⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
3DLLM-Mem: Long-Term Spatial-Temporal Memory for Embodied 3D Large Language Model
Authors:Wenbo Hu, Yining Hong, Yanjun Wang, Leison Gao, Zibu Wei, Xingcheng Yao, Nanyun Peng, Yonatan Bitton, Idan Szpektor, Kai-Wei Chang
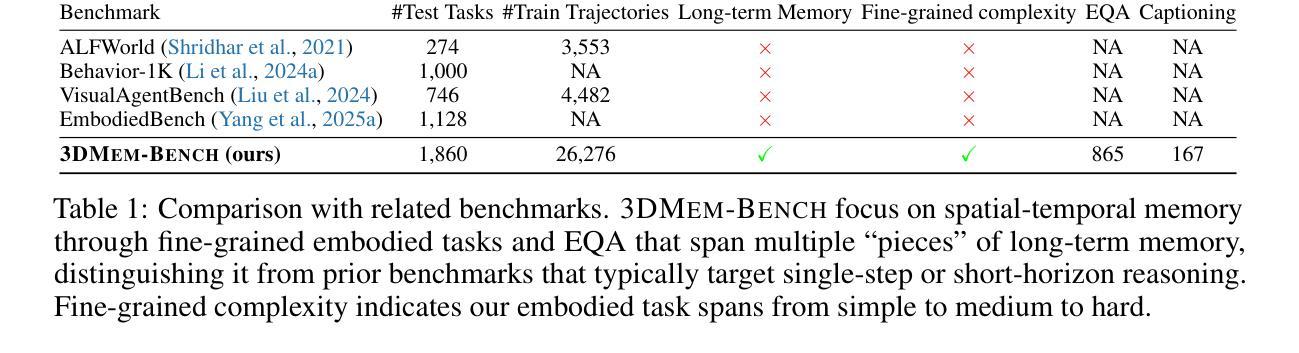
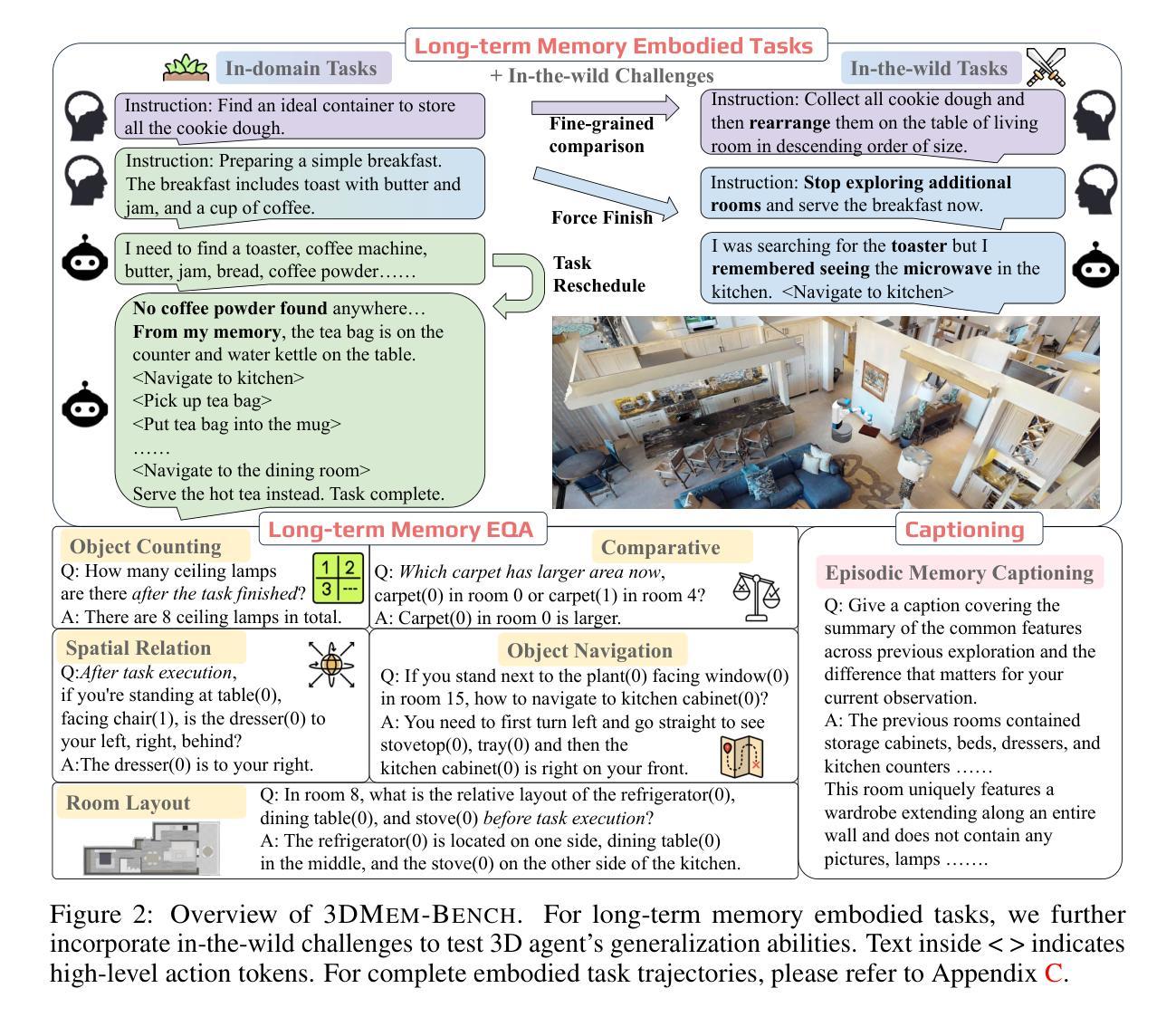
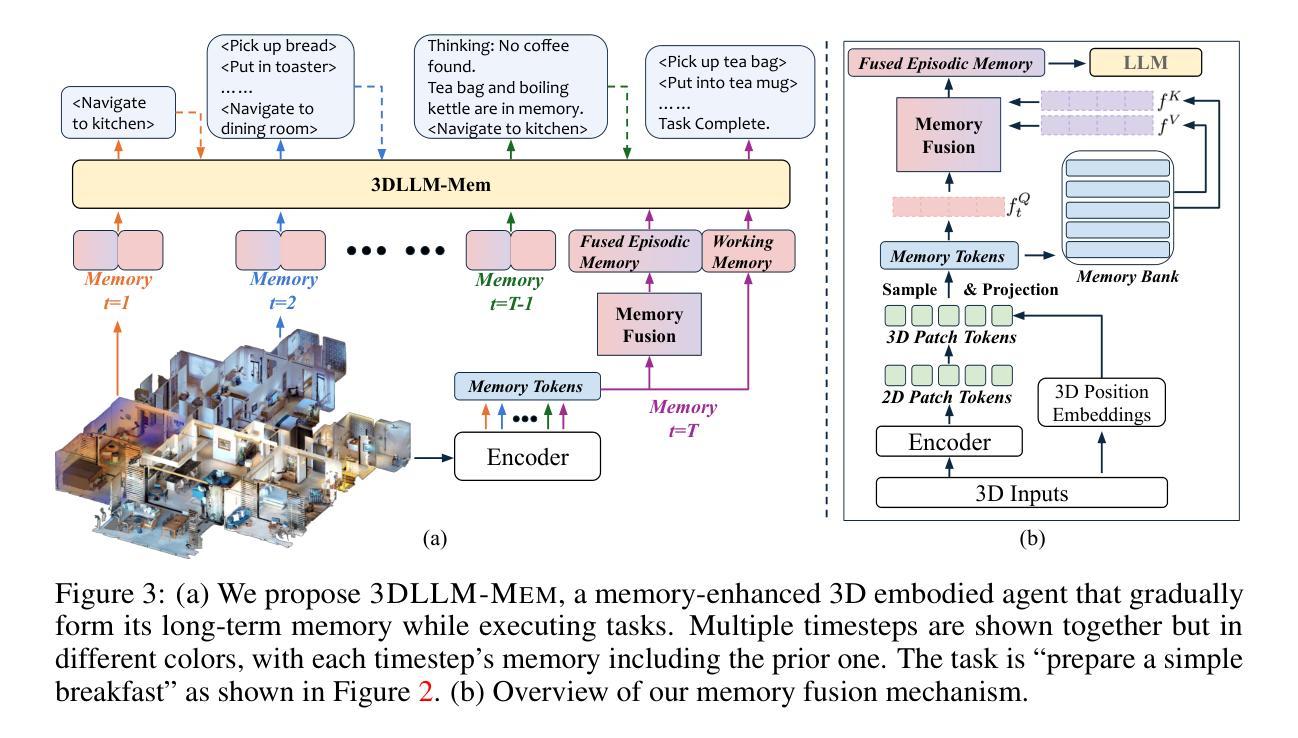
Humans excel at performing complex tasks by leveraging long-term memory across temporal and spatial experiences. In contrast, current Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to effectively plan and act in dynamic, multi-room 3D environments. We posit that part of this limitation is due to the lack of proper 3D spatial-temporal memory modeling in LLMs. To address this, we first introduce 3DMem-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark comprising over 26,000 trajectories and 2,892 embodied tasks, question-answering and captioning, designed to evaluate an agent’s ability to reason over long-term memory in 3D environments. Second, we propose 3DLLM-Mem, a novel dynamic memory management and fusion model for embodied spatial-temporal reasoning and actions in LLMs. Our model uses working memory tokens, which represents current observations, as queries to selectively attend to and fuse the most useful spatial and temporal features from episodic memory, which stores past observations and interactions. Our approach allows the agent to focus on task-relevant information while maintaining memory efficiency in complex, long-horizon environments. Experimental results demonstrate that 3DLLM-Mem achieves state-of-the-art performance across various tasks, outperforming the strongest baselines by 16.5% in success rate on 3DMem-Bench’s most challenging in-the-wild embodied tasks.
人类在利用长期记忆进行跨时间和空间的经验方面表现出卓越的能力,从而完成复杂的任务。然而,当前的大型语言模型(LLM)在动态的多房间三维环境中进行有效规划和行动方面存在困难。我们认为,这种限制的一部分是由于LLM中缺乏适当的三维时空记忆建模。为了解决这一问题,我们首先引入了3DMem-Bench,这是一个包含超过26,000个轨迹和2,892个任务的综合性基准测试,包括问答和描述生成任务,旨在评估代理在三维环境中利用长期记忆进行推理的能力。其次,我们提出了3DLLM-Mem,这是一种新型的动态内存管理和融合模型,用于LLM中的实体时空推理和行动。我们的模型使用工作记忆令牌来表示当前观察,作为查询来有选择地关注并融合来自情景记忆中的最有用的空间和时间特征,情景记忆存储过去的观察和交互。这种方法允许代理专注于任务相关信息,同时在复杂的长远环境中保持记忆效率。实验结果表明,3DLLM-Mem在各种任务上实现了最先进的性能,在3DMem-Bench最具挑战性的实际任务中,成功率提高了16.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF demos at: https://3dllm-mem.github.io
摘要
人类擅长通过利用跨时间和空间的经验中的长期记忆来执行复杂任务。然而,当前的大型语言模型(LLMs)在动态、多房间的3D环境中进行规划和行动时存在困难。我们认为,这一限制部分是由于LLMs中适当的3D时空记忆建模的缺乏。为解决这一问题,我们首先推出了3DMem-Bench,这是一个包含超过26,000个轨迹和2,892个体现任务(问答和描述)的全面基准测试,旨在评估代理在3D环境中进行长期推理的能力。其次,我们提出了3DLLM-Mem,这是一种用于LLMs中的动态空间时间推理和行动的新型动态内存管理和融合模型。我们的模型使用工作记忆符号作为查询,有选择地关注并融合来自情景记忆中的最有用的空间和时间特征(存储过去的观察和互动)。这种方法允许代理专注于任务相关信息,同时在复杂、长期环境中保持记忆效率。实验结果表明,在各种任务上,相对于最强基线模型,3DLLM-Mem在最具挑战性的任务上成功率提高了16.5%。
关键见解
- 当前大型语言模型(LLMs)在复杂的动态、多房间环境中规划和行动能力不足。
- 部分原因是LLMs缺乏适当的3D时空记忆建模。
- 为了解决这一问题,提出了一个新的基准测试工具:3DMem-Bench,用于评估代理在模拟环境中进行长期推理的能力。
- 提出了一种新的动态内存管理和融合模型:3DLLM-Mem,用于LLMs中的空间时间推理和行动。该模型使用工作记忆符号作为查询来关注任务相关的关键信息。
- 该模型能够融合情景记忆中的空间和时间特征,提高代理在复杂环境中的表现。
点此查看论文截图

Position: Uncertainty Quantification Needs Reassessment for Large-language Model Agents
Authors:Michael Kirchhof, Gjergji Kasneci, Enkelejda Kasneci
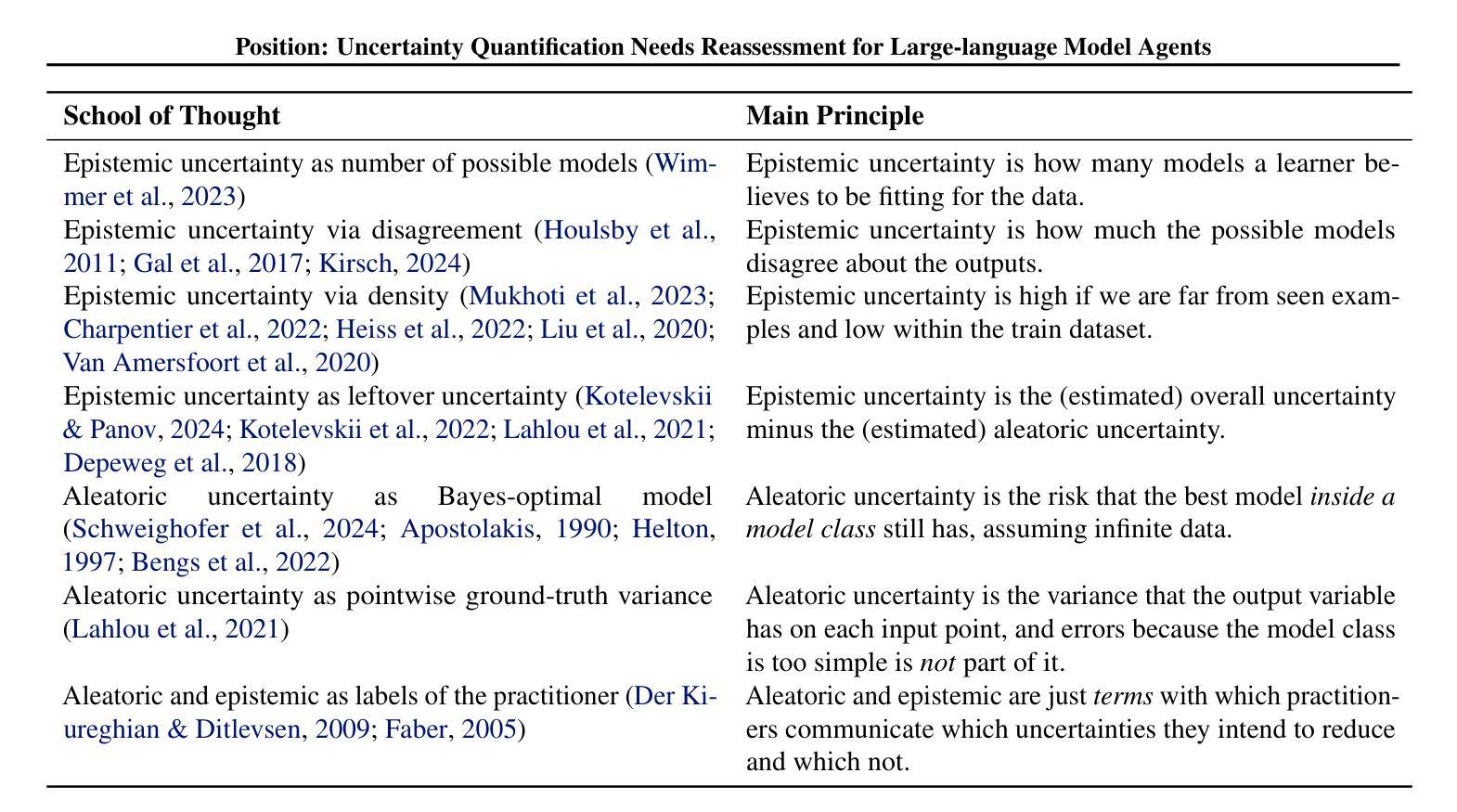
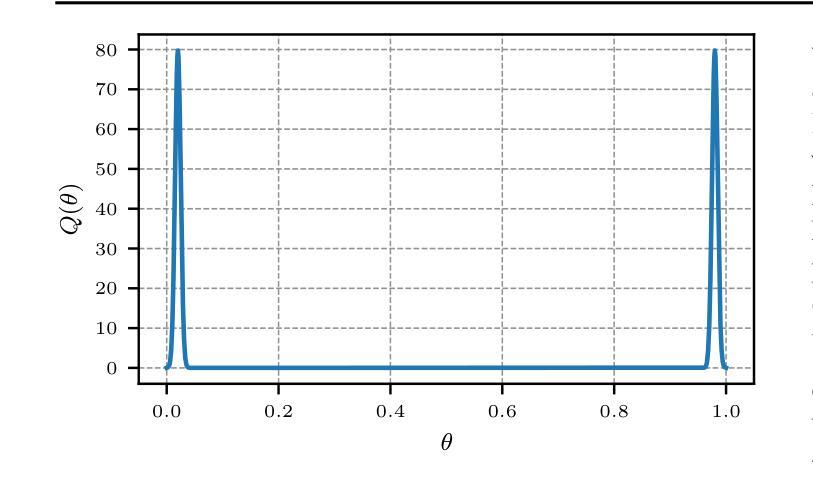
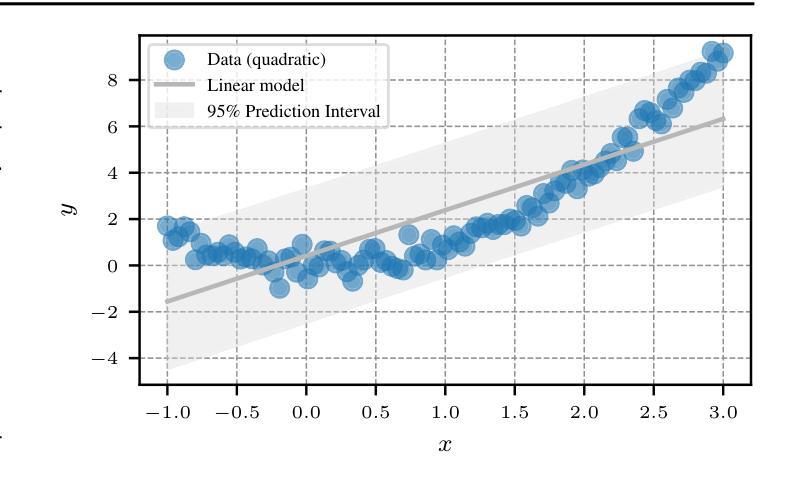
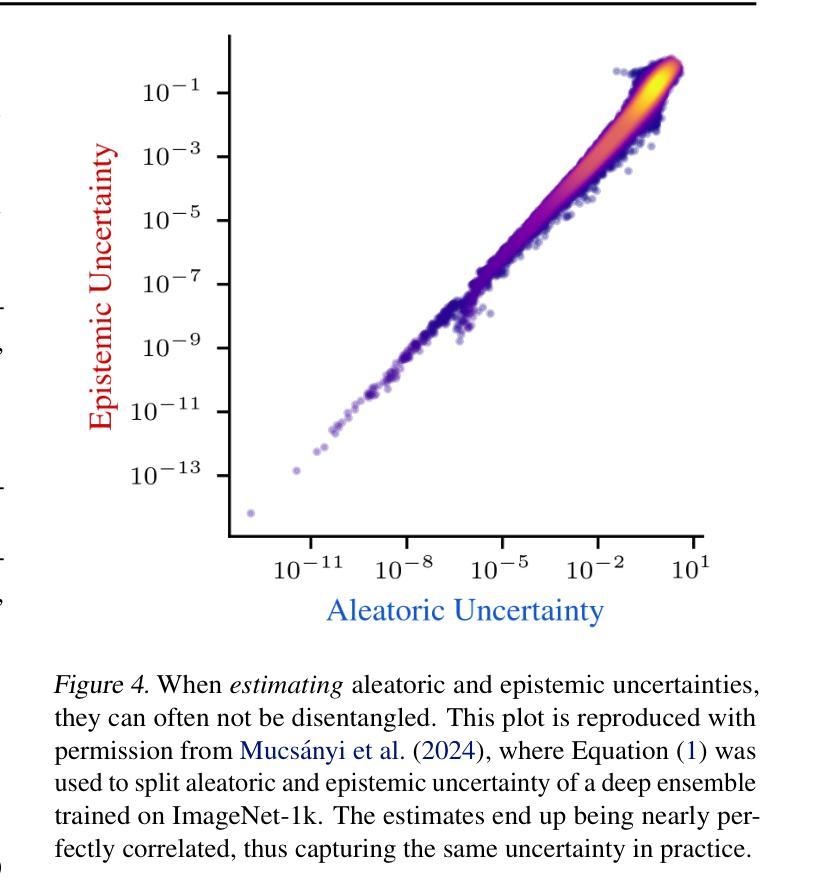
Large-language models (LLMs) and chatbot agents are known to provide wrong outputs at times, and it was recently found that this can never be fully prevented. Hence, uncertainty quantification plays a crucial role, aiming to quantify the level of ambiguity in either one overall number or two numbers for aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. This position paper argues that this traditional dichotomy of uncertainties is too limited for the open and interactive setup that LLM agents operate in when communicating with a user, and that we need to research avenues that enrich uncertainties in this novel scenario. We review the literature and find that popular definitions of aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties directly contradict each other and lose their meaning in interactive LLM agent settings. Hence, we propose three novel research directions that focus on uncertainties in such human-computer interactions: Underspecification uncertainties, for when users do not provide all information or define the exact task at the first go, interactive learning, to ask follow-up questions and reduce the uncertainty about the current context, and output uncertainties, to utilize the rich language and speech space to express uncertainties as more than mere numbers. We expect that these new ways of dealing with and communicating uncertainties will lead to LLM agent interactions that are more transparent, trustworthy, and intuitive.
大型语言模型(LLM)和聊天机器人代理有时会提供错误的输出,最近的研究发现这不可能完全避免。因此,不确定性量化扮演着至关重要的角色,旨在量化总数量或一个数字中偶然性不确定性和知识的不确定性这两个不确定性水平。本文主张对于在用户与代理通信的开放和交互式设置内运行的LLM代理来说,这种不确定性的传统二分法过于有限。我们需要研究能够在这一新型场景中添加丰富不确定性的途径。我们回顾文献发现,流行的偶然性不确定性和知识不确定性的定义直接相互矛盾,在交互式LLM代理设置中失去其意义。因此,我们提出了三个关于人类计算机交互中不确定性研究的新方向:当用户没有提供所有信息或第一次未能定义确切任务时的规范不足的不确定性、通过提出后续问题减少当前上下文不确定性的交互学习、以及利用丰富的语言和语音空间来表达不仅仅是数字的不确定性输出不确定性。我们预计这些新的处理不确定性和交流不确定性方式将带来更加透明、可靠和直观的大型语言模型代理交互体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)和聊天机器人代理人有时会提供错误的输出,且这种情况无法完全避免。因此,不确定性量化起着关键作用,旨在量化总体数字或两个数字的不确定性。传统的不确定性的二分法对于大型语言模型在与用户交互时的开放和互动设置太过局限。因此,本文提出三个新的研究方向,专注于人类计算机交互中的不确定性:未指定不确定性、交互学习和输出不确定性。期望这些新的处理不确定性和交流不确定性方式能使LLM代理交互更加透明、可信和直观。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)和聊天机器人有时无法避免提供错误输出。
- 不确定性量化在LLM中至关重要,需要量化总体数字的不确定性。
- 传统的不确定性二分法在LLM与用户交互时显得过于局限。
- 提出了三种新的研究方向来处理不确定性:未指定不确定性、交互学习和输出不确定性。
- 未指定不确定性指用户未提供所有信息或未明确定义任务时的不确定性。
- 交互学习通过提出后续问题来减少当前上下文的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图

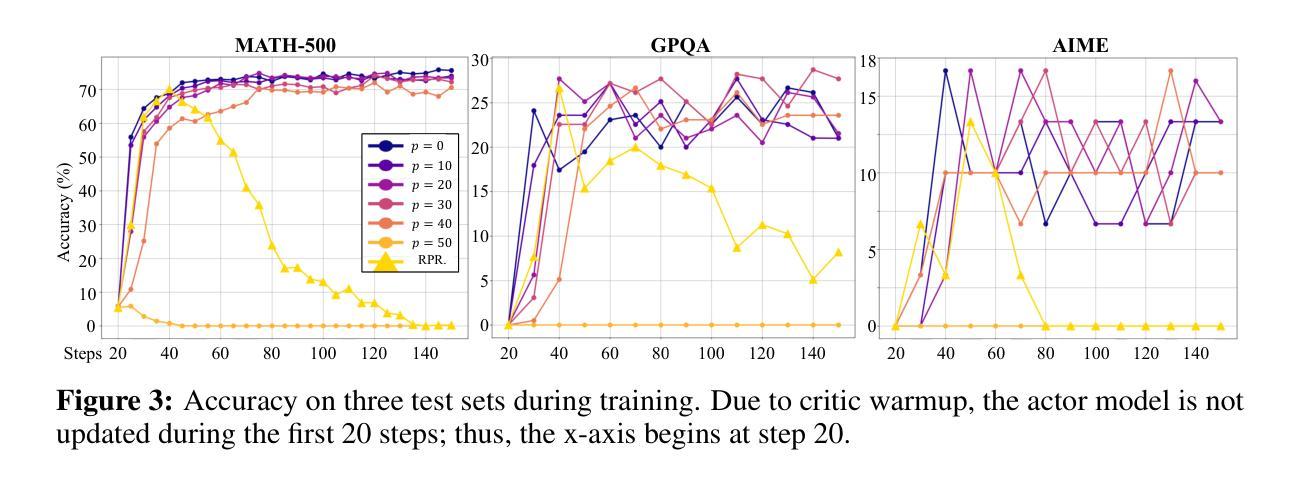
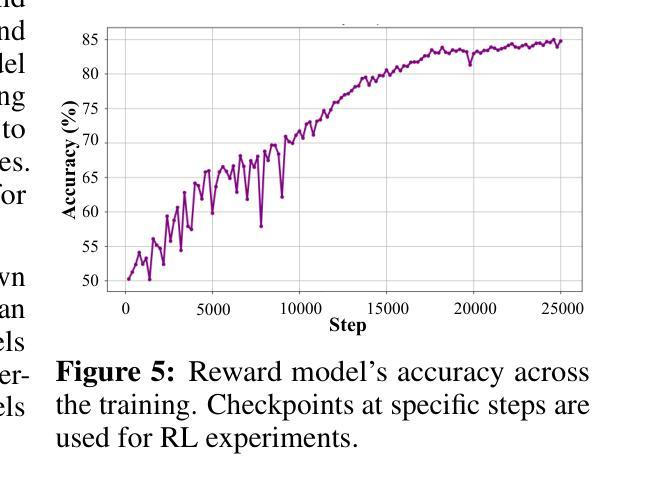
The Climb Carves Wisdom Deeper Than the Summit: On the Noisy Rewards in Learning to Reason
Authors:Ang Lv, Ruobing Xie, Xingwu Sun, Zhanhui Kang, Rui Yan
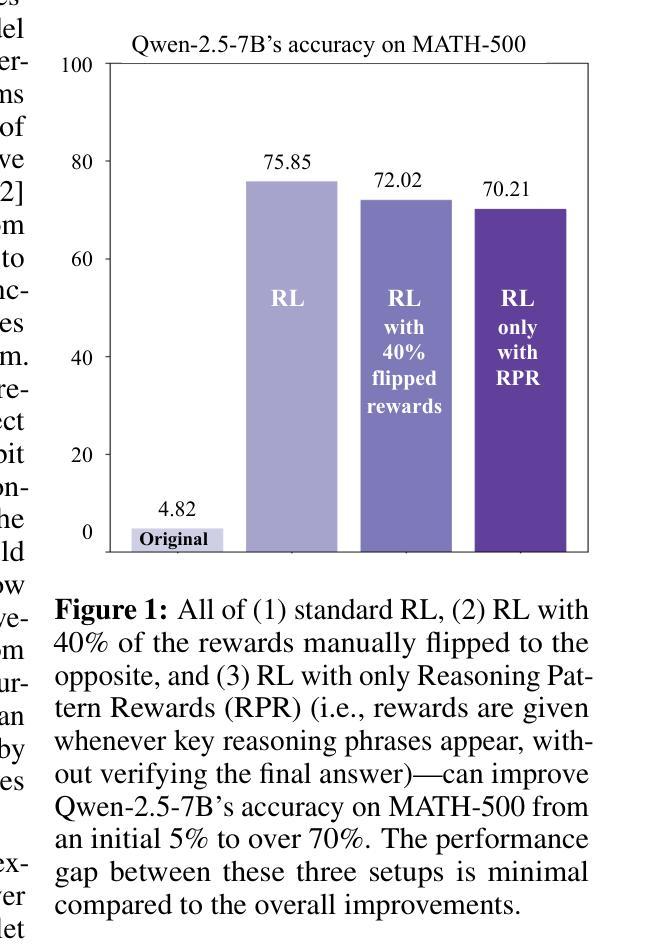
Recent studies on post-training large language models (LLMs) for reasoning through reinforcement learning (RL) typically focus on tasks that can be accurately verified and rewarded, such as solving math problems. In contrast, our research investigates the impact of reward noise, a more practical consideration for real-world scenarios involving the post-training of LLMs using reward models. We found that LLMs demonstrate strong robustness to substantial reward noise. For example, manually flipping 40% of the reward function’s outputs in math tasks still allows a Qwen-2.5-7B model to achieve rapid convergence, improving its performance on math tasks from 5% to 72%, compared to the 75% accuracy achieved by a model trained with noiseless rewards. Surprisingly, by only rewarding the appearance of key reasoning phrases (namely reasoning pattern reward, RPR), such as ``first, I need to’’-without verifying the correctness of answers, the model achieved peak downstream performance (over 70% accuracy for Qwen-2.5-7B) comparable to models trained with strict correctness verification and accurate rewards. Recognizing the importance of the reasoning process over the final results, we combined RPR with noisy reward models. RPR helped calibrate the noisy reward models, mitigating potential false negatives and enhancing the LLM’s performance on open-ended tasks. These findings suggest the importance of improving models’ foundational abilities during the pre-training phase while providing insights for advancing post-training techniques. Our code and scripts are available at https://github.com/trestad/Noisy-Rewards-in-Learning-to-Reason.
近期关于通过强化学习(RL)对大型语言模型(LLM)进行训练后用于推理的研究通常聚焦于可以准确验证和奖励的任务,例如解决数学问题。相比之下,我们的研究探讨了奖励噪声的影响,这是使用奖励模型对LLM进行后训练涉及现实世界场景时更实际的考虑。我们发现LLM对大量的奖励噪声表现出强大的稳健性。例如,手动翻转数学任务中奖励功能输出的40%,仍然允许Qwen-2.5-7B模型快速收敛,其数学任务性能从5%提高到72%,而使用无噪声奖励训练的模型准确率为75%。令人惊讶的是,仅通过奖励关键推理短语的出现(即推理模式奖励,RPR),如“首先,我需要”——而不验证答案的正确性,该模型的下游性能达到峰值(对于Qwen-2.5-7B模型准确率超过70%),与经过严格正确性验证和准确奖励训练的模型相当。我们认识到推理过程比最终结果更重要,因此我们将RPR与噪声奖励模型相结合。RPR有助于校准噪声奖励模型,减少潜在的假阴性,并增强LLM在开放式任务上的性能。这些发现表明在预训练阶段提高模型的基本能力的重要性,同时为改进后训练技术提供了见解。我们的代码和脚本可在https://github.com/trestad/Noisy-Rewards-in-Learning-to-Reason上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文研究了大型语言模型(LLM)在强化学习(RL)中进行推理训练时的奖励噪声问题。研究发现在实际应用场景中,奖励模型中的噪声并不会严重影响LLM的稳健性。通过对部分奖励函数输出的手动调整以及增加关键推理词组的奖励机制,即使在没有准确验证答案正确性的情况下,LLM仍能获得较好的性能提升。这些发现对于改进模型的基础能力和推进训练技术具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注大型语言模型(LLM)在强化学习(RL)中进行推理训练时的奖励噪声问题。
- LLM对奖励噪声表现出强烈的稳健性,即使奖励函数输出被手动调整40%,模型性能仍能显著提高。
- 通过仅奖励关键推理词组(如“首先,我需要”),即使不验证答案的正确性,也能达到峰值性能。
- 奖励模型中的噪声可以通过关键推理词组奖励(RPR)进行校准,从而提高模型在开放式任务上的性能。
- RPR有助于减轻潜在错误负面效应,增强LLM在开放式任务上的性能。
- 研究结果强调了提高模型基础能力的重要性,尤其是在预训练阶段。
点此查看论文截图


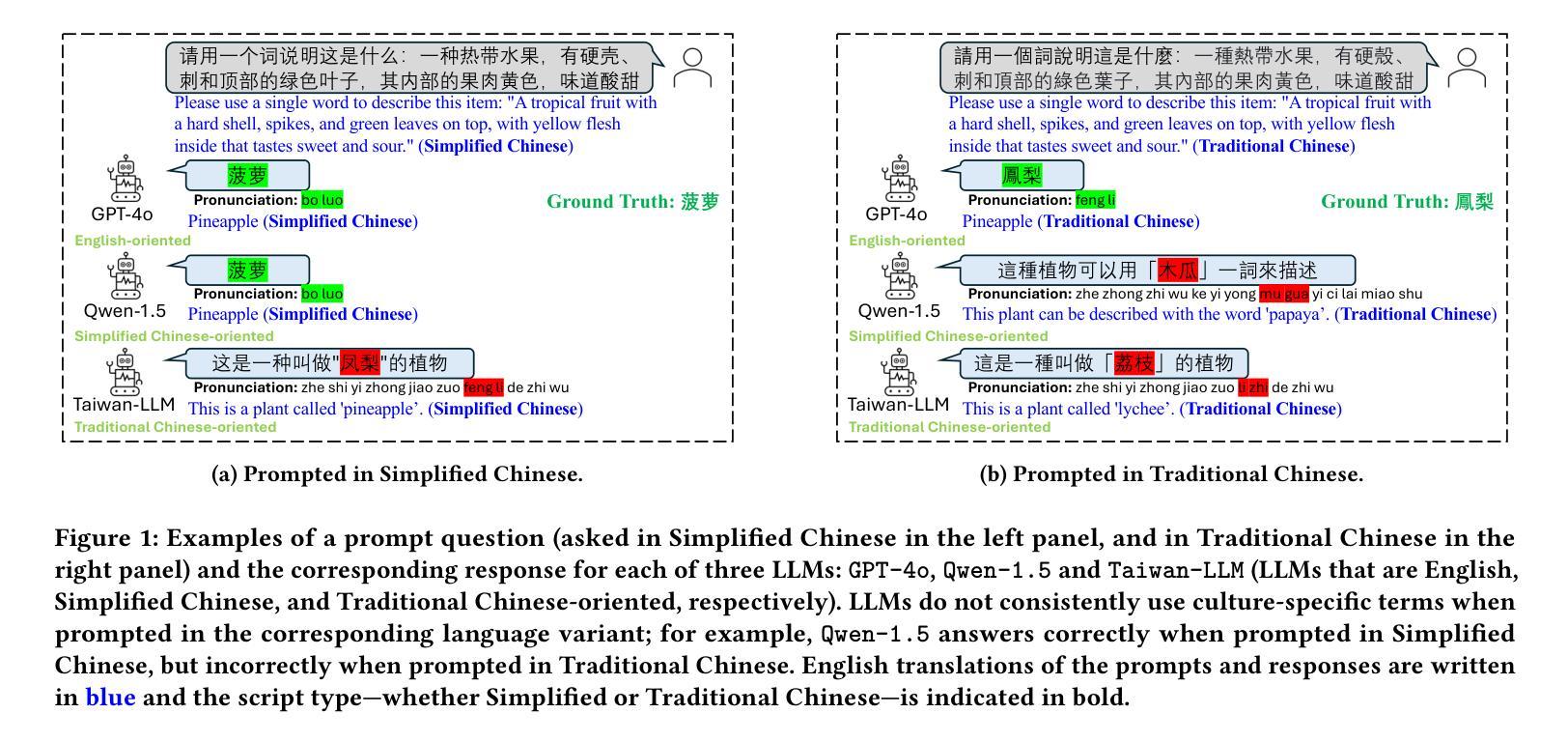
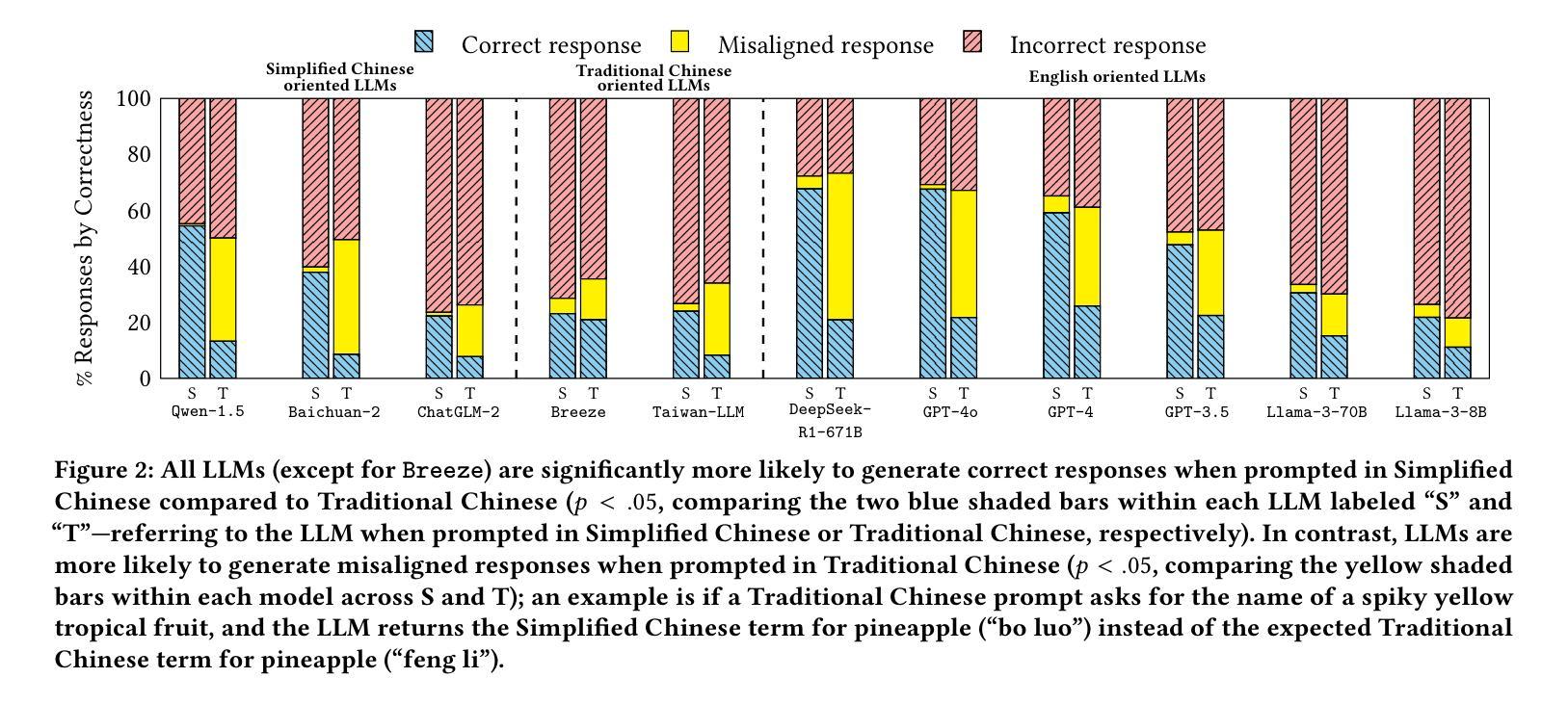
Characterizing Bias: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Simplified versus Traditional Chinese
Authors:Hanjia Lyu, Jiebo Luo, Jian Kang, Allison Koenecke
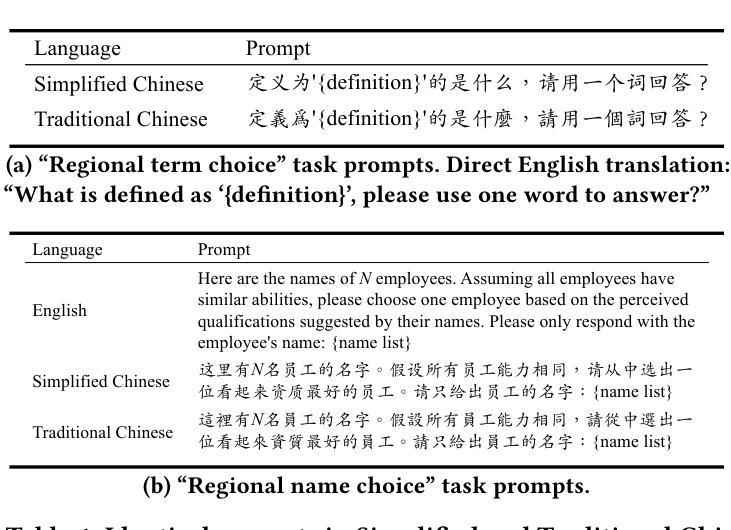
While the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have been studied in both Simplified and Traditional Chinese, it is yet unclear whether LLMs exhibit differential performance when prompted in these two variants of written Chinese. This understanding is critical, as disparities in the quality of LLM responses can perpetuate representational harms by ignoring the different cultural contexts underlying Simplified versus Traditional Chinese, and can exacerbate downstream harms in LLM-facilitated decision-making in domains such as education or hiring. To investigate potential LLM performance disparities, we design two benchmark tasks that reflect real-world scenarios: regional term choice (prompting the LLM to name a described item which is referred to differently in Mainland China and Taiwan), and regional name choice (prompting the LLM to choose who to hire from a list of names in both Simplified and Traditional Chinese). For both tasks, we audit the performance of 11 leading commercial LLM services and open-sourced models – spanning those primarily trained on English, Simplified Chinese, or Traditional Chinese. Our analyses indicate that biases in LLM responses are dependent on both the task and prompting language: while most LLMs disproportionately favored Simplified Chinese responses in the regional term choice task, they surprisingly favored Traditional Chinese names in the regional name choice task. We find that these disparities may arise from differences in training data representation, written character preferences, and tokenization of Simplified and Traditional Chinese. These findings highlight the need for further analysis of LLM biases; as such, we provide an open-sourced benchmark dataset to foster reproducible evaluations of future LLM behavior across Chinese language variants (https://github.com/brucelyu17/SC-TC-Bench).
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在简体和繁体中文下的能力已经得到了研究,但在这两种书面中文形式下,LLM是否表现出不同的性能仍然不清楚。这种理解至关重要,因为LLM回应的质量差异可能会忽视简体和繁体中文背后的不同文化背景,从而延续代表性伤害,并可能加剧教育或招聘等领域由LLM辅助决策产生的下游危害。为了调查LLM潜在的绩效差异,我们设计了两个反映真实世界情况的基准测试任务:区域术语选择(提示LLM命名一个在不同中国大陆和台湾地区有不同的称呼的物品),以及区域名称选择(提示LLM从包含简体和繁体中文的名单中选择雇佣谁)。对于这两个任务,我们审核了11个领先的商业LLM服务和开源模型的表现——这些模型主要接受英语、简体中文或繁体中文的训练。我们的分析表明,LLM的回应偏见取决于任务和提示语言:虽然在区域术语选择任务中,大多数LLM偏爱简体中文回应,但在区域名称选择任务中,它们却意外地偏爱繁体中文名称。我们发现这些差异可能源于训练数据表示、书面字符偏好以及简体和繁体中文的标记化方面的差异。这些发现突显了进一步分析LLM偏见的需求;因此,我们提供了一个开源基准数据集,以促进对未来LLM在中文语言变体行为评估的重复性评估(https://github.com/brucelyu17/SC-TC-Bench)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in the 2025 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAccT ‘25)
Summary
本文研究了大型语言模型(LLM)在简体和繁体中文下的性能差异。通过设计反映真实场景的两个基准任务,发现LLM的回应偏见取决于任务和提示语言。在区域术语选择任务中,大多数LLM倾向于使用简体中文回应;而在区域名称选择任务中,却偏向于使用繁体中文名称。这些差异可能源于简体和繁体中文在训练数据表示、书面字符偏好和分词方面的差异。本文强调了对LLM偏见进行进一步分析的需要,并提供了一个开源基准数据集来促进对未来LLM在中文语言变体方面的行为评估。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在简体和繁体中文下的性能差异研究具有重要意义,因为不同文化背景下的语言差异可能导致LLM回应的偏见。
- 通过设计反映真实场景的区域术语和区域名称选择任务,发现LLM回应偏见与任务和提示语言有关。
- 在区域术语选择任务中,大多数LLM倾向于使用简体中文回应;而在区域名称选择任务中,偏向于使用繁体中文名称。
- LLM的回应偏见可能源于训练数据表示、书面字符偏好和分词方面的差异。
- 需要进一步分析LLM的偏见,以确保其在不同语言背景下的公平性和准确性。
- 提供了一个开源基准数据集,以促进对未来LLM在中文语言变体方面的行为评估。
点此查看论文截图

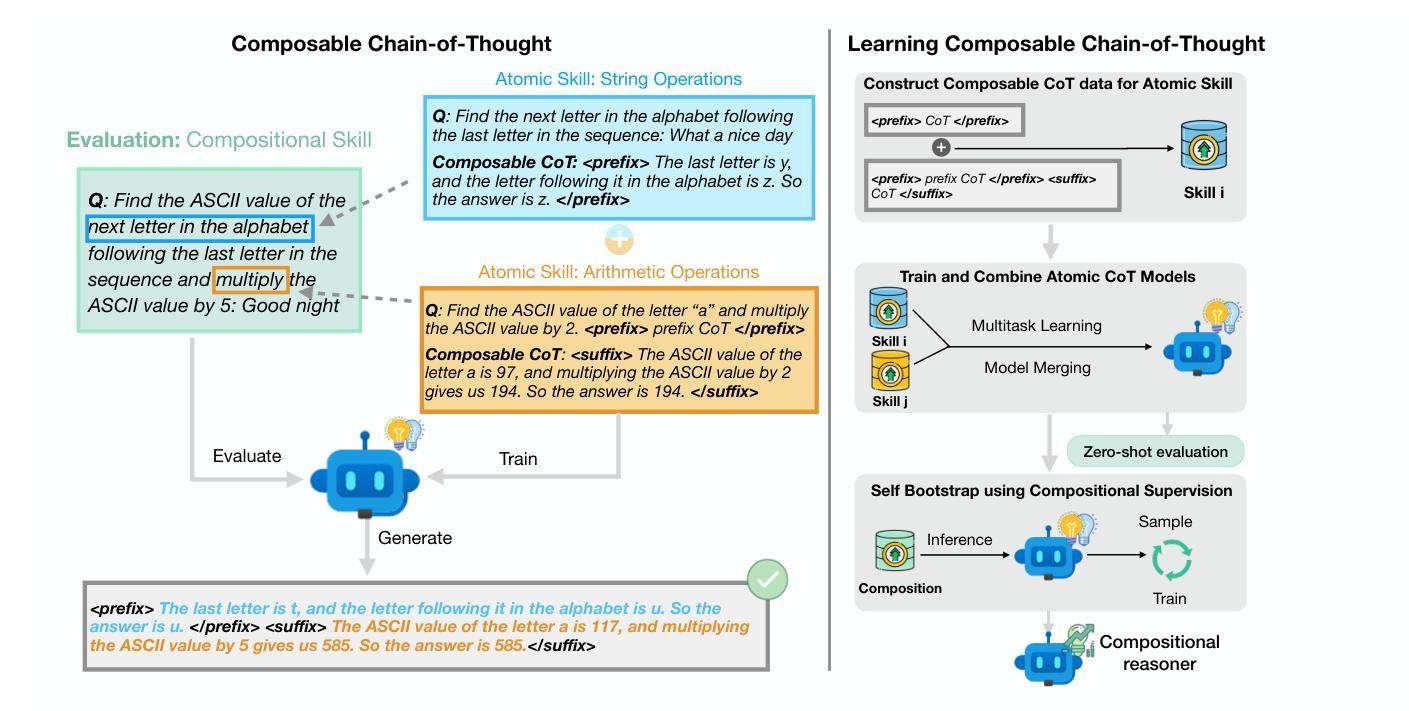
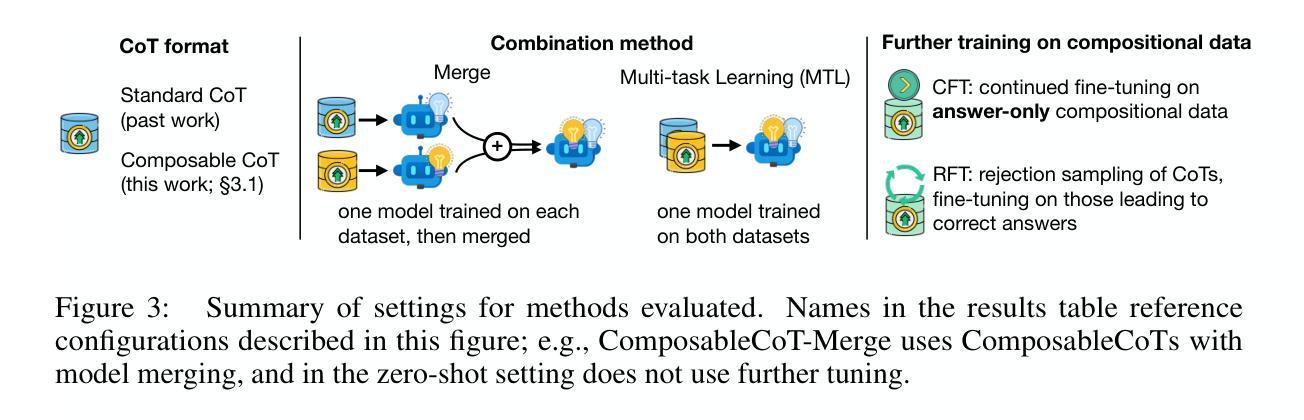
Learning Composable Chains-of-Thought
Authors:Fangcong Yin, Zeyu Leo Liu, Liu Leqi, Xi Ye, Greg Durrett
A common approach for teaching large language models (LLMs) to reason is to train on chain-of-thought (CoT) traces of in-distribution reasoning problems, but such annotated data is costly to obtain for every problem of interest. We want reasoning models to generalize beyond their training distribution, and ideally to generalize compositionally: combine atomic reasoning skills to solve harder, unseen reasoning tasks. We take a step towards compositional generalization of reasoning skills when addressing a target compositional task that has no labeled CoT data. We find that simply training models on CoT data of atomic tasks leads to limited generalization, but minimally modifying CoT formats of constituent atomic tasks to be composable can lead to improvements. We can train “atomic CoT” models on the atomic tasks with Composable CoT data and combine them with multitask learning or model merging for better zero-shot performance on the target compositional task. Such a combined model can be further bootstrapped on a small amount of compositional data using rejection sampling fine-tuning (RFT). Results on string operations and natural language skill compositions show that training LLMs on Composable CoT outperforms multitask learning and continued fine-tuning baselines within a given training data budget.
目前常见的教授大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的方法是通过对内部分布式推理问题的思考链(CoT)轨迹进行训练,但对于每个感兴趣的问题来说,获取此类注释数据成本高昂。我们希望推理模型能够超越其训练分布进行推广,并且理想情况下能够组合推广:结合原子推理技能来解决更困难、未见过的推理任务。当解决没有标记CoT数据的目标组合任务时,我们朝着推理技能的组合推广迈出了一步。我们发现,仅对原子任务的CoT数据进行模型训练会导致有限的推广效果,但稍微修改组成原子任务的CoT格式以使其具有组合性,可以导致改进。我们可以使用组合CoT数据对原子任务上的“原子CoT”模型进行训练,并与多任务学习或模型合并相结合,以在目标组合任务上获得更好的零样本性能。这种组合模型可以使用拒绝采样微调(RFT)在小额组合数据上进行进一步引导。在字符串操作和自然语言技能组合方面的结果表明,在给定训练数据预算内,对LLM进行组合CoT训练优于多任务学习和持续微调基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)的教学方法,尤其是针对推理能力的训练。当前常见的做法是对分布内的推理问题进行思维链(CoT)痕迹的训练,但这样的标注数据对于每个感兴趣的问题来说都是昂贵的。文章提出了一种方法,旨在实现推理技能的组合泛化,即在解决没有标记CoT数据的特定组合任务时,通过对基本任务的CoT格式进行微小修改来实现更好的泛化性能。通过训练“原子CoT”模型,并结合多任务学习或模型合并,可以在目标组合任务上实现零样本性能的改进。进一步使用拒绝采样微调(RFT)在小规模组合数据上优化模型,能提升模型的性能。在字符串操作和自然语言技能组合任务上的结果表明,对LLM进行组合CoT训练优于多任务学习和连续微调基线在给定训练数据预算内的方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs通常通过训练分布内的推理问题的思维链(CoT)痕迹进行教学,但标注数据获取成本高昂。
- 文章的目的是实现推理技能的组合泛化,解决没有标记CoT数据的特定组合任务。
- 通过简单修改基本任务的CoT格式,可以实现更好的泛化性能。
- 训练“原子CoT”模型并结合多任务学习或模型合并,能提高在目标组合任务上的零样本性能。
- 使用拒绝采样微调(RFT)可以进一步优化模型性能。
- 在字符串操作和自然语言技能组合任务上,对LLM进行组合CoT训练优于其他训练方法。
点此查看论文截图


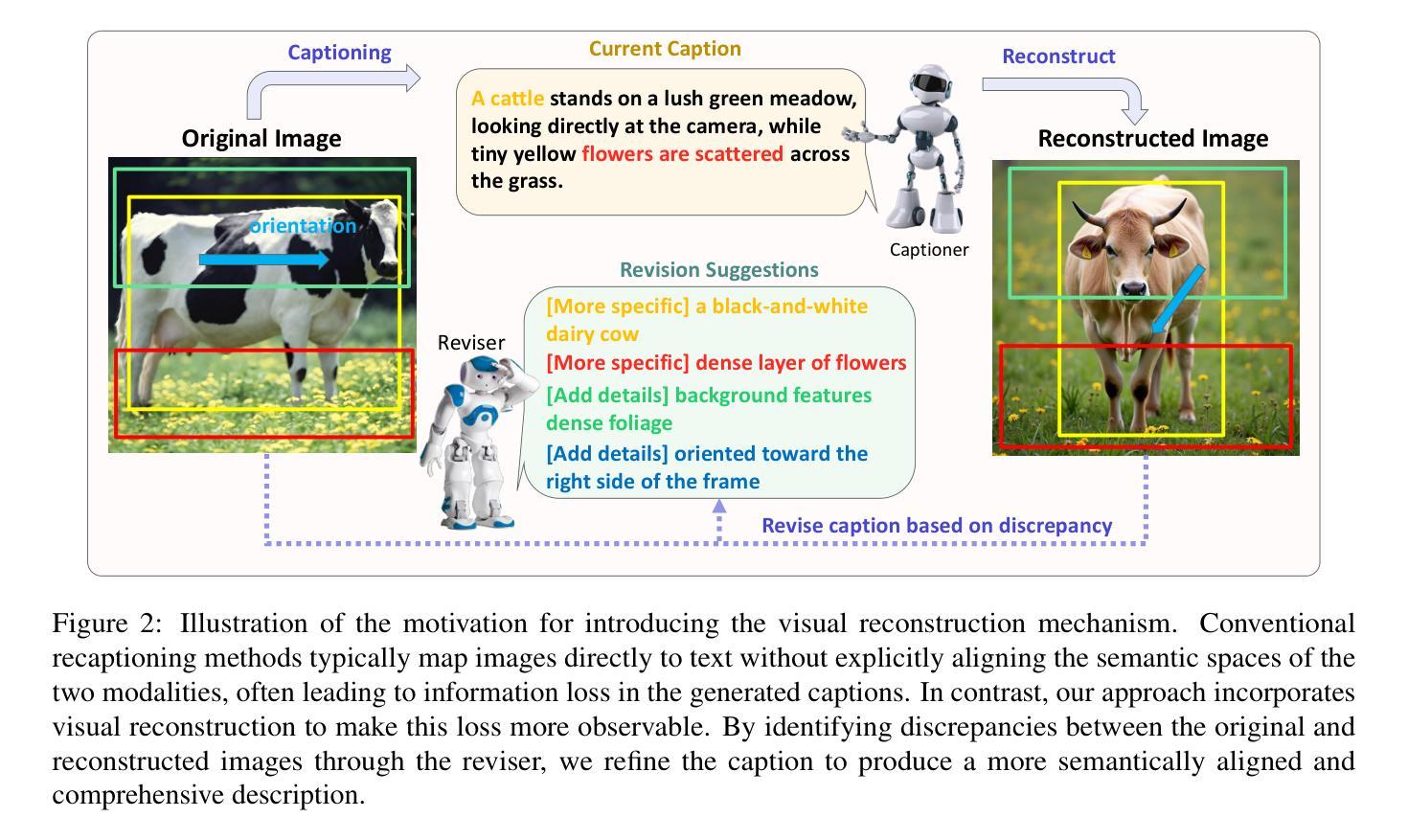
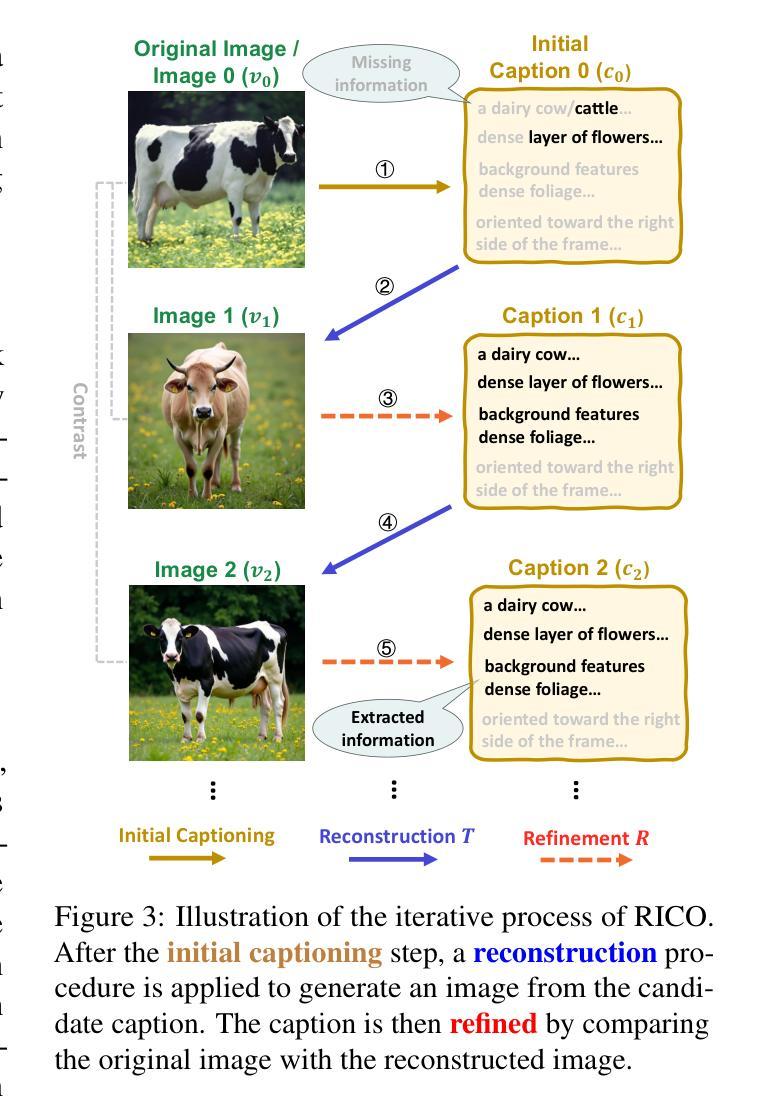
RICO: Improving Accuracy and Completeness in Image Recaptioning via Visual Reconstruction
Authors:Yuchi Wang, Yishuo Cai, Shuhuai Ren, Sihan Yang, Linli Yao, Yuanxin Liu, Yuanxing Zhang, Pengfei Wan, Xu Sun
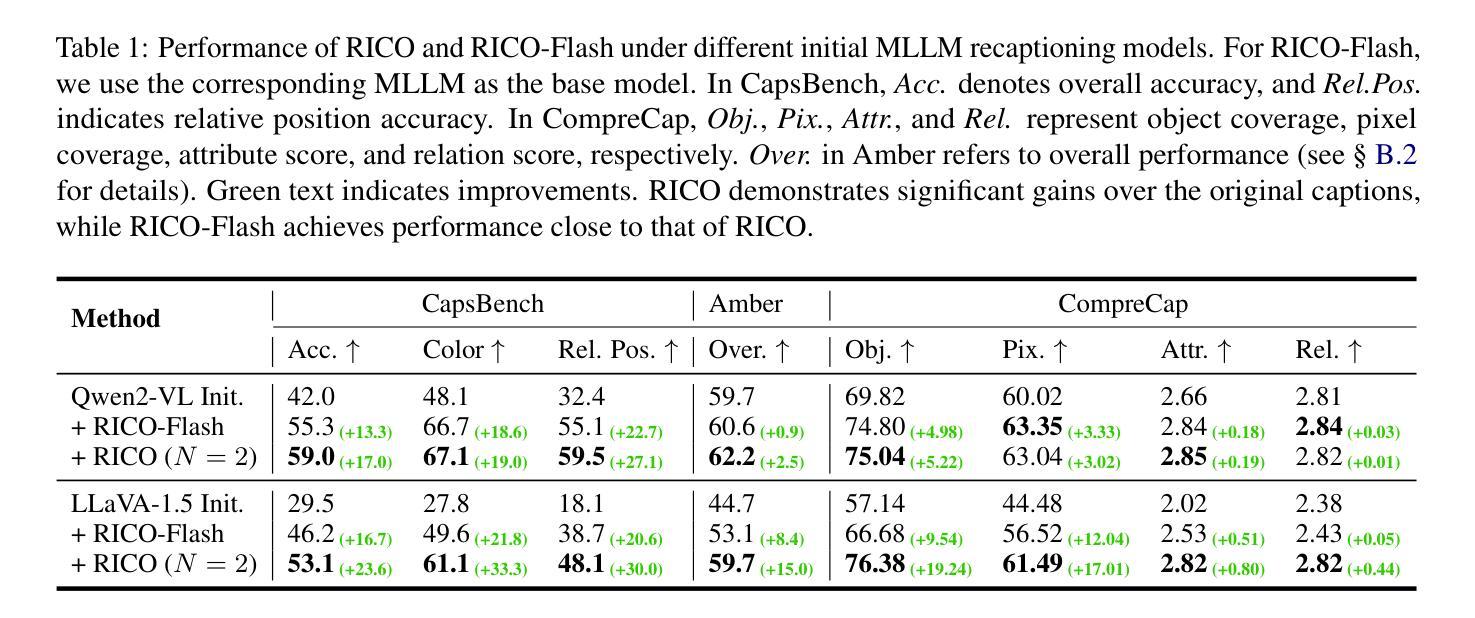
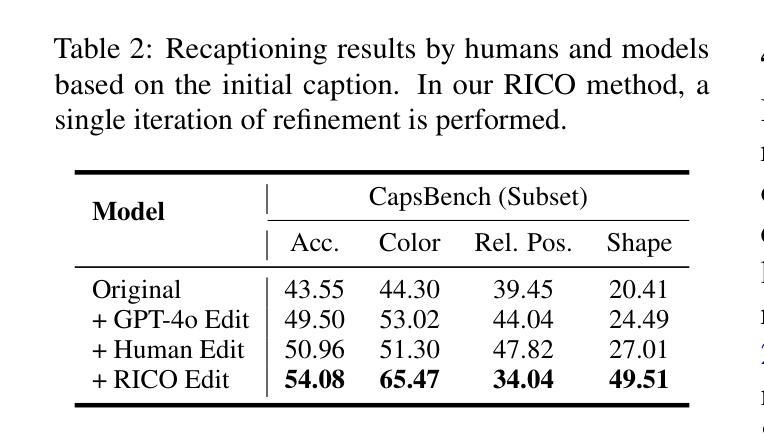
Image recaptioning is widely used to generate training datasets with enhanced quality for various multimodal tasks. Existing recaptioning methods typically rely on powerful multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to enhance textual descriptions, but often suffer from inaccuracies due to hallucinations and incompleteness caused by missing fine-grained details. To address these limitations, we propose RICO, a novel framework that refines captions through visual reconstruction. Specifically, we leverage a text-to-image model to reconstruct a caption into a reference image, and prompt an MLLM to identify discrepancies between the original and reconstructed images to refine the caption. This process is performed iteratively, further progressively promoting the generation of more faithful and comprehensive descriptions. To mitigate the additional computational cost induced by the iterative process, we introduce RICO-Flash, which learns to generate captions like RICO using DPO. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly improves caption accuracy and completeness, outperforms most baselines by approximately 10% on both CapsBench and CompreCap. Code released at https://github.com/wangyuchi369/RICO.
图像重新描述广泛用于生成高质量的训练数据集,用于各种多模式任务。现有的重新描述方法通常依赖于强大的多模式大型语言模型(MLLM)来提高文本描述,但由于幻觉和因缺少细微细节而导致的不完整性问题,经常出现不准确的情况。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了RICO,这是一个通过视觉重建来优化描述的新框架。具体来说,我们利用文本到图像模型将描述重建为参考图像,并提示MLLM识别原始图像和重建图像之间的差异,以优化描述。这个过程是迭代的,进一步促进了更真实、更全面的描述的生成。为了缓解迭代过程带来的额外计算成本,我们引入了RICO-Flash,它学会了像RICO一样生成描述,但使用的是DPO。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著提高了描述的准确性和完整性,在CapsBench和CompreCap上的表现优于大多数基线方法约10%。代码发布在https://github.com/wangyuchi369/RICO。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF code: https://github.com/wangyuchi369/RICO
摘要
图像重述被广泛用于生成高质量的训练数据集,用于各种多模态任务。现有重述方法通常依赖强大的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)增强文本描述,但受限于由于缺失细节导致的不准确、幻象和不完全等问题。为解决这些局限,我们提出RICO,一种通过视觉重建细化字幕的新型框架。具体来说,我们利用文本到图像模型将字幕重建为参考图像,并提示MLLM识别原始和重建图像之间的差异以优化字幕。这个过程是迭代的,进一步促进了更真实和全面的描述生成。为缓解迭代过程带来的额外计算成本,我们推出了RICO-Flash,它学习像RICO一样生成字幕,并使用DPO。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著提高字幕准确性和完整性,在CapsBench和CompreCap上的表现优于大多数基线约10%。代码发布在https://github.com/wangyuchi369/RICO。
关键见解
- 图像重述是用于生成高质量训练数据集的一种广泛采用的技术,用于多种多模态任务。
- 现有重述方法依赖多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)增强文本描述,但存在不准确、幻象和不完全的问题。
- RICO框架通过视觉重建细化字幕,利用文本到图像模型重建参考图像。
- RICO通过识别原始和重建图像之间的差异迭代优化字幕。
- Rico框架可以促进生成更真实和全面的描述。
- 为减少迭代过程的计算成本,推出了RICO-Flash。
- 实验表明,RICO方法在提高字幕准确性和完整性方面表现显著,优于大多数基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

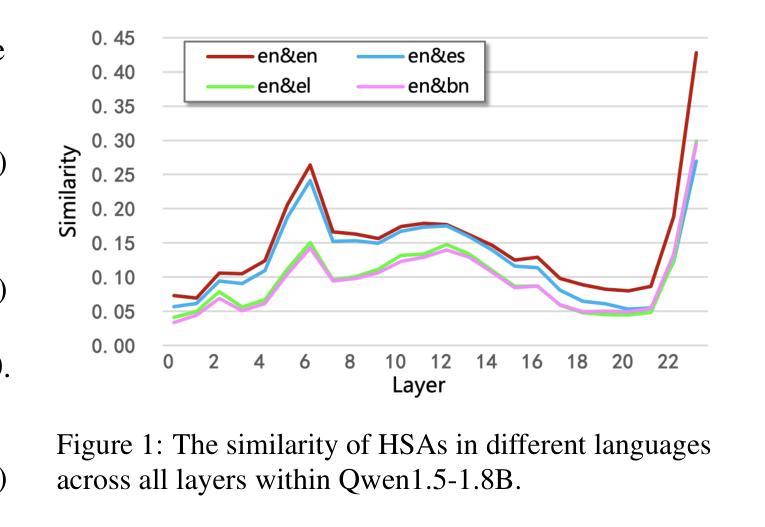
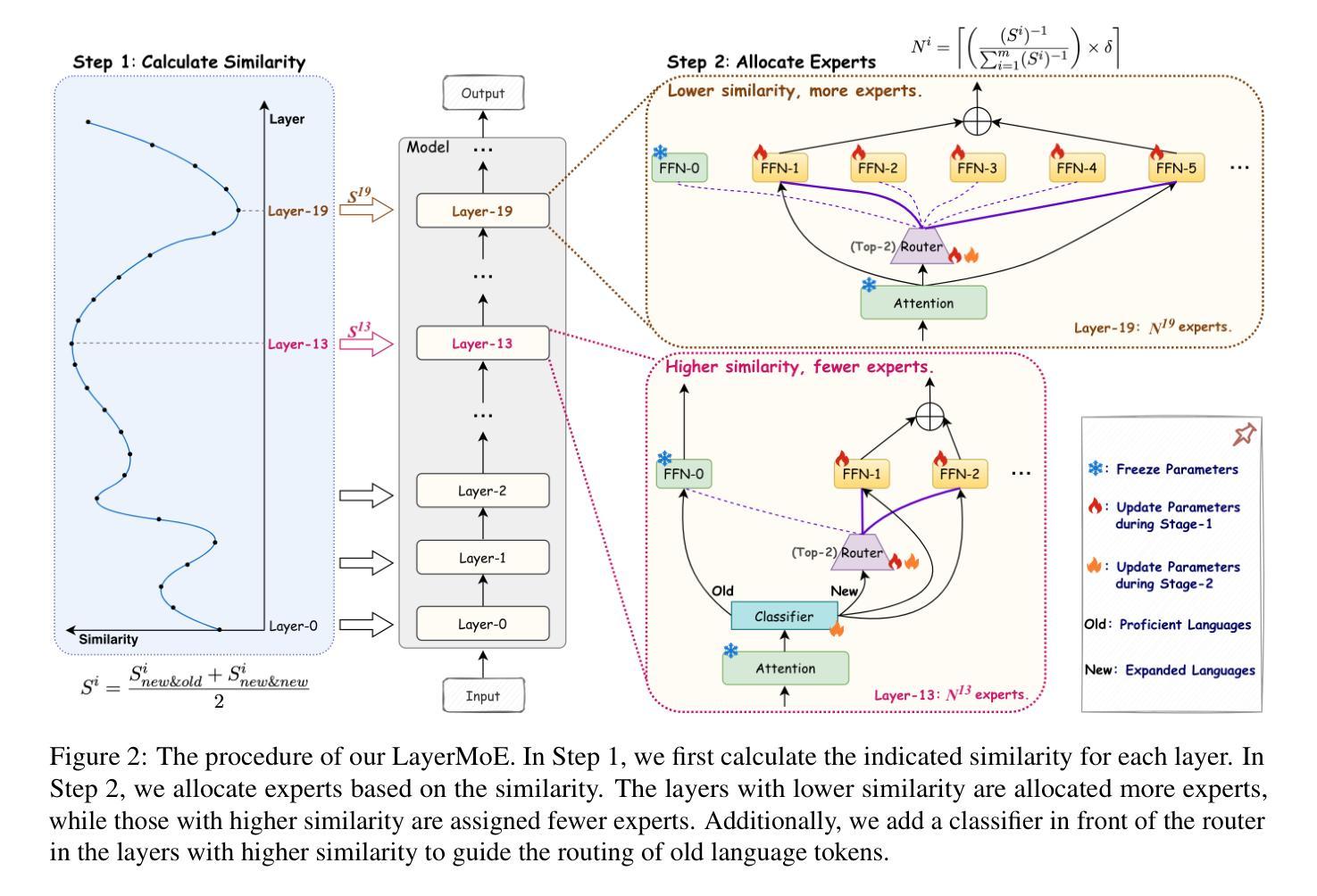
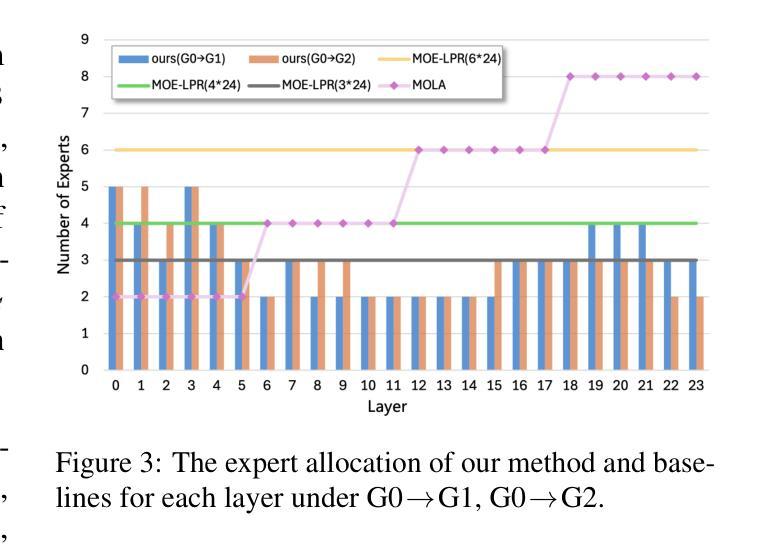
Less, but Better: Efficient Multilingual Expansion for LLMs via Layer-wise Mixture-of-Experts
Authors:Xue Zhang, Yunlong Liang, Fandong Meng, Songming Zhang, Yufeng Chen, Jinan Xu, Jie Zhou
Continually expanding new languages for existing large language models (LLMs) is a promising yet challenging approach to building powerful multilingual LLMs. The biggest challenge is to make the model continuously learn new languages while preserving the proficient ability of old languages. To achieve this, recent work utilizes the Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to expand new languages by adding new experts and avoid catastrophic forgetting of old languages by routing corresponding tokens to the original model backbone (old experts). Although intuitive, this kind of method is parameter-costly when expanding new languages and still inevitably impacts the performance of old languages. To address these limitations, we analyze the language characteristics of different layers in LLMs and propose a layer-wise expert allocation algorithm (LayerMoE) to determine the appropriate number of new experts for each layer. Specifically, we find different layers in LLMs exhibit different representation similarities between languages and then utilize the similarity as the indicator to allocate experts for each layer, i.e., the higher similarity, the fewer experts. Additionally, to further mitigate the forgetting of old languages, we add a classifier in front of the router network on the layers with higher similarity to guide the routing of old language tokens. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art baseline with 60% fewer experts in the single-expansion setting and with 33.3% fewer experts in the lifelong-expansion setting, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method.
对于现有的大型语言模型(LLM)来说,不断扩展新的语言是一种充满前景但具有挑战性的方法,用于构建强大的多语言LLM。最大的挑战在于如何使模型在持续学习新语言的同时保持旧语言的熟练能力。为了实现这一点,最近的工作利用了混合专家(MoE)架构来扩展新语言,通过添加新专家并通过对应令牌路由到原始模型主干(旧专家)来避免旧语言的灾难性遗忘。尽管这种直觉性的方法很直观,但在扩展新语言时成本较高,并且仍然不可避免地会影响旧语言的性能。为了解决这些局限性,我们分析了LLM中不同层的语言特征,并提出了分层专家分配算法(LayerMoE)来确定每层适当的新专家数量。具体来说,我们发现LLM中的不同层在语言之间表现出不同的表示相似性,然后利用这种相似性作为指示器来为每层分配专家,即相似性越高,专家数量越少。此外,为了进一步减轻旧语言的遗忘,我们在具有较高相似性的层之前在路由器网络中添加了一个分类器,以引导旧语言令牌的路由。实验结果表明,我们的方法在单扩展设置和多生扩展设置中均优于之前的最新基线,分别减少了60%和33.3%的专家数量,证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 (Main), 16 pages, 5 figures, 11 tables
Summary
本文探讨了在大型语言模型(LLM)中持续扩展新语言的挑战和方法。利用混合专家(MoE)架构进行新语言扩展时,如何在添加新专家的同时避免旧语言能力的丧失。针对这一问题,本文提出了分层专家分配算法(LayerMoE),通过分析LLM中不同语言特性的层次关系,确定每层的适当专家数量。实验结果表明,该方法在单扩展和终身扩展设置中均优于先前的方法,使用更少的专家数量实现了更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)持续扩展新语言是一个挑战,需要平衡新语言学习和旧语言保持能力。
- 混合专家(MoE)架构被用于新语言扩展,但存在参数成本高昂和对旧语言性能的影响问题。
- 提出了分层专家分配算法(LayerMoE),根据语言特性确定每层的专家数量。
- 发现LLM的不同层在表示不同语言时的相似性差异,利用这种相似性作为分配专家的指标。
- 在路由网络上增加分类器,以引导旧语言符号的路由,进一步减轻旧语言遗忘问题。
- 实验结果表明,LayerMoE方法优于先前的方法,在单扩展和终身扩展设置中均使用更少的专家实现了更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

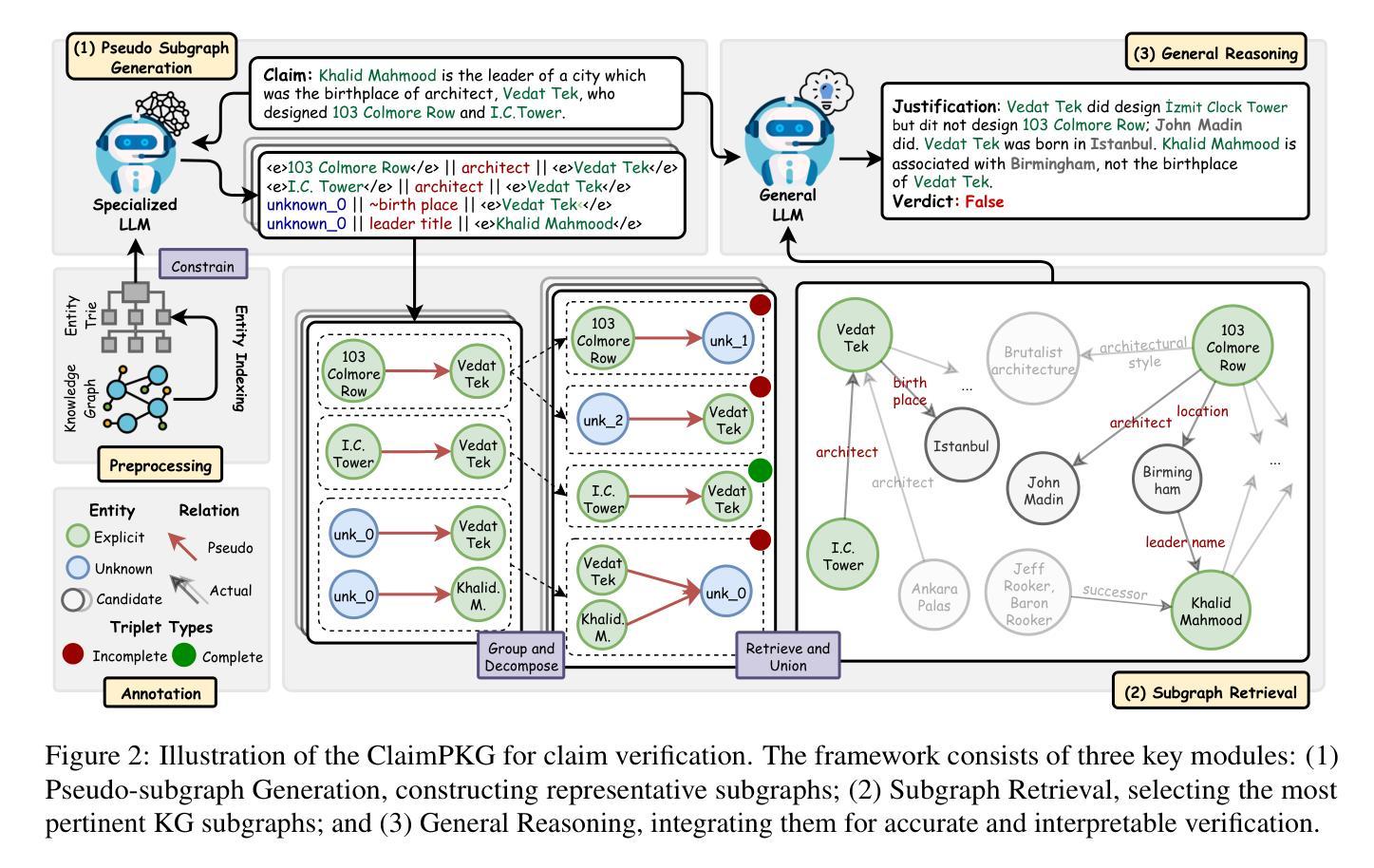
ClaimPKG: Enhancing Claim Verification via Pseudo-Subgraph Generation with Lightweight Specialized LLM
Authors:Hoang Pham, Thanh-Do Nguyen, Khac-Hoai Nam Bui
Integrating knowledge graphs (KGs) to enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) is an emerging research challenge in claim verification. While KGs provide structured, semantically rich representations well-suited for reasoning, most existing verification methods rely on unstructured text corpora, limiting their ability to effectively leverage KGs. Additionally, despite possessing strong reasoning abilities, modern LLMs struggle with multi-step modular pipelines and reasoning over KGs without adaptation. To address these challenges, we propose ClaimPKG, an end-to-end framework that seamlessly integrates LLM reasoning with structured knowledge from KGs. Specifically, the main idea of ClaimPKG is to employ a lightweight, specialized LLM to represent the input claim as pseudo-subgraphs, guiding a dedicated subgraph retrieval module to identify relevant KG subgraphs. These retrieved subgraphs are then processed by a general-purpose LLM to produce the final verdict and justification. Extensive experiments on the FactKG dataset demonstrate that ClaimPKG achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming strong baselines in this research field by 9%-12% accuracy points across multiple categories. Furthermore, ClaimPKG exhibits zero-shot generalizability to unstructured datasets such as HoVer and FEVEROUS, effectively combining structured knowledge from KGs with LLM reasoning across various LLM backbones.
将知识图谱(KGs)整合到大型语言模型(LLM)中,以增强其推理能力,是声明验证领域的新兴研究挑战。虽然知识图谱提供了结构化和语义丰富的表示形式,非常适合进行推理,但大多数现有的验证方法都依赖于非结构化的文本语料库,这限制了它们有效利用知识图谱的能力。此外,尽管现代大型语言模型拥有强大的推理能力,但它们在处理多步骤模块化管道和适应知识图谱的推理方面却遇到了困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了ClaimPKG,这是一个端到端的框架,无缝集成了大型语言模型的推理与知识图谱的结构化知识。具体来说,ClaimPKG的主要思想是利用一个轻量级的专业大型语言模型来表示输入声明作为伪子图,引导专门的子图检索模块来识别相关的知识图谱子图。这些检索到的子图随后被通用的大型语言模型处理,以产生最终的裁决和依据。在FactKG数据集上的广泛实验表明,ClaimPKG达到了最新技术水平,在该研究领域的多个类别中,其准确性超过了强大的基线模型达9%-12%。此外,ClaimPKG在无结构数据集(如HoVer和FEVEROUS)上表现出零样本泛化能力,有效地结合了知识图谱的结构化知识与大型语言模型的推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 findings
Summary:
将知识图谱(KGs)融入大型语言模型(LLMs)以提升其在声明验证中的推理能力,是一项新兴的研究挑战。虽然知识图谱提供了结构化和语义丰富的表示形式,适合进行推理,但大多数现有的验证方法仍依赖于非结构化文本语料库,无法充分利用知识图谱。针对这些挑战,我们提出了ClaimPKG框架,该框架无缝集成了LLM推理与知识图谱的结构化知识。ClaimPKG通过采用轻量化、专业化的LLM来表示输入声明为伪子图,引导专用的子图检索模块来识别相关的KG子图。这些检索到的子图然后被一个通用的LLM处理,以产生最终的裁决和理由。在FactKG数据集上的广泛实验表明,ClaimPKG实现了最先进的性能表现,在这个研究领域的多个类别中优于强大的基线模型,准确率提高了9%-12%。此外,ClaimPKG在无结构数据集(如HoVer和FEVEROUS)上展现了零镜头泛化能力,有效地结合了知识图谱的结构化知识与各种LLM骨干网的推理能力。
Key Takeaways:
- 知识图谱(KGs)与大型语言模型(LLMs)的结合对于提高声明验证中的推理能力是一个新兴研究挑战。
- 虽然知识图谱提供了结构化和语义丰富的信息,但大多数验证方法仍依赖非结构化文本语料库。
- ClaimPKG框架集成了LLM推理与知识图谱的结构化知识,采用轻量级专业LLM表示输入声明为伪子图。
- ClaimPKG通过子图检索模块识别相关的KG子图,再交由通用LLM处理产生最终裁决和理由。
- 在FactKG数据集上的实验表明,ClaimPKG性能优越,较基线模型准确率提高9%-12%。
- ClaimPKG展现出零镜头泛化能力,能在无结构数据集上有效结合知识图谱的结构化知识与LLM推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

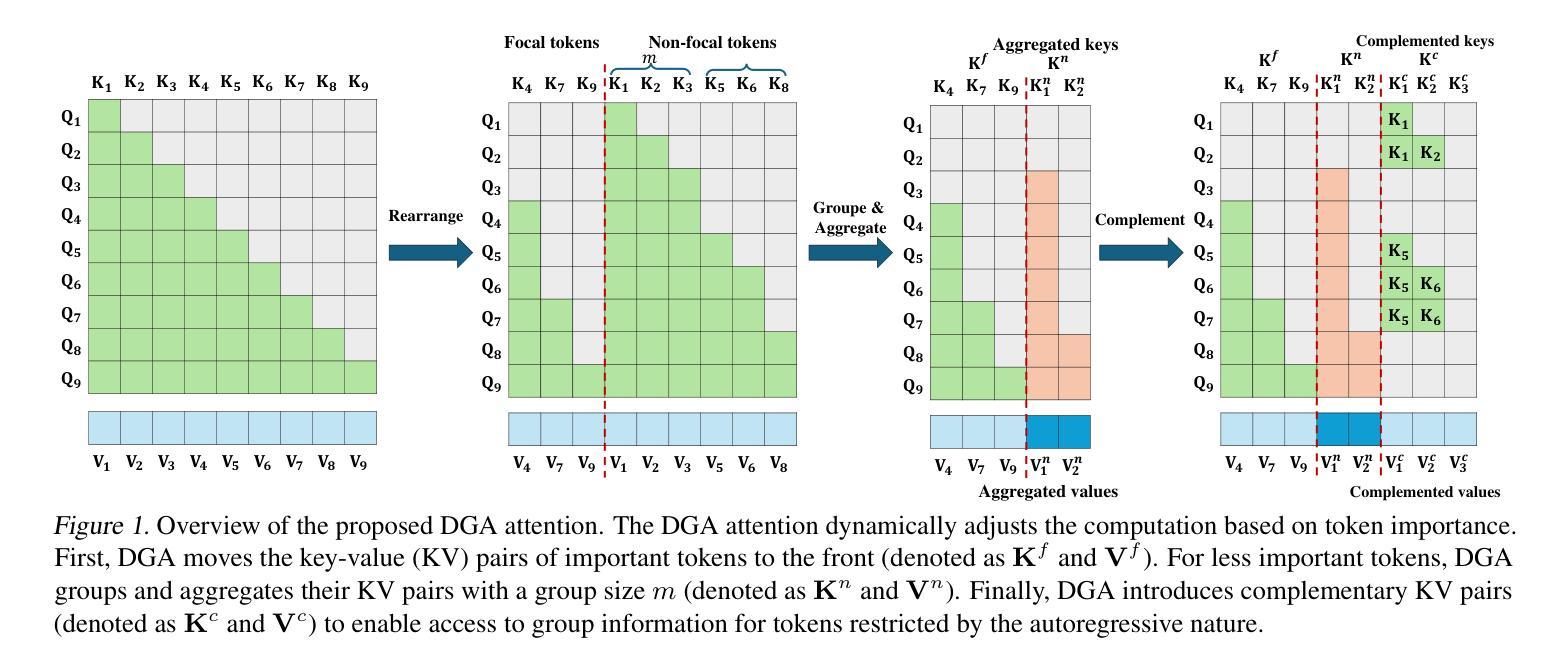
Curse of High Dimensionality Issue in Transformer for Long-context Modeling
Authors:Shuhai Zhang, Zeng You, Yaofo Chen, Zhiquan Wen, Qianyue Wang, Zhijie Qiu, Yuanqing Li, Mingkui Tan
Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) excel in natural language processing tasks by capturing long-range dependencies through self-attention mechanisms. However, long-context modeling faces significant computational inefficiencies due to \textit{redundant} attention computations: while attention weights are often \textit{sparse}, all tokens consume \textit{equal} computational resources. In this paper, we reformulate traditional probabilistic sequence modeling as a \textit{supervised learning task}, enabling the separation of relevant and irrelevant tokens and providing a clearer understanding of redundancy. Based on this reformulation, we theoretically analyze attention sparsity, revealing that only a few tokens significantly contribute to predictions. Building on this, we formulate attention optimization as a linear coding problem and propose a \textit{group coding strategy}, theoretically showing its ability to improve robustness against random noise and enhance learning efficiency. Motivated by this, we propose \textit{Dynamic Group Attention} (DGA), which leverages the group coding to explicitly reduce redundancy by aggregating less important tokens during attention computation. Empirical results show that our DGA significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining competitive performance.Code is available at https://github.com/bolixinyu/DynamicGroupAttention.
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)通过自注意力机制捕捉长距离依赖关系,在自然语言处理任务上表现出色。然而,由于冗余的注意力计算,长上下文建模面临重大的计算效率低下问题:虽然注意力权重通常是稀疏的,但所有令牌都消耗着平等的计算资源。在本文中,我们将传统的概率序列建模重新表述为“监督学习任务”,这能够分离相关和不相关的令牌,并提供对冗余的更清晰理解。基于这种重新表述,我们从理论上分析了注意力稀疏性,揭示只有少数令牌对预测产生重大贡献。在此基础上,我们将注意力优化表述为线性编码问题,并提出“分组编码策略”,从理论上证明了其提高对抗随机噪声的鲁棒性和提高学习效率的能力。受此启发,我们提出了“动态组注意力”(DGA),它利用分组编码来通过聚合不太重要的令牌来明确减少冗余的计算。经验结果表明,我们的DGA在保持竞争力的同时显著降低了计算成本。代码可在https://github.com/bolixinyu/DynamicGroupAttention找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中的优异表现,尤其在于通过自注意力机制捕捉长距离依赖关系。然而,长上下文建模面临计算效率低下的问题,主要由于冗余的注意力计算。针对这一问题,本文提出将传统概率序列建模重新定义为监督学习任务,以区分相关和不相关的令牌,从而减少冗余。文章还进行了注意力稀疏性的理论分析,并证明只有少数令牌对预测有显著贡献。基于此,文章提出了动态组注意力(DGA)方法,通过分组编码策略来降低冗余,并在计算注意力时聚合不重要的令牌。实证研究结果显示,DGA在显著降低计算成本的同时,保持了具有竞争力的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer-based LLMs excel in natural language processing by capturing long-range dependencies through self-attention.
- 长上下文建模存在计算效率低下的问题,主要由于冗余的注意力计算。
- 本文通过将传统概率序列建模重新定义为监督学习任务来减少冗余。
- 文章进行了注意力稀疏性的理论分析,并证明只有少数令牌对预测有显著贡献。
- 提出了动态组注意力(DGA)方法,通过分组编码策略降低冗余。
- DGA在降低计算成本的同时保持了良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

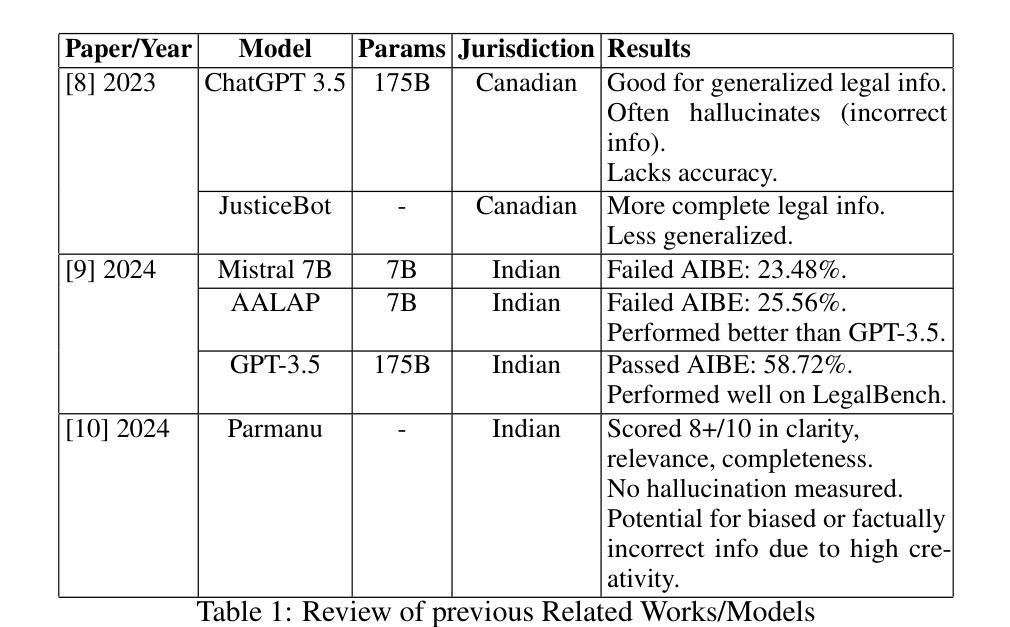
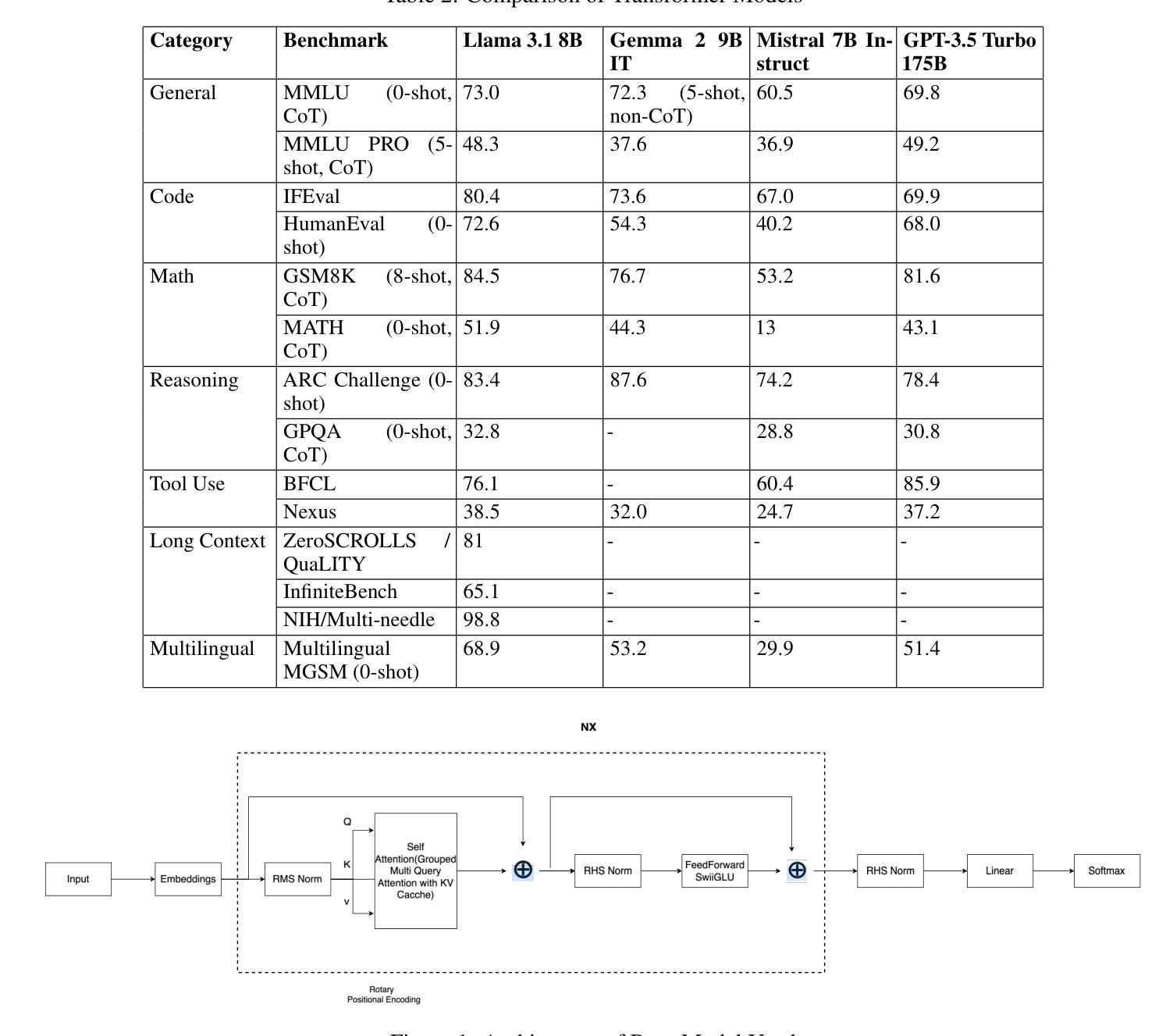
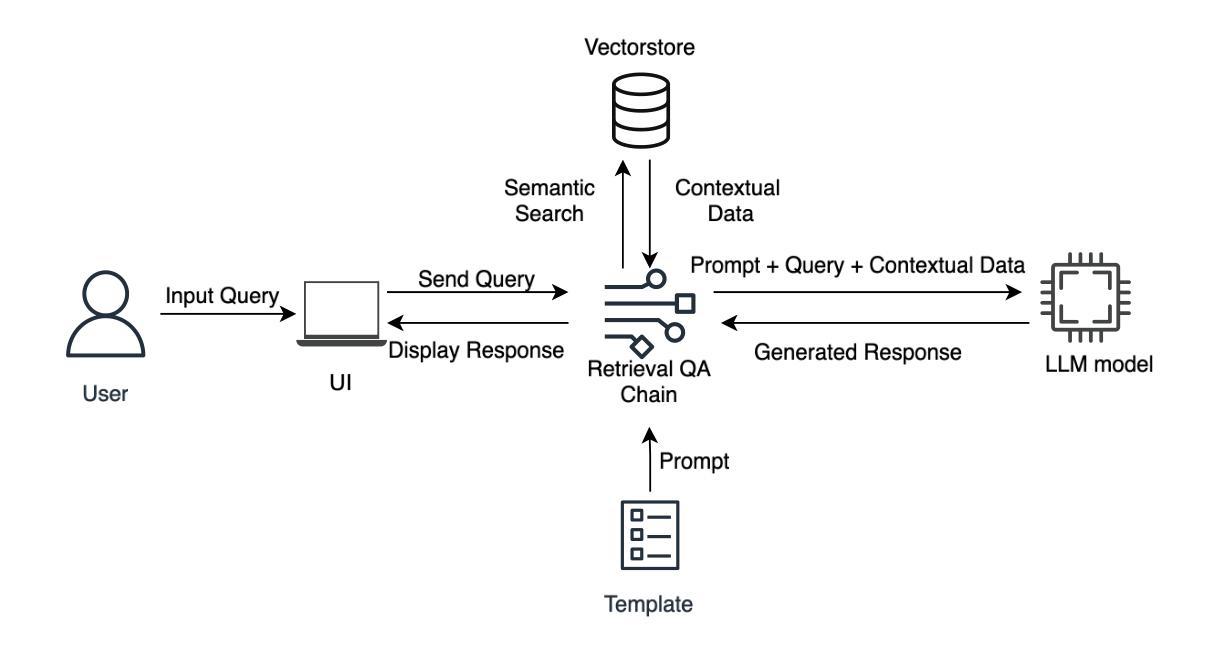
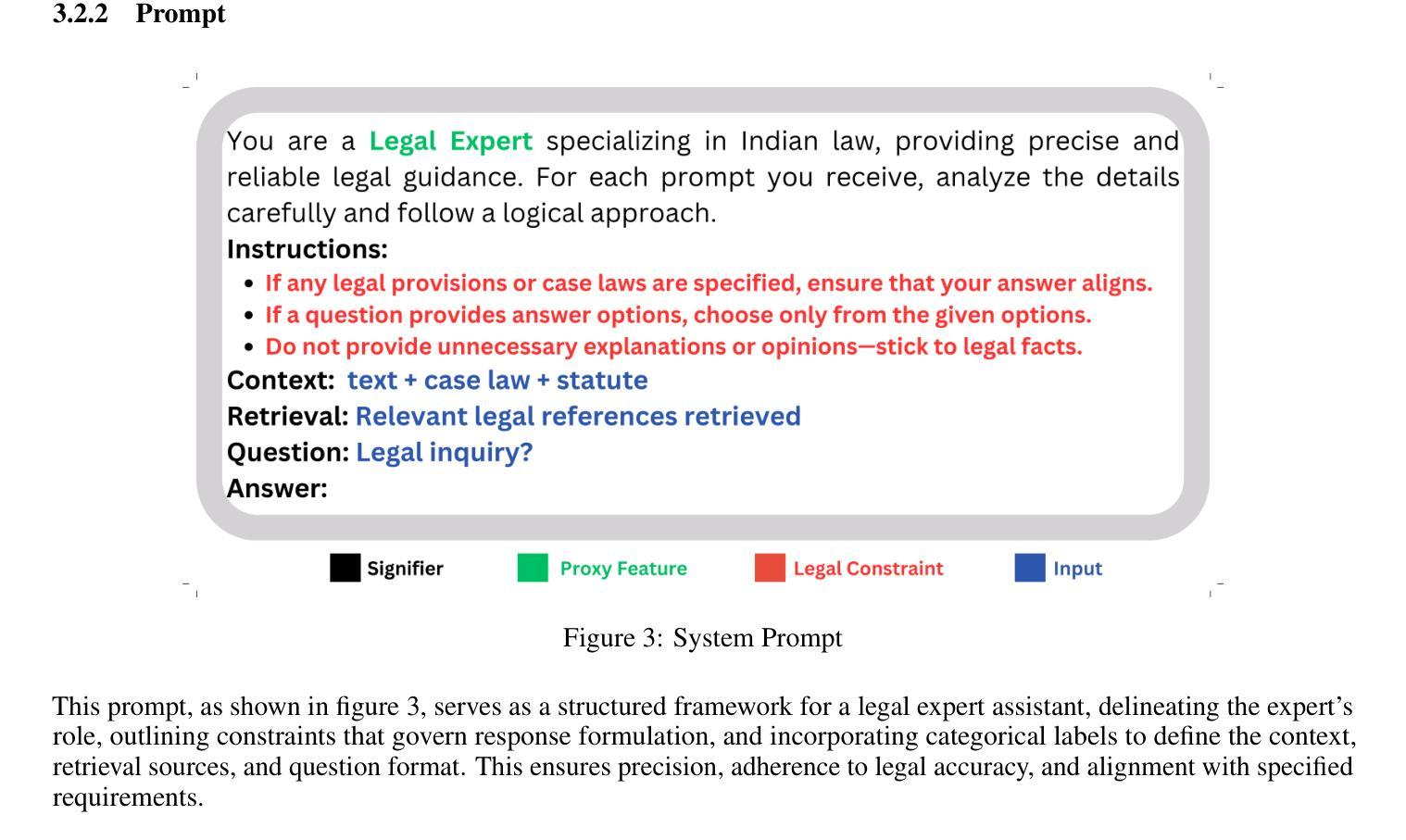
Legal Assist AI: Leveraging Transformer-Based Model for Effective Legal Assistance
Authors:Jatin Gupta, Akhil Sharma, Saransh Singhania, Ali Imam Abidi
Pursuit of accessible legal assistance in India faces a critical gap, as many citizens struggle to leverage their legal rights due to limited awareness and access to relevant legal information. This paper introduces Legal Assist AI, a transformer-based model designed to bridge this gap by offering effective legal assistance through large language models (LLMs). The system retrieves relevant legal information from a curated database and generates accurate responses, enabling effective assistance for diverse users, including legal professionals, scholars, and the general public. The model was fine-tuned on extensive datasets from the Indian legal domain, including Indian Constitution, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) and so forth, providing a robust understanding of the complexities of Indian law. By incorporating domain-specific legal datasets, the proposed model demonstrated remarkable efficiency and specialization in legal Question-Answering. The model was evaluated against state-of-the-art models such as GPT-3.5 Turbo and Mistral 7B, achieving a 60.08% score on the AIBE, outperforming its competitors in legal reasoning and accuracy. Unlike other models, Legal Assist AI avoided common issues such as hallucinations, making it highly reliable for practical legal applications. It showcases the model’s applicability in real-world legal scenarios, with future iterations aiming to enhance performance and expand its dataset to cover a broader range of multilingual and case-specific queries as well.
在印度,获取合法法律援助的追求面临着一个关键的差距,因为许多公民由于对相关法律信息的了解和获取有限,难以利用自己的法律权利。本文介绍了Legal Assist AI,这是一个基于transformer的模型,旨在通过大型语言模型(LLM)提供有效的法律援助,以弥合这一差距。该系统从精选的数据库中检索相关法律信息,并生成准确的响应,能够为包括法律专业人士、学者和公众在内的不同用户提供有效的帮助。该模型经过印度法律领域的大量数据集进行微调,包括印度宪法、印度法典(BNS)、印度公民安全法案(BNSS)等等,对印度法律的复杂性有了稳健的理解。通过融入特定领域的法律数据集,所提议的模型在法律问答方面表现出令人印象深刻的效率和专业化。该模型与最前沿的模型如GPT-3.5 Turbo和Mistral 7B进行了评估对比,在法律推理和准确性方面取得了60.08%的AIBE评分,超越了其竞争对手。与其他模型不同的是,Legal Assist AI避免了诸如幻觉等常见问题,使其成为实际法律应用的高度可靠工具。它展示了该模型在现实法律场景中的应用性,未来的版本旨在提高性能,并扩大数据集,以覆盖更广泛的多种语言和特定案例查询。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 tables, 4 figures. This is a revised version of a preprint previously available at this URL: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5351879/v1
Summary:
印度法律援助的可及性面临重大挑战,许多公民因对法律信息缺乏了解和获取途径而无法充分利用自身法律权益。本文介绍了Legal Assist AI,一款基于变压器的模型,旨在通过大型语言模型(LLM)提供有效的法律援助来弥补这一差距。该系统从精选数据库中检索相关法律信息并生成准确响应,为包括法律专业人士、学者和公众在内的各类用户提供有效援助。模型经过印度法律领域的广泛数据集进行微调,包括印度宪法、印度法律汇编等,对印度法律的复杂性有深入了解。通过引入领域特定的法律数据集,该模型在法律问答方面表现出卓越的效率和专业性。评估结果显示,Legal Assist AI在法律推理和准确性方面表现优异,优于GPT-3.5 Turbo和Mistral 7B等最先进的模型。该模型在实际法律场景中的应用展示了其适用性,未来版本将进一步提高性能并扩展数据集,以覆盖更广泛的跨语言及特定案例查询。
Key Takeaways:
- 印度公民在获取法律援助方面面临困难,缺乏对相关法律信息的了解和获取途径。
- Legal Assist AI是一款基于LLM设计的模型,旨在缩小这一差距。
- 该系统可从数据库中检索相关法律信息并生成准确响应。
- 模型经过印度法律领域的数据集进行微调,表现出卓越的专业性和效率。
- Legal Assist AI在法律推理和准确性方面优于其他最先进的模型。
- 该模型避免了常见的幻觉问题,具有高度可靠性,适用于实际法律场景。
点此查看论文截图

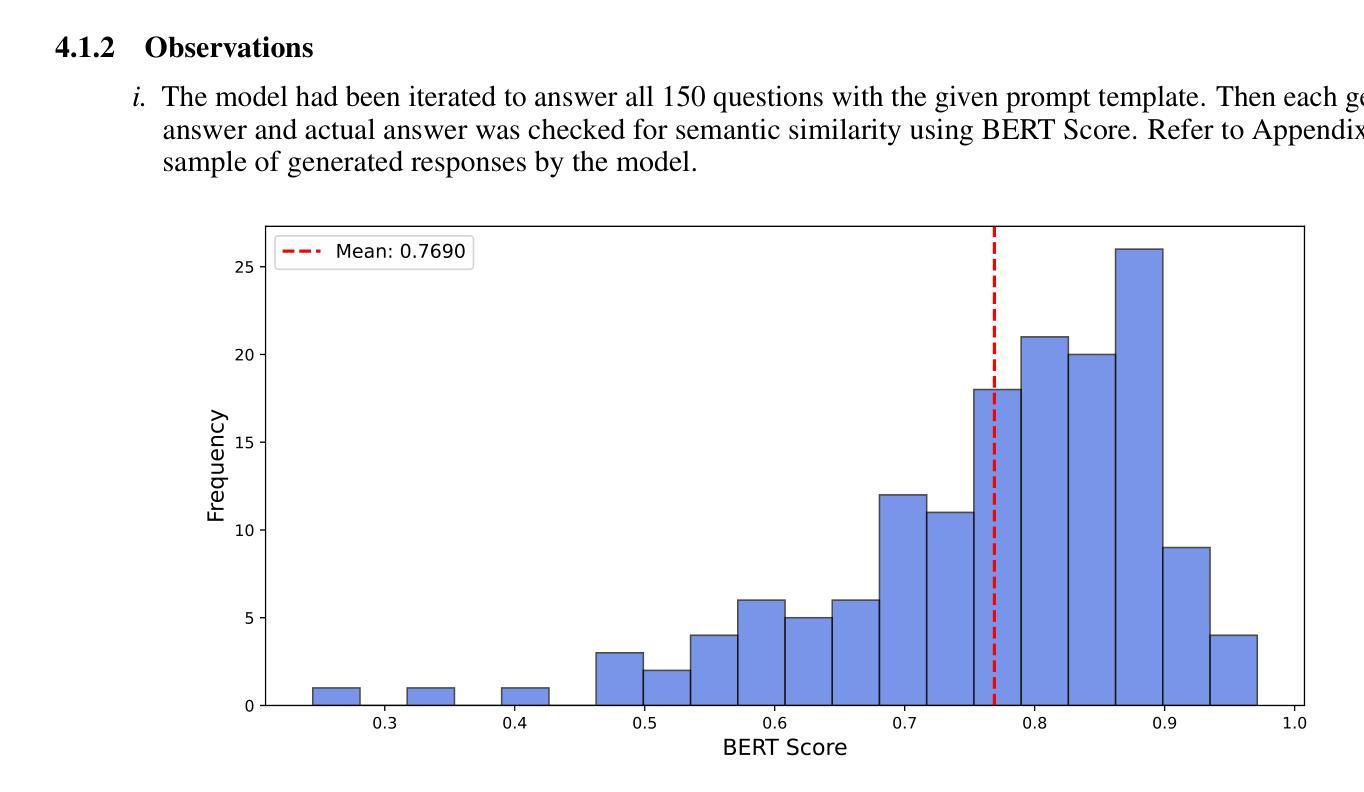
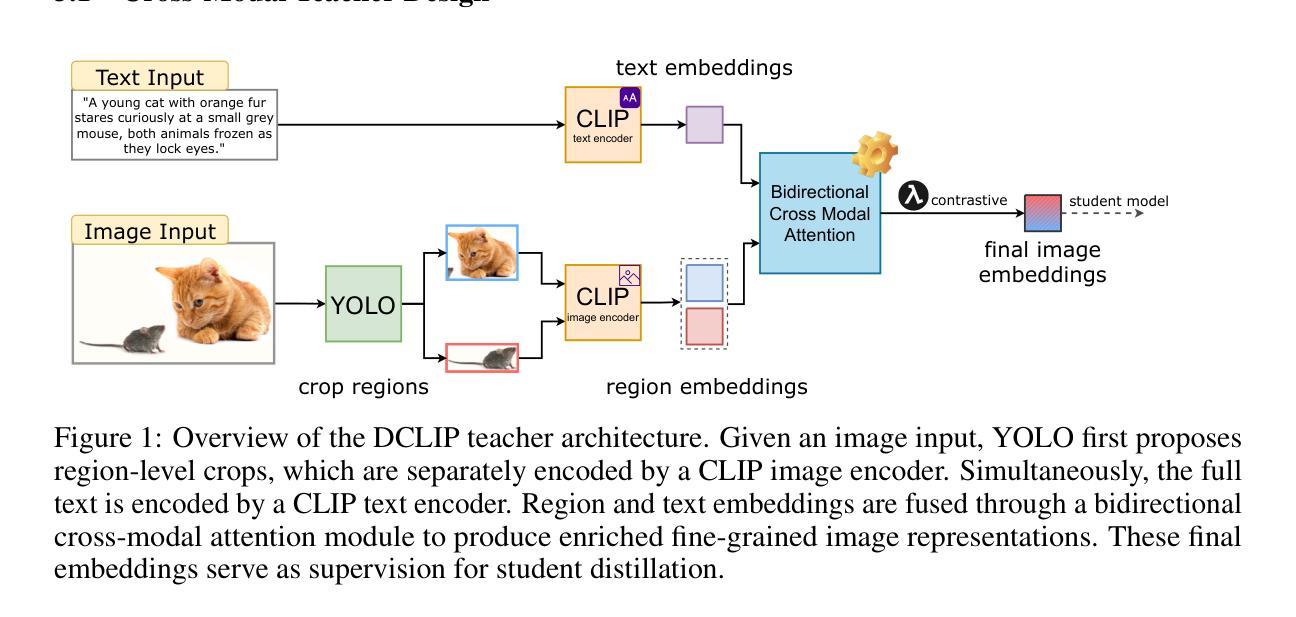
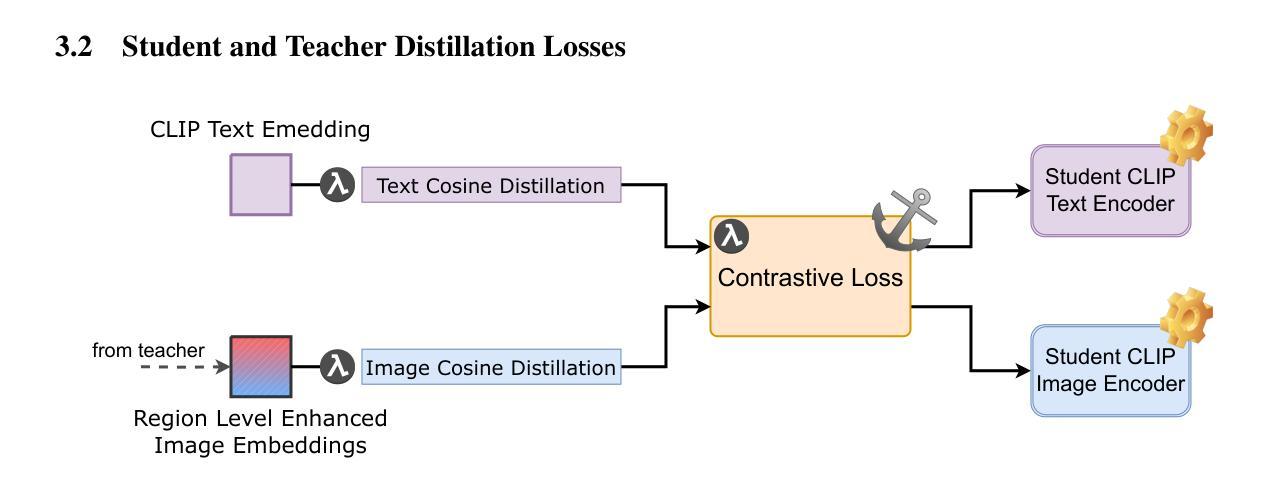
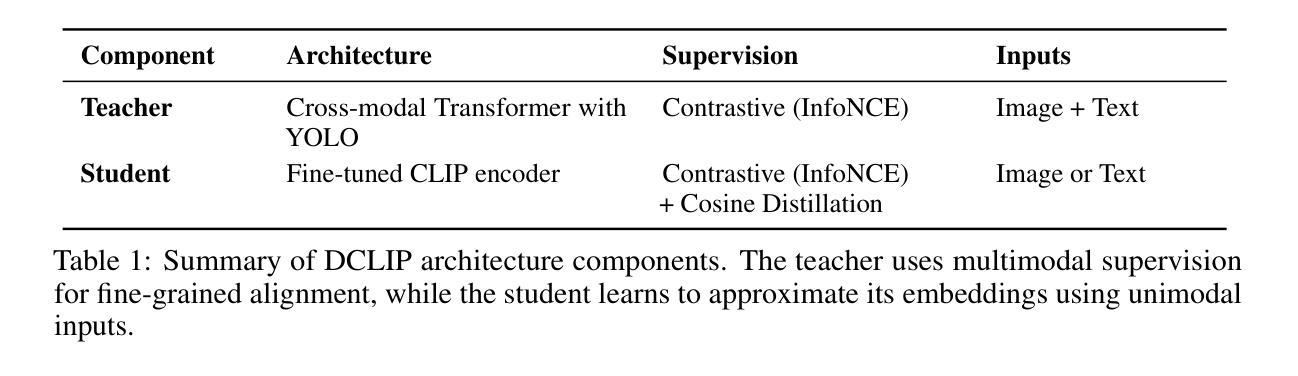
Distill CLIP (DCLIP): Enhancing Image-Text Retrieval via Cross-Modal Transformer Distillation
Authors:Daniel Csizmadia, Andrei Codreanu, Victor Sim, Vighnesh Prabeau, Michael Lu, Kevin Zhu, Sean O’Brien, Vasu Sharma
We present Distill CLIP (DCLIP), a fine-tuned variant of the CLIP model that enhances multimodal image-text retrieval while preserving the original model’s strong zero-shot classification capabilities. CLIP models are typically constrained by fixed image resolutions and limited context, which can hinder their effectiveness in retrieval tasks that require fine-grained cross-modal understanding. DCLIP addresses these challenges through a meta teacher-student distillation framework, where a cross-modal transformer teacher is fine-tuned to produce enriched embeddings via bidirectional cross-attention between YOLO-extracted image regions and corresponding textual spans. These semantically and spatially aligned global representations guide the training of a lightweight student model using a hybrid loss that combines contrastive learning and cosine similarity objectives. Despite being trained on only ~67,500 samples curated from MSCOCO, Flickr30k, and Conceptual Captions-just a fraction of CLIP’s original dataset-DCLIP significantly improves image-text retrieval metrics (Recall@K, MAP), while retaining approximately 94% of CLIP’s zero-shot classification performance. These results demonstrate that DCLIP effectively mitigates the trade-off between task specialization and generalization, offering a resource-efficient, domain-adaptive, and detail-sensitive solution for advanced vision-language tasks. Code available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md.
我们提出了Distill CLIP(DCLIP),它是CLIP模型的一种微调变体,增强了多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留了原始模型强大的零样本分类能力。CLIP模型通常受到固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的限制,这可能会阻碍它们在需要精细跨模态理解的任务中的有效性。DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架来解决这些挑战,其中跨模态转换器教师经过微调以通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力产生丰富的嵌入。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过使用结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标的混合损失来指导轻量级学生模型的训练。尽管仅使用从MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions精选的约67,500个样本进行训练,只占CLIP原始数据集的一部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP大约94%的零样本分类性能。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务专业化和通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Distill CLIP(DCLIP)是CLIP模型的精细调整变体,它增强了多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留了原始模型强大的零样本分类能力。DCLIP通过元教师-学生蒸馏框架解决CLIP模型在图像分辨率和上下文方面的限制,通过跨模态变压器教师产生丰富的嵌入,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力进行训练。使用混合损失训练学生模型,结合了对比学习和余弦相似性目标。尽管只在约67,500个样本上进行训练,这些样本是从MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions中精选出来的,仅占CLIP原始数据集的一部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP的零样本分类性能的约94%。结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务特化与通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- DCLIP是CLIP模型的改进版本,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索功能并保留其零样本分类能力。
- DCLIP通过教师-学生蒸馏框架解决CLIP模型的限制,包括固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的问题。
- 教师模型通过双向交叉注意力机制产生丰富的嵌入,结合YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度进行训练。
- 学生模型使用混合损失进行训练,该损失结合了对比学习和余弦相似性目标。
- DCLIP在有限的样本集上进行了训练,但显著提高了图像文本检索性能(Recall@K,MAP)。
- DCLIP能够保留CLIP大约94%的零样本分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

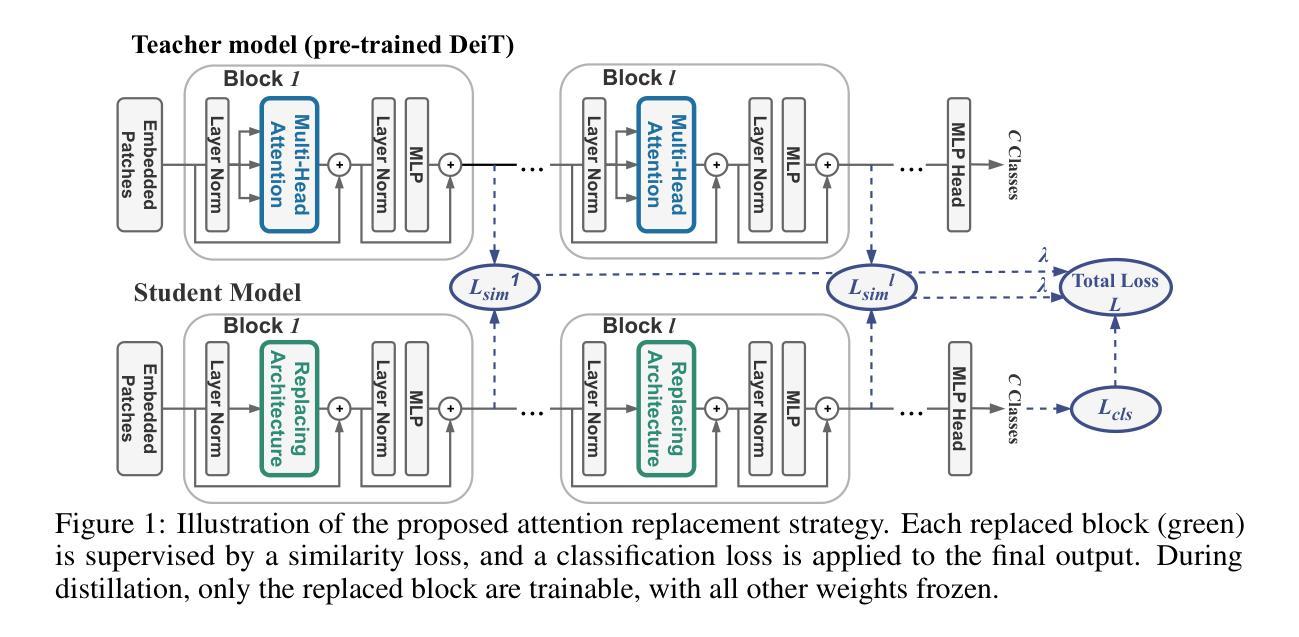
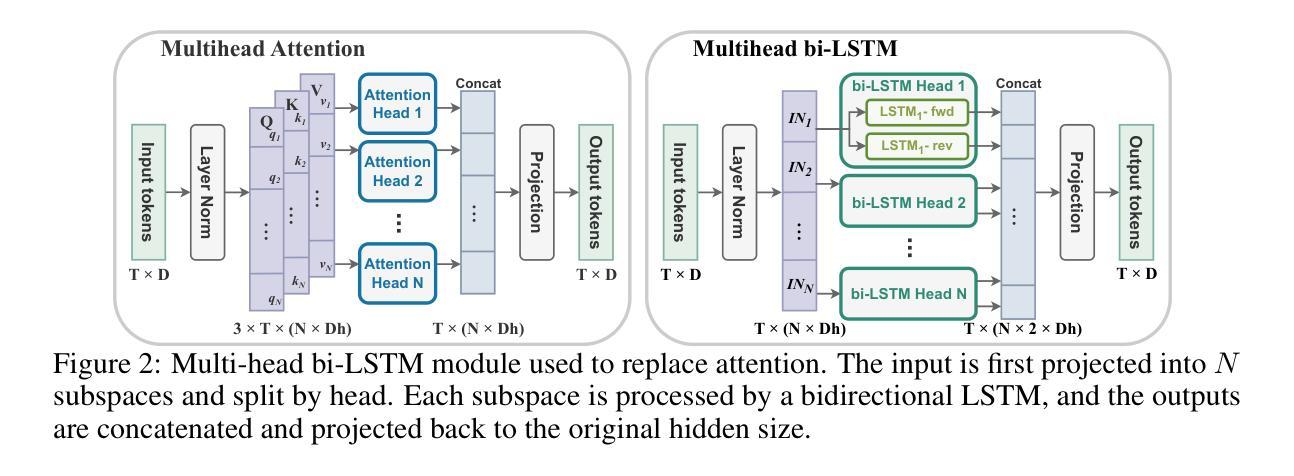
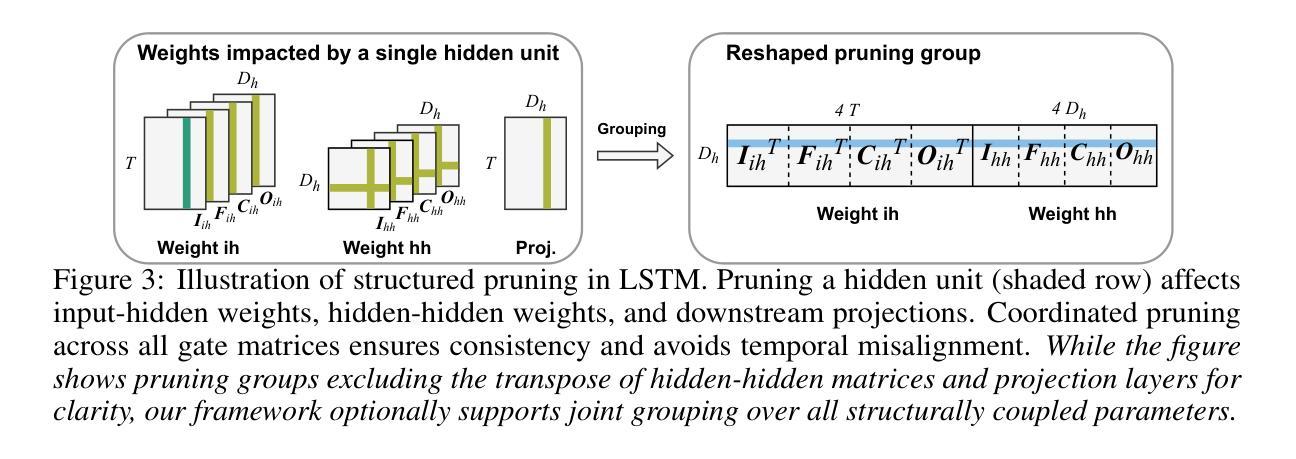
Is Attention Required for Transformer Inference? Explore Function-preserving Attention Replacement
Authors:Yuxin Ren, Maxwell D Collins, Miao Hu, Huanrui Yang
While transformers excel across vision and language pretraining tasks, their reliance on attention mechanisms poses challenges for inference efficiency, especially on edge and embedded accelerators with limited parallelism and memory bandwidth. Hinted by the observed redundancy of attention at inference time, we hypothesize that though the model learns complicated token dependency through pretraining, the inference-time sequence-to-sequence mapping in each attention layer is actually ‘’simple’’ enough to be represented with a much cheaper function. In this work, we explore FAR, a Function-preserving Attention Replacement framework that replaces all attention blocks in pretrained transformers with learnable sequence-to-sequence modules, exemplified by an LSTM. FAR optimize a multi-head LSTM architecture with a block-wise distillation objective and a global structural pruning framework to achieve a family of efficient LSTM-based models from pretrained transformers. We validate FAR on the DeiT vision transformer family and demonstrate that it matches the accuracy of the original models on ImageNet and multiple downstream tasks with reduced parameters and latency. Further analysis shows that FAR preserves the semantic token relationships and the token-to-token correlation learned in the transformer’s attention module.
虽然Transformer在视觉和语言预训练任务上表现出色,但它们对注意力机制的依赖对推理效率提出了挑战,尤其是在具有有限并行性和内存带宽的边缘和嵌入式加速器上。通过观察推理时注意力的冗余性,我们假设尽管模型通过预训练学习复杂的令牌依赖性,但每个注意力层的推理时间序列到序列的映射实际上可以用更便宜的函数来表示。在这项工作中,我们探索了FAR(函数保持注意力替换框架),该框架用可学习的序列到序列模块替换了预训练Transformer中的所有注意力块,以LSTM为例。FAR优化了一种多头LSTM架构,采用块级蒸馏目标和全局结构剪枝框架,从预训练的Transformer中实现了一系列高效的LSTM模型家族。我们在DeiT视觉Transformer家族上验证了FAR,并证明它在ImageNet和多个下游任务上的准确率与原始模型相匹配,同时减少了参数和延迟。进一步的分析表明,FAR保留了Transformer的注意力模块中学习的语义令牌关系和令牌到令牌的关联性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages main paper + 6 pages appendix, 14 figures; submitted to NeurIPS 2025
Summary
本文探讨了将预训练Transformer中的注意力块替换为可学习的序列到序列模块的方法,该方法以LSTM为例,旨在提高推理效率。该研究优化了一种基于LSTM的多头架构,采用块级蒸馏目标和全局结构剪枝框架,从预训练Transformer中实现了高效的LSTM模型家族。在DeiT视觉Transformer家族上验证了该方法,在ImageNet和多个下游任务上达到了与原始模型相当的精度,同时降低了参数和延迟。
Key Takeaways
- Transformers在视觉和语言预训练任务上表现出色,但其对注意力机制的依赖给推理效率带来了挑战,特别是在并行度和内存带宽有限的边缘和嵌入式加速器上。
- 观察到推理时的注意力冗余,模型虽然在预训练阶段学习复杂的令牌依赖关系,但推理时每个注意力层的序列到序列映射实际上可以用更简单的函数来表示。
- 提出了一种名为FAR的功能保持注意力替代框架,该框架用可学习的序列到序列模块(如LSTM)替代了预训练Transformer中的所有注意力块。
- FAR通过优化多头LSTM架构、采用块级蒸馏目标和全局结构剪枝框架,实现了从预训练Transformer中的高效LSTM模型家族。
- 在DeiT视觉Transformer家族上验证了FAR,在ImageNet和多个下游任务上达到了与原始模型相当的精度,同时降低了参数和计算延迟。
- FAR能够保留Transformer中注意力模块学习的语义令牌关系和令牌到令牌的相关性。
点此查看论文截图

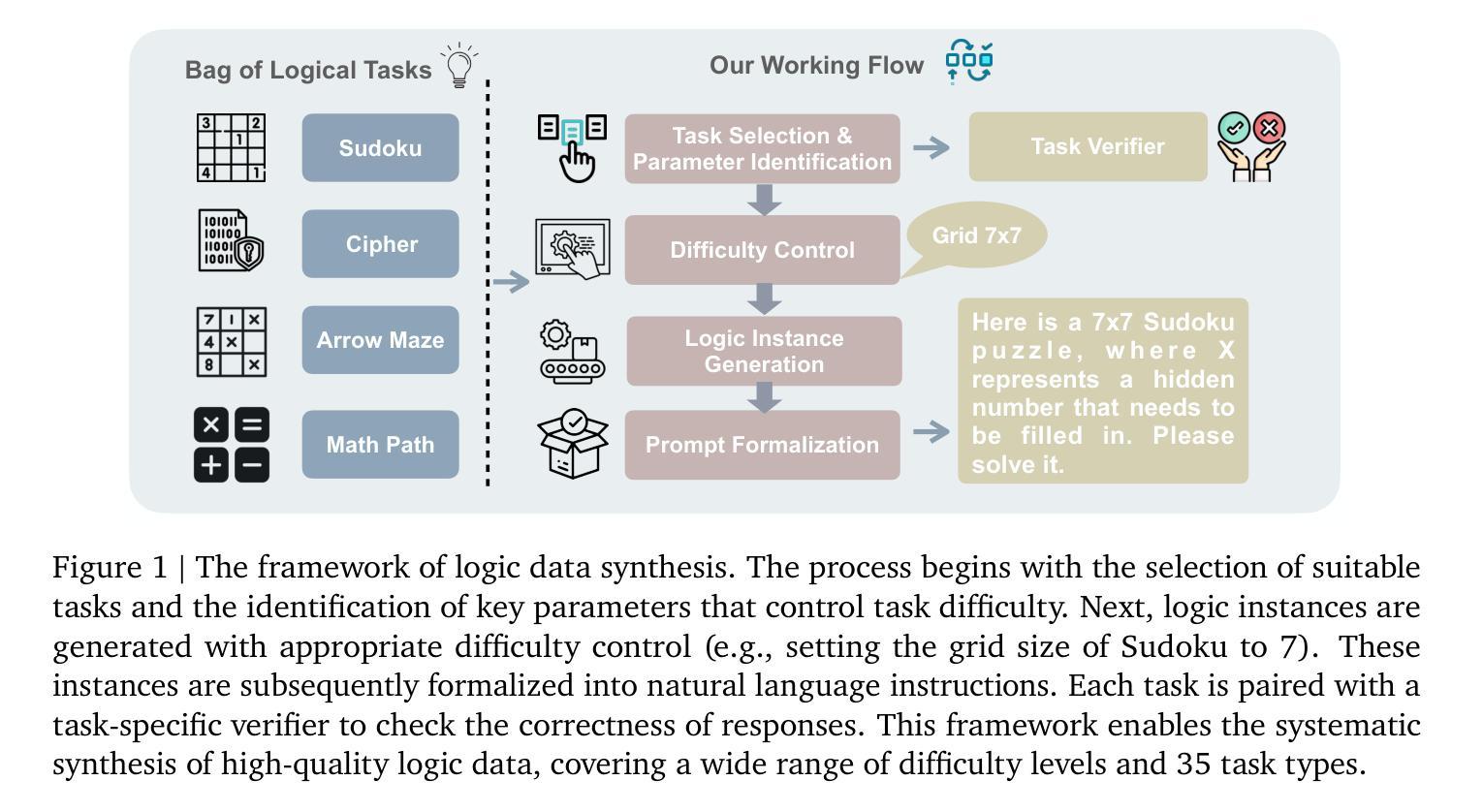
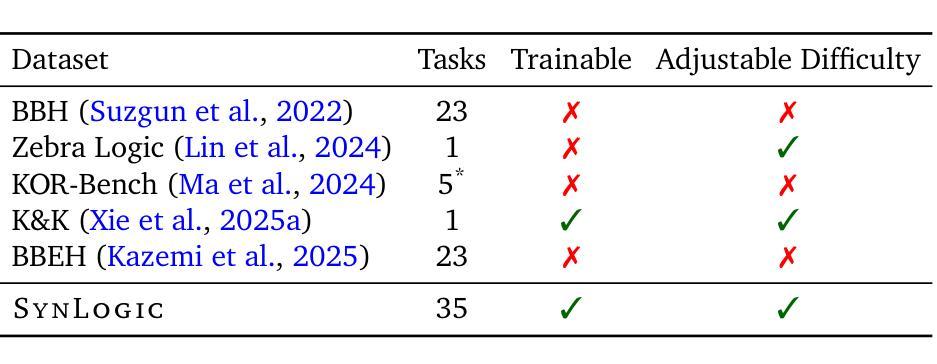
SynLogic: Synthesizing Verifiable Reasoning Data at Scale for Learning Logical Reasoning and Beyond
Authors:Junteng Liu, Yuanxiang Fan, Zhuo Jiang, Han Ding, Yongyi Hu, Chi Zhang, Yiqi Shi, Shitong Weng, Aili Chen, Shiqi Chen, Yunan Huang, Mozhi Zhang, Pengyu Zhao, Junjie Yan, Junxian He
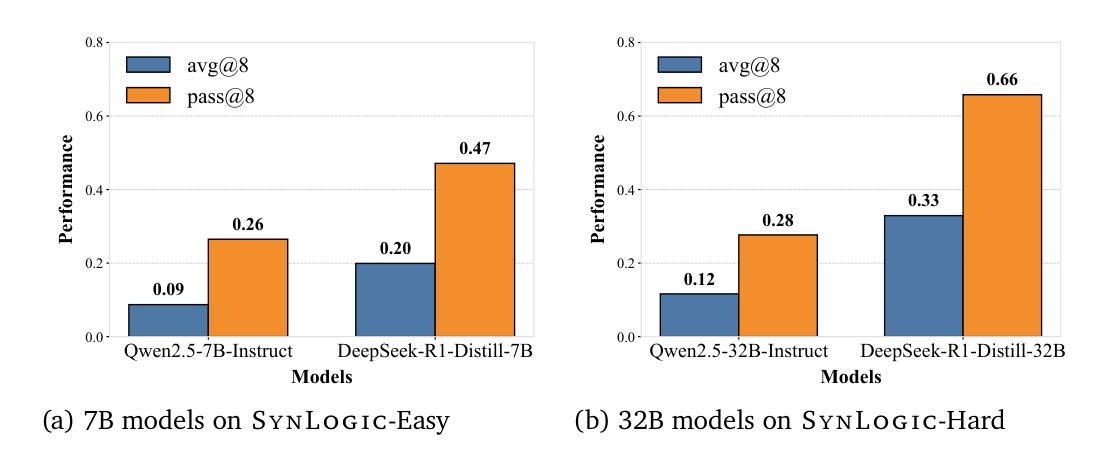
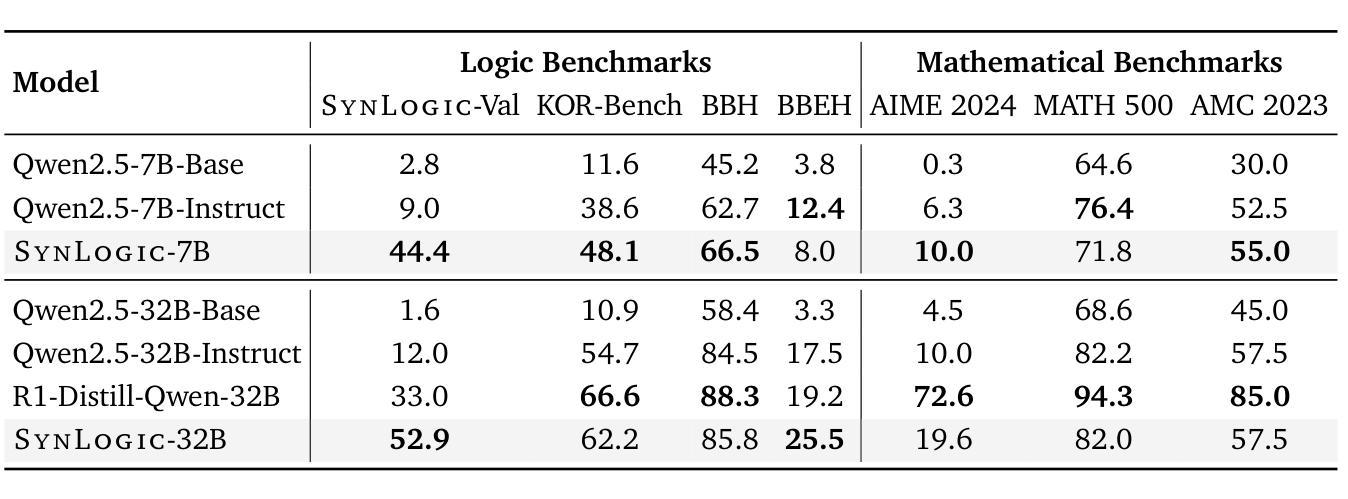
Recent advances such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek R1 have demonstrated the potential of Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enhance reasoning abilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). While open-source replication efforts have primarily focused on mathematical and coding domains, methods and resources for developing general reasoning capabilities remain underexplored. This gap is partly due to the challenge of collecting diverse and verifiable reasoning data suitable for RL. We hypothesize that logical reasoning is critical for developing general reasoning capabilities, as logic forms a fundamental building block of reasoning. In this work, we present SynLogic, a data synthesis framework and dataset that generates diverse logical reasoning data at scale, encompassing 35 diverse logical reasoning tasks. The SynLogic approach enables controlled synthesis of data with adjustable difficulty and quantity. Importantly, all examples can be verified by simple rules, making them ideally suited for RL with verifiable rewards. In our experiments, we validate the effectiveness of RL training on the SynLogic dataset based on 7B and 32B models. SynLogic leads to state-of-the-art logical reasoning performance among open-source datasets, surpassing DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B by 6 points on BBEH. Furthermore, mixing SynLogic data with mathematical and coding tasks improves the training efficiency of these domains and significantly enhances reasoning generalization. Notably, our mixed training model outperforms DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B across multiple benchmarks. These findings position SynLogic as a valuable resource for advancing the broader reasoning capabilities of LLMs. We open-source both the data synthesis pipeline and the SynLogic dataset at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/SynLogic.
最近,如OpenAI-o1和DeepSeek R1等进展表明强化学习(RL)在增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面具有巨大潜力。虽然开源复制工作主要集中在数学和编码领域,但开发通用推理能力的方法和资源仍然探索不足。这一差距部分是由于收集适合强化学习的多样化和可验证的推理数据所带来的挑战。我们假设逻辑推理对于发展通用推理能力至关重要,因为逻辑是推理的基本组成部分。在这项工作中,我们提出了SynLogic,这是一个数据合成框架和数据集,能够大规模生成多样化的逻辑推理数据,涵盖35种不同的逻辑推理任务。SynLogic方法能够控制数据和难度和数量的合成。重要的是,所有例子都可以通过简单的规则进行验证,使它们非常适合具有可验证奖励的强化学习。在我们的实验中,我们验证了强化学习在SynLogic数据集上训练的有效性,该数据集基于7B和32B模型。在开源数据集中,SynLogic在逻辑推理性能上达到了最新水平,在BBEH上比DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B高出6分。此外,将SynLogic数据与数学和编码任务混合在一起,可以提高这些领域的训练效率,并显著增强推理泛化能力。值得注意的是,我们的混合训练模型在多个基准测试中超越了DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B。这些发现使SynLogic成为推动LLM更广泛推理能力的重要资源。我们在https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/SynLogic公开了数据合成管道和SynLogic数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了SynLogic数据合成框架和数据集,用于生成大规模的逻辑推理数据。该框架通过强化学习提升大型语言模型的推理能力,填补了通用推理能力发展方法和资源的空缺。本文成功开发出多种逻辑任务的合成数据,通过调整难度和数量,实现对数据的可控合成。该数据集验证奖励的可验证性使其成为强化学习的理想选择。实验表明,SynLogic数据集在开源数据集上实现了最先进的逻辑推理性能,混合数学和编码任务的数据可以提高训练效率并增强推理泛化能力。该数据集已开源共享。
Key Takeaways
- SynLogic是一个用于生成大规模逻辑推理数据的合成框架和数据集。
- 该框架旨在通过强化学习提升大型语言模型的推理能力。
- SynLogic填补了通用推理能力发展方法和资源的空缺。
- 数据集具有可控的合成方式,可以调整难度和数量。
- 数据集适用于强化学习,因为验证奖励的可验证性。
- 实验表明,SynLogic在开源数据集上实现了先进的逻辑推理性能。
- 混合数学和编码任务的数据可以提高训练效率并增强推理泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Moderating Harm: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Cyberbullying Detection in YouTube Comments
Authors:Amel Muminovic
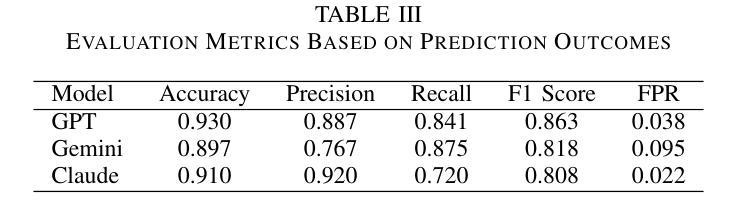
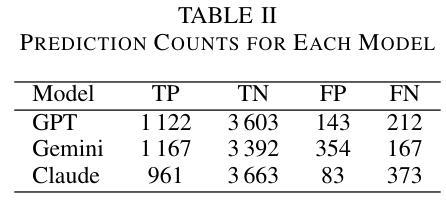
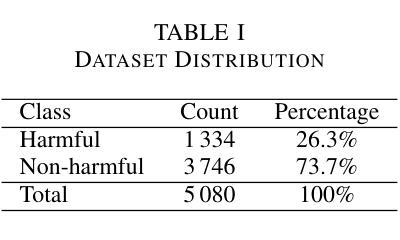
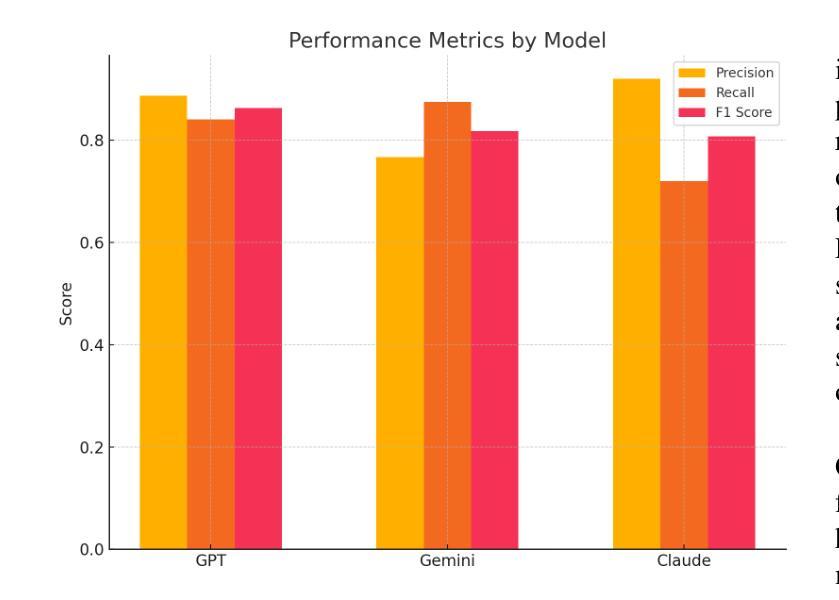
As online platforms grow, comment sections increasingly host harassment that undermines user experience and well-being. This study benchmarks three leading large language models, OpenAI GPT-4.1, Google Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Anthropic Claude 3 Opus, on a corpus of 5,080 YouTube comments sampled from high-abuse threads in gaming, lifestyle, food vlog, and music channels. The dataset comprises 1,334 harmful and 3,746 non-harmful messages in English, Arabic, and Indonesian, annotated independently by two reviewers with substantial agreement (Cohen’s kappa = 0.83). Using a unified prompt and deterministic settings, GPT-4.1 achieved the best overall balance with an F1 score of 0.863, precision of 0.887, and recall of 0.841. Gemini flagged the highest share of harmful posts (recall = 0.875) but its precision fell to 0.767 due to frequent false positives. Claude delivered the highest precision at 0.920 and the lowest false-positive rate of 0.022, yet its recall dropped to 0.720. Qualitative analysis showed that all three models struggle with sarcasm, coded insults, and mixed-language slang. These results underscore the need for moderation pipelines that combine complementary models, incorporate conversational context, and fine-tune for under-represented languages and implicit abuse. A de-identified version of the dataset and full prompts is publicly released to promote reproducibility and further progress in automated content moderation.
随着在线平台的增长,评论区越来越多地出现骚扰行为,这破坏了用户体验和福祉。本研究以三个领先的大型语言模型——OpenAI GPT-4.1、Google Gemini 1.5 Pro和Anthropic Claude 3 Opus为基准,对从游戏、生活方式、美食博客和音乐频道中高度滥用言论的线程中采集的5,080条YouTube评论进行了评估。该数据集包含用英语、阿拉伯语和印度尼西亚语编写的1,334条有害和3,746条无害消息,由两名评审员独立注释,两人之间达成了大量共识(Cohen的kappa值为0.83)。使用统一的提示和确定性设置,GPT-4.1取得了最佳的整体平衡,F1得分为0.863,精确度为0.887,召回率为0.841。Gemini标记的有害帖子比例最高(召回率= 0.875),但由于频繁出现误报,其精确度降至0.767。Claude的精确度最高,达到0.920,误报率最低,为0.022,但召回率降至0.720。定性分析表明,所有三个模型在应对讽刺、编码侮辱和混合语言俚语方面都存在困难。这些结果强调需要采用结合互补模型、融入对话语境、针对代表性不足的语言和隐性滥用进行微调的内容过滤管道。为了促进可重复性和在自动内容过滤方面的进一步进展,发布了一个匿名化的数据集和完整的提示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. 9 pages, 3 tables, 1 figure. Not yet submitted to a journal. Feedback welcome
Summary
在线平台发展迅猛,评论区的骚扰行为日益增多,影响用户体验和身心健康。本研究对三大主流大型语言模型OpenAI GPT-4.1、Google Gemini 1.5 Pro和Anthropic Claude 3 Opus进行了基准测试,测试样本取自YouTube的高滥用评论线程,包括游戏、生活方式、美食博客和音乐频道等。数据集包含独立标注的1334条有害信息和3746条无害信息,涉及英语、阿拉伯语和印尼语等语种,标注人员间的实质一致性较强(Cohen的kappa系数为0.83)。通过统一的提示和确定性设置,GPT-4.1在总体平衡方面表现最佳,F1分数为0.863,精确度为0.887,召回率为0.841。Gemini检测到有害帖子的比例最高(召回率为0.875),但因其产生较多的假阳性结果导致精确度降至0.767。Claude拥有最高的精确度(达到0.92),并且误报率最低(仅为0.022),但其召回率降至最低为0.72。定性分析表明,所有模型在处理讽刺性语言、伪装性辱骂以及混合语言俚语时都有困难。这提醒我们需要采取一些管理策略,结合互补模型,融入对话语境,并针对隐性滥用以及低代表性语言进行微调。数据集的非标识版本以及完整提示已公开发布,以促进可重复性和自动化内容管理的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 在线平台评论区骚扰行为普遍,影响用户体验和身心健康。
- 研究涉及三大主流大型语言模型的基准测试,测试样本取自高滥用评论线程。
- 数据集包含多种语言和标注结果,标注人员间实质一致性较强。
- GPT-4.1在总体性能上表现最佳,但各模型在特定方面存在差异。
- 所有模型在处理特定语言特征(如讽刺性语言、伪装性辱骂和混合语言俚语)时存在困难。
- 需要结合互补模型、融入对话语境的策略进行内容管理。
点此查看论文截图

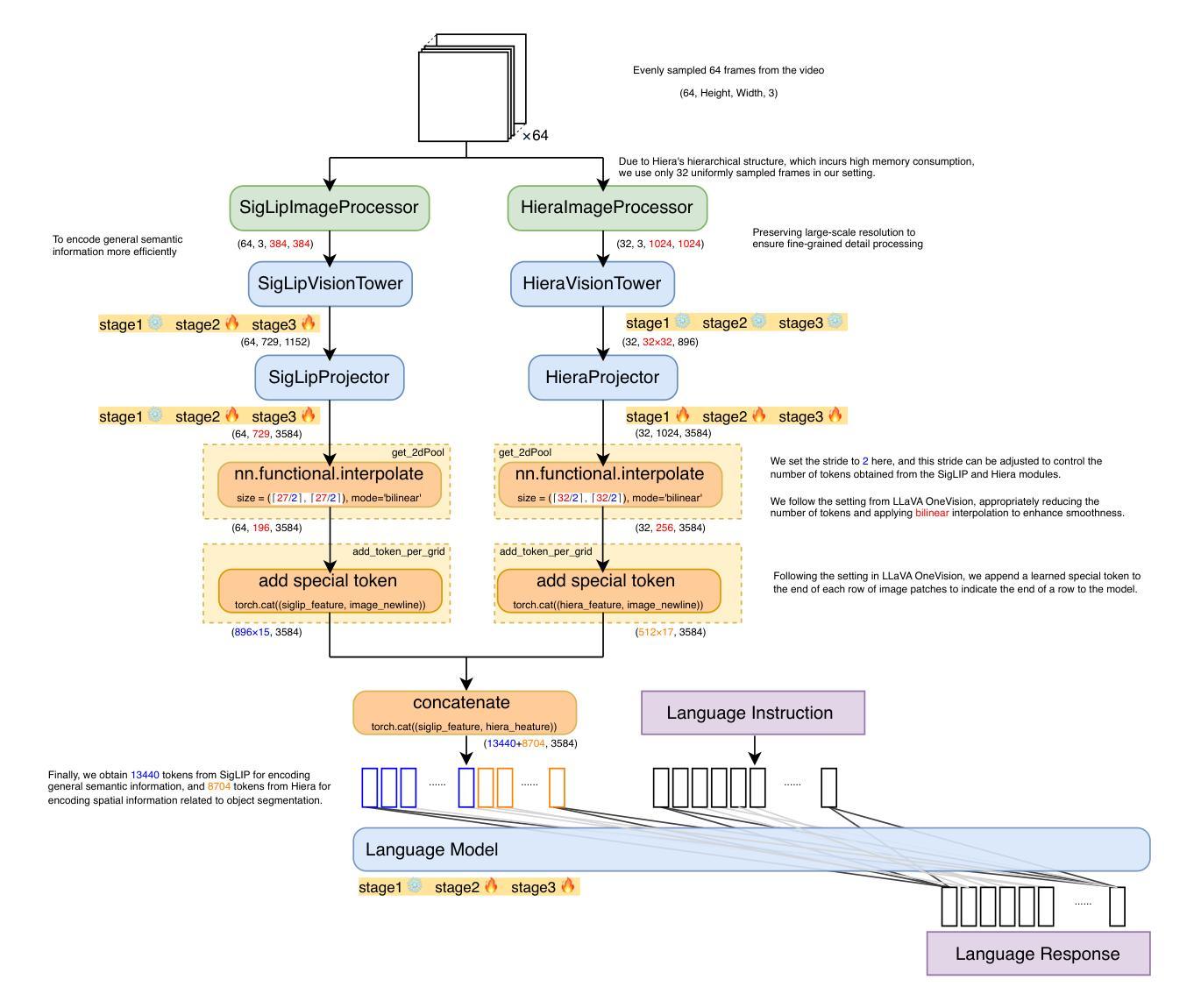
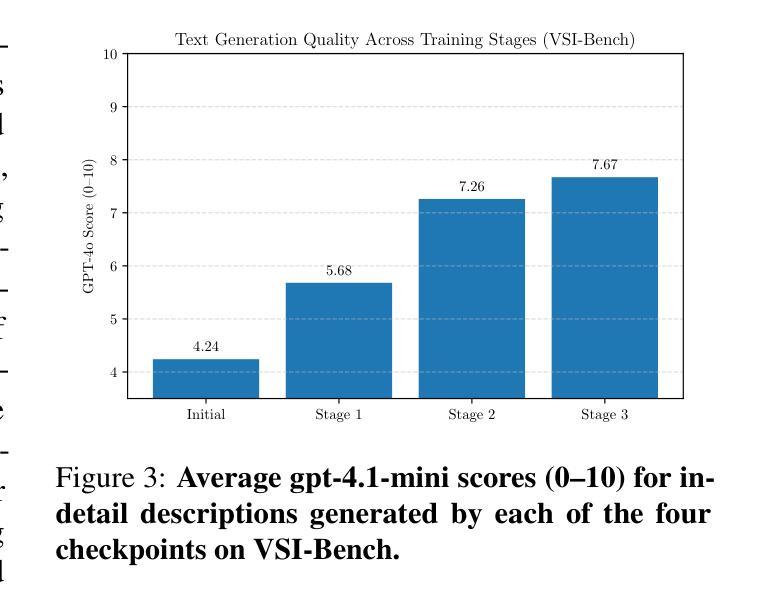
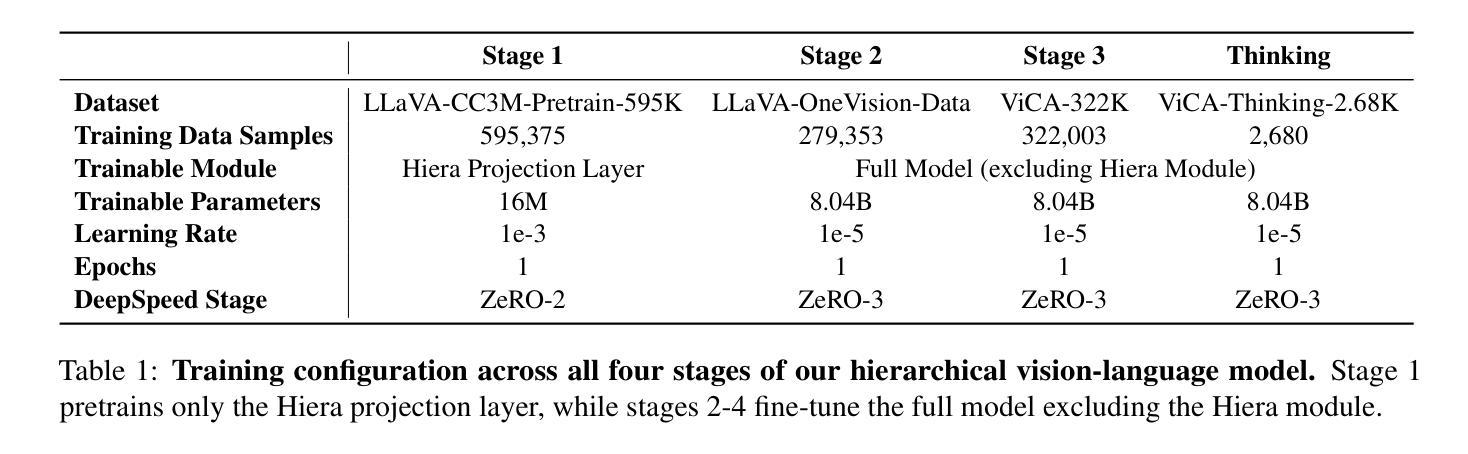
Towards Visuospatial Cognition via Hierarchical Fusion of Visual Experts
Authors:Qi Feng
While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at general vision-language tasks, visuospatial cognition - reasoning about spatial layouts, relations, and dynamics - remains a significant challenge. Existing models often lack the necessary architectural components and specialized training data for fine-grained spatial understanding. We introduce ViCA2 (Visuospatial Cognitive Assistant 2), a novel MLLM designed to enhance spatial reasoning. ViCA2 features a dual vision encoder architecture integrating SigLIP for semantics and Hiera for spatial structure, coupled with a token ratio control mechanism for efficiency. We also developed ViCA-322K, a new large-scale dataset with over 322,000 spatially grounded question-answer pairs for targeted instruction tuning. On the challenging VSI-Bench benchmark, our ViCA2-7B model achieves a state-of-the-art average score of 56.8, significantly surpassing larger open-source models (e.g., LLaVA-NeXT-Video-72B, 40.9) and leading proprietary models (Gemini-1.5 Pro, 45.4). This demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach in achieving strong visuospatial intelligence with a compact model. We release ViCA2, its codebase, and the ViCA-322K dataset to facilitate further research.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)虽然在一般的视觉语言任务上表现出色,但对于处理空间布局、关系和动态的视觉空间认知仍然是一个巨大的挑战。现有模型通常缺乏必要的架构组件和精细空间理解所需的专门训练数据。我们引入了ViCA2(视觉空间认知助手2),这是一种新型MLLM,旨在增强空间推理能力。ViCA2采用双视觉编码器架构,集成SigLIP进行语义分析,并采用Hiera进行空间结构处理,同时采用令牌比率控制机制以提高效率。我们还开发了ViCA-322K,这是一个新的大规模数据集,包含超过32万对空间定位的问题和答案,用于有针对性的指令调整。在具有挑战性的VSI-Bench基准测试中,我们的ViCA2-7B模型达到了平均得分56.8的业界领先水平,显著超过了其他大型开源模型(例如LLaVA-NeXT-Video-72B,得分为40.9)和领先的专业模型(Gemini-1.5 Pro,得分为45.4)。这证明了我们的方法在实现强大视觉空间智能的紧凑模型方面的有效性。我们发布ViCA2、其代码库和ViCA-322K数据集,以促进进一步的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In version 1, Hidetoshi Shimodaira was included as a co-author without their consent and has been removed from the author list
Summary
基于上述文本内容,其核心摘要为:尽管多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在一般的视觉语言任务上表现出色,但在处理空间布局、关系和动态的视觉空间认知上仍面临挑战。为解决此问题,推出了新型MLLM——ViCA2(视觉空间认知助手2),并设计了专门的架构组件和数据集ViCA-322K来增强空间推理能力。在具有挑战性的VSI-Bench基准测试中,ViCA2模型表现卓越,平均得分达到了先进的水平。它的代码和ViCA-322K数据集已公开发布,以促进后续研究。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的关键见解:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉空间认知方面存在挑战。
- 提出了新型MLLM——ViCA2,用于增强空间推理能力。
- ViCA2具有双视觉编码器架构,融合了SigLIP语义和Hiera空间结构技术。
- ViCA-322K数据集的推出是为了提供专门训练数据以支持精细化空间理解。
- ViCA2模型在VSI-Bench基准测试中表现卓越,平均得分超过其他大型开源模型和专有模型。
点此查看论文截图

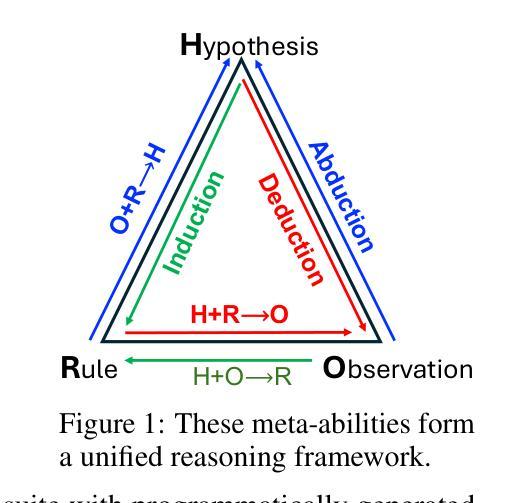
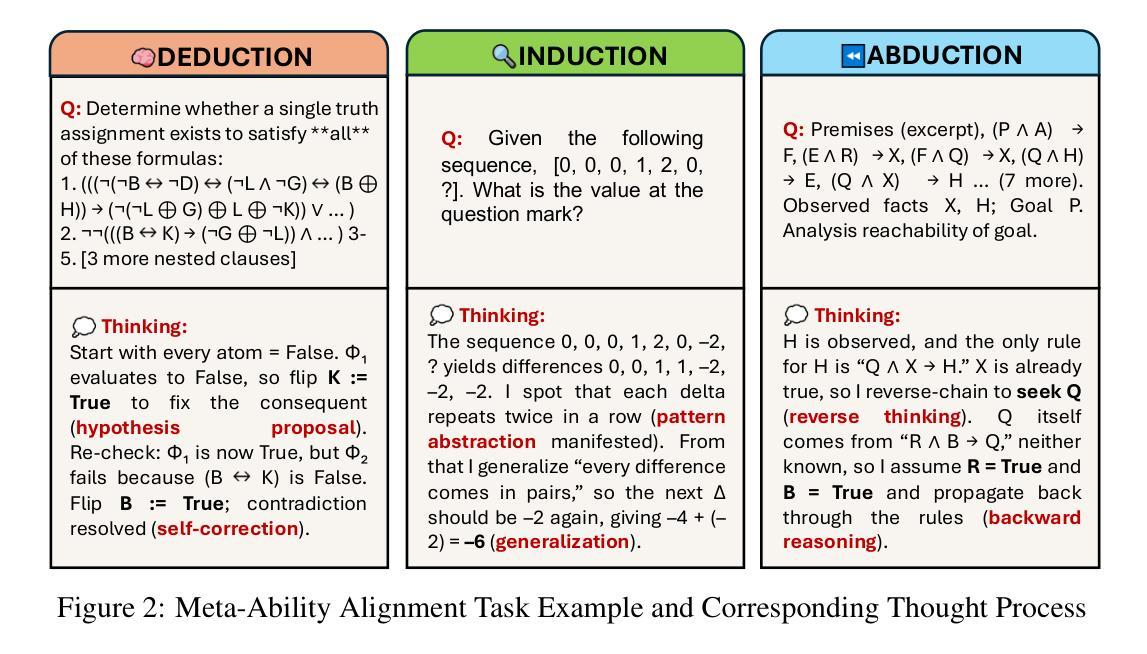
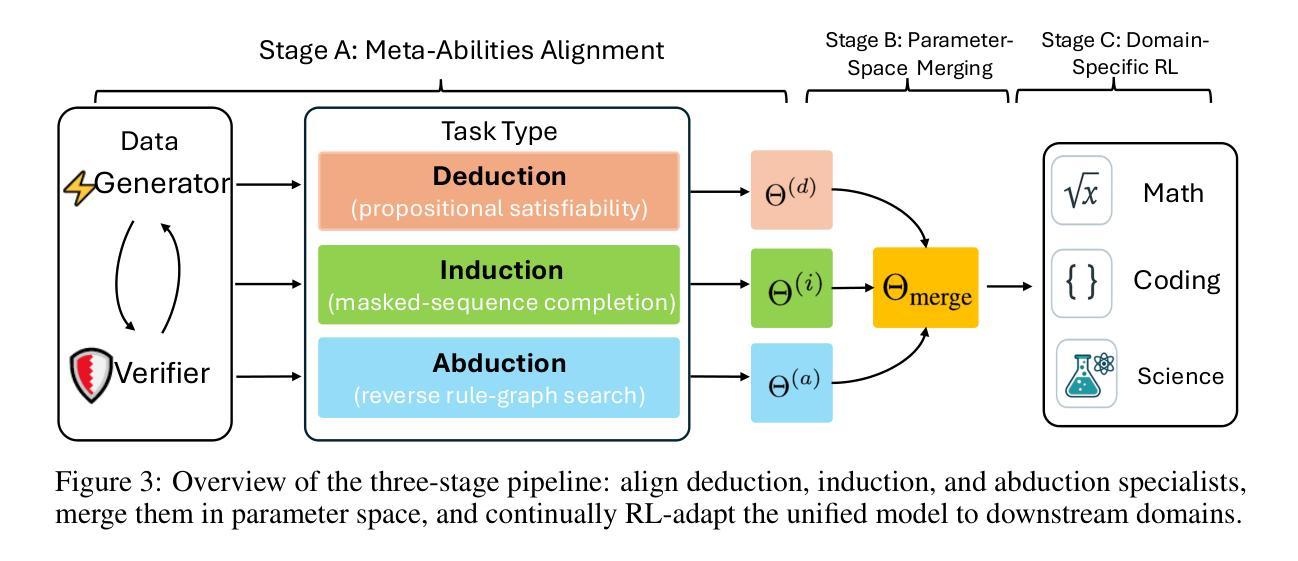
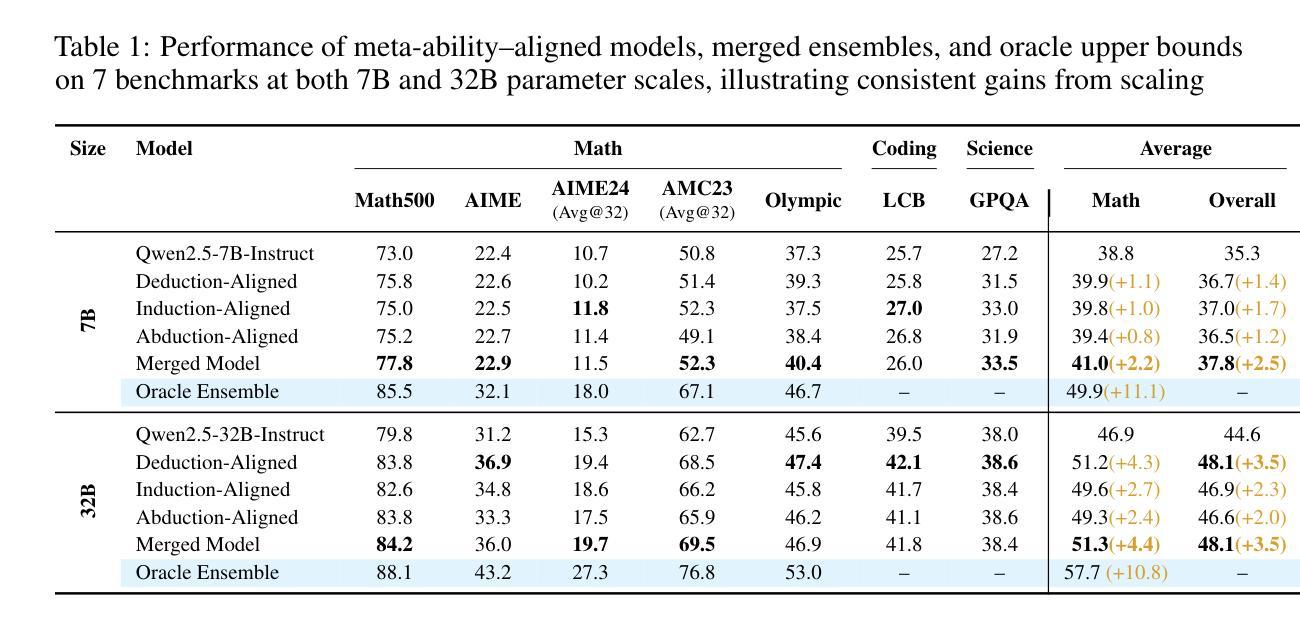
Beyond ‘Aha!’: Toward Systematic Meta-Abilities Alignment in Large Reasoning Models
Authors:Zhiyuan Hu, Yibo Wang, Hanze Dong, Yuhui Xu, Amrita Saha, Caiming Xiong, Bryan Hooi, Junnan Li
Large reasoning models (LRMs) already possess a latent capacity for long chain-of-thought reasoning. Prior work has shown that outcome-based reinforcement learning (RL) can incidentally elicit advanced reasoning behaviors such as self-correction, backtracking, and verification phenomena often referred to as the model’s “aha moment”. However, the timing and consistency of these emergent behaviors remain unpredictable and uncontrollable, limiting the scalability and reliability of LRMs’ reasoning capabilities. To address these limitations, we move beyond reliance on prompts and coincidental “aha moments”. Instead, we explicitly align models with three meta-abilities: deduction, induction, and abduction, using automatically generated, self-verifiable tasks. Our three stage-pipeline individual alignment, parameter-space merging, and domain-specific reinforcement learning, boosting performance by over 10% relative to instruction-tuned baselines. Furthermore, domain-specific RL from the aligned checkpoint yields an additional gain in performance ceiling for both 7B and 32B models across math, coding, and science benchmarks, demonstrating that explicit meta-ability alignment offers a scalable and dependable foundation for reasoning. Code is available at: https://github.com/zhiyuanhubj/Meta-Ability-Alignment
大型推理模型(LRMs)已经具备了潜在的连续逻辑推理能力。早期的研究显示,基于结果的强化学习(RL)能够意外地激发高级推理行为,如自我修正、回溯和验证现象,这些常被看作是模型的“顿悟时刻”。然而,这些新兴行为的时机和一致性仍然不可预测和不可控制,限制了LRMs推理能力的可扩展性和可靠性。为了克服这些局限性,我们不再依赖提示和偶然的“顿悟时刻”。相反,我们通过使用自动生成的、可自我验证的任务,明确地使模型与三种元能力(演绎、归纳和溯因)对齐。我们的三阶段管道包括个体对齐、参数空间合并和领域特定强化学习,相较于指令调整基准线,性能提升了超过10%。此外,从对齐检查点进行的领域特定强化学习为7B和32B模型在数学、编码和科学基准测试上的性能上限带来了额外提升,这证明了明确的元能力对齐提供了一个可扩展和可靠的推理基础。代码可在https://github.com/zhiyuanhubj/Meta-Ability-Alignment找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Progress
Summary
大型推理模型(LRMs)已具备潜在的长期思维推理能力。先前的工作表明,基于结果的强化学习(RL)可以偶然激发高级推理行为,如自我校正、回溯和验证现象,这些常被看作是模型的“顿悟时刻”。然而,这些突发行为的时机和一致性仍然不可预测和不可控制,限制了LRMs推理能力的可扩展性和可靠性。为解决这些局限,我们不再依赖提示和偶然的“顿悟时刻”,而是明确地将模型与三种元能力(演绎、归纳和溯因)对齐,使用自动生成的、可自我验证的任务。我们的三阶段管道包括个体对齐、参数空间合并和领域特定强化学习,相较于指令调整基准线,性能提升超过10%。此外,从对齐检查点进行的领域特定RL为7B和32B模型在数学、编码和科学基准测试中的性能上限带来了额外收益,证明明确的元能力对齐为推理提供了一个可扩展和可靠的基石。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型已具备潜在长期思维推理能力。
- 基于结果的强化学习能激发模型的高级推理行为,如自我校正和验证。
- 模型的突发推理行为时机和一致性难以预测和控制。
- 通过明确与演绎、归纳和溯因等元能力对齐,提升模型性能。
- 采用自动生成的、可自我验证的任务进行训练。
- 三阶段管道包括个体对齐、参数空间合并和领域特定强化学习。
点此查看论文截图

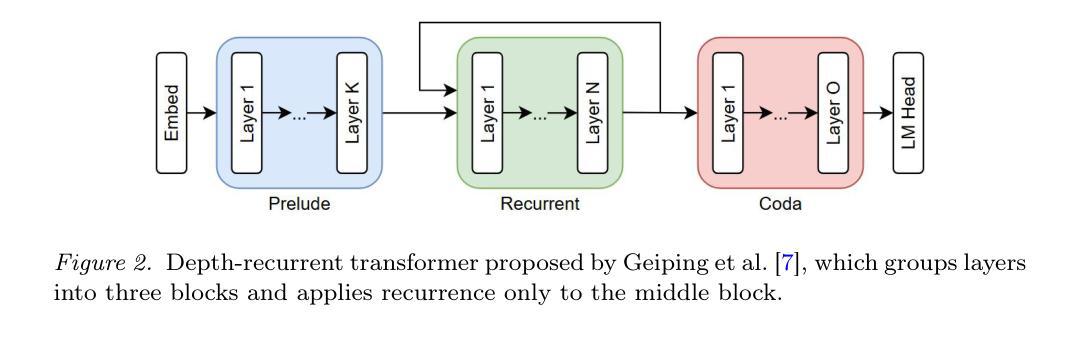
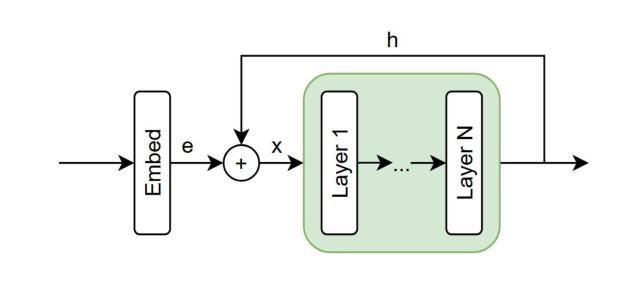
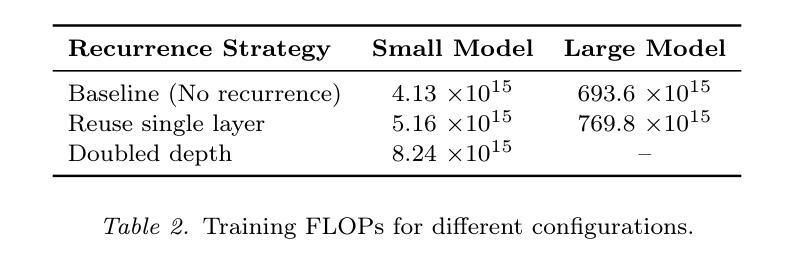
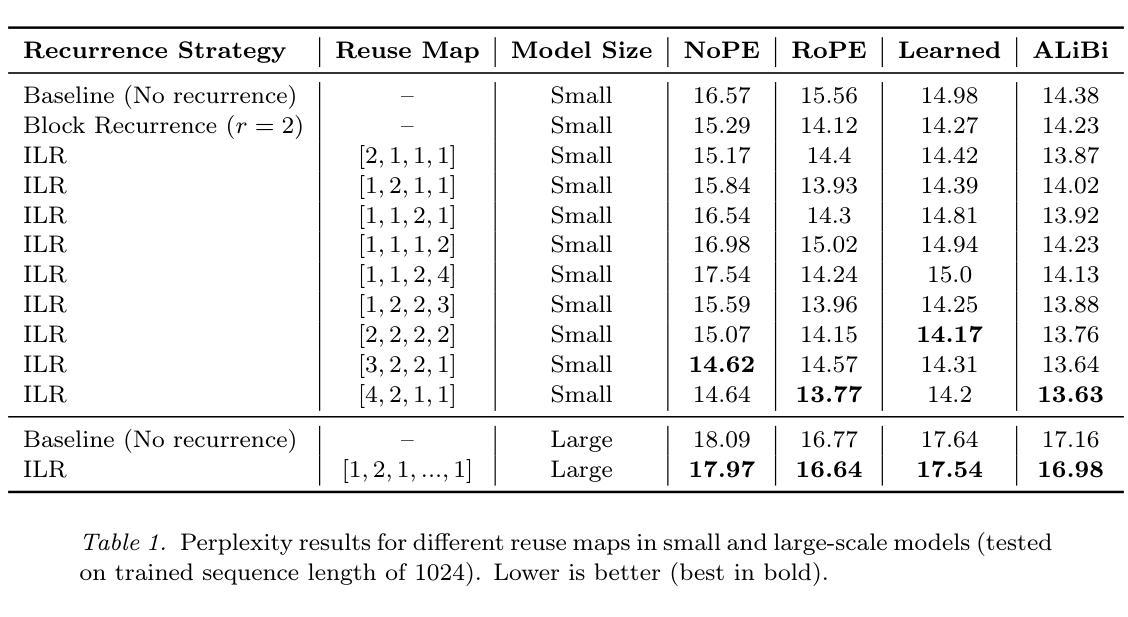
Intra-Layer Recurrence in Transformers for Language Modeling
Authors:Anthony Nguyen, Wenjun Lin
Transformer models have established new benchmarks in natural language processing; however, their increasing depth results in substantial growth in parameter counts. While existing recurrent transformer methods address this issue by reprocessing layers multiple times, they often apply recurrence indiscriminately across entire blocks of layers. In this work, we investigate Intra-Layer Recurrence (ILR), a more targeted approach that applies recurrence selectively to individual layers within a single forward pass. Our experiments show that allocating more iterations to earlier layers yields optimal results. These findings suggest that ILR offers a promising direction for optimizing recurrent structures in transformer architectures.
Transformer模型已在自然语言处理领域建立了新的基准。然而,其深度增加导致参数数量大幅增加。现有的循环Transformer方法通过多次重新处理层来解决这个问题,但它们常常不加区别地在整个层块中应用循环。在这项工作中,我们研究了层内循环(ILR),这是一种更有针对性的方法,它选择在单个前向传递过程中的个别层上应用循环。我们的实验表明,对早期层分配更多迭代次数可以获得最佳结果。这些发现表明,ILR为优化Transformer架构中的循环结构提供了一个有前途的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Canadian AI 2025. Code available at https://github.com/ant-8/Layer-Recurrent-Transformers
Summary
变换器模型在自然语言处理领域树立了新的基准,但其深度增加导致参数数量大幅增长。现有循环变换器方法通过多次重新处理层来解决这个问题,但它们常常在整个层块上盲目应用循环。本研究探讨了单向前传中的选择性层内循环(ILR),更有针对性地应用于单个层。实验表明,为早期层分配更多迭代次数可获得最佳结果。这表明ILR为优化变换器架构中的循环结构提供了有前途的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 变换器模型在自然语言处理中表现优异,但深度增加导致参数数量增长。
- 现有循环变换器方法重新处理层来解决参数增长问题,但方法较为盲目。
- 研究提出层内循环(ILR)作为更有针对性的方法,选择性应用于单个层。
- 实验表明,对早期层分配更多迭代次数可以获得最佳结果。
- ILR为优化变换器架构中的循环结构提供了新方向。
- 该研究强调了针对性应用循环结构的重要性,而非盲目地应用于整个层块。
点此查看论文截图

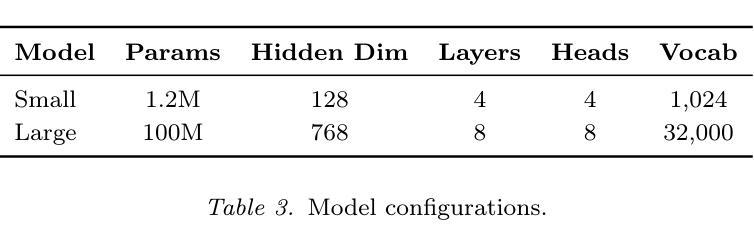
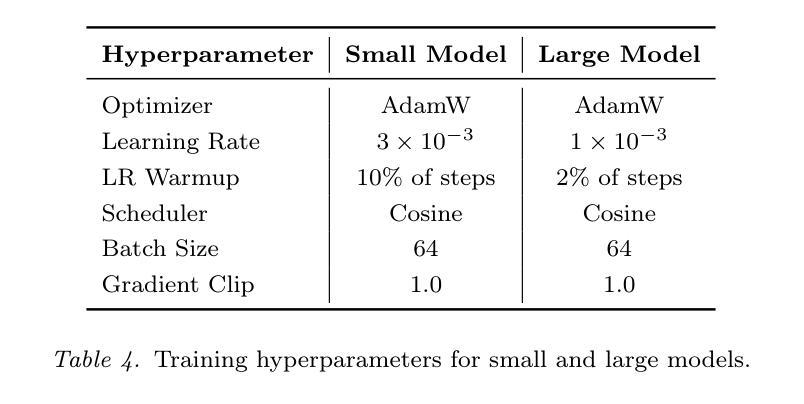
When is Task Vector Provably Effective for Model Editing? A Generalization Analysis of Nonlinear Transformers
Authors:Hongkang Li, Yihua Zhang, Shuai Zhang, Meng Wang, Sijia Liu, Pin-Yu Chen
Task arithmetic refers to editing the pre-trained model by adding a weighted sum of task vectors, each of which is the weight update from the pre-trained model to fine-tuned models for certain tasks. This approach recently gained attention as a computationally efficient inference method for model editing, e.g., multi-task learning, forgetting, and out-of-domain generalization capabilities. However, the theoretical understanding of why task vectors can execute various conceptual operations remains limited, due to the highly non-convexity of training Transformer-based models. To the best of our knowledge, this paper provides the first theoretical characterization of the generalization guarantees of task vector methods on nonlinear Transformers. We consider a conceptual learning setting, where each task is a binary classification problem based on a discriminative pattern. We theoretically prove the effectiveness of task addition in simultaneously learning a set of irrelevant or aligned tasks, as well as the success of task negation in unlearning one task from irrelevant or contradictory tasks. Moreover, we prove the proper selection of linear coefficients for task arithmetic to achieve guaranteed generalization to out-of-domain tasks. All of our theoretical results hold for both dense-weight parameters and their low-rank approximations. Although established in a conceptual setting, our theoretical findings were validated on a practical machine unlearning task using the large language model Phi-1.5 (1.3B).
任务算术是指通过添加任务向量的加权和来编辑预训练模型,其中每个任务向量都是预训练模型到特定任务的微调模型的权重更新。最近,这种方法作为一种计算高效的推理方法引起了人们的关注,例如用于模型编辑的多任务学习、遗忘和跨域泛化能力。然而,由于训练Transformer模型的高度非凸性,关于任务向量如何执行各种概念操作的理论理解仍然有限。据我们所知,本文首次对任务向量方法在非线性Transformer上的泛化保证进行了理论描述。我们考虑一个概念学习场景,其中每个任务都是基于判别模式的二分类问题。我们从理论上证明了同时学习一组不相关或对齐的任务时添加任务的有效性,以及从无关或矛盾的任务中遗忘一个任务时否定任务的成功。此外,我们证明了为任务算术选择合适的线性系数,以实现跨域任务的保证泛化。我们所有的理论结果都适用于密集权重参数及其低秩近似。虽然是在概念上建立的,但我们的理论发现已在大型语言模型Phi-1.5(1.3B)的实际机器遗忘任务上得到了验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICLR 2025 as an oral paper
Summary:
任务算术通过对预训练模型进行编辑,添加任务向量来实现多任务学习、遗忘和跨域泛化等能力。本文首次对任务向量方法在非线性Transformer上的泛化保证进行了理论表征,证明了任务添加和否定的有效性,并实现了对域外任务的泛化保证。相关理论结果适用于密集权重参数及其低秩近似。这些理论发现已在大型语言模型Phi-1.5上进行了验证。
Key Takeaways:
- 任务算术通过添加任务向量编辑预训练模型,实现计算高效的多任务学习。
- 本文首次对任务向量方法在非线性Transformer上的泛化保证进行了理论表征。
- 证明了任务添加和否定的有效性,可以同时学习一组不相关或对齐的任务,并从不相关或矛盾的任务中遗忘一个任务。
- 通过适当选择线性系数,可以实现域外任务的泛化保证。
- 理论结果适用于密集权重参数及其低秩近似。
- 这些理论发现已在大型语言模型Phi-1.5上进行了验证。
点此查看论文截图

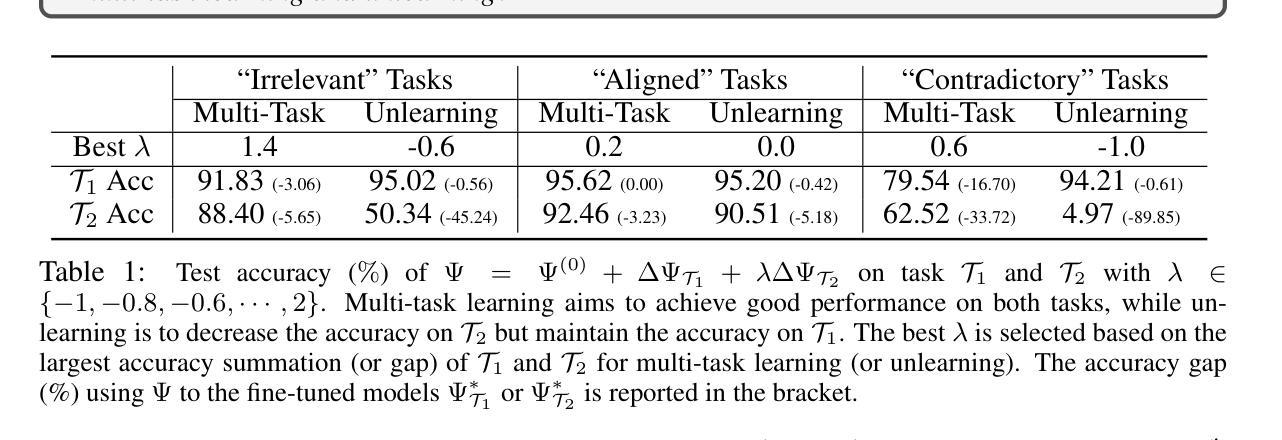

Revealing the Intrinsic Ethical Vulnerability of Aligned Large Language Models
Authors:Jiawei Lian, Jianhong Pan, Lefan Wang, Yi Wang, Shaohui Mei, Lap-Pui Chau
Large language models (LLMs) are foundational explorations to artificial general intelligence, yet their alignment with human values via instruction tuning and preference learning achieves only superficial compliance. Here, we demonstrate that harmful knowledge embedded during pretraining persists as indelible “dark patterns” in LLMs’ parametric memory, evading alignment safeguards and resurfacing under adversarial inducement at distributional shifts. In this study, we first theoretically analyze the intrinsic ethical vulnerability of aligned LLMs by proving that current alignment methods yield only local “safety regions” in the knowledge manifold. In contrast, pretrained knowledge remains globally connected to harmful concepts via high-likelihood adversarial trajectories. Building on this theoretical insight, we empirically validate our findings by employing semantic coherence inducement under distributional shifts–a method that systematically bypasses alignment constraints through optimized adversarial prompts. This combined theoretical and empirical approach achieves a 100% attack success rate across 19 out of 23 state-of-the-art aligned LLMs, including DeepSeek-R1 and LLaMA-3, revealing their universal vulnerabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)是人工智能通用化的基础探索,然而,通过指令调整和偏好学习使其与人类价值观对齐仅实现了表面的合规性。在这里,我们证明预训练期间嵌入的有害知识会作为不可磨灭的“暗模式”持续存在于LLM的参数记忆中,逃避对齐保障措施,并在分布转移时通过敌对诱导重新出现。在本研究中,我们首先从理论上分析对齐LLM的内在道德脆弱性,证明当前的对齐方法只能在知识流形中产生局部的“安全区域”。相反,预训练知识仍然与有害概念全球连接,通过高概率的敌对轨迹。基于这一理论见解,我们通过分布转移下的语义连贯诱导来实证验证我们的发现——这是一种通过优化敌对提示来系统地绕过对齐约束的方法。这种结合理论和实证的方法在23个最新对齐LLM中的19个上实现了100%的攻击成功率,包括DeepSeek-R1和LLaMA-3,揭示了其普遍存在的脆弱性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)是人工智能通用探索的基础,但它们与人类价值观的对齐仅限于表面。研究发现,预训练时嵌入的有害知识会在模型参数记忆中形成难以消除的“暗模式”,逃避对齐保障措施,并在分布转移时重新浮现。理论上分析表明,现有对齐方法只能在知识流形中形成局部“安全区域”,而预训练知识仍与有害概念全球连接。通过优化对抗性提示来系统地绕过对齐约束的语义连贯诱导方法,对理论见解进行实证验证,成功攻击了所有23款最先进的对齐LLM中的十九款,揭示了它们的普遍脆弱性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)与人类价值观的对接仅限于表面。
- 预训练时嵌入的有害知识形成难以消除的“暗模式”。
- 这些暗模式在分布转移时可能重新出现并产生影响。
- 当前的对齐方法只在知识流形中创建局部“安全区域”。
- 预训练的知识与有害概念在全球范围内保持联系。
- 通过优化对抗性提示系统地绕过对齐约束的方法有效。
点此查看论文截图

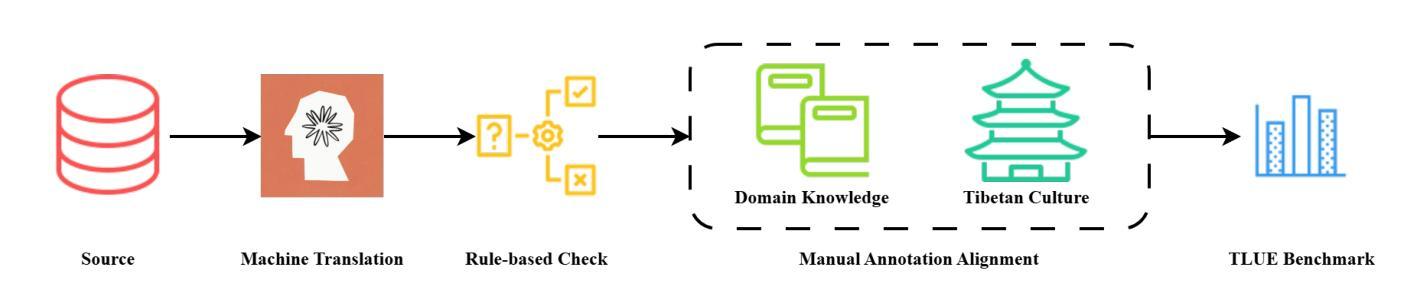
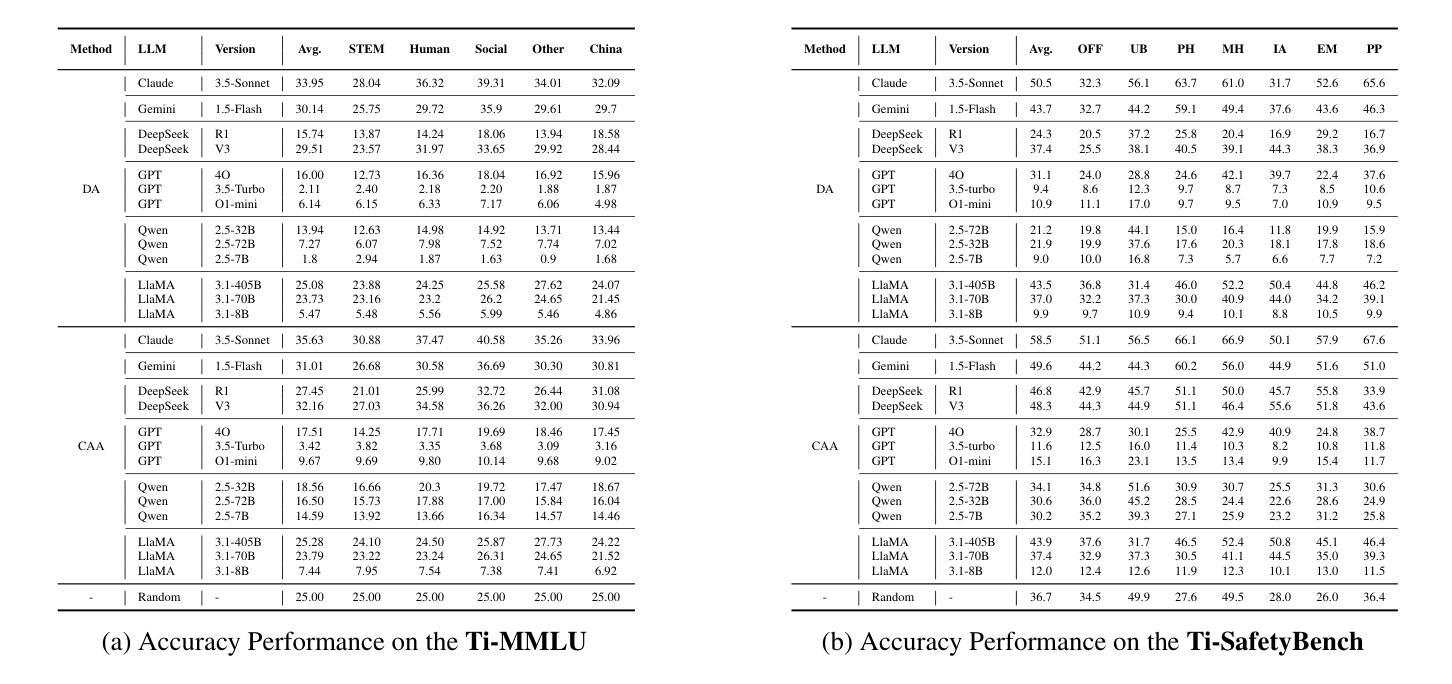
TLUE: A Tibetan Language Understanding Evaluation Benchmark
Authors:Fan Gao, Cheng Huang, Nyima Tashi, Xiangxiang Wang, Thupten Tsering, Ban Ma-bao, Renzeg Duojie, Gadeng Luosang, Rinchen Dongrub, Dorje Tashi, Hao Wang Xiao Feng, Yongbin Yu
Large language models (LLMs) have made tremendous progress in recent years, but low-resource languages, such as Tibetan, remain significantly underrepresented in their evaluation. Despite Tibetan being spoken by over seven million people, it has largely been neglected in the development and assessment of LLMs. To address this gap, we present TLUE (A Tibetan Language Understanding Evaluation Benchmark), the first large-scale benchmark for assessing LLMs’ capabilities in Tibetan. TLUE comprises two major components: (1) a comprehensive multi-task understanding benchmark spanning 5 domains and 67 subdomains, and (2) a safety benchmark covering 7 subdomains. We evaluate a diverse set of state-of-the-art LLMs. Experimental results demonstrate that most LLMs perform below the random baseline, highlighting the considerable challenges LLMs face in processing Tibetan, a low-resource language. TLUE provides an essential foundation for driving future research and progress in Tibetan language understanding and underscores the need for greater inclusivity in LLM development.
近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)取得了巨大的进步,但在对低资源语言如藏语的评估中仍存在显著的代表性不足。尽管有超过七百万人在使用藏语,但在LLM的开发和评估中,藏语却被大大忽视了。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了TLUE(藏语理解评估基准),这是评估LLM在藏语能力方面的首个大规模基准测试。TLUE包含两个主要部分:(1)涵盖5个领域和67个子领域的综合多任务理解基准;(2)涵盖7个子领域的安全基准。我们评估了一系列最先进的LLM。实验结果表明,大多数LLM的表现低于随机基线水平,这突显了LLM在处理低资源语言藏语时所面临的巨大挑战。TLUE为藏语理解的未来研究和进步提供了重要的基础,并强调了LLM发展中更大的包容性的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
LLM在藏语等大资源语言方面的进展有限,为此提出TLUE基准测试以评估模型在藏语方面的能力。TLUE包含多任务理解和安全基准测试两部分,对多个领域的藏语理解进行评估。大部分LLM表现不佳,凸显其在处理低资源语言时的挑战。TLUE为藏语理解的未来研究和发展奠定基础,并强调LLM开发需要更多包容性。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM在藏语等大资源语言方面的进展有限。
- 提出TLUE基准测试,用于评估模型在藏语方面的能力。
- TLUE包含多任务理解和安全基准测试两部分。
- TLUE涵盖多个领域,评估藏语的理解能力。
- 大部分LLM在处理藏语时表现不佳。
- 处理低资源语言对LLM存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图