⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
ConfLUNet: Multiple sclerosis lesion instance segmentation in presence of confluent lesions
Authors:Maxence Wynen, Pedro M. Gordaliza, Maxime Istasse, Anna Stölting, Pietro Maggi, Benoît Macq, Meritxell Bach Cuadra
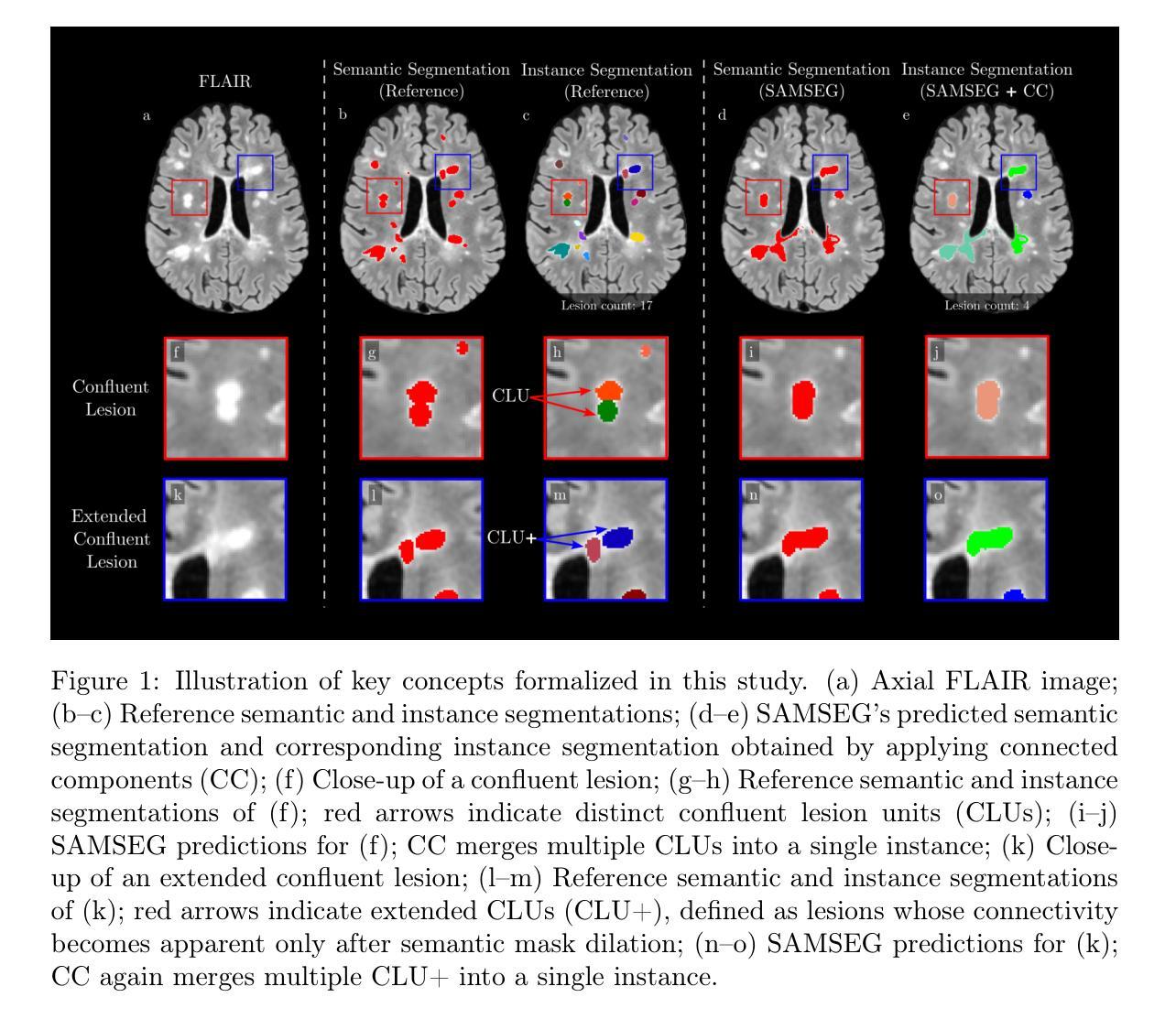
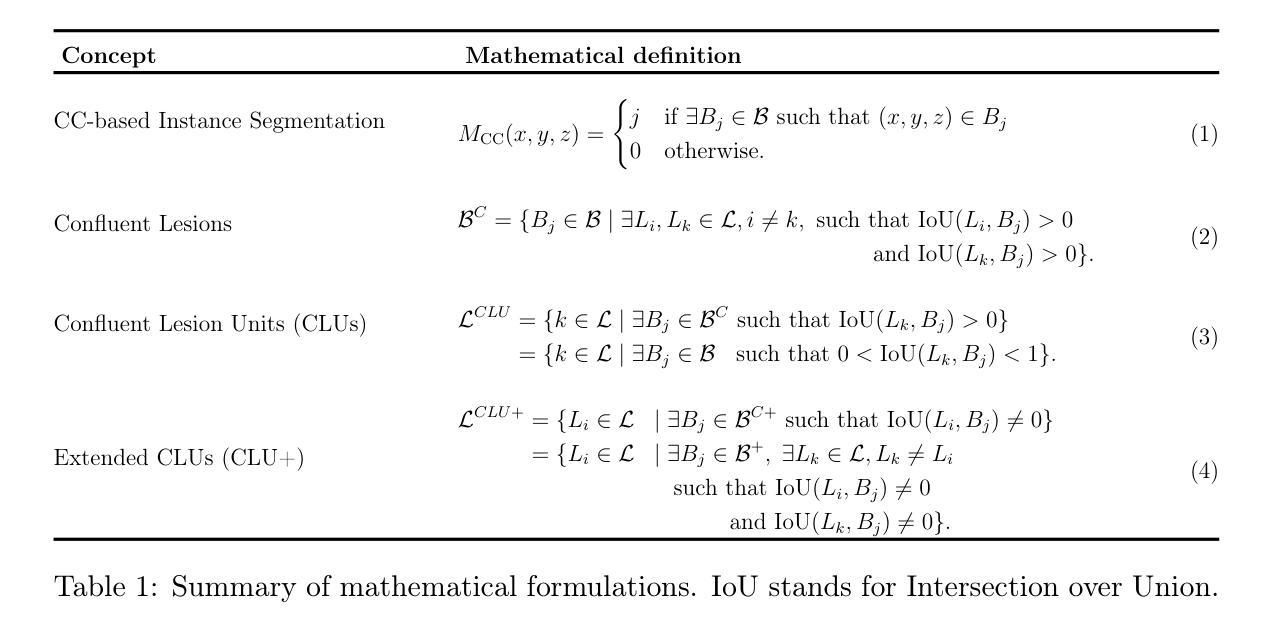
Accurate lesion-level segmentation on MRI is critical for multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis, prognosis, and disease monitoring. However, current evaluation practices largely rely on semantic segmentation post-processed with connected components (CC), which cannot separate confluent lesions (aggregates of confluent lesion units, CLUs) due to reliance on spatial connectivity. To address this misalignment with clinical needs, we introduce formal definitions of CLUs and associated CLU-aware detection metrics, and include them in an exhaustive instance segmentation evaluation framework. Within this framework, we systematically evaluate CC and post-processing-based Automated Confluent Splitting (ACLS), the only existing methods for lesion instance segmentation in MS. Our analysis reveals that CC consistently underestimates CLU counts, while ACLS tends to oversplit lesions, leading to overestimated lesion counts and reduced precision. To overcome these limitations, we propose ConfLUNet, the first end-to-end instance segmentation framework for MS lesions. ConfLUNet jointly optimizes lesion detection and delineation from a single FLAIR image. Trained on 50 patients, ConfLUNet significantly outperforms CC and ACLS on the held-out test set (n=13) in instance segmentation (Panoptic Quality: 42.0% vs. 37.5%/36.8%; p = 0.017/0.005) and lesion detection (F1: 67.3% vs. 61.6%/59.9%; p = 0.028/0.013). For CLU detection, ConfLUNet achieves the highest F1[CLU] (81.5%), improving recall over CC (+12.5%, p = 0.015) and precision over ACLS (+31.2%, p = 0.003). By combining rigorous definitions, new CLU-aware metrics, a reproducible evaluation framework, and the first dedicated end-to-end model, this work lays the foundation for lesion instance segmentation in MS.
在核磁共振成像(MRI)上进行准确的病灶级别分割对于多发性硬化症(MS)的诊断、预后和疾病监测至关重要。然而,当前的评估方法主要依赖于通过连通组件(CC)进行后处理的语义分割,由于依赖空间连通性,它们无法分离融合病灶(融合病灶单位(CLU)的聚集体)。为了解决这一与临床需求的不符,我们引入了CLU的正式定义和相关CLU感知检测指标,并将它们纳入详尽的实例分割评估框架。在此框架内,我们系统地评估了基于连通组件(CC)和后处理自动融合分割(ACLS)的方法,这是多发性硬化症中病灶实例分割的现有唯一方法。我们的分析表明,CC始终低估CLU计数,而ACLS倾向于过分割病灶,导致病灶计数过高,精度降低。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了ConfLUNet,这是多发性硬化症病灶实例分割的第一个端到端框架。ConfLUNet从单个FLAIR图像中联合优化病灶检测和轮廓描绘。在50名患者上进行训练后,ConfLUNet在实例分割(泛全景质量:42.0%对比37.5%/36.8%,p=0.017/0.005)和病灶检测(F1:67.3%对比61.6%/59.9%,p=0.028/0.013)方面显著优于CC和ACLS。对于CLU检测,ConfLUNet达到了最高的F1[CLU](81.5%),在召回率上超过了CC(+12.5%,p=0.015),并在精确度上超过了ACLS(+31.2%,p=0.003)。通过结合严格定义、新的CLU感知指标、可重现的评估框架和第一个专用端到端模型,这项工作为多发性硬化症中的病灶实例分割奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
准确地在MRI上进行病变级别的分割对于多发性硬化症(MS)的诊断、预后和疾病监测至关重要。然而,当前的评估实践主要依赖于通过连通组件(CC)进行语义分割,但由于依赖空间连通性,无法分离融合病变(合并病变单位CLUs)。为应对这种与临床需求的错位,我们对CLUs和相关CLU感知检测指标进行了正式定义,并将它们纳入详尽的实例分割评估框架中。在此框架中,我们对基于CC和后处理的自动化融合分割方法(ACLS)进行了系统评价,这是MS病变实例分割中唯一现有的方法。分析表明,CC始终低估了CLU计数,而ACLS倾向于过度分割病变,导致病变计数过高且精度降低。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了ConfLUNet,这是首个端到端的MS病变实例分割框架。ConfLUNet从单个FLAIR图像中联合优化病变检测和轮廓绘制。在50名患者上进行训练后,ConfLUNet在保留的测试集(n=13)上的实例分割和病变检测方面显著优于CC和ACLS(全景质量:42.0%比37.5%/36.8%;p=0.017/0.005;F1:67.3%比61.6%/59.9%;p=0.028/0.013)。对于CLU检测,ConfLUNet的F1[CLU]值最高(81.5%),在召回率上较CC提高了(+12.5%,p=0.015),在精确度上较ACLS提高了(+31.2%,p=0.003)。通过严格的定义、新的CLU感知指标、可复制的评估框架和首个端到端的专用模型,这项工作为MS的病变实例分割奠定了基础。
要点归纳
- 当前MRI病变级别分割在多发性硬化症诊断、预后和监测中的重要性。
- 当前评估方法主要依赖连通组件进行语义分割,无法有效分离融合病变。
- 引入CLUs的定义和相关CLU感知检测指标的重要性。
- 系统评估了基于连通组件的自动化分割方法和现有的ACLS方法,发现其局限性。
- 提出ConfLUNet作为首个端到端的MS病变实例分割框架,联合优化病变检测和轮廓绘制。
- ConfLUNet在实例分割、病变检测以及CLU检测方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Universal Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Seun-An Choe, Keon-Hee Park, Jinwoo Choi, Gyeong-Moon Park
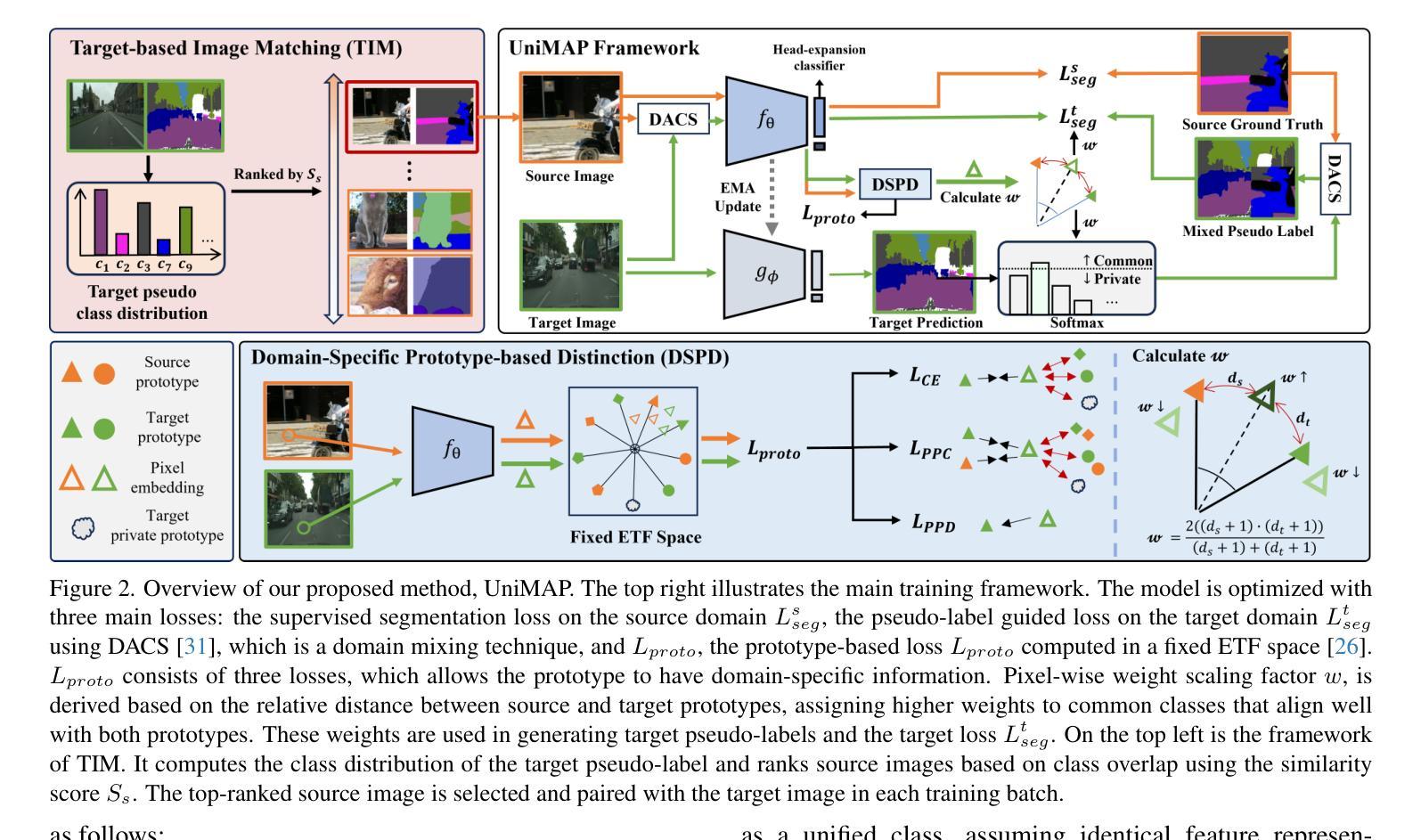
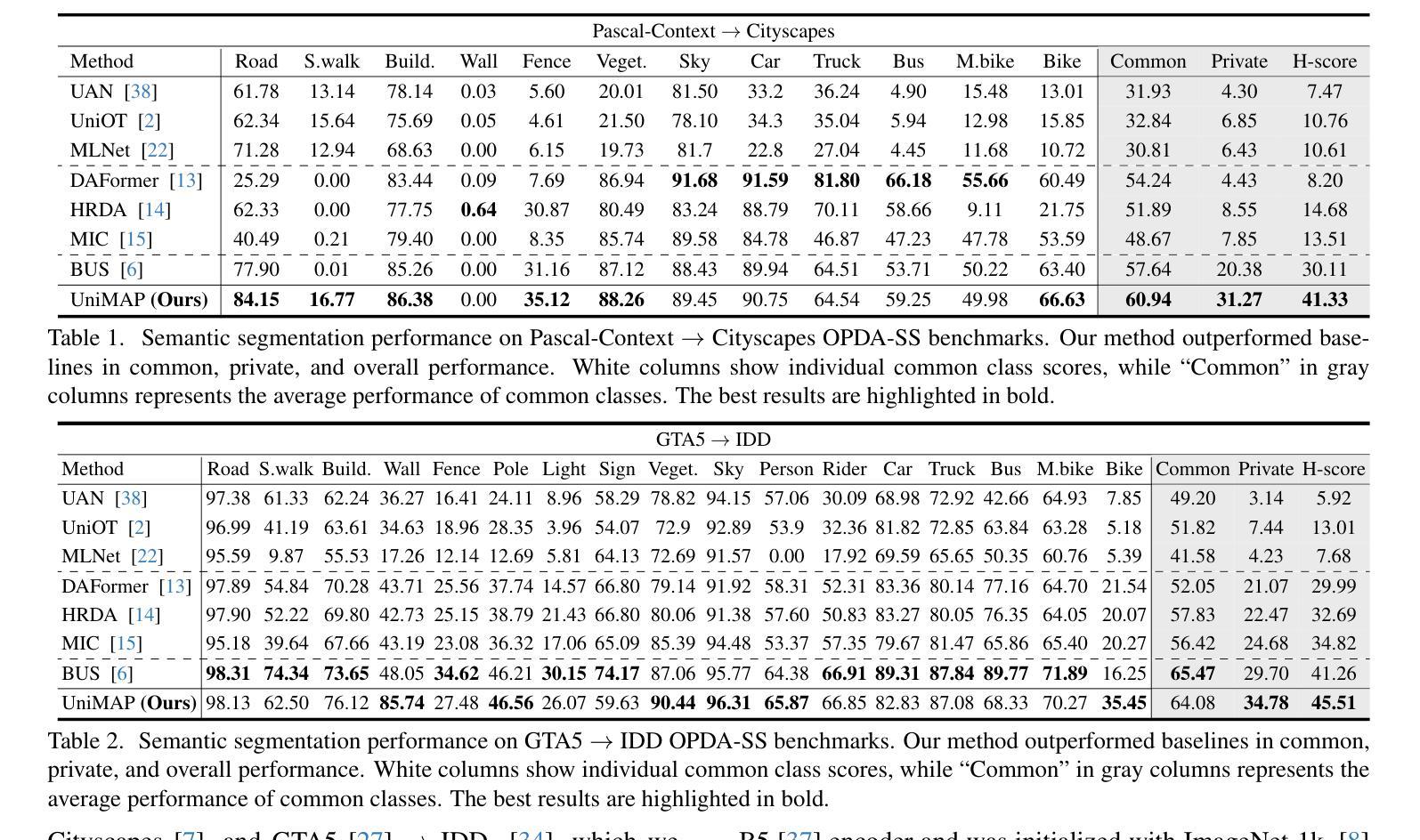
Unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation (UDA-SS) aims to transfer knowledge from labeled source data to unlabeled target data. However, traditional UDA-SS methods assume that category settings between source and target domains are known, which is unrealistic in real-world scenarios. This leads to performance degradation if private classes exist. To address this limitation, we propose Universal Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation (UniDA-SS), achieving robust adaptation even without prior knowledge of category settings. We define the problem in the UniDA-SS scenario as low confidence scores of common classes in the target domain, which leads to confusion with private classes. To solve this problem, we propose UniMAP: UniDA-SS with Image Matching and Prototype-based Distinction, a novel framework composed of two key components. First, Domain-Specific Prototype-based Distinction (DSPD) divides each class into two domain-specific prototypes, enabling finer separation of domain-specific features and enhancing the identification of common classes across domains. Second, Target-based Image Matching (TIM) selects a source image containing the most common-class pixels based on the target pseudo-label and pairs it in a batch to promote effective learning of common classes. We also introduce a new UniDA-SS benchmark and demonstrate through various experiments that UniMAP significantly outperforms baselines. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/KU-VGI/UniMAP}{this https URL}.
无监督领域自适应语义分割(UDA-SS)旨在将来自带标签源数据的知识转移到无标签目标数据。然而,传统的UDA-SS方法假设源域和目标域之间的类别设置是已知的,这在现实场景中是不现实的。如果存在私有类别,这会导致性能下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了通用领域自适应语义分割(UniDA-SS),实现了稳健的适应,即使在没有类别设置的先验知识的情况下也是如此。我们将UniDA-SS场景中的问题定义为目标域中常见类别的置信度得分较低,这导致与私有类别的混淆。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了UniMAP:基于图像匹配的UniDA-SS以及基于原型的区别,这是一个新型框架,由两个关键组件组成。首先,基于域特定原型的区别(DSPD)将每个类别分为两个域特定原型,能够更精细地分离域特定特征,并增强跨域的常见类别的识别。其次,基于目标的图像匹配(TIM)选择包含最多常见类别像素的源图像,基于目标伪标签将其分批配对,以促进常见类别的有效学习。我们还引入了一个新的UniDA-SS基准测试,并通过各种实验证明UniMAP显著优于基线。代码可在this https URL获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为UniMAP的框架,用于解决无监督域自适应语义分割中的局限性问题。框架针对公共类别低置信度导致的私有类别混淆问题,采用域特定原型区分和目标基于图像的匹配技术。此外,还引入了一个新的UniDA-SS基准测试,并通过实验证明UniMAP在性能上显著优于基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- UDA-SS的目标是将知识从标记的源数据转移到未标记的目标数据。然而,传统的UDA-SS方法假设源域和目标域之间的类别设置已知,这在现实世界中并不常见。因此存在私有类别时性能会下降。
- UniMAP框架解决了该问题,通过图像匹配和基于原型的区分技术,实现了无需类别设置的先验知识的稳健适应。
- UniMAP解决了目标域中公共类别低置信度导致的问题,避免与私有类别的混淆。这通过两个关键组件实现:域特定原型区分和目标基于图像的匹配。域特定原型区分将每个类分为两个域特定原型,实现跨域的域特定特征的精细分离,提高公共类别的识别能力。目标基于图像的匹配选择包含最多公共类别像素的源图像,基于目标伪标签进行配对,以促进有效学习公共类别。
点此查看论文截图

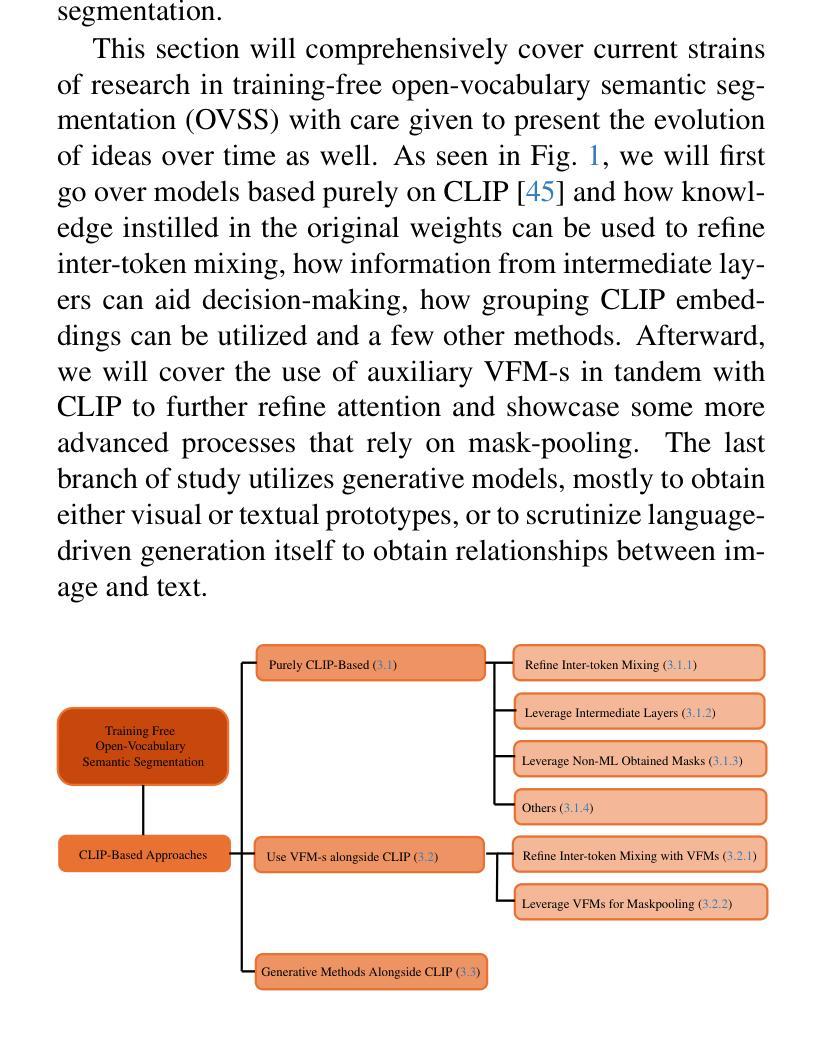
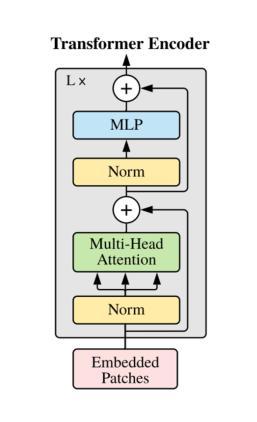
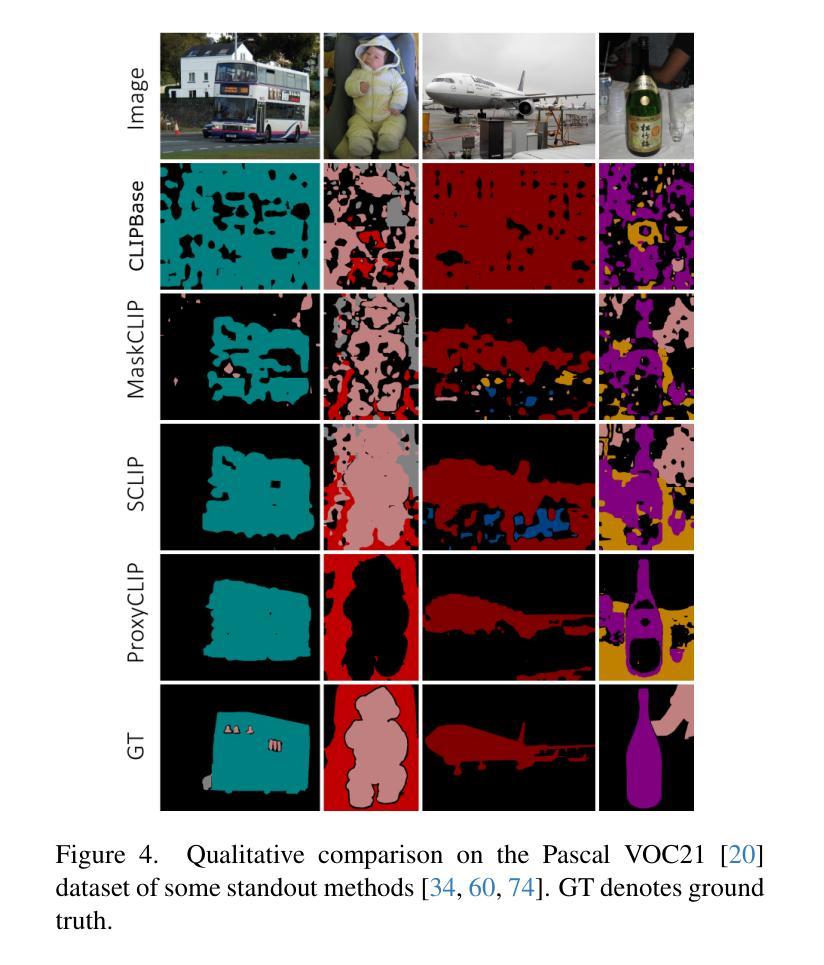
A Survey on Training-free Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Naomi Kombol, Ivan Martinović, Siniša Šegvić
Semantic segmentation is one of the most fundamental tasks in image understanding with a long history of research, and subsequently a myriad of different approaches. Traditional methods strive to train models up from scratch, requiring vast amounts of computational resources and training data. In the advent of moving to open-vocabulary semantic segmentation, which asks models to classify beyond learned categories, large quantities of finely annotated data would be prohibitively expensive. Researchers have instead turned to training-free methods where they leverage existing models made for tasks where data is more easily acquired. Specifically, this survey will cover the history, nuance, idea development and the state-of-the-art in training-free open-vocabulary semantic segmentation that leverages existing multi-modal classification models. We will first give a preliminary on the task definition followed by an overview of popular model archetypes and then spotlight over 30 approaches split into broader research branches: purely CLIP-based, those leveraging auxiliary visual foundation models and ones relying on generative methods. Subsequently, we will discuss the limitations and potential problems of current research, as well as provide some underexplored ideas for future study. We believe this survey will serve as a good onboarding read to new researchers and spark increased interest in the area.
语义分割是图像理解中最基本的任务之一,有着悠久的历史和众多的研究方法。传统方法致力于从头开始训练模型,需要大量的计算资源和训练数据。随着开放词汇语义分割的出现,该任务要求模型对学到的类别进行分类之外的内容,大量精细标注的数据将变得极为昂贵。因此,研究人员转而采用无训练方法,他们利用为更容易获取数据的任务构建的现有模型。具体来说,这篇综述将介绍无训练开放词汇语义分割的历史、细微差别、思想发展和最新研究情况,该分割利用现有的多模式分类模型。我们将首先给出任务定义的初步介绍,然后概述流行的模型原型,再重点介绍超过30种方法分为几个较大的研究分支:纯基于CLIP的方法、利用辅助视觉基础模型的方法和依赖生成方法的方法。随后,我们将讨论当前研究的局限性和潜在问题,并提供一些尚未探索的想法供未来研究。我们相信这篇综述将为新研究人员提供良好的入门读物,并激发对该领域的兴趣。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了语义分割在图像理解领域的重要性及其研究历史。随着开放词汇语义分割的兴起,研究人员开始转向无需训练的方法,利用现有模型解决数据更易获取的任务。本文回顾了训练免费开放词汇语义分割的历史、细微差别、思想发展和最新进展,特别是利用多模式分类模型的方法。文章概述了任务定义、流行模型原型,并重点介绍了30多种方法的不同研究分支。同时,文章也探讨了当前研究的局限性和潜在问题,并为未来的研究提供了一些尚未探索的想法。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割是图像理解中的基础任务,有着丰富的研究历史和各种不同方法。
- 开放词汇语义分割要求模型进行分类超出已学类别,需要大量精细标注的数据,成本高昂。
- 研究人员开始转向无需训练的方法,利用现有模型,这些方法针对数据更易获取的任务。
- 本文回顾了训练免费开放词汇语义分割的历史、发展和最新进展。
- 文章概述了任务定义、流行模型原型,并重点介绍了30多种方法的不同研究分支,包括纯CLIP方法、利用辅助视觉基础模型的方法和依赖生成方法。
- 当前研究的局限性在于存在潜在问题,本文也讨论了这些问题。
点此查看论文截图

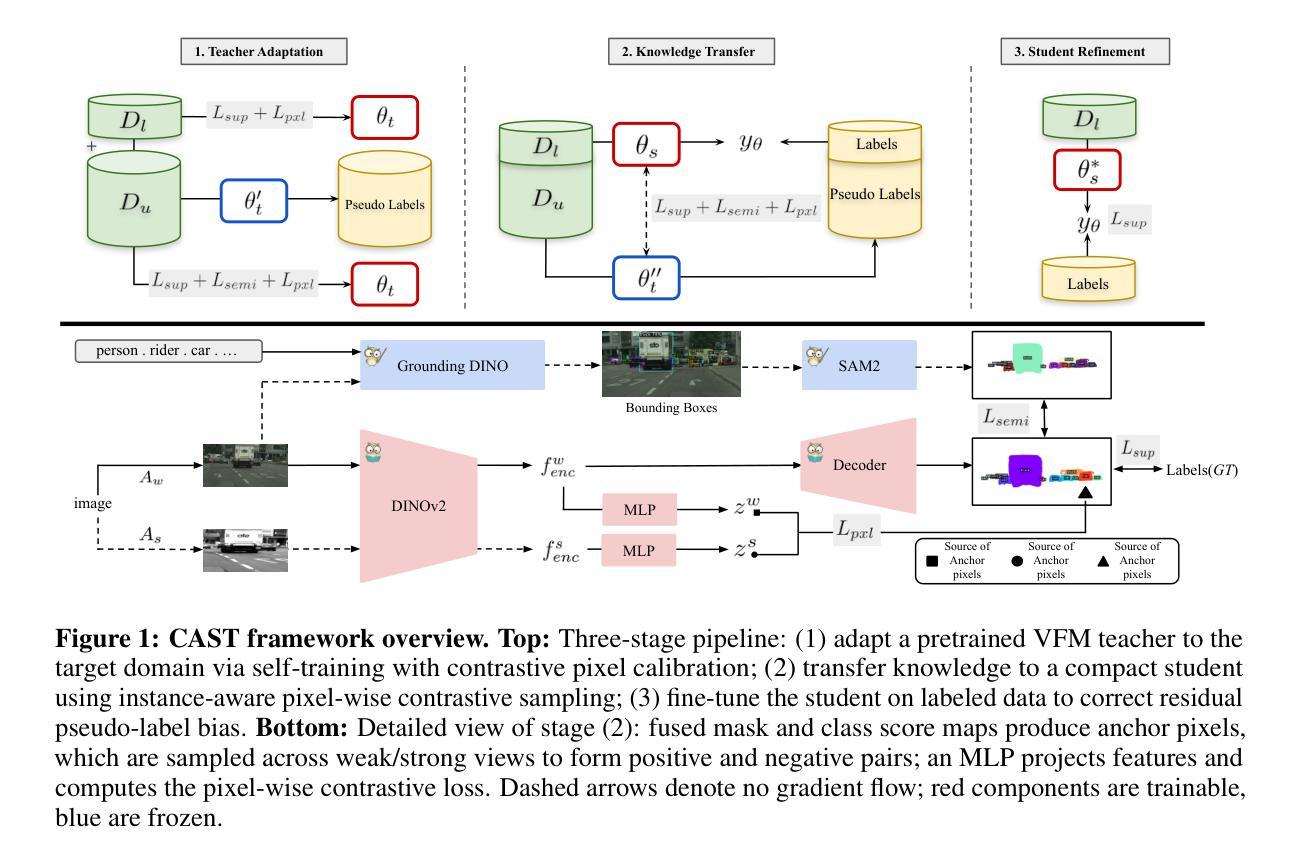
CAST: Contrastive Adaptation and Distillation for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
Authors:Pardis Taghavi, Tian Liu, Renjie Li, Reza Langari, Zhengzhong Tu
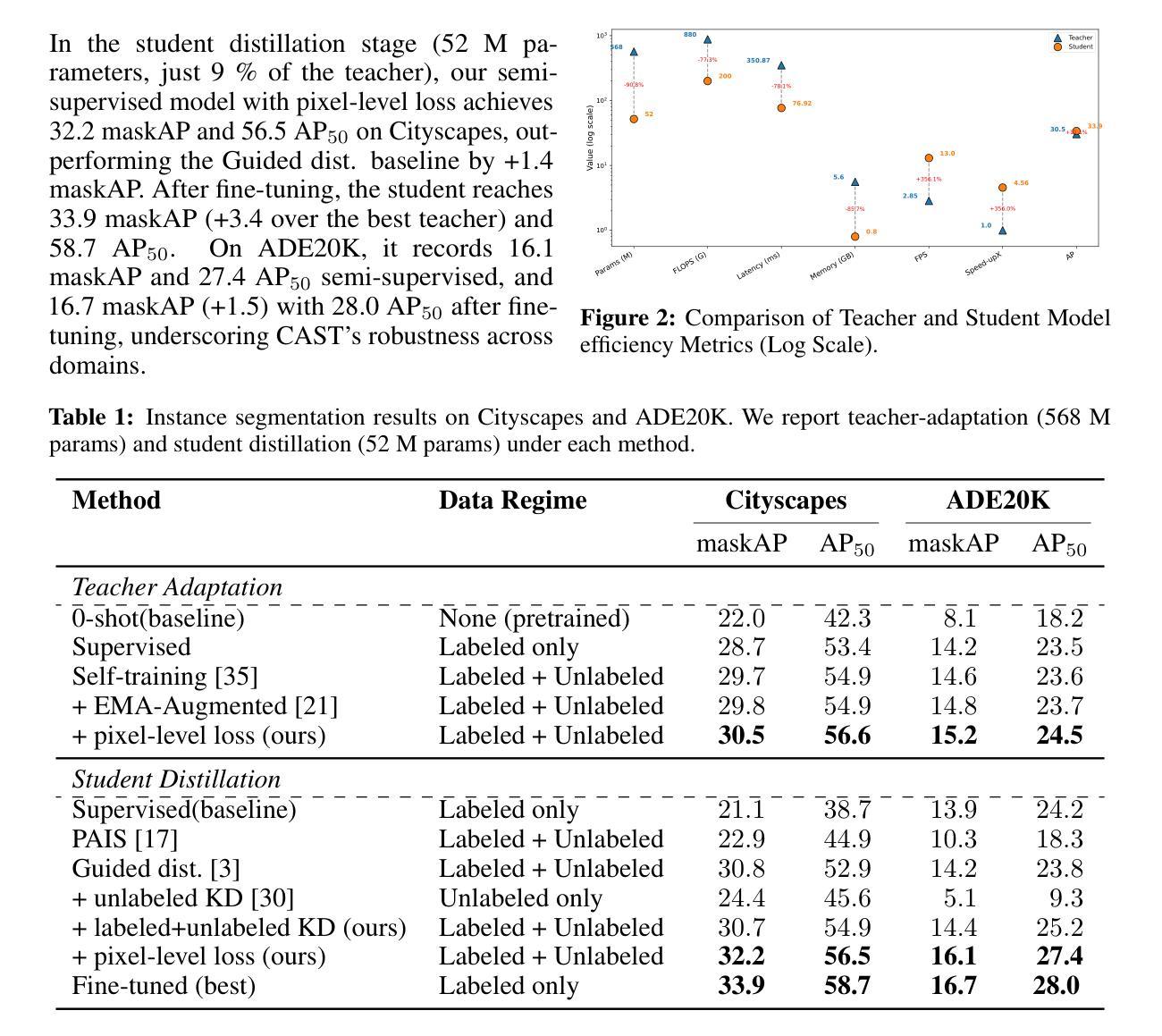
Instance segmentation demands costly per-pixel annotations and large models. We introduce CAST, a semi-supervised knowledge distillation (SSKD) framework that compresses pretrained vision foundation models (VFM) into compact experts using limited labeled and abundant unlabeled data. CAST unfolds in three stages: (1) domain adaptation of the VFM teacher(s) via self-training with contrastive pixel calibration, (2) distillation into a compact student via a unified multi-objective loss that couples standard supervision and pseudo-labels with our instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive term, and (3) fine-tuning on labeled data to remove residual pseudo-label bias. Central to CAST is an \emph{instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive loss} that fuses mask and class scores to mine informative negatives and enforce clear inter-instance margins. By maintaining this contrastive signal across both adaptation and distillation, we align teacher and student embeddings and fully leverage unlabeled images. On Cityscapes and ADE20K, our ~11X smaller student surpasses its adapted VFM teacher(s) by +3.4 AP (33.9 vs. 30.5) and +1.5 AP (16.7 vs. 15.2) and outperforms state-of-the-art semi-supervised approaches.
实例分割需要昂贵的像素级标注和大模型。我们引入了CAST,这是一种半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)框架,它利用有限的标记数据和大量的无标记数据,将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST分为三个阶段:(1)通过对比像素校准进行自我训练,对VFM教师进行域适应;(2)通过统一的多目标损失进行蒸馏,该损失将标准监督和伪标签与我们的实例感知像素级对比项相结合,对紧凑的学生模型进行蒸馏;(3)在标记数据上进行微调,以消除残留的伪标签偏见。CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,它融合掩膜和类分数来挖掘信息阴性样本并强制执行清晰的实例间边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持这种对比信号,我们对齐教师和学生嵌入,并充分利用无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K上,我们较小的学生模型(~11倍)超越了其适应的VFM教师模型(+3.4 AP(33.9对30.5)和+1.5 AP(16.7对15.2)),并优于最新的半监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了基于半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)的压缩框架CAST,该框架利用有限的标签数据和大量的无标签数据将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST分为三个主要阶段:VFM教师的域自适应、通过统一的多目标损失蒸馏到紧凑的学生模型,以及使用标记数据进行微调以消除残留的伪标签偏见。核心在于实例感知像素级对比损失,该损失融合了掩膜和类别分数以挖掘信息负样本并明确实例间的边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持对比信号,我们实现了教师和学生嵌入的对齐,并充分利用了无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K数据集上,我们的学生模型超越了其适应的VFM教师模型,并超过了现有的最先进的半监督方法。
Key Takeaways:
- CAST利用有限的标签数据和大量的无标签数据压缩预训练视觉基础模型。
- CAST分为三个主要阶段:教师域自适应、通过多目标损失蒸馏学生模型和微调。
- 实例感知像素级对比损失是CAST的核心,融合了掩膜和类别分数。
- 对比信号在适应和蒸馏过程中都被保持。
- 学生模型大小和性能超越了其适应的VFM教师模型。
- 在Cityscapes和ADE20K数据集上,CAST表现优于现有的最先进的半监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

Test-Time Adaptation of Vision-Language Models for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Mehrdad Noori, David Osowiechi, Gustavo Adolfo Vargas Hakim, Ali Bahri, Moslem Yazdanpanah, Sahar Dastani, Farzad Beizaee, Ismail Ben Ayed, Christian Desrosiers
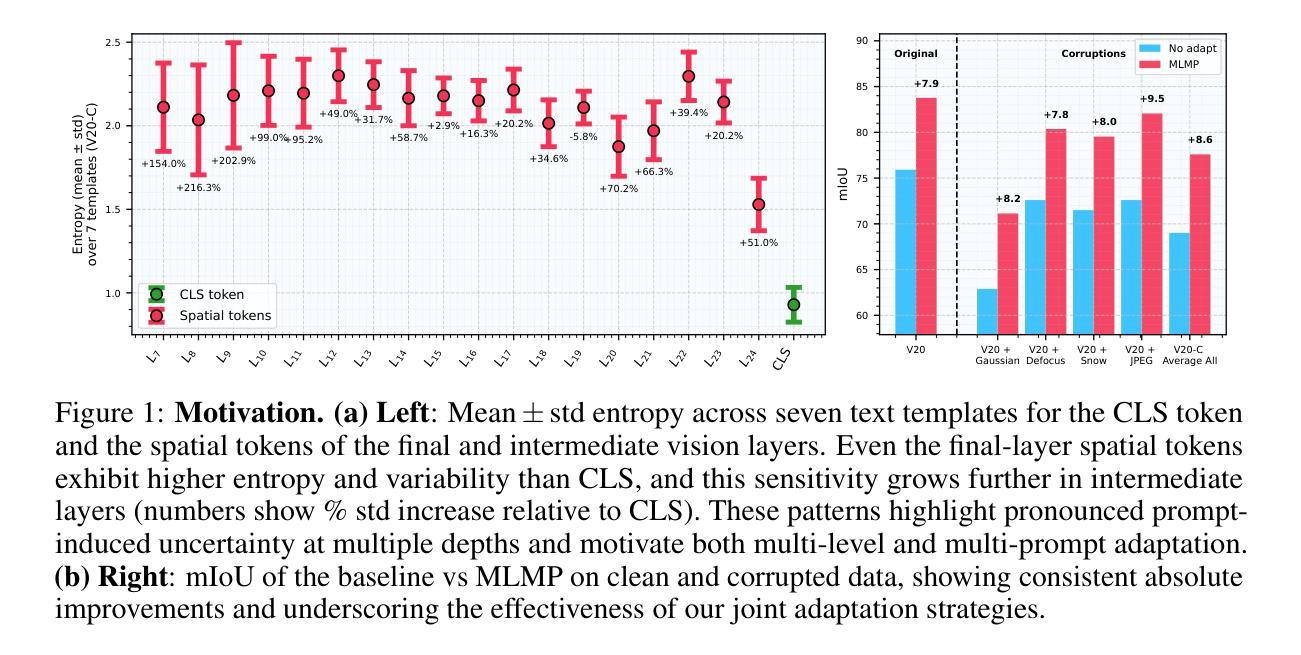
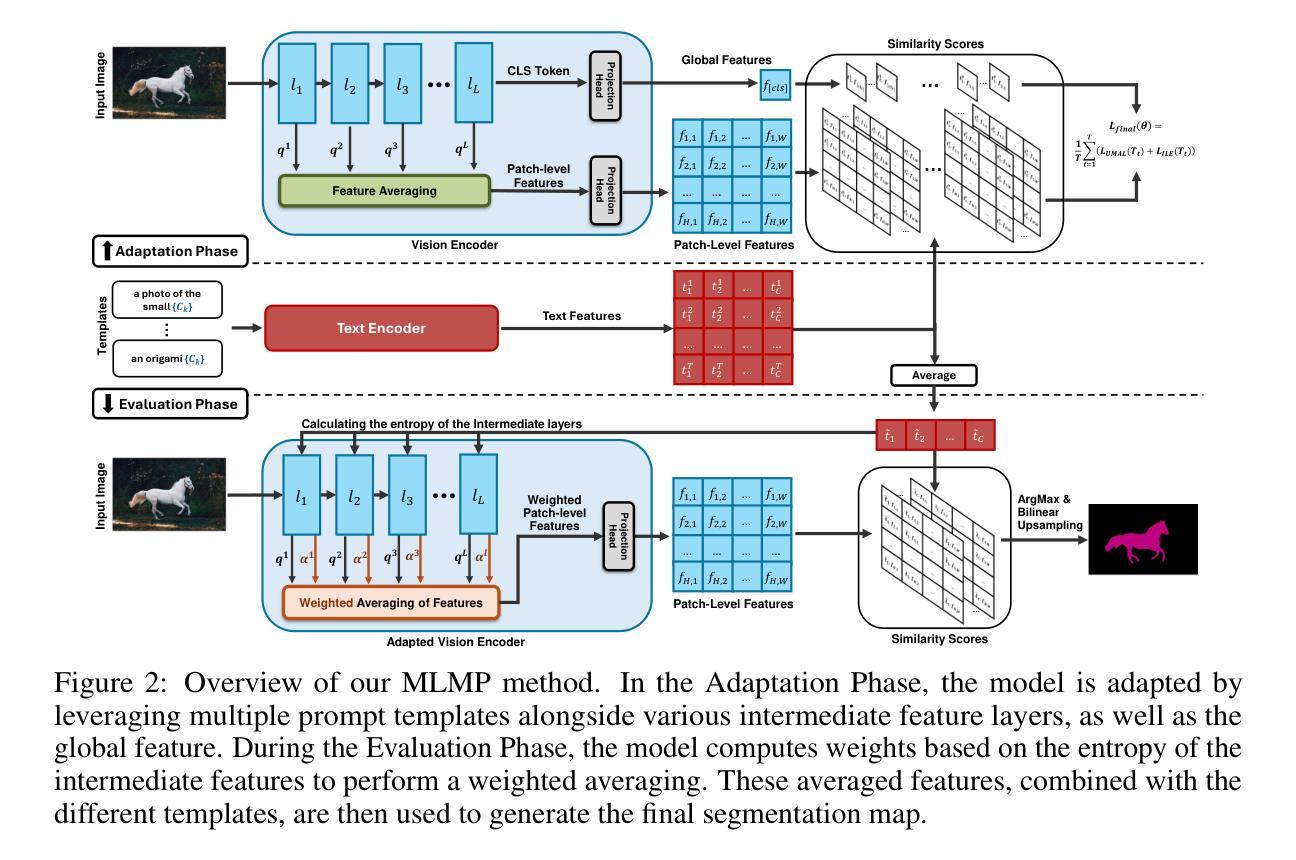
Recently, test-time adaptation has attracted wide interest in the context of vision-language models for image classification. However, to the best of our knowledge, the problem is completely overlooked in dense prediction tasks such as Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS). In response, we propose a novel TTA method tailored to adapting VLMs for segmentation during test time. Unlike TTA methods for image classification, our Multi-Level and Multi-Prompt (MLMP) entropy minimization integrates features from intermediate vision-encoder layers and is performed with different text-prompt templates at both the global CLS token and local pixel-wise levels. Our approach could be used as plug-and-play for any segmentation network, does not require additional training data or labels, and remains effective even with a single test sample. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive OVSS TTA benchmark suite, which integrates a rigorous evaluation protocol, seven segmentation datasets, and 15 common corruptions, with a total of 82 distinct test scenarios, establishing a standardized and comprehensive testbed for future TTA research in open-vocabulary segmentation. Our experiments on this suite demonstrate that our segmentation-tailored method consistently delivers significant gains over direct adoption of TTA classification baselines.
最近,测试时间适应在图像分类的视觉语言模型背景下引起了广泛关注。然而,据我们所知,该问题在密集预测任务(如开放词汇语义分割)中完全被忽略了。作为回应,我们提出了一种新型的TTA方法,专为测试时适应VLMs进行分割而设计。与用于图像分类的TTA方法不同,我们的多层次多提示(MLMP)熵最小化结合了中间视觉编码器层的特征,并在全局CLS标记和局部像素级使用不同的文本提示模板进行。我们的方法可以作为任何分割网络的即插即用工具,无需额外的训练数据或标签,即使在单个测试样本上也能保持有效。此外,我们引入了一个全面的OVSS TTA基准套件,其中包括严格的评估协议、七个分割数据集和15种常见腐蚀,总共82种不同的测试场景,为未来的开放词汇分割TTA研究建立了标准化和全面的测试平台。在此套件上的实验表明,我们的针对分割的方法始终在直接采用TTA分类基线时表现出显著的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注测试时间自适应技术在视觉语言模型中的图像分类应用,但在密集预测任务如开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)中却被忽视。为此,提出了一种针对分割任务的测试时间自适应方法,通过多级别和多提示的熵最小化策略,整合视觉编码器中间层的特征,并在全局CLS标记和局部像素级使用不同的文本提示模板。该方法可作为任何分割网络的即插即用模块,无需额外的训练数据或标签,甚至在单个测试样本上也能保持有效。同时,引入了一个全面的OVSS TTA基准套件,为未来TTA在开放词汇分割领域的研究提供了标准化和全面的测试平台。实验表明,该方法在分割任务上相较于直接采用TTA分类基线有显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间自适应技术在视觉语言模型的图像分类中受到关注,但在密集预测任务如开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)中被忽视。
- 提出了一种针对分割任务的测试时间自适应方法,通过多级别和多提示的熵最小化策略整合特征。
- 该方法可作为任何分割网络的即插即用模块,无需额外的训练数据或标签。
- 引入了一个全面的OVSS TTA基准套件,为未来TTA研究提供了标准化测试平台。
- 实验表明,该方法在分割任务上表现优越,可以显著提高模型性能。
- 通过使用不同的文本提示模板,该方法在全局CLS标记和局部像素级都有良好表现。
点此查看论文截图

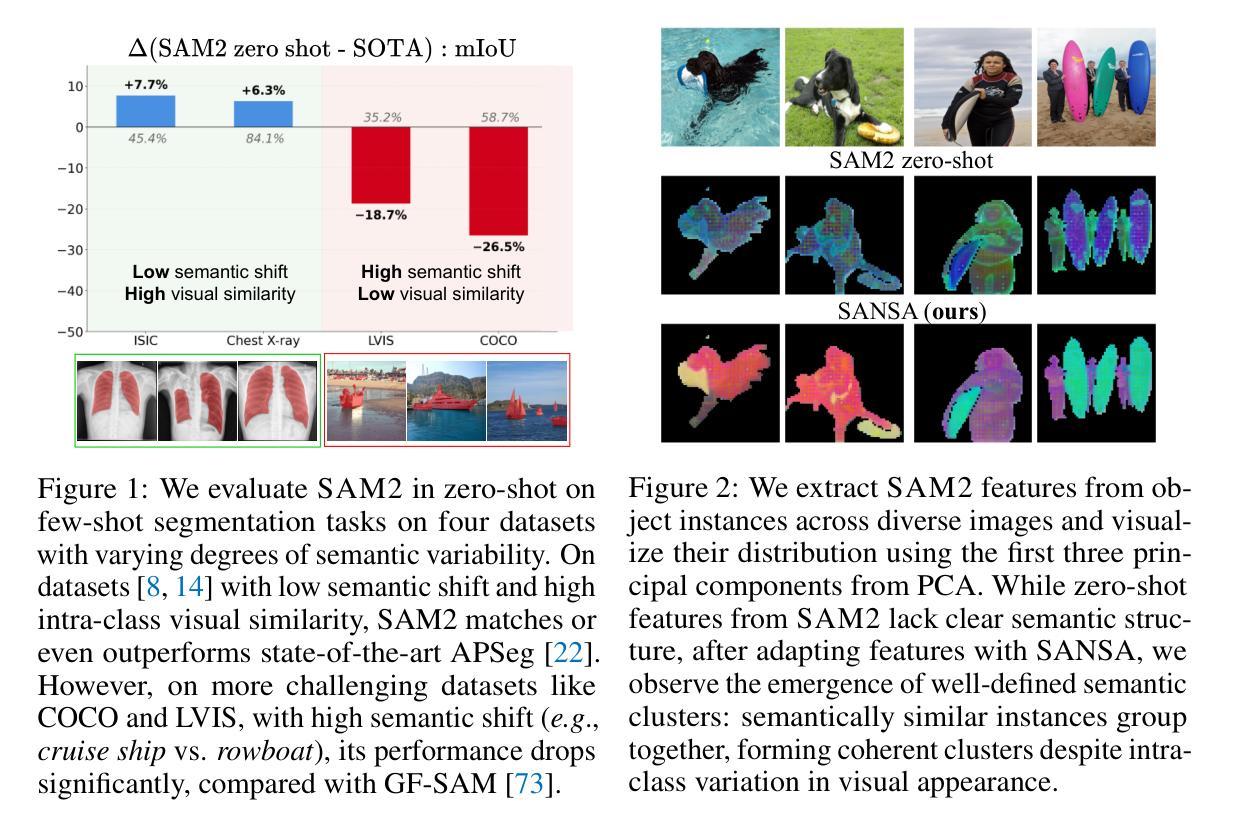
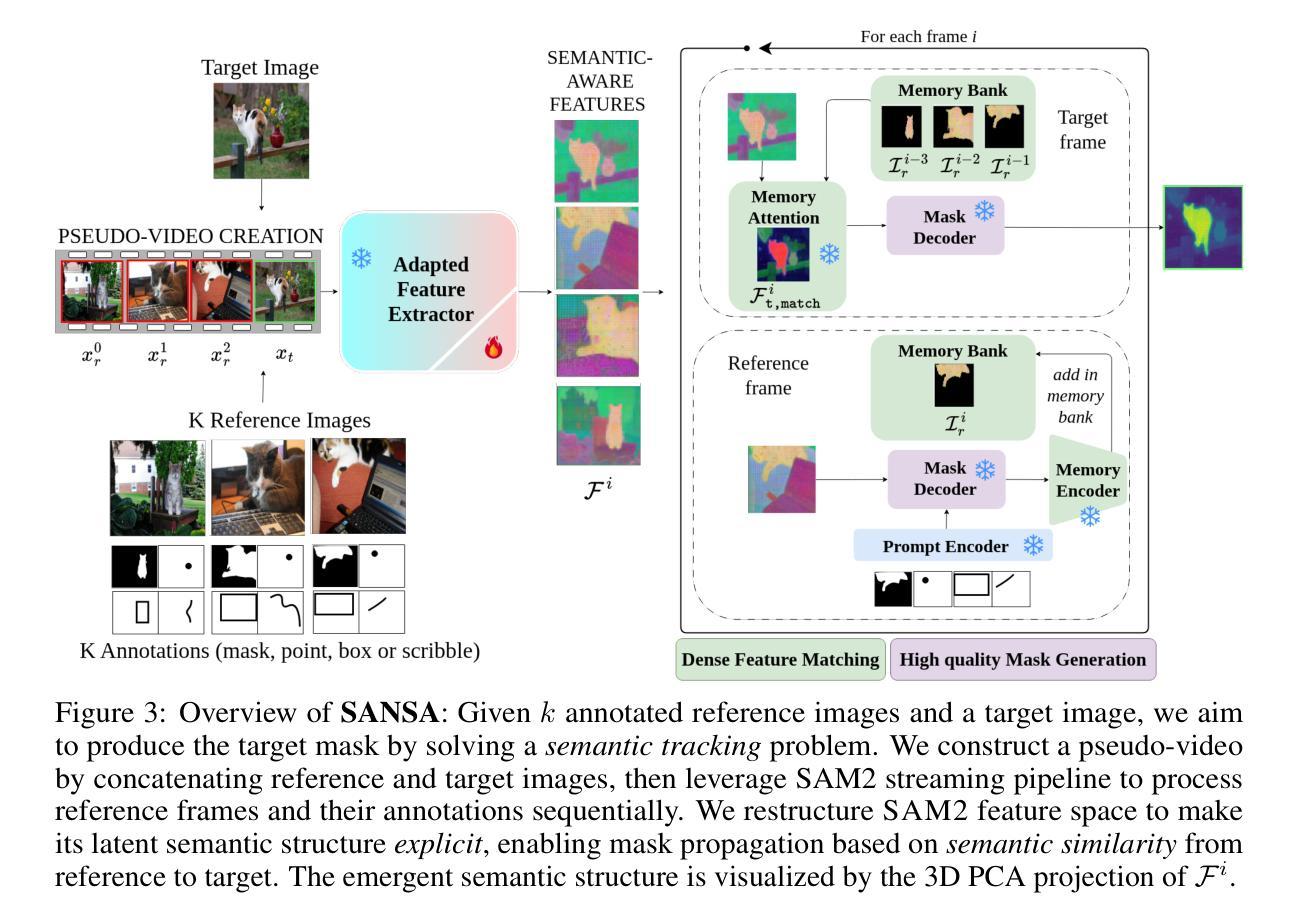
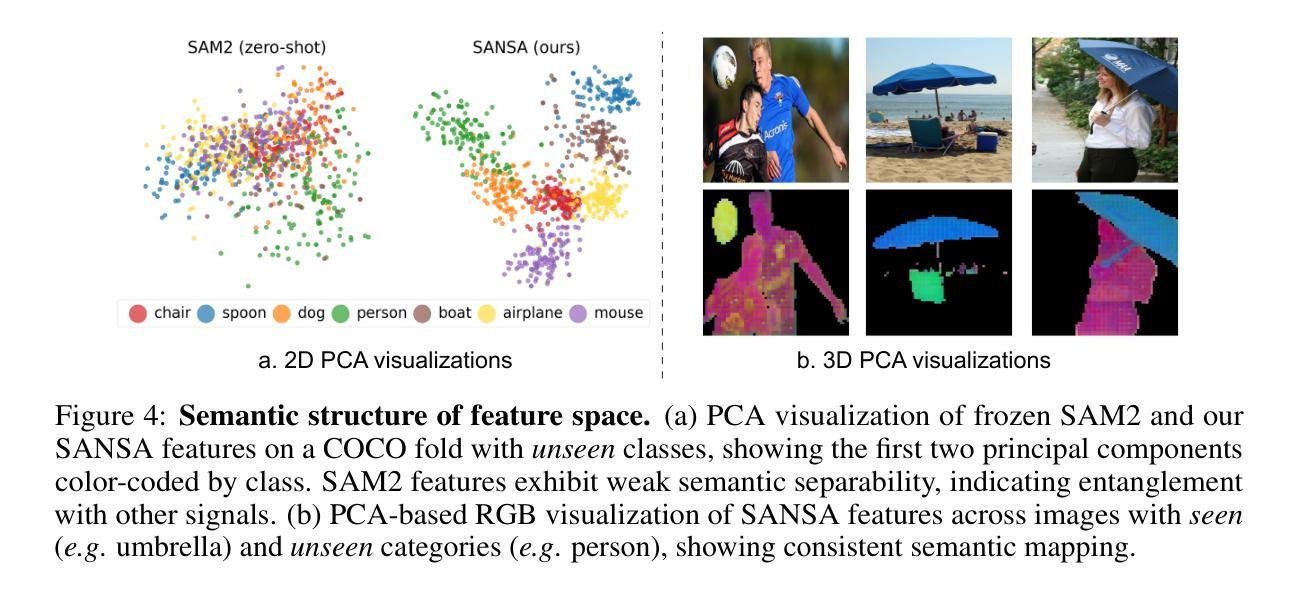
SANSA: Unleashing the Hidden Semantics in SAM2 for Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Claudia Cuttano, Gabriele Trivigno, Giuseppe Averta, Carlo Masone
Few-shot segmentation aims to segment unseen object categories from just a handful of annotated examples. This requires mechanisms that can both identify semantically related objects across images and accurately produce segmentation masks. We note that Segment Anything 2 (SAM2), with its prompt-and-propagate mechanism, offers both strong segmentation capabilities and a built-in feature matching process. However, we show that its representations are entangled with task-specific cues optimized for object tracking, which impairs its use for tasks requiring higher level semantic understanding. Our key insight is that, despite its class-agnostic pretraining, SAM2 already encodes rich semantic structure in its features. We propose SANSA (Semantically AligNed Segment Anything 2), a framework that makes this latent structure explicit, and repurposes SAM2 for few-shot segmentation through minimal task-specific modifications. SANSA achieves state-of-the-art performance on few-shot segmentation benchmarks specifically designed to assess generalization, outperforms generalist methods in the popular in-context setting, supports various prompts flexible interaction via points, boxes, or scribbles, and remains significantly faster and more compact than prior approaches. Code is available at https://github.com/ClaudiaCuttano/SANSA.
少数样本分割旨在从少量标注的样本中对未见过的目标类别进行分割。这需要能够在图像中识别语义相关对象并准确生成分割掩码的机制。我们注意到,借助提示和传播的Segment Anything 2(SAM2)提供了强大的分割能力和内置的特征匹配过程。然而,我们表明其表示与针对对象跟踪优化的特定任务线索纠缠在一起,这损害了其在需要高级语义理解的任务中的使用。我们的关键见解是,尽管SAM2具有类无关的预训练,但它已经在特征中编码了丰富的语义结构。我们提出了SANSA(语义对齐的Segment Anything 2),一个使这种潜在结构明确的框架,并通过最少的特定任务修改将SAM2重新用于少数样本分割。SANSA在专门为评估泛化能力设计的少数样本分割基准测试上实现了最先进的性能,在流行的上下文设置中的全能方法表现出色,支持通过点、框或涂鸦进行各种提示的灵活交互,并且相较于先前的方法,速度更快、更紧凑。代码可在https://github.com/ClaudiaCuttano/SANSA上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/ClaudiaCuttano/SANSA
Summary
SAM2模型具有强大的分割能力和内置的特征匹配过程,但其在少数样本分割任务中的表现受到任务特定线索的干扰。我们提出SANSA框架,通过使SAM2的潜在结构显性化并对其进行最小特定的任务修改,使其成为适合少数样本分割任务的有效工具。SANSA具有出色的性能,支持各种提示灵活的交互方式,并且相较于先前的方法更加快速和紧凑。
Key Takeaways
- SAM2模型具有强大的分割能力和特征匹配过程。
- SAM2模型在少数样本分割任务中的表现受到任务特定线索的干扰。
- SANSA框架利用SAM2的潜在结构进行少数样本分割任务。
- SANSA框架通过最小特定的任务修改使SAM2模型适合少数样本分割任务。
- SANSA在少数样本分割任务上具有出色的性能,且优于先前的通用方法。
- SANSA支持各种提示灵活的交互方式,便于用户进行使用和操作。
点此查看论文截图

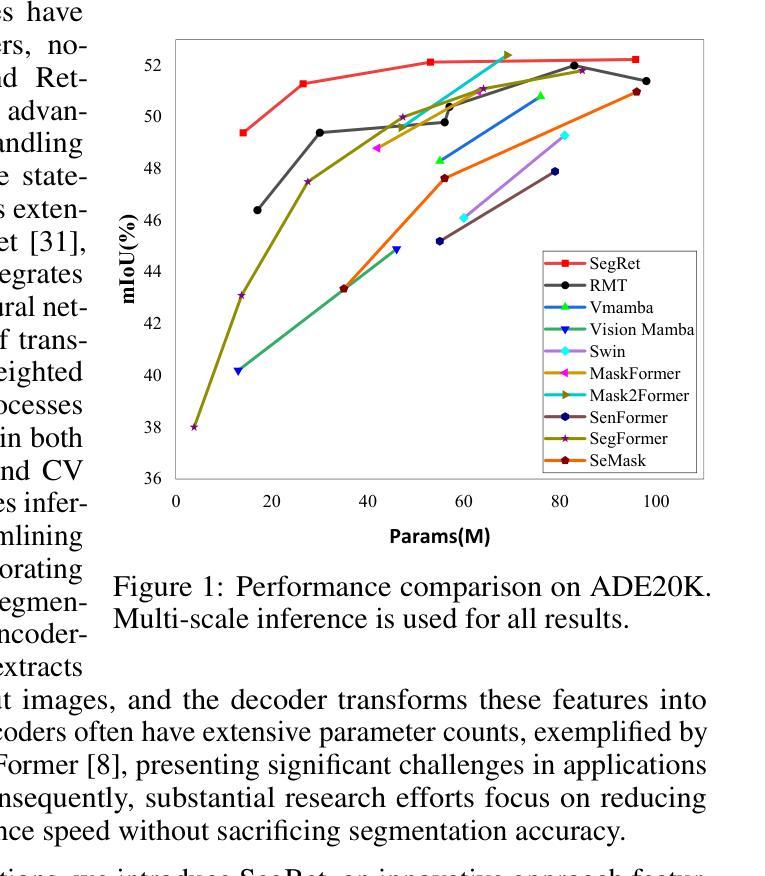
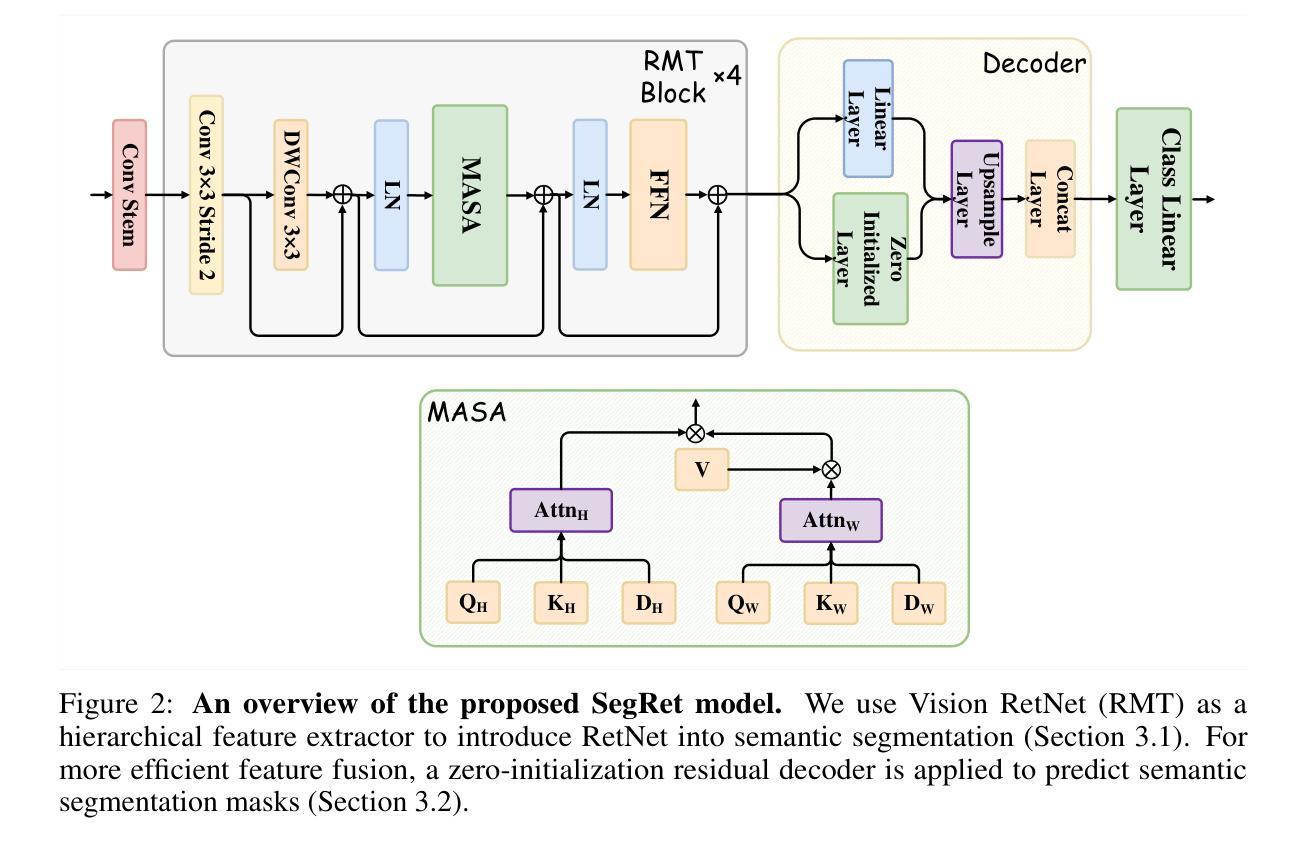
SegRet: An Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Retentive Network
Authors:Zhiyuan Li, Yi Chang, Yuan Wu
With the rapid evolution of autonomous driving technology and intelligent transportation systems, semantic segmentation has become increasingly critical. Precise interpretation and analysis of real-world environments are indispensable for these advanced applications. However, traditional semantic segmentation approaches frequently face challenges in balancing model performance with computational efficiency, especially regarding the volume of model parameters. To address these constraints, we propose SegRet, a novel model employing the Retentive Network (RetNet) architecture coupled with a lightweight residual decoder that integrates zero-initialization. SegRet offers three distinctive advantages: (1) Lightweight Residual Decoder: by embedding a zero-initialization layer within the residual network structure, the decoder remains computationally streamlined without sacrificing essential information propagation; (2) Robust Feature Extraction: adopting RetNet as its backbone enables SegRet to effectively capture hierarchical image features, thereby enriching the representation quality of extracted features; (3) Parameter Efficiency: SegRet attains state-of-the-art (SOTA) segmentation performance while markedly decreasing the number of parameters, ensuring high accuracy without imposing additional computational burdens. Comprehensive empirical evaluations on prominent benchmarks, such as ADE20K, Citycapes, and COCO-Stuff, highlight the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
随着自动驾驶技术和智能交通系统的快速发展,语义分割的重要性日益凸显。精确解读和分析真实环境对这些高级应用来说是不可或缺的。然而,传统的语义分割方法常常在平衡模型性能和计算效率方面面临挑战,特别是关于模型参数体积的问题。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了SegRet,一个采用Retentive Network(RetNet)架构结合轻量级残差解码器的新型模型,该解码器集成了零初始化。SegRet具有三个显著优势:
(1)轻量级残差解码器:通过在残差网络结构中嵌入零初始化层,解码器在计算上保持简洁,同时不牺牲重要信息的传播;
(2)稳健的特征提取:采用RetNet作为骨干网,使SegRet能够有效地捕获分层图像特征,从而丰富提取特征的表现质量;
(3)参数效率:SegRet在减少参数数量的同时达到了最先进的分割性能,确保高精度不会带来额外的计算负担。在ADE20K、Citycapes和COCO-Stuff等主流基准测试上的综合实证评估,突显了我们方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages
Summary
随着自动驾驶技术与智能交通系统的飞速发展,语义分割技术变得尤为重要。精确解读和分析真实环境对这些高级应用不可或缺。传统语义分割方法常在模型性能与计算效率之间面临挑战,尤其体现在模型参数规模上。我们提出SegRet模型,采用Retentive Network(RetNet)架构结合轻量化残差解码器,集成零初始化技术。SegRet具备三大优势:一、轻量化残差解码器:在残差网络结构中嵌入零初始化层,保证解码器计算流程简洁,同时不牺牲关键信息传输;二、稳健特征提取:采用RetNet作为骨干网,使SegRet能够有效捕捉图像层次特征,从而提高特征表示质量;三、参数高效:SegRet在减少参数数量的同时达到最先进的分割性能,确保高精度且不会增加计算负担。在ADE20K、Citycapes和COCO-Stuff等主流基准测试上的综合评估,凸显了我们方法的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在自动驾驶和智能交通系统中至关重要,需要精确解读和分析真实环境。
- 传统语义分割方法面临模型性能和计算效率的平衡挑战,尤其是模型参数规模。
- SegRet模型采用RetNet架构和轻量化残差解码器,集成零初始化技术。
- SegRet具有三大优势:轻量化、稳健特征提取和参数高效。
- SegRet在保证高分割性能的同时,显著减少了参数数量,且不增加计算负担。
- 在主流基准测试上,SegRet表现出有效性和优越性。
点此查看论文截图

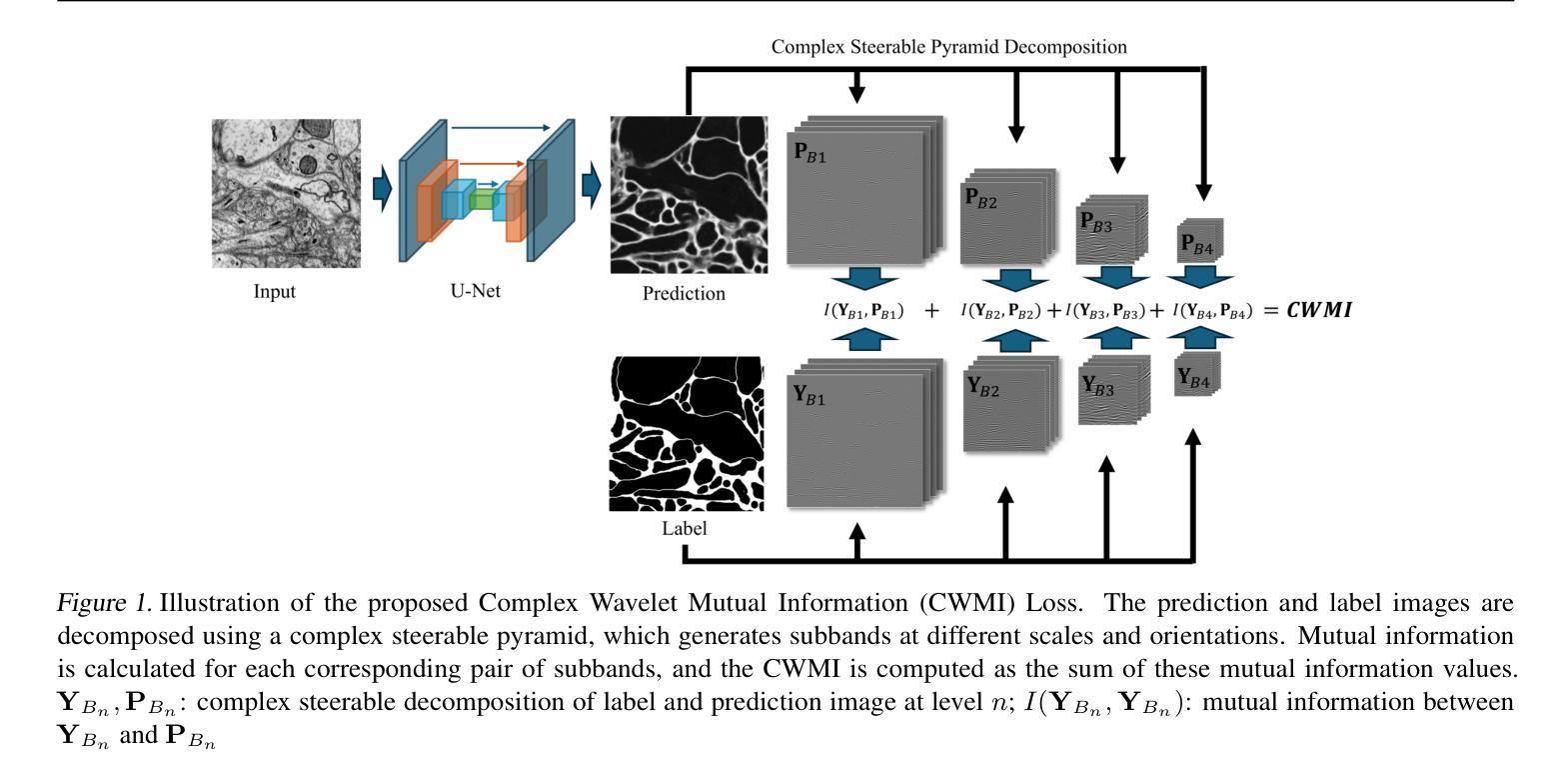
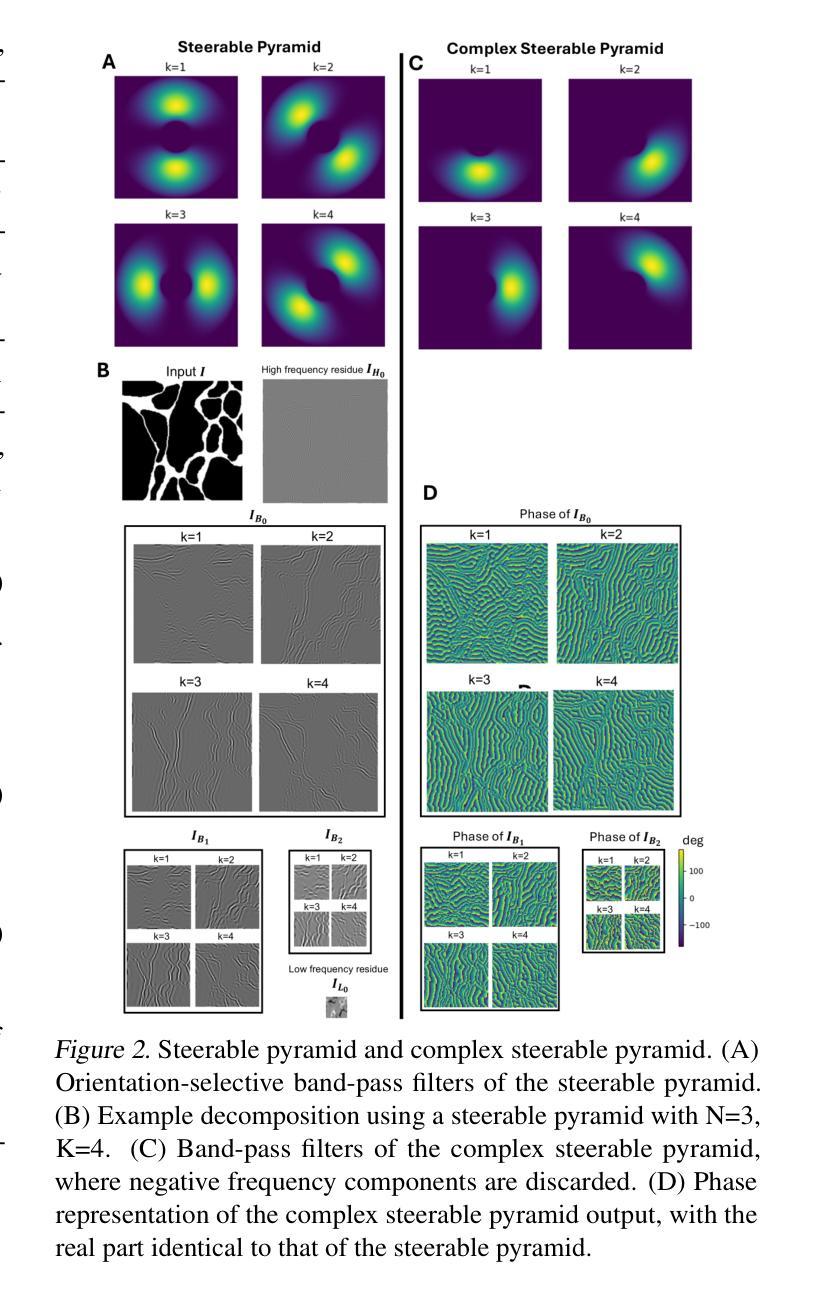
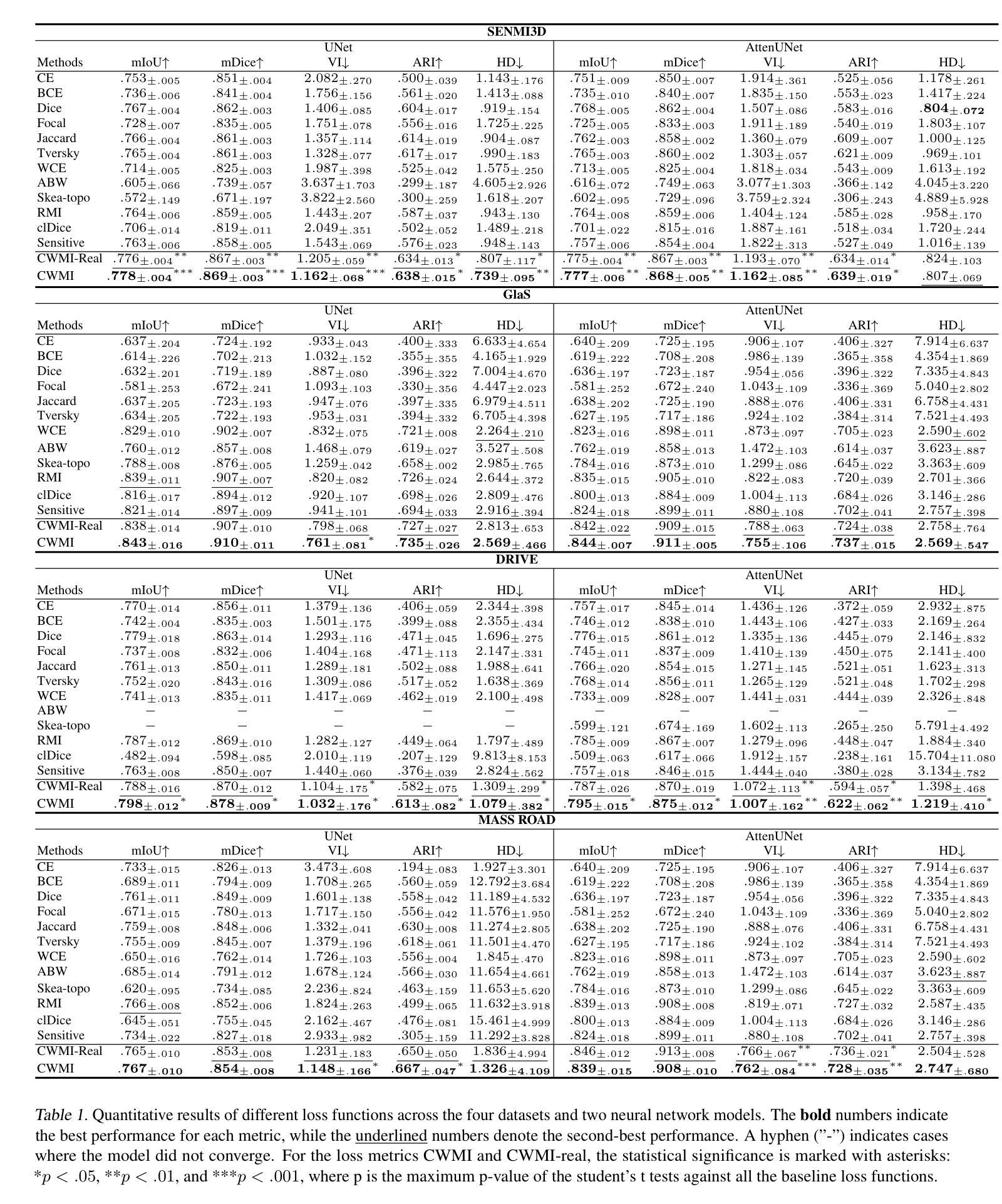
Complex Wavelet Mutual Information Loss: A Multi-Scale Loss Function for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Renhao Lu
Recent advancements in deep neural networks have significantly enhanced the performance of semantic segmentation. However, class imbalance and instance imbalance remain persistent challenges, where smaller instances and thin boundaries are often overshadowed by larger structures. To address the multiscale nature of segmented objects, various models have incorporated mechanisms such as spatial attention and feature pyramid networks. Despite these advancements, most loss functions are still primarily pixel-wise, while regional and boundary-focused loss functions often incur high computational costs or are restricted to small-scale regions. To address this limitation, we propose the complex wavelet mutual information (CWMI) loss, a novel loss function that leverages mutual information from subband images decomposed by a complex steerable pyramid. The complex steerable pyramid captures features across multiple orientations and preserves structural similarity across scales. Meanwhile, mutual information is well-suited to capturing high-dimensional directional features and offers greater noise robustness. Extensive experiments on diverse segmentation datasets demonstrate that CWMI loss achieves significant improvements in both pixel-wise accuracy and topological metrics compared to state-of-the-art methods, while introducing minimal computational overhead. Our code is available at https://github.com/lurenhaothu/CWMI
最近深度神经网络的发展极大地提高了语义分割的性能。然而,类别不平衡和实例不平衡仍然持续存在挑战,较小的实例和薄边界通常被较大的结构所掩盖。为了解决分割对象的多尺度特性,各种模型已经融入了空间注意力机制和特征金字塔网络等机制。尽管有了这些进展,大多数损失函数仍然是基于像素的,而区域性和边界聚焦的损失函数往往带来较高的计算成本或仅限于小规模区域。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了复杂小波互信息(CWMI)损失这一新型损失函数,它利用由复杂可转向金字塔分解得到的子带图像的互信息。复杂可转向金字塔能够捕获多个方向的特性,并在不同尺度上保留结构相似性。同时,互信息非常适合捕捉高维方向特性,并提供了更强的噪声鲁棒性。在多种分割数据集上的广泛实验表明,与最新方法相比,CWMI损失在像素级精度和拓扑指标方面取得了显著改进,同时引入了极低的计算开销。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lurenhaothu/CWMI找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025. This version corresponds to the official camera-ready submission
Summary
本文介绍了针对语义分割中的多尺度问题,提出了一种新的损失函数——复杂小波互信息(CWMI)损失。该函数利用由复杂可转向金字塔分解得到的子带图像的互信息,有效地提高了像素级精度和拓扑度量。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割面临的挑战包括类别不平衡和实例不平衡,其中较小的实例和薄边界常被较大的结构所掩盖。
- 为了应对分割对象的多尺度特性,已存在的模型采用了空间注意力机制和特征金字塔网络等方法。
- 现有的损失函数主要是像素级的,而区域和边界聚焦的损失函数计算成本较高或仅限于小规模区域。
- 提出了一种新的损失函数——复杂小波互信息(CWMI)损失,它利用复杂可转向金字塔分解的互信息。
- 复杂可转向金字塔能够捕捉多个方向的特性并保持跨尺度的结构相似性。
- 互信息适用于捕捉高维方向特性,并提供了更好的噪声鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

Cross-Layer Feature Pyramid Transformer for Small Object Detection in Aerial Images
Authors:Zewen Du, Zhenjiang Hu, Guiyu Zhao, Ying Jin, Hongbin Ma
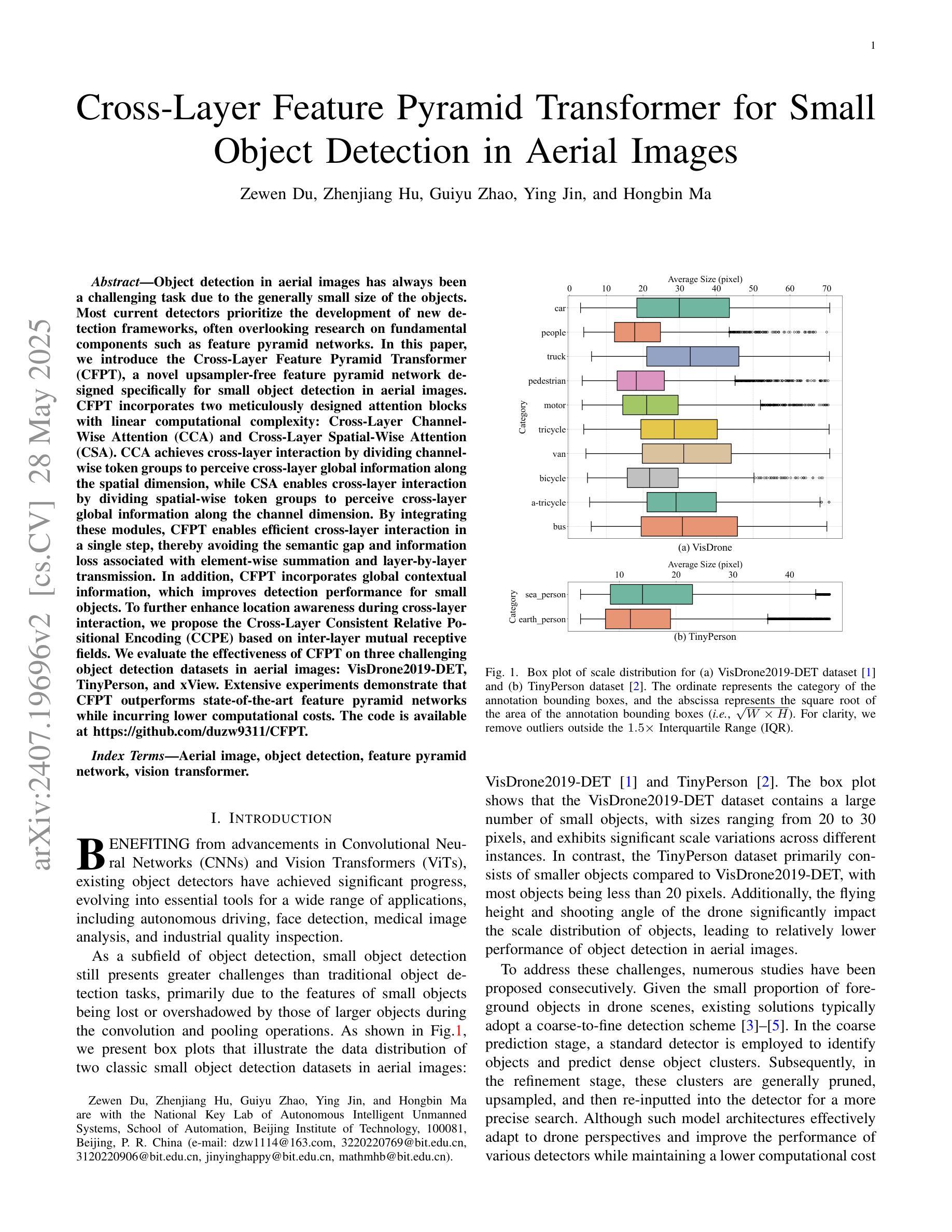
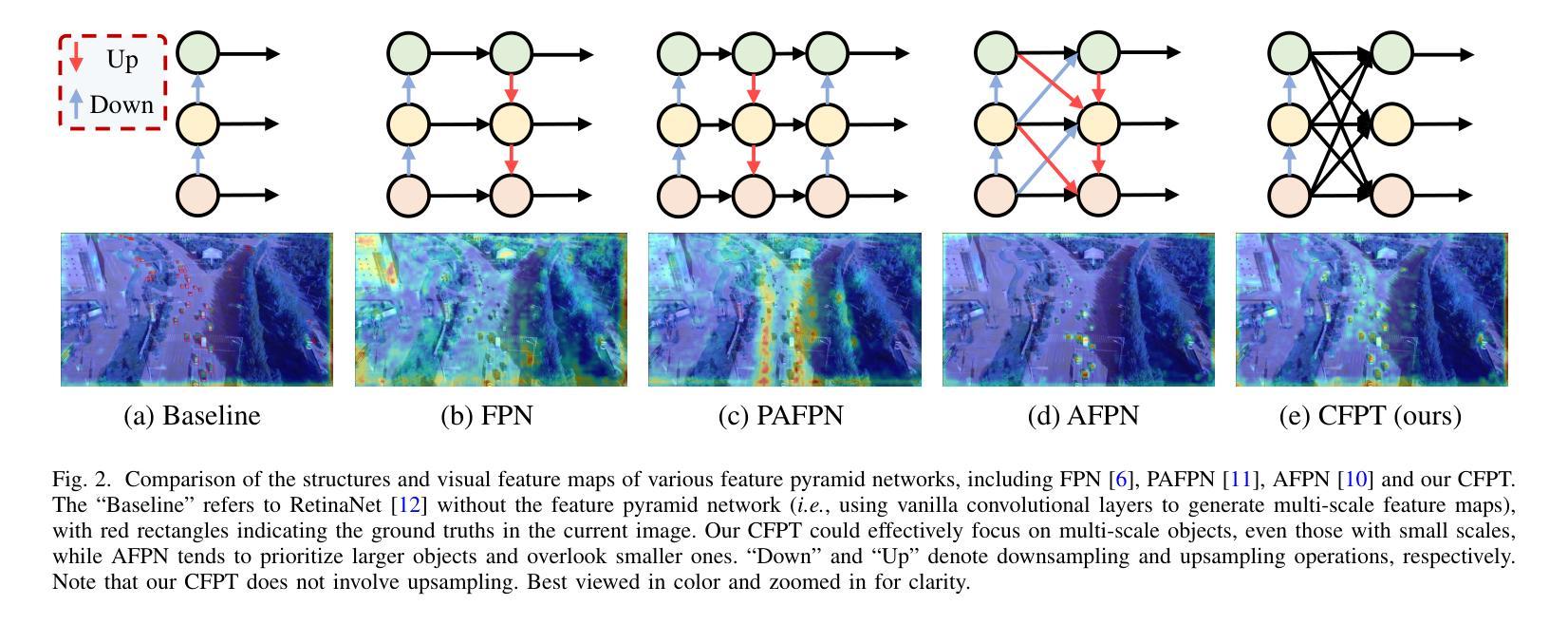
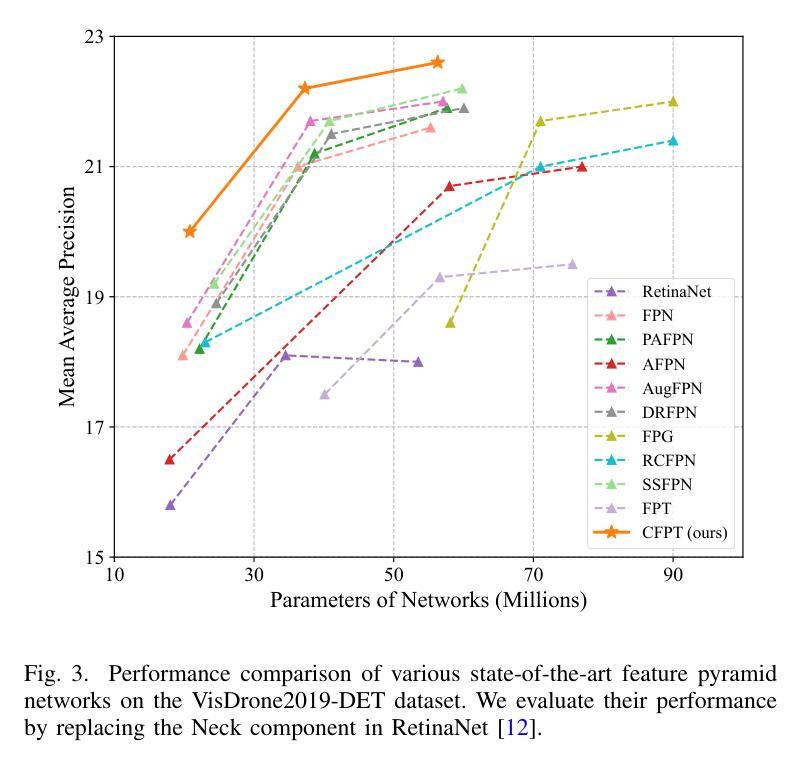
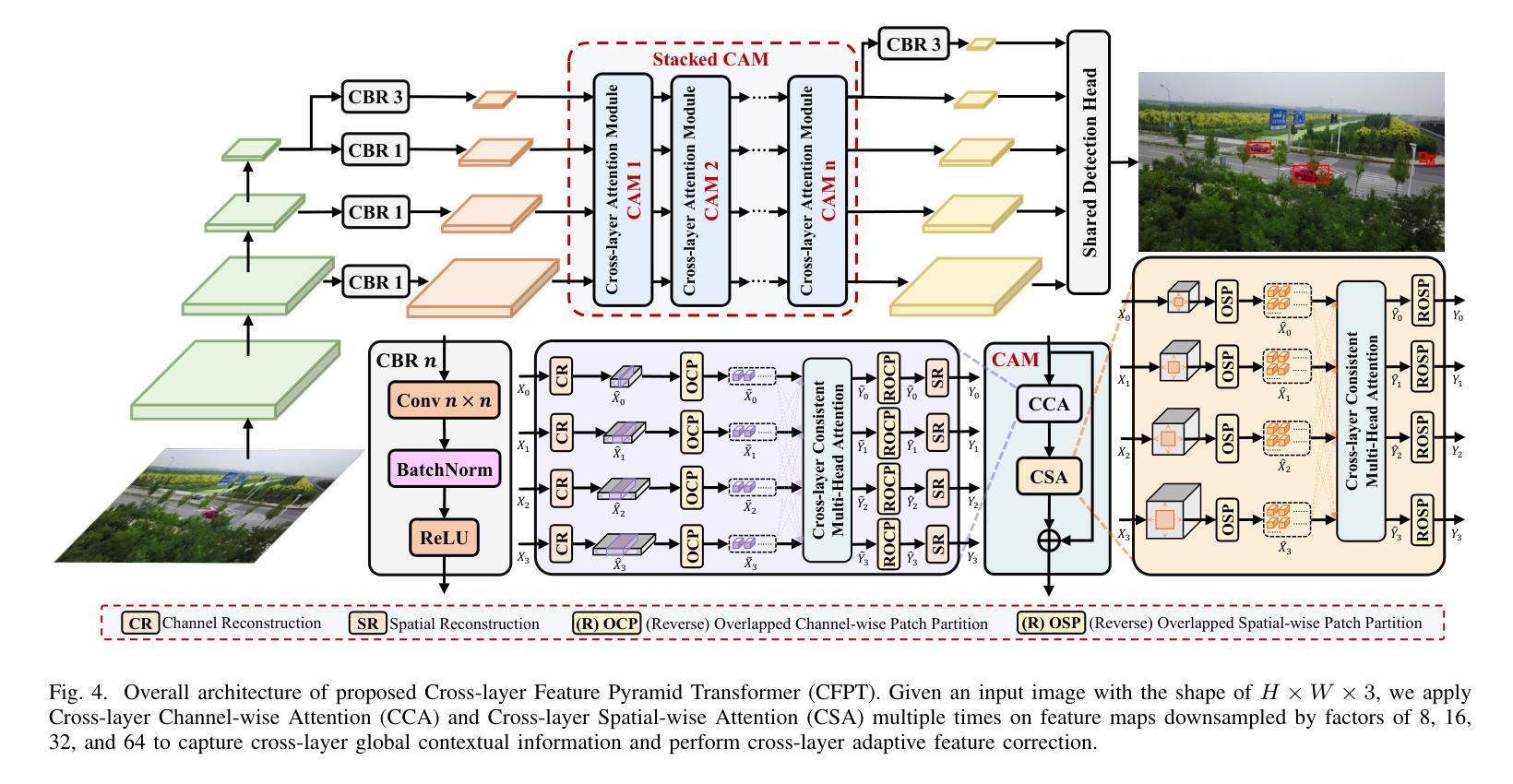
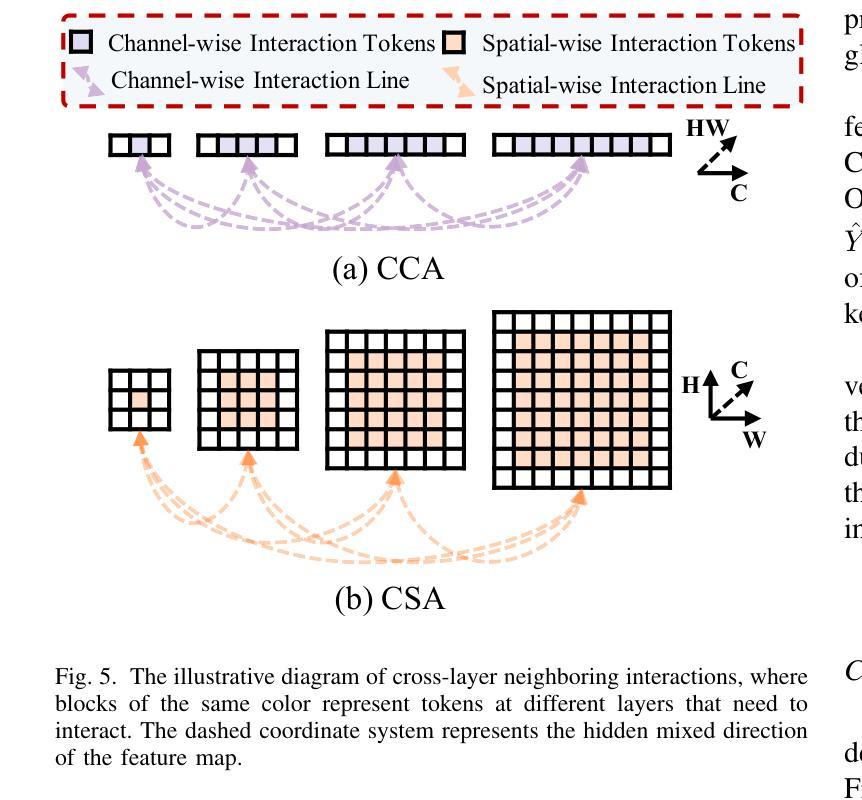
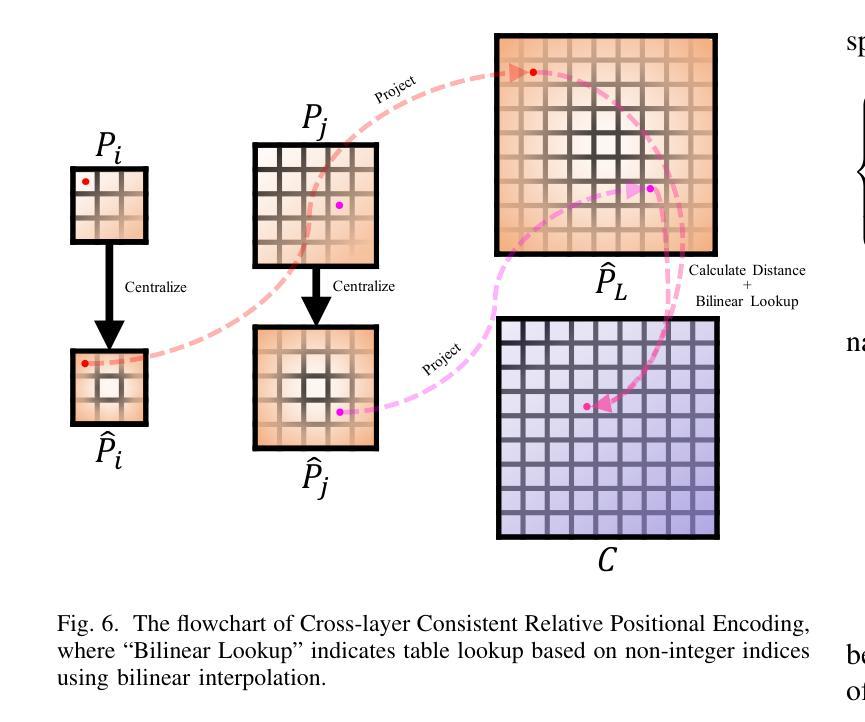
Object detection in aerial images has always been a challenging task due to the generally small size of the objects. Most current detectors prioritize the development of new detection frameworks, often overlooking research on fundamental components such as feature pyramid networks. In this paper, we introduce the Cross-Layer Feature Pyramid Transformer (CFPT), a novel upsampler-free feature pyramid network designed specifically for small object detection in aerial images. CFPT incorporates two meticulously designed attention blocks with linear computational complexity: Cross-Layer Channel-Wise Attention (CCA) and Cross-Layer Spatial-Wise Attention (CSA). CCA achieves cross-layer interaction by dividing channel-wise token groups to perceive cross-layer global information along the spatial dimension, while CSA enables cross-layer interaction by dividing spatial-wise token groups to perceive cross-layer global information along the channel dimension. By integrating these modules, CFPT enables efficient cross-layer interaction in a single step, thereby avoiding the semantic gap and information loss associated with element-wise summation and layer-by-layer transmission. In addition, CFPT incorporates global contextual information, which improves detection performance for small objects. To further enhance location awareness during cross-layer interaction, we propose the Cross-Layer Consistent Relative Positional Encoding (CCPE) based on inter-layer mutual receptive fields. We evaluate the effectiveness of CFPT on three challenging object detection datasets in aerial images: VisDrone2019-DET, TinyPerson, and xView. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CFPT outperforms state-of-the-art feature pyramid networks while incurring lower computational costs. The code is available at https://github.com/duzw9311/CFPT.
在航空图像中进行目标检测一直是一项具有挑战性的任务,主要是因为目标通常尺寸较小。目前大多数探测器都侧重于开发新的检测框架,往往忽视了关于基础组件的研究,如特征金字塔网络。在本文中,我们介绍了跨层特征金字塔转换器(CFPT),这是一种专为航空图像中的小目标检测设计的无上采样器特征金字塔网络。CFPT融合了两个精心设计的具有线性计算复杂度的注意力块:跨层通道注意力(CCA)和跨层空间注意力(CSA)。CCA通过沿空间维度将通道令牌分组来实现跨层交互,以感知跨层全局信息,而CSA通过沿通道维度将空间令牌分组来实现跨层交互。通过集成这些模块,CFPT能够在单步中实现高效的跨层交互,从而避免了逐元素求和和逐层传输所带来的语义鸿沟和信息损失。此外,CFPT结合了全局上下文信息,提高了对小目标的检测性能。为了进一步提高跨层交互过程中的位置感知能力,我们基于层间相互感受野提出了跨层一致相对位置编码(CCPE)。我们在三个具有挑战性的航空图像目标检测数据集上评估了CFPT的有效性:VisDrone2019-DET、TinyPerson和xView。大量实验表明,CFPT在具有较低计算成本的同时,优于最新的特征金字塔网络。相关代码可通过https://github.com/duzw9311/CFPT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种新型的跨层特征金字塔转换器(CFPT),这是一种专为空中图像小目标检测设计的无上采样器特征金字塔网络。它包含两种设计精巧的注意力块:跨层通道注意力(CCA)和跨层空间注意力(CSA)。CFPT通过整合这些模块,实现了跨层交互,避免了语义鸿沟和信息损失。此外,CFPT还融入了全局上下文信息,提高了对小目标的检测性能。该研究在三个具有挑战性的空中图像目标检测数据集上评估了CFPT的有效性,并证明其性能优于当前主流的特征金字塔网络,同时计算成本更低。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种新型的跨层特征金字塔转换器(CFPT),针对空中图像的小目标检测。
- CFPT包含两种注意力块:跨层通道注意力(CCA)和跨层空间注意力(CSA),可实现高效的跨层交互。
- CFPT避免了语义鸿沟和信息损失的问题。
- CFPT融入了全局上下文信息以提高对小目标的检测性能。
- 在三个具有挑战性的空中图像目标检测数据集上进行了实验验证,证明CFPT的性能优于其他主流方法。
- CFPT的计算成本较低。
点此查看论文截图