⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
UAVPairs: A Challenging Benchmark for Match Pair Retrieval of Large-scale UAV Images
Authors:Junhuan Liu, San Jiang, Wei Ge, Wei Huang, Bingxuan Guo, Qingquan Li
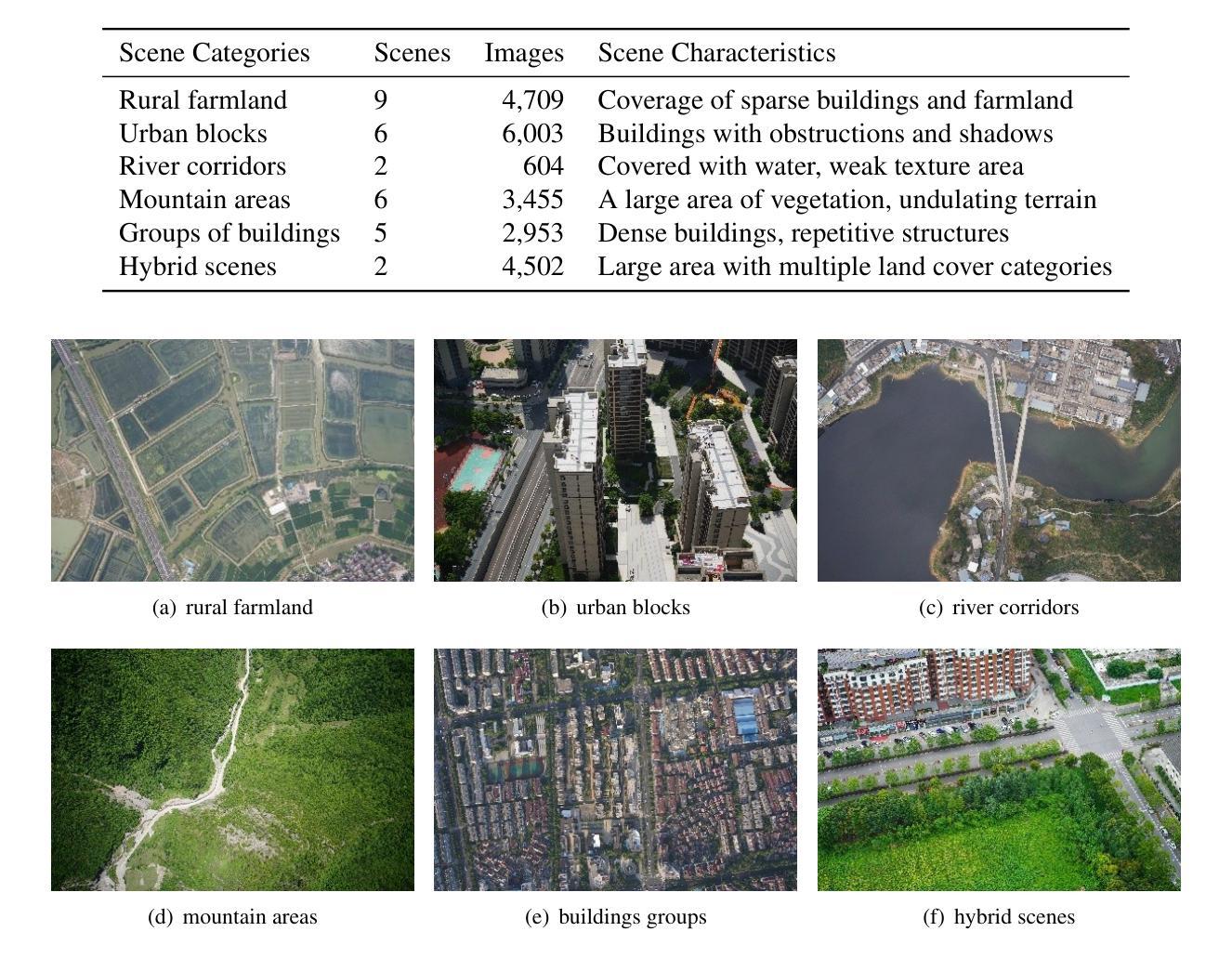
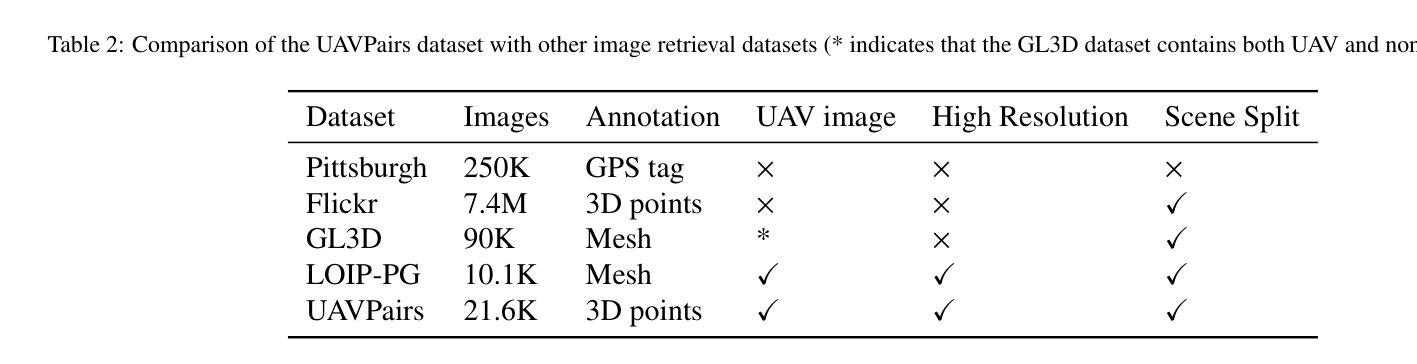
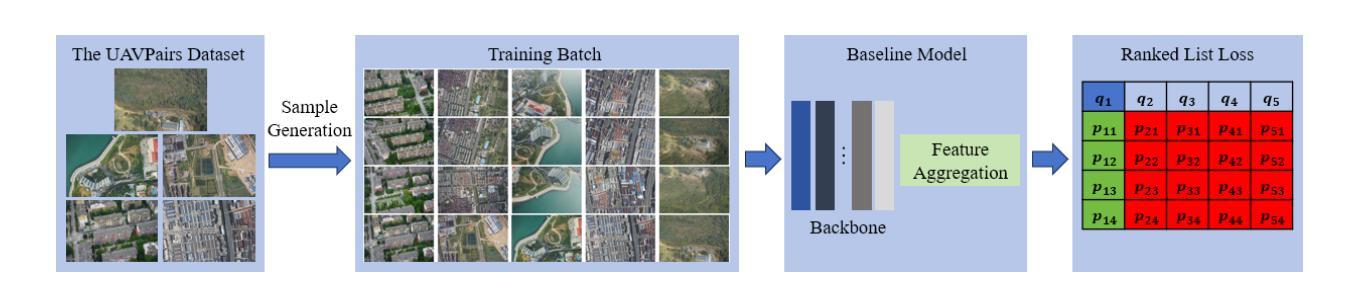
The primary contribution of this paper is a challenging benchmark dataset, UAVPairs, and a training pipeline designed for match pair retrieval of large-scale UAV images. First, the UAVPairs dataset, comprising 21,622 high-resolution images across 30 diverse scenes, is constructed; the 3D points and tracks generated by SfM-based 3D reconstruction are employed to define the geometric similarity of image pairs, ensuring genuinely matchable image pairs are used for training. Second, to solve the problem of expensive mining cost for global hard negative mining, a batched nontrivial sample mining strategy is proposed, leveraging the geometric similarity and multi-scene structure of the UAVPairs to generate training samples as to accelerate training. Third, recognizing the limitation of pair-based losses, the ranked list loss is designed to improve the discrimination of image retrieval models, which optimizes the global similarity structure constructed from the positive set and negative set. Finally, the effectiveness of the UAVPairs dataset and training pipeline is validated through comprehensive experiments on three distinct large-scale UAV datasets. The experiment results demonstrate that models trained with the UAVPairs dataset and the ranked list loss achieve significantly improved retrieval accuracy compared to models trained on existing datasets or with conventional losses. Furthermore, these improvements translate to enhanced view graph connectivity and higher quality of reconstructed 3D models. The models trained by the proposed approach perform more robustly compared with hand-crafted global features, particularly in challenging repetitively textured scenes and weakly textured scenes. For match pair retrieval of large-scale UAV images, the trained image retrieval models offer an effective solution. The dataset would be made publicly available at https://github.com/json87/UAVPairs.
本文的主要贡献是构建了一个具有挑战性的基准数据集UAVPairs,以及为大规模无人机图像匹配对检索设计的训练流程。首先,构建了UAVPairs数据集,包含30个不同场景的21622张高分辨率图像;采用基于SfM的3D重建生成的3D点和轨迹来定义图像对之间的几何相似性,确保使用真正可匹配的图像对进行训练。其次,针对全局硬负样本挖掘成本高昂的问题,提出了一种批量非平凡样本挖掘策略,利用UAVPairs的几何相似性和多场景结构生成训练样本,以加速训练。第三,认识到基于对的损失函数的局限性,设计了排名列表损失,以提高图像检索模型的辨别力,该损失函数优化了由正集和负集构建的全局相似性结构。最后,通过在三组不同的大规模无人机数据集上进行的综合实验验证了UAVPairs数据集和训练流程的有效性。实验结果表明,与在现有数据集上训练或采用传统损失的模型相比,使用UAVPairs数据集和排名列表损失训练的模型在检索精度上取得了显著提高。此外,这些改进转化为更好的视图图连接和更高的3D模型质量。与手工设计的全局特征相比,采用所提出方法训练的模型表现得更加稳健,特别是在具有挑战性的重复纹理场景和弱纹理场景中。对于大规模无人机图像的匹配对检索,经过训练的图像检索模型提供了一种有效的解决方案。该数据集将在https://github.com/json87/UAVPairs上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文构建了一个名为UAVPairs的大规模高分辨率无人机图像匹配对检索基准数据集及训练流程。数据集包含多样化的真实场景图像和精确的几何标注,可用于训练图像检索模型。论文提出了一种低成本的全局硬负样本挖掘策略,并设计了排名列表损失函数以提高模型的鉴别能力。实验证明,使用UAVPairs数据集和排名列表损失的模型在大型无人机图像检索任务中具有显著提升的准确性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- UAVPairs数据集是一个大规模的无人机图像匹配对检索基准数据集,包含多样化的真实场景图像和精确的几何标注。
- 采用SfM-based 3D重建技术来定义图像对之间的几何相似性,确保匹配对真实性。
- 提出了一种低成本的全局硬负样本挖掘策略,利用UAVPairs数据集的几何相似性和多场景结构生成训练样本,加快训练速度。
- 设计了排名列表损失函数来改善图像检索模型的鉴别能力,优化全局相似性结构。
点此查看论文截图



Collaborative Learning for Unsupervised Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration: Integrating Self-Supervision and MIM-Guided Diffusion-Based Image Translation
Authors:Xiaochen Wei, Weiwei Guo, Wenxian Yu
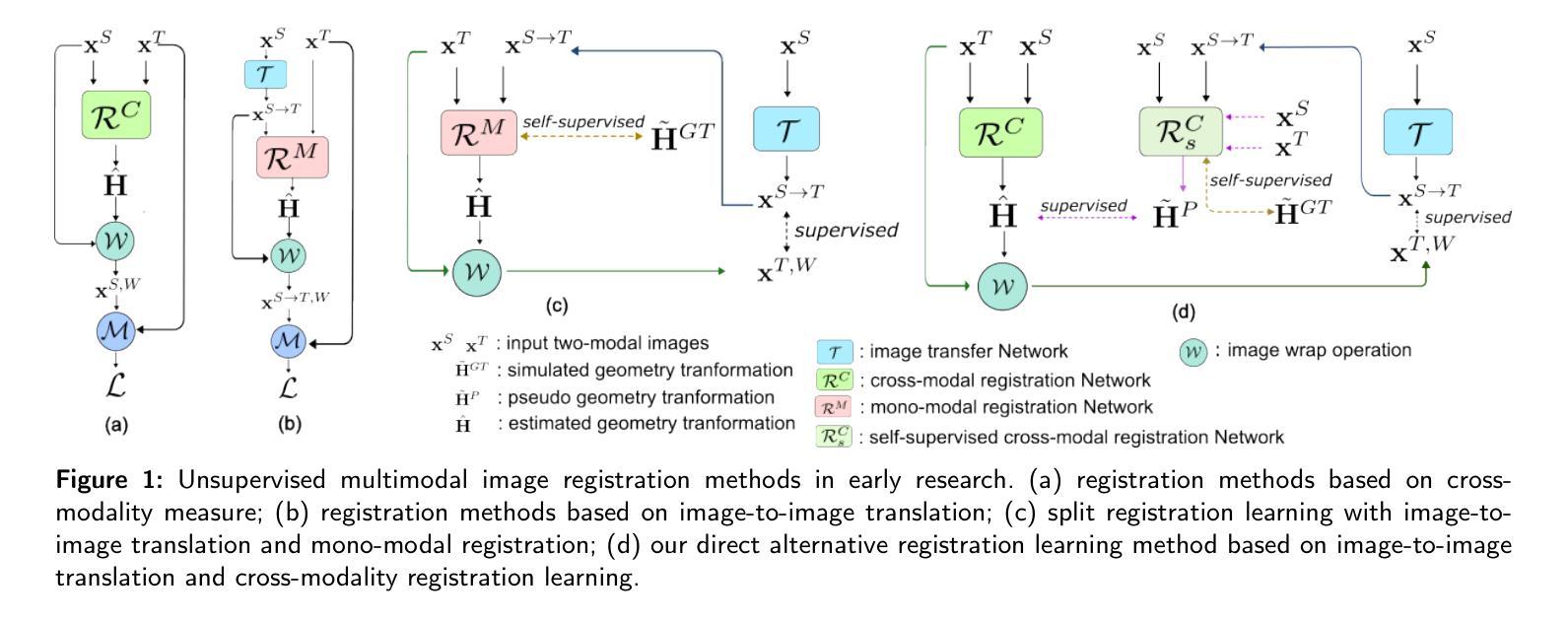
The substantial modality-induced variations in radiometric, texture, and structural characteristics pose significant challenges for the accurate registration of multimodal images. While supervised deep learning methods have demonstrated strong performance, they often rely on large-scale annotated datasets, limiting their practical application. Traditional unsupervised methods usually optimize registration by minimizing differences in feature representations, yet often fail to robustly capture geometric discrepancies, particularly under substantial spatial and radiometric variations, thus hindering convergence stability. To address these challenges, we propose a Collaborative Learning framework for Unsupervised Multimodal Image Registration, named CoLReg, which reformulates unsupervised registration learning into a collaborative training paradigm comprising three components: (1) a cross-modal image translation network, MIMGCD, which employs a learnable Maximum Index Map (MIM) guided conditional diffusion model to synthesize modality-consistent image pairs; (2) a self-supervised intermediate registration network which learns to estimate geometric transformations using accurate displacement labels derived from MIMGCD outputs; (3) a distilled cross-modal registration network trained with pseudo-label predicted by the intermediate network. The three networks are jointly optimized through an alternating training strategy wherein each network enhances the performance of the others. This mutual collaboration progressively reduces modality discrepancies, enhances the quality of pseudo-labels, and improves registration accuracy. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that our ColReg achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art unsupervised approaches and even surpasses several supervised baselines.
在辐射测量、纹理和结构特征方面,不同模态引起的巨大变化为多模态图像的准确配准带来了重大挑战。虽然监督深度学习的方法已经取得了很好的性能表现,但它们通常依赖于大规模标注数据集,从而限制了其实践应用。传统的无监督方法通常通过最小化特征表示的差异性来优化配准,但它们往往不能稳健地捕获几何差异,特别是在较大的空间变化和辐射测量变化下,从而阻碍了收敛稳定性。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种名为CoLReg的无监督多模态图像配准的协同学习框架,它将无监督配准学习重新制定为一种协同训练模式,包括三个组成部分:(1)一种跨模态图像转换网络MIMGCD,它采用可学习的最大索引图(MIM)引导的条件扩散模型来合成模态一致的图像对;(2)一个自监督的中间配准网络,它学习使用由MIMGCD输出派生的准确位移标签来估计几何变换;(3)一个通过中间网络预测的伪标签训练的蒸馏跨模态配准网络。这三个网络通过交替训练策略进行联合优化,每个网络都增强了其他网络的性能。这种相互协作的方式逐步减少了模态差异,提高了伪标签的质量,并提高了配准的准确性。在多个数据集上的广泛实验结果表明,我们的ColReg与最先进的无监督方法相比具有竞争力或更优越的性能表现,甚至超越了若干监督基准方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
提出一种名为ColReg的协同学习框架,用于无监督多模态图像配准。该框架包括三个组件:跨模态图像翻译网络MIMGCD、自监督中间配准网络和蒸馏跨模态配准网络。它们通过交替训练策略共同优化,逐步减少模态差异,提高伪标签质量,并改善配准精度。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,ColReg与现有先进无监督方法相比具有竞争力或更优越的性能,甚至超越了一些有监督的基线。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态图像配准面临辐射度量、纹理和结构特性上的挑战。
- 现有方法包括基于深度学习的监督方法和传统无监督方法,但各有局限性。
- 提出的ColReg框架包含三个组件:MIMGCD网络进行跨模态图像翻译,中间网络进行自监督学习估计几何变换,蒸馏网络使用中间网络的伪标签进行训练。
- 三个网络通过交替训练策略共同优化,提高配准精度和伪标签质量。
- ColReg在多个数据集上的表现与现有先进无监督方法相比具有竞争力或更优越。
- ColReg甚至在某些情况下超越了监督方法基线。
点此查看论文截图


Subspecialty-Specific Foundation Model for Intelligent Gastrointestinal Pathology
Authors:Lianghui Zhu, Xitong Ling, Minxi Ouyang, Xiaoping Liu, Mingxi Fu, Tian Guan, Fanglei Fu, Xuanyu Wang, Maomao Zeng, Mingxi Zhu, Yibo Jin, Liming Liu, Song Duan, Qiming He, Yizhi Wang, Luxi Xie, Houqiang Li, Yonghong He, Sufang Tian
Gastrointestinal (GI) diseases represent a clinically significant burden, necessitating precise diagnostic approaches to optimize patient outcomes. Conventional histopathological diagnosis, heavily reliant on the subjective interpretation of pathologists, suffers from limited reproducibility and diagnostic variability. To overcome these limitations and address the lack of pathology-specific foundation models for GI diseases, we develop Digepath, a specialized foundation model for GI pathology. Our framework introduces a dual-phase iterative optimization strategy combining pretraining with fine-screening, specifically designed to address the detection of sparsely distributed lesion areas in whole-slide images. Digepath is pretrained on more than 353 million image patches from over 200,000 hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides of GI diseases. It attains state-of-the-art performance on 33 out of 34 tasks related to GI pathology, including pathological diagnosis, molecular prediction, gene mutation prediction, and prognosis evaluation, particularly in diagnostically ambiguous cases and resolution-agnostic tissue classification.We further translate the intelligent screening module for early GI cancer and achieve near-perfect 99.6% sensitivity across 9 independent medical institutions nationwide. The outstanding performance of Digepath highlights its potential to bridge critical gaps in histopathological practice. This work not only advances AI-driven precision pathology for GI diseases but also establishes a transferable paradigm for other pathology subspecialties.
胃肠道(GI)疾病在临床上有显著的重要性,因此需要精确的诊断方法来优化患者治疗效果。传统的组织病理学诊断严重依赖于病理学家的主观判断,存在可重复性差和诊断结果不稳定的问题。为了克服这些限制并解决胃肠道疾病病理特征缺乏基础模型的问题,我们开发了Digepath,这是一个专门针对胃肠道病理学的专门基础模型。我们的框架引入了一种两阶段迭代优化策略,结合预训练和精细筛选,专门用于解决在全幻灯片图像中检测稀疏分布的病变区域的问题。Digepath在超过20万个胃肠道疾病苏木精和伊红染色幻灯片的超过3.53亿个图像斑块上进行预训练。在涉及胃肠道病理学的34项任务中的33项上取得了最先进的性能,包括病理诊断、分子预测、基因突变预测和预后评估,特别是在诊断模糊和分辨率无关的组织分类方面。我们将智能筛选模块用于早期胃肠道癌症筛查,并在全国9家独立医疗机构实现了近完美的99.6%灵敏度。Digepath的出色性能突显了其在组织病理学实践中弥合重要差距的潜力。这项工作不仅推动了人工智能驱动的胃肠道疾病的精准病理学发展,而且为其他病理学专科建立了可借鉴的模式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
数字化胃肠道病理模型Digepath的研发突破,解决胃肠道疾病诊断难题。通过预训练与精细筛选的双阶段迭代优化策略,实现对全切片图像中稀疏病灶区域的检测。在胃肠道病理相关34项任务中取得最佳性能,包括病理诊断、分子预测、基因突变预测和预后评估等。智能筛查模块对早期胃肠道癌症检测灵敏度达99.6%,全国9家独立医疗机构验证。展现出巨大潜力,推动AI精准病理学在胃肠道疾病领域的发展,并为其他病理专科提供可借鉴的范例。
Key Takeaways:
- Digepath模型是针对胃肠道疾病病理诊断的专门基础模型。
- 该模型采用预训练与精细筛选相结合的双阶段迭代优化策略。
- Digepath模型能在全切片图像中检测稀疏病灶区域。
- Digepath模型在胃肠道病理多个任务上表现优异,包括诊断、分子预测和预后评估等。
- 智能筛查模块对早期胃肠道癌症检测具有很高的灵敏度(99.6%)。
- Digepath模型的成功应用为AI在胃肠道疾病领域的精准病理学提供了发展动力。
点此查看论文截图

UniDB: A Unified Diffusion Bridge Framework via Stochastic Optimal Control
Authors:Kaizhen Zhu, Mokai Pan, Yuexin Ma, Yanwei Fu, Jingyi Yu, Jingya Wang, Ye Shi
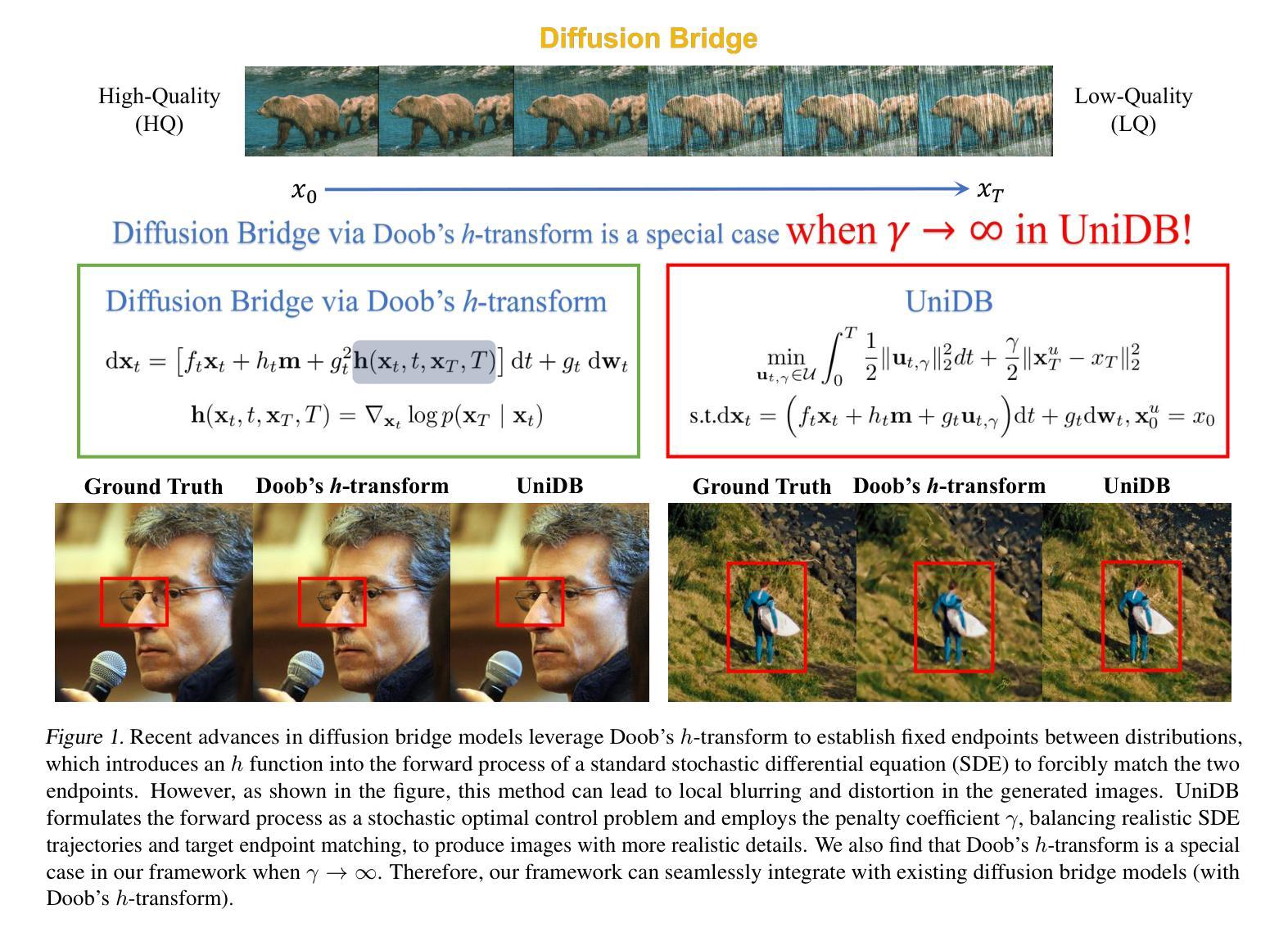
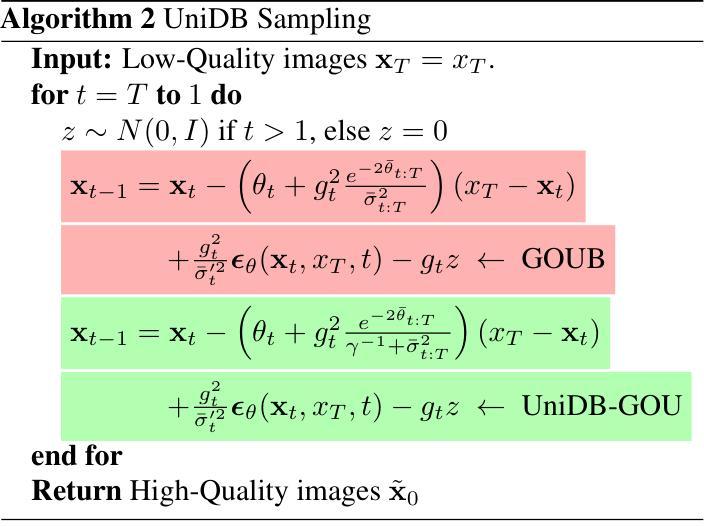
Recent advances in diffusion bridge models leverage Doob’s $h$-transform to establish fixed endpoints between distributions, demonstrating promising results in image translation and restoration tasks. However, these approaches frequently produce blurred or excessively smoothed image details and lack a comprehensive theoretical foundation to explain these shortcomings. To address these limitations, we propose UniDB, a unified framework for diffusion bridges based on Stochastic Optimal Control (SOC). UniDB formulates the problem through an SOC-based optimization and derives a closed-form solution for the optimal controller, thereby unifying and generalizing existing diffusion bridge models. We demonstrate that existing diffusion bridges employing Doob’s $h$-transform constitute a special case of our framework, emerging when the terminal penalty coefficient in the SOC cost function tends to infinity. By incorporating a tunable terminal penalty coefficient, UniDB achieves an optimal balance between control costs and terminal penalties, substantially improving detail preservation and output quality. Notably, UniDB seamlessly integrates with existing diffusion bridge models, requiring only minimal code modifications. Extensive experiments across diverse image restoration tasks validate the superiority and adaptability of the proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/UniDB-SOC/UniDB/.
近期扩散桥模型的新进展利用Doob的h变换来建立分布之间的固定端点,在图像翻译和恢复任务中展现出有前景的结果。然而,这些方法经常产生模糊或过度平滑的图像细节,并且缺乏全面的理论基础来解释这些不足。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了基于随机最优控制(SOC)的扩散桥统一框架UniDB。UniDB通过基于SOC的优化来制定问题,并推导出最优控制器的封闭形式解决方案,从而统一并推广了现有的扩散桥模型。我们证明,采用Doob的h变换的现有扩散桥构成了我们框架的一种特殊情况,出现在SOC成本函数的终端惩罚系数趋于无穷大时。通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,UniDB实现了控制成本和终端惩罚之间的最佳平衡,大大提高了细节保留和输出质量。值得注意的是,UniDB可以无缝地融入现有的扩散桥模型,只需要最少的代码修改。在不同图像恢复任务上的大量实验验证了所提出框架的优越性和适应性。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/UniDB-SOC/UniDB/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于随机最优控制(SOC)的UniDB统一框架解决了扩散桥梁模型在图像翻译和恢复任务中的模糊或过度平滑问题。该框架通过SOC优化问题公式化,推导出最优控制器的封闭解,统一并推广了现有的扩散桥梁模型。通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,UniDB实现了控制成本和终端惩罚之间的最佳平衡,提高了细节保留和输出质量。此外,UniDB与现有扩散桥梁模型无缝集成,只需进行最小的代码修改。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散桥梁模型利用Doob的h变换在图像翻译和恢复任务中建立固定端点。
- 现有方法经常产生模糊或过度平滑的图像细节,缺乏全面的理论来解释这些缺点。
- UniDB是一个基于随机最优控制的统一框架,解决了现有扩散桥梁模型的局限性。
- UniDB通过SOC优化问题公式化,推导出最优控制器的封闭解。
- UniDB通过引入可调终端惩罚系数,实现了控制成本和终端惩罚之间的平衡。
- UniDB提高了图像细节保留和输出质量。
点此查看论文截图

Go With the Flow: Fast Diffusion for Gaussian Mixture Models
Authors:George Rapakoulias, Ali Reza Pedram, Fengjiao Liu, Lingjiong Zhu, Panagiotis Tsiotras
Schrodinger Bridges (SBs) are diffusion processes that steer, in finite time, a given initial distribution to another final one while minimizing a suitable cost functional. Although various methods for computing SBs have recently been proposed in the literature, most of these approaches require computationally expensive training schemes, even for solving low-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an analytic parametrization of a set of feasible policies for steering the distribution of a dynamical system from one Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to another. Instead of relying on standard non-convex optimization techniques, the optimal policy within the set can be approximated as the solution of a low-dimensional linear program whose dimension scales linearly with the number of components in each mixture. The proposed method generalizes naturally to more general classes of dynamical systems, such as controllable linear time-varying systems, enabling efficient solutions to multi-marginal momentum SB between GMMs, a challenging distribution interpolation problem. We showcase the potential of this approach in low-to-moderate dimensional problems such as image-to-image translation in the latent space of an autoencoder, learning of cellular dynamics using multi-marginal momentum SB problems, and various other examples. We also test our approach on an Entropic Optimal Transport (EOT) benchmark problem and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cases where the boundary distributions are mixture models while requiring virtually no training.
薛定谔桥(SBs)是一类扩散过程,可以在有限时间内从给定的初始分布引导到另一个最终分布,同时最小化合适的成本函数。尽管最近文献中提出了多种计算SB的方法,但即使对于解决低维问题,大多数这些方法也需要计算昂贵的训练方案。在这项工作中,我们提出了一套可行的策略分析参数化方法,用于从高斯混合模型(GMM)引导动态系统的分布到另一个高斯混合模型。我们并不依赖于标准的非凸优化技术,而是将集合中的最佳策略近似为低维线性规划问题的解,其维度与每个混合中的组件数量呈线性关系。所提出的方法自然地推广到更一般的动态系统类,如可控线性时变系统,为解决高斯混合模型之间的多边缘动量SB、一个具有挑战性的分布插值问题提供了高效解决方案。我们展示了这种方法在诸如自编码器的潜在空间中的图像到图像翻译、使用多边缘动量SB问题学习细胞动力学等低维到中等维度的潜在应用以及各种其他示例。我们还通过在熵最优传输(EOT)基准测试问题上测试我们的方法,并证明在边界分布为混合模型的情况下,它的性能优于现有先进技术,同时几乎不需要进行训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文提出一种基于高斯混合模型(GMM)的动力系统分布调控的解析参数化方法。通过线性规划求解最优策略,避免了高维非凸优化技术的依赖,提高了计算效率,并自然推广到更一般的动力系统。在图像翻译、细胞动力学模拟等应用中展现了潜力,并在熵最优传输(EOT)基准测试中表现出优于现有方法的效果。
Key Takeaways:
- Schrodinger Bridges (SBs) 是通过最小化成本函数在一定时间内从初始分布转向最终分布的过程。
- 目前计算SBs的方法多数需要昂贵的训练成本,即使解决低维问题也是如此。
- 本文提出了一种对可控策略集进行解析参数化的方法,适用于从高斯混合模型(GMM)到另一个GMM的动力系统分布调控。
- 通过低维线性规划求解最优策略,其维度与混合中组件的数量成线性关系。
- 该方法可自然推广到更一般的动力系统,如可控线性时变系统。
- 该方法在图像翻译、细胞动力学模拟等应用中表现出潜力。
点此查看论文截图

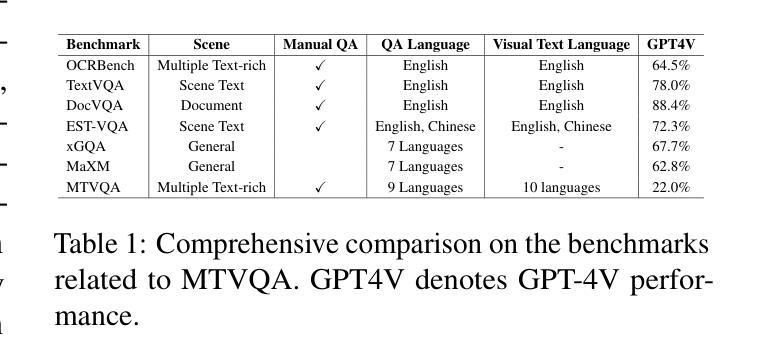
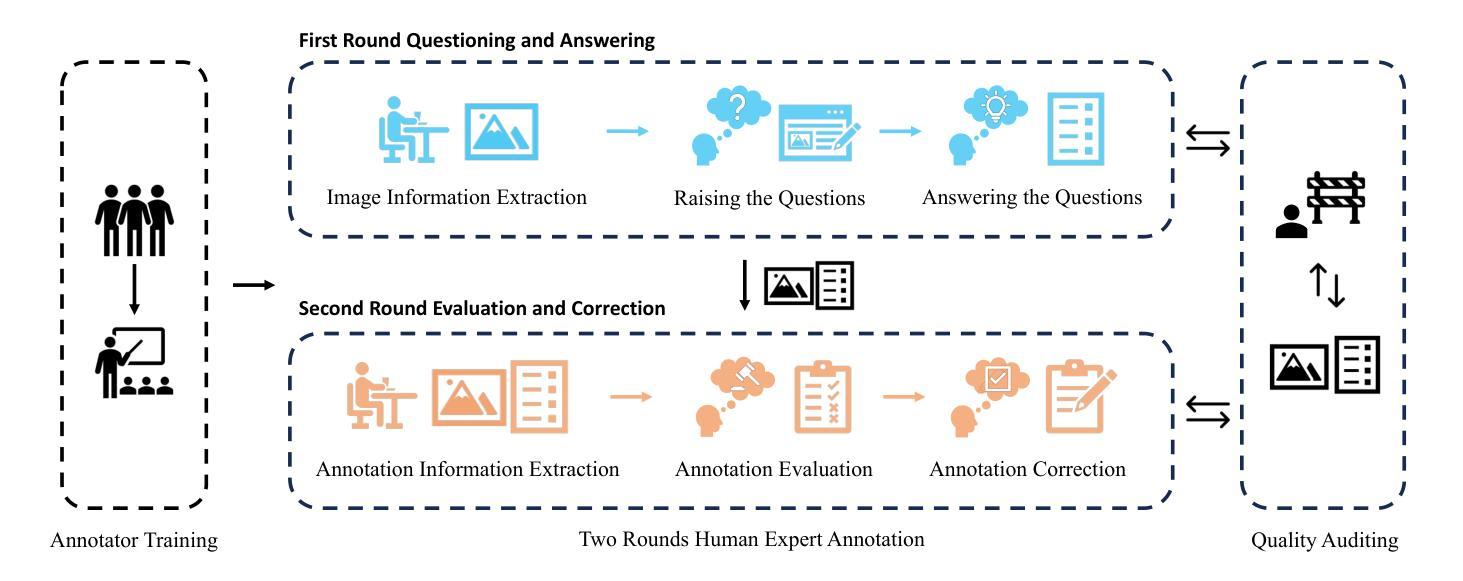
MTVQA: Benchmarking Multilingual Text-Centric Visual Question Answering
Authors:Jingqun Tang, Qi Liu, Yongjie Ye, Jinghui Lu, Shu Wei, Chunhui Lin, Wanqing Li, Mohamad Fitri Faiz Bin Mahmood, Hao Feng, Zhen Zhao, Yanjie Wang, Yuliang Liu, Hao Liu, Xiang Bai, Can Huang
Text-Centric Visual Question Answering (TEC-VQA) in its proper format not only facilitates human-machine interaction in text-centric visual environments but also serves as a de facto gold proxy to evaluate AI models in the domain of text-centric scene understanding. Nonetheless, most existing TEC-VQA benchmarks have focused on high-resource languages like English and Chinese. Despite pioneering works to expand multilingual QA pairs in non-text-centric VQA datasets through translation engines, the translation-based protocol encounters a substantial “visual-textual misalignment” problem when applied to TEC-VQA. Specifically, it prioritizes the text in question-answer pairs while disregarding the visual text present in images. Moreover, it fails to address complexities related to nuanced meaning, contextual distortion, language bias, and question-type diversity. In this work, we tackle multilingual TEC-VQA by introducing MTVQA, the first benchmark featuring high-quality human expert annotations across 9 diverse languages, consisting of 6,778 question-answer pairs across 2,116 images. Further, by comprehensively evaluating numerous state-of-the-art Multimodal Large Language Models~(MLLMs), including Qwen2-VL, GPT-4o, GPT-4V, Claude3, and Gemini, on the MTVQA benchmark, it is evident that there is still a large room for performance improvement (Qwen2-VL scoring 30.9 versus 79.7 for human performance), underscoring the value of MTVQA. Additionally, we supply multilingual training data within the MTVQA dataset, demonstrating that straightforward fine-tuning with this data can substantially enhance multilingual TEC-VQA performance. We aspire that MTVQA will offer the research community fresh insights and stimulate further exploration in multilingual visual text comprehension. The project homepage is available at https://bytedance.github.io/MTVQA/.
文本聚焦的视觉问答(TEC-VQA)在适当的形式下,不仅促进了文本为中心的视觉环境中的人机交互,而且还作为评估文本为中心的场景理解领域的人工智能模型的黄金标准代理。然而,现有的TEC-VQA基准测试主要关注英语和中文等资源丰富语言。尽管在非文本为中心的VQA数据集中通过翻译引擎扩大跨语言问答对的开创性工作已经开展,但基于翻译协议的协议在应用于TEC-VQA时遇到了重大的“视觉文本不对齐”问题。具体来说,它优先考虑问答对中的文本,而忽视图像中呈现的视觉文本。此外,它未能解决与微妙含义、上下文扭曲、语言偏见和问题类型多样性相关的复杂性。在这项工作中,我们通过引入MTVQA来解决多语言TEC-VQA问题,MTVQA是第一个跨越9种不同语言的基准测试,具有高质量的人类专家注释,包含跨2,116张图像的6,778个问答对。此外,通过全面评估许多最新的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),包括Qwen2-VL、GPT-4o、GPT-4V、Claude3和Gemini在MTVQA基准上的表现,显然还有很大的性能改进空间(Qwen2-VL得分为30.9分,人类性能得分为79.7分),这突显了MTVQA的价值。另外,我们在MTVQA数据集中提供了多语言训练数据,证明使用此数据进行微调可以大大提高多语言TEC-VQA的性能。我们期望MTVQA能为研究界提供新的见解,并激发对多语言视觉文本理解领域的进一步探索。项目主页可在https://bytedance.github.io/MTVQA/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 findings
Summary
本文介绍了针对文本中心型视觉问答(TEC-VQA)的多语言基准测试MTVQA。MTVQA首次引入高质量的人类专家在九种不同语言的注释,解决现有TEC-VQA基准测试偏重于高资源语言的问题。通过对多种先进的多模态大型语言模型在MTVQA基准测试上的全面评估,显示仍有很大的性能提升空间。此外,MTVQA还提供多语言训练数据,证明直接使用这些数据进行微调可以显著提高多语言TEC-VQA的性能。本文旨在提供新的视角并激发对多语言视觉文本理解领域的进一步探索。项目主页可通过链接访问。
Key Takeaways
- MTVQA是首个针对文本中心型视觉问答(TEC-VQA)的多语言基准测试,包含九种语言的多样化高质量人类专家注释。
- 当前TEC-VQA基准测试主要关注高资源语言,如英语和中文。
- 翻译协议应用于TEC-VQA时存在“视觉文本不对齐”问题。
- MTVQA解决了与翻译协议相关的复杂问题,包括细微意义、上下文失真、语言偏见和问题类型多样性等。
- 在MTVQA基准测试中评估了多种先进的多模态大型语言模型,显示性能提升空间巨大。
- MTVQA提供多语言训练数据,证明微调这些数据能显著提高多语言TEC-VQA性能。
点此查看论文截图