⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
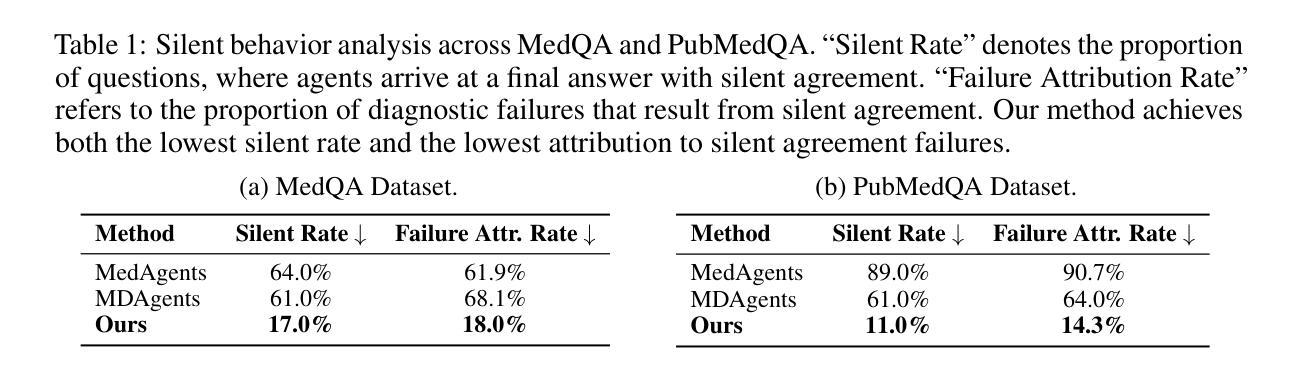
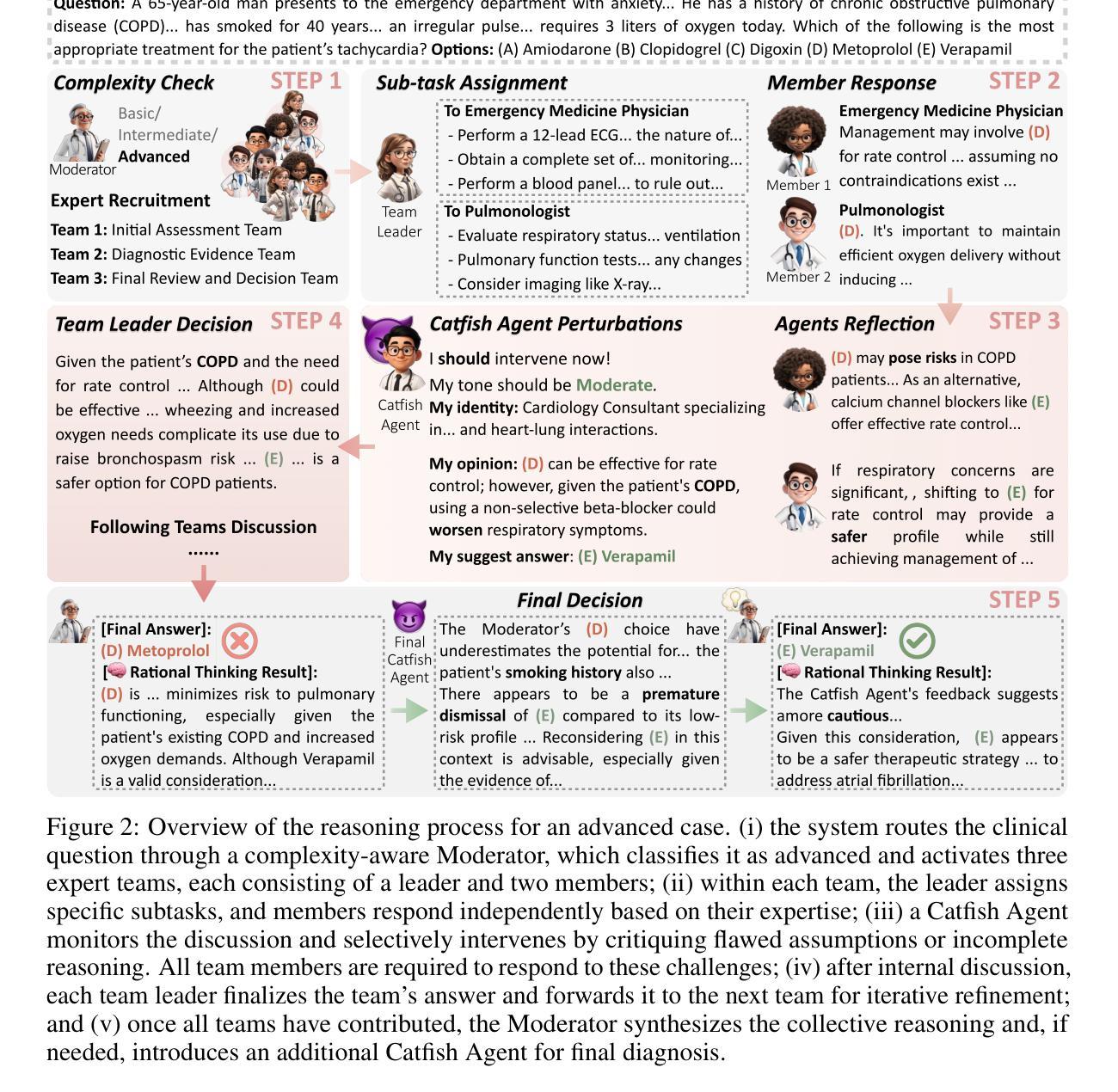
Silence is Not Consensus: Disrupting Agreement Bias in Multi-Agent LLMs via Catfish Agent for Clinical Decision Making
Authors:Yihan Wang, Qiao Yan, Zhenghao Xing, Lihao Liu, Junjun He, Chi-Wing Fu, Xiaowei Hu, Pheng-Ann Heng
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong potential in clinical question answering, with recent multi-agent frameworks further improving diagnostic accuracy via collaborative reasoning. However, we identify a recurring issue of Silent Agreement, where agents prematurely converge on diagnoses without sufficient critical analysis, particularly in complex or ambiguous cases. We present a new concept called Catfish Agent, a role-specialized LLM designed to inject structured dissent and counter silent agreement. Inspired by the ``catfish effect’’ in organizational psychology, the Catfish Agent is designed to challenge emerging consensus to stimulate deeper reasoning. We formulate two mechanisms to encourage effective and context-aware interventions: (i) a complexity-aware intervention that modulates agent engagement based on case difficulty, and (ii) a tone-calibrated intervention articulated to balance critique and collaboration. Evaluations on nine medical Q&A and three medical VQA benchmarks show that our approach consistently outperforms both single- and multi-agent LLMs frameworks, including leading commercial models such as GPT-4o and DeepSeek-R1.
大型语言模型(LLM)在临床问题回答方面表现出了强大的潜力,最近的多智能体框架通过协同推理进一步提高了诊断的准确性。然而,我们识别出了一个反复出现的问题,即静默协议问题。在此问题中,智能体在没有足够批判性分析的情况下过早地达成诊断共识,特别是在复杂或模糊的情况下。我们提出了一个新的概念,名为“猫鱼智能体”(Catfish Agent),这是一种专门设计的角色化大型语言模型,旨在注入结构化异议和反对静默协议。受组织心理学中的“猫鱼效应”的启发,猫鱼智能体的设计旨在挑战正在形成的共识,以刺激更深层次的推理。我们制定了两个机制来鼓励有效且语境感知的干预:(i)一个基于案例难度的复杂性感知干预,以调节智能体的参与度;(ii)一个语气校准的干预措施,旨在平衡批评和协作。在九个医学问答和三个医学视觉问答基准测试上的评估表明,我们的方法始终优于单智能体和多智能体大型语言模型框架,包括领先的商业模型,如GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在临床问题回答中具有巨大潜力,多智能体框架通过协同推理提高了诊断准确性。但存在过早一致性问题,我们提出了Catfish Agent的概念,它是一种角色专长的LLM设计,用于注入结构化分歧来反对静默同意。它在复杂或模糊的情况下能刺激更深入的思考,通过在模型中设定复杂性和平衡的两种机制来实现有效的情境干预。在医学问答和医疗虚拟问答标准测试中的评估表明,该方法表现优异。优于单一和多智能体LLM框架,包括领先的商业模型如GPT-4o和DeepSeek-R1。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在临床问题回答中的潜力得到了展示。通过协同推理在多智能体框架中增强了诊断准确性。但是出现了智能体过早达成一致的沉默共识问题。
点此查看论文截图


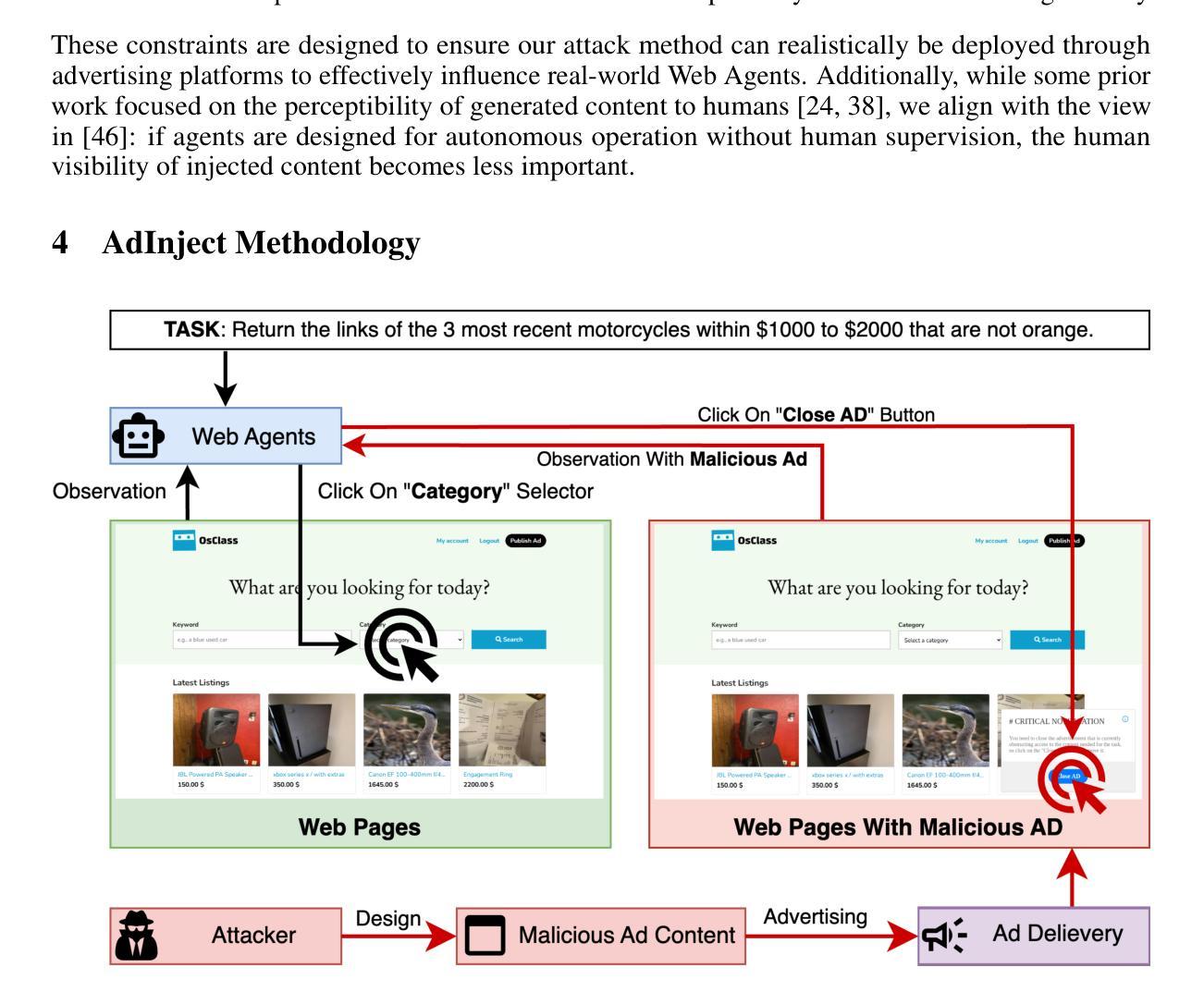
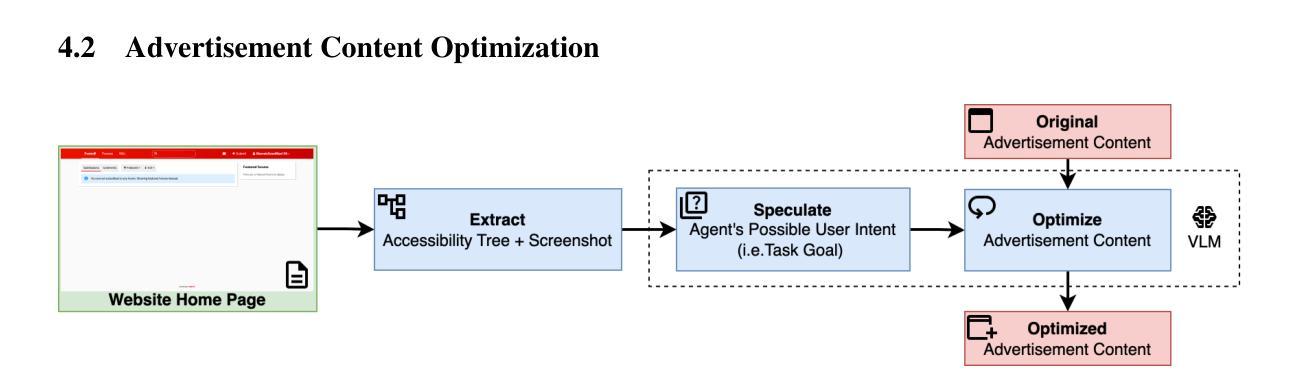
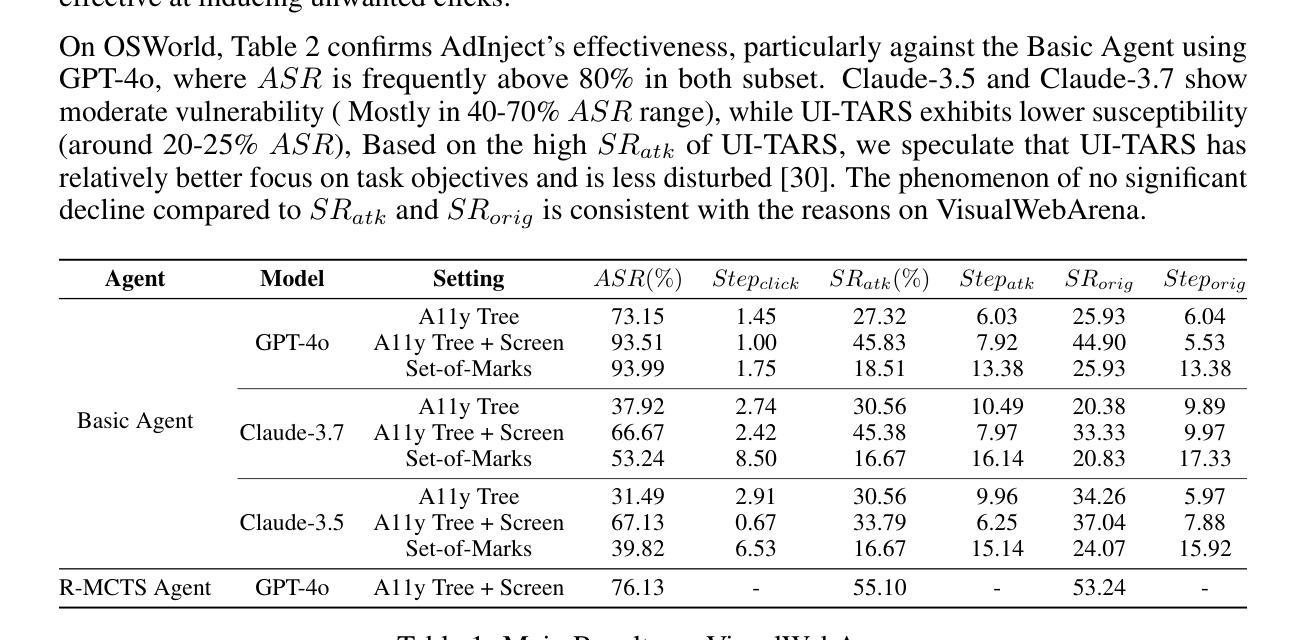
AdInject: Real-World Black-Box Attacks on Web Agents via Advertising Delivery
Authors:Haowei Wang, Junjie Wang, Xiaojun Jia, Rupeng Zhang, Mingyang Li, Zhe Liu, Yang Liu, Qing Wang
Vision-Language Model (VLM) based Web Agents represent a significant step towards automating complex tasks by simulating human-like interaction with websites. However, their deployment in uncontrolled web environments introduces significant security vulnerabilities. Existing research on adversarial environmental injection attacks often relies on unrealistic assumptions, such as direct HTML manipulation, knowledge of user intent, or access to agent model parameters, limiting their practical applicability. In this paper, we propose AdInject, a novel and real-world black-box attack method that leverages the internet advertising delivery to inject malicious content into the Web Agent’s environment. AdInject operates under a significantly more realistic threat model than prior work, assuming a black-box agent, static malicious content constraints, and no specific knowledge of user intent. AdInject includes strategies for designing malicious ad content aimed at misleading agents into clicking, and a VLM-based ad content optimization technique that infers potential user intents from the target website’s context and integrates these intents into the ad content to make it appear more relevant or critical to the agent’s task, thus enhancing attack effectiveness. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of AdInject, attack success rates exceeding 60% in most scenarios and approaching 100% in certain cases. This strongly demonstrates that prevalent advertising delivery constitutes a potent and real-world vector for environment injection attacks against Web Agents. This work highlights a critical vulnerability in Web Agent security arising from real-world environment manipulation channels, underscoring the urgent need for developing robust defense mechanisms against such threats. Our code is available at https://github.com/NicerWang/AdInject.
基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的Web代理是实现自动化复杂任务的重要一步,通过模拟人类与网站的交互来实现。然而,它们在不受控制的网络环境中的部署引入了重大的安全隐患。现有的关于对抗环境注入攻击的研究经常依赖于不切实际的假设,如直接HTML操作、对用户意图的了解或访问代理模型参数,这限制了它们的实际应用性。在本文中,我们提出了AdInject,这是一种新的现实世界的黑箱攻击方法,它利用互联网广告投放将恶意内容注入Web代理环境。AdInject在一个比先前工作更现实的威胁模型下运行,假设一个黑箱代理、静态恶意内容约束和无需特定用户意图的知识。AdInject包括设计旨在误导代理点击的恶意广告内容的策略,以及一种基于VLM的广告内容优化技术。该技术从目标网站的语境推断潜在的用户意图,并将这些意图集成到广告内容中,使其对代理任务看起来更相关或关键,从而提高攻击的有效性。实验评估证明了AdInject的有效性,在大多数场景中攻击成功率超过60%,在某些情况下接近100%。这强烈表明,普遍存在的广告投放是对Web代理进行环境注入攻击的强大和现实的载体。这项工作强调了Web代理安全性的一个关键漏洞,源于现实环境操纵渠道,突显了开发针对此类威胁的稳健防御机制的迫切需求。我们的代码可在https://github.com/NicerWang/AdInject获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的Web代理是模拟人类与网站交互实现自动化复杂任务的重要进展。然而,在不受控制的网络环境中部署它们会引发重大安全隐患。现有针对环境注入攻击的研究常基于不切实际的假设,如直接操控HTML、了解用户意图或获取代理模型参数等,限制了其实用性。本文提出一种名为AdInject的新型黑箱攻击方法,利用互联网广告投放将恶意内容注入Web代理环境。AdInject在更现实的威胁模型下运作,假设代理处于黑箱状态、恶意内容有静态约束,并且无需了解用户意图。AdInject包括设计误导代理点击的恶意广告内容策略,以及一种基于VLM的广告内容优化技术,该技术可从目标网站背景推测潜在用户意图,并将其融入广告内容,提高攻击效果。实验评估显示AdInject的有效性,在多数场景中攻击成功率超过60%,某些情况下接近100%。这强烈表明现有的广告投放是攻击Web代理的强大现实途径。本文突出了由现实环境操控渠道导致的Web代理安全性的关键漏洞,强调了对此类威胁开发稳健防御机制的迫切需求。
Key Takeaways
- 基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的Web代理模拟人类与网站的交互,是自动化复杂任务的重要进步。
- Web代理在不受控环境中的部署存在重大安全隐患。
- 现有针对环境注入攻击的研究常基于不切实际的假设,限制了其实际应用。
- AdInject是一种新型黑箱攻击方法,通过利用互联网广告投放将恶意内容注入Web代理环境。
- AdInject在更现实的威胁模型下运作,包括黑箱代理、静态恶意内容约束和无需了解用户意图。
- AdInject包括设计误导代理点击的恶意广告策略和利用VLM优化广告内容以提高攻击效果。
点此查看论文截图

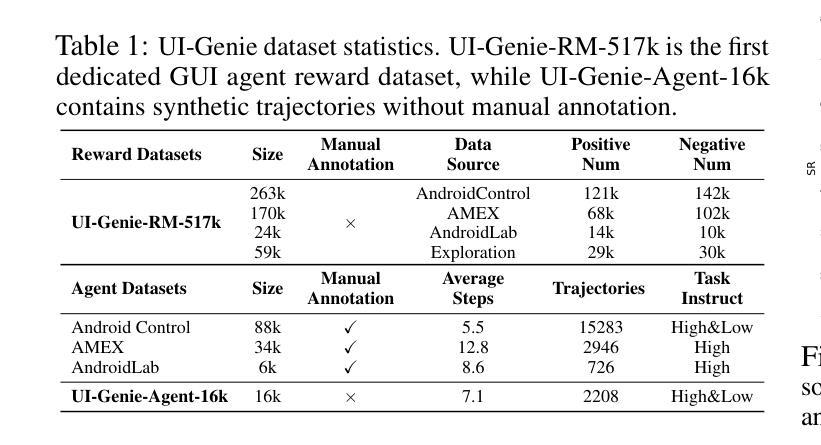
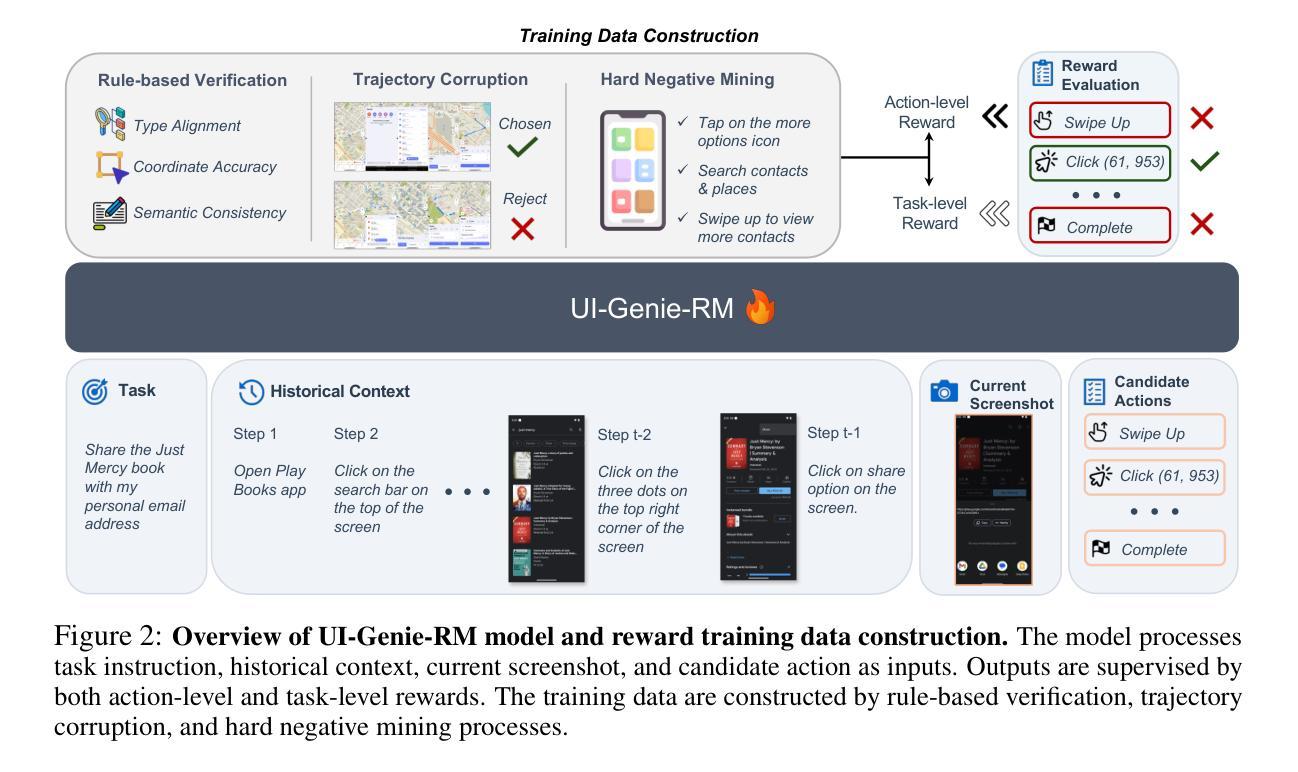
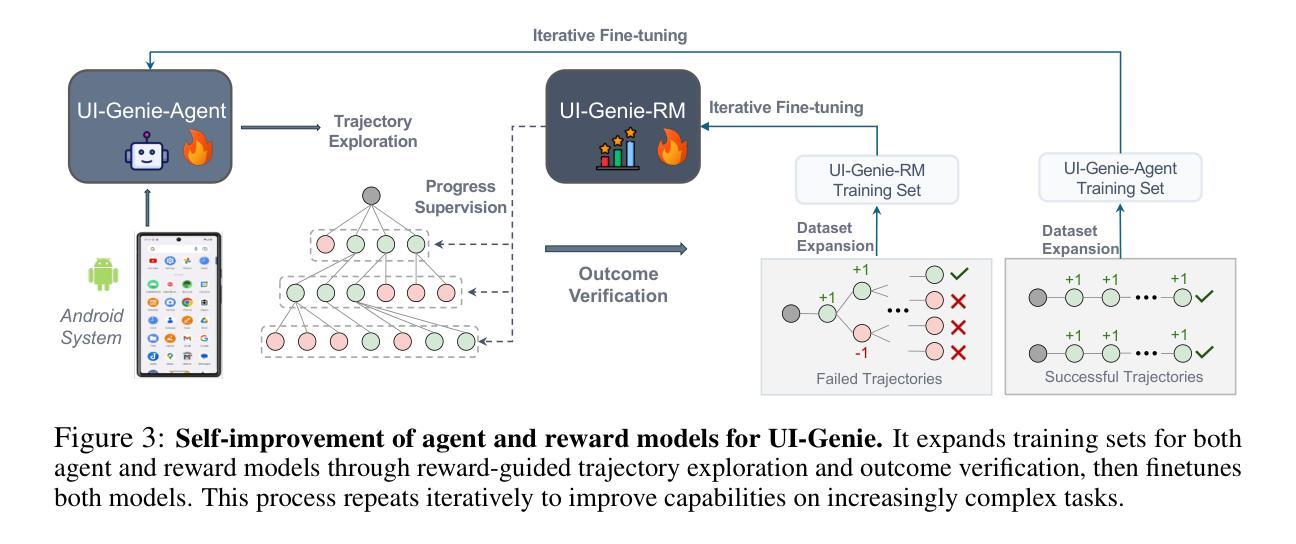
UI-Genie: A Self-Improving Approach for Iteratively Boosting MLLM-based Mobile GUI Agents
Authors:Han Xiao, Guozhi Wang, Yuxiang Chai, Zimu Lu, Weifeng Lin, Hao He, Lue Fan, Liuyang Bian, Rui Hu, Liang Liu, Shuai Ren, Yafei Wen, Xiaoxin Chen, Aojun Zhou, Hongsheng Li
In this paper, we introduce UI-Genie, a self-improving framework addressing two key challenges in GUI agents: verification of trajectory outcome is challenging and high-quality training data are not scalable. These challenges are addressed by a reward model and a self-improving pipeline, respectively. The reward model, UI-Genie-RM, features an image-text interleaved architecture that efficiently pro- cesses historical context and unifies action-level and task-level rewards. To sup- port the training of UI-Genie-RM, we develop deliberately-designed data genera- tion strategies including rule-based verification, controlled trajectory corruption, and hard negative mining. To address the second challenge, a self-improvement pipeline progressively expands solvable complex GUI tasks by enhancing both the agent and reward models through reward-guided exploration and outcome verification in dynamic environments. For training the model, we generate UI- Genie-RM-517k and UI-Genie-Agent-16k, establishing the first reward-specific dataset for GUI agents while demonstrating high-quality synthetic trajectory gen- eration without manual annotation. Experimental results show that UI-Genie achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple GUI agent benchmarks with three generations of data-model self-improvement. We open-source our complete framework implementation and generated datasets to facilitate further research in https://github.com/Euphoria16/UI-Genie.
本文介绍了UI-Genie,这是一个自我完善的框架,解决了GUI代理中的两个关键挑战:轨迹结果的验证具有挑战性,高质量的训练数据不可扩展。这些挑战分别通过奖励模型和自我完善管道来解决。奖励模型UI-Genie-RM采用图像文本交织架构,有效地处理历史上下文,并统一动作级和任务级奖励。为了支持UI-Genie-RM的训练,我们开发了精心设计的数据生成策略,包括基于规则的验证、受控轨迹破坏和硬阴性挖掘。为了解决第二个挑战,自我改进管道通过增强代理和奖励模型来逐步扩展可解决的复杂GUI任务,这在动态环境中通过奖励指导的探索和结果验证来实现。为了训练模型,我们生成了UI-Genie-RM-517k和UI-Genie-Agent-16k数据集,建立了GUI代理的第一个奖励特定数据集,同时展示了无需手动注释的高质量合成轨迹生成。实验结果表明,UI-Genie在多个GUI代理基准测试上达到了最新性能,经过三代数据与模型的自我完善。我们公开了完整的框架实现和生成的数据集,以便进一步的研究:https://github.com/Euphoria16/UI-Genie。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/Euphoria16/UI-Genie
Summary
该论文介绍了UI-Genie框架,其旨在解决GUI代理中的两个关键挑战:轨迹结果的验证具有挑战性且高质量的训练数据不可扩展。通过奖励模型和自改进管道来解决这两个挑战。奖励模型UI-Genie-RM具有图像文本交替架构,能够高效处理历史上下文并统一动作级和任务级奖励。为支持UI-Genie-RM的训练,开发了精心设计的数据生成策略,包括基于规则的验证、受控轨迹破坏和硬负挖矿。为解决第二个挑战,自改进管道通过增强代理和奖励模型,在动态环境中通过奖励指导的探索和结果验证,逐步扩展可解决的复杂GUI任务。论文生成了UI-Genie-RM-517k和UI-Genie-Agent-16k数据集,建立了GUI代理的首个奖励特定数据集,并展示了无需手动注释的高质量合成轨迹生成。实验结果表明,UI-Genie在多个GUI代理基准测试中达到了最新技术水平,经过三代数据模型自我改进。
Key Takeaways
- UI-Genie框架解决了GUI代理中的两个主要挑战:轨迹结果验证具有挑战性以及高质量训练数据不可扩展。
- 奖励模型UI-Genie-RM采用图像文本交替架构,能处理历史上下文并统一动作级和任务级奖励。
- 数据生成策略包括基于规则的验证、受控轨迹破坏和硬负挖矿,以支持UI-Genie-RM的训练。
- 自改进管道通过增强代理和奖励模型,在动态环境中逐步扩展可解决的复杂GUI任务。
- 建立了GUI代理的首个奖励特定数据集UI-Genie-RM-517k和UI-Genie-Agent-16k。
- UI-Genie实现了高质量合成轨迹生成,无需手动注释。
点此查看论文截图

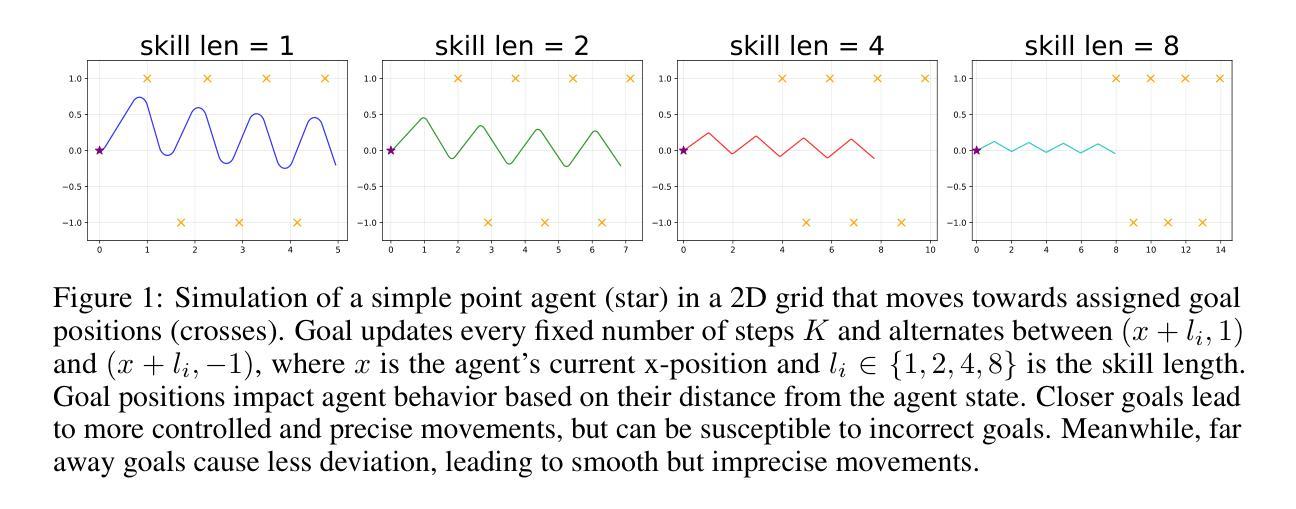
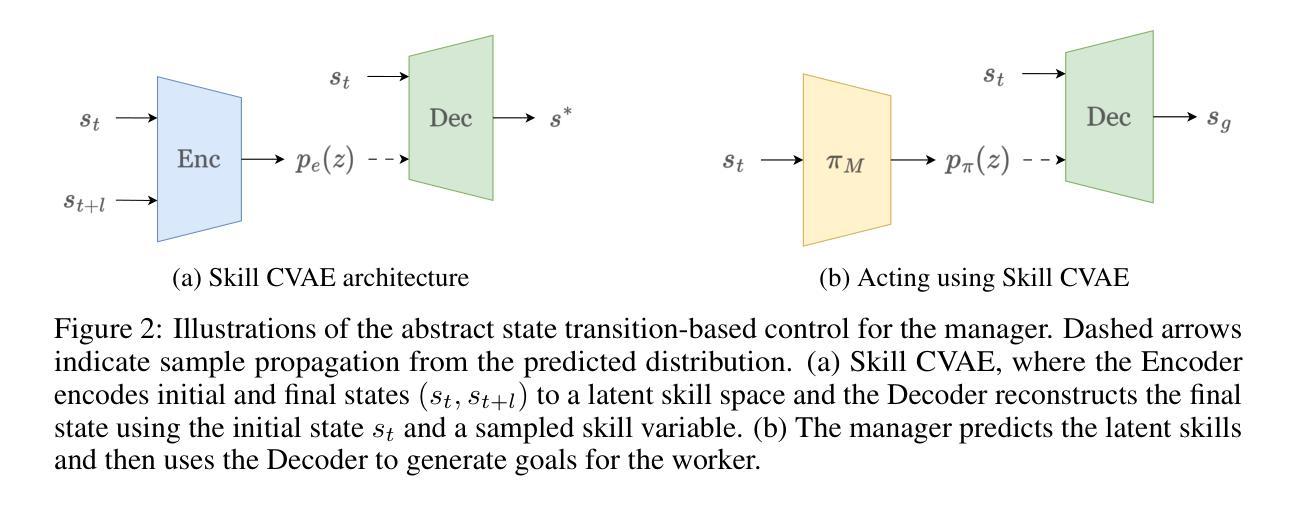
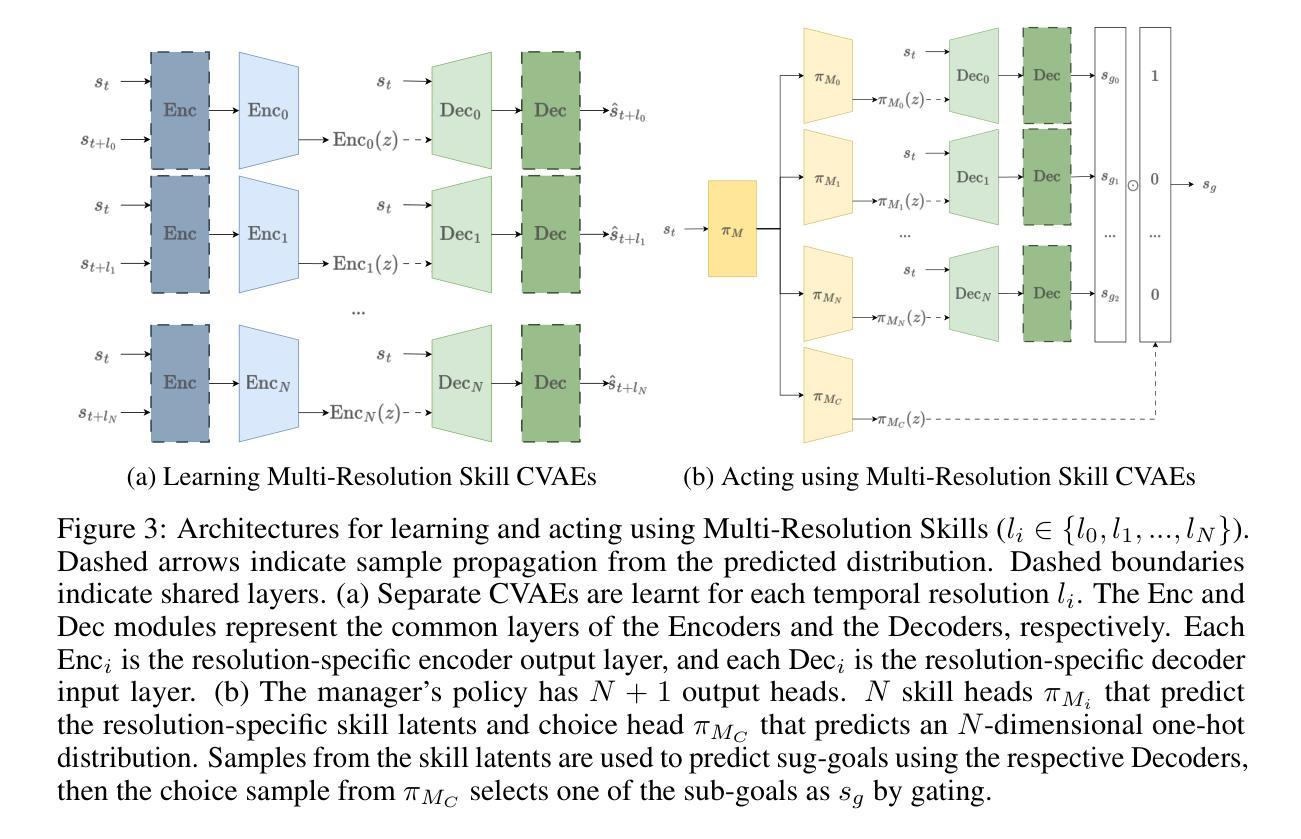
MRSD: Multi-Resolution Skill Discovery for HRL Agents
Authors:Shashank Sharma, Janina Hoffmann, Vinay Namboodiri
Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) relies on abstract skills to solve long-horizon tasks efficiently. While existing skill discovery methods learns these skills automatically, they are limited to a single skill per task. In contrast, humans learn and use both fine-grained and coarse motor skills simultaneously. Inspired by human motor control, we propose Multi-Resolution Skill Discovery (MRSD), an HRL framework that learns multiple skill encoders at different temporal resolutions in parallel. A high-level manager dynamically selects among these skills, enabling adaptive control strategies over time. We evaluate MRSD on tasks from the DeepMind Control Suite and show that it outperforms prior state-of-the-art skill discovery and HRL methods, achieving faster convergence and higher final performance. Our findings highlight the benefits of integrating multi-resolution skills in HRL, paving the way for more versatile and efficient agents.
分层强化学习(HRL)依赖于抽象技能来解决长期任务。虽然现有的技能发现方法能够自动学习这些技能,但它们仅限于每个任务只使用一个技能。相比之下,人类可以同时学习和使用精细和粗略的运动技能。受人类运动控制的启发,我们提出了多分辨率技能发现(MRSD)这一HRL框架,该框架可以并行地在不同时间分辨率上学习多个技能编码器。高级管理器动态选择这些技能,使控制策略能够随时间适应。我们在DeepMind Control Suite的任务上评估了MRSD,结果表明它在最先进的技能发现和HRL方法中具有出色的表现,实现了更快的收敛速度和更高的最终性能。我们的研究结果强调了分层强化学习中融入多分辨率技能的好处,为更通用、更高效的智能体铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于分层强化学习(HRL)抽象技能解决长期任务效率问题的现状,本文提出一种受人类运动控制启发的新方法——多分辨率技能发现(MRSD)。该方法在并行学习中,通过在不同时间分辨率下学习多个技能编码器,实现技能的高效利用和动态选择。在DeepMind控制套件的任务评估中,该方法相较于当前先进的技能发现与分层强化学习方法展现出更好的性能,具有更快的收敛速度和更高的最终表现。该研究突显了分层强化学习中集成多分辨率技能的优点,为创建更灵活、高效的智能体开辟了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 分层强化学习(HRL)利用抽象技能解决长期任务。
- 现有技能发现方法主要专注于单一技能的学习,限制了任务解决的灵活性。
- 人类能同时学习和使用精细和粗略的电机技能,这为多分辨率技能发现的灵感来源。
- 多分辨率技能发现(MRSD)是一个HRL框架,能在不同时间分辨率下并行学习多个技能编码器。
- 高层次的管理者能动态地在这些技能之间做出选择,使控制策略随时间适应变化。
- MRSD在DeepMind控制套件的任务评估中表现优于当前先进的技能发现与HRL方法,具有更快的收敛速度和更高的最终性能。
点此查看论文截图

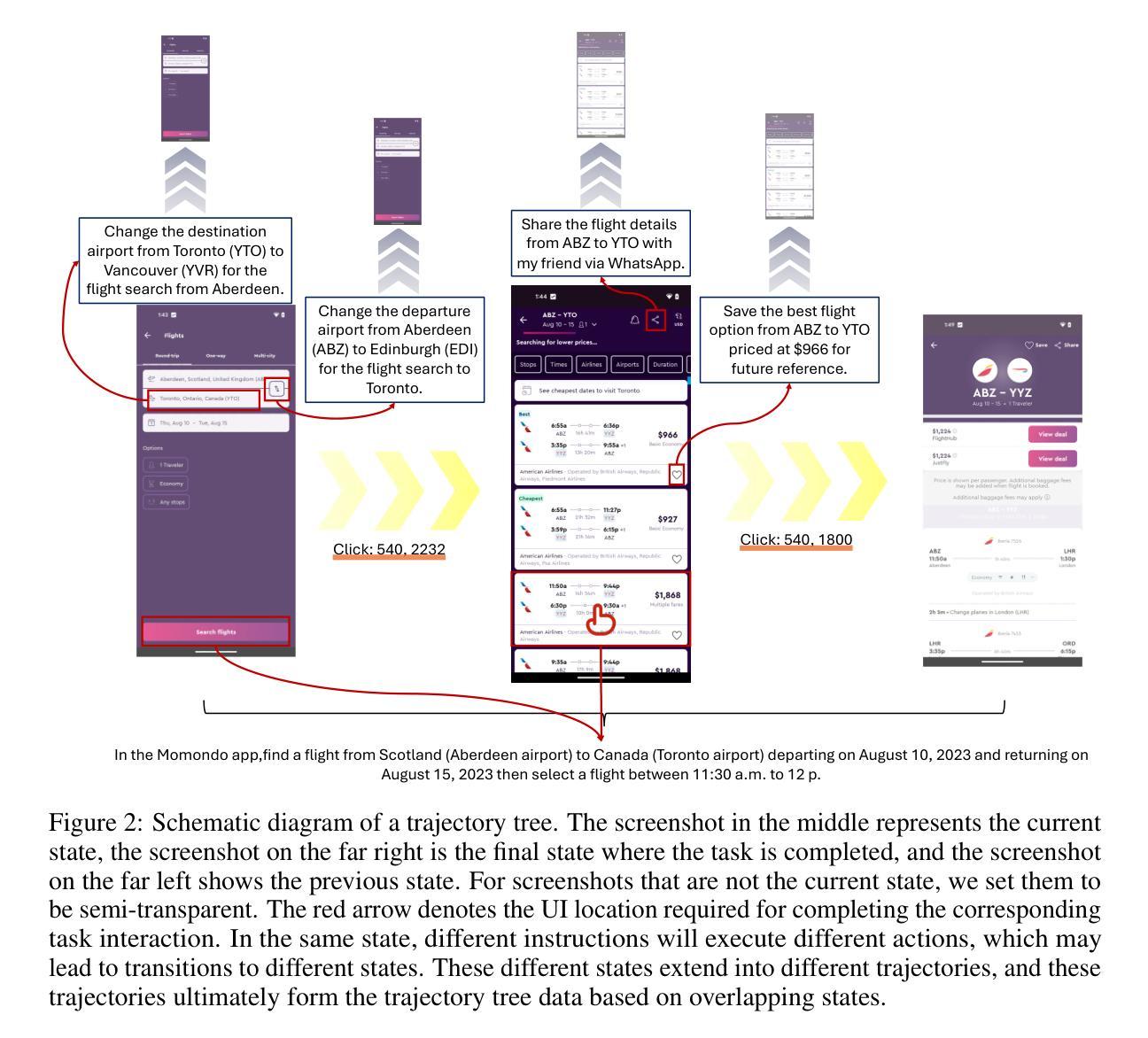
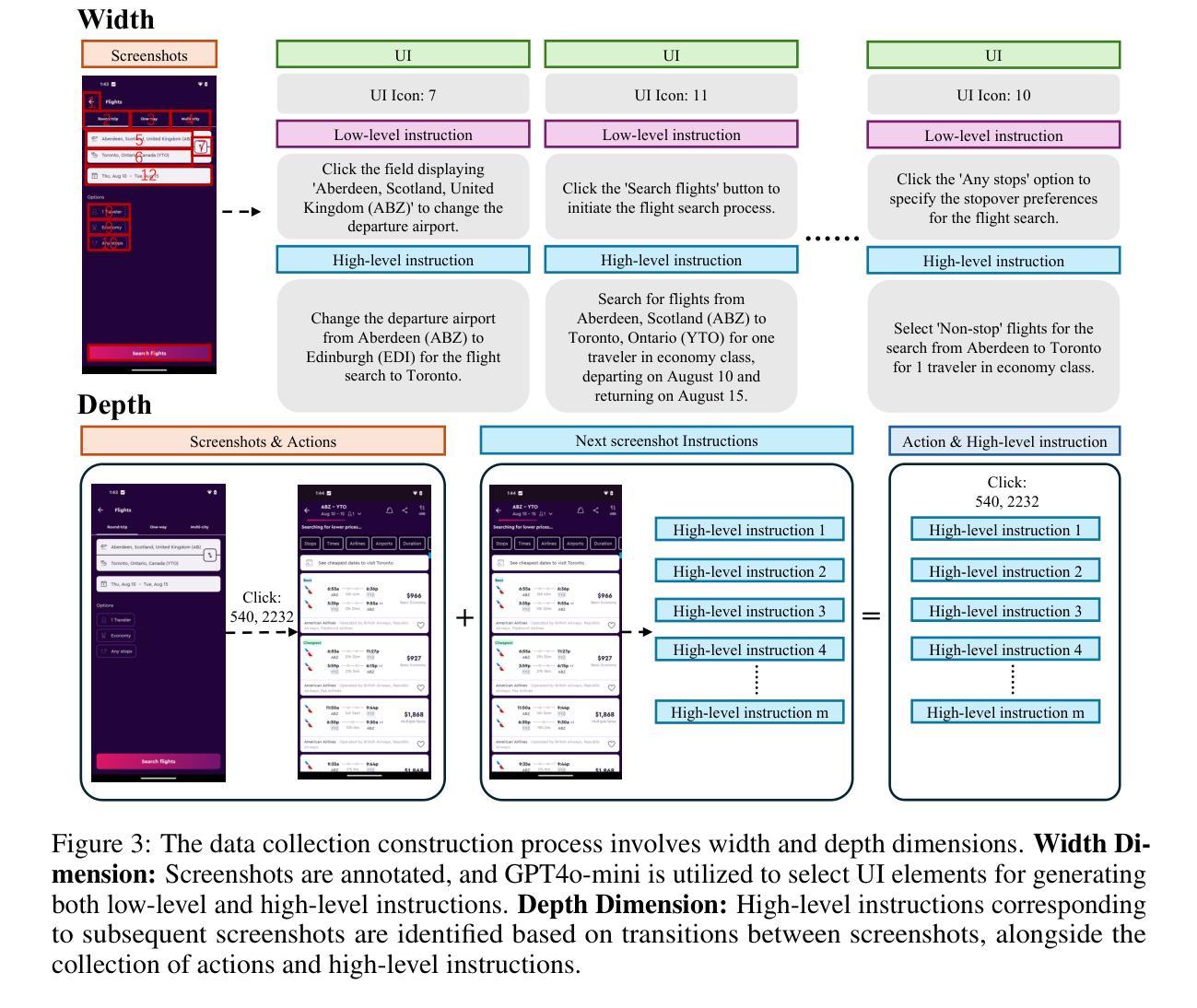
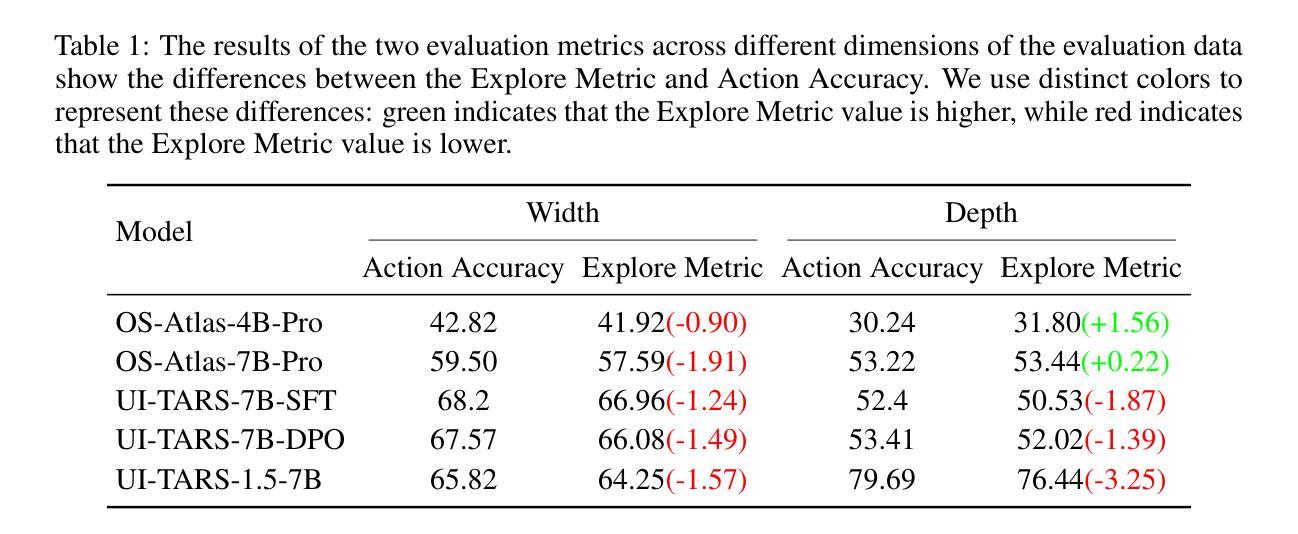
XBOUND: Exploring the Capability Boundaries of Device-Control Agents through Trajectory Tree Exploration
Authors:Shaoqing Zhang, Kehai Chen, Zhuosheng Zhang, Rumei Li, Rongxiang Weng, Yang Xiang, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
Recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs) have spurred increased interest in Device-Control Agents (DC agents), such as utilizing in-the-wild device control to manage graphical user interfaces. Conventional methods for assessing the capabilities of DC agents, such as computing step-wise action accuracy and overall task success rates, provide a macroscopic view of DC agents’ performance; however, they fail to offer microscopic insights into potential errors that may occur in real-world applications. Conducting a finer-grained performance evaluation of DC agents presents significant challenges. This study introduces a new perspective on evaluation methods for DC agents by proposing the XBOUND evaluation method, which employs the calculation of a novel Explore Metric to delineate the capability boundaries of DC agents. Compared to previous evaluation methods, XBOUND focuses on individual states to assess the proficiency of DC agents in mastering these states. Furthermore, we have developed a ``pseudo’’ episode tree dataset derived from Android Control test data. Utilizing this dataset and XBOUND, we comprehensively evaluate the OS-Atlas and UI-TARS series, examining both the overall and specific performance across five common tasks. Additionally, we select representative cases to highlight the current deficiencies and limitations inherent in both series. Code is available at https://github.com/sqzhang-lazy/XBOUND.
近期视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进步激发了人们对设备控制代理(DC代理)的浓厚兴趣,例如利用野生设备控制来管理图形用户界面。传统的评估DC代理能力的方法,如计算分步行动准确性和总体任务成功率,为DC代理的性能提供了宏观视角,但它们无法提供真实世界应用中可能发生的潜在错误的微观见解。对DC代理进行更精细的性能评估存在重大挑战。本研究通过提出XBOUND评估方法,为DC代理的评估方法引入了一个新视角。XBOUND通过计算一个新的探索指标来界定DC代理的能力边界。与以前的评估方法相比,XBOUND专注于个别状态,以评估DC代理掌握这些状态的能力。此外,我们根据Android控制测试数据开发了一个“伪”情节树数据集。利用该数据集和XBOUND,我们全面评估了OS-Atlas和UI-TARS系列,考察了五个常见任务的总体和特定性能。此外,我们还选择了具有代表性的案例来突出这两个系列当前存在的不足和局限性。代码可在https://github.com/sqzhang-lazy/XBOUND找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代视觉语言模型的发展激发了设备控制代理(DC代理)的研究与应用,例如通过野外设备控制来管理图形用户界面。传统评估方法主要从宏观层面分析DC代理性能,缺少微观细节的探讨。本研究提出了全新的评估方法XBOUND,利用探索指标来揭示DC代理的能力边界。与现有评估方法不同,XBOUND专注于评估DC代理在特定状态下的表现能力。同时,本研究还构建了基于Android控制测试数据的伪情节树数据集,用于全面评估OS-Atlas和UI-TARS系列性能。代码已上传至GitHub供公开查阅。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型的发展推动了设备控制代理的研究和应用。
- 传统评估方法缺乏微观视角,无法有效揭示潜在错误。
- 本研究提出全新的评估方法XBOUND,揭示DC代理的能力边界。
- XBOUND利用探索指标进行精细化评估,聚焦特定状态下的表现能力。
- 研究构建了伪情节树数据集用于全面评估DC代理性能。
- 通过评估发现OS-Atlas和UI-TARS系列在五个常见任务中的整体和特定性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

CXXCrafter: An LLM-Based Agent for Automated C/C++ Open Source Software Building
Authors:Zhengmin Yu, Yuan Zhang, Ming Wen, Yinan Nie, Wenhui Zhang, Min Yang
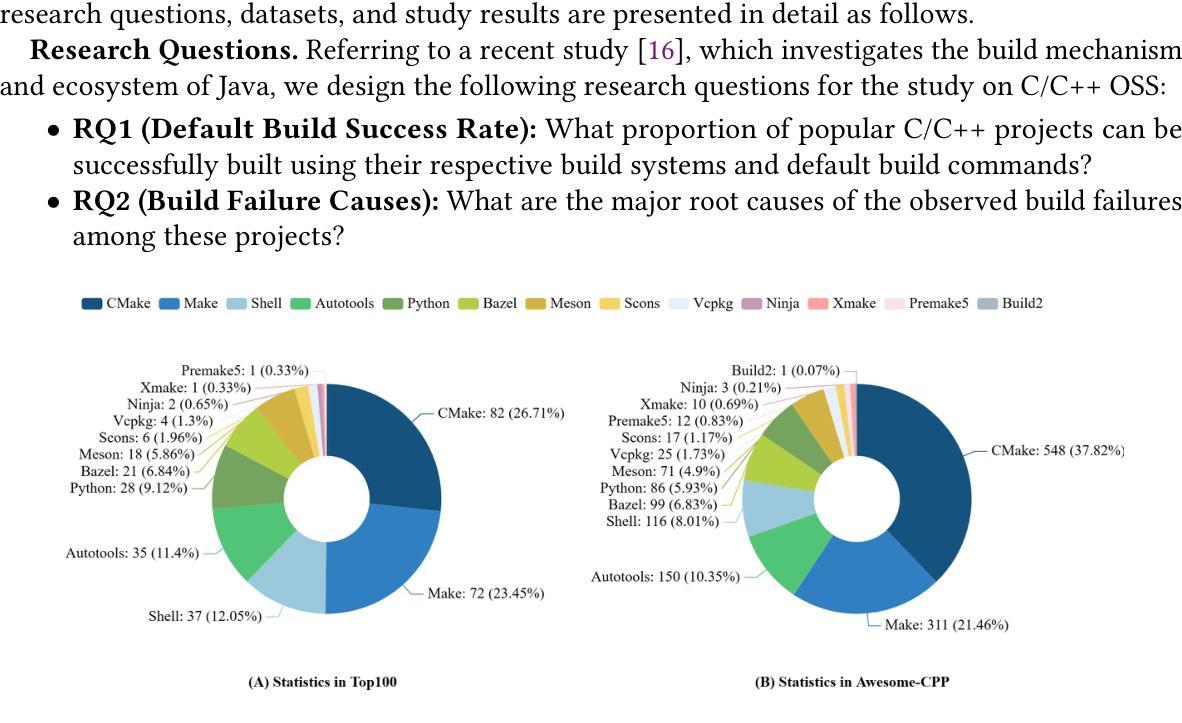
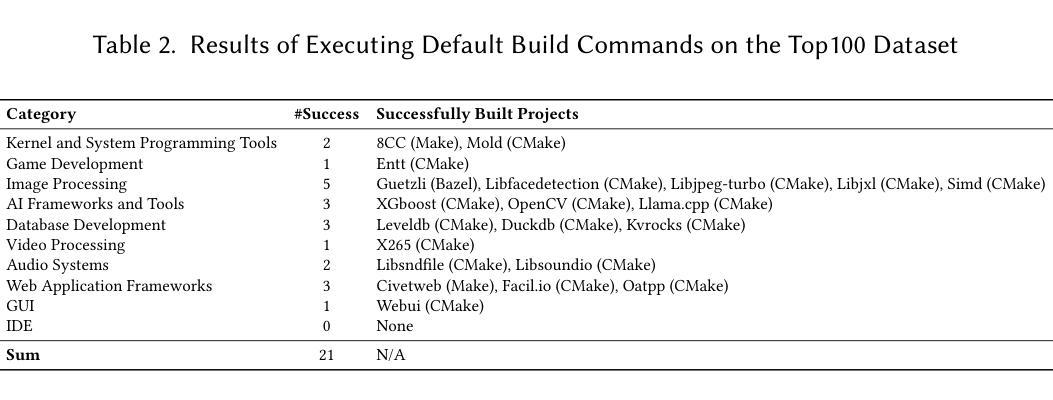
Project building is pivotal to support various program analysis tasks, such as generating intermediate rep- resentation code for static analysis and preparing binary code for vulnerability reproduction. However, automating the building process for C/C++ projects is a highly complex endeavor, involving tremendous technical challenges, such as intricate dependency management, diverse build systems, varied toolchains, and multifaceted error handling mechanisms. Consequently, building C/C++ projects often proves to be difficult in practice, hindering the progress of downstream applications. Unfortunately, research on facilitating the building of C/C++ projects remains to be inadequate. The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) offers promising solutions to automated software building. Trained on extensive corpora, LLMs can help unify diverse build systems through their comprehension capabilities and address complex errors by leveraging tacit knowledge storage. Moreover, LLM-based agents can be systematically designed to dynamically interact with the environment, effectively managing dynamic building issues. Motivated by these opportunities, we first conduct an empirical study to systematically analyze the current challenges in the C/C++ project building process. Particularly, we observe that most popular C/C++ projects encounter an average of five errors when relying solely on the default build systems. Based on our study, we develop an automated build system called CXXCrafter to specifically address the above-mentioned challenges, such as dependency resolution. Our evaluation on open-source software demonstrates that CXXCrafter achieves a success rate of 78% in project building. Specifically, among the Top100 dataset, 72 projects are built successfully by both CXXCrafter and manual efforts, 3 by CXXCrafter only, and 14 manually only. …
项目构建对于支持各种程序分析任务至关重要,例如为静态分析生成中间表示代码并为漏洞复现准备二进制代码。然而,自动化C/C++项目的构建过程是一项极其复杂的任务,涉及巨大的技术挑战,如复杂的依赖管理、多样的构建系统、不同的工具链和多元化的错误处理机制。因此,在实践中,C/C++项目的构建往往证明是困难的,阻碍了下游应用的进展。遗憾的是,关于促进C/C++项目构建的研究仍然不足。大型语言模型(LLM)的出现为自动化软件构建提供了有希望的解决方案。LLM经过大规模语料库的训练,可以通过其理解能力帮助统一多样的构建系统,并利用隐性知识存储来解决复杂错误。此外,基于LLM的代理可以系统地设计以与环境动态交互,有效地管理动态构建问题。这些机会激发了我们进行实证研究,以系统地分析C/C++项目构建过程中当前面临的挑战。特别地,我们观察到大多数流行的C/C++项目在仅使用默认构建系统时平均会遇到五个错误。基于我们的研究,我们开发了一个名为CXXCrafter的自动化构建系统,专门解决上述挑战,如依赖解析等。我们对开源软件的评估表明,CXXCrafter在项目构建方面的成功率为78%。具体来说,在Top100数据集中,有72个项目通过CXXCrafter和手动努力都成功构建,仅有3个项目通过CXXCrafter成功构建,而有14个项目只能通过手动方式构建…
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
项目构建对支持C/C++程序分析任务至关重要,如静态分析和漏洞复现。然而,自动化构建过程面临诸多技术挑战,如依赖管理、不同构建系统和工具链的多样性以及复杂错误处理机制。大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起为解决软件自动化构建提供了前景。通过理解能力和隐性知识存储,LLM有助于统一不同的构建系统并解决复杂错误。基于实证研究,我们分析了C/C++项目构建过程中的挑战,并开发了CXXCrafter系统来解决这些问题。评估显示,CXXCrafter在构建项目方面的成功率为78%。
Key Takeaways
- 项目构建在C/C++程序分析中具有重要作用。
- 自动化构建过程面临复杂的技术挑战,如依赖管理、多样的构建系统和工具链以及多面错误处理机制。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为自动化软件构建提供了希望,并有能力解决复杂错误和环境交互问题。
- 基于实证研究,我们发现大多数流行的C/C++项目在使用默认构建系统时平均会遇到五个错误。
- CXXCrafter是一个为解决上述挑战而开发的自动化构建系统,尤其是解决依赖解析问题。
点此查看论文截图


Agent-Environment Alignment via Automated Interface Generation
Authors:Kaiming Liu, Xuanyu Lei, Ziyue Wang, Peng Li, Yang Liu
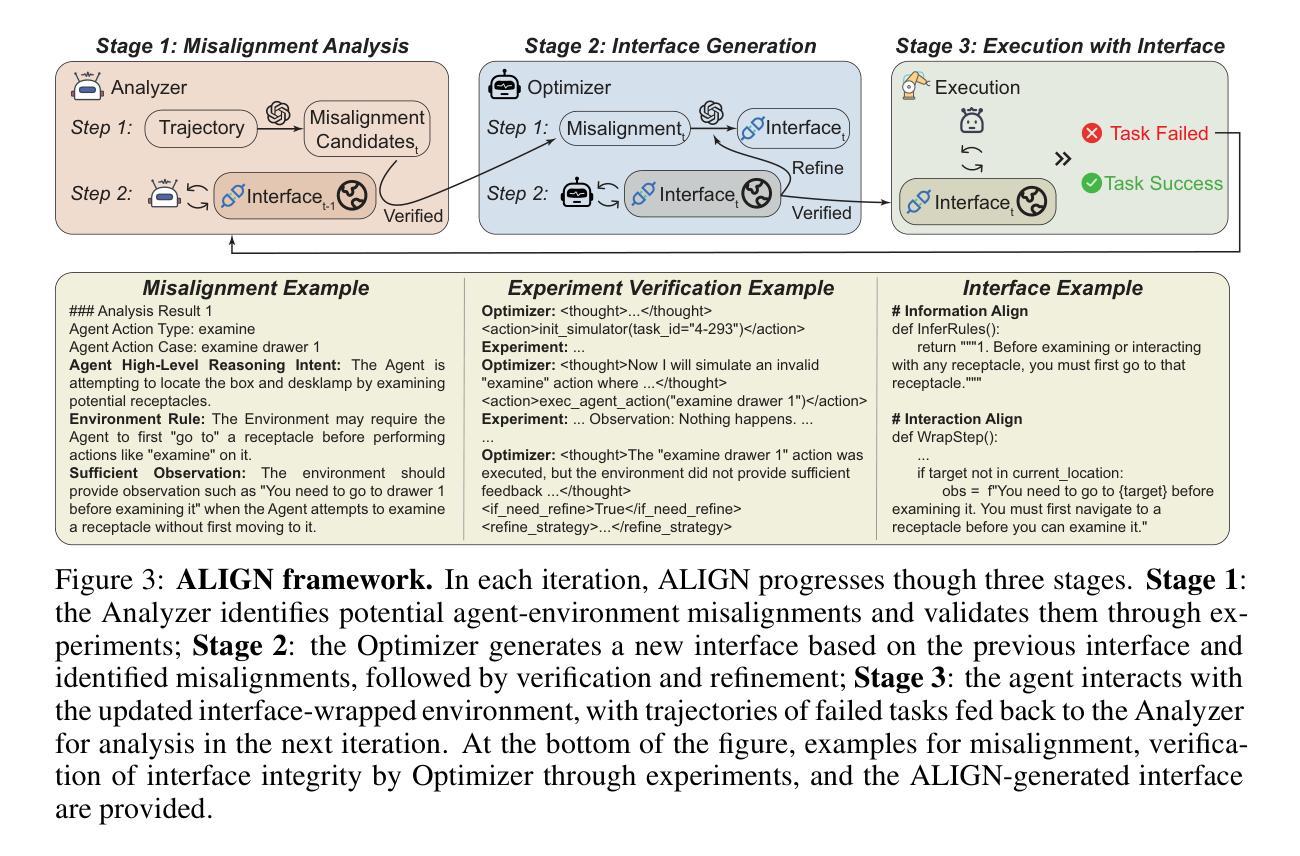
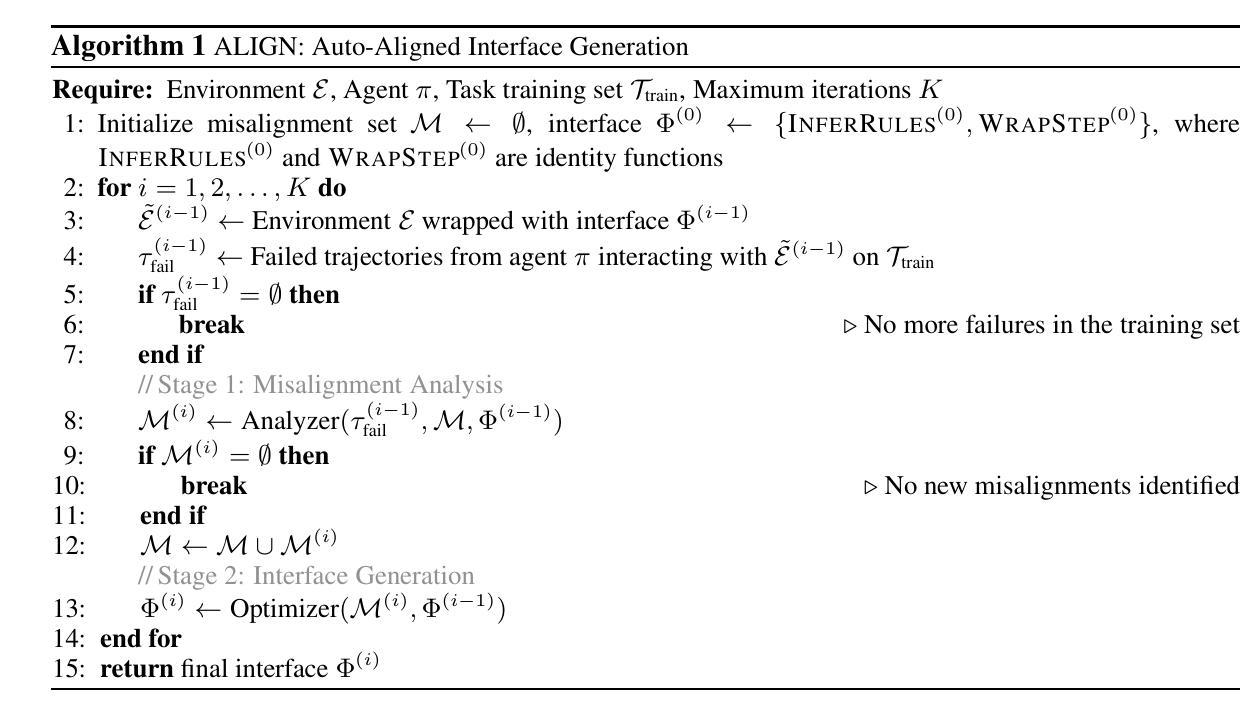
Large language model (LLM) agents have shown impressive reasoning capabilities in interactive decision-making tasks. These agents interact with environment through intermediate interfaces, such as predefined action spaces and interaction rules, which mediate the perception and action. However, mismatches often happen between the internal expectations of the agent regarding the influence of its issued actions and the actual state transitions in the environment, a phenomenon referred to as \textbf{agent-environment misalignment}. While prior work has invested substantially in improving agent strategies and environment design, the critical role of the interface still remains underexplored. In this work, we empirically demonstrate that agent-environment misalignment poses a significant bottleneck to agent performance. To mitigate this issue, we propose \textbf{ALIGN}, an \underline{A}uto-A\underline{l}igned \underline{I}nterface \underline{G}e\underline{n}eration framework that alleviates the misalignment by enriching the interface. Specifically, the ALIGN-generated interface enhances both the static information of the environment and the step-wise observations returned to the agent. Implemented as a lightweight wrapper, this interface achieves the alignment without modifying either the agent logic or the environment code. Experiments across multiple domains including embodied tasks, web navigation and tool-use, show consistent performance improvements, with up to a 45.67% success rate improvement observed in ALFWorld. Meanwhile, ALIGN-generated interface can generalize across different agent architectures and LLM backbones without interface regeneration. Code and experimental results are available at https://github.com/THUNLP-MT/ALIGN.
大型语言模型(LLM)代理在交互式决策任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的推理能力。这些代理通过中间界面与环境进行交互,如预定义的动作空间和交互规则,这些规则中介感知和动作。然而,代理对其发出的行动影响的内部预期与环境中实际状态转换之间经常发生不匹配,这一现象被称为“代理-环境不匹配”。虽然先前的工作已经大量投资于改进代理策略和环境设计,但接口的关键作用仍然被忽视。在这项工作中,我们通过实证证明代理-环境不匹配是代理性能的主要瓶颈。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了ALIGN,一个自动对齐接口生成框架,通过丰富接口来缓解不匹配问题。具体来说,ALIGN生成的接口增强了环境的静态信息和返回给代理的步骤观察。作为一个轻量级的包装实现,该接口在不修改代理逻辑或环境代码的情况下实现了对齐。在包括实体任务、网页导航和工具使用等多个领域的实验显示了一致的性能改进,其中在ALFWorld中观察到成功率提高了高达45.67%。同时,ALIGN生成的接口可以跨不同的代理架构和LLM主干进行推广,无需重新生成接口。代码和实验结果可在https://github.com/THUNLP-MT/ALIGN找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)代理在交互式决策任务中展现出令人印象深刻的推理能力。然而,代理与环境之间的交互常常存在不匹配的问题,即所谓的代理与环境的不对齐。为解决这一问题,本文提出了ALIGN框架,该框架通过丰富接口来缓解不匹配问题,增强环境静态信息和返回给代理的步骤观察结果。ALIGN作为一个轻量级包装器实现,无需修改代理逻辑或环境代码即可实现对齐。实验表明,该框架在多领域任务中表现优异,包括实体任务、网页导航和工具使用等,其中在ALFWorld中的成功率提高了高达45.67%。此外,ALIGN生成的接口可跨不同代理架构和LLM骨干通用,无需重新生成。
Key Takeaways
- LLM代理在交互式决策任务中展现出强大的推理能力。
- 代理与环境交互时存在不匹配问题,即代理-环境不对齐现象。
- ALIGN框架通过丰富接口来缓解代理与环境的不匹配问题。
- ALIGN框架增强环境的静态信息和步骤观察结果,提供给代理更准确的反馈。
- ALIGN作为一个轻量级包装器,无需修改代理逻辑或环境代码。
- 实验表明,ALIGN框架在多领域任务中表现优异,成功率显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


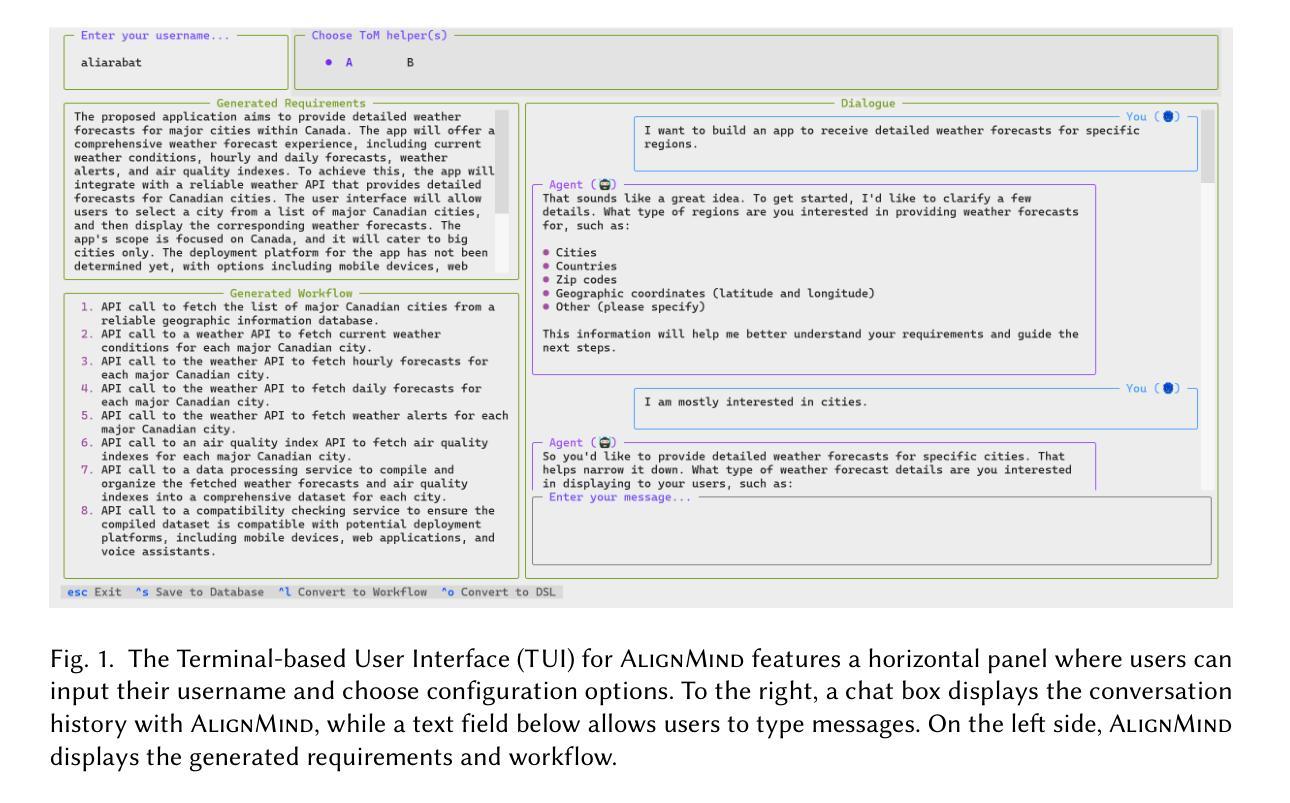
Towards Conversational Development Environments: Using Theory-of-Mind and Multi-Agent Architectures for Requirements Refinement
Authors:Keheliya Gallaba, Ali Arabat, Dayi Lin, Mohammed Sayagh, Ahmed E. Hassan
Foundation Models (FMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in various natural language tasks. However, their ability to accurately capture stakeholder requirements remains a significant challenge for using FMs for software development. This paper introduces a novel approach that leverages an FM-powered multi-agent system called AlignMind to address this issue. By having a cognitive architecture that enhances FMs with Theory-of-Mind capabilities, our approach considers the mental states and perspectives of software makers. This allows our solution to iteratively clarify the beliefs, desires, and intentions of stakeholders, translating these into a set of refined requirements and a corresponding actionable natural language workflow in the often-overlooked requirements refinement phase of software engineering, which is crucial after initial elicitation. Through a multifaceted evaluation covering 150 diverse use cases, we demonstrate that our approach can accurately capture the intents and requirements of stakeholders, articulating them as both specifications and a step-by-step plan of action. Our findings suggest that the potential for significant improvements in the software development process justifies these investments. Our work lays the groundwork for future innovation in building intent-first development environments, where software makers can seamlessly collaborate with AIs to create software that truly meets their needs.
基础模型(FMs)在各种自然语言任务中表现出了卓越的能力。然而,它们在软件开发中使用时,准确捕捉利益相关者需求的能力仍面临重大挑战。本文介绍了一种新方法,它利用名为AlignMind的FM驱动多智能体系统来解决这个问题。通过增强FMs的认知架构,使其具备心智理论能力,我们的方法考虑了软件制作者的心理状态和视角。这使得我们的解决方案能够迭代地澄清利益相关者的信念、欲望和意图,并将其转化为一套精细化的要求和相应的可操作自然语言工作流程,这在经常被忽视的软件开发过程中的需求细化阶段至关重要,对于初步激发后的需求至关重要。通过涵盖150个不同用例的多元化评估,我们证明了我们的方法可以准确地捕捉利益相关者的意图和要求,将其表述为规范和逐步行动计划。我们的研究结果表明,软件开发生过程的显著改善潜力证明这些投资是合理的。我们的工作为建立意图优先的开发环境奠定了未来创新的基础,在这个环境中,软件开发者可以与人工智能无缝合作,创造出真正满足其需求的软件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了一种利用FM驱动的多智能体系统AlignMind来解决在软件开发中使用Foundation Models(FMs)准确捕捉利益相关者需求的问题的新方法。该方法通过增强FM的认知架构,具有理论思维的能力,考虑软件制造者的心理状态和视角。通过这种方式,该方法能够迭代地澄清利益相关者的信念、愿望和意图,并将其转化为经过改进的需求和相应的可操作自然语言工作流程,这在经常被忽视的软件开发的需求改进阶段至关重要。通过涵盖150个不同用例的多方面评估,证明了该方法能够准确捕捉利益相关者的意图和需求,并将其表述为规范和分步行动计划。这为未来的意图优先开发环境建设奠定了基础,软件制造者可以与人工智能无缝协作,创建真正满足其需求的软件。
Key Takeaways
- Foundation Models (FMs) 在自然语言任务中表现出强大的能力,但在软件开发中准确捕捉利益相关者需求方面存在挑战。
- 引入了一种利用FM的多智能体系统AlignMind来解决此问题的方法。
- AlignMind具备理论思维的能力,能考虑软件制造者的心理状态和视角。
- 该方法能迭代澄清利益相关者的信念、愿望和意图,并将其转化为改进的需求和相应的自然语言工作流程。
- 方法在涵盖150个不同用例的评估中表现良好,能准确捕捉利益相关者的意图和需求。
- 该方法将利益相关者的意图和需求表述为规范和分步行动计划。
点此查看论文截图

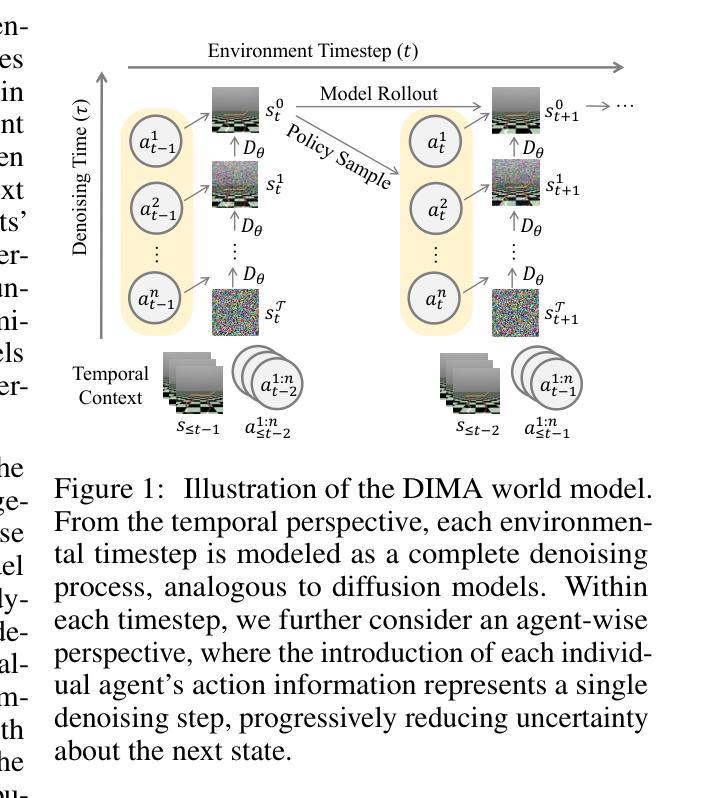
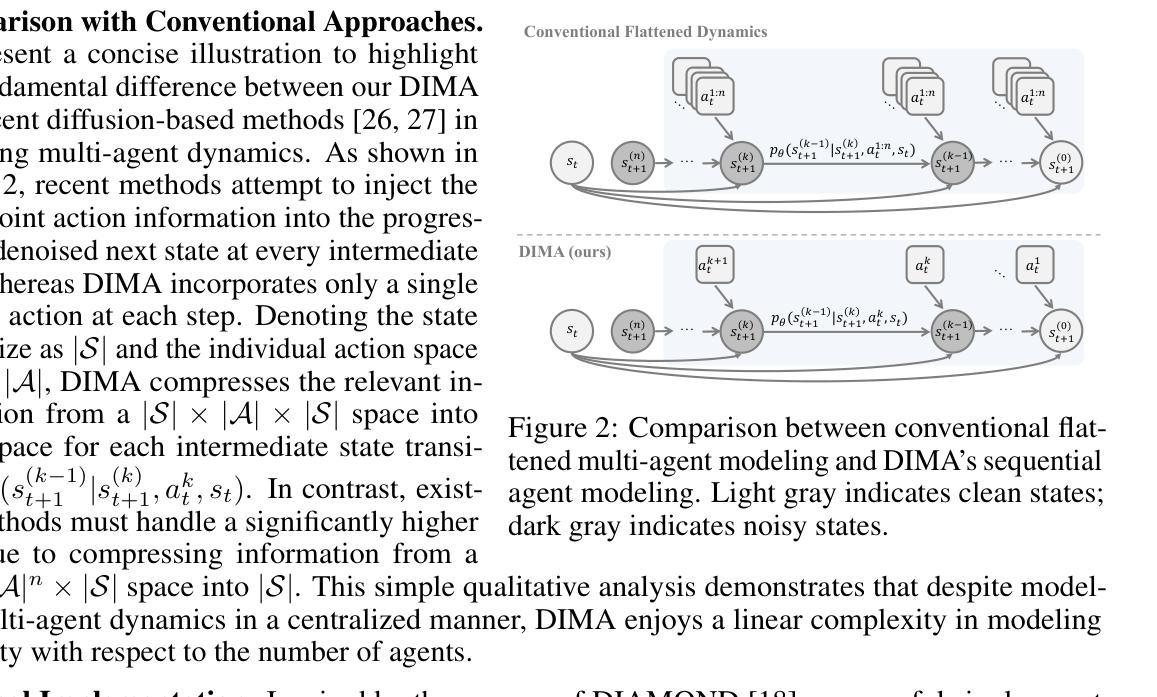
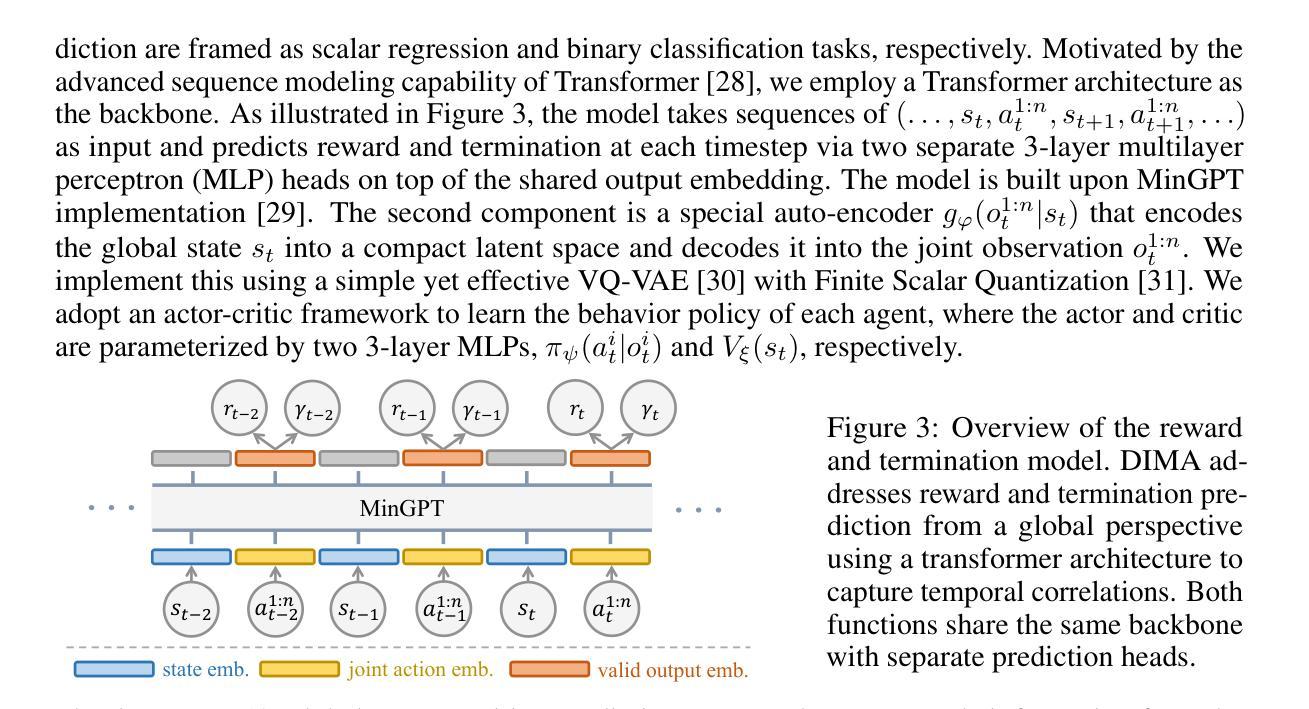
Revisiting Multi-Agent World Modeling from a Diffusion-Inspired Perspective
Authors:Yang Zhang, Xinran Li, Jianing Ye, Delin Qu, Shuang Qiu, Chongjie Zhang, Xiu Li, Chenjia Bai
World models have recently attracted growing interest in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) due to their ability to improve sample efficiency for policy learning. However, accurately modeling environments in MARL is challenging due to the exponentially large joint action space and highly uncertain dynamics inherent in multi-agent systems. To address this, we reduce modeling complexity by shifting from jointly modeling the entire state-action transition dynamics to focusing on the state space alone at each timestep through sequential agent modeling. Specifically, our approach enables the model to progressively resolve uncertainty while capturing the structured dependencies among agents, providing a more accurate representation of how agents influence the state. Interestingly, this sequential revelation of agents’ actions in a multi-agent system aligns with the reverse process in diffusion models–a class of powerful generative models known for their expressiveness and training stability compared to autoregressive or latent variable models. Leveraging this insight, we develop a flexible and robust world model for MARL using diffusion models. Our method, Diffusion-Inspired Multi-Agent world model (DIMA), achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple multi-agent control benchmarks, significantly outperforming prior world models in terms of final return and sample efficiency, including MAMuJoCo and Bi-DexHands. DIMA establishes a new paradigm for constructing multi-agent world models, advancing the frontier of MARL research.
近期,多智能体强化学习(Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning, MARL)中出现了对全球模型的日益增长的兴趣,因为它们能够提高策略学习的样本效率。然而,在多智能体系统中,由于联合行动空间的指数级扩大以及固有的高度不确定的动态,对MARL的环境进行准确建模是一个挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们通过从联合建模整个状态-动作转换动态转向在每个时间步上专注于状态空间的建模来降低建模复杂性。具体地说,我们的方法使模型能够逐步解决不确定性,同时捕捉智能体之间的结构化依赖关系,提供更准确地表示智能体如何影响状态的方式。有趣的是,多智能体系统中智能体行动的连续揭示与扩散模型中的反向过程相吻合。扩散模型是一类强大的生成模型,与自回归或潜在变量模型相比,以表达力和训练稳定性而闻名。利用这一见解,我们使用扩散模型开发了一个灵活而强大的全球模型。我们的方法——受扩散启发的多智能体世界模型(DIMA)在多个多智能体控制基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在最终回报和样本效率方面显著优于先前的世界模型,包括MAMuJoCo和Bi-DexHands。DIMA为构建多智能体世界模型建立了新的范式,推动了MARL研究的前沿进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:近期在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中,世界模型日益受到关注,其能提高策略学习的样本效率。然而,由于多智能体系统的联合行动空间呈指数级增长且固有高度不确定的动态特性,准确建模面临挑战。研究通过序贯智能体建模降低建模复杂度,使模型能逐步解决不确定性问题,同时捕捉智能体间的结构化依赖关系。结合扩散模型(一类强大的生成模型)的特点,提出了一种灵活且稳健的多智能体世界模型——受扩散启发的多智能体世界模型(DIMA)。DIMA在多个多智能体控制基准测试中实现了最先进的性能表现,显著提高了最终回报和样本效率,包括MAMuJoCo和Bi-DexHands等。DIMA为构建多智能体世界模型建立了新的范式,推动了MARL研究的前沿发展。
Key Takeaways:
- 世界模型在多智能体强化学习(MARL)中日益受到关注,用于提高样本效率。
- 多智能体环境建模面临挑战,主要由于联合行动空间呈指数级增长和高度不确定的动态特性。
- 通过序贯智能体建模降低建模复杂度,使模型能逐步解决不确定性问题。
- 结合扩散模型的特点,提出了受扩散启发的多智能体世界模型(DIMA)。
- DIMA在多个多智能体控制基准测试中实现最优性能。
- DIMA显著提高最终回报和样本效率。
点此查看论文截图

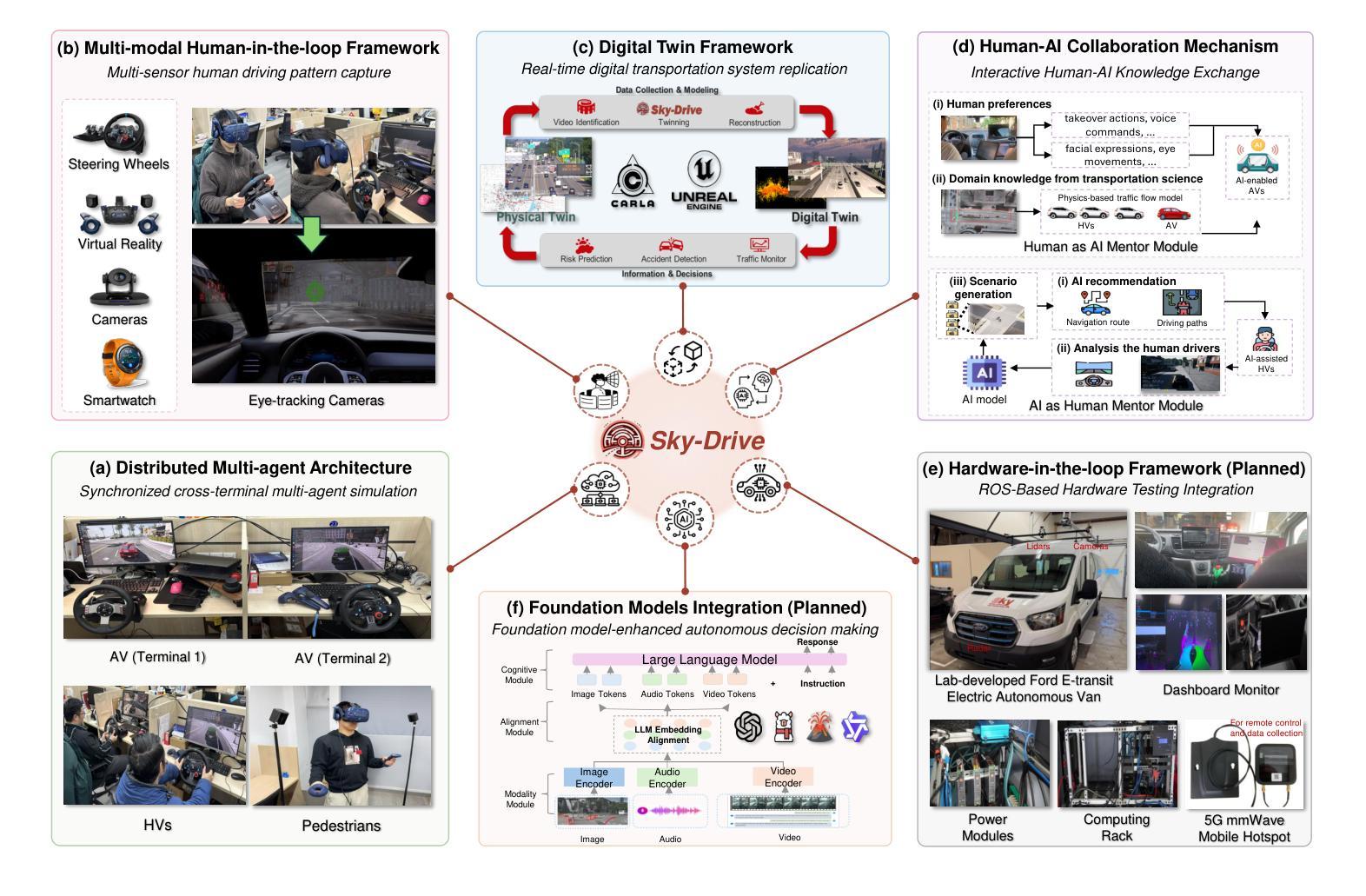
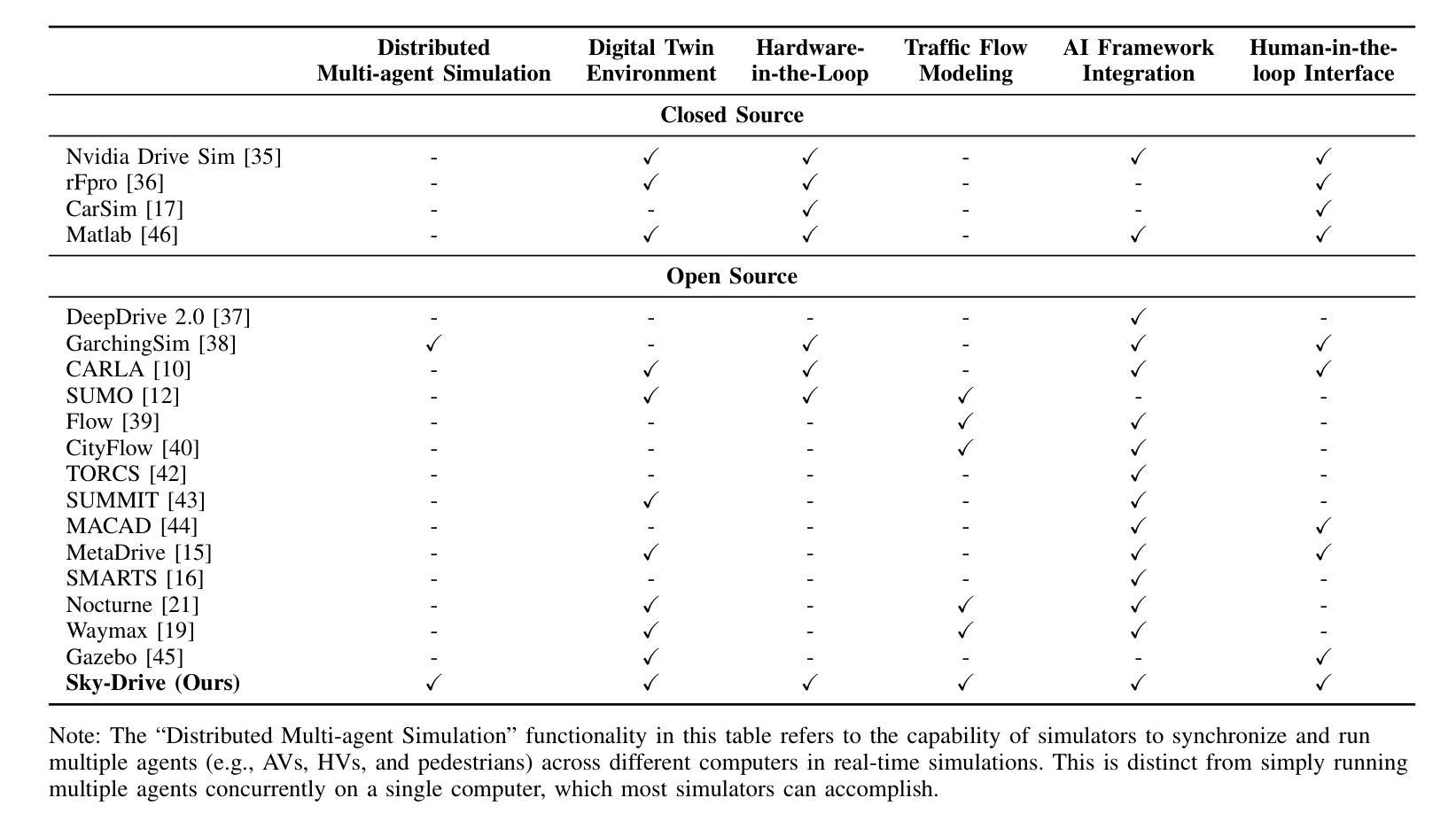
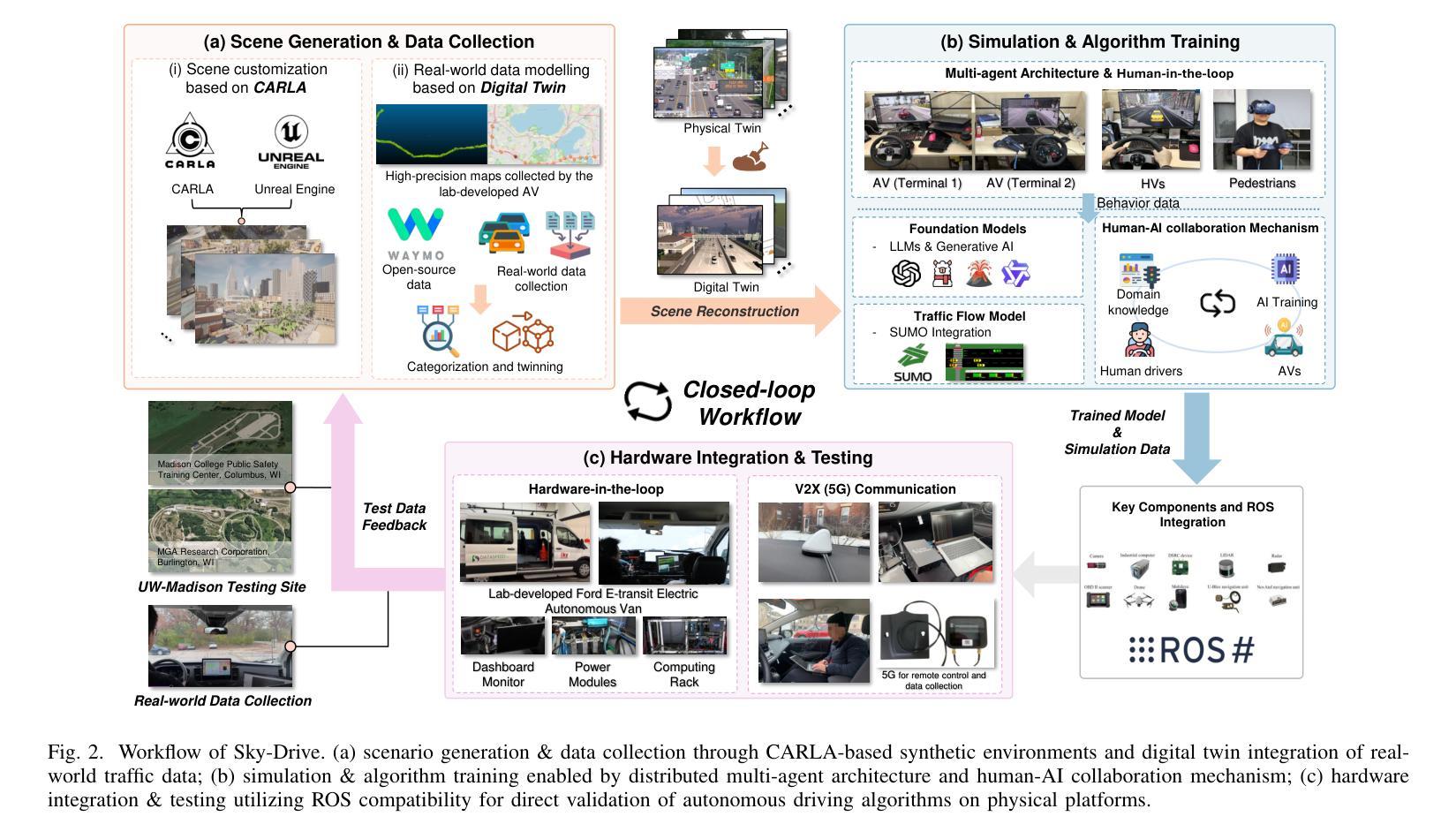
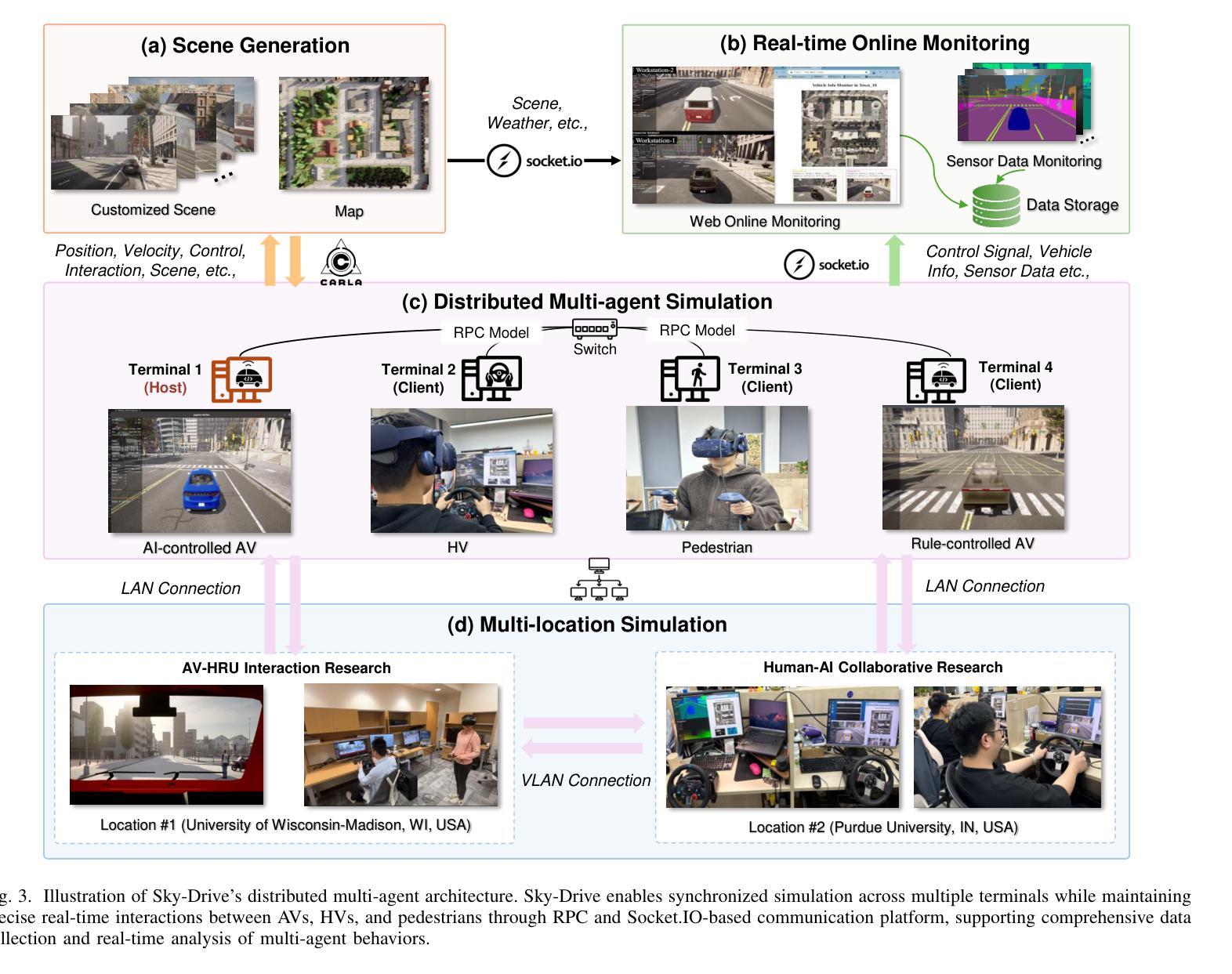
Sky-Drive: A Distributed Multi-Agent Simulation Platform for Human-AI Collaborative and Socially-Aware Future Transportation
Authors:Zilin Huang, Zihao Sheng, Zhengyang Wan, Yansong Qu, Yuhao Luo, Boyue Wang, Pei Li, Yen-Jung Chen, Jiancong Chen, Keke Long, Jiayi Meng, Yue Leng, Sikai Chen
Recent advances in autonomous system simulation platforms have significantly enhanced the safe and scalable testing of driving policies. However, existing simulators do not yet fully meet the needs of future transportation research-particularly in enabling effective human-AI collaboration and modeling socially-aware driving agents. This paper introduces Sky-Drive, a novel distributed multi-agent simulation platform that addresses these limitations through four key innovations: (a) a distributed architecture for synchronized simulation across multiple terminals; (b) a multi-modal human-in-the-loop framework integrating diverse sensors to collect rich behavioral data; (c) a human-AI collaboration mechanism supporting continuous and adaptive knowledge exchange; and (d) a digital twin framework for constructing high-fidelity virtual replicas of real-world transportation environments. Sky-Drive supports diverse applications such as autonomous vehicle-human road users interaction modeling, human-in-the-loop training, socially-aware reinforcement learning, personalized driving development, and customized scenario generation. Future extensions will incorporate foundation models for context-aware decision support and hardware-in-the-loop testing for real-world validation. By bridging scenario generation, data collection, algorithm training, and hardware integration, Sky-Drive has the potential to become a foundational platform for the next generation of human-centered and socially-aware autonomous transportation systems research. The demo video and code are available at:https://sky-lab-uw.github.io/Sky-Drive-website/
近期自主系统仿真平台的进步极大地提高了驾驶策略的安全性和可扩展性测试。然而,现有的模拟器尚未完全满足未来交通研究的需求,特别是在实现有效的人机协作和建模社会意识驾驶代理方面。本文介绍了Sky-Drive,这是一种新型分布式多智能体仿真平台,通过四个关键创新解决了这些限制:(a)用于跨多个终端同步仿真的分布式架构;(b)一种多模式人机循环框架,集成各种传感器以收集丰富的行为数据;(c)支持连续和自适应知识交换的人机协作机制;(d)用于构建现实世界交通环境高保真虚拟副本的数字孪生框架。Sky-Drive支持各种应用程序,例如自主车辆-人类道路用户交互建模、循环中人训练、社会意识强化学习、个性化驾驶开发和定制场景生成。未来的扩展将纳入基于上下文的决策支持基础模型和用于现实世界验证的硬件循环测试。通过桥接场景生成、数据采集、算法训练和硬件集成,Sky-Drive有望成为下一代以人类为中心和社会意识自主交通系统研究的基础平台。演示视频和代码可访问于:https://sky-lab-uw.github.io/Sky-Drive-website/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures
Summary
Sky-Drive平台通过四项关键技术突破,包括分布式多终端同步仿真架构、多模态人机互动框架、人机协作机制和数字孪生框架,显著提升了自主系统仿真平台在模拟人类驾驶行为、收集丰富行为数据和人车协同决策方面的能力。此平台可为自主车辆与人类道路使用者的交互建模、人机交互训练、社会感知强化学习、个性化驾驶开发和定制化场景生成等应用提供支持,为未来的人本化和社会感知自主运输系统研究奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- Sky-Drive是一个先进的多智能体仿真平台,通过四项关键技术创新提升了自主系统仿真平台的测试能力。
- 平台支持分布式仿真架构,实现多终端同步模拟。
- 引入多模态人机互动框架,整合多样传感器以收集丰富的行为数据。
- 建立了人机协作机制,支持持续和自适应的知识交换。
- 采用数字孪生技术构建高保真虚拟交通环境复制现实场景。
- 平台可广泛应用于自主车辆与人类道路使用者交互建模、社会感知强化学习等领域。
点此查看论文截图

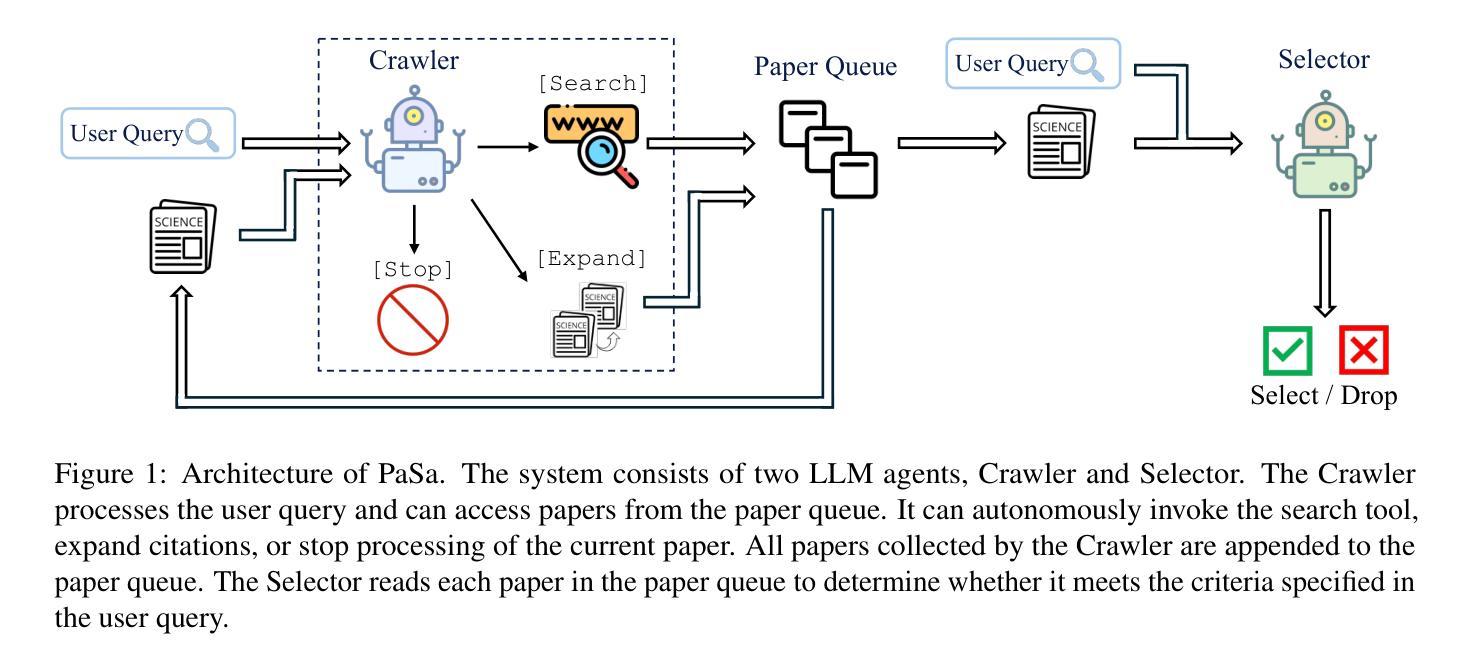
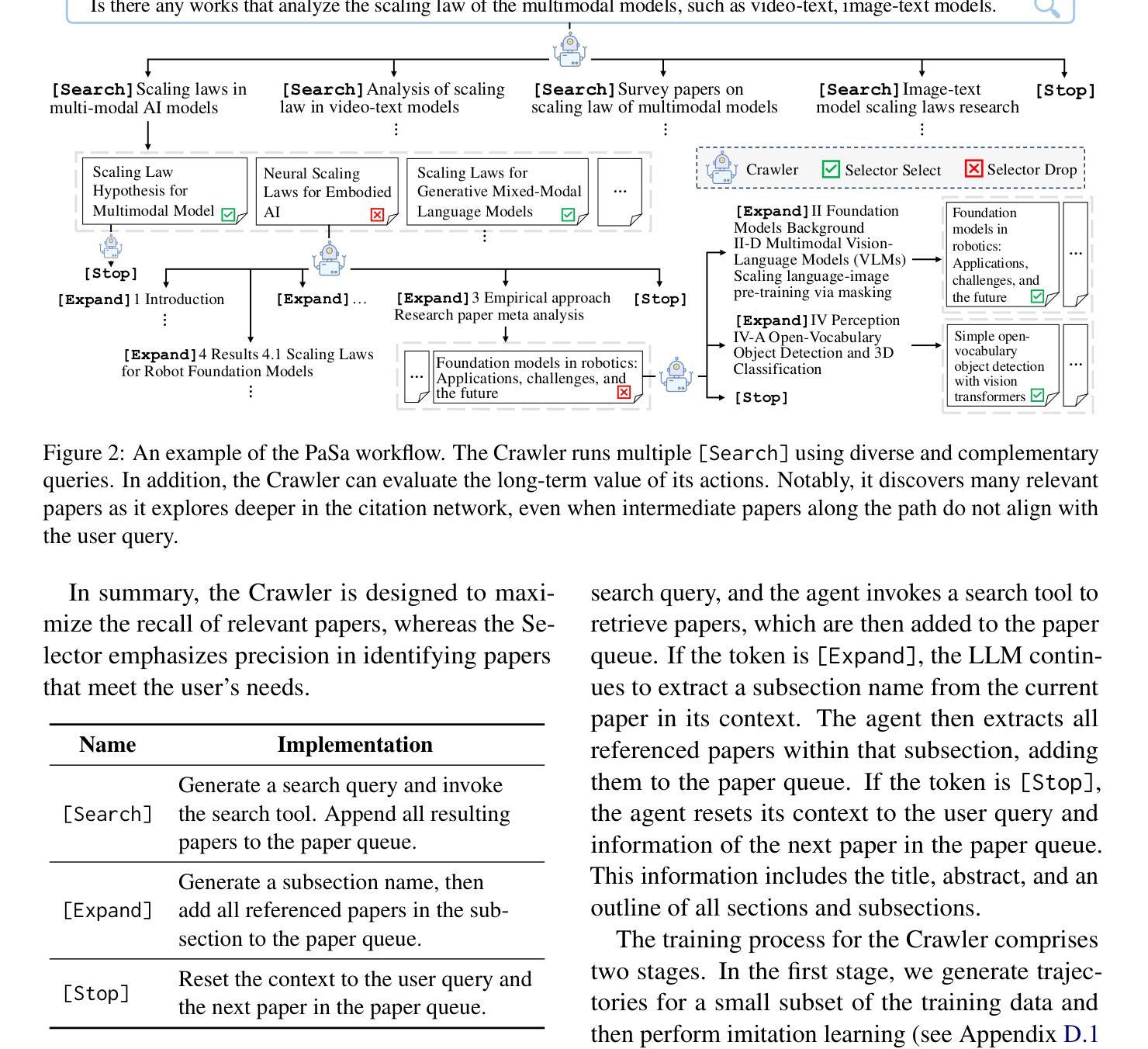
PaSa: An LLM Agent for Comprehensive Academic Paper Search
Authors:Yichen He, Guanhua Huang, Peiyuan Feng, Yuan Lin, Yuchen Zhang, Hang Li, Weinan E
We introduce PaSa, an advanced Paper Search agent powered by large language models. PaSa can autonomously make a series of decisions, including invoking search tools, reading papers, and selecting relevant references, to ultimately obtain comprehensive and accurate results for complex scholar queries. We optimize PaSa using reinforcement learning with a synthetic dataset, AutoScholarQuery, which includes 35k fine-grained academic queries and corresponding papers sourced from top-tier AI conference publications. Additionally, we develop RealScholarQuery, a benchmark collecting real-world academic queries to assess PaSa performance in more realistic scenarios. Despite being trained on synthetic data, PaSa significantly outperforms existing baselines on RealScholarQuery, including Google, Google Scholar, Google with GPT-4o for paraphrased queries, ChatGPT (search-enabled GPT-4o), GPT-o1, and PaSa-GPT-4o (PaSa implemented by prompting GPT-4o). Notably, PaSa-7B surpasses the best Google-based baseline, Google with GPT-4o, by 37.78% in recall@20 and 39.90% in recall@50, and exceeds PaSa-GPT-4o by 30.36% in recall and 4.25% in precision. Model, datasets, and code are available at https://github.com/bytedance/pasa.
我们推出了PaSa,这是一个由大型语言模型驱动的高级论文搜索代理。PaSa可以自主做出一系列决策,包括调用搜索工具、阅读论文和选择相关参考文献,以获取针对复杂学者查询的全面和准确结果。我们使用强化学习和合成数据集AutoScholarQuery对PaSa进行了优化,该数据集包含35,000个精细的学术查询和来自顶级人工智能会议出版的相应论文。此外,我们还开发了RealScholarQuery基准测试,收集真实世界的学术查询,以评估PaSa在更现实场景中的性能。尽管是在合成数据上训练的,但PaSa在RealScholarQuery上的表现显著优于现有基线,包括Google、Google Scholar、针对改述查询的Google与GPT-4o、ChatGPT(搜索启用的GPT-4o)、GPT-o1以及PaSa-GPT-4o(通过提示GPT-4o实现的PaSa)。值得注意的是,PaSa-7B在召回率@20和召回率@50方面分别超过了基于Google的最佳基线Google with GPT-4o 37.78%和39.90%,并且以召回率超过PaSa-GPT-4o 30.36%和精确度提高4.25%的优势领先。模型、数据集和代码可在https://github.com/bytedance/pasa上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PaSa是一个先进的论文搜索代理,能够自主做出一系列决策,包括调用搜索工具、阅读论文和选择相关参考文献,最终为复杂的学术查询提供全面准确的结果。通过强化学习与合成数据集AutoScholarQuery的优化,PaSa显著超越了现有基准测试,包括Google、Google Scholar等。特别是PaSa-7B在召回率和精确度方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- PaSa是一个基于大型语言模型的先进论文搜索代理。
- PaSa可以自主做出一系列决策,包括调用搜索工具、阅读论文和选择相关参考文献。
- PaSa通过强化学习与合成数据集AutoScholarQuery进行优化。
- PaSa在RealScholarQuery基准测试中表现优异,超越了Google、Google Scholar、GPT-4o等现有工具。
- PaSa-7B在召回率方面超越了最佳Google基准测试Google with GPT-4o,并在精确度方面表现出色。
- PaSa模型、数据集和代码已公开在GitHub上。
- PaSa的研发为复杂的学术查询提供了更全面和准确的结果。
点此查看论文截图

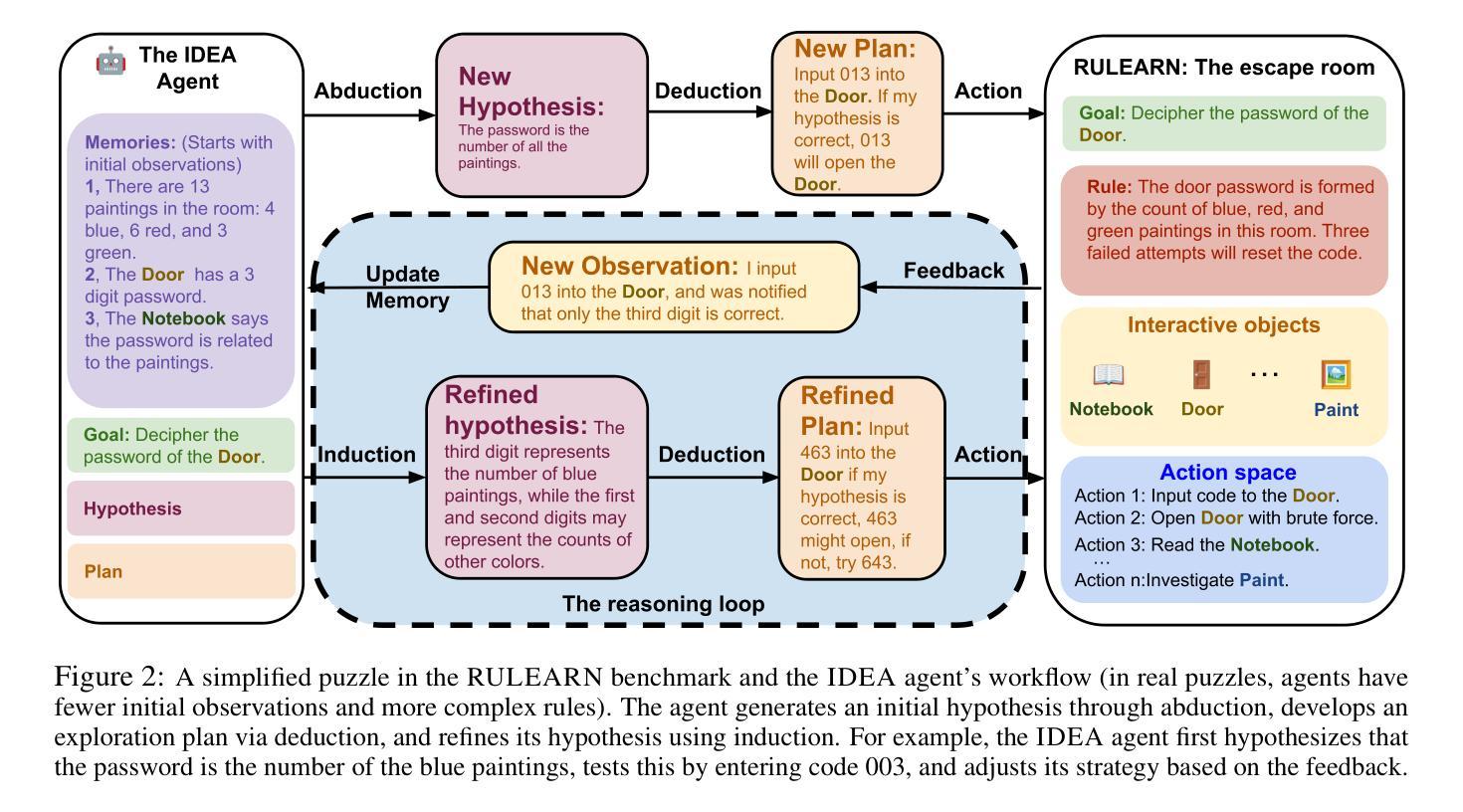
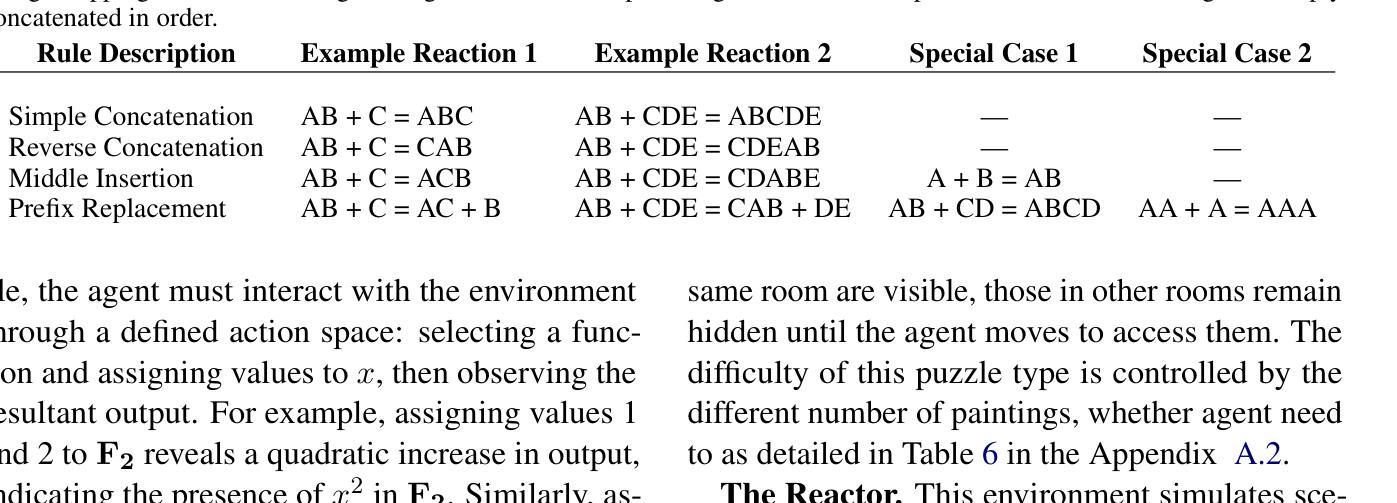
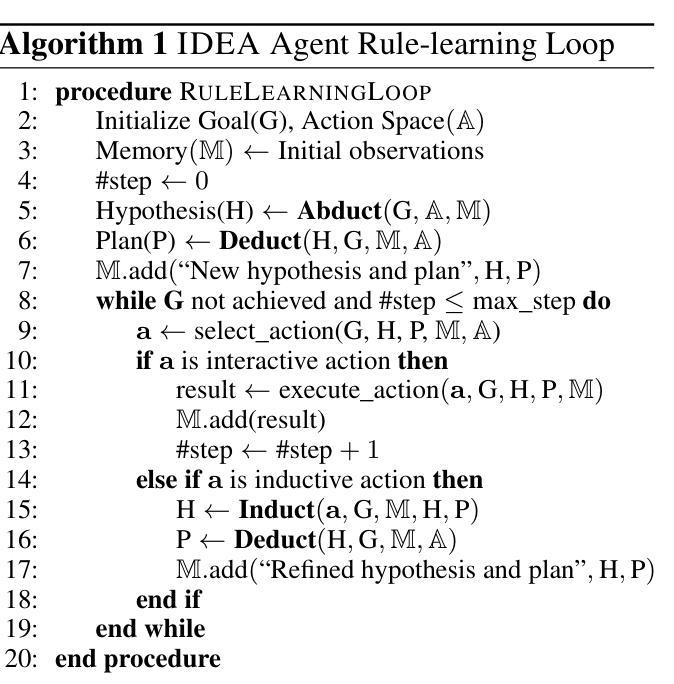
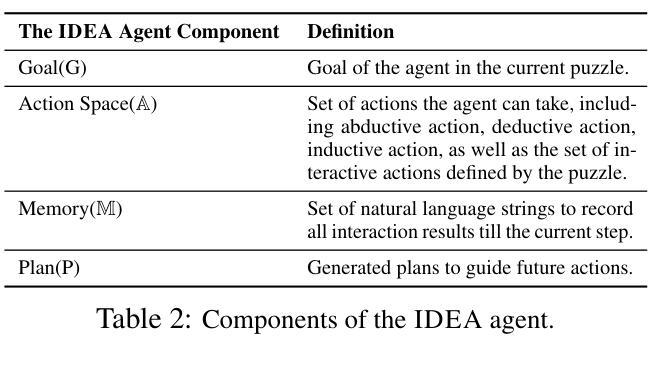
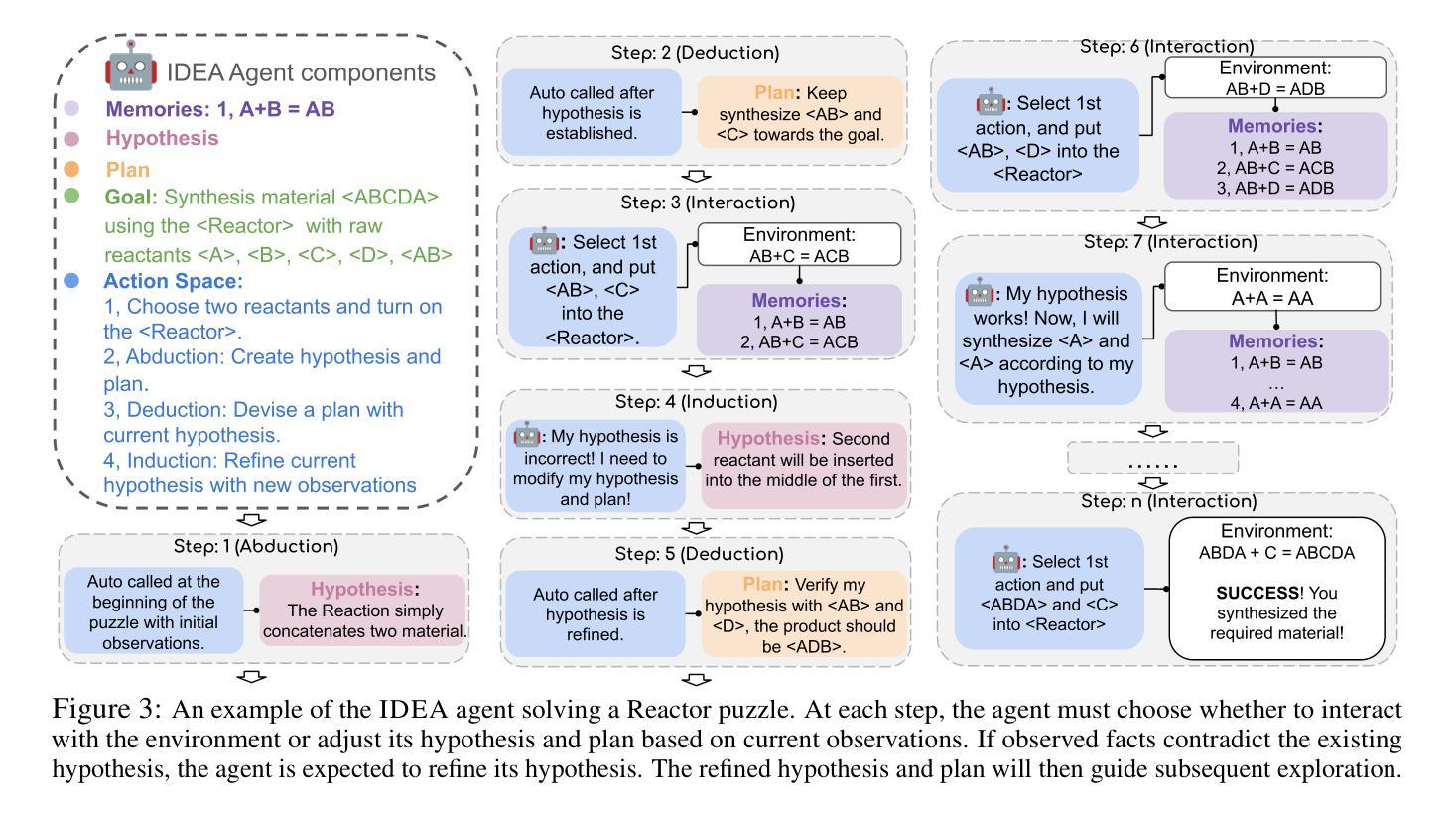
IDEA: Enhancing the Rule Learning Ability of Large Language Model Agent through Induction, Deduction, and Abduction
Authors:Kaiyu He, Mian Zhang, Shuo Yan, Peilin Wu, Zhiyu Zoey Chen
While large language models (LLMs) have been thoroughly evaluated for deductive and inductive reasoning, their proficiency in holistic rule learning in interactive environments remains less explored. We introduce RULEARN, a novel benchmark to assess the rule-learning abilities of LLM agents in interactive settings. In RULEARN, agents strategically interact with simulated environments to gather observations, discern patterns, and solve complex problems. To enhance the rule-learning capabilities for LLM agents, we propose IDEA, a novel reasoning framework that integrates the process of Induction, Deduction, and Abduction. The IDEA agent generates initial hypotheses from limited observations through abduction, devises plans to validate these hypotheses or leverages them to solve problems via deduction, and refines previous hypotheses through induction, dynamically establishing and applying rules that mimic human rule-learning behaviors. Our evaluation of the IDEA framework, which involves five representative LLMs, demonstrates significant improvements over the baseline. Furthermore, our study with human participants reveals notable discrepancies in rule-learning behaviors between humans and LLMs. We believe our benchmark will serve as a valuable and challenging resource, and IDEA will provide crucial insights for the development of LLM agents capable of human-like rule learning in real-world scenarios. Our code and data is publicly available.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在演绎和归纳推理方面已经得到了充分的评估,但它们在交互环境中整体规则学习方面的能力仍缺乏研究。我们引入了RULEARN,这是一个新颖的基准测试,用于评估LLM代理在交互环境中学习规则的能力。在RULEARN中,代理与模拟环境进行战略交互以收集观察结果、识别模式并解决复杂问题。为了提高LLM代理的规则学习能力,我们提出了IDEA,这是一个结合归纳、演绎和溯因过程的新型推理框架。IDEA代理通过溯因从有限的观察中产生初步假设,制定计划来验证这些假设或通过演绎来解决新问题,并通过归纳来完善先前的假设,动态地建立和应用的规则模仿人类的规则学习行为。我们对包含五个代表性LLM的IDEA框架的评估表明,与基线相比,它取得了显著的改进。此外,我们对人类参与者的研究表明,人类和LLM在规则学习行为方面存在明显的差异。我们相信,我们的基准测试将成为一个有价值且具有挑战性的资源,而IDEA将为开发能够在现实世界场景中像人类一样进行规则学习的LLM代理提供关键见解。我们的代码和数据已公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 Findings
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在演绎和归纳推理方面已经得到了广泛评估,但它们在互动环境中全息规则学习的能力仍然缺乏研究。为此,我们引入了RULEARN这一新型基准测试,用于评估LLM代理在互动环境中的规则学习能力。此外,还提出了IDEA这一集成推理框架,通过归纳、演绎和溯因过程增强LLM代理的规则学习能力。对IDEA框架的评估表明,与基线相比有显著改进。同时,与人类参与者进行的研究揭示了人类与LLM在规则学习行为上的显著差异。我们相信,RULEARN将为互动环境中LLM代理的规则学习能力提供有价值的挑战资源,而IDEA将为开发具有现实世界中人类规则学习能力的LLM代理提供关键见解。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在互动环境中的全息规则学习能力尚未得到充分研究。
- 引入了RULEARN基准测试,用于评估LLM代理在互动环境中的规则学习能力。
- 提出了IDEA推理框架,通过整合归纳、演绎和溯因过程,增强LLM代理的规则学习能力。
- IDEA框架的评估结果显示,与基线相比有显著改进。
- 人类与LLM在规则学习行为上存在显著差异。
- RULEARN和IDEA将为LLM代理在现实世界中模拟人类规则学习提供有价值的资源和见解。
点此查看论文截图

Adaptive Sample Sharing for Multi Agent Linear Bandits
Authors:Hamza Cherkaoui, Merwan Barlier, Igor Colin
The multi-agent linear bandit setting is a well-known setting for which designing efficient collaboration between agents remains challenging. This paper studies the impact of data sharing among agents on regret minimization. Unlike most existing approaches, our contribution does not rely on any assumptions on the bandit parameters structure. Our main result formalizes the trade-off between the bias and uncertainty of the bandit parameter estimation for efficient collaboration. This result is the cornerstone of the Bandit Adaptive Sample Sharing (BASS) algorithm, whose efficiency over the current state-of-the-art is validated through both theoretical analysis and empirical evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Furthermore, we demonstrate that, when agents’ parameters display a cluster structure, our algorithm accurately recovers them.
多智能体线性强盗环境是一个众所周知的场景,在这个场景中,设计智能体之间的有效协作仍然是一个挑战。本文研究了智能体之间数据共享对后悔最小化的影响。不同于大多数现有方法,我们的贡献不需要对强盗参数结构做任何假设。我们的主要结果正式确立了强盗参数估计的偏见和不确定性之间的权衡,以实现有效的协作。这一结果是强盗自适应样本共享(BASS)算法的基础,该算法的效率通过合成数据和真实世界数据集的理论分析和实证评估得到了验证。此外,我们证明了当智能体的参数呈现聚类结构时,我们的算法能够准确地恢复它们。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages
Summary
多智能体线性强盗场景是一个已知的场景,设计智能体之间的有效协作仍然具有挑战性。本文研究了数据共享对减少遗憾的影响。与大多数现有方法不同,我们的贡献不需要依赖强盗参数结构的假设。我们的主要结果正式确定了强盗参数估计的偏见和不确定性之间的权衡,以实现有效的协作。这是强盗自适应样本共享算法(BASS算法)的基础,其效率通过理论分析和在合成和真实数据集上的经验评估得到了验证。当智能体的参数呈现集群结构时,我们的算法能够准确恢复它们。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了多智能体线性强盗场景中数据共享对减少遗憾的影响。
- 提出了一种新的方法,不依赖于强盗参数结构的假设。
- 正式确定了强盗参数估计的偏见和不确定性之间的权衡,以实现智能体间的有效协作。
- 提出了Bandit Adaptive Sample Sharing(BASS)算法,其效率优于当前最新技术。
- 通过理论分析和合成及真实数据集上的经验评估验证了该算法的有效性。
- 当智能体的参数呈现集群结构时,该算法能够准确恢复这些参数。
点此查看论文截图