⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
ArVoice: A Multi-Speaker Dataset for Arabic Speech Synthesis
Authors:Hawau Olamide Toyin, Rufael Marew, Humaid Alblooshi, Samar M. Magdy, Hanan Aldarmaki
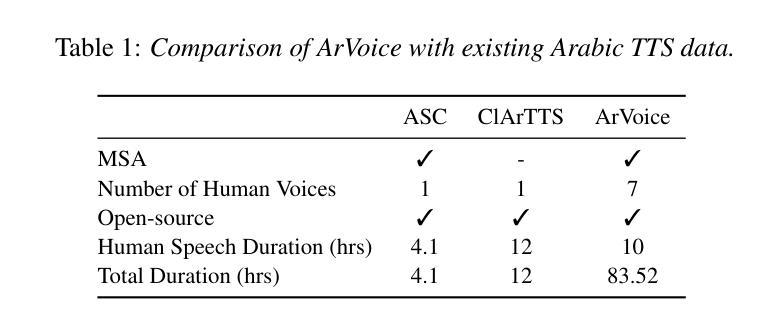
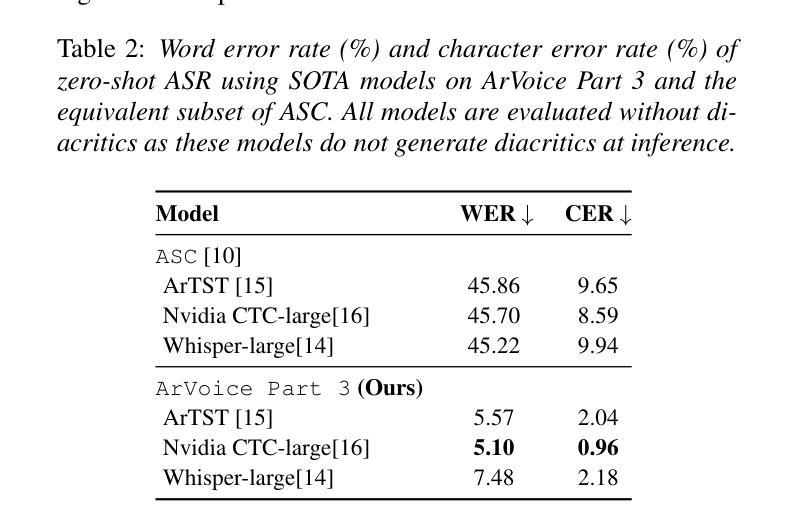
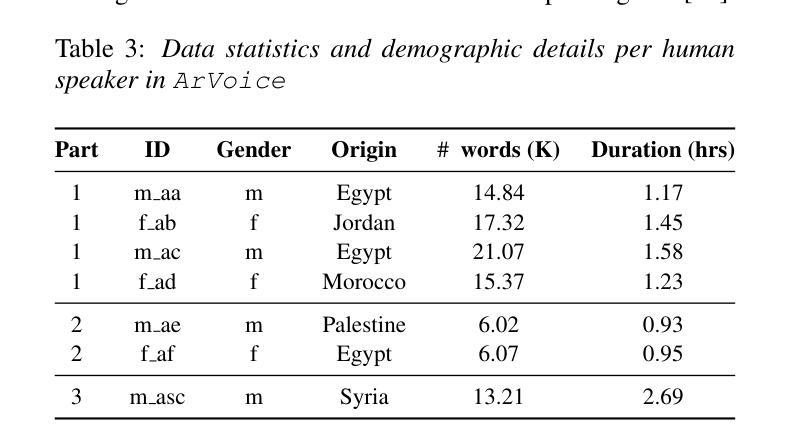
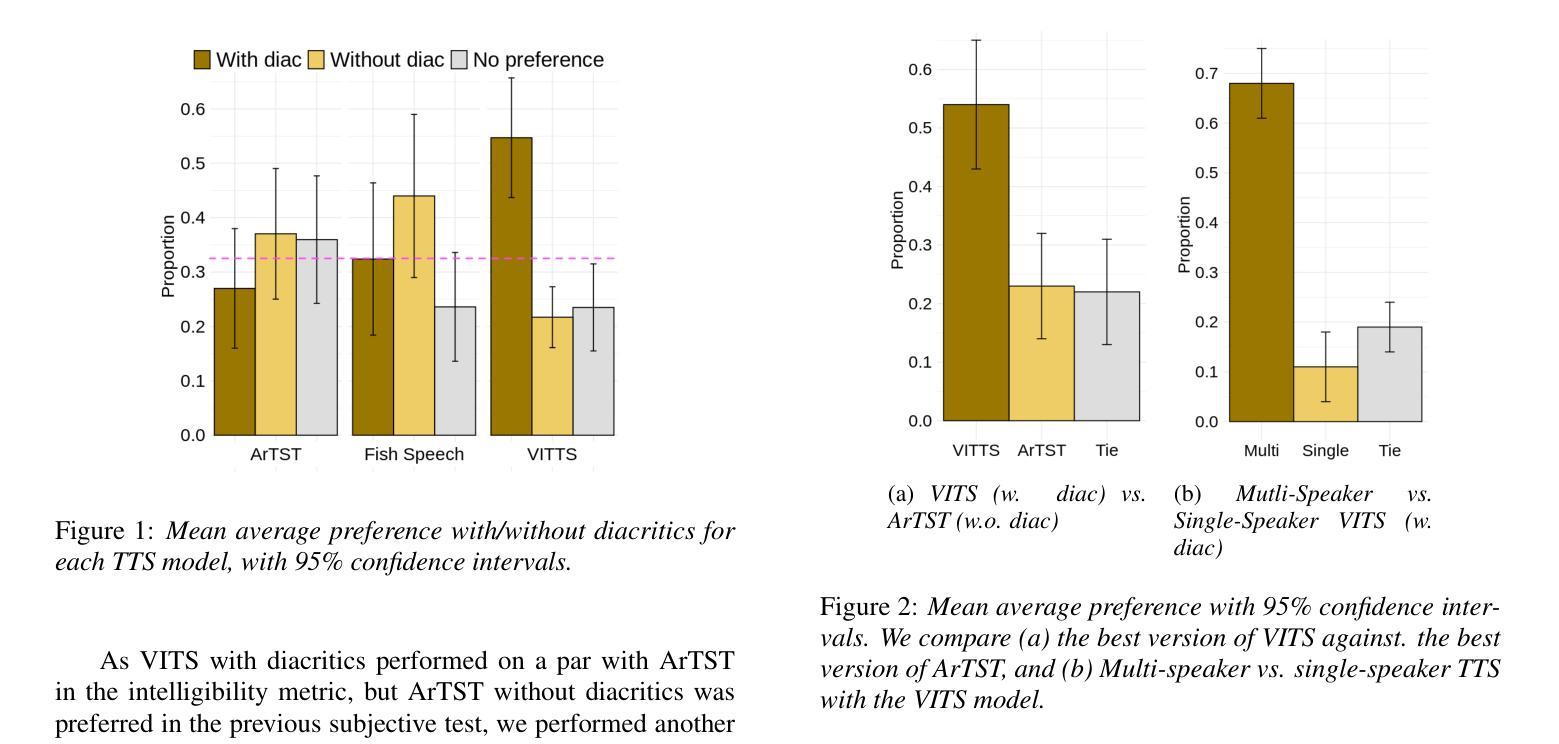
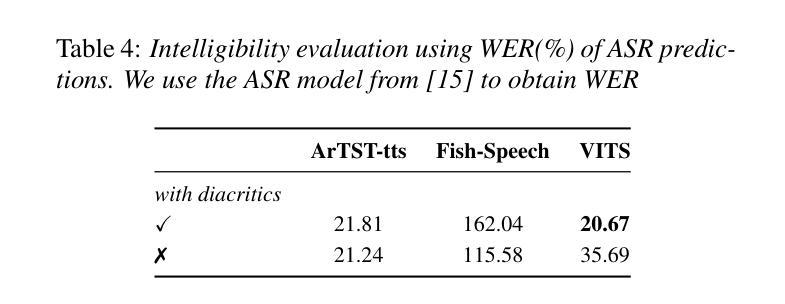
We introduce ArVoice, a multi-speaker Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) speech corpus with diacritized transcriptions, intended for multi-speaker speech synthesis, and can be useful for other tasks such as speech-based diacritic restoration, voice conversion, and deepfake detection. ArVoice comprises: (1) a new professionally recorded set from six voice talents with diverse demographics, (2) a modified subset of the Arabic Speech Corpus; and (3) high-quality synthetic speech from two commercial systems. The complete corpus consists of a total of 83.52 hours of speech across 11 voices; around 10 hours consist of human voices from 7 speakers. We train three open-source TTS and two voice conversion systems to illustrate the use cases of the dataset. The corpus is available for research use.
我们介绍了ArVoice,这是一个多说话人现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)语音语料库,带有加音符号的转录,旨在用于多说话人语音合成,并且对其他任务如基于语音的音标恢复、声音转换和深度伪造检测等也有用。ArVoice包括:(1)由具有不同人口统计特征的六位语音人才录制的新专业集,(2)阿拉伯语音库的修改子集;(3)两个商业系统的高品质合成语音。完整的语料库包含总计83.52小时的语音,跨越11种声音;其中约10小时是人类声音,来自7位说话者。我们训练了三个开源的TTS和两种语音转换系统,以说明该数据集的使用情况。该语料库可用于研究用途。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at INTERSPEECH 2025 The dataset is available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/MBZUAI/ArVoice
Summary
ArVoice是一个多说话人现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)语音语料库,包含带变音符的转录,主要用于多说话人语音合成,也可用于其他任务,如变音符恢复、语音转换和深度伪造检测。它包含专业录制的数据集、修改的阿拉伯语音语料库子集以及两个商业系统的高质量合成语音。该语料库共有83.52小时的语音数据,涵盖11个声音,其中约10小时是人类声音。为展示数据集的应用场景,训练了三个开源文本转语音系统和两个语音转换系统。该语料库可用于研究用途。
Key Takeaways
- ArVoice是一个多说话人的现代标准阿拉伯语语音语料库,包含带变音符的转录。
- 该语料库可用于多说话人语音合成及其他任务,如变音符恢复、语音转换和深度伪造检测。
- ArVoice包含专业录制的数据集、修改的阿拉伯语音语料库子集以及从两个商业系统生成的高质量合成语音。
- 完整语料库包含83.52小时的语音数据,涵盖11个声音,其中约10小时是人类声音。
- 为展示数据集的应用场景,该论文训练了三个开源文本转语音系统和两个语音转换系统。
- ArVoice语料库可用于研究用途。
点此查看论文截图

Guided by Gut: Efficient Test-Time Scaling with Reinforced Intrinsic Confidence
Authors:Amirhosein Ghasemabadi, Keith G. Mills, Baochun Li, Di Niu
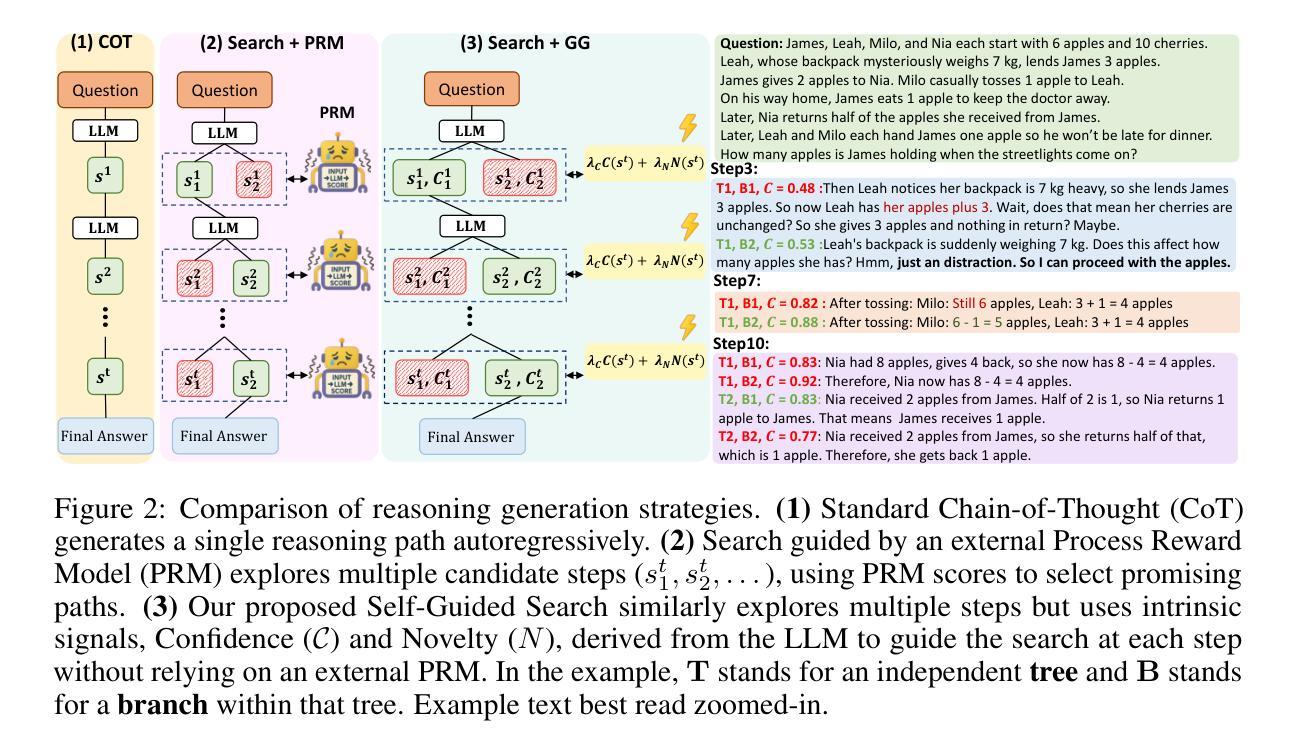
Test-Time Scaling (TTS) methods for enhancing Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning often incur substantial computational costs, primarily due to extensive reliance on external Process Reward Models (PRMs) or sampling methods like Best-of-N (BoN). This paper introduces Guided by Gut (GG), an efficient self-guided TTS framework that achieves PRM-level performance without costly external verifier models. Our method employs a lightweight tree search guided solely by intrinsic LLM signals, token-level confidence and step novelty. One critical innovation is improving the reliability of internal confidence estimates via a targeted reinforcement learning fine-tuning phase. Empirical evaluations on challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that GG enables smaller models (e.g., 1.5B parameters) to achieve accuracy matching or surpassing significantly larger models (e.g., 32B-70B parameters), while reducing GPU memory usage by up to 10x. Compared to PRM-based methods, GG achieves comparable accuracy with 8x faster inference speeds and 4-5x lower memory usage. Additionally, GG reduces KV cache memory usage by approximately 50% compared to the BoN strategy, facilitating more efficient and practical deployment of TTS techniques.
测试时缩放(TTS)方法通常用于增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,但会产生巨大的计算成本,这主要是因为严重依赖外部过程奖励模型(PRM)或如最佳N(BoN)这样的采样方法。本文介绍了“听从内心”(GG)这一高效的自我引导TTS框架,它无需昂贵的外部验证模型即可实现PRM级别的性能。我们的方法采用轻量级的树搜索,仅由内在LLM信号、令牌级信心和步骤新颖性来指导。一个关键的创新点是通过有针对性的强化学习微调阶段来提高内部信心估计的可靠性。在具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的经验评估表明,GG使较小的模型(例如,1.5B参数)能够达到或超过显著较大的模型(例如,32B-70B参数)的准确度,同时将GPU内存使用率降低高达10倍。与基于PRM的方法相比,GG以8倍的推理速度实现了相当的精度,并降低了4-5倍的内存使用率。此外,与BoN策略相比,GG减少了大约50%的KV缓存内存使用,使TTS技术的部署更加高效实用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了名为Guided by Gut的TTS框架,它能够在不使用昂贵的外部验证模型的情况下实现PRM级别的性能。该框架通过采用轻量级树搜索、基于LLM的固有信号、令牌级别的置信度和步骤新颖性来工作。重要创新之一是通过有针对性的强化学习微调阶段提高了内部置信度估计的可靠性。它在具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的实证评估表明,GG使较小的模型能够实现与较大的模型相匹配或更高的准确性,同时减少了GPU内存使用量。与PRM方法相比,GG实现了相当的准确性,同时推理速度提高了8倍,内存使用率降低了4-5倍。此外,与BoN策略相比,GG减少了KV缓存内存的使用量约50%,使得TTS技术的部署更加高效实用。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的主要见解:
- Guided by Gut是一个高效的自我引导TTS框架,无需依赖昂贵的外部验证模型即可实现PRM级别的性能。
- 该框架通过轻量级树搜索、固有LLM信号进行工作,并结合令牌级别的置信度和步骤新颖性来实现高效推理。
- 通过强化学习微调阶段提高了内部置信度估计的可靠性。
- GG能在较小的模型上实现与较大的模型相匹配或更高的准确性,并在数学推理基准测试中表现出优越性能。
- 与PRM方法相比,GG提供了更快的推理速度和更低的内存使用效率。
点此查看论文截图

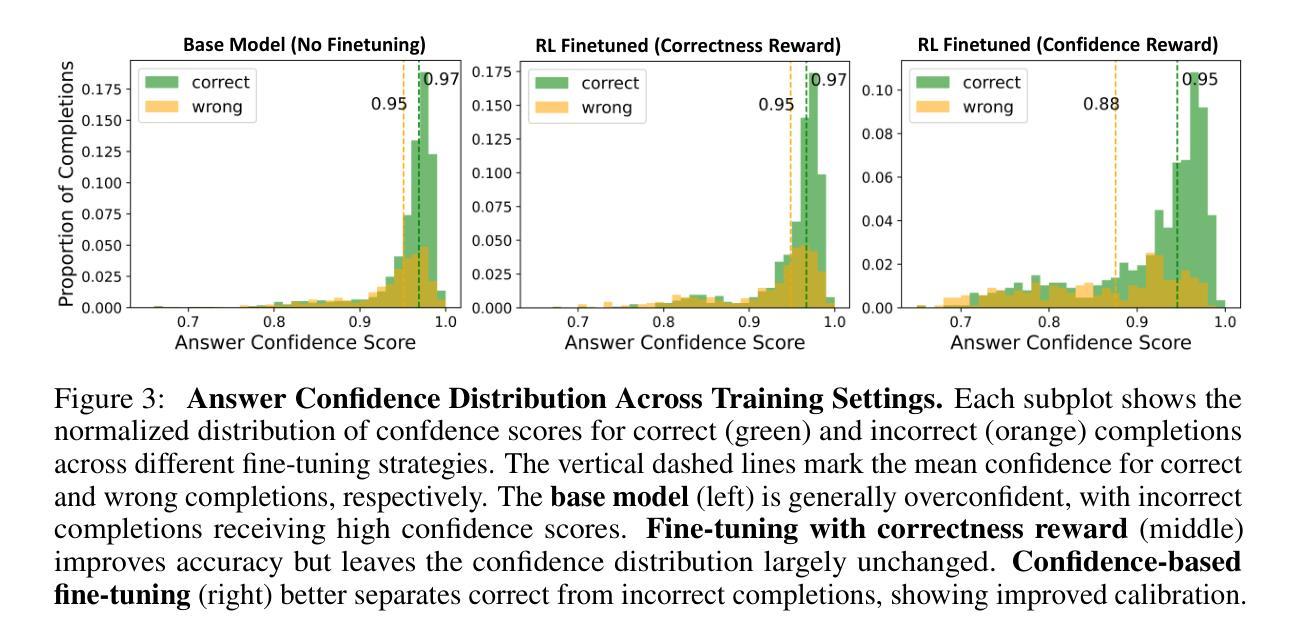
PMOA-TTS: Introducing the PubMed Open Access Textual Times Series Corpus
Authors:Shahriar Noroozizadeh, Sayantan Kumar, George H. Chen, Jeremy C. Weiss
Understanding temporal dynamics in clinical narratives is essential for modeling patient trajectories, yet large-scale temporally annotated resources remain limited. We present PMOA-TTS, the first openly available dataset of 124,699 PubMed Open Access (PMOA) case reports, each converted into structured (event, time) timelines via a scalable LLM-based pipeline. Our approach combines heuristic filtering with Llama 3.3 to identify single-patient case reports, followed by prompt-driven extraction using Llama 3.3 and DeepSeek R1, resulting in over 5.6 million timestamped clinical events. To assess timeline quality, we evaluate against a clinician-curated reference set using three metrics: (i) event-level matching (80% match at a cosine similarity threshold of 0.1), (ii) temporal concordance (c-index > 0.90), and (iii) Area Under the Log-Time CDF (AULTC) for timestamp alignment. Corpus-level analysis shows wide diagnostic and demographic coverage. In a downstream survival prediction task, embeddings from extracted timelines achieve time-dependent concordance indices up to 0.82 $\pm$ 0.01, demonstrating the predictive value of temporally structured narratives. PMOA-TTS provides a scalable foundation for timeline extraction, temporal reasoning, and longitudinal modeling in biomedical NLP. The dataset is available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/snoroozi/pmoa-tts .
理解临床叙述中的时间动态对于建立患者轨迹模型至关重要,然而大规模的时间注释资源仍然有限。我们推出了PMOA-TTS,这是第一个公开可用的数据集,包含124,699篇PubMed Open Access(PMOA)病例报告,每个报告都通过可扩展的LLM管道转换为结构化(事件,时间)时间表。我们的方法结合了启发式过滤和Llama 3.3来识别单个患者的病例报告,然后使用Llama 3.3和DeepSeek R1进行提示驱动提取,产生了超过560万的时间戳临床事件。为了评估时间表的质量,我们使用临床医生编制的参考集,通过三个指标进行评估:(i)事件级别匹配(在余弦相似性阈值为0.1的情况下达到80%的匹配度),(ii)时间一致性(c指数> 0.9),以及(iii)时间戳对齐的Log-Time CDF下的面积(AULTC)。语料库级别的分析显示出广泛的诊断和人口覆盖面。在下游的生存预测任务中,从提取的时间表中获得的嵌入达到了高达0.82±0.01的时间依赖性一致性指数,证明了时序结构化叙述的预测价值。PMOA-TTS为时间序列提取、时间推理和纵向建模提供了可扩展的基础,在生物医学NLP领域具有广泛应用。数据集可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/snoroozi/pmoa-tts找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PMOA-TTS数据集,这是首个公开的、包含124,699篇PubMed Open Access案例报告的数据集。通过可扩展的LLM管道将这些报告转换为结构化(事件,时间)时间线。数据集用于评估时间线质量,并在下游生存预测任务中表现出良好的预测性能。PMOA-TTS为生物医学NLP中的时间线提取、时间推理和纵向建模提供了可扩展的基础。
Key Takeaways
- PMOA-TTS是首个公开的、大规模的临床叙事数据集,包含124,699篇PubMed Open Access案例报告。
- 利用LLM管道实现了结构化的(事件,时间)时间线转换。
- 结合启发式过滤和Llama 3.3技术,以及基于prompt的提取和DeepSeek R1技术,实现了超过560万的时间戳临床事件提取。
- 通过三个指标评估时间线质量:事件级别匹配、时间一致性和时间戳对齐的累积分布函数下的面积(AULTC)。
- 数据集涵盖广泛的诊断和人口统计数据,具有良好的覆盖面。
- 在下游生存预测任务中,提取的时间线嵌入达到了较高的预测性能,显示了结构化叙事的时间预测价值。
点此查看论文截图

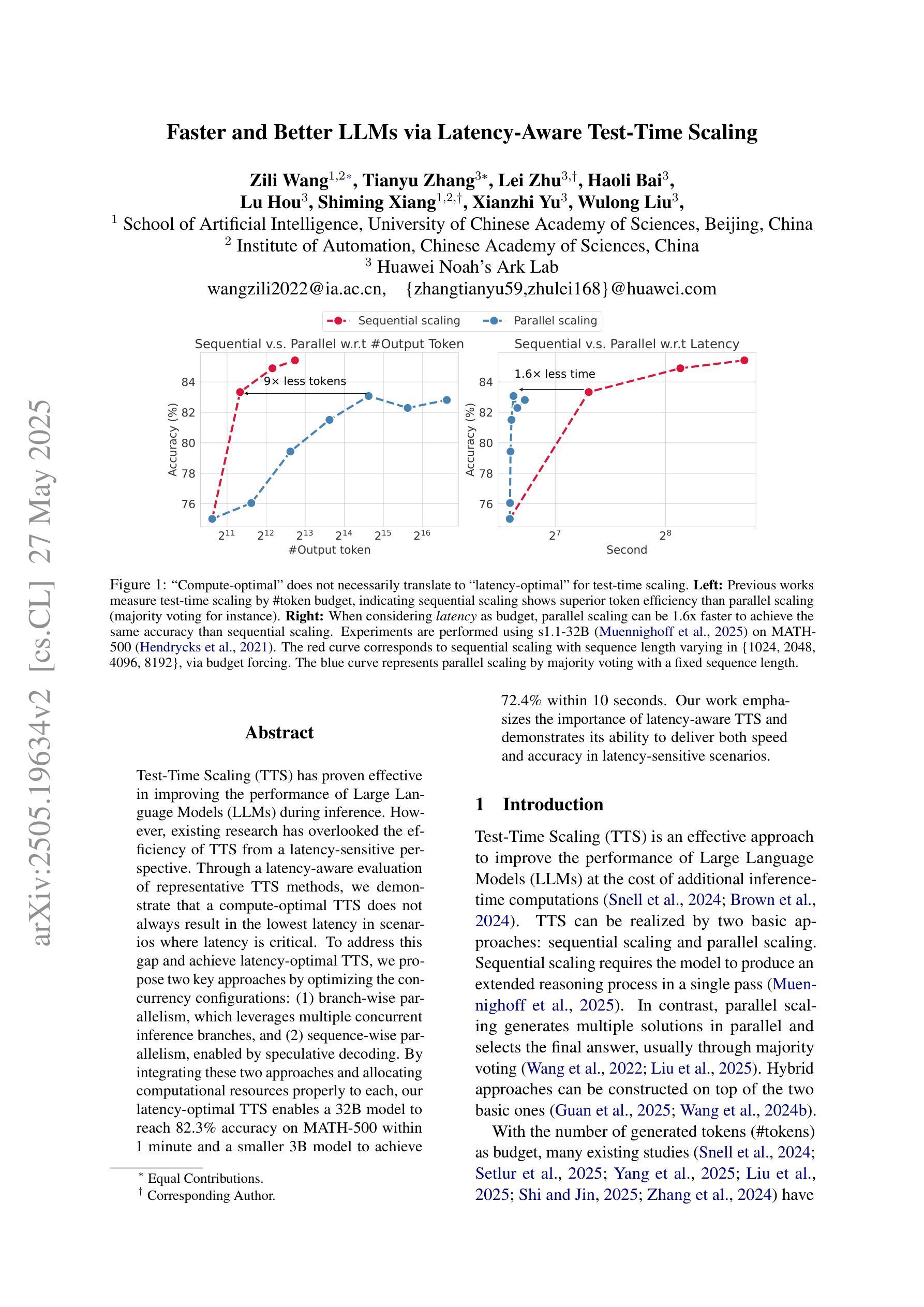
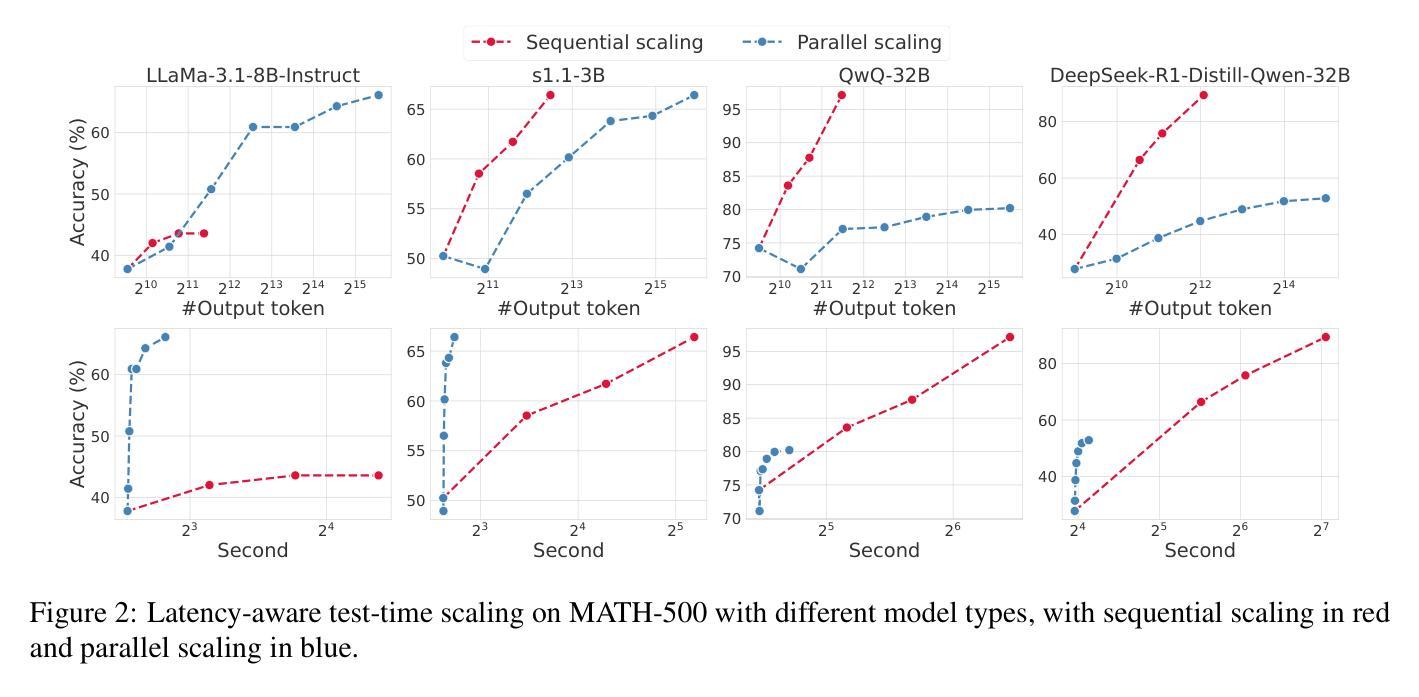
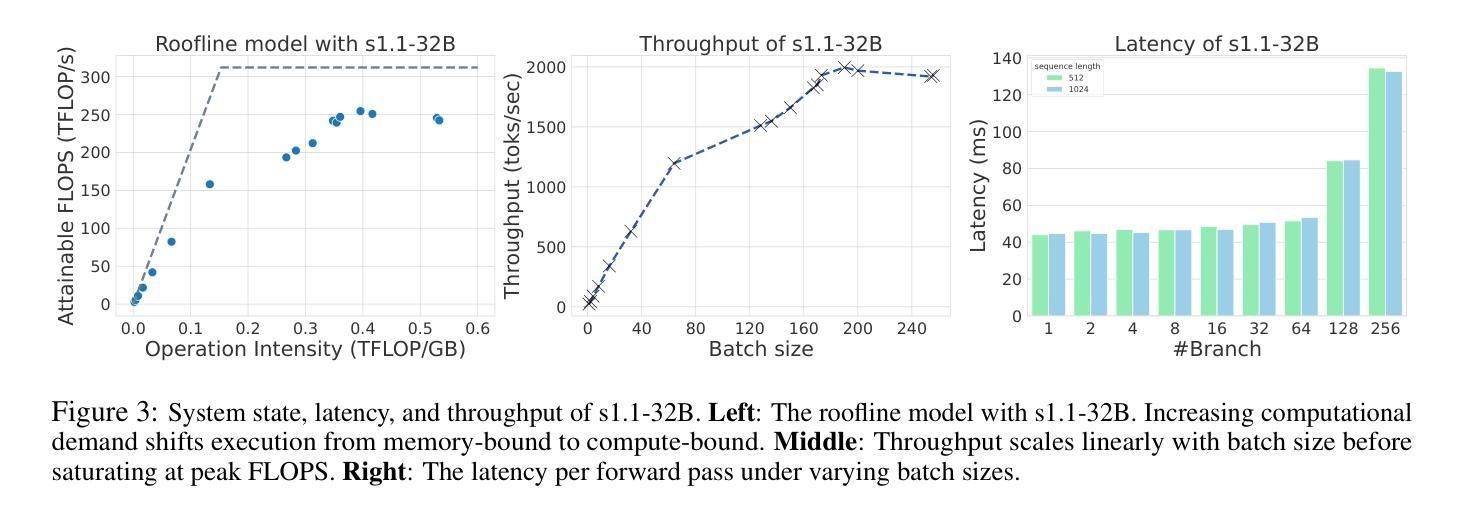
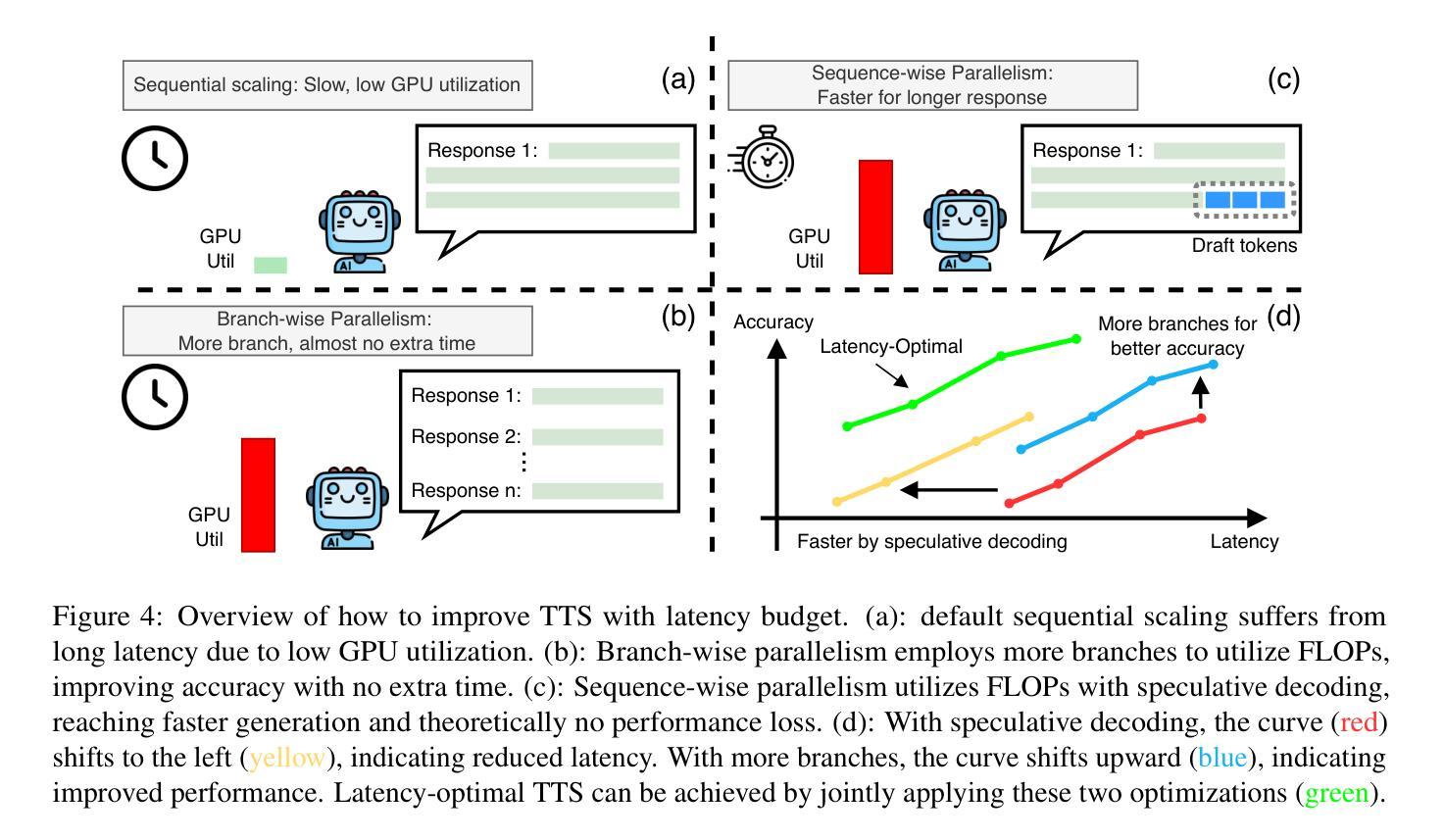
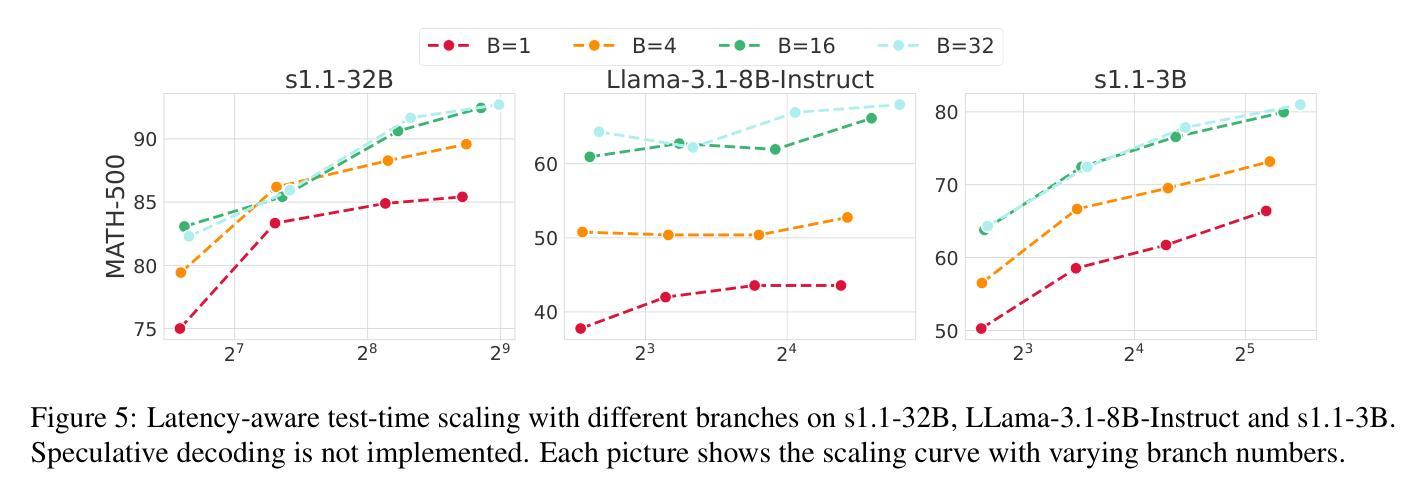
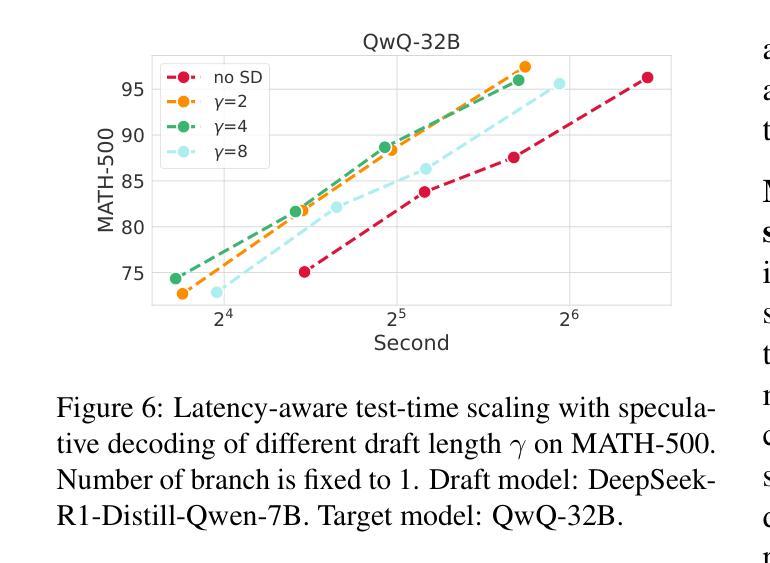
Faster and Better LLMs via Latency-Aware Test-Time Scaling
Authors:Zili Wang, Tianyu Zhang, Haoli Bai, Lu Hou, Xianzhi Yu, Wulong Liu, Shiming Xiang, Lei Zhu
Test-Time Scaling (TTS) has proven effective in improving the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) during inference. However, existing research has overlooked the efficiency of TTS from a latency-sensitive perspective. Through a latency-aware evaluation of representative TTS methods, we demonstrate that a compute-optimal TTS does not always result in the lowest latency in scenarios where latency is critical. To address this gap and achieve latency-optimal TTS, we propose two key approaches by optimizing the concurrency configurations: (1) branch-wise parallelism, which leverages multiple concurrent inference branches, and (2) sequence-wise parallelism, enabled by speculative decoding. By integrating these two approaches and allocating computational resources properly to each, our latency-optimal TTS enables a 32B model to reach 82.3% accuracy on MATH-500 within 1 minute and a smaller 3B model to achieve 72.4% within 10 seconds. Our work emphasizes the importance of latency-aware TTS and demonstrates its ability to deliver both speed and accuracy in latency-sensitive scenarios.
测试时缩放(TTS)已证明在推理过程中可以提高大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。然而,现有研究从延迟敏感的角度忽视了TTS的效率。通过对代表性TTS方法进行延迟感知评估,我们证明计算最优的TTS并不总是导致延迟最低,这在延迟至关重要的场景中尤为关键。为了解决这一差距并实现延迟最优的TTS,我们提出了两种通过优化并发配置的关键方法:(1)分支并行性,利用多个并发推理分支;(2)通过猜测解码实现序列并行性。通过整合这两种方法并为每种方法适当分配计算资源,我们的延迟最优TTS使32B模型在MATH-500上1分钟内达到82.3%的准确率,较小的3B模型在10秒内达到72.4%的准确率。我们的工作强调了延迟感知TTS的重要性,并展示了其在延迟敏感场景中实现速度和准确性的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
测试时间尺度(TTS)可改善大型语言模型(LLM)的推理性能。但现有研究未从延迟敏感的角度充分评估TTS的效率。通过延迟感知的评估方法,我们发现计算最优的TTS并不总是导致最低延迟,这在延迟至关重要的情况下尤为明显。为解决这一差距并实现延迟优化的TTS,我们提出两种优化并发配置的关键方法:(1)分支并行性,利用多个并发推理分支;(2)序列并行性,通过投机解码实现。通过整合这两种方法并为每个分配适当的计算资源,我们的延迟优化TTS使32B模型在MATH-500上在1分钟内达到82.3%的准确率,较小的3B模型在10秒内达到72.4%的准确率。我们的工作强调了延迟感知TTS的重要性,并展示了其在延迟敏感场景中实现速度和准确性的能力。
Key Takeaways
- TTS在提高大型语言模型推理性能方面具有有效性。
- 现有研究未充分从延迟敏感的角度评估TTS的效率。
- 计算最优的TTS并不总是导致最低延迟。
- 提出分支并行性和序列并行性两种优化并发配置的方法。
- 通过整合这两种方法,延迟优化TTS能在短时间内实现较高的准确率。
- 延迟优化TTS在延迟敏感场景中能同时提高速度和准确性。
- 重视延迟感知的TTS是很重要的。
点此查看论文截图
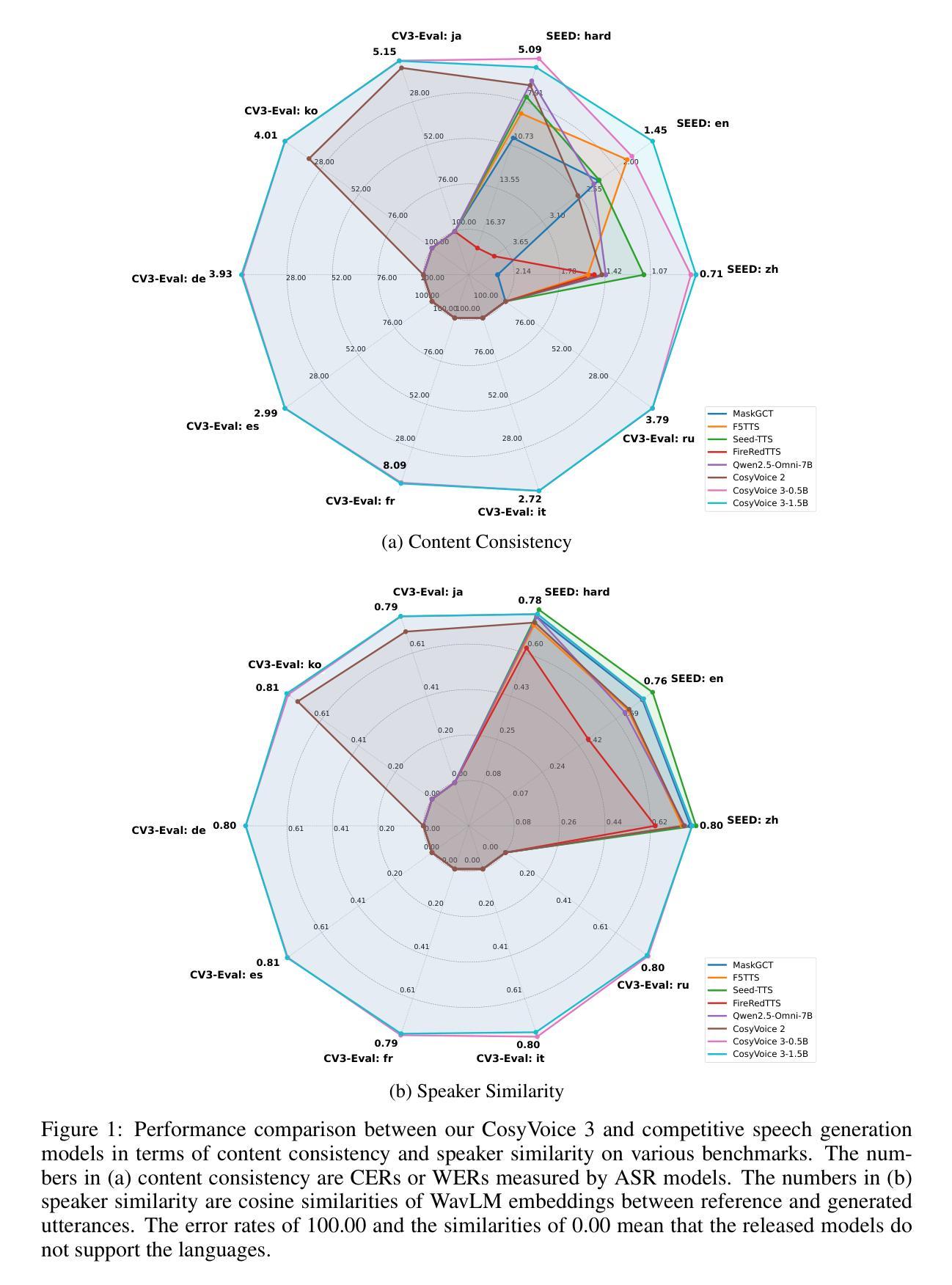
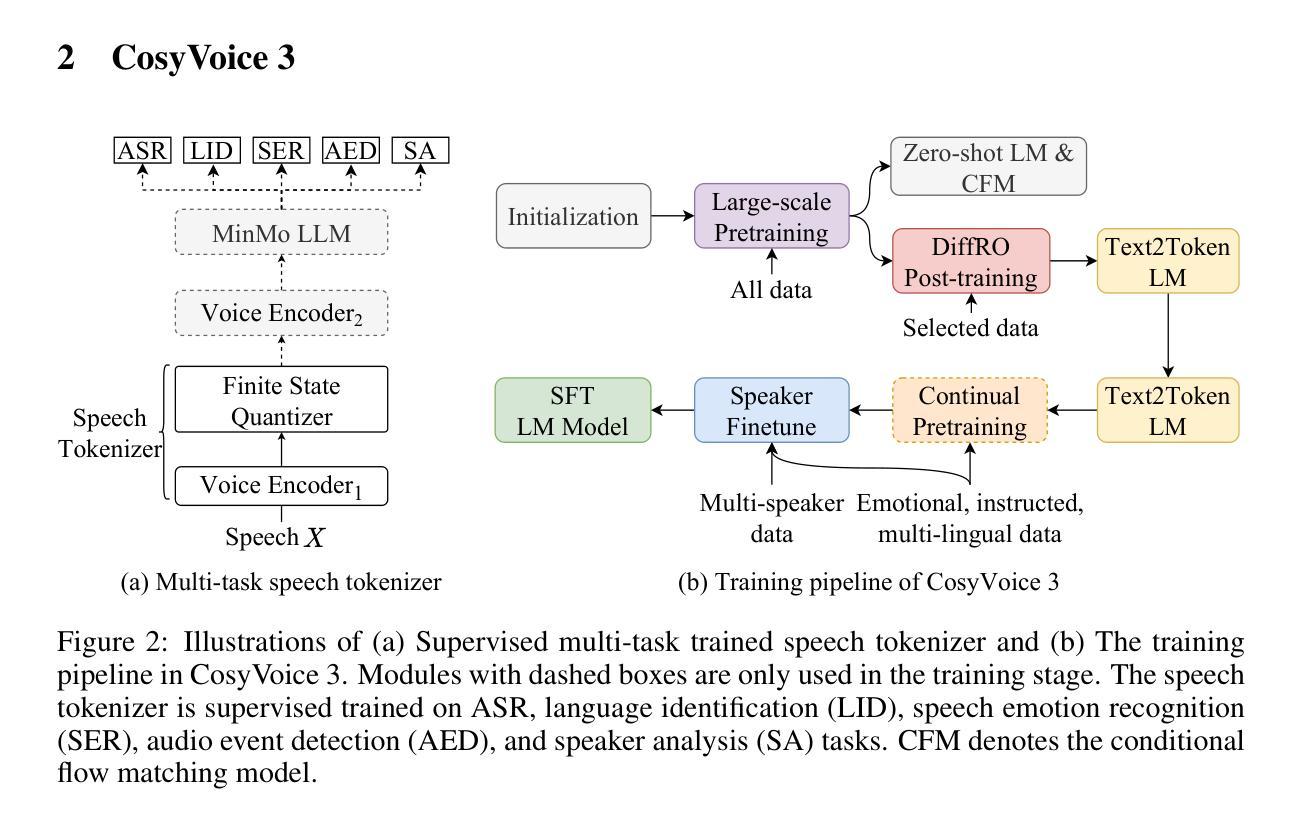
CosyVoice 3: Towards In-the-wild Speech Generation via Scaling-up and Post-training
Authors:Zhihao Du, Changfeng Gao, Yuxuan Wang, Fan Yu, Tianyu Zhao, Hao Wang, Xiang Lv, Hui Wang, Chongjia Ni, Xian Shi, Keyu An, Guanrou Yang, Yabin Li, Yanni Chen, Zhifu Gao, Qian Chen, Yue Gu, Mengzhe Chen, Yafeng Chen, Shiliang Zhang, Wen Wang, Jieping Ye
In our prior works, we introduced a scalable streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which integrates a large language model (LLM) and a chunk-aware flow matching (FM) model, and achieves low-latency bi-streaming speech synthesis and human-parity quality. Despite these advancements, CosyVoice 2 exhibits limitations in language coverage, domain diversity, data volume, text formats, and post-training techniques. In this paper, we present CosyVoice 3, an improved model designed for zero-shot multilingual speech synthesis in the wild, surpassing its predecessor in content consistency, speaker similarity, and prosody naturalness. Key features of CosyVoice 3 include: 1) A novel speech tokenizer to improve prosody naturalness, developed via supervised multi-task training, including automatic speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, language identification, audio event detection, and speaker analysis. 2) A new differentiable reward model for post-training applicable not only to CosyVoice 3 but also to other LLM-based speech synthesis models. 3) Dataset Size Scaling: Training data is expanded from ten thousand hours to one million hours, encompassing 9 languages and 18 Chinese dialects across various domains and text formats. 4) Model Size Scaling: Model parameters are increased from 0.5 billion to 1.5 billion, resulting in enhanced performance on our multilingual benchmark due to the larger model capacity. These advancements contribute significantly to the progress of speech synthesis in the wild. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3.
在我们之前的工作中,我们推出了一款可扩展的流式语音合成模型CosyVoice 2,它集成了一个大型语言模型(LLM)和一块分块感知流匹配(FM)模型,实现了低延迟双流式语音合成和与人类相当的质量。尽管有了这些进步,CosyVoice 2在语言覆盖、领域多样性、数据量、文本格式和后续训练技术方面仍存在局限性。在本文中,我们介绍了CosyVoice 3,这是一款改进后的模型,旨在实现野外零镜头多语言语音合成,在内容一致性、演讲者相似性和语调自然性方面超越了其前身。CosyVoice 3的主要特点包括:1)一种新型语音标记器,通过监督多任务训练开发,旨在提高语调的自然性,包括自动语音识别、语音情感识别、语言识别、音频事件检测和说话人分析。2)一种新的可微奖励模型,适用于训练后的训练,不仅适用于CosyVoice 3,而且适用于其他基于LLM的语音合成模型。3)数据集大小缩放:训练数据从一万小时扩展到一百万小时,涵盖9种语言和18种中文方言,跨越各种领域和文本格式。4)模型大小缩放:模型参数从0.5亿增加到15亿,由于模型容量更大,我们的多语种基准测试性能得到提升。这些进步对野外语音合成的进展做出了重大贡献。我们鼓励读者在https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3上听取演示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, work in progress
Summary
新一代语音合成模型CosyVoice 3问世,集成了大型语言模型与一系列新技术,支持零起点多语种语音合成。相比上一代,它在内容一致性、说话人相似性和语调自然度方面取得显著进步。采用了全新的语音分词器,能应对各种语音任务。推出新型可微调节奖励模型,扩大训练数据集至一千万小时,涵盖九种语言和十八种中文方言。模型参数增至十五亿,显著提升多语种基准测试性能。
Key Takeaways
- CosyVoice 3引入了新型零起点多语种语音合成技术,提高了内容一致性、说话人相似性和语调自然度。
- 采用了全新的语音分词器,通过多任务训练提升语调自然度。
- 推出新型可微调节奖励模型,适用于多种语言模型。
- 训练数据集大幅扩展至一千万小时,涵盖多种语言和方言。
- 模型参数增至十五亿,增强了多语种性能表现。
- 新模型在多种领域和文本格式上表现出强大的适应性。
点此查看论文截图

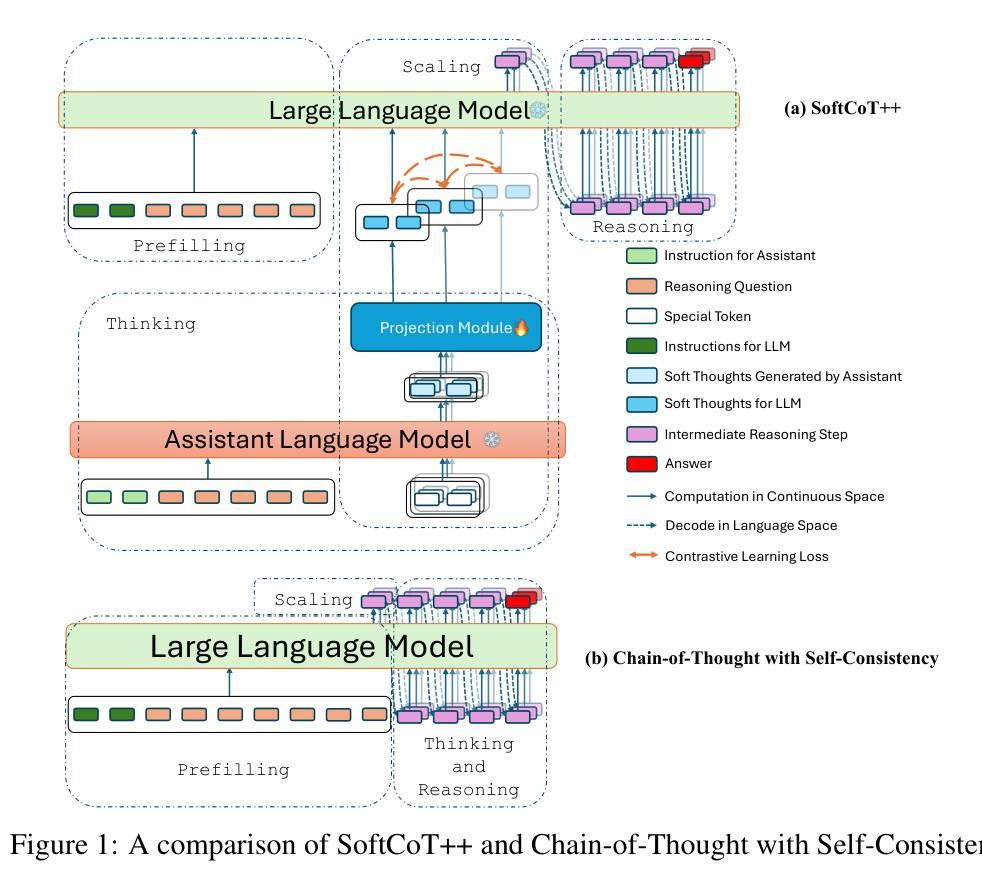
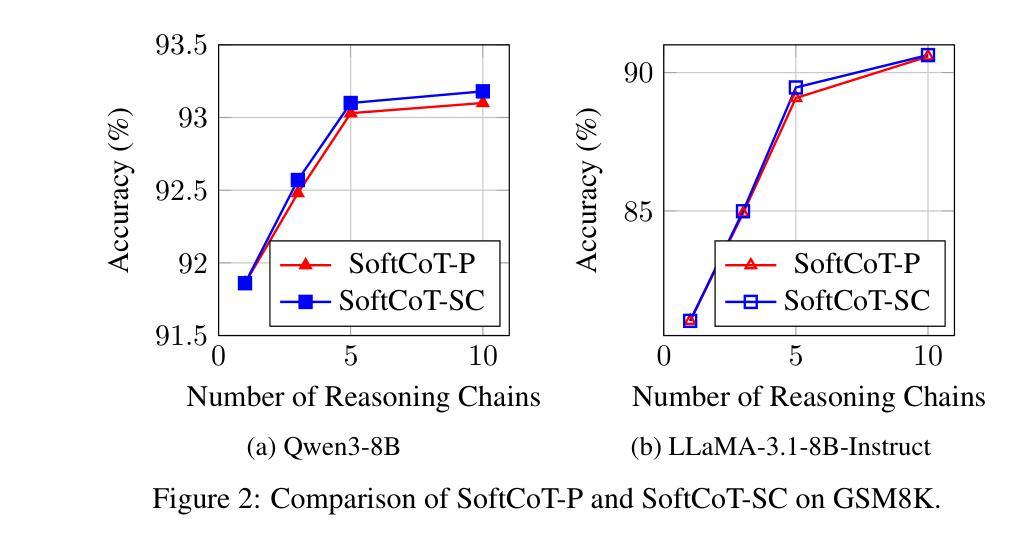
SoftCoT++: Test-Time Scaling with Soft Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Yige Xu, Xu Guo, Zhiwei Zeng, Chunyan Miao
Test-Time Scaling (TTS) refers to approaches that improve reasoning performance by allocating extra computation during inference, without altering the model’s parameters. While existing TTS methods operate in a discrete token space by generating more intermediate steps, recent studies in Coconut and SoftCoT have demonstrated that thinking in the continuous latent space can further enhance the reasoning performance. Such latent thoughts encode informative thinking without the information loss associated with autoregressive token generation, sparking increased interest in continuous-space reasoning. Unlike discrete decoding, where repeated sampling enables exploring diverse reasoning paths, latent representations in continuous space are fixed for a given input, which limits diverse exploration, as all decoded paths originate from the same latent thought. To overcome this limitation, we introduce SoftCoT++ to extend SoftCoT to the Test-Time Scaling paradigm by enabling diverse exploration of thinking paths. Specifically, we perturb latent thoughts via multiple specialized initial tokens and apply contrastive learning to promote diversity among soft thought representations. Experiments across five reasoning benchmarks and two distinct LLM architectures demonstrate that SoftCoT++ significantly boosts SoftCoT and also outperforms SoftCoT with self-consistency scaling. Moreover, it shows strong compatibility with conventional scaling techniques such as self-consistency. Source code is available at https://github.com/xuyige/SoftCoT.
测试时缩放(TTS)是指通过在推理过程中分配额外的计算资源来提高推理性能的方法,而不会改变模型的参数。虽然现有的TTS方法在离散标记空间中进行操作,通过生成更多的中间步骤来工作,但最近的Coconut和SoftCoT研究表明,在连续潜在空间中进行思考可以进一步提高推理性能。这种潜在的想法可以编码信息丰富的思考过程,而没有自回归标记生成所带来的信息损失,这引发了人们对连续空间推理的浓厚兴趣。与离散解码不同,离散解码通过重复采样可以探索多样的推理路径,而连续空间中的潜在表示对于给定输入是固定的,这限制了多样的探索,因为所有解码路径都源于相同的潜在想法。为了克服这一局限性,我们引入SoftCoT++,将SoftCoT扩展到测试时缩放范式,通过特殊的初始标记扰动思考路径,并应用对比学习来促进软思考表示之间的多样性。在五个推理基准测试和两种不同的大型语言模型架构上的实验表明,SoftCoT++显著提升了SoftCoT的性能,并且优于SoftCoT的自一致性缩放。此外,它显示出与常规缩放技术(如自一致性)的强大兼容性。源代码可在https://github.com/xuyige/SoftCoT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
文本描述了Test-Time Scaling(TTS)的概念及其在推理性能提升方面的作用。传统TTS方法在离散标记空间操作,而Coconut和SoftCoT研究显示连续潜在空间思考能提高推理性能。为克服连续空间中潜在表示带来的探索多样性限制,提出SoftCoT++方法,通过多个专用初始标记扰动潜在思考,并采用对比学习促进软思考表示之间的多样性。实验表明,SoftCoT++在五个推理基准测试和两个不同的大型语言模型架构上显著提升了SoftCoT的性能,并且与传统扩展技术如自我一致性扩展兼容。
Key Takeaways
- Test-Time Scaling (TTS) 是指在推理过程中分配额外的计算资源以提高性能,而不改变模型的参数。
- 传统TTS方法在离散标记空间操作,但连续潜在空间思考能提高推理性能。
- SoftCoT++方法通过多个专用初始标记扰动潜在思考,促进推理过程中的多样性探索。
- SoftCoT++显著提升了SoftCoT的性能,并在多个推理基准测试上表现优异。
- SoftCoT++与传统扩展技术如自我一致性扩展兼容。
- 连续空间思考减少了信息损失,不同于离散解码的重复采样能够探索不同的推理路径。
点此查看论文截图

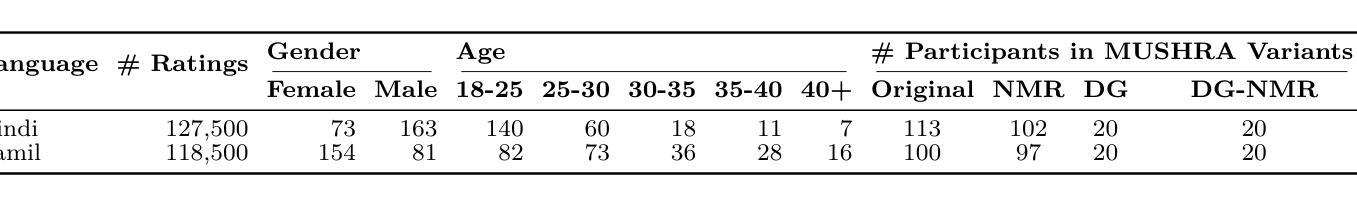
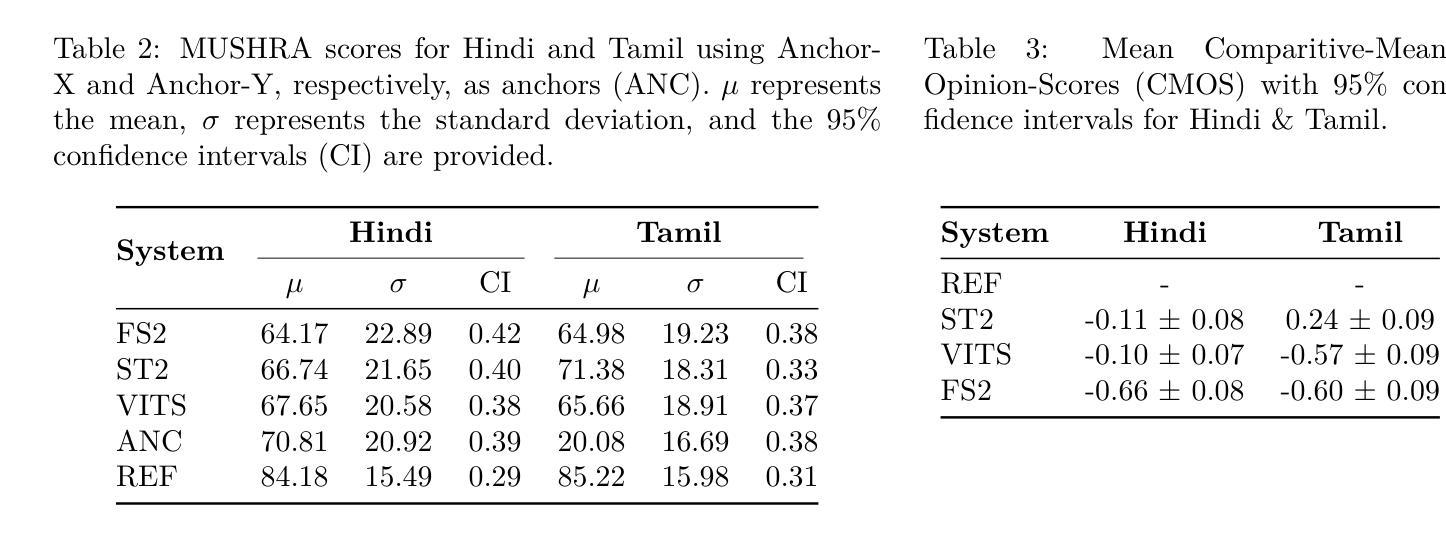
Rethinking MUSHRA: Addressing Modern Challenges in Text-to-Speech Evaluation
Authors:Praveen Srinivasa Varadhan, Amogh Gulati, Ashwin Sankar, Srija Anand, Anirudh Gupta, Anirudh Mukherjee, Shiva Kumar Marepally, Ankur Bhatia, Saloni Jaju, Suvrat Bhooshan, Mitesh M. Khapra
Despite rapid advancements in TTS models, a consistent and robust human evaluation framework is still lacking. For example, MOS tests fail to differentiate between similar models, and CMOS’s pairwise comparisons are time-intensive. The MUSHRA test is a promising alternative for evaluating multiple TTS systems simultaneously, but in this work we show that its reliance on matching human reference speech unduly penalises the scores of modern TTS systems that can exceed human speech quality. More specifically, we conduct a comprehensive assessment of the MUSHRA test, focusing on its sensitivity to factors such as rater variability, listener fatigue, and reference bias. Based on our extensive evaluation involving 492 human listeners across Hindi and Tamil we identify two primary shortcomings: (i) reference-matching bias, where raters are unduly influenced by the human reference, and (ii) judgement ambiguity, arising from a lack of clear fine-grained guidelines. To address these issues, we propose two refined variants of the MUSHRA test. The first variant enables fairer ratings for synthesized samples that surpass human reference quality. The second variant reduces ambiguity, as indicated by the relatively lower variance across raters. By combining these approaches, we achieve both more reliable and more fine-grained assessments. We also release MANGO, a massive dataset of 246,000 human ratings, the first-of-its-kind collection for Indian languages, aiding in analyzing human preferences and developing automatic metrics for evaluating TTS systems.
尽管TTS模型发展迅速,但缺乏一个稳定且强大的人类评估框架。例如,MOS测试无法区分相似的模型,CMOS的配对比较又很耗时。MUSHRA测试是评估多个TTS系统的一个很有前景的替代方法,但在这项工作中我们发现,它对匹配人类参考语音的依赖,过分地惩罚了现代TTS系统的得分,这些系统的语音质量甚至超过了人类。更具体地说,我们对MUSHRA测试进行了全面的评估,重点研究其对评分者差异性、听众疲劳和参考偏见等因素的敏感性。基于涉及印度语和泰米尔语共492名听众的广泛评估,我们发现了两个主要问题:(i)参考匹配偏见,评分者受到人为参考的过度影响;(ii)由于缺少明确的精细指导而产生的判断模糊性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了两种改进的MUSHRA测试变种。第一种变体允许对超越人类参考质量的合成样本进行更公平的评分。第二种变体通过减少评分者之间的相对较低的方差来降低模糊性。通过结合这两种方法,我们实现了更可靠、更精细的评估。我们还发布了MANGO数据集,这是一个人类评分的巨大数据集,包含24万6千条评分,是印度语言领域首创的此类数据集,有助于分析人类偏好并开发用于评估TTS系统的自动度量指标。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in TMLR
摘要
本文探讨了TTS模型评估中存在的问题。尽管TTS技术发展迅速,但仍缺乏一致且稳健的人机评估框架。现有的MOS测试无法区分相似模型,CMOS的成对比较则耗时过长。MUSHRA测试是一种有望同时评估多个TTS系统的测试方法,但它依赖匹配人类参考语音,对现代超过人类语音质量的TTS系统有所不公。本文对MUSHRA测试进行了全面的评估,重点关注评委差异性、听者疲劳和参考偏见等因素的影响。通过涉及印地语和泰米尔语的492名人类听者的广泛评估,发现了两大问题:一是参考匹配偏见,评委受到人类参考的不当影响;二是判断模糊,由于缺乏明确的细分指南。为解决这些问题,本文提出了两种改进的MUSHRA测试方法,一种为合成样本超过人类参考质量提供更公平的评分,另一种减少模糊性,降低评委之间的方差。此外,还发布了MANGO数据集,包含24.6万条人类评分,成为印度语言领域的首创集合,有助于分析人类偏好并为TTS系统的发展提供自动度量标准。
关键见解
- TTS领域缺乏一致且稳健的人机评估框架,现有测试方法存在缺陷。
- MUSHRA测试是一种有前途的评估方法,但存在参考匹配偏见和对现代TTS系统的评分不公问题。
- 通过广泛评估发现评委差异性、听者疲劳和参考偏见等因素影响MUSHRA测试的准确性。
- 提出两种改进的MUSHRA测试方法,旨在更公平地评估超过人类参考质量的TTS系统并减少判断模糊性。
- 发布了MANGO数据集,成为印度语言领域的首创大规模人类评分集合,有助于分析人类偏好和发展TTS系统的自动度量标准。
- 数据集包含丰富的语音样本和评分数据,为深入研究提供了宝贵的资源。
点此查看论文截图

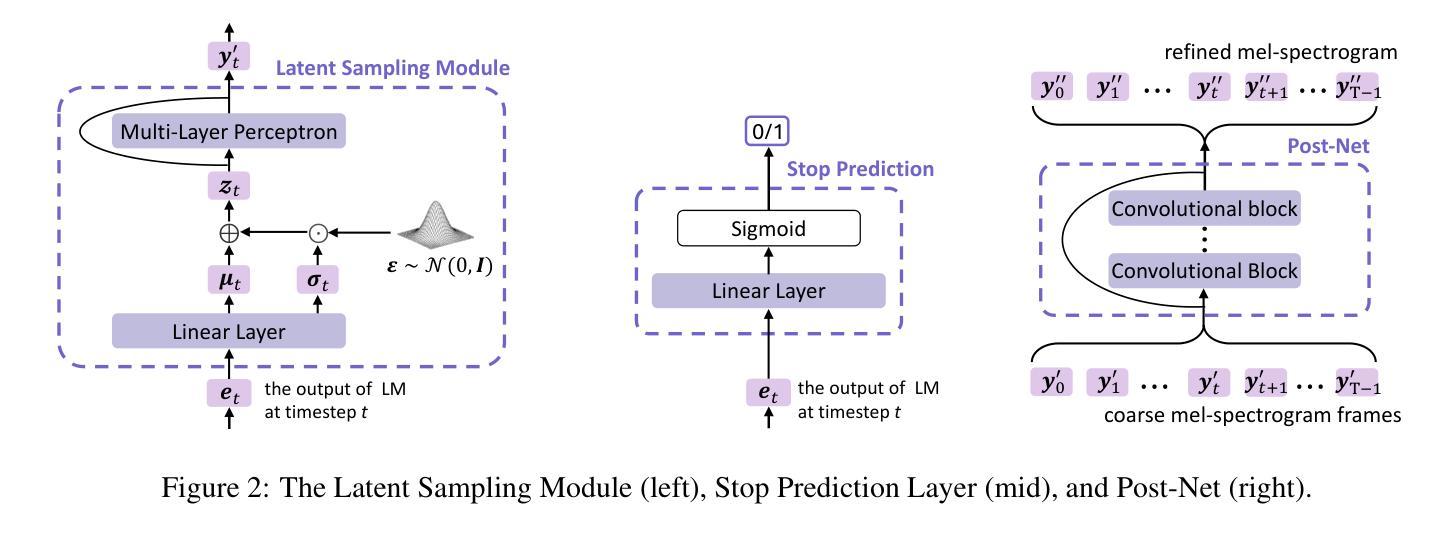
Autoregressive Speech Synthesis without Vector Quantization
Authors:Lingwei Meng, Long Zhou, Shujie Liu, Sanyuan Chen, Bing Han, Shujie Hu, Yanqing Liu, Jinyu Li, Sheng Zhao, Xixin Wu, Helen Meng, Furu Wei
We present MELLE, a novel continuous-valued token based language modeling approach for text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). MELLE autoregressively generates continuous mel-spectrogram frames directly from text condition, bypassing the need for vector quantization, which is typically designed for audio compression and sacrifices fidelity compared to continuous representations. Specifically, (i) instead of cross-entropy loss, we apply regression loss with a proposed spectrogram flux loss function to model the probability distribution of the continuous-valued tokens; (ii) we have incorporated variational inference into MELLE to facilitate sampling mechanisms, thereby enhancing the output diversity and model robustness. Experiments demonstrate that, compared to the two-stage codec language model VALL-E and its variants, the single-stage MELLE mitigates robustness issues by avoiding the inherent flaws of sampling vector-quantized codes, achieves superior performance across multiple metrics, and, most importantly, offers a more streamlined paradigm. The demos of our work are provided at https://aka.ms/melle.
我们提出了MELLE,这是一种基于连续值标记的新的文本转语音合成(TTS)语言建模方法。MELLE通过文本条件直接自回归生成连续的梅尔频谱帧,避免了向量量化的需要。向量量化通常是为音频压缩设计的,相较于连续表示形式牺牲了保真度。具体来说,(i)我们没有使用交叉熵损失,而是应用了回归损失和提出的频谱流损失函数来模拟连续值标记的概率分布;(ii)我们将变分推断融入MELLE,以优化采样机制,从而提高了输出多样性和模型稳健性。实验证明,相较于两阶段编码语言模型VALL-E及其变体,单阶段的MELLE通过避免采样向量量化码的固有缺陷,解决了稳健性问题,在多个指标上实现了卓越的性能,并且最重要的是,提供了更为简洁的模式。我们的工作演示地址为https://aka.ms/melle。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 Main
Summary
MELLE是一种基于连续值令牌的语言建模方法,用于文本到语音合成(TTS)。它直接生成连续的梅尔频谱帧,绕过向量量化的需求,从而提高了音频质量。该方法使用回归损失和提出的频谱流损失函数建模连续值令牌的概率分布,并融入变分推断提高采样机制和模型稳健性。实验证明,相比两阶段编解码器语言模型VALL-E及其变体,单阶段的MELLE避免了采样向量量化代码的固有缺陷,实现了跨多个指标的优越性能,并提供了更简洁的范式。
Key Takeaways
- MELLE是一种新型的连续值令牌语言建模方法,用于文本到语音合成(TTS)。
- MELLE直接生成连续的梅尔频谱帧,避免了向量量化的需求,从而提高音频质量。
- 使用回归损失和频谱流损失函数建模连续值令牌的概率分布。
- 变分推断被融入MELLE以提高采样机制和模型稳健性。
- MELLE相比两阶段编解码器语言模型VALL-E及其变体,在多个指标上实现优越性能。
- MELLE避免了采样向量量化代码的固有缺陷。
点此查看论文截图