⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
Be Decisive: Noise-Induced Layouts for Multi-Subject Generation
Authors:Omer Dahary, Yehonathan Cohen, Or Patashnik, Kfir Aberman, Daniel Cohen-Or
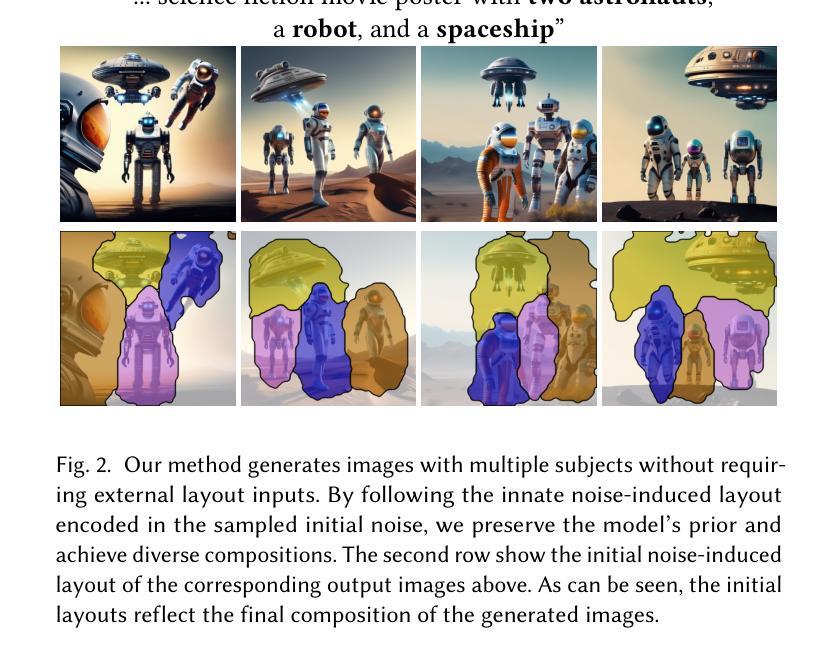
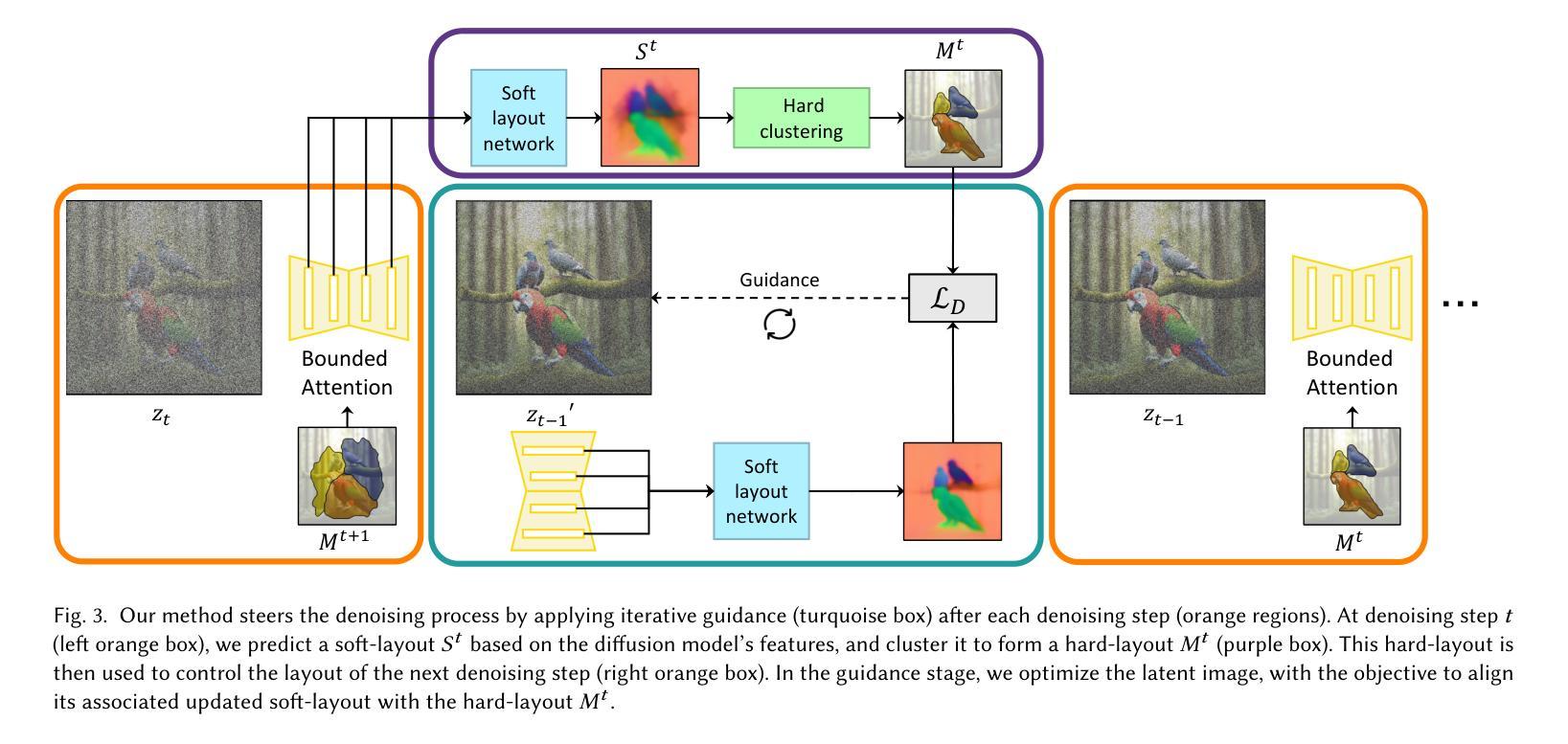
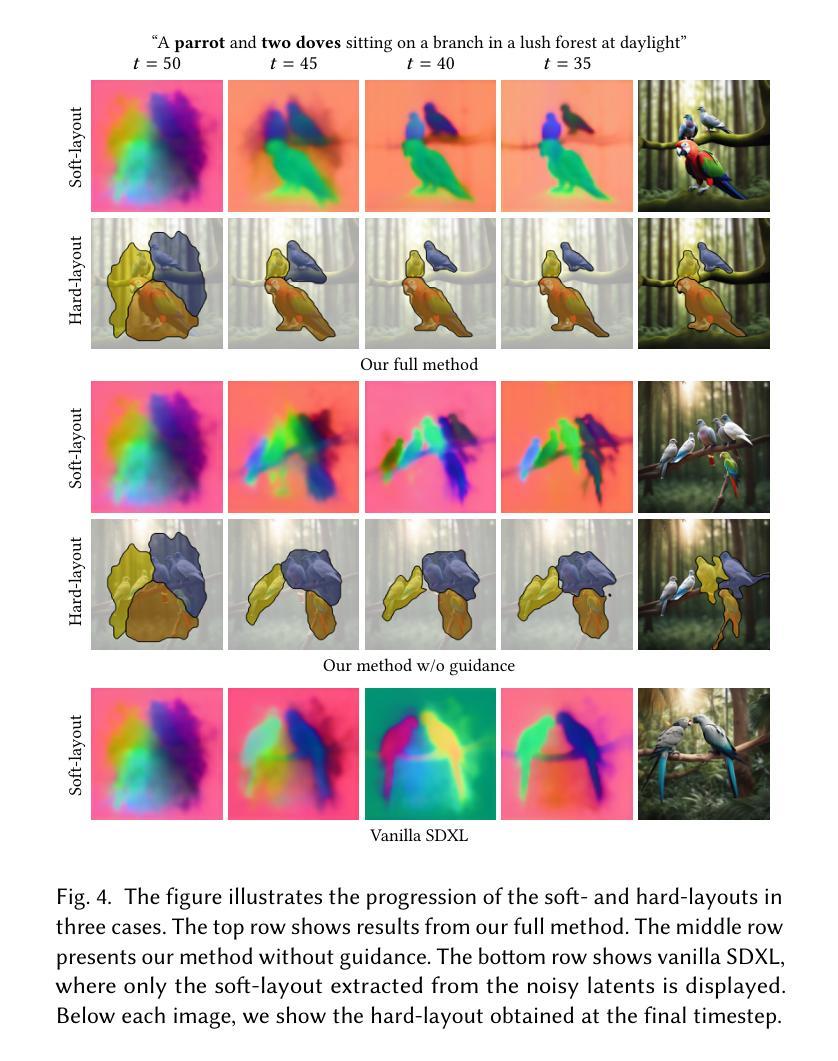
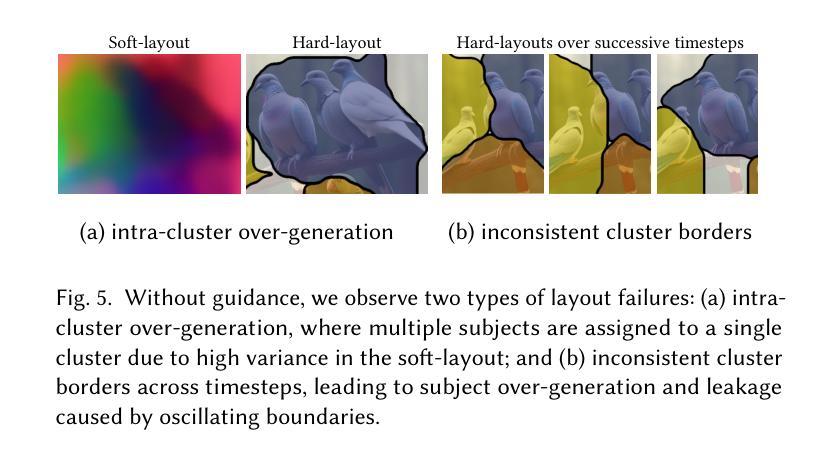
Generating multiple distinct subjects remains a challenge for existing text-to-image diffusion models. Complex prompts often lead to subject leakage, causing inaccuracies in quantities, attributes, and visual features. Preventing leakage among subjects necessitates knowledge of each subject’s spatial location. Recent methods provide these spatial locations via an external layout control. However, enforcing such a prescribed layout often conflicts with the innate layout dictated by the sampled initial noise, leading to misalignment with the model’s prior. In this work, we introduce a new approach that predicts a spatial layout aligned with the prompt, derived from the initial noise, and refines it throughout the denoising process. By relying on this noise-induced layout, we avoid conflicts with externally imposed layouts and better preserve the model’s prior. Our method employs a small neural network to predict and refine the evolving noise-induced layout at each denoising step, ensuring clear boundaries between subjects while maintaining consistency. Experimental results show that this noise-aligned strategy achieves improved text-image alignment and more stable multi-subject generation compared to existing layout-guided techniques, while preserving the rich diversity of the model’s original distribution.
生成多个不同的主题仍然是现有文本到图像扩散模型的挑战。复杂的提示往往会导致主题泄漏,从而导致数量、属性和视觉特征的不准确。防止主题之间的泄漏需要了解每个主题的空间位置。最近的方法通过外部布局控制提供这些空间位置。然而,强制实施规定的布局往往与由采样初始噪声决定的固有布局相冲突,导致与模型先验不一致。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新方法,该方法可以预测与提示对齐的空间布局,该布局由初始噪声导出,并在去噪过程中对其进行改进。通过依赖这种噪声引起的布局,我们避免了与外部强制实施的布局冲突,并更好地保留了模型的先验知识。我们的方法使用一个小神经网络来预测和精炼在每个去噪步骤中不断发展的噪声引起的布局,从而在保持主题一致性的同时确保主题之间的清晰边界。实验结果表明,与现有的布局引导技术相比,这种与噪声对齐的策略实现了更好的文本图像对齐和更稳定的多主题生成,同时保留了模型原始分布的丰富多样性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025. Project page: https://omer11a.github.io/be-decisive/
摘要
文本到图像的扩散模型在生成多个不同主题时面临挑战。复杂提示会导致主题泄露,影响数量、属性和视觉特征准确性。防止主题间泄露需要了解每个主题的空间位置。最近的方法通过外部布局控制提供这些空间位置,但强制执行规定的布局往往与由采样初始噪声决定的固有布局冲突,导致与模型先验的不对齐。本文介绍了一种新方法,该方法根据提示预测与提示对齐的空间布局,并从初始噪声中派生出来,在消噪过程中对其进行优化。通过依赖这种噪声引起的布局,避免了与外部施加的布局冲突,并更好地保持了模型的先验。我们的方法使用小型神经网络来预测和精炼每个消噪步骤中的噪声引起的布局的演变,确保主题之间的清晰界限,同时保持一致性。实验结果表明,与现有的布局指导技术相比,这种与噪声对齐的策略实现了更好的文本图像对齐和更稳定的多主题生成,同时保留了模型的原始分布的丰富多样性。
关键见解
- 文本到图像的扩散模型在生成多个主题时存在挑战,需要解决主题泄露问题。
- 主题泄露问题需要通过了解每个主题的空间位置来预防。
- 最近的解决方法是使用外部布局控制提供空间位置,但这种方法存在与模型先验冲突的问题。
- 本文提出了一种新方法,根据初始噪声预测并与提示对齐的空间布局。
- 该方法通过依赖噪声引起的布局,避免了与外部布局的冲突,并保持了模型的先验。
- 使用小型神经网络在消噪过程中预测和精炼噪声引起的布局的演变。
点此查看论文截图


MagicTryOn: Harnessing Diffusion Transformer for Garment-Preserving Video Virtual Try-on
Authors:Guangyuan Li, Siming Zheng, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Junsheng Luan, Binkai Ou, Lei Zhao, Bo Li, Peng-Tao Jiang
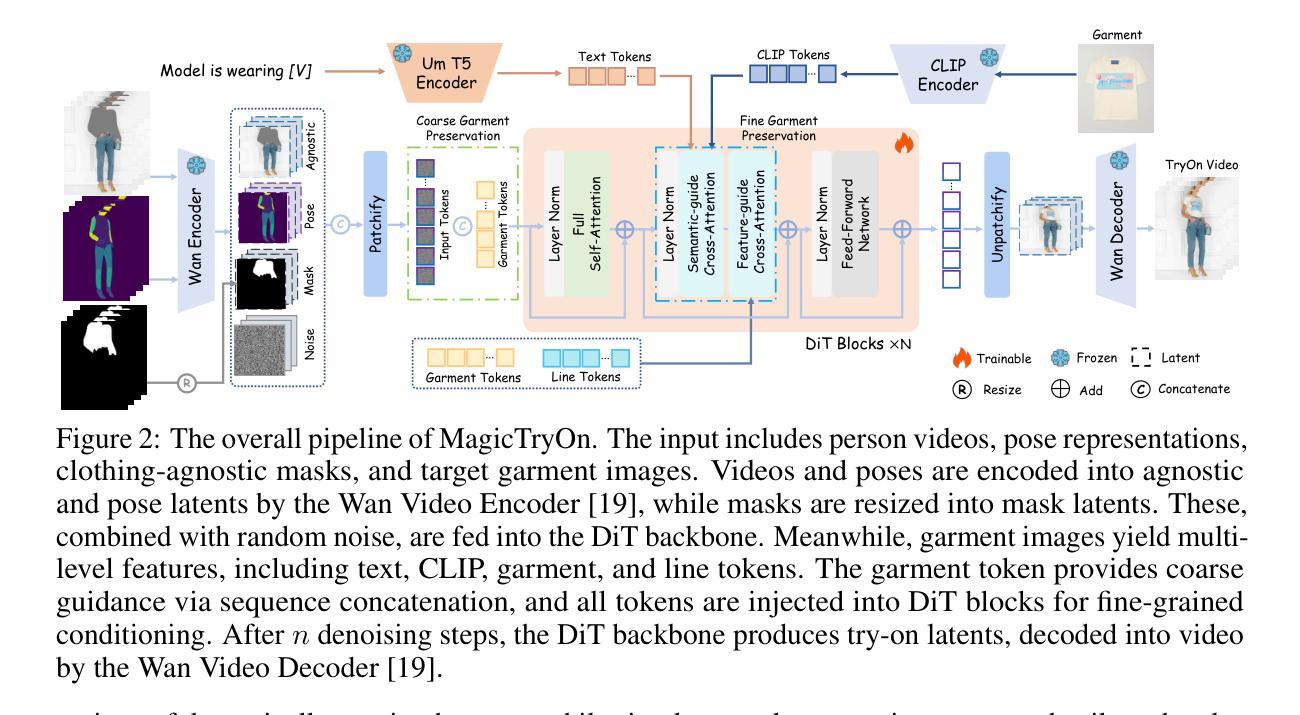
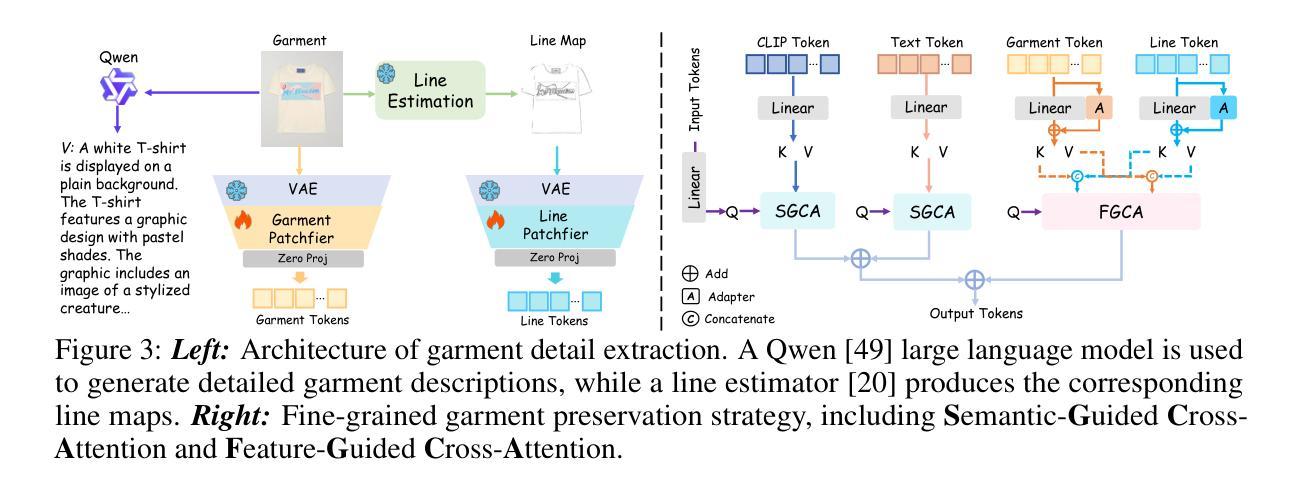
Video Virtual Try-On (VVT) aims to simulate the natural appearance of garments across consecutive video frames, capturing their dynamic variations and interactions with human body motion. However, current VVT methods still face challenges in terms of spatiotemporal consistency and garment content preservation. First, they use diffusion models based on the U-Net, which are limited in their expressive capability and struggle to reconstruct complex details. Second, they adopt a separative modeling approach for spatial and temporal attention, which hinders the effective capture of structural relationships and dynamic consistency across frames. Third, their expression of garment details remains insufficient, affecting the realism and stability of the overall synthesized results, especially during human motion. To address the above challenges, we propose MagicTryOn, a video virtual try-on framework built upon the large-scale video diffusion Transformer.We replace the U-Net architecture with a diffusion Transformer and combine full self-attention to jointly model the spatiotemporal consistency of videos. We design a coarse-to-fine garment preservation strategy. The coarse strategy integrates garment tokens during the embedding stage, while the fine strategy incorporates multiple garment-based conditions, such as semantics, textures, and contour lines during the denoising stage. Moreover, we introduce a mask-aware loss to further optimize garment region fidelity. Extensive experiments on both image and video try-on datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing SOTA methods in comprehensive evaluations and generalizes to in-the-wild scenarios.
视频虚拟试穿(VVT)旨在模拟衣物在连续视频帧中的自然外观,捕捉其动态变化和与人类动作之间的交互。然而,当前的VVT方法仍面临时空一致性和服装内容保留方面的挑战。首先,它们使用基于U-Net的扩散模型,其表达能力有限,难以重建复杂的细节。其次,它们采用空间和时间的分离建模方法,这阻碍了跨帧的结构关系和动态一致性的有效捕捉。第三,它们对服装细节的表达仍然不足,影响了合成结果的逼真度和稳定性,尤其是在人体运动期间。为了应对上述挑战,我们提出了MagicTryOn,这是一个基于大规模视频扩散Transformer的视频虚拟试穿框架。我们采用扩散Transformer替代U-Net架构,并结合全自注意力来联合建模视频的时空一致性。我们设计了一种由粗到细的服装保留策略。粗策略在嵌入阶段集成服装令牌,而细策略在降噪阶段融入多种基于服装的条件,如语义、纹理和轮廓线。此外,我们引入了一个掩膜损失来进一步优化服装区域的保真度。在图像和视频试穿数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在综合评估中优于现有最先进的方法,并可以推广到野外场景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视频虚拟试穿(VVT)的挑战及解决方案。针对现有VVT方法在时空一致性及服装内容保存方面的问题,提出了MagicTryOn框架,基于大规模视频扩散Transformer。采用全自注意力机制联合建模视频时空一致性,设计由粗到细的服装保存策略,并引入掩膜感知损失优化服装区域保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 视频虚拟试穿(VVT)旨在模拟服装在连续视频帧中的自然外观,捕捉其动态变化和与人体运动的交互。
- 当前VVT方法在时空一致性和服装内容保存方面存在挑战。
- MagicTryOn框架使用基于大规模视频扩散Transformer的模型,替代了U-Net架构。
- 全自注意力机制用于联合建模视频的时空一致性。
- 服装保存策略采用由粗到细的设计,整合服装标记并考虑多种服装条件。
- 引入掩膜感知损失以优化服装区域的保真度。
点此查看论文截图

Sci-Fi: Symmetric Constraint for Frame Inbetweening
Authors:Liuhan Chen, Xiaodong Cun, Xiaoyu Li, Xianyi He, Shenghai Yuan, Jie Chen, Ying Shan, Li Yuan
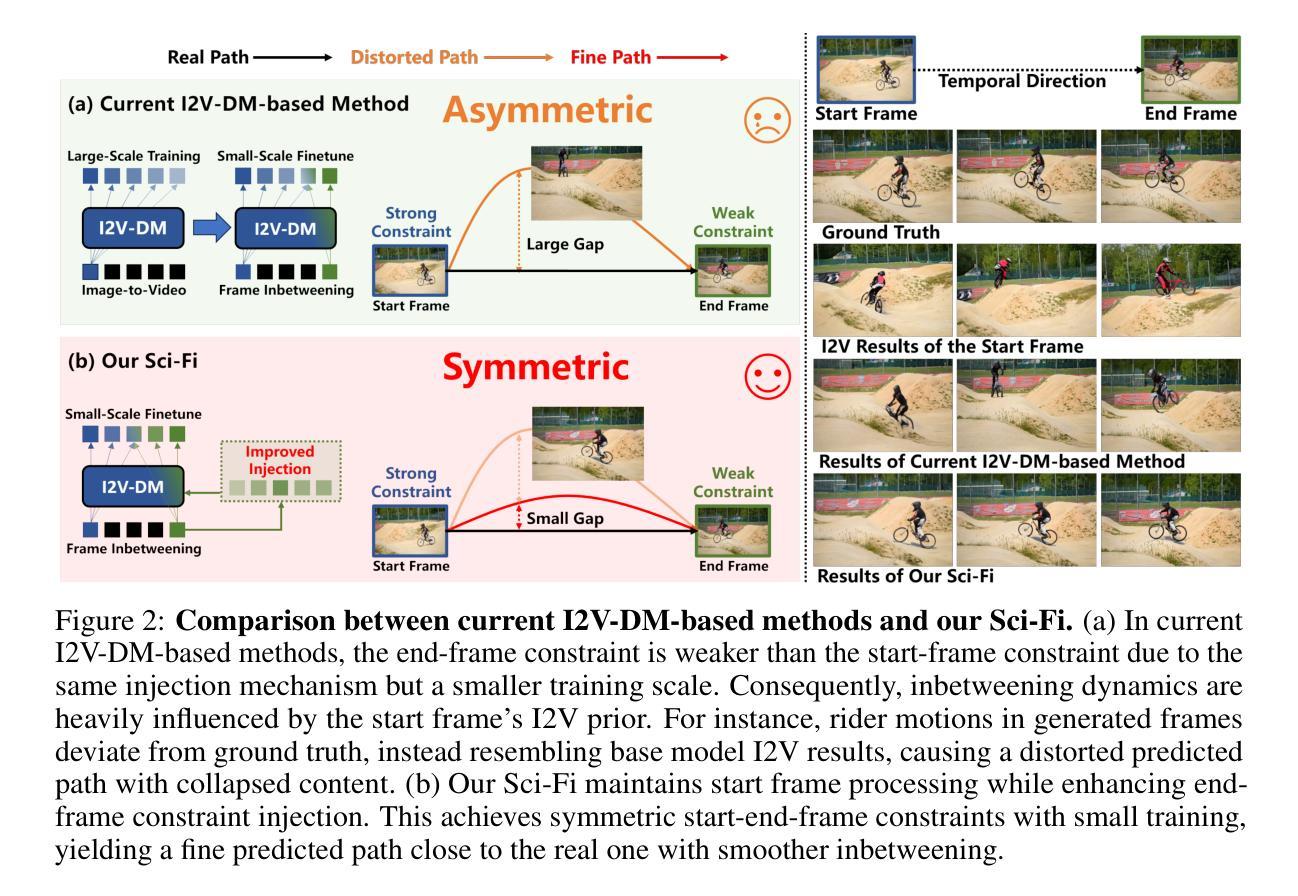
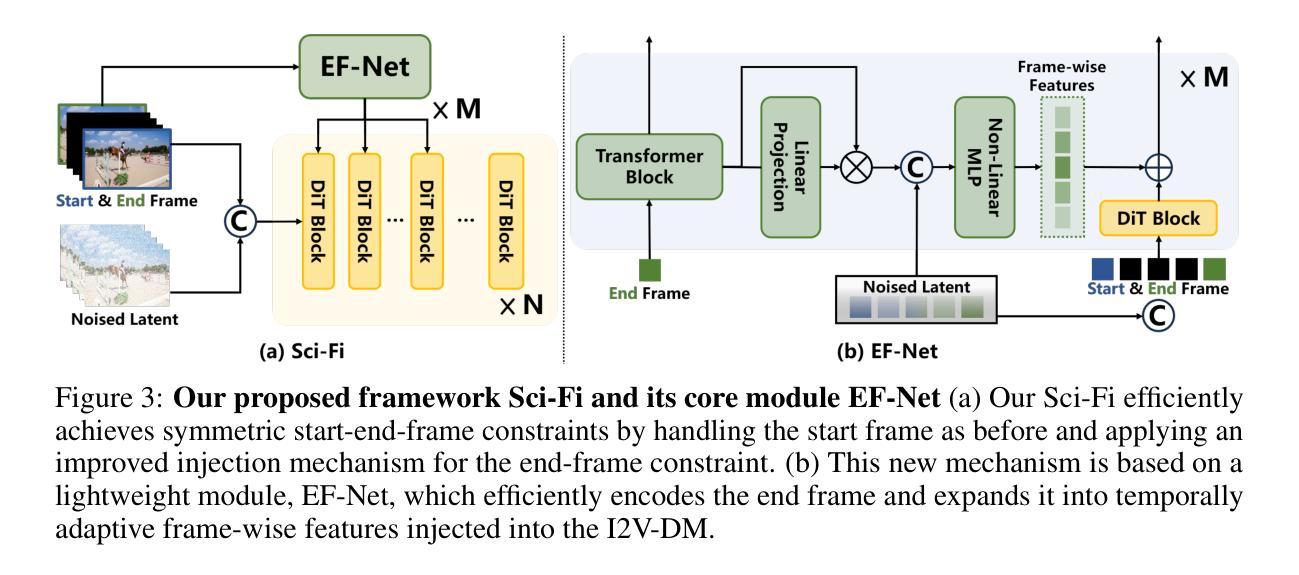
Frame inbetweening aims to synthesize intermediate video sequences conditioned on the given start and end frames. Current state-of-the-art methods mainly extend large-scale pre-trained Image-to-Video Diffusion models (I2V-DMs) by incorporating end-frame constraints via directly fine-tuning or omitting training. We identify a critical limitation in their design: Their injections of the end-frame constraint usually utilize the same mechanism that originally imposed the start-frame (single image) constraint. However, since the original I2V-DMs are adequately trained for the start-frame condition in advance, naively introducing the end-frame constraint by the same mechanism with much less (even zero) specialized training probably can’t make the end frame have a strong enough impact on the intermediate content like the start frame. This asymmetric control strength of the two frames over the intermediate content likely leads to inconsistent motion or appearance collapse in generated frames. To efficiently achieve symmetric constraints of start and end frames, we propose a novel framework, termed Sci-Fi, which applies a stronger injection for the constraint of a smaller training scale. Specifically, it deals with the start-frame constraint as before, while introducing the end-frame constraint by an improved mechanism. The new mechanism is based on a well-designed lightweight module, named EF-Net, which encodes only the end frame and expands it into temporally adaptive frame-wise features injected into the I2V-DM. This makes the end-frame constraint as strong as the start-frame constraint, enabling our Sci-Fi to produce more harmonious transitions in various scenarios. Extensive experiments prove the superiority of our Sci-Fi compared with other baselines.
帧间插值旨在根据给定的起始帧和结束帧合成中间视频序列。当前最先进的方法主要是通过融入端帧约束来扩展大规模预训练图像到视频扩散模型(I2V-DMs),这包括直接微调或省略训练。我们发现了它们设计中的一个关键局限:它们注入端帧约束通常使用与原来施加起始帧(单张图像)约束相同的机制。然而,由于原始的I2V-DMs已经提前对起始帧条件进行了充分的训练,因此,通过几乎没有任何(甚至零)专门训练的相同机制简单地引入端帧约束可能无法使端帧对中间内容产生与起始帧一样强烈的影响。这种对中间内容控制力的不对称性可能导致生成帧的运动不一致或外观崩溃。为了有效地实现起始帧和结束帧的对称约束,我们提出了一种新型框架,称为Sci-Fi,它通过较小的训练规模应用更强的约束注入。具体来说,它像过去一样处理起始帧约束,同时用一个改进的机制引入端帧约束。新机制基于一个精心设计的轻量级模块,名为EF-Net,它只编码端帧,并将其扩展为注入到I2V-DM中的时间自适应帧级特征。这使得端帧约束与起始帧约束一样强烈,从而让我们的Sci-Fi能够在各种场景中产生更和谐的过渡。大量实验证明,我们的Sci-Fi相较于其他基准测试表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 9 figures
Summary
当前主流的视频插帧方法主要基于预训练的图像到视频的扩散模型(I2V-DMs)。然而,这些方法在引入结束帧约束时存在设计上的局限性,即它们通常使用与开始帧相同的机制来引入约束,但这样的方式导致了对中间内容的控制力不足。为此,我们提出了一个新的框架Sci-Fi,通过设计一种更强大的注入机制来实现对开始和结束帧的对称约束。该机制包含一个轻量级的EF-Net模块,仅对结束帧进行编码并扩展为时间自适应的帧级特征,注入到I2V-DMs中。这使得结束帧的约束与开始帧相同,从而提高了过渡的自然性。实验证明,Sci-Fi相较于其他基线方法表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 当前先进的方法主要基于大型预训练图像到视频扩散模型进行视频插帧。
- 这些方法存在设计上的局限性,即在引入结束帧约束时未能充分利用其影响力。
- 对开始和结束帧的约束不对称可能导致生成的中间内容不一致。
- 提出的Sci-Fi框架旨在通过加强结束帧的约束来改进这一问题。
- EF-Net模块用于对结束帧进行编码并扩展为时间自适应的帧级特征。
- EF-Net注入机制使得结束帧的约束与开始帧相同,增强了中间过渡的自然性。
点此查看论文截图

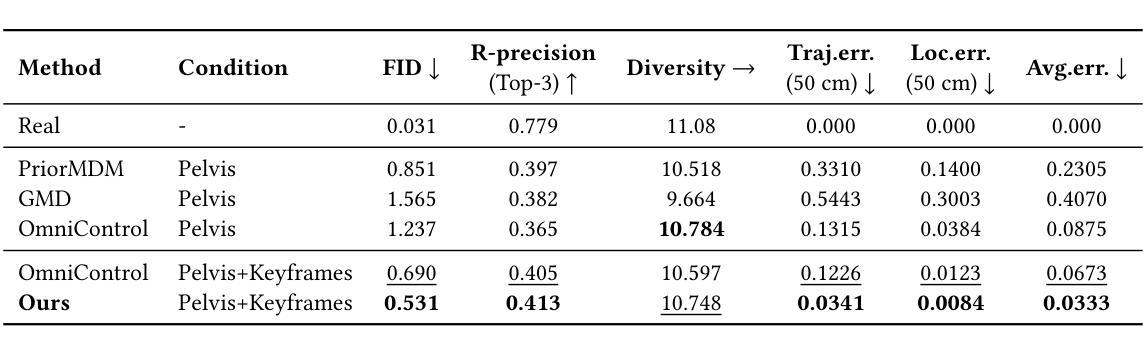
IKMo: Image-Keyframed Motion Generation with Trajectory-Pose Conditioned Motion Diffusion Model
Authors:Yang Zhao, Yan Zhang, Xubo Yang
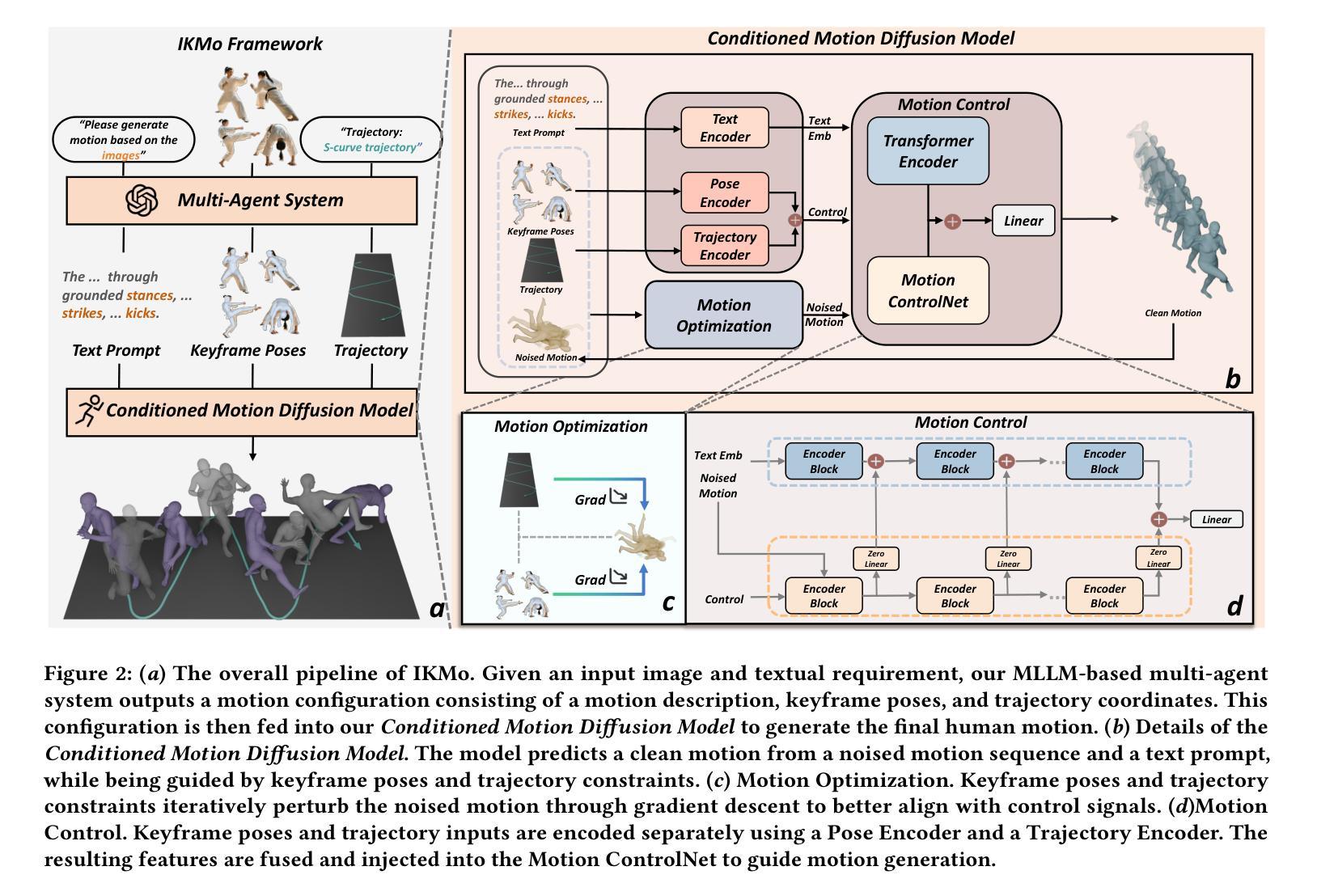
Existing human motion generation methods with trajectory and pose inputs operate global processing on both modalities, leading to suboptimal outputs. In this paper, we propose IKMo, an image-keyframed motion generation method based on the diffusion model with trajectory and pose being decoupled. The trajectory and pose inputs go through a two-stage conditioning framework. In the first stage, the dedicated optimization module is applied to refine inputs. In the second stage, trajectory and pose are encoded via a Trajectory Encoder and a Pose Encoder in parallel. Then, motion with high spatial and semantic fidelity is guided by a motion ControlNet, which processes the fused trajectory and pose data. Experiment results based on HumanML3D and KIT-ML datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art on all metrics under trajectory-keyframe constraints. In addition, MLLM-based agents are implemented to pre-process model inputs. Given texts and keyframe images from users, the agents extract motion descriptions, keyframe poses, and trajectories as the optimized inputs into the motion generation model. We conducts a user study with 10 participants. The experiment results prove that the MLLM-based agents pre-processing makes generated motion more in line with users’ expectation. We believe that the proposed method improves both the fidelity and controllability of motion generation by the diffusion model.
现有的人运动生成方法使用轨迹和姿态输入,对两种模式进行全局处理,导致生成结果不理想。在本文中,我们提出了基于扩散模型的图像关键帧运动生成方法IKMo,该方法将轨迹和姿态解耦。轨迹和姿态输入经过两阶段条件框架处理。在第一阶段,应用专用优化模块对输入进行细化。在第二阶段,轨迹和姿态通过轨迹编码器和姿态编码器并行编码。然后,由运动控制网络引导产生具有高空间和语义保真度的运动,该网络处理融合的轨迹和姿态数据。基于HumanML3D和KIT-ML数据集的实验结果表明,在轨迹关键帧约束下,所提方法在各项指标上均优于最新技术。此外,还实现了基于MLLM的代理来预处理模型输入。给定用户提供的文本和关键帧图像,代理提取运动描述、关键帧姿态和轨迹,作为优化后的输入放入运动生成模型中。我们对10名参与者进行了一项用户研究。实验结果证明,基于MLLM的代理预处理使得生成的运动更符合用户的预期。我们相信,该方法提高了扩散模型在运动生成方面的保真度和可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于扩散模型的图像关键帧运动生成方法IKMo,该方法将轨迹和姿态输入解耦,并通过两阶段条件框架对输入进行优化处理。在控制网络指导下生成具有高度空间和时间忠实度的运动。实验证明,该方法在轨迹关键帧约束下优于现有技术,并通过用户研究验证了预处理的MLLM代理能使生成的运动更贴近用户期望。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的运动生成方法IKMo,基于扩散模型,将轨迹和姿态输入解耦处理。
- 采用了两阶段条件框架,首先对输入进行精细化处理。
- 通过运动控制网络生成具有高度空间和时间忠实度的运动。
- 在HumanML3D和KIT-ML数据集上的实验结果证明,该方法在轨迹关键帧约束下优于现有技术。
- 引入了MLLM-based代理预处理模型输入,包括从用户提取运动描述、关键帧姿态和轨迹等优化输入。
- 用户研究证明了预处理使生成的运动更符合用户期望。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Single Index Models with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Anqi Tang, Youming Chen, Shuchen Xue, Zhaoqiang Liu
Diffusion models (DMs) have demonstrated remarkable ability to generate diverse and high-quality images by efficiently modeling complex data distributions. They have also been explored as powerful generative priors for signal recovery, resulting in a substantial improvement in the quality of reconstructed signals. However, existing research on signal recovery with diffusion models either focuses on specific reconstruction problems or is unable to handle nonlinear measurement models with discontinuous or unknown link functions. In this work, we focus on using DMs to achieve accurate recovery from semi-parametric single index models, which encompass a variety of popular nonlinear models that may have {\em discontinuous} and {\em unknown} link functions. We propose an efficient reconstruction method that only requires one round of unconditional sampling and (partial) inversion of DMs. Theoretical analysis on the effectiveness of the proposed methods has been established under appropriate conditions. We perform numerical experiments on image datasets for different nonlinear measurement models. We observe that compared to competing methods, our approach can yield more accurate reconstructions while utilizing significantly fewer neural function evaluations.
扩散模型(DMs)已经显示出生成多样且高质量图像的强大能力,能够高效地建模复杂的数据分布。它们还被探索为信号恢复的强大生成先验,从而大大提高了重建信号的质量。然而,现有的关于使用扩散模型进行信号恢复的研究要么集中在特定的重建问题上,要么无法处理具有不连续或未知链接函数的非线性测量模型。在这项工作中,我们专注于使用扩散模型实现半参数单索引模型的精确恢复,该模型涵盖了各种流行的非线性模型,这些模型可能具有不连续和未知的链接函数。我们提出了一种有效的重建方法,只需进行一轮无条件采样和扩散模型的(部分)反演。在适当的条件下,对提出的方法的有效性进行了理论分析。我们在不同的非线性测量模型的图像数据集上进行了数值实验。我们的观察结果是,与竞争方法相比,我们的方法在进行神经网络功能评估时,可以产生更准确的重建结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在生成多样且高质量图像方面表现出显著能力,通过有效建模复杂数据分布。此外,它们还被探索为信号恢复的强大先验,大大提高了重建信号的质量。本研究关注使用扩散模型实现半参数单索引模型的精确恢复,涵盖各种可能具有间断和未知链接函数的非线性模型。我们提出了一种有效的重建方法,只需一轮无条件采样和(部分)反转扩散模型。在适当条件下,对方法的有效性进行了理论分析。对图像数据集的不同非线性测量模型进行的数值实验表明,与竞争方法相比,我们的方法可以实现更准确的重建,同时大大减少神经网络功能评估的使用。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)能高效生成多样且高质量图像。
- 扩散模型作为信号恢复的强大先验,能显著提高重建信号质量。
- 研究关注使用扩散模型实现半参数单索引模型的精确恢复,适用于具有间断和未知链接函数的非线性模型。
- 提出一种有效的重建方法,只需一轮无条件采样和(部分)反转扩散模型。
- 在适当条件下,对方法的有效性进行了理论分析。
- 数值实验表明,与其他方法相比,该方法能更准确地重建信号。
点此查看论文截图

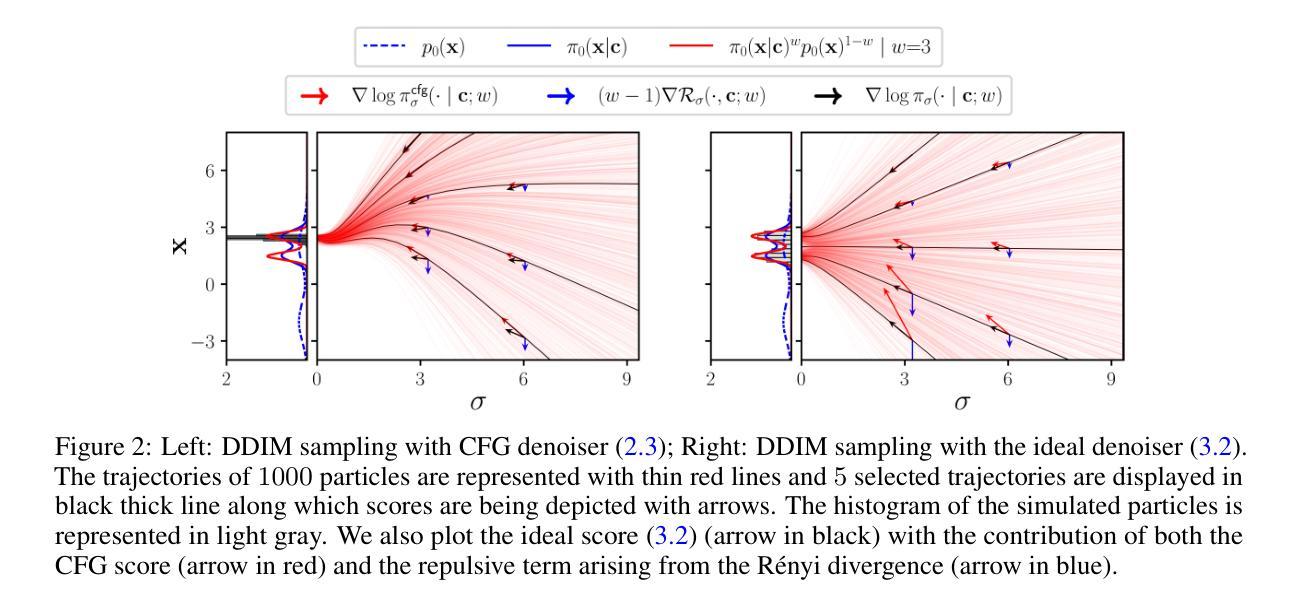
Conditional Diffusion Models with Classifier-Free Gibbs-like Guidance
Authors:Badr Moufad, Yazid Janati, Alain Durmus, Ahmed Ghorbel, Eric Moulines, Jimmy Olsson
Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) is a widely used technique for improving conditional diffusion models by linearly combining the outputs of conditional and unconditional denoisers. While CFG enhances visual quality and improves alignment with prompts, it often reduces sample diversity, leading to a challenging trade-off between quality and diversity. To address this issue, we make two key contributions. First, CFG generally does not correspond to a well-defined denoising diffusion model (DDM). In particular, contrary to common intuition, CFG does not yield samples from the target distribution associated with the limiting CFG score as the noise level approaches zero – where the data distribution is tilted by a power $w \gt 1$ of the conditional distribution. We identify the missing component: a R'enyi divergence term that acts as a repulsive force and is required to correct CFG and render it consistent with a proper DDM. Our analysis shows that this correction term vanishes in the low-noise limit. Second, motivated by this insight, we propose a Gibbs-like sampling procedure to draw samples from the desired tilted distribution. This method starts with an initial sample from the conditional diffusion model without CFG and iteratively refines it, preserving diversity while progressively enhancing sample quality. We evaluate our approach on both image and text-to-audio generation tasks, demonstrating substantial improvements over CFG across all considered metrics. The code is available at https://github.com/yazidjanati/cfgig
无分类器引导(CFG)是一种广泛应用于改进条件扩散模型的线性组合输出技术的技术。通过将有条件和无条件的去噪器结合起来使用,CFG在提高视觉质量的同时也能改善与提示的对齐性。然而,CFG往往减少了样本的多样性,因此在质量和多样性之间产生了挑战性的权衡问题。为了解决这个问题,我们做出了两个重要的贡献。首先,CFG通常并不对应一个定义良好的去噪扩散模型(DDM)。尤其重要的是,与常识相反,当噪声水平接近零时,CFG并不会从目标分布中生成样本,这个分布与条件分布的幂次方$w \gt 1$相对应。我们确定了缺失的部分:一个起着排斥力作用的Rényi散度项是必需的,用来纠正CFG并使其与适当的DDM保持一致。我们的分析表明,这个修正项在噪声水平较低时会消失。其次,基于这一见解,我们提出了一种类似Gibbs的采样程序,从所需的倾斜分布中绘制样本。这种方法以条件扩散模型中的初始样本开始,不带CFG进行迭代改进,从而保持了多样性并逐步提高了样本质量。我们在图像和文本到音频生成任务上评估了我们的方法,在所有考虑的指标上都显著优于CFG。代码可在https://github.com/yazidjanati/cfgig找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
本文介绍了Classifier-Free Guidance(CFG)在条件扩散模型中的应用,通过线性组合条件和无条件去噪器的输出来提高模型的性能。虽然CFG能提高视觉质量和与提示的对齐度,但它往往减少了样本的多样性,需要在质量和多样性之间做出权衡。为解决这一问题,本文做出了两个关键贡献。首先,CFG并不对应于一个定义明确的去噪扩散模型(DDM)。通过深入的分析,本文确定了缺失的组件:一个起到排斥作用的Rényi散度项,这是修正CFG并使其与适当的DDM一致的必要条件。其次,基于这一见解,本文提出了一种Gibbs样式的采样程序,从所需的倾斜分布中绘制样本。该方法从条件扩散模型中的无CFG初始样本开始,进行迭代优化,既保持多样性又逐步提高样本质量。在图像和文本到音频生成任务上的评估表明,该方法在各项指标上均优于CFG。
Key Takeaways
- Classifier-Free Guidance(CFG)用于提高条件扩散模型的性能,但存在质量和多样性之间的权衡问题。
- CFG并不直接对应于一个明确的去噪扩散模型(DDM)。
- 识别出缺失的组件:一个起到排斥作用的Rényi散度项,用于修正CFG并使其与DDM一致。
- 提出了一种基于Gibbs采样的方法,可以从所需的倾斜分布中绘制样本,既提高样本质量又保持多样性。
- 修正后的方法在图像和文本到音频生成任务上显著优于CFG。
- 相关的代码已实现并公开可用。
点此查看论文截图


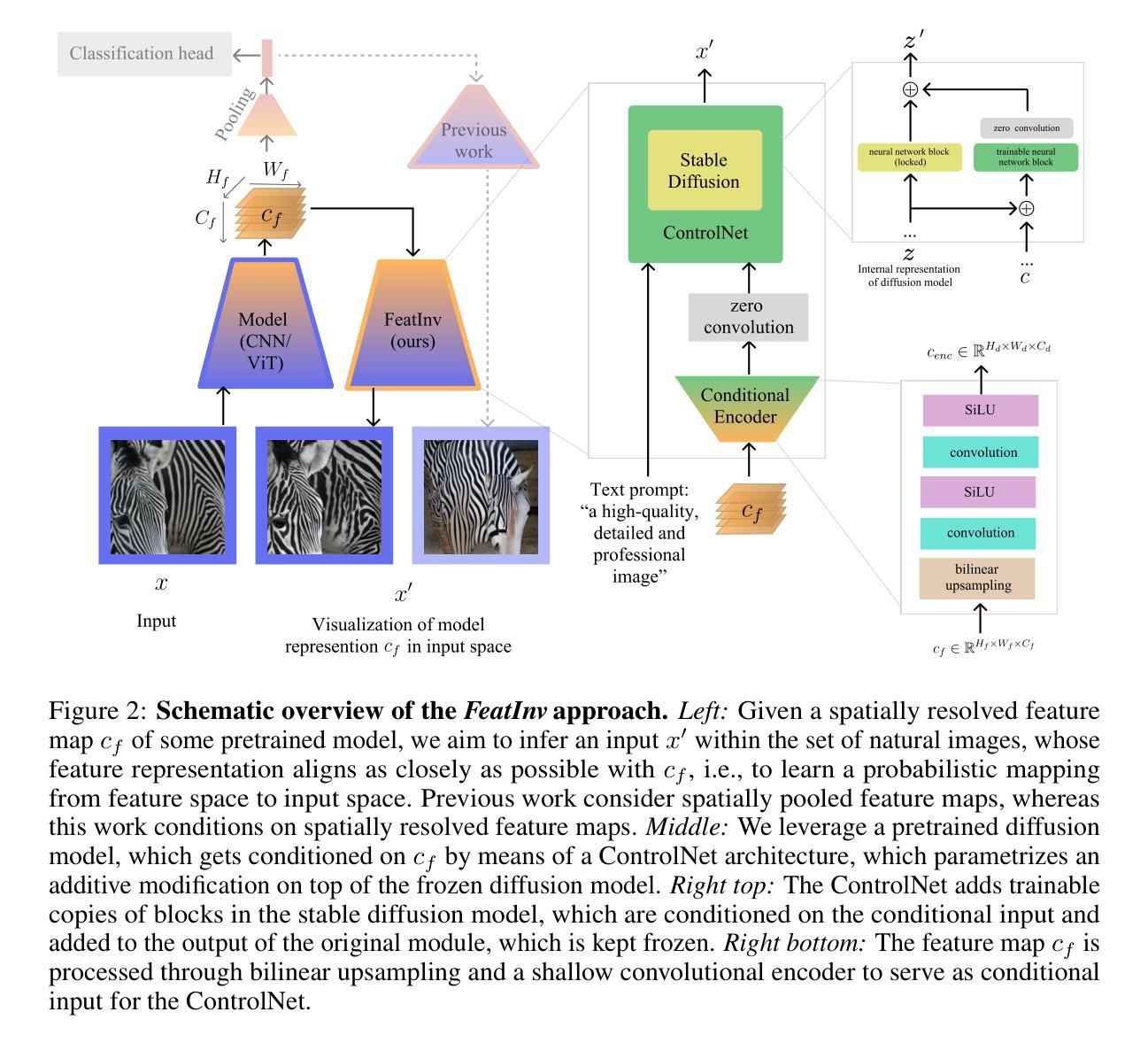
FeatInv: Spatially resolved mapping from feature space to input space using conditional diffusion models
Authors:Nils Neukirch, Johanna Vielhaben, Nils Strodthoff
Internal representations are crucial for understanding deep neural networks, such as their properties and reasoning patterns, but remain difficult to interpret. While mapping from feature space to input space aids in interpreting the former, existing approaches often rely on crude approximations. We propose using a conditional diffusion model - a pretrained high-fidelity diffusion model conditioned on spatially resolved feature maps - to learn such a mapping in a probabilistic manner. We demonstrate the feasibility of this approach across various pretrained image classifiers from CNNs to ViTs, showing excellent reconstruction capabilities. Through qualitative comparisons and robustness analysis, we validate our method and showcase possible applications, such as the visualization of concept steering in input space or investigations of the composite nature of the feature space. This approach has broad potential for improving feature space understanding in computer vision models.
内部表征对于理解深度神经网络(例如其属性和推理模式)至关重要,但仍难以解释。从特征空间到输入空间的映射有助于解释前者,而现有方法通常依赖于粗略的近似。我们建议使用条件扩散模型——一个以空间解析特征图为条件的预训练高保真扩散模型,以概率方式学习这种映射。我们通过各种预训练图像分类器的实例证明了该方法的可行性,这些分类器涵盖了从卷积神经网络到视觉变换器的范围,显示出出色的重建能力。通过定性和稳健性分析,我们验证了我们的方法,并展示了可能的应用,例如在输入空间中可视化概念导向或研究特征空间的复合性质。该方法在改进计算机视觉模型中特征空间的理解方面具有广阔潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures, code is available at https://github.com/AI4HealthUOL/FeatInv
Summary
基于深度神经网络内部表征的重要性,当前对于映射从特征空间到输入空间的解释方法仍存在困难。我们提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的概率映射方法,这种方法通过空间解析的特征映射条件预训练的高保真扩散模型。这种方法在不同的预训练图像分类器中的应用表现优异,如CNN和ViTs等。我们的方法验证了其可行性和稳健性,并展示了在可视化输入空间中的概念导向以及探究特征空间的复合性质等应用。该方法具有提高计算机视觉模型在特征空间理解的广泛应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 内部表征对于深度神经网络的理解和探究至关重要,它反映了模型的性质和推理模式。
- 从特征空间到输入空间的映射对于解释神经网络的工作原理很重要,但现有的方法往往依赖于粗略的近似。
- 提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的概率映射方法,利用预训练的高保真扩散模型进行映射。
- 方法在多种预训练图像分类器上表现出良好的重建能力,包括CNN和ViTs等。
- 通过定性比较和稳健性分析验证了方法的可行性。
- 该方法具有可视化输入空间中的概念导向以及探究特征空间的复合性质的潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图

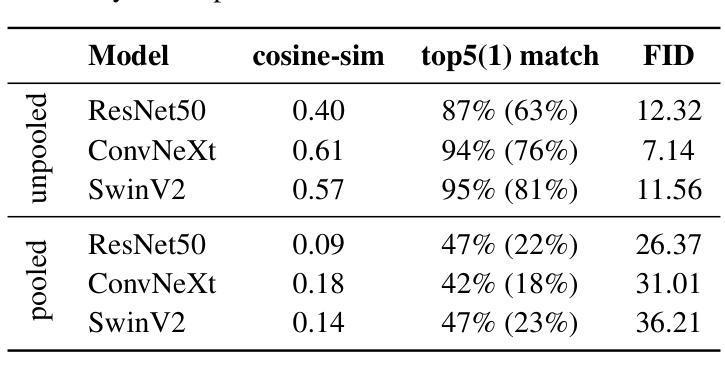

Facial Attribute Based Text Guided Face Anonymization
Authors:Mustafa İzzet Muştu, Hazım Kemal Ekenel
The increasing prevalence of computer vision applications necessitates handling vast amounts of visual data, often containing personal information. While this technology offers significant benefits, it should not compromise privacy. Data privacy regulations emphasize the need for individual consent for processing personal data, hindering researchers’ ability to collect high-quality datasets containing the faces of the individuals. This paper presents a deep learning-based face anonymization pipeline to overcome this challenge. Unlike most of the existing methods, our method leverages recent advancements in diffusion-based inpainting models, eliminating the need for training Generative Adversarial Networks. The pipeline employs a three-stage approach: face detection with RetinaNet, feature extraction with VGG-Face, and realistic face generation using the state-of-the-art BrushNet diffusion model. BrushNet utilizes the entire image, face masks, and text prompts specifying desired facial attributes like age, ethnicity, gender, and expression. This enables the generation of natural-looking images with unrecognizable individuals, facilitating the creation of privacy-compliant datasets for computer vision research.
随着计算机视觉应用的日益普及,需要处理包含个人信息的海量视觉数据。虽然这项技术带来了巨大的好处,但它不应该损害隐私。数据隐私规定强调处理个人数据时需要个人同意,这阻碍了研究人员收集包含个人面部的高质量数据集的能力。本文针对这一挑战,提出了一种基于深度学习的面部匿名化管道。与大多数现有方法不同,我们的方法利用基于扩散的修复模型的最新进展,无需训练生成对抗网络。该管道采用三阶段方法:使用RetinaNet进行面部检测,使用VGG-Face进行特征提取,以及使用最先进的BrushNet扩散模型进行逼真的面部生成。BrushNet利用整个图像、面部遮挡和文本提示来指定所需的面部属性,如年龄、种族、性别和表情。这能够生成看似自然但无法识别个人的图像,为计算机视觉研究创建符合隐私要求的数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5 figures, published in the Proceedings of the Joint visuAAL-GoodBrother Conference on Trustworthy Video- and Audio-Based Assistive Technologies
Summary
本文提出一种基于深度学习的面部匿名化管道,以应对计算机视觉应用中涉及隐私保护的挑战。该方法采用扩散基去噪模型,无需训练生成对抗网络,包括面部检测、特征提取和基于BrushNet扩散模型的逼真面部生成三个阶段。能够生成具有不可识别个体的自然图像,为计算机视觉研究创建符合隐私保护要求的数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机视觉应用需要处理大量包含个人信息的视觉数据。
- 隐私保护是处理个人数据的关键问题,数据隐私法规强调个人同意的必要性。
- 现有方法在处理个人数据隐私时面临挑战,本文提出了一种基于深度学习的面部匿名化管道来应对这一挑战。
- 该方法利用扩散基去噪模型,不需要训练生成对抗网络。
- 管道包括三个阶段:使用RetinaNet进行面部检测,使用VGG-Face进行特征提取,以及使用BrushNet扩散模型进行逼真的面部生成。
- BrushNet利用整个图像、面部掩码和指定面部属性的文本提示,如年龄、种族、性别和表情。
点此查看论文截图



Generative Image Compression by Estimating Gradients of the Rate-variable Feature Distribution
Authors:Minghao Han, Weiyi You, Jinhua Zhang, Leheng Zhang, Ce Zhu, Shuhang Gu
While learned image compression (LIC) focuses on efficient data transmission, generative image compression (GIC) extends this framework by integrating generative modeling to produce photo-realistic reconstructed images. In this paper, we propose a novel diffusion-based generative modeling framework tailored for generative image compression. Unlike prior diffusion-based approaches that indirectly exploit diffusion modeling, we reinterpret the compression process itself as a forward diffusion path governed by stochastic differential equations (SDEs). A reverse neural network is trained to reconstruct images by reversing the compression process directly, without requiring Gaussian noise initialization. This approach achieves smooth rate adjustment and photo-realistic reconstructions with only a minimal number of sampling steps. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing generative image compression approaches across a range of metrics, including perceptual distortion, statistical fidelity, and no-reference quality assessments.
传统的图像压缩(LIC)侧重于高效数据传输,而生成式图像压缩(GIC)则通过集成生成模型来产生逼真的重建图像,从而扩展了这一框架。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于扩散的生成模型框架,该框架专为生成式图像压缩设计。与以往基于扩散的方法间接利用扩散建模不同,我们将压缩过程本身重新解释为受随机微分方程(SDEs)控制的正向扩散路径。训练一个反向神经网络直接反转压缩过程进行图像重建,无需高斯噪声初始化。这种方法实现了平滑的速率调整,只需极少的采样步骤就能实现逼真的重建。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在感知失真、统计保真和无参考质量评估等多个指标上,都优于现有的生成式图像压缩方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的生成图像压缩框架。不同于间接利用扩散模型的先前方法,本文将压缩过程本身重新解释为由随机微分方程(SDEs)控制的正向扩散路径。通过训练反向神经网络直接反转压缩过程,无需高斯噪声初始化,实现平滑率调整和逼真的图像重建,采样步骤数量最小化。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法在感知失真、统计保真度和无参考质量评估等多个指标上优于现有生成图像压缩方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一个基于扩散模型的生成图像压缩框架,结合了图像压缩和生成建模。
- 不同于其他方法,本文直接将压缩过程解释为正向扩散路径,受随机微分方程(SDEs)控制。
- 使用反向神经网络反转压缩过程,无需高斯噪声初始化,实现高效且高质量的图像重建。
- 该方法实现了率的平滑调整,可以在不同压缩率下保持图像质量。
- 与现有生成图像压缩方法相比,该方法在感知失真、统计保真度和无参考质量评估等方面表现更优。
- 该方法通过最小化采样步骤数量,提高了生成图像压缩的效率。
点此查看论文截图

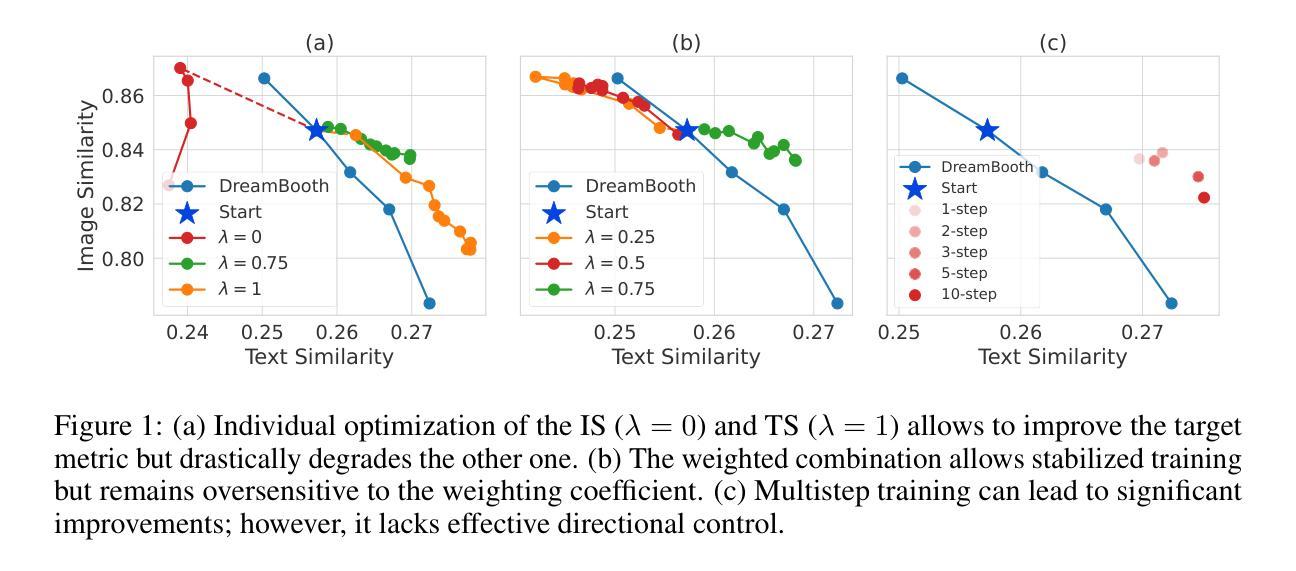
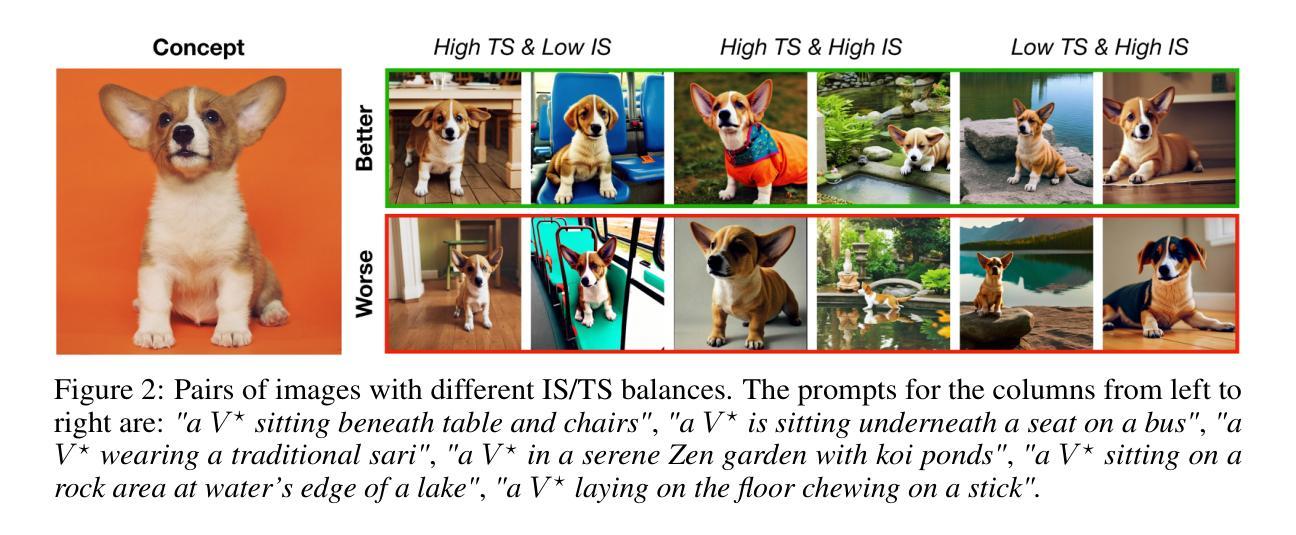
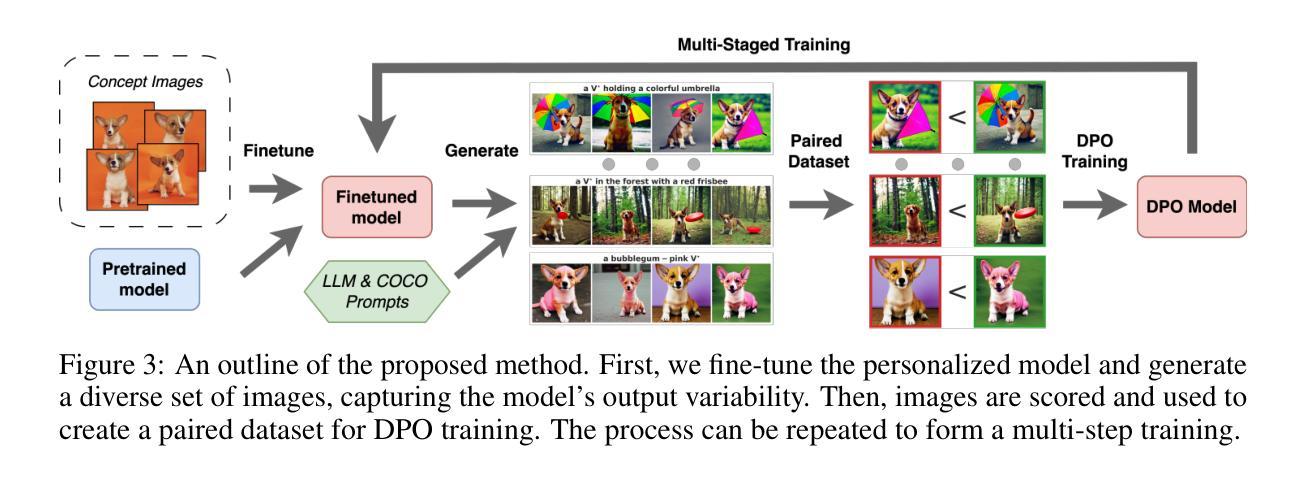
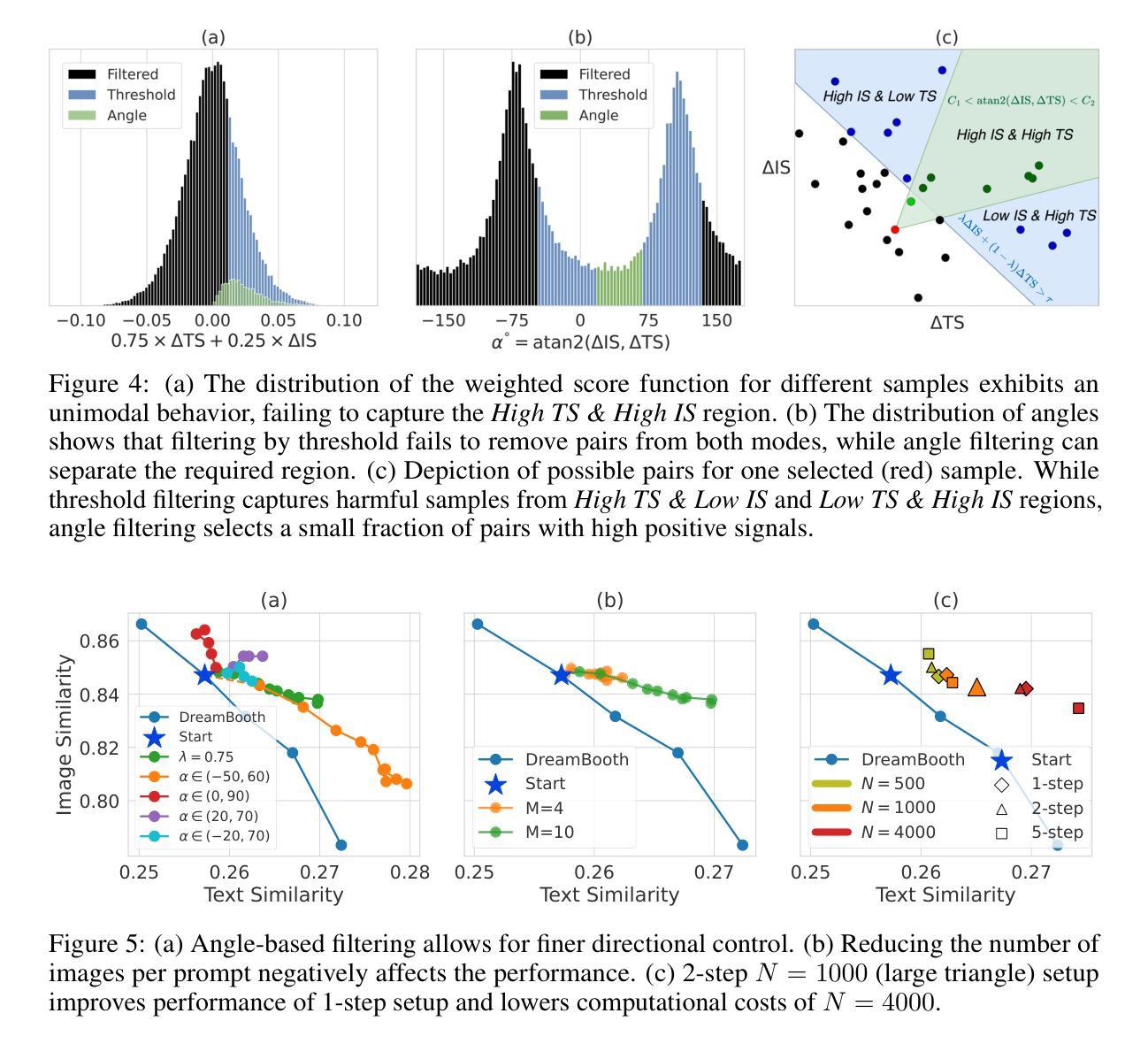
DreamBoothDPO: Improving Personalized Generation using Direct Preference Optimization
Authors:Shamil Ayupov, Maksim Nakhodnov, Anastasia Yaschenko, Andrey Kuznetsov, Aibek Alanov
Personalized diffusion models have shown remarkable success in Text-to-Image (T2I) generation by enabling the injection of user-defined concepts into diverse contexts. However, balancing concept fidelity with contextual alignment remains a challenging open problem. In this work, we propose an RL-based approach that leverages the diverse outputs of T2I models to address this issue. Our method eliminates the need for human-annotated scores by generating a synthetic paired dataset for DPO-like training using external quality metrics. These better-worse pairs are specifically constructed to improve both concept fidelity and prompt adherence. Moreover, our approach supports flexible adjustment of the trade-off between image fidelity and textual alignment. Through multi-step training, our approach outperforms a naive baseline in convergence speed and output quality. We conduct extensive qualitative and quantitative analysis, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method across various architectures and fine-tuning techniques. The source code can be found at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/DreamBoothDPO.
个性化扩散模型在文本到图像(T2I)生成中表现出了显著的成功,通过将用户定义的概念注入到不同的上下文中。然而,在概念保真度和上下文对齐之间找到平衡仍然是一个具有挑战性的开放问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于强化学习的方法,利用T2I模型的多样化输出来解决这个问题。我们的方法通过生成一个合成配对数据集,用于DPO类似训练的外部质量指标评估,从而消除了对人工标注分数的需求。这些优劣对特地被构建用来改进概念保真度和提示符合度。此外,我们的方法支持灵活地调整图像保真度和文本对齐之间的权衡。通过多步训练,我们的方法比简单基线在收敛速度和输出质量上表现更好。我们进行了广泛的定性和定量分析,证明我们的方法在各种架构和微调技术上的有效性。源代码可以在https://github.com/ControlGenAI/DreamBoothDPO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally. The source code can be found at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/DreamBoothDPO
Summary
本文探讨了个性化扩散模型在文本到图像生成中的成功应用,并指出平衡概念保真与上下文对齐的难题。为此,研究团队提出了一种基于强化学习的方法,利用文本到图像模型的多样输出来解决这一问题。该方法通过生成合成配对数据集进行类似DPO的训练,改进了概念保真和提示遵循。此外,该研究支持在图像保真度和文本对齐之间灵活调整权衡。通过多步训练,该研究的方法在收敛速度和输出质量上超越了简单基线,并在各种架构和微调技术方面展示了方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 个性化扩散模型在文本到图像生成中展现出色成功。
- 平衡概念保真与上下文对齐是当前面临的挑战。
- 研究团队提出基于强化学习的方法来解决这一问题。
- 该方法通过生成合成配对数据集进行DPO式训练,改进概念保真和提示遵循。
- 方法支持在图像保真度和文本对齐之间灵活调整权衡。
- 通过多步训练,该方法在收敛速度和输出质量上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

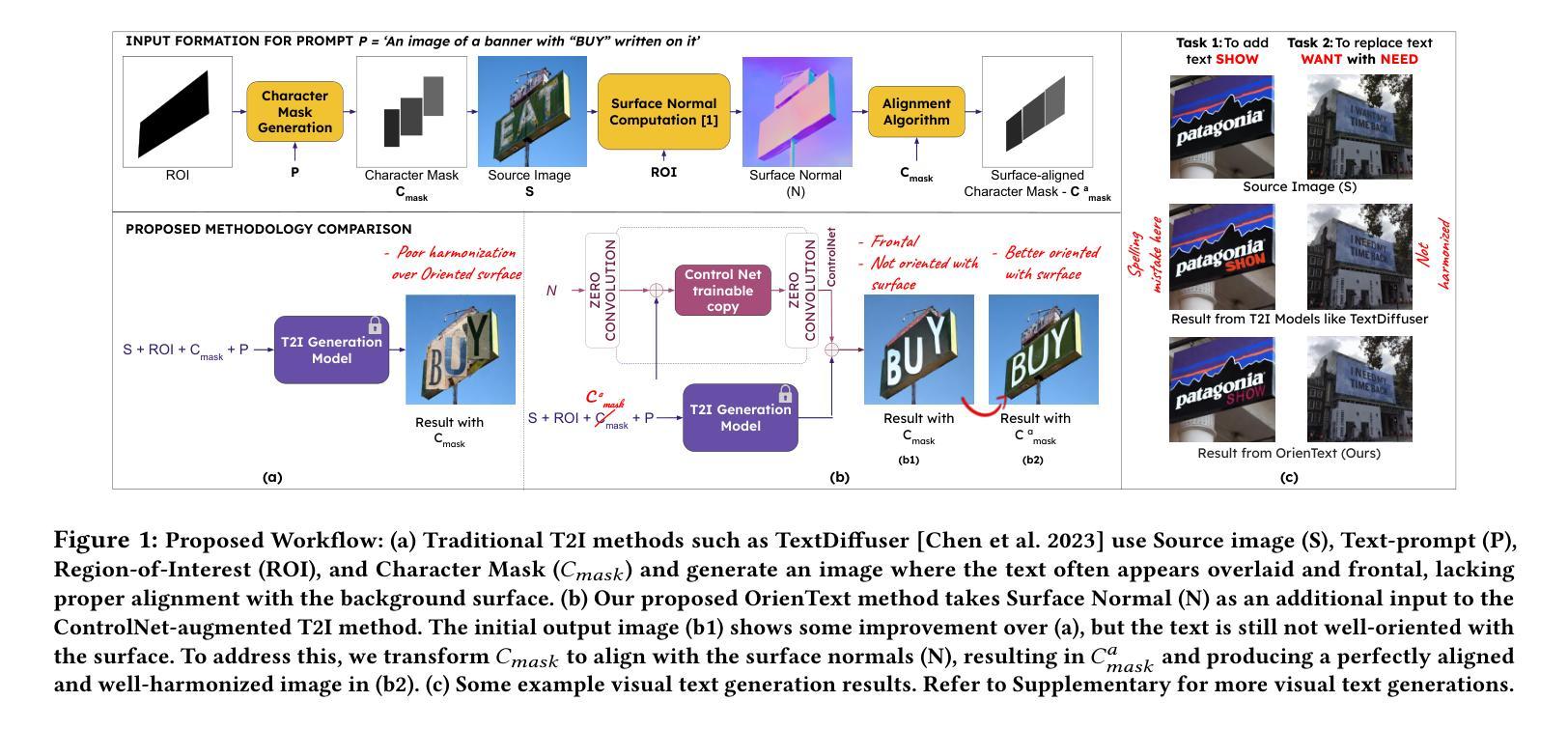
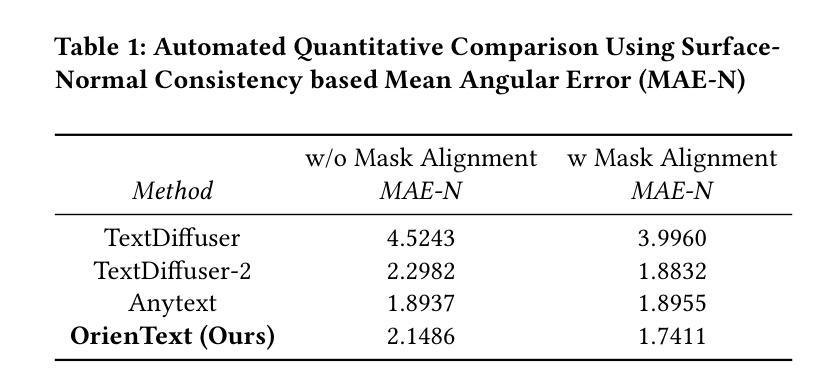
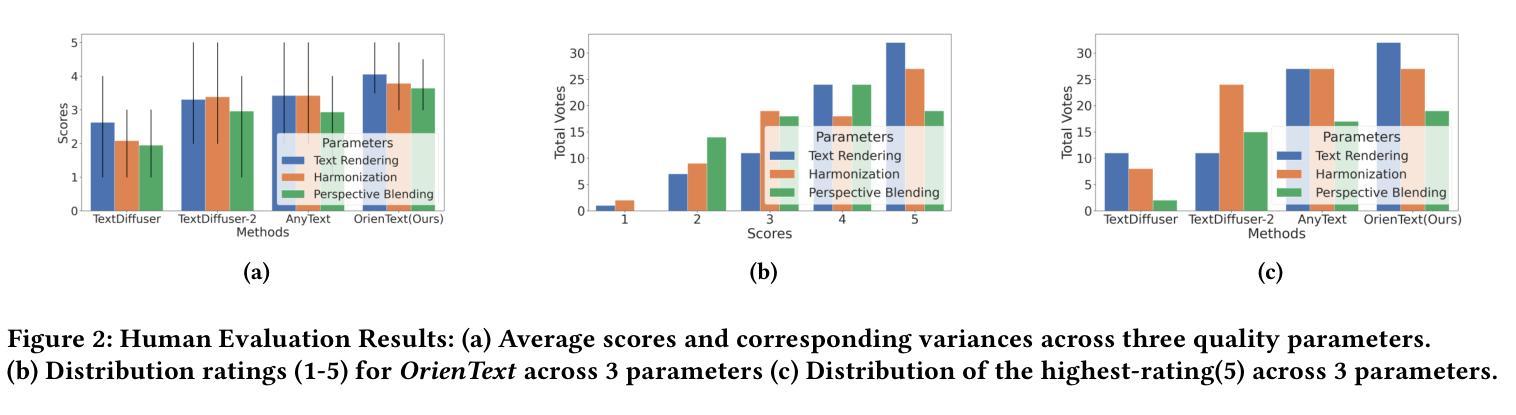
OrienText: Surface Oriented Textual Image Generation
Authors:Shubham Singh Paliwal, Arushi Jain, Monika Sharma, Vikram Jamwal, Lovekesh Vig
Textual content in images is crucial in e-commerce sectors, particularly in marketing campaigns, product imaging, advertising, and the entertainment industry. Current text-to-image (T2I) generation diffusion models, though proficient at producing high-quality images, often struggle to incorporate text accurately onto complex surfaces with varied perspectives, such as angled views of architectural elements like buildings, banners, or walls. In this paper, we introduce the Surface Oriented Textual Image Generation (OrienText) method, which leverages region-specific surface normals as conditional input to T2I generation diffusion model. Our approach ensures accurate rendering and correct orientation of the text within the image context. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the OrienText method on a self-curated dataset of images and compare it against the existing textual image generation methods.
图像中的文本内容在电子商务领域至关重要,特别是在营销、产品图像、广告和娱乐行业。当前的文本到图像(T2I)生成扩散模型虽然擅长生成高质量图像,但在将文本准确融入具有不同视角的复杂表面时往往遇到困难,例如建筑物的倾斜视图、横幅或墙壁等。在本文中,我们引入了面向表面的文本图像生成(OrienText)方法,该方法利用区域特定的表面法线作为条件输入应用于T2I生成扩散模型。我们的方法确保了图像上下文中文本的准确渲染和正确方向。我们在自己整理的图像数据集上展示了OrienText方法的有效性,并将其与现有的文本图像生成方法进行了比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Technical Communications
Summary
文本内容中的图像在电子商务领域尤为关键,特别是在营销、产品影像、广告和娱乐产业中。现有的文本到图像生成扩散模型虽然能够生成高质量图像,但在将文本准确地融入到具有不同视角的复杂表面上时,常常面临挑战,如建筑元素、横幅或墙壁的倾斜视图等。本文介绍了面向表面的文本图像生成(OrienText)方法,该方法利用区域特定的表面法线作为条件输入到文本到图像生成的扩散模型中,确保文本在图像上下文中的准确渲染和正确方向。我们在自制的图像数据集上验证了OrienText方法的有效性,并将其与现有的文本图像生成方法进行了比较。
Key Takeaways
- 文本内容在图像中的准确性对电子商务领域至关重要,尤其在营销、产品影像、广告和娱乐产业中。
- 当前文本到图像生成扩散模型在处理复杂视角的文本集成时面临挑战。
- OrienText方法利用区域特定的表面法线作为条件输入,以提高文本在图像中的渲染准确性。
- OrienText方法确保了文本在图像上下文中的正确方向和准确渲染。
- 论文在自制的图像数据集上验证了OrienText方法的有效性。
- OrienText方法与现有的文本图像生成方法相比,表现出更高的有效性。
- 该方法对于改进文本到图像生成技术在复杂表面上的表现具有积极意义。
点此查看论文截图




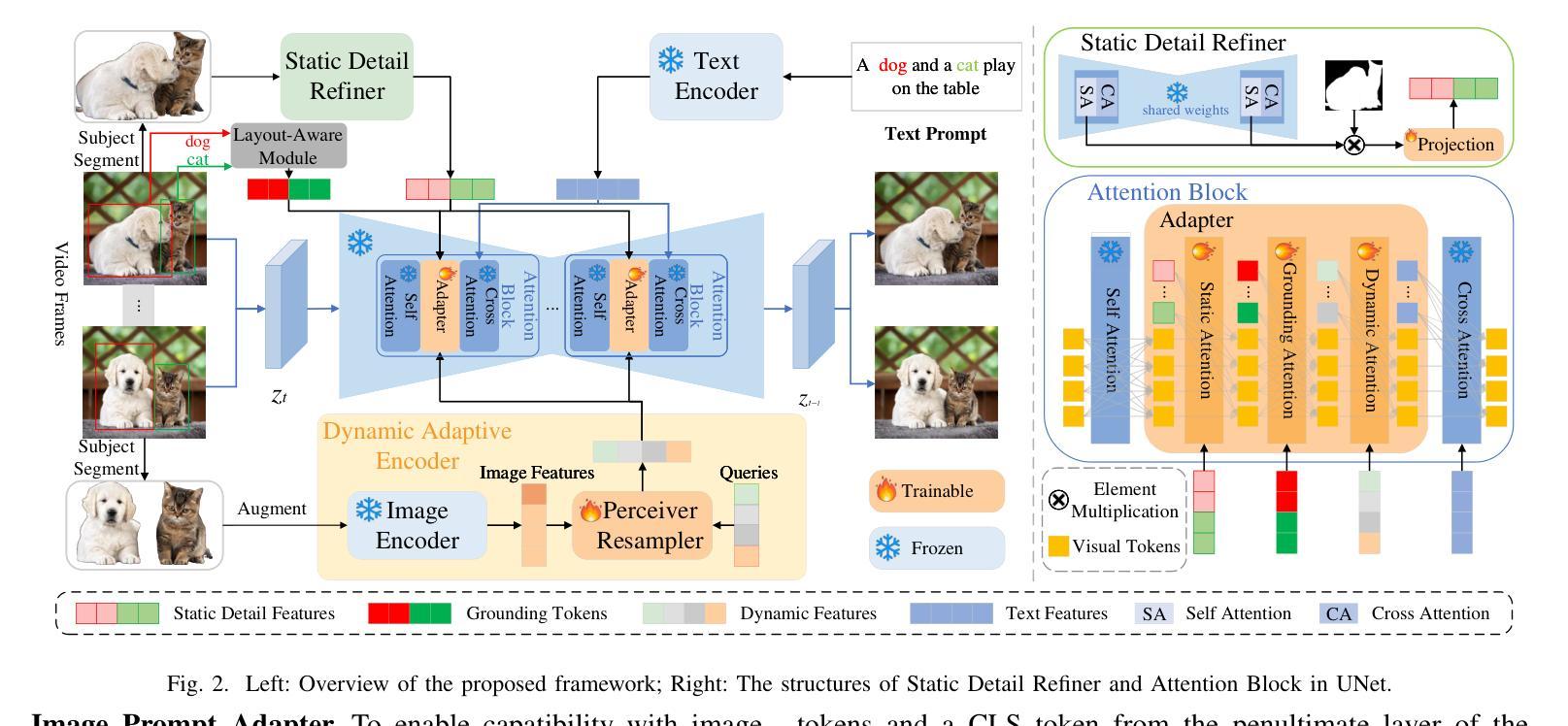
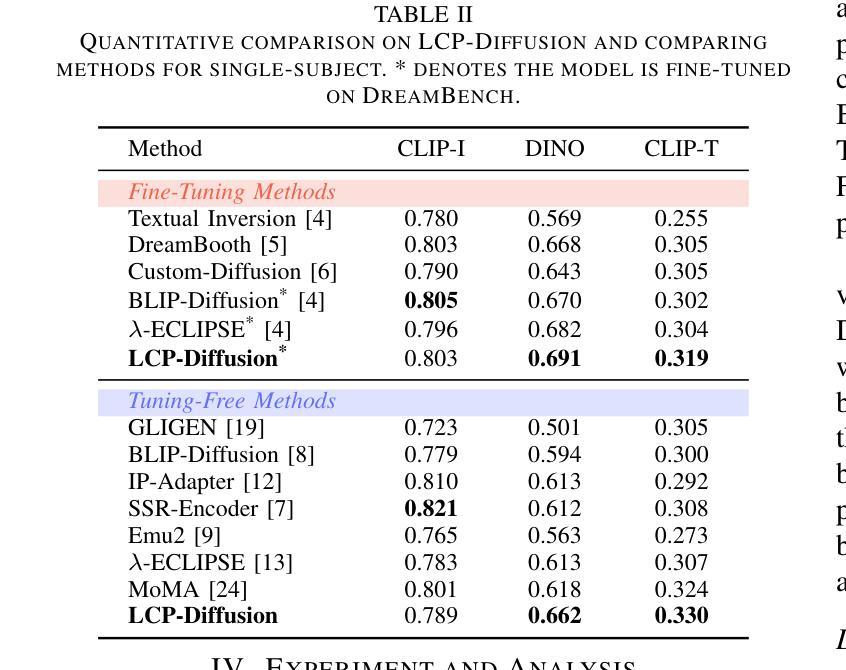
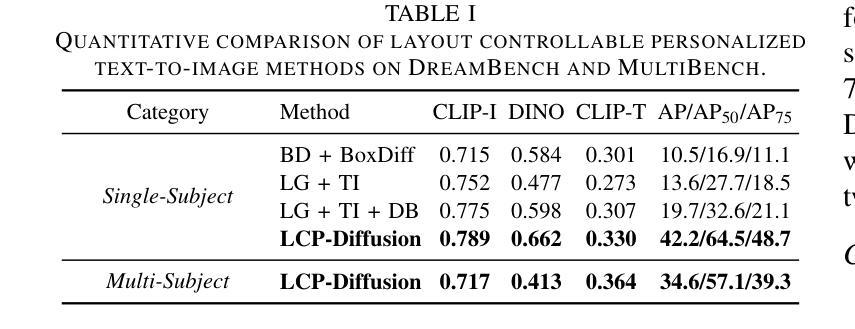
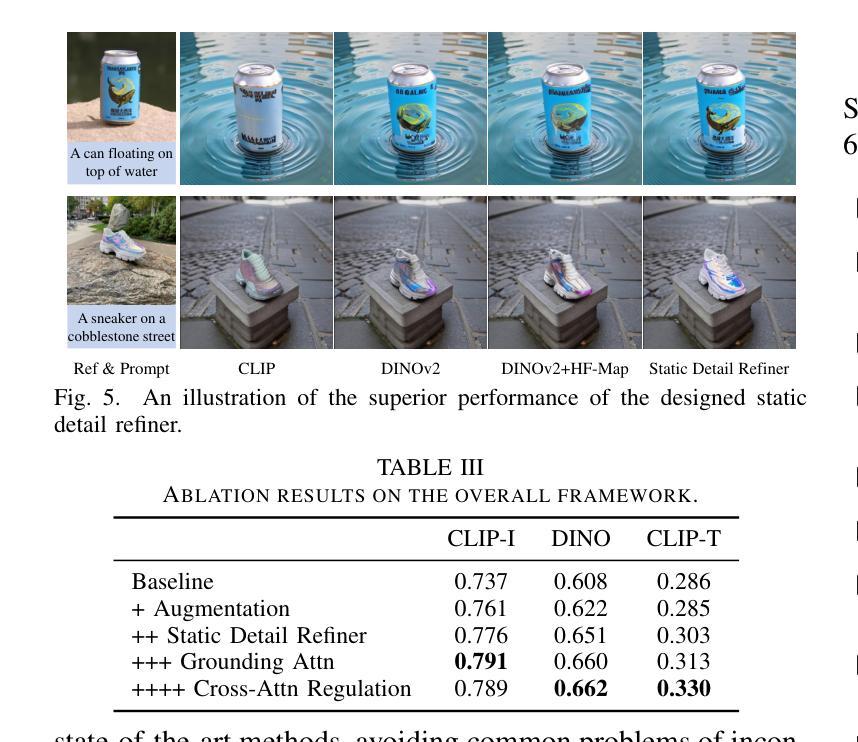
Create Anything Anywhere: Layout-Controllable Personalized Diffusion Model for Multiple Subjects
Authors:Wei Li, Hebei Li, Yansong Peng, Siying Wu, Yueyi Zhang, Xiaoyan Sun
Diffusion models have significantly advanced text-to-image generation, laying the foundation for the development of personalized generative frameworks. However, existing methods lack precise layout controllability and overlook the potential of dynamic features of reference subjects in improving fidelity. In this work, we propose Layout-Controllable Personalized Diffusion (LCP-Diffusion) model, a novel framework that integrates subject identity preservation with flexible layout guidance in a tuning-free approach. Our model employs a Dynamic-Static Complementary Visual Refining module to comprehensively capture the intricate details of reference subjects, and introduces a Dual Layout Control mechanism to enforce robust spatial control across both training and inference stages. Extensive experiments validate that LCP-Diffusion excels in both identity preservation and layout controllability. To the best of our knowledge, this is a pioneering work enabling users to “create anything anywhere”.
扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面取得了显著进展,为个性化生成框架的发展奠定了基础。然而,现有方法缺乏精确的布局可控性,并忽视了参考主题动态特征在提高保真度方面的潜力。在这项工作中,我们提出了布局可控个性化扩散(LCP-Diffusion)模型,这是一个新型框架,以无调整的方式将主题身份保留与灵活布局指导相结合。我们的模型采用动态静态互补视觉细化模块,全面捕捉参考主题的复杂细节,并引入双重布局控制机制,在训练和推理阶段实施稳健的空间控制。大量实验验证表明,LCP-Diffusion在身份保留和布局控制方面都表现出色。据我们所知,这是一项开创性工作,使用户能够“在任何地方创建任何内容”。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICME 2025
Summary
扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面取得了显著进展,为个性化生成框架的发展奠定了基础。然而,现有方法缺乏精确的布局可控性,忽视了参考主体动态特征在提高保真度方面的潜力。本研究提出了Layout-Controllable Personalized Diffusion(LCP-Diffusion)模型,这是一种结合主体身份保留与灵活布局指导的全新框架,采用无调整的方法。该模型通过动态静态互补视觉细化模块全面捕捉参考主体的细节,并引入双重布局控制机制,在训练和推理阶段实现稳健的空间控制。实验证明,LCP-Diffusion在身份保留和布局可控性方面表现出色,这是一项开创性工作,使用户能够“在任何地方创建任何内容”。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成方面取得显著进展,为个性化生成框架奠定基础。
- 现有方法缺乏精确的布局可控性。
- LCP-Diffusion模型结合了主体身份保留与灵活布局指导。
- 动态静态互补视觉细化模块全面捕捉参考主体的细节。
- 双重布局控制机制在训练和推理阶段实现稳健的空间控制。
- LCP-Diffusion模型在身份保留和布局可控性方面表现出色。
点此查看论文截图


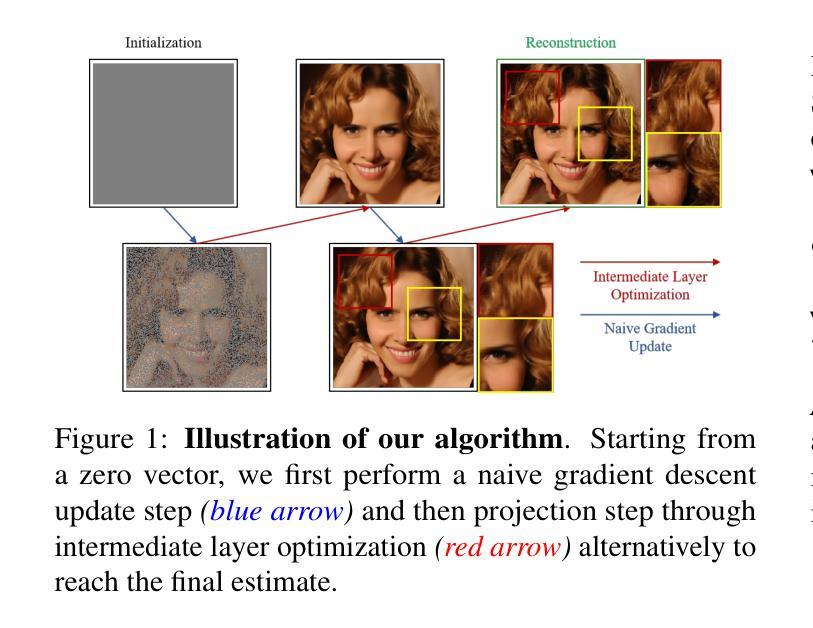
Integrating Intermediate Layer Optimization and Projected Gradient Descent for Solving Inverse Problems with Diffusion Models
Authors:Yang Zheng, Wen Li, Zhaoqiang Liu
Inverse problems (IPs) involve reconstructing signals from noisy observations. Traditional approaches often rely on handcrafted priors, which can fail to capture the complexity of real-world data. The advent of pre-trained generative models has introduced new paradigms, offering improved reconstructions by learning rich priors from data. Among these, diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as a powerful framework, achieving remarkable reconstruction performance across numerous IPs. However, existing DM-based methods frequently encounter issues such as heavy computational demands and suboptimal convergence. In this work, building upon the idea of the recent work DMPlug~\cite{wang2024dmplug}, we propose two novel methods, DMILO and DMILO-PGD, to address these challenges. Our first method, DMILO, employs intermediate layer optimization (ILO) to alleviate the memory burden inherent in DMPlug. Additionally, by introducing sparse deviations, we expand the range of DMs, enabling the exploration of underlying signals that may lie outside the range of the diffusion model. We further propose DMILO-PGD, which integrates ILO with projected gradient descent (PGD), thereby reducing the risk of suboptimal convergence. We provide an intuitive theoretical analysis of our approach under appropriate conditions and validate its superiority through extensive experiments on diverse image datasets, encompassing both linear and nonlinear IPs. Our results demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the effectiveness of DMILO and DMILO-PGD in addressing common challenges in DM-based IP solvers.
逆问题(IPs)涉及从噪声观察中重建信号。传统方法通常依赖于手工设计的先验知识,这可能无法捕捉真实世界数据的复杂性。预训练生成模型的出现引入了新的范式,通过从数据中学习丰富的先验知识,提供了改进的重构。其中,扩散模型(DMs)作为一种强大的框架脱颖而出,在多个IPs中实现了显著的重构性能。然而,现有的基于DM的方法经常面临计算需求大、收敛性不佳等问题。在这项工作中,我们基于最近的工作DMPlug(Wang et al., 2024)提出了两种新方法:DMILO和DMILO-PGD,以应对这些挑战。我们的第一种方法DMILO采用中间层优化(ILO)来缓解DMPlug固有的内存负担。此外,通过引入稀疏偏差,我们扩大了DM的范围,能够探索可能位于扩散模型范围之外的潜在信号。我们进一步提出了DMILO-PGD,它将ILO与投影梯度下降法(PGD)相结合,从而降低了收敛到局部最优解的风险。我们在适当条件下直观地分析了我们的方法,并通过对各种图像数据集的大量实验验证了其优越性,这些实验涵盖了线性和非线性IPs。我们的结果证明了与最新技术相比的显著性能提升,突显了DMILO和DMILO-PGD在解决基于DM的IP求解器中的常见挑战时的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
摘要
本文主要介绍了扩散模型在处理逆问题中的最新进展。传统的逆处理方法依赖手工设计的先验知识,难以捕捉真实世界的复杂性。随着预训练生成模型的出现,新的方法如扩散模型(DMs)已经在许多逆问题中展现出强大的重建性能。然而,现有的DM方法常常面临计算量大和收敛性不佳的问题。本文基于DMPlug工作提出了两种新方法DMILO和DMILO-PGD来解决这些问题。DMILO通过中间层优化(ILO)减轻DMPlug的内存负担,并引入稀疏偏差来扩展DM的范围。而DMILO-PGD则结合了ILO和投影梯度下降法(PGD),降低了次优收敛的风险。本文在多种图像数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证,显示所提方法在解决线性及非线性逆问题时,性能显著优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 扩散模型在处理逆问题中展现出强大的重建性能。
- 现有扩散模型方法面临计算量大和收敛性不佳的挑战。
- DMILO方法通过中间层优化和引入稀疏偏差来解决这些问题。
- DMILO-PGD结合了中间层优化和投影梯度下降法,降低次优收敛风险。
- 本文提出的两种新方法在多种图像数据集上进行了广泛实验验证,性能显著优于现有方法。
- 本文方法对解决线性及非线性逆问题均有效。
点此查看论文截图



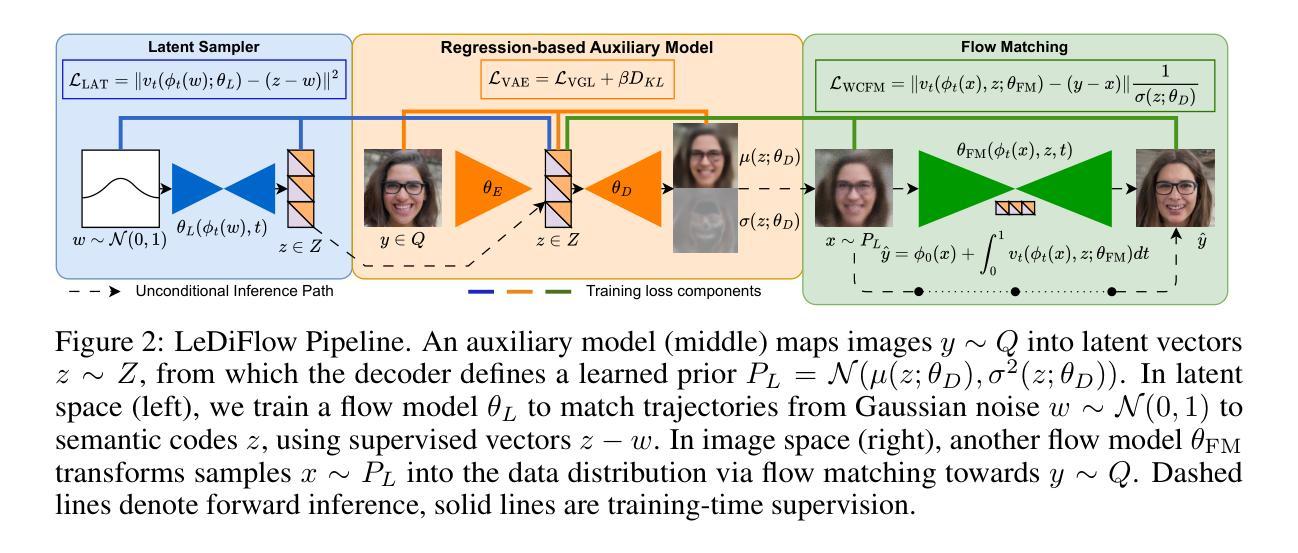
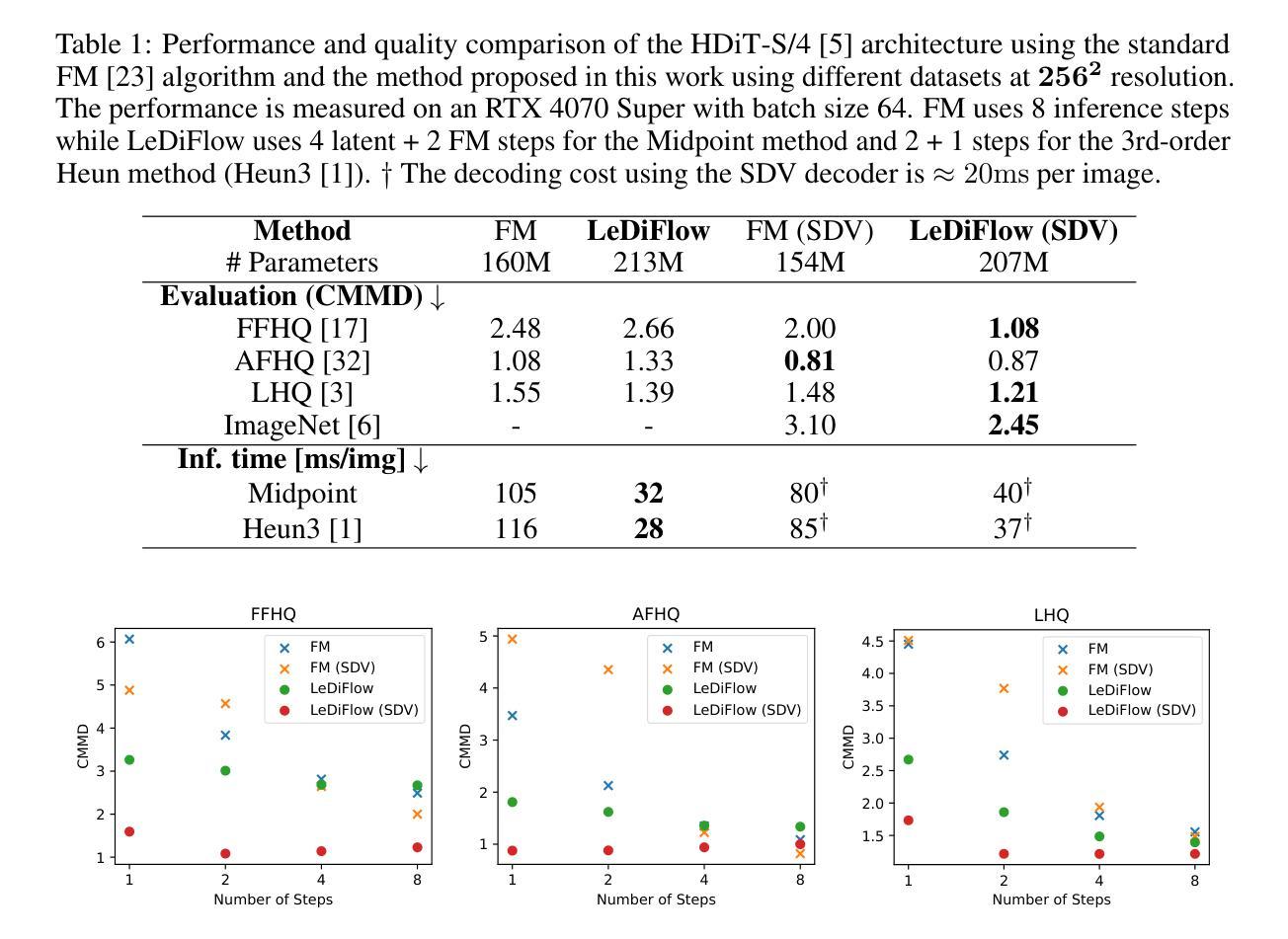
LeDiFlow: Learned Distribution-guided Flow Matching to Accelerate Image Generation
Authors:Pascal Zwick, Nils Friederich, Maximilian Beichter, Lennart Hilbert, Ralf Mikut, Oliver Bringmann
Enhancing the efficiency of high-quality image generation using Diffusion Models (DMs) is a significant challenge due to the iterative nature of the process. Flow Matching (FM) is emerging as a powerful generative modeling paradigm based on a simulation-free training objective instead of a score-based one used in DMs. Typical FM approaches rely on a Gaussian distribution prior, which induces curved, conditional probability paths between the prior and target data distribution. These curved paths pose a challenge for the Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) solver, requiring a large number of inference calls to the flow prediction network. To address this issue, we present Learned Distribution-guided Flow Matching (LeDiFlow), a novel scalable method for training FM-based image generation models using a better-suited prior distribution learned via a regression-based auxiliary model. By initializing the ODE solver with a prior closer to the target data distribution, LeDiFlow enables the learning of more computationally tractable probability paths. These paths directly translate to fewer solver steps needed for high-quality image generation at inference time. Our method utilizes a State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) transformer architecture combined with latent space sampling and can be trained on a consumer workstation. We empirically demonstrate that LeDiFlow remarkably outperforms the respective FM baselines. For instance, when operating directly on pixels, our model accelerates inference by up to 3.75x compared to the corresponding pixel-space baseline. Simultaneously, our latent FM model enhances image quality on average by 1.32x in CLIP Maximum Mean Discrepancy (CMMD) metric against its respective baseline.
使用扩散模型(DMs)提高高质量图像生成的效率是一个巨大的挑战,因为该过程具有迭代性。流匹配(FM)正崭露头角,成为一种基于模拟自由训练目标的强大生成建模范式,而不是DMs中使用的基于评分的目标。典型的FM方法依赖于高斯分布先验,这会在先验和目标数据分布之间产生弯曲的条件概率路径。这些弯曲的路径对常微分方程(ODE)求解器构成了挑战,需要多次调用流预测网络的推理。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于学习分布引导流匹配(LeDiFlow)的FM图像生成模型的新型可扩展方法,该方法使用通过基于回归的辅助模型学习的更适合的先验分布。通过用更接近目标数据分布的先验初始化ODE求解器,LeDiFlow能够学习更易于计算的概率路径。这些路径直接转化为在推理时高质量图像生成所需的更少的求解器步骤。我们的方法利用最先进的变压器架构,结合潜在空间采样,可以在消费者工作站上进行训练。我们实证表明,LeDiFlow显著优于各自的FM基线。例如,当直接在像素上操作时,我们的模型将推理加速了高达3.75倍,相对于相应的像素空间基线。同时,我们的潜在FM模型在CLIP最大平均差异(CMMD)指标上平均提高了图像质量1.32倍,超过了其相应的基线模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的高效率高质量图像生成面临挑战,主要是由于其迭代性质。流匹配(FM)作为一种基于模拟的无训练目标的生成建模范式正在兴起,相对于扩散模型使用的基于分数的训练目标,它具有潜力。典型的FM方法依赖于高斯分布先验,这会在先验和目标数据分布之间产生弯曲的条件概率路径。针对这一问题,我们提出了基于学习分布引导流匹配(LeDiFlow)的解决方法,这是一种用于训练基于FM的图像生成模型的新方法,通过采用更适合的先验分布来提高效率。LeDiFlow使用回归辅助模型来学习先验分布,通过使ODE求解器的初始状态更接近目标数据分布,从而学习更易于计算的概率路径。这些路径直接转化为在推理时生成高质量图像所需的更少求解器步骤。我们的方法结合了最先进的转换器架构和潜在空间采样,可以在消费者工作站上进行训练。实验表明,LeDiFlow显著优于相应的FM基线。例如,直接在像素上操作时,我们的模型将推理速度提高了3.75倍;而在潜在空间上操作时,我们的模型提高了图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配(FM)是一种新兴的生成建模方法,基于模拟无训练目标,潜力巨大。
- 典型的FM方法使用高斯分布先验,导致与目解先验的分布之间出现弯曲的条件概率路径问题。
- LeDiFlow作为一种新型可扩展方法,采用回归辅助模型学习更适合的先验分布来解决上述问题。
- LeDiFlow通过使ODE求解器的初始状态更接近目标数据分布,提高了计算效率并减少了推理时间所需的求解器步骤。
- LeDiFlow结合了最先进的转换器架构和潜在空间采样技术。
- LeDiFlow显著优于现有的FM基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

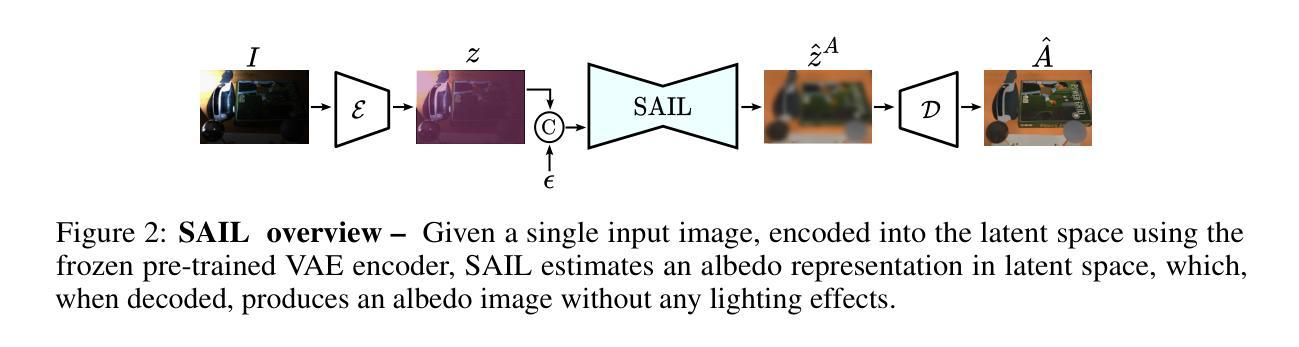
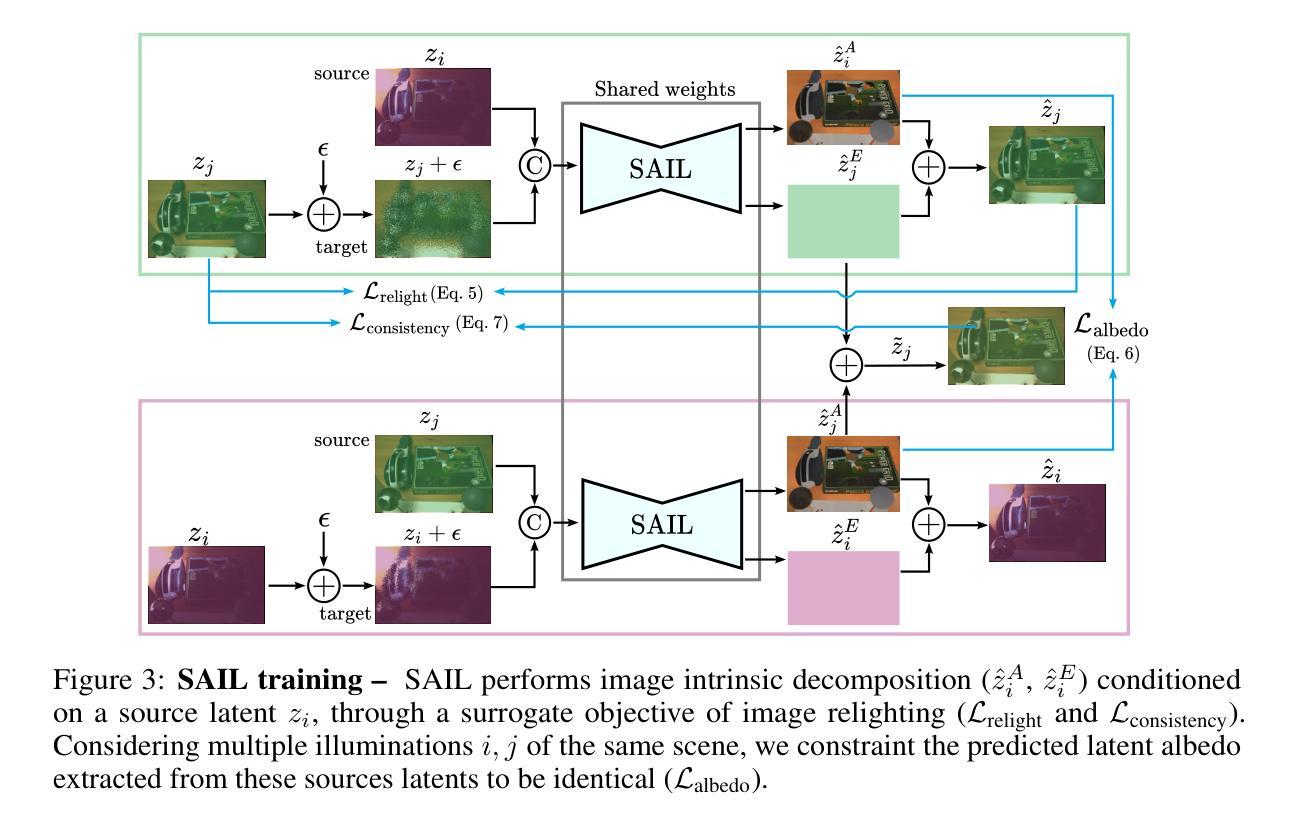
SAIL: Self-supervised Albedo Estimation from Real Images with a Latent Diffusion Model
Authors:Hala Djeghim, Nathan Piasco, Luis Roldão, Moussab Bennehar, Dzmitry Tsishkou, Céline Loscos, Désiré Sidibé
Intrinsic image decomposition aims at separating an image into its underlying albedo and shading components, isolating the base color from lighting effects to enable downstream applications such as virtual relighting and scene editing. Despite the rise and success of learning-based approaches, intrinsic image decomposition from real-world images remains a significant challenging task due to the scarcity of labeled ground-truth data. Most existing solutions rely on synthetic data as supervised setups, limiting their ability to generalize to real-world scenes. Self-supervised methods, on the other hand, often produce albedo maps that contain reflections and lack consistency under different lighting conditions. To address this, we propose SAIL, an approach designed to estimate albedo-like representations from single-view real-world images. We repurpose the prior knowledge of a latent diffusion model for unconditioned scene relighting as a surrogate objective for albedo estimation. To extract the albedo, we introduce a novel intrinsic image decomposition fully formulated in the latent space. To guide the training of our latent diffusion model, we introduce regularization terms that constrain both the lighting-dependent and independent components of our latent image decomposition. SAIL predicts stable albedo under varying lighting conditions and generalizes to multiple scenes, using only unlabeled multi-illumination data available online.
内在图像分解旨在将图像分离为其基本的材质反射(albedo)和阴影组件,从而将基础颜色从光照效果中分离出来,以支持下游应用,例如虚拟照明和场景编辑。尽管基于学习的方法的兴起并取得了成功,但从真实世界的图像中进行内在图像分解仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为缺乏标记的真实数据。现有的大多数解决方案依赖于合成数据作为监督设置,这限制了它们对真实场景的泛化能力。另一方面,自监督的方法通常产生的材质反射图包含反射,并且在不同的光照条件下缺乏一致性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SAIL(一种从单视图真实世界图像估计类似材质反射的表示方法)。我们利用潜在扩散模型的先验知识作为无条件场景照明代理目标来进行材质反射估计。为了提取材质反射,我们在潜在空间中引入了一种新型内在图像分解方法。为了引导潜在扩散模型的训练,我们引入了正则化项,以约束潜在图像分解的光照依赖和独立组件。SAIL可以在不同的光照条件下预测稳定的材质反射,并适用于多个场景,仅使用在线可用的无标签多照明数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://hala-djeghim.github.io/SAIL/
Summary
本文提出了SAIL方法,旨在从单视角真实图像中估计出类似材质的表示。该方法利用潜在扩散模型的先验知识作为无条件场景补光的替代目标来进行材质估计。通过引入新的内在图像分解方法,完全在潜在空间中完成分解。同时,通过引入正则化项来约束潜在图像分解中的光照依赖和独立成分,从而指导潜在扩散模型的训练。SAIL能够在不同的光照条件下预测稳定的材质,并可以推广到多个场景,仅使用在线可用的无标签多光照数据。
Key Takeaways
- 内在图像分解旨在分离图像的底层材质和阴影成分,为虚拟补光和场景编辑等下游应用提供基础。
- 学习方法虽然成功,但由于缺乏真实数据的标签,从真实图像中进行内在图像分解仍然是一个重大挑战。
- 现有解决方案大多依赖于合成数据作为监督设置,限制了其在真实场景中的泛化能力。
- 自监督方法产生的材质图通常包含反射,并且在不同光照条件下缺乏一致性。
- SAIL方法利用潜在扩散模型的先验知识来估计从单视角真实图像中得出的材质表示。
- SAIL在潜在空间中完成内在图像分解,并通过引入正则化项来约束其光照依赖和独立成分。
点此查看论文截图

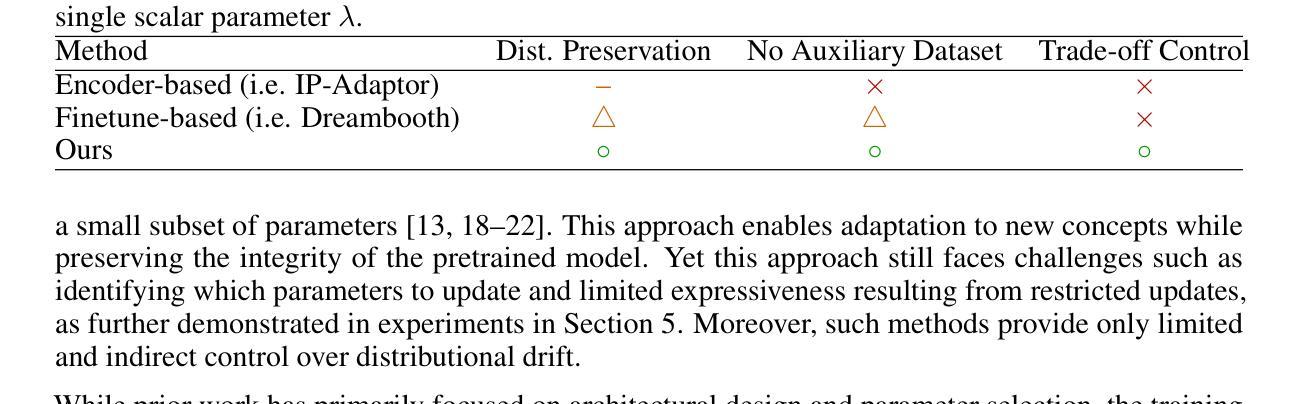
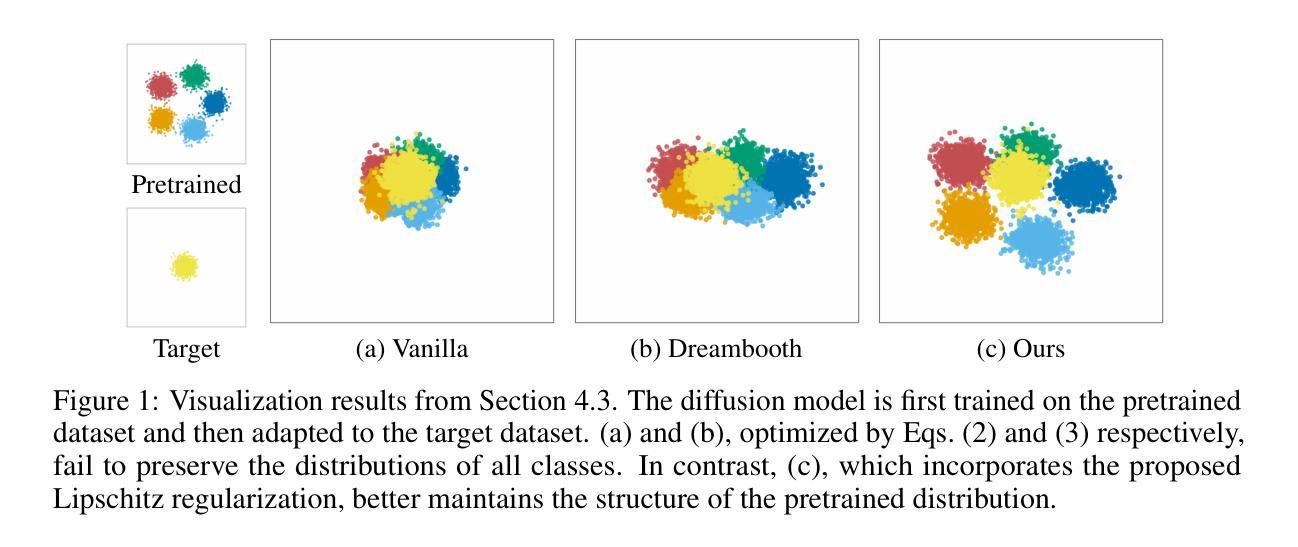
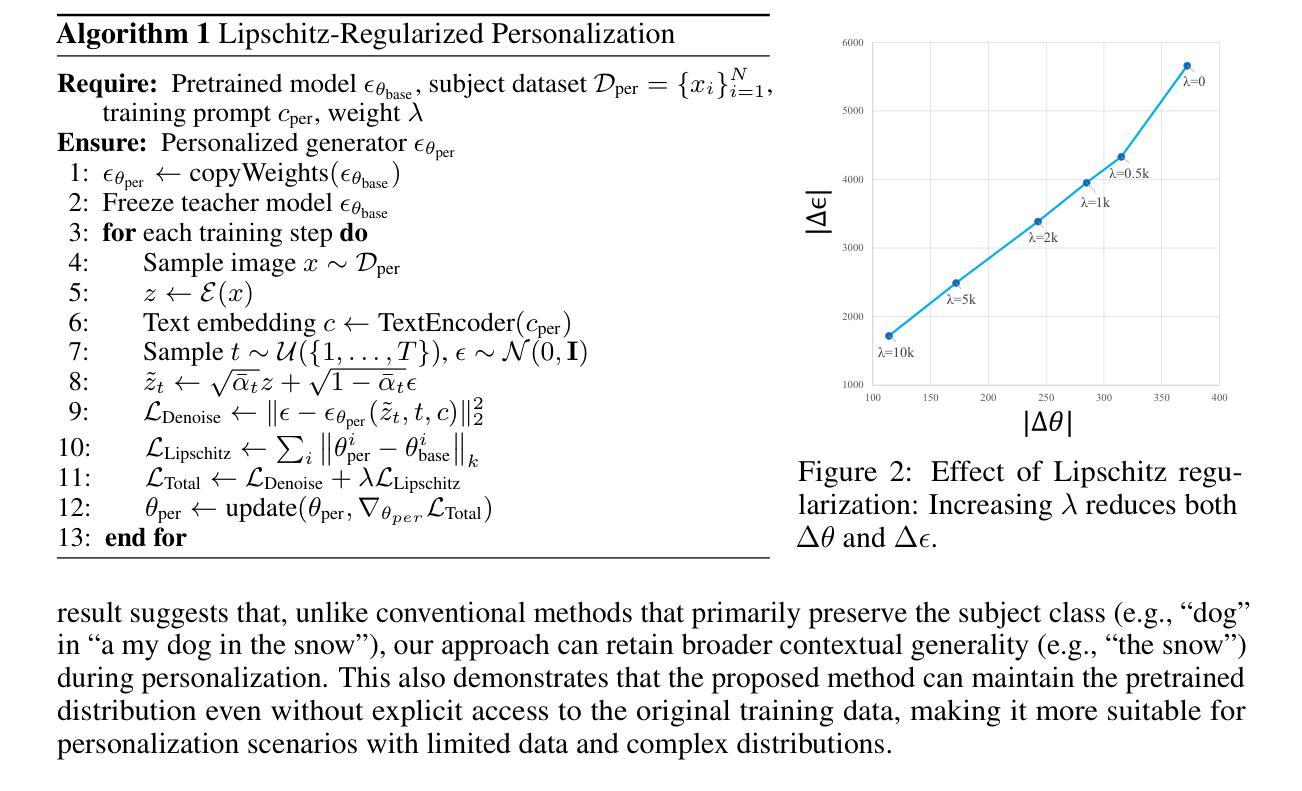
Regularized Personalization of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models without Distributional Drift
Authors:Gihoon Kim, Hyungjin Park, Taesup Kim
Personalization using text-to-image diffusion models involves adapting a pretrained model to novel subjects with only a few image examples. This task presents a fundamental challenge, as the model must not only learn the new subject effectively but also preserve its ability to generate diverse and coherent outputs across a wide range of prompts. In other words, successful personalization requires integrating new concepts without forgetting previously learned generative capabilities. Forgetting denotes unintended distributional drift, where the model’s output distribution deviates from that of the original pretrained model. In this paper, we provide an analysis of this issue and identify a mismatch between standard training objectives and the goals of personalization. To address this, we propose a new training objective based on a Lipschitz-bounded formulation that explicitly constrains deviation from the pretrained distribution. Our method provides improved control over distributional drift and performs well even in data-scarce scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing personalization methods, achieving higher CLIP-T, CLIP-I, and DINO scores.
使用文本到图像扩散模型进行个性化涉及使用仅少数图像示例来适应预训练模型以进行新型主题处理。此任务呈现了一个基本挑战,因为模型不仅需要有效地学习新主题,而且还要保持其在广泛提示中生成多样化和连贯输出的能力。换句话说,成功的个性化要求集成新概念而不会忘记先前学习的生成能力。遗忘表示意外的分布漂移,即模型输出分布偏离原始预训练模型的分布。在本文中,我们对此问题进行了分析,并确定了标准训练目标与个性化目标之间的不匹配。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于Lipschitz界定的新训练目标,该目标显式约束了预训练分布的偏差。我们的方法在控制分布漂移方面提供了更好的控制,即使在数据稀缺的情况下也能表现良好。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于现有的个性化方法,实现了更高的CLIP-T、CLIP-I和DINO分数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练文本到图像扩散模型的个性化适应是一大挑战,需要模型不仅高效学习新主题,还要保持对各种提示生成多样化和连贯性输出的能力。个人化过程中会出现意外分布漂移的问题,即模型输出分布偏离原始预训练模型的分布。本文分析这一问题,发现标准训练目标与个性化目标之间存在不匹配。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于Lipschitz约束的新训练目标,该目标能够明确控制分布偏离。实验结果表明,该方法在数据稀缺的场景下表现良好,一致优于现有个性化方法,达到更高的CLIP-T、CLIP-I和DINO评分。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练文本到图像扩散模型的个性化适应是一个挑战,需要模型学习新主题并保持生成能力。
- 在个性化过程中存在分布漂移问题,即模型输出分布偏离预训练模型的分布。
- 本文分析了标准训练目标与个性化目标之间的不匹配问题。
- 提出了一种基于Lipschitz约束的新训练目标,以控制分布偏离。
- 方法在数据稀缺的场景下表现良好。
- 该方法在实验评估中一致优于现有个性化方法。
点此查看论文截图

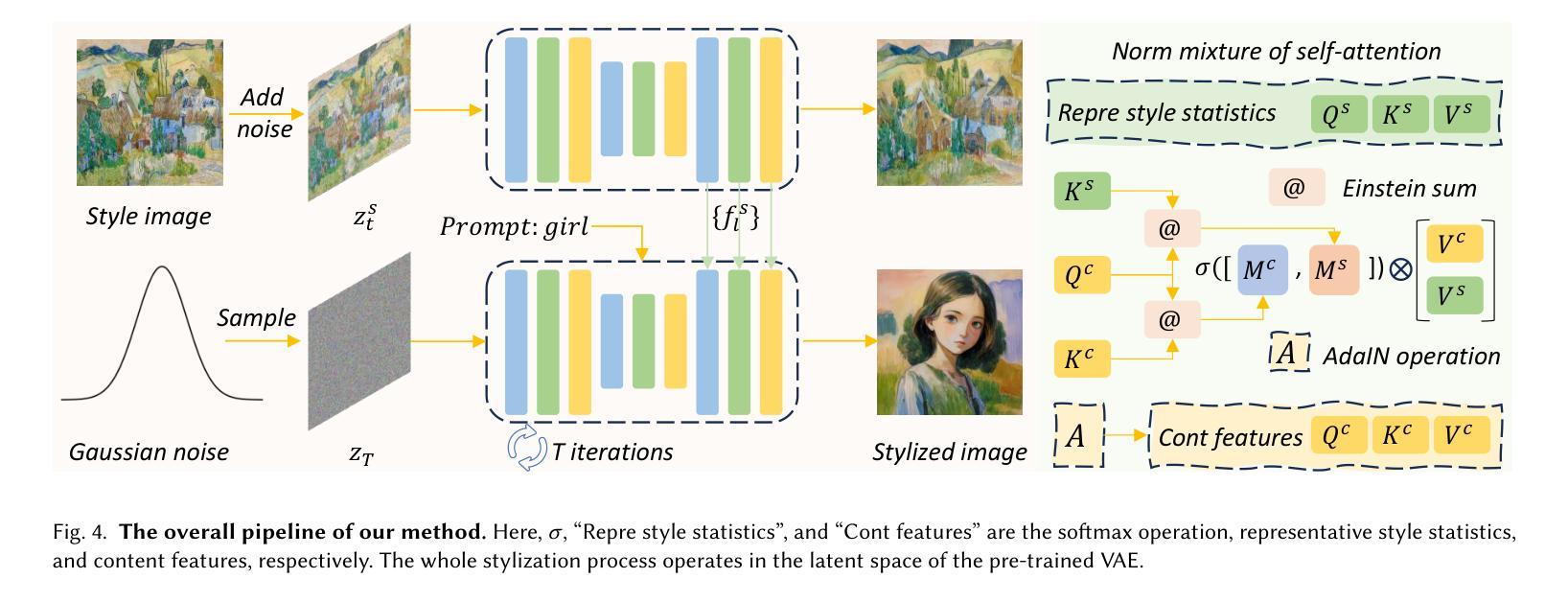
Training-free Stylized Text-to-Image Generation with Fast Inference
Authors:Xin Ma, Yaohui Wang, Xinyuan Chen, Tien-Tsin Wong, Cunjian Chen
Although diffusion models exhibit impressive generative capabilities, existing methods for stylized image generation based on these models often require textual inversion or fine-tuning with style images, which is time-consuming and limits the practical applicability of large-scale diffusion models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel stylized image generation method leveraging a pre-trained large-scale diffusion model without requiring fine-tuning or any additional optimization, termed as OmniPainter. Specifically, we exploit the self-consistency property of latent consistency models to extract the representative style statistics from reference style images to guide the stylization process. Additionally, we then introduce the norm mixture of self-attention, which enables the model to query the most relevant style patterns from these statistics for the intermediate output content features. This mechanism also ensures that the stylized results align closely with the distribution of the reference style images. Our qualitative and quantitative experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
尽管扩散模型展现出令人印象深刻的生成能力,但基于这些模型的风格化图像生成现有方法通常需要文本反转或使用风格图像进行微调,这既耗时又限制了大规模扩散模型的实际应用性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种新的风格化图像生成方法,该方法利用预训练的大规模扩散模型,无需微调或任何额外优化,被称为OmniPainter。具体来说,我们利用潜在一致性模型的自洽性属性,从参考风格图像中提取代表性风格统计信息来指导风格化过程。此外,我们还引入了自注意力机制的范数混合,使模型能够为中间输出内容特征查询最相关的风格模式。这种机制还确保风格化结果与参考风格图像的分布紧密对齐。我们的定性和定量实验结果都表明,所提出的方法优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://maxin-cn.github.io/omnipainter_project
Summary
本文提出一种利用预训练的大型扩散模型进行风格化图像生成的新方法,无需微调或其他额外优化,称为OmniPainter。它利用潜在一致性模型的自洽性,从参考风格图像中提取代表性风格统计信息来指导风格化过程。此外,还引入了自注意力机制的范数混合,使模型能够为中间输出内容特征查询最相关的风格模式。该方法生成的风格化结果与参考风格图像分布紧密对齐,实验证明其优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- OmniPainter利用预训练的大型扩散模型进行风格化图像生成,无需额外优化或微调。
- 该方法利用潜在一致性模型的自洽性提取参考风格图像中的代表性风格统计信息。
- 引入范数混合自注意力机制,使模型能够查询最相关的风格模式与中间输出内容特征相匹配。
- OmniPainter确保风格化结果与参考风格图像分布紧密对齐。
- 实验证明OmniPainter在风格化图像生成方面优于现有方法。
- 该方法大大减少了生成风格化图像所需的时间和复杂性。
点此查看论文截图


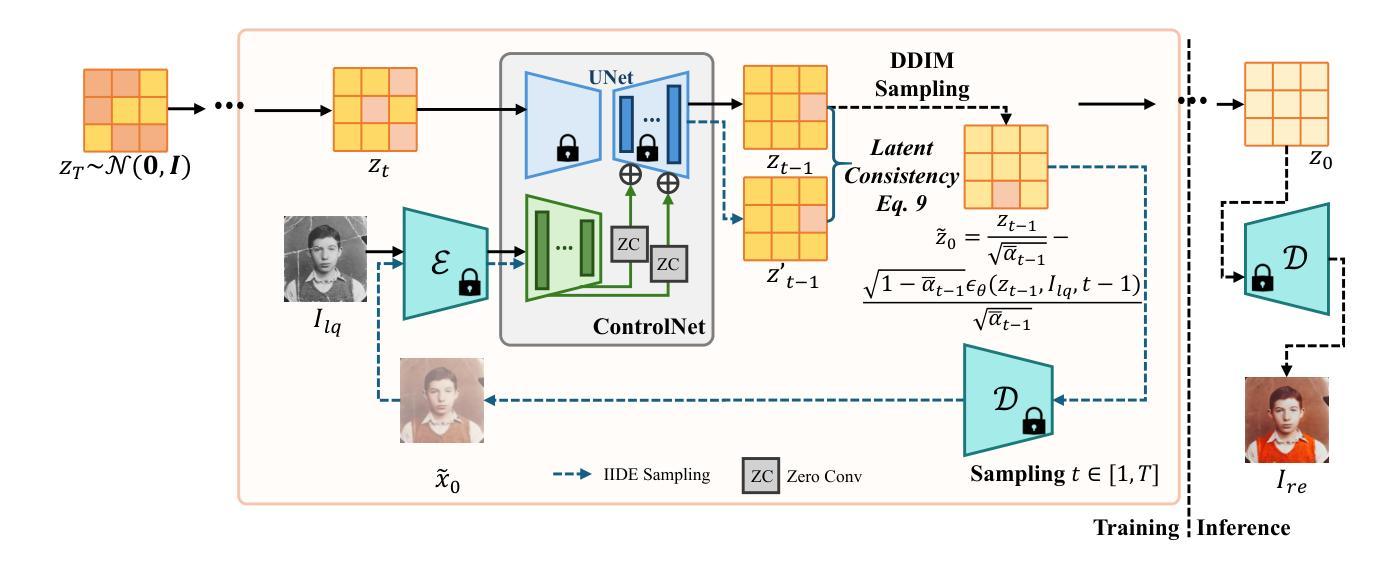
Restoring Real-World Images with an Internal Detail Enhancement Diffusion Model
Authors:Peng Xiao, Hongbo Zhao, Yijun Wang, Jianxin Lin
Restoring real-world degraded images, such as old photographs or low-resolution images, presents a significant challenge due to the complex, mixed degradations they exhibit, such as scratches, color fading, and noise. Recent data-driven approaches have struggled with two main challenges: achieving high-fidelity restoration and providing object-level control over colorization. While diffusion models have shown promise in generating high-quality images with specific controls, they often fail to fully preserve image details during restoration. In this work, we propose an internal detail-preserving diffusion model for high-fidelity restoration of real-world degraded images. Our method utilizes a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model as a generative prior, eliminating the need to train a model from scratch. Central to our approach is the Internal Image Detail Enhancement (IIDE) technique, which directs the diffusion model to preserve essential structural and textural information while mitigating degradation effects. The process starts by mapping the input image into a latent space, where we inject the diffusion denoising process with degradation operations that simulate the effects of various degradation factors. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models in both qualitative assessments and perceptual quantitative evaluations. Additionally, our approach supports text-guided restoration, enabling object-level colorization control that mimics the expertise of professional photo editing.
恢复真实世界中的退化图像,如旧照片或低分辨率图像,是一个巨大的挑战,因为它们表现出的复杂混合退化,如划痕、颜色褪色和噪声。最近的数据驱动方法面临两个主要挑战:实现高保真恢复和提供颜色化的对象级控制。尽管扩散模型在生成具有特定控制的高质量图像方面显示出潜力,但它们通常在恢复过程中无法完全保留图像细节。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种内部细节保留的扩散模型,用于高保真地恢复真实世界的退化图像。我们的方法利用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型作为生成先验,无需从头开始训练模型。我们的方法的核心是内部图像细节增强(IIDE)技术,该技术指导扩散模型在保留基本结构和纹理信息的同时,减轻退化效果。该过程首先将通过输入图像映射到潜在空间,然后我们在扩散去噪过程中注入退化操作,以模拟各种退化因素的影响。大量实验表明,我们的方法在定性和定量评估方面都显著优于最新模型。此外,我们的方法还支持文本引导的恢复,能够实现对象级的颜色控制,模拟专业照片编辑的专业水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于内部细节保留的扩散模型,用于恢复真实世界退化图像。该研究利用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型作为生成先验,无需从头开始训练模型。通过内部图像细节增强(IIDE)技术,该模型能够在扩散过程中保留重要的结构和纹理信息,同时减轻退化效果。实验证明,该方法在定性和感知定量评估方面都显著优于现有模型,并支持文本引导的恢复,能够实现对象级别的色彩化控制,模拟专业照片编辑的专长。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于内部细节保留的扩散模型,用于恢复真实世界退化图像。
- 利用预训练的Stable Diffusion模型作为生成先验,无需重新训练。
- 通过IIDE技术,能够在扩散过程中保留重要的结构和纹理信息。
- 减轻了图像退化效果,如划痕、颜色褪色和噪音。
- 在定性和定量评估方面都显著优于现有模型。
- 支持文本引导的恢复,实现对象级别的色彩化控制。
点此查看论文截图
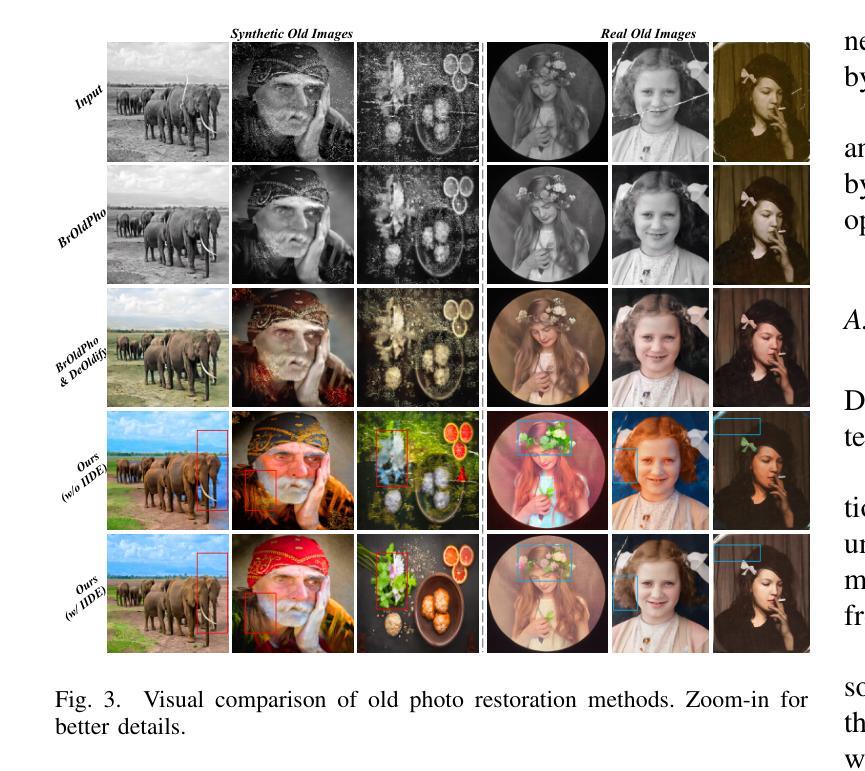


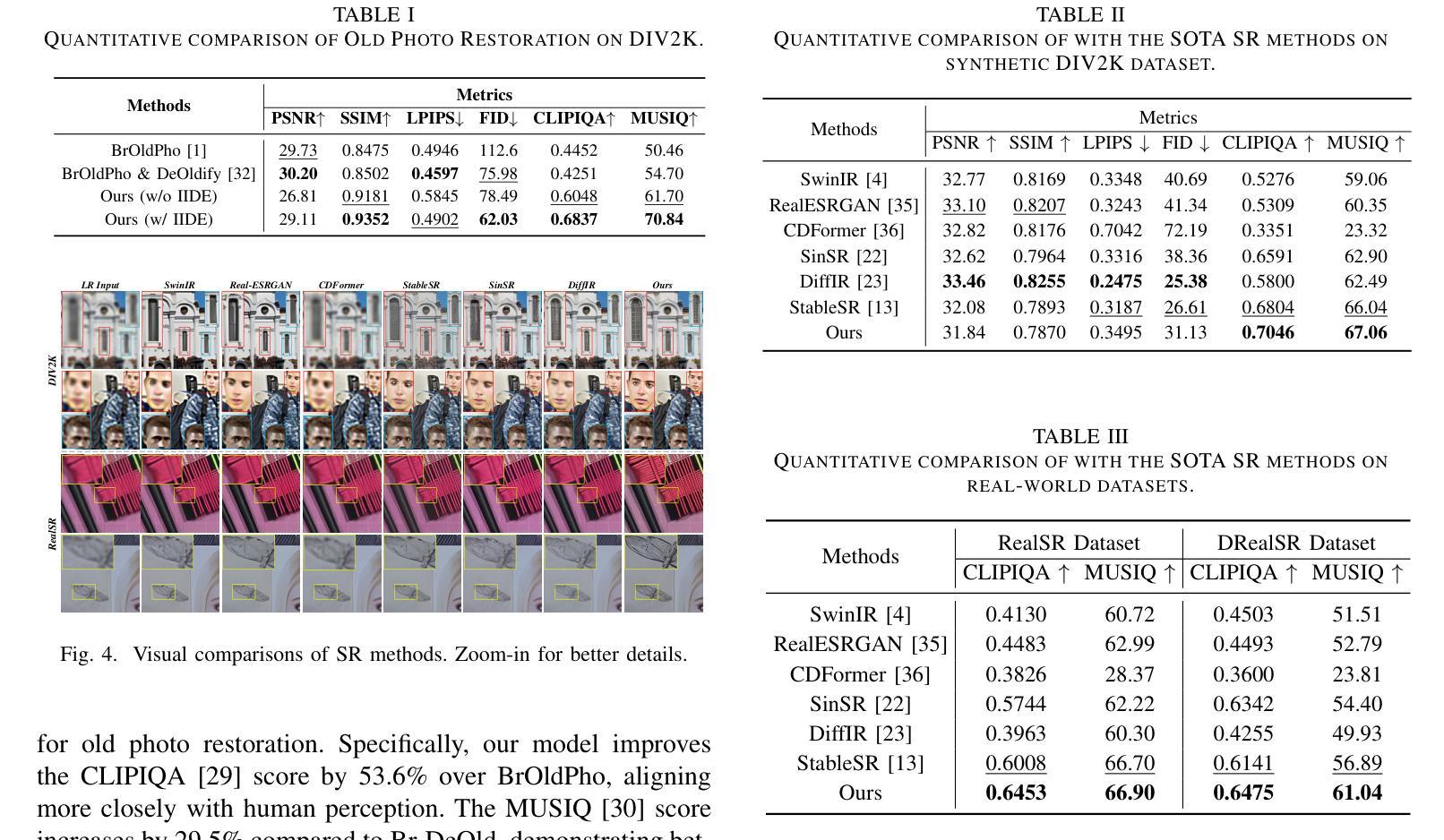
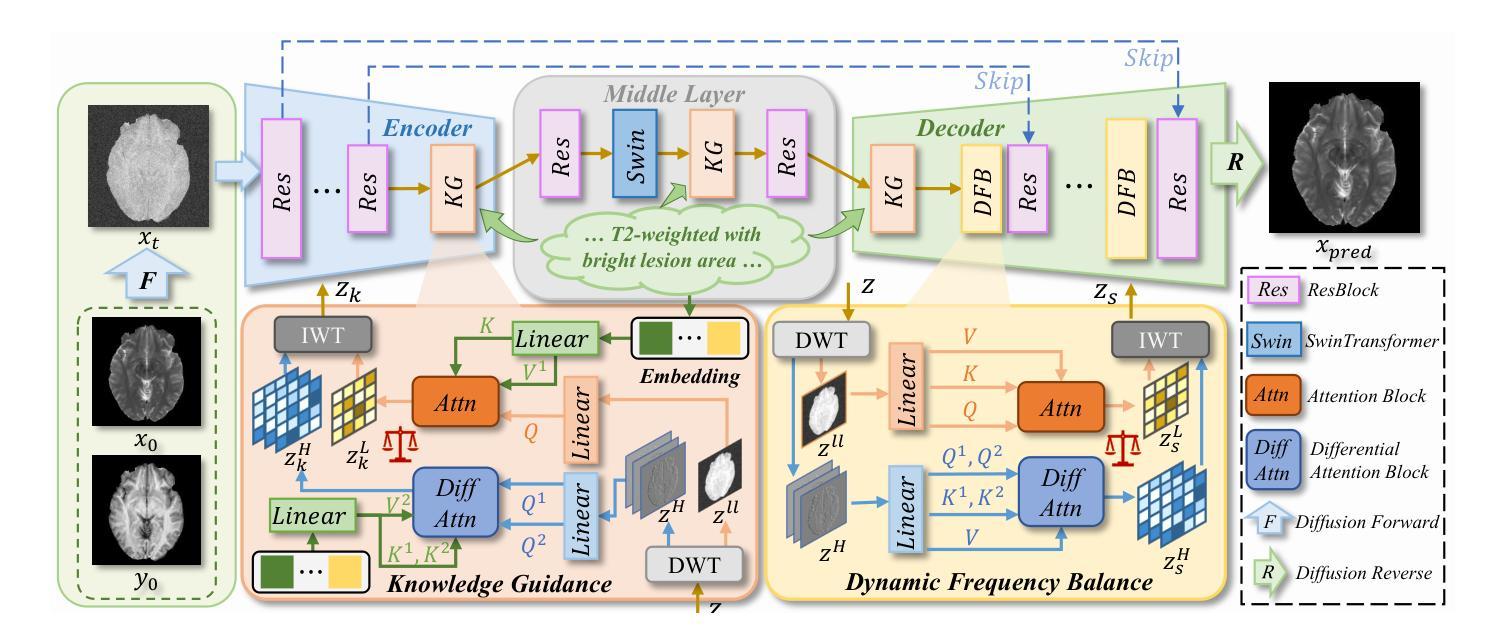
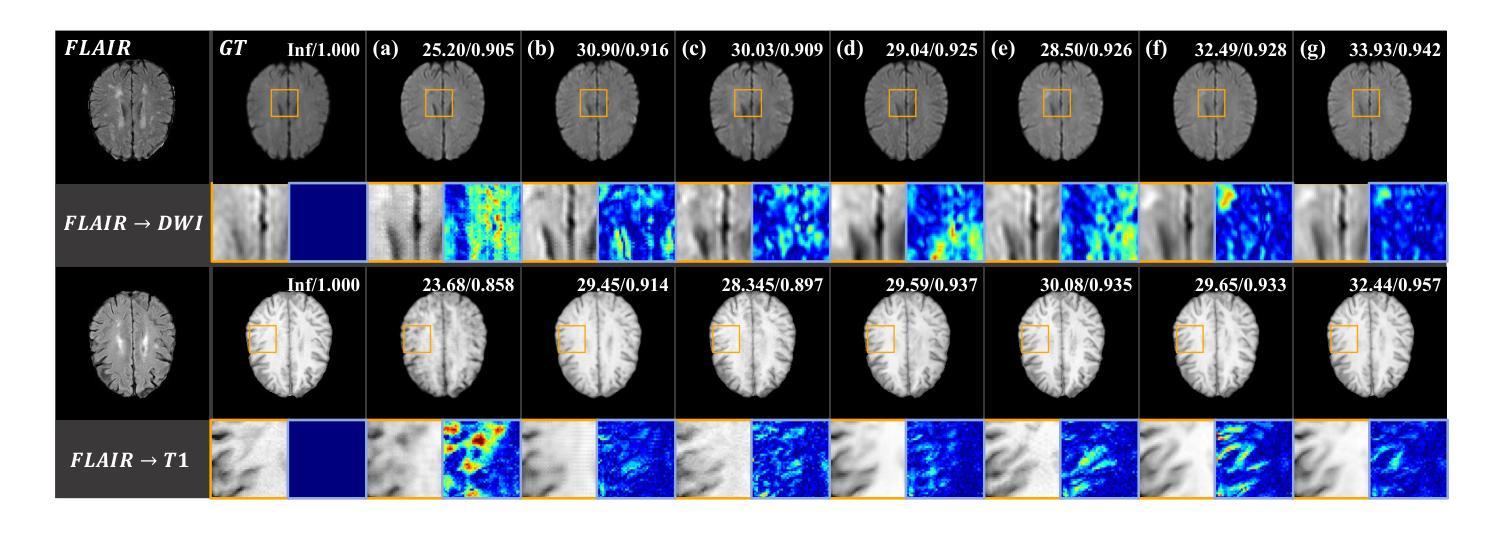
Structure-Accurate Medical Image Translation via Dynamic Frequency Balance and Knowledge Guidance
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Multimodal medical images play a crucial role in the precise and comprehensive clinical diagnosis. Diffusion model is a powerful strategy to synthesize the required medical images. However, existing approaches still suffer from the problem of anatomical structure distortion due to the overfitting of high-frequency information and the weakening of low-frequency information. Thus, we propose a novel method based on dynamic frequency balance and knowledge guidance. Specifically, we first extract the low-frequency and high-frequency components by decomposing the critical features of the model using wavelet transform. Then, a dynamic frequency balance module is designed to adaptively adjust frequency for enhancing global low-frequency features and effective high-frequency details as well as suppressing high-frequency noise. To further overcome the challenges posed by the large differences between different medical modalities, we construct a knowledge-guided mechanism that fuses the prior clinical knowledge from a visual language model with visual features, to facilitate the generation of accurate anatomical structures. Experimental evaluations on multiple datasets show the proposed method achieves significant improvements in qualitative and quantitative assessments, verifying its effectiveness and superiority.
多模态医学图像在精确全面的临床诊断中起着至关重要的作用。扩散模型是合成所需医学图像的一种强大策略。然而,现有方法仍存在因高频信息过度拟合而导致解剖结构失真以及低频信息减弱的问题。因此,我们提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识指导的新方法。具体来说,我们首先通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征来提取低频和高频成分。然后,设计了一个动态频率平衡模块,该模块可以自适应地调整频率,以增强全局低频特征和有效的高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。为了克服不同医学模态之间巨大差异所带来的挑战,我们构建了一个知识引导机制,该机制融合了来自视觉语言模型的先验临床知识与视觉特征,以促进准确解剖结构的生成。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,所提出的方法在定性和定量评估方面取得了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical image translation, Diffusion model, 16 pages
Summary
基于扩散模型的多模态医学图像合成在临床医学诊断中发挥着重要作用。针对现有方法存在的解剖结构扭曲问题,本文提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识引导的新方法。通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征,提取低频和高频成分,设计动态频率平衡模块自适应调整频率,增强全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。此外,本文构建了知识引导机制,融合了视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,以生成准确的解剖结构,解决了不同医学模态之间的差异问题。实验评估显示,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的定性定量改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像在临床诊断中的关键作用以及扩散模型在医学图像合成中的强大策略。
- 现有方法存在的解剖结构扭曲问题,主要是由于高频信息的过拟合和低频信息的减弱。
- 本文通过小波变换分解模型特征,提取低频和高频成分。
- 设计了动态频率平衡模块,自适应调整频率,以增强全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。
- 构建知识引导机制,融合视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,解决不同医学模态之间的差异问题。
- 实验评估显示,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进。
点此查看论文截图


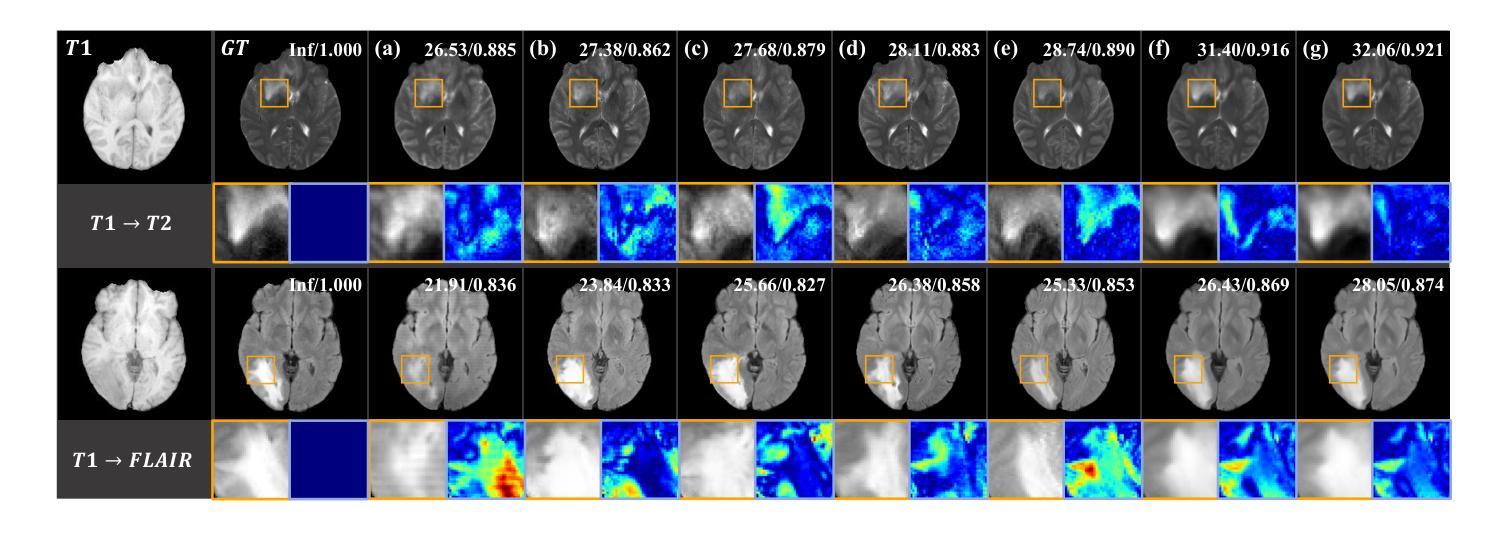
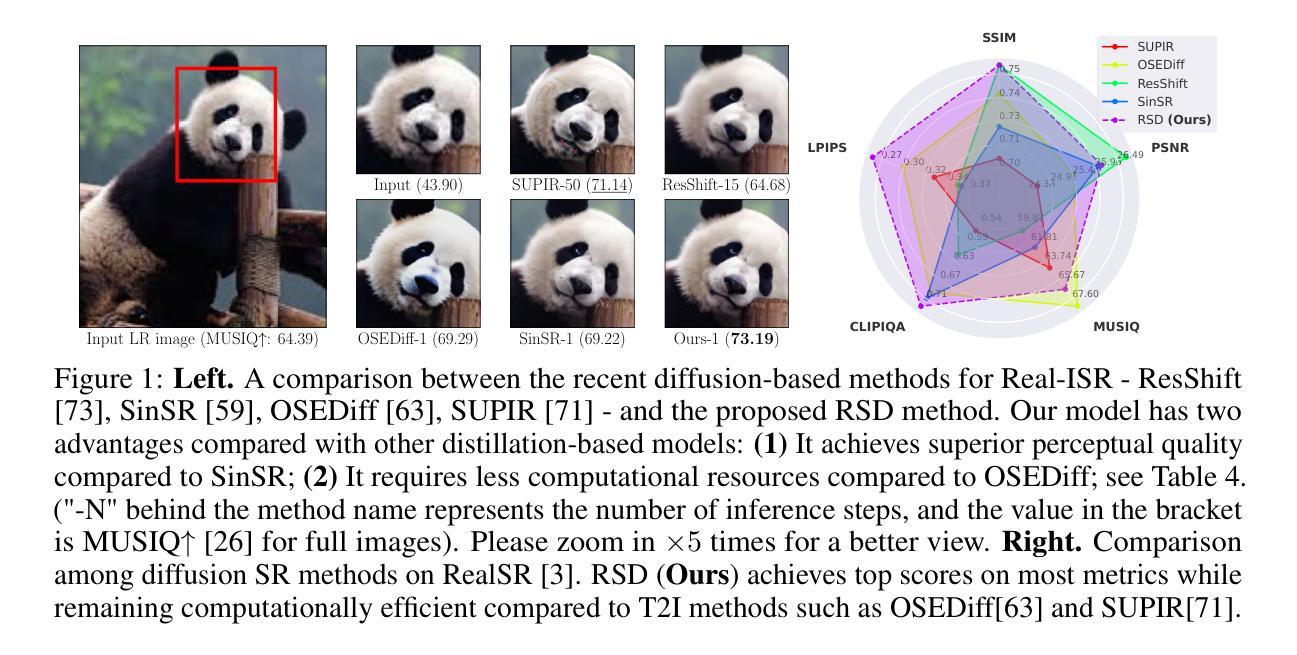
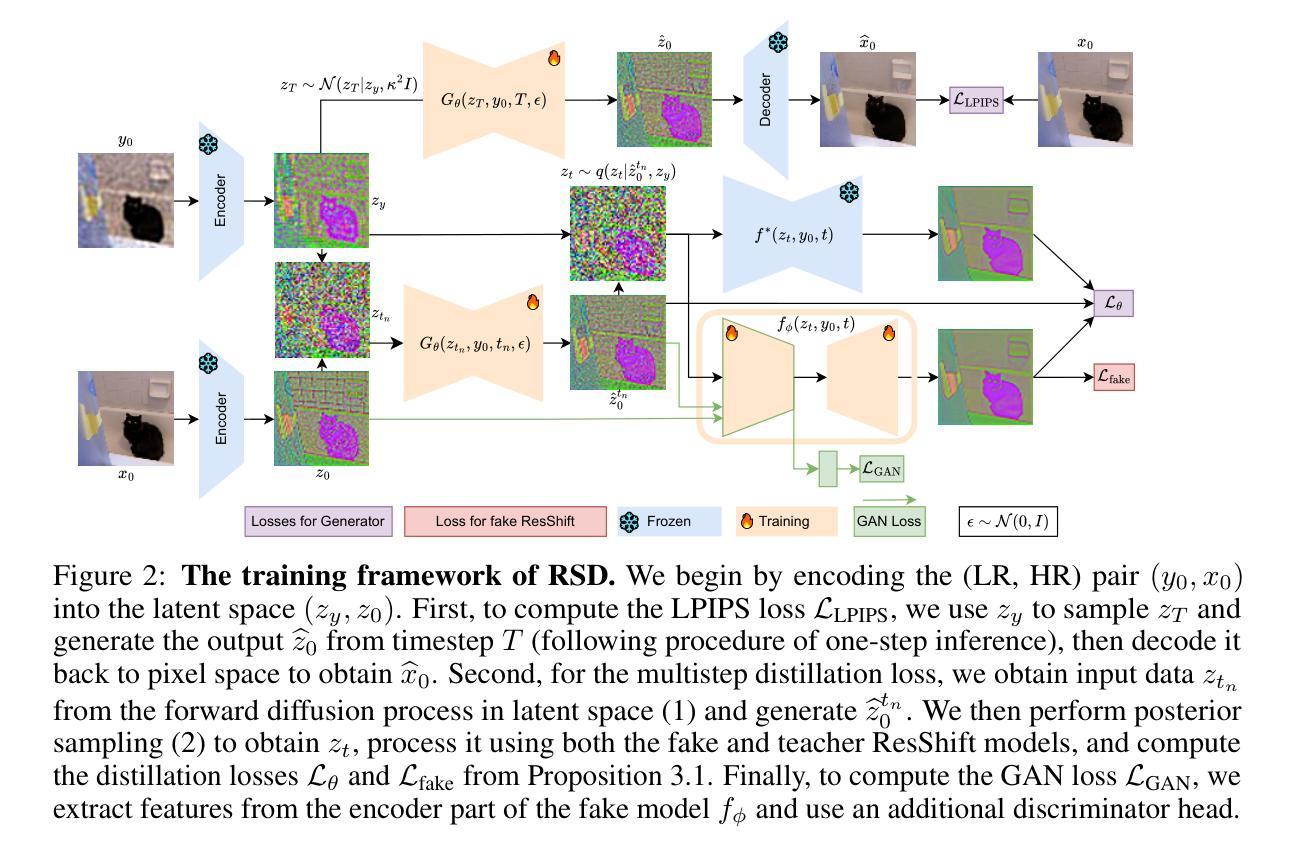
One-Step Residual Shifting Diffusion for Image Super-Resolution via Distillation
Authors:Daniil Selikhanovych, David Li, Aleksei Leonov, Nikita Gushchin, Sergei Kushneriuk, Alexander Filippov, Evgeny Burnaev, Iaroslav Koshelev, Alexander Korotin
Diffusion models for super-resolution (SR) produce high-quality visual results but require expensive computational costs. Despite the development of several methods to accelerate diffusion-based SR models, some (e.g., SinSR) fail to produce realistic perceptual details, while others (e.g., OSEDiff) may hallucinate non-existent structures. To overcome these issues, we present RSD, a new distillation method for ResShift, one of the top diffusion-based SR models. Our method is based on training the student network to produce such images that a new fake ResShift model trained on them will coincide with the teacher model. RSD achieves single-step restoration and outperforms the teacher by a large margin. We show that our distillation method can surpass the other distillation-based method for ResShift - SinSR - making it on par with state-of-the-art diffusion-based SR distillation methods. Compared to SR methods based on pre-trained text-to-image models, RSD produces competitive perceptual quality, provides images with better alignment to degraded input images, and requires fewer parameters and GPU memory. We provide experimental results on various real-world and synthetic datasets, including RealSR, RealSet65, DRealSR, ImageNet, and DIV2K.
扩散模型在超分辨率(SR)处理中能够产生高质量的视觉效果,但需要昂贵的计算成本。尽管已经开发了几种方法来加速基于扩散的SR模型,但一些方法(例如SinSR)无法产生逼真的感知细节,而其他方法(例如OSEDiff)可能会虚构不存在的结构。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了RSD,这是一种针对顶级基于扩散的SR模型之一ResShift的新型蒸馏方法。我们的方法基于训练学生网络来产生图像,这些图像会通过一个在新图像上训练的假冒ResShift模型与教师模型相吻合。RSD实现了单步恢复,并大幅超越了教师模型。我们展示了我们的蒸馏方法可以超越用于ResShift的其他基于蒸馏的方法——SinSR——使其与最先进的基于扩散的SR蒸馏方法相媲美。与基于预训练文本到图像模型的SR方法相比,RSD产生的感知质量具有竞争力,为退化输入图像提供了更好的图像对齐,并且需要更少的参数和GPU内存。我们在各种真实和合成数据集上提供了实验结果,包括RealSR、RealSet65、DRealSR、ImageNet和DIV2K。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在超分辨率(SR)处理中能够产生高质量图像,但计算成本较高。尽管已有多种加速扩散模型的方法,但仍存在一些问题,如SinSR无法产生真实的感知细节,而OSEDiff会产生不存在的结构。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的蒸馏方法RSD,用于顶级的扩散模型ResShift。该方法基于训练学生网络产生图像,使基于这些图像训练的新假ResShift模型与教师模型一致。RSD实现了单步恢复,并大幅超越了教师模型。实验结果显示,我们的蒸馏方法能超越SinSR等其它蒸馏方法,达到先进水平的扩散SR模型表现。与基于预训练文本图像的SR方法相比,RSD感知质量高,更贴合输入的低分辨率图像,并且需要的参数和GPU内存更小。实验效果在不同真实世界和合成数据集上得到验证。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在超分辨率处理中能产生高质量图像,但计算成本较高。
- 当前存在的加速扩散模型方法存在缺陷,如无法产生真实细节或产生不存在的结构。
- RSD是一种新型的蒸馏方法,用于优化顶级扩散模型ResShift的表现。
- RSD基于训练学生网络产生图像,使新假ResShift模型与教师模型一致。
- RSD实现了单步恢复,并大幅超越了教师模型的表现。
- RSD的蒸馏方法能超越其他蒸馏方法,达到先进水平的扩散SR模型表现。
- 与其他SR方法相比,RSD具有更高的感知质量、更贴合输入的低分辨率图像,且参数和GPU内存需求较小。实验效果在不同数据集上得到验证。
点此查看论文截图