⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
Learning Fine-Grained Geometry for Sparse-View Splatting via Cascade Depth Loss
Authors:Wenjun Lu, Haodong Chen, Anqi Yi, Yuk Ying Chung, Zhiyong Wang, Kun Hu
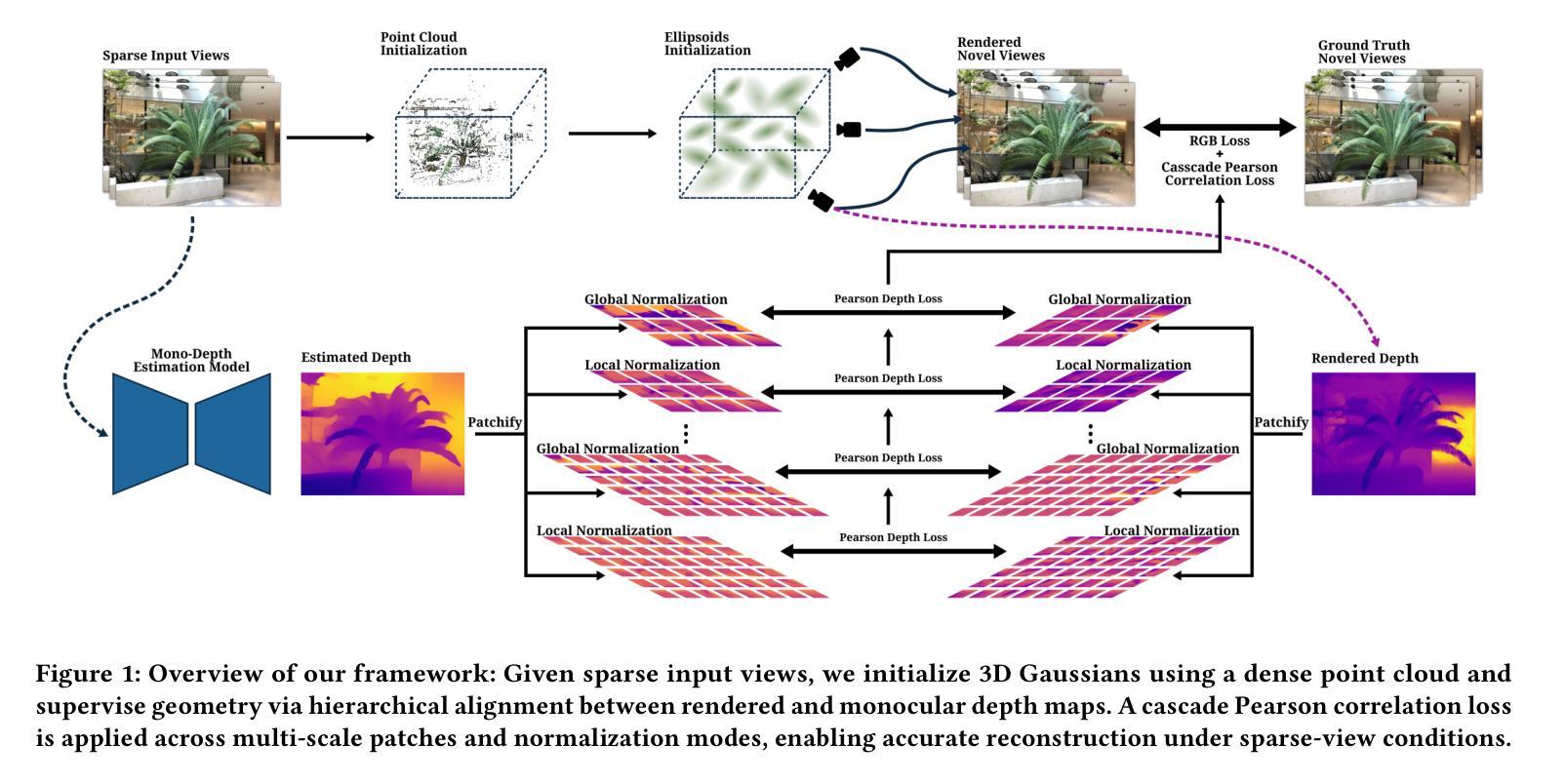
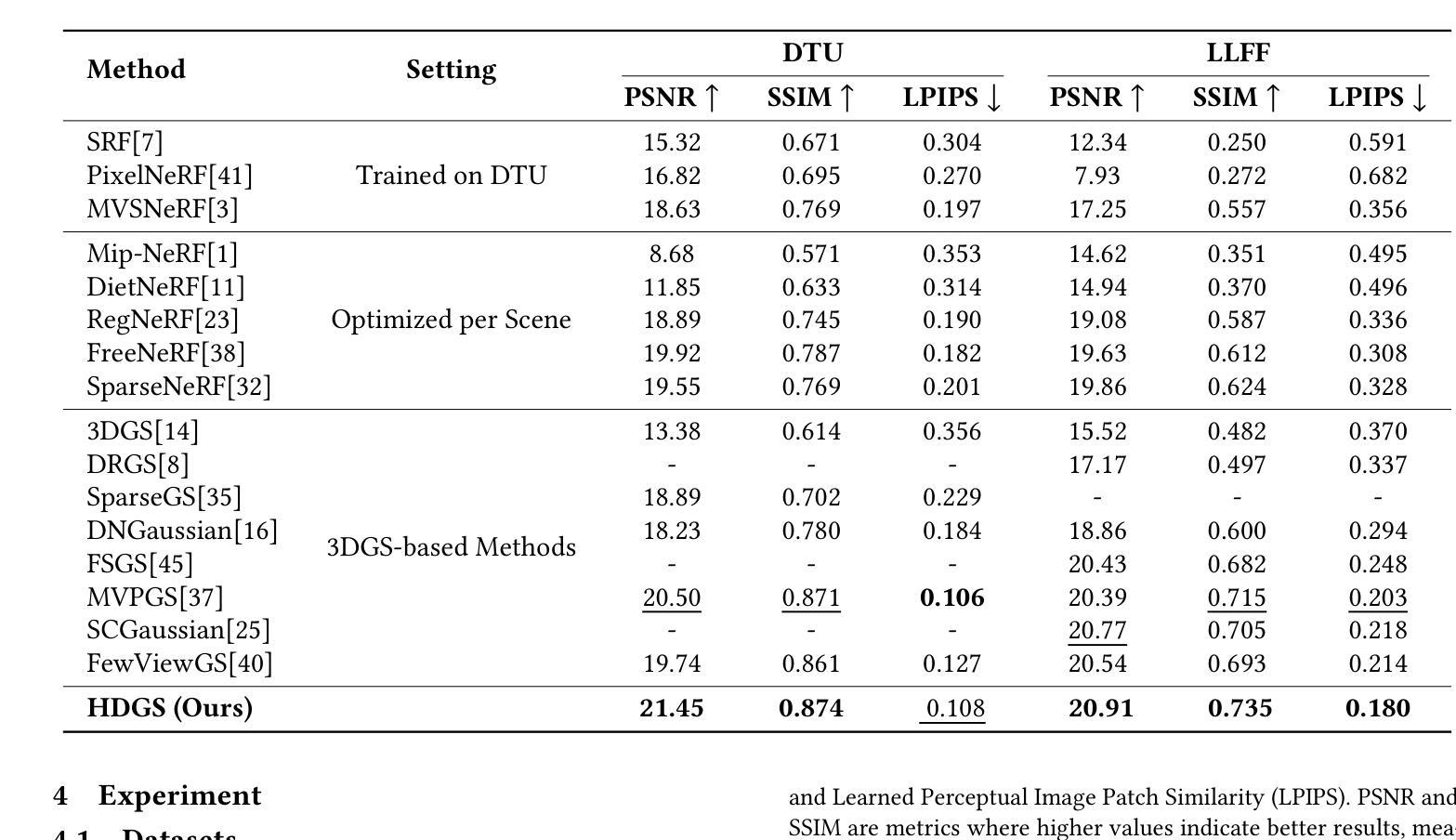
Novel view synthesis is a fundamental task in 3D computer vision that aims to reconstruct realistic images from a set of posed input views. However, reconstruction quality degrades significantly under sparse-view conditions due to limited geometric cues. Existing methods, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and the more recent 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), often suffer from blurred details and structural artifacts when trained with insufficient views. Recent works have identified the quality of rendered depth as a key factor in mitigating these artifacts, as it directly affects geometric accuracy and view consistency. In this paper, we address these challenges by introducing Hierarchical Depth-Guided Splatting (HDGS), a depth supervision framework that progressively refines geometry from coarse to fine levels. Central to HDGS is a novel Cascade Pearson Correlation Loss (CPCL), which aligns rendered and estimated monocular depths across multiple spatial scales. By enforcing multi-scale depth consistency, our method substantially improves structural fidelity in sparse-view scenarios. Extensive experiments on the LLFF and DTU benchmarks demonstrate that HDGS achieves state-of-the-art performance under sparse-view settings while maintaining efficient and high-quality rendering
新颖视角合成是3D计算机视觉中的一项基本任务,旨在从一组设定好的输入视角重建真实图像。然而,在稀疏视角条件下,由于有限的几何线索,重建质量会显著下降。现有方法,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和最新的3D高斯喷涂(3DGS),在训练视角不足时,往往会出现细节模糊和结构伪影。近期的研究工作已经识别出渲染深度质量是减轻这些伪影的关键因素,因为它直接影响几何精度和视角一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种针对稀疏视图条件下重建质量下降的问题的解决方案。通过引入层次深度引导溅射法(HDGS)和级联皮尔逊相关系数损失(CPCL),该方法能够在多个空间尺度上渐进地优化几何结构,提高结构保真度。在LLFF和DTU基准测试中,HDGS在稀疏视图条件下实现了卓越的性能,同时保持了高效高质量的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏视图条件下,重建质量会显著下降,因为可用的几何线索有限。
- 现有方法如NeRF和3DGS在训练时如果视图不足,会出现模糊细节和结构伪影。
- 渲染深度质量是减轻这些伪影的关键因素,直接影响几何准确性和视图一致性。
- HDGS是一种深度监督框架,可从粗到细逐步优化几何结构。
- CPCL是HDGS的核心,它能在多个空间尺度上对齐渲染和估计的单眼深度。
- 通过强制执行多尺度深度一致性,HDGS大大提高了稀疏视图场景中的结构保真度。
点此查看论文截图

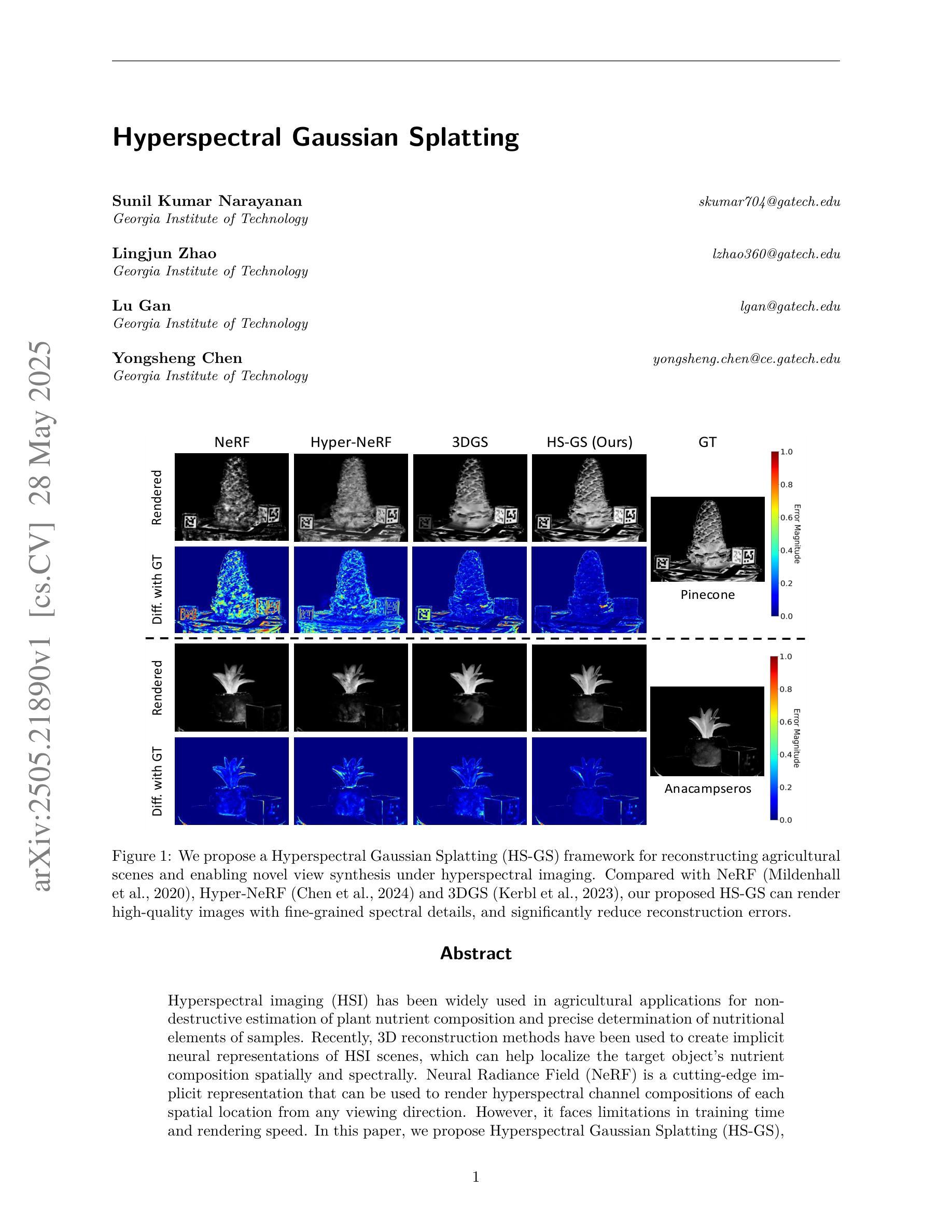
Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Sunil Kumar Narayanan, Lingjun Zhao, Lu Gan, Yongsheng Chen
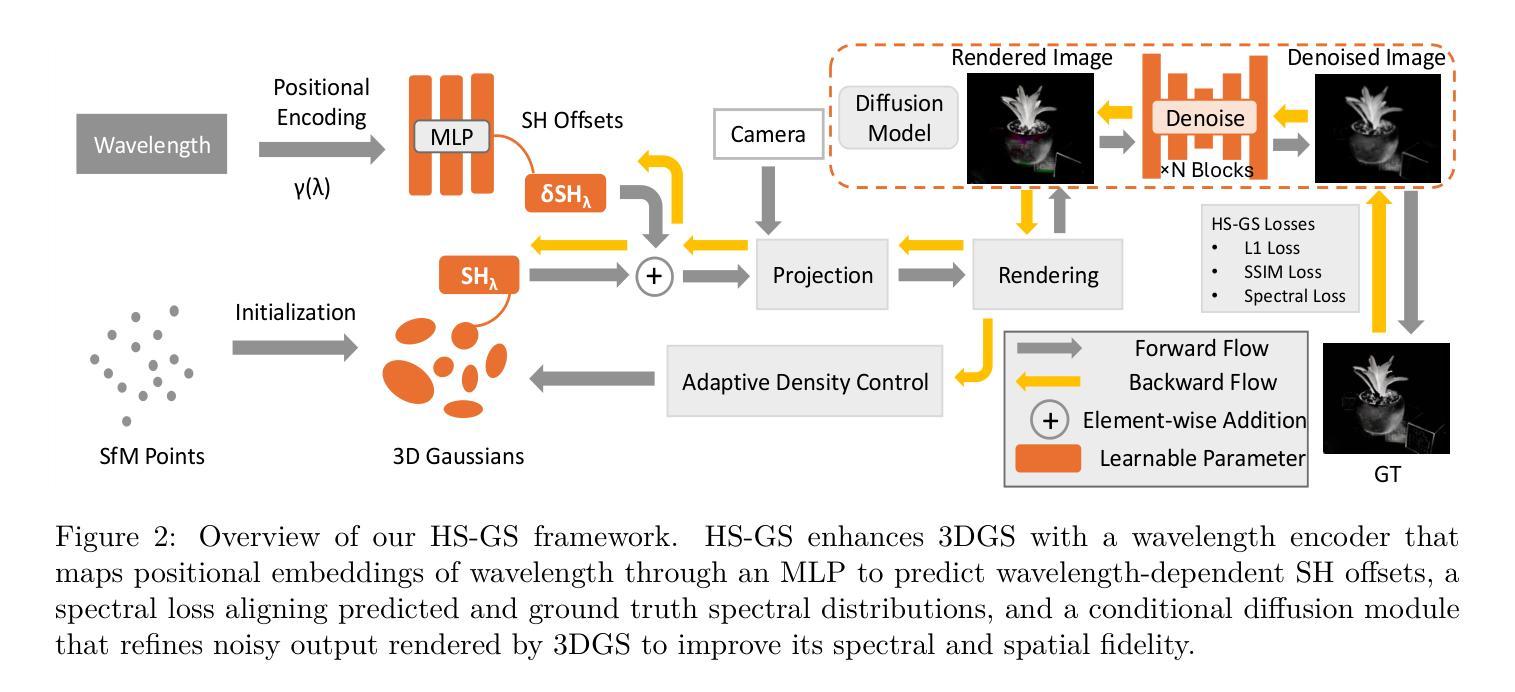
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has been widely used in agricultural applications for non-destructive estimation of plant nutrient composition and precise determination of nutritional elements in samples. Recently, 3D reconstruction methods have been used to create implicit neural representations of HSI scenes, which can help localize the target object’s nutrient composition spatially and spectrally. Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) is a cutting-edge implicit representation that can render hyperspectral channel compositions of each spatial location from any viewing direction. However, it faces limitations in training time and rendering speed. In this paper, we propose Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting (HS-GS), which combines the state-of-the-art 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with a diffusion model to enable 3D explicit reconstruction of the hyperspectral scenes and novel view synthesis for the entire spectral range. To enhance the model’s ability to capture fine-grained reflectance variations across the light spectrum and leverage correlations between adjacent wavelengths for denoising, we introduce a wavelength encoder to generate wavelength-specific spherical harmonics offsets. We also introduce a novel Kullback–Leibler divergence-based loss to mitigate the spectral distribution gap between the rendered image and the ground truth. A diffusion model is further applied for denoising the rendered images and generating photorealistic hyperspectral images. We present extensive evaluations on five diverse hyperspectral scenes from the Hyper-NeRF dataset to show the effectiveness of our proposed HS-GS framework. The results demonstrate that HS-GS achieves new state-of-the-art performance among all previously published methods. Code will be released upon publication.
高光谱成像(HSI)在农业应用中得到广泛应用,用于非破坏性估计植物养分组成和精确确定样品中的营养元素。最近,三维重建方法已用于创建HSI场景的隐式神经表示,这有助于在空间上定位目标对象的养分组成。神经辐射场(NeRF)是一种前沿的隐式表示方法,可以从任何观看方向呈现每个空间位置的高光谱通道组成。然而,它在训练时间和渲染速度方面存在局限性。在本文中,我们提出了高光谱高斯涂斑法(HS-GS),它将最新的三维高斯涂斑法(3DGS)与扩散模型相结合,实现对高光谱场景的三维显式重建和整个光谱范围的全新视图合成。为了增强模型捕捉光谱中精细反射率变化的能力,并利用相邻波长之间的相关性进行去噪,我们引入了波长编码器来生成特定波长的球面谐波偏移。我们还引入了一种新型的基于Kullback-Leibler散度损失的损失函数,以减轻渲染图像与真实图像之间的光谱分布差距。扩散模型进一步应用于对渲染图像进行去噪,并生成逼真的高光谱图像。我们在Hyper-NeRF数据集上的五个不同高光谱场景进行了广泛评估,以展示我们提出HS-GS框架的有效性。结果表明,HS-GS在所有已发布的方法中达到了新的最先进的性能。代码将在发布时公布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Hyperspectral Gaussian Splatting(HS-GS)的方法,结合先进的3D Gaussian Splatting技术与扩散模型,实现高分辨率的隐式重建和整个光谱范围的全新视角合成。通过引入波长编码器和基于Kullback-Leibler散度的损失函数,提高捕捉光谱细微反射变化和利用相邻波长去噪的能力。HS-GS在Hyper-NeRF数据集上的五个不同场景表现优异,达到最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- HSI在农业应用中的重要作用:用于非破坏性估计植物养分组成和精确确定样本中的营养元素。
- NeRF是先进的隐式表示方法,能从任何视角渲染每个空间位置的超光谱通道组成。
- HS-GS方法结合了先进的3D Gaussian Splatting技术和扩散模型,实现隐式重建和全新视角的合成。
- HS-GS引入波长编码器以捕捉光谱细微反射变化并利用相邻波长去噪。
- 采用基于Kullback-Leibler散度的损失函数来缩小渲染图像与真实图像之间的光谱分布差距。
- 扩散模型用于对渲染图像进行去噪并生成逼真的超光谱图像。
点此查看论文截图