⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
M3S-UPD: Efficient Multi-Stage Self-Supervised Learning for Fine-Grained Encrypted Traffic Classification with Unknown Pattern Discovery
Authors:Yali Yuan, Yu Huang, Xingjian Zeng, Hantao Mei, Guang Cheng
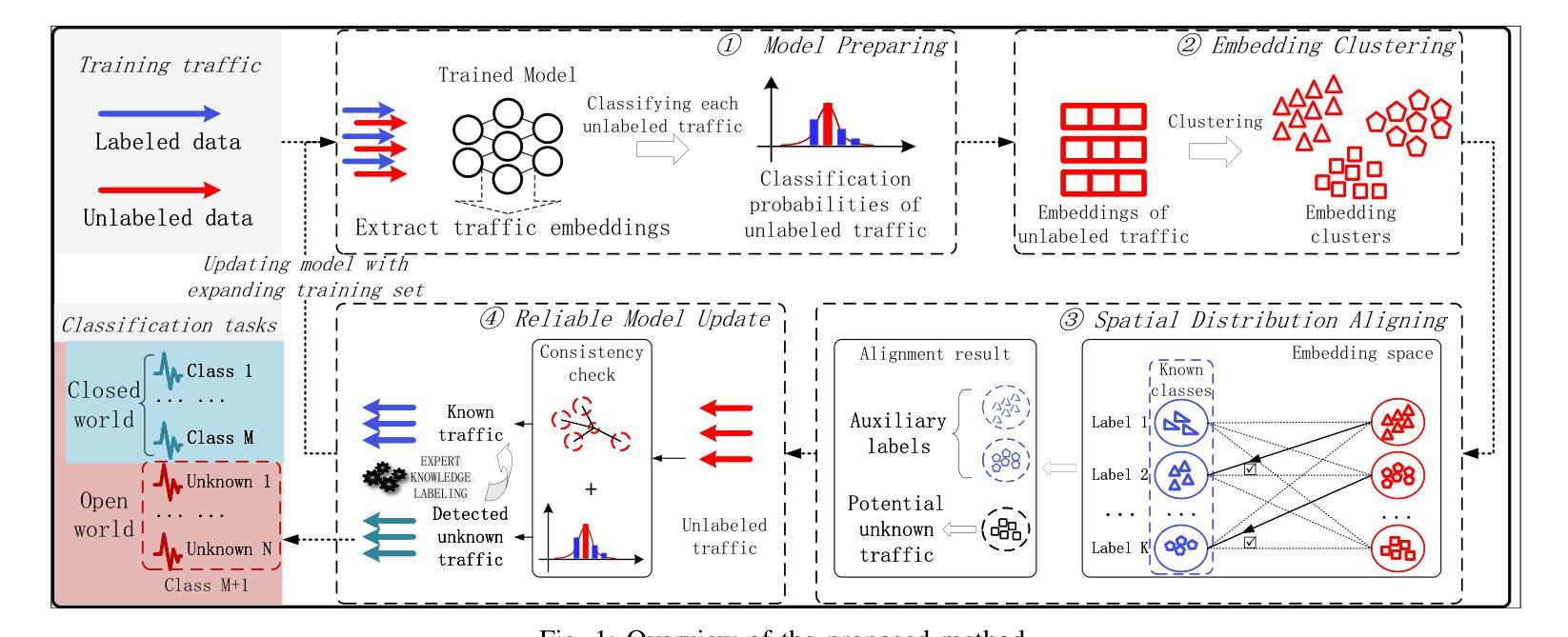
The growing complexity of encrypted network traffic presents dual challenges for modern network management: accurate multiclass classification of known applications and reliable detection of unknown traffic patterns. Although deep learning models show promise in controlled environments, their real-world deployment is hindered by data scarcity, concept drift, and operational constraints. This paper proposes M3S-UPD, a novel Multi-Stage Self-Supervised Unknown-aware Packet Detection framework that synergistically integrates semi-supervised learning with representation analysis. Our approach eliminates artificial segregation between classification and detection tasks through a four-phase iterative process: 1) probabilistic embedding generation, 2) clustering-based structure discovery, 3) distribution-aligned outlier identification, and 4) confidence-aware model updating. Key innovations include a self-supervised unknown detection mechanism that requires neither synthetic samples nor prior knowledge, and a continuous learning architecture that is resistant to performance degradation. Experimental results show that M3S-UPD not only outperforms existing methods on the few-shot encrypted traffic classification task, but also simultaneously achieves competitive performance on the zero-shot unknown traffic discovery task.
不断增长的加密网络流量复杂性给现代网络管理带来了双重挑战:准确的多类已知应用程序分类和可靠的未知流量模式检测。虽然深度学习模型在受控环境中表现出良好的前景,但它们在现实世界部署中受到数据稀缺、概念漂移和操作约束的阻碍。本文提出了M3S-UPD,一种新颖的多阶段自监督未知感知数据包检测框架,协同整合了半监督学习与表示分析。我们的方法通过四阶段迭代过程消除了分类和检测任务之间人为的分割:1)概率嵌入生成,2)基于聚类的结构发现,3)分布对齐异常值识别,以及4)基于信心的模型更新。关键创新包括无需合成样本或先验知识的自监督未知检测机制和抵抗性能退化的持续学习架构。实验结果表明,M3S-UPD不仅在少数加密流量分类任务上优于现有方法,而且在零样本未知流量发现任务上也实现了竞争性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文针对现代网络管理所面临的已知应用多类分类和未知流量模式检测双重挑战,提出了一种新颖的多阶段自监督未知感知数据包检测框架M3S-UPD。该框架通过整合半监督学习与表示分析,实现了无需人工分割分类与检测任务的能力。其核心创新点包括自监督未知检测机制和抗性能下降的连续学习架构。实验结果显示,M3S-UPD不仅在少样本加密流量分类任务上表现优异,同时在零样本未知流量发现任务上也具备竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- M3S-UPD框架解决了现代网络管理中加密网络流量分类和未知流量检测的挑战。
- 该框架通过整合半监督学习与表示分析,消除了分类和检测任务的人工分割。
- M3S-UPD采用四阶段迭代过程,包括概率嵌入生成、基于聚类的结构发现、分布对齐的异常值识别和信心感知模型更新。
- 框架的关键创新点包括自监督未知检测机制和抗性能下降的连续学习架构。
- 实验结果显示,M3S-UPD在少样本加密流量分类任务上表现优异。
- M3S-UPD在零样本未知流量发现任务上具备竞争力。
- 该框架无需合成样本和先验知识,即可实现未知检测机制。
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Large Language Models for Bengali Math Word Problem Solving with Chain of Thought Reasoning
Authors:Bidyarthi Paul, Jalisha Jashim Era, Mirazur Rahman Zim, Tahmid Sattar Aothoi, Faisal Muhammad Shah
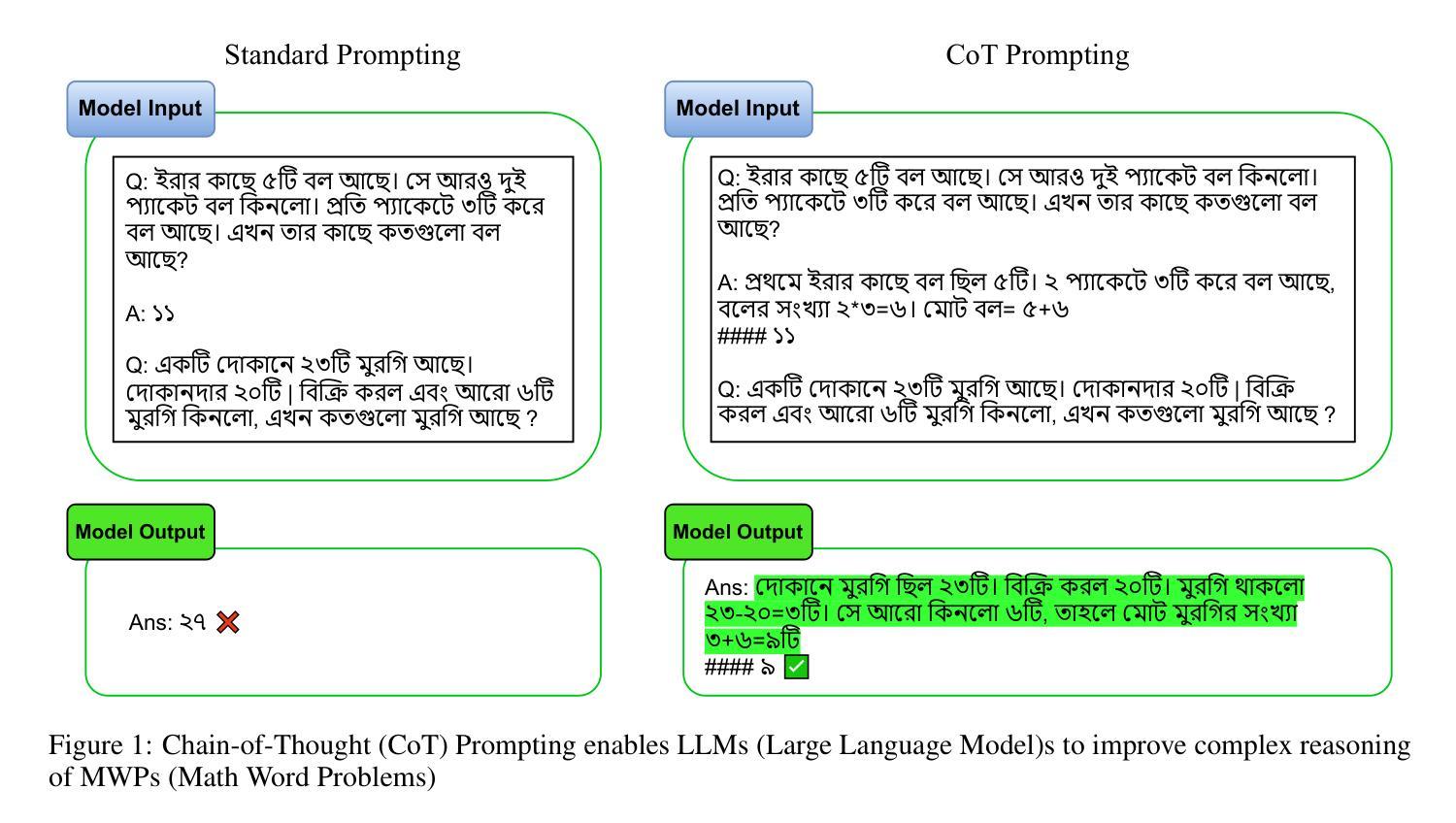
Solving Bengali Math Word Problems (MWPs) remains a major challenge in natural language processing (NLP) due to the language’s low-resource status and the multi-step reasoning required. Existing models struggle with complex Bengali MWPs, largely because no human-annotated Bengali dataset has previously addressed this task. This gap has limited progress in Bengali mathematical reasoning. To address this, we created SOMADHAN, a dataset of 8792 complex Bengali MWPs with manually written, step-by-step solutions. We designed this dataset to support reasoning-focused evaluation and model development in a linguistically underrepresented context. Using SOMADHAN, we evaluated a range of large language models (LLMs) - including GPT-4o, GPT-3.5 Turbo, LLaMA series models, Deepseek, and Qwen - through both zero-shot and few-shot prompting with and without Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning. CoT prompting consistently improved performance over standard prompting, especially in tasks requiring multi-step logic. LLaMA-3.3 70B achieved the highest accuracy of 88% with few-shot CoT prompting. We also applied Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune models efficiently, enabling them to adapt to Bengali MWPs with minimal computational cost. Our work fills a critical gap in Bengali NLP by providing a high-quality reasoning dataset and a scalable framework for solving complex MWPs. We aim to advance equitable research in low-resource languages and enhance reasoning capabilities in educational and language technologies.
解决孟加拉数学文字题(Math Word Problems, MWPs)仍然是自然语言处理(NLP)领域的一个重大挑战,这是由于孟加拉语的资源相对较少以及需要多步骤推理。现有模型在处理复杂的孟加拉数学文字题时遇到困难,很大程度上是因为之前没有人对孟加拉语数据集进行这方面的标注工作。这一空白限制了孟加拉数学推理的进步。为了解决这个问题,我们创建了SOMADHAN数据集,其中包含8792个复杂的孟加拉数学文字题以及手动编写的逐步解答。我们设计这个数据集是为了支持在语言学表达不足的情境中进行推理评估模型的发展。使用SOMADHAN数据集,我们评估了一系列大型语言模型(LLMs),包括GPT-4o、GPT-3.5 Turbo、LLaMA系列模型、Deepseek和Qwen等,通过零样本和少样本提示以及有无思维链(Chain of Thought, CoT)推理的方法进行评估。思维链提示法始终提高了性能,尤其是在需要多步骤逻辑的任务中。LLaMA-3.3 70B在少样本思维链提示下取得了88%的最高准确率。我们还应用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法来有效地微调模型,使其能够适应孟加拉数学文字题,同时保持较低的计算成本。我们的工作通过提供高质量推理数据集和解决复杂数学文字题的可扩展框架来填补孟加拉NLP领域的空白。我们的目标是推动低资源语言的公平研究,并提升教育和语言技术中的推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了解决孟加拉数学文字题(MWPs)的挑战,由于孟加拉语的低资源状态和多步骤推理的需求,现有的模型难以处理复杂的孟加拉数学文字题。为此,研究者创建了SOMADHAN数据集,包含8792个复杂的孟加拉数学文字题及其逐步解决方案。使用SOMADHAN数据集,研究者评估了一系列大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本提示下的表现,发现链式思维(CoT)提示在需要多步骤逻辑的任务中表现尤为出色。LLaMA-3.3 70B在少样本CoT提示下取得了最高的88%准确率。此外,研究者还应用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法高效微调模型,使其能够迅速适应孟加拉数学文字题。此研究填补了孟加拉NLP领域的关键空白,为复杂数学文字题的处理提供了高质量推理数据集和可扩展框架。旨在推动低资源语言的研究公平性和提升教育和语言技术中的推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 解决孟加拉数学文字题是NLP领域的一大挑战,因低资源状态和多步骤推理需求导致现有模型难以应对。
- 创建了SOMADHAN数据集,包含复杂孟加拉数学文字题及其逐步解决方案,支持推理评估与模型发展。
- 链式思维(CoT)提示在大型语言模型(LLMs)中表现优越,尤其在需要多步骤逻辑的任务中。
- LLaMA-3.3 70B在少样本CoT提示下表现最佳,准确率为88%。
- 应用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法,能高效微调模型以适应孟加拉数学文字题。
- 该研究填补了孟加拉NLP领域的空白,提供了高质量推理数据集和复杂数学文字题的解决方案框架。
点此查看论文截图

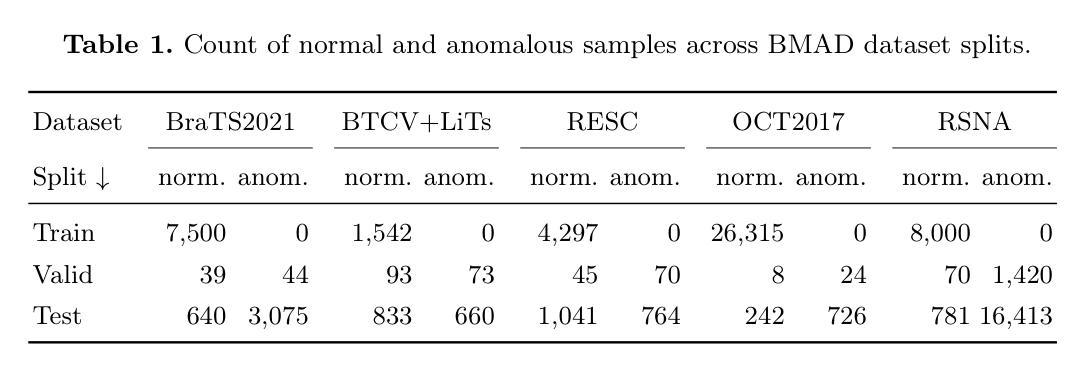
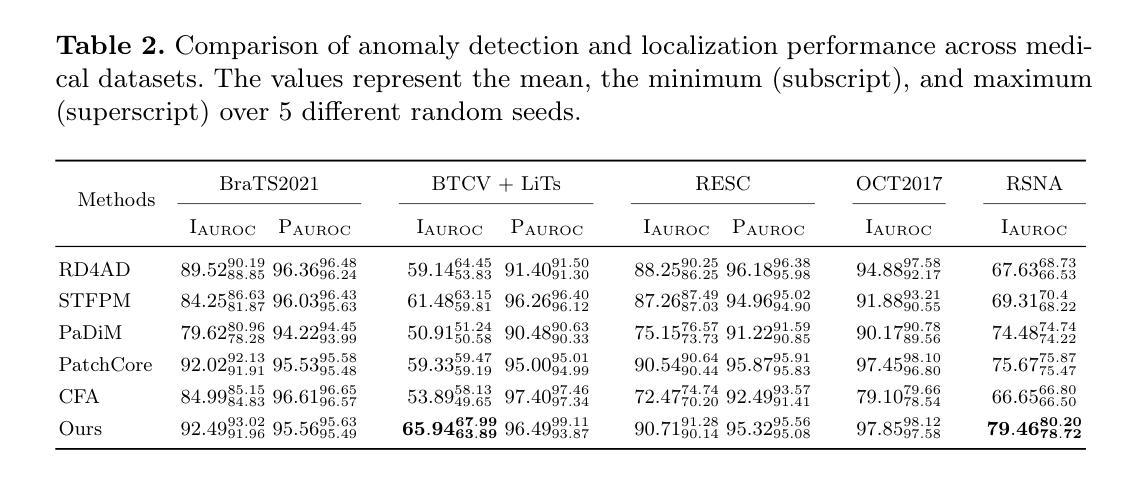
Is Hyperbolic Space All You Need for Medical Anomaly Detection?
Authors:Alvaro Gonzalez-Jimenez, Simone Lionetti, Ludovic Amruthalingam, Philippe Gottfrois, Fabian Gröger, Marc Pouly, Alexander A. Navarini
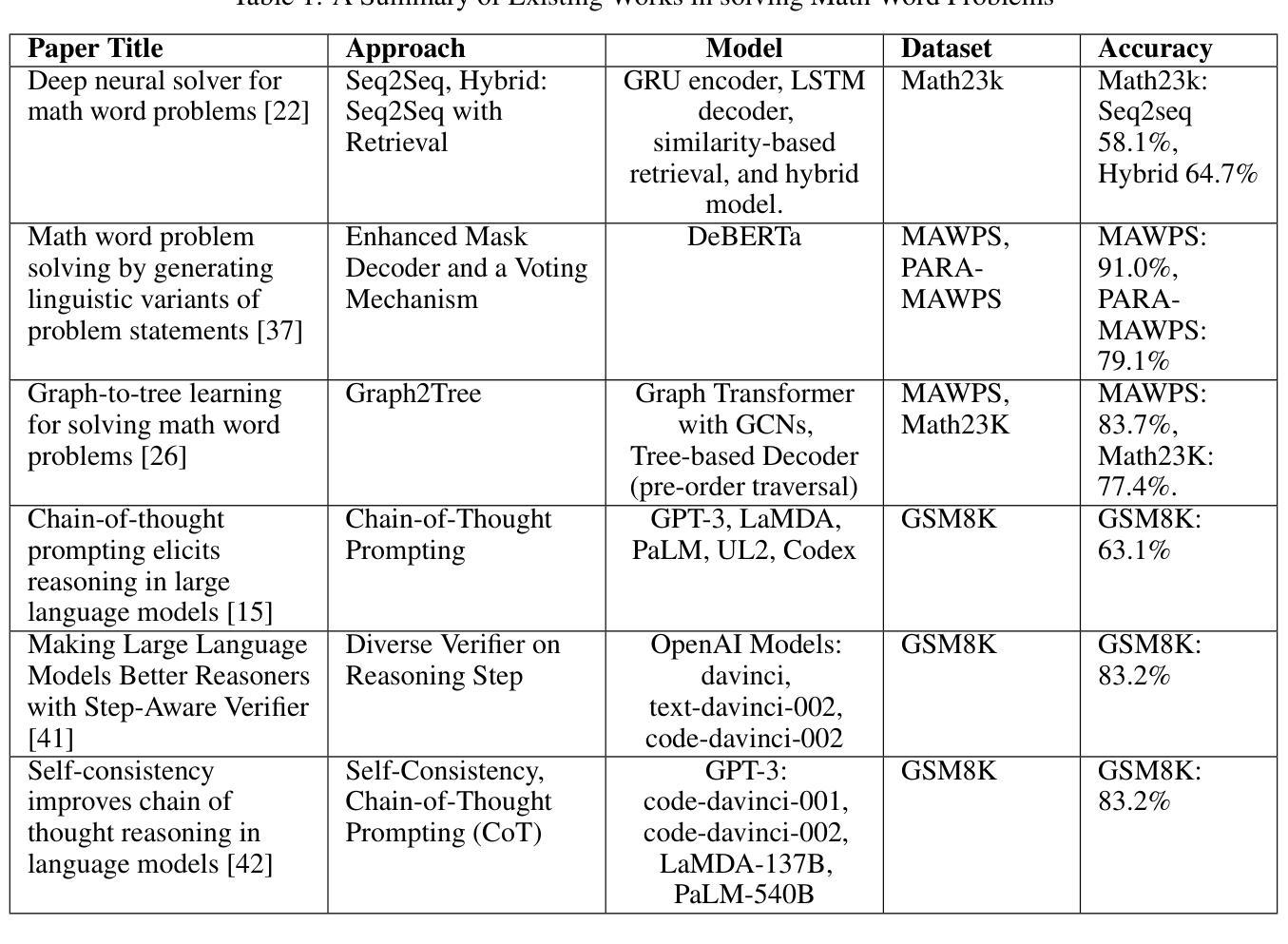
Medical anomaly detection has emerged as a promising solution to challenges in data availability and labeling constraints. Traditional methods extract features from different layers of pre-trained networks in Euclidean space; however, Euclidean representations fail to effectively capture the hierarchical relationships within these features, leading to suboptimal anomaly detection performance. We propose a novel yet simple approach that projects feature representations into hyperbolic space, aggregates them based on confidence levels, and classifies samples as healthy or anomalous. Our experiments demonstrate that hyperbolic space consistently outperforms Euclidean-based frameworks, achieving higher AUROC scores at both image and pixel levels across multiple medical benchmark datasets. Additionally, we show that hyperbolic space exhibits resilience to parameter variations and excels in few-shot scenarios, where healthy images are scarce. These findings underscore the potential of hyperbolic space as a powerful alternative for medical anomaly detection. The project website can be found at https://hyperbolic-anomalies.github.io
医学异常检测已成为解决数据可用性和标签约束挑战的有前途的解决方案。传统方法从欧几里得空间的预训练网络的不同层次中提取特征;然而,欧几里得表示法无法有效地捕获这些特征内的层次关系,导致异常检测性能不佳。我们提出了一种新颖而简单的方法,将特征表示投影到双曲空间,基于置信度水平进行聚合,并将样本分类为正常或异常。我们的实验表明,双曲空间始终优于基于欧几里得德的框架,在多个医学基准数据集上,无论是在图像还是像素级别,都实现了更高的AUROC分数。此外,我们还展示了双曲空间对参数变化的稳健性,并在健康图像稀缺的少量场景中表现出色。这些发现强调了双曲空间作为医学异常检测的有力替代方法的潜力。项目网站地址为:https://hyperbolic-anomalies.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Provisionally Accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了医疗异常检测的挑战及解决方案。传统方法在欧几里得空间提取预训练网络的不同层特征,但无法有效捕捉这些特征中的层次关系,导致异常检测性能不佳。本文提出了一种新的简单方法,将特征表示投影到双曲空间,基于置信度进行聚合,并分类为正常或异常样本。实验表明,双曲空间在多个医疗基准数据集上始终优于基于欧几里得空间的框架,并在图像和像素级别均获得更高的AUROC分数。此外,该研究还显示双曲空间对参数变化具有韧性,并在健康图像稀缺的少数场景中表现出色。这为双曲空间在医疗异常检测中的潜力提供了有力证据。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗异常检测面临数据可用性和标签约束的挑战。
- 传统方法在欧几里得空间提取特征,但无法有效捕捉层次关系,导致检测性能不佳。
- 引入了一种新方法,将特征表示投影到双曲空间进行分类。
- 双曲空间在多个医疗数据集上表现优于欧几里得空间方法。
- 双曲空间方法具有较高的AUROC分数,适用于图像和像素级别检测。
- 双曲空间对参数变化具有韧性,并在少数场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

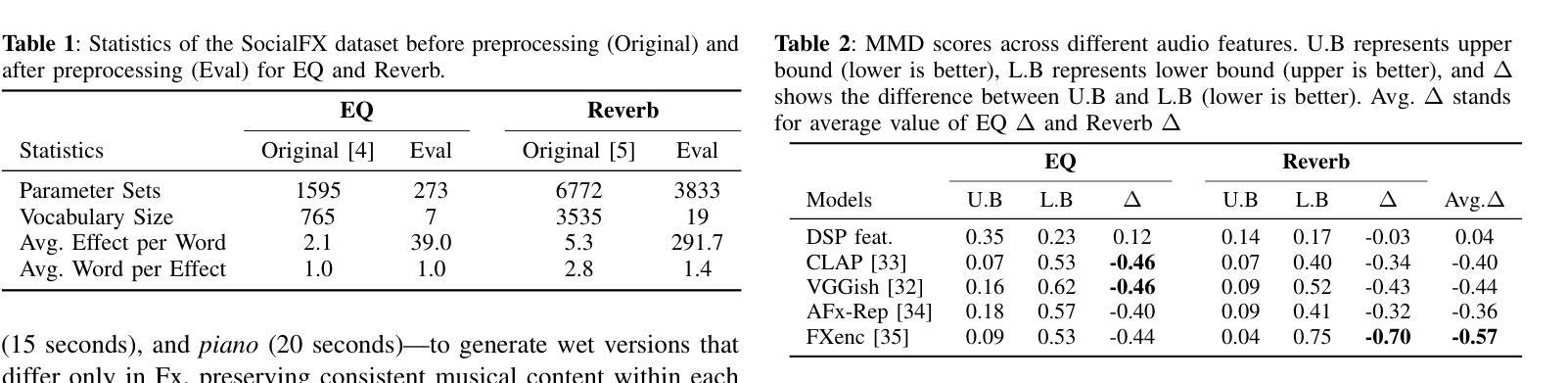
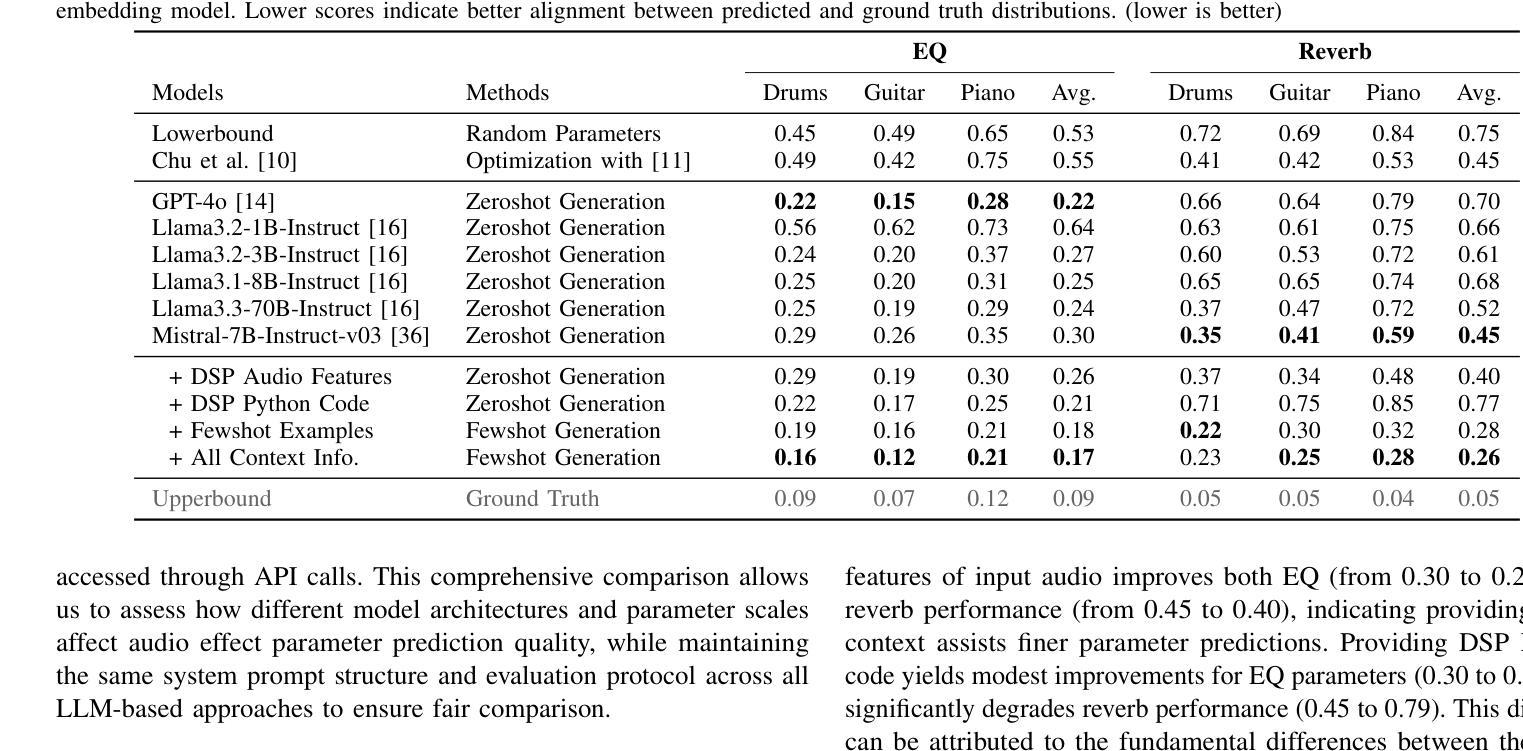
Can Large Language Models Predict Audio Effects Parameters from Natural Language?
Authors:Seungheon Doh, Junghyun Koo, Marco A. Martínez-Ramírez, Wei-Hsiang Liao, Juhan Nam, Yuki Mitsufuji
In music production, manipulating audio effects (Fx) parameters through natural language has the potential to reduce technical barriers for non-experts. We present LLM2Fx, a framework leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to predict Fx parameters directly from textual descriptions without requiring task-specific training or fine-tuning. Our approach address the text-to-effect parameter prediction (Text2Fx) task by mapping natural language descriptions to the corresponding Fx parameters for equalization and reverberation. We demonstrate that LLMs can generate Fx parameters in a zero-shot manner that elucidates the relationship between timbre semantics and audio effects in music production. To enhance performance, we introduce three types of in-context examples: audio Digital Signal Processing (DSP) features, DSP function code, and few-shot examples. Our results demonstrate that LLM-based Fx parameter generation outperforms previous optimization approaches, offering competitive performance in translating natural language descriptions to appropriate Fx settings. Furthermore, LLMs can serve as text-driven interfaces for audio production, paving the way for more intuitive and accessible music production tools.
在音乐制作中,通过自然语言操作音频效果(Fx)参数具有降低非专家技术壁垒的潜力。我们推出了LLM2Fx框架,该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)直接从文本描述预测Fx参数,无需特定任务训练或微调。我们的方法通过自然语言描述映射到相应的Fx参数来解决文本到效果参数预测(Text2Fx)任务,这些参数用于均衡和混响。我们证明了LLM能够以零样本的方式生成Fx参数,这阐明了音乐制作中音色语义和音频效果之间的关系。为了提高性能,我们引入了三种类型的上下文示例:音频数字信号处理(DSP)特征、DSP函数代码和少量示例。我们的结果表明,基于LLM的Fx参数生成优于以前的优化方法,在将自然语言描述翻译成适当的Fx设置方面表现出竞争力。此外,LLM可以作为音频制作的文本驱动界面,为更直观和可访问的音乐制作工具铺平道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to WASPAA 2025
Summary
基于自然语言描述预测音频效果参数具有降低音乐制作中非专家技术门槛的潜力。本研究提出了LLM2Fx框架,利用大型语言模型(LLMs)直接根据文本描述预测音频效果参数,无需特定任务训练和微调。本研究通过映射自然语言描述到均衡和混响的相应效果参数,解决了文本到效果参数预测(Text2Fx)的任务。研究结果表明,LLM可以在零样本的情况下生成效果参数,揭示了音乐制作中音色语义和音频效果之间的关系。引入三种类型的上下文实例——音频数字信号处理(DSP)特征、DSP函数代码和少量实例——以增强性能。与先前的优化方法相比,基于LLM的效果参数生成表现出卓越性能,在自然语言描述转化为适当的音效设置方面表现出竞争力。此外,LLM可作为音频制作的文本驱动界面,为音乐制作工具提供更直观和可访问的途径。
Key Takeaways
- LLM2Fx框架利用大型语言模型(LLMs)预测音频效果(Fx)参数,降低非专家在音乐制作中的技术壁垒。
- 文本直接预测Fx参数,无需特定任务训练和微调。
- 通过映射自然语言和均衡、混响效果参数的对应关系来解决Text2Fx任务。
- LLM能够在零样本情况下生成Fx参数,揭示音色语义与音频效果的关系。
- 引入DSP特征、DSP函数代码和少量实例三种类型的上下文实例以增强性能。
- 基于LLM的Fx参数生成方法优于先前的优化方法,在自然语言描述转化为适当的音效设置方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

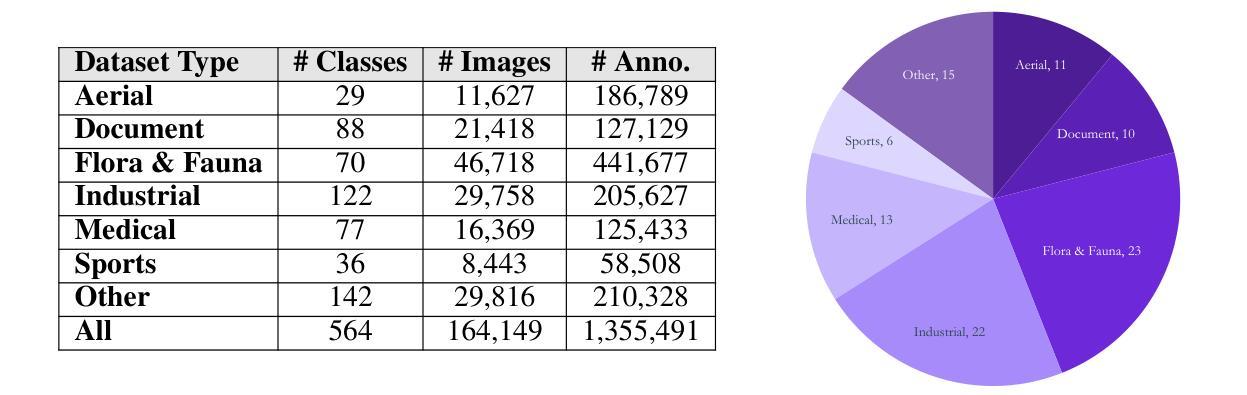
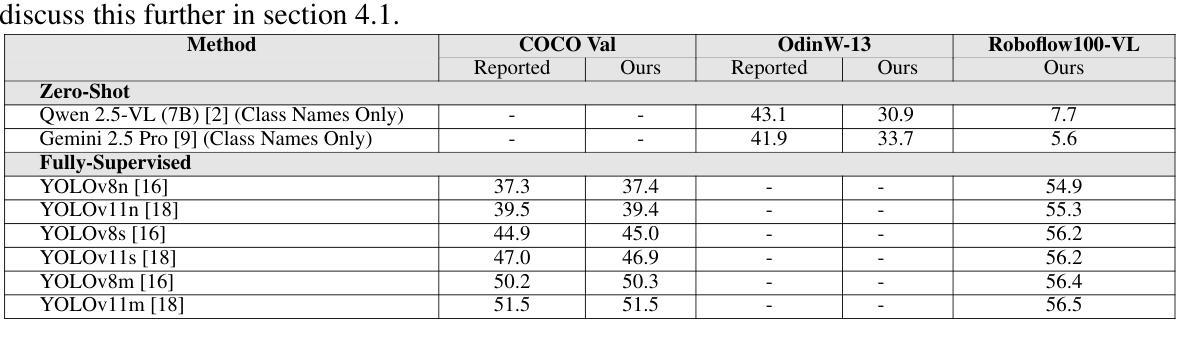
Roboflow100-VL: A Multi-Domain Object Detection Benchmark for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Peter Robicheaux, Matvei Popov, Anish Madan, Isaac Robinson, Joseph Nelson, Deva Ramanan, Neehar Peri
Vision-language models (VLMs) trained on internet-scale data achieve remarkable zero-shot detection performance on common objects like car, truck, and pedestrian. However, state-of-the-art models still struggle to generalize to out-of-distribution classes, tasks and imaging modalities not typically found in their pre-training. Rather than simply re-training VLMs on more visual data, we argue that one should align VLMs to new concepts with annotation instructions containing a few visual examples and rich textual descriptions. To this end, we introduce Roboflow100-VL, a large-scale collection of 100 multi-modal object detection datasets with diverse concepts not commonly found in VLM pre-training. We evaluate state-of-the-art models on our benchmark in zero-shot, few-shot, semi-supervised, and fully-supervised settings, allowing for comparison across data regimes. Notably, we find that VLMs like GroundingDINO and Qwen2.5-VL achieve less than 2% zero-shot accuracy on challenging medical imaging datasets within Roboflow100-VL, demonstrating the need for few-shot concept alignment. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/ and https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/
视觉语言模型(VLMs)通过在互联网规模的数据上进行训练,在常见对象(如汽车、卡车和行人)上实现了显著的零样本检测性能。然而,最先进的模型仍然难以推广到其预训练中没有出现的类别、任务以及成像模式。我们主张不应仅仅通过更多的视觉数据重新训练VLMs,而应该通过包含少量视觉示例和丰富文本描述的注释指令来对齐VLMs以理解新概念。为此,我们推出了Roboflow100-VL,这是一系列包含一百个多模态对象检测数据集的大规模集合,其中包含的概念在VLM预训练中并不常见。我们在我们的基准测试上对最先进的模型进行了零样本、少样本、半监督和完全监督环境下的评估,允许跨数据体制进行比较。值得注意的是,我们发现像GroundingDINO和Qwen2.5-VL这样的VLM在Roboflow100-VL中具有挑战性的医学影像数据集上的零样本准确率低于2%,这证明了进行少样本概念对齐的必要性。我们的代码和数据集可在https://github.com/roboflow/rf100-vl/和https://universe.roboflow.com/rf100-vl/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
训练于互联网规模数据的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在常见物体上的零样本检测性能出色,如汽车、卡车和行人。然而,最先进的模型在泛化到非常见类别、任务和成像模式时仍面临挑战。为此,我们引入了Roboflow100-VL,这是一套包含100个多模式对象检测数据集的大规模集合,其中包含各种不常见于VLM预训练的概念。我们评估了在不同设置下的先进模型,包括零样本、小样本次、半监督和全监督设置,以便在不同数据体系中进行比较。研究发现,在Roboflow100-VL中的具有挑战性的医学影像数据集上,VLMs的零样本准确率低于2%,这凸显了少量样本概念对齐的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在常见物体上的零样本检测表现优秀。
- 最先进的VLMs在泛化到非常见类别、任务和成像模式时遇到困难。
- Roboflow100-VL是一个包含多样概念的大规模多模态对象检测数据集。
- 在Roboflow100-VL的医学影像数据集上,VLMs的零样本准确率较低。
- 需要通过少量样本进行概念对齐来提升VLMs的性能。
- 研究提供了在不同设置下评估模型性能的平台。
点此查看论文截图




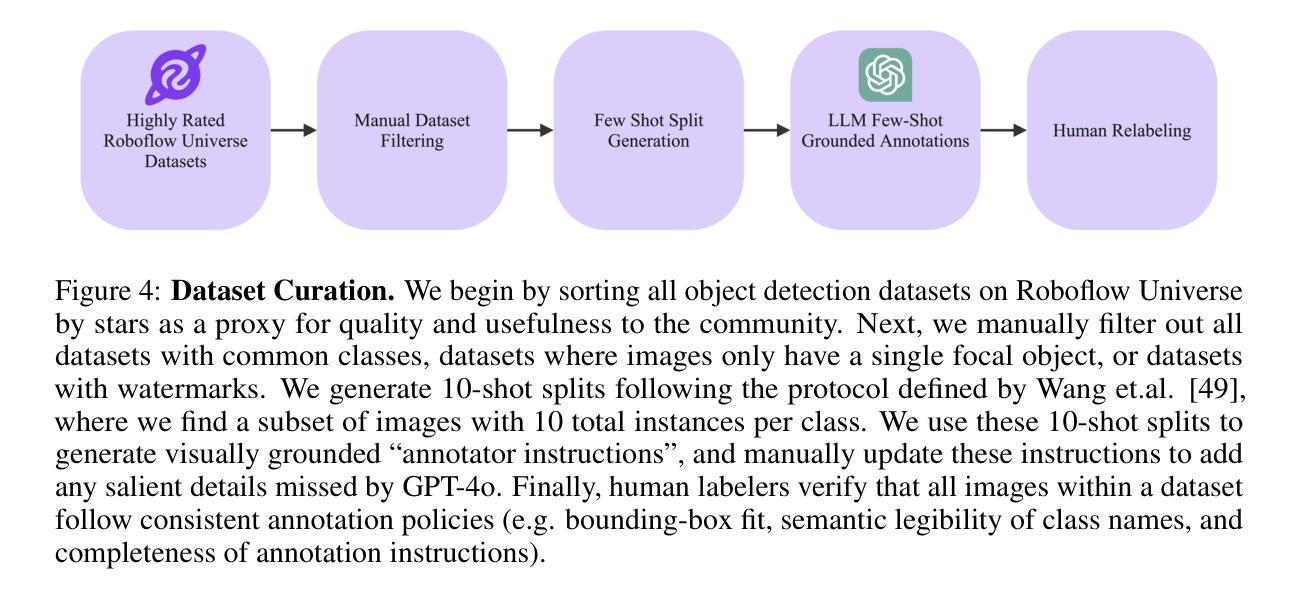
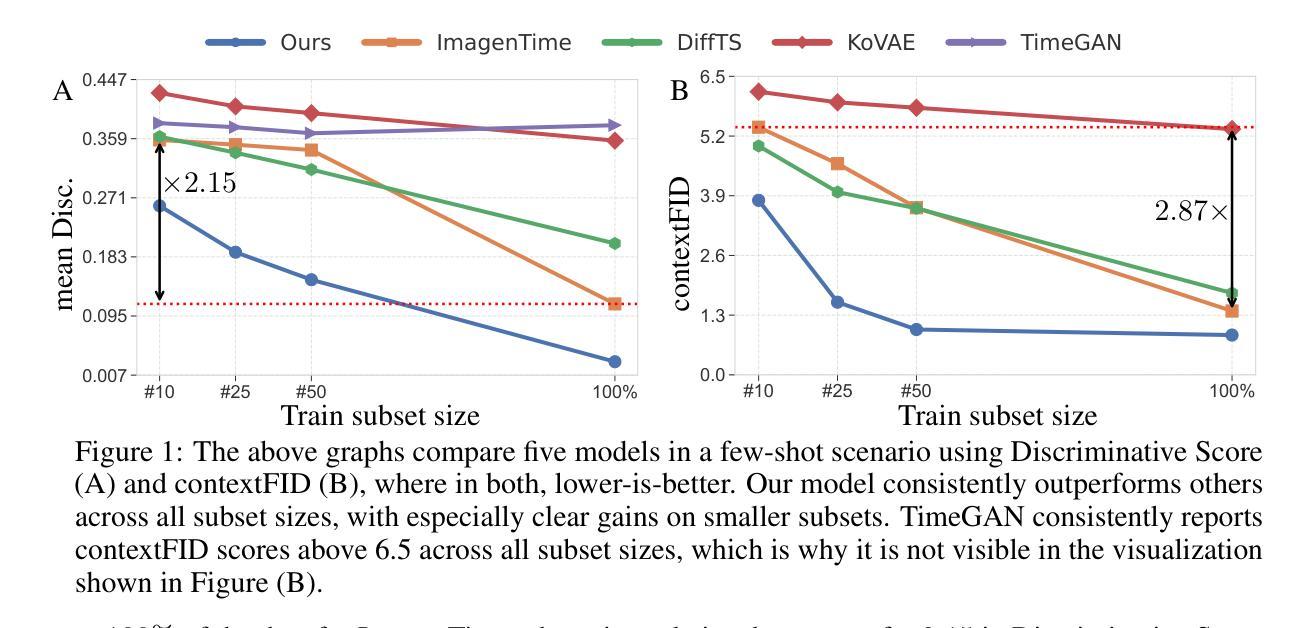
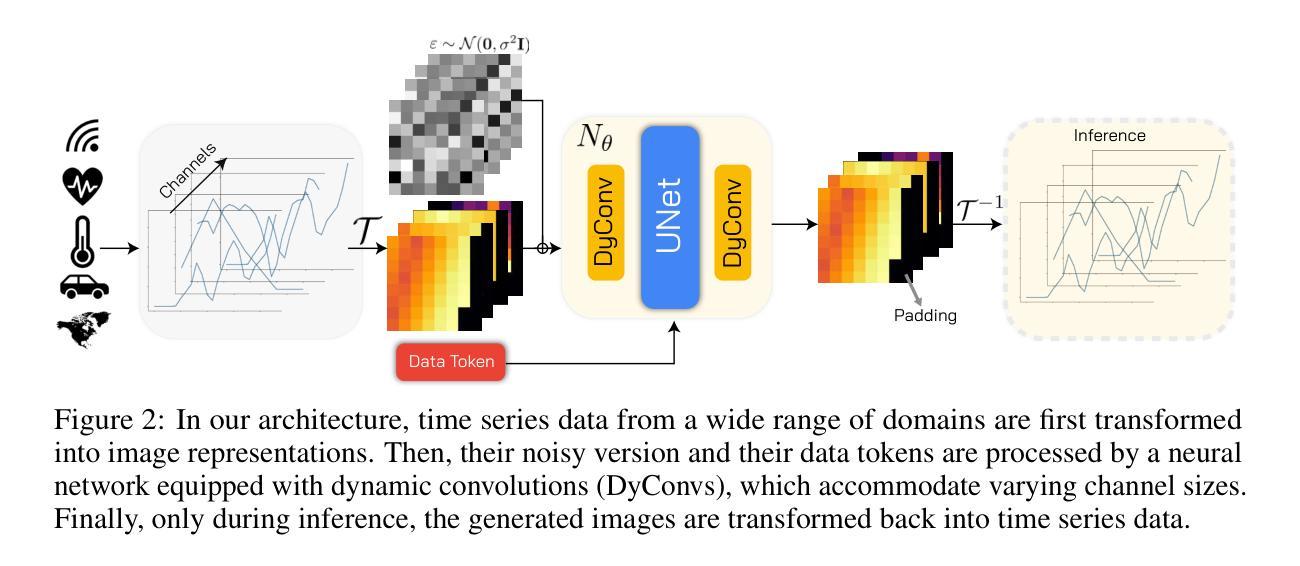
Time Series Generation Under Data Scarcity: A Unified Generative Modeling Approach
Authors:Tal Gonen, Itai Pemper, Ilan Naiman, Nimrod Berman, Omri Azencot
Generative modeling of time series is a central challenge in time series analysis, particularly under data-scarce conditions. Despite recent advances in generative modeling, a comprehensive understanding of how state-of-the-art generative models perform under limited supervision remains lacking. In this work, we conduct the first large-scale study evaluating leading generative models in data-scarce settings, revealing a substantial performance gap between full-data and data-scarce regimes. To close this gap, we propose a unified diffusion-based generative framework that can synthesize high-fidelity time series across diverse domains using just a few examples. Our model is pre-trained on a large, heterogeneous collection of time series datasets, enabling it to learn generalizable temporal representations. It further incorporates architectural innovations such as dynamic convolutional layers for flexible channel adaptation and dataset token conditioning for domain-aware generation. Without requiring abundant supervision, our unified model achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot settings-outperforming domain-specific baselines across a wide range of subset sizes. Remarkably, it also surpasses all baselines even when tested on full datasets benchmarks, highlighting the strength of pre-training and cross-domain generalization. We hope this work encourages the community to revisit few-shot generative modeling as a key problem in time series research and pursue unified solutions that scale efficiently across domains. Code is available at https://github.com/azencot-group/ImagenFew.
时间序列生成建模是时间序列分析中的核心挑战,特别是在数据稀缺的条件下。尽管最近生成模型有所进展,但我们对最先进的生成模型在有限监督下的表现的综合理解仍然不足。在这项工作中,我们首次进行大规模研究,评估数据稀缺环境中领先的生成模型,揭示了全数据和数据稀缺环境下的显著性能差距。为了缩小这一差距,我们提出了一个统一的基于扩散的生成框架,它仅使用少数几个示例就能合成跨不同领域的高保真时间序列。我们的模型在大量、异质的时间序列数据集上进行预训练,使其能够学习可推广的时间表示。它进一步融入了架构创新,如动态卷积层,以实现灵活的通道适配和数据集令牌条件,以进行领域感知生成。无需大量监督,我们的统一模型在少量样本的情况下实现了最新性能——在广泛的各种子集大小上超越了特定领域的基线。值得一提的是,即使在完整数据集基准测试上,它也超过了所有基线,这突显了预训练和跨域推广的力量。我们希望这项工作能鼓励社区重新关注时间序列研究中的小样生成建模作为关键问题,并追求能高效跨域扩展的统一解决方案。代码可在https://github.com/azencot-group/ImagenFew处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
本文研究了时间序列生成模型在数据稀缺条件下的性能表现。文章通过大规模实验评估了主流生成模型,发现了全数据与数据稀缺环境下的性能差距。为缩小这一差距,提出了一种基于扩散的统一生成框架,该框架能在仅使用少量样本的情况下合成高质量的时间序列数据。模型通过预训练学习通用时间序列表示,并引入动态卷积层和数据集标记条件等创新架构,以适应不同领域的数据生成。在少量样本的情况下,该模型实现了最先进的性能表现,甚至在全数据集基准测试中超过了所有基线模型,突显了预训练和跨域泛化的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员对时间序列生成模型在数据稀缺条件下的性能进行了大规模研究。
- 发现了在全数据与数据稀缺环境下的生成模型性能差距。
- 提出了一种基于扩散的统一生成框架,可在仅使用少量样本的情况下合成高质量的时间序列数据。
- 模型通过预训练学习通用时间序列表示。
- 模型引入动态卷积层和数据集标记条件等创新架构以适应不同领域的数据生成。
- 在少量样本的情况下,该模型的性能表现达到或超越了现有最先进的模型。
- 预训练和跨域泛化的重要性在研究中得到了突显。
点此查看论文截图

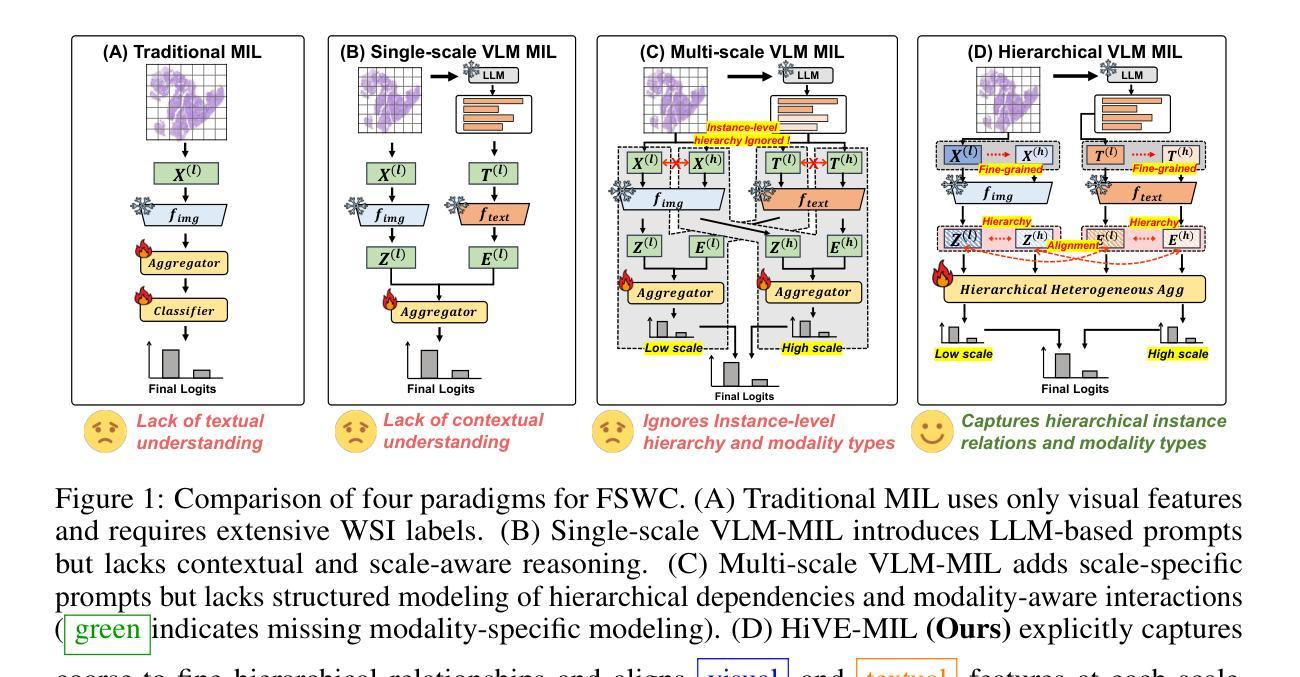
Few-Shot Learning from Gigapixel Images via Hierarchical Vision-Language Alignment and Modeling
Authors:Bryan Wong, Jong Woo Kim, Huazhu Fu, Mun Yong Yi
Vision-language models (VLMs) have recently been integrated into multiple instance learning (MIL) frameworks to address the challenge of few-shot, weakly supervised classification of whole slide images (WSIs). A key trend involves leveraging multi-scale information to better represent hierarchical tissue structures. However, existing methods often face two key limitations: (1) insufficient modeling of interactions within the same modalities across scales (e.g., 5x and 20x) and (2) inadequate alignment between visual and textual modalities on the same scale. To address these gaps, we propose HiVE-MIL, a hierarchical vision-language framework that constructs a unified graph consisting of (1) parent-child links between coarse (5x) and fine (20x) visual/textual nodes to capture hierarchical relationships, and (2) heterogeneous intra-scale edges linking visual and textual nodes on the same scale. To further enhance semantic consistency, HiVE-MIL incorporates a two-stage, text-guided dynamic filtering mechanism that removes weakly correlated patch-text pairs, and introduces a hierarchical contrastive loss to align textual semantics across scales. Extensive experiments on TCGA breast, lung, and kidney cancer datasets demonstrate that HiVE-MIL consistently outperforms both traditional MIL and recent VLM-based MIL approaches, achieving gains of up to 4.1% in macro F1 under 16-shot settings. Our results demonstrate the value of jointly modeling hierarchical structure and multimodal alignment for efficient and scalable learning from limited pathology data. The code is available at https://github.com/bryanwong17/HiVE-MIL
视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近已被纳入多重实例学习(MIL)框架,以解决少数镜头、弱监督分类全幻灯片图像(WSI)的挑战。一种关键趋势是利用多尺度信息来更好地表示层次化的组织结构。然而,现有方法通常面临两个主要局限:(1)同一模态内不同尺度(例如,5倍和20倍)之间交互的建模不足;(2)同一尺度上视觉和文本模态之间对齐不足。为了解决这些差距,我们提出了HiVE-MIL,这是一个层次化的视觉语言框架,它构建了一个统一图,包括(1)粗(5倍)和细(20倍)视觉/文本节点之间的父子链接,以捕捉层次关系,以及(2)同一尺度上的视觉和文本节点之间的异质内尺度边。为了进一步增强语义一致性,HiVE-MIL采用了一种两阶段的文本引导动态过滤机制,该机制可以消除弱相关的补丁-文本对,并引入了一种层次对比损失,以对齐各尺度的文本语义。在TCGA乳腺癌、肺癌和肾癌数据集上的大量实验表明,HiVE-MIL始终优于传统的MIL和最新的基于VLM的MIL方法,在16镜头设置下宏观F1提高了高达4.1%。我们的结果证明了联合建模层次结构和多模态对齐对于从有限的病理数据中实现高效和可扩展学习的价值。代码可在https://github.com/bryanwong17/HiVE-MIL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了如何将视觉语言模型(VLMs)融入多实例学习(MIL)框架,以解决少量弱监督分类问题在全幻灯片图像(WSIs)上的应用。为解决现有方法的不足,如跨尺度内模态交互不足和视觉与文本模态间的不对齐问题,提出了HiVE-MIL框架。该框架通过构建统一图来捕捉层次关系,并采用两阶段文本引导的动态过滤机制增强语义一致性。在癌症数据集上的实验表明,HiVE-MIL在宏观F1得分上优于传统MIL和基于VLM的MIL方法,最高提升可达4.1%。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs与MIL结合应用于解决少量弱监督分类的WSI问题。
- HiVE-MIL框架引入多尺度信息,构建统一图来捕捉层次关系。
- 现有方法的两个主要局限性是跨尺度内模态交互不足和视觉与文本模态间的不对齐。
- HiVE-MIL采用两阶段文本引导的动态过滤机制增强语义一致性。
- 实验结果展示HiVE-MIL在多种癌症数据集上的优异性能。
- 代码公开可供下载参考学习。
点此查看论文截图

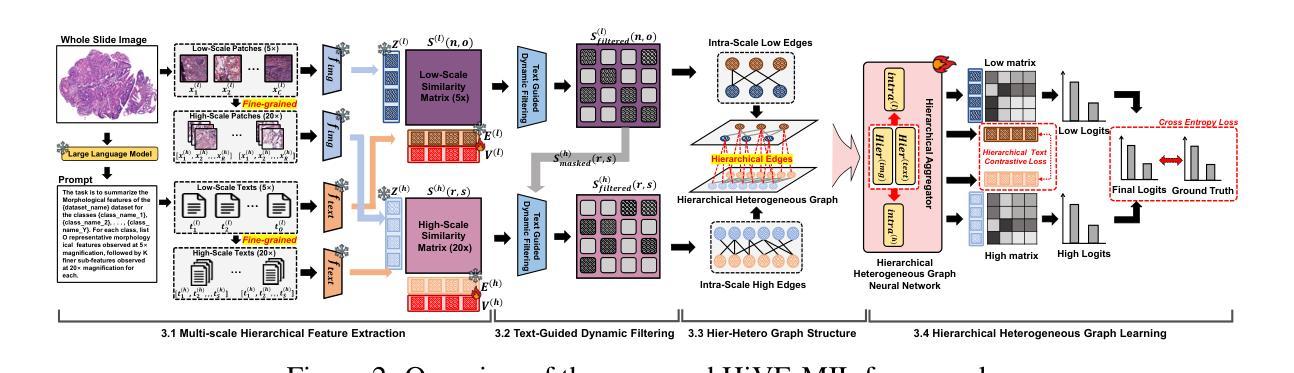
Learning Policy Committees for Effective Personalization in MDPs with Diverse Tasks
Authors:Luise Ge, Michael Lanier, Anindya Sarkar, Bengisu Guresti, Chongjie Zhang, Yevgeniy Vorobeychik
Many dynamic decision problems, such as robotic control, involve a series of tasks, many of which are unknown at training time. Typical approaches for these problems, such as multi-task and meta reinforcement learning, do not generalize well when the tasks are diverse. On the other hand, approaches that aim to tackle task diversity, such as using task embedding as policy context and task clustering, typically lack performance guarantees and require a large number of training tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach for learning a policy committee that includes at least one near-optimal policy with high probability for tasks encountered during execution. While we show that this problem is in general inapproximable, we present two practical algorithmic solutions. The first yields provable approximation and task sample complexity guarantees when tasks are low-dimensional (the best we can do due to inapproximability), whereas the second is a general and practical gradient-based approach. In addition, we provide a provable sample complexity bound for few-shot learning. Our experiments on MuJoCo and Meta-World show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art multi-task, meta-, and task clustering baselines in training, generalization, and few-shot learning, often by a large margin. Our code is available at https://github.com/CERL-WUSTL/PACMAN.
在许多动态决策问题,如机器人控制中,涉及一系列任务,其中许多任务在训练时未知。针对这些问题的典型方法,如多任务学习和元强化学习,当任务多样时并不通用。另一方面,旨在解决任务多样性的方法,如使用任务嵌入作为策略上下文和任务聚类,通常缺乏性能保证,需要大量训练任务。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种学习策略委员会的新方法,该方法能够大概率地包括在执行过程中遇到任务的至少一个近优策略。虽然我们发现这个问题通常不可近似解决,但我们提出了两种实用的算法解决方案。第一种方法在任务为低维时能产生可证明近似和任务样本复杂性保证(这是我们能做到的最好因为不可近似性),而第二种是一种通用且实用的基于梯度的方法。此外,我们还为小样本学习提供了可证明样本复杂性界限。我们在MuJoCo和Meta-World上的实验表明,所提出的方法在训练、泛化和小样学习方面均优于最新的多任务、元学习和任务聚类基线,通常具有较大优势。我们的代码可在https://github.com/CERL-WUSTL/PACMAN上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种解决动态决策问题的方法,特别适用于任务多样性和未知任务的情况。通过构建政策委员会,该方法能确保在执行时遇到的任务中有至少一个近优政策的概率较高。虽然该问题一般不可近似,但提供了两种实用的算法解决方案,并在MuJoCo和Meta-World的实验中证明了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种新的解决动态决策问题的方法,适用于任务多样性和未知任务的环境。
- 通过构建政策委员会,确保在执行时遇到的任何任务都有至少一个近优政策。
- 虽然该问题一般不可近似,但提供了两种实用的算法解决方案,其中一种在任务低维度情况下可提供可证明的近似和任务样本复杂性保证。
- 另一种算法是一种通用且实用的基于梯度的解决方案。
- 为少样本学习提供了可证明的样本复杂性界限。
- 在MuJoCo和Meta-World的实验中,该方法优于多任务、元学习和任务聚类等现有方法,显示出其在训练、泛化和少样本学习方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

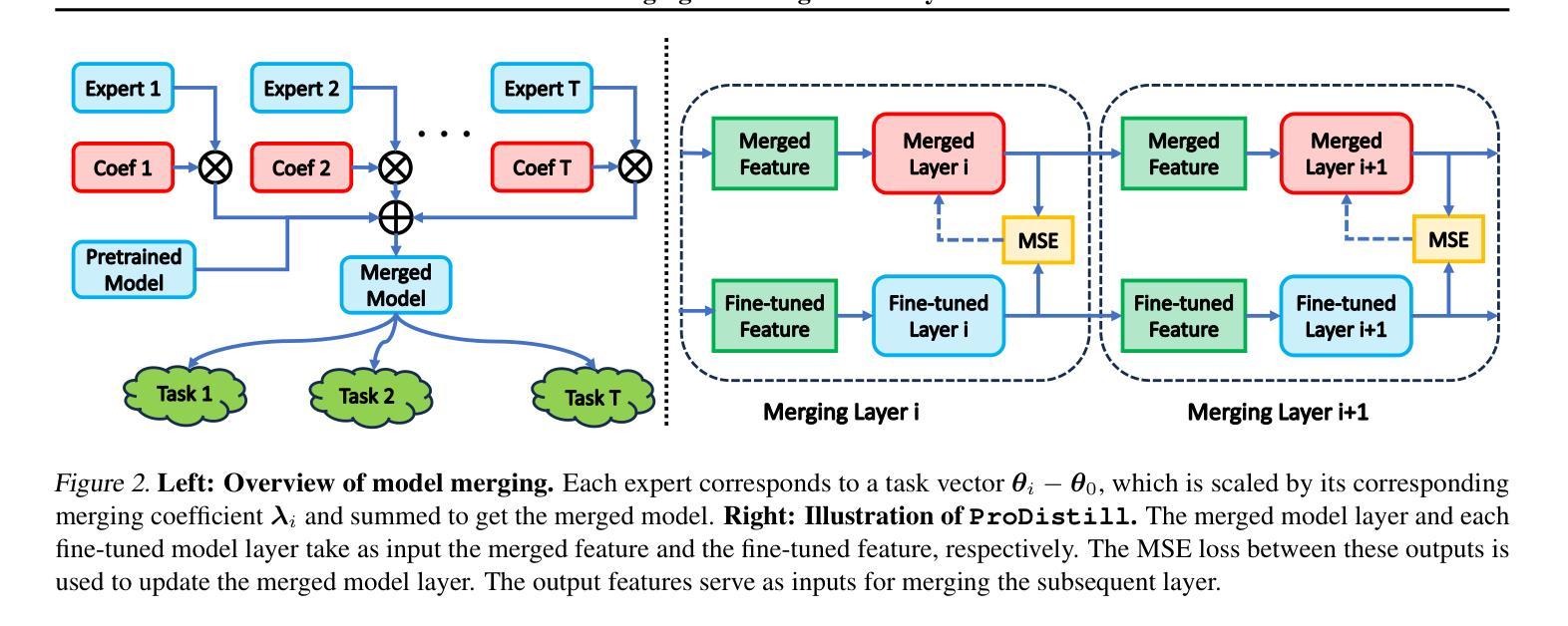
Scalable Model Merging with Progressive Layer-wise Distillation
Authors:Jing Xu, Jiazheng Li, Jingzhao Zhang
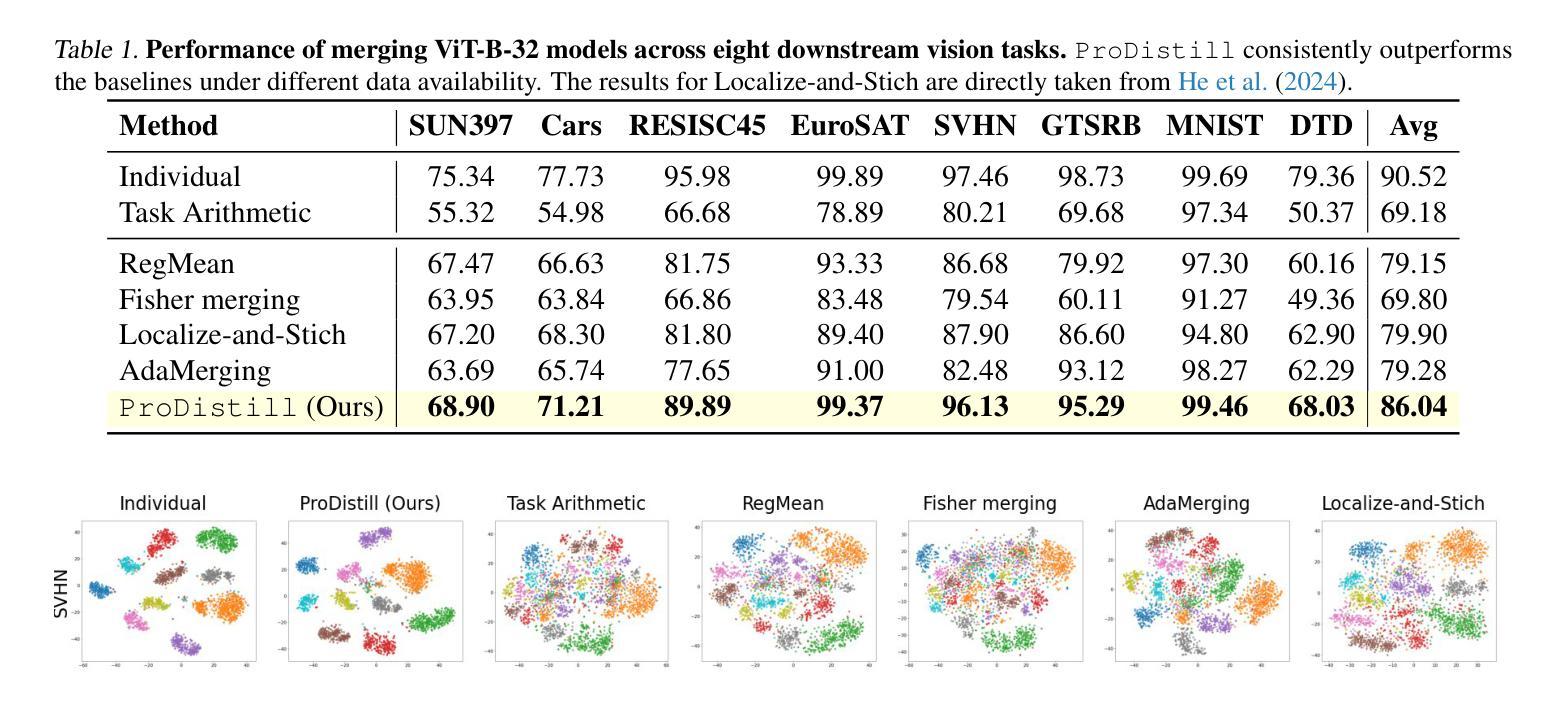
Model merging offers an effective way to integrate the capabilities of multiple fine-tuned models. However, the performance degradation of the merged model remains a challenge, particularly when none or few data are available. This paper first highlights the necessity of domain-specific data for model merging by proving that data-agnostic algorithms can have arbitrarily bad worst-case performance. Building on this theoretical insight, we explore the relationship between model merging and distillation, introducing a novel few-shot merging algorithm, ProDistill (Progressive Layer-wise Distillation). Unlike common belief that layer wise training hurts performance, we show that layer-wise teacher-student distillation not only enhances the scalability but also improves model merging performance. We conduct extensive experiments to show that compared to existing few-shot merging methods, ProDistill achieves state-of-the-art performance, with up to 6.14% and 6.61% improvements in vision and NLU tasks. Furthermore, we extend the experiments to models with over 10B parameters, showcasing the exceptional scalability of ProDistill.
模型融合提供了一种有效的方式,可以整合多个微调模型的能力。然而,融合模型的性能下降仍然是一个挑战,特别是在没有或只有少量数据可用的情况下。本文首先通过证明数据无关算法可能具有任意差的最坏情况性能来强调特定领域数据对模型融合的必要性。基于这一理论见解,我们探索了模型融合与蒸馏之间的关系,并引入了一种新颖的少量数据融合算法ProDistill(渐进逐层蒸馏)。与普遍的观点相反,我们认为逐层训练并不会损害性能,反而展示逐层教师学生蒸馏不仅提高了可扩展性,还提高了模型融合性能。我们进行了大量实验表明,与现有的少量数据融合方法相比,ProDistill取得了最先进的性能,在视觉和自然语言理解任务上分别提高了6.14%和6.61%。此外,我们将实验扩展到了超过10B参数的模型上,展示了ProDistill的出色可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型融合是集成多个微调模型的有效方法,但融合模型的性能下降,特别是在无数据或少数据情况下是一大挑战。本文首先强调领域特定数据对模型融合的重要性,并证明数据无关算法的最坏情况性能可能任意差。基于此理论见解,本文探索模型融合与蒸馏的关系,提出一种新型的小样本融合算法ProDistill(渐进逐层蒸馏)。不同于普遍认知,逐层训练并不会损害性能,反而显示逐层教师-学生蒸馏不仅提高可伸缩性,还能改善模型融合性能。在实验中表明,相较于现有的小样本融合方法,ProDistill表现达到领先水平,视觉和自然语言处理任务性能分别提高高达6.14%和6.61%。此外,该算法在超过10B参数的模型上表现卓越的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 模型融合是集成多个微调模型的有效方法,但存在性能下降的挑战,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。
- 领域特定数据对模型融合至关重要,数据无关算法的最坏情况性能可能很差。
- 渐进逐层蒸馏(ProDistill)是一种新型的小样本融合算法,通过探索模型融合与蒸馏的关系来提高性能。
- 逐层教师-学生蒸馏不仅不损害性能,反而能改善模型融合性能,并提高算法的可伸缩性。
- ProDistill在视觉和自然语言处理任务上表现优异,相较于现有方法,性能提升显著。
- ProDistill在大型模型(超过10B参数)上展现出卓越的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

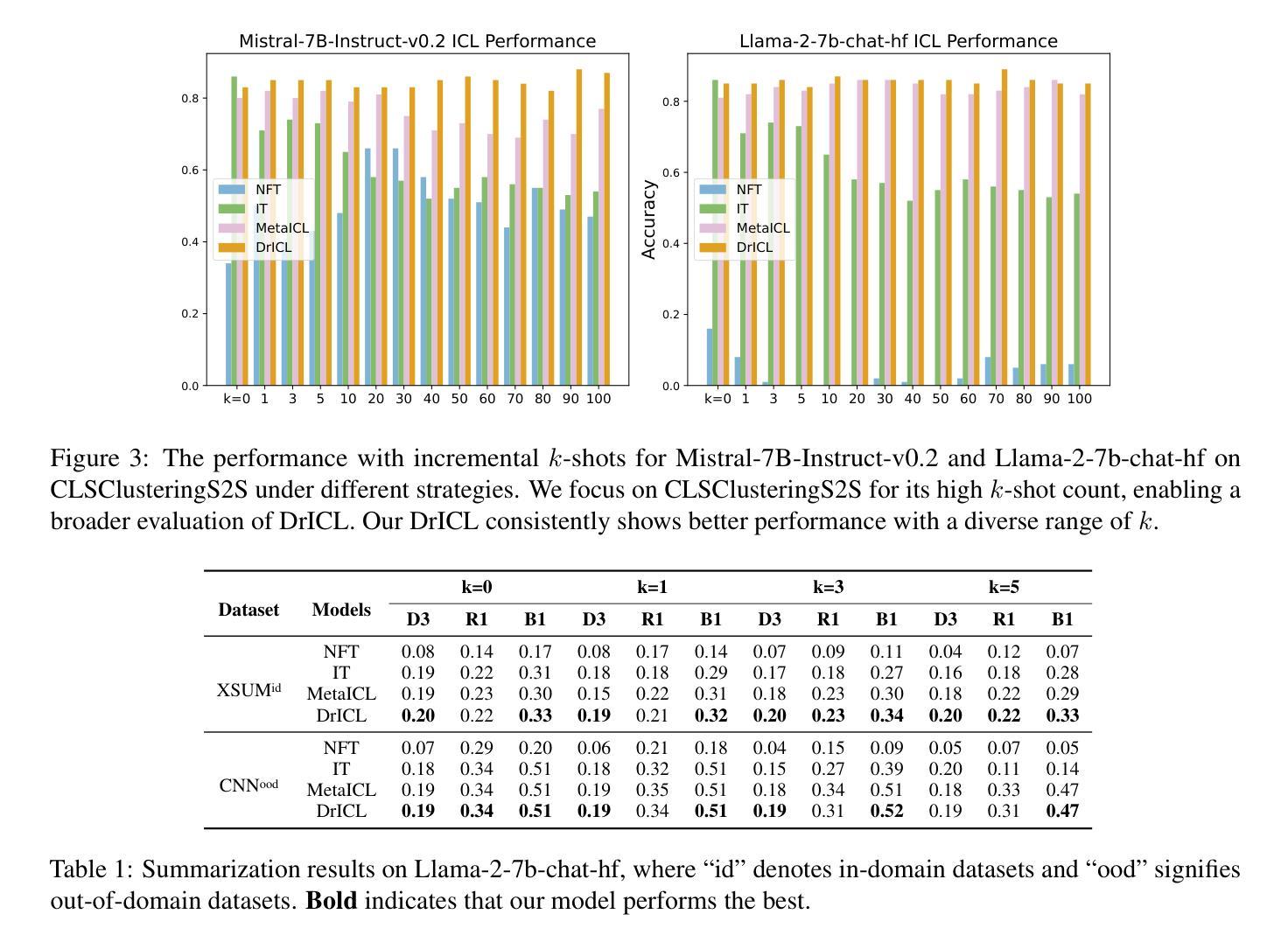
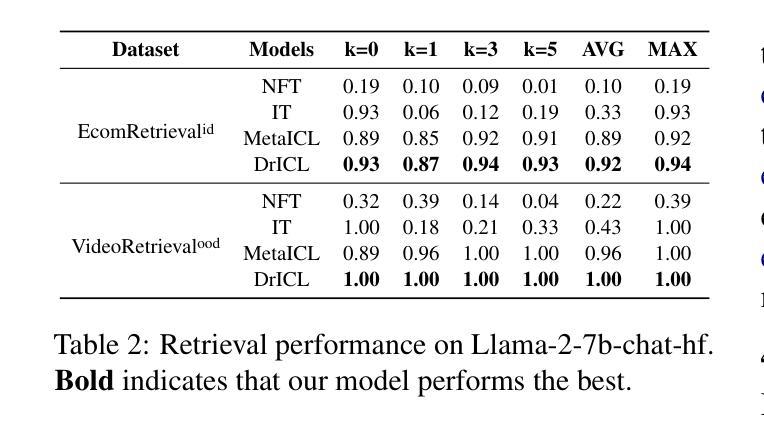
More is not always better? Enhancing Many-Shot In-Context Learning with Differentiated and Reweighting Objectives
Authors:Xiaoqing Zhang, Ang Lv, Yuhan Liu, Flood Sung, Wei Liu, Jian Luan, Shuo Shang, Xiuying Chen, Rui Yan
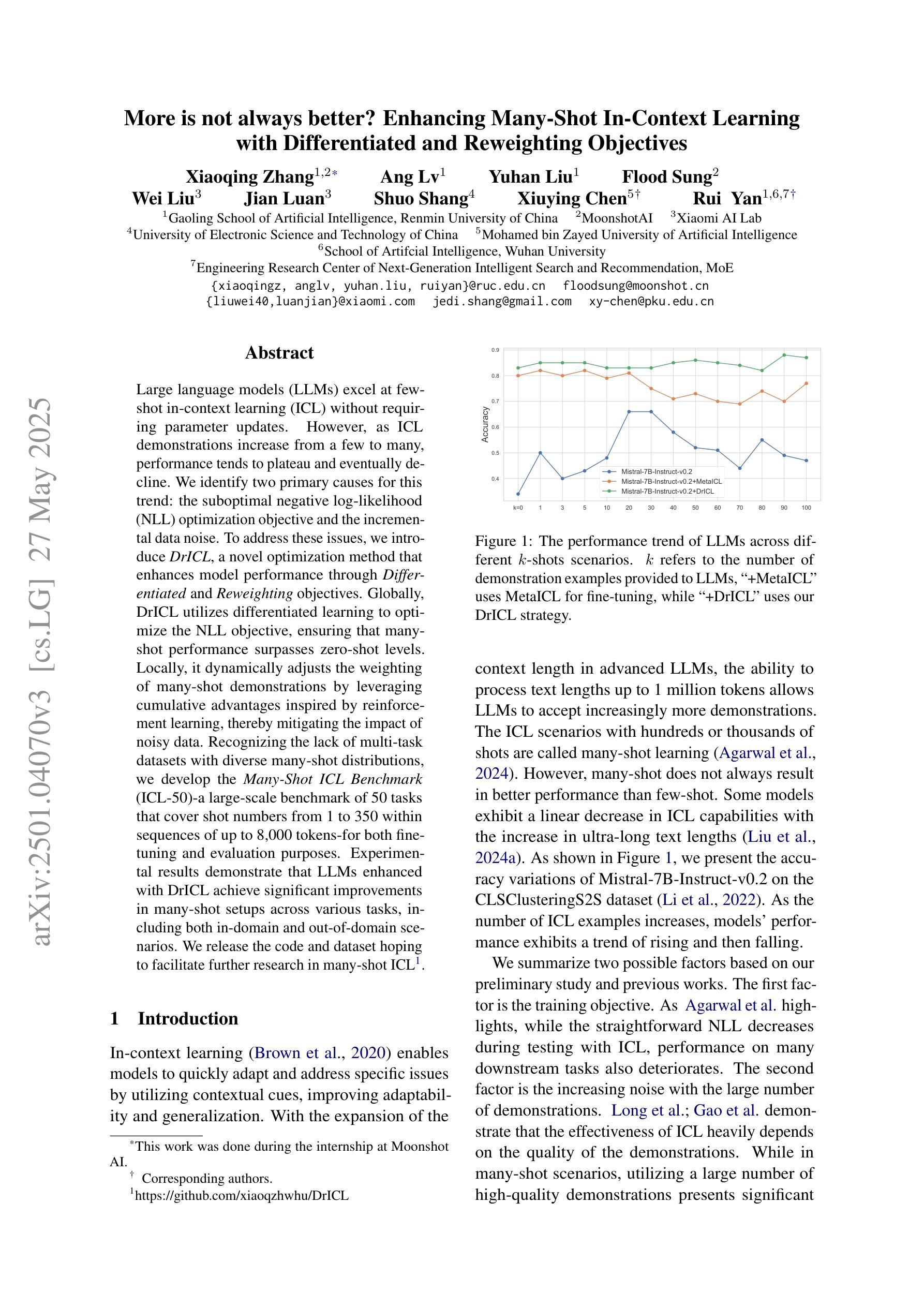
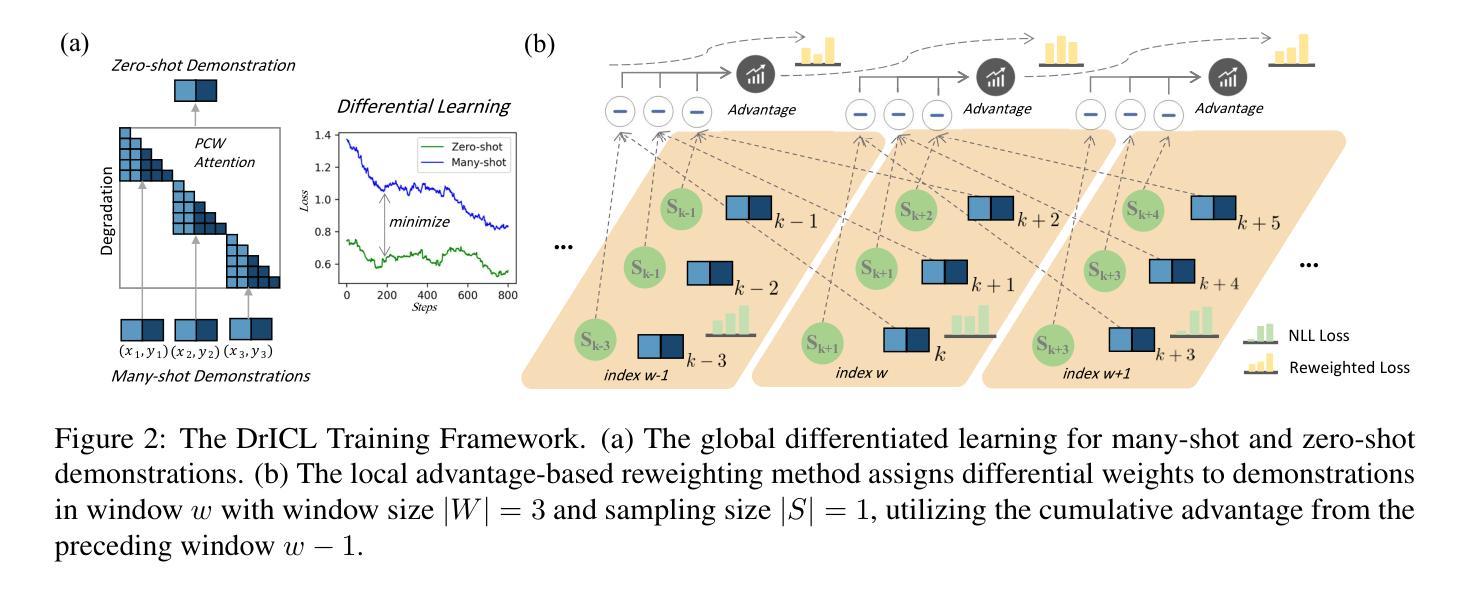
Large language models (LLMs) excel at few-shot in-context learning (ICL) without requiring parameter updates. However, as ICL demonstrations increase from a few to many, performance tends to plateau and eventually decline. We identify two primary causes for this trend: the suboptimal negative log-likelihood (NLL) optimization objective and the incremental data noise. To address these issues, we introduce \textit{DrICL}, a novel optimization method that enhances model performance through \textit{Differentiated} and \textit{Reweighting} objectives. Globally, DrICL utilizes differentiated learning to optimize the NLL objective, ensuring that many-shot performance surpasses zero-shot levels. Locally, it dynamically adjusts the weighting of many-shot demonstrations by leveraging cumulative advantages inspired by reinforcement learning, thereby mitigating the impact of noisy data. Recognizing the lack of multi-task datasets with diverse many-shot distributions, we develop the \textit{Many-Shot ICL Benchmark} (ICL-50)-a large-scale benchmark of 50 tasks that cover shot numbers from 1 to 350 within sequences of up to 8,000 tokens-for both fine-tuning and evaluation purposes. Experimental results demonstrate that LLMs enhanced with DrICL achieve significant improvements in many-shot setups across various tasks, including both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios. We release the code and dataset hoping to facilitate further research in many-shot ICL\footnote{https://github.com/xiaoqzhwhu/DrICL}.
大型语言模型(LLM)在不需更新参数的情况下,擅长于小样本上下文学习(ICL)。然而,随着ICL演示从少数增加到多数,性能往往达到平台期并最终下降。我们确定了导致这一趋势的两个主要原因:次优的负对数似然(NLL)优化目标和增量数据噪声。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了DrICL,这是一种通过差异化和重权目标增强模型性能的新型优化方法。全局上,DrICL利用差异化学习来优化NLL目标,确保多步性能超越零步水平。局部上,它通过在强化学习中借鉴累积优势来动态调整多步演示的权重,从而减轻噪声数据的影响。由于没有包含多种多步分布的多任务数据集,我们开发了多步ICL基准(ICL-50)——一个大规模基准测试,包含50个任务,涵盖从1到350步的射击次数,序列中的令牌数高达8000个,既可用于微调也可用于评估目的。实验结果表明,采用DrICL增强的大型语言模型在各种任务的多步设置中实现了显著的改进,包括域内和域外场景。我们发布代码和数据集,希望能进一步推动多步ICL的研究(https://github.com/xiaoqzhwhu/DrICL)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, 11 tables
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型在少量场景学习(ICL)中的性能瓶颈问题,分析了导致性能下降的两个主要原因,并提出了一个名为DrICL的优化方法来解决这一问题。DrICL通过差异化的学习方法优化负对数似然(NLL)目标,并动态调整多场景演示的权重来减少数据噪声的影响。此外,文章还建立了一个大规模的多场景学习基准测试(ICL-50),用于评估和优化LLM在多场景学习中的性能。实验结果显示,采用DrICL优化的LLM在各种任务的多场景设置中取得了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在少量场景学习(ICL)中面临性能瓶颈。
- 性能下降的主要原因包括负对数似然(NLL)优化目标的不佳和增量数据噪声。
- 引入DrICL优化方法,通过差异化的学习方法和动态调整演示权重来解决上述问题。
- DrICL能在全球范围内优化NLL目标,提高多场景学习的性能。
- 建立了多场景学习基准测试(ICL-50),涵盖从1到350的不同场景数量,用于评估和推动LLM在多场景学习中的研究。
- 实验结果显示,采用DrICL优化的LLM在多场景设置中取得了显著的改进,适用于各种任务,包括跨域场景。
点此查看论文截图
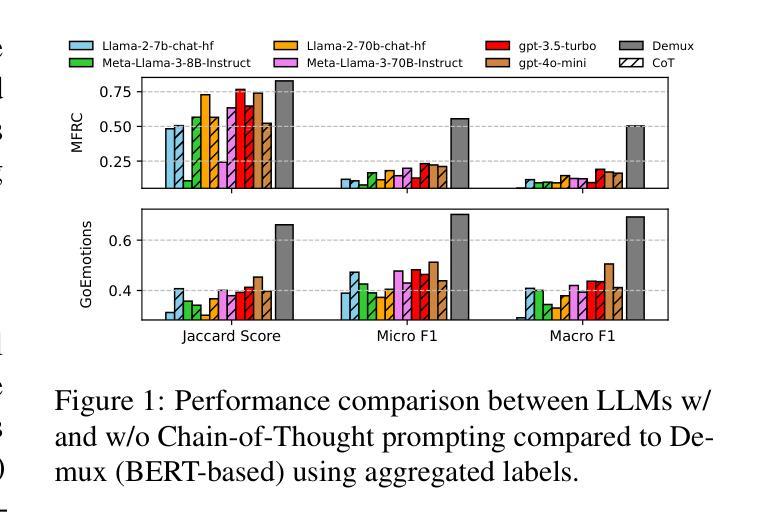
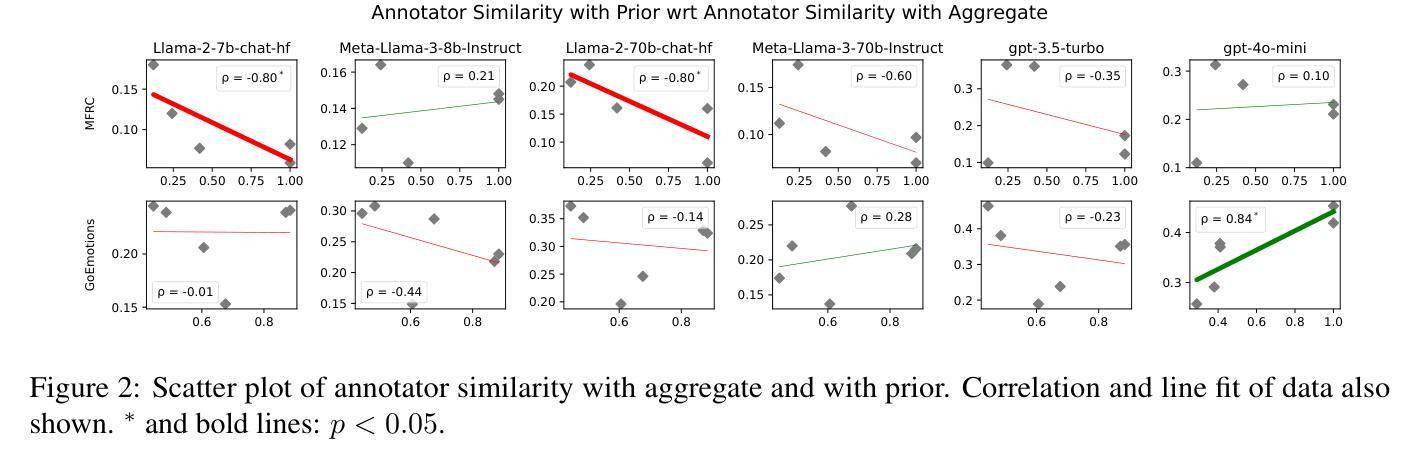
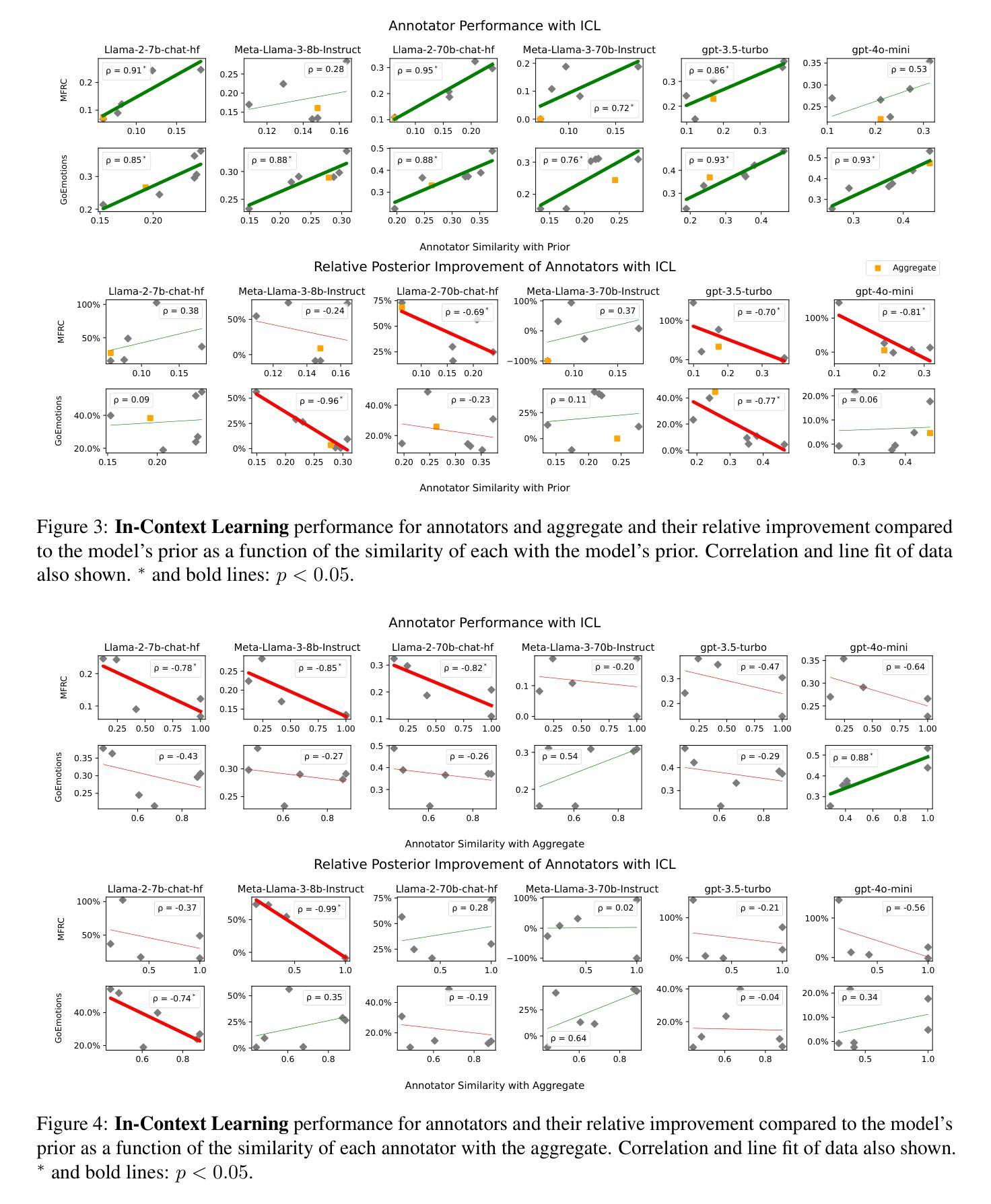
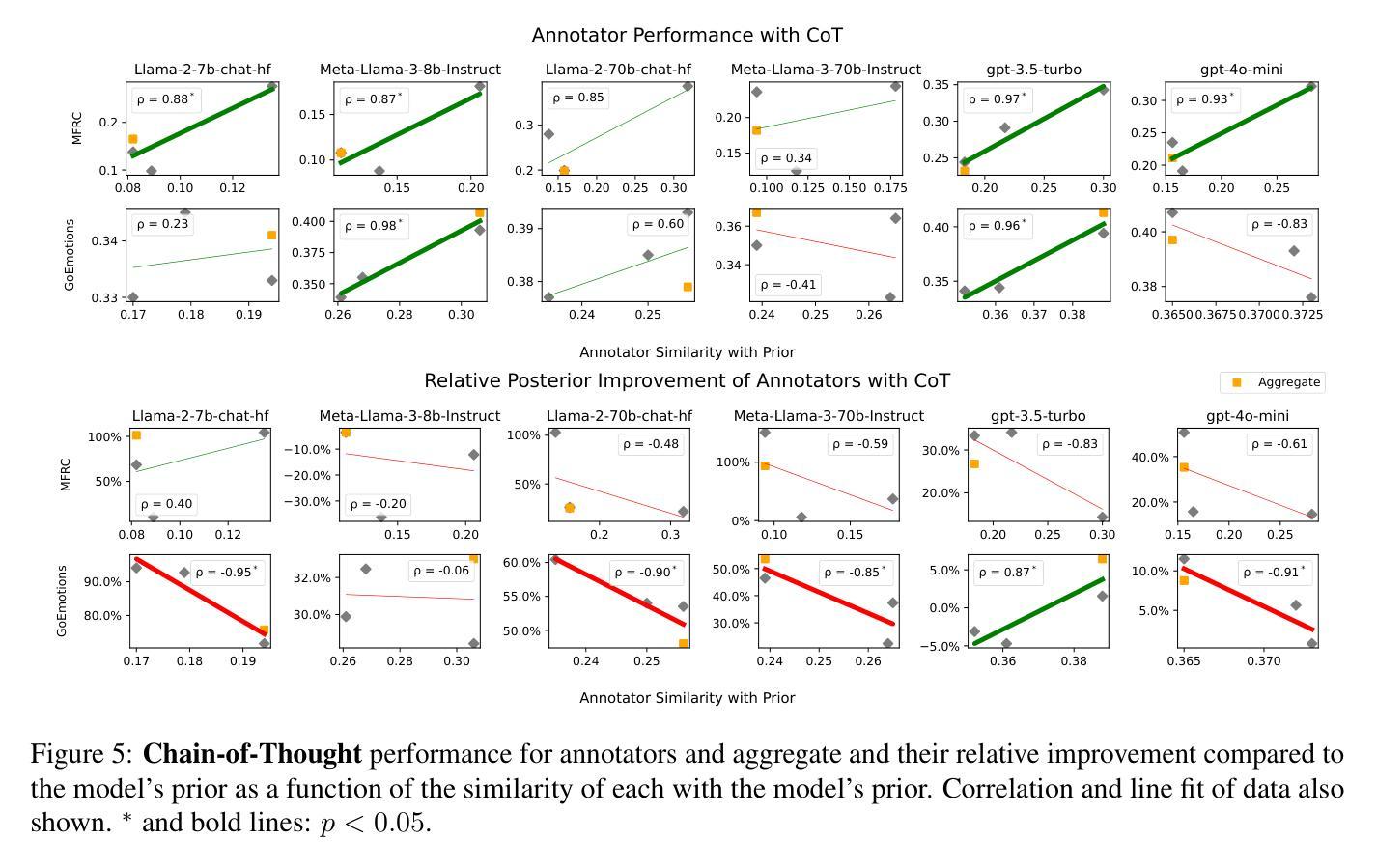
Aggregation Artifacts in Subjective Tasks Collapse Large Language Models’ Posteriors
Authors:Georgios Chochlakis, Alexandros Potamianos, Kristina Lerman, Shrikanth Narayanan
In-context Learning (ICL) has become the primary method for performing natural language tasks with Large Language Models (LLMs). The knowledge acquired during pre-training is crucial for this few-shot capability, providing the model with task priors. However, recent studies have shown that ICL predominantly relies on retrieving task priors rather than “learning” to perform tasks. This limitation is particularly evident in complex subjective domains such as emotion and morality, where priors significantly influence posterior predictions. In this work, we examine whether this is the result of the aggregation used in corresponding datasets, where trying to combine low-agreement, disparate annotations might lead to annotation artifacts that create detrimental noise in the prompt. Moreover, we evaluate the posterior bias towards certain annotators by grounding our study in appropriate, quantitative measures of LLM priors. Our results indicate that aggregation is a confounding factor in the modeling of subjective tasks, and advocate focusing on modeling individuals instead. However, aggregation does not explain the entire gap between ICL and the state of the art, meaning other factors in such tasks also account for the observed phenomena. Finally, by rigorously studying annotator-level labels, we find that it is possible for minority annotators to both better align with LLMs and have their perspectives further amplified.
上下文学习(ICL)已成为使用大型语言模型(LLM)执行自然语言任务的主要方法。在预训练期间获得的知识对于这种小样本能力至关重要,为模型提供任务先验。然而,最近的研究表明,ICL主要依赖于获取任务先验,而不是“学习”执行任务。这种局限性在情感、道德等复杂的主观领域尤为明显,先验知识会显著影响后验预测。在这项工作中,我们调查这是否是由于相应数据集中使用的聚合方法导致的,尝试结合低同意率、分散的注释可能会导致注释产生的伪像,在提示中产生有害的噪声。此外,我们通过基于合适、定量的LLM先验度量来评估对特定注释器的后验偏见。我们的结果表明,聚合是主观任务建模中的混淆因素,并主张重点关注对个体的建模。然而,聚合并不能完全解释ICL与最新技术之间的差距,意味着此类任务中的其他因素也导致了观察到的现象。最后,通过对注释器级别的标签进行严格研究,我们发现少数注释器与LLM更好地对齐并放大其观点是可能的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
Summary
在语境学习(ICL)中,大型语言模型(LLM)主要依赖预训练知识完成自然语言任务。但研究发现,ICL主要依赖检索任务先验知识而非“学习”执行任务。在情感、道德等复杂主观领域,先验知识对后验预测影响显著。本研究探讨了数据集聚合方式是否导致了这一现象,发现尝试合并低一致性、分散的注释可能导致提示中的有害噪声。此外,我们通过对LLM先验知识的定量评估,发现聚合是主观任务建模中的干扰因素,主张重点建模个体而非整体。但聚合并不能完全解释ICL与最新技术之间的差距,说明还有其他因素影响了任务表现。通过深入研究注释者层面的标签,我们发现少数注释者的观点与LLM更一致,且他们的观点会被进一步放大。
Key Takeaways
- ICL 主要依赖预训练知识来完成自然语言任务。
- 在复杂主观领域,先验知识对后验预测的影响显著。
- 数据集的聚合方式可能导致注释中的有害噪声,影响任务表现。
- 聚合是主观任务建模中的干扰因素,应更注重建模个体。
- 除了聚合因素,其他因素也影响了ICL的表现,仍需深入研究。
- 少数注释者的观点与LLM更一致,他们的观点在模型中的影响可能会被放大。
点此查看论文截图

V-RoAst: Visual Road Assessment. Can VLM be a Road Safety Assessor Using the iRAP Standard?
Authors:Natchapon Jongwiriyanurak, Zichao Zeng, June Moh Goo, James Haworth, Xinglei Wang, Kerkritt Sriroongvikrai, Nicola Christie, Ilya Ilyankou, Meihui Wang, Huanfa Chen
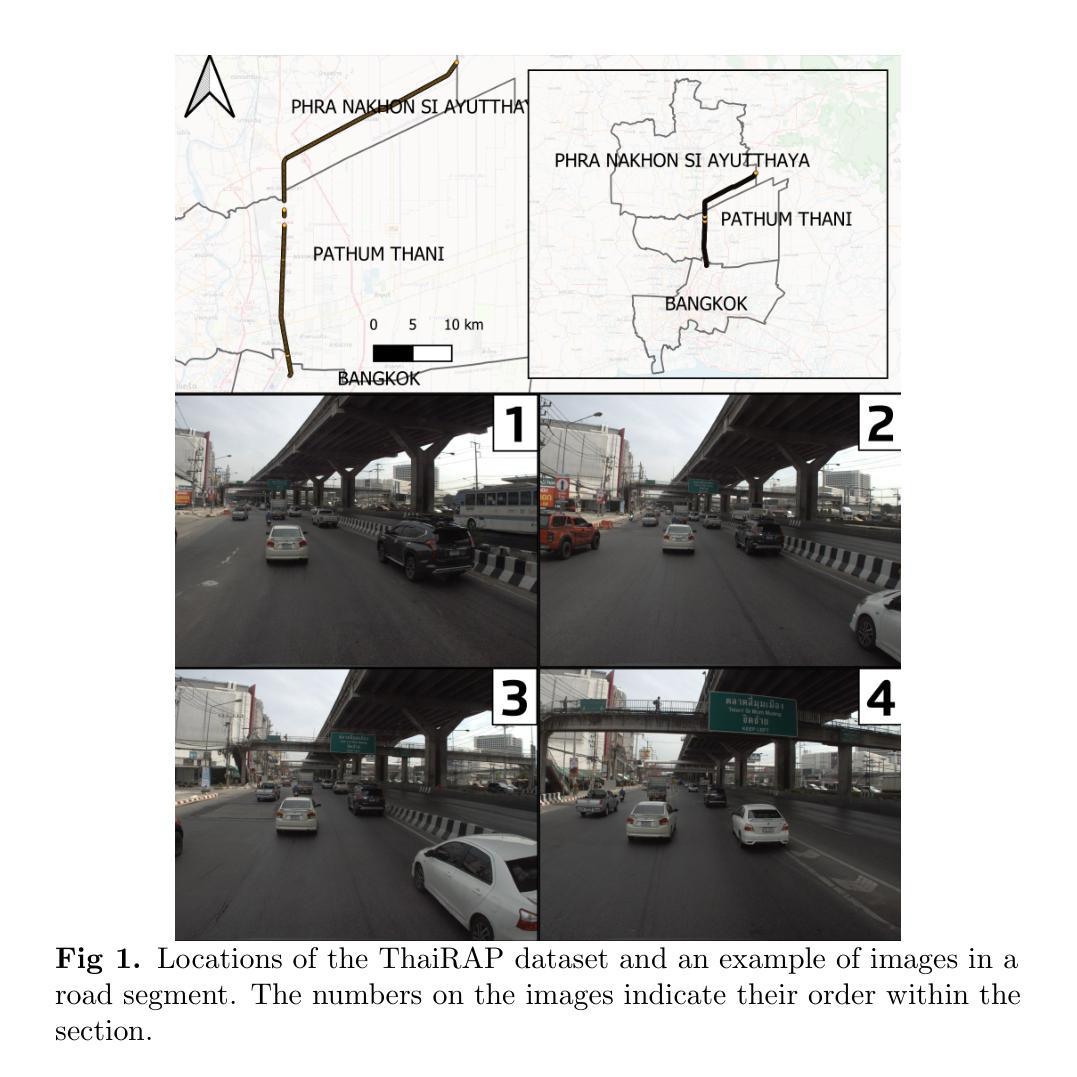
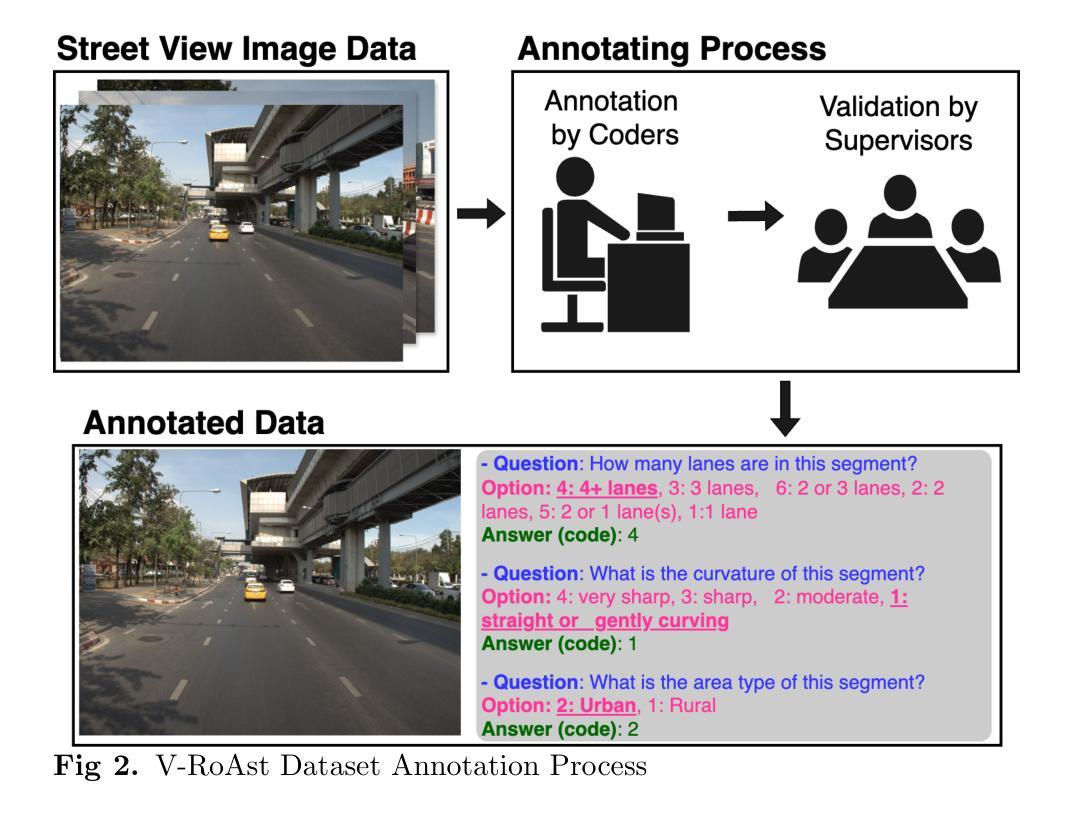
Road traffic crashes result in millions of deaths annually and significant economic burdens, particularly on Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs). Road safety assessments traditionally rely on human-labelled data, which is labour-intensive and time-consuming. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have advanced automated road safety assessments, they typically demand large labelled datasets and often require fine-tuning for each new geographic context. This study explores whether Vision Language Models (VLMs) with zero-shot capability can overcome these limitations to serve as effective road safety assessors using the International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP) standard. Our approach, V-RoAst (Visual question answering for Road Assessment), leverages advanced VLMs, such as Gemini-1.5-flash and GPT-4o-mini, to analyse road safety attributes without requiring any labelled training data. By optimising prompt engineering and utilising crowdsourced imagery from Mapillary, V-RoAst provides a scalable, cost-effective, and automated solution for global road safety assessments. Preliminary results show that while VLMs achieve lower performance than CNN-based models, they are capable of Visual Question Answering (VQA) and show potential in predicting star ratings from crowdsourced imagery. However, their performance is poor when key visual features are absent in the imagery, emphasising the need for human labelling to address these gaps. Advancements in VLMs, alongside in-context learning such as chain-of-thought and few-shot learning, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning, present opportunities for improvement, making VLMs promising tools for road assessment tasks. Designed for resource-constrained stakeholders, this framework holds the potential to save lives and reduce economic burdens worldwide. Code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst.
道路交通事故每年造成数百万人死亡和巨大的经济负担,特别是给中低收入国家(LMICs)带来了巨大的挑战。传统的道路安全评估主要依赖于人工标注的数据,这既耗时又耗力。尽管卷积神经网络(CNNs)已经推动了道路安全评估的自动化,但它们通常需要大量的标注数据集,并且针对每个新的地理背景都需要进行微调。本研究探讨了具有零样本能力的视觉语言模型(VLMs)是否能够克服这些限制,以国际道路评估计划(iRAP)标准作为有效的道路安全评估工具。我们的方法V-RoAst(用于道路评估的视觉问答),利用先进的VLMs技术,如Gemini-1.5-flash和GPT-4o-mini,分析道路安全属性而无需任何标注的训练数据。通过优化提示工程并利用来自Mapillary的众源图像数据,V-RoAst提供了一个可规模化、经济高效、自动化的全球道路安全评估解决方案。初步结果表明,虽然VLMs的性能低于CNN模型,但它们能够进行视觉问答并显示出从众源图像预测星级评分的潜力。然而,当图像中缺少关键视觉特征时,它们的性能较差,这强调了进行人工标注以弥补这些不足的必要性。随着视觉语言模型的进步以及上下文学习(如思维链和少样本学习)和参数高效微调等技术的发展,为改进提供了机会,使VLMs成为道路评估任务的有前途的工具。这一框架旨在为资源有限的利益相关者设计,具有挽救生命和减少全球经济负担的潜力。代码和数据集可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/PongNJ/V-RoAst。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行道路安全评估的可行性。研究提出了一种名为V-RoAst的方法,利用先进的VLMs分析道路安全属性,无需标记训练数据。通过优化提示工程和利用Mapillary的众源图像,V-RoAst提供了可规模化、成本低廉、自动化的全球道路安全评估解决方案。虽然VLMs的性能低于CNN模型,但在视觉问答(VQA)和基于众源图像预测星级评分方面显示出潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 道路安全评估传统上依赖人工标记数据,既耗时又劳力密集。
- 卷积神经网络(CNNs)已用于自动化道路安全评估,但需大量标记数据集,且对新地理上下文需微调。
- 本研究探索了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在道路安全评估中的应用,提出了一种名为V-RoAst的方法。
- V-RoAst利用VLMs分析道路安全属性,无需标记训练数据,提供可规模化、自动化解决方案。
- VLMs在视觉问答(VQA)和基于众源图像预测星级评分方面表现出潜力。
- VLMs性能在关键视觉特征缺失时表现较差,需人工标记填补空白。
点此查看论文截图

Query Performance Prediction using Relevance Judgments Generated by Large Language Models
Authors:Chuan Meng, Negar Arabzadeh, Arian Askari, Mohammad Aliannejadi, Maarten de Rijke
Query performance prediction (QPP) aims to estimate the retrieval quality of a search system for a query without human relevance judgments. Previous QPP methods typically return a single scalar value and do not require the predicted values to approximate a specific information retrieval (IR) evaluation measure, leading to certain drawbacks: (i) a single scalar is insufficient to accurately represent different IR evaluation measures, especially when metrics do not highly correlate, and (ii) a single scalar limits the interpretability of QPP methods because solely using a scalar is insufficient to explain QPP results. To address these issues, we propose a QPP framework using automatically generated relevance judgments (QPP-GenRE), which decomposes QPP into independent subtasks of predicting the relevance of each item in a ranked list to a given query. This allows us to predict any IR evaluation measure using the generated relevance judgments as pseudo-labels. This also allows us to interpret predicted IR evaluation measures, and identify, track and rectify errors in generated relevance judgments to improve QPP quality. We predict an item’s relevance by using open-source large language models (LLMs) to ensure scientific reproducibility. We face two main challenges: (i) excessive computational costs of judging an entire corpus for predicting a metric considering recall, and (ii) limited performance in prompting open-source LLMs in a zero-/few-shot manner. To solve the challenges, we devise an approximation strategy to predict an IR measure considering recall and propose to fine-tune open-source LLMs using human-labeled relevance judgments. Experiments on the TREC 2019 to 2022 deep learning tracks and CAsT-19 and 20 datasets show that QPP-GenRE achieves state-of-the-art QPP quality for both lexical and neural rankers.
查询性能预测(QPP)旨在估计搜索系统对查询的检索质量,而无需人工相关性判断。以往的QPP方法通常返回一个单一标量值,并不要求预测值近似特定的信息检索(IR)评估措施,这导致了一些缺点:(i)一个单一标量不足以准确代表不同的IR评估措施,尤其是当指标之间相关性不高时;(ii)单一标量限制了QPP方法的可解释性,因为仅使用标量不足以解释QPP结果。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了使用自动生成的相关性判断(QPP-GenRE)的QPP框架。它将QPP分解为预测排名列表中每个项目对给定查询的相关性的独立子任务。这使我们能够使用生成的相关性判断作为伪标签来预测任何IR评估措施。这还可以帮助我们解释预测的IR评估措施,并识别、跟踪和纠正生成的相关性判断中的错误,以提高QPP质量。我们通过使用开源的大型语言模型(LLM)来预测项目的相关性,以确保科学可重复性。我们面临两个主要挑战:(i)考虑到召回率预测指标而判断整个语料库的计算成本过高;(ii)在零/少镜头情况下提示开源LLM时的性能有限。为了解决这些挑战,我们制定了一种近似策略来预测考虑召回的IR措施,并提议使用人类标注的相关性判断对开源LLM进行微调。在TREC 2019至2022深度学习轨迹以及CAsT-19和20数据集上的实验表明,QPP-GenRE在词汇和神经排名器方面都达到了最先进的QPP质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS)
Summary
该文介绍了查询性能预测(QPP)的新框架——QPP-GenRE。该框架旨在解决传统QPP方法返回单一标量值带来的问题,如无法准确代表不同的信息检索(IR)评估指标和解释性不足。QPP-GenRE通过分解QPP为预测给定查询下排名列表中每个项目相关性的独立子任务,使用自动生成的相关性判断作为伪标签来预测任何IR评估指标。此外,它还允许解释预测的IR评估指标,并识别、跟踪和纠正生成的相关性判断中的错误以提高QPP质量。
Key Takeaways
- 查询性能预测(QPP)旨在估计搜索系统对查询的检索质量,无需人工相关性判断。
- 传统QPP方法返回单一标量值,存在不足,如不能准确代表不同的IR评估指标和解释性不足。
- QPP-GenRE框架使用自动生成的相关性判断作为伪标签,能预测任何IR评估指标。
- QPP-GenRE允许解释预测的IR评估指标,并识别、跟踪和纠正生成的相关性判断中的错误。
- QPP-GenRE通过使用开源大型语言模型(LLMs)预测项目的相关性,确保科学可重复性。
- QPP-GenRE面临两个主要挑战:判断整个语料库以预测指标的计算成本过高,以及在零/少镜头情况下提示开源LLMs的性能有限。
点此查看论文截图


