⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-30 更新
Beyond 1D: Vision Transformers and Multichannel Signal Images for PPG-to-ECG Reconstruction
Authors:Xiaoyan Li, Shixin Xu, Faisal Habib, Arvind Gupta, Huaxiong Huang
Reconstructing ECG from PPG is a promising yet challenging task. While recent advancements in generative models have significantly improved ECG reconstruction, accurately capturing fine-grained waveform features remains a key challenge. To address this, we propose a novel PPG-to-ECG reconstruction method that leverages a Vision Transformer (ViT) as the core network. Unlike conventional approaches that rely on single-channel PPG, our method employs a four-channel signal image representation, incorporating the original PPG, its first-order difference, second-order difference, and area under the curve. This multi-channel design enriches feature extraction by preserving both temporal and physiological variations within the PPG. By leveraging the self-attention mechanism in ViT, our approach effectively captures both inter-beat and intra-beat dependencies, leading to more robust and accurate ECG reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing 1D convolution-based approaches, achieving up to 29% reduction in PRD and 15% reduction in RMSE. The proposed approach also produces improvements in other evaluation metrics, highlighting its robustness and effectiveness in reconstructing ECG signals. Furthermore, to ensure a clinically relevant evaluation, we introduce new performance metrics, including QRS area error, PR interval error, RT interval error, and RT amplitude difference error. Our findings suggest that integrating a four-channel signal image representation with the self-attention mechanism of ViT enables more effective extraction of informative PPG features and improved modeling of beat-to-beat variations for PPG-to-ECG mapping. Beyond demonstrating the potential of PPG as a viable alternative for heart activity monitoring, our approach opens new avenues for cyclic signal analysis and prediction.
从光体积脉搏波图(PPG)重建心电图(ECG)是一项前景广阔但具有挑战性的任务。虽然生成模型的最新进展已显着提高了ECG重建的准确度,但准确捕捉精细波形特征仍然是一个关键挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的PPG到ECG重建方法。与传统的依赖单通道PPG的方法不同,我们的方法采用四通道信号图像表示,结合了原始PPG、其一阶差分、二阶差分和曲线下的面积。这种多通道设计通过保留PPG中的时间和生理变化来丰富特征提取。通过利用ViT中的自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地捕捉了心搏间和心搏内的依赖关系,从而实现更稳健和准确的ECG重建。实验结果表明,我们的方法始终优于现有的基于1D卷积的方法,在PRD上减少了高达29%,在RMSE上减少了15%。所提出的方法在其他评估指标上也取得了改进,这突显了其在重建ECG信号方面的稳健性和有效性。此外,为了确保临床上相关的评估,我们引入了新的性能指标,包括QRS面积误差、PR间隔误差、RT间隔误差和RT振幅差异误差。我们的研究结果表明,将四通道信号图像表示与ViT的自注意力机制相结合,能够更有效地提取有用的PPG特征,并改进心搏到心搏变化的建模,用于PPG到ECG的映射。我们的方法不仅证明了PPG作为心脏活动监测的可行替代方案的潜力,而且为循环信号分析和预测开辟了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种利用Vision Transformer(ViT)为核心网络的新型PPG到ECG重建方法。不同于传统依赖单通道PPG的方法,该方法采用四通道信号图像表示,融合了原始PPG、一阶差分、二阶差分和曲线下面积等信息。利用ViT的自注意力机制,该方法能有效捕捉心跳间和心跳内的依赖关系,实现更稳健和准确的ECG重建。实验结果显示,该方法优于现有的基于一维卷积的方法,在PRD和RMSE指标上分别降低了29%和15%。此外,为确保临床相关的评估,引入了新的性能评价指标,包括QRS面积误差、PR间隔误差、RT间隔误差和RT振幅差异误差。研究发现,将四通道信号图像表示与ViT的自注意力机制相结合,能有效提取PPG特征,提高心跳间变化的建模能力,为PPG在心脏活动监测中的替代应用提供了潜力,同时为循环信号分析和预测提供了新的途径。
关键见解
- 提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的PPG到ECG重建新方法。
- 采用四通道信号图像表示,融合了原始PPG及其一阶、二阶差值和曲线下面积信息,丰富了特征提取。
- 利用ViT的自注意力机制捕捉心跳间和心跳内的依赖关系,实现更准确和稳健的ECG重建。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在多个评价指标上优于现有方法。
- 引入了新的性能评价指标,以进行更临床相关的评估。
- 结合四通道信号图像表示和ViT自注意力机制的方法在提取PPG特征和建模心跳间变化方面更有效。
- 研究为PPG在心脏活动监测中的替代应用以及循环信号分析和预测提供了新的途径。
点此查看论文截图

Geometric Feature Prompting of Image Segmentation Models
Authors:Kenneth Ball, Erin Taylor, Nirav Patel, Andrew Bartels, Gary Koplik, James Polly, Jay Hineman
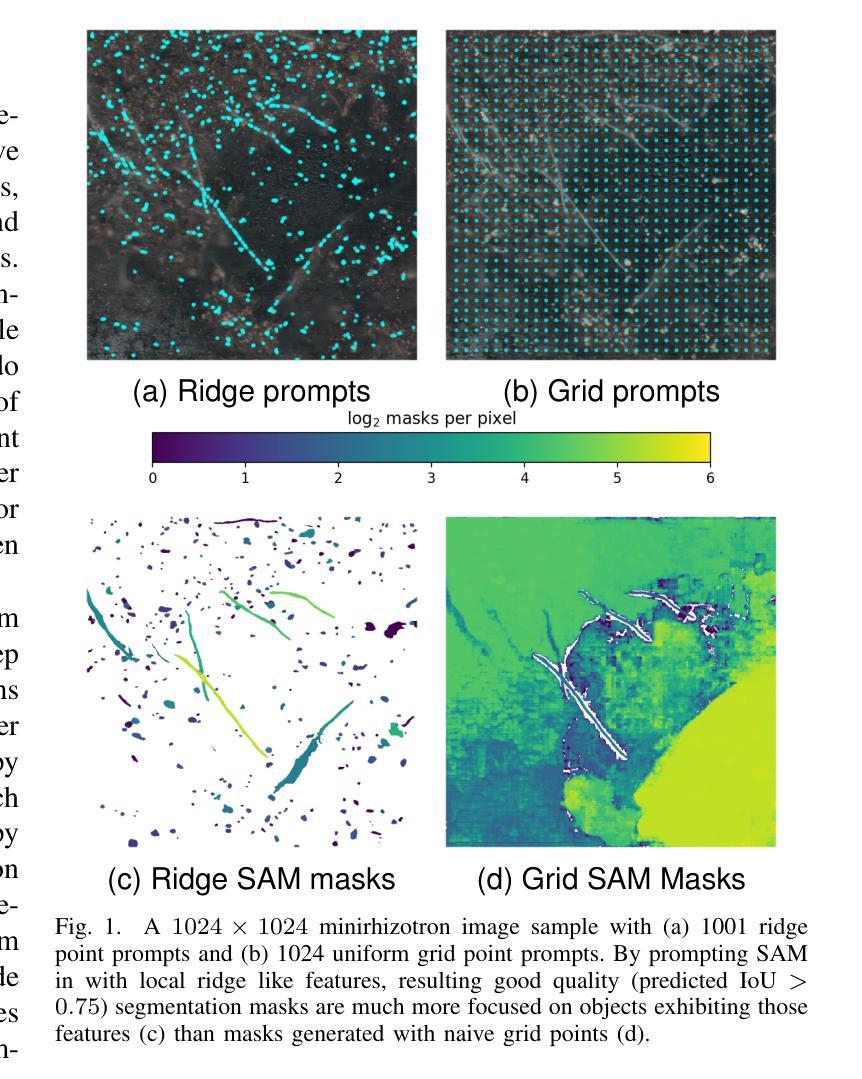
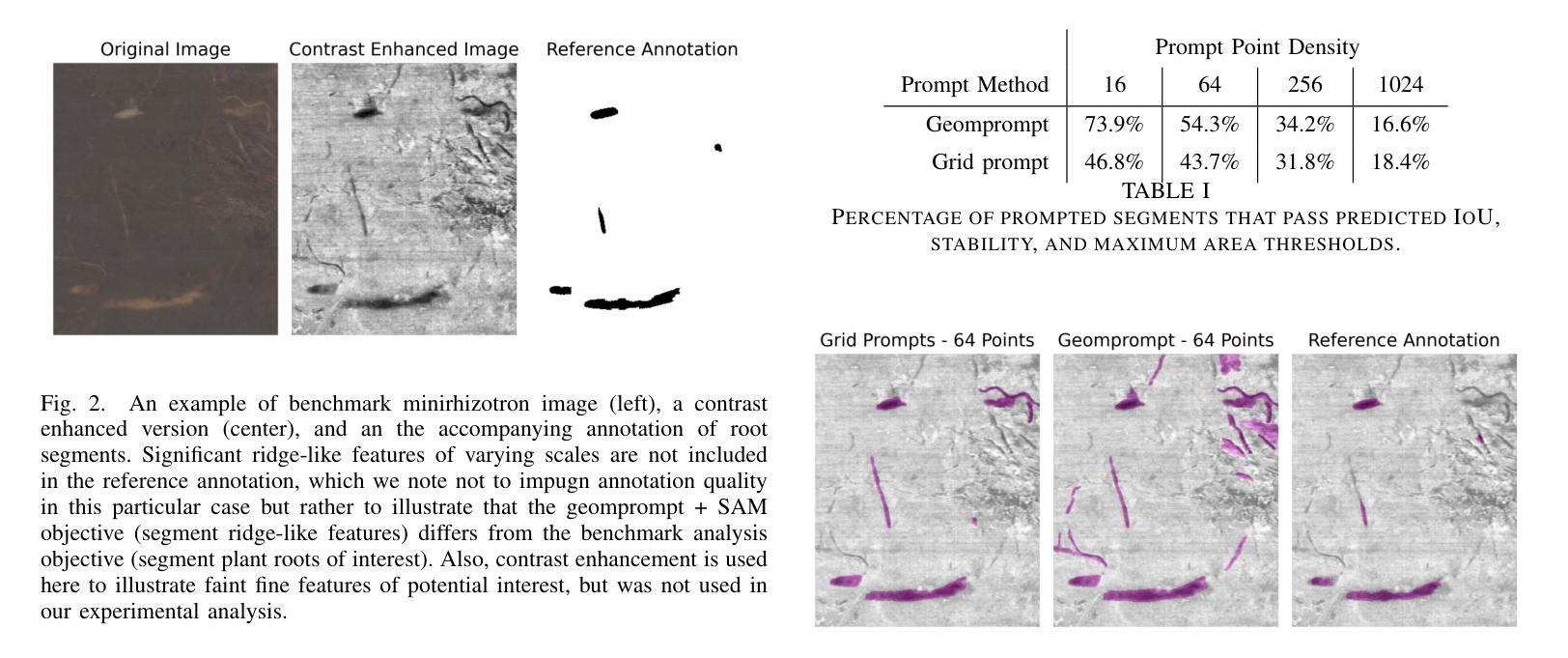
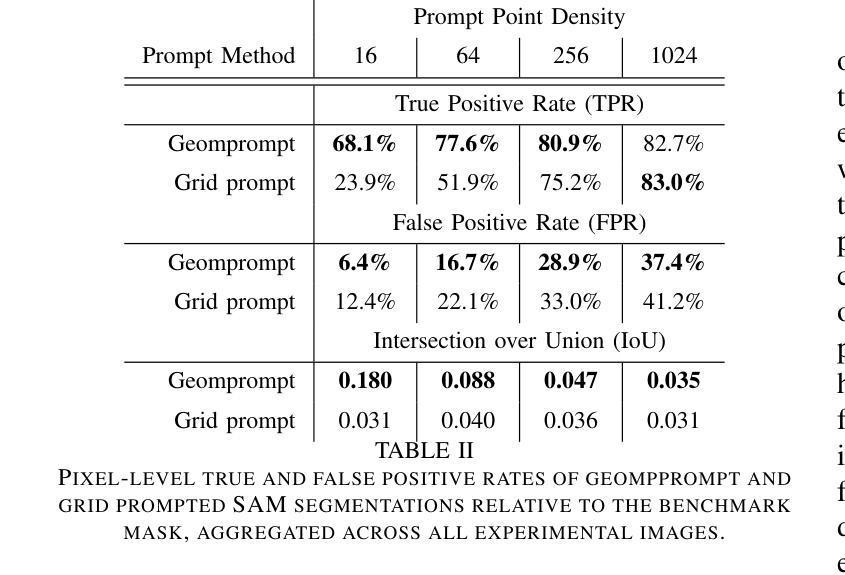
Advances in machine learning, especially the introduction of transformer architectures and vision transformers, have led to the development of highly capable computer vision foundation models. The segment anything model (known colloquially as SAM and more recently SAM 2), is a highly capable foundation model for segmentation of natural images and has been further applied to medical and scientific image segmentation tasks. SAM relies on prompts – points or regions of interest in an image – to generate associated segmentations. In this manuscript we propose the use of a geometrically motivated prompt generator to produce prompt points that are colocated with particular features of interest. Focused prompting enables the automatic generation of sensitive and specific segmentations in a scientific image analysis task using SAM with relatively few point prompts. The image analysis task examined is the segmentation of plant roots in rhizotron or minirhizotron images, which has historically been a difficult task to automate. Hand annotation of rhizotron images is laborious and often subjective; SAM, initialized with GeomPrompt local ridge prompts has the potential to dramatically improve rhizotron image processing. The authors have concurrently released an open source software suite called geomprompt https://pypi.org/project/geomprompt/ that can produce point prompts in a format that enables direct integration with the segment-anything package.
机器学习的发展,特别是引入了Transformer架构和视觉Transformer,催生了高度强大的计算机视觉基础模型的发展。片段任何东西模型(俗称SAM,最近称为SAM 2)是一种高度强大的自然图像分割基础模型,并已进一步应用于医学和科学图像分割任务。SAM依赖于提示——图像中的点或感兴趣区域——来生成相关的分割。在本文中,我们提出了一种几何动机提示生成器的使用,以产生与特定特征共定位的提示点。有针对性的提示可以使用SAM和相对较少的点提示,在科学研究图像分析任务中自动生成敏感和特定的分割。研究的图像分析任务是根系图像的根系分段或迷你根系图像分析,这历来是一个自动化困难的任务。根系图像的手动标注很费时且经常带有主观性;使用GeomPrompt初始化局部脊线提示的SAM有可能极大地改进根系图像的处理过程。作者同时发布了一个名为geomprompt的开源软件套件,该软件套件可以产生点提示的格式,能够直接与片段任何东西软件包集成:https://pypi.org/project/geomprompt/ 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习和变压器架构的进展,特别是视觉变压器的引入,推动了计算机视觉基础模型的发展。本文提出的分段任何模型(SAM)是一种高度专业的自然图像分割基础模型,并已应用于医学和科研图像分割任务。SAM依赖于提示点或图像中的感兴趣区域来生成相关的分割。本文建议使用几何动机提示生成器来产生与特定特征共定位的提示点,在科研图像分析任务中实现敏感和特定的自动分割,使用SAM仅需相对较少的点提示即可完成。所研究的图像分析任务是分割植物根系图像,这项工作在过去很难自动化完成。几何提示工具同时发布的开源软件包geomprompt可以用于生成直接集成到分段包中的点提示。几何提示可以大幅度改善根系图像的处理效率。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉变压器的发展推动了计算机视觉的进步,使得对自然、医学和科研图像的分割能力显著提高。
- SAM模型通过依赖提示点或图像中的感兴趣区域进行图像分割,为科研图像分析提供了强大的工具。
- 几何动机提示生成器能够产生与特定特征共定位的提示点,提高了自动分割的准确性和敏感性。
- 在植物根系图像分析中,使用SAM和geomprompt工具可以大幅度提高图像处理的自动化程度。
- 使用geomprompt软件套件的开源性质可以简化与其他软件包的集成,进一步提高工作效率。
- SAM模型和geomprompt工具的应用有助于减少手动标注图像的工作量,提高标注的一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Do We Need All the Synthetic Data? Towards Targeted Synthetic Image Augmentation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Dang Nguyen, Jiping Li, Jinghao Zheng, Baharan Mirzasoleiman
Synthetically augmenting training datasets with diffusion models has been an effective strategy for improving generalization of image classifiers. However, existing techniques struggle to ensure the diversity of generation and increase the size of the data by up to 10-30x to improve the in-distribution performance. In this work, we show that synthetically augmenting part of the data that is not learned early in training outperforms augmenting the entire dataset. By analyzing a two-layer CNN, we prove that this strategy improves generalization by promoting homogeneity in feature learning speed without amplifying noise. Our extensive experiments show that by augmenting only 30%-40% of the data, our method boosts the performance by up to 2.8% in a variety of scenarios, including training ResNet, ViT and DenseNet on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and TinyImageNet, with a range of optimizers including SGD and SAM. Notably, our method applied with SGD outperforms the SOTA optimizer, SAM, on CIFAR-100 and TinyImageNet. It can also easily stack with existing weak and strong augmentation strategies to further boost the performance.
通过扩散模型对训练数据集进行合成增强,是提高图像分类器泛化能力的有效策略。然而,现有技术在确保生成的多样性和通过扩大数据集规模(高达10-30倍)以提高内部性能分布方面遇到了困难。在这项工作中,我们表明,仅对训练早期未学到的部分数据进行合成增强,优于增强整个数据集。通过分析两层卷积神经网络,我们证明该策略通过促进特征学习速度的均质性,提高了泛化能力,而不会放大噪声。我们的大量实验表明,通过仅增强30%-40%的数据,我们的方法在多种场景下提高了性能,包括在CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上训练ResNet、ViT和DenseNet,以及一系列优化器,包括SGD和SAM。值得注意的是,我们的方法与SGD相结合,在CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上的性能超过了当前最佳优化器SAM。它还可以轻松地与现有的弱增强和强增强策略相结合,进一步提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据增强是提升图像分类器泛化性能的有效策略。现有技术难以确保生成数据的多样性并扩大数据集大小。本文发现,仅对训练初期未学到的数据进行数据增强优于对整个数据集进行增强。通过两层卷积神经网络的分析,证明该策略通过促进特征学习速度的均匀性来提高泛化能力,且不会放大噪声。通过仅对数据的30%-40%进行增强,本文方法在多种场景下提升了性能,包括在CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上训练ResNet、ViT和DenseNet等模型,以及使用SGD和SAM等优化器。特别是与SAM这一当前最佳优化器相比,使用SGD的方法在CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上表现更佳。此方法还可轻松结合现有弱增强和强增强策略进一步提升性能。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强是提高图像分类器泛化性能的有效策略。
- 现有数据增强技术难以同时确保生成数据的多样性和扩大数据集规模。
- 仅对训练初期未学到的数据进行数据增强能够提升模型的泛化性能。
- 该策略通过促进特征学习速度的均匀性来提高模型性能,同时不会放大噪声。
- 方法在多种模型和数据集上进行了实验验证,包括ResNet、ViT、DenseNet等,以及CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet等。
- 使用SGD的方法在某些场景下表现优于当前最佳优化器SAM。
点此查看论文截图

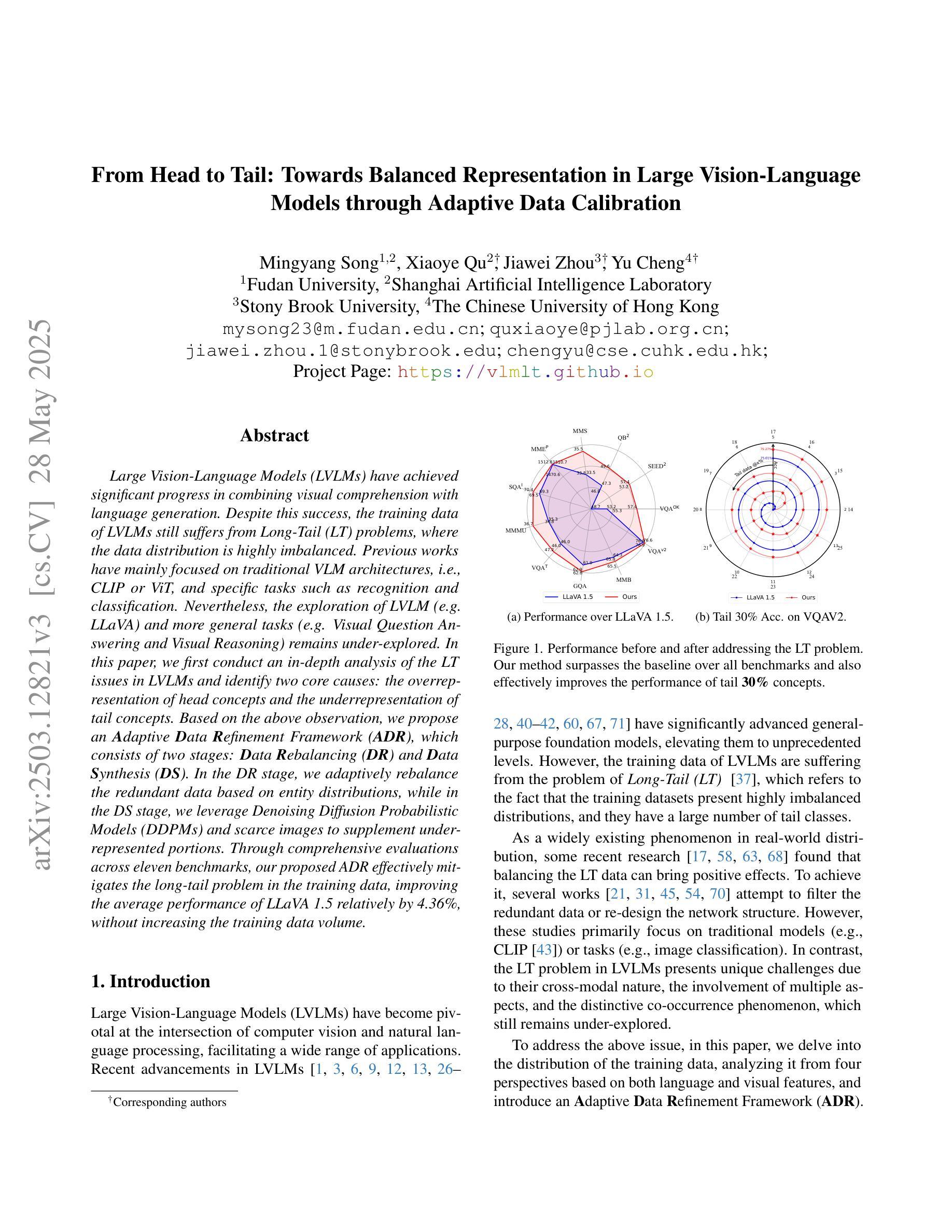
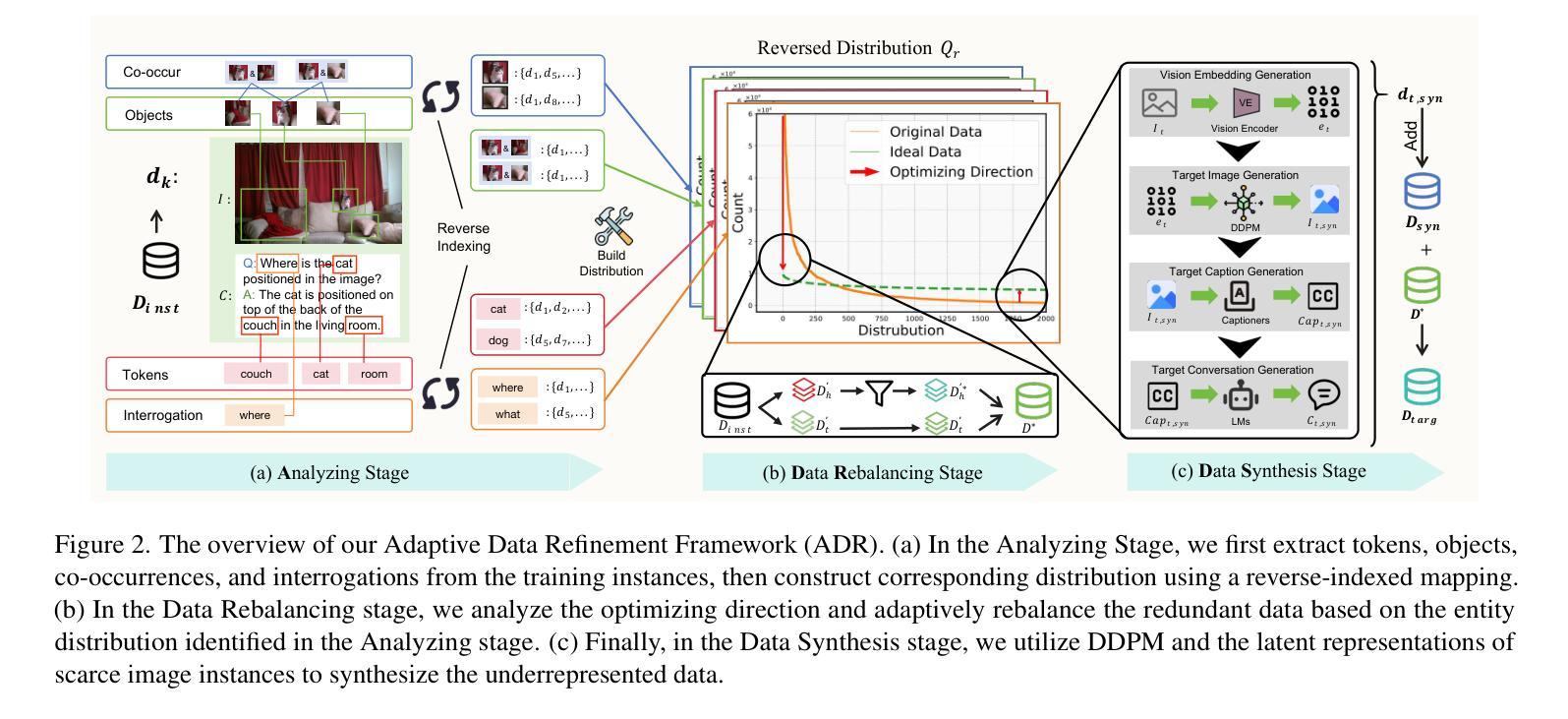
From Head to Tail: Towards Balanced Representation in Large Vision-Language Models through Adaptive Data Calibration
Authors:Mingyang Song, Xiaoye Qu, Jiawei Zhou, Yu Cheng
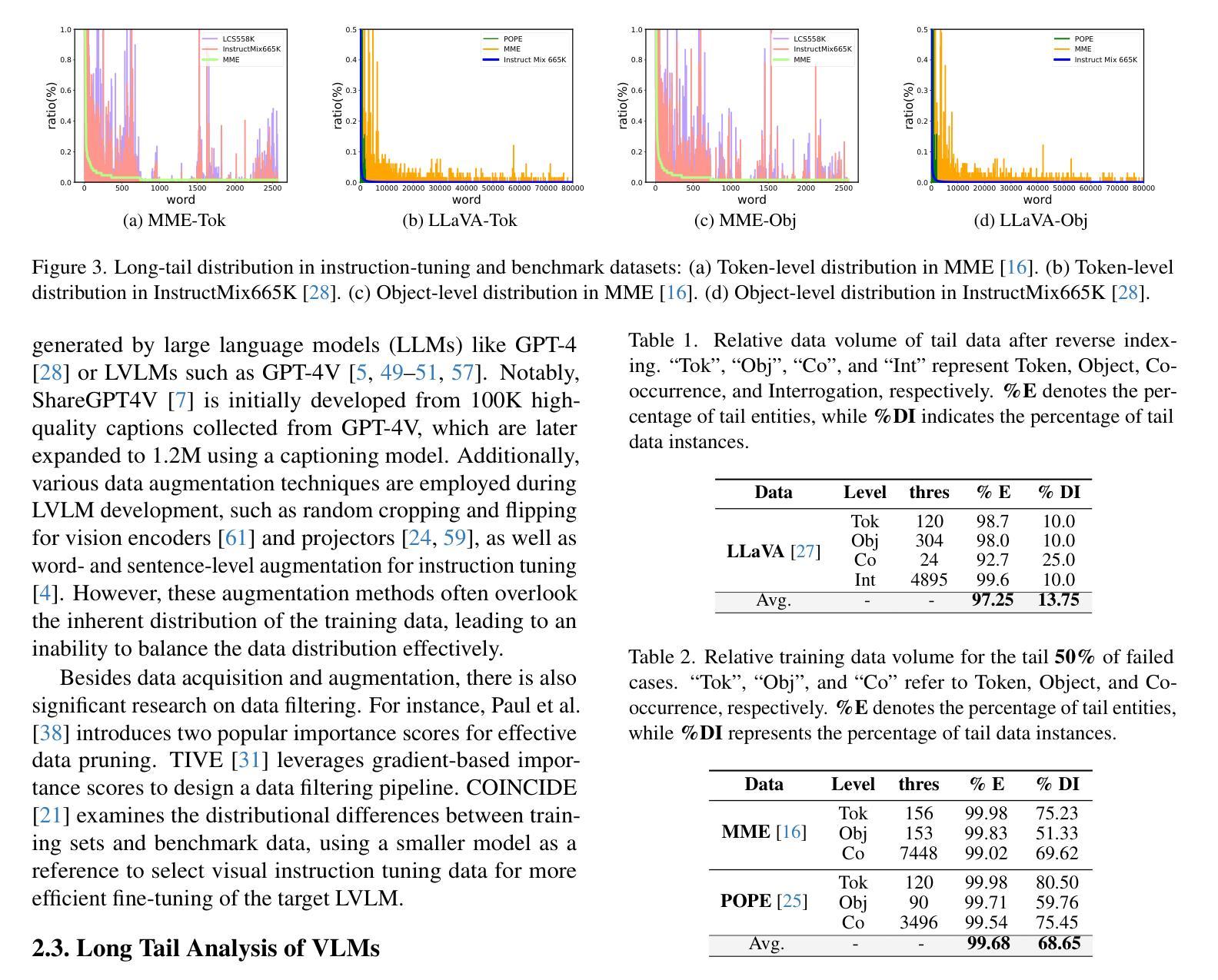
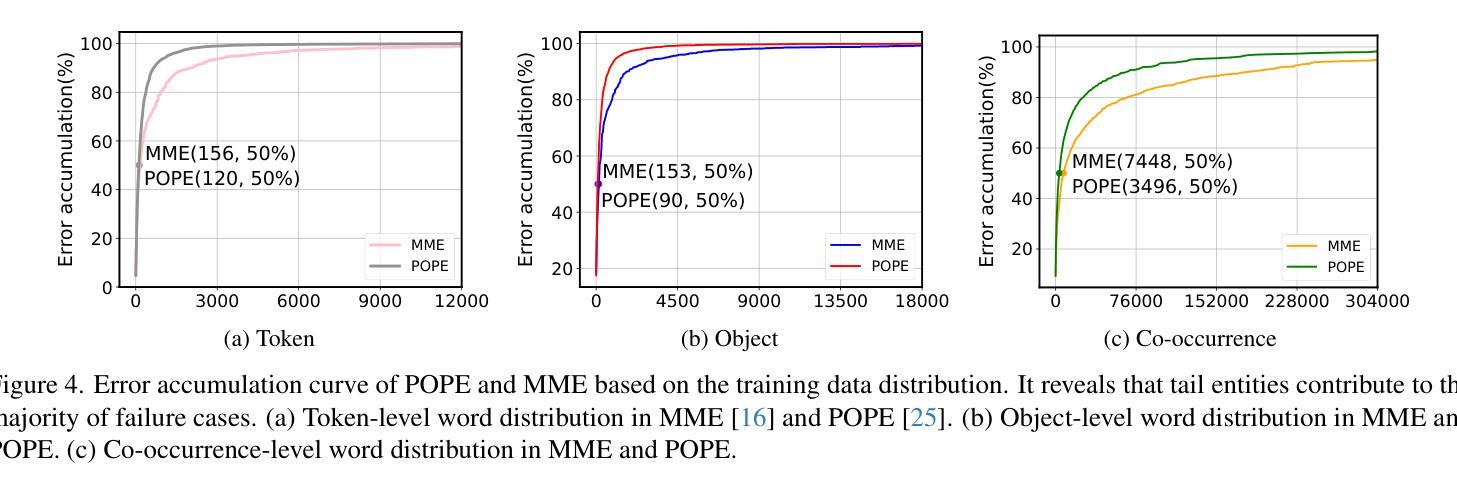
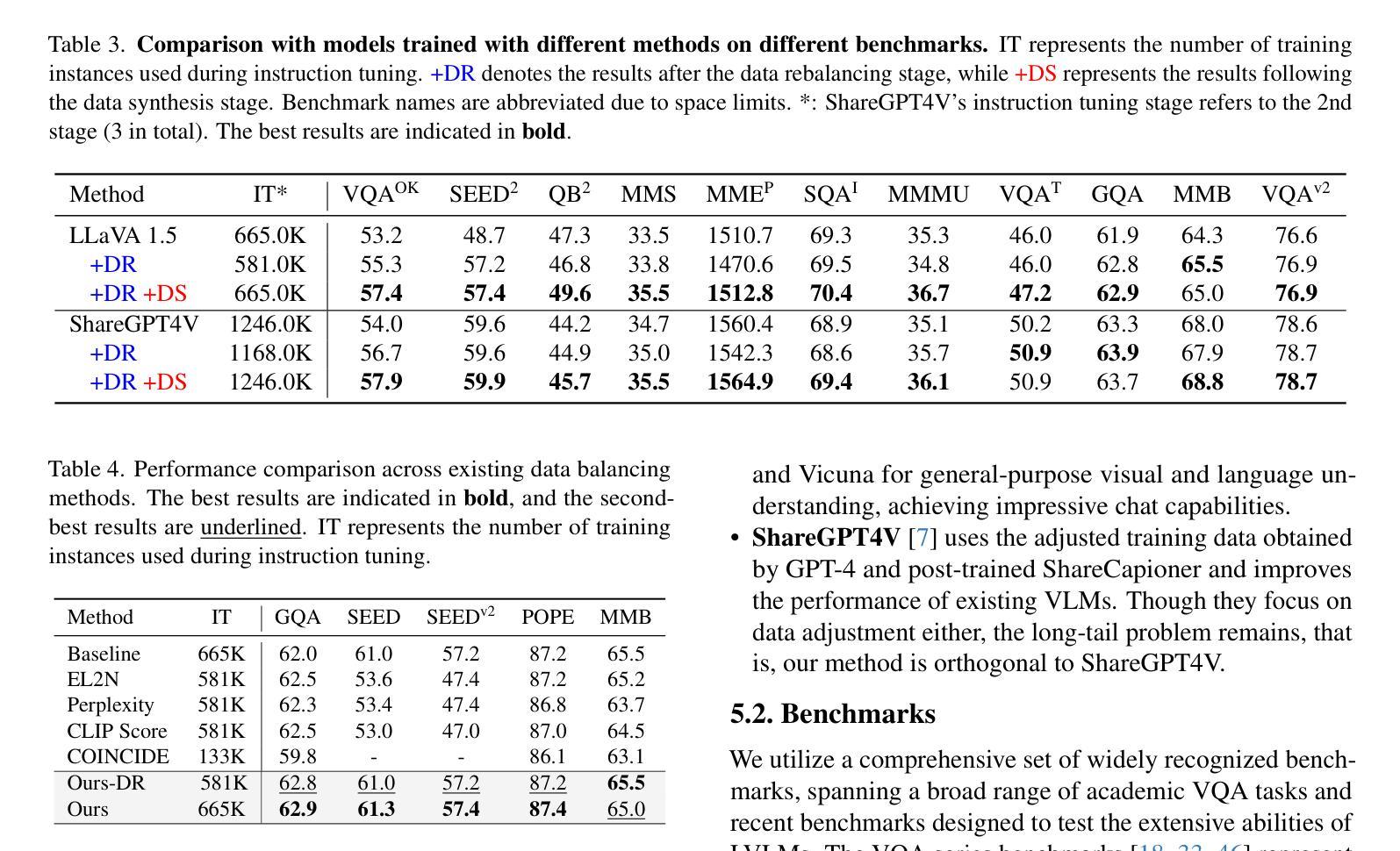
Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved significant progress in combining visual comprehension with language generation. Despite this success, the training data of LVLMs still suffers from Long-Tail (LT) problems, where the data distribution is highly imbalanced. Previous works have mainly focused on traditional VLM architectures, i.e., CLIP or ViT, and specific tasks such as recognition and classification. Nevertheless, the exploration of LVLM (e.g. LLaVA) and more general tasks (e.g. Visual Question Answering and Visual Reasoning) remains under-explored. In this paper, we first conduct an in-depth analysis of the LT issues in LVLMs and identify two core causes: the overrepresentation of head concepts and the underrepresentation of tail concepts. Based on the above observation, we propose an $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{R}$efinement Framework ($\textbf{ADR}$), which consists of two stages: $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{R}$ebalancing ($\textbf{DR}$) and $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{S}$ynthesis ($\textbf{DS}$). In the DR stage, we adaptively rebalance the redundant data based on entity distributions, while in the DS stage, we leverage Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) and scarce images to supplement underrepresented portions. Through comprehensive evaluations across eleven benchmarks, our proposed ADR effectively mitigates the long-tail problem in the training data, improving the average performance of LLaVA 1.5 relatively by 4.36%, without increasing the training data volume.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在结合视觉理解与语言生成方面取得了显著进展。然而,尽管取得了成功,LVLM的训练数据仍然面临长尾(LT)问题,即数据分布极度不平衡。之前的研究主要集中于传统的VLM架构,例如CLIP或ViT,以及特定的任务,如识别和分类。然而,对于LVLM(例如LLaVA)和更一般的任务(例如视觉问答和视觉推理)的探索仍然不足。
在本文中,我们首先对LVLMs中的LT问题进行了深入分析,并确定了两个核心原因:头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。基于上述观察,我们提出了一个自适应数据精炼框架(ADR),它由两个阶段组成:数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)。在DR阶段,我们根据实体分布自适应地重新平衡冗余数据,而在DS阶段,我们利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和稀缺图像来补充表示不足的部分。通过对十一个基准的全面评估,我们提出的ADR有效地缓解了训练数据中的长尾问题,相对提高了LLaVA 1.5的平均性能4.36%,且没有增加训练数据量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文深入探讨了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)面临的Long-Tail(LT)问题,并指出其两大核心原因:头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。为解决这一问题,本文提出了自适应数据优化框架(ADR),包含数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)两个阶段。DR阶段根据实体分布自适应地重新平衡数据,而DS阶段则利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和稀缺图像来补充被低估的部分。在多个基准测试上的综合评估表明,ADR框架有效地缓解了训练数据中的长尾问题,相对提升了LLaVA 1.5模型的平均性能4.36%,且未增加训练数据量。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)面临Long-Tail(LT)问题,数据分布高度不平衡。
- 问题的核心在于头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。
- 提出了自适应数据优化框架(ADR)来解决这一问题。
- ADR包含数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)两个阶段。
- DR阶段自适应地重新平衡数据,基于实体分布。
- DS阶段利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和稀缺图像补充被低估的数据部分。
- 综合评估显示,ADR框架有效缓解了训练数据中的长尾问题,提升了模型的平均性能,且未增加训练数据量。
点此查看论文截图