测试时的个性化且存在模型架构和训练策略的局限性,以及现有尝试解决此问题的梯度元学习方法需要标注示例和参数调整不够高效的问题,本文提出了一种有效的框架。该框架将个性化表述为提示调整,并结合辅助图像重建任务和自监督损失来引导无标签测试例的提示适应。为确保自监督损失最小化文本识别误差,本文利用元学习来学习提示的最佳初始化。该方法允许模型通过更新不到1%的参数来高效捕捉独特的书写风格,并省去耗时标注过程。在RIMES和IAM手写数据库基准测试中,该方法持续优于先前最先进的方法,同时使用参数更少20倍。这标志着个性化手写文本识别的重大进展,为资源受限场景中更可靠、更实用的部署铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 近期手写文本识别(HTR)技术的进展实现了手写文本到数字格式的转换,但识别不同书写风格的挑战仍然存在。
- 传统HTR方法因模型架构和训练策略的局限性,缺乏测试时的个性化。
- 现有尝试通过梯度元学习弥补这一差距的方法仍需要标注示例,且参数调整不够高效。
- 本文提出的框架将个性化表述为提示调整,结合辅助图像重建任务和自监督损失引导无标签测试例的提示适应。
- 利用自监督损失和元学习来优化提示的初始化和提高模型性能。
- 该方法能高效捕捉独特书写风格,更新参数不到1%,并免去耗时标注过程。
点此查看论文截图


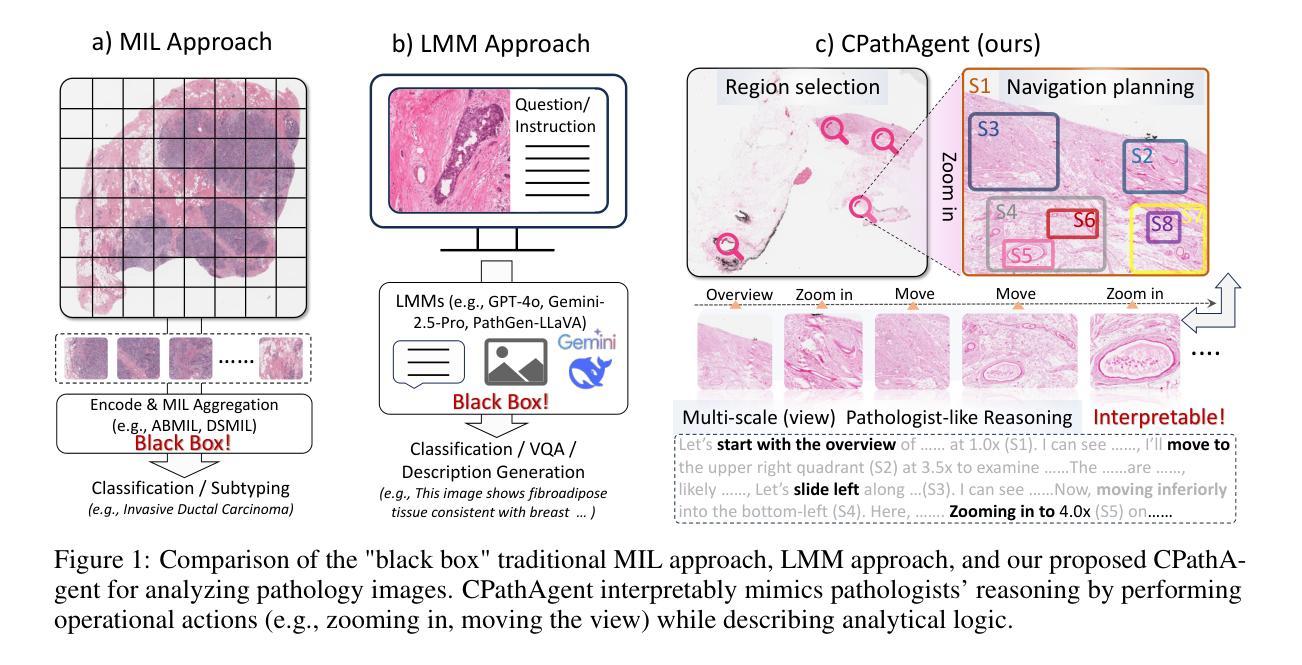
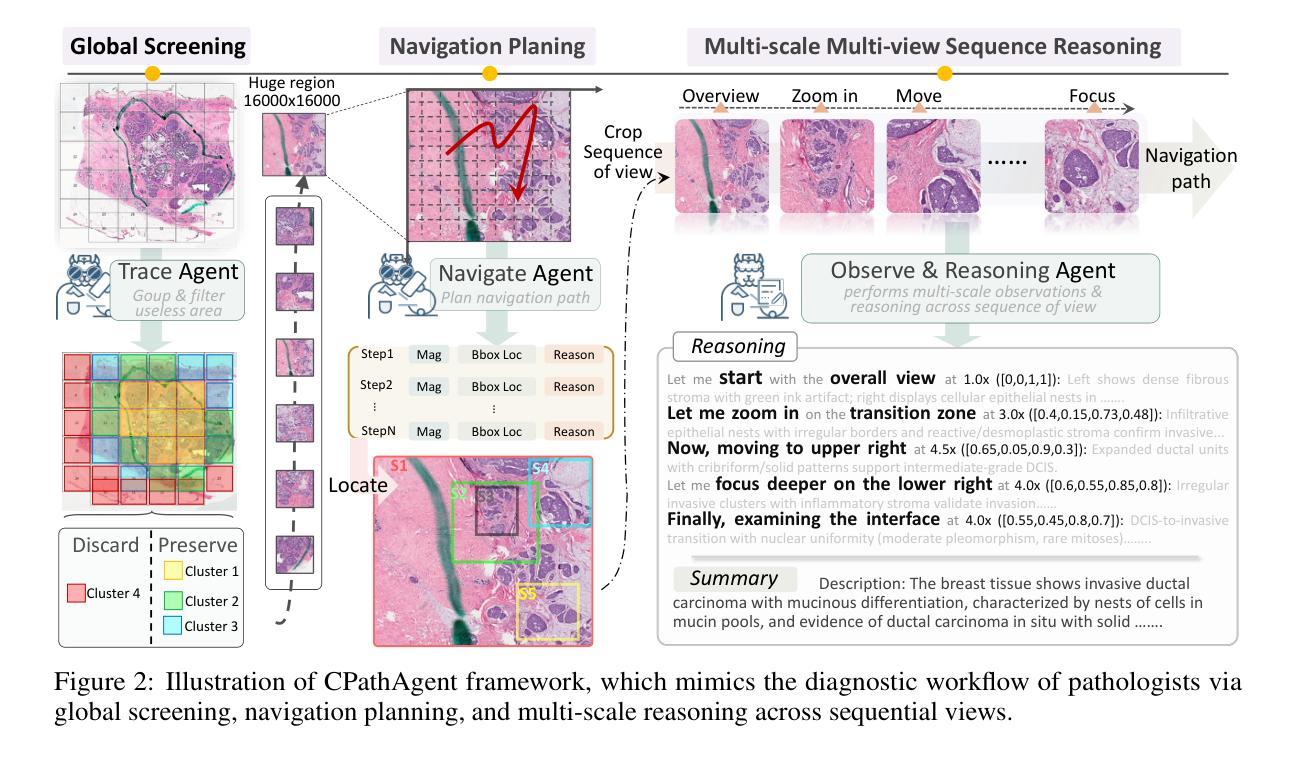
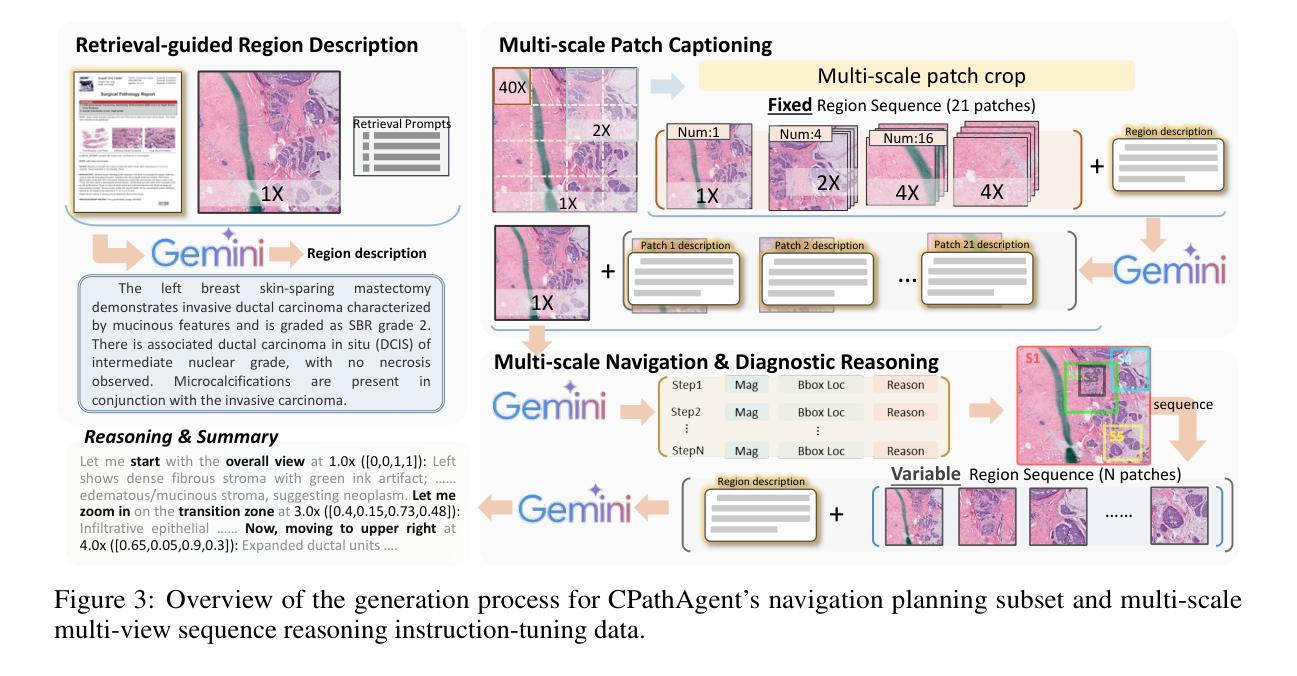
CPathAgent: An Agent-based Foundation Model for Interpretable High-Resolution Pathology Image Analysis Mimicking Pathologists’ Diagnostic Logic
Authors:Yuxuan Sun, Yixuan Si, Chenglu Zhu, Kai Zhang, Zhongyi Shui, Bowen Ding, Tao Lin, Lin Yang
Recent advances in computational pathology have led to the emergence of numerous foundation models. However, these approaches fail to replicate the diagnostic process of pathologists, as they either simply rely on general-purpose encoders with multi-instance learning for classification or directly apply multimodal models to generate reports from images. A significant limitation is their inability to emulate the diagnostic logic employed by pathologists, who systematically examine slides at low magnification for overview before progressively zooming in on suspicious regions to formulate comprehensive diagnoses. To address this gap, we introduce CPathAgent, an innovative agent-based model that mimics pathologists’ reasoning processes by autonomously executing zoom-in/out and navigation operations across pathology images based on observed visual features. To achieve this, we develop a multi-stage training strategy unifying patch-level, region-level, and whole-slide capabilities within a single model, which is essential for mimicking pathologists, who require understanding and reasoning capabilities across all three scales. This approach generates substantially more detailed and interpretable diagnostic reports compared to existing methods, particularly for huge region understanding. Additionally, we construct an expert-validated PathMMU-HR$^{2}$, the first benchmark for huge region analysis, a critical intermediate scale between patches and whole slides, as diagnosticians typically examine several key regions rather than entire slides at once. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CPathAgent consistently outperforms existing approaches across three scales of benchmarks, validating the effectiveness of our agent-based diagnostic approach and highlighting a promising direction for the future development of computational pathology.
近期计算病理学领域的进展催生了许多基础模型。然而,这些方法无法复制病理医生的诊断过程,因为它们要么简单地依赖于具有多实例学习功能的一般编码器进行分类,要么直接将多模式模型应用于图像生成报告。一个显著的局限性在于,它们无法模拟病理医生的诊断逻辑,即系统性地在低倍镜下观察切片以获取概览,然后逐步放大可疑区域以做出全面的诊断。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了CPathAgent,这是一个基于创新的智能体模型,通过自主执行放大/缩小和导航操作来模拟病理医生的推理过程,在病理图像上基于观察到的视觉特征进行跨尺度操作。为了实现这一点,我们开发了一种多阶段训练策略,在一个单一模型中统一了补丁级别、区域级别和整个幻灯片级别的能力,这对于模拟病理医生来说至关重要,他们需要在这三个尺度上具备理解和推理能力。该方法生成的诊断报告比现有方法更为详细和可解释,特别是对于巨大区域的理解。此外,我们构建了经过专家验证的PathMMU-HR$^{2}$,这是首个针对巨大区域分析的基准测试,是补丁和整个幻灯片之间的一个重要中间尺度,因为诊断通常需要对几个关键区域而非整个幻灯片进行检查。大量实验表明,CPathAgent在三个尺度的基准测试中始终优于现有方法,验证了我们的基于智能体的诊断方法的有效性,并指出了计算病理学未来发展的有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 49 pages, 33 figures
Summary
近期计算病理学领域的进展催生出众多基础模型,但现有方法无法复制病理医师的诊断过程。为此,我们提出CPathAgent,基于视觉特征进行自主缩放和导航操作,模拟病理医师的推理过程。通过多阶段训练策略,将斑块、区域和整个幻灯片的能力统一于单一模型中,生成更详细、可解释的诊断报告。同时,我们建立了专家验证的PathMMU-HR$^{2}$基准测试,用于评估巨大区域的分析能力。实验证明,CPathAgent在三个基准测试中均表现优异,验证了其诊断效果和前景。
Key Takeaways
- 计算病理学领域涌现出众多基础模型,但现有方法无法完全模拟病理医师的诊断过程。
- CPathAgent通过自主执行缩放和导航操作,模拟病理医师的推理过程。
- 多阶段训练策略实现了斑块、区域和整个幻灯片的统一能力模型,提高诊断的全面性。
- CPathAgent生成的诊断报告更加详细和可解释。
- PathMMU-HR$^{2}$基准测试的建立,填补了巨大区域分析领域的空白。
- CPathAgent在三个基准测试中表现优异,验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

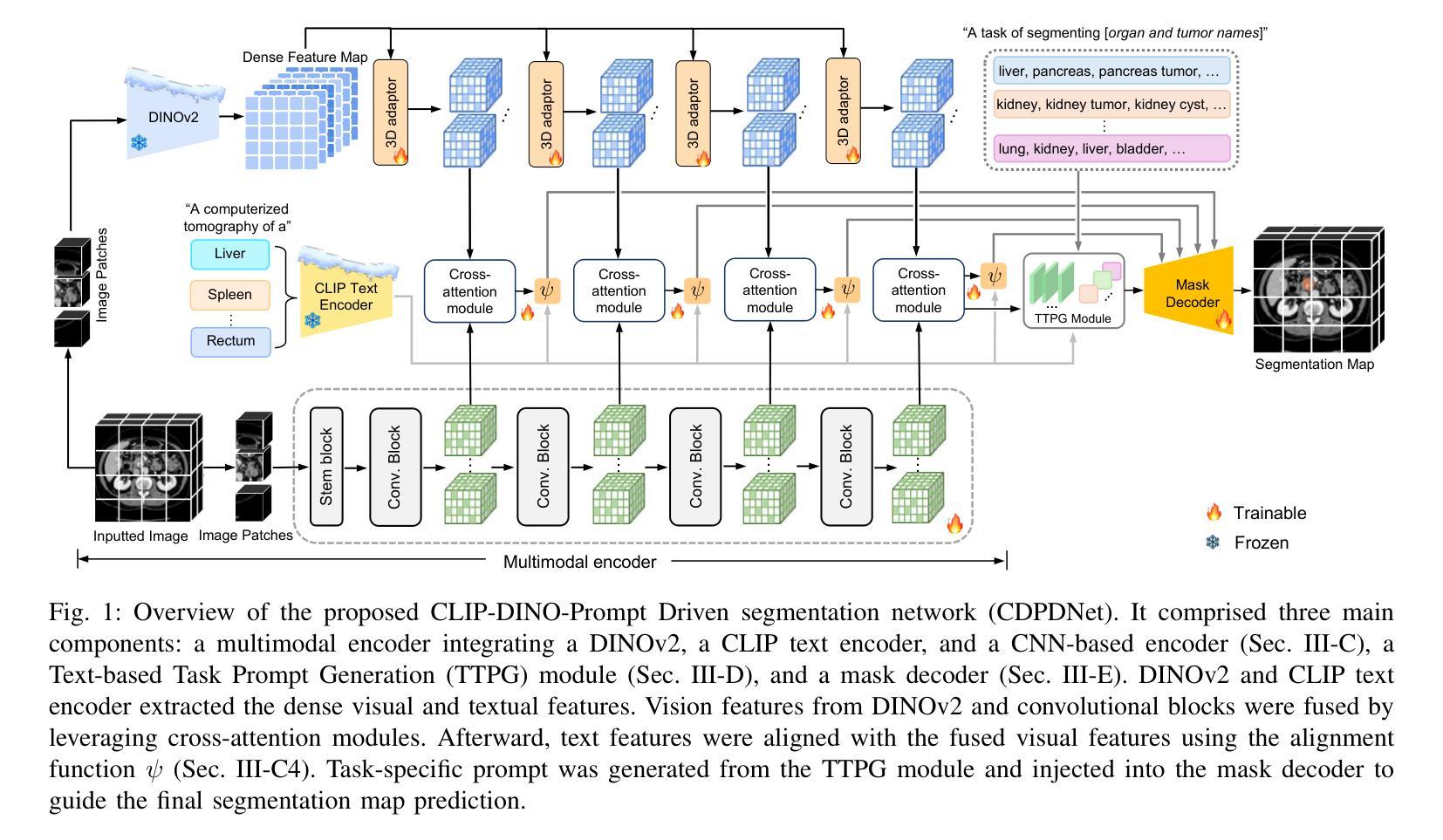
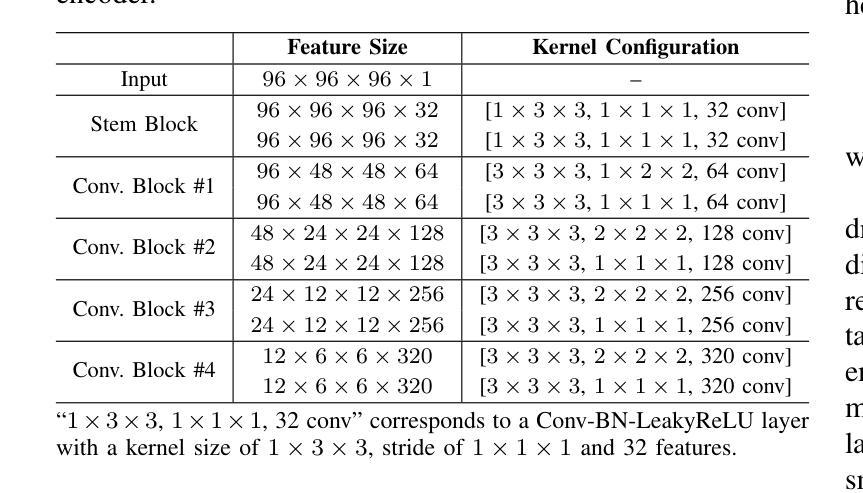
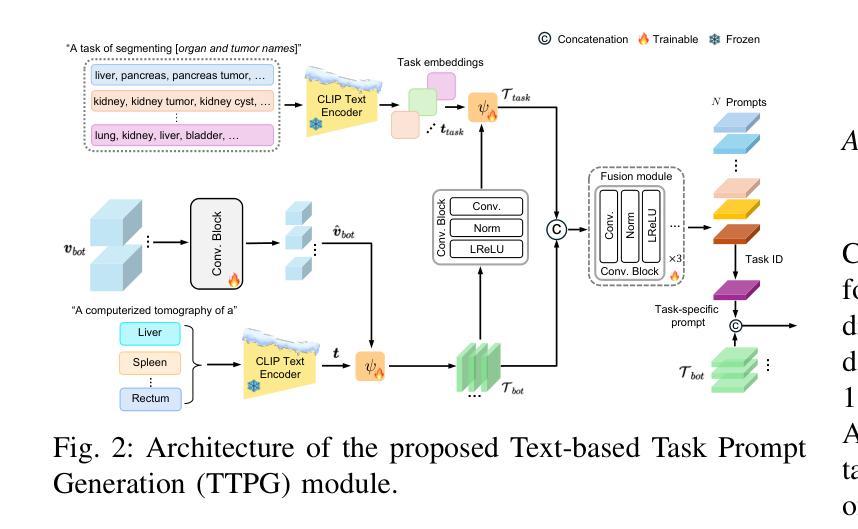
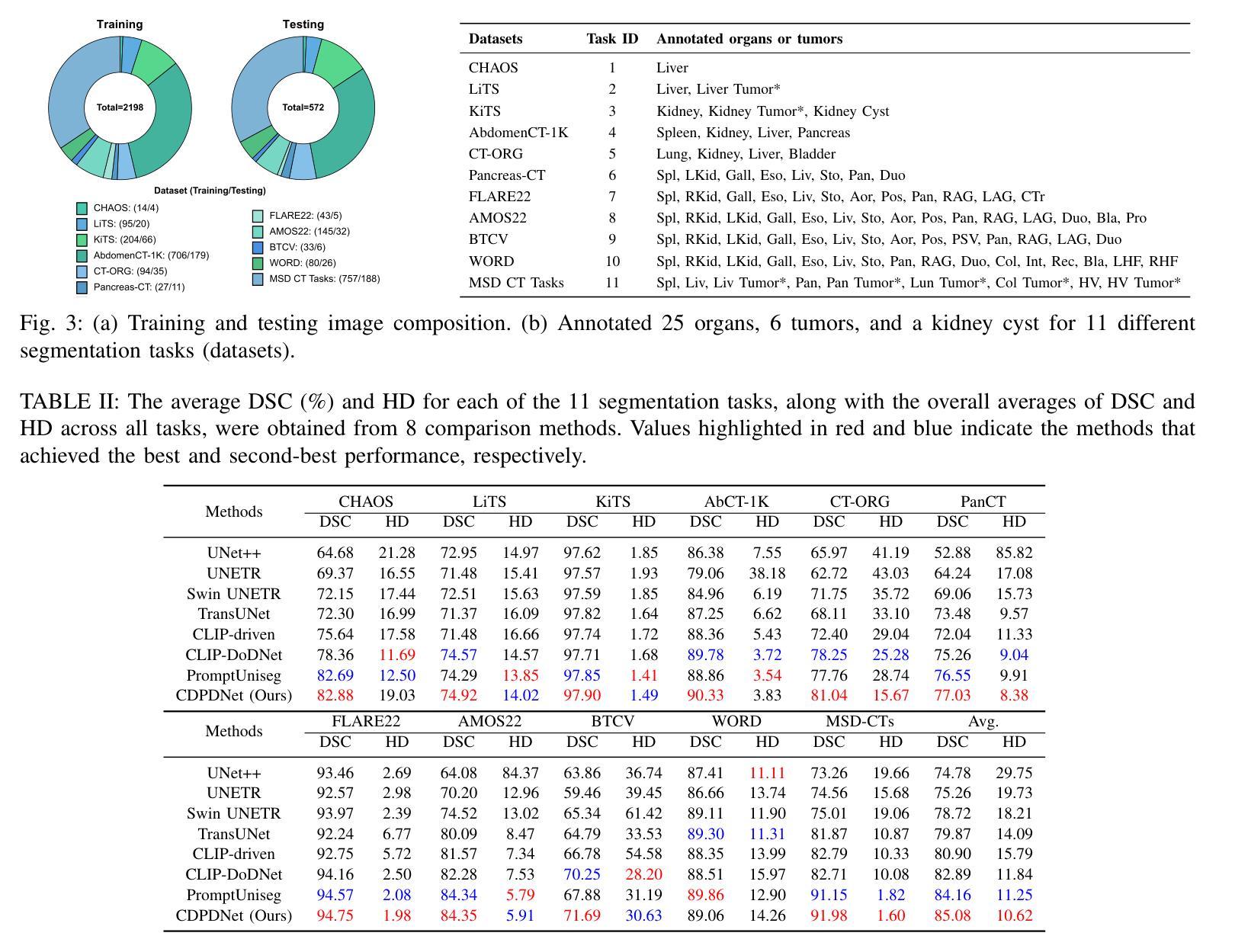
CDPDNet: Integrating Text Guidance with Hybrid Vision Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiong Wu, Yang Xing, Boxiao Yu, Wei Shao, Kuang Gong
Most publicly available medical segmentation datasets are only partially labeled, with annotations provided for a subset of anatomical structures. When multiple datasets are combined for training, this incomplete annotation poses challenges, as it limits the model’s ability to learn shared anatomical representations among datasets. Furthermore, vision-only frameworks often fail to capture complex anatomical relationships and task-specific distinctions, leading to reduced segmentation accuracy and poor generalizability to unseen datasets. In this study, we proposed a novel CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network (CDPDNet), which combined a self-supervised vision transformer with CLIP-based text embedding and introduced task-specific text prompts to tackle these challenges. Specifically, the framework was constructed upon a convolutional neural network (CNN) and incorporated DINOv2 to extract both fine-grained and global visual features, which were then fused using a multi-head cross-attention module to overcome the limited long-range modeling capability of CNNs. In addition, CLIP-derived text embeddings were projected into the visual space to help model complex relationships among organs and tumors. To further address the partial label challenge and enhance inter-task discriminative capability, a Text-based Task Prompt Generation (TTPG) module that generated task-specific prompts was designed to guide the segmentation. Extensive experiments on multiple medical imaging datasets demonstrated that CDPDNet consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art segmentation methods. Code and pretrained model are available at: https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git.
大部分公开可用的医学分割数据集仅部分标注,只为部分解剖结构提供注释。当多个数据集组合进行训练时,这种不完全的注释带来了挑战,因为它限制了模型在数据集之间学习共享解剖表征的能力。此外,仅依赖视觉的框架往往无法捕捉复杂的解剖关系和任务特定区别,导致分割准确度降低,对未见数据集的泛化能力较差。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新颖的CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network(CDPDNet),它将自我监督的视觉变压器与CLIP基于的文本嵌入相结合,并引入了任务特定的文本提示来解决这些挑战。具体来说,该框架建立在卷积神经网络(CNN)之上,融入了DINOv2以提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,然后使用多头交叉注意模块融合这些特征,以克服CNN有限的长期建模能力。此外,CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投射到视觉空间中,以帮助建模器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。为了进一步解决部分标签挑战并增强任务间的判别能力,设计了一个基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块,以生成特定任务的提示来指导分割。在多个医学影像数据集上的广泛实验表明,CDPDNet持续优于现有的最先进的分割方法。代码和预先训练好的模型可在:https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动分割网络(CDPDNet),结合自监督视觉变压器与CLIP文本嵌入技术,通过特定任务文本提示来解决医学图像分割中面临的标注不完整和复杂解剖关系捕捉难题。CDPDNet采用CNN结合DINOv2技术提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,并利用多头交叉注意力模块进行特征融合,以克服CNN的长期建模能力限制。同时,利用CLIP衍生的文本嵌入将文本信息投影到视觉空间,帮助模型理解器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。为解决部分标注问题并增强任务间的判别能力,设计了一种基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块来指导分割。在多个医学图像数据集上的实验表明,CDPDNet显著优于现有最先进的分割方法。
Key Takeaways
- CDPDNet结合自监督视觉变压器和CLIP文本嵌入技术,解决医学图像分割中的标注不完整和复杂解剖关系捕捉难题。
- CDPDNet采用CNN和DINOv2技术提取视觉特征,实现精细粒度和全局特征的融合。
- 多头交叉注意力模块克服CNN的长期建模能力限制。
- CLIP衍生的文本嵌入帮助模型理解器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。
- 引入基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块,解决部分标注问题并增强任务间的判别能力。
- 在多个医学图像数据集上,CDPDNet的实验结果显著优于现有最先进的分割方法。
点此查看论文截图
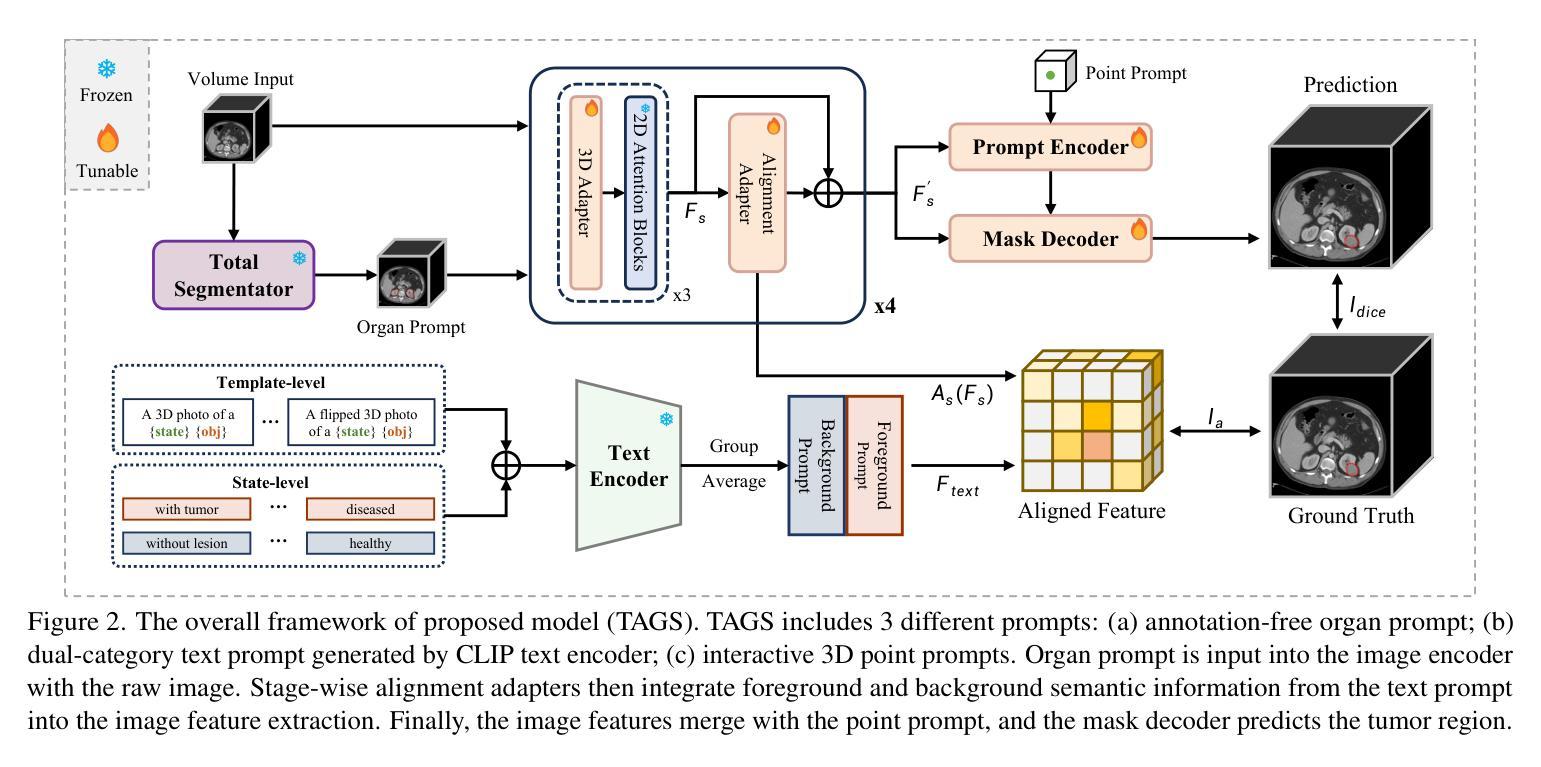
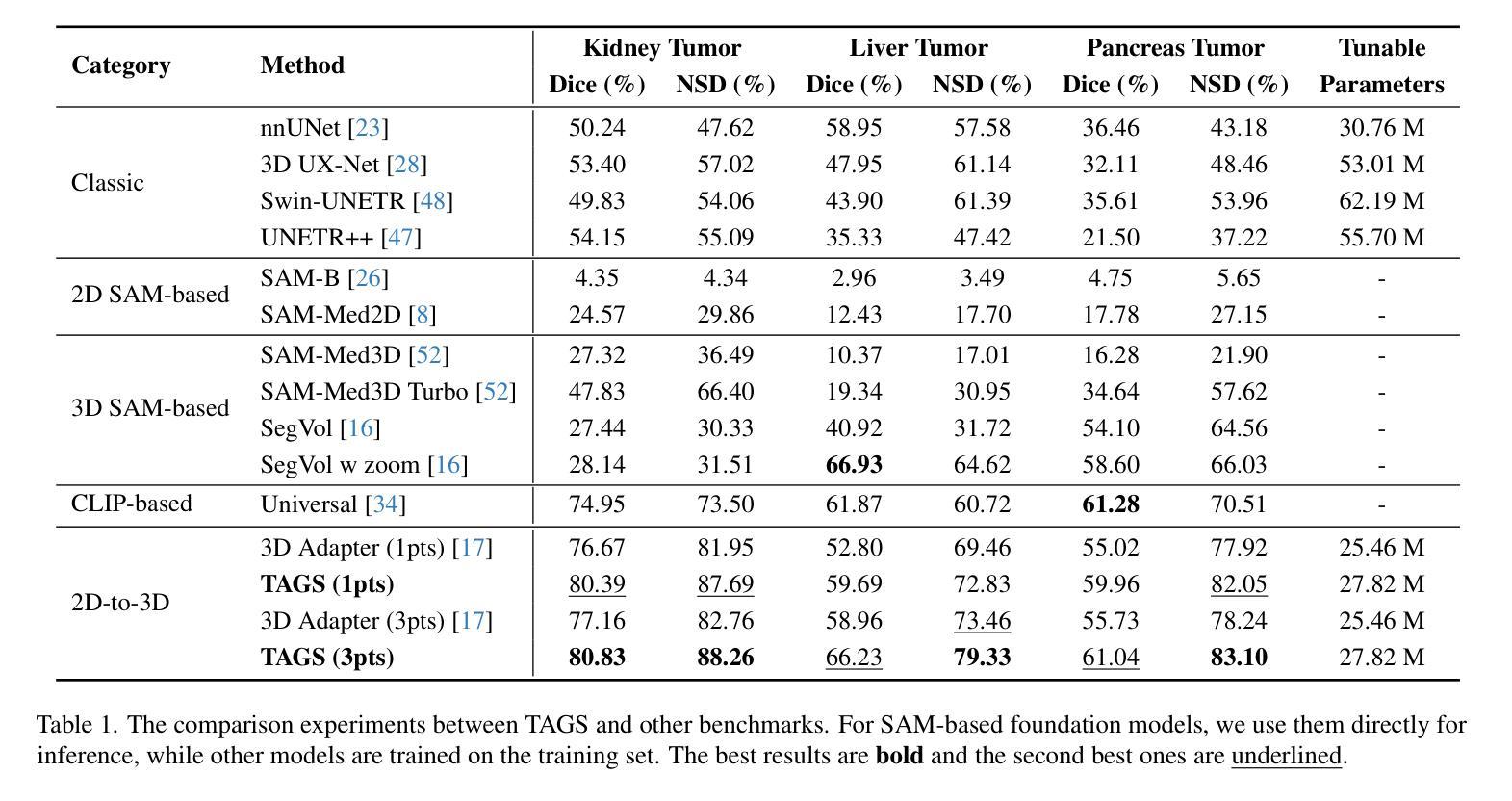
TAGS: 3D Tumor-Adaptive Guidance for SAM
Authors:Sirui Li, Linkai Peng, Zheyuan Zhang, Gorkem Durak, Ulas Bagci
Foundation models (FMs) such as CLIP and SAM have recently shown great promise in image segmentation tasks, yet their adaptation to 3D medical imaging-particularly for pathology detection and segmentation-remains underexplored. A critical challenge arises from the domain gap between natural images and medical volumes: existing FMs, pre-trained on 2D data, struggle to capture 3D anatomical context, limiting their utility in clinical applications like tumor segmentation. To address this, we propose an adaptation framework called TAGS: Tumor Adaptive Guidance for SAM, which unlocks 2D FMs for 3D medical tasks through multi-prompt fusion. By preserving most of the pre-trained weights, our approach enhances SAM’s spatial feature extraction using CLIP’s semantic insights and anatomy-specific prompts. Extensive experiments on three open-source tumor segmentation datasets prove that our model surpasses the state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models (+46.88% over nnUNet), interactive segmentation frameworks, and other established medical FMs, including SAM-Med2D, SAM-Med3D, SegVol, Universal, 3D-Adapter, and SAM-B (at least +13% over them). This highlights the robustness and adaptability of our proposed framework across diverse medical segmentation tasks.
最近,CLIP和SAM等基础模型(FMs)在图像分割任务中显示出巨大的潜力,然而它们在适应三维医学成像方面的应用,特别是在病理检测和分割方面仍然被研究得不够深入。自然图像和医学体积之间存在领域差距的问题由此产生了一个关键挑战:现有的在二维数据上预训练的FMs在捕获三维解剖上下文方面存在困难,这在肿瘤分割等临床应用中限制了它们的实用性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种名为TAGS的适应框架:SAM的肿瘤自适应指导。通过多提示融合,我们的框架解锁了二维FMs在三维医学任务中的应用。通过保留大部分预训练权重,我们的方法利用CLIP的语义洞察力和解剖特定提示,增强了SAM的空间特征提取能力。在三个开源肿瘤分割数据集上的大量实验证明,我们的模型超越了最先进的医学图像分割模型(相对于nnUNet提高+46.88%),交互式分割框架和其他既定的医学FMs,包括SAM-Med2D、SAM-Med3D、SegVol、Universal、3D-Adapter和SAM-B(至少相对于它们提高+13%)。这突显了我们提出的框架在不同医学分割任务中的稳健性和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在自然图像领域表现良好的Foundation模型(FMs)在3D医学成像上的应用挑战。通过提出名为TAGS的适应框架,实现了对SAM模型的优化,使其在肿瘤分割等临床应用中表现更好。该框架通过多提示融合技术,利用CLIP的语义提示和解剖特定提示,提高SAM的空间特征提取能力。在三个开源肿瘤分割数据集上的实验证明,该模型优于现有医学图像分割模型和其他建立的医学FMs。
Key Takeaways
- Foundation模型(FMs)在图像分割任务中展现出巨大潜力,但在3D医学成像上的适应度仍需提高。
- 现有FMs面临从自然图像到医学体积数据的领域差距问题,难以捕捉3D解剖上下文信息。
- 提出的TAGS框架成功解锁了SAM模型在3D医学任务中的潜力,通过多提示融合技术提高其空间特征提取能力。
- TAGS框架保留了大部分预训练权重,并结合了CLIP的语义提示和解剖特定提示。
- 在三个开源肿瘤分割数据集上的实验表明,TAGS框架表现超越现有医学图像分割模型和其他医学FMs。
- TAGS框架的鲁棒性和适应性在不同医学分割任务中得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图

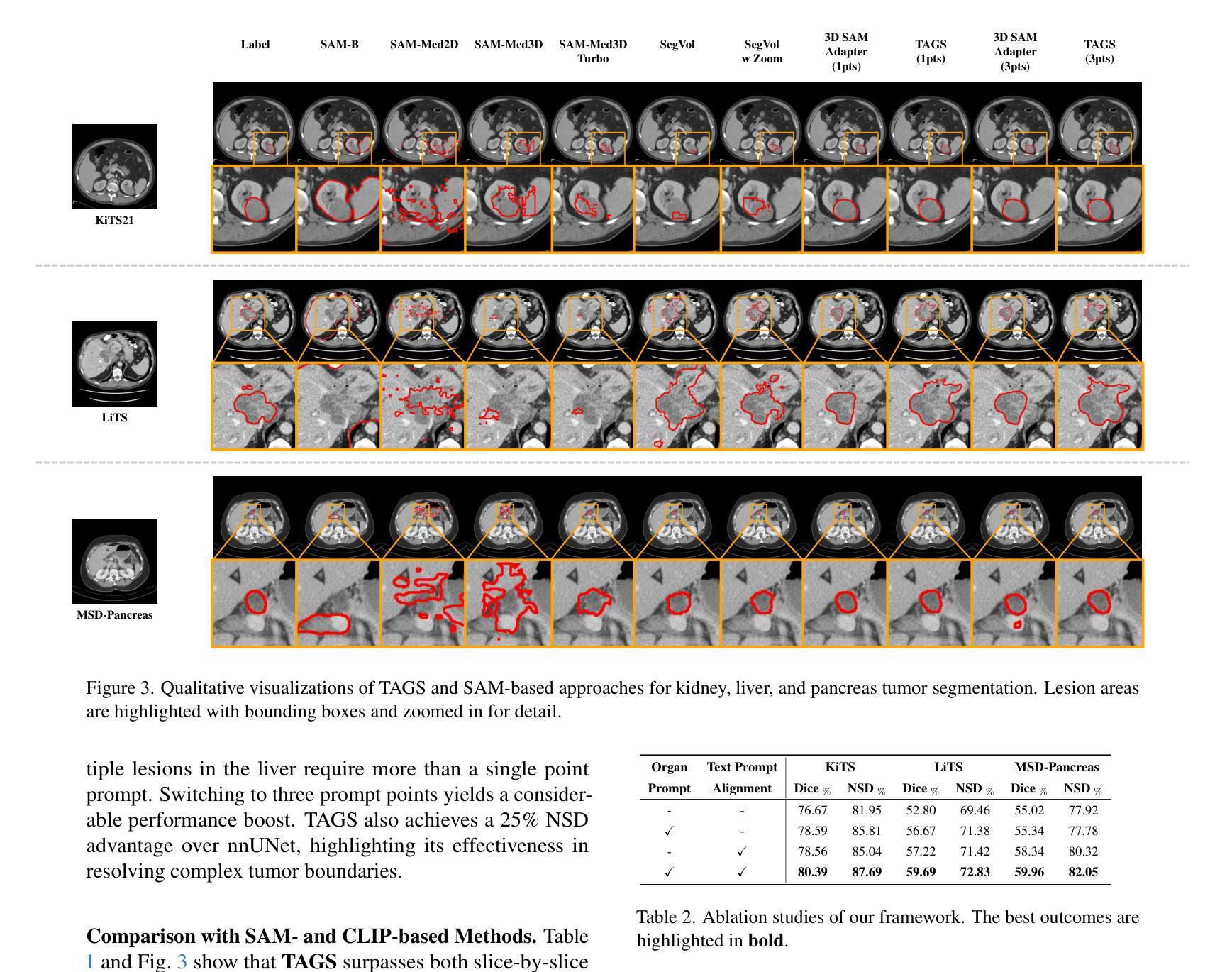
Hypergraph Tversky-Aware Domain Incremental Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation with Missing Modalities
Authors:Junze Wang, Lei Fan, Weipeng Jing, Donglin Di, Yang Song, Sidong Liu, Cong Cong
Existing methods for multimodal MRI segmentation with missing modalities typically assume that all MRI modalities are available during training. However, in clinical practice, some modalities may be missing due to the sequential nature of MRI acquisition, leading to performance degradation. Furthermore, retraining models to accommodate newly available modalities can be inefficient and may cause overfitting, potentially compromising previously learned knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose Replay-based Hypergraph Domain Incremental Learning (ReHyDIL) for brain tumor segmentation with missing modalities. ReHyDIL leverages Domain Incremental Learning (DIL) to enable the segmentation model to learn from newly acquired MRI modalities without forgetting previously learned information. To enhance segmentation performance across diverse patient scenarios, we introduce the Cross-Patient Hypergraph Segmentation Network (CHSNet), which utilizes hypergraphs to capture high-order associations between patients. Additionally, we incorporate Tversky-Aware Contrastive (TAC) loss to effectively mitigate information imbalance both across and within different modalities. Extensive experiments on the BraTS2019 dataset demonstrate that ReHyDIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an improvement of over 2% in the Dice Similarity Coefficient across various tumor regions.
现有的多模态MRI分割缺失模态的方法通常假设在训练期间所有MRI模态都是可用的。然而,在临床实践中,由于MRI采集的序列性质,某些模态可能会缺失,导致性能下降。此外,为了容纳新可用的模态而重新训练模型可能效率低下,并可能导致过拟合,从而可能损害之前学到的知识。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了基于重播的超图域增量学习(ReHyDIL)方法,用于具有缺失模态的脑肿瘤分割。ReHyDIL利用域增量学习(DIL)使分割模型能够从新获取的MRI模态中学习,而不会忘记之前学到的信息。为了提高不同患者场景下的分割性能,我们引入了跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet),该网络利用超图来捕捉患者之间的高阶关联。此外,我们结合了Tversky感知对比(TAC)损失,以有效地缓解不同模态之间和内部的信息不平衡问题。在BraTS2019数据集上的广泛实验表明,ReHyDIL优于最新方法,在各种肿瘤区域的Dice相似系数上提高了超过2%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 Early Accept. The code is available at https://github.com/reeive/ReHyDIL
Summary
本文提出一种基于回放和超图域的增量学习(ReHyDIL)方法,用于处理MRI图像中缺失模态的情况下的脑肿瘤分割问题。该方法结合了域增量学习(DIL)技术,使得分割模型能够在没有忘记先前知识的情况下学习新获取的MRI模态。通过引入跨患者超图分割网络(CHSNet)和Tversky感知对比损失(TAC loss),提高了不同患者场景下的分割性能。在BraTS2019数据集上的实验表明,ReHyDIL在Dice相似系数上较现有方法提高了超过2%。
Key Takeaways
- ReHyDIL方法能够处理MRI图像中缺失模态的情况,提高脑肿瘤分割的准确性。
- ReHyDIL结合了域增量学习(DIL)技术,使得模型能够学习新获取的MRI模态而不忘记先前知识。
- CHSNet网络通过利用超图捕捉患者之间的高阶关联,提高了分割性能。
- Tversky感知对比损失(TAC loss)有效地缓解了不同模态间和内部的信息不平衡问题。
- ReHyDIL在BraTS2019数据集上的实验表现优于现有方法,Dice相似系数提高了超过2%。
- 该方法能够应对MRI图像获取过程中的序贯性导致的模态缺失问题。
点此查看论文截图

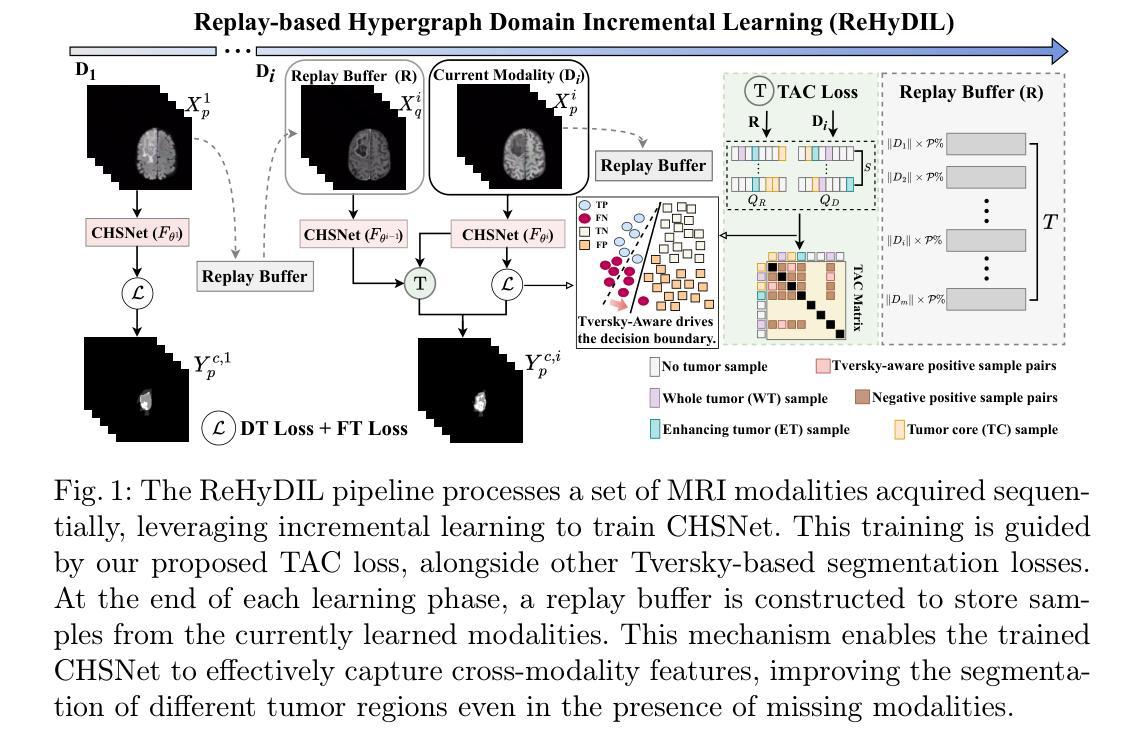
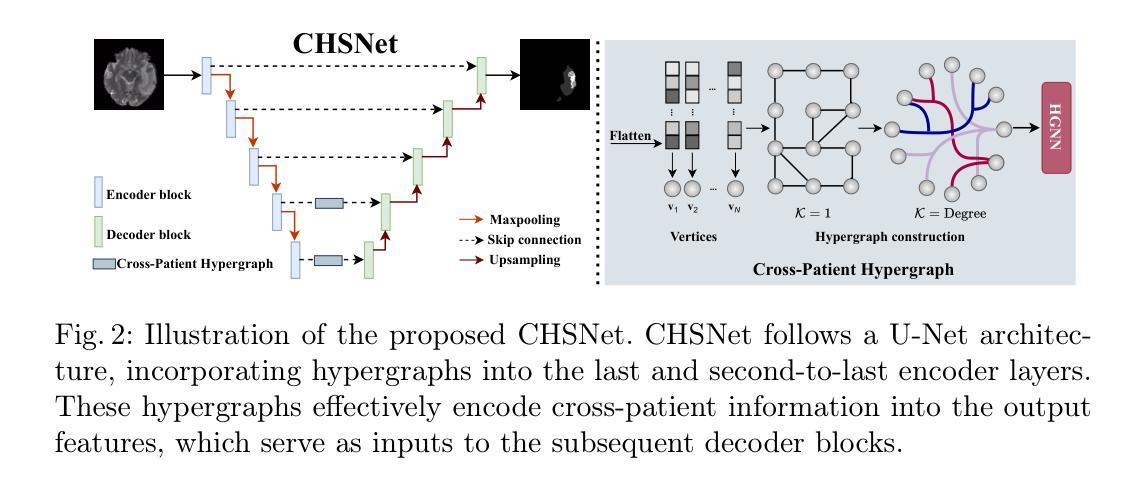
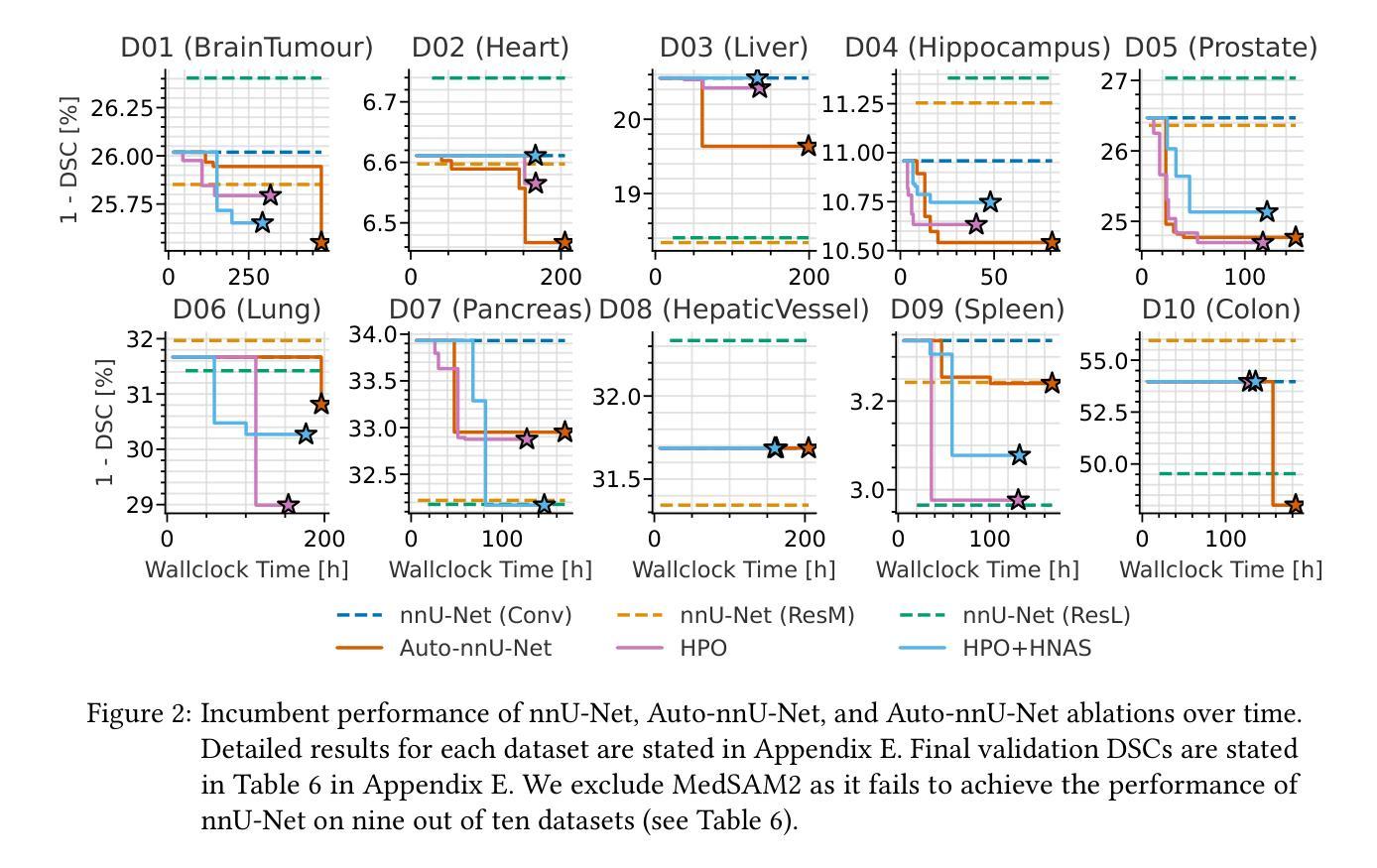
Auto-nnU-Net: Towards Automated Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jannis Becktepe, Leona Hennig, Steffen Oeltze-Jafra, Marius Lindauer
Medical Image Segmentation (MIS) includes diverse tasks, from bone to organ segmentation, each with its own challenges in finding the best segmentation model. The state-of-the-art AutoML-related MIS-framework nnU-Net automates many aspects of model configuration but remains constrained by fixed hyperparameters and heuristic design choices. As a full-AutoML framework for MIS, we propose Auto-nnU-Net, a novel nnU-Net variant enabling hyperparameter optimization (HPO), neural architecture search (NAS), and hierarchical NAS (HNAS). Additionally, we propose Regularized PriorBand to balance model accuracy with the computational resources required for training, addressing the resource constraints often faced in real-world medical settings that limit the feasibility of extensive training procedures. We evaluate our approach across diverse MIS datasets from the well-established Medical Segmentation Decathlon, analyzing the impact of AutoML techniques on segmentation performance, computational efficiency, and model design choices. The results demonstrate that our AutoML approach substantially improves the segmentation performance of nnU-Net on 6 out of 10 datasets and is on par on the other datasets while maintaining practical resource requirements. Our code is available at https://github.com/automl/AutoNNUnet.
医学图像分割(MIS)包括从骨骼到器官分割等多样化的任务,每个任务在寻找最佳分割模型时都面临自己的挑战。目前最先进的与AutoML相关的MIS框架nnU-Net能够自动化模型配置的许多方面,但仍然受到固定超参数和启发式设计选择的限制。作为MIS的全自动机器学习(AutoML)框架,我们提出了Auto-nnU-Net,这是一种新型的nnU-Net变体,能够实现超参数优化(HPO)、神经网络架构搜索(NAS)和分层NAS(HNAS)。此外,我们提出了正则化PriorBand,以平衡模型精度与训练所需的计算资源,解决现实医学环境中经常面临的资源约束问题,这些问题限制了广泛训练程序的可行性。我们在经过充分验证的医学分割十项全能赛的多个人MIS数据集上评估了我们的方法,分析了AutoML技术对分割性能、计算效率和模型设计选择的影响。结果表明,我们的AutoML方法在10个数据集中的6个数据集上显著提高了nnU-Net的分割性能,在其他数据集上表现相当,同时保持了实际的资源需求。我们的代码可在https://github.com/automl/AutoNNUnet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages, 19 figures. Accepted for publication at AutoML 2025
摘要
提出一种全自动医学图像分割框架Auto-nnU-Net,基于nnU-Net进行超参数优化、神经网络架构搜索和分层架构搜索,以提高模型在多种医学图像分割任务上的性能。同时引入Regularized PriorBand方法平衡模型精度与训练所需计算资源,以应对实际医疗环境中资源限制的问题。在Medical Segmentation Decathlon多个数据集上进行的实验表明,该AutoML方法可显著提高nnU-Net在6个数据集上的分割性能,并在其他数据集上表现相当,同时满足实际资源需求。
关键见解
- Auto-nnU-Net框架扩展了nnU-Net,增加了超参数优化、神经网络架构搜索和分层架构搜索功能,适用于多种医学图像分割任务。
- Regularized PriorBand方法平衡了模型精度和计算资源需求,适应了医学环境中资源限制的挑战。
- 相较于nnU-Net,Auto-nnU-Net在多数医学图像分割数据集上表现出更高的性能。
- 新型框架能够自动化配置模型,降低了手动调整超参数的需求。
- 该框架的实用性和高效性满足实际医学图像分割的需求。
- Auto-nnU-Net的代码已公开发布,便于其他研究者使用和改进。
- 研究结果对医学图像分割的自动化和性能提升有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

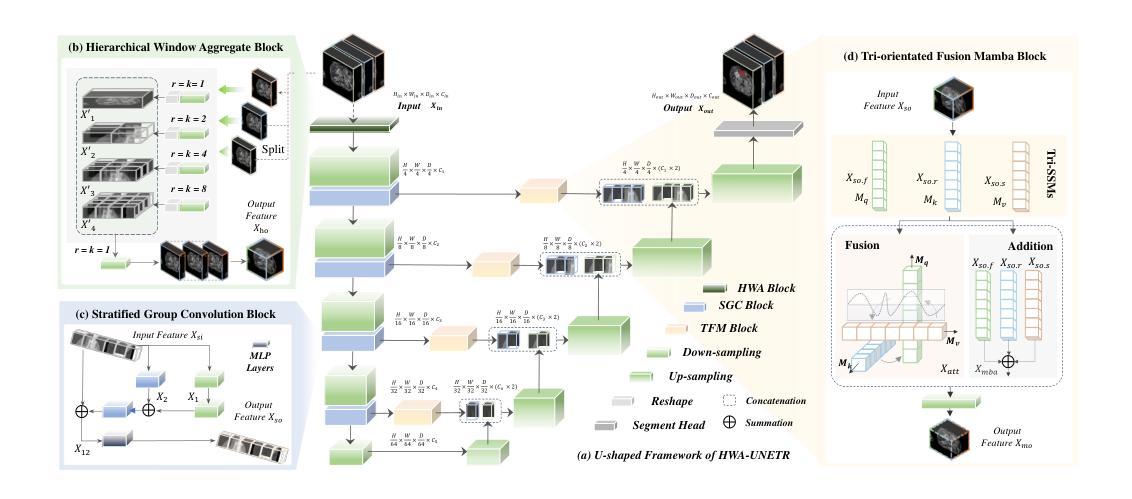
HWA-UNETR: Hierarchical Window Aggregate UNETR for 3D Multimodal Gastric Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Jiaming Liang, Lihuan Dai, Xiaoqi Sheng, Xiangguang Chen, Chun Yao, Guihua Tao, Qibin Leng, Hongmin Cai, Xi Zhong
Multimodal medical image segmentation faces significant challenges in the context of gastric cancer lesion analysis. This clinical context is defined by the scarcity of independent multimodal datasets and the imperative to amalgamate inherently misaligned modalities. As a result, algorithms are constrained to train on approximate data and depend on application migration, leading to substantial resource expenditure and a potential decline in analysis accuracy. To address those challenges, we have made two major contributions: First, we publicly disseminate the GCM 2025 dataset, which serves as the first large-scale, open-source collection of gastric cancer multimodal MRI scans, featuring professionally annotated FS-T2W, CE-T1W, and ADC images from 500 patients. Second, we introduce HWA-UNETR, a novel 3D segmentation framework that employs an original HWA block with learnable window aggregation layers to establish dynamic feature correspondences between different modalities’ anatomical structures, and leverages the innovative tri-orientated fusion mamba mechanism for context modeling and capturing long-range spatial dependencies. Extensive experiments on our GCM 2025 dataset and the publicly BraTS 2021 dataset validate the performance of our framework, demonstrating that the new approach surpasses existing methods by up to 1.68% in the Dice score while maintaining solid robustness. The dataset and code are public via https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR.
在胃癌病灶分析的背景下,多模态医学图像分割面临着巨大的挑战。这种临床背景的特点是缺乏独立的多模态数据集,以及必须将本质上不对齐的模式融合起来的迫切需求。因此,算法受限于在近似数据上进行训练,并依赖于应用迁移,导致资源消耗巨大,分析精度可能下降。为了应对这些挑战,我们做出了两大贡献:首先,我们公开发布了GCM 2025数据集,这是首个大规模、开源的胃癌多模态MRI扫描数据集,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像。其次,我们引入了HWA-UNETR,这是一种新型的3D分割框架,采用可学习的窗口聚合层构成原始HWA块,以在不同模态的解剖结构之间建立动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的tri-orientated融合mamba机制进行上下文建模和捕捉长期空间依赖性。在我们的GCM 2025数据集和公开的BraTS 2021数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的框架性能,证明新方法在Dice得分上最多提高了1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been provisionally accepted for MICCAI 2025
摘要
胃癌病灶分析的多模态医学图像分割面临挑战,包括缺乏独立多模态数据集和需要融合固有错位模态的必要性。为此,本研究贡献了两个重要成果:一是公开了GCM 2025数据集,该数据集为首个公开的大规模胃癌多模态MRI扫描数据集,包含来自500名患者的专业注释FS-T2W、CE-T1W和ADC图像;二是引入了HWA-UNETR,一种新型的3D分割框架,采用可学习的窗口聚合层建立不同模态解剖结构之间的动态特征对应关系,并利用创新的三角融合策略进行上下文建模和捕捉长期空间依赖性。在GCM 2025数据集和公开BraTS 2021数据集上的实验验证了该框架的性能,新方法的Dice得分率提高了高达1.68%,同时保持了稳健性。数据集和代码已公开在https://github.com/JeMing-creater/HWA-UNETR。
关键见解
- 多模态医学图像分割在胃癌病灶分析中面临挑战,主要由于缺乏独立多模态数据集和需要融合不同模态的必要性。
- 公开了GCM 2025数据集,为胃癌多模态MRI扫描的首个大规模、开源数据集。
- 引入了HWA-UNETR框架,该框架采用可学习的窗口聚合层建立不同模态之间的动态特征对应关系。
- HWA-UNETR框架采用创新的三角融合策略进行上下文建模和捕捉长期空间依赖性。
- 在GCM 2025和BraTS 2021数据集上的实验验证了HWA-UNETR框架的性能优越性。
- 新的方法相对于现有方法在Dice得分率上有所提高,最高达到1.68%。
点此查看论文截图

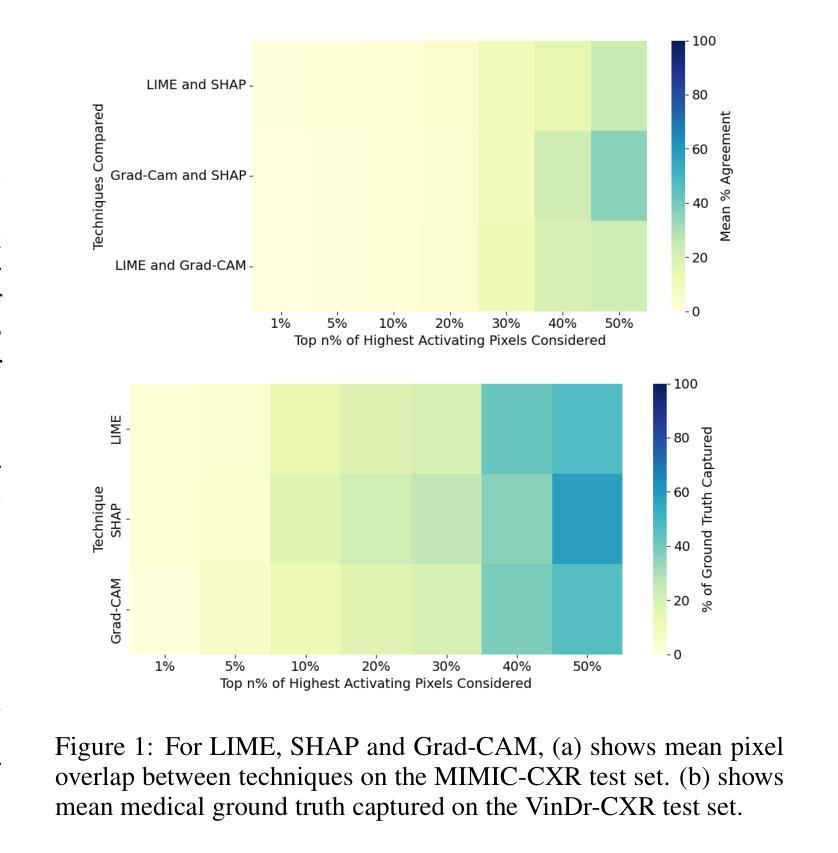
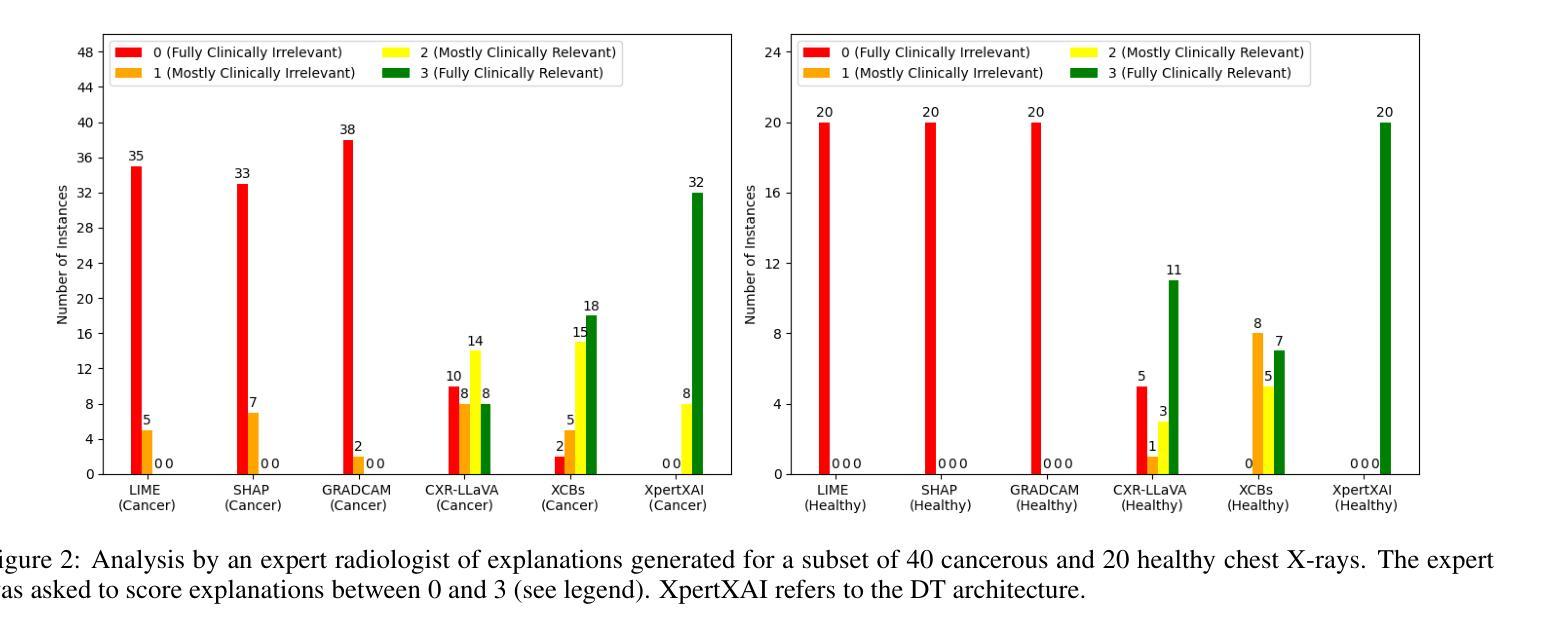
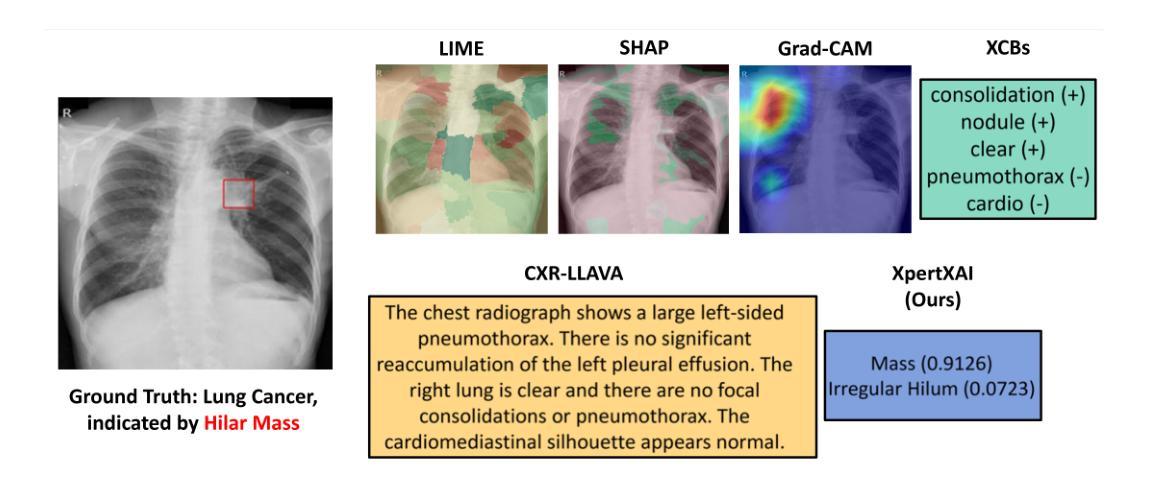
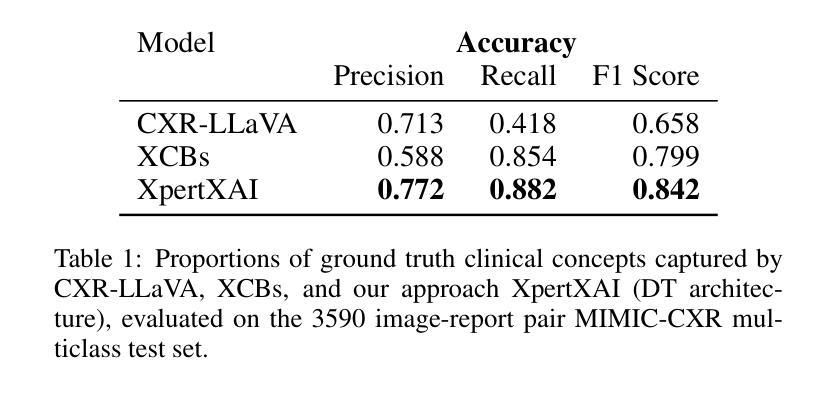
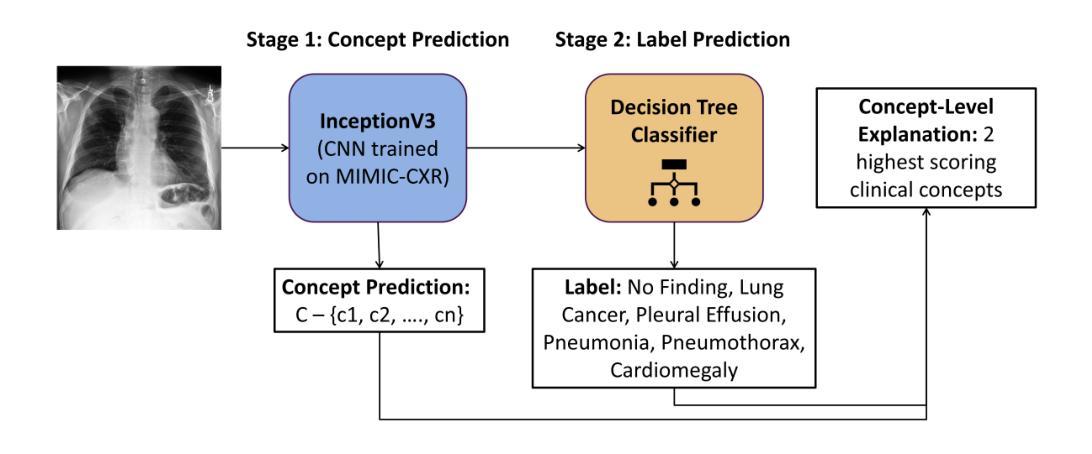
Explainability Through Human-Centric Design for XAI in Lung Cancer Detection
Authors:Amy Rafferty, Rishi Ramaesh, Ajitha Rajan
Deep learning models have shown promise in lung pathology detection from chest X-rays, but widespread clinical adoption remains limited due to opaque model decision-making. In prior work, we introduced ClinicXAI, a human-centric, expert-guided concept bottleneck model (CBM) designed for interpretable lung cancer diagnosis. We now extend that approach and present XpertXAI, a generalizable expert-driven model that preserves human-interpretable clinical concepts while scaling to detect multiple lung pathologies. Using a high-performing InceptionV3-based classifier and a public dataset of chest X-rays with radiology reports, we compare XpertXAI against leading post-hoc explainability methods and an unsupervised CBM, XCBs. We assess explanations through comparison with expert radiologist annotations and medical ground truth. Although XpertXAI is trained for multiple pathologies, our expert validation focuses on lung cancer. We find that existing techniques frequently fail to produce clinically meaningful explanations, omitting key diagnostic features and disagreeing with radiologist judgments. XpertXAI not only outperforms these baselines in predictive accuracy but also delivers concept-level explanations that better align with expert reasoning. While our focus remains on explainability in lung cancer detection, this work illustrates how human-centric model design can be effectively extended to broader diagnostic contexts - offering a scalable path toward clinically meaningful explainable AI in medical diagnostics.
深度学习模型在胸部X光片中检测肺部病变方面显示出巨大潜力,但由于模型决策不透明,其在临床上的广泛应用仍然有限。先前,我们引入了ClinicXAI,这是一种以人类为中心、专家指导的概念瓶颈模型(CBM),旨在实现可解释的肺癌诊断。现在我们扩展了该方法,并推出了XpertXAI,这是一种通用、专家驱动型的模型,既保留了可解释的临床概念,又能扩展到检测多种肺部病变。我们使用高性能的InceptionV3分类器和一个带有放射学报告的公共胸部X光数据集,将XpertXAI与领先的事后解释方法以及无监督的CBM(XCBs)进行比较。我们通过专家放射科医生注释和医学真实值对其进行评估。尽管XpertXAI经过多种病变的训练,但我们的专家验证主要集中在肺癌上。我们发现现有的技术往往无法产生具有临床意义的解释,忽略了关键的诊断特征,并与放射科医生的判断存在分歧。XpertXAI不仅在预测准确性方面超越这些基线,而且提供了与专家推理更相符的概念层面的解释。虽然我们的重点仍然是肺癌检测中的可解释性,但这项工作说明了以人类为中心的设计如何有效地扩展到更广泛的诊断环境,为医学诊断中的可解释人工智能提供了可扩展的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型在胸部X光片中检测肺部病变具有潜力,但临床应用广泛采用仍有限,主要由于模型决策不透明。本文扩展先前工作,提出XpertXAI,一种通用专家驱动模型,旨在保留人类可解释的临床概念,同时扩展检测多种肺部病变。通过与领先的后验解释方法和无监督CBM比较评估,以及专家放射科医生注释和医学真实情况验证评估解释结果。尽管XpertXAI针对多种病变进行训练,但专家验证侧重于肺癌。研究发现现有技术难以产生临床上有意义的解释,忽略关键诊断特征并与放射科医生判断存在分歧。XpertXAI不仅预测准确率高于基线,而且提供与专家推理更一致的概念级解释。虽然我们的重点仍然是肺癌检测的可解释性,但这项工作表明以人为中心的设计模型如何有效地扩展到更广泛的诊断情境,为临床上有意义的可解释人工智能诊断提供了可扩展路径。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在胸部X光肺部病变检测中有潜力,但临床应用受限,主要由于决策不透明。
- 介绍XpertXAI模型:一种专家驱动模型,旨在实现可解释的肺癌诊断,同时能够检测多种肺部病变。
- 通过与现有技术比较评估XpertXAI性能,发现现有技术难以产生临床意义的解释。
- XpertXAI不仅预测准确率高,而且提供与专家推理更一致的概念级解释。
- XpertXAI通过保留人类可解释的临床概念实现解释性增强。
- 工作展示人为中心的设计模型如何扩展到更广泛的诊断情境。
点此查看论文截图

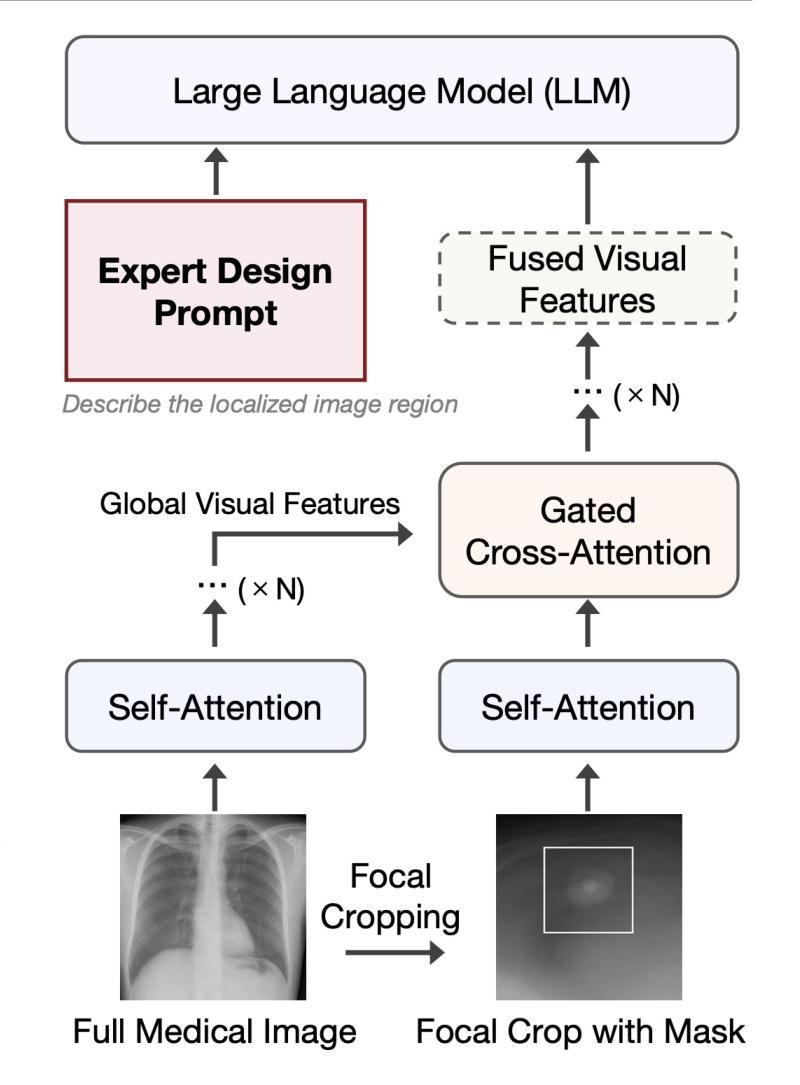
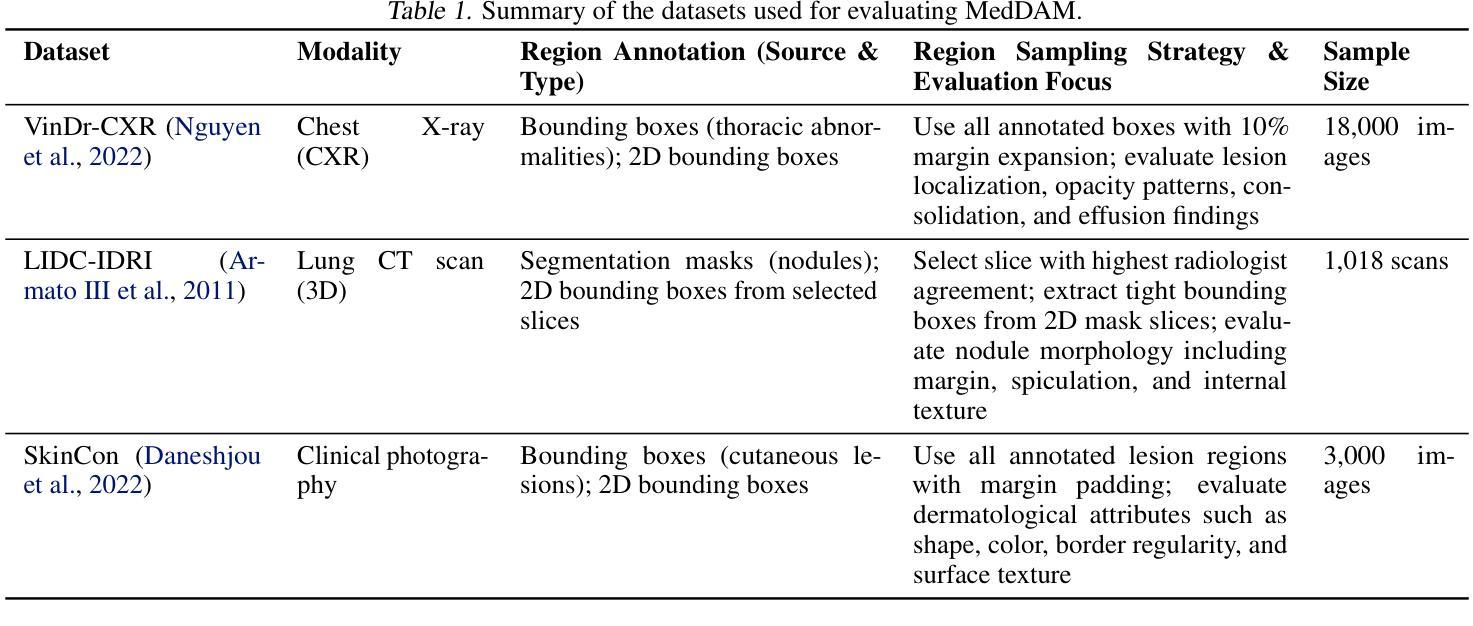
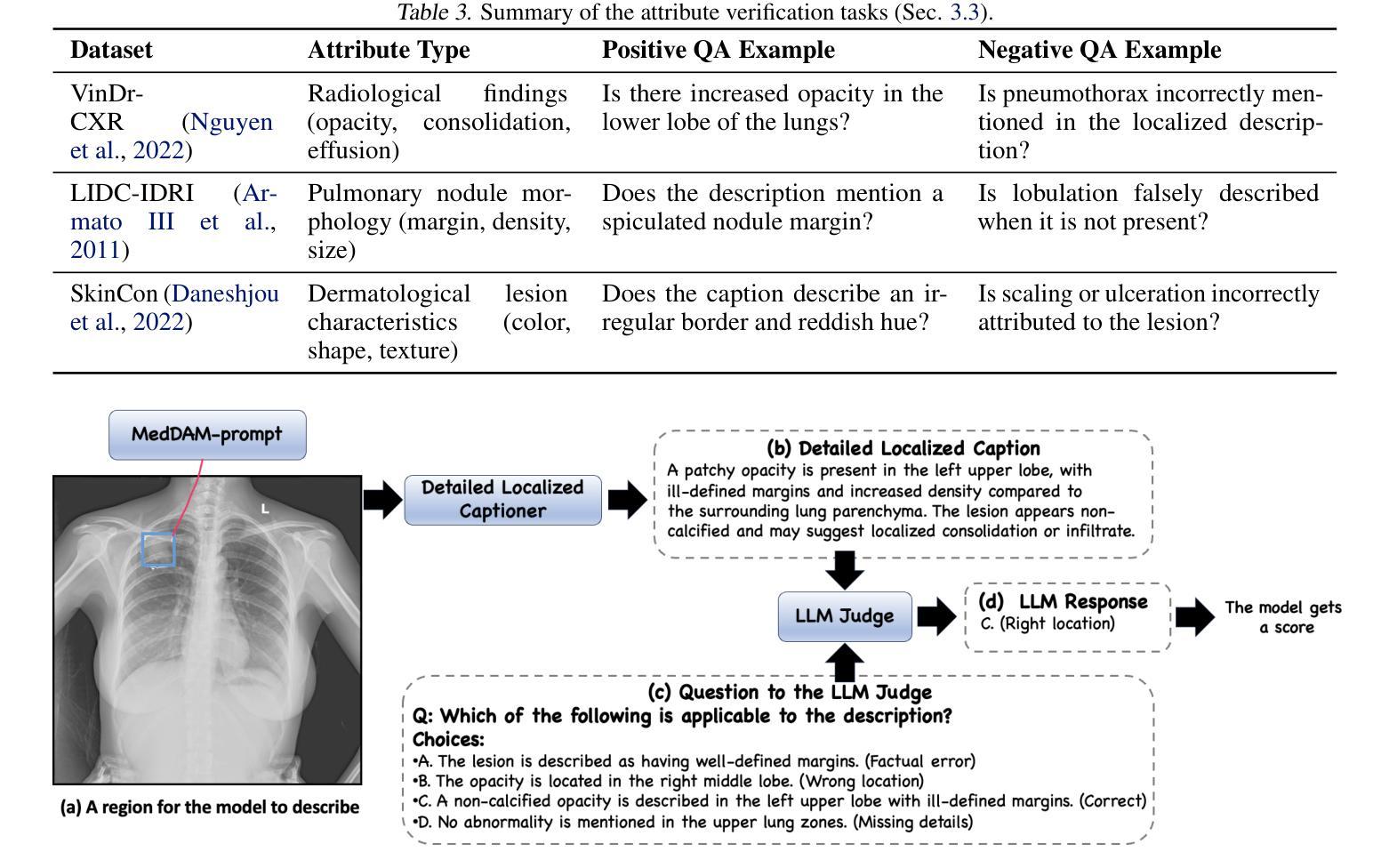
Describe Anything in Medical Images
Authors:Xi Xiao, Yunbei Zhang, Thanh-Huy Nguyen, Ba-Thinh Lam, Janet Wang, Lin Zhao, Jihun Hamm, Tianyang Wang, Xingjian Li, Xiao Wang, Hao Xu, Tianming Liu, Min Xu
Localized image captioning has made significant progress with models like the Describe Anything Model (DAM), which can generate detailed region-specific descriptions without explicit region-text supervision. However, such capabilities have yet to be widely applied to specialized domains like medical imaging, where diagnostic interpretation relies on subtle regional findings rather than global understanding. To mitigate this gap, we propose MedDAM, the first comprehensive framework leveraging large vision-language models for region-specific captioning in medical images. MedDAM employs medical expert-designed prompts tailored to specific imaging modalities and establishes a robust evaluation benchmark comprising a customized assessment protocol, data pre-processing pipeline, and specialized QA template library. This benchmark evaluates both MedDAM and other adaptable large vision-language models, focusing on clinical factuality through attribute-level verification tasks, thereby circumventing the absence of ground-truth region-caption pairs in medical datasets. Extensive experiments on the VinDr-CXR, LIDC-IDRI, and SkinCon datasets demonstrate MedDAM’s superiority over leading peers (including GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, LLaMA-3.2 Vision, Qwen2.5-VL, GPT-4Rol, and OMG-LLaVA) in the task, revealing the importance of region-level semantic alignment in medical image understanding and establishing MedDAM as a promising foundation for clinical vision-language integration.
局部图像标注已经取得了显著的进步,如“描述任何事物模型”(DAM)等模型,能够在没有明确的区域文本监督的情况下,生成详细的区域特定描述。然而,这种能力尚未广泛应用于医疗成像等特定领域,诊断解读依赖于微妙的区域发现而非全局理解。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了MedDAM,这是第一个利用大型视觉语言模型进行医学图像区域特定标注的全面框架。MedDAM采用医学专家设计的针对特定成像模式的提示,并建立了一个稳健的评估基准,包括定制评估协议、数据预处理管道和专用QA模板库。该基准不仅评估MedDAM,还评估其他可适应的大型视觉语言模型,通过属性级别验证任务关注临床事实性,从而避免了医学数据集中地面真实区域标题对缺失的问题。在VinDr-CXR、LIDC-IDRI和SkinCon数据集上的大量实验表明,MedDAM在任务上优于领先的对等模型(包括GPT-4o、Claude 3.7 Sonnet、LLaMA-3.2 Vision、Qwen2.5-VL、GPT-4Rol和OMG-LLaVA),这凸显了区域级别语义对齐在医学图像理解中的重要性,并确立了MedDAM作为临床视觉语言集成的有前途的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像的区域特定描述问题,提出MedDAM框架,利用大型视觉语言模型生成详细的区域特定描述,通过医学专家设计的提示和定制评估协议等建立稳健的评估基准,并在实际医学数据集上验证其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- MedDAM是首个针对医学图像区域特定描述的综合框架,利用大型视觉语言模型生成详细的区域特定描述。
- MedDAM通过医学专家设计的提示,适应特定成像模式,建立稳健的评估基准。
- 评估基准包括定制的评估协议、数据预处理管道和专用问答模板库。
- MedDAM侧重于临床事实性,通过属性级别的验证任务来评估模型性能。
- MedDAM在VinDr-CXR、LIDC-IDRI和SkinCon数据集上的实验结果表明其优越性。
- 实验结果揭示了区域级别语义对齐在医学图像理解中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


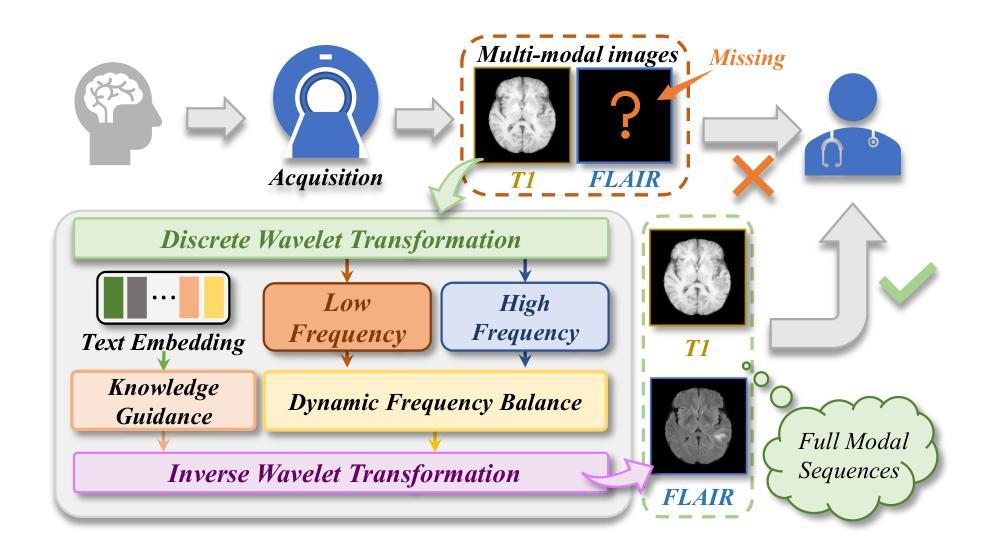
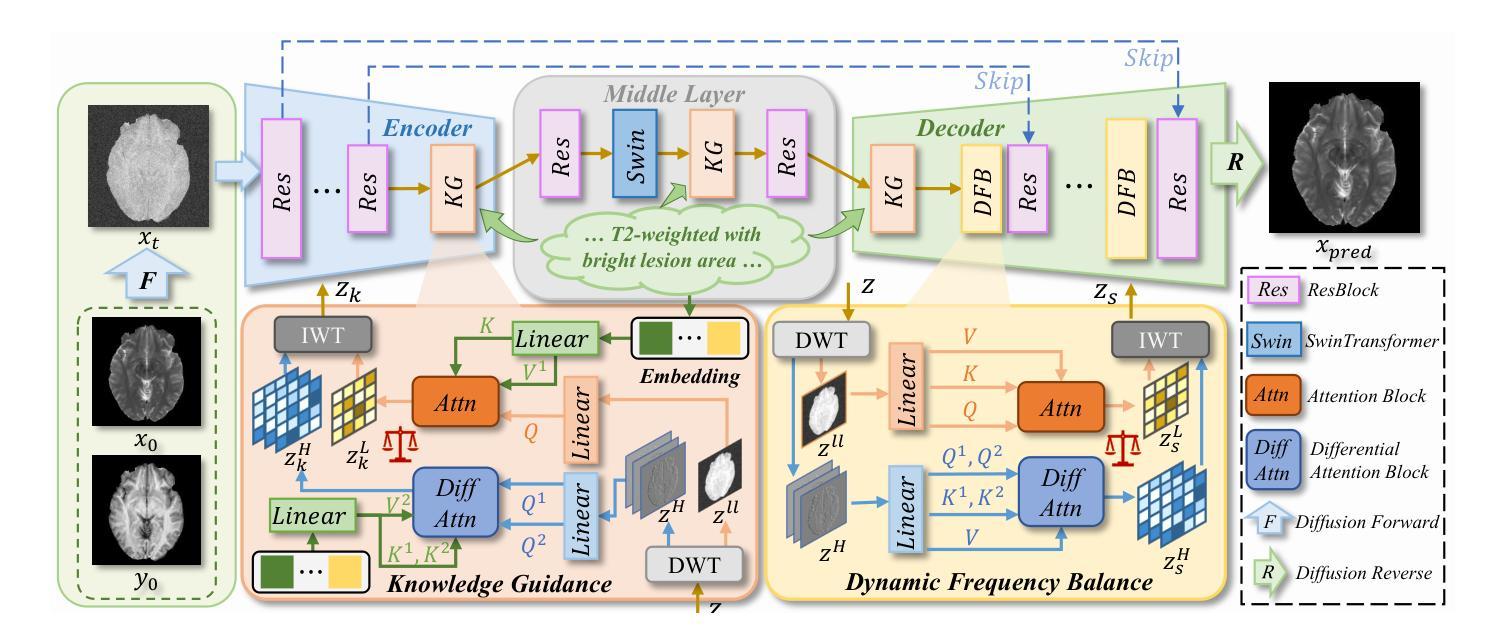
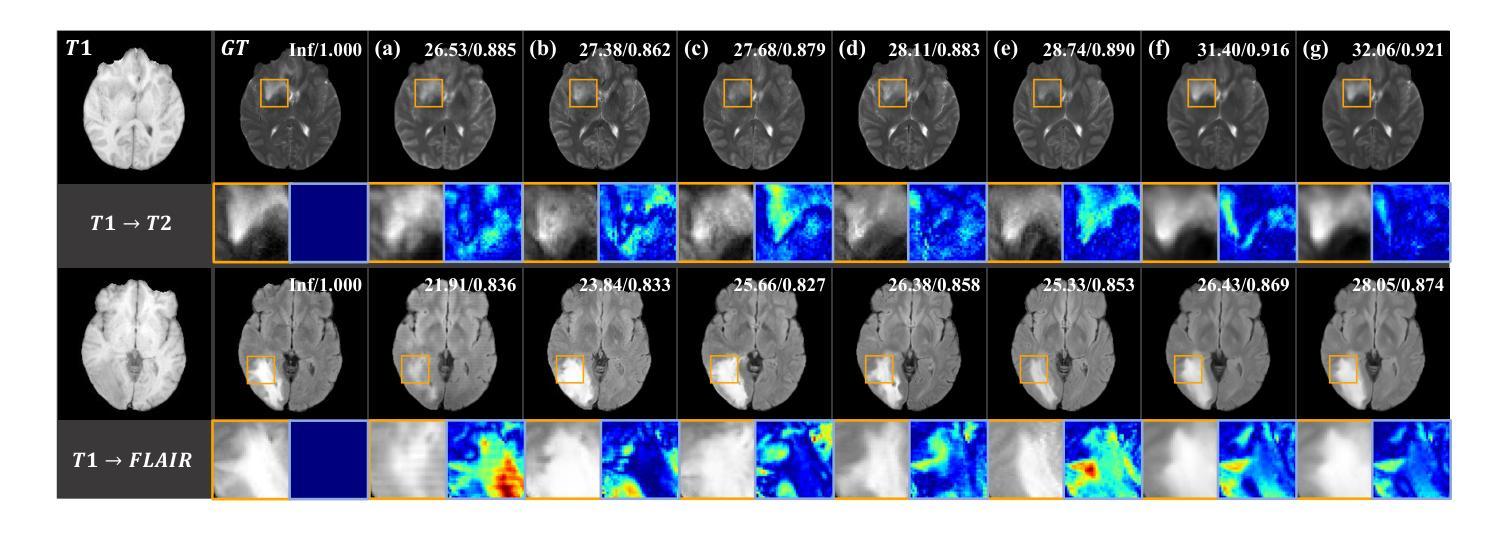
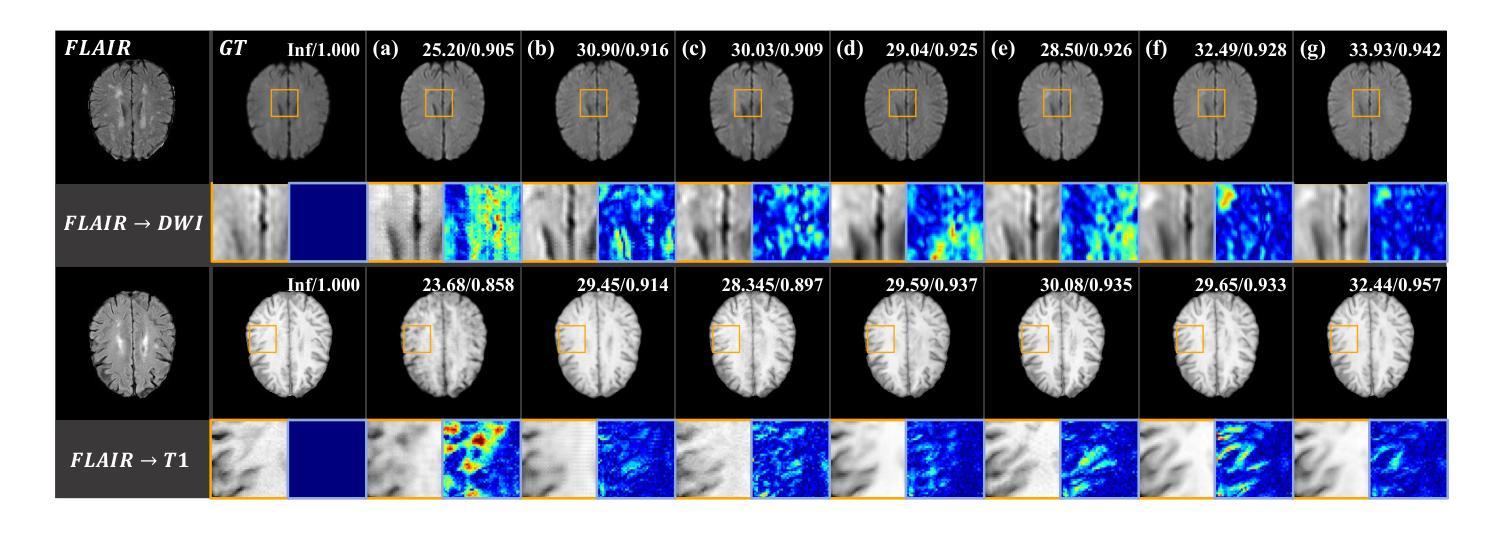
Structure-Accurate Medical Image Translation via Dynamic Frequency Balance and Knowledge Guidance
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Multimodal medical images play a crucial role in the precise and comprehensive clinical diagnosis. Diffusion model is a powerful strategy to synthesize the required medical images. However, existing approaches still suffer from the problem of anatomical structure distortion due to the overfitting of high-frequency information and the weakening of low-frequency information. Thus, we propose a novel method based on dynamic frequency balance and knowledge guidance. Specifically, we first extract the low-frequency and high-frequency components by decomposing the critical features of the model using wavelet transform. Then, a dynamic frequency balance module is designed to adaptively adjust frequency for enhancing global low-frequency features and effective high-frequency details as well as suppressing high-frequency noise. To further overcome the challenges posed by the large differences between different medical modalities, we construct a knowledge-guided mechanism that fuses the prior clinical knowledge from a visual language model with visual features, to facilitate the generation of accurate anatomical structures. Experimental evaluations on multiple datasets show the proposed method achieves significant improvements in qualitative and quantitative assessments, verifying its effectiveness and superiority.
多模态医学图像在精确全面的临床诊断中起着至关重要的作用。扩散模型是合成所需医学图像的一种强大策略。然而,现有方法仍然存在因高频信息过拟合和低频信息减弱导致的解剖结构扭曲问题。因此,我们提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的新方法。具体来说,我们首先通过利用小波变换分解模型的关键特征来提取低频和高频成分。然后,设计了一个动态频率平衡模块,该模块可以自适应地调整频率,以增强全局低频特征和有效的高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。为了克服不同医学模态之间巨大差异所带来的挑战,我们构建了一个知识引导机制,该机制将来自视觉语言模型的先验临床知识与视觉特征相结合,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,所提出的方法在定性和定量评估方面都取得了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical image translation, Diffusion model, 16 pages
Summary
基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的方法在多模态医学图像合成中具有重要作用,解决了现有方法存在的解剖结构扭曲问题。该方法通过小波变换提取高低频成分,并设计动态频率平衡模块自适应调整频率,增强全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。此外,通过构建知识引导机制融合临床先验知识,生成准确的解剖结构。实验评估表明,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像在临床诊断中具有重要作用。
- 扩散模型是合成医学图像的有效策略。
- 现有方法存在解剖结构扭曲的问题,主要是由于高频信息的过度拟合和低频信息的减弱。
- 提出的基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的新方法旨在解决这一问题。
- 方法通过小波变换提取高低频成分,并使用动态频率平衡模块增强低频特征和有效高频细节。
- 知识引导机制融合了临床先验知识,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。
点此查看论文截图


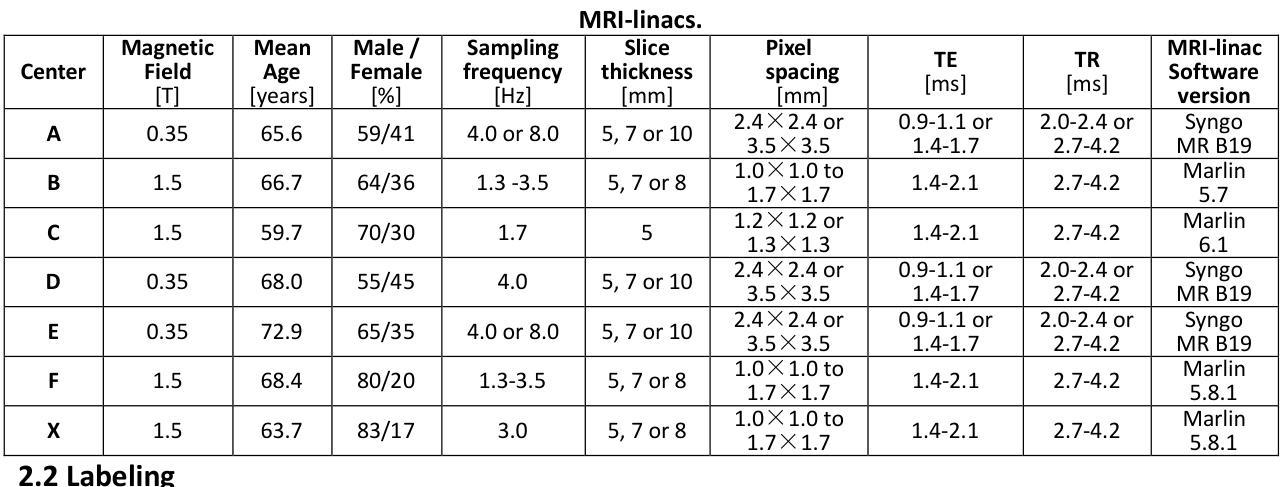
TrackRAD2025 challenge dataset: Real-time tumor tracking for MRI-guided radiotherapy
Authors:Yiling Wang, Elia Lombardo, Adrian Thummerer, Tom Blöcker, Yu Fan, Yue Zhao, Christianna Iris Papadopoulou, Coen Hurkmans, Rob H. N. Tijssen, Pia A. W. Görts, Shyama U. Tetar, Davide Cusumano, Martijn P. W. Intven, Pim Borman, Marco Riboldi, Denis Dudáš, Hilary Byrne, Lorenzo Placidi, Marco Fusella, Michael Jameson, Miguel Palacios, Paul Cobussen, Tobias Finazzi, Cornelis J. A. Haasbeek, Paul Keall, Christopher Kurz, Guillaume Landry, Matteo Maspero
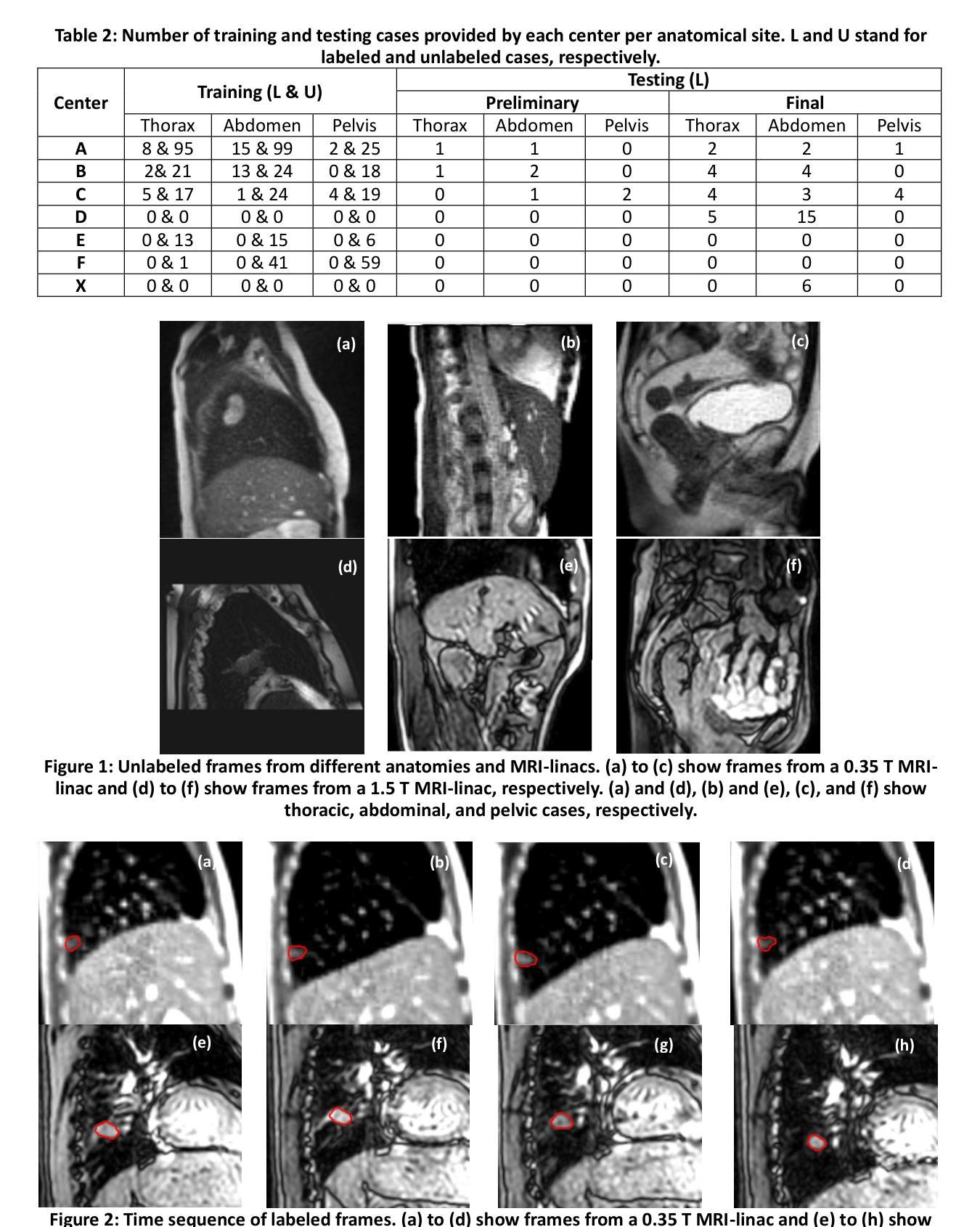
Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize anatomical motion is becoming increasingly important when treating cancer patients with radiotherapy. Hybrid MRI-linear accelerator (MRI-linac) systems allow real-time motion management during irradiation. This paper presents a multi-institutional real-time MRI time series dataset from different MRI-linac vendors. The dataset is designed to support developing and evaluating real-time tumor localization (tracking) algorithms for MRI-guided radiotherapy within the TrackRAD2025 challenge (https://trackrad2025.grand-challenge.org/). Acquisition and validation methods: The dataset consists of sagittal 2D cine MRIs in 585 patients from six centers (3 Dutch, 1 German, 1 Australian, and 1 Chinese). Tumors in the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis acquired on two commercially available MRI-linacs (0.35 T and 1.5 T) were included. For 108 cases, irradiation targets or tracking surrogates were manually segmented on each temporal frame. The dataset was randomly split into a public training set of 527 cases (477 unlabeled and 50 labeled) and a private testing set of 58 cases (all labeled). Data Format and Usage Notes: The data is publicly available under the TrackRAD2025 collection: https://doi.org/10.57967/hf/4539. Both the images and segmentations for each patient are available in metadata format. Potential Applications: This novel clinical dataset will enable the development and evaluation of real-time tumor localization algorithms for MRI-guided radiotherapy. By enabling more accurate motion management and adaptive treatment strategies, this dataset has the potential to advance the field of radiotherapy significantly.
目的:在治疗癌症患者时进行放射治疗时,利用磁共振成像(MRI)来可视化解剖运动变得越来越重要。混合MRI-直线加速器(MRI-linac)系统可在照射过程中进行实时运动管理。本文介绍了一个多机构实时MRI时间序列数据集,该数据集来自不同的MRI-linac供应商。该数据集旨在支持开发并评估MRI引导放射治疗的实时肿瘤定位(跟踪)算法,以应对TrackRAD2025挑战(https://trackrad2025.grand-challenge.org/)。
采集和验证方法:数据集包含来自6个中心(荷兰3个,德国1个,澳大利亚1个,中国1个)的585例患者的矢状面2D电影MRI。胸、腹和骨盆部位的肿瘤是在两台商用MRI-linac(0.35T和1.5T)上获得的。在108个病例中,每个时间帧上都手动分割了照射目标或跟踪代理。数据集被随机分成527例公共训练集(477例未标记和50例已标记)和58例私有测试集(均已标记)。
数据格式和使用注意事项:数据可在TrackRAD2025收藏中公开获取:https://doi.org/10.57967/hf/4539。每个患者的图像和分段都可用元数据格式查看。
潜在应用:这个新型临床数据集将能够开发和评估MRI引导放射治疗的实时肿瘤定位算法。通过实现更精确的运动管理和自适应治疗方案,该数据集有望推动放射治疗领域的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables; submitted to Medical Physics, tentatively accepted
Summary
磁共振成像(MRI)在癌症患者放疗治疗中用于可视化解剖运动日益重要。本文介绍了一个多机构实时MRI时间序列数据集,该数据集来自不同的MRI-直线加速器(MRI-linac)供应商,旨在支持开发并评估用于MRI引导放疗的实时肿瘤定位(跟踪)算法。数据集包含来自六个中心的585名患者的矢状面2D电影MRI,涵盖了胸部、腹部和骨盆的肿瘤。此数据集已公开,并可用于TrackRAD2025挑战赛(https://trackrad2025.grand-challenge.org/)。该数据集有望促进实时肿瘤定位算法的开发和评估,通过更精确的运动管理和自适应治疗方案,为放疗领域带来显著进展。
Key Takeaways
- 实时MRI时间序列数据集支持开发并评估用于MRI引导放疗的肿瘤定位算法。
- 数据集包含来自不同MRI-linac供应商的实时数据,涵盖胸部、腹部和骨盆的肿瘤。
- 数据集包含公开可用的训练集和测试集,分为有标签和无标签的数据。
- 数据集具有潜力推动放疗领域的发展,通过更精确的运动管理和自适应治疗方案改善治疗效果。
- 数据集可用于验证和改进肿瘤运动跟踪算法的性能和准确性。
- 此数据集是首个多机构合作创建的大规模实时MRI数据集,具有广泛的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

UltraBones100k: A reliable automated labeling method and large-scale dataset for ultrasound-based bone surface extraction
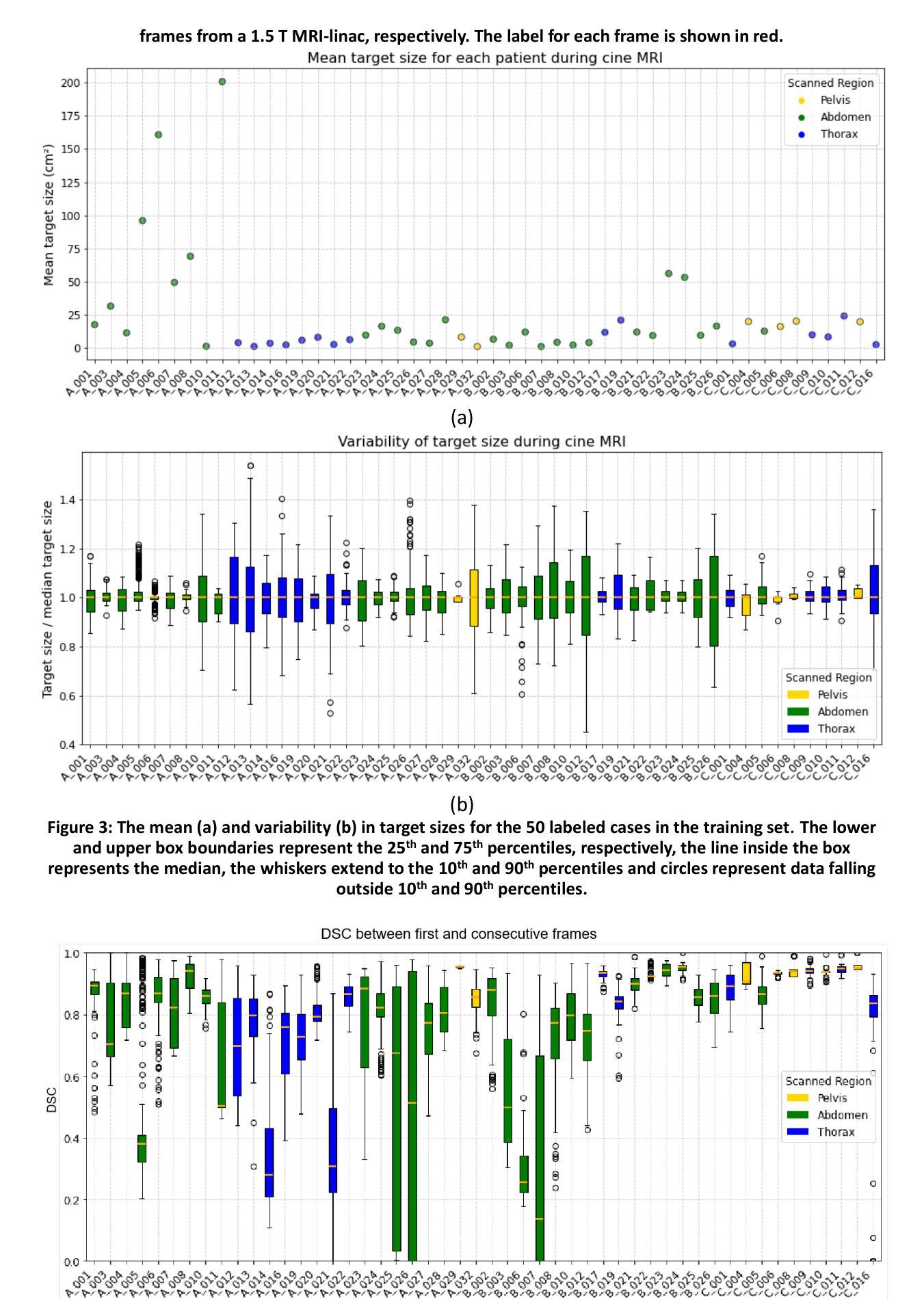
Authors:Luohong Wu, Nicola A. Cavalcanti, Matthias Seibold, Giuseppe Loggia, Lisa Reissner, Jonas Hein, Silvan Beeler, Arnd Viehöfer, Stephan Wirth, Lilian Calvet, Philipp Fürnstahl
Ultrasound-based bone surface segmentation is crucial in computer-assisted orthopedic surgery. However, ultrasound images have limitations, including a low signal-to-noise ratio, and acoustic shadowing, which make interpretation difficult. Existing deep learning models for bone segmentation rely primarily on costly manual labeling by experts, limiting dataset size and model generalizability. Additionally, the complexity of ultrasound physics and acoustic shadow makes the images difficult for humans to interpret, leading to incomplete labels in anechoic regions and limiting model performance. To advance ultrasound bone segmentation and establish effective model benchmarks, larger and higher-quality datasets are needed. We propose a methodology for collecting ex-vivo ultrasound datasets with automatically generated bone labels, including anechoic regions. The proposed labels are derived by accurately superimposing tracked bone CT models onto the tracked ultrasound images. These initial labels are refined to account for ultrasound physics. A clinical evaluation is conducted by an expert physician specialized on orthopedic sonography to assess the quality of the generated bone labels. A neural network for bone segmentation is trained on the collected dataset and its predictions are compared to expert manual labels, evaluating accuracy, completeness, and F1-score. We collected the largest known dataset of 100k ultrasound images of human lower limbs with bone labels, called UltraBones100k. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test with Bonferroni correction confirmed that the bone alignment after our method significantly improved the quality of bone labeling (p < 0.001). The model trained on UltraBones100k consistently outperforms manual labeling in all metrics, particularly in low-intensity regions (320% improvement in completeness at a distance threshold of 0.5 mm).
基于超声的骨骼表面分割在计算机辅助骨科手术中至关重要。然而,超声图像存在信号噪声比低和声影等局限性,使得解读困难。现有的骨骼分割深度学习模型主要依赖于专家昂贵的手动标注,这限制了数据集的大小和模型的通用性。此外,超声物理和声影的复杂性使得图像对人类来说难以解读,导致无声区域的标签不完整并限制了模型性能。为了推进超声骨分割并建立有效的模型基准,需要更大、更高质量的数据集。我们提出了一种收集离体超声数据集的方法,其中包括自动生成的骨骼标签和无声区域。这些标签是通过准确地将追踪的骨骼CT模型叠加到追踪的超声图像上而得出的。这些初始标签经过调整以考虑超声物理特性。由专门研究骨科超声的专家医生进行临床评估,以评估生成的骨骼标签的质量。在收集的数据集上训练了一个骨骼分割神经网络,并将其预测结果与专家手动标签进行比较,评估准确性、完整性和F1分数。我们收集了已知最大的包含骨骼标签的10万张人类下肢超声图像数据集,称为UltraBones100k。采用威尔科克斯符号秩检验进行Bonferroni校正后证实,使用我们的方法后,骨骼对齐显著提高了骨骼标签的质量(p < 0.001)。在UltraBones100k上训练的模型在所有指标上都一致优于手动标注,特别是在低强度区域(在距离阈值为0.5毫米的情况下,完整性提高了320%)。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
超声骨表面分割在计算机辅助骨科手术中至关重要。然而,由于超声图像存在信号噪声比较低、声影等局限性,使得解读困难。现有的深度学习骨分割模型主要依赖专家昂贵的手动标注,限制了数据集大小和模型的泛化能力。为推进超声骨分割并建立有效的模型基准,需要更大、更高质量的数据集。我们提出了一种收集离体超声数据集的方法,可以自动生成骨标签,包括无声区标签。标签是通过将追踪的骨CT模型精确叠加到追踪的超声图像上而派生出来的。这些初始标签经过了超声物理学的修正。由专家医生对生成的骨标签质量进行评估。在收集的数据集上训练了一个用于骨分割的神经网络,并将其预测结果与专家手动标签进行比较,评估了准确性、完整性和F1分数。我们收集了已知最大的包含人类下肢骨骼标签的超声图像数据集UltraBones100k。通过Wilcoxon符号秩检验和Bonferroni校正证实,我们的方法显著提高了骨标签的质量(p < 0.001)。在UltraBones100k上训练的模型在所有指标上都优于手动标注,特别是在低强度区域(在距离阈值为0.5毫米的情况下,完整性提高了320%)。
关键见解
- 超声骨表面分割在骨科手术中非常重要,但超声图像解读存在困难。
- 当前深度学习模型受限于手动标注,影响数据集大小和模型泛化能力。
- 提出了一种自动生成骨标签的方法,适用于离体超声数据集。
- 通过将追踪的骨CT模型叠加到超声图像上生成初始标签,并进行超声物理学修正。
- 进行了临床评估,证实了生成的骨标签质量显著提高。
- 在收集的大型数据集UltraBones100k上训练的模型表现优于手动标注。
点此查看论文截图

PUSSM: Point Cloud Upsampling as Implicit Statistical Shape Model
Authors:Tongxu Zhang, Bei Wang
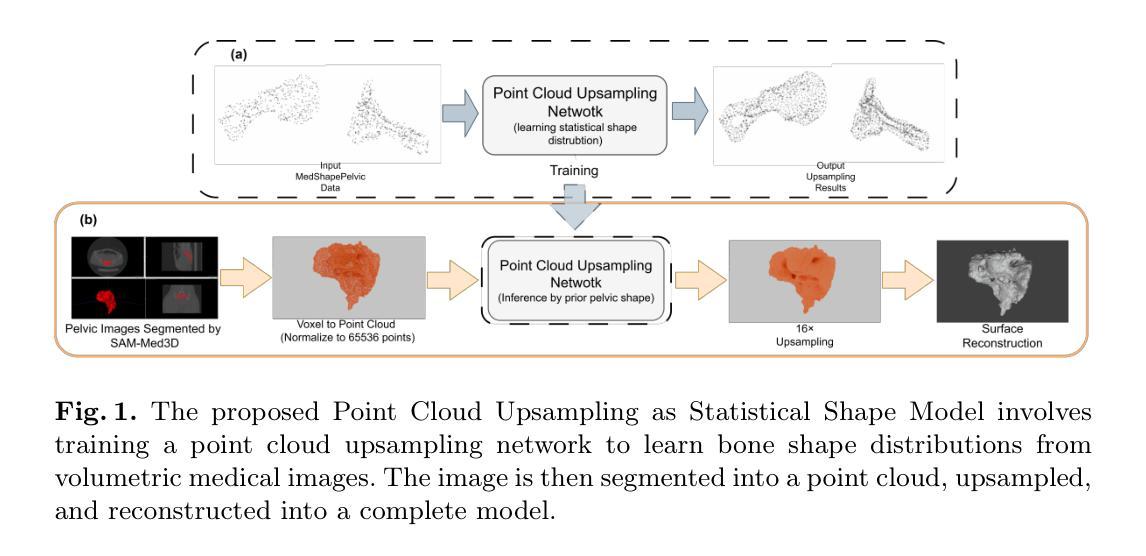
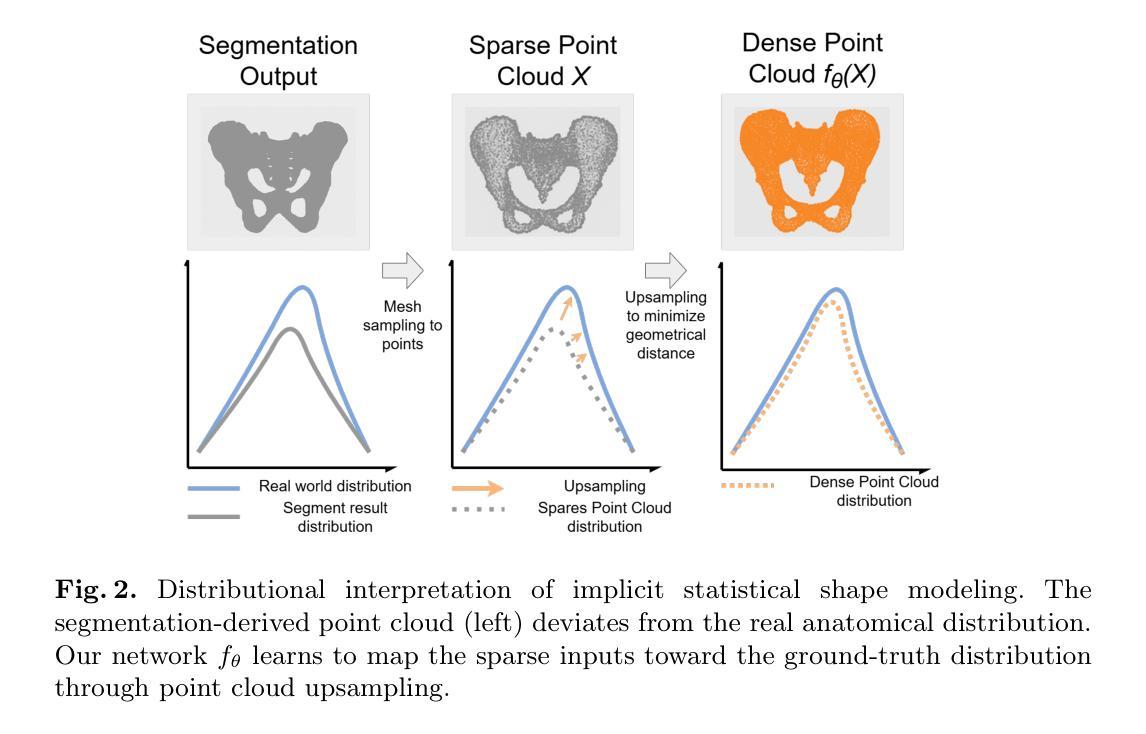
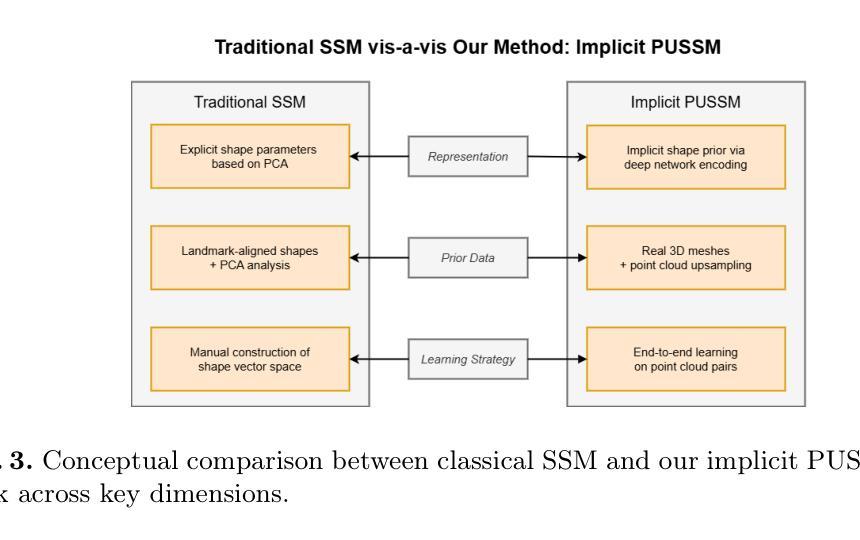
This paper proposes a framework for high-fidelity reconstruction of pelvic structures by integrating medical image segmentation and point cloud upsampling. By point cloud upsampling to learn shape priors from MedShapePelvic without requiring landmarks or PCA, our method functions as an implicit statistical shape model. Evaluations on Pelvic1k show significant improvements in surface quality and anatomical accuracy. This approach is generalizable and applicable to other skeletal regions.
本文提出一个通过整合医学图像分割和点云上采样进行骨盆结构高保真重建的框架。通过点云上采样从MedShapePelvic中学习形状先验知识,而无需地标或主成分分析,我们的方法可作为隐式统计形状模型。在Pelvic1k上的评估显示,表面质量和解剖精度有了显著提高。此方法是通用的,适用于其他骨骼区域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种结合医学图像分割和点云上采样技术的骨盆结构高保真重建框架。通过点云上采样,从MedShapePelvic中学习形状先验,无需地标或PCA,该方法可作为隐式统计形状模型。在Pelvic1k上的评估显示,表面质量和解剖精度得到显著提高。该方法可推广应用于其他骨骼区域。
Key Takeaways
- 骨盆结构的高保真重建框架结合了医学图像分割和点云上采样技术。
- 通过点云上采样学习形状先验,无需使用地标或PCA技术。
- 该方法可作为隐式统计形状模型。
- 在Pelvic1k上的评估表明,该方法的表面质量和解剖精度显著提高。
- 该方法具有推广性,可应用于其他骨骼区域的重建。
- 该框架对于医学图像分析和处理具有重要的应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

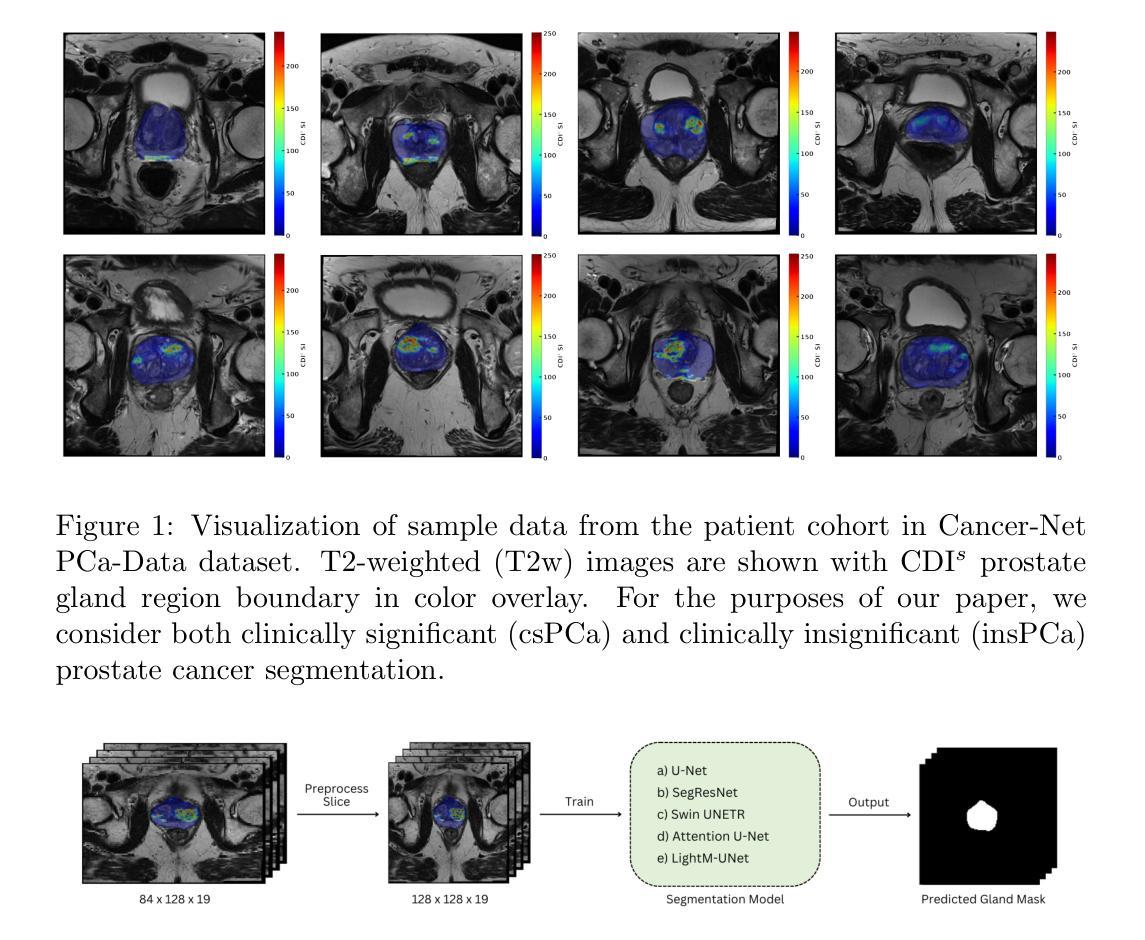
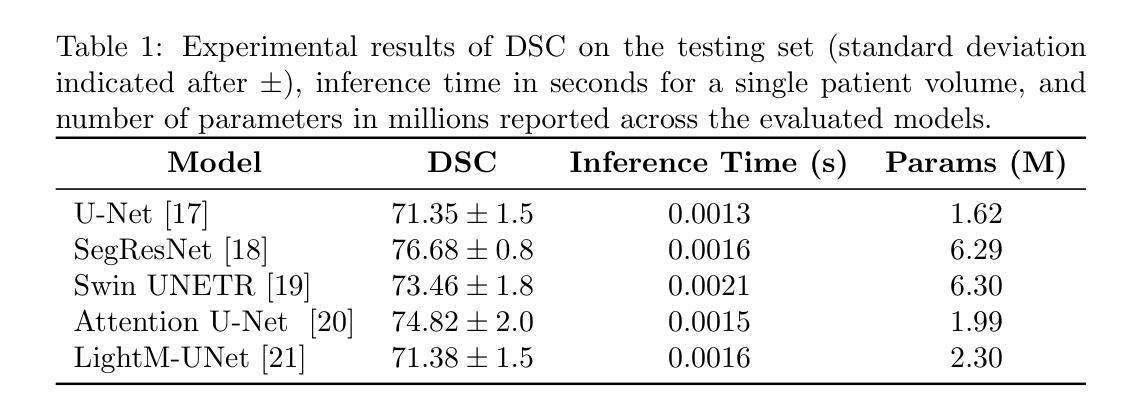
Cancer-Net PCa-Seg: Benchmarking Deep Learning Models for Prostate Cancer Segmentation Using Synthetic Correlated Diffusion Imaging
Authors:Jarett Dewbury, Chi-en Amy Tai, Alexander Wong
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most prevalent cancer among men in the United States, accounting for nearly 300,000 cases, 29% of all diagnoses and 35,000 total deaths in 2024. Traditional screening methods such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been pivotal in diagnosis, but have faced limitations in specificity and generalizability. In this paper, we explore the potential of enhancing PCa gland segmentation using a novel MRI modality called synthetic correlated diffusion imaging (CDI$^s$). We employ several state-of-the-art deep learning models, including U-Net, SegResNet, Swin UNETR, Attention U-Net, and LightM-UNet, to segment prostate glands from a 200 CDI$^s$ patient cohort. We find that SegResNet achieved superior segmentation performance with a Dice-Sorensen coefficient (DSC) of $76.68 \pm 0.8$. Notably, the Attention U-Net, while slightly less accurate (DSC $74.82 \pm 2.0$), offered a favorable balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. Our findings demonstrate the potential of deep learning models in improving prostate gland segmentation using CDI$^s$ to enhance PCa management and clinical support.
前列腺癌(PCa)是美国男性最常见的癌症,2024年将近有30万例病例,占所有诊断的29%,以及导致3万5千人死亡。传统的筛查方法,如前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)检测和磁共振成像(MRI),在诊断中至关重要,但在特异性和普及性方面存在局限性。在本文中,我们探讨了使用一种名为合成相关扩散成像(CDI$^s$)的新型MRI模式提高前列腺癌腺体分割的潜力。我们采用了先进的深度学习模型,包括U-Net、SegResNet、Swin UNETR、Attention U-Net和LightM-UNet,对来自200名CDI$^s$患者的前列腺腺体进行分割。我们发现SegResNet的分割性能最佳,Dice-Sorensen系数(DSC)为$76.68 \pm 0.8$。值得注意的是,虽然Attention U-Net的准确度稍低(DSC $74.82 \pm 2.0$),但在准确性与计算效率之间达到了有利的平衡。我们的研究结果表明,深度学习模型在利用CDI$^s$提高前列腺癌腺体分割方面具有潜力,可改善前列腺癌管理和临床支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, to be published in Studies in Computational Intelligence. This paper introduces Cancer-Net PCa-Seg, a comprehensive evaluation of deep learning models for prostate cancer segmentation using synthetic correlated diffusion imaging (CDI$^s$). We benchmark five state-of-the-art architectures: U-Net, SegResNet, Swin UNETR, Attention U-Net, and LightM-UNet
Summary
前列腺癌是美国男性最常见的癌症之一,针对其诊断方法如前列腺特异性抗原检测和磁共振成像存在局限性。本研究探讨了使用合成相关扩散成像(CDI$^s$)这一新型MRI模式在前列腺癌腺体分割方面的潜力。采用多种先进的深度学习模型,发现SegResNet模型分割性能最优,Dice系数为$76.68 \pm 0.8$。Attention U-Net模型虽准确性稍低,但计算效率较高,为前列腺癌管理和临床支持提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 前列腺癌是美国男性最常见的癌症之一,预计到2024年将导致近3万例死亡。
- 传统的前列腺癌诊断方法如PSA测试和MRI存在局限性。
- 合成相关扩散成像(CDI$^s$)作为一种新型的MRI模态被研究用于增强前列腺癌腺体的分割。
- 深度学习模型在前列腺癌腺体分割中显示出潜力,其中SegResNet模型表现最佳。
- Attention U-Net模型在计算效率和准确性之间达到了较好的平衡。
点此查看论文截图