⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation for Segmentation and Signal Unmixing
Authors:Nikola Andrejic, Milica Spasic, Igor Mihajlovic, Petra Milosavljevic, Djordje Pavlovic, Filip Milisavljevic, Uros Milivojevic, Danilo Delibasic, Ivana Mikic, Sinisa Todorovic
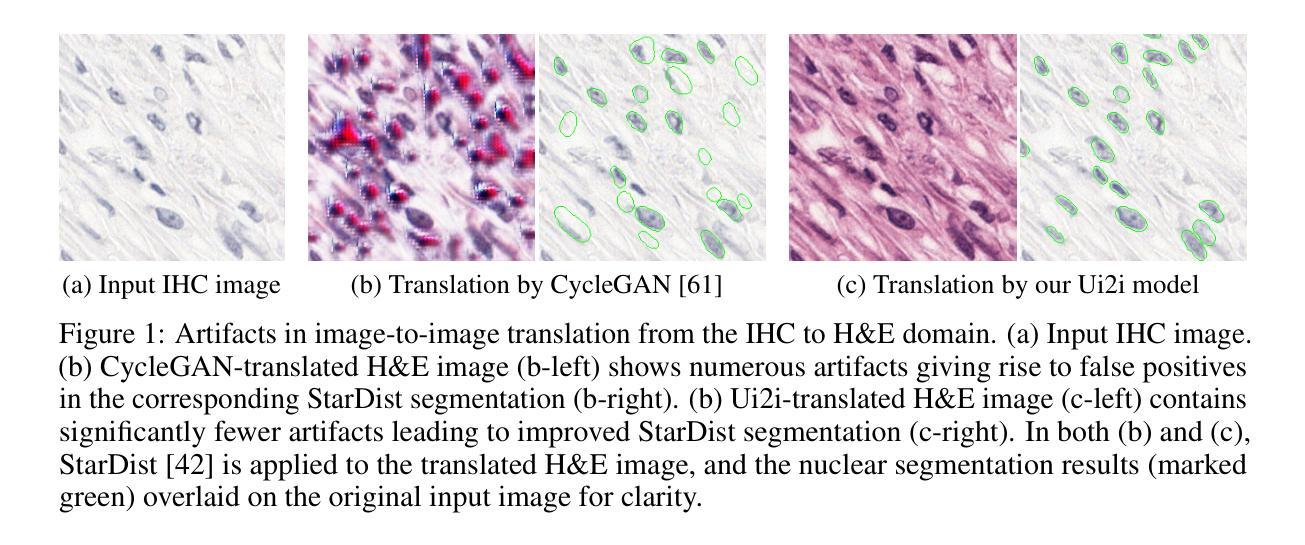
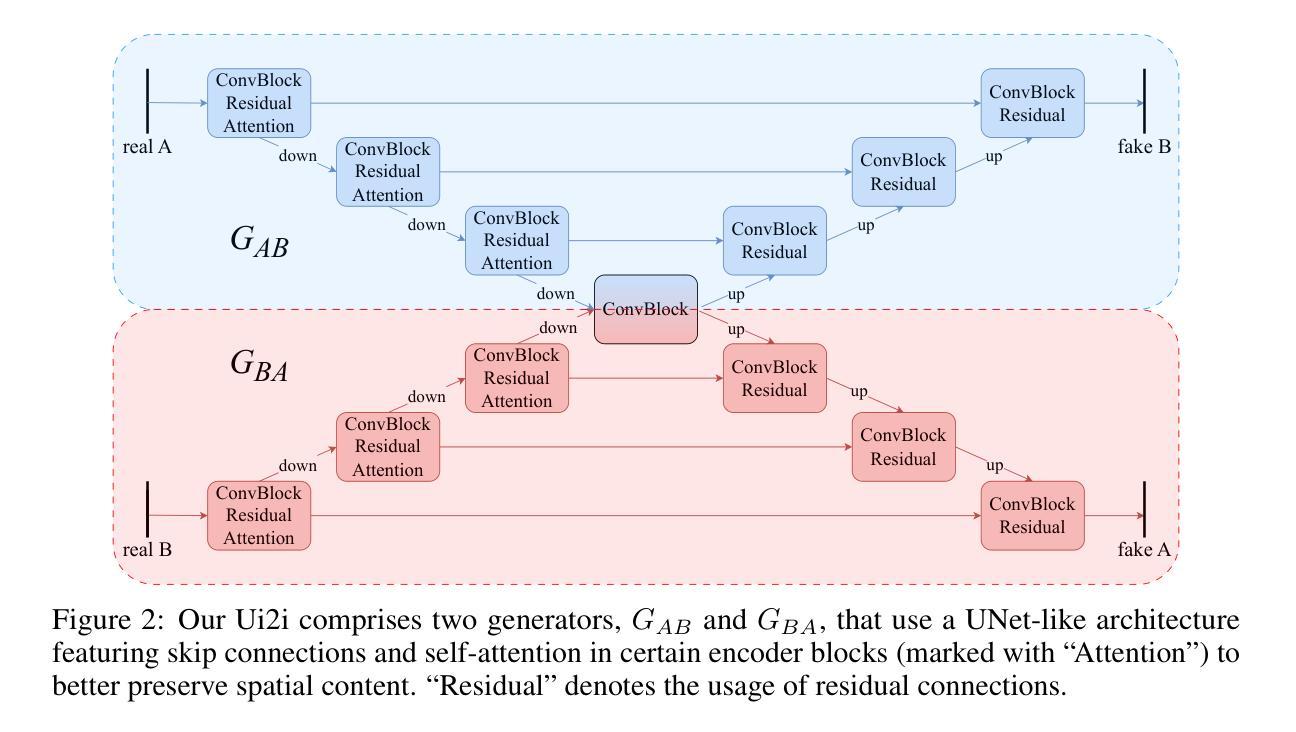
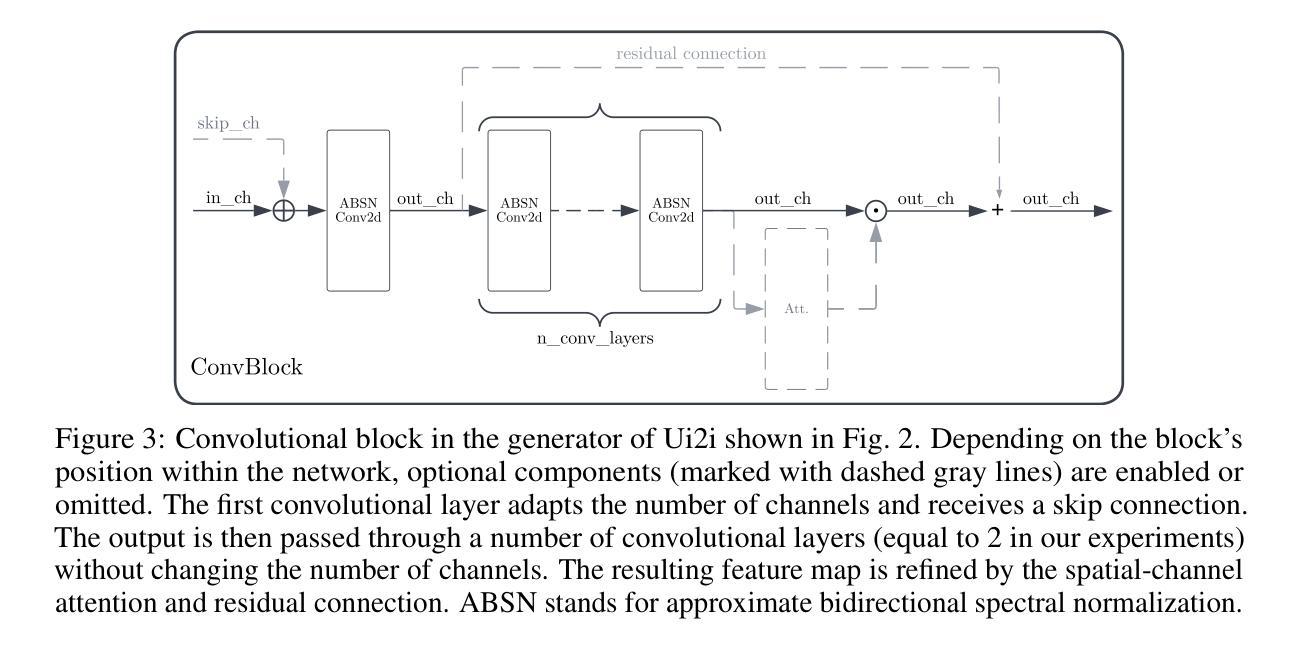
This work introduces Ui2i, a novel model for unpaired image-to-image translation, trained on content-wise unpaired datasets to enable style transfer across domains while preserving content. Building on CycleGAN, Ui2i incorporates key modifications to better disentangle content and style features, and preserve content integrity. Specifically, Ui2i employs U-Net-based generators with skip connections to propagate localized shallow features deep into the generator. Ui2i removes feature-based normalization layers from all modules and replaces them with approximate bidirectional spectral normalization – a parameter-based alternative that enhances training stability. To further support content preservation, channel and spatial attention mechanisms are integrated into the generators. Training is facilitated through image scale augmentation. Evaluation on two biomedical tasks – domain adaptation for nuclear segmentation in immunohistochemistry (IHC) images and unmixing of biological structures superimposed in single-channel immunofluorescence (IF) images – demonstrates Ui2i’s ability to preserve content fidelity in settings that demand more accurate structural preservation than typical translation tasks. To the best of our knowledge, Ui2i is the first approach capable of separating superimposed signals in IF images using real, unpaired training data.
本文介绍了Ui2i,这是一种新型的无配对图像到图像翻译模型。该模型在内容无配对数据集上进行训练,能够在跨域进行风格转移的同时保留内容。Ui2i基于CycleGAN构建,进行了关键修改,以更好地分离内容和风格特征,并保留内容完整性。具体来说,Ui2i采用基于U-Net的生成器,通过跳过连接将局部浅层特征深入传播到生成器中。Ui2i从所有模块中移除了基于特征的归一化层,并用基于参数的双向谱归一化替换它们——这是一种增强训练稳定性的参数化替代方案。为了进一步支持内容保留,将通道和空间注意力机制集成到生成器中。通过图像尺度增强来促进训练。在两项生物医学任务上的评估——免疫组织化学(IHC)图像中的核分割域适应和单通道免疫荧光(IF)图像中叠加生物结构的解混——证明了Ui2i在需要比典型翻译任务更精确的结构保留的设置中保留内容保真度的能力。据我们所知,Ui2i是第一个能够使用真实的、无配对的训练数据在IF图像中分离叠加信号的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to NeurIPs 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Ui2i这一新型的无配对图像到图像翻译模型。该模型在内容无关的未配对数据集上进行训练,能够在不同领域间实现风格转换的同时保留内容。Ui2i基于CycleGAN构建,进行了关键性修改以更好地分离内容和风格特征,并保留内容的完整性。通过采用U-Net基础的生成器与跳过连接,Ui2i能将局部浅层特征深入传播到生成器中。此外,Ui2i移除了所有模块的特征标准化层,并用基于参数的双向谱标准化替代,增强了训练稳定性。为了进一步增强内容保留能力,生成器中集成了通道和空间注意力机制。通过图像尺度增强进行训练。在免疫组织化学(IHC)图像的核分割和单通道免疫荧光(IF)图像的生物结构混合两项生物医学任务上的评估,展示了Ui2i在需要更高精确度结构保留的翻译任务中保持内容保真度的能力。据我们所知,Ui2i是首个能够使用真实、未配对的训练数据在IF图像中分离叠加信号的方法。
Key Takeaways
- Ui2i是一种新型的未配对图像到图像翻译模型,能够进行风格转换并保留内容。
- Ui2i基于CycleGAN构建,并进行改进以更好地分离内容和风格特征。
- Ui2i使用U-Net基础的生成器,利用跳过连接深入传播局部浅层特征。
- Ui2i通过替换特征标准化层并采用基于参数的双向谱标准化,增强了训练稳定性。
- Ui2i集成了通道和空间注意力机制以保留内容。
- Ui2i通过图像尺度增强进行训练。
点此查看论文截图

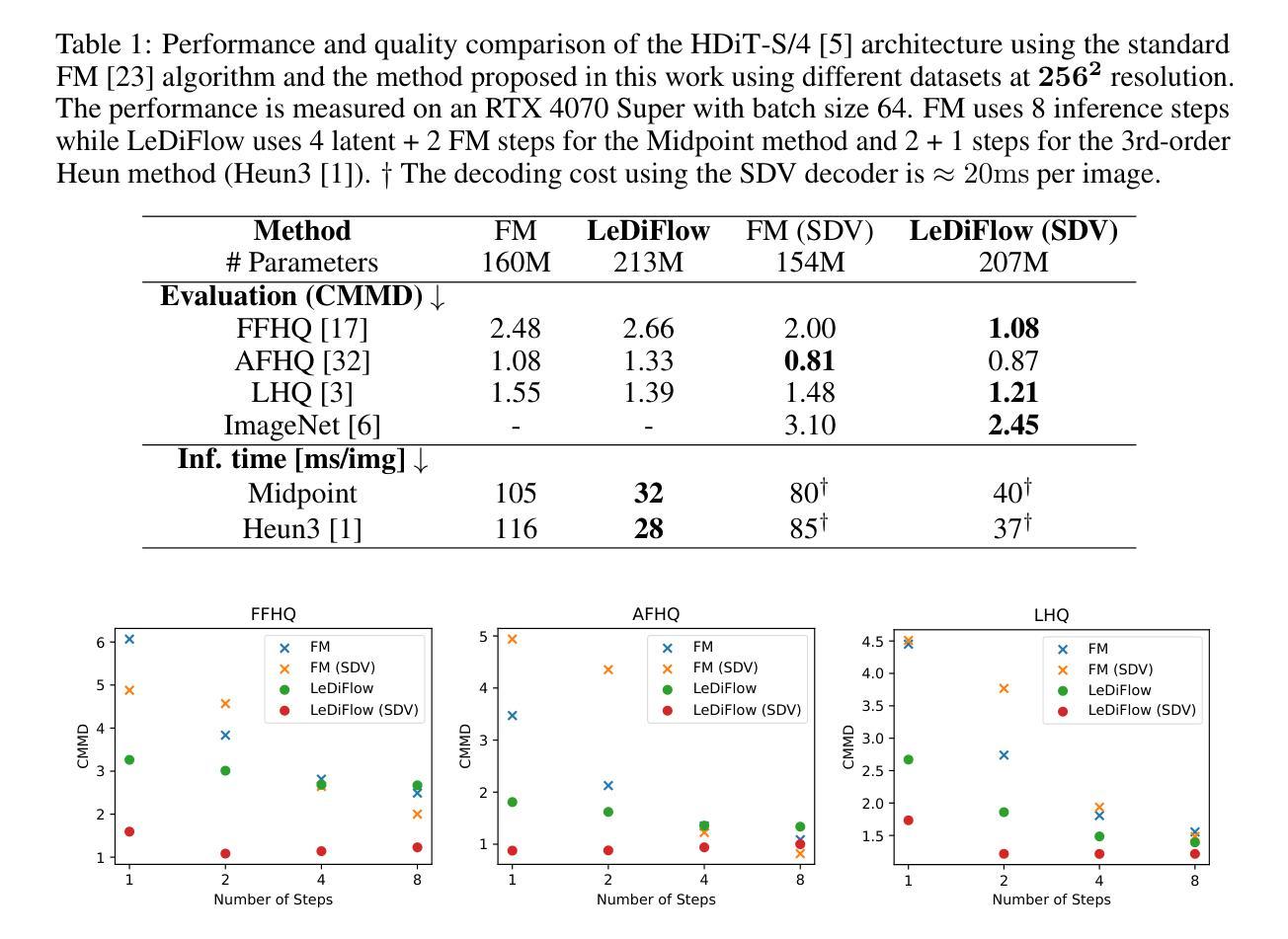
LeDiFlow: Learned Distribution-guided Flow Matching to Accelerate Image Generation
Authors:Pascal Zwick, Nils Friederich, Maximilian Beichter, Lennart Hilbert, Ralf Mikut, Oliver Bringmann
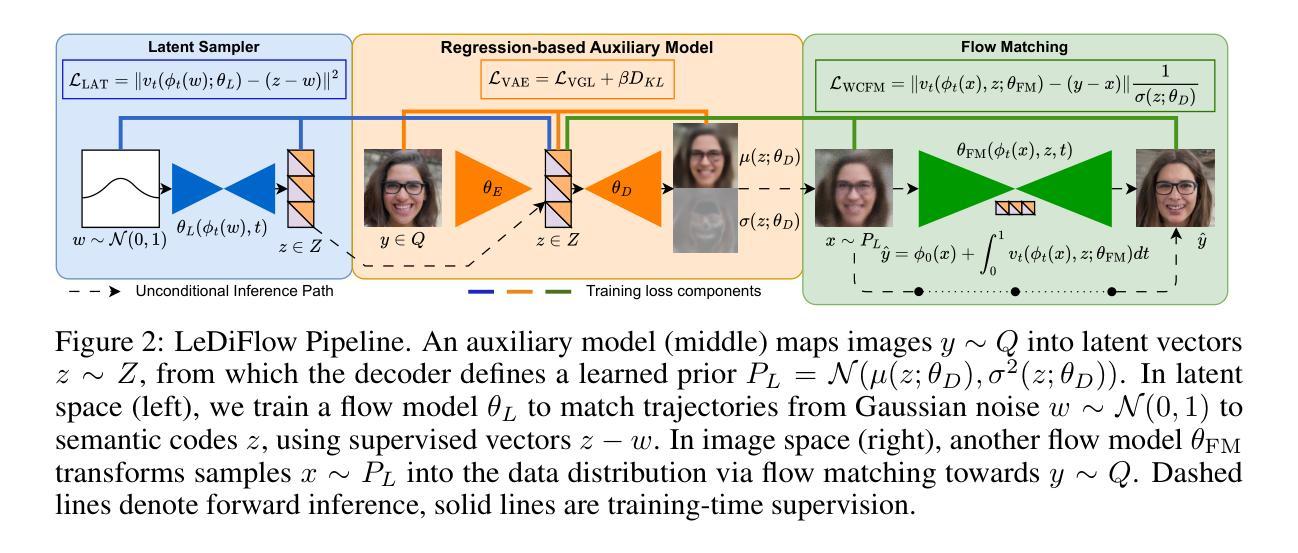
Enhancing the efficiency of high-quality image generation using Diffusion Models (DMs) is a significant challenge due to the iterative nature of the process. Flow Matching (FM) is emerging as a powerful generative modeling paradigm based on a simulation-free training objective instead of a score-based one used in DMs. Typical FM approaches rely on a Gaussian distribution prior, which induces curved, conditional probability paths between the prior and target data distribution. These curved paths pose a challenge for the Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) solver, requiring a large number of inference calls to the flow prediction network. To address this issue, we present Learned Distribution-guided Flow Matching (LeDiFlow), a novel scalable method for training FM-based image generation models using a better-suited prior distribution learned via a regression-based auxiliary model. By initializing the ODE solver with a prior closer to the target data distribution, LeDiFlow enables the learning of more computationally tractable probability paths. These paths directly translate to fewer solver steps needed for high-quality image generation at inference time. Our method utilizes a State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) transformer architecture combined with latent space sampling and can be trained on a consumer workstation. We empirically demonstrate that LeDiFlow remarkably outperforms the respective FM baselines. For instance, when operating directly on pixels, our model accelerates inference by up to 3.75x compared to the corresponding pixel-space baseline. Simultaneously, our latent FM model enhances image quality on average by 1.32x in CLIP Maximum Mean Discrepancy (CMMD) metric against its respective baseline.
提高使用扩散模型(DMs)生成高质量图像的效率是一个重大挑战,因为该过程具有迭代性。流匹配(FM)正崭露头角,成为一种基于无仿真训练目标的强大生成建模范式,而不是DMs中使用的基于分数的范式。典型的FM方法依赖于高斯分布先验,这会在先验和目标数据分布之间产生弯曲的条件概率路径。这些弯曲的路径对常微分方程(ODE)求解器构成了挑战,需要多次调用流预测网络的推理。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于学习分布引导流匹配(LeDiFlow)的新型可扩展方法,用于使用通过基于回归的辅助模型学习到的更合适先验分布来训练FM基于图像的生成模型。通过用更接近目标数据分布的先验来初始化ODE求解器,LeDiFlow能够学习计算上更可行的概率路径。这些路径直接转化为在推理时生成高质量图像所需的更少求解器步骤。我们的方法利用最先进的变压器架构,结合潜在空间采样,可以在消费者工作站上进行训练。我们实证地证明了LeDiFlow显著优于各自的FM基线。例如,直接在像素上操作时,我们的模型将推理加速至最高达3.75倍,相较于相应的像素空间基线。同时,我们的潜在FM模型在CLIP最大均值差异(CMMD)指标上平均提高了图像质量1.32倍,超过了其相应基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于学习分布引导流匹配(LeDiFlow)的方法,用于提高基于流匹配(FM)的图像生成模型的效率。该方法通过使用回归辅助模型学习更合适的先验分布,解决普通微分方程(ODE)求解器面临的挑战。LeDiFlow通过初始化ODE求解器以更接近目标数据分布,学习更具计算可行性的概率路径,从而减少推理时高质量图像生成所需的求解器步骤。实验表明,LeDiFlow显著优于传统FM方法,可直接在像素上操作时加速推理,提高图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配(FM)是一种基于模拟免费训练目标的生成建模范式,挑战在于其迭代性质。
- 传统FM方法依赖于高斯分布先验,导致概率路径弯曲,对ODE求解器构成挑战。
- LeDiFlow通过使用回归辅助模型学习更合适的先验分布来解决这个问题。
- LeDiFlow初始化ODE求解器以更接近目标数据分布,使学习更具计算可行性的概率路径成为可能。
- LeDiFlow方法使用最先进的转换器架构,结合潜伏空间采样,可在消费者工作站上进行训练。
- LeDiFlow显著提高了基于FM的图像生成模型的效率,并可在像素操作时加速推理。
点此查看论文截图

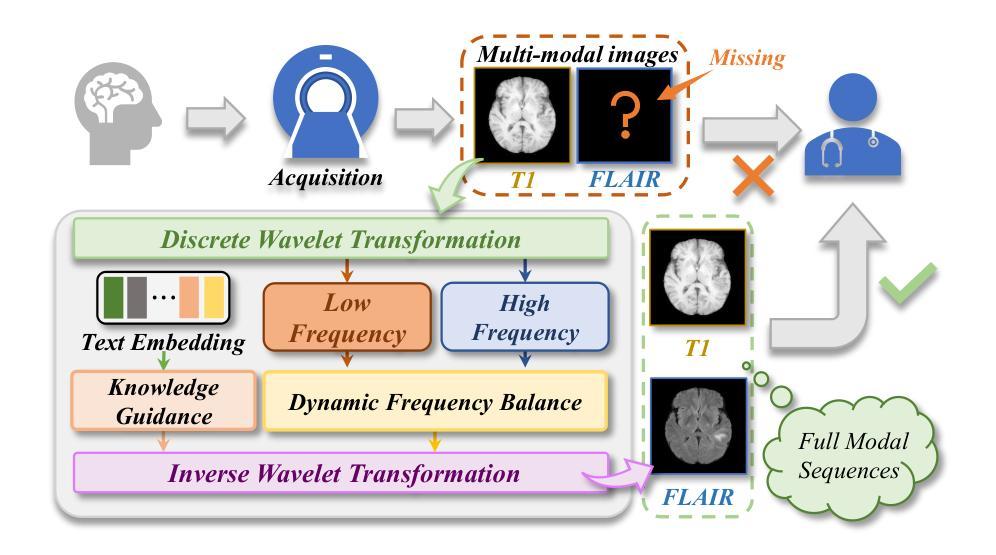
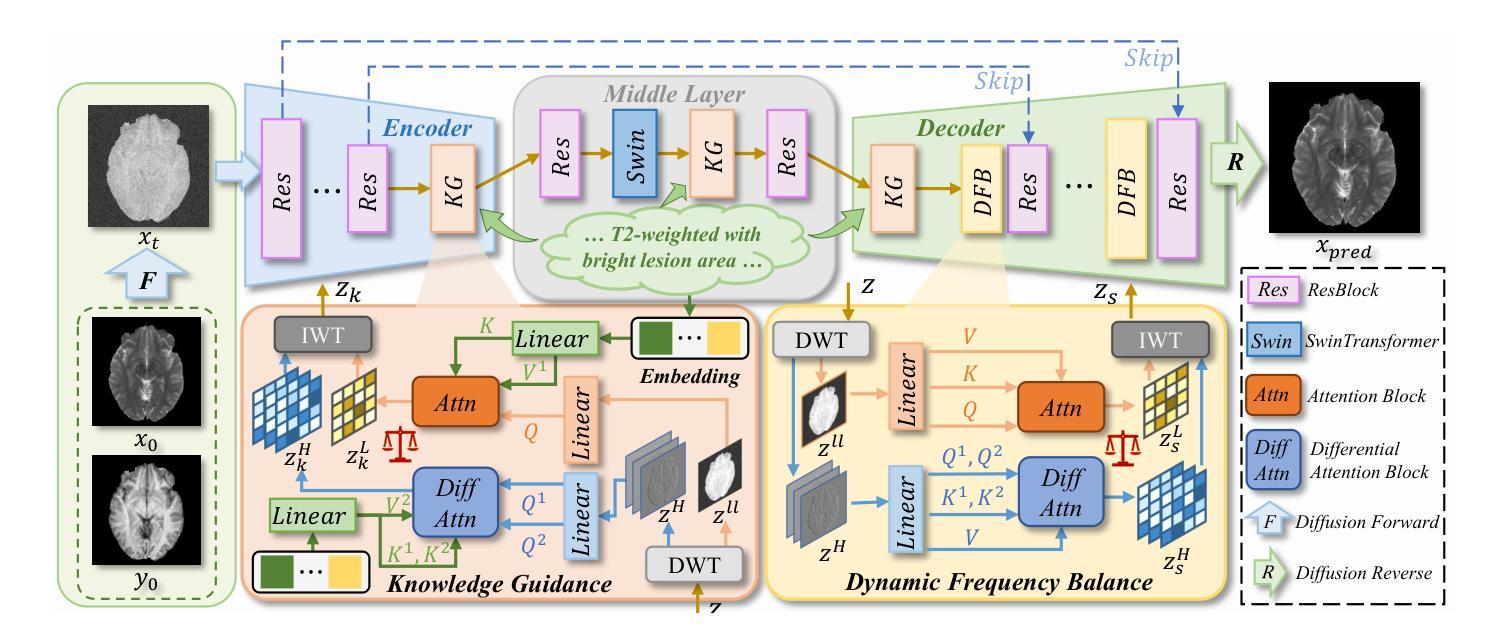
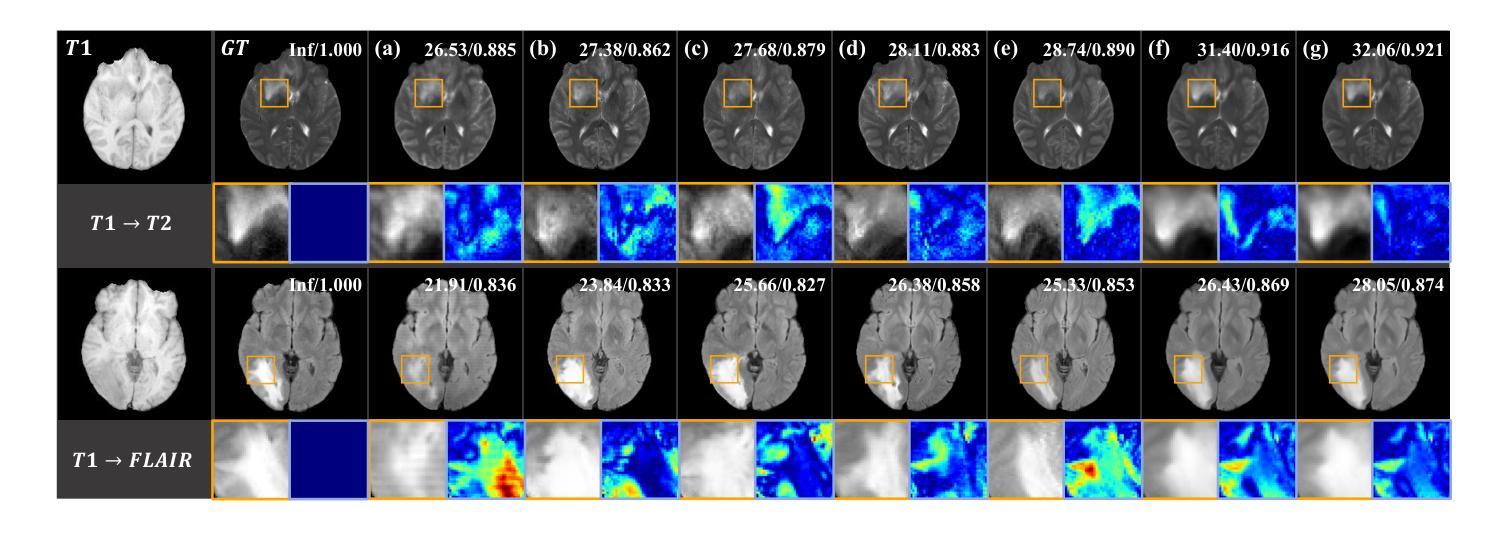
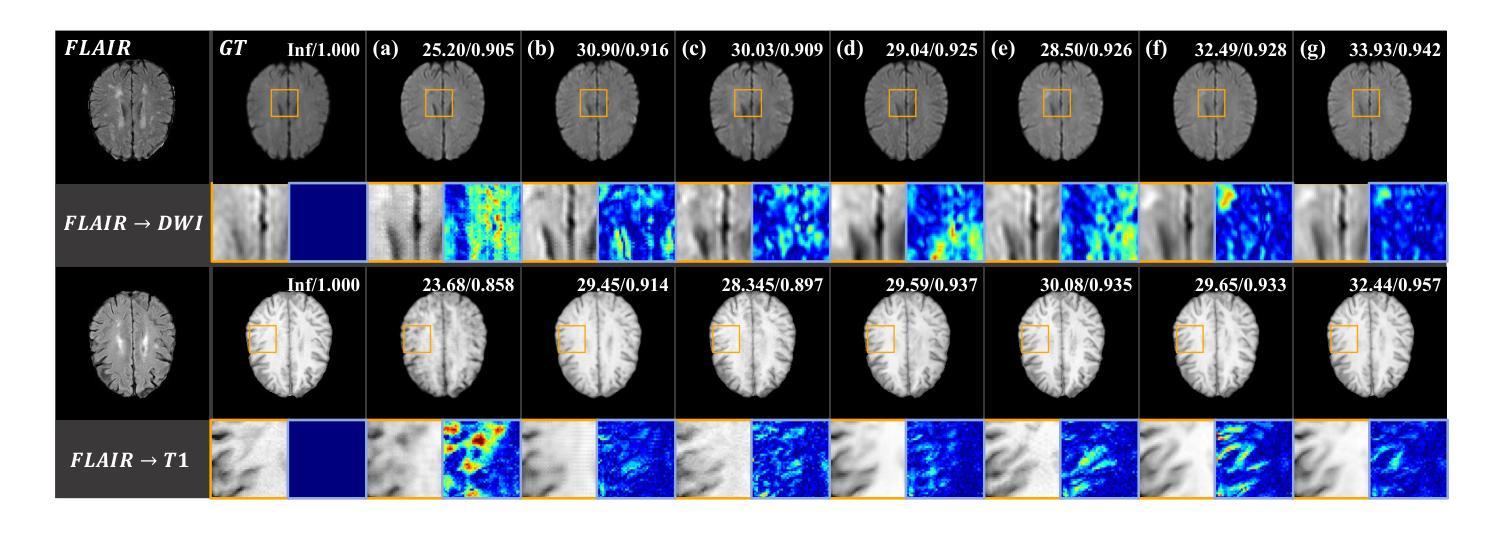
Structure-Accurate Medical Image Translation via Dynamic Frequency Balance and Knowledge Guidance
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Multimodal medical images play a crucial role in the precise and comprehensive clinical diagnosis. Diffusion model is a powerful strategy to synthesize the required medical images. However, existing approaches still suffer from the problem of anatomical structure distortion due to the overfitting of high-frequency information and the weakening of low-frequency information. Thus, we propose a novel method based on dynamic frequency balance and knowledge guidance. Specifically, we first extract the low-frequency and high-frequency components by decomposing the critical features of the model using wavelet transform. Then, a dynamic frequency balance module is designed to adaptively adjust frequency for enhancing global low-frequency features and effective high-frequency details as well as suppressing high-frequency noise. To further overcome the challenges posed by the large differences between different medical modalities, we construct a knowledge-guided mechanism that fuses the prior clinical knowledge from a visual language model with visual features, to facilitate the generation of accurate anatomical structures. Experimental evaluations on multiple datasets show the proposed method achieves significant improvements in qualitative and quantitative assessments, verifying its effectiveness and superiority.
多模态医学图像在精确全面的临床诊断中起着至关重要的作用。扩散模型是合成所需医学图像的一种强大策略。然而,现有方法仍存在因过度拟合高频信息而导致解剖结构失真,以及低频信息减弱的问题。因此,我们提出了一种基于动态频率平衡和知识指导的新方法。具体来说,我们首先通过小波变换分解模型的关键特征来提取低频和高频成分。然后,设计了一个动态频率平衡模块,自适应地调整频率,以增强全局低频特征和有效的高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。为了进一步克服不同医学模态之间巨大差异带来的挑战,我们构建了一个知识引导机制,该机制将视觉语言模型中的先验临床知识与视觉特征相结合,有助于生成准确的解剖结构。在多个数据集上的实验评估表明,该方法在定性和定量评估方面都取得了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical image translation, Diffusion model, 16 pages
Summary
基于动态频率平衡和知识指导的方法在多模态医学图像合成中实现了精确且全面的临床诊断。通过对模型关键特征进行小波变换分解来提取低频和高频成分,并设计动态频率平衡模块自适应调整频率,强化全局低频特征和有效高频细节,同时抑制高频噪声。此外,构建知识引导机制融合视觉语言模型的先验临床知识,克服不同医学模态之间的差异,生成准确的解剖结构。实验评估表明,该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进,验证了其有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态医学图像在临床诊断中扮演重要角色,扩散模型是合成医学图像的有效策略。
- 现有方法存在因过度拟合高频信息而忽略低频信息导致的解剖结构扭曲问题。
- 引入动态频率平衡模块,自适应调整频率以强化低频和有效高频细节,并抑制高频噪声。
- 提出知识引导机制,融合先验临床知识,促进准确解剖结构的生成。
- 方法通过小波变换分解模型关键特征以提取低频和高频成分。
- 实验评估显示该方法在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进。
点此查看论文截图


Overcoming Spurious Solutions in Semi-Dual Neural Optimal Transport: A Smoothing Approach for Learning the Optimal Transport Plan
Authors:Jaemoo Choi, Jaewoong Choi, Dohyun Kwon
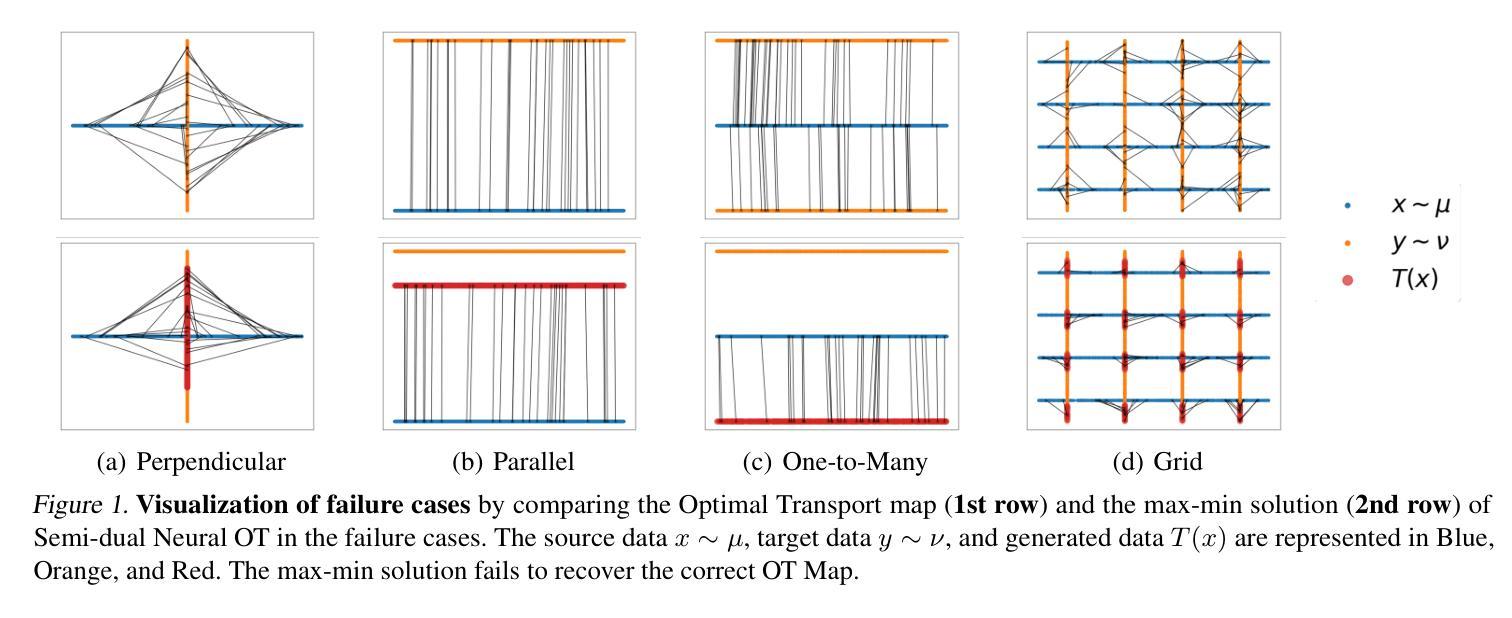
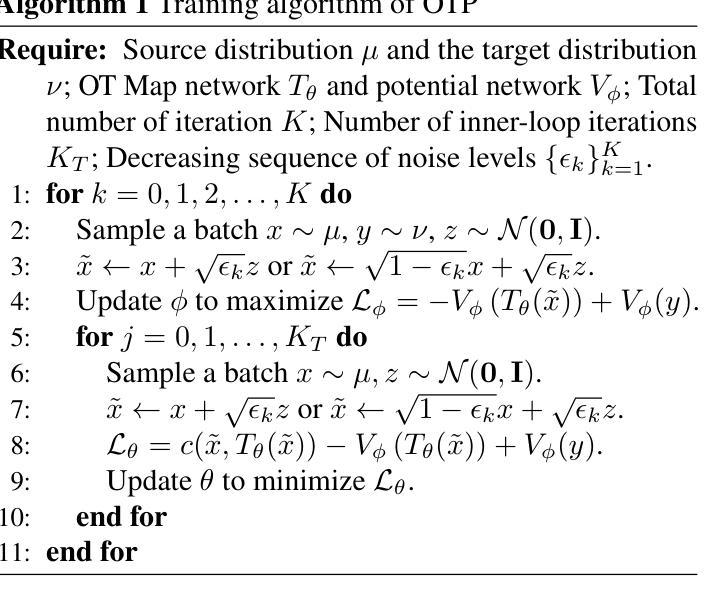
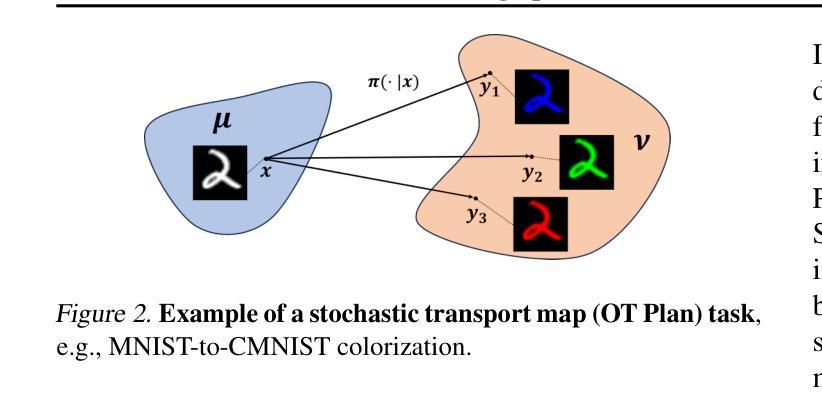
We address the convergence problem in learning the Optimal Transport (OT) map, where the OT Map refers to a map from one distribution to another while minimizing the transport cost. Semi-dual Neural OT, a widely used approach for learning OT Maps with neural networks, often generates spurious solutions that fail to transfer one distribution to another accurately. We identify a sufficient condition under which the max-min solution of Semi-dual Neural OT recovers the true OT Map. Moreover, to address cases when this sufficient condition is not satisfied, we propose a novel method, OTP, which learns both the OT Map and the Optimal Transport Plan, representing the optimal coupling between two distributions. Under sharp assumptions on the distributions, we prove that our model eliminates the spurious solution issue and correctly solves the OT problem. Our experiments show that the OTP model recovers the optimal transport map where existing methods fail and outperforms current OT-based models in image-to-image translation tasks. Notably, the OTP model can learn stochastic transport maps when deterministic OT Maps do not exist, such as one-to-many tasks like colorization.
我们解决了在学习最佳传输(OT)映射中遇到的收敛问题。OT映射指的是从一个分布到另一个分布的映射,同时最小化传输成本。半双神经网络OT(一种广泛用于学习OT映射的神经网络方法)经常会产生虚假解决方案,无法准确地将一个分布转移到另一个分布。我们确定了半双神经网络OT的最大最小解恢复真实OT映射的充分条件。此外,为了解决不满足此充分条件的情况,我们提出了一种新方法OTP,它同时学习OT映射和最佳传输计划,代表两个分布之间的最佳耦合。在关于分布的尖锐假设下,我们证明我们的模型消除了虚假解决方案并正确解决了OT问题。我们的实验表明,在现有方法失败的情况下,OTP模型恢复了最佳传输映射,并在图像到图像的翻译任务中表现出优于当前基于OT的模型。值得注意的是,当确定性OT映射不存在时,例如一对一至多任务的彩色化问题中,OTP模型可以学习随机传输映射。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文解决了学习最优传输(OT)映射中的收敛问题。文章指出半双神经网络OT在生成OT映射时可能出现伪解问题。为解决此问题,文章提出了一个充分条件,在该条件下半双神经网络OT的最大最小解可以恢复真实的OT映射。同时,为满足不满足此充分条件的情况,文章提出了一种新方法OTP,该方法同时学习OT映射和最优传输计划,代表两个分布之间的最优耦合。在分布假设下,文章证明了OTP模型消除了伪解问题并正确解决了OT问题。实验表明,OTP模型在图像转换任务中优于当前基于OT的模型,并能在确定性OT映射不存在时学习随机传输映射,如色彩化等一对一至多任务。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了学习最优传输(OT)映射中的收敛问题。
- 半双神经网络OT在生成OT映射时可能出现伪解问题。
- 提出了一个充分条件,在该条件下半双神经网络OT的最大最小解可以恢复真实的OT映射。
- 为解决不满足充分条件的情况,提出了一种新方法OTP,同时学习OT映射和最优传输计划。
- OTP模型在分布假设下能消除伪解问题并正确解决OT问题。
- 实验表明,OTP模型在图像转换任务中优于当前基于OT的模型。
点此查看论文截图