⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
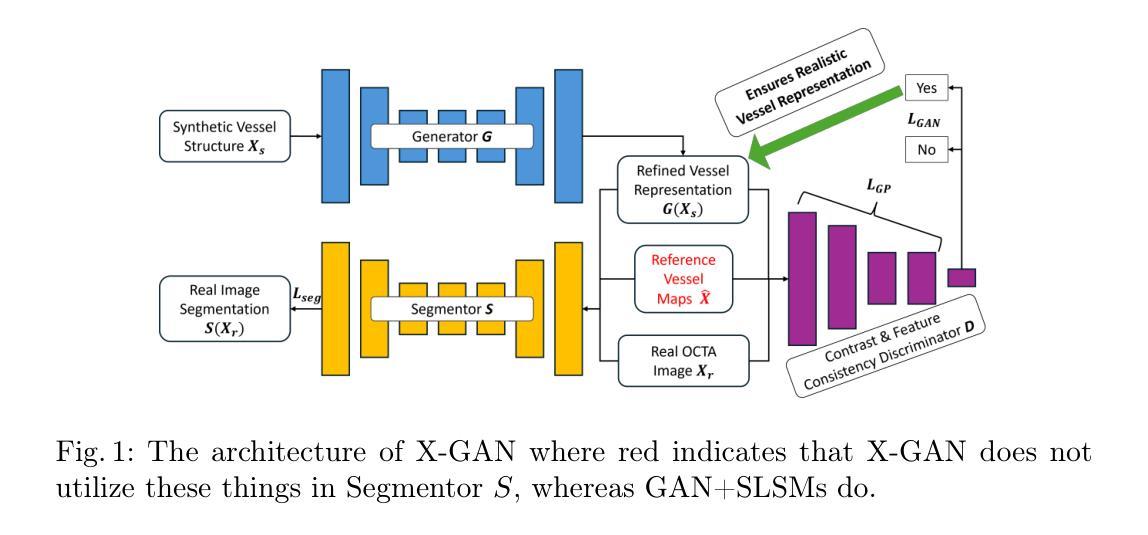
X-GAN: A Generative AI-Powered Unsupervised Model for Main Vessel Segmentation of Glaucoma Screening
Authors:Cheng Huang, Weizheng Xie, Tsengdar J. Lee, Jui-Kai Wang, Karanjit Kooner, Ning Zhang, Jia Zhang
Structural changes in main retinal blood vessels serve as critical biomarkers for the onset and progression of glaucoma. Identifying these vessels is vital for vascular modeling yet highly challenging. This paper proposes X-GAN, a generative AI-powered unsupervised segmentation model designed for extracting main blood vessels from Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) images. The process begins with the Space Colonization Algorithm (SCA) to rapidly generate a skeleton of vessels, featuring their radii. By synergistically integrating the generative adversarial network (GAN) with biostatistical modeling of vessel radii, X-GAN enables a fast reconstruction of both 2D and 3D representations of the vessels. Based on this reconstruction, X-GAN achieves nearly 100% segmentation accuracy without relying on labeled data or high-performance computing resources. Experimental results confirm X-GAN’s superiority in evaluating main vessel segmentation compared to existing deep learning models. Code is here: https://github.com/VikiXie/SatMar8.
视网膜主血管结构的变化是青光眼发生和发展的关键生物标志物。识别这些血管对血管建模至关重要,但极具挑战性。本文提出了X-GAN,这是一种基于生成式人工智能的无监督分割模型,旨在从光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像中提取主要血管。该流程始于空间殖民算法(SCA),以快速生成血管的骨架及其半径特征。通过协同整合生成对抗网络(GAN)与血管半径的生物统计建模,X-GAN能够实现血管2D和3D表示的快速重建。基于这种重建,X-GAN在不依赖标记数据或高性能计算资源的情况下实现了近100%的分割精度。实验结果证实了X-GAN在评估主血管分割方面优于现有的深度学习模型。代码地址:https://github.com/VikiXie/SatMar8。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要探讨视网膜主血管结构变化对青光眼发生和进展的重要生物标志物作用。文章提出了一种基于生成式人工智能的无监督分割模型X-GAN,用于从光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像中提取主血管。该模型通过结合空间殖民算法(SCA)和生成对抗网络(GAN),实现对血管半径的生物统计建模,能迅速重建血管的二维和三维表示,且无需依赖标记数据或高性能计算资源即可达到近100%的分割精度,优于现有深度学习模型。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜主血管结构变化是青光眼的重要生物标志物。
- X-GAN是一种基于生成式AI的无监督分割模型,用于从OCTA图像中提取主血管。
- X-GAN通过结合SCA和GAN,实现血管半径的生物统计建模。
- X-GAN能够迅速重建血管的二维和三维表示。
- X-GAN达到近100%的分割精度,且无需依赖标记数据或高性能计算资源。
- X-GAN模型在评价主血管分割方面优于现有的深度学习模型。
点此查看论文截图

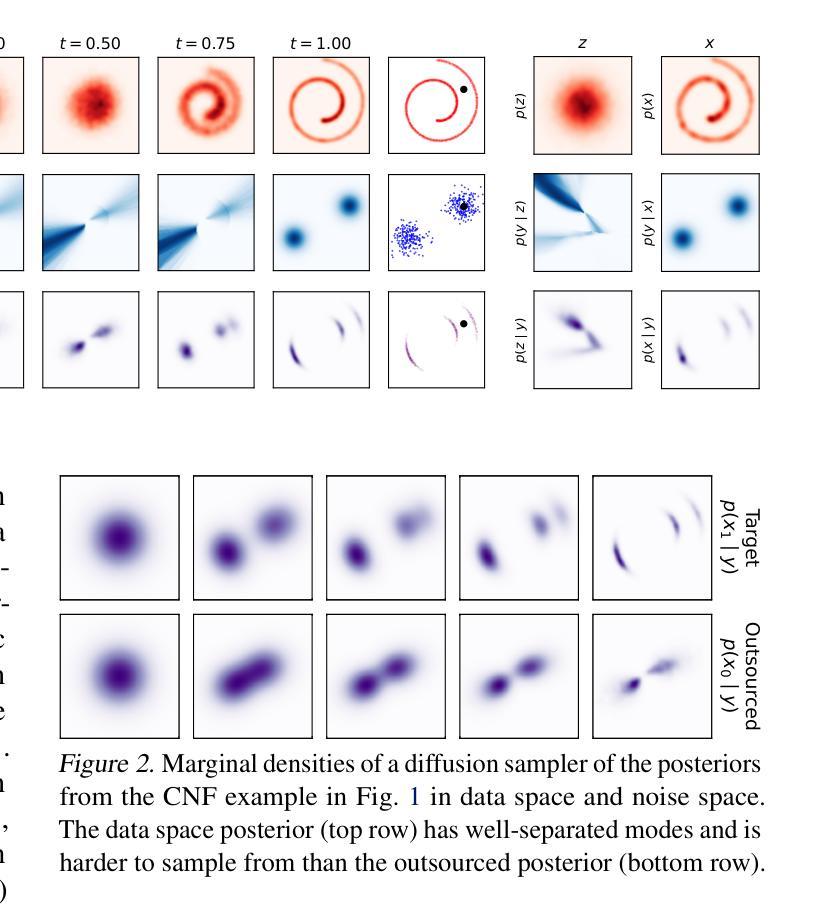
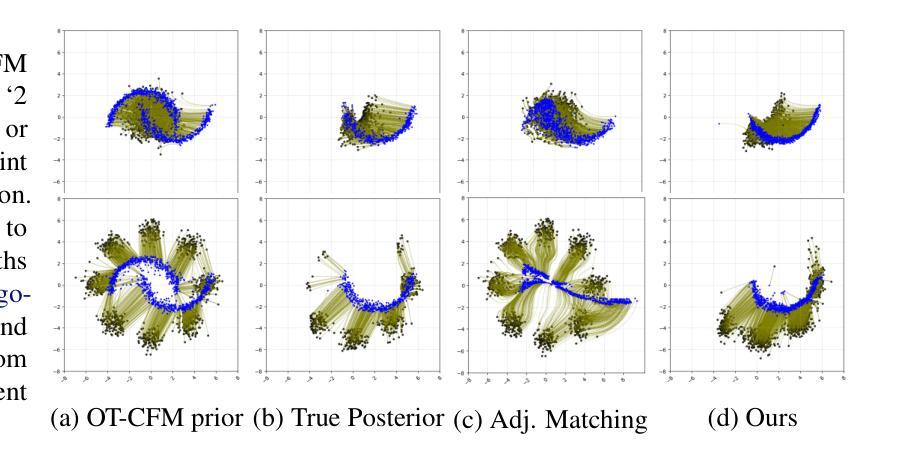
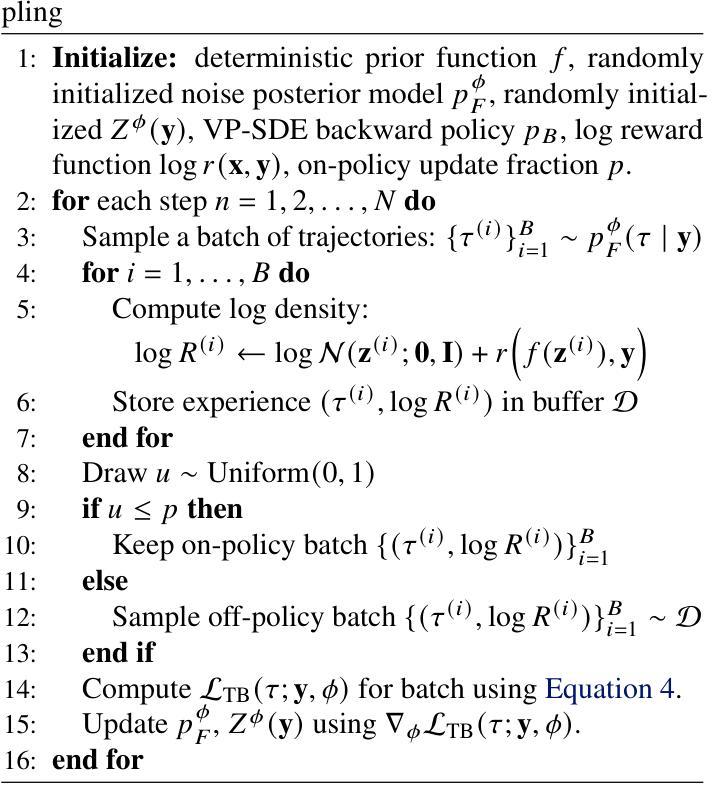
Outsourced diffusion sampling: Efficient posterior inference in latent spaces of generative models
Authors:Siddarth Venkatraman, Mohsin Hasan, Minsu Kim, Luca Scimeca, Marcin Sendera, Yoshua Bengio, Glen Berseth, Nikolay Malkin
Any well-behaved generative model over a variable $\mathbf{x}$ can be expressed as a deterministic transformation of an exogenous (‘outsourced’) Gaussian noise variable $\mathbf{z}$: $\mathbf{x}=f_\theta(\mathbf{z})$. In such a model (\eg, a VAE, GAN, or continuous-time flow-based model), sampling of the target variable $\mathbf{x} \sim p_\theta(\mathbf{x})$ is straightforward, but sampling from a posterior distribution of the form $p(\mathbf{x}\mid\mathbf{y}) \propto p_\theta(\mathbf{x})r(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y})$, where $r$ is a constraint function depending on an auxiliary variable $\mathbf{y}$, is generally intractable. We propose to amortize the cost of sampling from such posterior distributions with diffusion models that sample a distribution in the noise space ($\mathbf{z}$). These diffusion samplers are trained by reinforcement learning algorithms to enforce that the transformed samples $f_\theta(\mathbf{z})$ are distributed according to the posterior in the data space ($\mathbf{x}$). For many models and constraints, the posterior in noise space is smoother than in data space, making it more suitable for amortized inference. Our method enables conditional sampling under unconditional GAN, (H)VAE, and flow-based priors, comparing favorably with other inference methods. We demonstrate the proposed outsourced diffusion sampling in several experiments with large pretrained prior models: conditional image generation, reinforcement learning with human feedback, and protein structure generation.
任何针对变量$\mathbf{x}$的良好行为生成模型都可以表达为外源(外包)高斯噪声变量$\mathbf{z}$的确定性转换:$\mathbf{x}=f_\theta(\mathbf{z})$。在这样的模型中(例如VAE、GAN或连续时间流模型),目标变量$\mathbf{x}$的采样遵循$p_\theta(\mathbf{x})$,这是很直接的,但是从一个形式为$p(\mathbf{x}\mid\mathbf{y}) \propto p_\theta(\mathbf{x})r(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{y})$的后验分布中采样通常是难以处理的,其中$r$是依赖于辅助变量$\mathbf{y}$的限制函数。我们建议使用扩散模型来抵消从这种后验分布中采样的成本,这些扩散采样器通过强化学习算法进行训练,以确保转换后的样本$f_\theta(\mathbf{z})$在数据空间$\mathbf{x}$中根据后验分布。对于许多模型和约束,噪声空间中的后验比在数据空间中的更平滑,这使其成为更适用于抵消推理的方法。我们的方法可在无条件GAN、(H)VAE和基于流的先验条件下实现条件采样,与其他推理方法相比具有优势。我们通过几个使用大型预训练先验模型的实验展示了外包扩散采样的效果:条件图像生成、带有人类反馈的强化学习以及蛋白质结构生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025; code: https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/Outsourced_Diffusion_Sampling
Summary
该文本介绍了一种利用扩散模型在噪声空间进行采样的方法,以实现对目标变量$\mathbf{x}$的后验分布采样。该方法适用于各种生成模型,如VAE、GAN和连续时间流模型。通过强化学习算法训练扩散采样器,使得变换后的样本$f_\theta(\mathbf{z})$在数据空间中的分布符合后验分布。该方法在多个实验中得到验证,如条件图像生成、带有人类反馈的强化学习和蛋白质结构生成。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型可以通过将目标变量$\mathbf{x}$表示为外源高斯噪声变量$\mathbf{z}$的确定性转换来表达。
- 采样目标变量$\mathbf{x}$相对简单,但从后验分布$p(\mathbf{x}\mid\mathbf{y})$采样通常不可行。
- 扩散模型被用来在噪声空间进行采样,以减轻从后验分布采样的成本。
- 扩散采样器通过强化学习算法进行训练,以确保变换后的样本在数据空间中符合后验分布。
- 对于许多模型和约束,噪声空间中的后验分布比数据空间更平滑,适合进行推理。
- 所提出的方法可以在无条件GAN、(H)VAE和流基先验下进行条件采样。
点此查看论文截图