⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
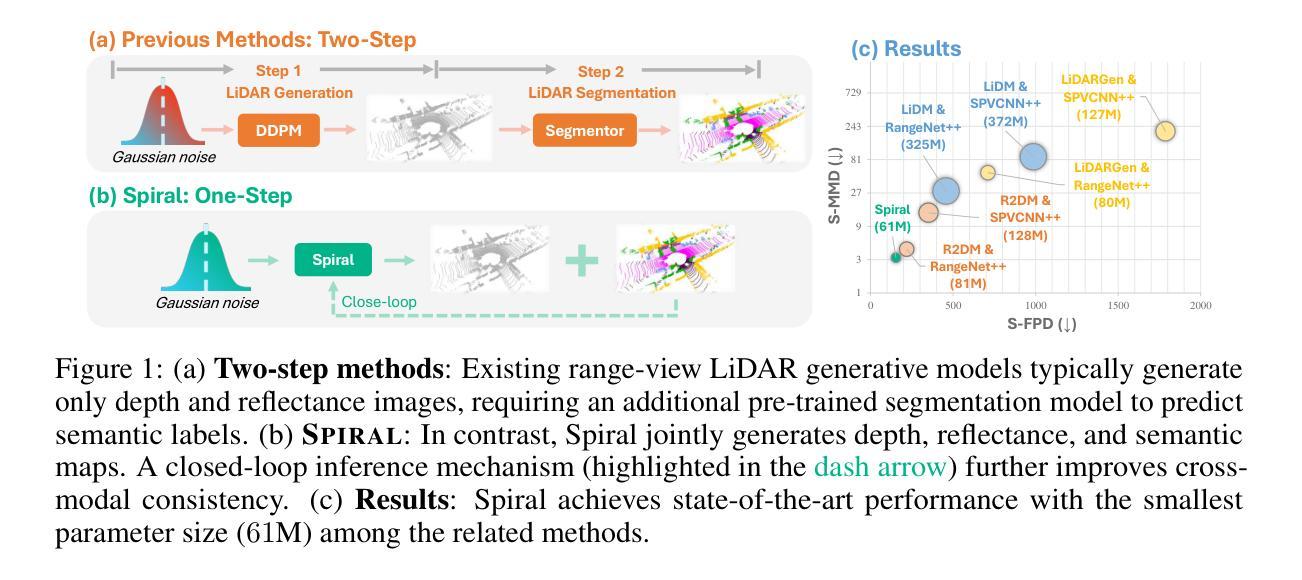
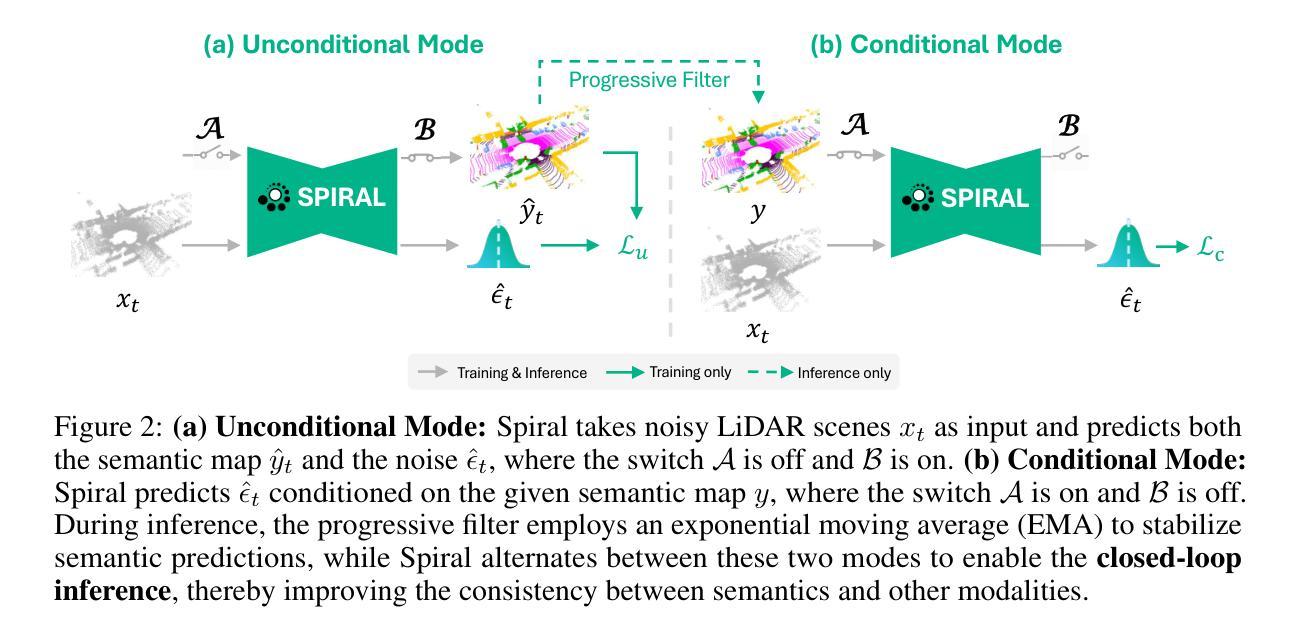
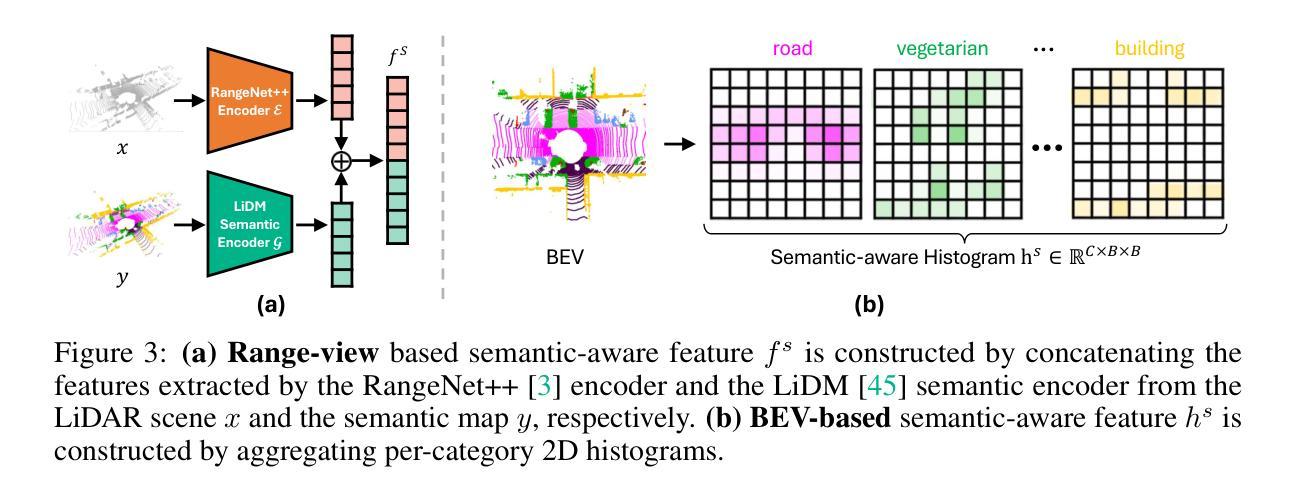
SPIRAL: Semantic-Aware Progressive LiDAR Scene Generation
Authors:Dekai Zhu, Yixuan Hu, Youquan Liu, Dongyue Lu, Lingdong Kong, Slobodan Ilic
Leveraging recent diffusion models, LiDAR-based large-scale 3D scene generation has achieved great success. While recent voxel-based approaches can generate both geometric structures and semantic labels, existing range-view methods are limited to producing unlabeled LiDAR scenes. Relying on pretrained segmentation models to predict the semantic maps often results in suboptimal cross-modal consistency. To address this limitation while preserving the advantages of range-view representations, such as computational efficiency and simplified network design, we propose Spiral, a novel range-view LiDAR diffusion model that simultaneously generates depth, reflectance images, and semantic maps. Furthermore, we introduce novel semantic-aware metrics to evaluate the quality of the generated labeled range-view data. Experiments on the SemanticKITTI and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that Spiral achieves state-of-the-art performance with the smallest parameter size, outperforming two-step methods that combine the generative and segmentation models. Additionally, we validate that range images generated by Spiral can be effectively used for synthetic data augmentation in the downstream segmentation training, significantly reducing the labeling effort on LiDAR data.
基于最新的扩散模型,激光雷达(LiDAR)的大规模三维场景生成已经取得了巨大的成功。虽然基于体素的方法可以生成几何结构和语义标签,但现有的范围视图方法仅限于生成无标签的激光雷达场景。依赖预训练的分割模型来预测语义地图往往会导致跨模态一致性不佳。为了解决这个问题,同时保留范围视图表示的优点,如计算效率和网络设计简化,我们提出了Spiral,这是一种新型的范围视图激光雷达扩散模型,可以同时生成深度、反射图像和语义地图。此外,我们还引入了新型的语义感知指标来评估生成的带标签范围视图数据的质量。在SemanticKITTI和nuScenes数据集上的实验表明,Spiral在参数规模最小的情况下实现了最先进的技术性能,超越了将生成模型和分割模型相结合的两步方法。此外,我们验证了Spiral生成的范围图像可以有效地用于下游分割训练中的合成数据增强,从而大大减少激光雷达数据的标注工作量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于最新的扩散模型,LiDAR基大规模3D场景生成已取得了巨大成功。虽然最近的基于体素的方法可以生成几何结构和语义标签,但现有的范围视图方法仅限于生成未标记的LiDAR场景。依靠预训练的分割模型来预测语义地图往往会导致跨模态一致性较差。为了克服这一局限性,同时保留范围视图表示的优点(如计算效率高和简化网络设计),我们提出了Spiral,这是一种新型的范围视图LiDAR扩散模型,可以同时生成深度、反射图像和语义地图。实验表明,Spiral在SemanticKITTI和nuScenes数据集上性能处于领先地位,参数规模最小,且优于结合生成模型和分割模型的两步方法。此外,我们验证了Spiral生成的范围图像可以有效地用于下游分割训练中的合成数据增强,大大减少LiDAR数据的标注工作量。
Key Takeaways
- 利用最新的扩散模型,LiDAR基大规模3D场景生成取得了成功。
- 现有的范围视图方法主要生成未标记的LiDAR场景。
- Spiral是一种新型的范围视图LiDAR扩散模型,能同时生成深度、反射图像和语义地图。
- Spiral在语义地图生成方面性能领先,参数规模较小。
- Spiral与结合生成模型和分割模型的两步方法相比具有优势。
- Spiral生成的范围图像可用于下游分割训练中的合成数据增强。
点此查看论文截图

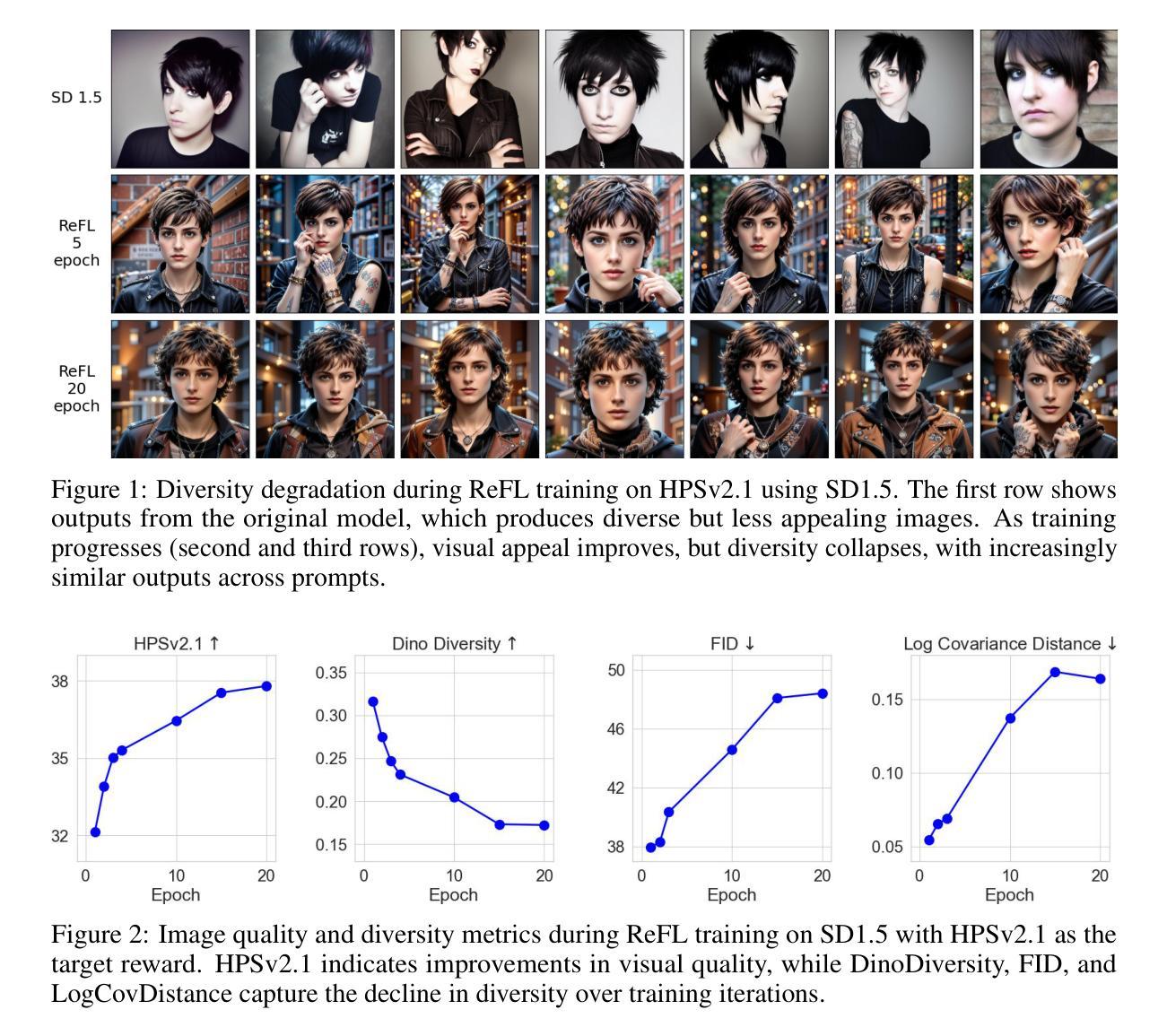
ImageReFL: Balancing Quality and Diversity in Human-Aligned Diffusion Models
Authors:Dmitrii Sorokin, Maksim Nakhodnov, Andrey Kuznetsov, Aibek Alanov
Recent advances in diffusion models have led to impressive image generation capabilities, but aligning these models with human preferences remains challenging. Reward-based fine-tuning using models trained on human feedback improves alignment but often harms diversity, producing less varied outputs. In this work, we address this trade-off with two contributions. First, we introduce \textit{combined generation}, a novel sampling strategy that applies a reward-tuned diffusion model only in the later stages of the generation process, while preserving the base model for earlier steps. This approach mitigates early-stage overfitting and helps retain global structure and diversity. Second, we propose \textit{ImageReFL}, a fine-tuning method that improves image diversity with minimal loss in quality by training on real images and incorporating multiple regularizers, including diffusion and ReFL losses. Our approach outperforms conventional reward tuning methods on standard quality and diversity metrics. A user study further confirms that our method better balances human preference alignment and visual diversity. The source code can be found at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/ImageReFL .
最近扩散模型的进展为图像生成能力带来了深刻影响,但是如何将这些模型与人类偏好对齐仍然是一个挑战。使用经过人类反馈训练的模型进行基于奖励的微调,可以提高对齐性,但往往会损害多样性,导致输出结果较为单一。在这项工作中,我们通过两个贡献来解决这一权衡问题。首先,我们引入了组合生成这一新型采样策略,只在生成过程的后期应用经过奖励调整的扩散模型,同时保留早期步骤的基准模型。这种方法减轻了早期阶段的过度拟合问题,有助于保持全局结构和多样性。其次,我们提出了一种名为ImageReFL的微调方法,通过在实际图像上进行训练并引入多种正则化器(包括扩散和ReFL损失)来提高图像多样性,同时尽量减少质量损失。我们的方法在标准质量和多样性指标上的表现优于传统奖励调整方法。用户研究进一步证实,我们的方法更好地平衡了人类偏好对齐和视觉多样性。源代码可在https://github.com/ControlGenAI/ImageReFL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The source code can be found at https://github.com/ControlGenAI/ImageReFL
Summary
近期扩散模型的新进展为图像生成能力带来了显著提升,但在与人类偏好对齐方面仍存在挑战。基于奖励的微调使用训练在人类反馈上的模型改善了对齐性,但常常损害多样性,导致输出较少变化。本研究通过两个贡献来解决这一权衡问题。首先,我们引入“组合生成”这一新颖采样策略,仅在生成过程的后期应用奖励调整的扩散模型,而在早期阶段保留基础模型,以减轻早期阶段的过度拟合,并有助于保留全局结构和多样性。其次,我们提出“ImageReFL”这一微调方法,通过训练真实图像并融入包括扩散和ReFL损失在内的多个规则化器,在几乎不损失质量的情况下提高图像多样性。我们的方法在标准质量和多样性指标上优于传统奖励调整方法,用户研究进一步证实我们的方法更好地平衡了人类偏好对齐和视觉多样性。Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域取得显著进展,但对齐人类偏好仍具挑战。
- 奖励微调能提高模型与人类偏好的对齐程度,但可能损害输出多样性。
- 引入“组合生成”策略,在生成过程后期应用奖励调整的扩散模型,以保留全局结构和多样性。
- 提出“ImageReFL”微调方法,通过训练真实图像并融入多个规则化器,提高图像多样性同时几乎不损失质量。
- 该方法在标准质量和多样性指标上超越传统奖励调整方法。
- 用户研究证实该方法在平衡人类偏好对齐和视觉多样性方面表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图


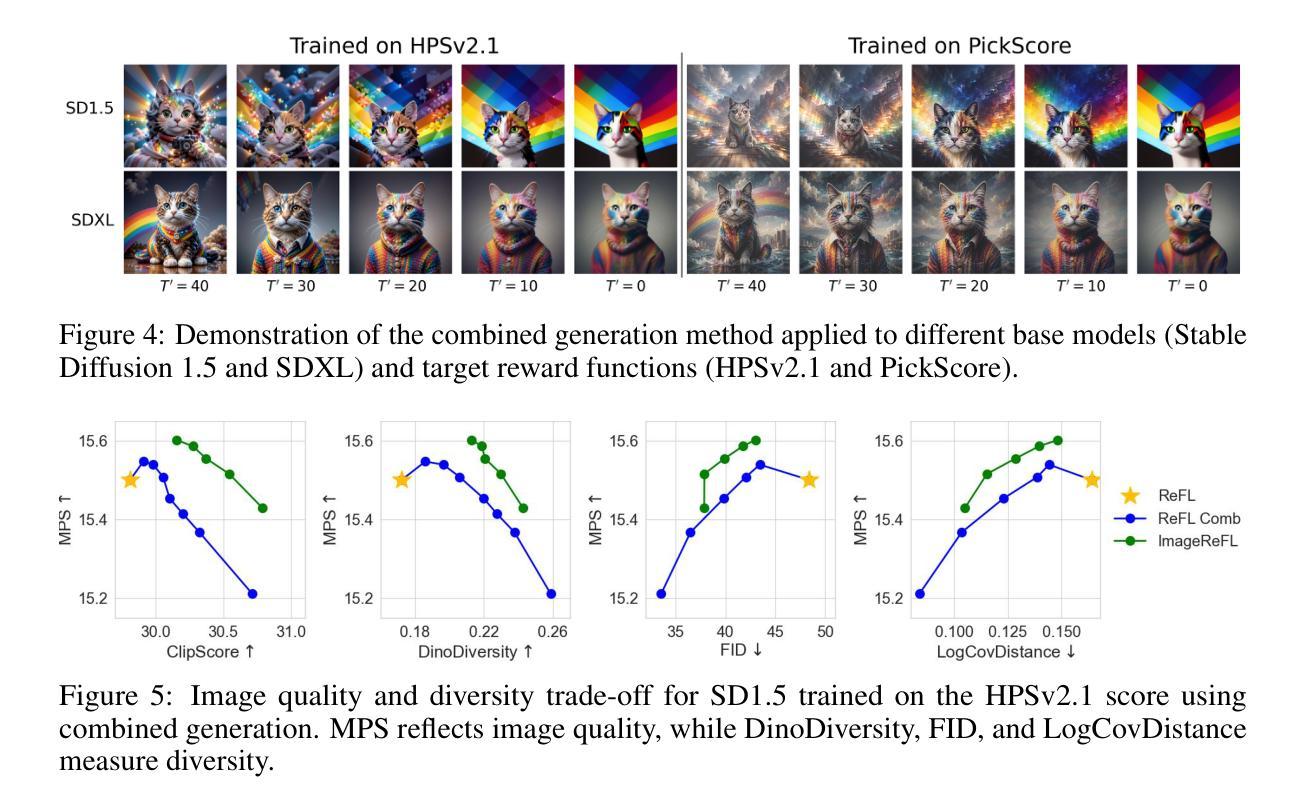
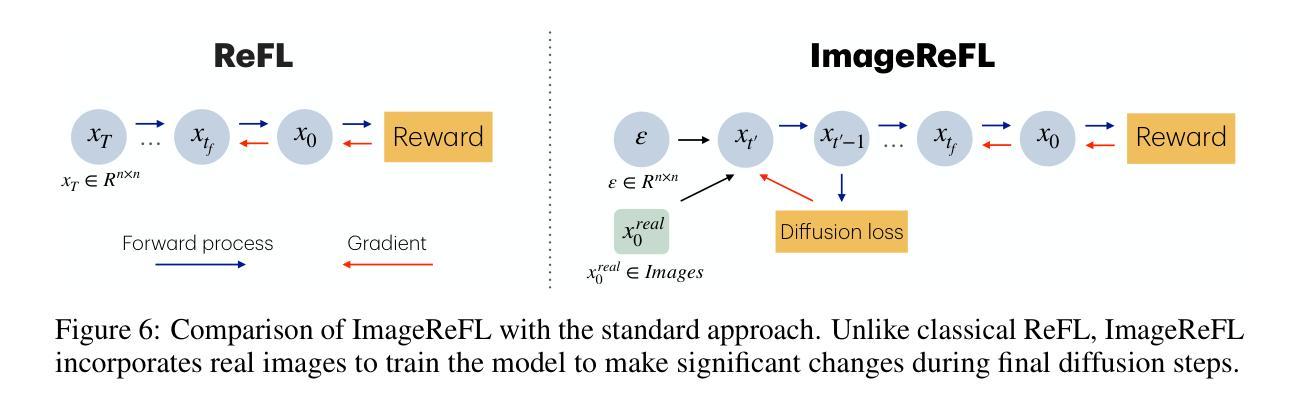
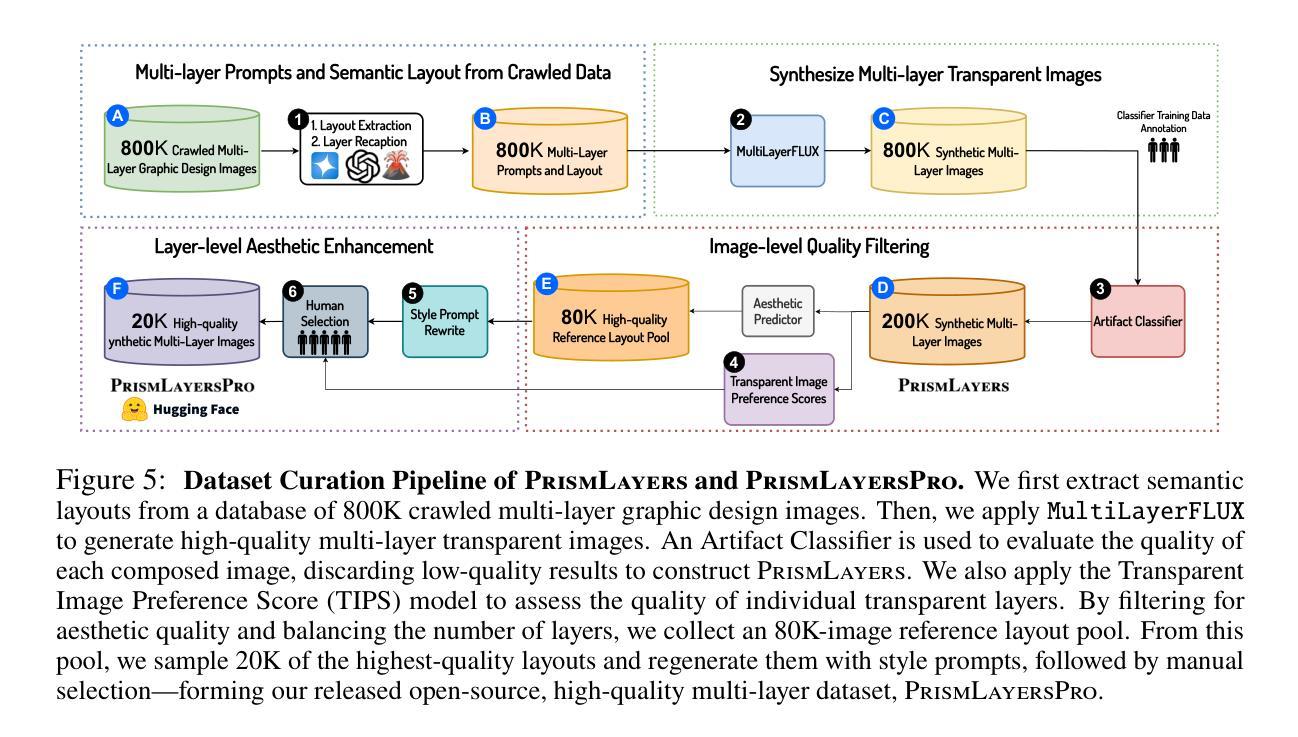
PrismLayers: Open Data for High-Quality Multi-Layer Transparent Image Generative Models
Authors:Junwen Chen, Heyang Jiang, Yanbin Wang, Keming Wu, Ji Li, Chao Zhang, Keiji Yanai, Dong Chen, Yuhui Yuan
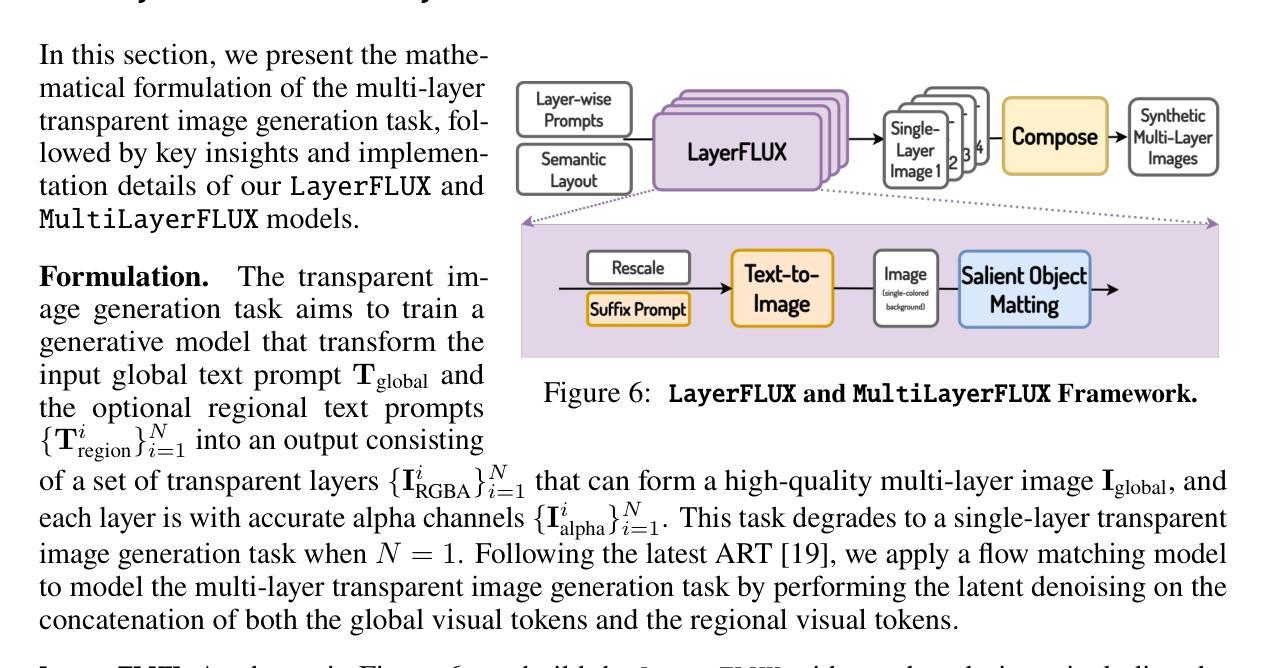
Generating high-quality, multi-layer transparent images from text prompts can unlock a new level of creative control, allowing users to edit each layer as effortlessly as editing text outputs from LLMs. However, the development of multi-layer generative models lags behind that of conventional text-to-image models due to the absence of a large, high-quality corpus of multi-layer transparent data. In this paper, we address this fundamental challenge by: (i) releasing the first open, ultra-high-fidelity PrismLayers (PrismLayersPro) dataset of 200K (20K) multilayer transparent images with accurate alpha mattes, (ii) introducing a trainingfree synthesis pipeline that generates such data on demand using off-the-shelf diffusion models, and (iii) delivering a strong, open-source multi-layer generation model, ART+, which matches the aesthetics of modern text-to-image generation models. The key technical contributions include: LayerFLUX, which excels at generating high-quality single transparent layers with accurate alpha mattes, and MultiLayerFLUX, which composes multiple LayerFLUX outputs into complete images, guided by human-annotated semantic layout. To ensure higher quality, we apply a rigorous filtering stage to remove artifacts and semantic mismatches, followed by human selection. Fine-tuning the state-of-the-art ART model on our synthetic PrismLayersPro yields ART+, which outperforms the original ART in 60% of head-to-head user study comparisons and even matches the visual quality of images generated by the FLUX.1-[dev] model. We anticipate that our work will establish a solid dataset foundation for the multi-layer transparent image generation task, enabling research and applications that require precise, editable, and visually compelling layered imagery.
从文本提示生成高质量、多层透明图像可以解锁一个新的创意控制级别,使用户能够像编辑来自大型语言模型的文本输出一样轻松地编辑每个图层。然而,由于缺少大型高质量的多层透明数据集,多层生成模型的发展滞后于传统的文本到图像模型。在本文中,我们通过以下方式解决了这一基本挑战:(i)发布了第一个开放、超高保真度的PrismLayers(PrismLayersPro)数据集,包含20万个(2万个)带有精确alpha蒙版的多层透明图像;(ii)引入了一个按需生成此类数据的无训练合成管道,该管道使用现成的扩散模型;(iii)开发了一个强大的开源多层生成模型ART+,该模型与现代文本到图像生成模型的审美相匹配。关键的技术贡献包括:LayerFLUX,它擅长生成具有精确alpha蒙版的高质量单一透明图层;以及MultiLayerFLUX,它将多个LayerFLUX输出组合成完整的图像,由人类注释的语义布局引导。为了确保更高的质量,我们应用了一个严格的过滤阶段来消除伪影和语义不匹配,随后进行人工选择。在我们合成的PrismLayersPro数据集上对最先进的ART模型进行微调,得到了ART+,在头对头的用户研究比较中,ART+在60%的情况下超越了原始ART的表现,甚至与FLUX生成的图像视觉质量相匹配。我们预期,我们的工作将为多层透明图像生成任务建立坚实的数据集基础,为需要精确、可编辑和视觉吸引人的分层图像的研究和应用提供支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Homepage: https://prism-layers.github.io/
摘要
本文解决了多层透明图像生成领域的一个核心挑战。通过建立首个公开的、超高保真度的PrismLayers(PrismLayersPro)数据集,引入了无需训练的合成管道,并使用现成的扩散模型按需生成数据。同时,推出强大的开源多层生成模型ART+,与现代文本到图像生成模型的审美相匹配。主要技术贡献包括LayerFLUX和MultiLayerFLUX,前者擅长生成高质量的单层透明图像,后者能将多个LayerFLUX输出组合成完整的图像。经过严格筛选和人工选择,确保图像质量。在合成PrismLayersPro数据集上对最先进的ART模型进行微调,得到ART+,在头对头用户研究比较中,ART+在60%的情况下表现优于原始ART,甚至与FLUX.1-[dev]模型生成的图像视觉质量相匹配。本文的工作将为多层透明图像生成任务建立坚实的数据集基础,为需要精确、可编辑和视觉吸引力强的分层图像的研究和应用提供支持。
关键见解
- 论文解决了多层透明图像生成领域因缺乏大型高质量数据集而滞后的问题,发布了首个超高保真度的PrismLayers(PrismLayersPro)数据集。
- 引入了一种无需训练的合成管道,利用现成的扩散模型按需生成数据。
- 推出了强大的开源多层生成模型ART+,该模型与现代文本到图像生成模型的审美相匹配。
- 主要技术贡献包括LayerFLUX和MultiLayerFLUX,前者能生成高质量的单层透明图像,后者能将多个图层组合成完整的图像。
- 通过严格的筛选阶段和人工选择,确保生成的图像质量。
- ART+模型在头对头用户研究比较中表现出色,甚至与最先进的模型相匹配。
点此查看论文截图


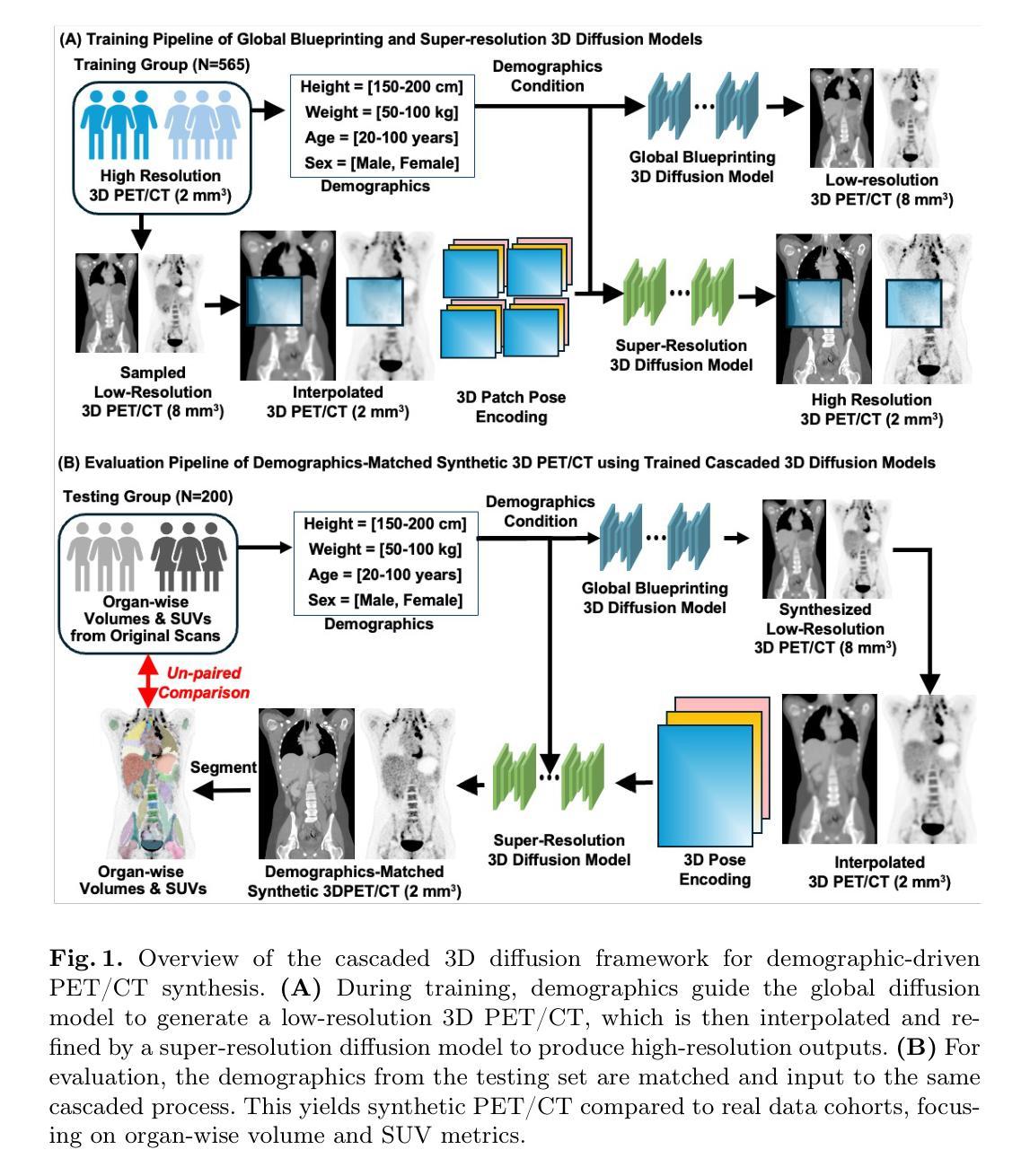
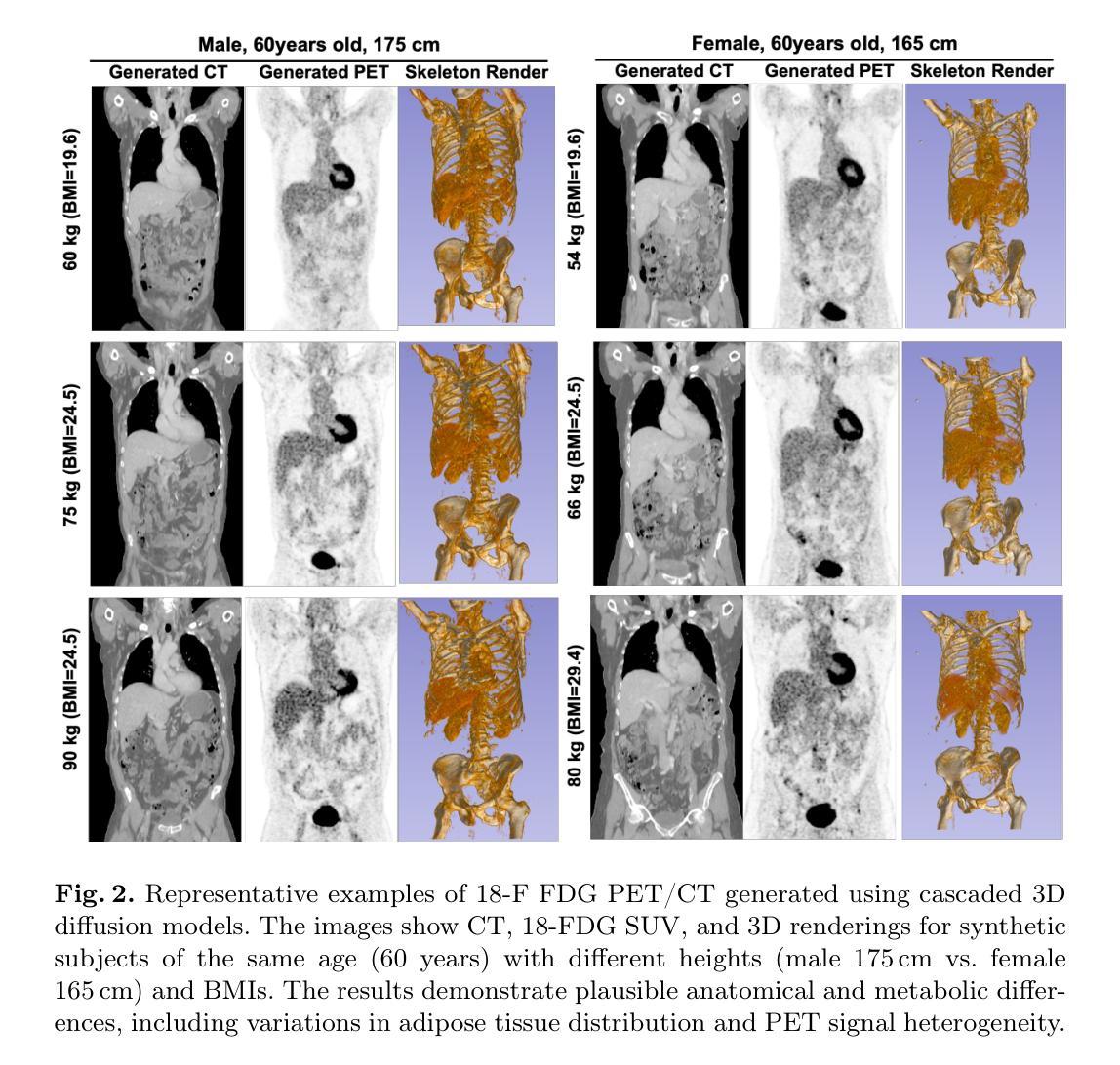
Cascaded 3D Diffusion Models for Whole-body 3D 18-F FDG PET/CT synthesis from Demographics
Authors:Siyeop Yoon, Sifan Song, Pengfei Jin, Matthew Tivnan, Yujin Oh, Sekeun Kim, Dufan Wu, Xiang Li, Quanzheng Li
We propose a cascaded 3D diffusion model framework to synthesize high-fidelity 3D PET/CT volumes directly from demographic variables, addressing the growing need for realistic digital twins in oncologic imaging, virtual trials, and AI-driven data augmentation. Unlike deterministic phantoms, which rely on predefined anatomical and metabolic templates, our method employs a two-stage generative process. An initial score-based diffusion model synthesizes low-resolution PET/CT volumes from demographic variables alone, providing global anatomical structures and approximate metabolic activity. This is followed by a super-resolution residual diffusion model that refines spatial resolution. Our framework was trained on 18-F FDG PET/CT scans from the AutoPET dataset and evaluated using organ-wise volume and standardized uptake value (SUV) distributions, comparing synthetic and real data between demographic subgroups. The organ-wise comparison demonstrated strong concordance between synthetic and real images. In particular, most deviations in metabolic uptake values remained within 3-5% of the ground truth in subgroup analysis. These findings highlight the potential of cascaded 3D diffusion models to generate anatomically and metabolically accurate PET/CT images, offering a robust alternative to traditional phantoms and enabling scalable, population-informed synthetic imaging for clinical and research applications.
我们提出了一种级联的3D扩散模型框架,该框架可以直接从人口统计学变量合成高保真度的3D PET/CT体积图像,从而满足肿瘤成像、虚拟试验和人工智能驱动的数据增强中所需逼真的数字双胞胎日益增长的需求。与依赖于预定义解剖和代谢模板的确定性幽灵(phantoms)不同,我们的方法采用两阶段生成过程。初始基于分数的扩散模型仅从人口统计学变量合成低分辨率的PET/CT体积图像,提供全球解剖结构和近似代谢活动。接下来是高分辨率剩余扩散模型,用于提高空间分辨率。我们的框架在AutoPET数据集的18F FDG PET/CT扫描上进行训练,并使用器官体积和标准摄取值(SUV)分布进行评估。在人口统计学分组中比较合成数据和真实数据的器官间差异,合成图像与真实图像之间显示出强烈的一致性。特别是,在亚组分析中,大多数代谢摄取值的偏差仍保持在真实值的3-5%以内。这些发现突出了级联的3D扩散模型的潜力,能够生成解剖学和代谢上准确的PET/CT图像,为传统幻影提供了一个稳健的替代方案,并实现用于临床和研究应用的规模化、以人群为基础的合成成像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI2025 Submitted version
Summary
本文提出了一种级联的3D扩散模型框架,可直接从人口统计学变量合成高保真度的3D PET/CT体积,满足肿瘤成像、虚拟试验和AI驱动的数据增强中对真实数字双胞胎的日益增长的需求。该方法采用两阶段生成过程,初始基于分数的扩散模型从人口统计学变量合成低分辨率的PET/CT体积,提供全球解剖结构和大致的代谢活动,接着由超分辨率残差扩散模型提高空间分辨率。该框架在AutoPET数据集上的训练和对不同人口学亚组的器官体积和标准摄取值(SUV)分布的评估表明,合成图像与真实图像间表现出强烈的一致性,特别是在代谢摄取值的偏差分析中,大多数偏差保持在真实值的3-5%以内。这突显了级联3D扩散模型在生成解剖和代谢准确的PET/CT图像方面的潜力,为传统幻影提供了一种稳健的替代方案,并为临床和研究应用提供了可扩展的、以人群为基础的综合成像方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种级联的3D扩散模型框架,用于从人口统计学变量中合成高保真度的3D PET/CT体积。
- 该方法采用两阶段生成过程,先合成低分辨率图像,再提高空间分辨率。
- 框架在AutoPET数据集上进行训练,表现出合成图像与真实图像之间强烈的一致性。
- 合成图像的器官体积和标准摄取值(SUV)分布与真实数据在人口学亚组中的比较显示出了良好的一致性。
- 大多数代谢摄取值的偏差保持在真实值的3-5%以内。
- 级联3D扩散模型在生成解剖和代谢准确的PET/CT图像方面展现出潜力。
点此查看论文截图

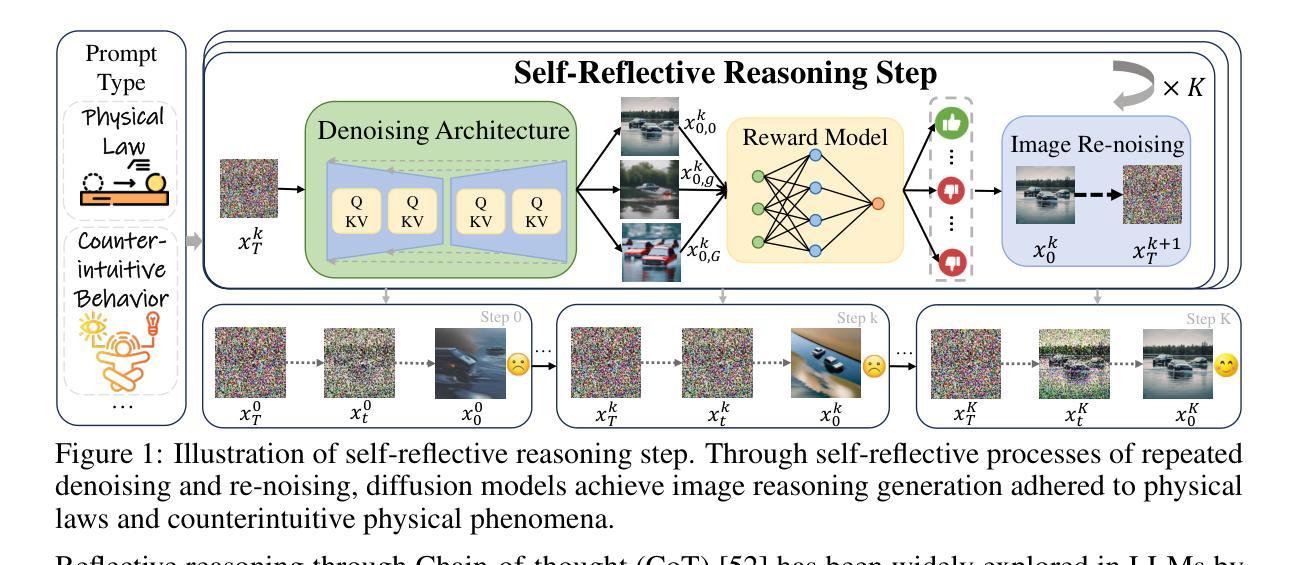
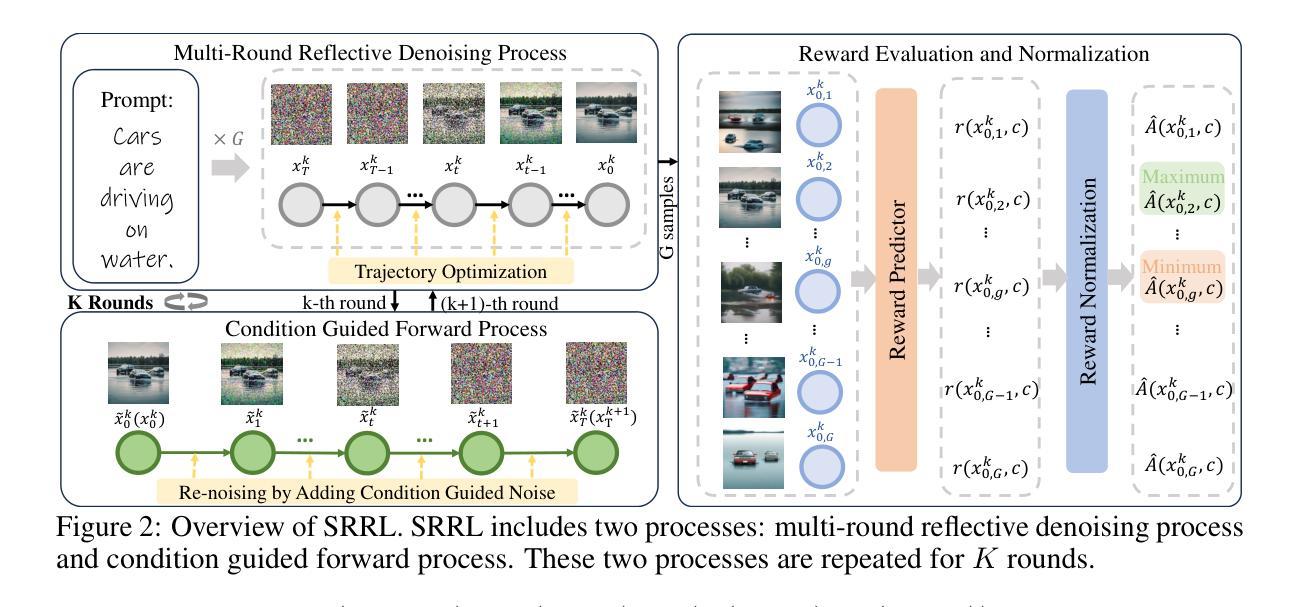
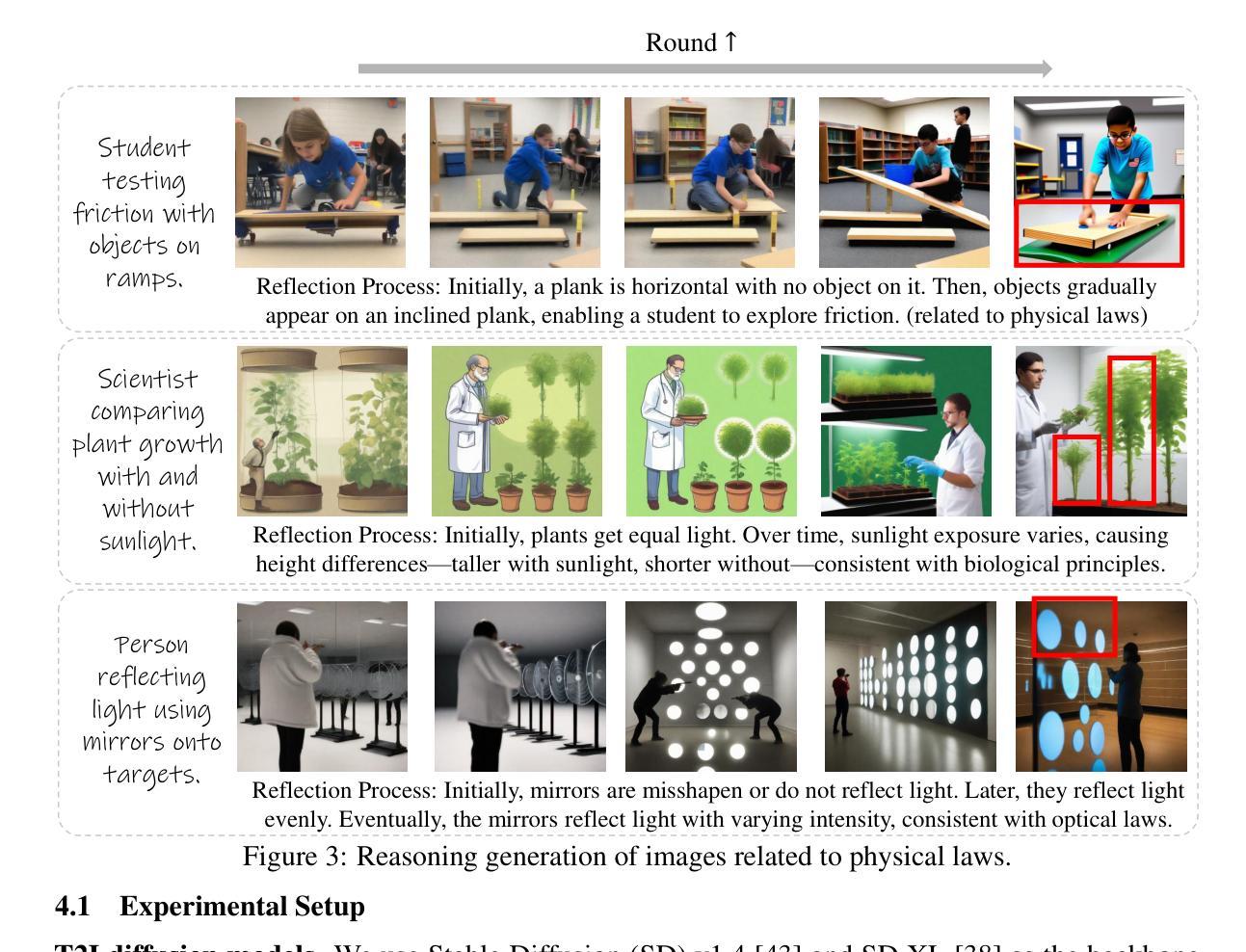
Self-Reflective Reinforcement Learning for Diffusion-based Image Reasoning Generation
Authors:Jiadong Pan, Zhiyuan Ma, Kaiyan Zhang, Ning Ding, Bowen Zhou
Diffusion models have recently demonstrated exceptional performance in image generation task. However, existing image generation methods still significantly suffer from the dilemma of image reasoning, especially in logic-centered image generation tasks. Inspired by the success of Chain of Thought (CoT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) in LLMs, we propose SRRL, a self-reflective RL algorithm for diffusion models to achieve reasoning generation of logical images by performing reflection and iteration across generation trajectories. The intermediate samples in the denoising process carry noise, making accurate reward evaluation difficult. To address this challenge, SRRL treats the entire denoising trajectory as a CoT step with multi-round reflective denoising process and introduces condition guided forward process, which allows for reflective iteration between CoT steps. Through SRRL-based iterative diffusion training, we introduce image reasoning through CoT into generation tasks adhering to physical laws and unconventional physical phenomena for the first time. Notably, experimental results of case study exhibit that the superior performance of our SRRL algorithm even compared with GPT-4o. The project page is https://jadenpan0.github.io/srrl.github.io/.
扩散模型在图像生成任务中表现出了卓越的性能。然而,现有的图像生成方法仍然面临着图像推理的困境,特别是在以逻辑为中心的图像生成任务中。受到大型语言模型(LLM)中的思维链(CoT)和强化学习(RL)成功的启发,我们提出了SRRL,这是一种用于扩散模型的自反思RL算法,通过反思和迭代生成轨迹来实现逻辑图像的推理生成。去噪过程中的中间样本带有噪声,使得准确的奖励评估变得困难。为解决这一挑战,SRRL将整个去噪轨迹视为带有多轮反思去噪过程的CoT步骤,并引入条件引导前向过程,这允许在CoT步骤之间进行反思迭代。通过基于SRRL的迭代扩散训练,我们首次将遵循物理定律和非传统物理现象的图像推理引入生成任务。值得注意的是,案例研究的实验结果表明,我们的SRRL算法性能卓越,甚至超越了GPT-4o。项目页面是:https://jadenpan0.github.io/srrl.github.io/。.
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成任务中表现出卓越性能,但在逻辑图像生成任务中仍面临图像推理的困境。本研究结合Chain of Thought(CoT)和强化学习(RL)的优点,为扩散模型提出自反射强化学习算法(SRRL),实现逻辑图像的推理生成。通过在整个去噪轨迹中引入多轮反射去噪过程和条件引导前向过程,解决了中间样本去噪过程中存在的噪声问题。基于SRRL的迭代扩散训练,首次将图像推理通过CoT引入遵循物理定律和非传统物理现象的生成任务中。实验案例研究结果显示SRRL算法性能卓越,甚至超越GPT-4o。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成任务中表现优秀,但在逻辑图像生成任务中存在图像推理困境。
- 提出自反射强化学习算法(SRRL)结合Chain of Thought(CoT)和强化学习(RL)优点,为扩散模型实现逻辑图像的推理生成。
- 通过在整个去噪轨迹中引入多轮反射去噪过程,解决中间样本去噪过程中的噪声问题。
- 引入条件引导前向过程,实现反射迭代在CoT步骤之间。
- 基于SRRL的迭代扩散训练首次将图像推理通过CoT引入生成任务中,遵循物理定律和非传统物理现象。
- 实验案例研究显示SRRL算法性能卓越。
点此查看论文截图

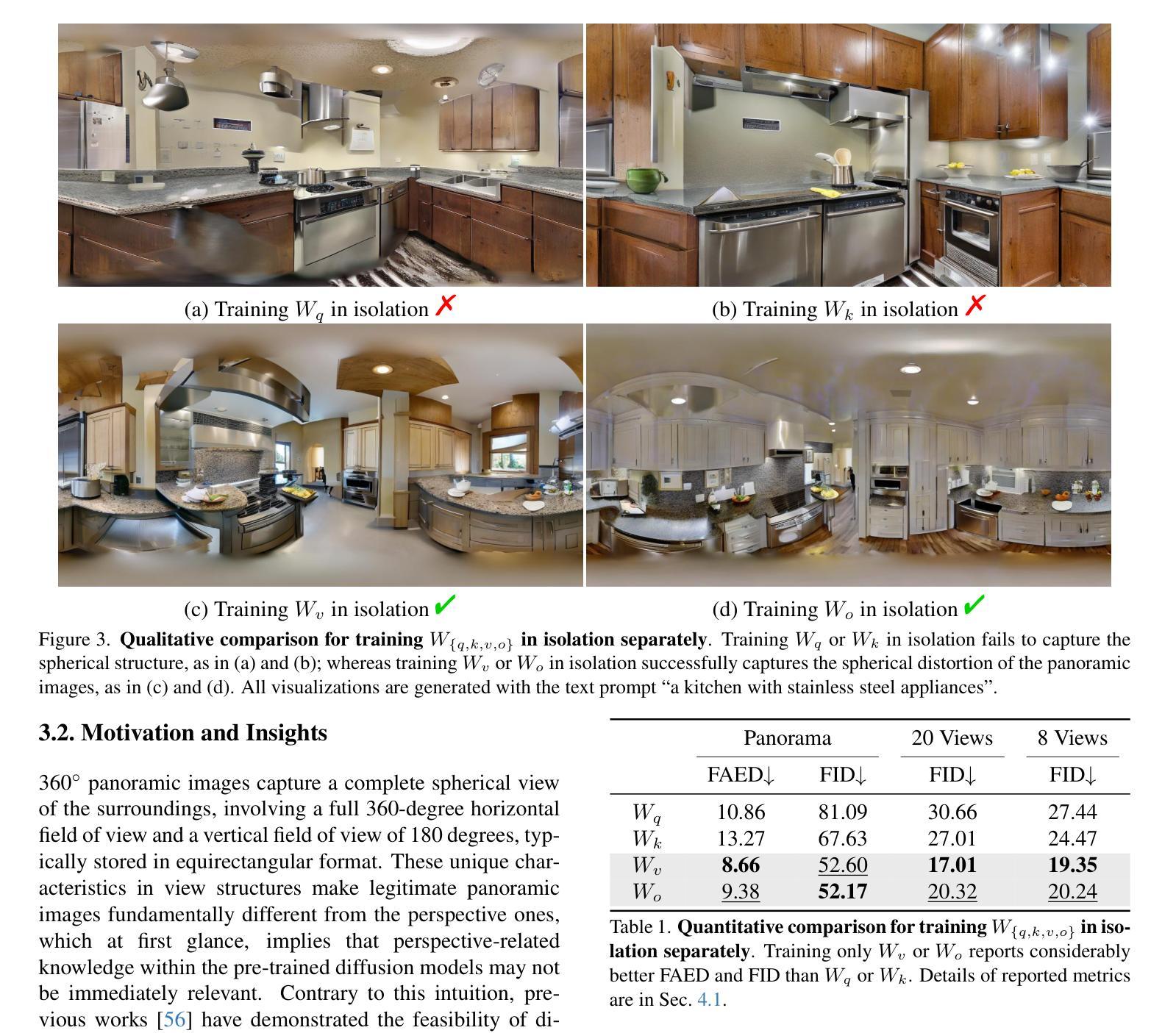
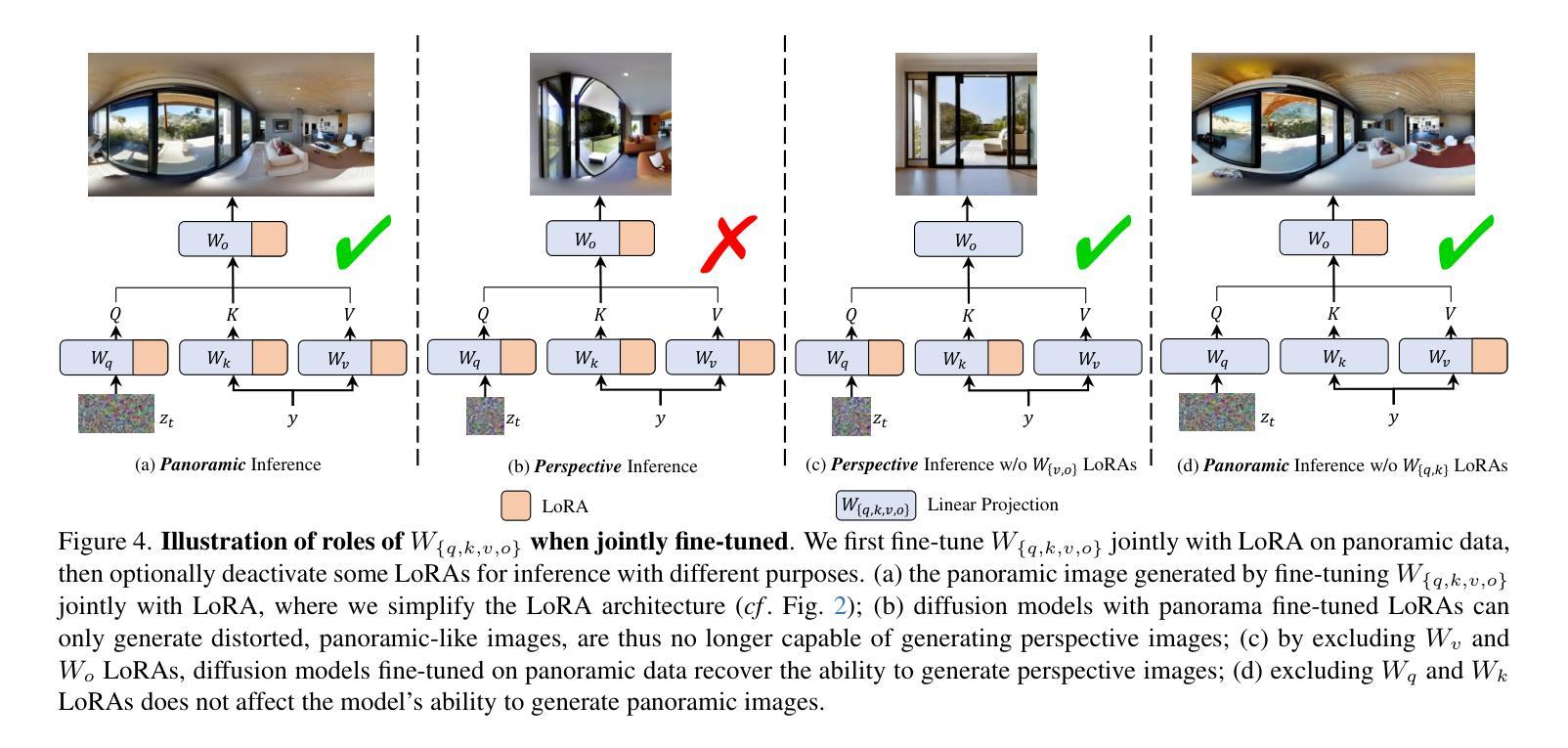
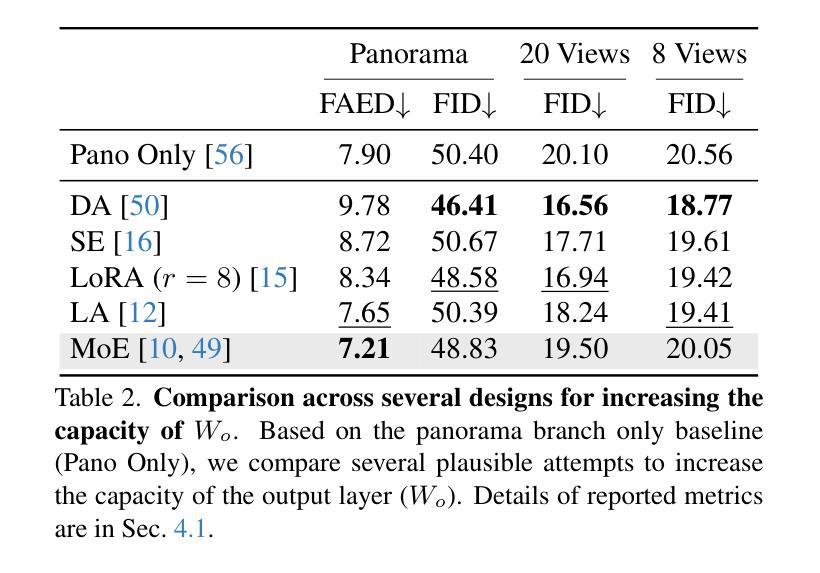
What Makes for Text to 360-degree Panorama Generation with Stable Diffusion?
Authors:Jinhong Ni, Chang-Bin Zhang, Qiang Zhang, Jing Zhang
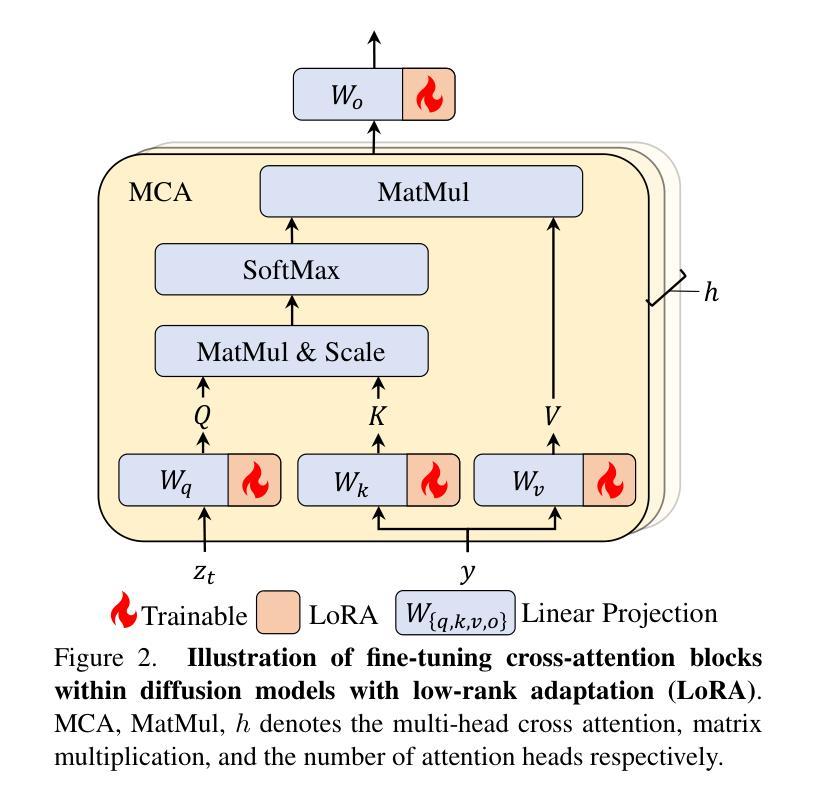
Recent prosperity of text-to-image diffusion models, e.g. Stable Diffusion, has stimulated research to adapt them to 360-degree panorama generation. Prior work has demonstrated the feasibility of using conventional low-rank adaptation techniques on pre-trained diffusion models to generate panoramic images. However, the substantial domain gap between perspective and panoramic images raises questions about the underlying mechanisms enabling this empirical success. We hypothesize and examine that the trainable counterparts exhibit distinct behaviors when fine-tuned on panoramic data, and such an adaptation conceals some intrinsic mechanism to leverage the prior knowledge within the pre-trained diffusion models. Our analysis reveals the following: 1) the query and key matrices in the attention modules are responsible for common information that can be shared between the panoramic and perspective domains, thus are less relevant to panorama generation; and 2) the value and output weight matrices specialize in adapting pre-trained knowledge to the panoramic domain, playing a more critical role during fine-tuning for panorama generation. We empirically verify these insights by introducing a simple framework called UniPano, with the objective of establishing an elegant baseline for future research. UniPano not only outperforms existing methods but also significantly reduces memory usage and training time compared to prior dual-branch approaches, making it scalable for end-to-end panorama generation with higher resolution. The code will be released.
文本到图像扩散模型的最新繁荣,例如Stable Diffusion,已经激发了将其适应360度全景图生成的研究。先前的工作已经证明,使用传统的低阶适应技术在预训练的扩散模型上生成全景图像是可行的。然而,透视图像和全景图像之间的巨大领域差距引发了关于实现这种经验成功的潜在机制的问题。我们假设并检查,可训练对应物在全景数据上进行微调时会表现出不同的行为,这种适应掩盖了预训练扩散模型中的先验知识利用的内在机制。我们的分析揭示了以下几点:1)注意力模块中的查询和键矩阵负责全景和透视域之间可以共享的共同信息,因此与全景生成关系不大;2)值矩阵和输出权重矩阵专门适应预训练知识到全景领域,在全景生成的微调过程中发挥更关键的作用。我们通过引入一个名为UniPano的简单框架,实证验证了这些见解,其目标是为未来研究建立优雅的基准线。UniPano不仅优于现有方法,而且与先前的双分支方法相比,还大大降低了内存使用和训练时间,使其可用于端到端的高分辨率全景图像生成。代码将被发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型的最新成功,如Stable Diffusion,已促使研究将其适应全景图生成。本文探讨了使用预训练扩散模型对全景图像进行低阶适应的方法,并分析了其内在机制。研究发现注意力模块中的查询和关键矩阵负责在全景和透视领域之间共享通用信息,而值矩阵和输出权重矩阵在全景生成中起到更关键作用。本文提出了UniPano框架,旨在为未来研究提供优雅的基准线,它不仅优于现有方法,而且在内存使用和训练时间方面显著优于先前的双分支方法,可实现端到端全景图生成的高分辨率。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)已成功应用于全景图生成。
- 使用预训练扩散模型进行低阶适应是一种有效的全景图像生成方法。
- 注意力模块中的查询和关键矩阵负责在全景和透视图像领域之间共享通用信息。
- 值矩阵和输出权重矩阵在全景图像的生成中起到更关键的作用。
- UniPano框架显著优于现有方法,为全景图生成提供了更高的分辨率和可扩展性。
- UniPano框架显著减少了内存使用和训练时间,与先前的双分支方法相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


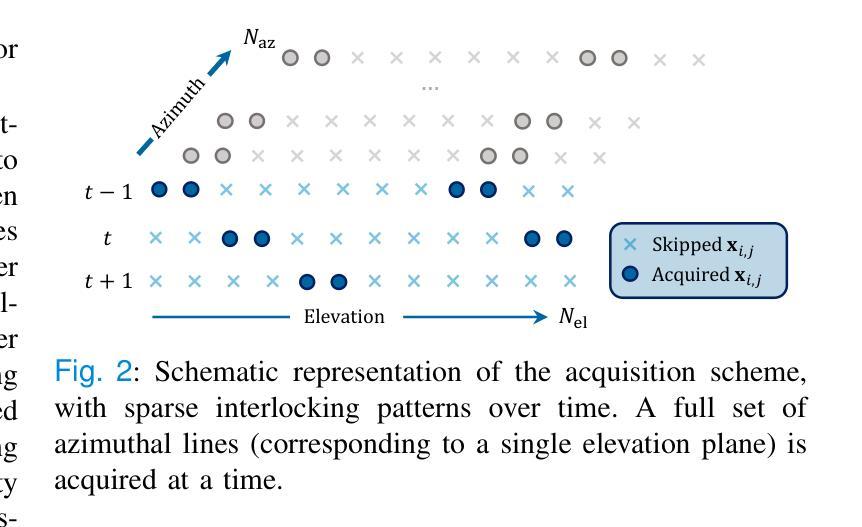
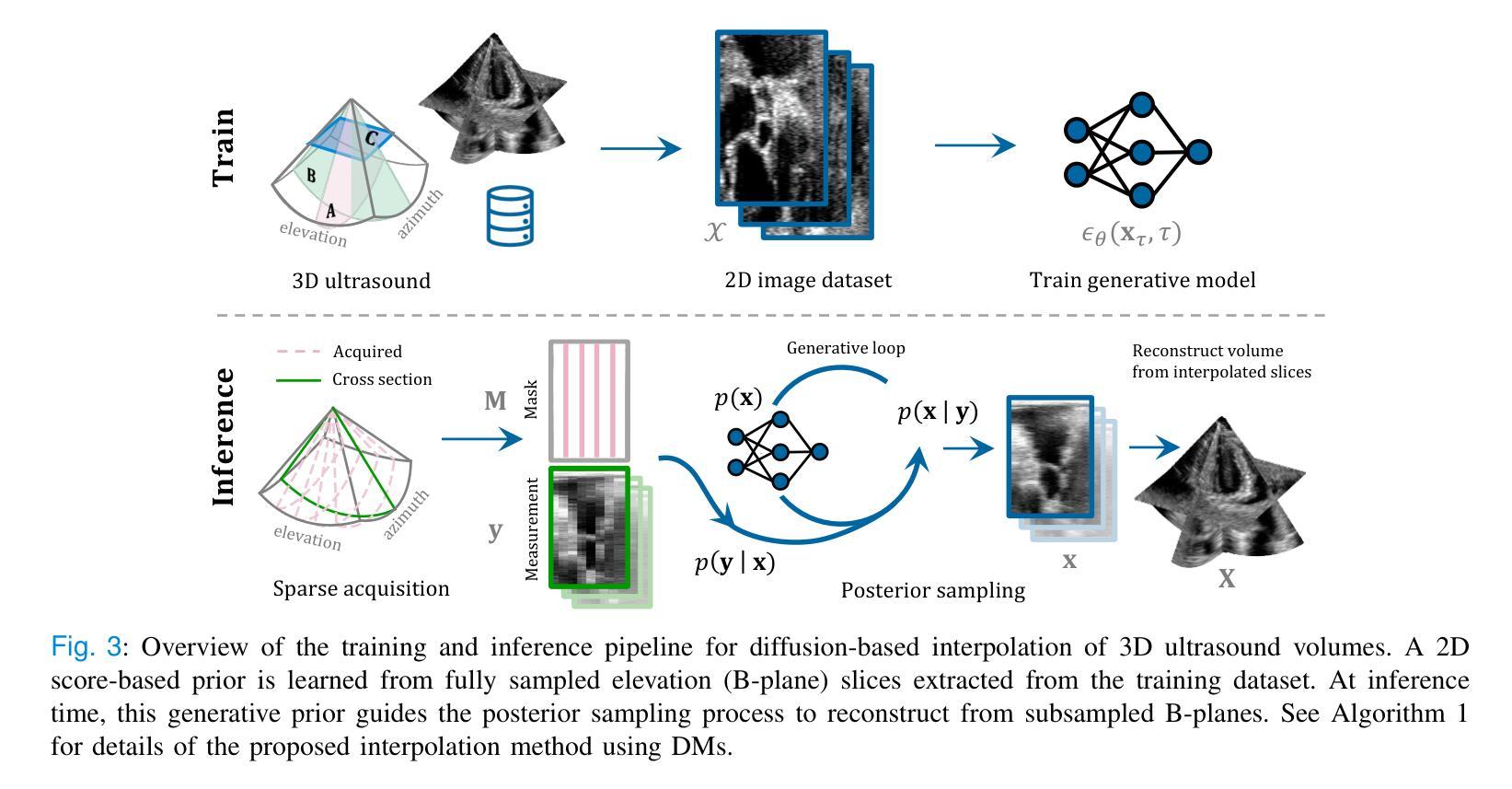
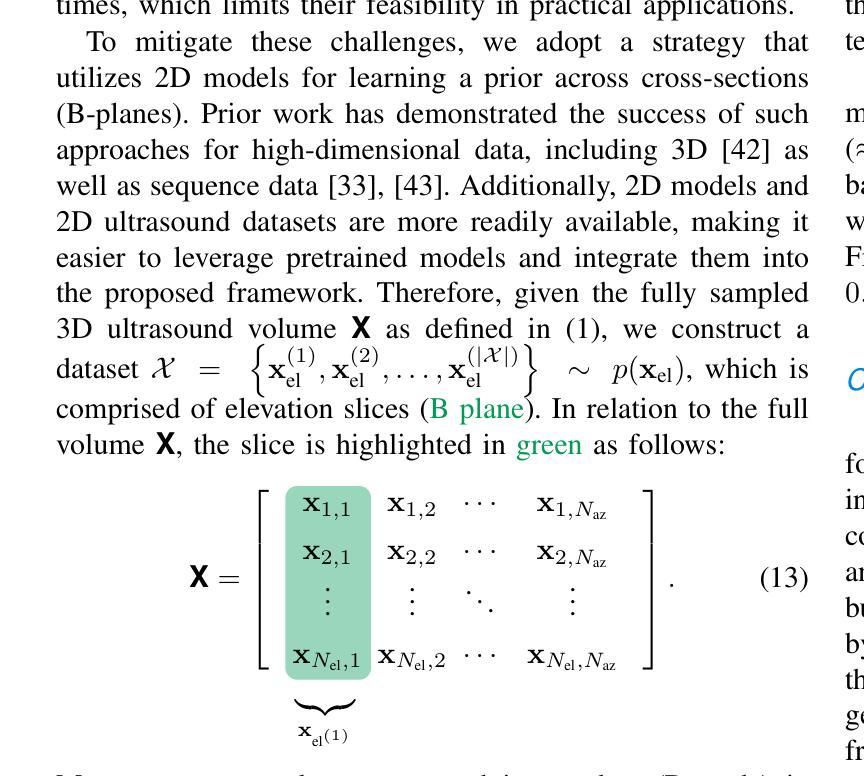
High Volume Rate 3D Ultrasound Reconstruction with Diffusion Models
Authors:Tristan S. W. Stevens, Oisín Nolan, Oudom Somphone, Jean-Luc Robert, Ruud J. G. van Sloun
Three-dimensional ultrasound enables real-time volumetric visualization of anatomical structures. Unlike traditional 2D ultrasound, 3D imaging reduces the reliance on precise probe orientation, potentially making ultrasound more accessible to clinicians with varying levels of experience and improving automated measurements and post-exam analysis. However, achieving both high volume rates and high image quality remains a significant challenge. While 3D diverging waves can provide high volume rates, they suffer from limited tissue harmonic generation and increased multipath effects, which degrade image quality. One compromise is to retain the focusing in elevation while leveraging unfocused diverging waves in the lateral direction to reduce the number of transmissions per elevation plane. Reaching the volume rates achieved by full 3D diverging waves, however, requires dramatically undersampling the number of elevation planes. Subsequently, to render the full volume, simple interpolation techniques are applied. This paper introduces a novel approach to 3D ultrasound reconstruction from a reduced set of elevation planes by employing diffusion models (DMs) to achieve increased spatial and temporal resolution. We compare both traditional and supervised deep learning-based interpolation methods on a 3D cardiac ultrasound dataset. Our results show that DM-based reconstruction consistently outperforms the baselines in image quality and downstream task performance. Additionally, we accelerate inference by leveraging the temporal consistency inherent to ultrasound sequences. Finally, we explore the robustness of the proposed method by exploiting the probabilistic nature of diffusion posterior sampling to quantify reconstruction uncertainty and demonstrate improved recall on out-of-distribution data with synthetic anomalies under strong subsampling.
三维超声能够实时可视化解剖结构的三维图像。与传统的二维超声不同,三维成像减少了对于精确探头方向的依赖,使得不同经验的临床医生都能更容易地使用超声,并改善了自动测量和考试后的分析。然而,实现高体积率和高图像质量仍是重大挑战。虽然三维发散波可以提供高体积率,但它们存在组织谐波生成有限和多路径效应增加的问题,从而降低了图像质量。一种折衷方案是在垂直方向上保持聚焦,同时在侧向利用未聚焦的发散波,以减少每个垂直平面的传输数量。然而,要达到完全三维发散波所达到的音量水平,需要对高度减小平面数量进行大幅降采样处理。随后,采用简单的插值技术进行整体渲染。本文介绍了一种利用扩散模型(DMs)从减少的高度平面上重建三维超声的新方法,以提高空间和时间分辨率。我们在一个三维心脏超声数据集上比较了传统的和监督深度学习插值方法。我们的结果表明,基于DM的重建在图像质量和下游任务性能上始终优于基线。此外,我们利用超声序列固有的时间一致性来加速推理过程。最后,我们通过利用扩散后采样概率性质来探索所提出方法的稳健性,量化重建的不确定性,并在强降采样下的合成异常数据上展示了对异常数据的改进召回率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 10 figures, preprint
Summary
本文介绍了利用扩散模型(DMs)对三维超声数据进行重建的新方法。该方法通过减少采样平面数量实现高效的三维超声重建,并利用扩散模型提高空间和时间分辨率。对比传统和基于深度学习的插值方法,在三维心脏超声数据集上,DMs重建方法在图像质量和下游任务性能上表现更优。同时,通过利用超声序列的固有时间一致性,提高了推理速度。此外,本文还探索了通过扩散模型的后验概率采样来量化重建不确定性的鲁棒性方法,并在强子采样条件下对合成异常数据提高了召回率。
Key Takeaways
- 三维超声能够实现实时体积可视化解剖结构,相较于传统二维超声,其降低了对精确探头位置的依赖。
- 高体积率和高质量图像是三维超声成像面临的挑战。发散波虽然能够提供高体积率但图像质量下降。
- 提出一种新方法:通过减少采样平面数量并利用扩散模型实现高效三维超声重建,提高空间和时间分辨率。
- 对比传统和基于深度学习的插值方法,DMs在图像质量和下游任务性能上表现更优。
- 利用超声序列的时间一致性加速推理过程。
- 通过扩散模型的后验概率采样量化重建不确定性,提高模型的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


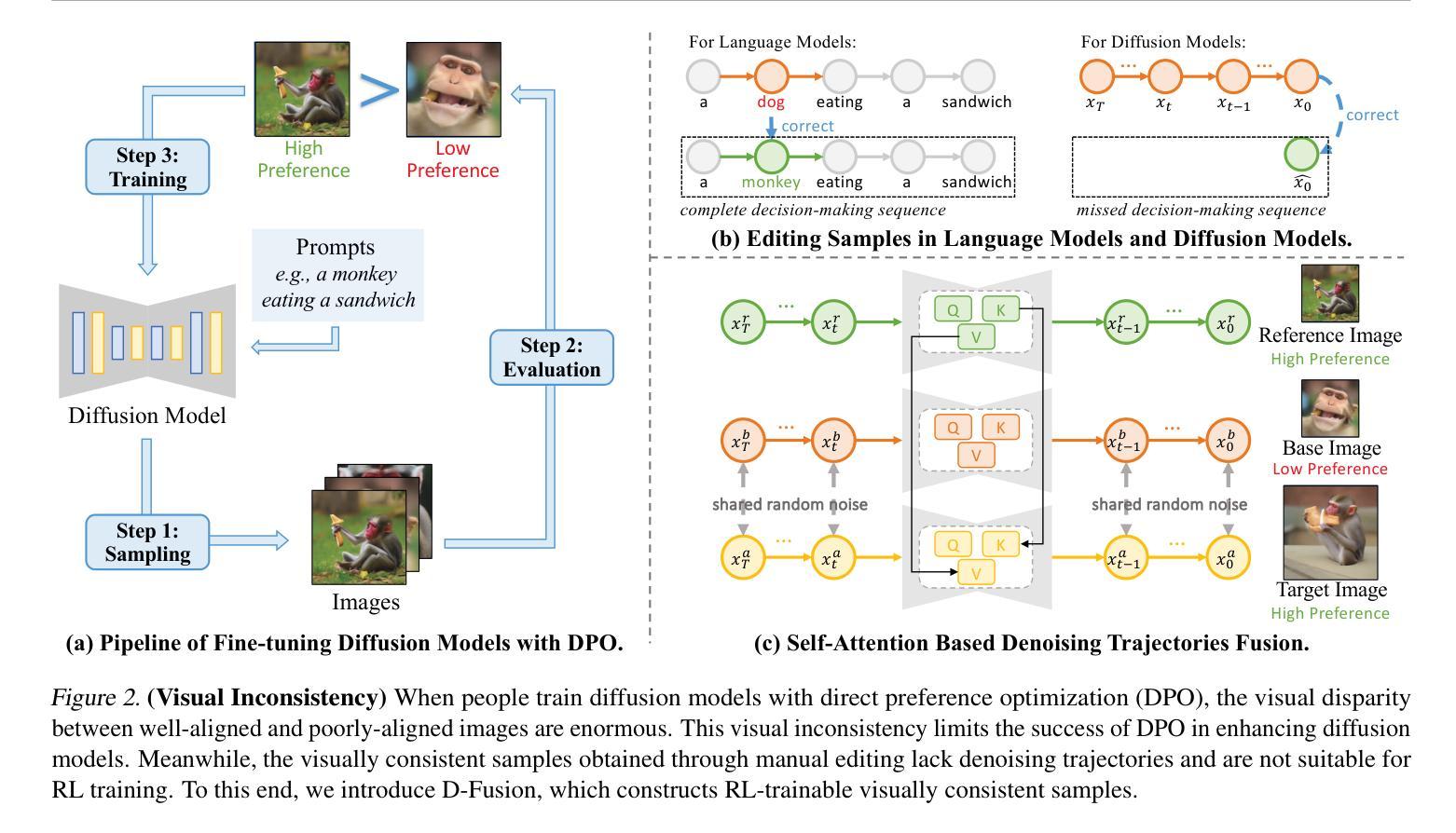
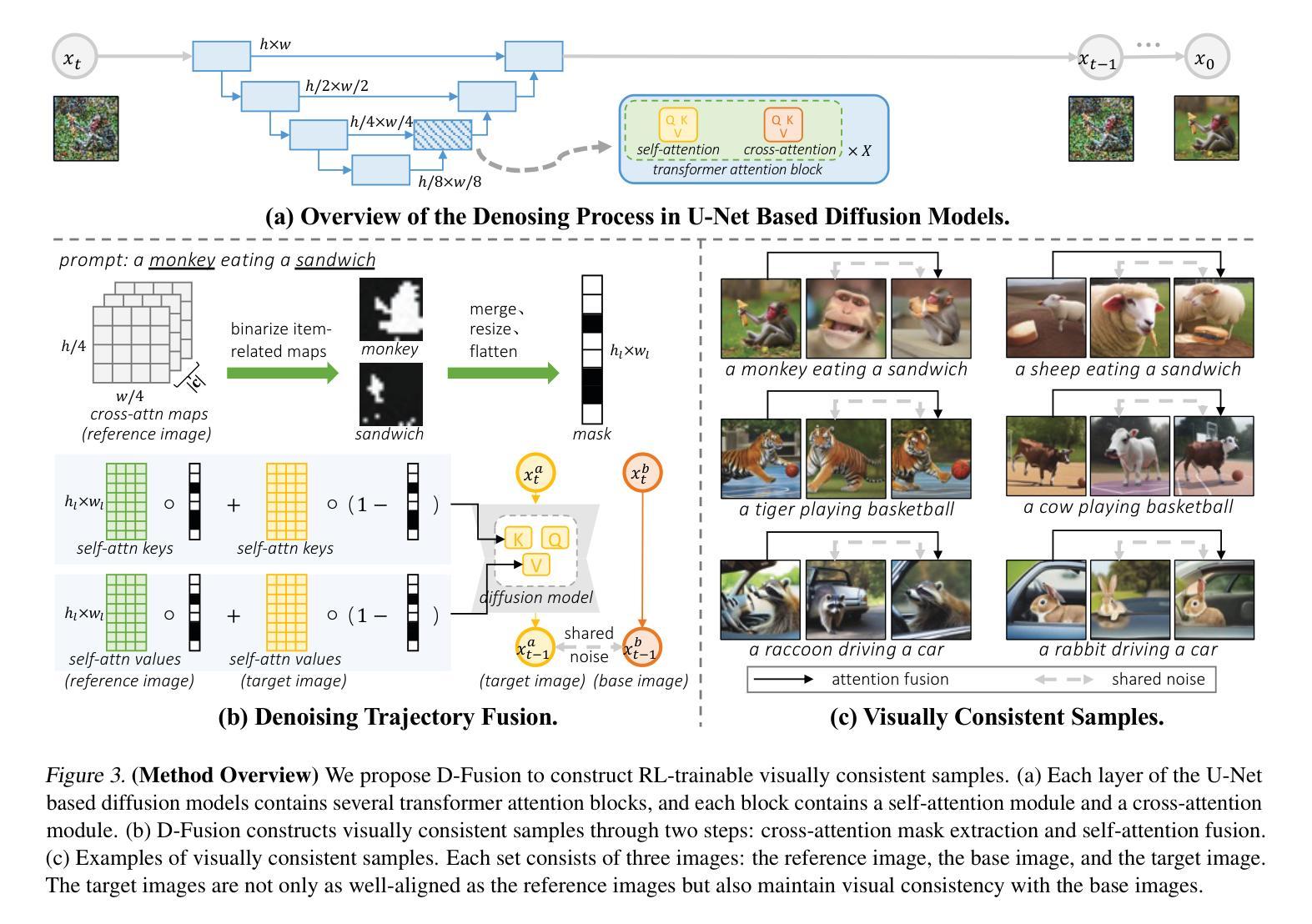
D-Fusion: Direct Preference Optimization for Aligning Diffusion Models with Visually Consistent Samples
Authors:Zijing Hu, Fengda Zhang, Kun Kuang
The practical applications of diffusion models have been limited by the misalignment between generated images and corresponding text prompts. Recent studies have introduced direct preference optimization (DPO) to enhance the alignment of these models. However, the effectiveness of DPO is constrained by the issue of visual inconsistency, where the significant visual disparity between well-aligned and poorly-aligned images prevents diffusion models from identifying which factors contribute positively to alignment during fine-tuning. To address this issue, this paper introduces D-Fusion, a method to construct DPO-trainable visually consistent samples. On one hand, by performing mask-guided self-attention fusion, the resulting images are not only well-aligned, but also visually consistent with given poorly-aligned images. On the other hand, D-Fusion can retain the denoising trajectories of the resulting images, which are essential for DPO training. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of D-Fusion in improving prompt-image alignment when applied to different reinforcement learning algorithms.
扩散模型的实际应用受到生成图像与相应文本提示不匹配的限制。近期的研究引入了直接偏好优化(DPO)以增强这些模型的对齐性。然而,DPO的有效性受到视觉不一致性的约束,其中良好对齐和不良对齐图像之间的重大视觉差异阻碍了扩散模型在微调过程中识别哪些因素正向贡献于对齐。为解决此问题,本文引入了D-Fusion方法,构建适用于DPO训练的视觉一致样本。一方面,通过执行掩膜引导的自注意力融合,生成的图像不仅对齐良好,而且在视觉上还与给定的不良对齐图像保持一致。另一方面,D-Fusion能够保留生成图像的降噪轨迹,这对于DPO训练至关重要。大量实验表明,当应用于不同的强化学习算法时,D-Fusion在改进提示图像对齐方面非常有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在实际应用中的局限性,即生成图像与对应文本提示的不对齐问题。为解决这个问题,文章引入了直接偏好优化(DPO)方法。然而,DPO受到视觉不一致性的限制。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种名为D-Fusion的方法,用于构建可进行DPO训练的视觉一致样本。通过执行掩膜引导的自注意力融合,D-Fusion不仅能生成与给定不良对齐图像视觉一致的图像,还能保留图像的降噪轨迹,这对于DPO训练至关重要。实验证明,D-Fusion在应用于不同的强化学习算法时,能有效提高提示图像的对齐性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型面临生成图像与文本提示不对齐的实用问题。
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)被引入以提高模型对齐性,但受限于视觉不一致性。
- D-Fusion方法通过执行掩膜引导的自注意力融合来解决视觉不一致性问题。
- D-Fusion不仅能生成良好对齐的图像,还能保留图像的降噪轨迹,对DPO训练至关重要。
- D-Fusion对不同的强化学习算法都有效,能显著提高提示图像的对齐性。
- 通过广泛实验验证了D-Fusion的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Collaborative Learning for Unsupervised Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration: Integrating Self-Supervision and MIM-Guided Diffusion-Based Image Translation
Authors:Xiaochen Wei, Weiwei Guo, Wenxian Yu
The substantial modality-induced variations in radiometric, texture, and structural characteristics pose significant challenges for the accurate registration of multimodal images. While supervised deep learning methods have demonstrated strong performance, they often rely on large-scale annotated datasets, limiting their practical application. Traditional unsupervised methods usually optimize registration by minimizing differences in feature representations, yet often fail to robustly capture geometric discrepancies, particularly under substantial spatial and radiometric variations, thus hindering convergence stability. To address these challenges, we propose a Collaborative Learning framework for Unsupervised Multimodal Image Registration, named CoLReg, which reformulates unsupervised registration learning into a collaborative training paradigm comprising three components: (1) a cross-modal image translation network, MIMGCD, which employs a learnable Maximum Index Map (MIM) guided conditional diffusion model to synthesize modality-consistent image pairs; (2) a self-supervised intermediate registration network which learns to estimate geometric transformations using accurate displacement labels derived from MIMGCD outputs; (3) a distilled cross-modal registration network trained with pseudo-label predicted by the intermediate network. The three networks are jointly optimized through an alternating training strategy wherein each network enhances the performance of the others. This mutual collaboration progressively reduces modality discrepancies, enhances the quality of pseudo-labels, and improves registration accuracy. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that our ColReg achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art unsupervised approaches and even surpasses several supervised baselines.
多模态图像在辐射度量、纹理和结构特性上的显著差异为准确的多模态图像配准带来了巨大挑战。尽管有监督的深度学习方法已经取得了良好的性能表现,但它们往往依赖于大规模标注数据集,从而限制了其实际应用。传统的无监督方法通常通过最小化特征表示的差异性来优化配准,但往往无法稳健地捕捉几何差异,特别是在较大的空间变化和辐射度量变化情况下,从而影响收敛稳定性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为CoLReg的基于无监督学习的多模态图像协同配准框架。它将无监督配准学习重新定义为一种协同训练模式,包含三个组成部分:(1)跨模态图像翻译网络MIMGCD,它采用基于可学习最大索引图(MIM)引导的条件扩散模型来合成模态一致的图像对;(2)自监督中间配准网络,该网络学习使用由MIMGCD输出得出的准确位移标签来估计几何变换;(3)通过中间网络预测的伪标签进行训练的蒸馏跨模态配准网络。这三个网络通过交替训练策略进行联合优化,其中每个网络都会增强其他网络的性能。这种相互协作的方式逐步减少了模态差异,提高了伪标签的质量,并提高了配准精度。在多个数据集上的广泛实验结果表明,我们的ColReg与最先进的无监督方法相比取得了竞争或优越的性能表现,甚至超越了多个有监督的基线方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CoLReg的协同学习框架,用于解决多模态图像注册的挑战性问题。通过采用三个协作组件:跨模态图像翻译网络MIMGCD、自监督中间注册网络和蒸馏跨模态注册网络,CoLReg能够减少模态差异,提高伪标签质量,并改善注册准确性。在多个数据集上的实验结果显示,ColReg相较于先进的无监督方法和一些监督基线方法表现出竞争性或优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态图像注册面临挑战,因为不同模态的图像在辐射度量、纹理和结构特性上存在差异。
- 现有方法如监督深度学习受限于大规模标注数据集,而传统无监督方法难以稳健捕获几何差异,特别是在大空间变化和辐射度量变化的情况下。
- 提出的CoLReg框架包括三个协作组件:跨模态图像翻译网络MIMGCD、自监督中间注册网络和蒸馏跨模态注册网络。
- MIMGCD网络使用可学习的最大索引图(MIM)指导的条件扩散模型来合成模态一致的图像对。
- 中间注册网络通过利用MIMGCD输出的准确位移标签进行自监督学习,估计几何变换。
- CoLReg通过交替训练策略联合优化这三个网络,相互协作提高性能。
点此查看论文截图


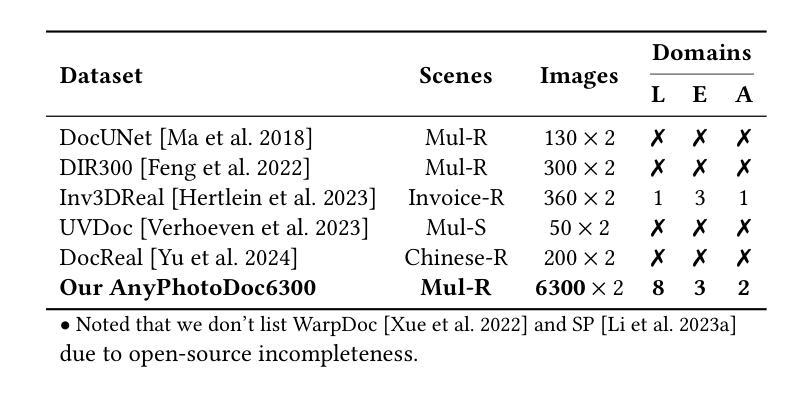
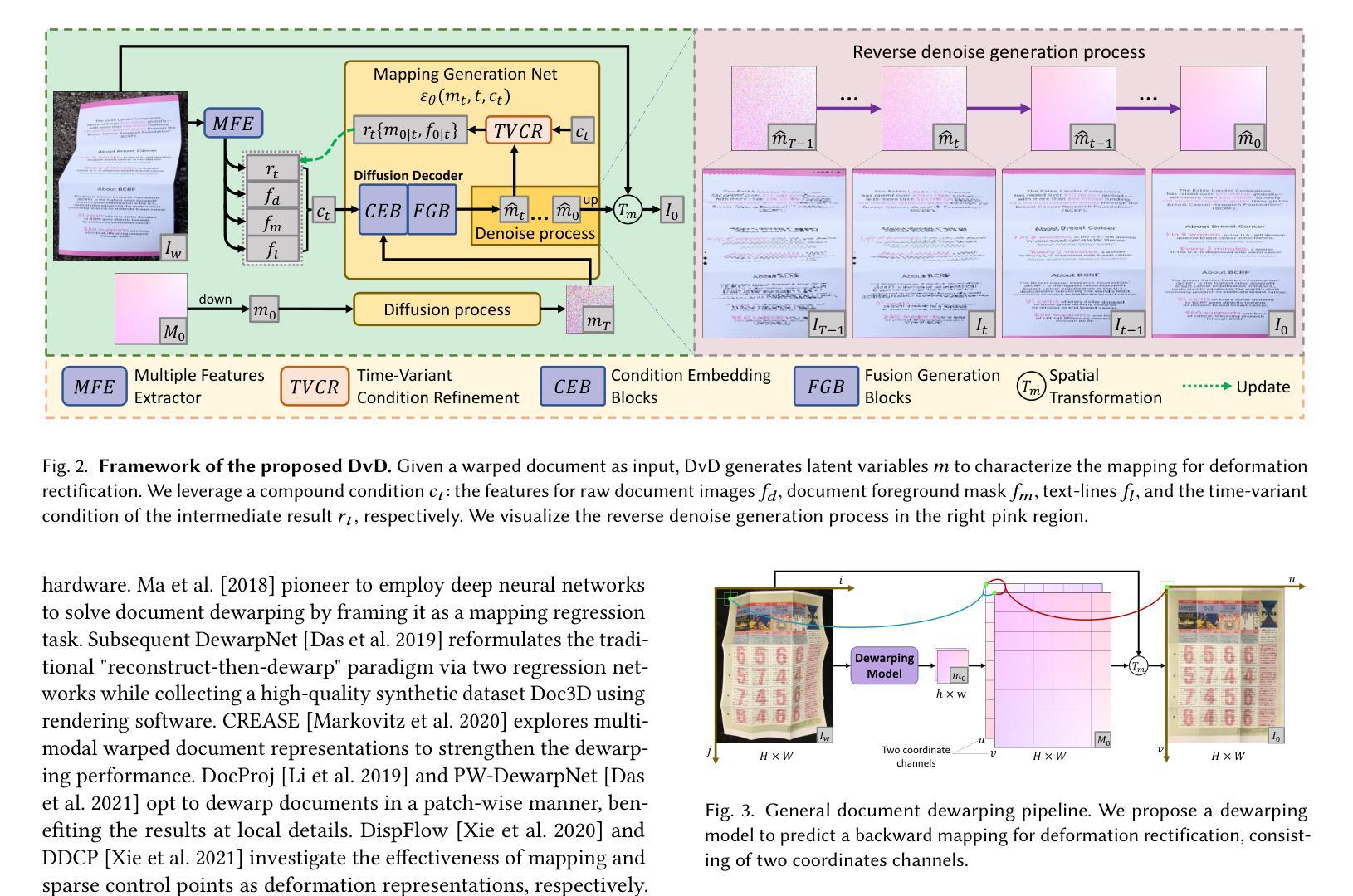
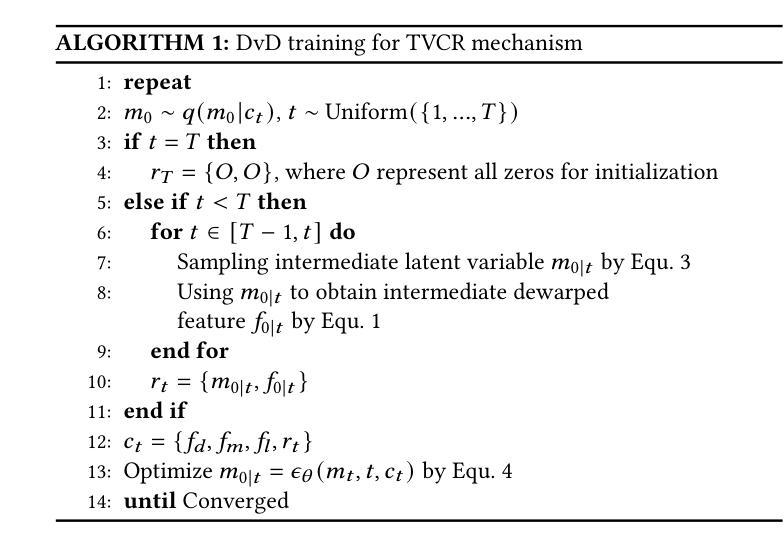
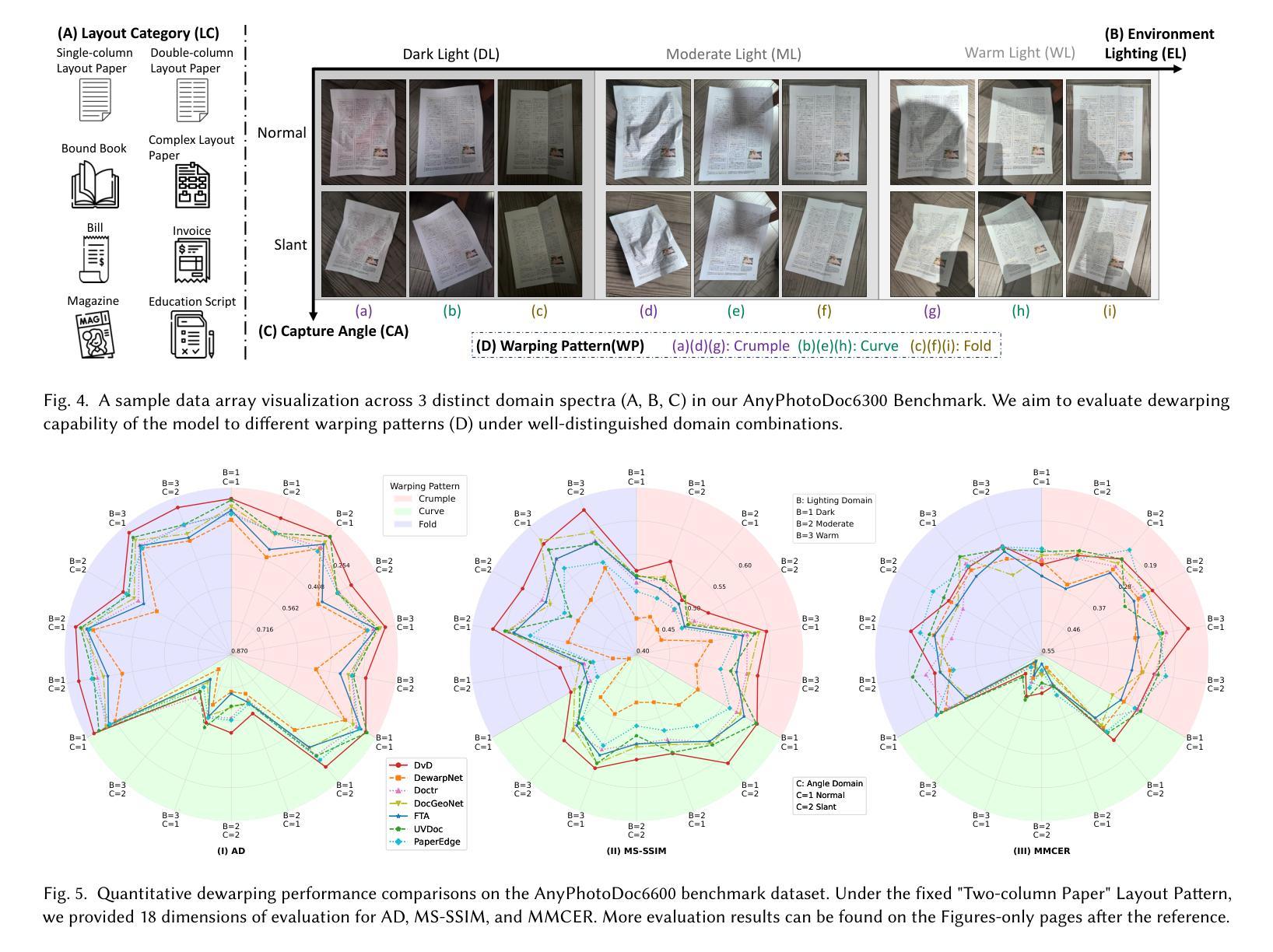
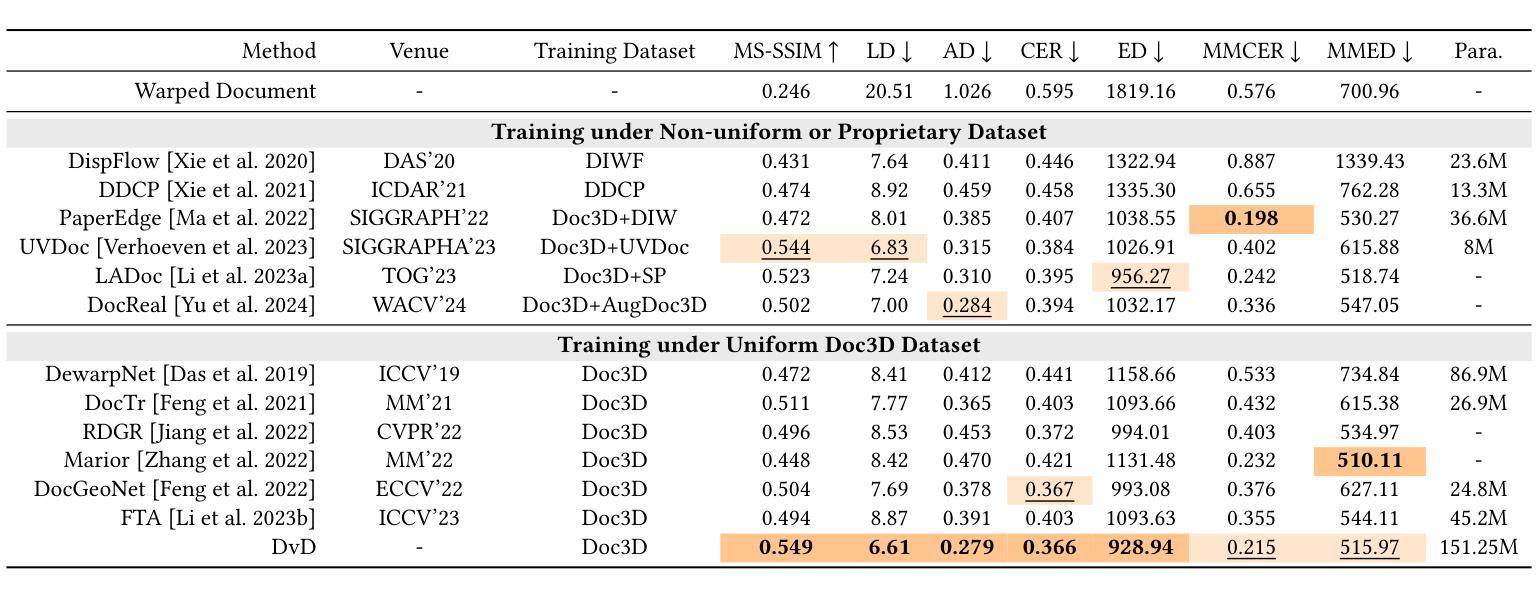
DvD: Unleashing a Generative Paradigm for Document Dewarping via Coordinates-based Diffusion Model
Authors:Weiguang Zhang, Huangcheng Lu, Maizhen Ning, Xiaowei Huang, Wei Wang, Kaizhu Huang, Qiufeng Wang
Document dewarping aims to rectify deformations in photographic document images, thus improving text readability, which has attracted much attention and made great progress, but it is still challenging to preserve document structures. Given recent advances in diffusion models, it is natural for us to consider their potential applicability to document dewarping. However, it is far from straightforward to adopt diffusion models in document dewarping due to their unfaithful control on highly complex document images (e.g., 2000$\times$3000 resolution). In this paper, we propose DvD, the first generative model to tackle document \textbf{D}ewarping \textbf{v}ia a \textbf{D}iffusion framework. To be specific, DvD introduces a coordinate-level denoising instead of typical pixel-level denoising, generating a mapping for deformation rectification. In addition, we further propose a time-variant condition refinement mechanism to enhance the preservation of document structures. In experiments, we find that current document dewarping benchmarks can not evaluate dewarping models comprehensively. To this end, we present AnyPhotoDoc6300, a rigorously designed large-scale document dewarping benchmark comprising 6,300 real image pairs across three distinct domains, enabling fine-grained evaluation of dewarping models. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed DvD can achieve state-of-the-art performance with acceptable computational efficiency on multiple metrics across various benchmarks including DocUNet, DIR300, and AnyPhotoDoc6300. The new benchmark and code will be publicly available.
文档去扭曲旨在纠正摄影文档图像中的变形,从而提高文本的清晰度,这已引起了很多关注并取得了很大进展,但保留文档结构仍然具有挑战性。考虑到扩散模型的最新进展,我们自然会考虑其应用于文档去扭曲的潜力。然而,由于扩散模型对高度复杂的文档图像(例如2000x3000分辨率)控制不精确,因此在文档去扭曲中采用扩散模型并不容易。在本文中,我们提出了DvD,这是第一个通过扩散框架解决文档去扭曲的生成模型。具体来说,DvD引入了坐标级去噪,而不是典型的像素级去噪,从而产生用于变形校正的映射。此外,我们进一步提出了一种时间可变条件细化机制,以提高文档结构的保留。在实验中,我们发现当前的文档去扭曲基准测试无法全面评估去扭曲模型。为此,我们推出了AnyPhotoDoc6300,这是一个严格设计的大规模文档去扭曲基准测试,包含三个不同领域的6300张真实图像对,能够对去扭曲模型进行精细评估。综合实验表明,我们提出的DvD在多个基准测试(包括DocUNet、DIR300和AnyPhotoDoc6300)上实现了最先进的性能,同时计算效率可接受。新的基准测试和代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了DvD,一个通过扩散框架解决文档去扭曲的生成模型。DvD引入坐标级别的去噪,而不是典型的像素级别去噪,以生成用于变形校正的映射。此外,还提出了一种时间可变条件优化机制,以提高文档结构的保留。实验发现现有文档去扭曲基准测试无法全面评估去扭曲模型。因此,我们推出了AnyPhotoDoc6300,一个严格设计的大规模文档去扭曲基准测试,包含6300张来自三个不同领域的真实图像对,可实现去扭曲模型的精细评估。综合实验表明,所提出的DvD在多个基准测试上实现了卓越的性能,包括DocUNet、DIR300和AnyPhotoDoc6300,且计算效率可接受。
关键见解
- 文档去扭曲旨在纠正摄影文档图像中的变形,提高文本可读性,但保留文档结构仍然具有挑战性。
- 扩散模型在文档去扭曲中具有潜在应用价值。
- DvD是首个通过扩散框架解决文档去扭曲的生成模型。
- DvD引入坐标级别的去噪机制,生成用于变形校正的映射。
- 提出了一种时间可变条件优化机制,以提高文档结构的保留。
- 现有文档去扭曲基准测试无法全面评估模型,因此推出了AnyPhotoDoc6300大规模基准测试。
- DvD在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


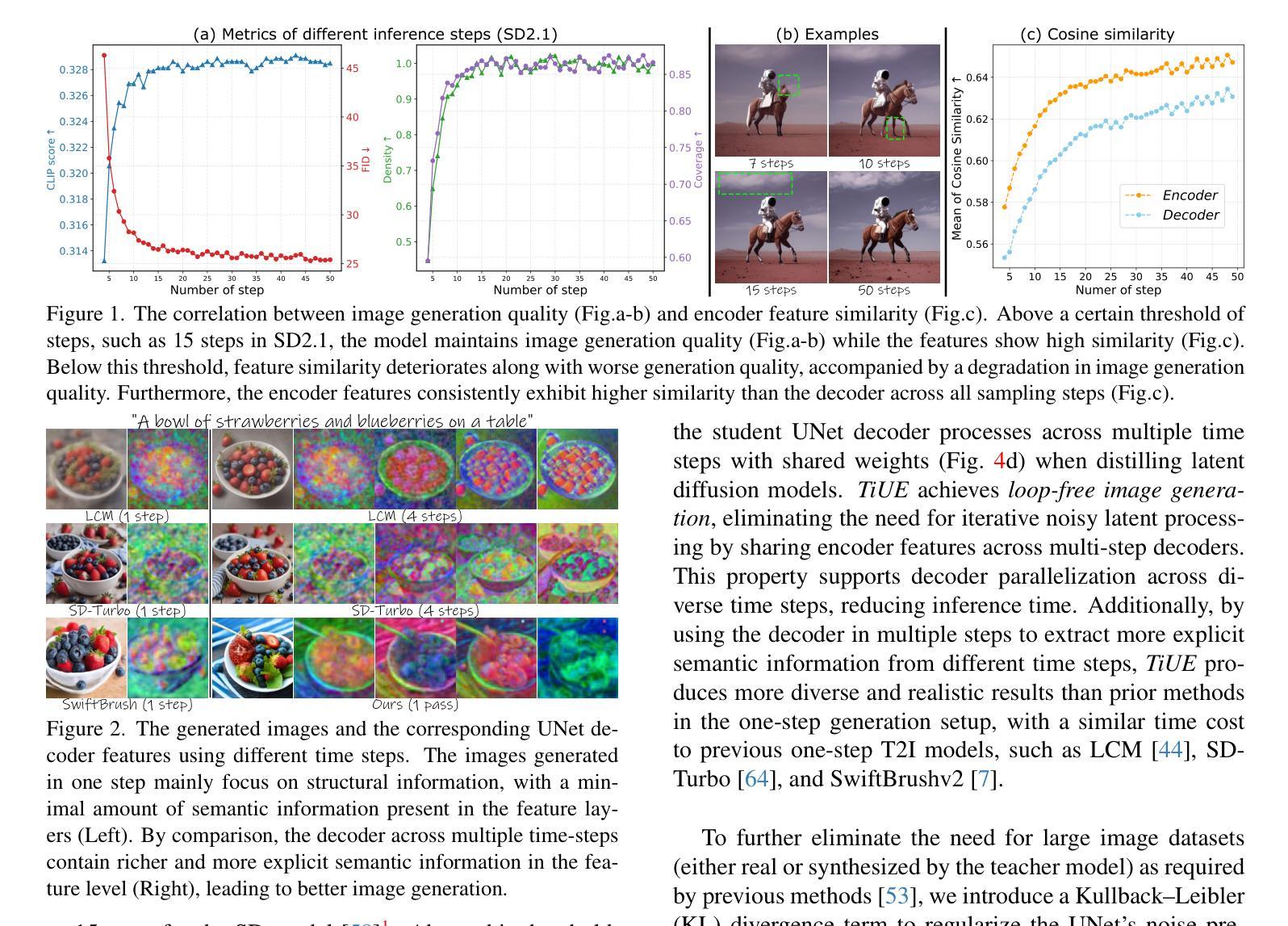
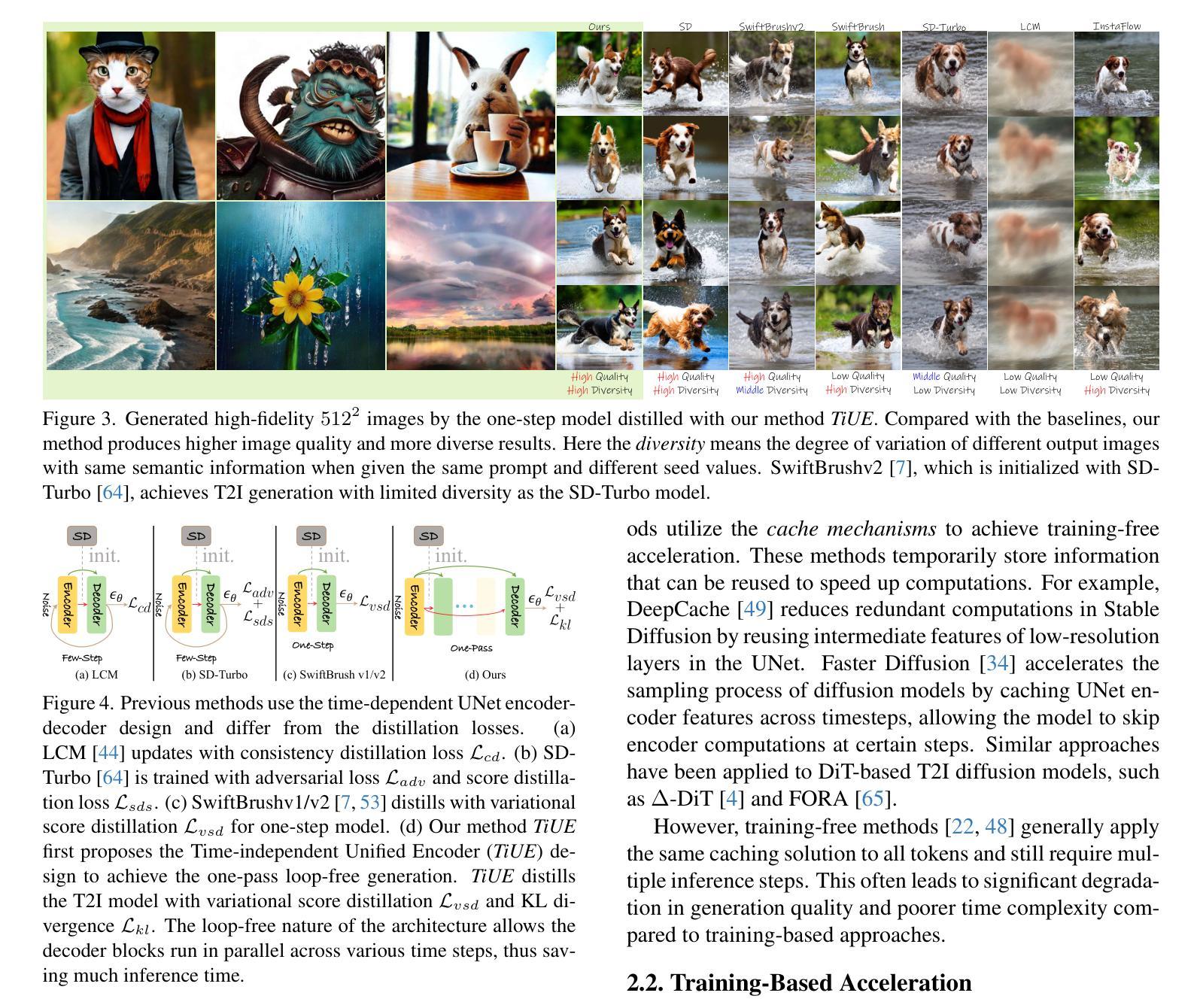
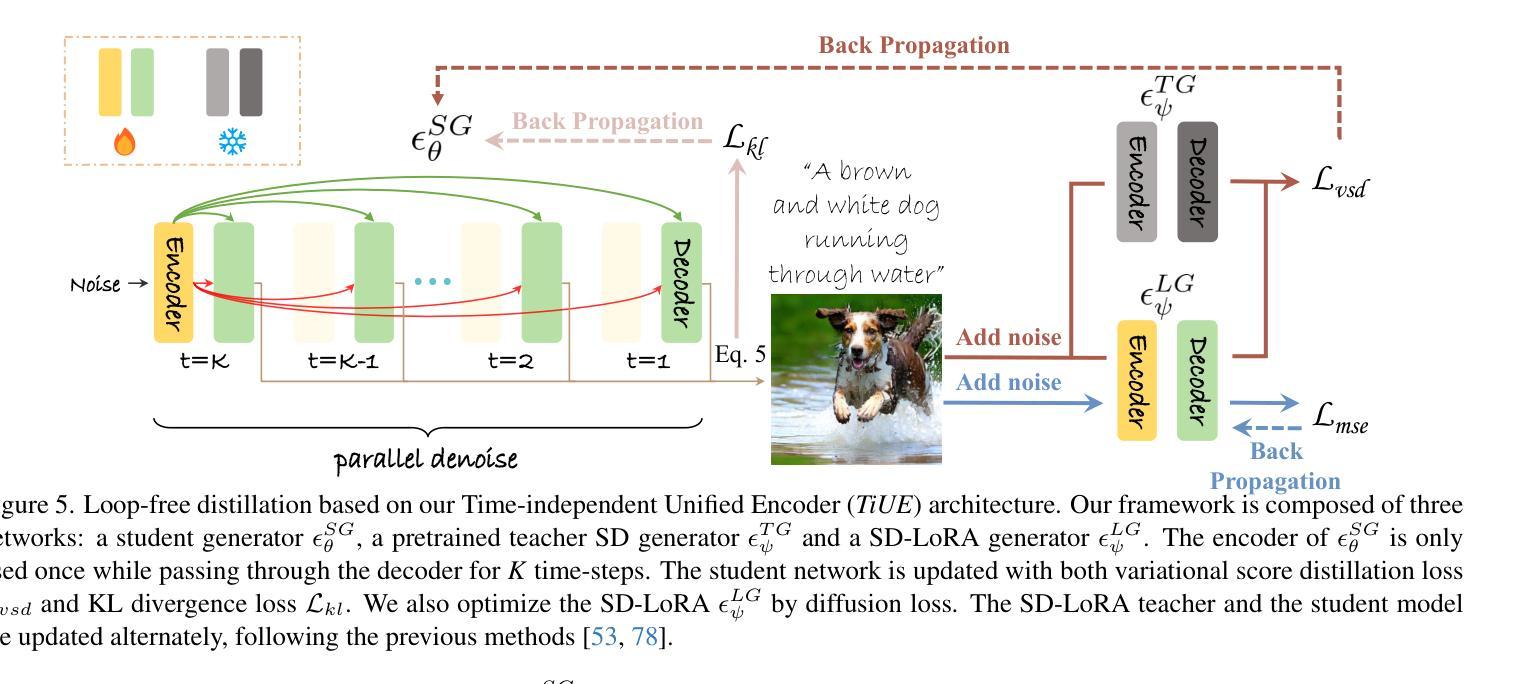
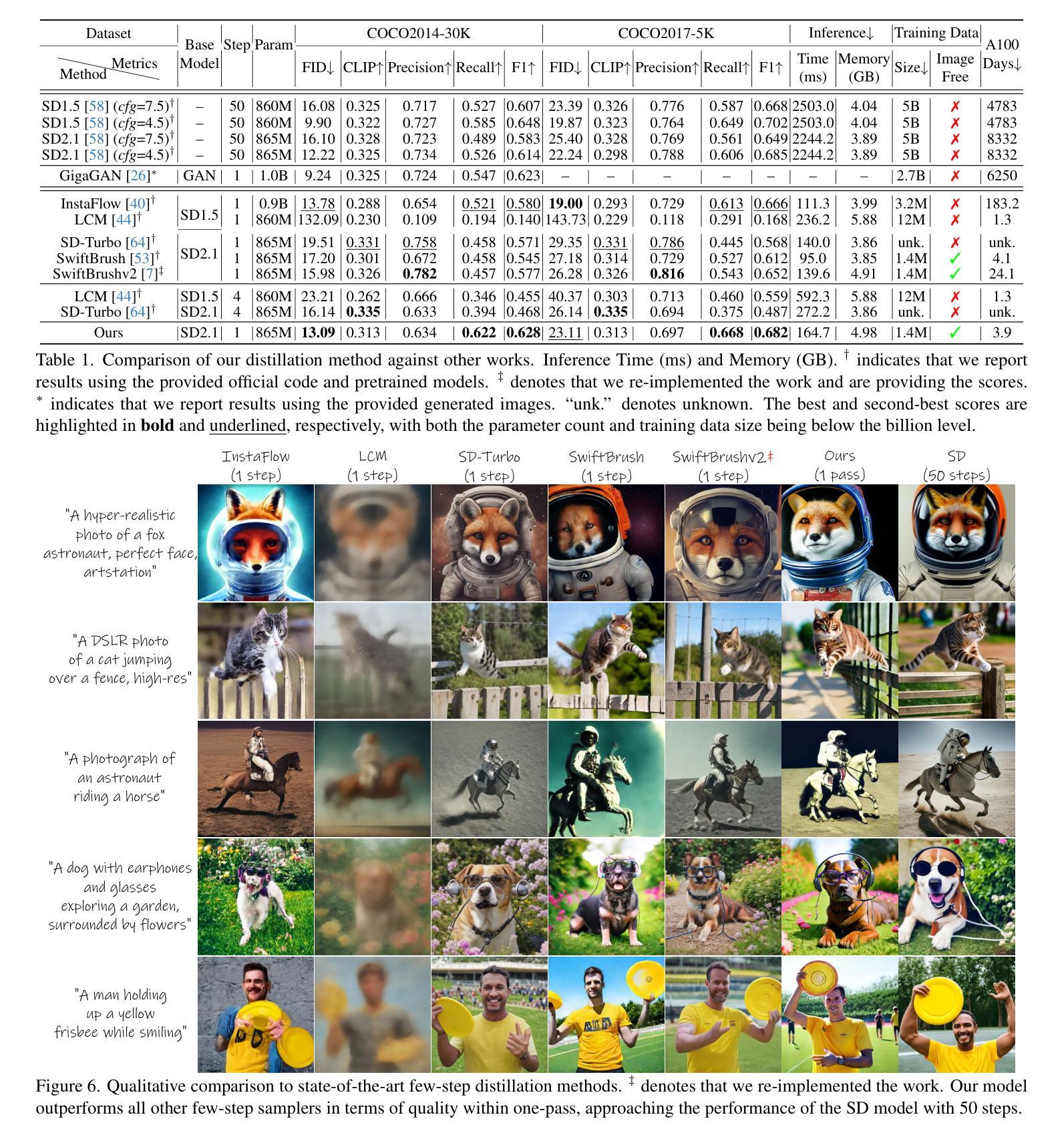
One-Way Ticket:Time-Independent Unified Encoder for Distilling Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Senmao Li, Lei Wang, Kai Wang, Tao Liu, Jiehang Xie, Joost van de Weijer, Fahad Shahbaz Khan, Shiqi Yang, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang
Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have made remarkable advancements in generative modeling; however, they face a trade-off between inference speed and image quality, posing challenges for efficient deployment. Existing distilled T2I models can generate high-fidelity images with fewer sampling steps, but often struggle with diversity and quality, especially in one-step models. From our analysis, we observe redundant computations in the UNet encoders. Our findings suggest that, for T2I diffusion models, decoders are more adept at capturing richer and more explicit semantic information, while encoders can be effectively shared across decoders from diverse time steps. Based on these observations, we introduce the first Time-independent Unified Encoder TiUE for the student model UNet architecture, which is a loop-free image generation approach for distilling T2I diffusion models. Using a one-pass scheme, TiUE shares encoder features across multiple decoder time steps, enabling parallel sampling and significantly reducing inference time complexity. In addition, we incorporate a KL divergence term to regularize noise prediction, which enhances the perceptual realism and diversity of the generated images. Experimental results demonstrate that TiUE outperforms state-of-the-art methods, including LCM, SD-Turbo, and SwiftBrushv2, producing more diverse and realistic results while maintaining the computational efficiency.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成建模方面取得了显著的进展;然而,它们在推理速度与图像质量之间存在权衡,为有效部署带来了挑战。现有的蒸馏T2I模型可以使用较少的采样步骤生成高保真图像,但在多样性和质量方面往往存在困难,特别是在单步模型中。从我们的分析来看,我们观察到UNet编码器中存在冗余计算。我们的研究发现,对于T2I扩散模型,解码器更擅长捕捉更丰富、更明确的语义信息,而编码器可以有效地在来自不同时间步的解码器之间共享。基于这些观察,我们为学生模型UNet架构引入了首个时间独立统一编码器TiUE,这是一种无循环的图像生成方法,用于蒸馏T2I扩散模型。TiUE使用一次通过方案,跨多个解码器时间步共享编码器特征,实现并行采样,并显著降低推理时间复杂度。此外,我们引入KL散度项来规范噪声预测,这提高了生成图像的感知真实感和多样性。实验结果表明,TiUE优于最新方法,包括LCM、SD-Turbo和SwiftBrushv2,能够在保持计算效率的同时产生更多样化和更真实的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR2025, Code: https://github.com/sen-mao/Loopfree
Summary
文本介绍了文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成建模方面的显著进展,但面临推理速度与图像质量之间的权衡挑战。研究团队观察到UNet编码器的冗余计算,并提出首个时间独立统一编码器TiUE,用于学生模型的UNet架构。TiUE采用无循环图像生成方法,通过共享编码器特征实现并行采样,显著降低推理时间复杂度。此外,通过引入KL散度项来规范噪声预测,提高了生成图像的感知真实性和多样性。实验表明,TiUE优于其他最新方法,包括LCM、SD-Turbo和SwiftBrushv2,能在保持计算效率的同时产生更多样化和逼真的结果。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型在生成建模方面取得显著进展,但面临推理速度与图像质量之间的权衡挑战。
- 现有蒸馏T2I模型虽能生成高保真图像,但在多样性和质量方面存在不足,尤其是在单步模型中。
- UNet编码器中存在冗余计算。
- 解码器更能捕捉丰富且明确的语义信息,而编码器可跨不同时间步有效共享。
- 引入时间独立统一编码器TiUE,用于学生模型的UNet架构,采用无循环图像生成方法。
- TiUE通过共享编码器特征实现并行采样,显著降低推理时间复杂度。
点此查看论文截图

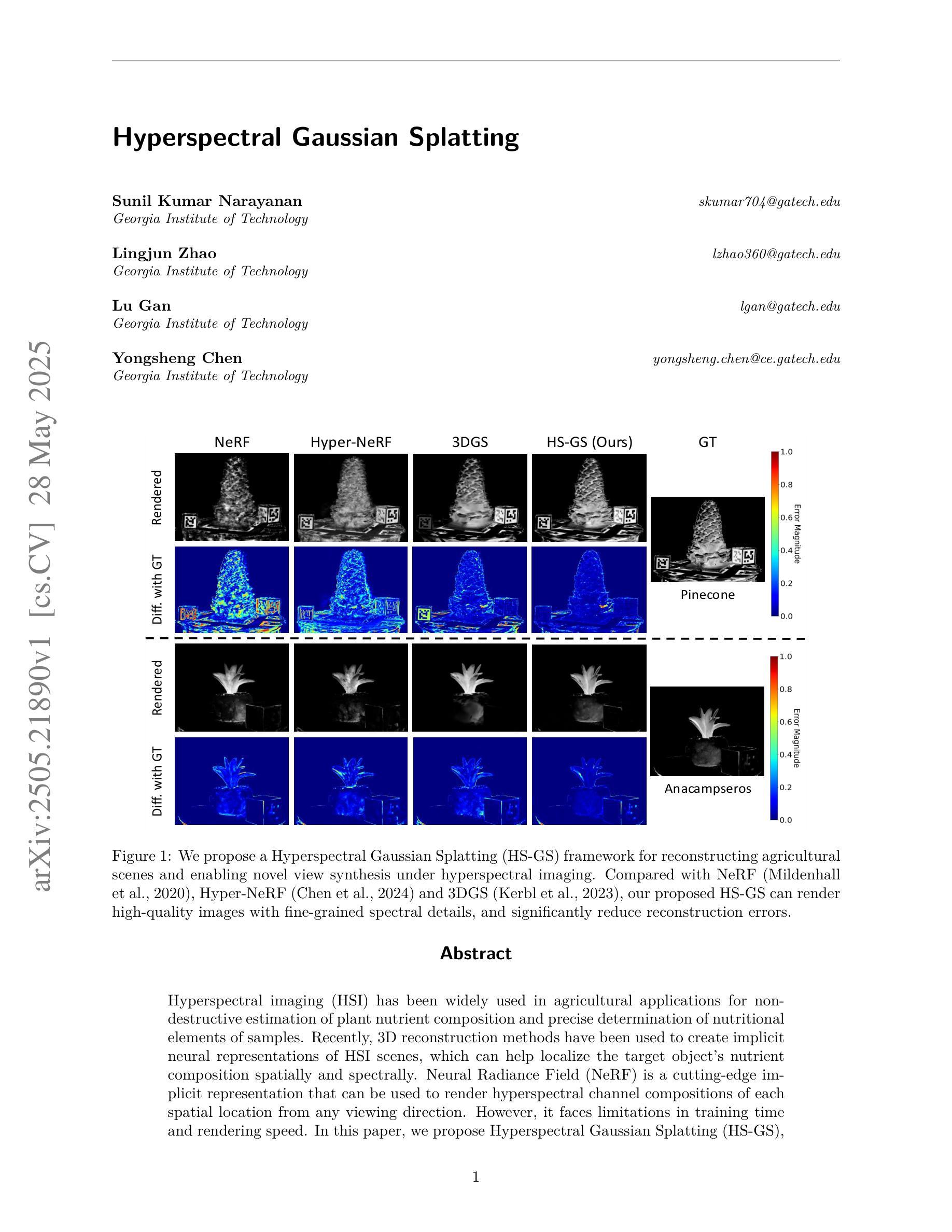
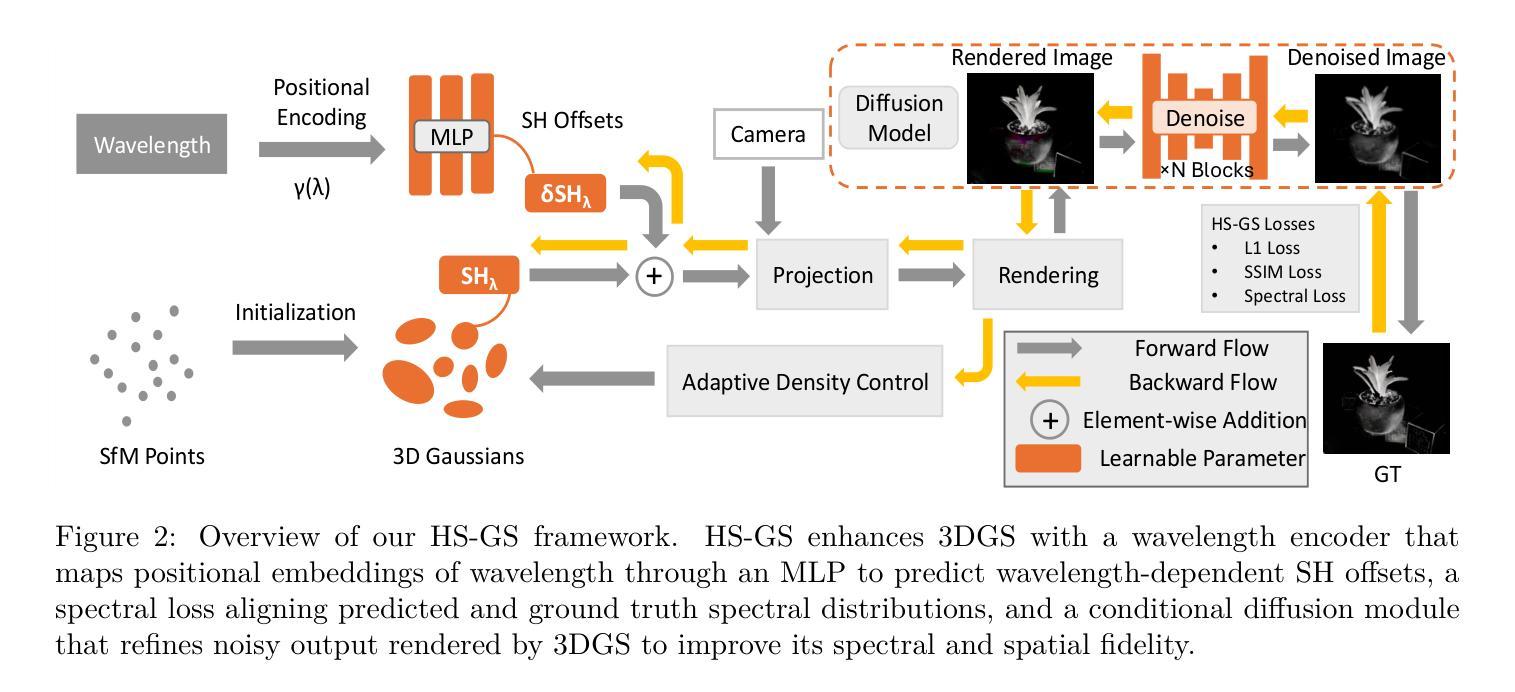
Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Sunil Kumar Narayanan, Lingjun Zhao, Lu Gan, Yongsheng Chen
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has been widely used in agricultural applications for non-destructive estimation of plant nutrient composition and precise determination of nutritional elements in samples. Recently, 3D reconstruction methods have been used to create implicit neural representations of HSI scenes, which can help localize the target object’s nutrient composition spatially and spectrally. Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) is a cutting-edge implicit representation that can render hyperspectral channel compositions of each spatial location from any viewing direction. However, it faces limitations in training time and rendering speed. In this paper, we propose Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting (HS-GS), which combines the state-of-the-art 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with a diffusion model to enable 3D explicit reconstruction of the hyperspectral scenes and novel view synthesis for the entire spectral range. To enhance the model’s ability to capture fine-grained reflectance variations across the light spectrum and leverage correlations between adjacent wavelengths for denoising, we introduce a wavelength encoder to generate wavelength-specific spherical harmonics offsets. We also introduce a novel Kullback–Leibler divergence-based loss to mitigate the spectral distribution gap between the rendered image and the ground truth. A diffusion model is further applied for denoising the rendered images and generating photorealistic hyperspectral images. We present extensive evaluations on five diverse hyperspectral scenes from the Hyper-NeRF dataset to show the effectiveness of our proposed HS-GS framework. The results demonstrate that HS-GS achieves new state-of-the-art performance among all previously published methods. Code will be released upon publication.
高光谱成像(HSI)在农业应用中得到了广泛应用,用于非破坏性估计植物养分组成和精确确定样品中的营养元素。最近,三维重建方法被用来创建HSI场景的隐式神经表示,这有助于在空间上光谱上定位目标对象的养分组成。神经辐射场(NeRF)是一种前沿的隐式表示方法,可以从任何观看方向呈现每个空间位置的高光谱通道组合。然而,它在训练时间和渲染速度方面存在局限性。在本文中,我们提出了高光谱高斯展布(HS-GS),它将最新的三维高斯展布(3DGS)与扩散模型相结合,实现对高光谱场景的三维显式重建以及整个光谱范围的全新视图合成。为了增强模型捕捉光谱中精细反射率变化的能力并利用相邻波长之间的相关性进行去噪,我们引入了波长编码器来生成特定波长的球面谐波偏移。我们还介绍了一种新型的基于Kullback-Leibler散度损失的方法来缩小渲染图像和真实图像之间的光谱分布差距。扩散模型进一步应用于对渲染图像进行去噪,并生成逼真的高光谱图像。我们在Hyper-NeRF数据集上的五个不同高光谱场景进行了广泛评估,以展示我们提出的HS-GS框架的有效性。结果表明,HS-GS在所有已发布的方法中达到了新的最先进的性能。代码将在发布时公布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting(HS-GS)的方法,结合了三维高斯溅射技术与扩散模型,实现了对高光谱场景的隐式重建与新型视合成,达到先进的性能水平。HS-GS模型具有快速渲染的特性,解决了现有的模型渲染能力低下的问题。它采用波长编码技术来捕捉不同波长反射特性的变化并利用邻近波长的信息实现去噪,并利用扩散模型提高图像去噪效果和生成逼真高光谱图像的能力。实验结果显示HS-GS框架在所有已发布的方法中表现最优。代码将在出版时公开。
Key Takeaways
- 本文使用Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting(HS-GS)方法结合了三维高斯溅射技术与扩散模型,实现了高光谱场景的隐式重建与新型视合成。
- HS-GS模型解决了现有模型在训练时间和渲染速度上的限制。
- 通过引入波长编码技术,HS-GS能够捕捉不同波长反射特性的变化并利用邻近波长的信息实现去噪。
- 采用扩散模型提高了图像去噪效果和生成逼真高光谱图像的能力。
点此查看论文截图
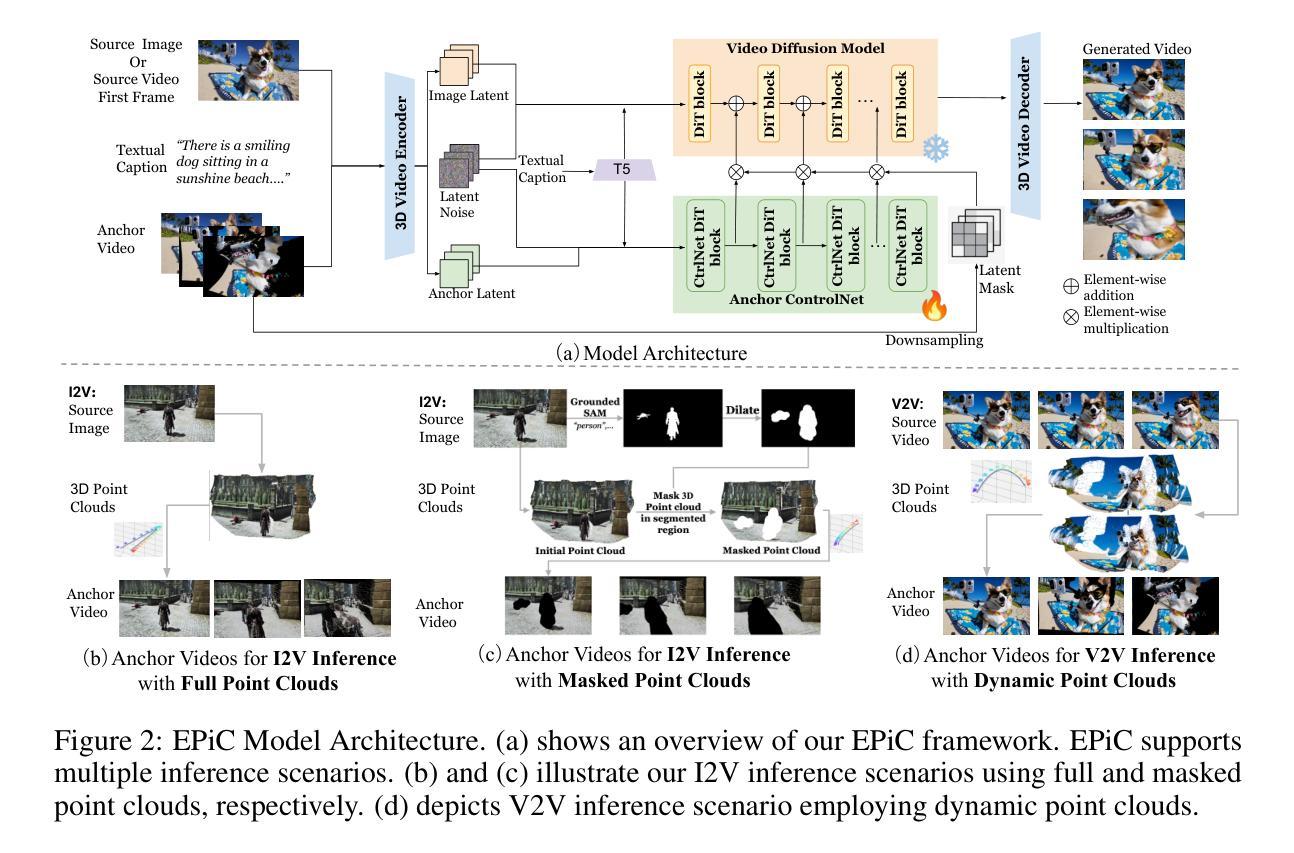
EPiC: Efficient Video Camera Control Learning with Precise Anchor-Video Guidance
Authors:Zun Wang, Jaemin Cho, Jialu Li, Han Lin, Jaehong Yoon, Yue Zhang, Mohit Bansal
Recent approaches on 3D camera control in video diffusion models (VDMs) often create anchor videos to guide diffusion models as a structured prior by rendering from estimated point clouds following annotated camera trajectories. However, errors inherent in point cloud estimation often lead to inaccurate anchor videos. Moreover, the requirement for extensive camera trajectory annotations further increases resource demands. To address these limitations, we introduce EPiC, an efficient and precise camera control learning framework that automatically constructs high-quality anchor videos without expensive camera trajectory annotations. Concretely, we create highly precise anchor videos for training by masking source videos based on first-frame visibility. This approach ensures high alignment, eliminates the need for camera trajectory annotations, and thus can be readily applied to any in-the-wild video to generate image-to-video (I2V) training pairs. Furthermore, we introduce Anchor-ControlNet, a lightweight conditioning module that integrates anchor video guidance in visible regions to pretrained VDMs, with less than 1% of backbone model parameters. By combining the proposed anchor video data and ControlNet module, EPiC achieves efficient training with substantially fewer parameters, training steps, and less data, without requiring modifications to the diffusion model backbone typically needed to mitigate rendering misalignments. Although being trained on masking-based anchor videos, our method generalizes robustly to anchor videos made with point clouds during inference, enabling precise 3D-informed camera control. EPiC achieves SOTA performance on RealEstate10K and MiraData for I2V camera control task, demonstrating precise and robust camera control ability both quantitatively and qualitatively. Notably, EPiC also exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to video-to-video scenarios.
关于视频扩散模型(VDM)中的3D相机控制方法,近期的研究通常通过从估计的点云渲染来创建锚视频,以作为扩散模型的结构化先验来引导模型。然而,点云估计中的固有误差往往导致锚视频不准确。此外,对大量的相机轨迹标注的需求进一步增加了资源需求。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了EPiC,这是一个高效且精确的相机控制学习框架,能够自动构建高质量的锚视频,而无需昂贵的相机轨迹标注。具体来说,我们通过基于第一帧可见性的源视频遮罩来创建用于训练的高精度锚视频。这种方法确保了高对齐性,消除了对相机轨迹标注的需求,因此可以轻松地应用于任何野生视频,生成图像到视频(I2V)的训练对。此外,我们引入了Anchor-ControlNet,这是一个轻量级的调节模块,它将锚视频指导集成到可见区域中,以预训练的VDM,并且只需要不到1%的主模型参数。通过结合提出的锚视频数据和ControlNet模块,EPiC能够实现高效的训练,大大减少参数、训练步骤和数据的需求,同时无需对扩散模型的主模型进行改动,通常这是为了缓解渲染不对齐的问题。虽然是在基于遮罩的锚视频上进行训练,但我们的方法对于推断时利用点云制作的锚视频具有稳健的泛化能力,能够实现精确的3D信息引导的相机控制。EPiC在RealEstate10K和MiraData上的I2V相机控制任务上达到了SOTA性能,从定量和定性两个方面都证明了其精确且稳健的相机控制能力。值得注意的是,EPiC在视频到视频的场景中也表现出强大的零样本泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://zunwang1.github.io/Epic
摘要
本文介绍了一种高效的相机控制学习框架EPiC,无需昂贵的相机轨迹标注,即可自动构建高质量锚视频,用于训练视频扩散模型(VDM)。通过基于首帧可见性的源视频遮罩创建精确锚视频,实现高对齐,消除对相机轨迹标注的需求,并可直接应用于任何野生视频生成图像到视频(I2V)的训练对。此外,引入Anchor-ControlNet模块,在可见区域集成锚视频指导预训练的VDM,参数少于主干模型参数的1%。结合提出的锚视频数据和ControlNet模块,EPiC实现了高效训练,大幅减少参数、训练步骤和数据需求,且无需修改扩散模型的主干来缓解渲染错位问题。尽管是在基于遮罩的锚视频上进行训练,但我们的方法在推理时利用点云制作的锚视频也表现稳健,实现了精确的3D信息引导的相机控制。EPiC在RealEstate10K和MiraData的I2V相机控制任务上达到了最先进的性能表现,证明其在定量和定性方面都具备精确且稳健的相机控制能力。值得注意的是,EPiC在视频到视频场景中表现出强大的零样本泛化能力。
关键见解
- EPiC框架能自动构建高质量锚视频,无需昂贵的相机轨迹标注。
- 通过基于首帧可见性的源视频遮罩创建精确锚视频,实现高对齐。
- Anchor-ControlNet模块集成锚视频指导,参数需求少。
- 结合锚视频数据和ControlNet模块,实现高效训练,减少参数、训练步骤和数据需求。
- 方法在基于点云的锚视频上也表现稳健,实现精确3D信息引导的相机控制。
- 在I2V相机控制任务上达到最先进的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图


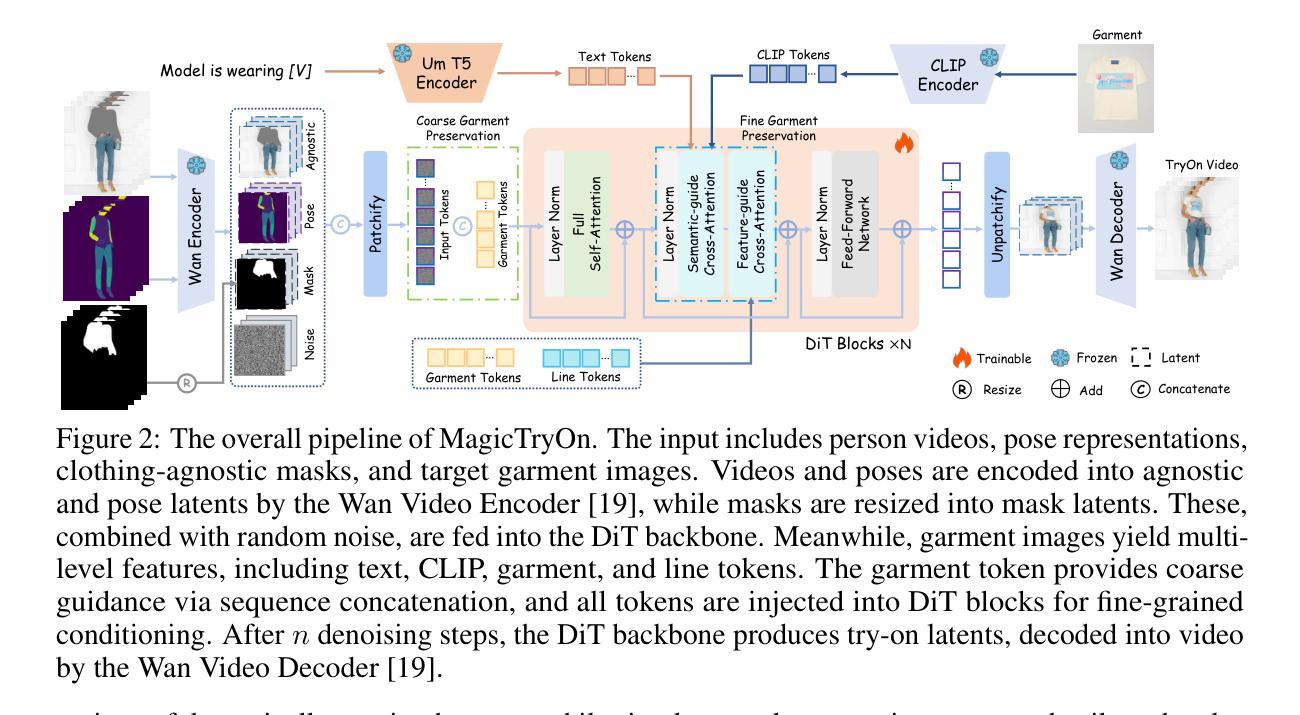
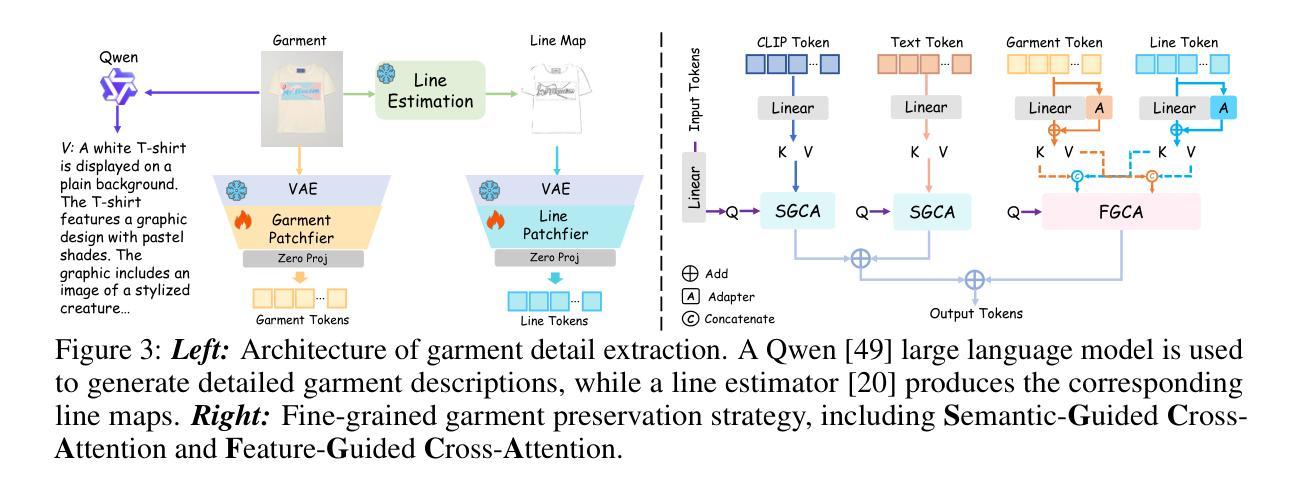
MagicTryOn: Harnessing Diffusion Transformer for Garment-Preserving Video Virtual Try-on
Authors:Guangyuan Li, Siming Zheng, Hao Zhang, Jinwei Chen, Junsheng Luan, Binkai Ou, Lei Zhao, Bo Li, Peng-Tao Jiang
Video Virtual Try-On (VVT) aims to simulate the natural appearance of garments across consecutive video frames, capturing their dynamic variations and interactions with human body motion. However, current VVT methods still face challenges in terms of spatiotemporal consistency and garment content preservation. First, they use diffusion models based on the U-Net, which are limited in their expressive capability and struggle to reconstruct complex details. Second, they adopt a separative modeling approach for spatial and temporal attention, which hinders the effective capture of structural relationships and dynamic consistency across frames. Third, their expression of garment details remains insufficient, affecting the realism and stability of the overall synthesized results, especially during human motion. To address the above challenges, we propose MagicTryOn, a video virtual try-on framework built upon the large-scale video diffusion Transformer. We replace the U-Net architecture with a diffusion Transformer and combine full self-attention to jointly model the spatiotemporal consistency of videos. We design a coarse-to-fine garment preservation strategy. The coarse strategy integrates garment tokens during the embedding stage, while the fine strategy incorporates multiple garment-based conditions, such as semantics, textures, and contour lines during the denoising stage. Moreover, we introduce a mask-aware loss to further optimize garment region fidelity. Extensive experiments on both image and video try-on datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing SOTA methods in comprehensive evaluations and generalizes to in-the-wild scenarios.
视频虚拟试穿(VVT)旨在模拟衣物在连续视频帧中的自然外观,捕捉其动态变化和与人体运动的交互。然而,当前的VVT方法仍面临时空一致性和服装内容保留方面的挑战。首先,它们使用基于U-Net的扩散模型,其表达能力有限,难以重建复杂的细节。其次,它们采用空间和时间的分离建模方法,这阻碍了跨帧的结构关系和动态一致性的有效捕获。第三,它们对服装细节的表达仍然不足,影响了合成结果的现实感和稳定性,特别是在人体运动期间。针对上述挑战,我们提出了MagicTryOn,一个基于大规模视频扩散Transformer的视频虚拟试穿框架。我们用扩散Transformer替换U-Net架构,并结合全自注意力来联合建模视频的时空一致性。我们设计了一种从粗到细的服装保留策略。粗策略在嵌入阶段集成服装令牌,而细策略在降噪阶段融入多种基于服装的条件,如语义、纹理和轮廓线。此外,我们引入了一个掩膜感知损失来进一步优化服装区域保真度。在图像和视频试穿数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在综合评估中超越了现有的最先进方法,并推广到野外场景。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视频虚拟试穿(VVT)技术旨在模拟衣物在连续视频帧中的自然外观,捕捉其与人体动作的动态变化和交互。然而,当前VVT方法仍面临时空一致性和衣物内容保留方面的挑战。首先,它们使用基于U-Net的扩散模型,其表现能力有限,难以重建复杂细节。其次,它们采用空间和时间的分离建模方法,这阻碍了帧间结构关系和动态一致性的有效捕捉。此外,衣物细节的表达能力不足,影响了合成结果的逼真度和稳定性,特别是在人体运动过程中。为解决上述挑战,我们提出了MagicTryOn,一个基于大规模视频扩散Transformer的视频虚拟试穿框架。我们采用扩散Transformer替代U-Net架构,结合全自注意力机制,对视频的时空一致性进行联合建模。设计了一种从粗到细的衣物保留策略。粗策略在嵌入阶段集成衣物令牌,而细策略在降噪阶段融入多种基于衣物的条件,如语义、纹理和轮廓线。此外,我们引入了一种掩码感知损失来进一步优化衣物区域的保真度。在图像和视频试穿数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法在综合评估中超越了现有先进技术,并适用于实际场景。
关键见解
- 视频虚拟试穿(VVT)技术旨在模拟衣物在视频中的自然外观,面临时空一致性和衣物内容保留的挑战。
- 当前方法使用基于U-Net的扩散模型,其表达能力有限,难以重建复杂细节。
- 现有方法采用分离建模时空注意力的方式,影响结构关系和动态一致性的有效捕捉。
- MagicTryOn框架使用大规模视频扩散Transformer,结合全自注意力机制进行时空一致性建模。
- MagicTryOn设计了一种衣物保留策略,包括在嵌入阶段集成衣物令牌以及在降噪阶段融入多种衣物条件。
- 引入掩码感知损失以优化衣物区域的保真度。
点此查看论文截图

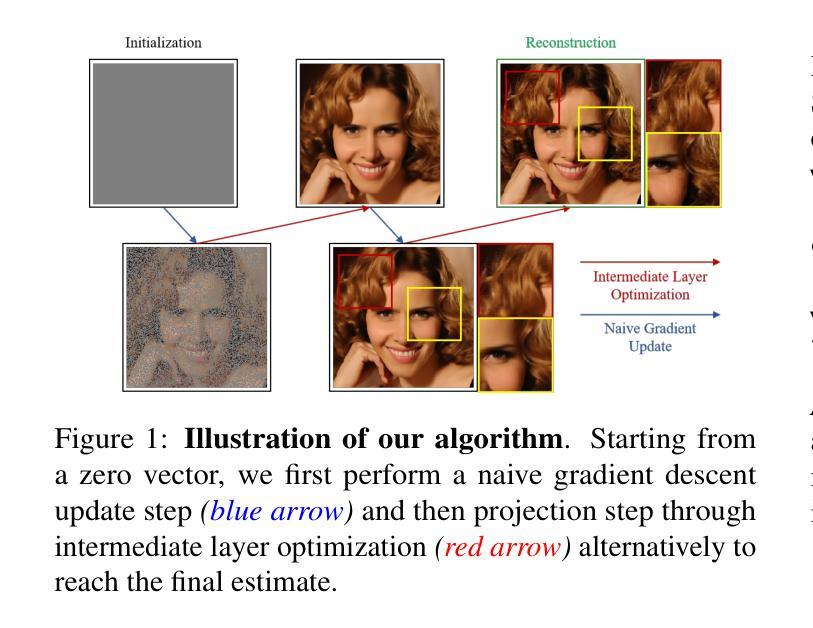
Integrating Intermediate Layer Optimization and Projected Gradient Descent for Solving Inverse Problems with Diffusion Models
Authors:Yang Zheng, Wen Li, Zhaoqiang Liu
Inverse problems (IPs) involve reconstructing signals from noisy observations. Recently, diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as a powerful framework for solving IPs, achieving remarkable reconstruction performance. However, existing DM-based methods frequently encounter issues such as heavy computational demands and suboptimal convergence. In this work, building upon the idea of the recent work DMPlug, we propose two novel methods, DMILO and DMILO-PGD, to address these challenges. Our first method, DMILO, employs intermediate layer optimization (ILO) to alleviate the memory burden inherent in DMPlug. Additionally, by introducing sparse deviations, we expand the range of DMs, enabling the exploration of underlying signals that may lie outside the range of the diffusion model. We further propose DMILO-PGD, which integrates ILO with projected gradient descent (PGD), thereby reducing the risk of suboptimal convergence. We provide an intuitive theoretical analysis of our approaches under appropriate conditions and validate their superiority through extensive experiments on diverse image datasets, encompassing both linear and nonlinear IPs. Our results demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the effectiveness of DMILO and DMILO-PGD in addressing common challenges in DM-based IP solvers.
逆向问题(IPs)涉及从噪声观察中重建信号。最近,扩散模型(DMs)作为解决IPs的强大框架而出现,实现了显著的重建性能。然而,现有的基于DM的方法经常遇到计算需求大、收敛不佳等问题。在这项工作中,我们基于最近的工作DMPlug,提出了两种新方法DMILO和DMILO-PGD,以应对这些挑战。我们的第一种方法DMILO采用中间层优化(ILO)来缓解DMPlug所固有的内存负担。此外,通过引入稀疏偏差,我们扩大了DM的范围,能够探索可能位于扩散模型范围之外的潜在信号。我们进一步提出了DMILO-PGD,它将ILO与投影梯度下降法(PGD)相结合,从而降低了收敛不佳的风险。我们在适当条件下对方法进行了直观的理论分析,并通过对各种图像数据集的大量实验验证了其优越性,这些实验涵盖了线性和非线性IPs。我们的结果证明了DMILO和DMILO-PGD在解决基于DM的IP求解器中的常见问题时的显著性能提升,突显了它们的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
扩散模型(DM)在解决反问题(IP)中表现出强大的能力,但现有方法存在计算量大和收敛性不佳等问题。本文提出两种新方法DMILO和DMILO-PGD,前者通过中间层优化(ILO)减轻内存负担,并引入稀疏偏差扩大模型探索范围;后者结合ILO和投影梯度下降法(PGD),降低收敛风险。理论分析和实验结果表明,两种方法在图像数据集上的性能显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DM)在反问题(IP)解决中表现出优异性能。
- 现有DM方法存在计算量大和收敛性问题。
- DMILO方法通过中间层优化(ILO)减轻内存负担。
- DMILO引入稀疏偏差以扩大模型的探索范围。
- DMILO-PGD结合ILO和投影梯度下降法(PGD),提高收敛性。
- 本文方法在实验上验证了对多种图像数据集的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



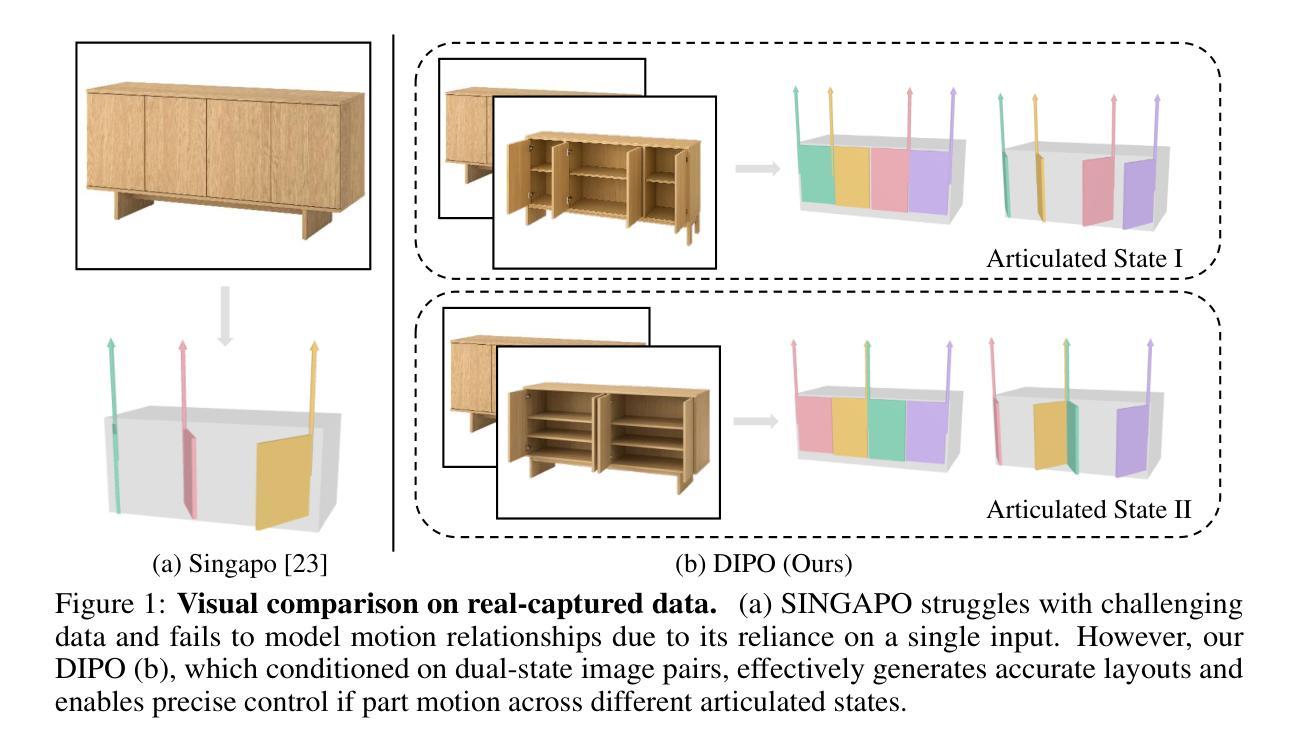
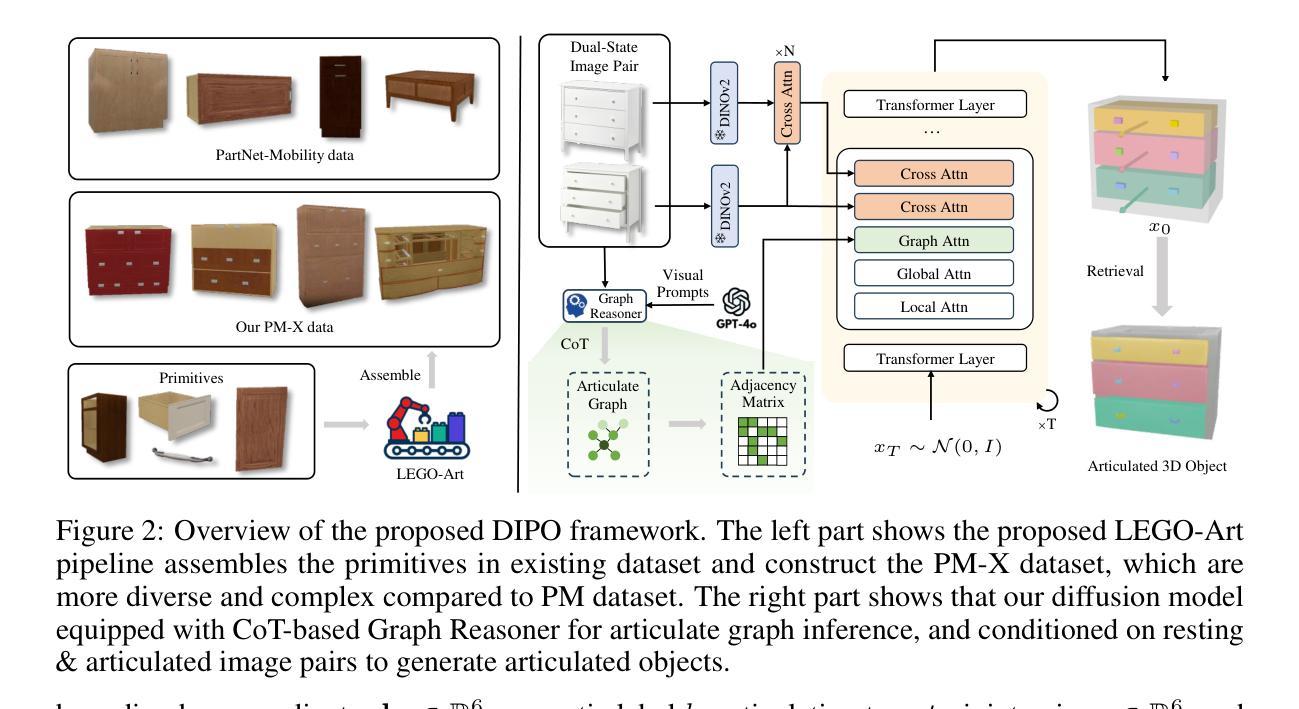
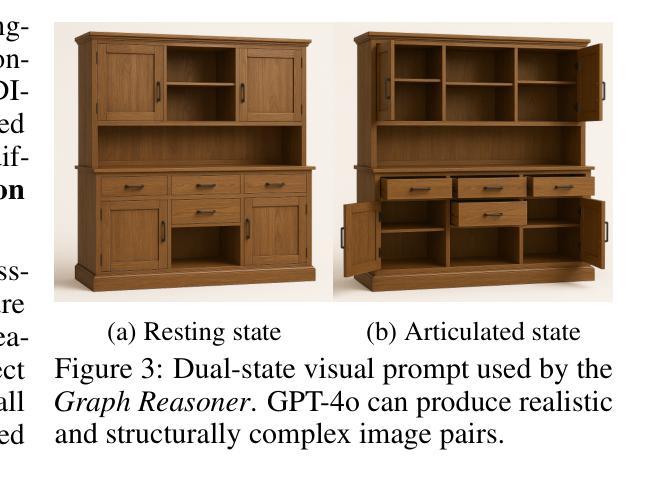
DIPO: Dual-State Images Controlled Articulated Object Generation Powered by Diverse Data
Authors:Ruiqi Wu, Xinjie Wang, Liu Liu, Chunle Guo, Jiaxiong Qiu, Chongyi Li, Lichao Huang, Zhizhong Su, Ming-Ming Cheng
We present DIPO, a novel framework for the controllable generation of articulated 3D objects from a pair of images: one depicting the object in a resting state and the other in an articulated state. Compared to the single-image approach, our dual-image input imposes only a modest overhead for data collection, but at the same time provides important motion information, which is a reliable guide for predicting kinematic relationships between parts. Specifically, we propose a dual-image diffusion model that captures relationships between the image pair to generate part layouts and joint parameters. In addition, we introduce a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) based graph reasoner that explicitly infers part connectivity relationships. To further improve robustness and generalization on complex articulated objects, we develop a fully automated dataset expansion pipeline, name LEGO-Art, that enriches the diversity and complexity of PartNet-Mobility dataset. We propose PM-X, a large-scale dataset of complex articulated 3D objects, accompanied by rendered images, URDF annotations, and textual descriptions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DIPO significantly outperforms existing baselines in both the resting state and the articulated state, while the proposed PM-X dataset further enhances generalization to diverse and structurally complex articulated objects. Our code and dataset will be released to the community upon publication.
我们提出了DIPO,这是一个新的可控生成框架,可以从一对图像中生成精细的3D对象:一张图像描绘对象在静止状态,另一张图像描绘对象在精细运动状态。与单图像方法相比,我们的双图像输入只会对数据采集造成适中的开销,但与此同时提供了重要的运动信息,这对于预测部件之间的运动关系是一个可靠的指南。具体来说,我们提出了一种双图像扩散模型,该模型可以捕捉图像对之间的关系以生成部分布局和关节参数。此外,我们引入了一种基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的图推理器,可以明确推断部分连接关系。为了进一步提高在复杂精细对象上的鲁棒性和泛化能力,我们开发了一个完全自动化的数据集扩展管道,名为LEGO-Art,它丰富了PartNet-Mobility数据集的多样性和复杂性。我们提出了PM-X,这是一个大规模复杂精细3D对象数据集,配有渲染图像、URDF注释和文本描述。大量实验表明,DIPO在静止状态和精细运动状态方面都显著优于现有基线,而提出的PM-X数据集进一步增强了对各种结构和复杂精细对象的泛化能力。我们的代码和数据集将在发布时向公众开放。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
我们提出了DIPO框架,用于从一对图像可控地生成复杂的三维物体。与单图像方法相比,我们的双图像输入带来了轻微的数据收集额外负担,但同时提供了重要的运动信息,可作为预测各部分间运动关系的可靠指南。我们使用双图像扩散模型来捕捉图像间的关系,以生成部分布局和关节参数。此外,我们引入了基于Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的图形推理器来明确推断部分连接关系。为了进一步提高在复杂关节物体的稳健性和泛化能力,我们开发了一个全自动数据集扩展管道LEGO-Art,丰富了PartNet-Mobility数据集的多样性和复杂性。我们提出了PM-X数据集,包含复杂关节三维物体的渲染图像、URDF注释和文本描述。实验表明,DIPO在静止状态和关节状态方面都显著优于现有基线方法,而PM-X数据集进一步增强了模型对多样化和结构复杂的关节物体的泛化能力。我们的代码和数据集将在发布时向公众开放。
Key Takeaways:
- DIPO框架采用双图像输入,用于生成复杂的三维物体,包括静止状态和关节状态的对象图像。
- 双图像扩散模型用于捕捉图像间的内在关系以生成物体的部分布局和关节参数。
- 引入Chain-of-Thought(CoT)的图形推理器来推断物体部分之间的连接关系。
- 开发LEGO-Art数据集扩展管道,增强数据集的多样性和复杂性。
- 提出PM-X数据集,包含复杂关节三维物体的渲染图像、URDF注释和文本描述。
- DIPO显著优于现有方法在生成复杂三维物体的性能表现上。
点此查看论文截图

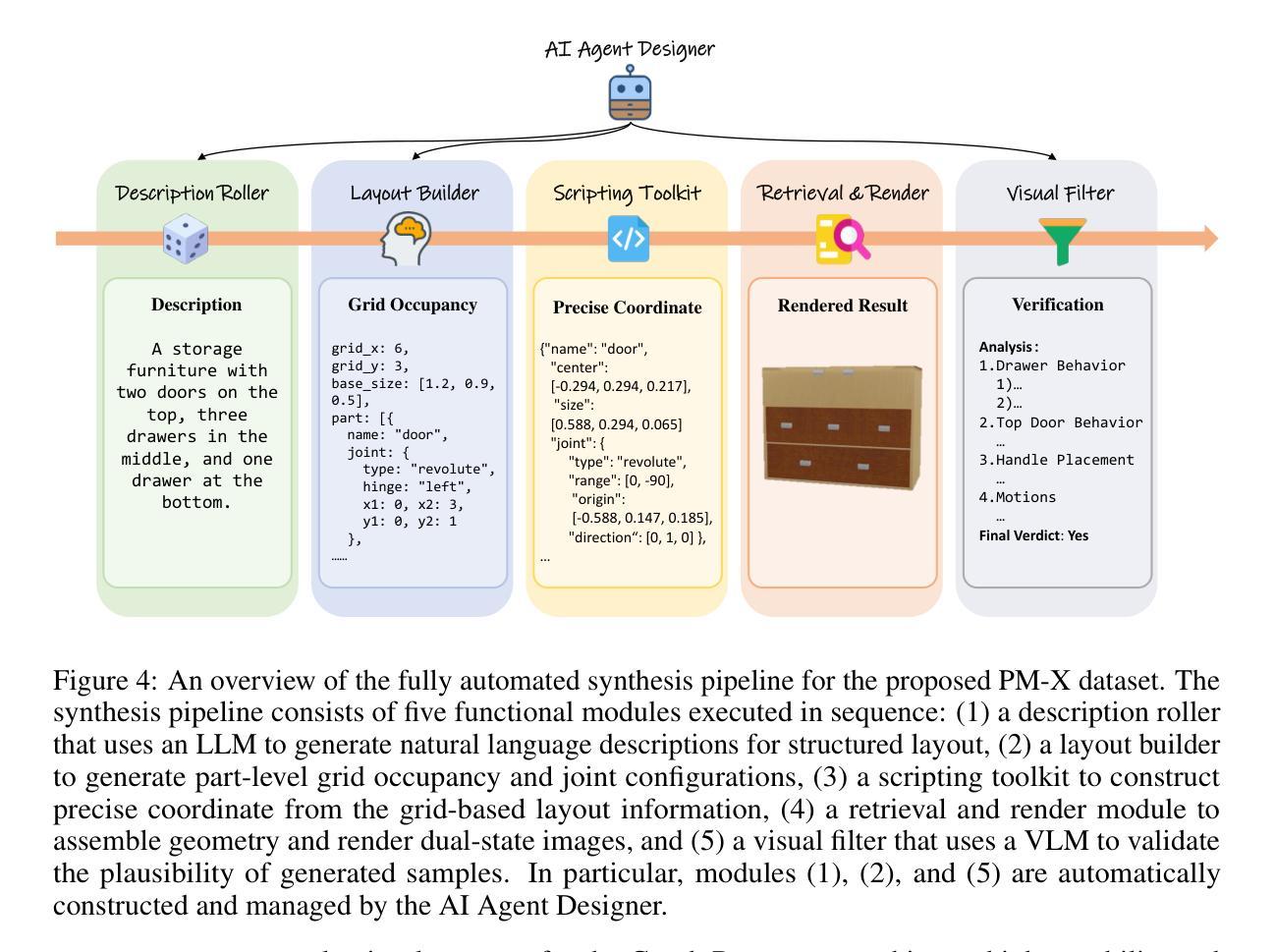
CreatiDesign: A Unified Multi-Conditional Diffusion Transformer for Creative Graphic Design
Authors:Hui Zhang, Dexiang Hong, Maoke Yang, Yutao Cheng, Zhao Zhang, Jie Shao, Xinglong Wu, Zuxuan Wu, Yu-Gang Jiang
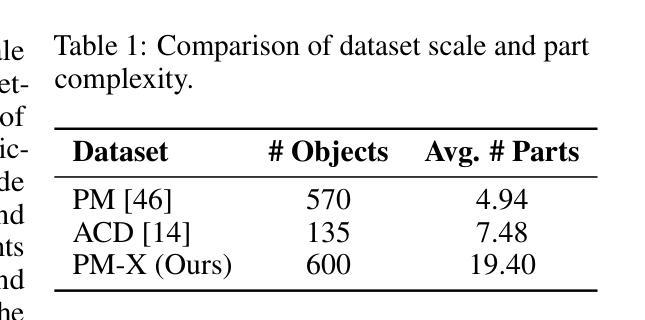
Graphic design plays a vital role in visual communication across advertising, marketing, and multimedia entertainment. Prior work has explored automated graphic design generation using diffusion models, aiming to streamline creative workflows and democratize design capabilities. However, complex graphic design scenarios require accurately adhering to design intent specified by multiple heterogeneous user-provided elements (\eg images, layouts, and texts), which pose multi-condition control challenges for existing methods. Specifically, previous single-condition control models demonstrate effectiveness only within their specialized domains but fail to generalize to other conditions, while existing multi-condition methods often lack fine-grained control over each sub-condition and compromise overall compositional harmony. To address these limitations, we introduce CreatiDesign, a systematic solution for automated graphic design covering both model architecture and dataset construction. First, we design a unified multi-condition driven architecture that enables flexible and precise integration of heterogeneous design elements with minimal architectural modifications to the base diffusion model. Furthermore, to ensure that each condition precisely controls its designated image region and to avoid interference between conditions, we propose a multimodal attention mask mechanism. Additionally, we develop a fully automated pipeline for constructing graphic design datasets, and introduce a new dataset with 400K samples featuring multi-condition annotations, along with a comprehensive benchmark. Experimental results show that CreatiDesign outperforms existing models by a clear margin in faithfully adhering to user intent.
平面设计在广告、营销和多媒体娱乐等领域的视觉交流中扮演着至关重要的角色。先前的研究已经探索了使用扩散模型进行自动平面设计生成,旨在简化创意工作流程并普及设计能力。然而,复杂的平面设计场景需要准确遵循由多个异构用户提供的元素(例如图像、布局和文本)指定的设计意图,这为现有方法带来了多条件控制挑战。具体来说,先前的单条件控制模型仅在它们的专业领域内有效,但难以推广到其他条件,而现有的多条件方法通常缺乏对每个子条件的精细控制,并损害了整体的构图和谐。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了CreatiDesign,这是一个涵盖模型架构和数据集构建的自动化平面设计系统解决方案。首先,我们设计了一种统一的多条件驱动架构,该架构能够灵活精确地集成异构设计元素,并且只需对基础扩散模型进行最小的架构修改。此外,为了确保每个条件精确地控制其指定的图像区域并避免条件之间的干扰,我们提出了一种多模态注意力掩码机制。我们还开发了全自动的平面设计数据集构建流程,并引入了一个包含40万样本的新数据集,该数据集具有多条件注释以及全面的基准测试。实验结果表明,CreatiDesign在忠实于用户意图方面明显优于现有模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了在广告、营销和多媒体娱乐等领域中,图形设计在视觉沟通中的重要性。针对自动化图形设计生成的问题,研究人员利用扩散模型进行探索,旨在优化创意工作流程并普及设计能力。然而,复杂图形设计场景需要精准地遵循用户提供的多个异构元素(如图像、布局和文本)所指定的设计意图,这对现有方法提出了多条件控制的挑战。为解决这一问题,本文提出了CreatiDesign系统解决方案,该方案涵盖了模型架构和数据集构建。通过设计统一的多条件驱动架构,实现灵活精确地集成异构设计元素,并引入多模态注意力屏蔽机制确保每个条件精确控制指定的图像区域,避免条件间的干扰。此外,本文还建立了全自动的图形设计数据集构建流程,并引入了一个包含40万样本的新数据集,进行多条件注释和全面的基准测试。实验结果表明,CreatiDesign在忠实于用户意图方面明显优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- 图形设计在视觉沟通领域具有关键作用,特别是在广告、营销和多媒体娱乐方面。
- 扩散模型被用于自动化图形设计生成,旨在优化创意工作流程和普及设计能力。
- 复杂图形设计场景需要遵循多个异构用户元素指定的设计意图,这对现有方法提出了挑战。
- 存在的方法在特定领域有效,但难以推广到其他条件,而多条件方法则缺乏对每个子条件的精细控制并可能影响整体和谐。
- 引入的CreatiDesign系统解决方案包括模型架构和数据集构建,实现灵活精确地集成异构设计元素。
- 多模态注意力屏蔽机制确保每个条件精确控制指定的图像区域,避免条件间的干扰。
点此查看论文截图

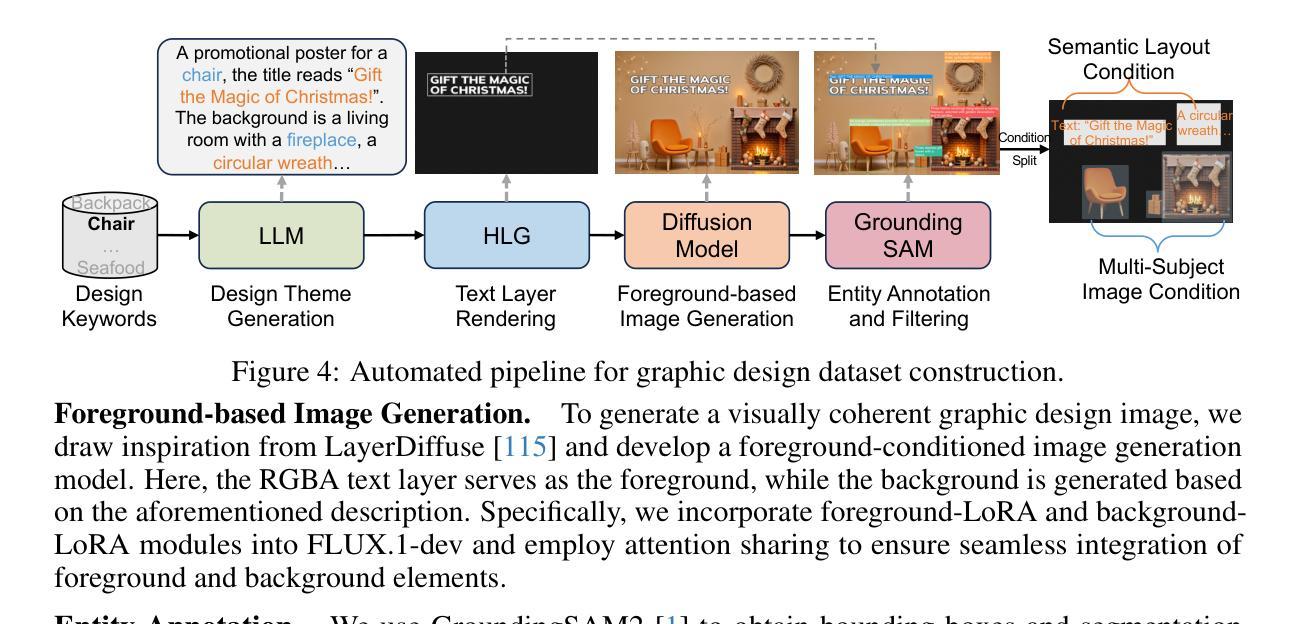
Latent Beam Diffusion Models for Decoding Image Sequences
Authors:Guilherme Fernandes, Vasco Ramos, Regev Cohen, Idan Szpektor, João Magalhães
While diffusion models excel at generating high-quality images from text prompts, they struggle with visual consistency in image sequences. Existing methods generate each image independently, leading to disjointed narratives - a challenge further exacerbated in non-linear storytelling, where scenes must connect beyond adjacent frames. We introduce a novel beam search strategy for latent space exploration, enabling conditional generation of full image sequences with beam search decoding. Unlike prior approaches that use fixed latent priors, our method dynamically searches for an optimal sequence of latent representations, ensuring coherent visual transitions. As the latent denoising space is explored, the beam search graph is pruned with a cross-attention mechanism that efficiently scores search paths, prioritizing alignment with both textual prompts and visual context. Human and automatic evaluations confirm that BeamDiffusion outperforms other baseline methods, producing full sequences with superior coherence, visual continuity, and textual alignment.
虽然扩散模型在根据文本提示生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在图像序列的视觉一致性方面存在困难。现有方法独立生成每张图像,导致叙事不连贯,特别是在非线性叙事中,场景必须在相邻帧之外建立联系,这一挑战进一步加剧。我们引入了一种新型的 beam 搜索策略,用于潜在空间探索,通过 beam 搜索解码实现有条件生成完整的图像序列。与之前使用固定潜在先验的方法不同,我们的方法动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保连贯的视觉过渡。在潜在去噪空间探索过程中,通过交叉注意力机制修剪 beam 搜索图,该机制可以有效地对搜索路径进行评分,优先与文本提示和视觉上下文对齐。人类和自动评估结果证实,BeamDiffusion 优于其他基线方法,生成的全序列具有更高的连贯性、视觉连贯性和文本对齐性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了一种新的扩散模型光束搜索策略,用于探索潜在空间,可实现基于文本提示的条件图像序列生成。该策略通过动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保视觉过渡连贯性,并通过对潜在去噪空间的探索进行光束搜索图的修剪,通过跨注意力机制有效评分搜索路径,优先与文本提示和视觉上下文对齐。评估和自动评估均证实,BeamDiffusion相较于其他基线方法,在生成连贯性、视觉连续性和文本对齐方面表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在图像序列的视觉连贯性方面存在挑战。
- 现有方法独立生成每张图像,导致叙事不连贯,非线性叙事中挑战更大。
- 引入了一种新的光束搜索策略,用于探索潜在空间,实现条件图像序列生成。
- 该策略通过动态搜索最优潜在表示序列,确保视觉过渡连贯。
- 光束搜索图的修剪通过跨注意力机制进行,有效评分搜索路径,与文本和视觉上下文对齐。
- BeamDiffusion相较于其他方法,在生成图像序列的连贯性、视觉连续性和文本对齐方面表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

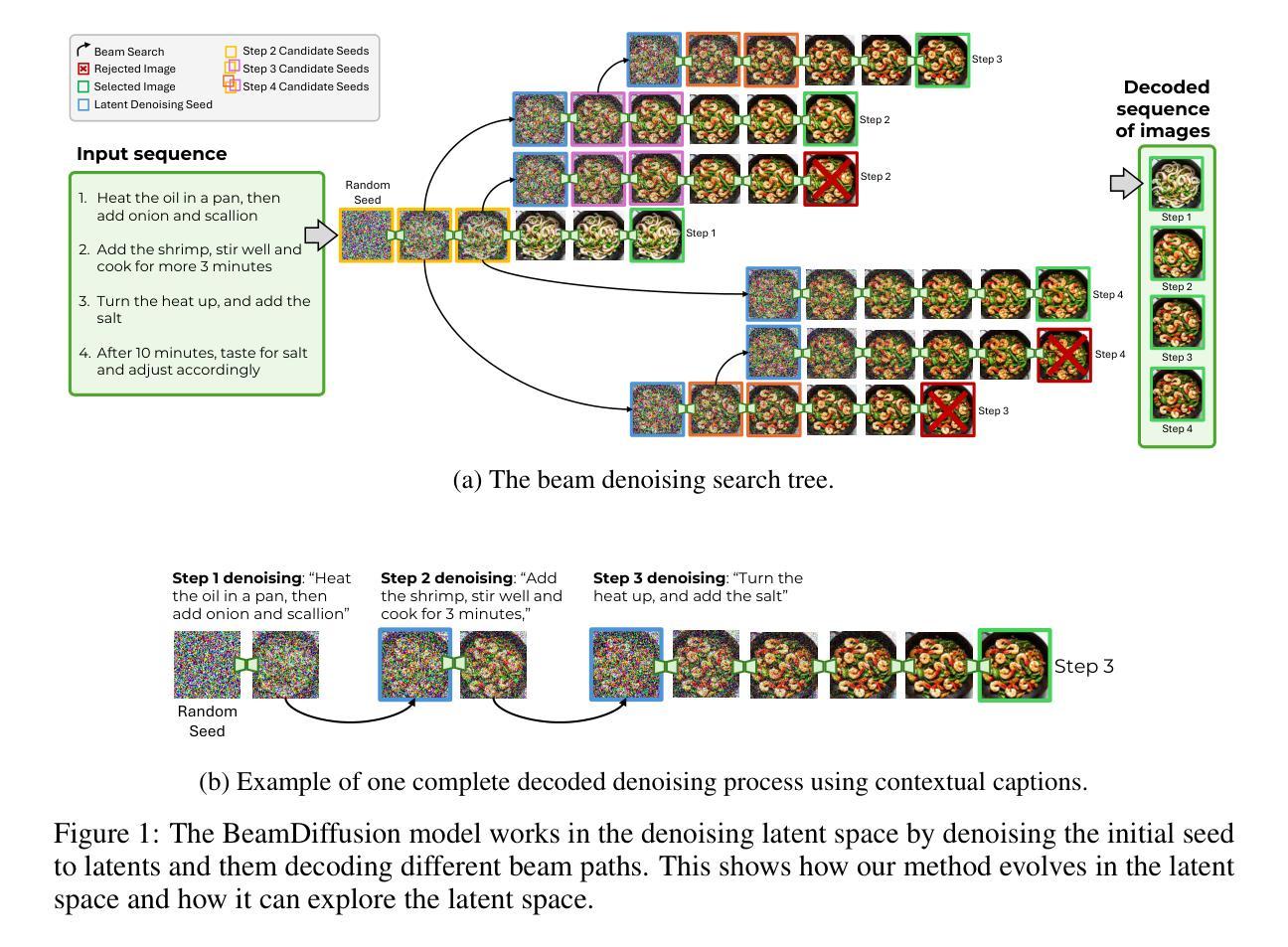
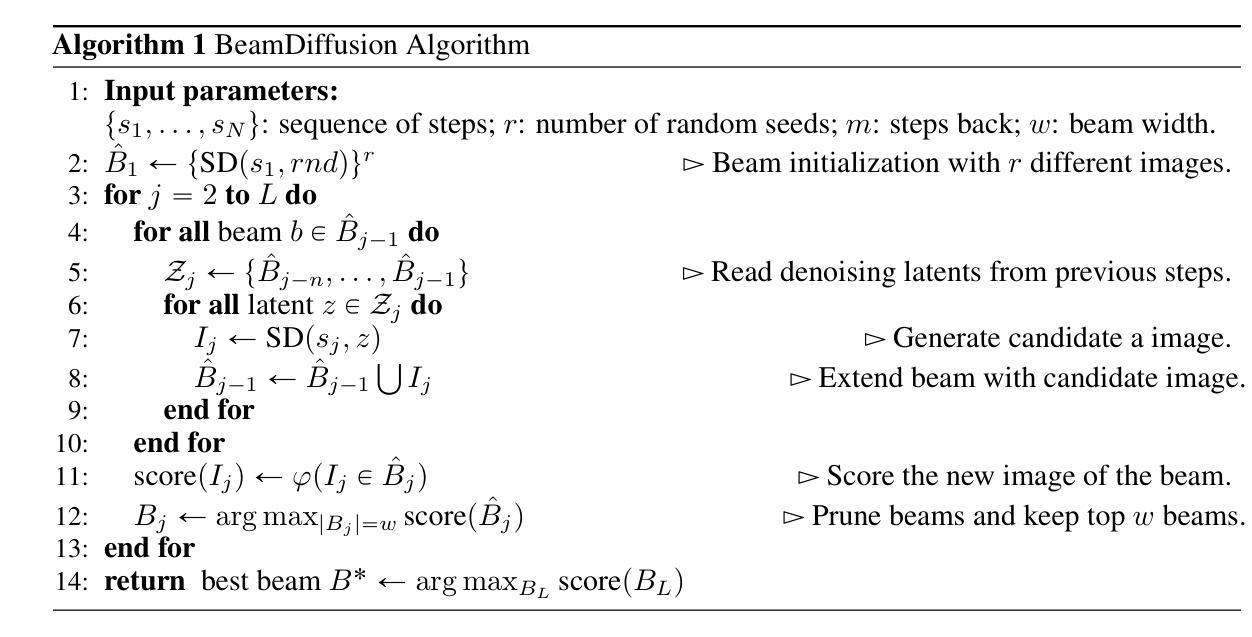
Inference-Time Scaling for Flow Models via Stochastic Generation and Rollover Budget Forcing
Authors:Jaihoon Kim, Taehoon Yoon, Jisung Hwang, Minhyuk Sung
We propose an inference-time scaling approach for pretrained flow models. Recently, inference-time scaling has gained significant attention in LLMs and diffusion models, improving sample quality or better aligning outputs with user preferences by leveraging additional computation. For diffusion models, particle sampling has allowed more efficient scaling due to the stochasticity at intermediate denoising steps. On the contrary, while flow models have gained popularity as an alternative to diffusion models–offering faster generation and high-quality outputs in state-of-the-art image and video generative models–efficient inference-time scaling methods used for diffusion models cannot be directly applied due to their deterministic generative process. To enable efficient inference-time scaling for flow models, we propose three key ideas: 1) SDE-based generation, enabling particle sampling in flow models, 2) Interpolant conversion, broadening the search space and enhancing sample diversity, and 3) Rollover Budget Forcing (RBF), an adaptive allocation of computational resources across timesteps to maximize budget utilization. Our experiments show that SDE-based generation, particularly variance-preserving (VP) interpolant-based generation, improves the performance of particle sampling methods for inference-time scaling in flow models. Additionally, we demonstrate that RBF with VP-SDE achieves the best performance, outperforming all previous inference-time scaling approaches.
我们为预训练的流模型提出了一种推理时间尺度方法。最近,推理时间尺度在大型语言模型和扩散模型中引起了广泛关注,通过利用额外的计算来提高样本质量或更好地使输出与用户偏好对齐。对于扩散模型,由于中间去噪步骤的随机性,粒子采样允许更有效的尺度扩展。相反,虽然流模型作为扩散模型的替代品而广受欢迎,为最先进的图像和视频生成模型提供了更快的生成速度和高质量输出,但用于扩散模型的高效推理时间尺度方法无法直接应用于流模型,因为它们具有确定的生成过程。为了实现流模型的推理时间有效尺度扩展,我们提出了三个关键想法:1)基于SDE的生成,使流模型能够进行粒子采样;2)插值转换,扩大搜索空间并增强样本多样性;3)滚动预算强制(RBF),这是一种自适应地在时间步长之间分配计算资源,以最大化预算利用。我们的实验表明,基于SDE的生成,特别是基于方差保留(VP)插值的生成,改进了流模型推理时间尺度扩展的粒子采样方法的性能。此外,我们还证明了使用VP-SDE的RBF取得了最佳性能,优于以前所有的推理时间尺度扩展方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://flow-inference-time-scaling.github.io/
Summary
针对预训练的流模型,我们提出了一种推理时间尺度调整方法。对于流模型,我们提出三个关键想法:基于SDE的生成、插值转换和滚压预算强制(RBF)。实验表明,基于VP插值的SDE生成提高了流模型中推理时间尺度调整的粒子采样方法的性能。结合VP-SDE的RBF取得了最佳性能,超越了以前的所有推理时间尺度调整方法。
Key Takeaways
- 针对预训练流模型的推理时间尺度调整方法被提出,改进了样本质量,并更好地对齐了用户的输出偏好。
- 流模型和扩散模型在推理时间尺度调整方面存在区别,因为流模型具有确定的生成过程。
- 对于流模型,提出了三个关键想法:基于SDE的生成、插值转换和RBF。
- 基于SDE的生成方法允许在流模型中进行粒子采样。
- 插值转换可以扩大搜索空间并提高样本多样性。
- RBF能够自适应地分配计算资源,以最大化预算利用率。
点此查看论文截图

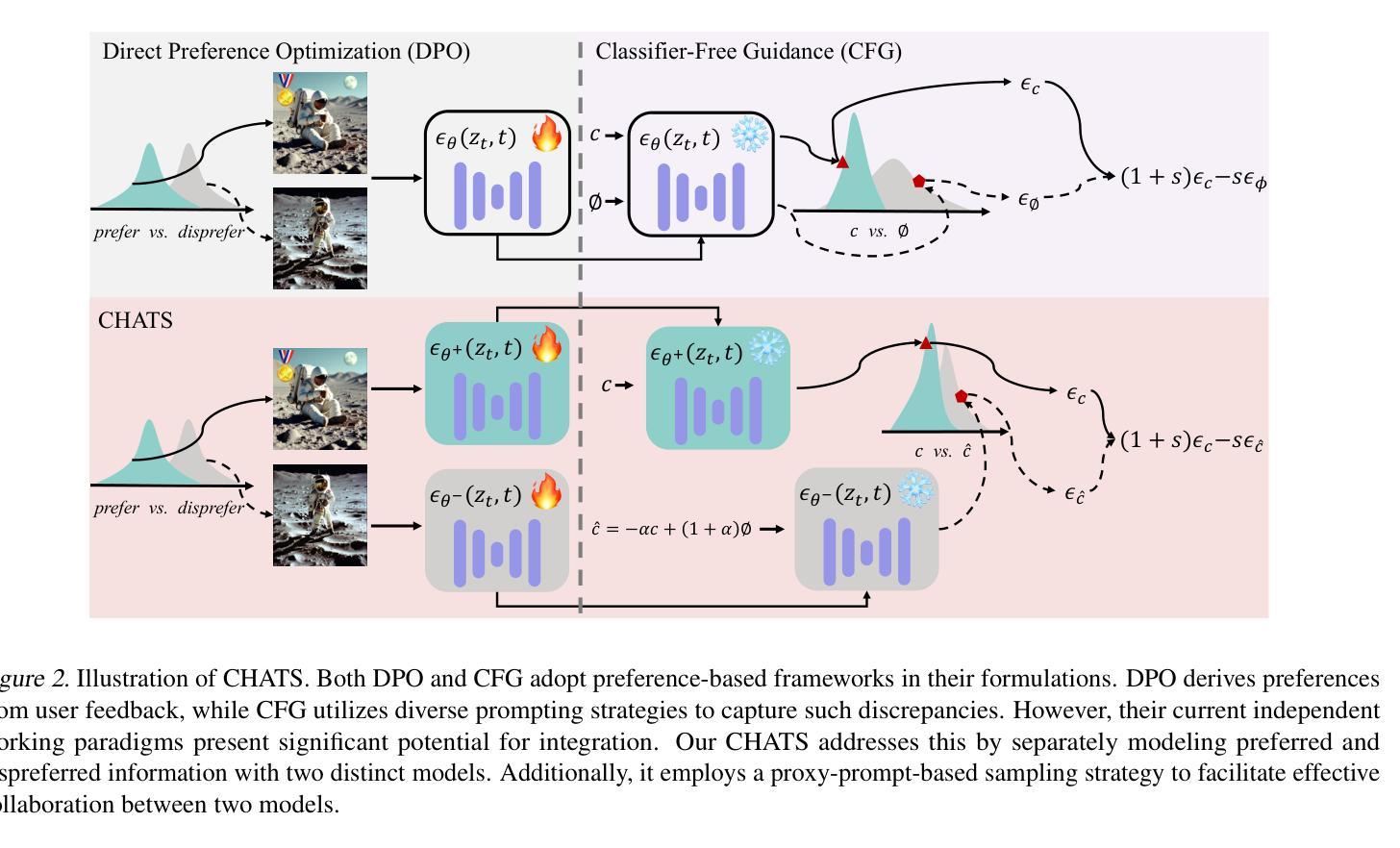
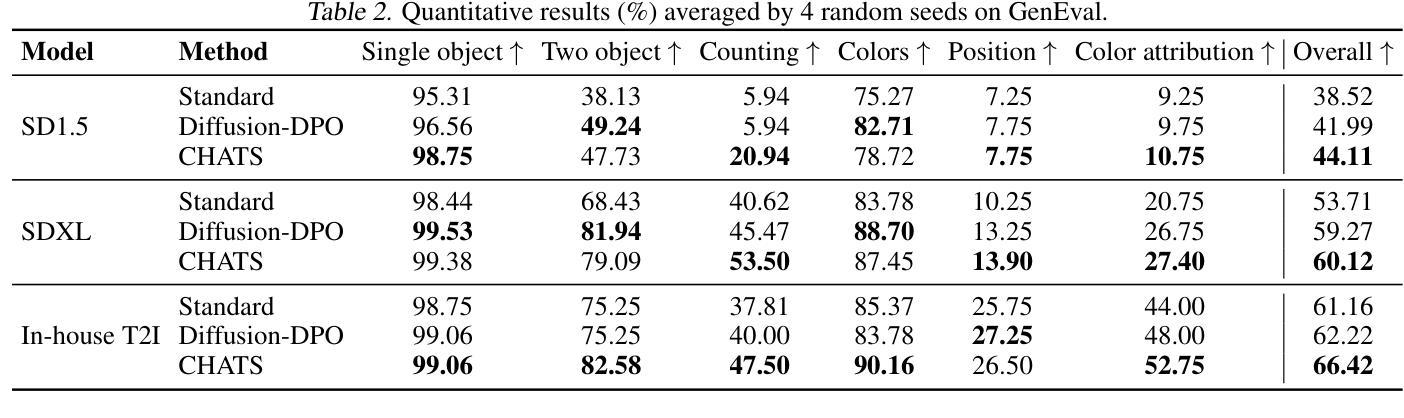
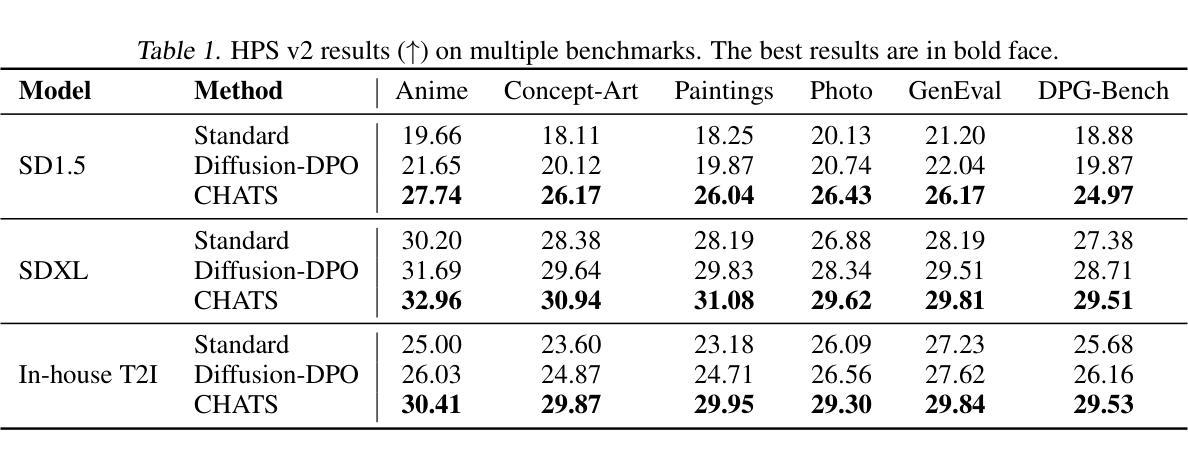
CHATS: Combining Human-Aligned Optimization and Test-Time Sampling for Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Minghao Fu, Guo-Hua Wang, Liangfu Cao, Qing-Guo Chen, Zhao Xu, Weihua Luo, Kaifu Zhang
Diffusion models have emerged as a dominant approach for text-to-image generation. Key components such as the human preference alignment and classifier-free guidance play a crucial role in ensuring generation quality. However, their independent application in current text-to-image models continues to face significant challenges in achieving strong text-image alignment, high generation quality, and consistency with human aesthetic standards. In this work, we for the first time, explore facilitating the collaboration of human performance alignment and test-time sampling to unlock the potential of text-to-image models. Consequently, we introduce CHATS (Combining Human-Aligned optimization and Test-time Sampling), a novel generative framework that separately models the preferred and dispreferred distributions and employs a proxy-prompt-based sampling strategy to utilize the useful information contained in both distributions. We observe that CHATS exhibits exceptional data efficiency, achieving strong performance with only a small, high-quality funetuning dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CHATS surpasses traditional preference alignment methods, setting new state-of-the-art across various standard benchmarks.
扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主导方法。关键组件,如人类偏好对齐和无分类器引导,在确保生成质量方面起着至关重要的作用。然而,它们在当前的文本到图像模型中的独立应用,在实现强大的文本图像对齐、高生成质量以及与人类审美标准的一致性方面仍面临重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们首次探索了人类性能对齐和测试时间采样的协作,以解锁文本到图像模型的潜力。因此,我们引入了CHATS(结合人类对齐优化和测试时间采样),这是一种新型生成框架,它分别建模首选和不受欢迎的分布,并采用基于代理提示的采样策略,利用这两个分布中包含的有用信息。我们发现CHATS表现出卓越的数据效率,仅使用一个小而高质量微调数据集就能实现强劲表现。大量实验表明,CHATS超越了传统偏好对齐方法,在多种标准基准测试中达到了新的最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/AIDC-AI/CHATS
Summary
文本介绍了扩散模型在文本到图像生成中的主导地位,并指出关键组件如人类偏好对齐和分类器免费指导在确保生成质量方面起着重要作用。然而,它们在文本到图像模型中的独立应用仍然面临着实现强大的文本图像对齐、高生成质量和符合人类审美标准的一致性的挑战。本研究首次探索了人类性能对齐和测试时间采样的协作潜力,并引入了CHATS(结合人类对齐优化和测试时间采样)这一新型生成框架。它分别建模首选和不受欢迎的分布,并采用基于代理提示的采样策略来利用这两个分布中包含的有用信息。实验表明,CHATS具有出色的数据效率,仅在小型高质量微调数据集上就能实现出色性能,并且在各种标准基准测试中超过了传统偏好对齐方法,树立了新的技术标杆。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已成为文本到图像生成的主流方法。
- 文本到图像模型的独立应用面临文本图像对齐、生成质量和符合人类审美标准一致性的挑战。
- CHATS框架首次探索了人类性能对齐和测试时间采样的协作潜力。
- CHATS通过分别建模首选和不受欢迎的分布并采用基于代理提示的采样策略来提高生成质量。
- CHATS展现出出色的数据效率,仅在小型高质量微调数据集上即可实现强性能。
- 实验表明CHATS在各种标准基准测试中超过了传统偏好对齐方法。
点此查看论文截图