⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
MV-CoLight: Efficient Object Compositing with Consistent Lighting and Shadow Generation
Authors:Kerui Ren, Jiayang Bai, Linning Xu, Lihan Jiang, Jiangmiao Pang, Mulin Yu, Bo Dai
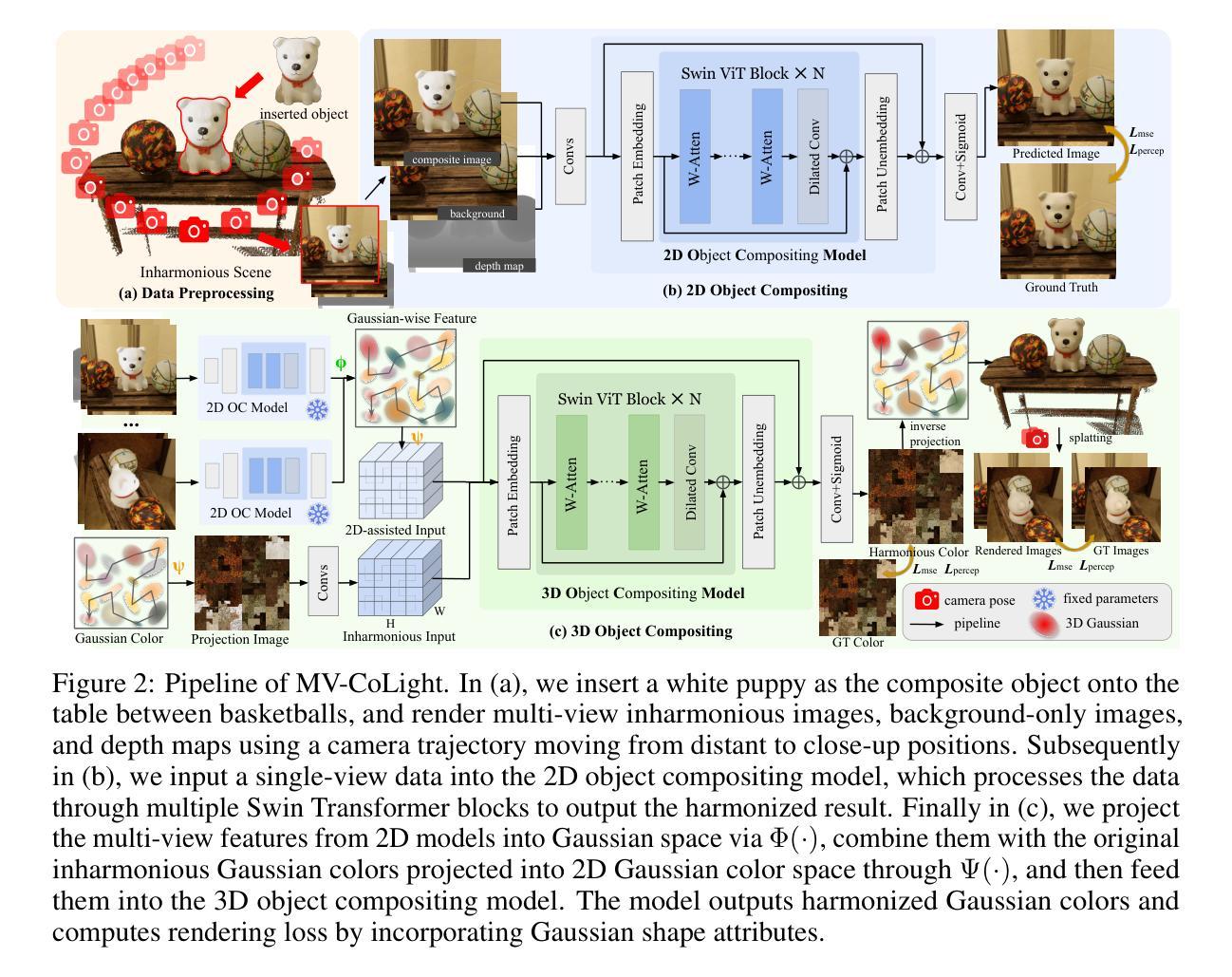
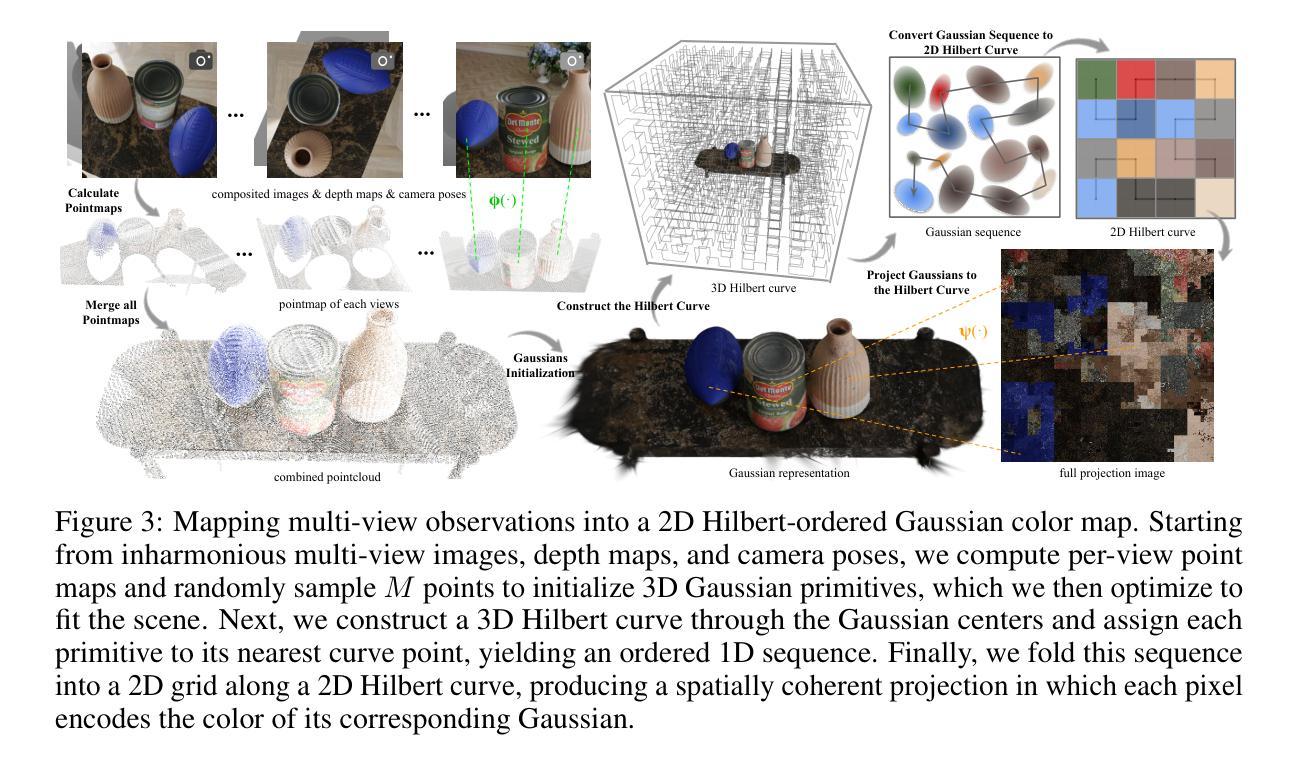
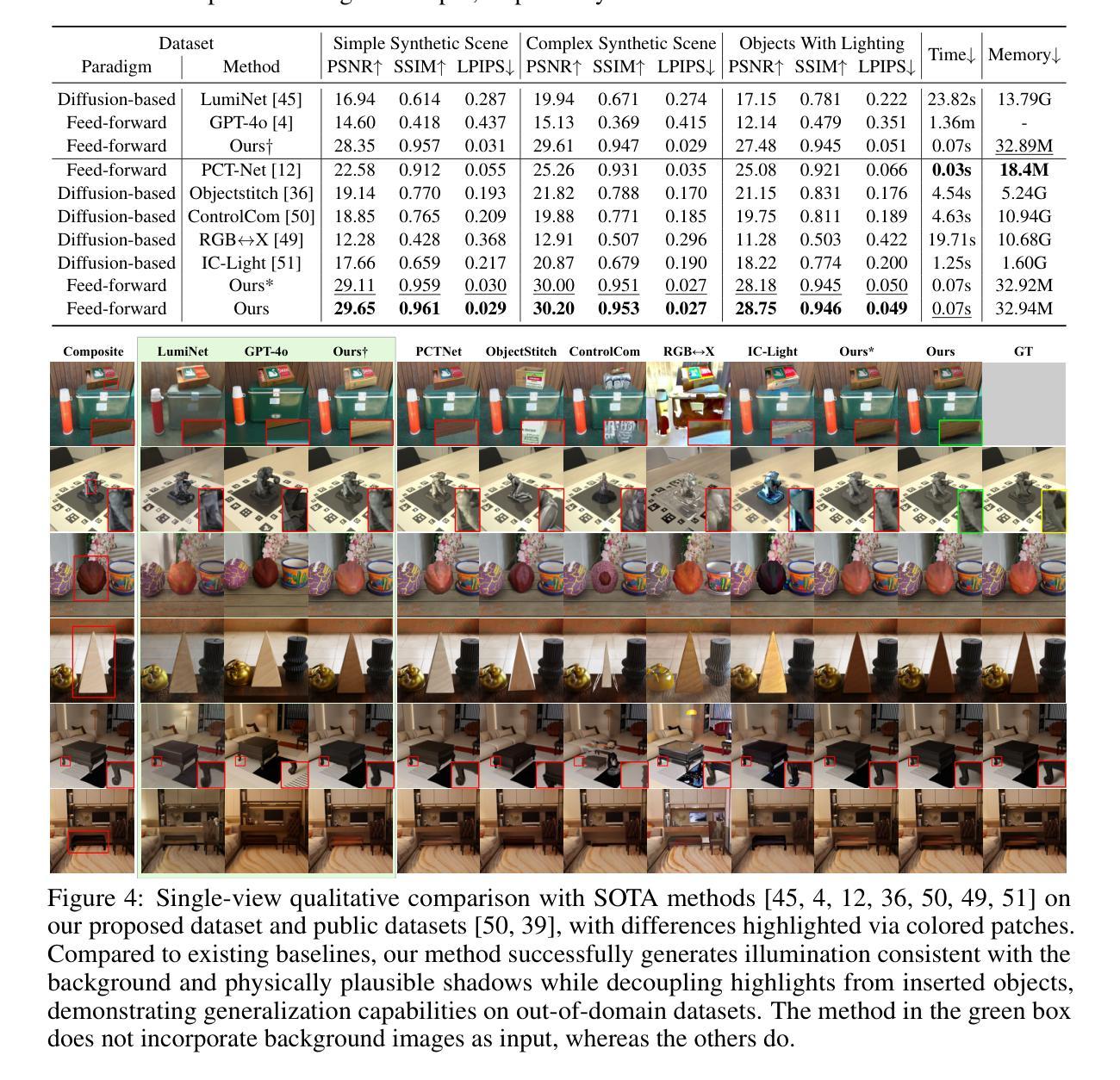
Object compositing offers significant promise for augmented reality (AR) and embodied intelligence applications. Existing approaches predominantly focus on single-image scenarios or intrinsic decomposition techniques, facing challenges with multi-view consistency, complex scenes, and diverse lighting conditions. Recent inverse rendering advancements, such as 3D Gaussian and diffusion-based methods, have enhanced consistency but are limited by scalability, heavy data requirements, or prolonged reconstruction time per scene. To broaden its applicability, we introduce MV-CoLight, a two-stage framework for illumination-consistent object compositing in both 2D images and 3D scenes. Our novel feed-forward architecture models lighting and shadows directly, avoiding the iterative biases of diffusion-based methods. We employ a Hilbert curve-based mapping to align 2D image inputs with 3D Gaussian scene representations seamlessly. To facilitate training and evaluation, we further introduce a large-scale 3D compositing dataset. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art harmonized results across standard benchmarks and our dataset, as well as casually captured real-world scenes demonstrate the framework’s robustness and wide generalization.
对象合成技术在增强现实(AR)和智能实体应用方面显示出巨大的潜力。现有的方法主要集中在单图像场景或内在分解技术上,面临多视角一致性、复杂场景和多变光照条件下的挑战。最近的逆向渲染技术进展,如基于三维高斯和扩散的方法,提高了一致性,但受限于可扩展性、繁重的数据需求或每个场景的重建时间延长。为了扩大其应用范围,我们引入了MV-CoLight,这是一个两阶段的照明一致性对象合成框架,适用于二维图像和三维场景。我们新颖的前馈架构直接对光线和阴影进行建模,避免了基于扩散方法的迭代偏见。我们采用基于Hilbert曲线的映射,无缝地将二维图像输入与三维高斯场景表示对齐。为了促进训练和评估,我们还引入了一个大规模的三维合成数据集。实验表明,我们的方法在标准基准测试集和我们自己的数据集上都达到了最先进的和谐结果,而在随意捕捉的真实世界场景中也证明了该框架的稳健性和广泛通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
对象合成技术在增强现实(AR)和具身智能应用方面展现出巨大潜力。现有方法主要关注单场景或内在分解技术,面临多视图一致性、复杂场景和多变光照条件下的挑战。近期逆向渲染技术的进展,如3D高斯和扩散方法,提高了一致性,但受限于可扩展性、大量数据需求或重建时间。为扩大其应用范围,我们提出MV-CoLight框架,用于二维图像和三维场景的光照一致性对象合成。我们的新型前馈架构直接建模光照和阴影,避免了扩散方法的迭代偏差。采用Hilbert曲线映射无缝对接二维图像输入和三维高斯场景表示。为进一步训练和评估,我们还引入大规模三维合成数据集。实验证明,该方法在标准基准测试及数据集中均表现优异,并且在日常捕获的真实场景中证明了该框架的鲁棒性和广泛适应性。
要点掌握
- 对象合成技术对于增强现实和具身智能应用具有巨大潜力。
- 现有方法面临多视图一致性、复杂场景和多变光照条件的挑战。
- MV-CoLight框架通过前馈架构直接建模光照和阴影,提高了一致性。
- 采用Hilbert曲线映射实现二维图像和三维场景的无缝对接。
- 引入大规模三维合成数据集用于训练和评估。
- 实验结果表明该方法在标准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

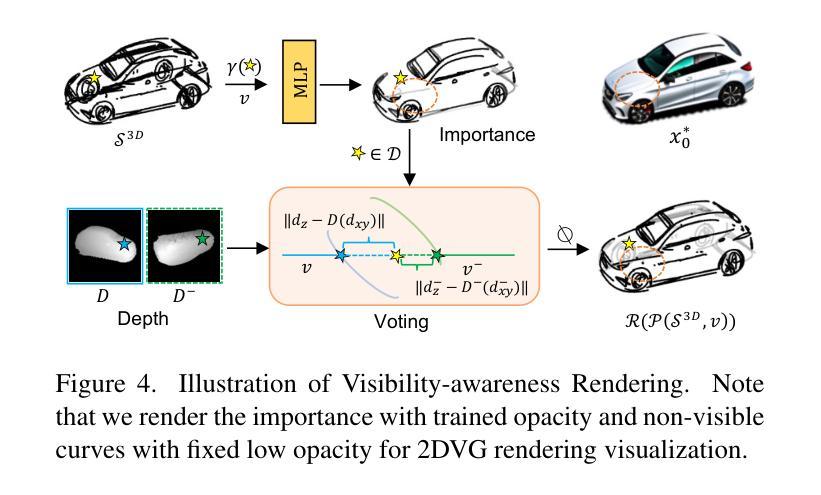
Empowering Vector Graphics with Consistently Arbitrary Viewing and View-dependent Visibility
Authors:Yidi Li, Jun Xiao, Zhengda Lu, Yiqun Wang, Haiyong Jiang
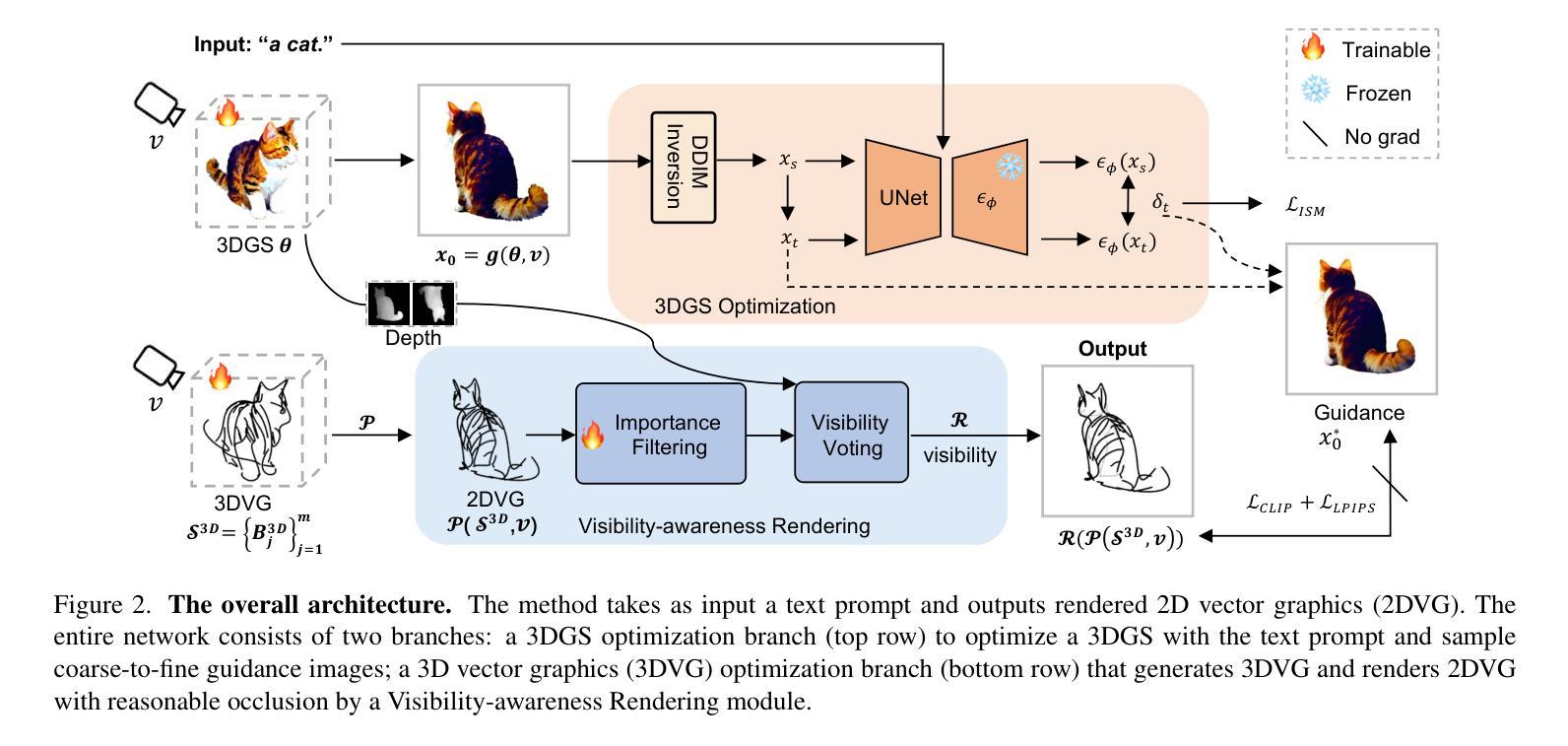
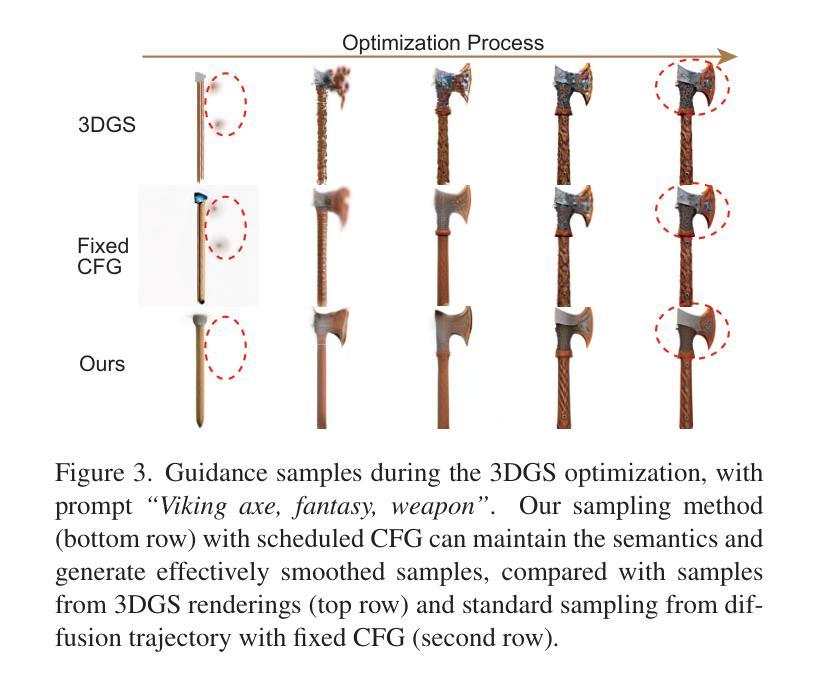
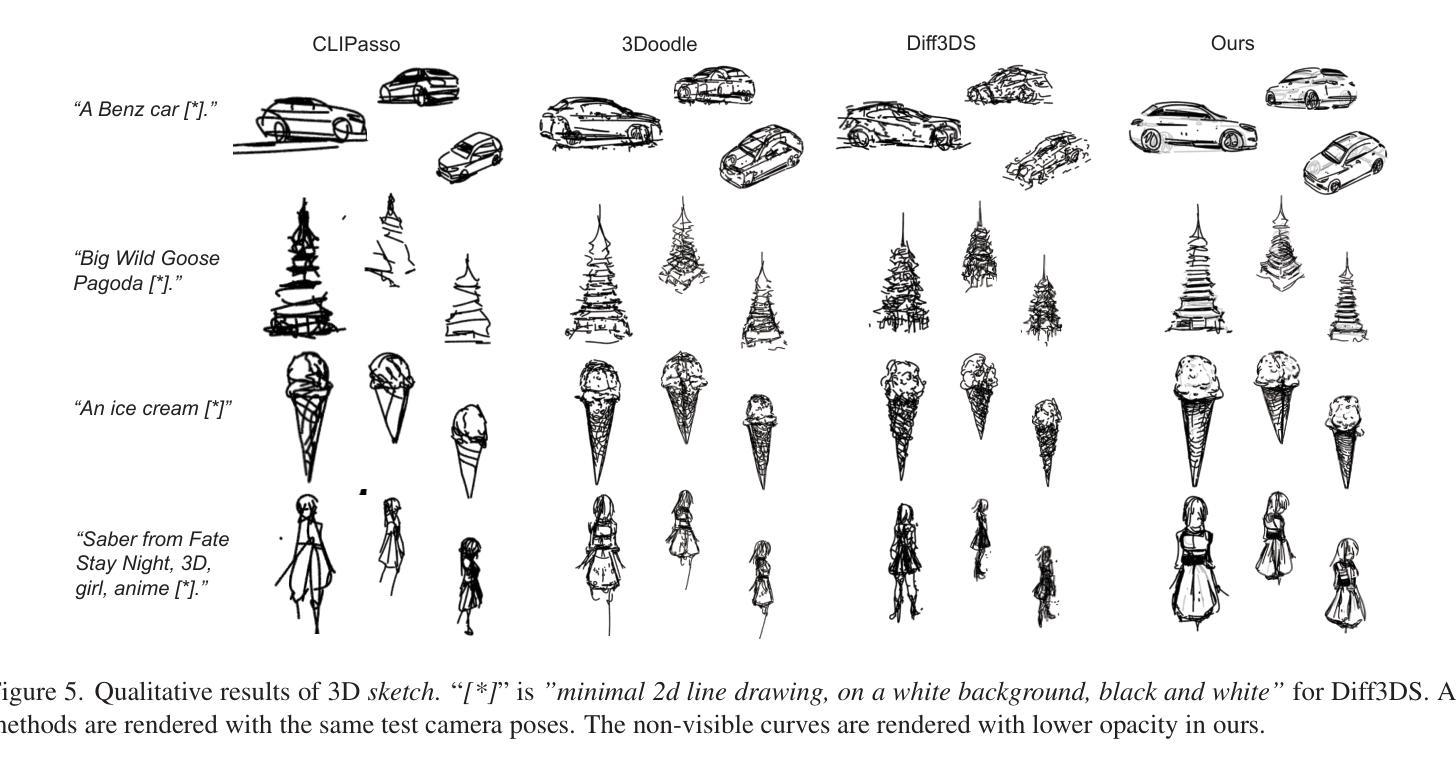
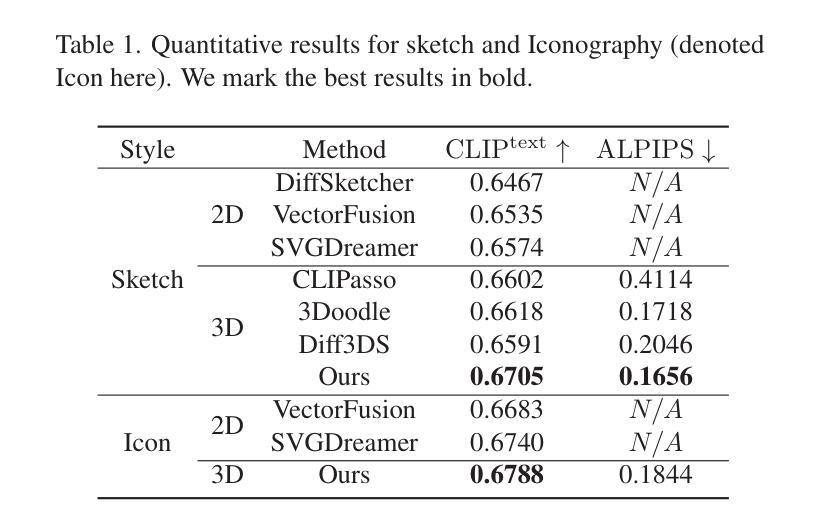
This work presents a novel text-to-vector graphics generation approach, Dream3DVG, allowing for arbitrary viewpoint viewing, progressive detail optimization, and view-dependent occlusion awareness. Our approach is a dual-branch optimization framework, consisting of an auxiliary 3D Gaussian Splatting optimization branch and a 3D vector graphics optimization branch. The introduced 3DGS branch can bridge the domain gaps between text prompts and vector graphics with more consistent guidance. Moreover, 3DGS allows for progressive detail control by scheduling classifier-free guidance, facilitating guiding vector graphics with coarse shapes at the initial stages and finer details at later stages. We also improve the view-dependent occlusions by devising a visibility-awareness rendering module. Extensive results on 3D sketches and 3D iconographies, demonstrate the superiority of the method on different abstraction levels of details, cross-view consistency, and occlusion-aware stroke culling.
本文提出了一种新型的文本到矢量图形的生成方法Dream3DVG,它支持任意视角观看、渐进的细节优化和视相关的遮挡意识。我们的方法是一个双分支优化框架,包括一个辅助的3D高斯喷绘优化分支和一个3D矢量图形优化分支。引入的3DGS分支能够填补文本提示和矢量图形之间的领域差距,提供更一致的指导。此外,3DGS通过调度无分类指导来实现渐进的细节控制,便于在初始阶段引导具有粗略形状的矢量图形,在后续阶段引导更精细的细节。我们还通过设计可见性感知渲染模块来改善视相关的遮挡问题。在3D草图和三维图标的大量结果中,该方法在不同抽象层次上的细节、跨视图一致性和遮挡感知笔画剔除方面的优越性得到了证明。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的文本到矢量图形的生成方法Dream3DVG,支持任意视角浏览、渐进的细节优化和视角相关的遮挡感知。该方法采用双分支优化框架,包括辅助的3D高斯平铺优化分支和3D矢量图形优化分支。引入的3DGS分支能够缩小文本提示和矢量图形之间的领域差距,提供更一致的指导。此外,3DGS通过调度无分类指导来实现渐进的细节控制,便于在早期阶段以粗略形状引导矢量图形,在后期加入更精细的细节。同时,通过设计可见性感知渲染模块,提高了视角相关的遮挡处理效果。在3D草图和三维图标上的广泛结果表明,该方法在不同层次的细节、跨视角一致性和遮挡感知描边剔除方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Dream3DVG是一种新型的文本到矢量图形的生成方法,支持任意视角浏览。
- 该方法采用双分支优化框架,包括3D高斯平铺优化分支和3D矢量图形优化分支。
- 3DGS分支能够缩小文本提示和矢量图形之间的领域差距,提供更一致的指导。
- 3DGS实现渐进的细节优化,早期以粗略形状引导矢量图形,后期加入更精细的细节。
- 通过设计可见性感知渲染模块,提高了视角相关的遮挡处理效果。
- Dream3DVG在3D草图和三维图标上的表现经过广泛测试。
点此查看论文截图

Structure from Collision
Authors:Takuhiro Kaneko
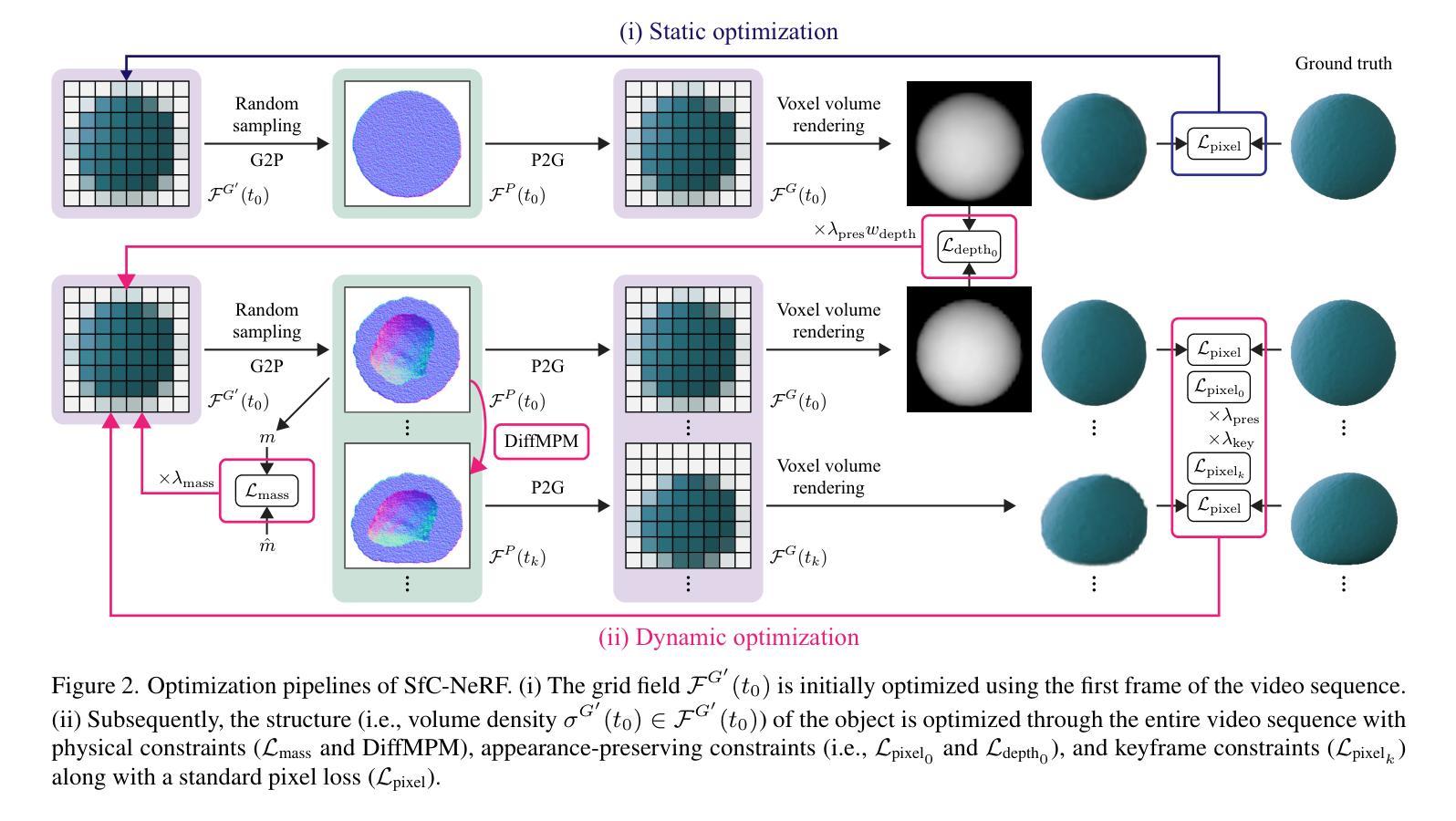
Recent advancements in neural 3D representations, such as neural radiance fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS), have enabled the accurate estimation of 3D structures from multiview images. However, this capability is limited to estimating the visible external structure, and identifying the invisible internal structure hidden behind the surface is difficult. To overcome this limitation, we address a new task called Structure from Collision (SfC), which aims to estimate the structure (including the invisible internal structure) of an object from appearance changes during collision. To solve this problem, we propose a novel model called SfC-NeRF that optimizes the invisible internal structure of an object through a video sequence under physical, appearance (i.e., visible external structure)-preserving, and keyframe constraints. In particular, to avoid falling into undesirable local optima owing to its ill-posed nature, we propose volume annealing; that is, searching for global optima by repeatedly reducing and expanding the volume. Extensive experiments on 115 objects involving diverse structures (i.e., various cavity shapes, locations, and sizes) and material properties revealed the properties of SfC and demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed SfC-NeRF.
近期,神经三维表示技术(如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯贴图(3DGS))的进展,已经能够实现通过多视角图像准确估计三维结构。然而,这种能力仅限于估计可见的外部结构,识别隐藏在表面之后的不可见内部结构仍然很困难。为了克服这一局限性,我们解决了一项新的任务,称为从碰撞中重建结构(SfC),旨在通过碰撞过程中的外观变化来估计物体的结构(包括不可见的内部结构)。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型模型SfC-NeRF,它通过视频序列优化物体的不可见内部结构,同时遵守物理、外观(即,可见的外部结构)保留和关键帧约束。尤其为了避免因问题不适定而陷入不良的局部最优解,我们提出了体积退火方法,即通过反复减小和扩大体积来寻找全局最优解。在涉及多种结构(例如各种腔室形状、位置和大小)和材料特性的13个物体上进行的广泛实验揭示了SfC的特性,并证明了所提出SfC-NeRF模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025 (Highlight). Project page: https://www.kecl.ntt.co.jp/people/kaneko.takuhiro/projects/sfc/
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯涂斑(3DGS)等神经三维表示的最新进展,已经能够准确地从多视角图像估计三维结构。然而,这项能力仅限于估计可见外部结构,对于隐藏在表面之后的不可见内部结构难以识别。为了克服这一局限性,本文提出了一个新的任务——碰撞结构(SfC),旨在从碰撞过程中的外观变化估计物体的结构(包括不可见的内部结构)。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新型模型SfC-NeRF,通过视频序列在物理和外观保留以及关键帧约束下优化物体的不可见内部结构。为避免因问题不适定而陷入局部最优解,本文提出了体积退火方法,即通过反复缩小和扩大体积来寻找全局最优解。对涉及多种结构和材料特性的115个物体的广泛实验揭示了SfC的特性,并验证了所提出的SfC-NeRF的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经三维表示技术如NeRF和3DGS能够从多视角图像准确估计三维结构。
- 当前技术主要局限于估计可见外部结构,难以识别不可见内部结构。
- 提出新的任务SfC,旨在从碰撞过程中的外观变化估计物体的完整结构。
- 为解决SfC问题,提出SfC-NeRF模型,结合视频序列在物理和外观约束下优化物体的内部结构。
- 采用体积退火方法避免陷入局部最优解,通过反复缩小和扩大体积来寻找全局最优解。
点此查看论文截图

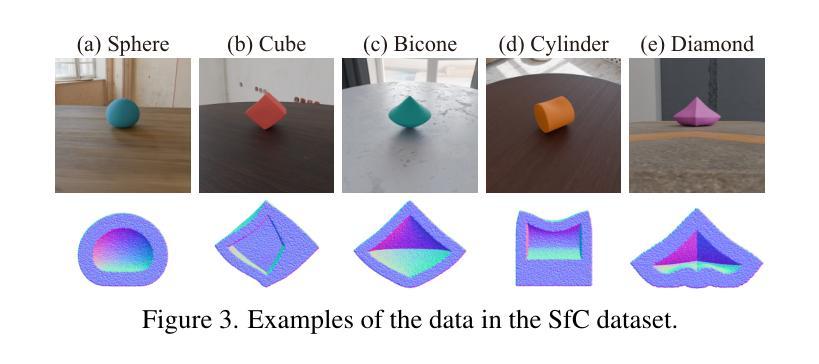
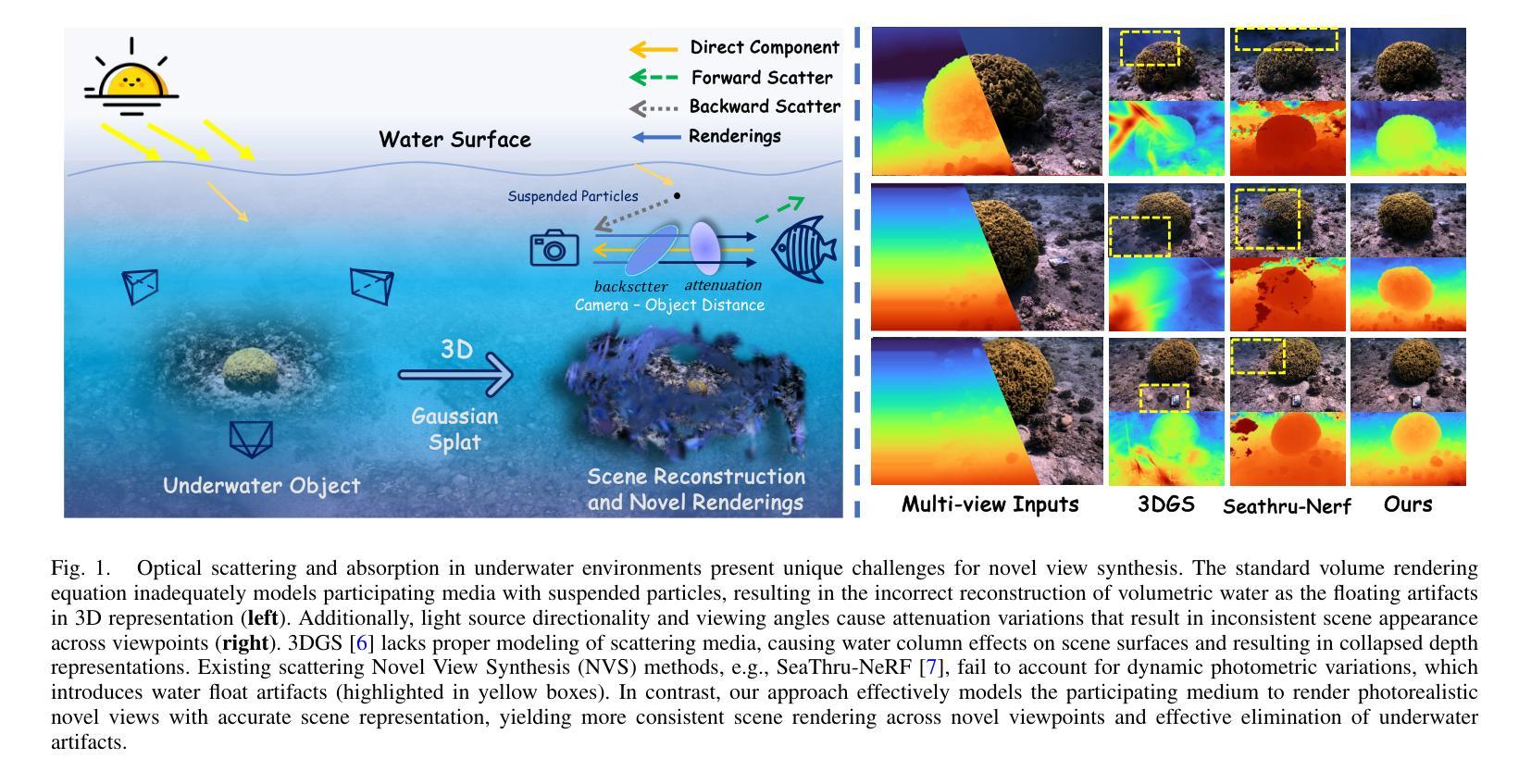
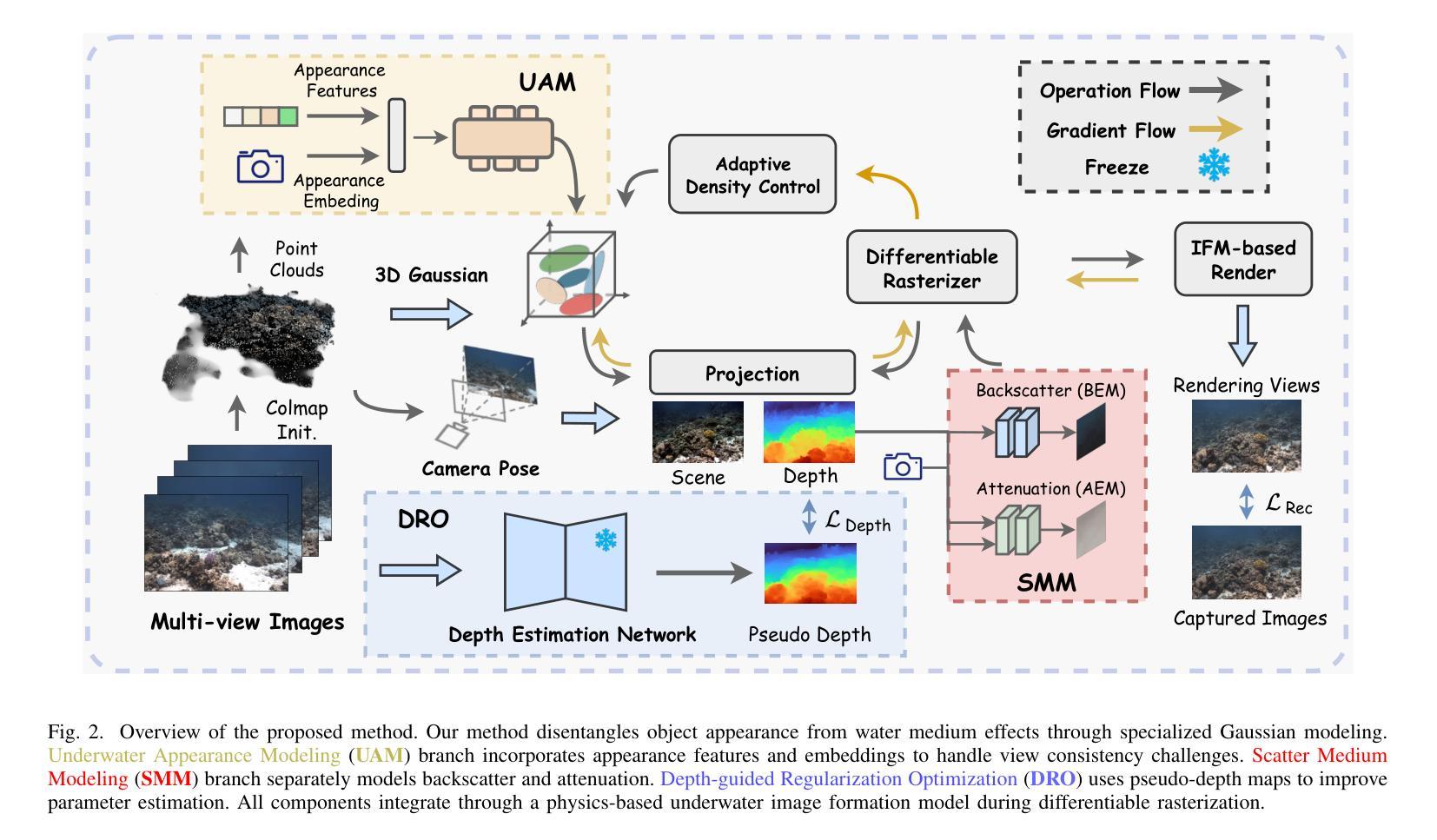
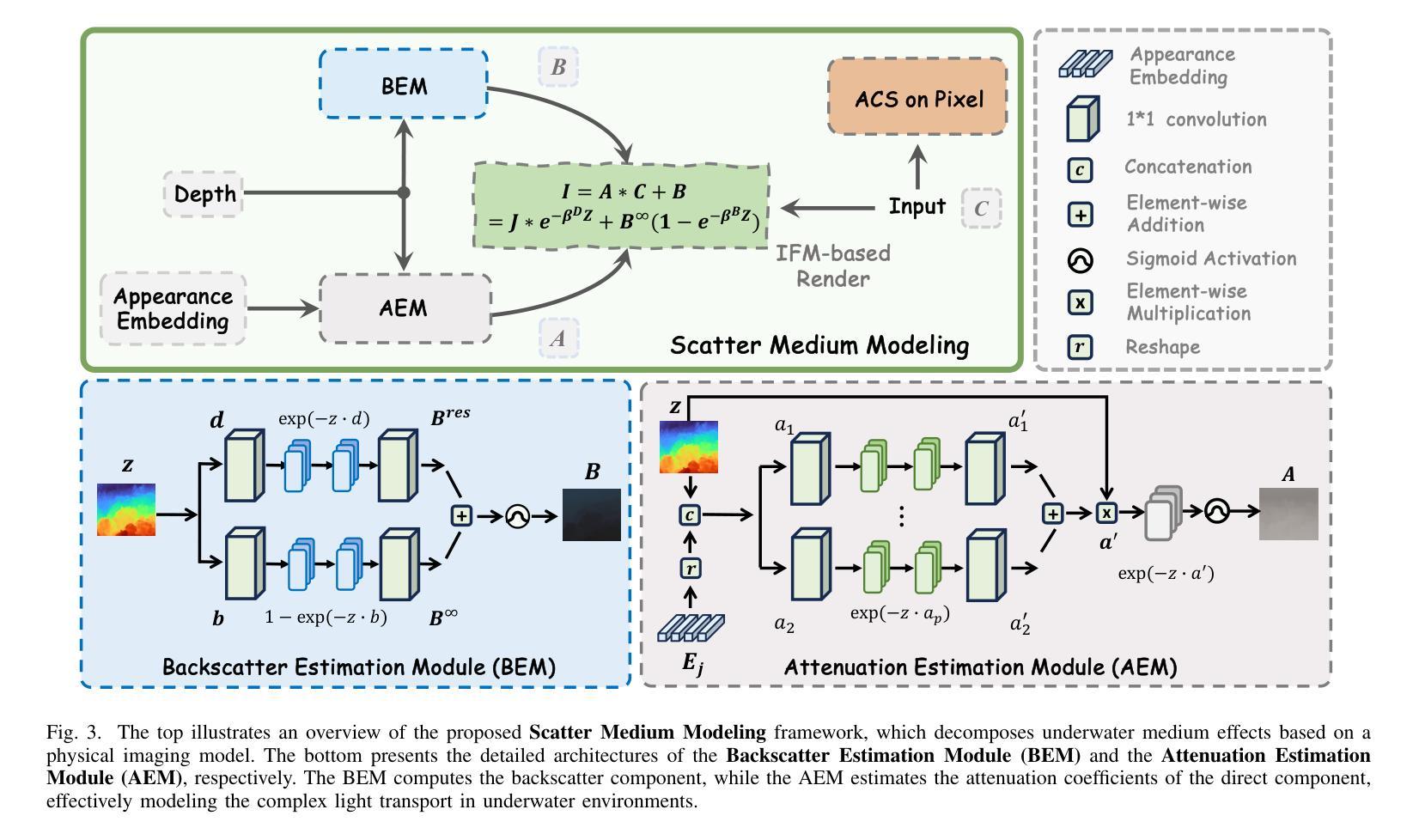
3D-UIR: 3D Gaussian for Underwater 3D Scene Reconstruction via Physics-Based Appearance-Medium Decouplin
Authors:Jieyu Yuan, Yujun Li, Yuanlin Zhang, Chunle Guo, Xiongxin Tang, Ruixing Wang, Chongyi Li
Novel view synthesis for underwater scene reconstruction presents unique challenges due to complex light-media interactions. Optical scattering and absorption in water body bring inhomogeneous medium attenuation interference that disrupts conventional volume rendering assumptions of uniform propagation medium. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) offers real-time rendering capabilities, it struggles with underwater inhomogeneous environments where scattering media introduce artifacts and inconsistent appearance. In this study, we propose a physics-based framework that disentangles object appearance from water medium effects through tailored Gaussian modeling. Our approach introduces appearance embeddings, which are explicit medium representations for backscatter and attenuation, enhancing scene consistency. In addition, we propose a distance-guided optimization strategy that leverages pseudo-depth maps as supervision with depth regularization and scale penalty terms to improve geometric fidelity. By integrating the proposed appearance and medium modeling components via an underwater imaging model, our approach achieves both high-quality novel view synthesis and physically accurate scene restoration. Experiments demonstrate our significant improvements in rendering quality and restoration accuracy over existing methods. The project page is available at \href{https://bilityniu.github.io/3D-UIR}{https://bilityniu.github.io/3D-UIR
水下场景重建的新型视图合成面临着独特的挑战,这是由于复杂的光媒交互造成的。水体中的光学散射和吸收带来了非均匀介质衰减干扰,破坏了传统体积渲染关于均匀传播介质的假设。虽然3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)提供了实时渲染功能,但在水下非均匀环境中,散射介质会引入伪影和外观不一致的问题。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个基于物理的框架,通过定制的高斯建模来分离物体外观和水介质效果。我们的方法引入了外观嵌入,这是后向散射和衰减的明确介质表示,提高了场景的一致性。此外,我们提出了一种距离引导优化策略,利用伪深度图作为监督,通过深度正则化和尺度惩罚项来提高几何保真度。通过整合提出的外观和介质建模组件,借助水下成像模型,我们的方法实现了高质量的新型视图合成和物理准确的场景恢复。实验表明,与现有方法相比,我们的方法在渲染质量和恢复精度方面都有显著提高。项目页面可在https://bilityniu.github.io/3D-UIR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
水下场景重建的新型视图合成面临独特挑战,因光与媒介的复杂交互导致。水体中的光学散射和吸收造成非均匀介质衰减干扰,破坏了传统体积渲染假设的均匀传播介质。3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)虽具备实时渲染能力,但在水下非均匀环境中,散射媒介会引发伪影和外观不一致问题。本研究提出一个基于物理的框架,通过定制的高斯建模来分离物体外观和水介质效果。引入外观嵌入作为后向散射和衰减的明确介质表示,提高场景一致性。此外,提出距离引导优化策略,利用伪深度图作为监督,结合深度正则化和尺度惩罚项,提高几何保真度。通过整合提出的外观和介质建模组件,借助水下成像模型,该方法实现了高质量的新型视图合成和物理准确的场景恢复。实验证明,该方法在渲染质量和恢复精度上较现有方法有明显改进。
Key Takeaways
- 水下场景重建面临复杂的光-媒介交互挑战。
- 光学散射和吸收导致非均匀介质衰减干扰。
- 3D高斯拼贴在处理水下非均匀环境时存在挑战。
- 提出基于物理的框架,通过定制的高斯建模分离物体外观和水介质效果。
- 引入外观嵌入以明确表示后向散射和衰减。
- 提出距离引导优化策略,利用伪深度图提高几何保真度。
点此查看论文截图

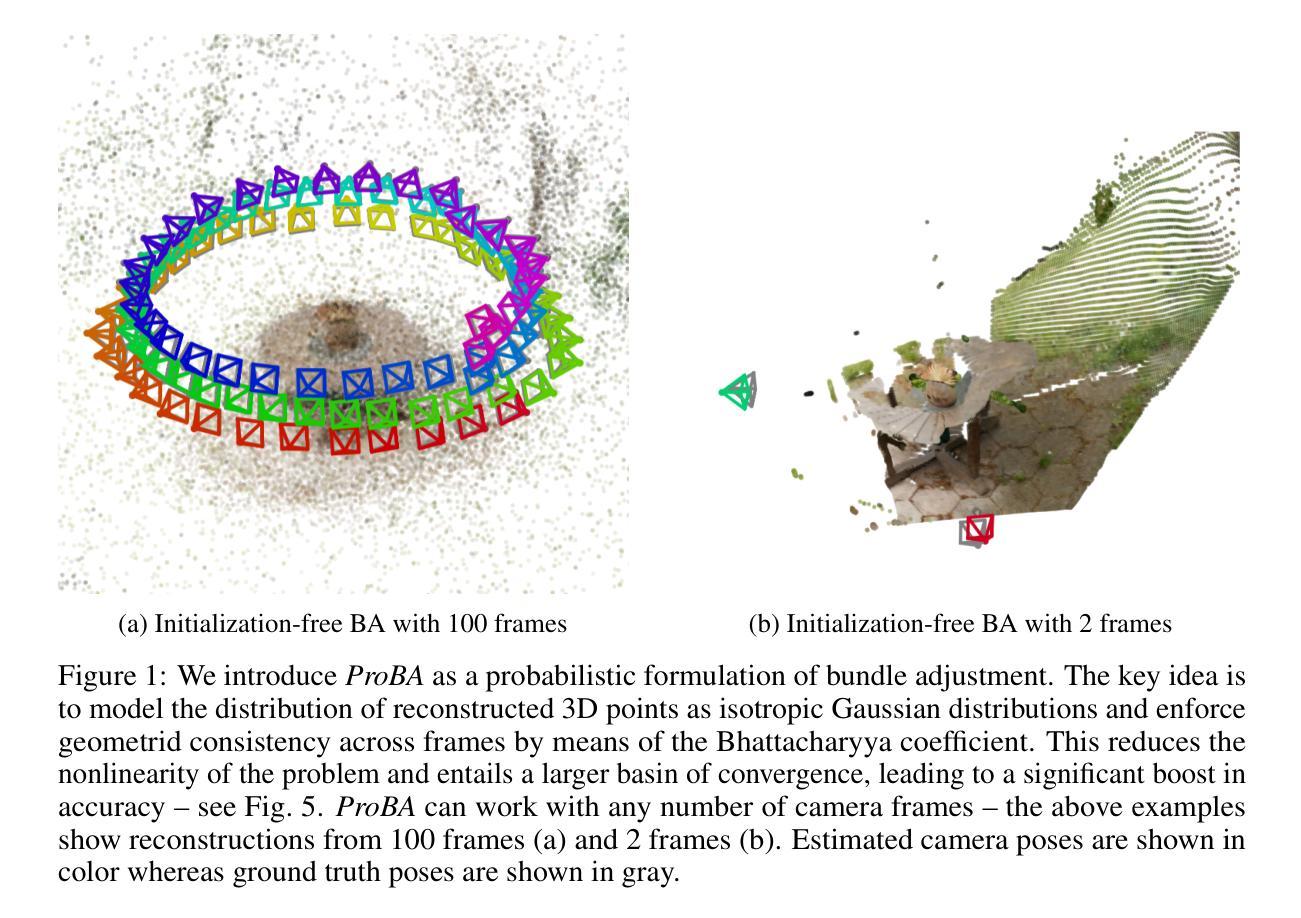
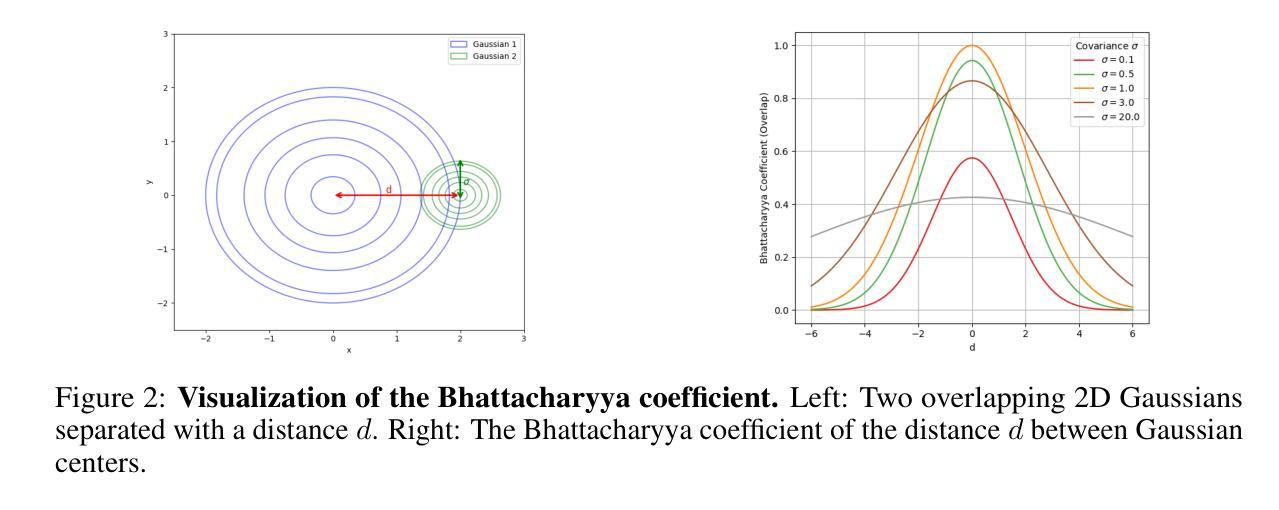
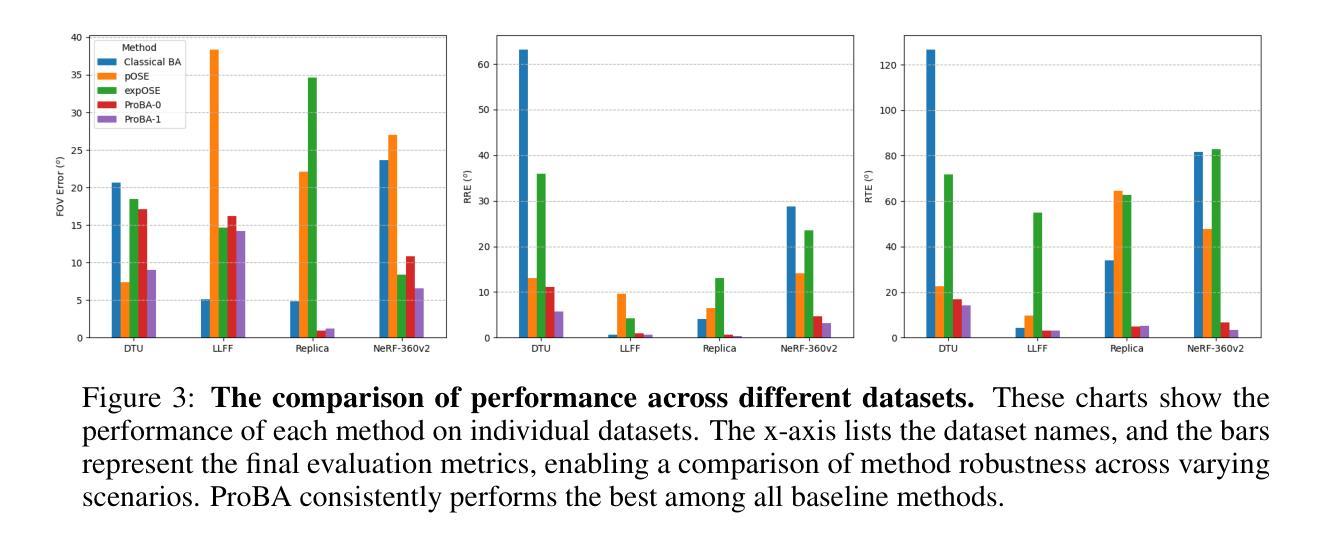
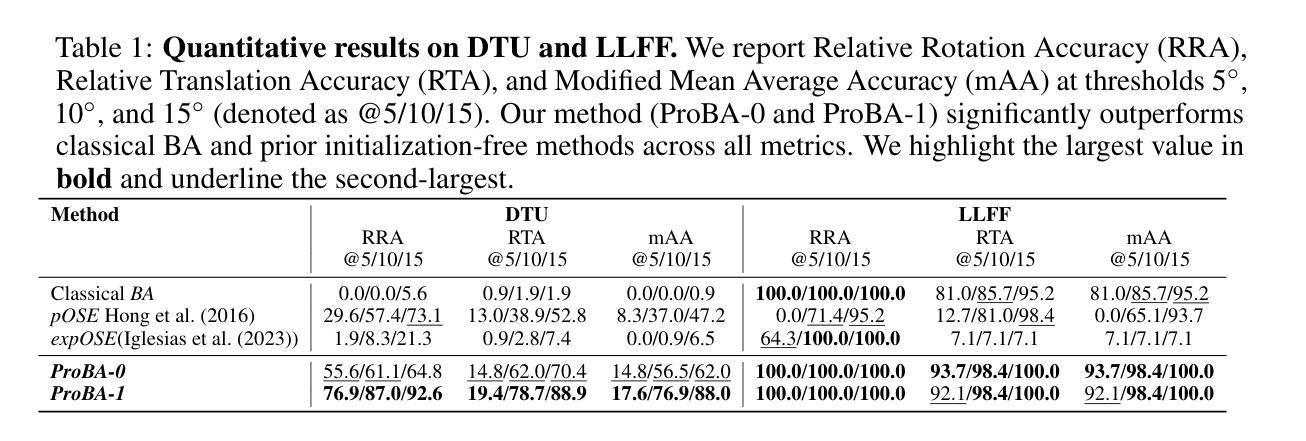
ProBA: Probabilistic Bundle Adjustment with the Bhattacharyya Coefficient
Authors:Jason Chui, Daniel Cremers
Classical Bundle Adjustment (BA) methods require accurate initial estimates for convergence and typically assume known camera intrinsics, which limits their applicability when such information is uncertain or unavailable. We propose a novel probabilistic formulation of BA (ProBA) that explicitly models and propagates uncertainty in both the 2D observations and the 3D scene structure, enabling optimization without any prior knowledge of camera poses or focal length. Our method uses 3D Gaussians instead of point-like landmarks and we introduce uncertainty-aware reprojection losses by projecting the 3D Gaussians onto the 2D image space, and enforce geometric consistency across multiple 3D Gaussians using the Bhattacharyya coefficient to encourage overlap between their corresponding Gaussian distributions. This probabilistic framework leads to more robust and reliable optimization, even in the presence of outliers in the correspondence set, reducing the likelihood of converging to poor local minima. Experimental results show that \textit{ProBA} outperforms traditional methods in challenging real-world conditions. By removing the need for strong initialization and known intrinsics, ProBA enhances the practicality of SLAM systems deployed in unstructured environments.
传统的Bundle Adjustment(BA)方法需要准确的初始估计值以实现收敛,并且通常假设已知相机内参,这在相关信息不确定或不可用的情况下限制了其适用性。我们提出了一种新型的BA概率公式(ProBA),该公式能够明确建模并传播2D观测和3D场景结构中的不确定性,从而实现无需事先了解相机姿态或焦距的优化。我们的方法使用3D高斯分布代替点状地标,并通过将3D高斯分布投影到2D图像空间来引入感知不确定性的重投影损失,并使用Bhattacharyya系数强制多个3D高斯分布之间的几何一致性,以鼓励其相应高斯分布之间的重叠。这种概率框架即使在对应集存在异常值的情况下,也能实现更稳健和可靠的优化,降低了陷入糟糕局部最小值的可能性。实验结果表明,在具有挑战性的现实条件下,ProBA优于传统方法。通过不再需要强大的初始化程序和已知的内参,ProBA提高了在复杂环境中部署的SLAM系统的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 14 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出一种新型的概率论Bundle Adjustment(ProBA)方法,该方法能够显式地模拟并传播2D观测和3D场景结构的不确定性,无需任何关于相机姿态或焦距的先验知识即可进行优化。通过引入基于不确定性感知的重投影损失和几何一致性约束,使得该方法更为稳健可靠,即使对应集存在异常值也能优化。实验结果表明,在复杂真实环境下,ProBA的性能优于传统方法,增强了在无结构环境中部署的SLAM系统的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- ProBA是一种新型的Bundle Adjustment方法,适用于相机参数不确定或不可用的情况。
- ProBA显式地模拟并传播观测和场景结构的不确定性。
- ProBA使用3D高斯分布代替点状地标进行优化。
- ProBA引入基于不确定性感知的重投影损失,通过将3D高斯分布投影到2D图像空间来执行。
- 使用Bhattacharyya系数来确保多个3D高斯之间的几何一致性,从而促进其相应高斯分布之间的重叠。
- ProBA更为稳健可靠,即使在对应集中存在异常值也能优化。
点此查看论文截图

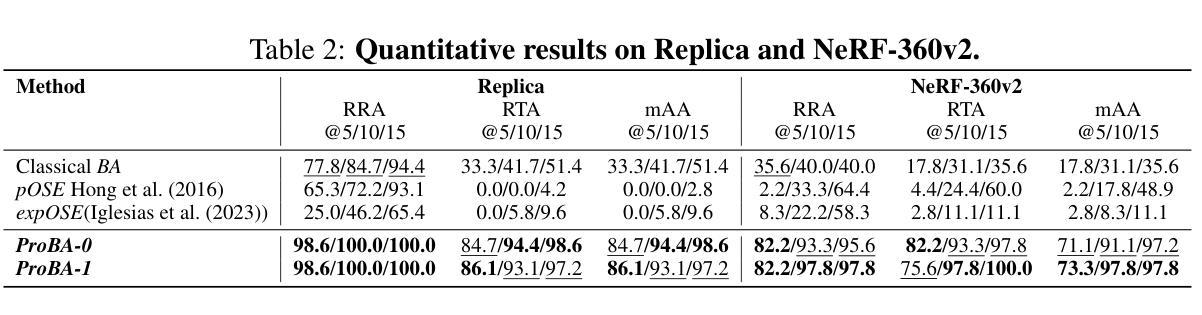
Intern-GS: Vision Model Guided Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Xiangyu Sun, Runnan Chen, Mingming Gong, Dong Xu, Tongliang Liu
Sparse-view scene reconstruction often faces significant challenges due to the constraints imposed by limited observational data. These limitations result in incomplete information, leading to suboptimal reconstructions using existing methodologies. To address this, we present Intern-GS, a novel approach that effectively leverages rich prior knowledge from vision foundation models to enhance the process of sparse-view Gaussian Splatting, thereby enabling high-quality scene reconstruction. Specifically, Intern-GS utilizes vision foundation models to guide both the initialization and the optimization process of 3D Gaussian splatting, effectively addressing the limitations of sparse inputs. In the initialization process, our method employs DUSt3R to generate a dense and non-redundant gaussian point cloud. This approach significantly alleviates the limitations encountered by traditional structure-from-motion (SfM) methods, which often struggle under sparse-view constraints. During the optimization process, vision foundation models predict depth and appearance for unobserved views, refining the 3D Gaussians to compensate for missing information in unseen regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Intern-GS achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality across diverse datasets, including both forward-facing and large-scale scenes, such as LLFF, DTU, and Tanks and Temples.
稀疏视角场景重建常常由于有限的观测数据所带来的约束而面临重大挑战。这些限制导致信息不完整,使用现有方法进行的重建效果不理想。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Intern-GS,这是一种利用丰富的先验知识,有效提升稀疏视角高斯延展过程的新方法,从而实现高质量的场景重建。具体来说,Intern-GS利用视觉基础模型来指导3D高斯延展的初始化和优化过程,有效解决稀疏输入的局限性。在初始化过程中,我们的方法采用DUSt3R生成密集且非冗余的高斯点云。这种方法极大地缓解了传统结构从运动(SfM)方法在稀疏视角约束下经常遇到的局限。在优化过程中,视觉基础模型预测未观测视角的深度和外观,对3D高斯进行微调以补偿未观测区域的缺失信息。大量实验表明,Intern-GS在多种数据集上实现了最先进的渲染质量,包括正面和大规模场景,如LLFF、DTU和坦克与神庙等。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于稀疏视角的场景重建常常面临由于观测数据有限导致的重大挑战。由于信息不完整,现有方法的重建效果往往不尽如人意。针对这一问题,我们提出了Intern-GS这一新方法,它通过利用视觉基础模型中的丰富先验知识,有效提升了稀疏视角的高斯拼贴过程,从而实现了高质量的场景重建。
Key Takeaways
- Intern-GS利用视觉基础模型的先验知识来解决稀疏视角场景重建中的挑战。
- 通过在初始化过程中使用DUSt3R生成密集且非冗余的高斯点云,有效缓解传统结构从运动(SfM)方法在稀疏视角约束下的局限性。
- 在优化过程中,利用视觉基础模型预测未观测视角的深度和外观,对3D高斯进行细化以补偿未见区域的缺失信息。
- Intern-GS在多种数据集上实现了最先进的渲染质量,包括正面场景、大规模场景,如LLFF、DTU和Tanks and Temples。
- 该方法能有效利用已有的丰富数据资源,通过结合先验知识和实时数据,提高场景重建的准确性和效率。
- 通过密集且非冗余的高斯点云生成,提升了场景结构的表示能力,使得重建结果更加精细。
点此查看论文截图


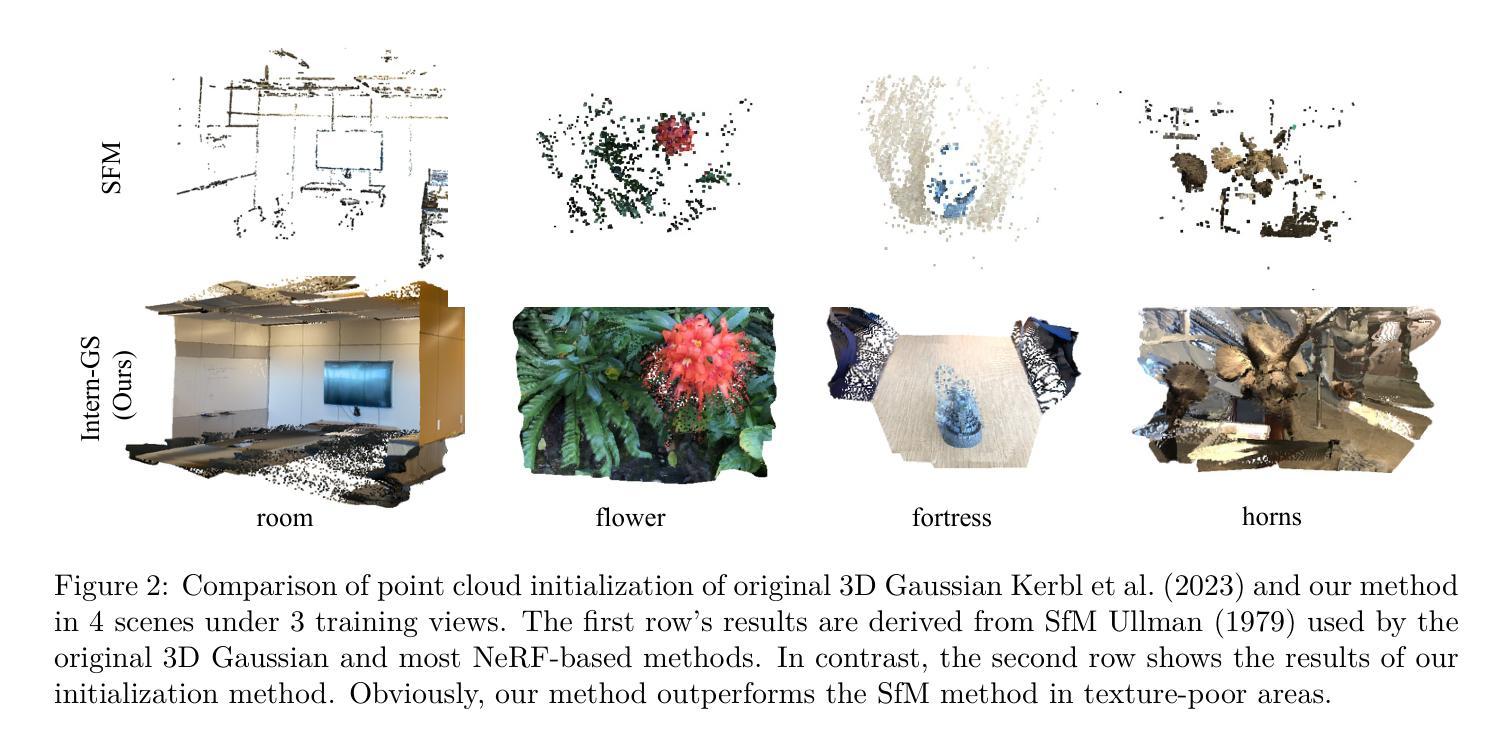
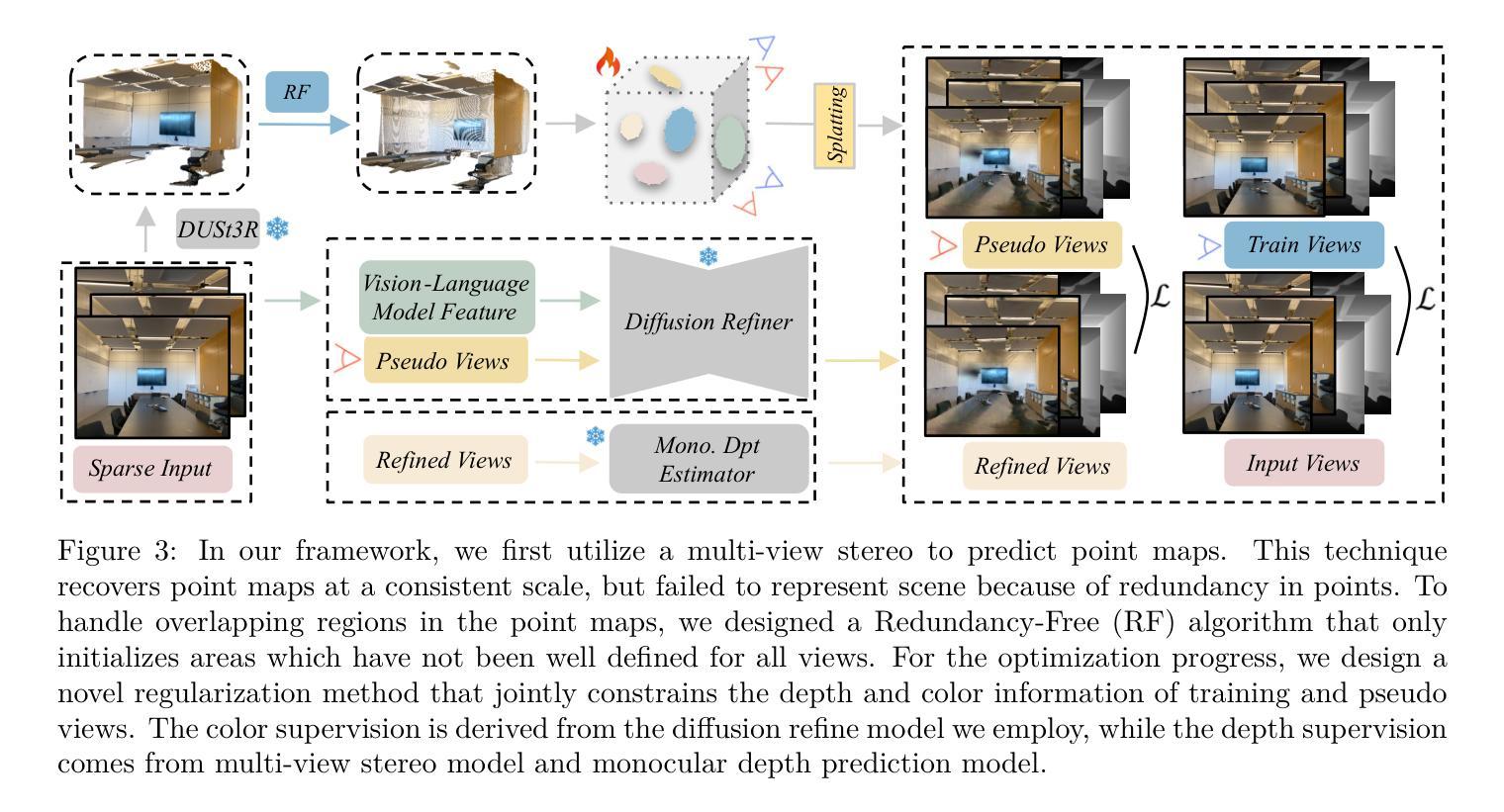
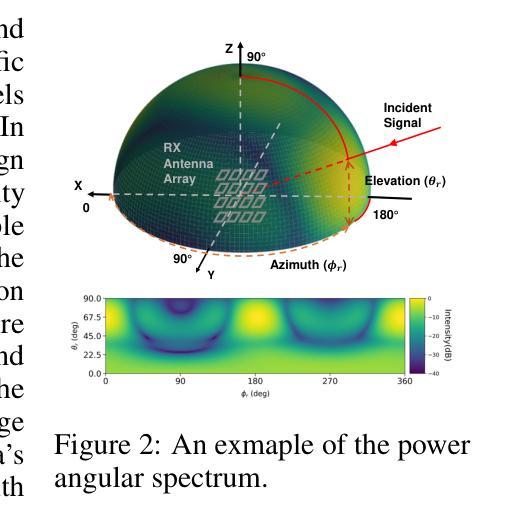
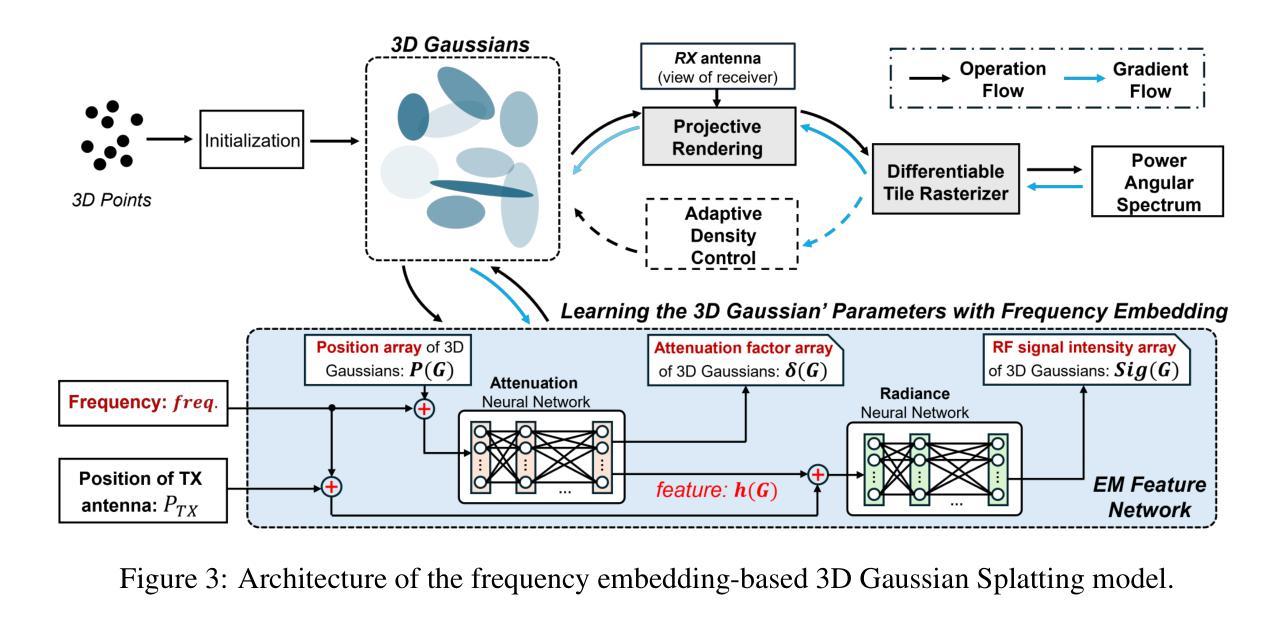
Wideband RF Radiance Field Modeling Using Frequency-embedded 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zechen Li, Lanqing Yang, Yiheng Bian, Hao Pan, Yongjian Fu, Yezhou Wang, Yi-Chao Chen, Guangtao Xue, Ju Ren
This paper presents an innovative frequency-embedded 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) algorithm for wideband radio-frequency (RF) radiance field modeling, offering an advancement over the existing works limited to single-frequency modeling. Grounded in fundamental physics, we uncover the complex relationship between EM wave propagation behaviors and RF frequencies. Inspired by this, we design an EM feature network with attenuation and radiance modules to learn the complex relationships between RF frequencies and the key properties of each 3D Gaussian, specifically the attenuation factor and RF signal intensity. By training the frequency-embedded 3DGS model, we can efficiently reconstruct RF radiance fields at arbitrary unknown frequencies within a given 3D environment. Finally, we propose a large-scale power angular spectrum (PAS) dataset containing 50000 samples ranging from 1 to 100 GHz in 6 indoor environments, and conduct extensive experiments to verify the effectiveness of our method. Our approach achieves an average Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) up to 0.72, and a significant improvement up to 17.8% compared to the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods trained on individual test frequencies. Additionally, our method achieves an SSIM of 0.70 without prior training on these frequencies, which represents only a 2.8% performance drop compared to models trained with full PAS data. This demonstrates our model’s capability to estimate PAS at unknown frequencies. For related code and datasets, please refer to https://github.com/sim-2-real/Wideband3DGS.
本文提出了一种创新的频率嵌入三维高斯扩展(3DGS)算法,用于宽带射频(RF)辐射场建模。相较于现有仅限于单频率建模的工作,该算法是一种进步。该算法基于物理学基本原理,揭示了电磁波传播行为与射频频率之间的复杂关系。受其启发,我们设计了一个具有衰减和辐射模块的电磁特征网络,以学习射频频率与每个三维高斯的关键属性之间的复杂关系,特别是衰减因子和射频信号强度。通过训练频率嵌入的3DGS模型,我们可以有效地在给定三维环境内的任意未知频率上重建射频辐射场。最后,我们提出了一个大规模功率角谱(PAS)数据集,包含6个室内环境中的50000个样本,频率范围从1到100 GHz,并进行了大量实验来验证我们的方法的有效性。我们的方法达到了平均结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)高达0.72,与当前最先进的(SOTA)方法相比,在个别测试频率上进行训练时,有了高达17.8%的显著改善。此外,我们的方法在未经这些频率预先训练的情况下达到了0.70的SSIM,与用全PAS数据训练的模型相比,性能仅下降了2.8%,这证明了我们模型在未知频率上估计PAS的能力。相关代码和数据集请参考:https://github.com/sim-2-real/Wideband3DGS。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种创新的频率嵌入三维高斯模糊算法(Frequency-Embedded 3D Gaussian Splatting,简称FE-3DGS),用于宽频射频辐射场建模。该算法突破了现有仅适用于单频建模的限制,通过设计电磁特征网络学习射频频率与三维高斯关键属性之间的复杂关系,能高效地在任意未知频率下重建射频辐射场。实验结果显示,该方法较当前最优算法有显著提升,且具备在未知频率上估算功率角谱的能力。相关代码与数据集可在相应链接下载。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种频率嵌入的三维高斯模糊算法(FE-3DGS),用于宽频射频辐射场建模。
- 突破了单频建模的限制,通过电磁特征网络学习射频频率与三维高斯属性的复杂关系。
- 能高效地在任意未知频率下重建射频辐射场。
- 实验结果显示该方法较当前最优算法有显著提升。
- 模型具备在未知频率上估算功率角谱的能力。
点此查看论文截图

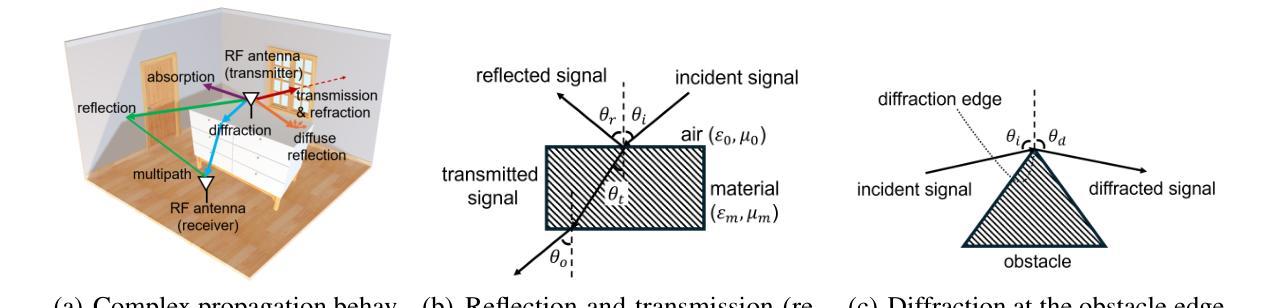
OmniIndoor3D: Comprehensive Indoor 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Xiaobao Wei, Xiaoan Zhang, Hao Wang, Qingpo Wuwu, Ming Lu, Wenzhao Zheng, Shanghang Zhang
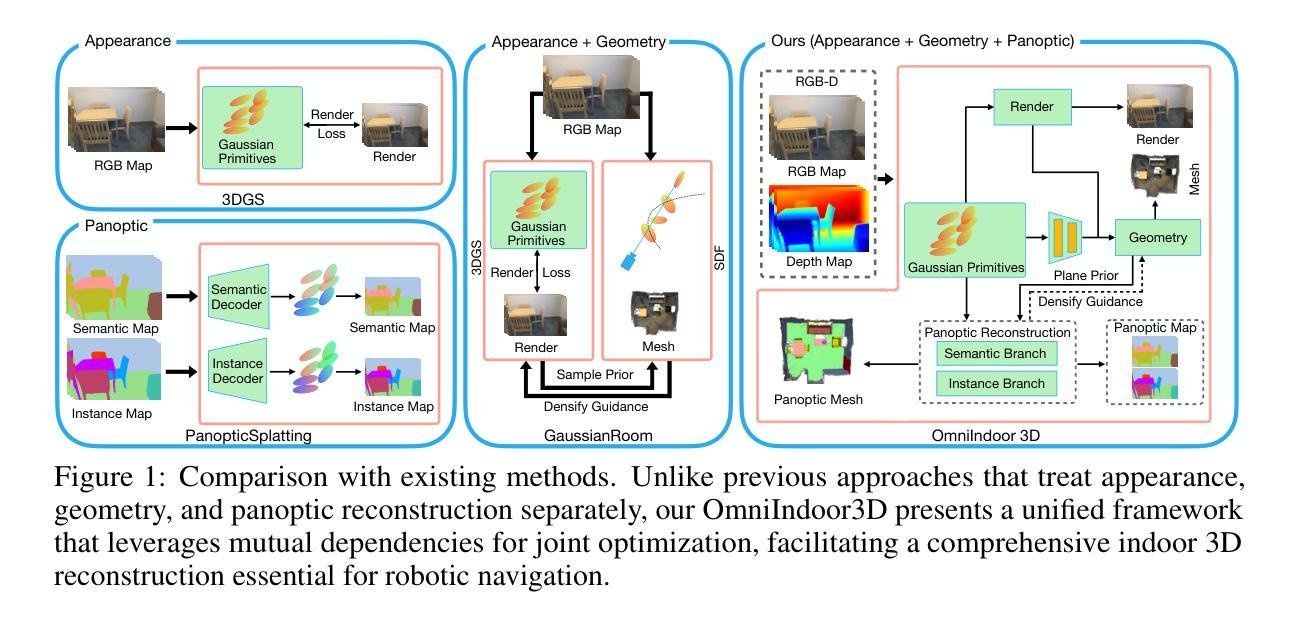
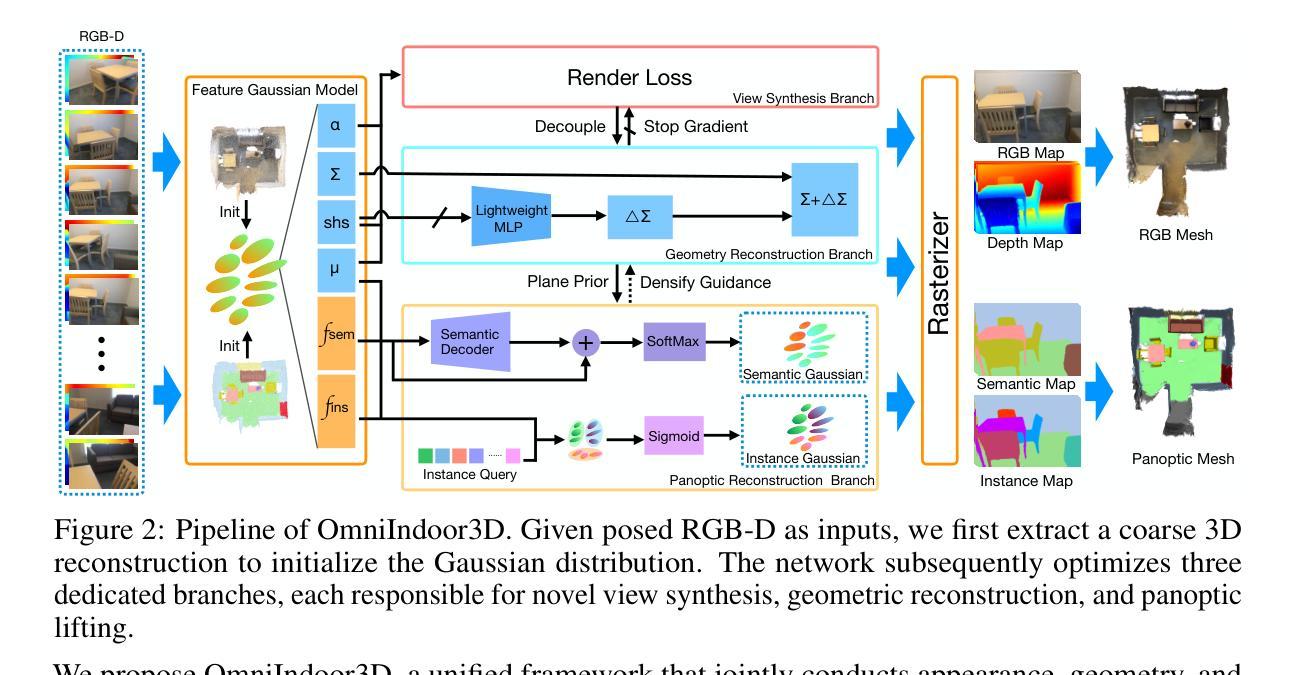
We propose a novel framework for comprehensive indoor 3D reconstruction using Gaussian representations, called OmniIndoor3D. This framework enables accurate appearance, geometry, and panoptic reconstruction of diverse indoor scenes captured by a consumer-level RGB-D camera. Since 3DGS is primarily optimized for photorealistic rendering, it lacks the precise geometry critical for high-quality panoptic reconstruction. Therefore, OmniIndoor3D first combines multiple RGB-D images to create a coarse 3D reconstruction, which is then used to initialize the 3D Gaussians and guide the 3DGS training. To decouple the optimization conflict between appearance and geometry, we introduce a lightweight MLP that adjusts the geometric properties of 3D Gaussians. The introduced lightweight MLP serves as a low-pass filter for geometry reconstruction and significantly reduces noise in indoor scenes. To improve the distribution of Gaussian primitives, we propose a densification strategy guided by panoptic priors to encourage smoothness on planar surfaces. Through the joint optimization of appearance, geometry, and panoptic reconstruction, OmniIndoor3D provides comprehensive 3D indoor scene understanding, which facilitates accurate and robust robotic navigation. We perform thorough evaluations across multiple datasets, and OmniIndoor3D achieves state-of-the-art results in appearance, geometry, and panoptic reconstruction. We believe our work bridges a critical gap in indoor 3D reconstruction. The code will be released at: https://ucwxb.github.io/OmniIndoor3D/
我们提出了一种使用高斯表示进行室内全面三维重建的新型框架,称为OmniIndoor3D。该框架能够利用消费级RGB-D相机捕获的多种室内场景,实现精确的外观、几何和全景重建。由于3DGS主要面向逼真的渲染进行优化,因此在高质量全景重建方面缺乏精确几何结构。因此,OmniIndoor3D首先结合多个RGB-D图像创建粗略的三维重建,然后用于初始化三维高斯并引导3DGS训练。为了消除外观和几何之间的优化冲突,我们引入了一个轻量级的MLP来调整三维高斯几何属性。引入的轻量级MLP作为几何重建的低通滤波器,显著减少了室内场景的噪声。为了提高高斯原始数据的分布,我们提出了一种由全景先验引导的致密化策略,以鼓励平面表面的平滑性。通过外观、几何和全景重建的联合优化,OmniIndoor3D提供了全面的室内三维场景理解,促进了准确可靠的机器人导航。我们在多个数据集上进行了全面评估,OmniIndoor3D在外观、几何和全景重建方面取得了最新结果。我们相信这项工作填补了室内三维重建的关键空白。代码发布地址为:[https://ucwxb.github.io/OmniIndoor3D/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯表示的新型室内三维重建框架OmniIndoor3D。该框架可实现通过消费级RGB-D相机捕获的多样化室内场景的准确外观、几何和全景重建。OmniIndoor3D结合多个RGB-D图像创建粗略的三维重建,进而初始化三维高斯分布并引导三维几何场景网络的训练。引入的轻量级多层感知器解决了外观和几何优化之间的冲突,作为几何重建的低通滤波器,显著降低了室内场景的噪声。通过全景先验指导的高斯原始分布加密策略,促进了平面表面的平滑性。通过外观、几何和全景重建的联合优化,OmniIndoor3D提供了全面的室内三维场景理解,促进了准确和稳健的机器人导航。在多个数据集上的评估表明,OmniIndoor3D在外观、几何和全景重建方面均达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型室内三维重建框架OmniIndoor3D,利用高斯表示实现准确重建。
- 结合RGB-D图像进行粗略三维重建,初始化三维高斯分布,引导后续训练。
- 引入轻量级多层感知器解决外观和几何优化间的冲突,提升几何重建质量。
- 采用低通滤波策略降低室内场景噪声,提高几何重建的准确性。
- 提出基于全景先验的高斯原始分布加密策略,促进平面表面的平滑性。
- 通过联合优化外观、几何和全景重建,OmniIndoor3D提供全面的室内三维场景理解。
点此查看论文截图

CCL-LGS: Contrastive Codebook Learning for 3D Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Lei Tian, Xiaomin Li, Liqian Ma, Hefei Huang, Zirui Zheng, Hao Yin, Taiqing Li, Huchuan Lu, Xu Jia
Recent advances in 3D reconstruction techniques and vision-language models have fueled significant progress in 3D semantic understanding, a capability critical to robotics, autonomous driving, and virtual/augmented reality. However, methods that rely on 2D priors are prone to a critical challenge: cross-view semantic inconsistencies induced by occlusion, image blur, and view-dependent variations. These inconsistencies, when propagated via projection supervision, deteriorate the quality of 3D Gaussian semantic fields and introduce artifacts in the rendered outputs. To mitigate this limitation, we propose CCL-LGS, a novel framework that enforces view-consistent semantic supervision by integrating multi-view semantic cues. Specifically, our approach first employs a zero-shot tracker to align a set of SAM-generated 2D masks and reliably identify their corresponding categories. Next, we utilize CLIP to extract robust semantic encodings across views. Finally, our Contrastive Codebook Learning (CCL) module distills discriminative semantic features by enforcing intra-class compactness and inter-class distinctiveness. In contrast to previous methods that directly apply CLIP to imperfect masks, our framework explicitly resolves semantic conflicts while preserving category discriminability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCL-LGS outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. Our project page is available at https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/.
近期三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的进步极大地推动了三维语义理解的发展,这对于机器人技术、自动驾驶以及虚拟现实/增强现实技术至关重要。然而,依赖二维先验的方法面临着一项重大挑战:由遮挡、图像模糊和视角相关变化引起的跨视图语义不一致性。这些不一致性通过投影监督传播时,会恶化三维高斯语义场的品质,并在渲染输出中引入伪像。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了CCL-LGS这一新型框架,它通过整合多视图语义线索来实施视图一致的语义监督。具体来说,我们的方法首先采用零样本追踪器来对齐一组由SAM生成的二维掩膜并可靠地识别出它们对应的类别。然后,我们使用CLIP来提取跨视图的稳健语义编码。最后,我们的对比代码本学习(CCL)模块通过执行类内紧凑性和类间差异性来提炼出判别语义特征。与前人直接对不完整掩膜应用CLIP的方法不同,我们的框架能够显式解决语义冲突,同时保留类别鉴别能力。大量实验表明,CCL-LGS优于以前的最先进方法。我们的项目页面可通过https://epsilontl.github.io/CCL-LGS/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了近期三维重建技术和视觉语言模型的发展对三维语义理解的重要性及其在机器人、自动驾驶、虚拟现实等领域的应用。然而,依赖于二维先验的方法面临着因遮挡、图像模糊和视角变化导致的跨视图语义不一致性挑战。为解决这一问题,本文提出了CCL-LGS框架,通过集成多视图语义线索来实施视图一致语义监督。实验证明,CCL-LGS相较于现有先进技术表现出优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D语义理解在机器人、自动驾驶、虚拟现实等领域具有关键作用。
- 当前方法依赖于二维先验,面临跨视图语义不一致的挑战。
- CCL-LGS框架通过多视图语义线索实施视图一致语义监督来克服这一挑战。
- CCL-LGS采用零镜头追踪器对齐SAM生成的二维掩膜并识别对应的类别。
- 使用CLIP提取跨视图的稳健语义编码。
- 对比代码本学习(CCL)模块通过执行类内紧凑性和类间区分性来提炼判别语义特征。
- CCL-LGS框架显式解决语义冲突,同时保留类别辨别能力。
点此查看论文截图

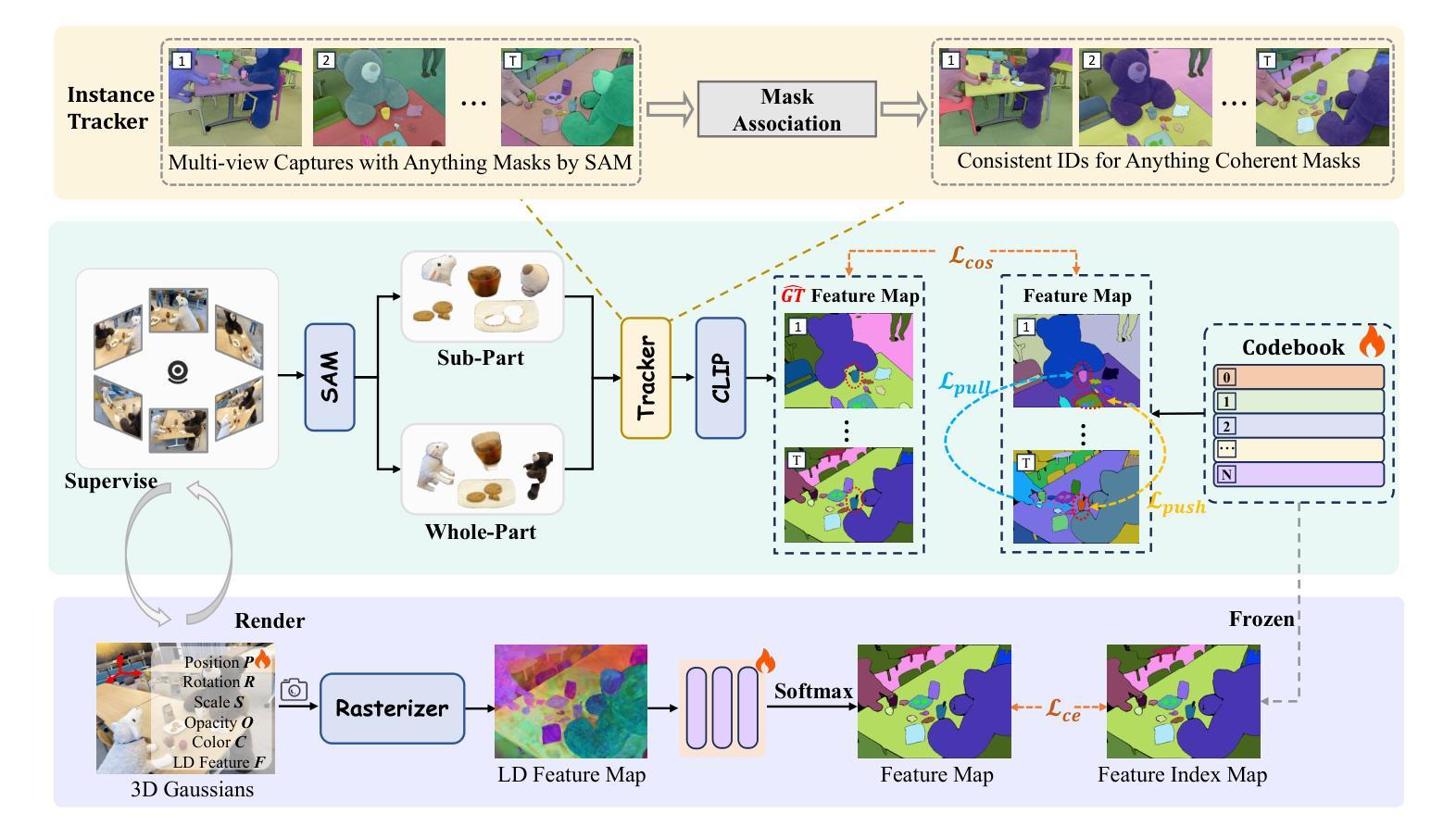
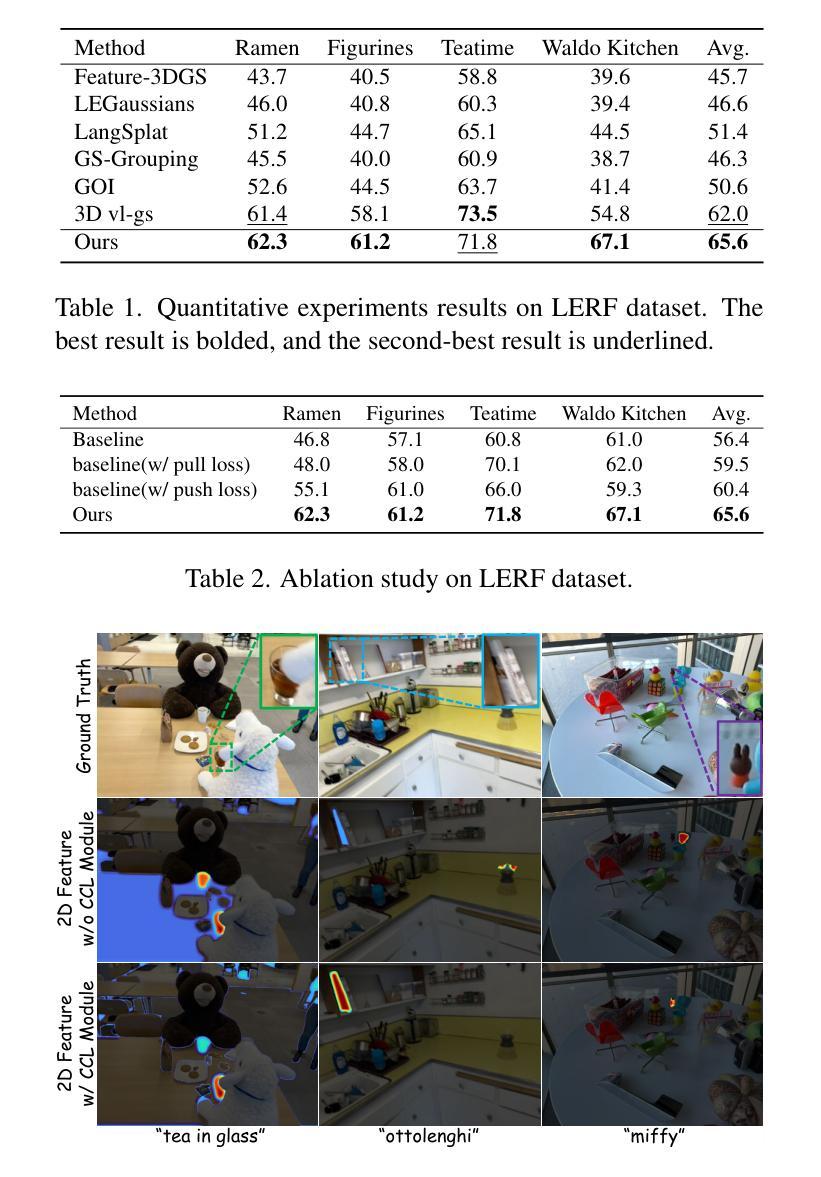
ParticleGS: Particle-Based Dynamics Modeling of 3D Gaussians for Prior-free Motion Extrapolation
Authors:Jinsheng Quan, Chunshi Wang, Yawei Luo
This paper aims to model the dynamics of 3D Gaussians from visual observations to support temporal extrapolation. Existing dynamic 3D reconstruction methods often struggle to effectively learn underlying dynamics or rely heavily on manually defined physical priors, which limits their extrapolation capabilities. To address this issue, we propose a novel dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting prior-free motion extrapolation framework based on particle dynamics systems. The core advantage of our method lies in its ability to learn differential equations that describe the dynamics of 3D Gaussians, and follow them during future frame extrapolation. Instead of simply fitting to the observed visual frame sequence, we aim to more effectively model the gaussian particle dynamics system. To this end, we introduce a dynamics latent state vector into the standard Gaussian kernel and design a dynamics latent space encoder to extract initial state. Subsequently, we introduce a Neural ODEs-based dynamics module that models the temporal evolution of Gaussian in dynamics latent space. Finally, a Gaussian kernel space decoder is used to decode latent state at the specific time step into the deformation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves comparable rendering quality with existing approaches in reconstruction tasks, and significantly outperforms them in future frame extrapolation. Our code is available at https://github.com/QuanJinSheng/ParticleGS.
本文旨在从视觉观察中对3D高斯动态进行建模,以支持时间外推。现有的动态3D重建方法往往难以有效地学习潜在动态,或者严重依赖于手动定义的物理先验,这限制了其外推能力。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于粒子动力学系统的新型动态3D高斯Splatting无先验运动外推框架。我们的方法的核心优势在于能够学习描述3D高斯动态的微分方程,并在未来帧外推过程中遵循这些方程。我们的目标不是简单地拟合观察到的视觉帧序列,而是更有效地对高斯粒子动力学系统进行建模。为此,我们在标准高斯核中引入了一个动态潜伏状态向量,并设计了一个动态潜伏空间编码器来提取初始状态。随后,我们引入了一个基于神经ODE的动态模块,该模块对动态潜伏空间中的高斯时间演化进行建模。最后,使用高斯核空间解码器将特定时间步长的潜伏状态解码为变形。实验结果表明,该方法在重建任务上的渲染质量与现有方法相当,并在未来帧外推方面显著优于它们。我们的代码可在https://github.com/QuanJinSheng/ParticleGS上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于粒子动力学系统的动态3D高斯Splatting无先验运动外推框架,用于从视觉观测中建模3D高斯的动力学以支持时间外推。该方法的核心优势在于能够学习描述3D高斯动力学的微分方程,并在未来帧外推过程中跟踪这些方程。实验结果表明,该方法在重建任务中的渲染质量可与现有方法相媲美,并在未来帧外推方面显著优于它们。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文旨在通过建模3D高斯的动力学来解决现有动态3D重建方法在外推能力上的局限性。
- 论文提出了一种基于粒子动力学系统的动态3D高斯Splatting无先验运动外推框架。
- 该方法通过学习描述3D高斯动力学的微分方程,并在未来帧外推过程中跟踪这些方程来提升外推能力。
- 论文引入了动力学潜在状态向量和动力学潜在空间编码器来提取初始状态。
- 使用基于神经ODE的动力学模块来模拟高斯在动力学潜在空间中的时间演化。
- 论文使用高斯核空间解码器将特定时间步长的潜在状态解码为变形。
点此查看论文截图

Sparse2DGS: Sparse-View Surface Reconstruction using 2D Gaussian Splatting with Dense Point Cloud
Authors:Natsuki Takama, Shintaro Ito, Koichi Ito, Hwann-Tzong Chen, Takafumi Aoki
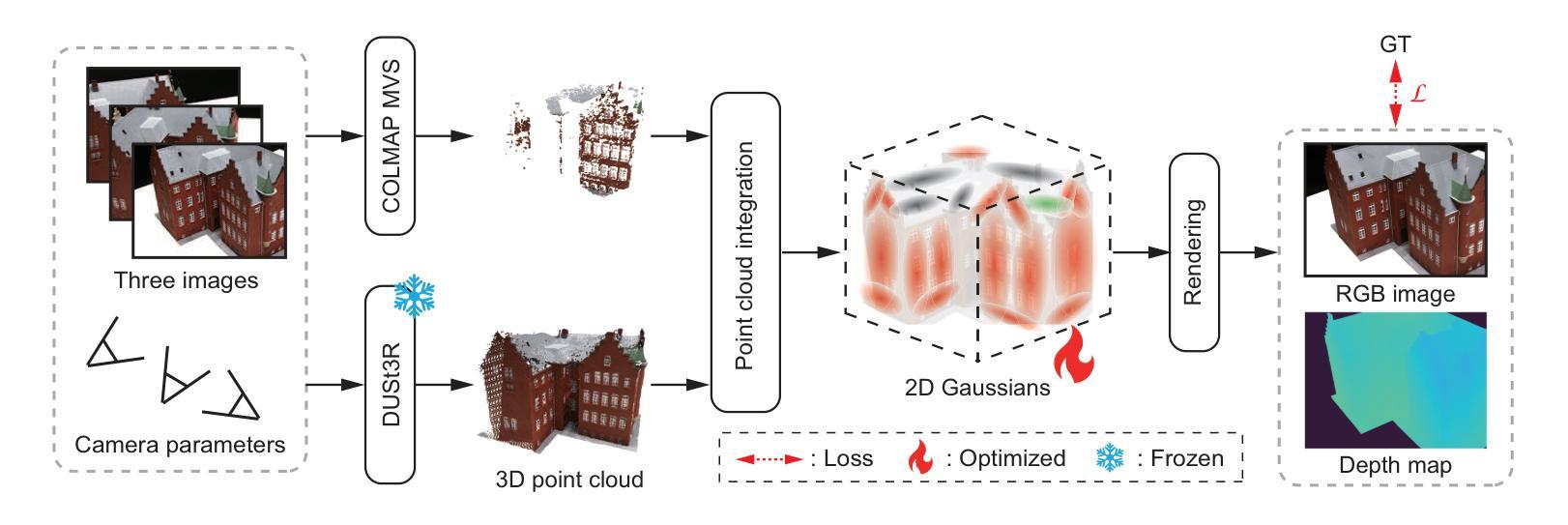
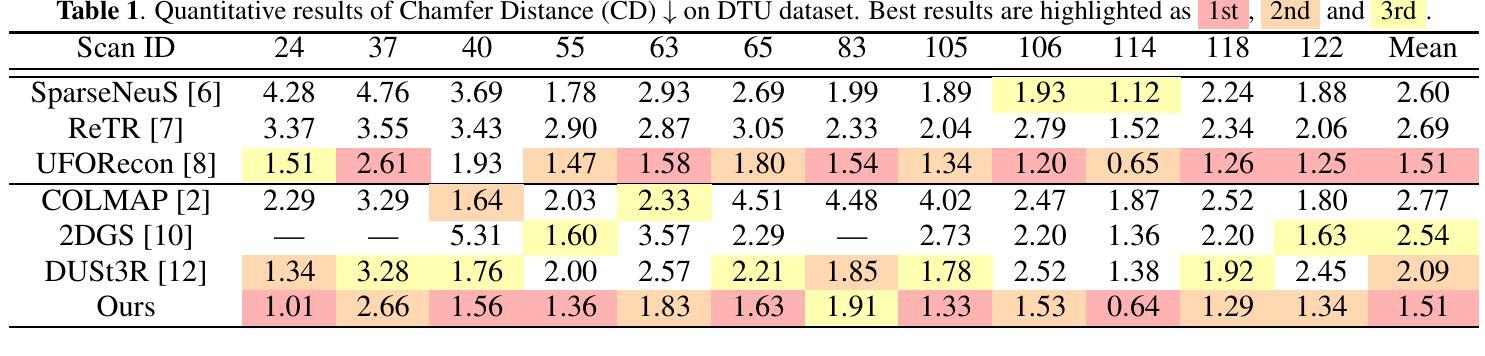
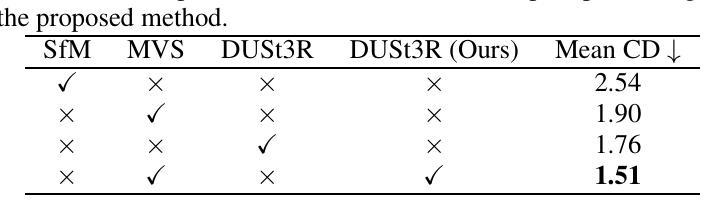
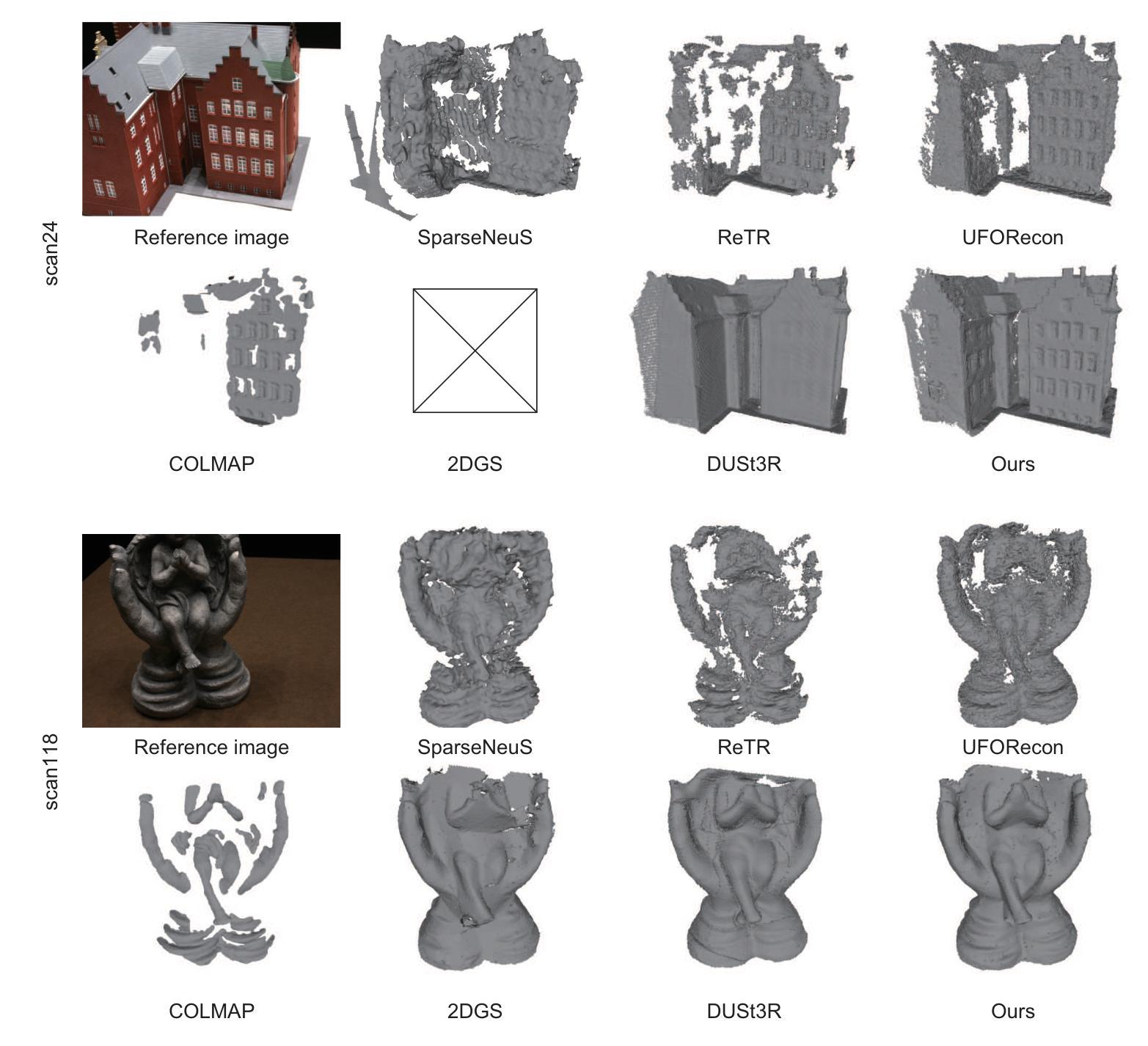
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has gained attention as a fast and effective method for novel view synthesis. It has also been applied to 3D reconstruction using multi-view images and can achieve fast and accurate 3D reconstruction. However, GS assumes that the input contains a large number of multi-view images, and therefore, the reconstruction accuracy significantly decreases when only a limited number of input images are available. One of the main reasons is the insufficient number of 3D points in the sparse point cloud obtained through Structure from Motion (SfM), which results in a poor initialization for optimizing the Gaussian primitives. We propose a new 3D reconstruction method, called Sparse2DGS, to enhance 2DGS in reconstructing objects using only three images. Sparse2DGS employs DUSt3R, a fundamental model for stereo images, along with COLMAP MVS to generate highly accurate and dense 3D point clouds, which are then used to initialize 2D Gaussians. Through experiments on the DTU dataset, we show that Sparse2DGS can accurately reconstruct the 3D shapes of objects using just three images.
高斯贴片(GS)作为一种快速有效的方法,已经引起了人们对新型视图合成技术的关注。它也被应用于使用多视图图像的3D重建,并能实现快速准确的3D重建。然而,GS假定输入包含大量多视图图像,因此当只有有限数量的输入图像可用时,重建精度会大大降低。主要原因之一是通过运动结构(SfM)获得的稀疏点云中的3D点数不足,这导致高斯原始值的优化初始化较差。我们提出了一种新的3D重建方法,称为Sparse2DGS,以增强仅使用三幅图像进行对象重建的2DGS。Sparse2DGS采用适用于立体图像的DUSt3R基本模型,结合COLMAP MVS生成高度准确且密集的3D点云,然后用于初始化2D高斯。通过对DTU数据集的实验,我们证明Sparse2DGS仅使用三幅图像就能准确重建对象的3D形状。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP 2025
摘要
本文提出一种名为Sparse2DGS的改进方法,针对仅有少量输入图像时Gaussian Splatting(GS)在3D重建中的不足进行优化。Sparse2DGS通过结合DUSt3R立体图像基础模型和COLMAP MVS技术,生成高精度密集三维点云,用于初始化二维高斯分布。实验证明,Sparse2DGS仅使用三张图像即可准确重建物体三维形状。
要点总结
- Gaussian Splatting (GS) 在快速有效的三维重建方面展现出良好性能,但它在输入图像数量有限时的重建精度会显著降低。
- 主要原因在于稀疏点云导致的初始化不佳,这些稀疏点云是通过从运动结构(SfM)获得的。
- Sparse2DGS方法被提出以改善上述问题,此方法能够在使用仅三张图像的情况下重建物体。
- Sparse2DGS结合了DUSt3R立体图像基础模型和COLMAP MVS技术,生成高度准确且密集的三维点云。
- 这些密集的点云用于初始化二维高斯分布,为后续的三维重建提供更准确的初始信息。
- 实验证明,Sparse2DGS方法能在仅使用三张图像的情况下,实现物体的三维形状准确重建。
- Sparse2DGS有望为在有限图像输入条件下的三维重建提供新的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

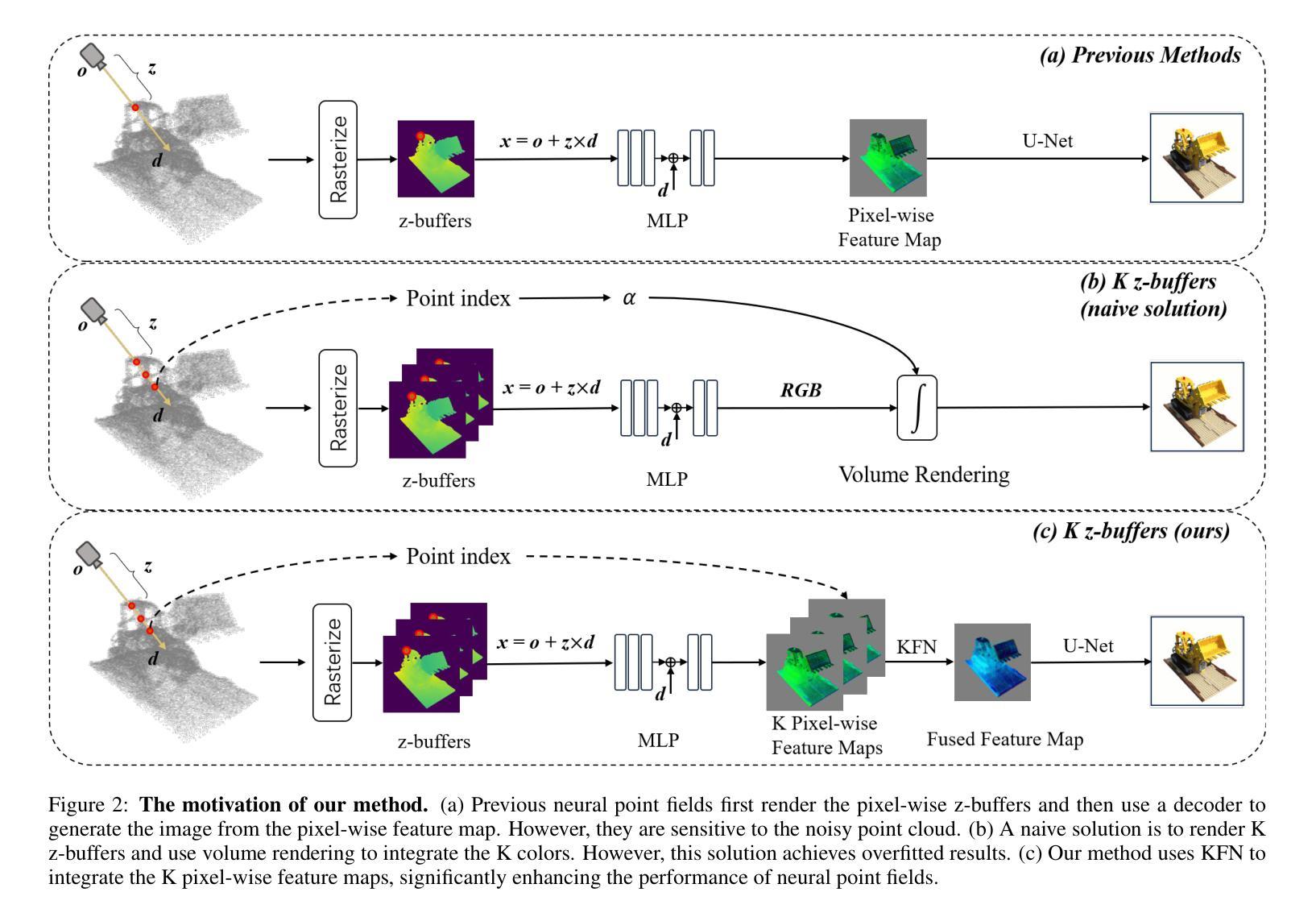
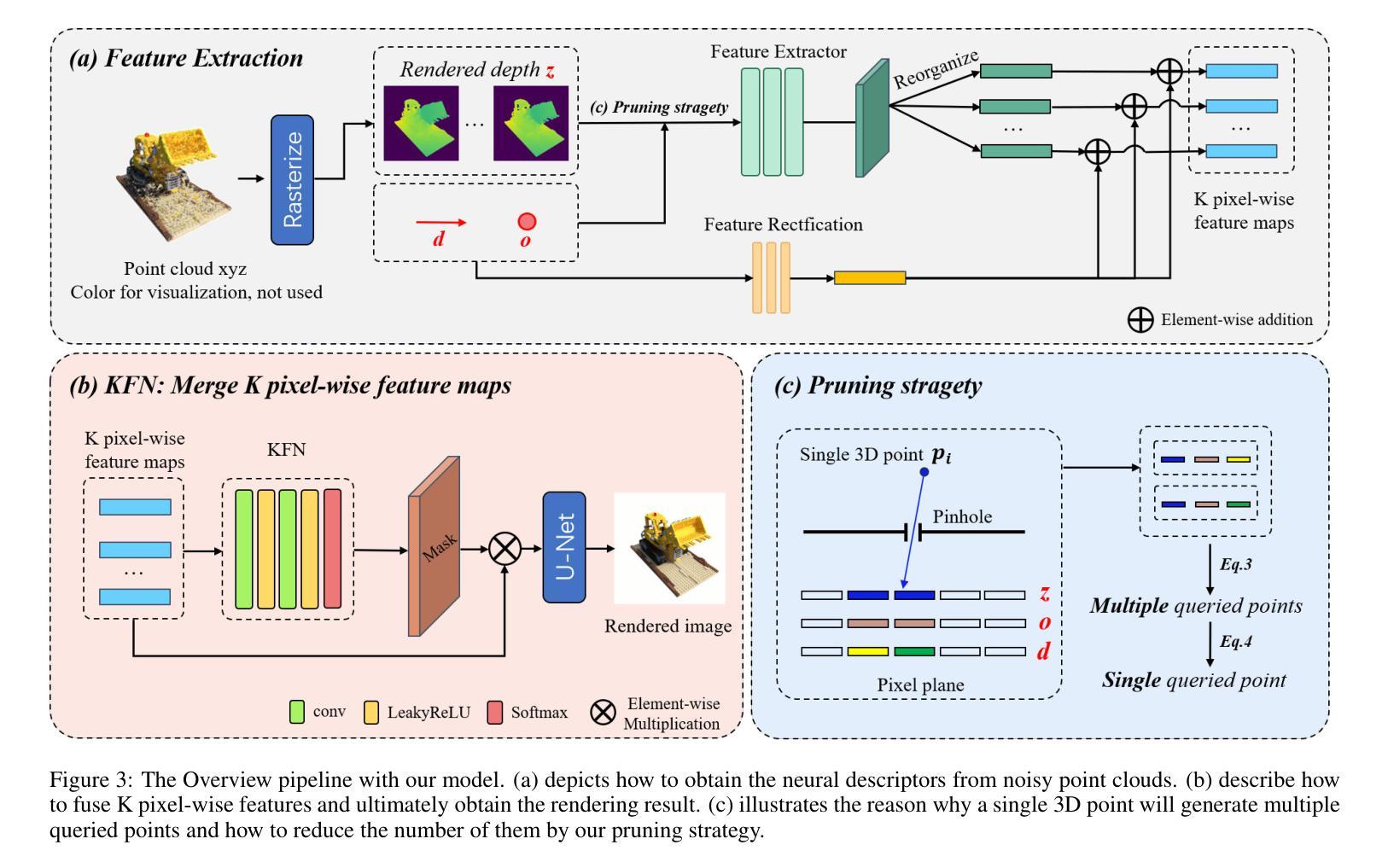
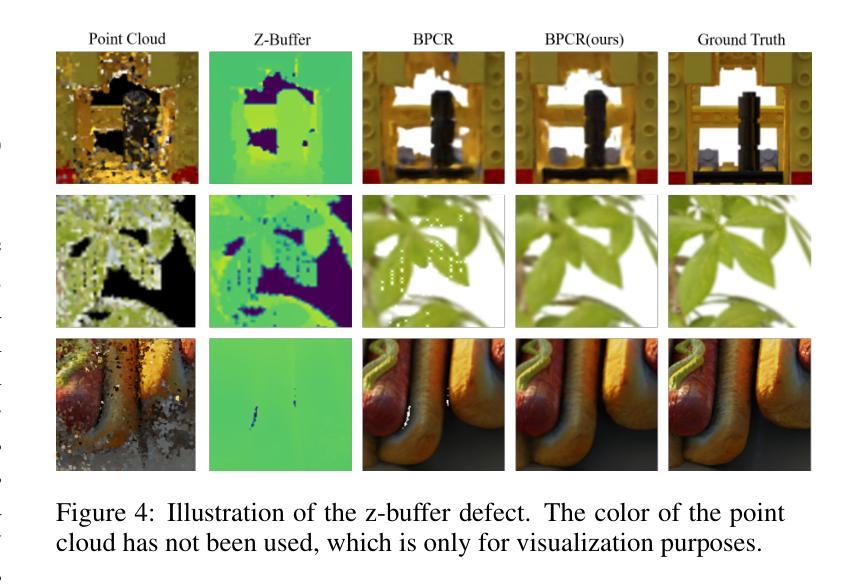
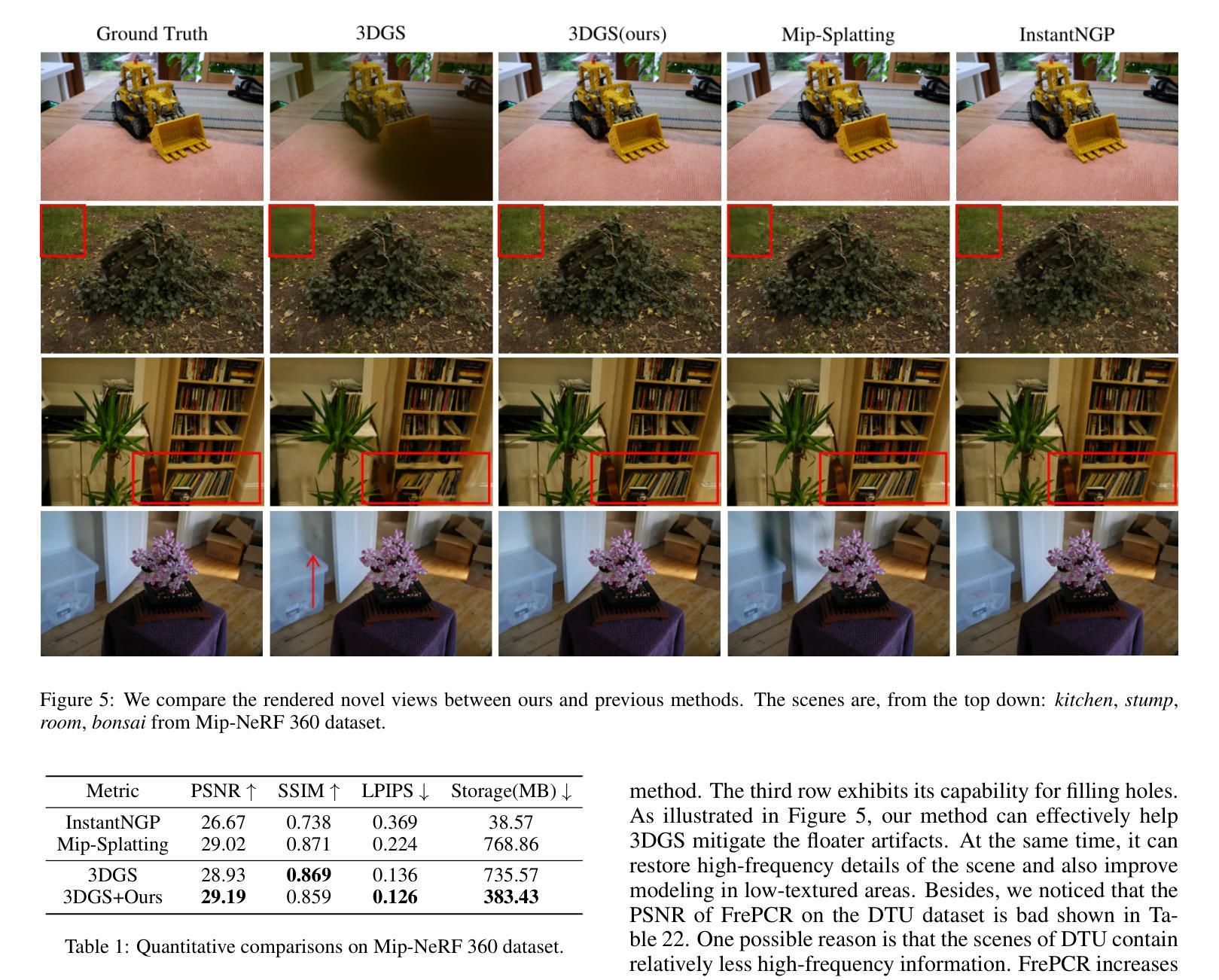
K-Buffers: A Plug-in Method for Enhancing Neural Fields with Multiple Buffers
Authors:Haofan Ren, Zunjie Zhu, Xiang Chen, Ming Lu, Rongfeng Lu, Chenggang Yan
Neural fields are now the central focus of research in 3D vision and computer graphics. Existing methods mainly focus on various scene representations, such as neural points and 3D Gaussians. However, few works have studied the rendering process to enhance the neural fields. In this work, we propose a plug-in method named K-Buffers that leverages multiple buffers to improve the rendering performance. Our method first renders K buffers from scene representations and constructs K pixel-wise feature maps. Then, We introduce a K-Feature Fusion Network (KFN) to merge the K pixel-wise feature maps. Finally, we adopt a feature decoder to generate the rendering image. We also introduce an acceleration strategy to improve rendering speed and quality. We apply our method to well-known radiance field baselines, including neural point fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively enhances the rendering performance of neural point fields and 3DGS.
神经场现在已成为3D视觉和计算机图形学研究的中心焦点。现有方法主要集中在各种场景表示上,如神经点和3D高斯等。然而,很少有工作研究渲染过程以增强神经场。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种名为K-Buffers的插件方法,它利用多个缓冲区来提高渲染性能。我们的方法首先从场景表示中渲染K个缓冲区,并构建K个像素级特征图。然后,我们引入了一个K特征融合网络(KFN)来合并这些像素级特征图。最后,我们采用一个特征解码器来生成渲染图像。我们还介绍了一种加速策略来提高渲染的速度和质量。我们将该方法应用于著名的辐射场基线,包括神经点场和3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)。大量实验表明,我们的方法有效地提高了神经点场和3DGS的渲染性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures, IJCAI 2025
Summary
神经网络领域现在是3D视觉和计算机图形学研究的中心。现有方法主要关注场景表示,如神经点和3D高斯。然而,很少有工作研究渲染过程以增强神经网络领域的效果。本研究提出了一种名为K-Buffers的插件方法,利用多个缓冲区提高渲染性能。该方法首先根据场景表示生成K个缓冲区,并构建K个像素级特征图。接着,引入K特征融合网络(KFN)融合这些特征图。最后,采用特征解码器生成渲染图像。还介绍了一种加速策略来提高渲染速度和品质。将该方法应用于神经点场和3D高斯喷射(3DGS)等著名辐射场基线,实验表明,该方法有效提高神经点场和3DGS的渲染性能。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络领域是当前3D视觉和计算机图形学研究的重点。
- 现有方法主要关注场景表示,如神经点和3D高斯,但对增强神经网络领域的渲染性能研究较少。
- 提出了一种名为K-Buffers的插件方法,利用多个缓冲区来提高渲染性能。
- K-Buffers方法包括生成K个缓冲区、构建像素级特征图、融合特征图以及生成渲染图像等步骤。
- 引入了一种加速策略来提高渲染速度和品质。
- 将K-Buffers方法应用于神经点场和3DGS等辐射场基线,实验证明其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

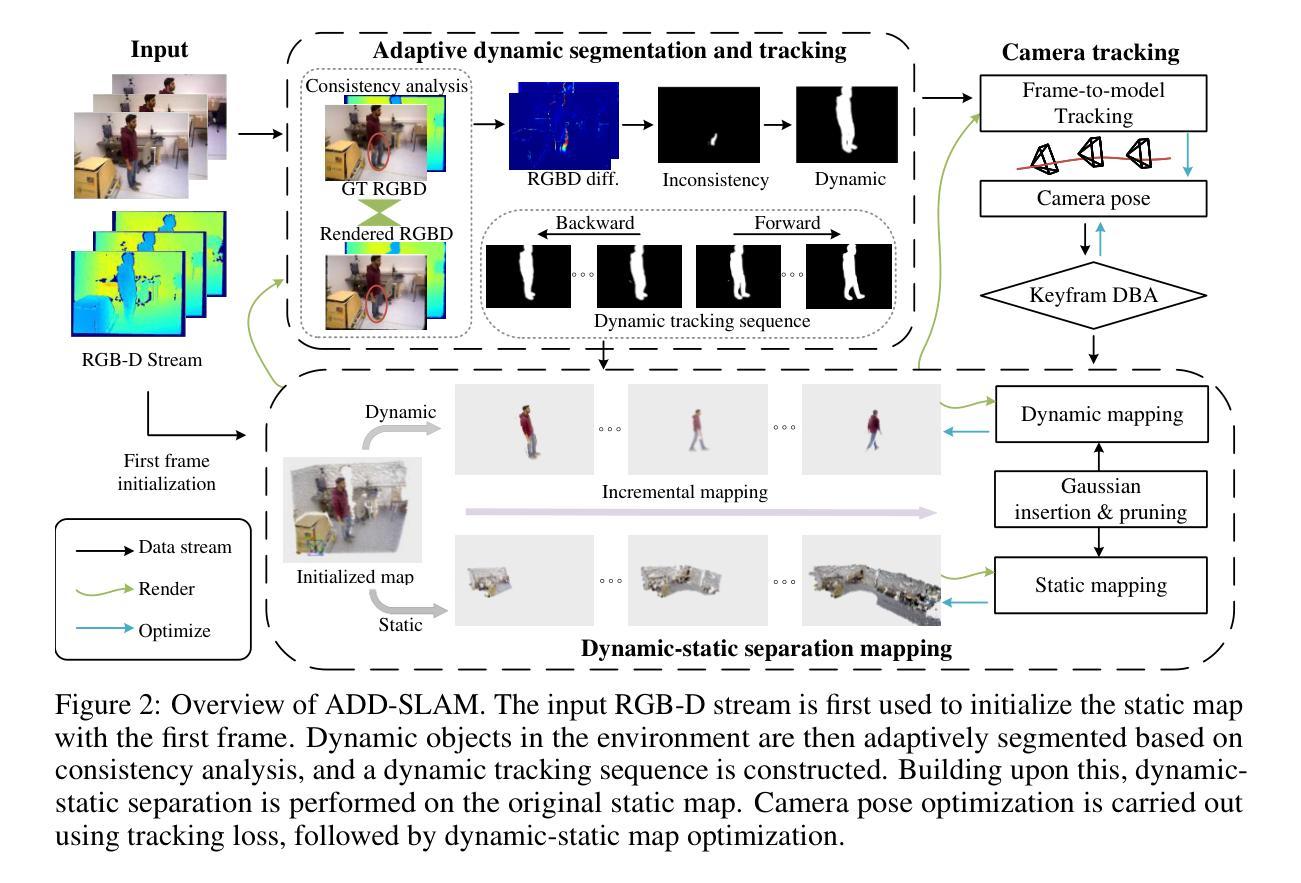
ADD-SLAM: Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Wenhua Wu, Chenpeng Su, Siting Zhu, Tianchen Deng, Zhe Liu, Hesheng Wang
Recent advancements in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods have demonstrated exceptional localization precision and remarkable dense mapping performance. However, dynamic objects introduce critical challenges by disrupting scene consistency, leading to tracking drift and mapping artifacts. Existing methods that employ semantic segmentation or object detection for dynamic identification and filtering typically rely on predefined categorical priors, while discarding dynamic scene information crucial for robotic applications such as dynamic obstacle avoidance and environmental interaction. To overcome these challenges, we propose ADD-SLAM: an Adaptive Dynamic Dense SLAM framework based on Gaussian splitting. We design an adaptive dynamic identification mechanism grounded in scene consistency analysis, comparing geometric and textural discrepancies between real-time observations and historical maps. Ours requires no predefined semantic category priors and adaptively discovers scene dynamics. Precise dynamic object recognition effectively mitigates interference from moving targets during localization. Furthermore, we propose a dynamic-static separation mapping strategy that constructs a temporal Gaussian model to achieve online incremental dynamic modeling. Experiments conducted on multiple dynamic datasets demonstrate our method’s flexible and accurate dynamic segmentation capabilities, along with state-of-the-art performance in both localization and mapping.
最近,神经辐射场(NeRF)和基于3D高斯的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法的进展,已经展示了出色的定位精度和令人印象深刻的密集映射性能。然而,动态物体通过破坏场景一致性,引入了关键挑战,导致跟踪漂移和映射伪影。现有采用语义分割或目标检测进行动态识别和过滤的方法通常依赖于预定义的分类先验知识,同时丢弃了对于机器人应用(如动态避障和环境交互)至关重要的动态场景信息。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了ADD-SLAM:一种基于高斯分裂的自适应动态密集SLAM框架。我们设计了一种基于场景一致性分析的自适应动态识别机制,通过比较实时观察与历史地图之间的几何和纹理差异。我们的方法不需要预定义的语义类别先验知识,并能自适应地发现场景动态。精确的动态目标识别有效地减轻了移动目标在定位过程中的干扰。此外,我们提出了一种动静分离映射策略,建立了一个临时高斯模型,以实现在线增量动态建模。在多个动态数据集上进行的实验证明了我们方法在动态分割方面的灵活性和准确性,以及在定位和映射方面的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最近NeRF和基于3D高斯SLAM方法的发展显示出卓越的定位精度和显著的密集映射性能。然而,动态物体破坏了场景的一致性,导致跟踪漂移和映射伪影,给技术实施带来挑战。现有方法依靠预先设定的分类先验进行动态识别和过滤,却忽视了机器人应用中至关重要的动态场景信息。为应对这些挑战,我们提出基于高斯分裂的ADD-SLAM自适应动态密集SLAM框架。通过场景一致性分析设计自适应动态识别机制,对比实时观测和历史地图之间的几何和纹理差异。我们的方法无需预设语义类别先验,可自适应发现场景动态性。精确的动态目标识别可有效减轻移动目标在定位过程中的干扰。此外,我们提出动态静态分离映射策略,构建临时高斯模型实现在线增量动态建模。在多个动态数据集上的实验证明,我们的方法具有灵活准确的动态分割能力,同时在定位和映射方面达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和基于3D高斯SLAM方法的最新进展提供了卓越的定位精度和密集映射性能。
- 动态物体对场景一致性造成干扰,影响跟踪和映射,成为技术挑战。
- 现有方法依赖预先设定的分类先验进行动态识别,但缺乏自适应性和动态场景信息的利用。
- ADD-SLAM框架通过场景一致性分析进行自适应动态识别,无需预设语义类别先验。
- 精确的动态目标识别减轻移动目标干扰定位过程。
- 动态静态分离映射策略利用临时高斯模型实现动态建模的在线增量更新。
点此查看论文截图


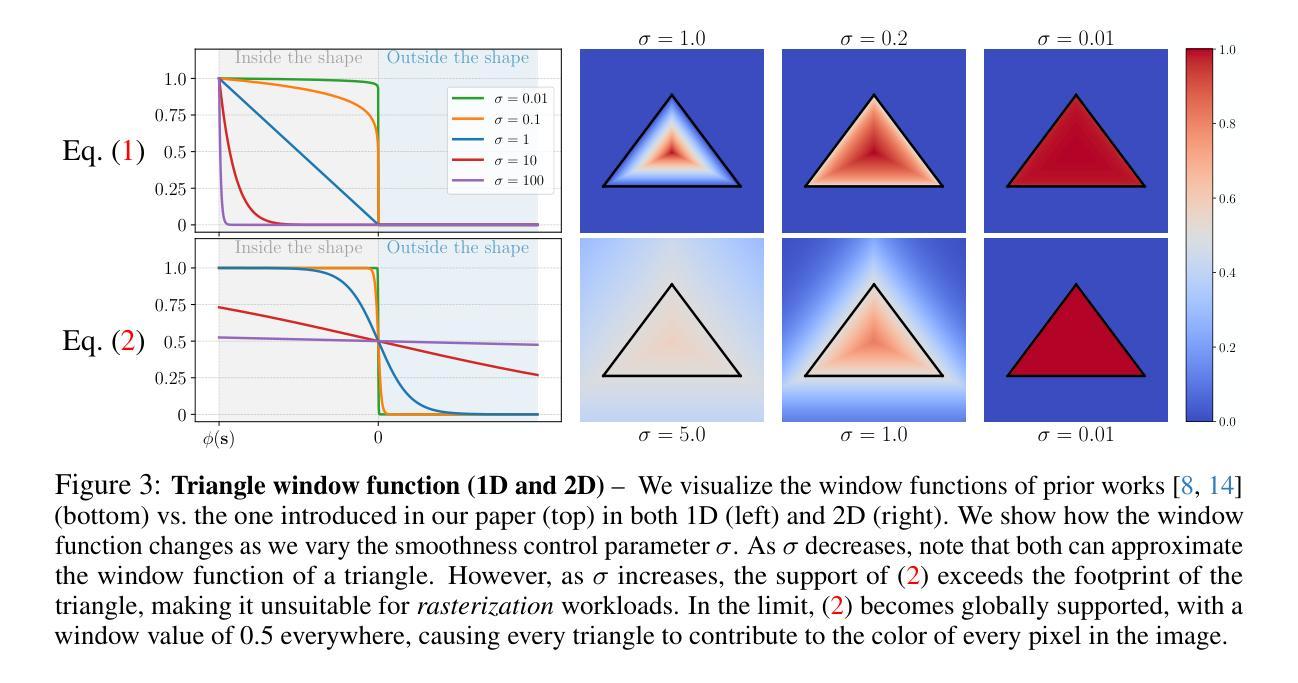
Triangle Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
Authors:Jan Held, Renaud Vandeghen, Adrien Deliege, Abdullah Hamdi, Silvio Giancola, Anthony Cioppa, Andrea Vedaldi, Bernard Ghanem, Andrea Tagliasacchi, Marc Van Droogenbroeck
The field of computer graphics was revolutionized by models such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, displacing triangles as the dominant representation for photogrammetry. In this paper, we argue for a triangle comeback. We develop a differentiable renderer that directly optimizes triangles via end-to-end gradients. We achieve this by rendering each triangle as differentiable splats, combining the efficiency of triangles with the adaptive density of representations based on independent primitives. Compared to popular 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting methods, our approach achieves higher visual fidelity, faster convergence, and increased rendering throughput. On the Mip-NeRF360 dataset, our method outperforms concurrent non-volumetric primitives in visual fidelity and achieves higher perceptual quality than the state-of-the-art Zip-NeRF on indoor scenes. Triangles are simple, compatible with standard graphics stacks and GPU hardware, and highly efficient: for the \textit{Garden} scene, we achieve over 2,400 FPS at 1280x720 resolution using an off-the-shelf mesh renderer. These results highlight the efficiency and effectiveness of triangle-based representations for high-quality novel view synthesis. Triangles bring us closer to mesh-based optimization by combining classical computer graphics with modern differentiable rendering frameworks. The project page is https://trianglesplatting.github.io/
计算机图形学领域经历了Neural Radiance Fields和3D Gaussian Splatting等模型的革命性变革,这些模型取代了三角形在摄影测量中的主导地位。在本文中,我们主张三角形的回归。我们开发了一种可微分的渲染器,该渲染器通过端到端梯度直接优化三角形。我们通过将每个三角形渲染为可微分的平面来实现这一点,结合了三角形的效率和基于独立原始数据的自适应密度表示。与流行的2D和3D高斯平面方法相比,我们的方法实现了更高的视觉保真度、更快的收敛速度和增加的渲染吞吐量。在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,我们的方法在视觉保真度方面超越了当前的非体积原始数据,并在室内场景上实现了比最新技术Zip-NeRF更高的感知质量。三角形简单、兼容标准图形堆栈和GPU硬件,并且效率极高:对于“花园”场景,我们使用现成的网格渲染器在1280x720分辨率下实现了超过2400帧每秒的帧率。这些结果突出了基于三角形的表示在高质量新型视图合成中的效率和效果。通过结合经典计算机图形学与现代可微分渲染框架,三角形使我们离基于网格的优化更近了一步。项目页面是https://trianglesplatting.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures, 10 tables
Summary
本文主张三角形的回归,提出了一种可微分渲染器,该渲染器可直接优化三角形,通过端到端的梯度实现。该方法结合了三角形的效率和基于独立原始数据的自适应密度表示,实现了高视觉保真度、快速收敛和增加的渲染吞吐量。在Mip-NeRF360数据集上,该方法在视觉保真度方面优于并发非体积原始数据,并且在室内场景上实现了高于现有技术Zip-NeRF的感知质量。三角形简单、兼容标准图形堆栈和GPU硬件,并且高效。对于花园场景,使用现成的网格渲染器在1280x720分辨率下实现了超过2400帧的帧率。此研究强调基于三角形表示的高质量新颖视图合成的效率和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文主张三角形的回归,在计算机图形领域提出一种可微分渲染器。
- 该渲染器可直接优化三角形,通过端到端的梯度实现。
- 方法结合了三角形的效率和基于独立原始数据的自适应密度表示。
- 与其他方法相比,该方法在视觉保真度、收敛速度和渲染吞吐量方面具有优势。
- 在Mip-NeRF360数据集上的实验结果优于并发非体积原始数据方法。
- 在室内场景的感知质量上实现了高于现有技术Zip-NeRF的表现。
点此查看论文截图



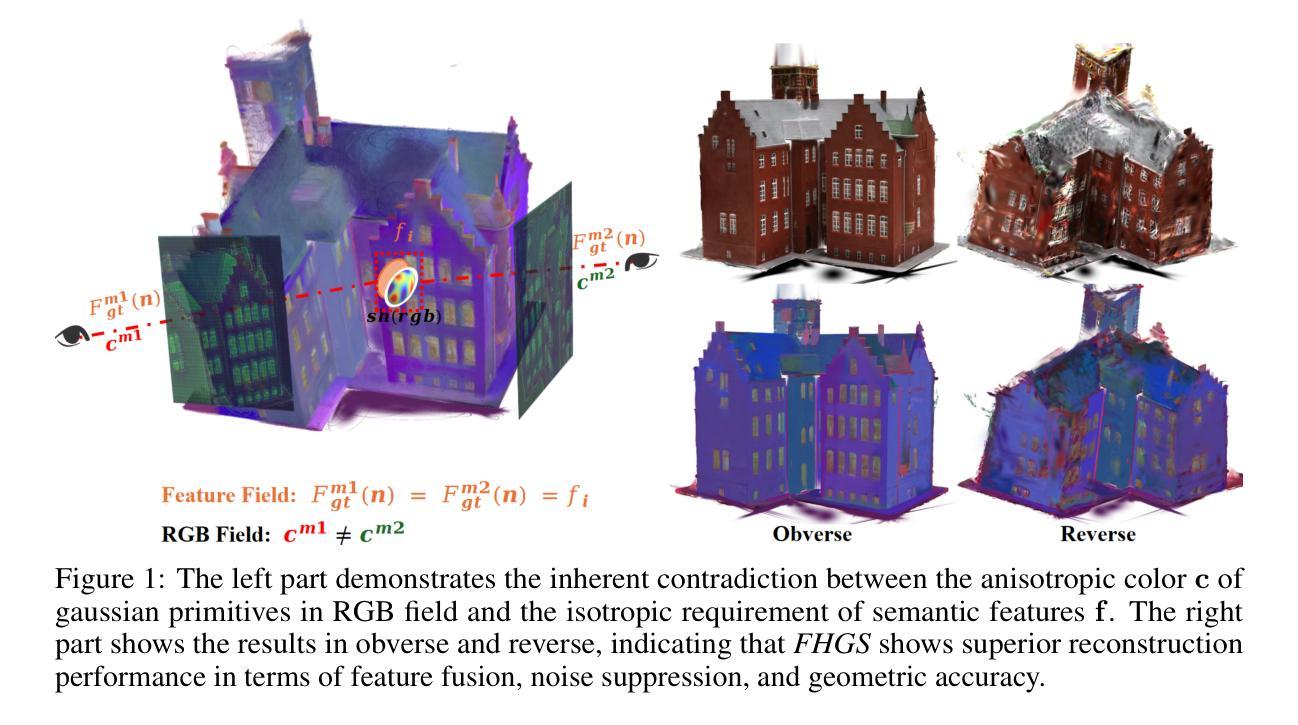
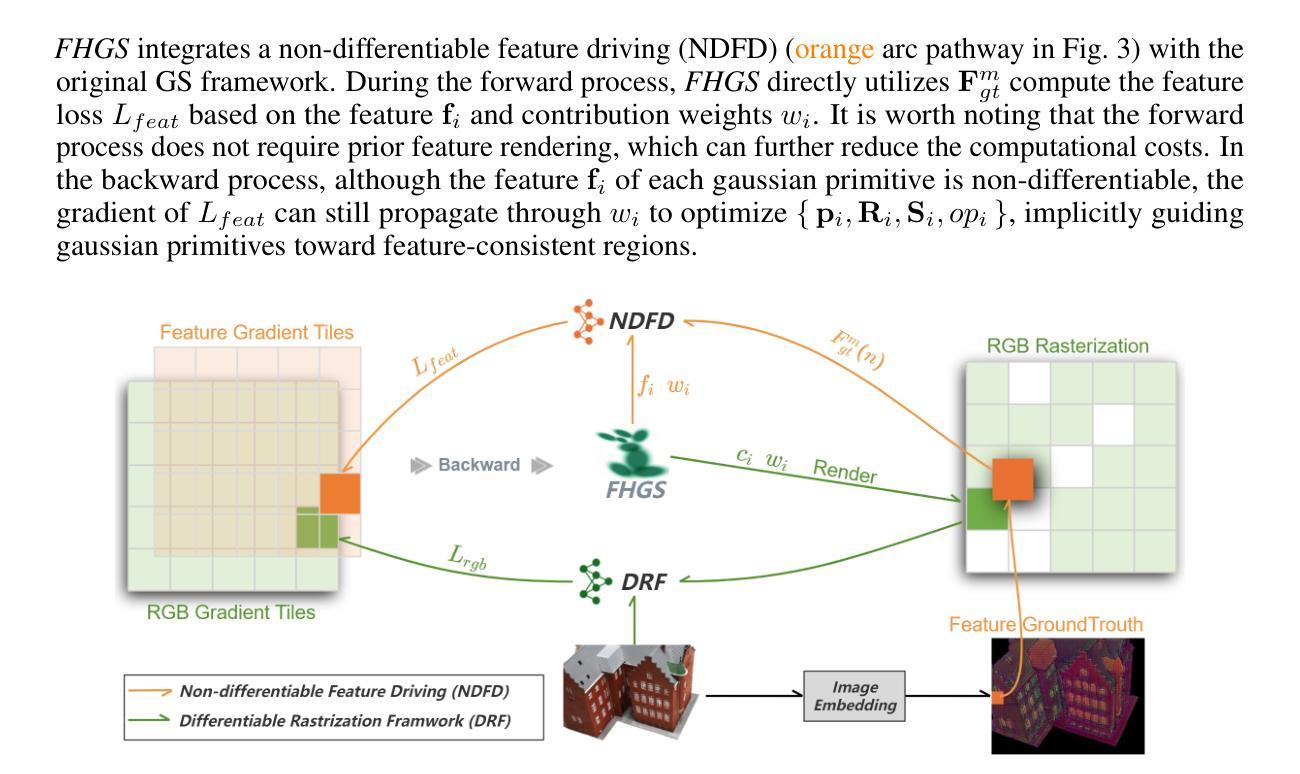
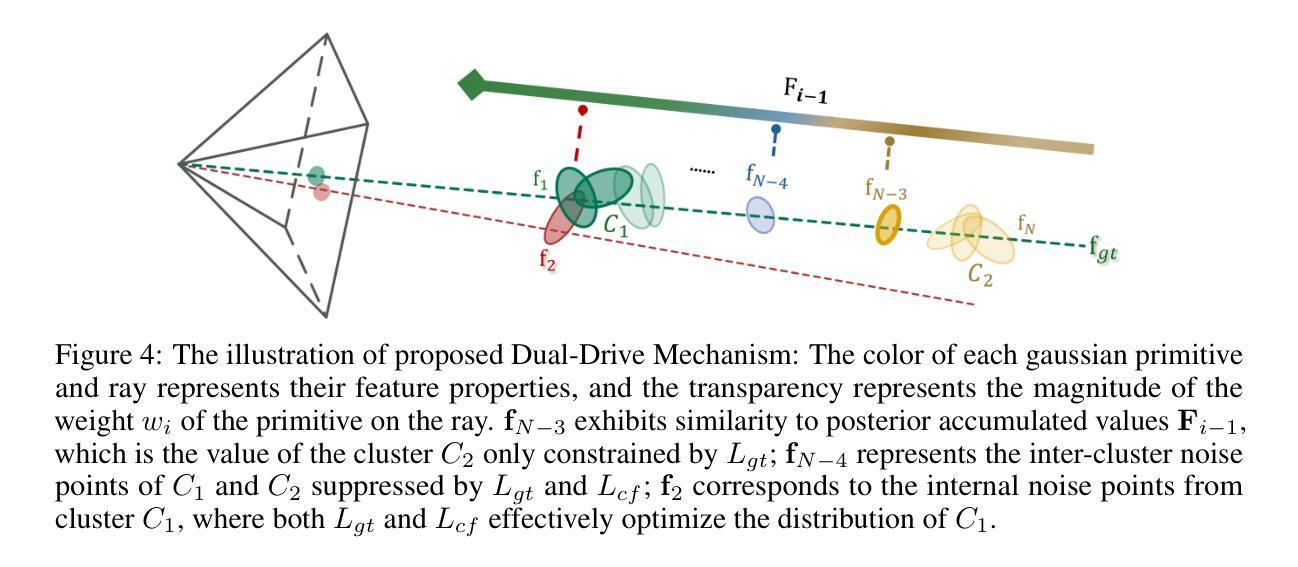
FHGS: Feature-Homogenized Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Q. G. Duan, Benyun Zhao, Mingqiao Han Yijun Huang, Ben M. Chen
Scene understanding based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently achieved notable advances. Although 3DGS related methods have efficient rendering capabilities, they fail to address the inherent contradiction between the anisotropic color representation of gaussian primitives and the isotropic requirements of semantic features, leading to insufficient cross-view feature consistency. To overcome the limitation, we proposes $\textit{FHGS}$ (Feature-Homogenized Gaussian Splatting), a novel 3D feature fusion framework inspired by physical models, which can achieve high-precision mapping of arbitrary 2D features from pre-trained models to 3D scenes while preserving the real-time rendering efficiency of 3DGS. Specifically, our $\textit{FHGS}$ introduces the following innovations: Firstly, a universal feature fusion architecture is proposed, enabling robust embedding of large-scale pre-trained models’ semantic features (e.g., SAM, CLIP) into sparse 3D structures. Secondly, a non-differentiable feature fusion mechanism is introduced, which enables semantic features to exhibit viewpoint independent isotropic distributions. This fundamentally balances the anisotropic rendering of gaussian primitives and the isotropic expression of features; Thirdly, a dual-driven optimization strategy inspired by electric potential fields is proposed, which combines external supervision from semantic feature fields with internal primitive clustering guidance. This mechanism enables synergistic optimization of global semantic alignment and local structural consistency. More interactive results can be accessed on: https://fhgs.cuastro.org/.
基于3D高斯展布(3DGS)的场景理解最近取得了显著的进展。尽管与3DGS相关的方法具有高效的渲染能力,但它们无法解决高斯基元的方向性颜色表示与语义特征的同构性要求之间的固有矛盾,导致跨视图特征一致性不足。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了受物理模型启发的特征同质化高斯展布(FHGS)这一新型3D特征融合框架,它可以实现从预训练模型到3D场景的任意2D特征的高精度映射,同时保留3DGS的实时渲染效率。具体来说,我们的FHGS引入了以下创新点:首先,提出了一种通用特征融合架构,使大规模预训练模型的语义特征(如SAM、CLIP)能够稳健地嵌入到稀疏的3D结构中;其次,引入了一种不可微分的特征融合机制,使语义特征呈现出与视点无关的同构分布。这从根本上平衡了高斯基元的方向性渲染和特征的同构表达;最后,提出了一种受电场启发的双驱动优化策略,结合了语义特征场的外部监督与内部基元聚类指导。该机制实现了全局语义对齐和局部结构一致性的协同优化。更多互动结果可访问:https://fhgs.cuastro.org/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3D高斯描摹(3DGS)的场景理解已经取得了显著的进展。然而,相关方法虽具有高效的渲染能力,但在处理高斯基元的各向异性与语义特征各向同性要求之间的内在矛盾时存在不足,导致跨视图特征一致性不足。为克服这一局限,本文提出一种受物理模型启发的特征同质化高斯描摹(FHGS)新型三维特征融合框架,它能在保留3DGS实时渲染效率的同时,实现预训练模型中任意二维特征的高精度映射到三维场景。FHGS的创新点包括:通用特征融合架构、非可微特征融合机制及受电场启发的双驱动优化策略。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在场景理解方面取得显著进展,但存在高斯基元各向异性与语义特征各向同性要求的矛盾,导致跨视图特征一致性不足。
- 提出FHGS新型三维特征融合框架,结合物理模型实现高效渲染与高精度映射。
- FHGS包含通用特征融合架构,能嵌入大规模预训练模型的语义特征到稀疏三维结构。
- 引入非可微特征融合机制,使语义特征展现视点独立各向同性分布,平衡高斯基元的各向异性与特征的各向同性表达。
点此查看论文截图

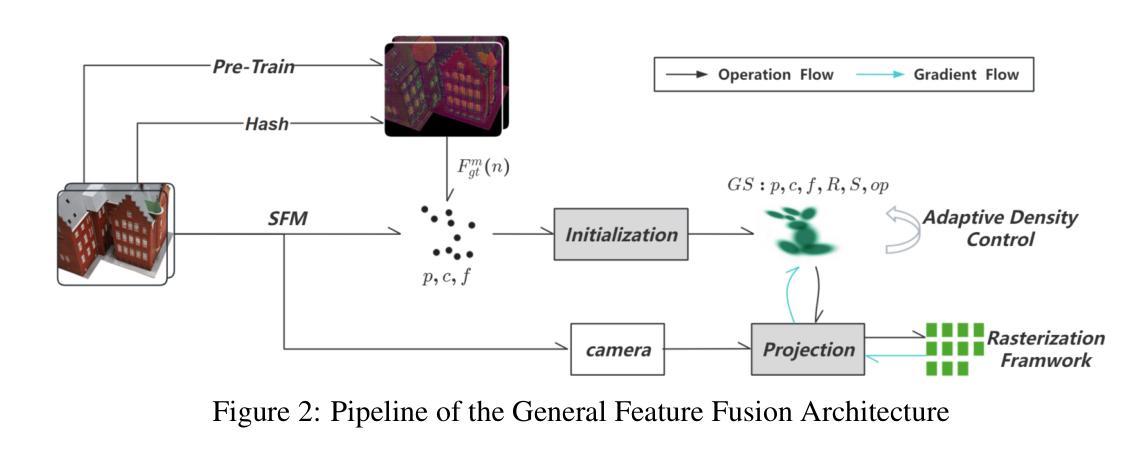
VPGS-SLAM: Voxel-based Progressive 3D Gaussian SLAM in Large-Scale Scenes
Authors:Tianchen Deng, Wenhua Wu, Junjie He, Yue Pan, Xirui Jiang, Shenghai Yuan, Danwei Wang, Hesheng Wang, Weidong Chen
3D Gaussian Splatting has recently shown promising results in dense visual SLAM. However, existing 3DGS-based SLAM methods are all constrained to small-room scenarios and struggle with memory explosion in large-scale scenes and long sequences. To this end, we propose VPGS-SLAM, the first 3DGS-based large-scale RGBD SLAM framework for both indoor and outdoor scenarios. We design a novel voxel-based progressive 3D Gaussian mapping method with multiple submaps for compact and accurate scene representation in large-scale and long-sequence scenes. This allows us to scale up to arbitrary scenes and improves robustness (even under pose drifts). In addition, we propose a 2D-3D fusion camera tracking method to achieve robust and accurate camera tracking in both indoor and outdoor large-scale scenes. Furthermore, we design a 2D-3D Gaussian loop closure method to eliminate pose drift. We further propose a submap fusion method with online distillation to achieve global consistency in large-scale scenes when detecting a loop. Experiments on various indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate the superiority and generalizability of the proposed framework. The code will be open source on https://github.com/dtc111111/vpgs-slam.
3D高斯糊化最近在密集视觉SLAM中显示出有前景的结果。然而,现有的基于3DGS的SLAM方法都局限于小场景,并在大规模场景和长序列中面临内存爆炸的问题。为此,我们提出VPGS-SLAM,它是基于3DGS的室内外场景大型RGBD SLAM框架。我们设计了一种基于体素的多子图渐进式3D高斯映射方法,用于大型和长序列场景的紧凑和准确场景表示。这使我们能够扩展到任意场景并提高稳健性(即使在姿态漂移的情况下)。此外,我们提出了一种2D-3D融合相机跟踪方法,以实现室内外大型场景的稳健和精确相机跟踪。为了进一步消除姿态漂移,我们设计了一种基于混合Gauss循环的检测方法。我们还提出了一种带有在线蒸馏的子图融合方法,以实现大规模场景中检测到循环时的全局一致性。在各种室内和室外数据集上的实验证明了所提出框架的优越性和通用性。代码将在https://github.com/dtc111111/vpgs-slam上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为VPGS-SLAM的大型室内外RGBD SLAM框架,采用基于体素的方法构建场景模型,支持多子图融合实现紧凑且准确的场景表示,适用于大规模和长序列场景。设计了一种有效的摄像机追踪算法和二三维融合方法以及高斯环闭合策略。
Key Takeaways
- VPGS-SLAM是一种适用于大规模场景的RGBD SLAM框架,可以扩展到任何规模的场景并增强其稳健性。
- 利用新颖的基于体素的渐进式三维高斯建模方法和多子图融合策略,提高了场景的准确性和紧凑性。
- 设计了适用于室内外大规模场景的二维-三维融合相机跟踪方法,确保鲁棒性和准确性。
- 通过创新的二维-三维高斯环闭合方法消除了姿态漂移问题。
- 提出了一种子图融合方法,通过在线蒸馏实现大规模场景中的全局一致性检测。
- 在各种室内外数据集上的实验证明了该框架的优越性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



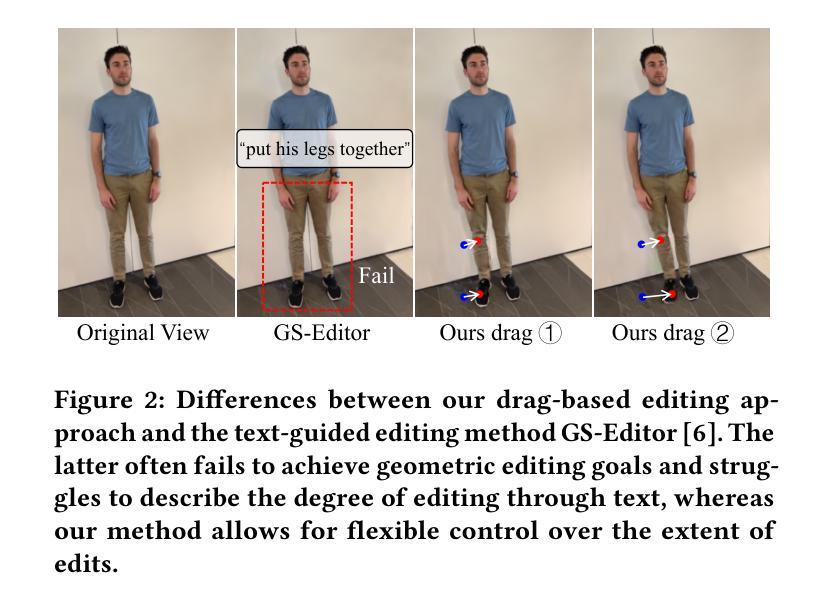
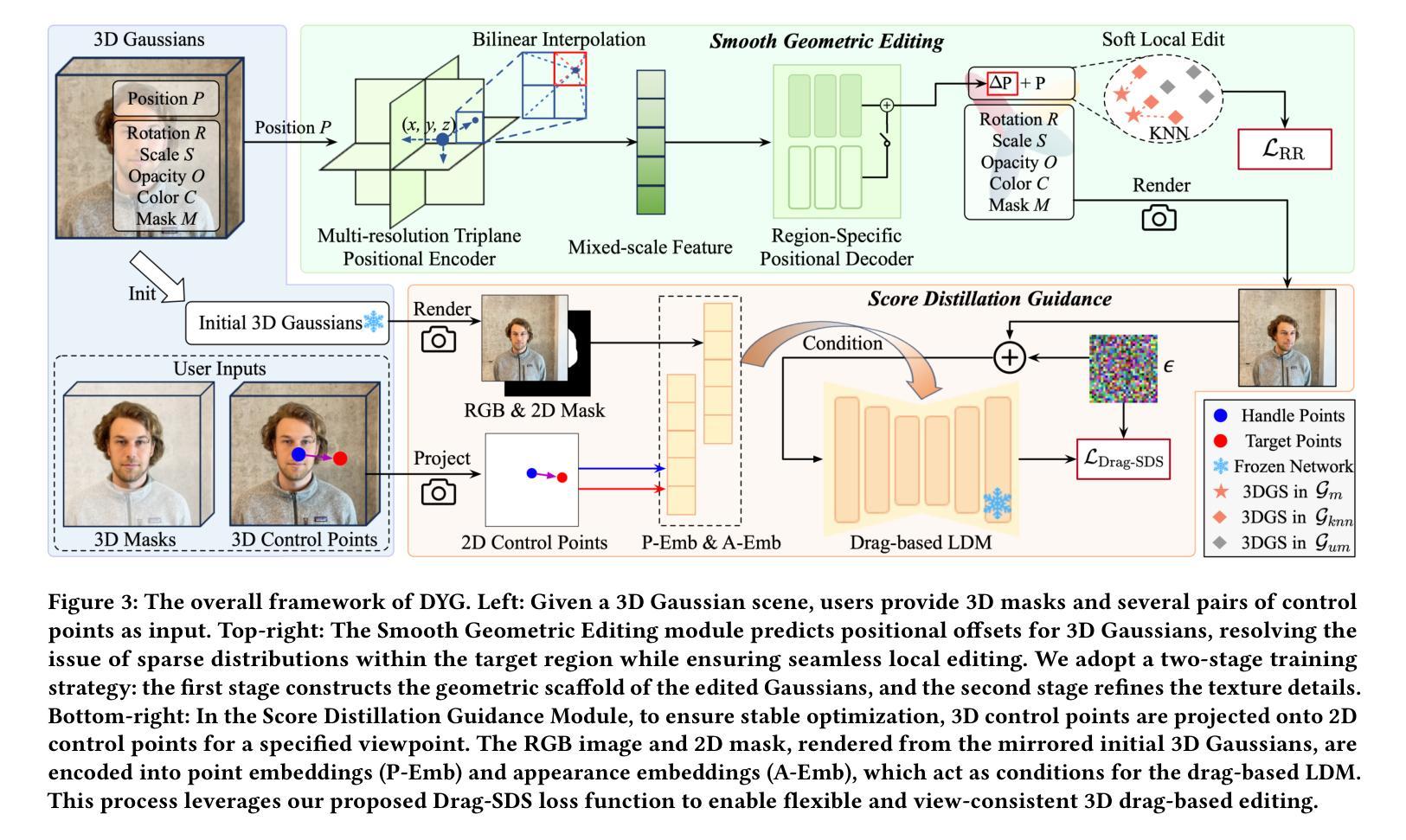
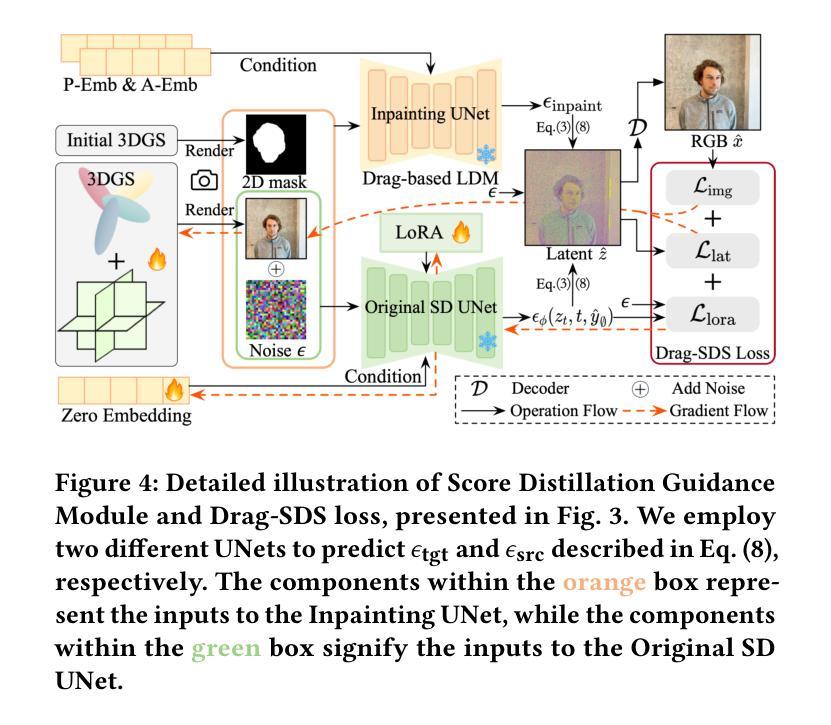
Drag Your Gaussian: Effective Drag-Based Editing with Score Distillation for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yansong Qu, Dian Chen, Xinyang Li, Xiaofan Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
Recent advancements in 3D scene editing have been propelled by the rapid development of generative models. Existing methods typically utilize generative models to perform text-guided editing on 3D representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). However, these methods are often limited to texture modifications and fail when addressing geometric changes, such as editing a character’s head to turn around. Moreover, such methods lack accurate control over the spatial position of editing results, as language struggles to precisely describe the extent of edits. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DYG, an effective 3D drag-based editing method for 3D Gaussian Splatting. It enables users to conveniently specify the desired editing region and the desired dragging direction through the input of 3D masks and pairs of control points, thereby enabling precise control over the extent of editing. DYG integrates the strengths of the implicit triplane representation to establish the geometric scaffold of the editing results, effectively overcoming suboptimal editing outcomes caused by the sparsity of 3DGS in the desired editing regions. Additionally, we incorporate a drag-based Latent Diffusion Model into our method through the proposed Drag-SDS loss function, enabling flexible, multi-view consistent, and fine-grained editing. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DYG conducts effective drag-based editing guided by control point prompts, surpassing other baselines in terms of editing effect and quality, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian.
最近,三维场景编辑的进展得益于生成模型的快速发展。现有方法通常利用生成模型对三维表示进行文本引导编辑,例如三维高斯平铺(3DGS)。然而,这些方法通常仅限于纹理修改,在应对几何变化时常常失效,比如编辑角色头部使其旋转。此外,这些方法在控制编辑结果的空间位置方面不够精确,因为语言很难精确描述编辑的程度。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了DYG,这是一种针对三维高斯平铺的有效基于拖拽的三维编辑方法。它使用户可以通过输入三维掩码和控制点对,方便地指定所需的编辑区域和拖拽方向,从而实现对编辑程度的精确控制。DYG结合了隐式triplane表示法的优点,建立编辑结果的三维骨架,有效克服了在所需编辑区域内,3DGS稀疏导致的编辑结果不理想问题。此外,我们通过提出的Drag-SDS损失函数,将基于拖拽的潜在扩散模型融入我们的方法,实现了灵活、多视角一致、精细的编辑。大量实验表明,DYG通过控制点提示进行有效的基于拖拽的编辑,在编辑效果和品质方面都超过了其他基线方法。请访问我们的项目页面https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian了解详情。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Visit our project page at https://quyans.github.io/Drag-Your-Gaussian
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D拖放编辑方法的突破性研究,该方法针对3D高斯样条(3DGS)进行改进,通过引入拖放编辑和隐式triplane表示,实现了对3D场景的精确编辑。用户可以通过输入3D遮罩和控制点来指定编辑区域和拖动方向,从而实现精确的编辑控制。此外,该研究还结合了基于拖动的潜在扩散模型,通过提出的Drag-SDS损失函数,实现了灵活、多视角一致和精细的编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 引入拖放编辑方法以克服现有3D场景编辑方法的局限性。
- 使用输入3D遮罩和控制点来指定编辑区域和拖动方向,实现精确编辑控制。
- 结合隐式triplane表示建立编辑结果几何框架,克服3DGS在编辑区域的稀疏性问题。
- 融入基于拖动的潜在扩散模型,通过Drag-SDS损失函数实现灵活、多视角一致和精细的编辑。
- 该方法超越了其他基线方法,在编辑效果和品质上表现出优势。
- 项目页面提供了更多详细信息和资源。
- 此方法有助于推动3D场景编辑技术的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图


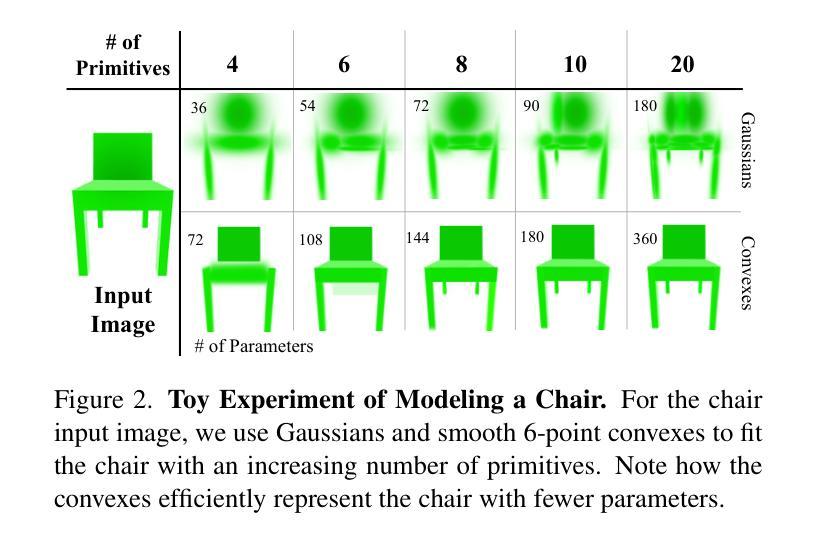
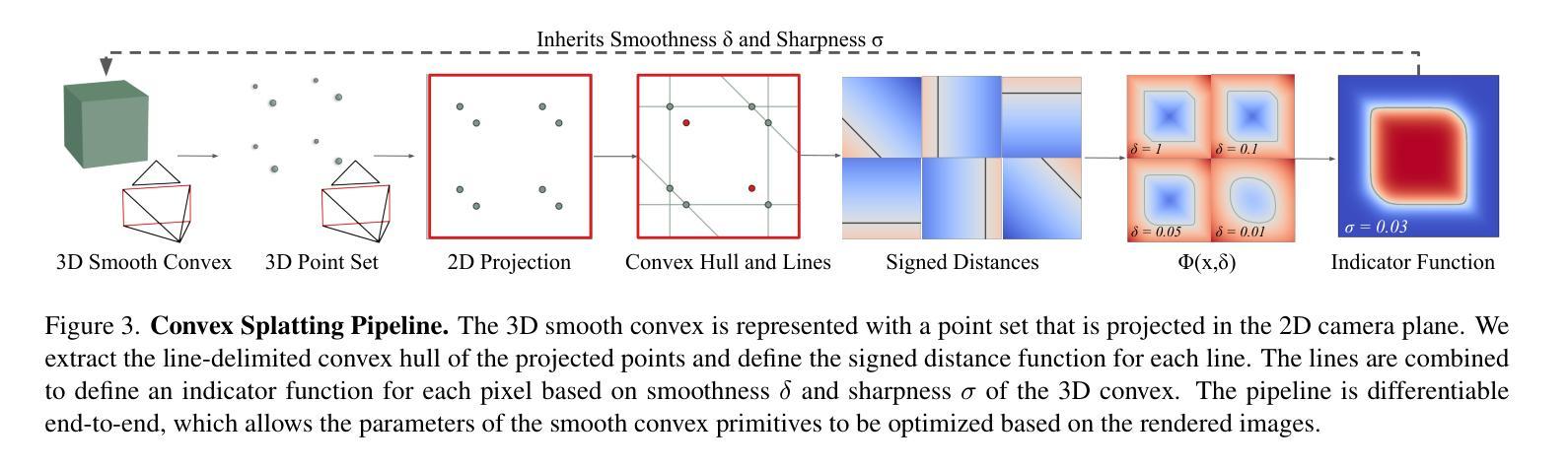
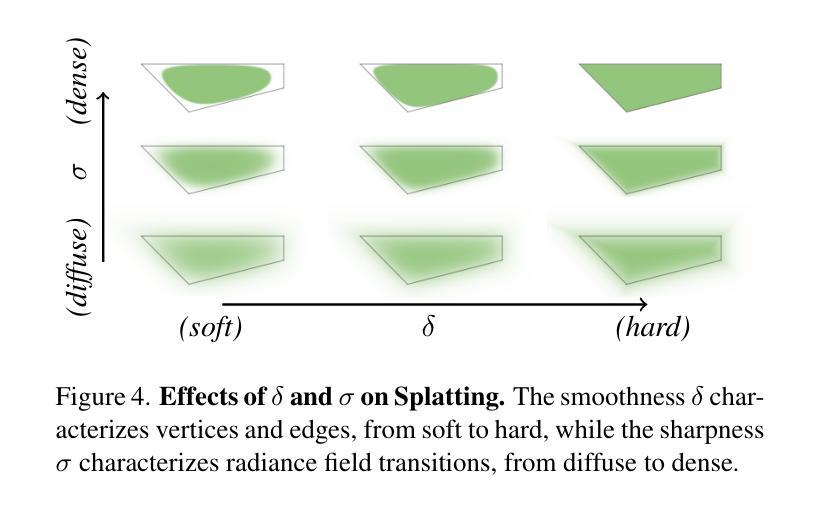
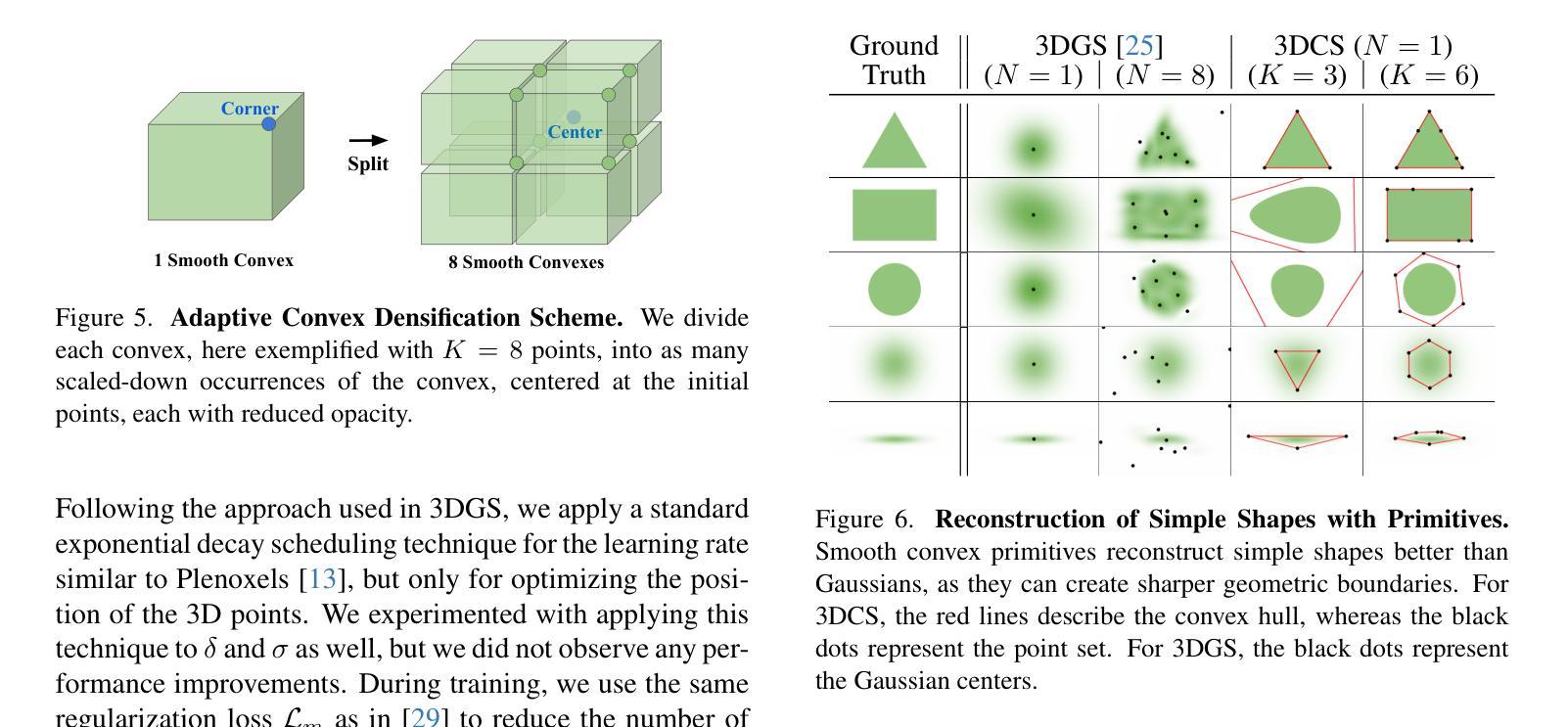
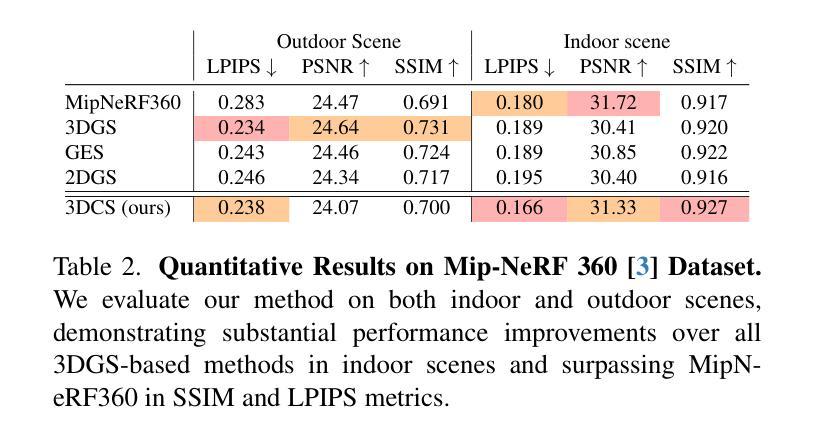
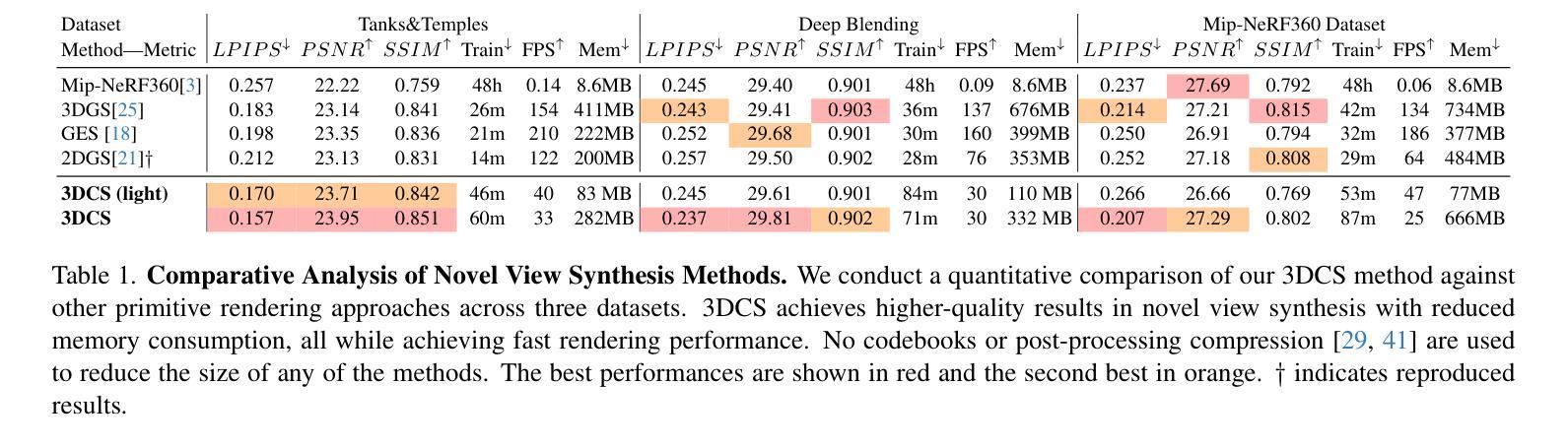
3D Convex Splatting: Radiance Field Rendering with 3D Smooth Convexes
Authors:Jan Held, Renaud Vandeghen, Abdullah Hamdi, Adrien Deliege, Anthony Cioppa, Silvio Giancola, Andrea Vedaldi, Bernard Ghanem, Marc Van Droogenbroeck
Recent advances in radiance field reconstruction, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), have achieved high-quality novel view synthesis and fast rendering by representing scenes with compositions of Gaussian primitives. However, 3D Gaussians present several limitations for scene reconstruction. Accurately capturing hard edges is challenging without significantly increasing the number of Gaussians, creating a large memory footprint. Moreover, they struggle to represent flat surfaces, as they are diffused in space. Without hand-crafted regularizers, they tend to disperse irregularly around the actual surface. To circumvent these issues, we introduce a novel method, named 3D Convex Splatting (3DCS), which leverages 3D smooth convexes as primitives for modeling geometrically-meaningful radiance fields from multi-view images. Smooth convex shapes offer greater flexibility than Gaussians, allowing for a better representation of 3D scenes with hard edges and dense volumes using fewer primitives. Powered by our efficient CUDA-based rasterizer, 3DCS achieves superior performance over 3DGS on benchmarks such as Mip-NeRF360, Tanks and Temples, and Deep Blending. Specifically, our method attains an improvement of up to 0.81 in PSNR and 0.026 in LPIPS compared to 3DGS while maintaining high rendering speeds and reducing the number of required primitives. Our results highlight the potential of 3D Convex Splatting to become the new standard for high-quality scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Project page: convexsplatting.github.io.
近期在辐射场重建方面的进展,如3D高斯喷射(3DGS),通过使用高斯基本体的组合来表示场景,实现了高质量的新视角合成和快速渲染。然而,3D高斯对于场景重建存在若干局限性。准确地捕捉硬边缘是一个挑战,因为高斯函数的数量难以显著增加以避免过大的内存占用。此外,由于它们在空间中会扩散,因此难以表示平面表面。如果没有手工制定的正则化器,它们往往会围绕实际表面不规则地分散。为了克服这些问题,我们引入了一种新方法,称为3D凸喷射(3DCS),它利用3D平滑凸体作为基本体,从多视角图像对几何意义的辐射场进行建模。平滑的凸形提供了比高斯更大的灵活性,允许使用较少的原始基本体更好地表示具有硬边缘和密集体积的3D场景。通过基于CUDA的高效光栅化器的支持,3DCS在Mip-NeRF360、坦克与寺庙以及深度混合等基准测试上的性能优于3DGS。具体来说,我们的方法与3DGS相比,在PSNR上提高了高达0.81,在LPIPS上提高了0.026,同时保持了高渲染速度并减少了所需原始基本体的数量。我们的结果突显了3D凸喷射在高质量场景重建和新视角合成方面的潜力,有望成为新的标准。项目页面:convexsplatting.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025 as Highlight. 13 pages, 13 figures, 10 tables
Summary
基于最新的三维凸块模型技术的3D Convex Splatting(简称3DCS)方法在三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面展现出卓越性能。相较于传统的三维高斯模型技术(如3DGS),其采用平滑凸体作为基本单位,能更灵活地表示具有硬边缘和密集体积的三维场景。此外,借助CUDA优化后的光线跟踪器,使其在多种标准基准测试中的性能明显优于现有的同类方法,有望取代其他重建和合成方法成为新标准。详情请访问项目主页。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图