⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-29 更新
FeatInv: Spatially resolved mapping from feature space to input space using conditional diffusion models
Authors:Nils Neukirch, Johanna Vielhaben, Nils Strodthoff
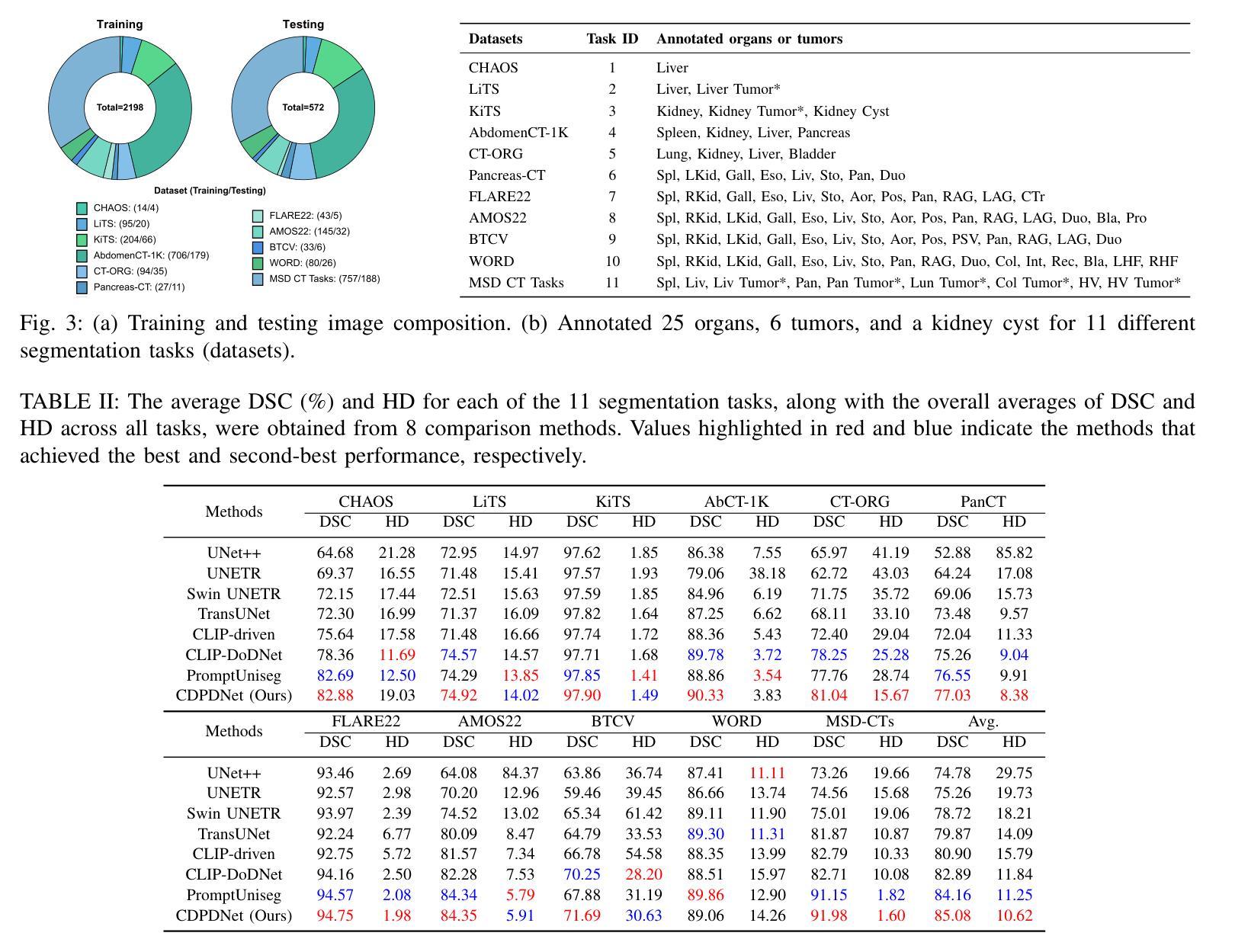
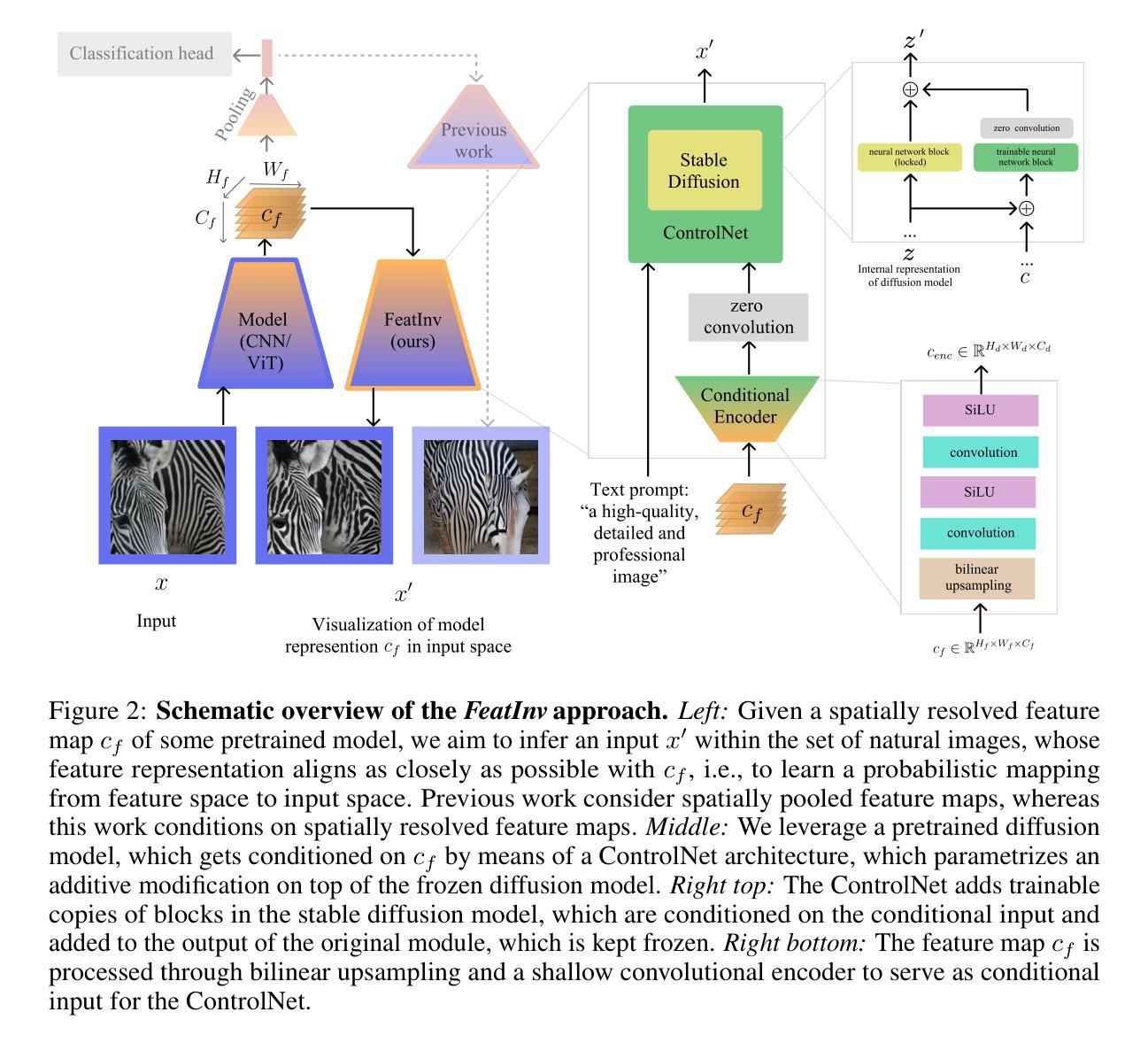
Internal representations are crucial for understanding deep neural networks, such as their properties and reasoning patterns, but remain difficult to interpret. While mapping from feature space to input space aids in interpreting the former, existing approaches often rely on crude approximations. We propose using a conditional diffusion model - a pretrained high-fidelity diffusion model conditioned on spatially resolved feature maps - to learn such a mapping in a probabilistic manner. We demonstrate the feasibility of this approach across various pretrained image classifiers from CNNs to ViTs, showing excellent reconstruction capabilities. Through qualitative comparisons and robustness analysis, we validate our method and showcase possible applications, such as the visualization of concept steering in input space or investigations of the composite nature of the feature space. This approach has broad potential for improving feature space understanding in computer vision models.
内部表征对于理解深度神经网络(如属性和推理模式)至关重要,但仍难以解释。虽然从特征空间到输入空间的映射有助于解释前者,但现有方法通常依赖于粗略近似。我们提出了一种基于条件扩散模型的方法,该模型是在空间解析的特征图上预训练的高保真扩散模型,以概率方式学习这种映射。我们展示了该方法在从CNN到ViT的各种预训练图像分类器中的可行性,表现出出色的重建能力。通过定性比较和稳健性分析,我们验证了我们的方法,并展示了可能的应用,如在输入空间中的概念导向可视化或特征空间复合性质的研究。该方法在改进计算机视觉模型的特征空间理解方面具有广泛潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures, code is available at https://github.com/AI4HealthUOL/FeatInv
Summary
研究团队提出使用条件扩散模型来从特征空间映射到输入空间,以理解深度神经网络(如CNN和ViT等)的内部表示。该方法以概率方式学习映射,具有优秀的重建能力,并展示了在可视化输入空间中的概念导向和特征空间的复合性质等方面的潜力。此方法的提出有望改善计算机视觉模型中特征空间的理解。
Key Takeaways
- 条件扩散模型被用于从特征空间映射到输入空间,以增强对深度神经网络内部表示的理解。
- 该方法基于预训练的高保真扩散模型,该模型在时空特征映射上得到条件化。
- 此方法适用于各种预训练图像分类器,包括CNN和ViT等,展现出优秀的重建能力。
- 通过定性比较和稳健性分析验证了该方法的可行性。
- 此方法可以用于可视化输入空间中的概念导向,研究特征空间的复合性质。
- 所提出的方法对于改善计算机视觉模型中特征空间的理解具有广阔潜力。
点此查看论文截图


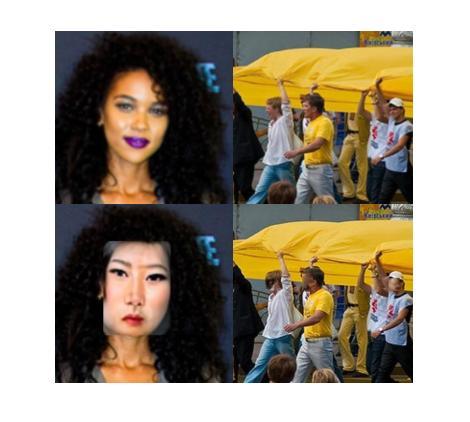
Facial Attribute Based Text Guided Face Anonymization
Authors:Mustafa İzzet Muştu, Hazım Kemal Ekenel
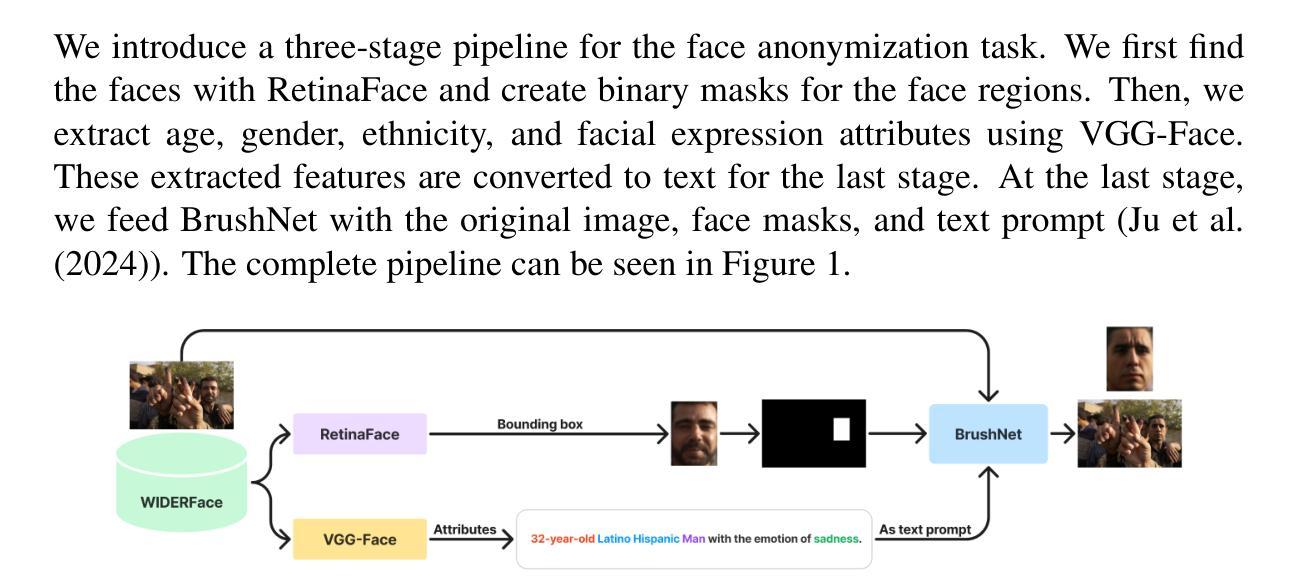
The increasing prevalence of computer vision applications necessitates handling vast amounts of visual data, often containing personal information. While this technology offers significant benefits, it should not compromise privacy. Data privacy regulations emphasize the need for individual consent for processing personal data, hindering researchers’ ability to collect high-quality datasets containing the faces of the individuals. This paper presents a deep learning-based face anonymization pipeline to overcome this challenge. Unlike most of the existing methods, our method leverages recent advancements in diffusion-based inpainting models, eliminating the need for training Generative Adversarial Networks. The pipeline employs a three-stage approach: face detection with RetinaNet, feature extraction with VGG-Face, and realistic face generation using the state-of-the-art BrushNet diffusion model. BrushNet utilizes the entire image, face masks, and text prompts specifying desired facial attributes like age, ethnicity, gender, and expression. This enables the generation of natural-looking images with unrecognizable individuals, facilitating the creation of privacy-compliant datasets for computer vision research.
随着计算机视觉应用的日益普及,需要处理包含个人信息的海量视觉数据。虽然这项技术带来了巨大的好处,但它不应该损害隐私。数据隐私规定强调处理个人数据时需要个人同意,这阻碍了研究人员收集包含个人面部的高质量数据集的能力。本文提出了一种基于深度学习的面部匿名化管道来应对这一挑战。与其他大多数现有方法不同,我们的方法利用基于扩散的修复模型的最新进展,无需训练生成对抗网络。该管道采用三阶段方法:使用RetinaNet进行面部检测,使用VGG-Face进行特征提取,以及使用最先进的BrushNet扩散模型进行逼真的面部生成。BrushNet利用整个图像、面部遮挡和文本提示来指定所需的面部属性,如年龄、种族、性别和表情。这能够生成具有不可识别个体的自然图像,促进了计算机视觉研究中的符合隐私要求的数据集创建。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 5 figures, published in the Proceedings of the Joint visuAAL-GoodBrother Conference on Trustworthy Video- and Audio-Based Assistive Technologies
Summary
提供计算机视觉技术挑战的分析和解决方法,为了解决涉及隐私的个人数据的收集问题,提出一种基于深度学习的面部匿名化管道。利用最新的扩散式修复模型技术,通过RetinaNet进行面部检测,使用VGG-Face进行特征提取,并利用先进的BrushNet扩散模型生成逼真的面部图像。通过整个图像、面部掩模和文字提示进行所需面部特征的筛选组合。保证了个人隐私保护的同时也产生了优质数据集,可为计算机视觉研究提供参考。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图



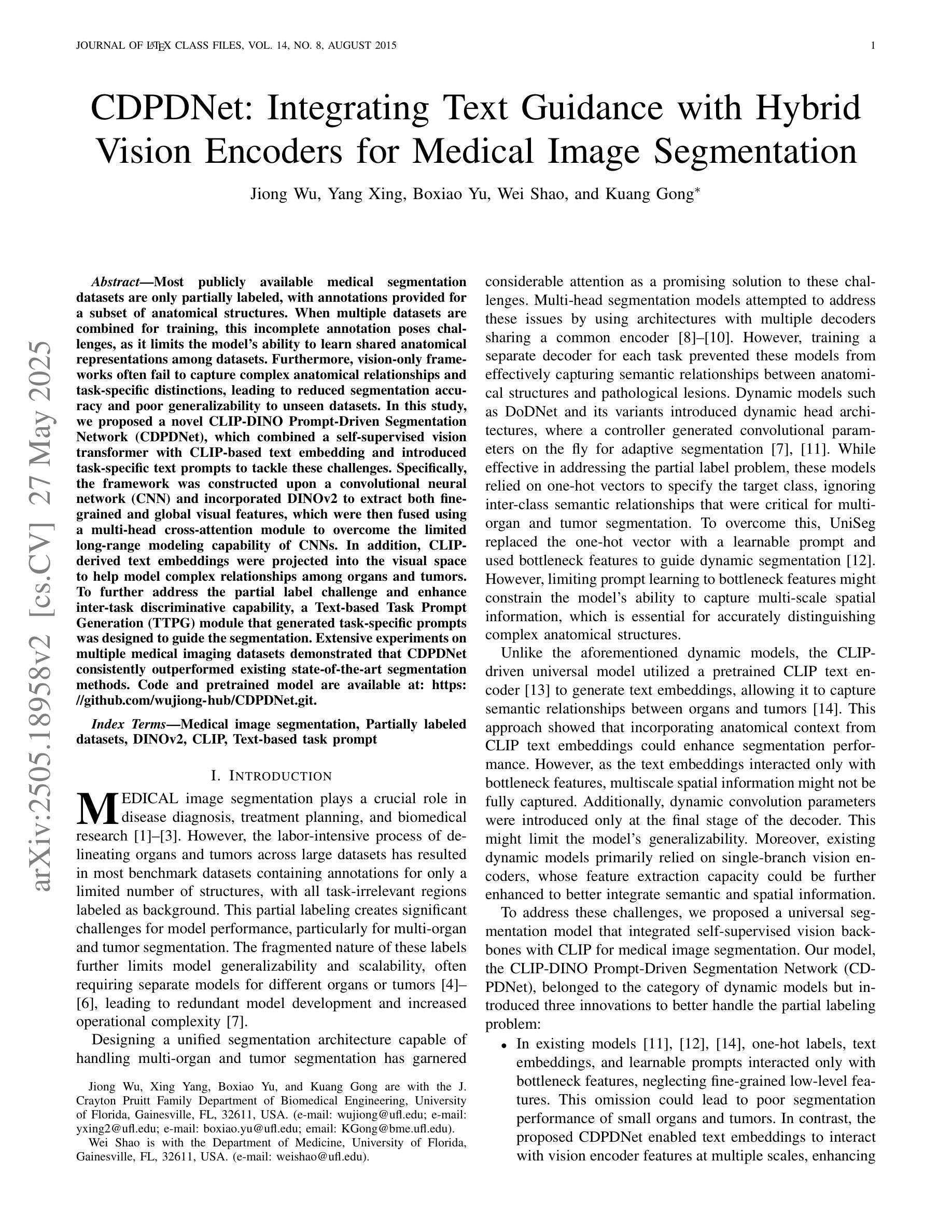
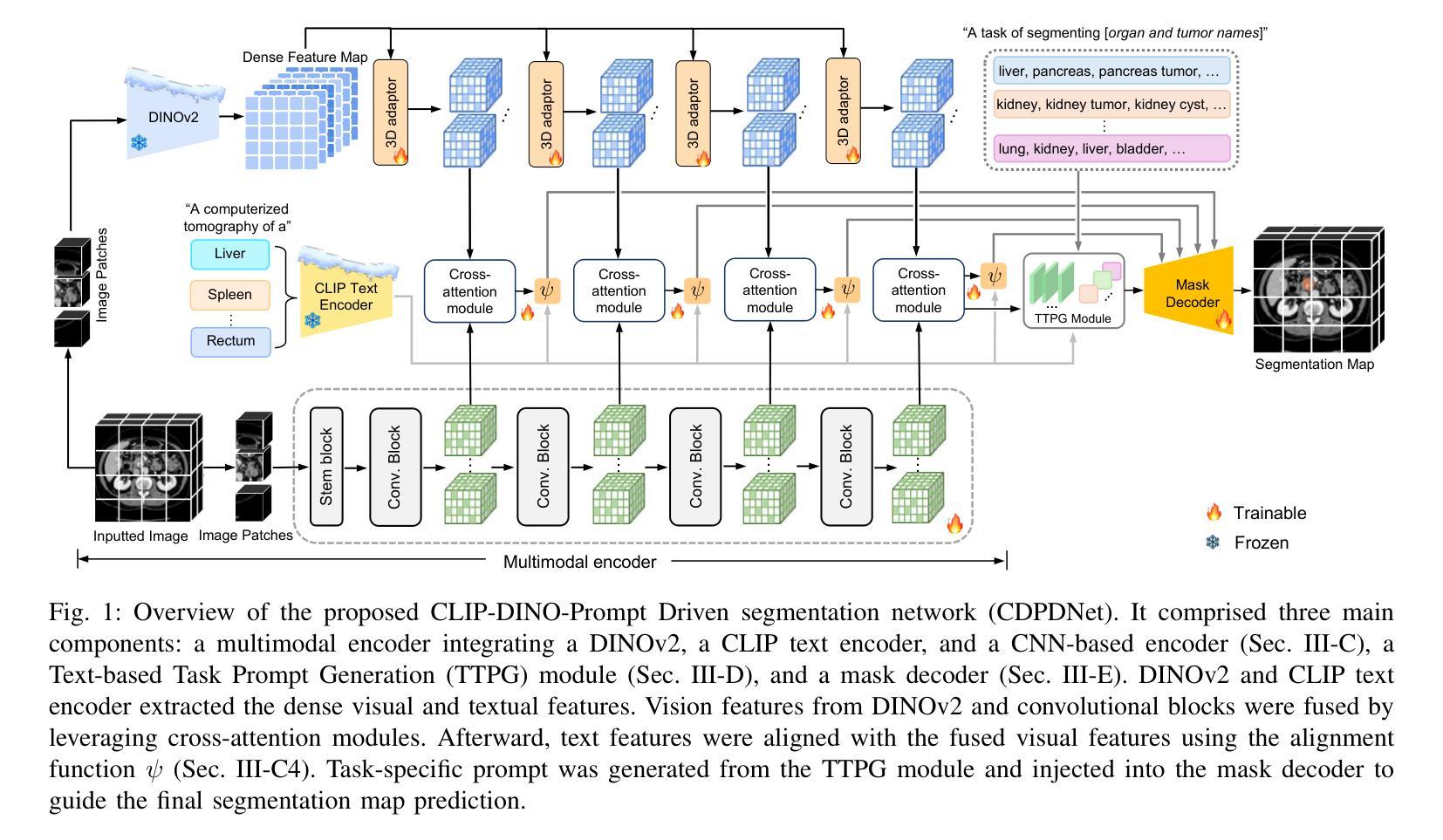
CDPDNet: Integrating Text Guidance with Hybrid Vision Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiong Wu, Yang Xing, Boxiao Yu, Wei Shao, Kuang Gong
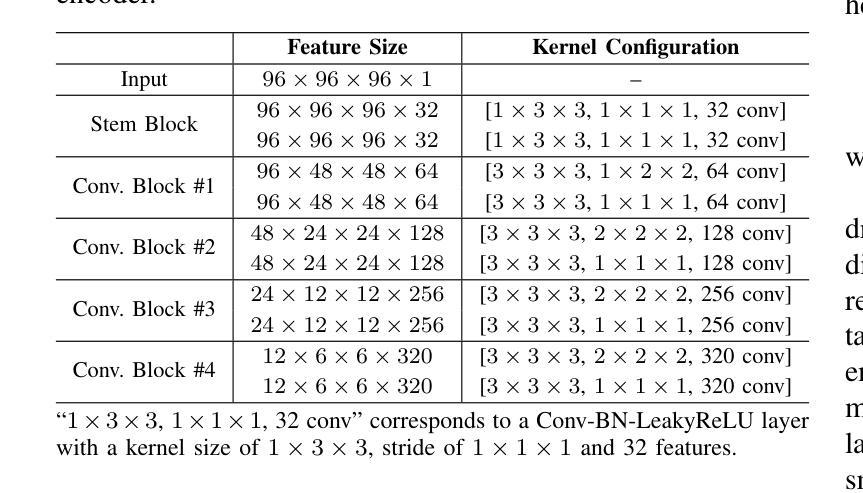
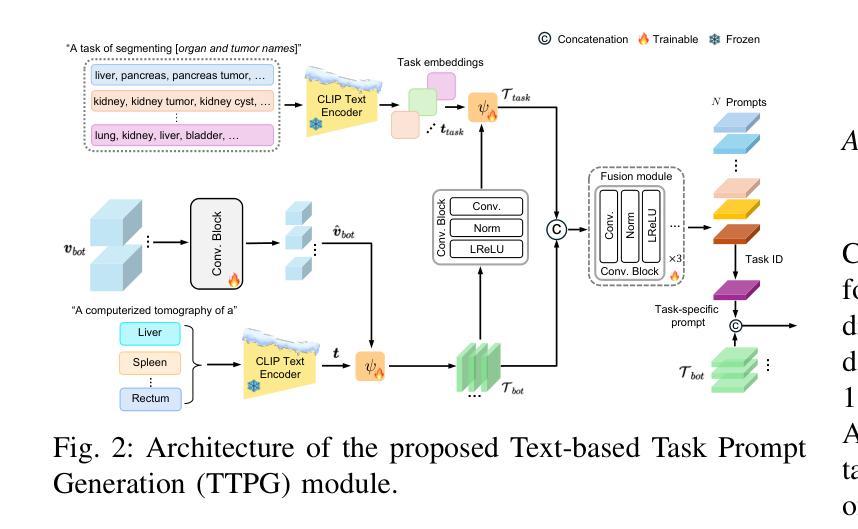
Most publicly available medical segmentation datasets are only partially labeled, with annotations provided for a subset of anatomical structures. When multiple datasets are combined for training, this incomplete annotation poses challenges, as it limits the model’s ability to learn shared anatomical representations among datasets. Furthermore, vision-only frameworks often fail to capture complex anatomical relationships and task-specific distinctions, leading to reduced segmentation accuracy and poor generalizability to unseen datasets. In this study, we proposed a novel CLIP-DINO Prompt-Driven Segmentation Network (CDPDNet), which combined a self-supervised vision transformer with CLIP-based text embedding and introduced task-specific text prompts to tackle these challenges. Specifically, the framework was constructed upon a convolutional neural network (CNN) and incorporated DINOv2 to extract both fine-grained and global visual features, which were then fused using a multi-head cross-attention module to overcome the limited long-range modeling capability of CNNs. In addition, CLIP-derived text embeddings were projected into the visual space to help model complex relationships among organs and tumors. To further address the partial label challenge and enhance inter-task discriminative capability, a Text-based Task Prompt Generation (TTPG) module that generated task-specific prompts was designed to guide the segmentation. Extensive experiments on multiple medical imaging datasets demonstrated that CDPDNet consistently outperformed existing state-of-the-art segmentation methods. Code and pretrained model are available at: https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git.
大部分公开可用的医学分割数据集仅部分标注,只为部分解剖结构提供注释。当多个数据集组合用于训练时,这种不完全的注释带来了挑战,因为它限制了模型在数据集之间学习共享解剖表征的能力。此外,仅依赖视觉的框架往往无法捕捉复杂的解剖关系和任务特定的区别,从而导致分割精度降低,以及对未见数据集的泛化能力较差。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新颖的CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动分割网络(CDPDNet),它将自监督视觉变压器与CLIP基于文本嵌入相结合,并引入任务特定的文本提示来解决这些挑战。具体来说,该框架建立在卷积神经网络(CNN)之上,并融入DINOv2来提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,然后使用多头交叉注意模块融合这些特征,以克服CNN有限的远程建模能力。此外,CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投射到视觉空间中,以帮助模型模拟器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。为了进一步解决部分标签挑战并增强任务间的判别能力,设计了一个基于文本的任务提示生成(TTPG)模块,以生成特定任务的提示来指导分割。在多个医学成像数据集上的广泛实验表明,CDPDNet持续优于现有的最先进的分割方法。代码和预训练模型可在:https://github.com/wujiong-hub/CDPDNet.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于CLIP-DINO Prompt驱动的分段网络(CDPDNet),用于解决医学图像分割中的挑战。该网络结合了自监督视觉变压器与CLIP文本嵌入技术,并引入特定任务的文本提示。CDPDNet解决了现有数据集标注不完整的问题,并在多个医学成像数据集上表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- CDPDNet结合了自监督视觉变压器和CLIP文本嵌入技术来解决医学图像分割中的挑战。
- 提出了基于任务的文本提示来指导图像分割,以克服部分标签数据的问题。
- 使用卷积神经网络(CNN)和DINOv2提取精细粒度和全局视觉特征,并通过多头交叉注意力模块进行融合。
- CLIP衍生的文本嵌入被投影到视觉空间,帮助建模器官和肿瘤之间的复杂关系。
- 通过多个医学成像数据集的实验验证,CDPDNet在性能上超越了现有的先进分割方法。
- 代码和预先训练的模型已公开发布,便于研究者和开发者使用。
- 该研究为解决医学图像分割中的不完全标注问题提供了一个有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图