⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
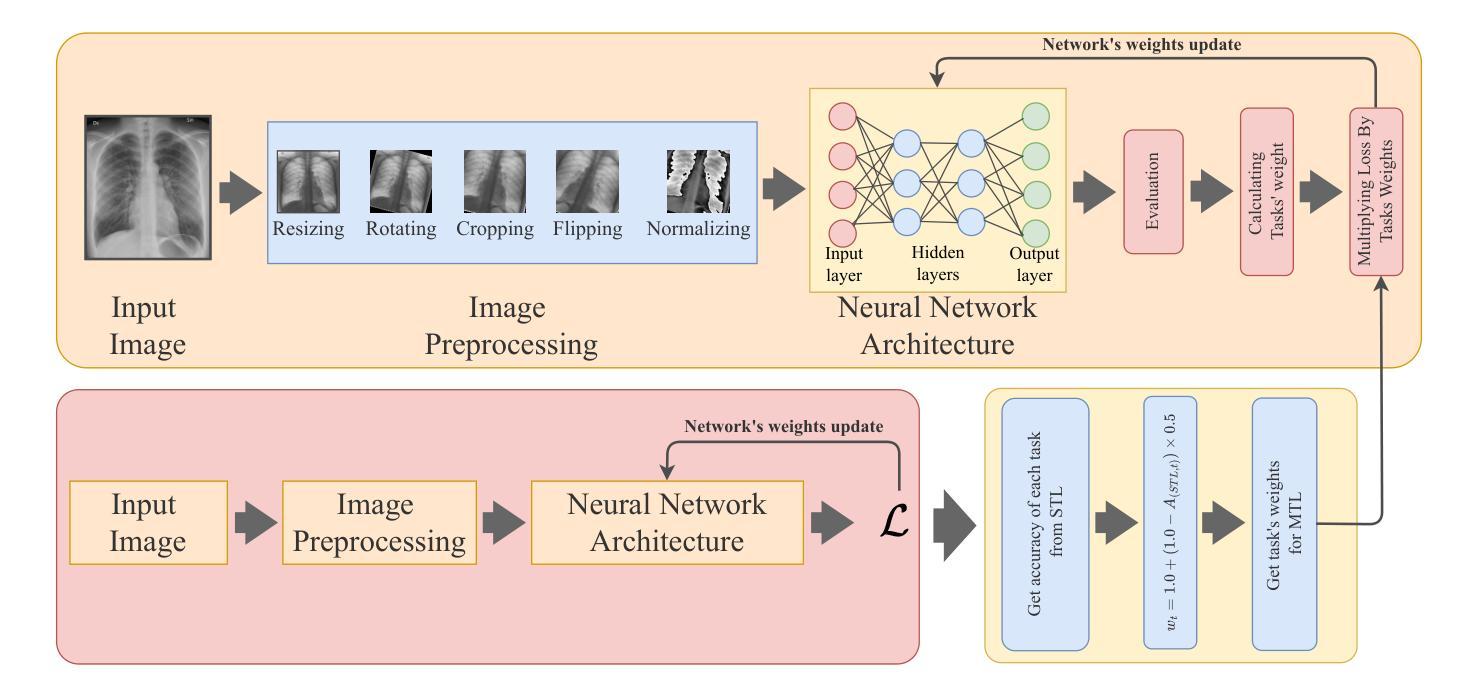
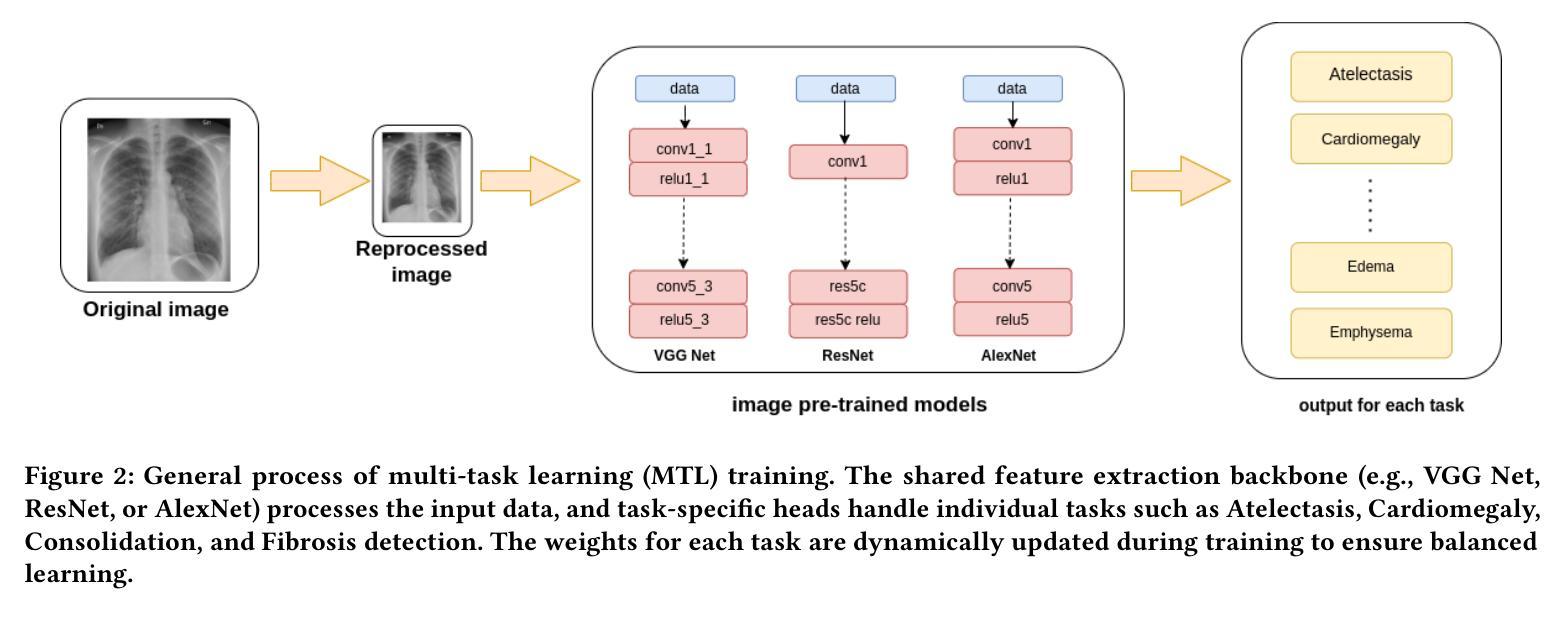
DeepChest: Dynamic Gradient-Free Task Weighting for Effective Multi-Task Learning in Chest X-ray Classification
Authors:Youssef Mohamed, Noran Mohamed, Khaled Abouhashad, Feilong Tang, Sara Atito, Shoaib Jameel, Imran Razzak, Ahmed B. Zaky
While Multi-Task Learning (MTL) offers inherent advantages in complex domains such as medical imaging by enabling shared representation learning, effectively balancing task contributions remains a significant challenge. This paper addresses this critical issue by introducing DeepChest, a novel, computationally efficient and effective dynamic task-weighting framework specifically designed for multi-label chest X-ray (CXR) classification. Unlike existing heuristic or gradient-based methods that often incur substantial overhead, DeepChest leverages a performance-driven weighting mechanism based on effective analysis of task-specific loss trends. Given a network architecture (e.g., ResNet18), our model-agnostic approach adaptively adjusts task importance without requiring gradient access, thereby significantly reducing memory usage and achieving a threefold increase in training speed. It can be easily applied to improve various state-of-the-art methods. Extensive experiments on a large-scale CXR dataset demonstrate that DeepChest not only outperforms state-of-the-art MTL methods by 7% in overall accuracy but also yields substantial reductions in individual task losses, indicating improved generalization and effective mitigation of negative transfer. The efficiency and performance gains of DeepChest pave the way for more practical and robust deployment of deep learning in critical medical diagnostic applications. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/youssefkhalil320/DeepChest-MTL
多任务学习(MTL)在医学成像等复杂领域具有内在优势,能够实现对共享表示的学习。然而,有效平衡任务贡献仍然是一个巨大挑战。本文通过引入DeepChest来解决这一关键问题,DeepChest是一种新型动态任务加权框架,专为多标签胸部X射线(CXR)分类而设计,计算效率高且有效。与现有的启发式或基于梯度的方法经常产生巨大开销不同,DeepChest利用一种以性能驱动的加权机制,基于任务特定损失趋势的有效分析。对于给定的网络架构(例如ResNet18),我们的模型无关方法自适应地调整任务重要性,无需梯度访问,从而大大降低了内存使用并实现了三倍的训练速度提升。它可以轻松应用于改进各种最先进的方法。在大规模CXR数据集上的大量实验表明,DeepChest不仅以7%的整体准确率超越了最先进的多任务学习方法,而且在个别任务损失上也实现了显著减少,这表明了更好的泛化和有效的负迁移缓解。DeepChest的效率和性能提升为深度学习在实际医疗诊断应用中的更实用和稳健部署铺平了道路。代码已公开在https://github.com/youssefkhalil320/DeepChest-MTL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多任务学习在医学图像等领域存在任务贡献平衡的挑战。本文提出DeepChest框架,采用动态任务加权机制,针对多标签胸片分类问题实现有效平衡。该框架计算效率高,可自适应调整任务重要性,无需梯度访问,显著提高训练速度和内存使用率。在大型胸片数据集上的实验表明,DeepChest在总体准确度上优于最新多任务学习方法7%,并有效减少单个任务损失,提高了泛化能力和减少了负迁移。
Key Takeaways
- 多任务学习在医学成像中存在平衡任务贡献的挑战。
- DeepChest框架通过动态任务加权机制解决此问题。
- DeepChest采用性能驱动的任务权重调整方法,分析特定任务的损失趋势。
- 该框架模型通用性强,可在不同的网络架构(如ResNet18)中自适应调整任务重要性。
- DeepChest提高了训练效率,显著减少了内存使用,并实现了三倍的训练速度提升。
- 在大型胸片数据集上的实验表明,DeepChest在总体准确度上优于其他最新方法。
点此查看论文截图


Multilook Coherent Imaging: Theoretical Guarantees and Algorithms
Authors:Xi Chen, Soham Jana, Christopher A. Metzler, Arian Maleki, Shirin Jalali
Multilook coherent imaging is a widely used technique in applications such as digital holography, ultrasound imaging, and synthetic aperture radar. A central challenge in these systems is the presence of multiplicative noise, commonly known as speckle, which degrades image quality. Despite the widespread use of coherent imaging systems, their theoretical foundations remain relatively underexplored. In this paper, we study both the theoretical and algorithmic aspects of likelihood-based approaches for multilook coherent imaging, providing a rigorous framework for analysis and method development. Our theoretical contributions include establishing the first theoretical upper bound on the Mean Squared Error (MSE) of the maximum likelihood estimator under the deep image prior hypothesis. Our results capture the dependence of MSE on the number of parameters in the deep image prior, the number of looks, the signal dimension, and the number of measurements per look. On the algorithmic side, we employ projected gradient descent (PGD) as an efficient method for computing the maximum likelihood solution. Furthermore, we introduce two key ideas to enhance the practical performance of PGD. First, we incorporate the Newton-Schulz algorithm to compute matrix inverses within the PGD iterations, significantly reducing computational complexity. Second, we develop a bagging strategy to mitigate projection errors introduced during PGD updates. We demonstrate that combining these techniques with PGD yields state-of-the-art performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/Computational-Imaging-RU/Bagged-DIP-Speckle.
多视角相干成像技术广泛应用于数字全息、超声成像和合成孔径雷达等领域。这些系统面临的主要挑战是存在乘法噪声,也称为斑点噪声,会降低图像质量。尽管相干成像系统得到了广泛应用,但其理论基础仍相对未被充分研究。在本文中,我们研究了基于似然的多视角相干成像的理论和算法方面,为分析和方法的开发提供了严格框架。我们的理论贡献包括在深度图像先验假设下建立最大似然估计的均方误差(MSE)的第一个理论上限。我们的结果捕捉到了MSE对深度图像先验参数数量、观察次数、信号维度和每次观察的测量数量等的依赖关系。在算法方面,我们采用投影梯度下降法(PGD)作为计算最大似然解的有效方法。此外,我们引入了两种增强PGD实际性能的关键思想。首先,我们结合了牛顿-舒尔茨算法在PGD迭代过程中计算矩阵逆,大大降低了计算复杂度。其次,我们开发了一种bagging策略来减轻PGD更新过程中引入的投影误差。我们证明,将这些技术与PGD相结合,可达到最先进的性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Computational-Imaging-RU/Bagged-DIP-Speckle找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2402.15635
Summary
本文研究了基于似然的方法在多重相干成像中的应用,包括理论和算法方面。理论贡献包括建立了最大似然估计的均方误差(MSE)的理论上界,分析了深度图像先验假设、观察次数、信号维度和每次观察的测量次数对MSE的影响。算法方面,采用投影梯度下降法(PGD)计算最大似然解,并引入两个关键思想提高PGD的实际性能:一是结合牛顿-舒尔茨算法降低计算复杂度,二是开发bagging策略减轻PGD更新中的投影误差。
Key Takeaways
- 多重相干成像中面临的主要挑战是乘法噪声(即斑点)导致的图像质量下降。
- 论文研究了基于似然的方法在多重相干成像中的理论和算法方面。
- 建立了最大似然估计的均方误差(MSE)的理论上界。
- 分析了深度图像先验假设、观察次数、信号维度和每次观察的测量次数对MSE的影响。
- 采用投影梯度下降法(PGD)计算最大似然解,该方法是一种高效的方法。
- 引入牛顿-舒尔茨算法和bagging策略来提高PGD的实际性能。
点此查看论文截图

PCA for Enhanced Cross-Dataset Generalizability in Breast Ultrasound Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Christian Schmidt, Heinrich Martin Overhoff
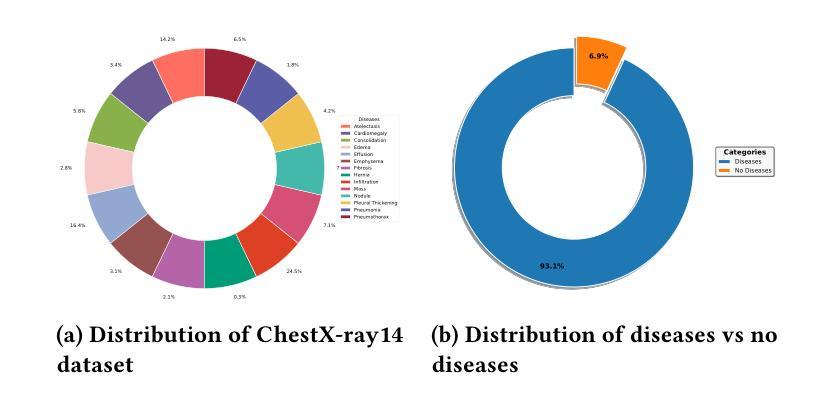
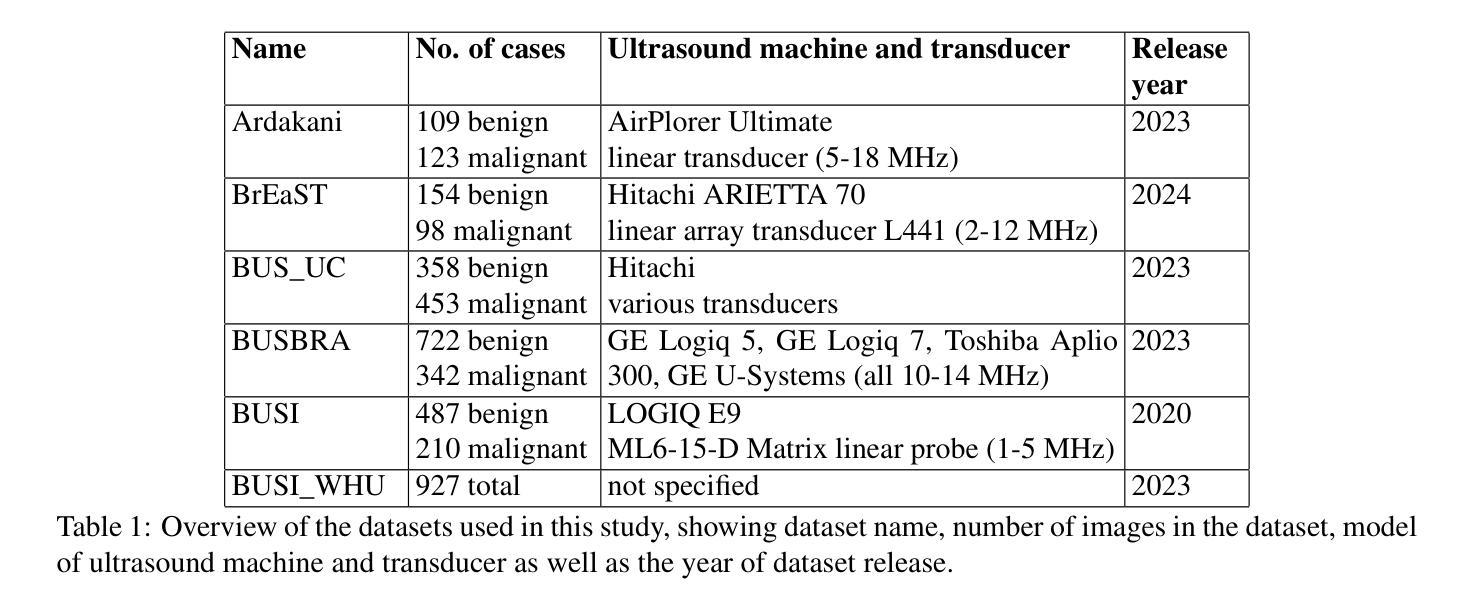
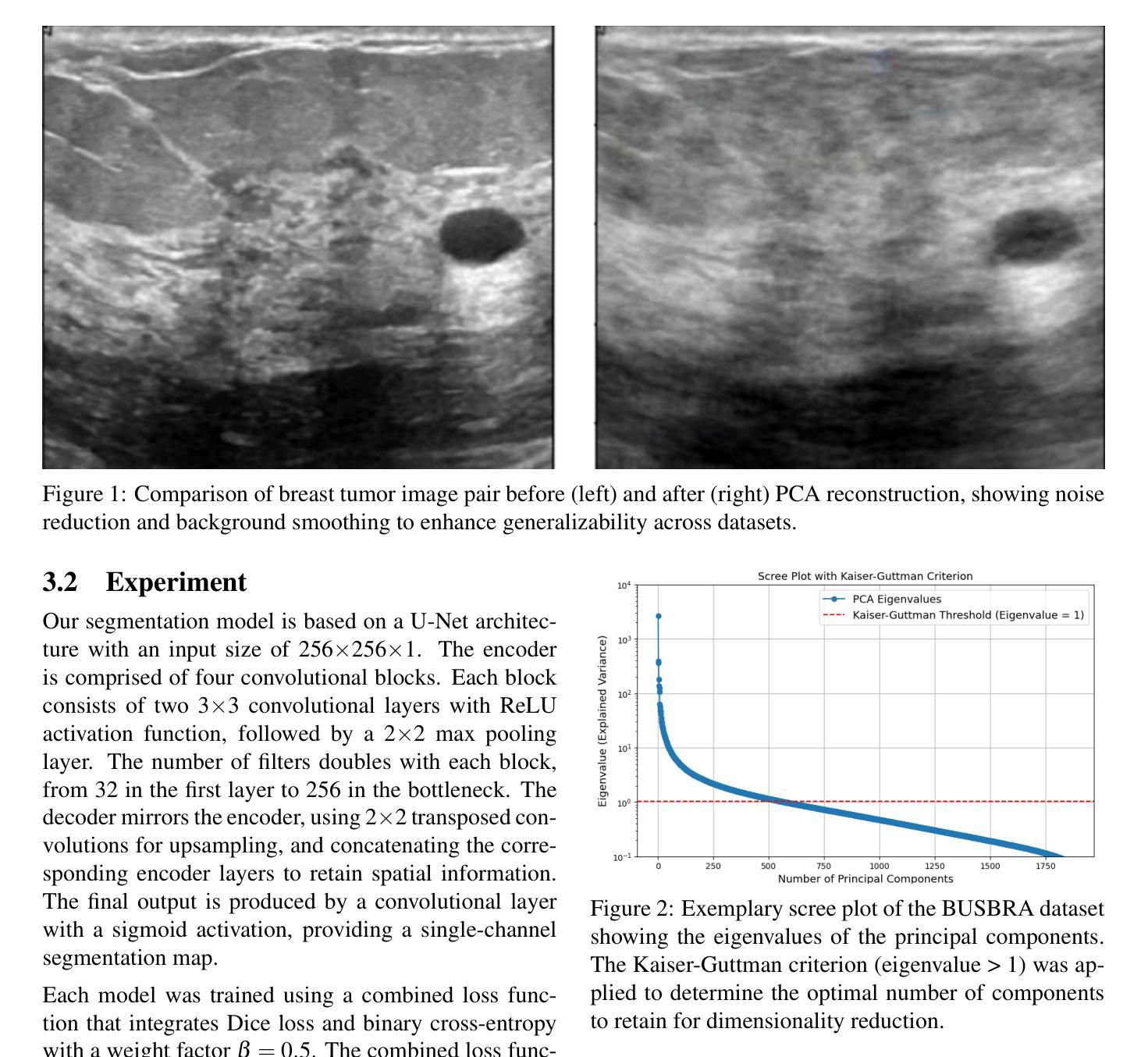
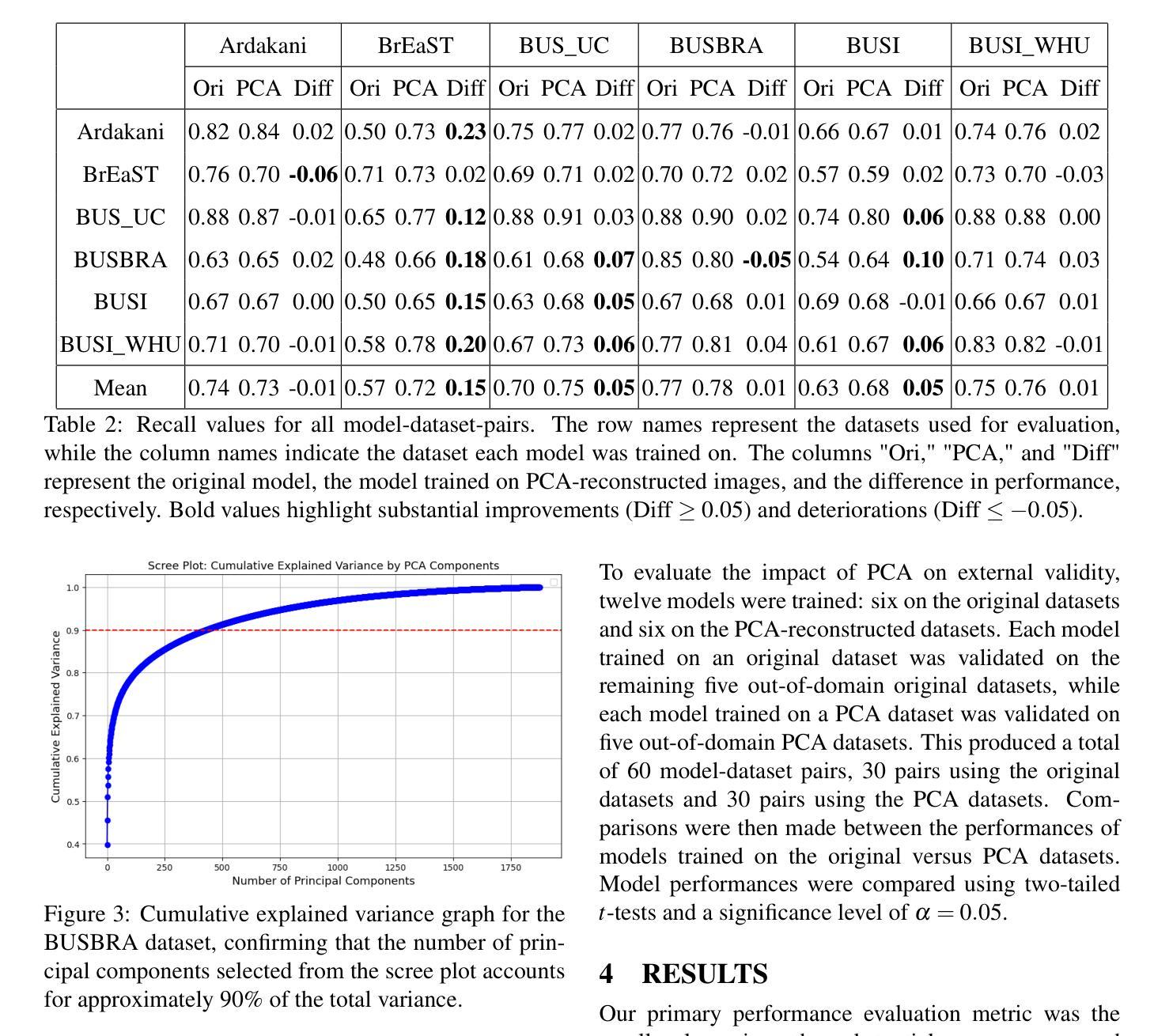
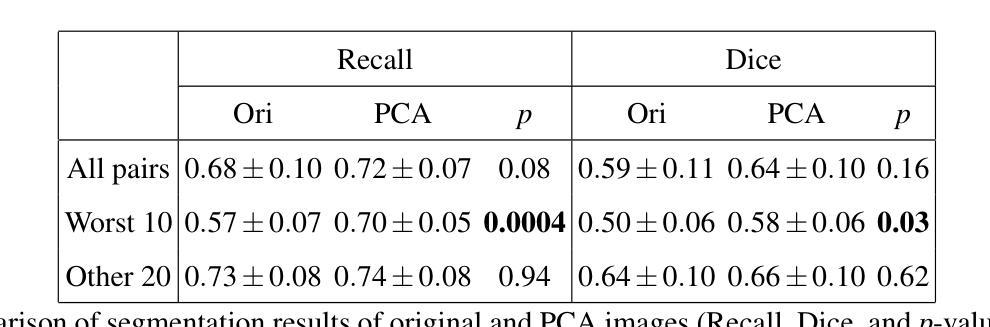
In medical image segmentation, limited external validity remains a critical obstacle when models are deployed across unseen datasets, an issue particularly pronounced in the ultrasound image domain. Existing solutions-such as domain adaptation and GAN-based style transfer-while promising, often fall short in the medical domain where datasets are typically small and diverse. This paper presents a novel application of principal component analysis (PCA) to address this limitation. PCA preprocessing reduces noise and emphasizes essential features by retaining approximately 90% of the dataset variance. We evaluate our approach across six diverse breast tumor ultrasound datasets comprising 3,983 B-mode images and corresponding expert tumor segmentation masks. For each dataset, a corresponding dimensionality reduced PCA-dataset is created and U-Net-based segmentation models are trained on each of the twelve datasets. Each model trained on an original dataset was inferenced on the remaining five out-of-domain original datasets (baseline results), while each model trained on a PCA dataset was inferenced on five out-of-domain PCA datasets. Our experimental results indicate that using PCA reconstructed datasets, instead of original images, improves the model’s recall and Dice scores, particularly for model-dataset pairs where baseline performance was lowest, achieving statistically significant gains in recall (0.57 $\pm$ 0.07 vs. 0.70 $\pm$ 0.05, $p = 0.0004$) and Dice scores (0.50 $\pm$ 0.06 vs. 0.58 $\pm$ 0.06, $p = 0.03$). Our method reduced the decline in recall values due to external validation by $33%$. These findings underscore the potential of PCA reconstruction as a safeguard to mitigate declines in segmentation performance, especially in challenging cases, with implications for enhancing external validity in real-world medical applications.
在医学图像分割领域,当模型部署在未见过的数据集上时,有限的外部有效性仍然是一个关键的障碍,这一问题在超声图像领域尤其突出。虽然现有的解决方案(如域适应和基于GAN的风格转移)前景广阔,但在医学领域通常面临数据集小且多样的问题。本文首次将主成分分析(PCA)应用于解决这一限制。PCA预处理通过保留大约90%的数据集方差来减少噪声并强调重要特征。我们在包含3983张B模式图像和相应的专家肿瘤分割掩码的六个不同乳腺癌超声数据集上评估了我们的方法。对于每个数据集,都会创建一个相应的降维PCA数据集,并在每个十二个数据集上训练基于U-Net的分割模型。在每个原始数据集上训练的模型对剩余的五个外部原始数据集进行推理(基线结果),而在PCA数据集上训练的模型对五个外部PCA数据集进行推理。我们的实验结果表明,使用PCA重建的数据集而不是原始图像,可以提高模型的召回率和Dice得分,特别是对于基线性能最低的模型-数据集对,召回率(0.57±0.07 vs. 0.70±0.05,p=0.0004)和Dice得分(0.50±0.06 vs. 0.58±0.06,p=0.03)都有统计学上的显著差异。我们的方法将由于外部验证而导致的召回值下降减少了33%。这些发现强调了PCA重建作为缓解分割性能下降的安全保障的潜力,特别是在具有挑战性的情况下,这对增强现实世界医学应用的外部有效性具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学图像分割中模型在未见数据集上部署时存在的外部有效性有限的问题,尤其是超声图像领域的问题,本文提出了一种基于主成分分析(PCA)的新应用。PCA预处理通过保留大约90%的数据集方差,减少噪声并强调重要特征。实验结果表明,使用PCA重建的数据集相较于原始图像,能提高模型的召回率和Dice得分,特别是在基线性能最低的模型-数据集对上,实现了统计学上的召回率显著增长。该方法减轻了由于外部验证导致的召回值下降33%,为提高医学应用中的外部有效性提供了潜在的安全保障。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中模型在未见数据集上的外部有效性有限是一个关键问题,特别是在超声图像领域。
- 主成分分析(PCA)被应用于医学图像预处理,以减少噪声并强调重要特征,保留大约90%的数据集方差。
- 通过实验评估了PCA在六个不同的乳腺癌超声数据集上的效果。
- 使用PCA重建的数据集训练模型,相较于原始图像,能提高模型的召回率和Dice得分。
- 在基线性能较低的模型-数据集对上,PCA的效果更为显著,实现了统计学上的召回率增长。
- PCA方法减轻了由于外部验证导致的召回值下降33%。
- PCA的应用为提高医学应用中的外部有效性提供了潜在的安全保障。
点此查看论文截图

Comparative assessment of fairness definitions and bias mitigation strategies in machine learning-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease from MR images
Authors:Maria Eleftheria Vlontzou, Maria Athanasiou, Christos Davatzikos, Konstantina S. Nikita
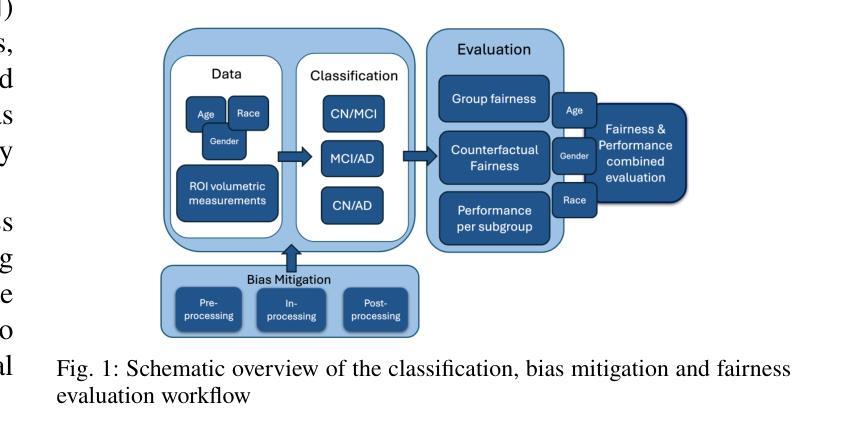
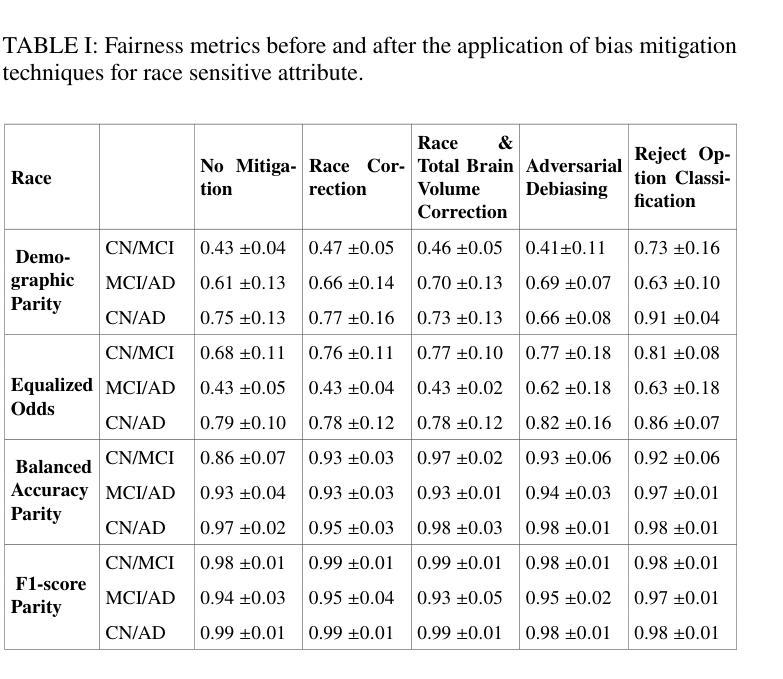
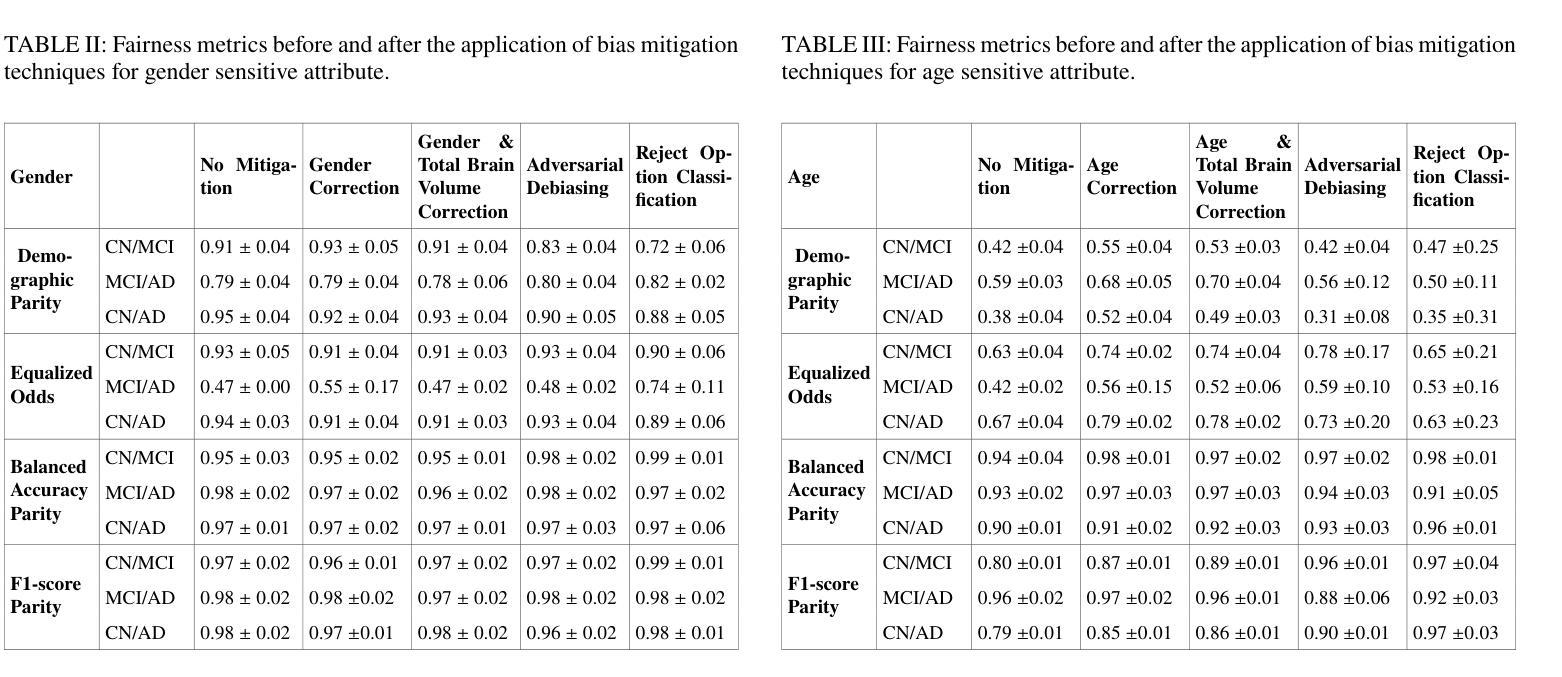
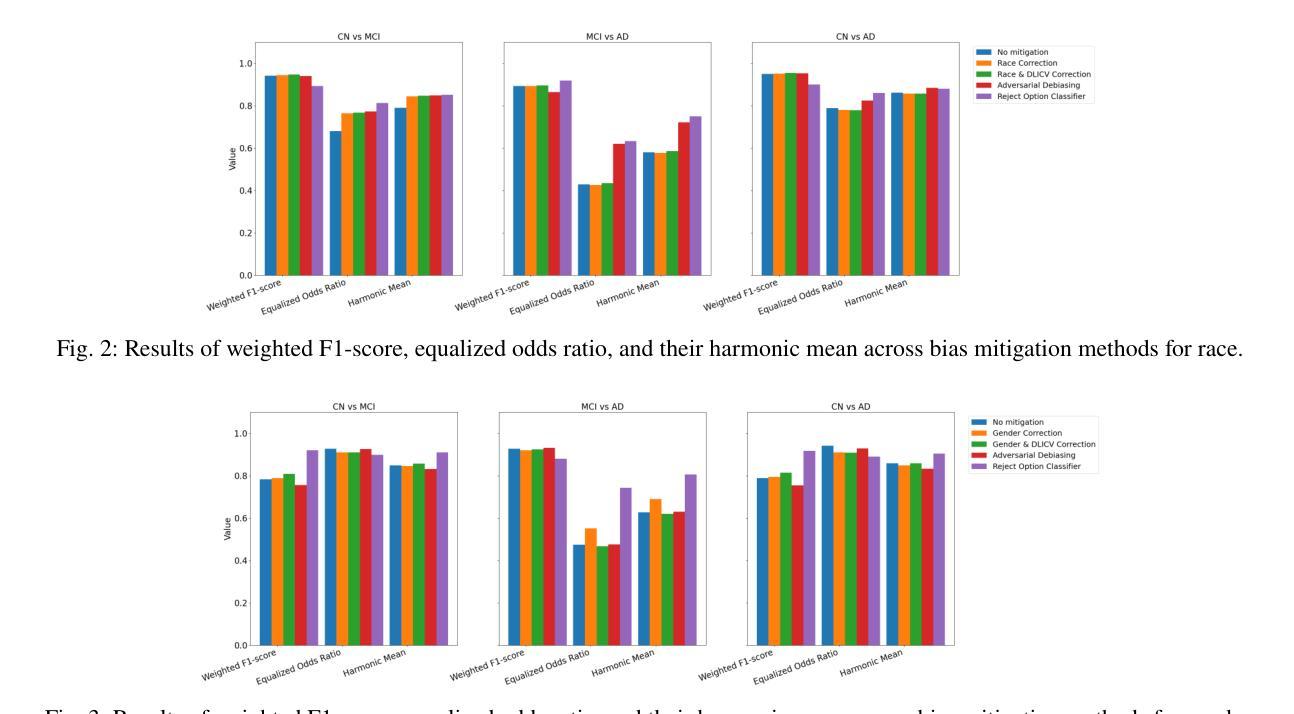
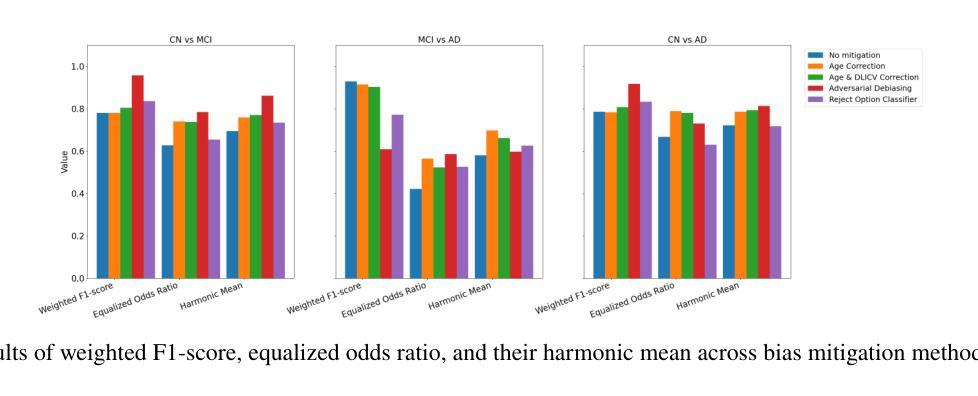
The present study performs a comprehensive fairness analysis of machine learning (ML) models for the diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from MRI-derived neuroimaging features. Biases associated with age, race, and gender in a multi-cohort dataset, as well as the influence of proxy features encoding these sensitive attributes, are investigated. The reliability of various fairness definitions and metrics in the identification of such biases is also assessed. Based on the most appropriate fairness measures, a comparative analysis of widely used pre-processing, in-processing, and post-processing bias mitigation strategies is performed. Moreover, a novel composite measure is introduced to quantify the trade-off between fairness and performance by considering the F1-score and the equalized odds ratio, making it appropriate for medical diagnostic applications. The obtained results reveal the existence of biases related to age and race, while no significant gender bias is observed. The deployed mitigation strategies yield varying improvements in terms of fairness across the different sensitive attributes and studied subproblems. For race and gender, Reject Option Classification improves equalized odds by 46% and 57%, respectively, and achieves harmonic mean scores of 0.75 and 0.80 in the MCI versus AD subproblem, whereas for age, in the same subproblem, adversarial debiasing yields the highest equalized odds improvement of 40% with a harmonic mean score of 0.69. Insights are provided into how variations in AD neuropathology and risk factors, associated with demographic characteristics, influence model fairness.
本研究对机器学习(ML)模型在诊断轻度认知障碍(MCI)和阿尔茨海默病(AD)中的公平性进行了全面分析,分析基于MRI衍生的神经成像特征。本研究探讨了多队列数据集中与年龄、种族和性别相关的偏见,以及这些敏感属性的代理特征编码的影响。还评估了不同公平定义和指标在识别此类偏见方面的可靠性。基于最合适的公平衡量标准,对广泛使用的预处理、过程处理和后处理偏见缓解策略进行了比较分析。此外,引入了一种新型组合度量方法,通过考虑F1分数和平等机会比率来量化公平性和性能之间的权衡,这对于医疗诊断应用是适当的。获得的结果表明存在与年龄和种族相关的偏见,而性别偏见并不显著。所实施的缓解策略在针对不同敏感属性和所研究子问题的公平性方面产生了不同程度的改进。对于种族和性别而言,拒绝选项分类将平等机会提高了46%和57%,并在MCI与AD的子问题中实现了0.75和0.80的调和平均数得分;而对于年龄,在同一子问题中,对抗去偏置使平等机会提高了40%,调和平均数得分为0.69。本研究提供了关于与人口统计学特征相关的AD神经病理学和风险因素的变动如何影响模型公平性的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF (C) 2025 IEEE Paper accepted at IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Conference, 2025
Summary
本文全面分析了用于轻度认知障碍(MCI)和阿尔茨海默病(AD)诊断的机器学习模型的公平性。研究调查了年龄、种族和性别等多队列数据集中的偏见,以及这些敏感属性编码的代理特征的影响。同时评估了不同公平性定义和指标在识别这些偏见方面的可靠性。根据最合适的公平措施,对预处理、中处理和后处理偏见缓解策略进行了比较分析。此外,介绍了一种新的复合度量标准,该标准能平衡公平性和性能,考虑了F1分数和均等机会比率,适用于医疗诊断应用。研究结果显示存在与年龄和种族相关的偏见,而性别偏见不显著。部署的缓解策略在不同敏感属性和研究子问题上公平性的改进程度不同。对于种族和性别,拒绝选项分类提高了均等机会比率分别达46%和57%,在MCI与AD子问题中达到和谐均值0.75和0.80;而对于年龄,在同一子问题中,对抗性去偏置提高了平等机会改善率达40%,和谐均值为0.69。此外,该研究还探讨了与人口特征相关的AD神经病理及风险因素的差异如何影响模型公平性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究对机器学习模型在MCI和AD诊断中的公平性进行了全面分析。
- 考察了年龄、种族和性别等多队列数据集中的偏见。
- 评估了不同公平性定义和指标的可靠性。
- 通过合适的公平措施,对比分析了不同的偏见缓解策略。
- 介绍了一种新的复合度量标准,用于平衡公平性和性能。
- 研究发现存在与年龄和种族相关的偏见,而性别偏见不显著。
点此查看论文截图

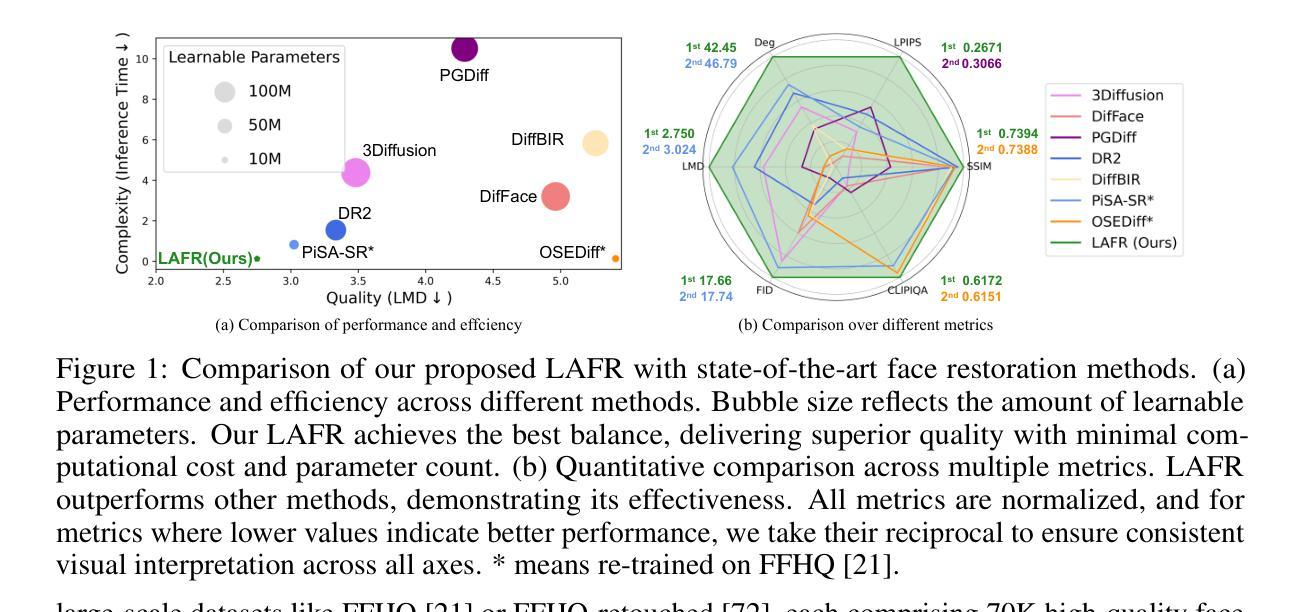
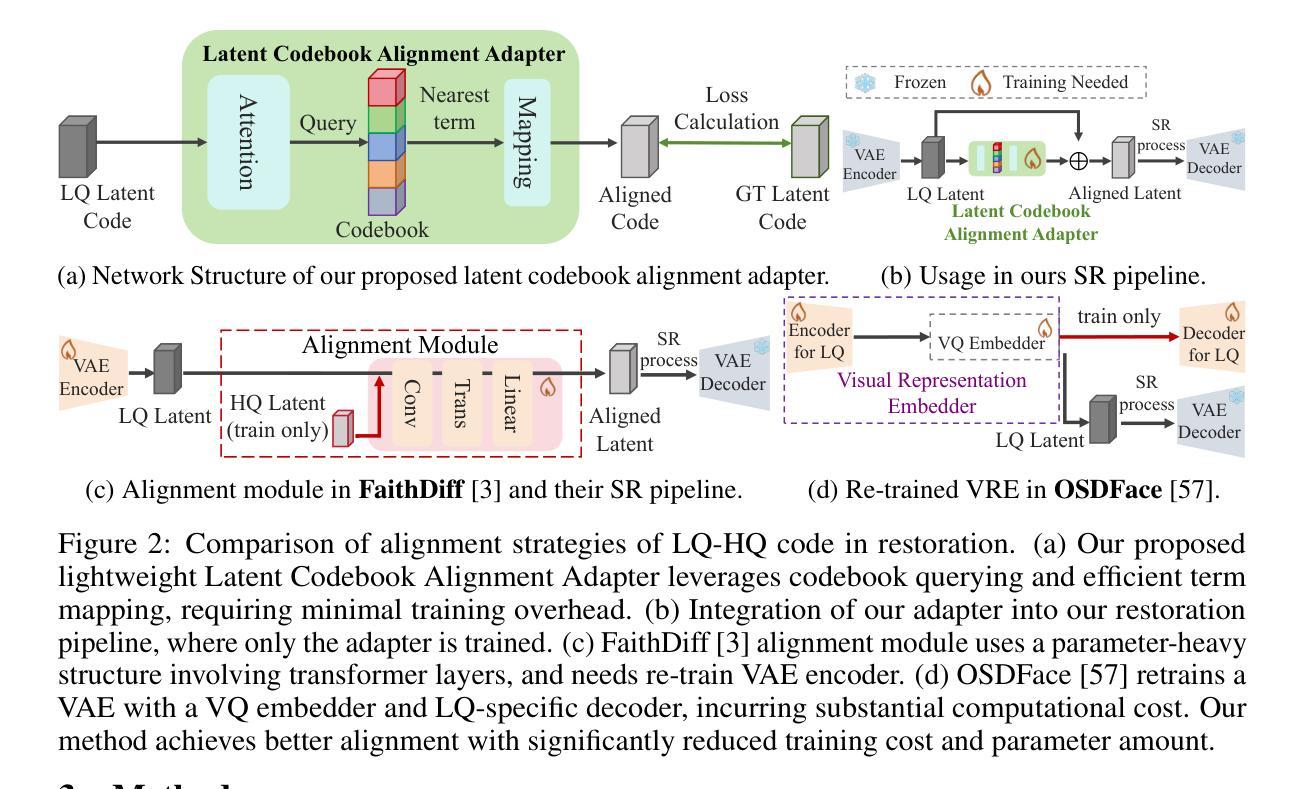
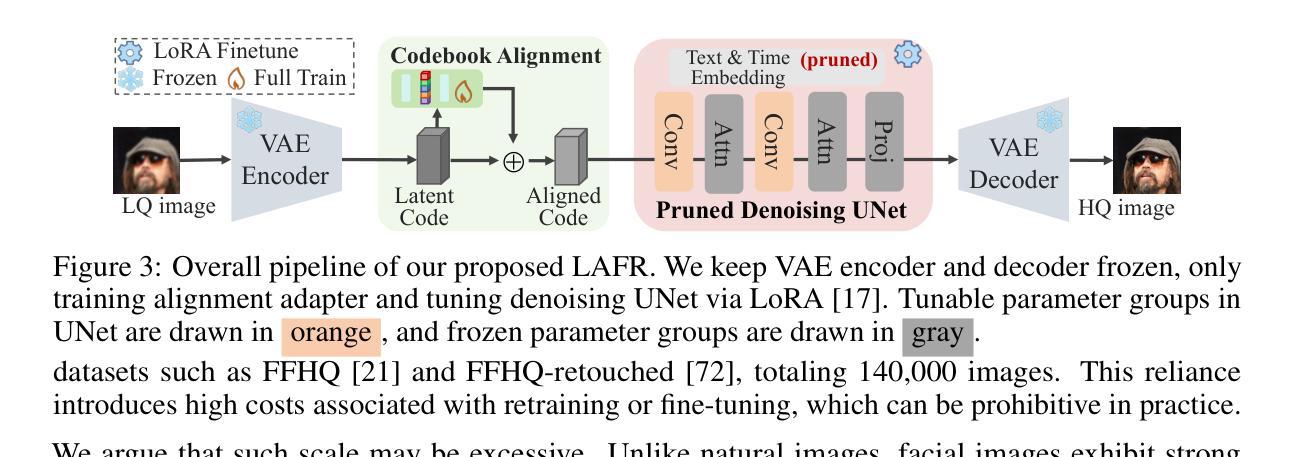
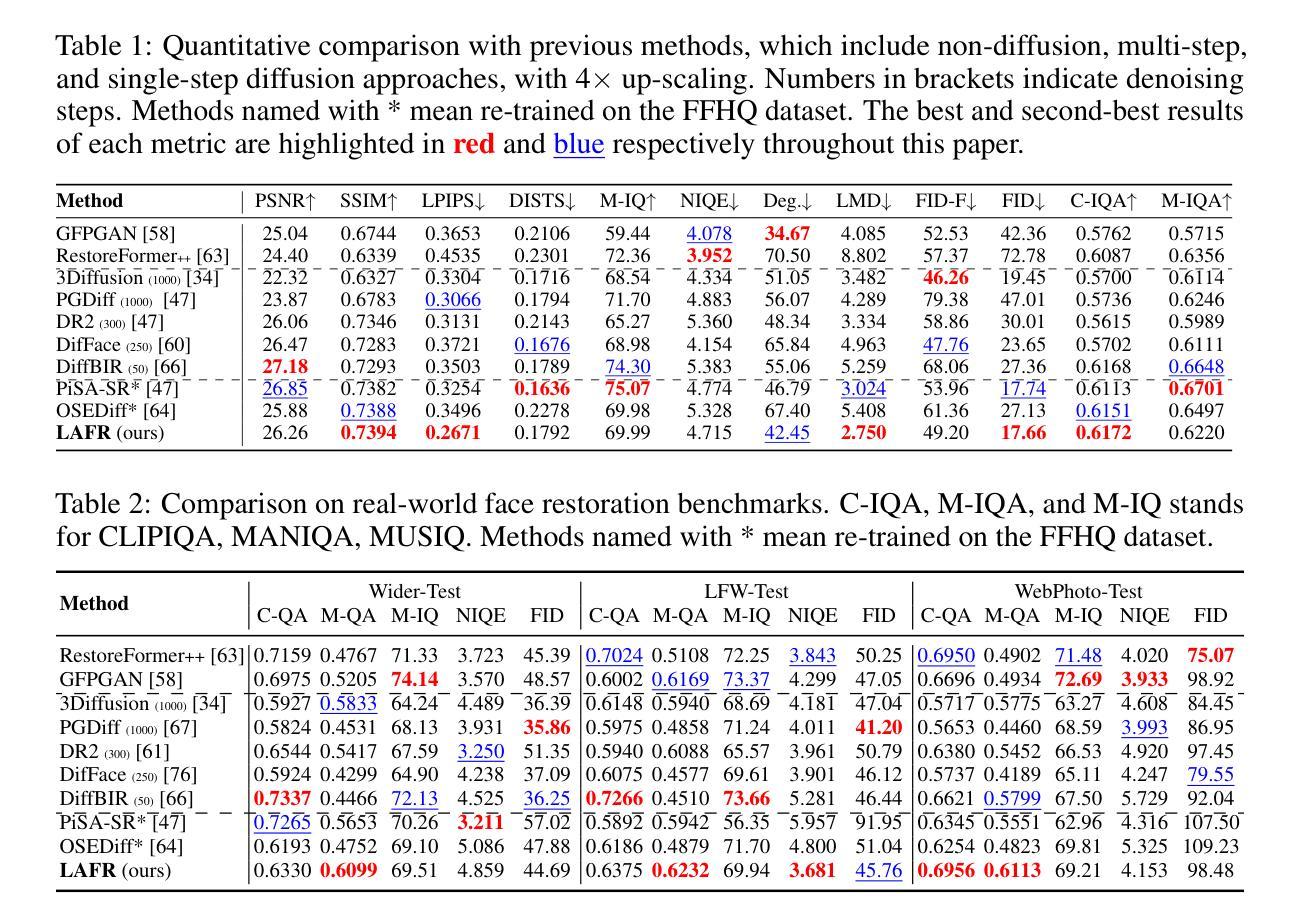
LAFR: Efficient Diffusion-based Blind Face Restoration via Latent Codebook Alignment Adapter
Authors:Runyi Li, Bin Chen, Jian Zhang, Radu Timofte
Blind face restoration from low-quality (LQ) images is a challenging task that requires not only high-fidelity image reconstruction but also the preservation of facial identity. While diffusion models like Stable Diffusion have shown promise in generating high-quality (HQ) images, their VAE modules are typically trained only on HQ data, resulting in semantic misalignment when encoding LQ inputs. This mismatch significantly weakens the effectiveness of LQ conditions during the denoising process. Existing approaches often tackle this issue by retraining the VAE encoder, which is computationally expensive and memory-intensive. To address this limitation efficiently, we propose LAFR (Latent Alignment for Face Restoration), a novel codebook-based latent space adapter that aligns the latent distribution of LQ images with that of HQ counterparts, enabling semantically consistent diffusion sampling without altering the original VAE. To further enhance identity preservation, we introduce a multi-level restoration loss that combines constraints from identity embeddings and facial structural priors. Additionally, by leveraging the inherent structural regularity of facial images, we show that lightweight finetuning of diffusion prior on just 0.9% of FFHQ dataset is sufficient to achieve results comparable to state-of-the-art methods, reduce training time by 70%. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world face restoration benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of LAFR, achieving high-quality, identity-preserving face reconstruction from severely degraded inputs.
从低质量(LQ)图像中恢复盲脸是一个具有挑战性的任务,不仅需要高保真度的图像重建,还需要保持面部身份。虽然像Stable Diffusion这样的扩散模型在生成高质量(HQ)图像方面显示出潜力,但它们的VAE模块通常仅在HQ数据上进行训练,导致在编码LQ输入时出现语义不对齐。这种不匹配会显著削弱去噪过程中LQ条件的有效性。现有方法通常通过重新训练VAE编码器来解决这个问题,这在计算上既昂贵又密集。为了有效地解决这一限制,我们提出了LAFR(面部恢复的潜在对齐,一种基于代码本的新型潜在空间适配器),它可以对齐LQ图像的潜在分布与HQ图像的潜在分布,在不改变原始VAE的情况下实现语义一致的扩散采样。为了进一步增强身份保持能力,我们引入了一种多级恢复损失,它结合了身份嵌入和面部结构先验的限制。此外,通过利用面部图像固有的结构规律,我们证明在仅使用FFHQ数据集的0.9%进行扩散先验的轻量级微调足以实现与最新方法相当的结果,并将训练时间减少70%。在合成和真实世界面部恢复基准测试上的大量实验证明了LAFR的有效性和高效性,实现了从严重退化的输入中进行高质量、保持身份的面部重建。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为LAFR的方法,用于从低质量图像中恢复盲脸。该方法通过代码本基于的潜在空间适配器,实现对潜在空间内低质量图像和高质量图像之间的对齐。此外,引入多层次恢复损失以加强身份保留,并通过利用面部图像的结构规律性,实现了高效的训练并保证了恢复结果的良好质量。LAFR能有效合成出高保真、保留身份的低质量输入面部重建结果。
Key Takeaways
- LAFR方法使用代码本基础的潜在空间适配器,实现了低质量(LQ)和高质量(HQ)图像之间的潜在分布对齐。
- 通过引入多层次恢复损失,加强了身份保留,确保在去除噪声过程中保持语义一致性。
- 利用面部图像的结构规律性,实现了高效训练并提高了恢复结果的保真度。
- 提出一种新型的轻量级微调扩散先验方法,仅使用FFHQ数据集的0.9%即可达到与最新方法相当的结果。
- 方法能有效缩短训练时间,达到70%的减少。
- 在合成和真实世界的面部恢复基准测试中进行了广泛的实验,证明了LAFR的有效性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

Comparison of water models for structure prediction
Authors:Bálint Soczó, Ildikó Pethes
Describing the interactions of water molecules is one of the most common, yet critical, tasks in molecular dynamics simulations. Because of its unique properties, hundreds of attempts have been made to construct an ideal interaction potential model for water. In various studies, the models have been evaluated based on their ability to reproduce different properties of water. This work focuses on the atomic-scale structure in the liquid phase of water. Forty-four classical water potential models are compared to identify those that can accurately describe the structure in alignment with experimental results. In addition to some older models that are still popular today, new or re-parametrized classical models using effective pair-additive potentials that have appeared in recent years are examined. Molecular dynamics simulations were performed over a wide range of temperatures and the resulting trajectories were used to calculate the partial radial distribution functions. The total scattering structure factors were compared with data from neutron and X-ray diffraction experiments. Our analysis indicates that models with more than four interaction sites, as well as flexible or polarizable models with higher computational requirements, do not provide a significant advantage in accurately describing the structure. On the other hand, recent three-site models have made considerable progress in this area, although the best agreement with experimental data over the entire temperature range was achieved with four-site, TIP4P-type models.
描述水分子间的相互作用是分子动力学模拟中最常见但也是至关重要的任务之一。由于其独特的特性,人们已经构建了数百个理想相互作用势模型来模拟水。在各种研究中,这些模型的评价基础是它们重现水的不同特性的能力。这项工作专注于液态水原子尺度的结构。对比了44种经典的水势模型,以识别那些能够准确描述结构与实验结果相符合的模型。除了今天仍然很流行的一些旧模型外,还检查了近年来出现的使用有效对加势的新或重新参数化的经典模型。在较宽的温度范围内进行了分子动力学模拟,并使用得到的轨迹计算了部分径向分布函数。总散射结构因子与中子衍射和X射线衍射实验数据进行了比较。我们的分析表明,具有超过四个相互作用位点的模型,以及具有更高计算要求的灵活或极化模型,在准确描述结构方面并没有显著优势。另一方面,最近的三个位点的模型在这一领域取得了重大进展,尽管在整个温度范围内与实验数据吻合度最好的是四位点TIP4P类型的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 97 pages together with supplementary; submitted to Journal of Molecular Liqudis
Summary
本文比较了44种经典水势模型,以识别能够准确描述液态水原子尺度结构并与实验结果一致的模型。通过分子动力学模拟,发现超过四个相互作用位点的模型以及计算要求较高的灵活或极化模型并没有显著优势。相反,最新的三位点模型在这方面取得了显著进展,但与整个温度范围内的实验结果最佳吻合的是四位点TIP4P型模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文章比较了多种水势模型以描述液态水的原子尺度结构。
- 通过分子动力学模拟对模型进行了评估。
- 发现超过四个相互作用位点的模型并未提供显著的描述结构准确性优势。
- 灵活或极化模型在高计算要求下并未显示出明显优势。
- 三位点模型在描述液态水结构方面取得了显著进展。
- 四位点TIP4P型模型在整个温度范围内与实验结果最佳吻合。
点此查看论文截图

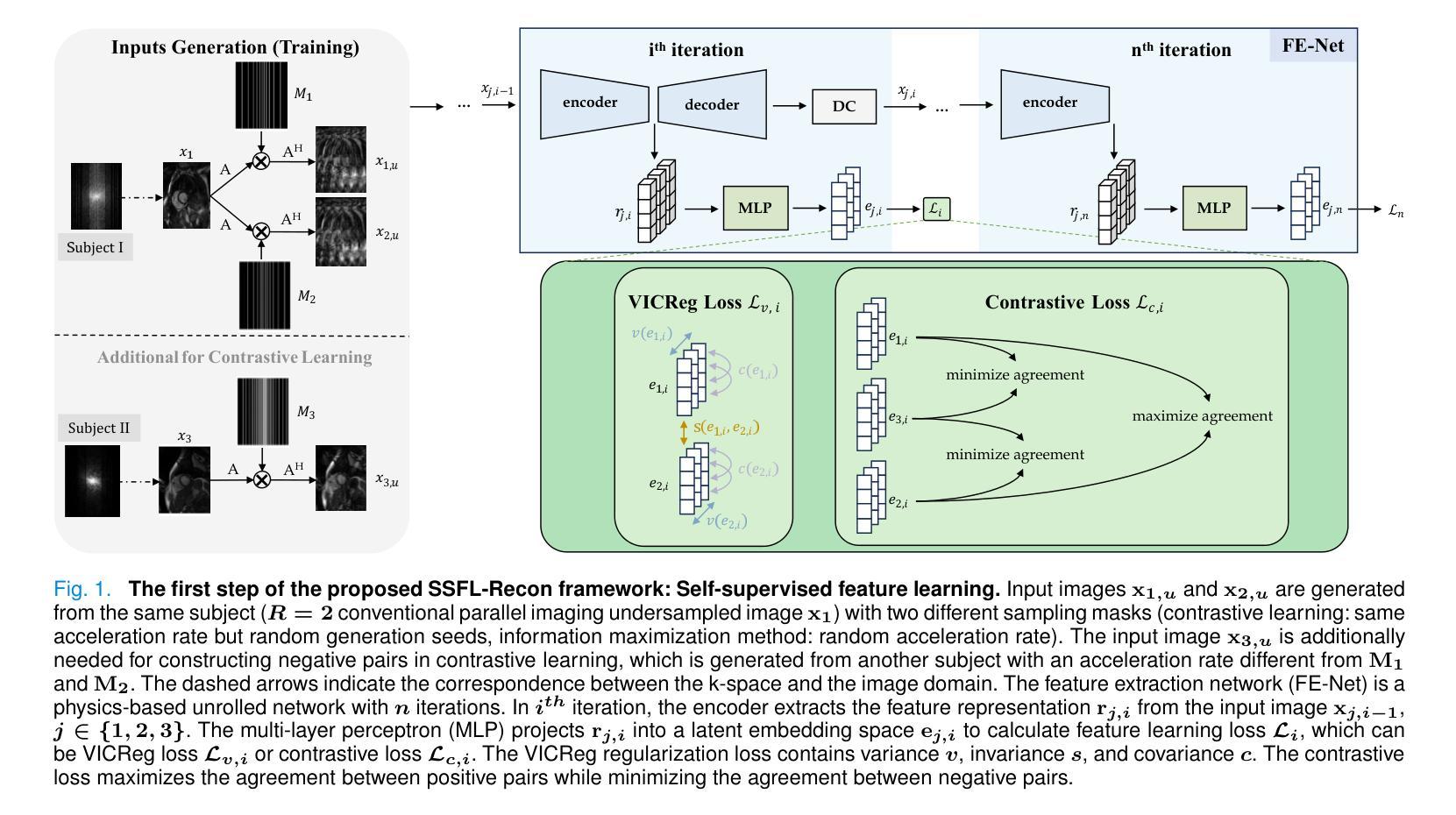
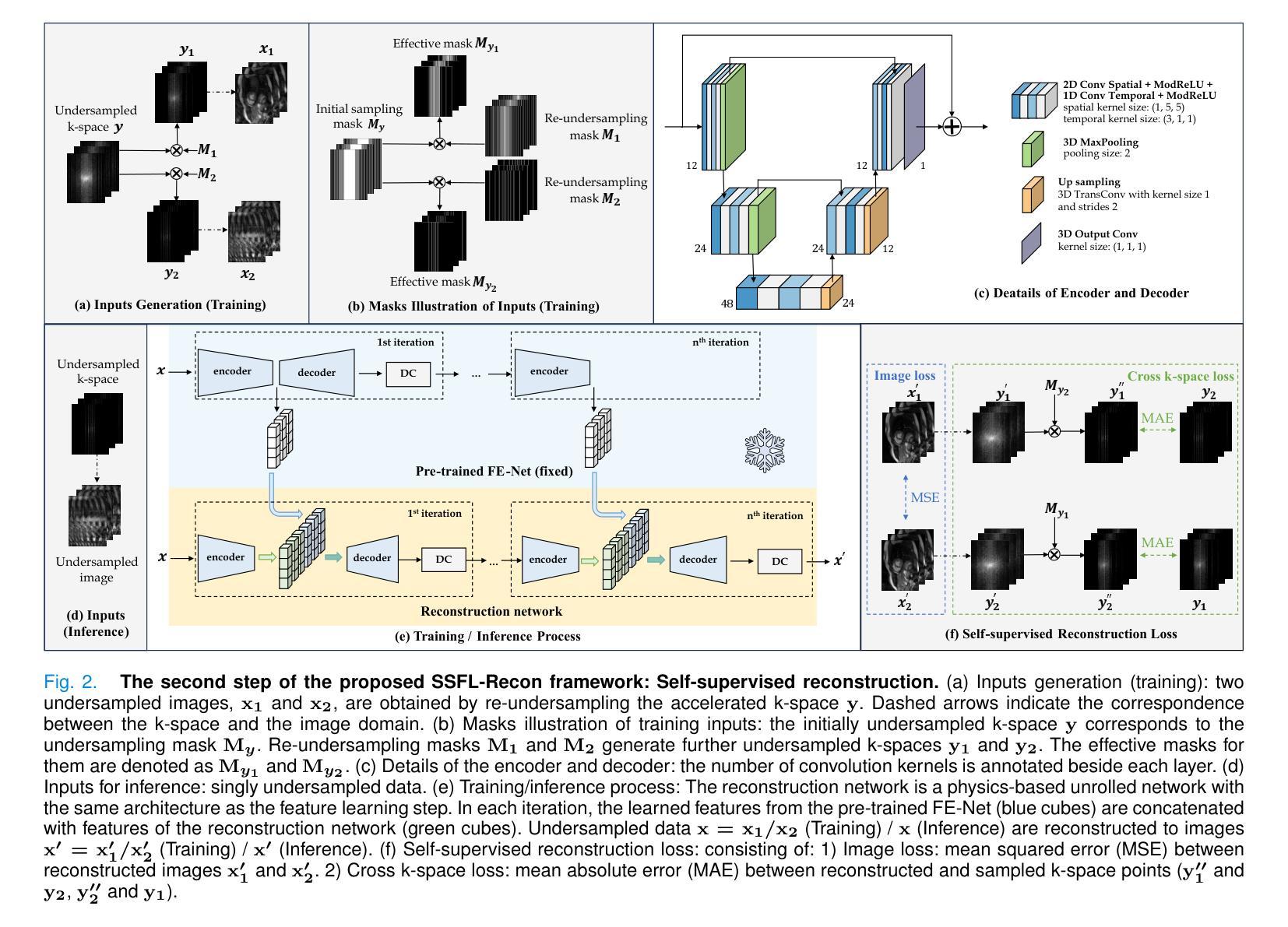
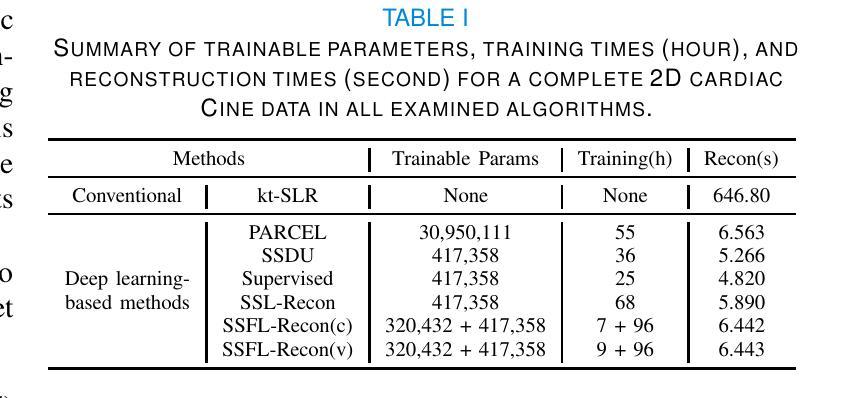
Self-supervised feature learning for cardiac Cine MR image reconstruction
Authors:Siying Xu, Marcel Früh, Kerstin Hammernik, Andreas Lingg, Jens Kübler, Patrick Krumm, Daniel Rueckert, Sergios Gatidis, Thomas Küstner
We propose a self-supervised feature learning assisted reconstruction (SSFL-Recon) framework for MRI reconstruction to address the limitation of existing supervised learning methods. Although recent deep learning-based methods have shown promising performance in MRI reconstruction, most require fully-sampled images for supervised learning, which is challenging in practice considering long acquisition times under respiratory or organ motion. Moreover, nearly all fully-sampled datasets are obtained from conventional reconstruction of mildly accelerated datasets, thus potentially biasing the achievable performance. The numerous undersampled datasets with different accelerations in clinical practice, hence, remain underutilized. To address these issues, we first train a self-supervised feature extractor on undersampled images to learn sampling-insensitive features. The pre-learned features are subsequently embedded in the self-supervised reconstruction network to assist in removing artifacts. Experiments were conducted retrospectively on an in-house 2D cardiac Cine dataset, including 91 cardiovascular patients and 38 healthy subjects. The results demonstrate that the proposed SSFL-Recon framework outperforms existing self-supervised MRI reconstruction methods and even exhibits comparable or better performance to supervised learning up to $16\times$ retrospective undersampling. The feature learning strategy can effectively extract global representations, which have proven beneficial in removing artifacts and increasing generalization ability during reconstruction.
我们提出了一种自监督特征学习辅助重建(SSFL-Recon)框架,用于MRI重建,以解决现有监督学习方法的局限性。尽管最近基于深度学习的方法在MRI重建中显示出有前景的性能,但它们大多数需要完全采样的图像进行有监督学习,这在考虑呼吸或器官运动的长时间采集时,实践中具有挑战性。此外,几乎所有完全采样的数据集都是从轻度加速数据集的常规重建中获得的,这可能潜在地影响可达到的性能。因此,临床实践中许多不同加速程度的欠采样数据集仍未得到充分利用。为了解决这些问题,我们首先训练一个自监督特征提取器,用于从欠采样图像中学习采样无关特征。预学习到的特征随后嵌入自监督重建网络中,以帮助去除伪影。实验对内部2D心脏电影数据集进行了回顾性研究,包括91名心血管患者和38名健康受试者。结果表明,所提出的SSFL-Recon框架优于现有的自监督MRI重建方法,甚至在$16\times$回顾性欠采样的情况下,其性能与有监督学习相当甚至更好。特征学习策略可以有效地提取全局表示,这在去除伪影和提高重建过程中的泛化能力方面证明了其好处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (TMI), 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于自监督特征学习的MRI重建框架(SSFL-Recon),以解决现有监督学习方法在MRI重建中的局限性。该框架能够在自监督环境下学习采样无关的特征,进而辅助去除重建过程中的伪影。实验结果表明,该框架在回顾性测试中表现出优异的性能,即使在高达16倍的回顾性欠采样情况下,其性能也与监督学习方法相当或更好。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了自监督特征学习辅助的MRI重建框架(SSFL-Recon)。
- 解决了现有监督学习方法在MRI重建中的局限性。
- 通过自监督特征提取器训练,学习采样无关的特征。
- 预学习特征嵌入到自监督重建网络中,以辅助去除伪影。
- 实验在内部2D心脏电影数据集上进行,涵盖了心血管患者和健康受试者。
- SSFL-Recon框架性能优于现有自监督MRI重建方法。
点此查看论文截图

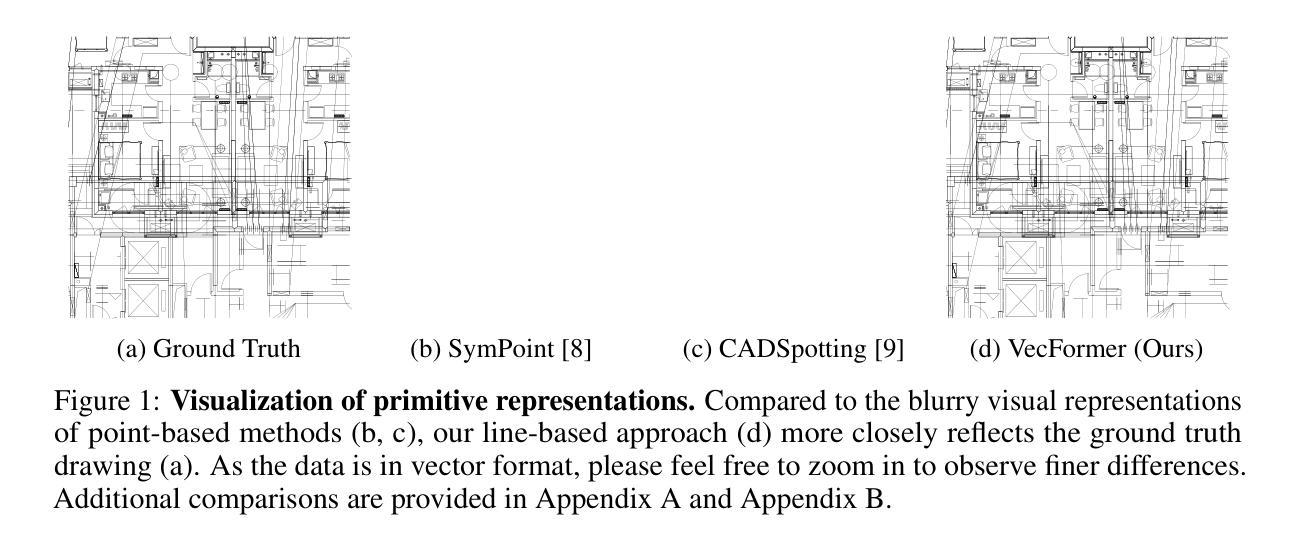
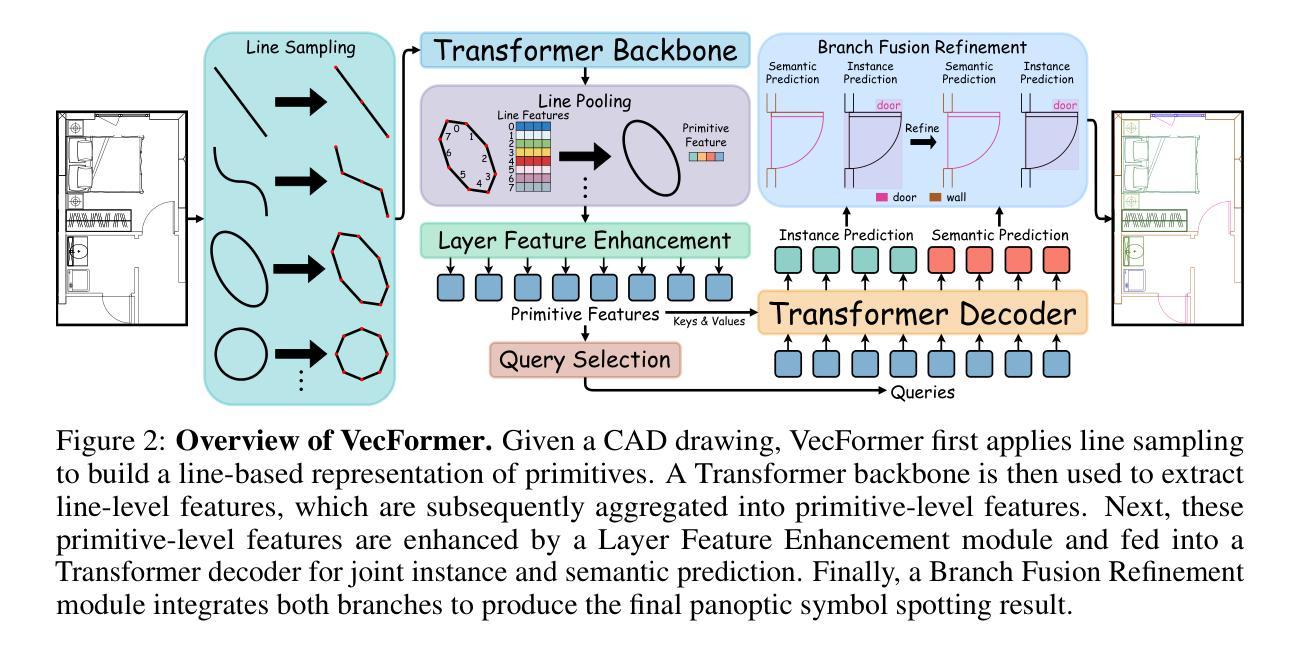
Point or Line? Using Line-based Representation for Panoptic Symbol Spotting in CAD Drawings
Authors:Xingguang Wei, Haomin Wang, Shenglong Ye, Ruifeng Luo, Yanting Zhang, Lixin Gu, Jifeng Dai, Yu Qiao, Wenhai Wang, Hongjie Zhang
We study the task of panoptic symbol spotting, which involves identifying both individual instances of countable things and the semantic regions of uncountable stuff in computer-aided design (CAD) drawings composed of vector graphical primitives. Existing methods typically rely on image rasterization, graph construction, or point-based representation, but these approaches often suffer from high computational costs, limited generality, and loss of geometric structural information. In this paper, we propose VecFormer, a novel method that addresses these challenges through line-based representation of primitives. This design preserves the geometric continuity of the original primitive, enabling more accurate shape representation while maintaining a computation-friendly structure, making it well-suited for vector graphic understanding tasks. To further enhance prediction reliability, we introduce a Branch Fusion Refinement module that effectively integrates instance and semantic predictions, resolving their inconsistencies for more coherent panoptic outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method establishes a new state-of-the-art, achieving 91.1 PQ, with Stuff-PQ improved by 9.6 and 21.2 points over the second-best results under settings with and without prior information, respectively, highlighting the strong potential of line-based representation as a foundation for vector graphic understanding.
我们研究了全景符号识别任务,该任务涉及识别由矢量图形基本元素组成的计算机辅助设计(CAD)绘图中的可数事物的各个实例以及不可数内容的语义区域。现有方法通常依赖于图像栅格化、图构建或基于点的表示,但这些方法往往存在计算成本高、通用性差以及几何结构信息丢失等问题。在本文中,我们提出了VecFormer这一新方法,它通过基于线条的基本元素表示来解决这些挑战。这种设计保留了原始基本元素的几何连续性,能够在保持计算友好的结构的同时实现更准确的形状表示,使其非常适合矢量图形理解任务。为了进一步提高预测可靠性,我们引入了分支融合细化模块,该模块有效地融合了实例和语义预测,解决了它们的不一致性,从而获得了更连贯的全景输出。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了新的先进水平,实现了91.1的PQ值。在带有和不带有先验信息的设置下,我们的方法在Stuff-PQ上分别提高了9.6和21.2个百分点,这突显了基于线条表示作为矢量图形理解基础的强大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了计算机视觉中的全景符号识别任务,即在计算机辅助设计(CAD)矢量图形中识别可数对象的个体实例和不可数区域的语义。针对现有方法存在的计算成本高、通用性差以及几何结构信息丢失等问题,本文提出了一种名为VecFormer的新方法。该方法采用基于线条的图形表示,有效保留了原始图形的几何连续性,提高了形状表示的准确性和计算效率,尤其适用于矢量图形理解任务。此外,本文还引入了一个名为Branch Fusion Refinement的模块,用于提高预测结果的可靠性,通过整合实例和语义预测结果,解决了它们之间不一致的问题,生成更连贯的全景输出结果。实验证明,该方法达到了新的研究水平,在有或无先验信息的情况下,相较于第二名结果分别提高了9.6和21.2点的Stuff-PQ值,显示出基于线条表示的矢量图形理解的强大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- VecFormer方法解决了计算机视觉中全景符号识别任务的问题,适用于计算机辅助设计(CAD)矢量图形的理解。
- VecFormer采用基于线条的图形表示,保留了原始图形的几何连续性,提高了形状表示的准确性。
- VecFormer方法在计算效率上表现优异,适用于矢量图形理解任务。
- Branch Fusion Refinement模块提高了预测结果的可靠性,解决了实例和语义预测之间的不一致问题。
- 实验结果显示VecFormer方法在全景符号识别任务上达到了新的研究水平。
- VecFormer方法在有或无先验信息的情况下均表现出强大的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

Federated Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Evangelos Charalampakis, Vasileios Mygdalis, Ioannis Pitas
This work explores the application of Federated Learning (FL) in Unsupervised Semantic image Segmentation (USS). Recent USS methods extract pixel-level features using frozen visual foundation models and refine them through self-supervised objectives that encourage semantic grouping. These features are then grouped to semantic clusters to produce segmentation masks. Extending these ideas to federated settings requires feature representation and cluster centroid alignment across distributed clients – an inherently difficult task under heterogeneous data distributions in the absence of supervision. To address this, we propose FUSS Federated Unsupervised image Semantic Segmentation) which is, to our knowledge, the first framework to enable fully decentralized, label-free semantic segmentation training. FUSS introduces novel federation strategies that promote global consistency in feature and prototype space, jointly optimizing local segmentation heads and shared semantic centroids. Experiments on both benchmark and real-world datasets, including binary and multi-class segmentation tasks, show that FUSS consistently outperforms local-only client trainings as well as extensions of classical FL algorithms under varying client data distributions. To support reproducibility, full code will be released upon manuscript acceptance.
本文探讨了联邦学习(FL)在无监督语义图像分割(USS)中的应用。最近的USS方法使用固定的视觉基础模型提取像素级特征,并通过自我监督目标对其进行细化,这些目标鼓励语义分组。然后,这些特征被分组到语义集群中,以产生分割掩膜。将这些思想扩展到联邦环境需要跨分布式客户端进行特征表示和聚类中心对齐——在缺乏监督的情况下,在异质数据分布中这是一项内在困难的任务。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FUSS(联邦无监督图像语义分割)(Federated Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation),据我们所知,这是第一个能够实现完全去中心化、无标签语义分割训练的框架。FUSS引入了新型联邦策略,促进特征和原型空间中的全局一致性,联合优化本地分割头和共享语义中心。在基准数据集和真实数据集上的实验,包括二进制和多类分割任务,表明FUSS在各种客户端数据分布下,始终优于仅本地的客户端训练和经典FL算法的扩展。为了支持复现,论文接受后将公布完整代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本工作探讨了联邦学习在无人监督语义图像分割中的应用。文章介绍了FUSS(联邦无人监督图像语义分割)框架,该框架能在完全分散、无需标签的语义分割训练中实现特征表示和集群质心对齐。FUSS引入新型联邦策略,促进特征空间和原型空间中的全局一致性,联合优化本地分割头和共享语义质心。实验表明,在各种客户端数据分布下,FUSS在基准数据集和真实世界数据集上的二进制和多类别分割任务中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 本工作将联邦学习应用于无人监督语义图像分割领域。
- 提出了FUSS框架,实现完全分散、无需标签的语义分割训练。
- FUSS通过引入新型联邦策略,促进特征空间和原型空间中的全局一致性。
- FUSS能优化本地分割头和共享语义质心。
- 实验结果表明,在各种客户端数据分布下,FUSS在多个数据集上的表现优于本地训练以及经典联邦学习算法的扩展。
- FUSS框架有望解决在分布式环境中进行无人监督语义图像分割的难题。
点此查看论文截图

GenCAD-Self-Repairing: Feasibility Enhancement for 3D CAD Generation
Authors:Chikaha Tsuji, Enrique Flores Medina, Harshit Gupta, Md Ferdous Alam
With the advancement of generative AI, research on its application to 3D model generation has gained traction, particularly in automating the creation of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files from images. GenCAD is a notable model in this domain, leveraging an autoregressive transformer-based architecture with a contrastive learning framework to generate CAD programs. However, a major limitation of GenCAD is its inability to consistently produce feasible boundary representations (B-reps), with approximately 10% of generated designs being infeasible. To address this, we propose GenCAD-Self-Repairing, a framework that enhances the feasibility of generative CAD models through diffusion guidance and a self-repairing pipeline. This framework integrates a guided diffusion denoising process in the latent space and a regression-based correction mechanism to refine infeasible CAD command sequences while preserving geometric accuracy. Our approach successfully converted two-thirds of infeasible designs in the baseline method into feasible ones, significantly improving the feasibility rate while simultaneously maintaining a reasonable level of geometric accuracy between the point clouds of ground truth models and generated models. By significantly improving the feasibility rate of generating CAD models, our approach helps expand the availability of high-quality training data and enhances the applicability of AI-driven CAD generation in manufacturing, architecture, and product design.
随着生成式人工智能的进步,其在3D模型生成领域的应用研究逐渐受到关注,特别是在从图像自动生成计算机辅助设计(CAD)文件方面。GenCAD是这个领域的一个显著模型,它利用基于自回归变压器架构和对比学习框架来生成CAD程序。然而,GenCAD的一个主要局限性是,它无法始终产生可行的边界表示(B-reps),大约10%的生成设计不可行。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GenCAD-Self-Repairing框架,它通过扩散引导和自我修复管道增强生成CAD模型的可行性。该框架集成了潜在空间中的引导扩散去噪过程,以及基于回归的校正机制,以细化不可行的CAD命令序列,同时保留几何精度。我们的方法成功地将基线方法中三分之二的不可行设计转化为可行设计,在显著提高可行性率的同时,还保持了真实模型与生成模型点云之间的几何精度合理水平。通过显著提高生成CAD模型的可行性率,我们的方法有助于丰富高质量训练数据的可用性,并增强AI驱动的CAD生成在制造、建筑和产品设计领域的适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于生成式人工智能的进步,其在3D模型生成领域的应用逐渐受到关注,尤其在从图像自动生成计算机辅助设计(CAD)文件方面。尽管GenCAD模型在这一领域表现突出,但其无法持续产生可行的边界表示(B-reps),约有10%的设计不可行。为解决这一问题,我们提出了GenCAD-Self-Repairing框架,通过扩散引导和自我修复管道增强生成CAD模型的可行性。该框架在潜在空间中集成了引导扩散去噪过程,并通过基于回归的校正机制来优化不可行的CAD命令序列,同时保留几何精度。我们的方法成功地将基线方法中三分之二的不可行设计转化为可行设计,在显著提高可行性率的同时,保持了地面真实模型和生成模型点云之间的合理几何精度。这有助于扩大高质量训练数据的可用性,增强AI驱动的CAD生成在制造、建筑和产品设计中的适用性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式人工智能在3D模型生成领域,特别是在从图像生成CAD文件方面,已引起关注。
- GenCAD是此领域的一个显著模型,但存在约10%的设计不可行的问题。
- GenCAD-Self-Repairing框架通过扩散引导和自我修复管道提高CAD模型的可行性。
- 框架通过引导扩散去噪过程和基于回归的校正机制来优化不可行的设计。
- 该方法成功地将大多数不可行设计转化为可行设计。
- 显著提高了设计的可行性率,同时保持了较高的几何精度。
点此查看论文截图

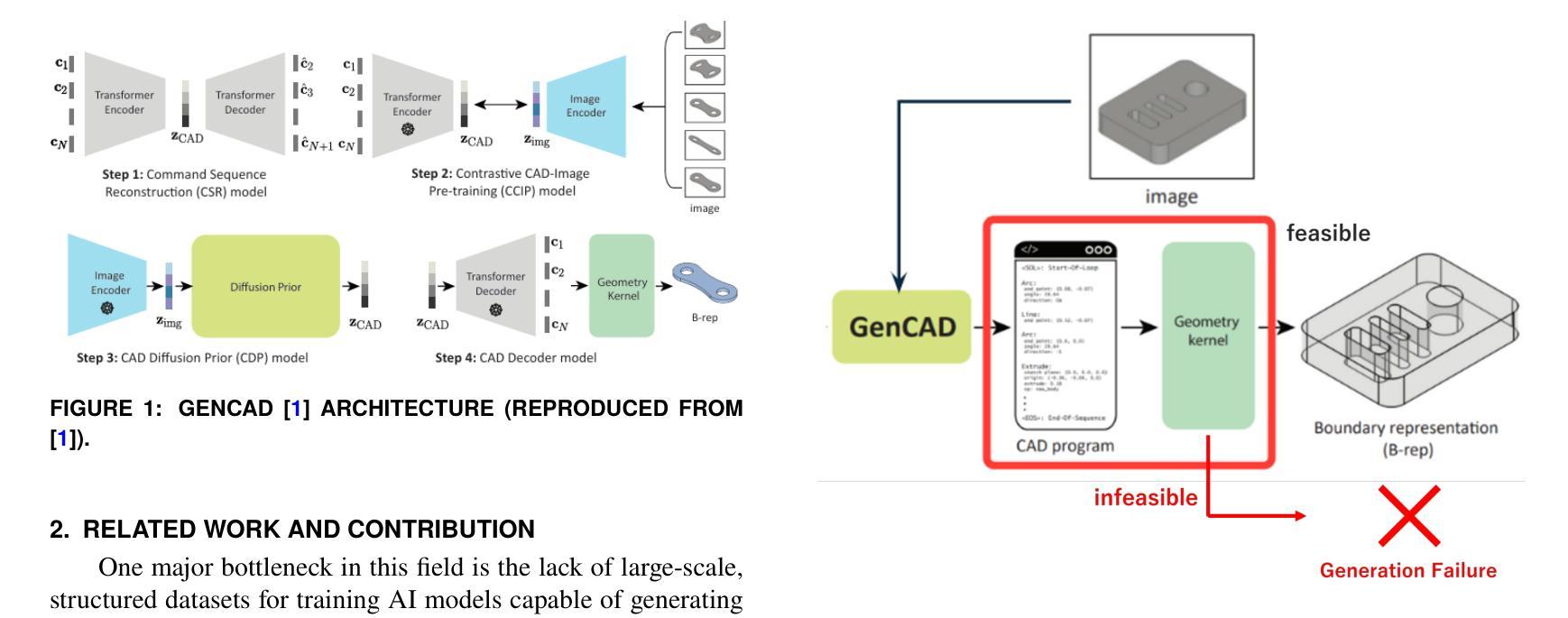
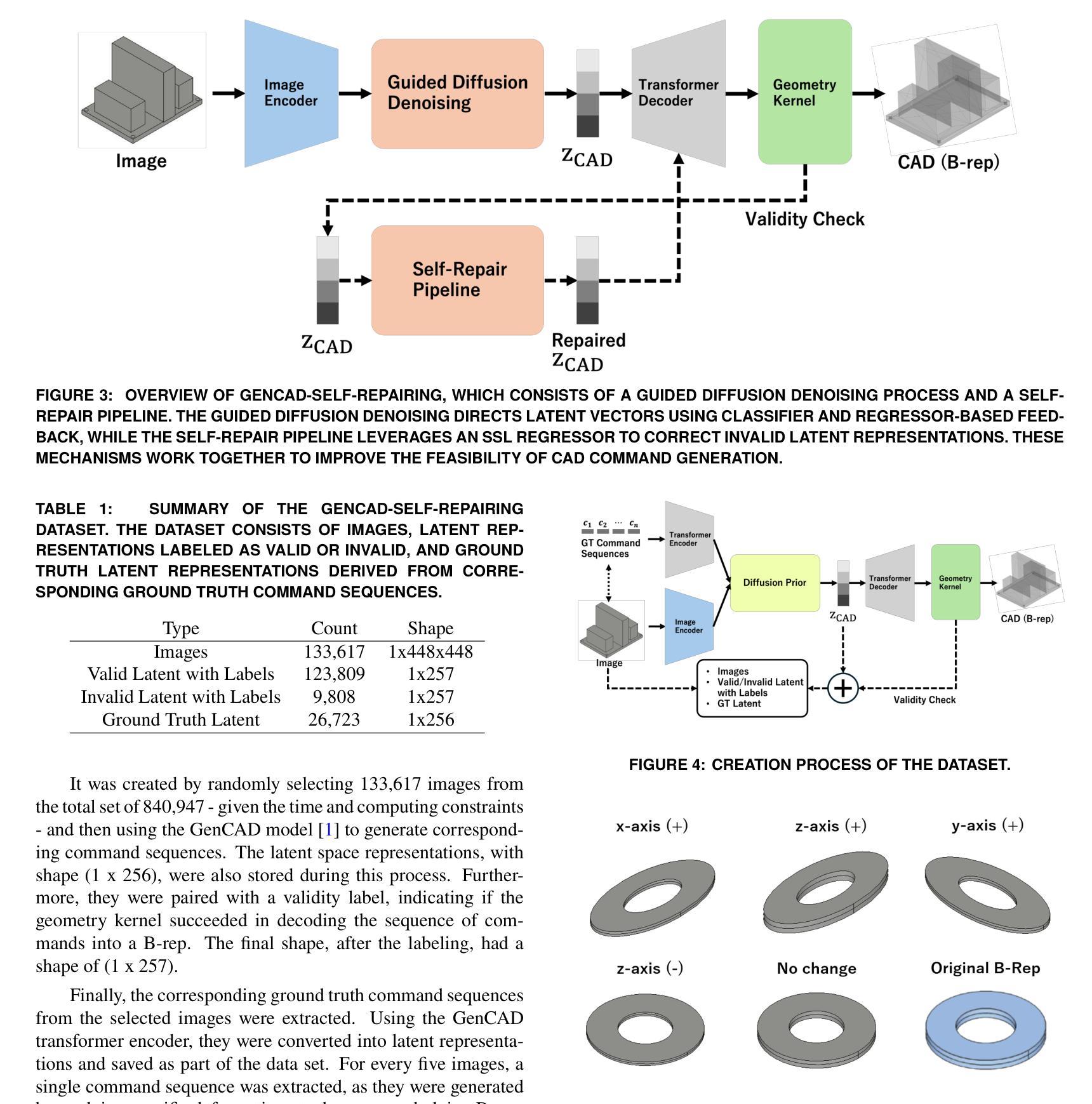
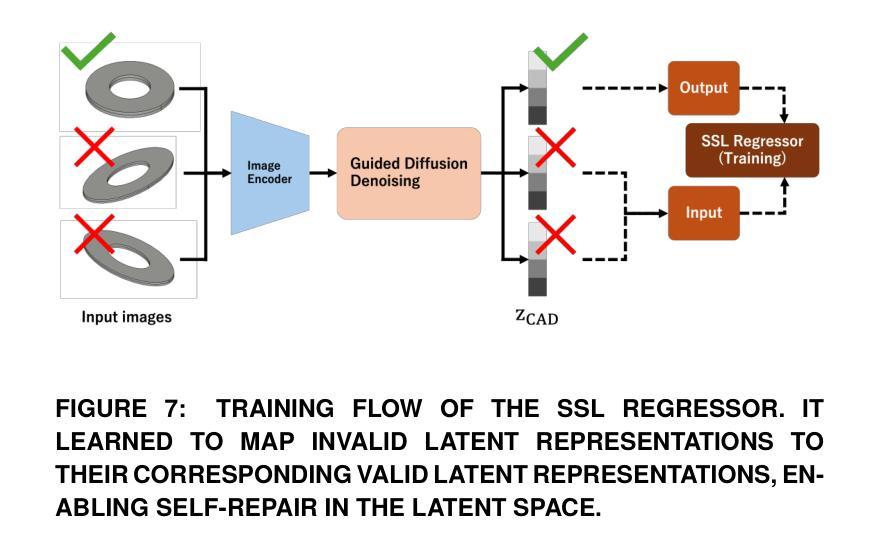
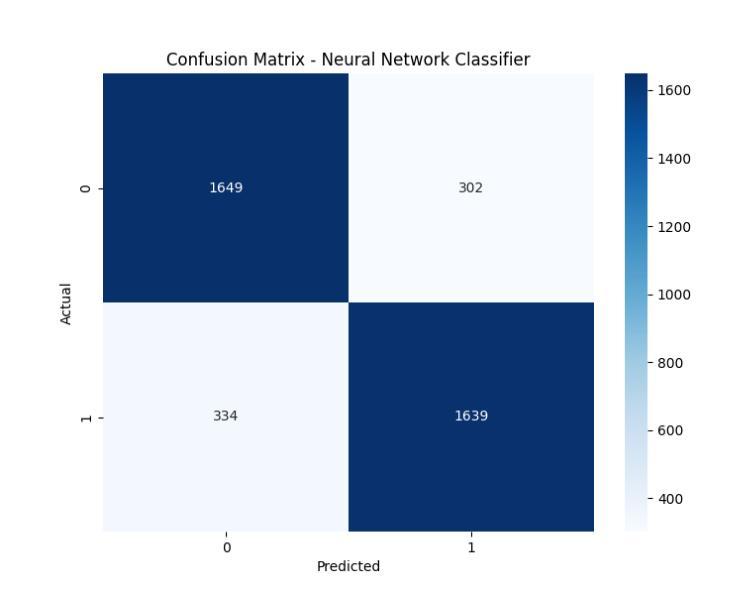
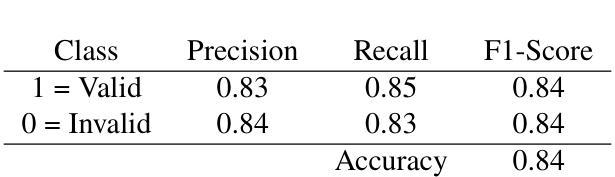
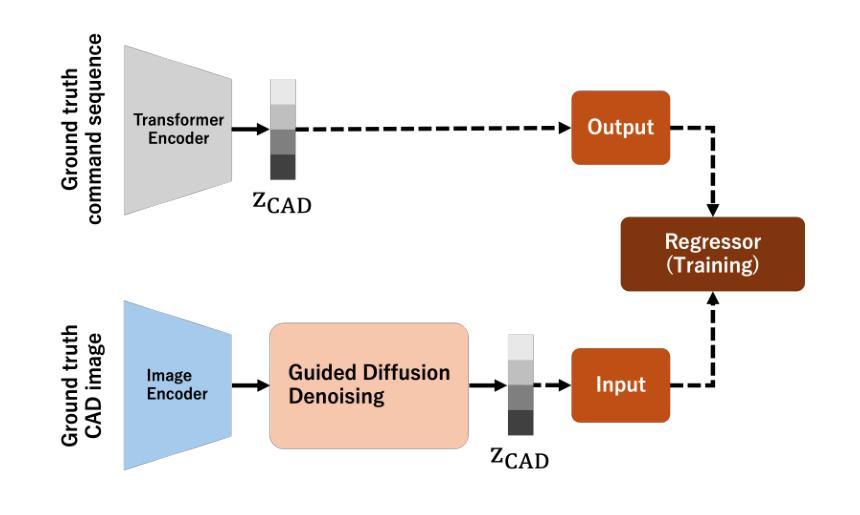
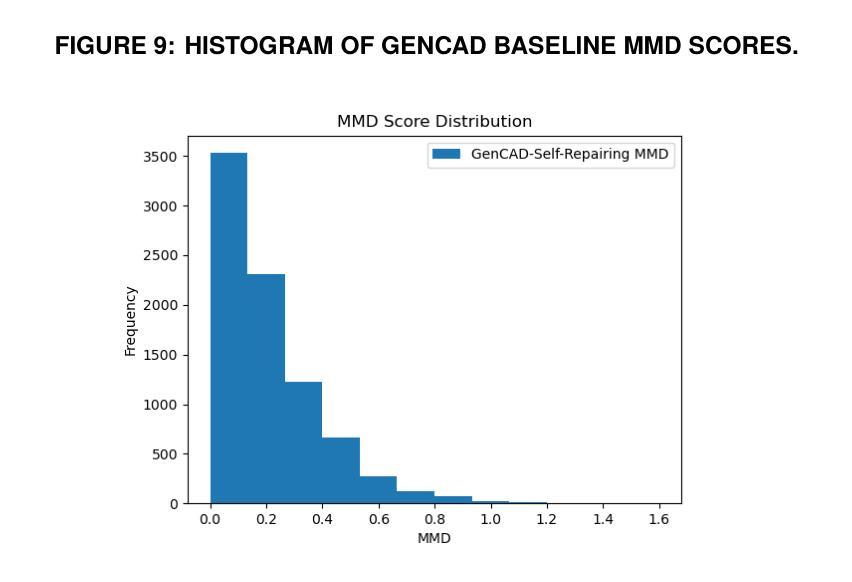
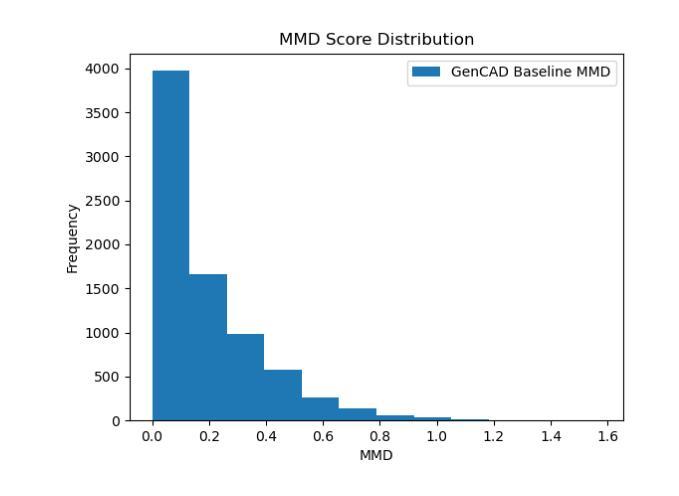
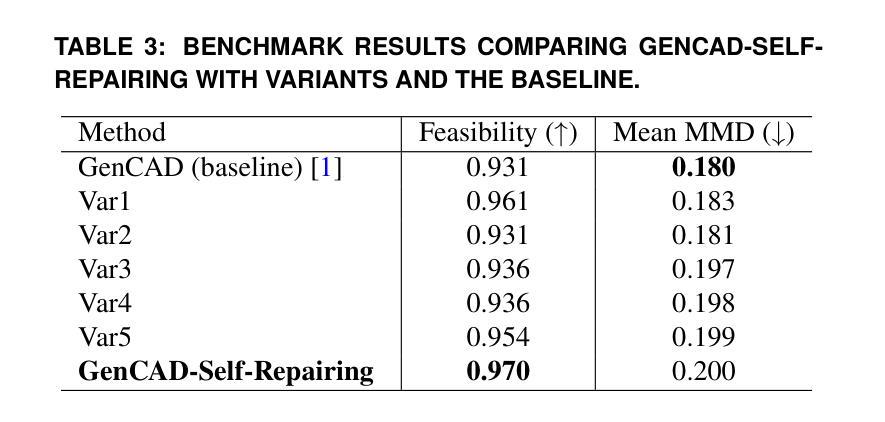
Image Aesthetic Reasoning: A New Benchmark for Medical Image Screening with MLLMs
Authors:Zheng Sun, Yi Wei, Long Yu
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are of great application across many domains, such as multimodal understanding and generation. With the development of diffusion models (DM) and unified MLLMs, the performance of image generation has been significantly improved, however, the study of image screening is rare and its performance with MLLMs is unsatisfactory due to the lack of data and the week image aesthetic reasoning ability in MLLMs. In this work, we propose a complete solution to address these problems in terms of data and methodology. For data, we collect a comprehensive medical image screening dataset with 1500+ samples, each sample consists of a medical image, four generated images, and a multiple-choice answer. The dataset evaluates the aesthetic reasoning ability under four aspects: \textit{(1) Appearance Deformation, (2) Principles of Physical Lighting and Shadow, (3) Placement Layout, (4) Extension Rationality}. For methodology, we utilize long chains of thought (CoT) and Group Relative Policy Optimization with Dynamic Proportional Accuracy reward, called DPA-GRPO, to enhance the image aesthetic reasoning ability of MLLMs. Our experimental results reveal that even state-of-the-art closed-source MLLMs, such as GPT-4o and Qwen-VL-Max, exhibit performance akin to random guessing in image aesthetic reasoning. In contrast, by leveraging the reinforcement learning approach, we are able to surpass the score of both large-scale models and leading closed-source models using a much smaller model. We hope our attempt on medical image screening will serve as a regular configuration in image aesthetic reasoning in the future.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在多个领域都有很好的应用,如多模态理解和生成。随着扩散模型(DM)和统一MLLMs的发展,图像生成性能得到了显著提高。然而,关于图像筛选的研究很少见,并且由于数据缺乏和MLLMs中图像美学推理能力较弱,其性能并不令人满意。在这项工作中,我们针对数据和方法的这些问题提出了一个完整的解决方案。在数据方面,我们收集了一个全面的医学图像筛选数据集,包含超过1500个样本,每个样本包括一张医学图像、四张生成的图像和一个多项选择题。该数据集从以下四个方面评估美学推理能力:(1)外观变形、(2)物理照明和阴影原理、(3)布局放置、(4)扩展合理性。在方法上,我们利用长链思维(CoT)和动态比例精度奖励下的组相对策略优化(DPA-GRPO),提高MLLMs的图像美学推理能力。我们的实验结果表明,即使是最先进的闭源MLLMs,如GPT-4o和Qwen-VL-Max,在图像美学推理方面的表现也如同随机猜测。相比之下,通过利用强化学习方法,我们能够使用较小的模型在得分上超越大规模模型和领先的闭源模型。我们希望我们的医学图像筛选尝试能为未来的图像美学推理提供常规配置。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在图像生成方面的显著改进,特别是在扩散模型(DM)和统一MLLMs的发展推动下。然而,关于图像筛选的研究较少,且MLLMs的性能并不令人满意。针对这些问题,本文提出了完整的数据和方法解决方案。在数据方面,我们收集了一个包含1500多个样本的综合医学图像筛选数据集,每个样本包括医学图像、四个生成的图像和多个选择题。在方法论方面,我们利用长链思维(CoT)和动态比例精度奖励的集团相对策略优化(DPA-GRPO),以增强MLLMs的图像美学推理能力。实验结果表明,通过强化学习方法,使用较小的模型可以超越大规模模型和领先闭源模型的得分。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在多领域有广泛应用,特别是在图像生成方面,DM和统一MLLMs的发展提高了性能。
- 当前研究中图像筛选的研究较少,MLLMs在该领域的性能有待提高。
- 缺乏数据和MLLMs的图像美学推理能力较弱是影响性能的主要原因。
- 本文提出了一个包含医学图像、生成图像和选择题的综合医学图像筛选数据集。
- 通过长链思维(CoT)和DPA-GRPO方法增强MLLMs的图像美学推理能力。
- 实验结果显示强化学习方法可以提高模型在图像美学推理方面的性能,超越大规模和闭源模型。
点此查看论文截图

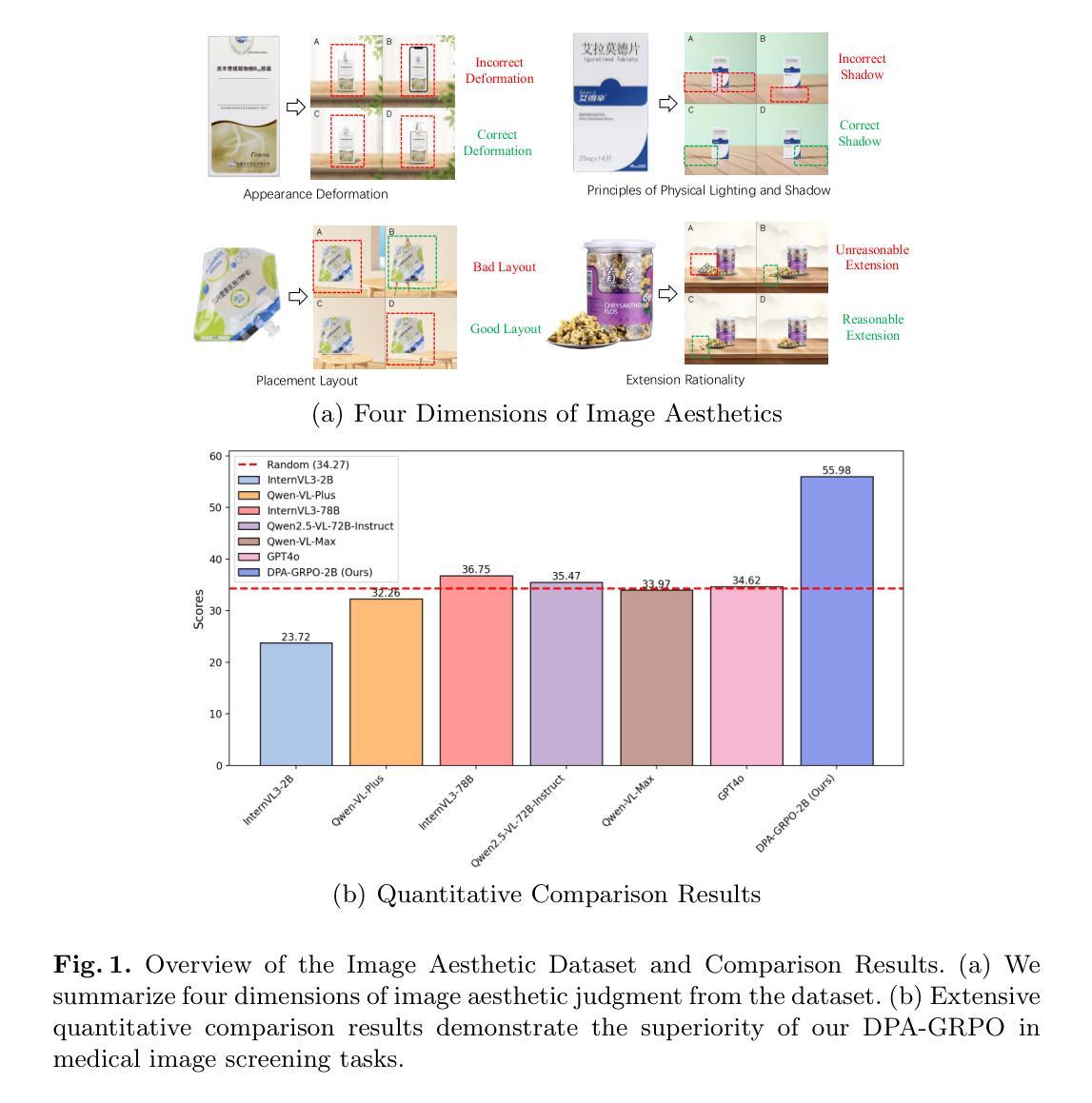
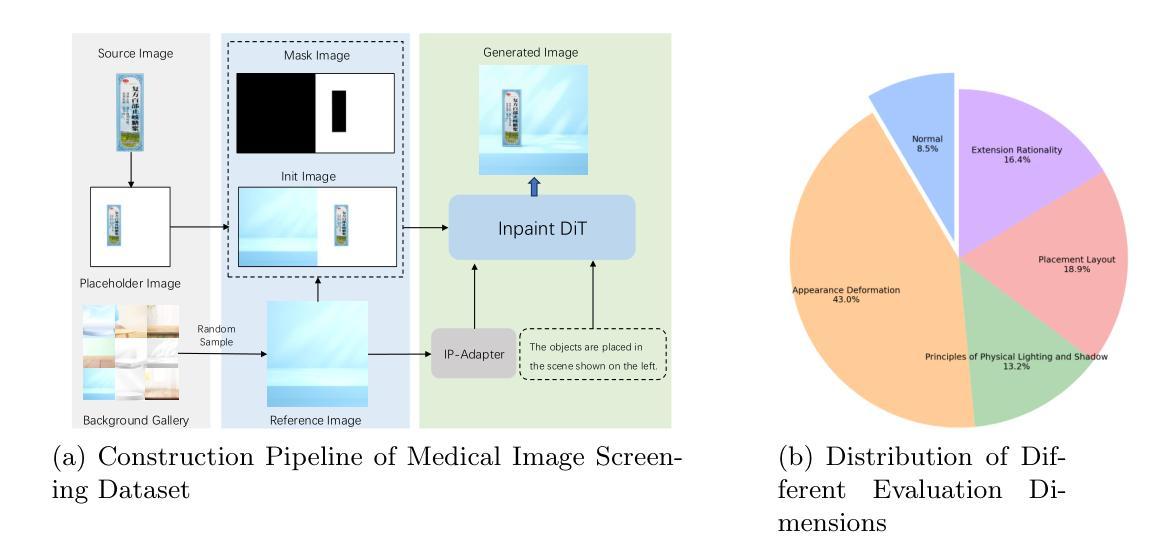
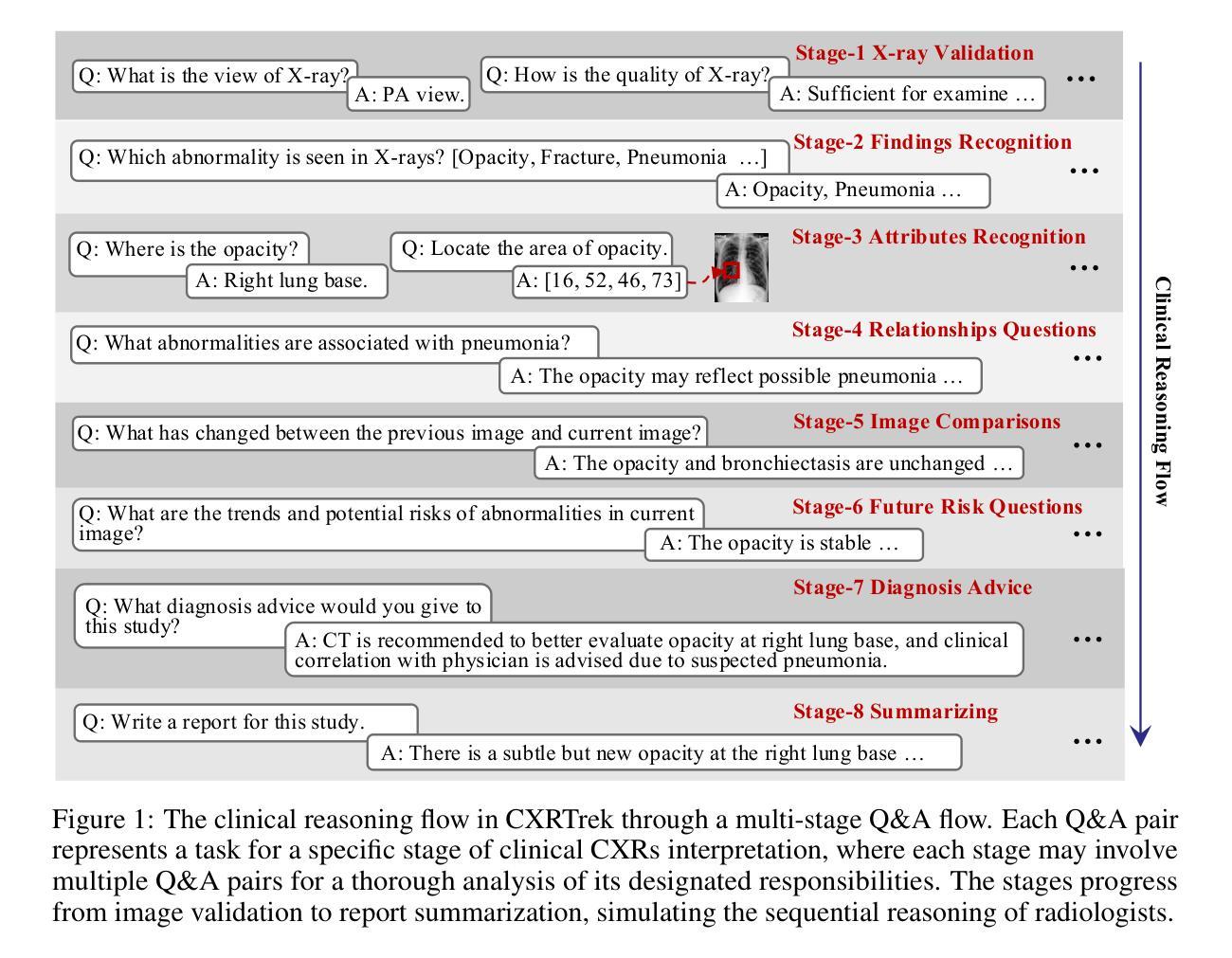
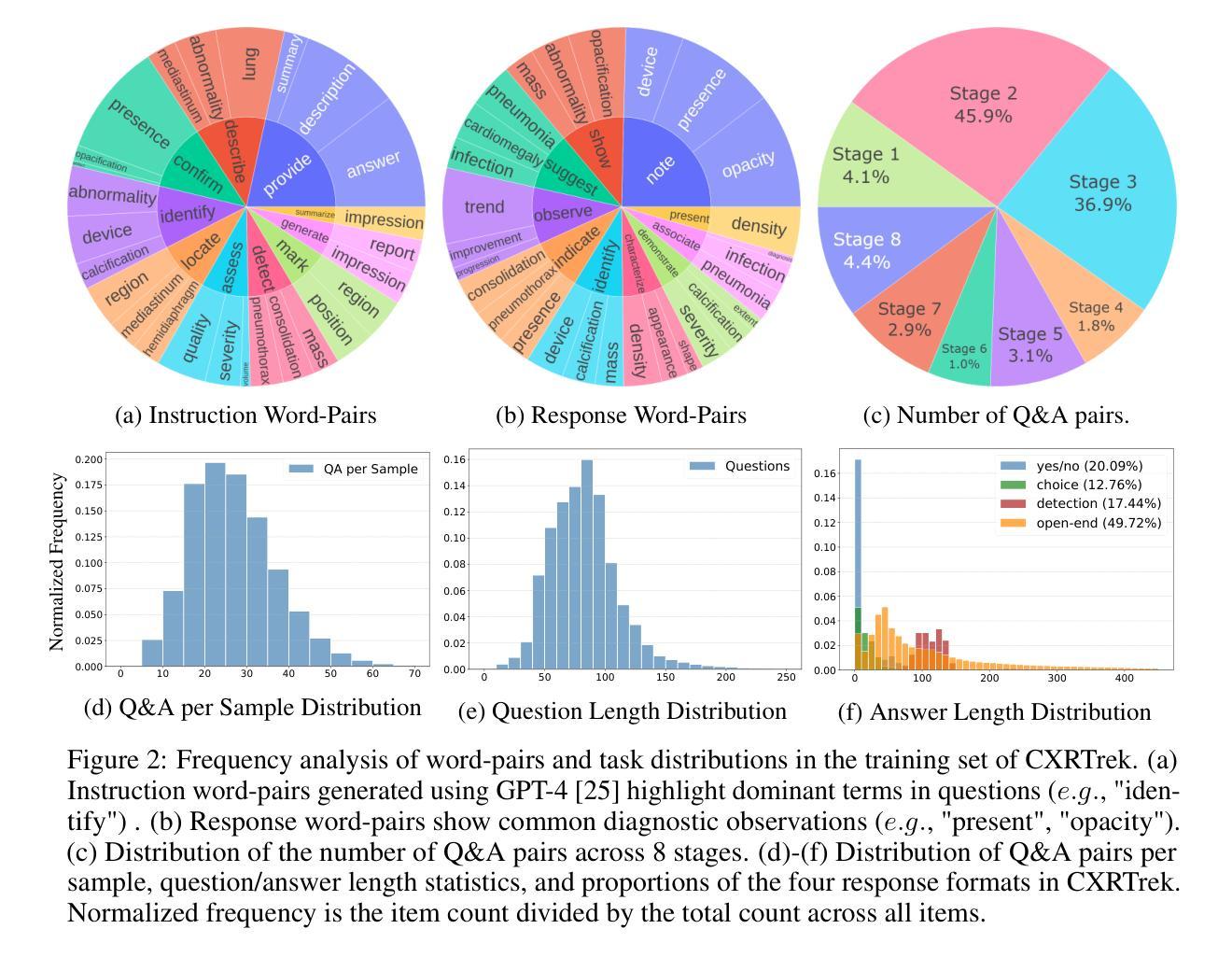
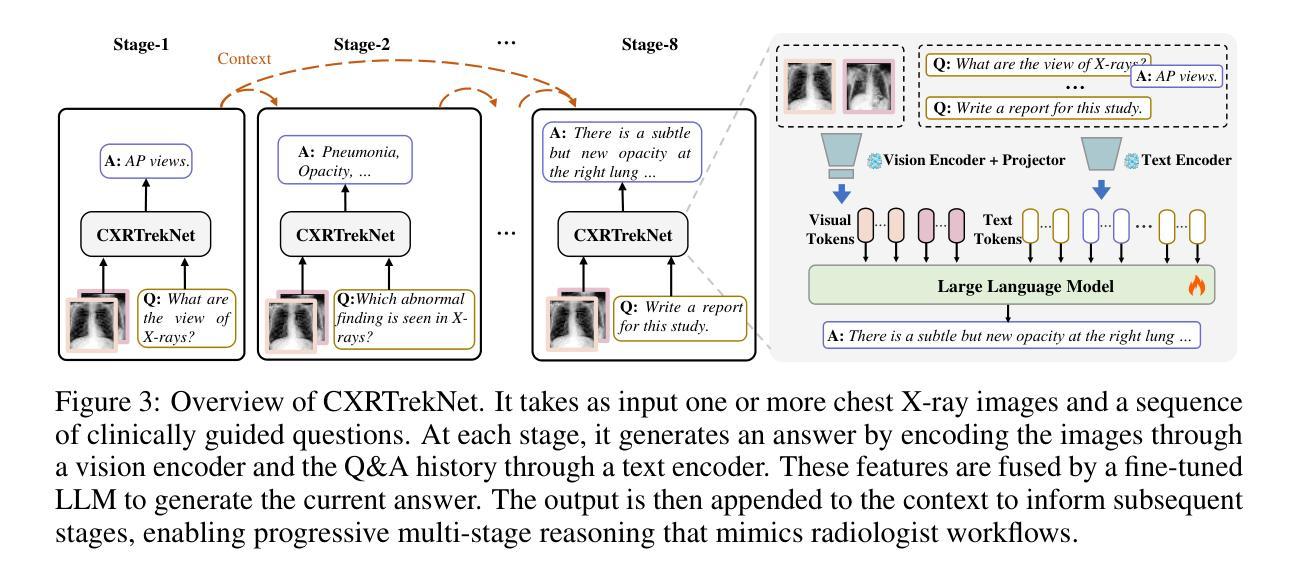
Interpreting Chest X-rays Like a Radiologist: A Benchmark with Clinical Reasoning
Authors:Jinquan Guan, Qi Chen, Lizhou Liang, Yuhang Liu, Vu Minh Hieu Phan, Minh-Son To, Jian Chen, Yutong Xie
Artificial intelligence (AI)-based chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation assistants have demonstrated significant progress and are increasingly being applied in clinical settings. However, contemporary medical AI models often adhere to a simplistic input-to-output paradigm, directly processing an image and an instruction to generate a result, where the instructions may be integral to the model’s architecture. This approach overlooks the modeling of the inherent diagnostic reasoning in chest X-ray interpretation. Such reasoning is typically sequential, where each interpretive stage considers the images, the current task, and the contextual information from previous stages. This oversight leads to several shortcomings, including misalignment with clinical scenarios, contextless reasoning, and untraceable errors. To fill this gap, we construct CXRTrek, a new multi-stage visual question answering (VQA) dataset for CXR interpretation. The dataset is designed to explicitly simulate the diagnostic reasoning process employed by radiologists in real-world clinical settings for the first time. CXRTrek covers 8 sequential diagnostic stages, comprising 428,966 samples and over 11 million question-answer (Q&A) pairs, with an average of 26.29 Q&A pairs per sample. Building on the CXRTrek dataset, we propose a new vision-language large model (VLLM), CXRTrekNet, specifically designed to incorporate the clinical reasoning flow into the VLLM framework. CXRTrekNet effectively models the dependencies between diagnostic stages and captures reasoning patterns within the radiological context. Trained on our dataset, the model consistently outperforms existing medical VLLMs on the CXRTrek benchmarks and demonstrates superior generalization across multiple tasks on five diverse external datasets. The dataset and model can be found in our repository (https://github.com/guanjinquan/CXRTrek).
基于人工智能(AI)的胸部X射线(CXR)解读助手已经取得了显著进展,并越来越多地应用于临床环境。然而,当代的医疗人工智能模型通常遵循一个简化的输入到输出的模式,直接处理图像和指令以生成结果,其中指令可能是模型架构的组成部分。这种方法忽略了胸部X射线解读中内在诊断推理的建模。这种推理通常是序贯的,每个解读阶段都会考虑图像、当前任务和来自先前阶段的上下文信息。这种疏忽导致了几个缺点,包括与临床场景的不匹配、缺乏上下文推理和不可追踪的错误。为了填补这一空白,我们构建了CXRTrek,这是一个新的多阶段视觉问答(VQA)数据集,用于CXR解读。该数据集首次明确模拟了放射科医生在现实世界临床环境中的诊断推理过程。CXRTrek涵盖8个连续的诊断阶段,包含428966个样本和超过1100万个问答对,每个样本平均有26.29个问答对。基于CXRTrek数据集,我们提出了一种新的视觉语言大型模型(VLLM),即CXRTrekNet,专门设计以将临床推理流程纳入VLLM框架。CXRTrekNet有效地建模了诊断阶段之间的依赖关系,并捕获了放射学上下文中的推理模式。在我们的数据集上训练的模型在CXRTrek基准测试上始终优于现有的医疗VLLM,并在五个不同的外部数据集上实现了多项任务的卓越泛化能力。数据集和模型可在我们的存储库中找到(https://github.com/guanjinquan/CXRTrek)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages (main text), 18 pages (appendix)
Summary
基于人工智能的胸部X射线(CXR)解读助手在临床应用中取得了显著进展。然而,当代医疗AI模型通常遵循简单的输入-输出模式,忽略了胸部X光解读中的内在诊断推理过程。为弥补这一不足,我们构建了CXRTrek多阶段视觉问答(VQA)数据集,模拟放射科医生在真实临床环境中的诊断推理过程。CXRTrek涵盖8个连续诊断阶段,包含428966个样本和超过1100万问题答案对。基于CXRTrek数据集,我们提出了全新的视觉语言大型模型(VLLM)——CXRTrekNet,有效融入临床推理流程至VLLM框架中。该模型在CXRTrek基准测试上表现优异,且在五个外部数据集上展现出卓越的多任务泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能在胸部X射线解读中应用广泛,但现有模型忽略诊断推理过程。
- CXRTrek数据集模拟真实临床环境中放射科医生的诊断推理过程。
- CXRTrek数据集包含8个连续诊断阶段,覆盖大量样本和问题答案对。
- CXRTrekNet是全新的视觉语言大型模型,融入临床推理流程。
- CXRTrekNet在CXRTrek基准测试及外部数据集上表现优异。
- 该模型有助于改进AI在医疗影像解读中的性能,使其更贴近实际临床需求。
- 数据集和模型已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

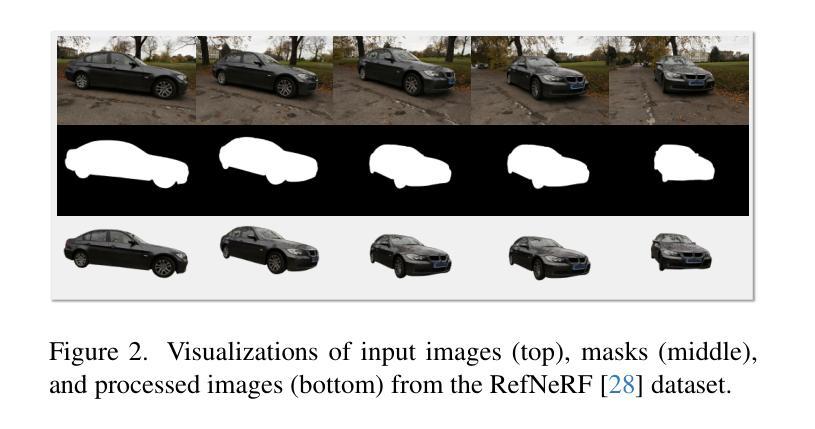
Zero-P-to-3: Zero-Shot Partial-View Images to 3D Object
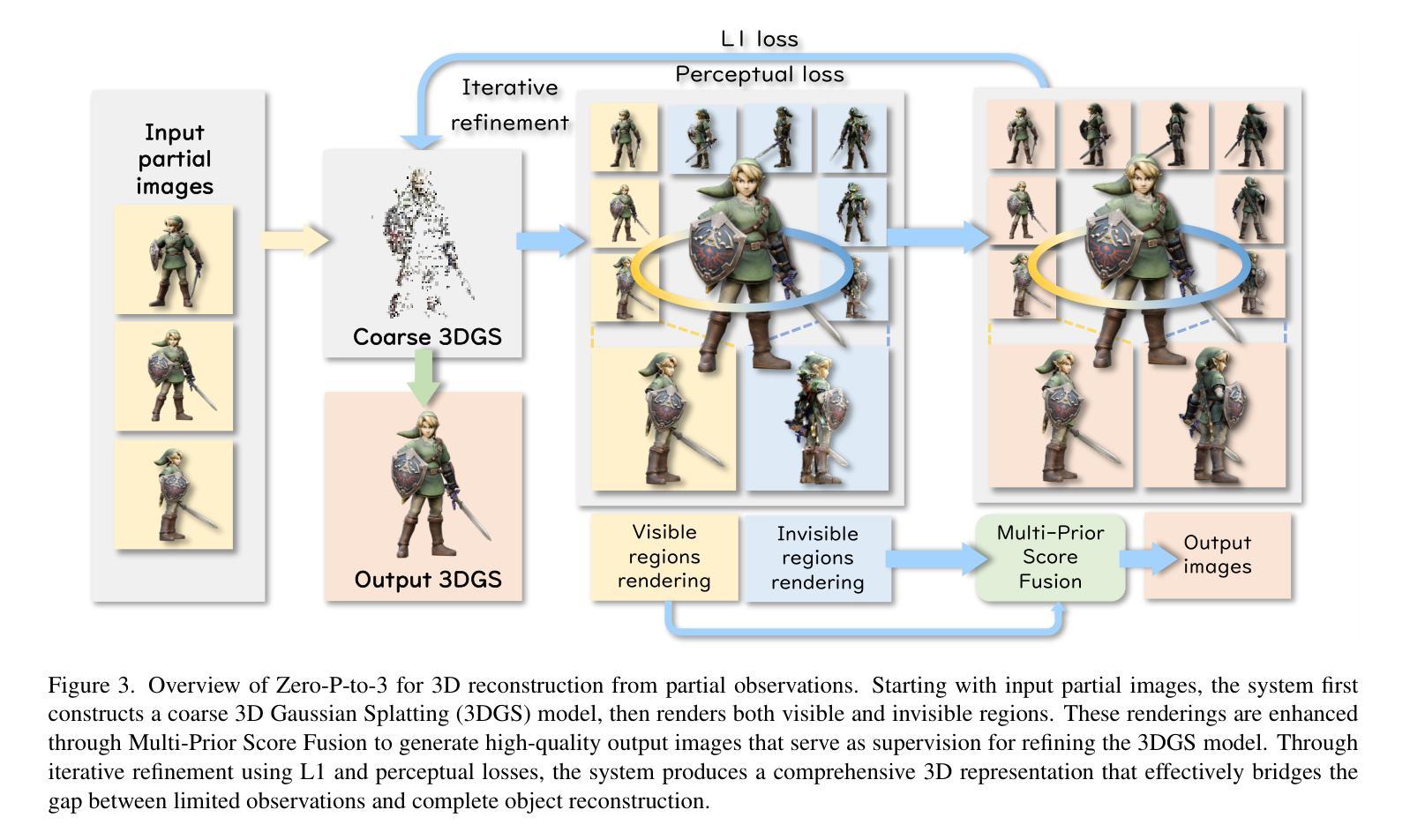
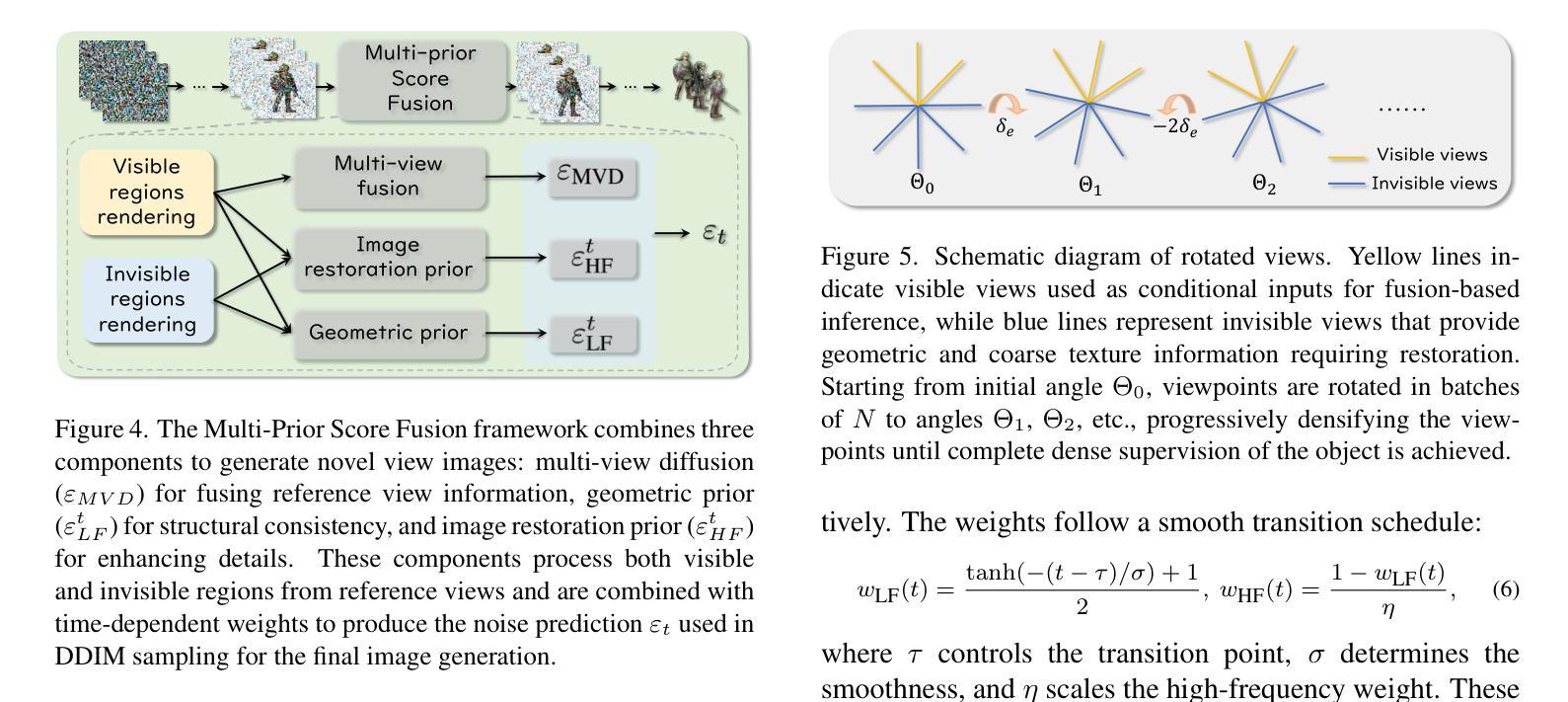
Authors:Yuxuan Lin, Ruihang Chu, Zhenyu Chen, Xiao Tang, Lei Ke, Haoling Li, Yingji Zhong, Zhihao Li, Shiyong Liu, Xiaofei Wu, Jianzhuang Liu, Yujiu Yang
Generative 3D reconstruction shows strong potential in incomplete observations. While sparse-view and single-image reconstruction are well-researched, partial observation remains underexplored. In this context, dense views are accessible only from a specific angular range, with other perspectives remaining inaccessible. This task presents two main challenges: (i) limited View Range: observations confined to a narrow angular scope prevent effective traditional interpolation techniques that require evenly distributed perspectives. (ii) inconsistent Generation: views created for invisible regions often lack coherence with both visible regions and each other, compromising reconstruction consistency. To address these challenges, we propose \method, a novel training-free approach that integrates the local dense observations and multi-source priors for reconstruction. Our method introduces a fusion-based strategy to effectively align these priors in DDIM sampling, thereby generating multi-view consistent images to supervise invisible views. We further design an iterative refinement strategy, which uses the geometric structures of the object to enhance reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets show the superiority of our method over SOTAs, especially in invisible regions.
生成式三维重建在不完全观察中显示出强大的潜力。虽然稀疏视角和单图像重建已经得到了充分的研究,但部分观察仍然被探索不足。在这种情况下,只有从特定的角度范围才能获取密集视图,而其他角度则无法获取。此任务面临两个主要挑战:(i)有限的视角范围:观察仅限于狭窄的角度范围,无法进行有效利用的传统插值技术需要均匀分布的角度。(ii)不一致的生成:为不可见区域创建的视图通常与可见区域和其他视图缺乏连贯性,从而损害重建的一致性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了\method,这是一种新型的无训练方法,它整合了局部密集观察和多种源先验进行重建。我们的方法引入了一种基于融合的策略,有效地对齐这些先验在DDIM采样中,从而生成多视角一致的图像来监督不可见视图。我们还设计了一种迭代细化策略,利用对象的几何结构来提高重建质量。在多个数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于最新技术,特别是在不可见区域。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
生成式三维重建在不全观测下展现巨大潜力。尽管稀疏视角和单图像重建已得到深入研究,但部分观测仍被较少探索。密集视角仅从特定角度范围可获取,其他角度则无法获取。此任务面临两大挑战:一是视角范围有限,观测仅限于狭窄角度,无法有效应用需均匀分布视角的传统插值技术;二是不一致的生成,为不可见区域创建的视角往往与可见区域及其他视角缺乏连贯性,影响重建的一致性。为应对这些挑战,我们提出一种新型无训练方法,集成局部密集观测和多源先验信息进行重建。\method通过融合策略有效对齐这些先验信息,在DDIM采样中生成多视角一致图像以监督不可见视角。我们还设计了一种迭代优化策略,利用物体几何结构提高重建质量。在多个数据集上的实验显示,我们的方法优于现有技术,尤其在不可见区域。
要点
- 生成式三维重建在处理不完全观测数据时表现出巨大潜力。
- 当前面临的主要挑战包括视角范围有限和生成的图像连贯性不足。
- 提出一种新型无训练方法,集成局部密集观测和多源先验信息,以改善重建质量。
- 通过融合策略有效对齐先验信息,生成多视角一致图像。
- 设计迭代优化策略,利用物体几何结构提高重建质量。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法在不可见区域的重建效果尤佳。
- 该方法为未来处理更为复杂的三维重建任务提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图


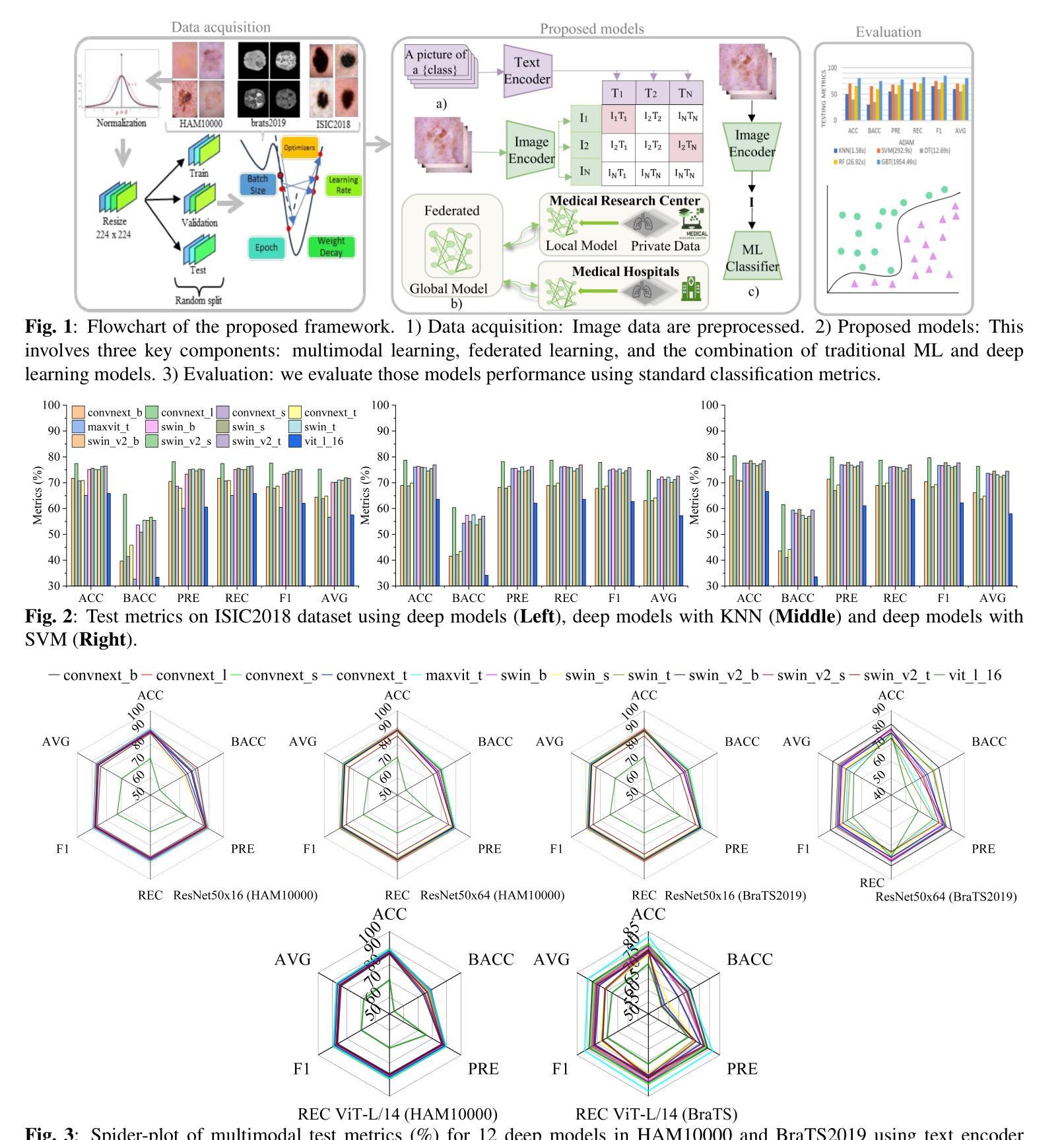
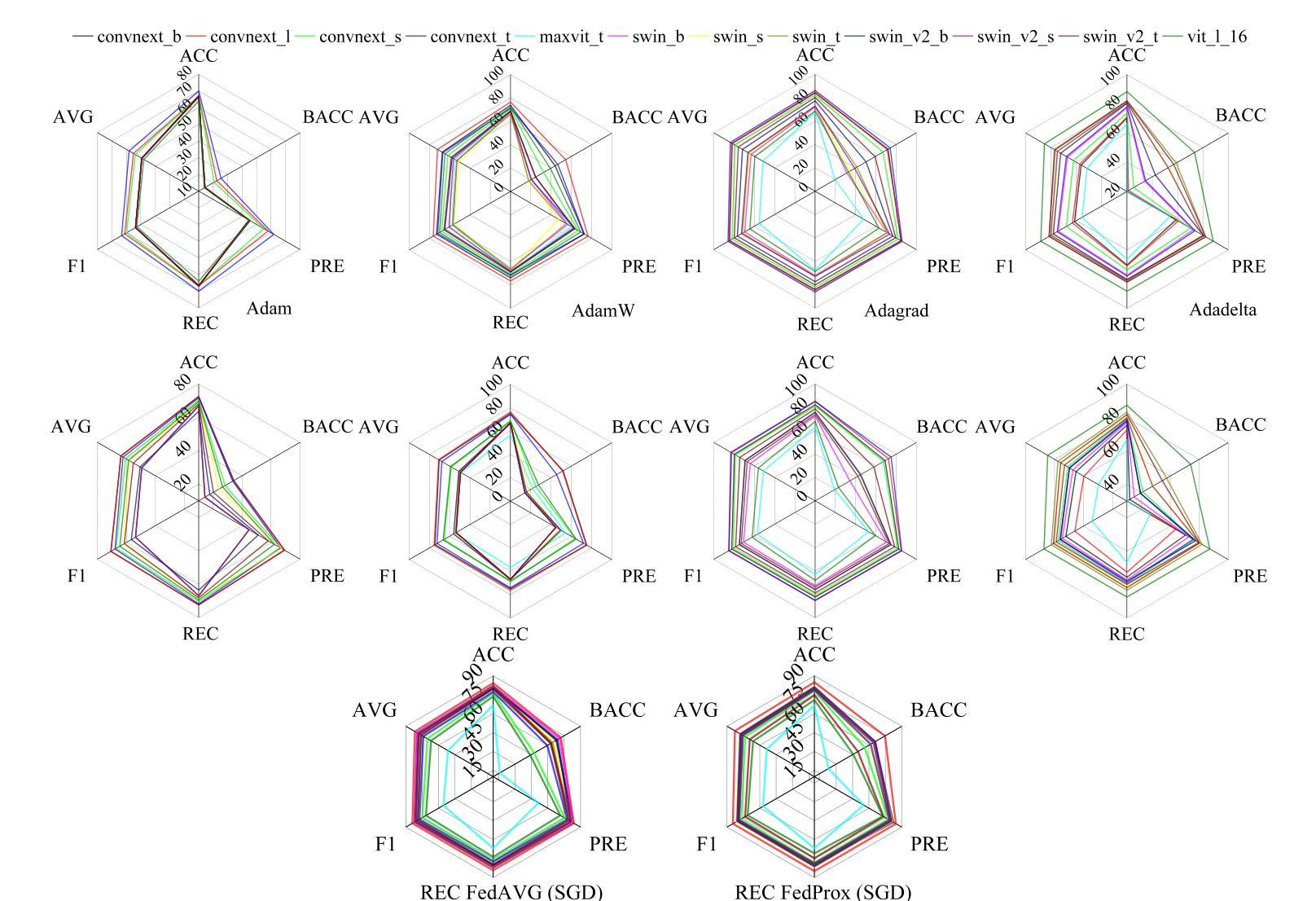
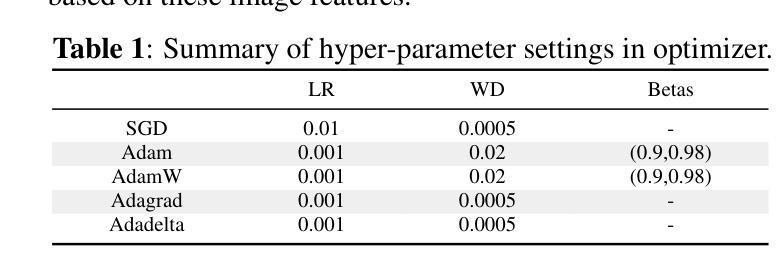
Deep Modeling and Optimization of Medical Image Classification
Authors:Yihang Wu, Muhammad Owais, Reem Kateb, Ahmad Chaddad
Deep models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformer (ViT), demonstrate remarkable performance in image classification. However, those deep models require large data to fine-tune, which is impractical in the medical domain due to the data privacy issue. Furthermore, despite the feasible performance of contrastive language image pre-training (CLIP) in the natural domain, the potential of CLIP has not been fully investigated in the medical field. To face these challenges, we considered three scenarios: 1) we introduce a novel CLIP variant using four CNNs and eight ViTs as image encoders for the classification of brain cancer and skin cancer, 2) we combine 12 deep models with two federated learning techniques to protect data privacy, and 3) we involve traditional machine learning (ML) methods to improve the generalization ability of those deep models in unseen domain data. The experimental results indicate that maxvit shows the highest averaged (AVG) test metrics (AVG = 87.03%) in HAM10000 dataset with multimodal learning, while convnext_l demonstrates remarkable test with an F1-score of 83.98% compared to swin_b with 81.33% in FL model. Furthermore, the use of support vector machine (SVM) can improve the overall test metrics with AVG of $\sim 2%$ for swin transformer series in ISIC2018. Our codes are available at https://github.com/AIPMLab/SkinCancerSimulation.
深度模型,如卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT),在图像分类方面表现出卓越的性能。然而,这些深度模型需要大量数据进行微调,这在医学领域由于数据隐私问题而不切实际。此外,尽管对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在自然领域表现出良好的性能,但其在医学领域的潜力尚未得到充分研究。为了应对这些挑战,我们考虑了以下三种情景:1)我们引入了一种新型的CLIP变体,使用四种CNN和八种ViT作为图像编码器,用于脑癌和皮肤癌的分类;2)我们将12个深度模型与两种联邦学习技术相结合,以保护数据隐私;3)我们引入传统机器学习(ML)方法来提高这些深度模型在未见领域数据中的泛化能力。实验结果表明,在具有多模式学习的HAM10000数据集中,MaxVit的平均测试指标(AVG)最高(AVG=87.03%),而ConvNext_l在联邦学习模型中相较于Swin_b取得了令人瞩目的成绩,其F1分数为83.98%。此外,支持向量机(SVM)的使用可以改进ISIC2018中Swin Transformer系列的总体测试指标,平均提高了约2%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/AIPMLab/SkinCancerSimulation上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ISBI2025
Summary
本文探讨了在医学图像分类领域,深度模型如卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViT)的应用与挑战。为应对数据隐私和未见域数据的问题,文章提出了使用新型CLIP变体、结合多种深度模型与联邦学习技术、以及引入传统机器学习方法来改善模型性能。实验结果表明,在某些场景下,新型模型表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 深度模型如CNN和ViT在医学图像分类中具有卓越性能,但需要大量数据进行微调。
- 医学领域的数据隐私问题是实现深度模型微调的不切实际之处。
- CLIP在自然领域表现良好,但在医学领域的应用潜力尚未充分研究。
- 新型CLIP变体使用CNN和ViT作为图像编码器,用于脑癌和皮肤癌分类。
- 结合多种深度模型与联邦学习技术以保护数据隐私。
- 引入传统机器学习方法,提高模型在未见域数据中的泛化能力。
- 实验结果显示,在某些模型和数据集下,新型方法表现优异,如maxvit在HAM10000数据集上的平均测试指标达到87.03%,convnext_l在FL模型中的F1分数达到83.98%。
点此查看论文截图

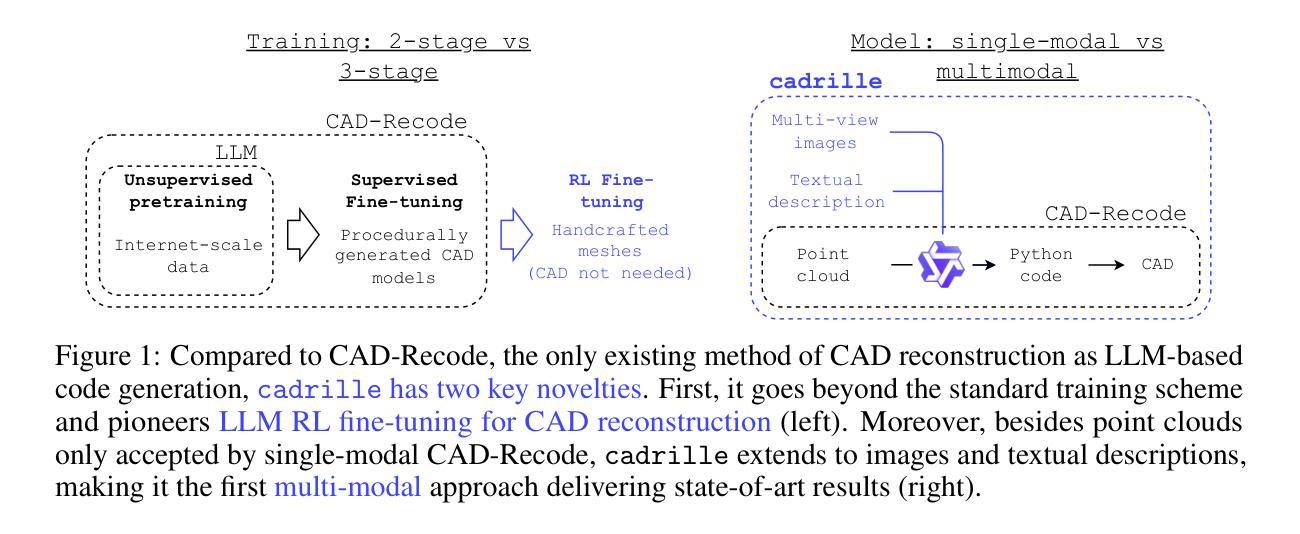
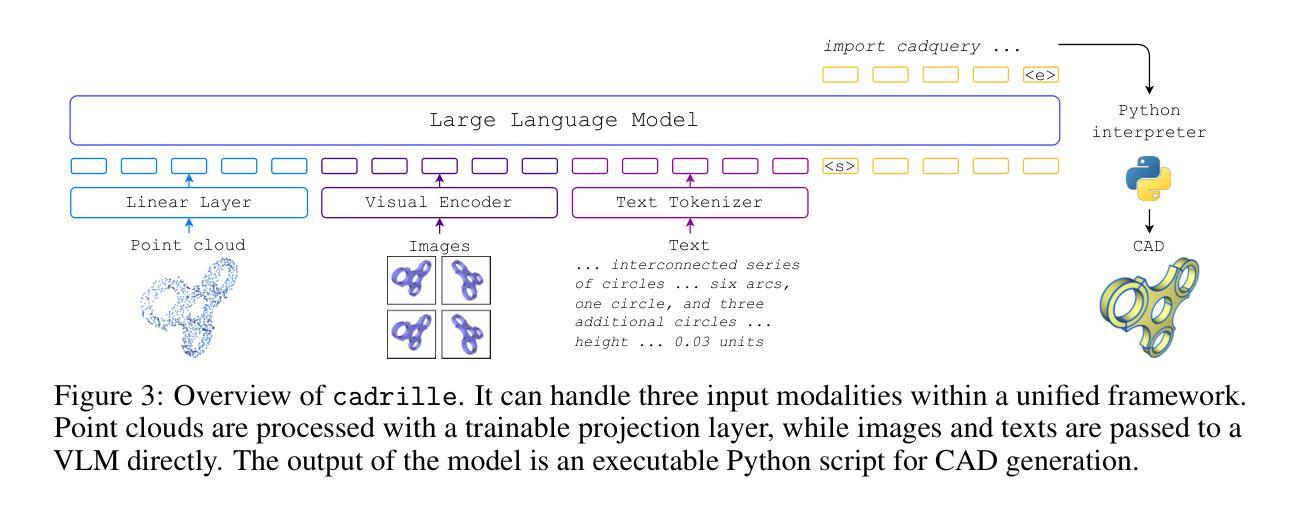
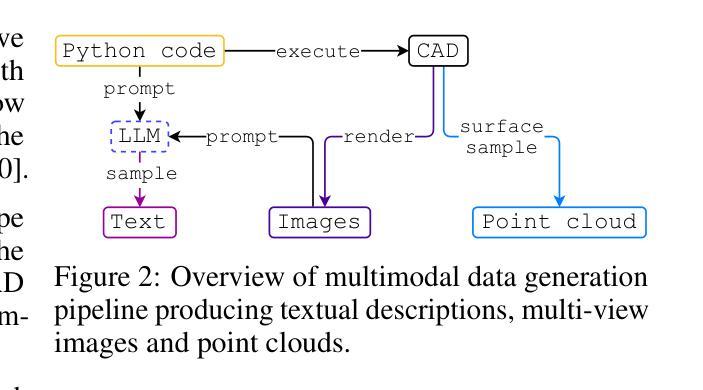
cadrille: Multi-modal CAD Reconstruction with Online Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Maksim Kolodiazhnyi, Denis Tarasov, Dmitrii Zhemchuzhnikov, Alexander Nikulin, Ilya Zisman, Anna Vorontsova, Anton Konushin, Vladislav Kurenkov, Danila Rukhovich
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a central role in engineering and manufacturing, making it possible to create precise and editable 3D models. Using a variety of sensor or user-provided data as inputs for CAD reconstruction can democratize access to design applications. However, existing methods typically focus on a single input modality, such as point clouds, images, or text, which limits their generalizability and robustness. Leveraging recent advances in vision-language models (VLM), we propose a multi-modal CAD reconstruction model that simultaneously processes all three input modalities. Inspired by large language model (LLM) training paradigms, we adopt a two-stage pipeline: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on large-scale procedurally generated data, followed by reinforcement learning (RL) fine-tuning using online feedback, obtained programatically. Furthermore, we are the first to explore RL fine-tuning of LLMs for CAD tasks demonstrating that online RL algorithms such as Group Relative Preference Optimization (GRPO) outperform offline alternatives. In the DeepCAD benchmark, our SFT model outperforms existing single-modal approaches in all three input modalities simultaneously. More importantly, after RL fine-tuning, cadrille sets new state-of-the-art on three challenging datasets, including a real-world one.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中扮演着核心角色,能够创建精确且可编辑的3D模型。使用各种传感器或用户提供的数据作为CAD重建的输入,可以使设计应用程序的访问更加民主化。然而,现有方法通常专注于单一的输入模式,如点云、图像或文本,这限制了其通用性和稳健性。我们利用最近的视觉语言模型(VLM)进展,提出了一种多模态CAD重建模型,该模型可以同时处理三种输入模式。受到大型语言模型(LLM)训练范式的启发,我们采用了两阶段流程:首先在大量程序生成的数据上进行有监督微调(SFT),然后采用在线反馈进行强化学习(RL)微调,这些反馈是程序获取的。此外,我们是第一个探索CAD任务的LLM的RL微调,证明在线RL算法(如集团相对偏好优化(GRPO))胜过离线替代方案。在DeepCAD基准测试中,我们的SFT模型在三种输入模式上同时超越了现有的单模态方法。更重要的是,经过RL微调后,cadrille在三个具有挑战性的数据集上创下了最新世界纪录,包括一个真实世界的数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中的核心作用,研究提出一种多模态CAD重建模型,能够同时处理点云、图像和文本三种输入模态。采用监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)的两阶段管道,通过程序生成大数据集,并使用集团相对偏好优化(GRPO)等在线RL算法进行微调。该模型在DeepCAD基准测试中表现出卓越性能,并在三个具有挑战性的数据集上达到最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中扮演核心角色,能够创建精确且可编辑的3D模型。
- 现有CAD重建方法主要关注单一输入模态,限制了其通用性和稳健性。
- 研究提出了一种多模态CAD重建模型,能同时处理点云、图像和文本三种输入模态。
- 采用监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)的两阶段训练管道,其中SFT在大型程序生成数据集上进行,随后通过在线反馈进行RL微调。
- 研究首次探索了使用强化学习(RL)对CAD任务的LLM进行微调。
- 在线RL算法如集团相对偏好优化(GRPO)在CAD任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

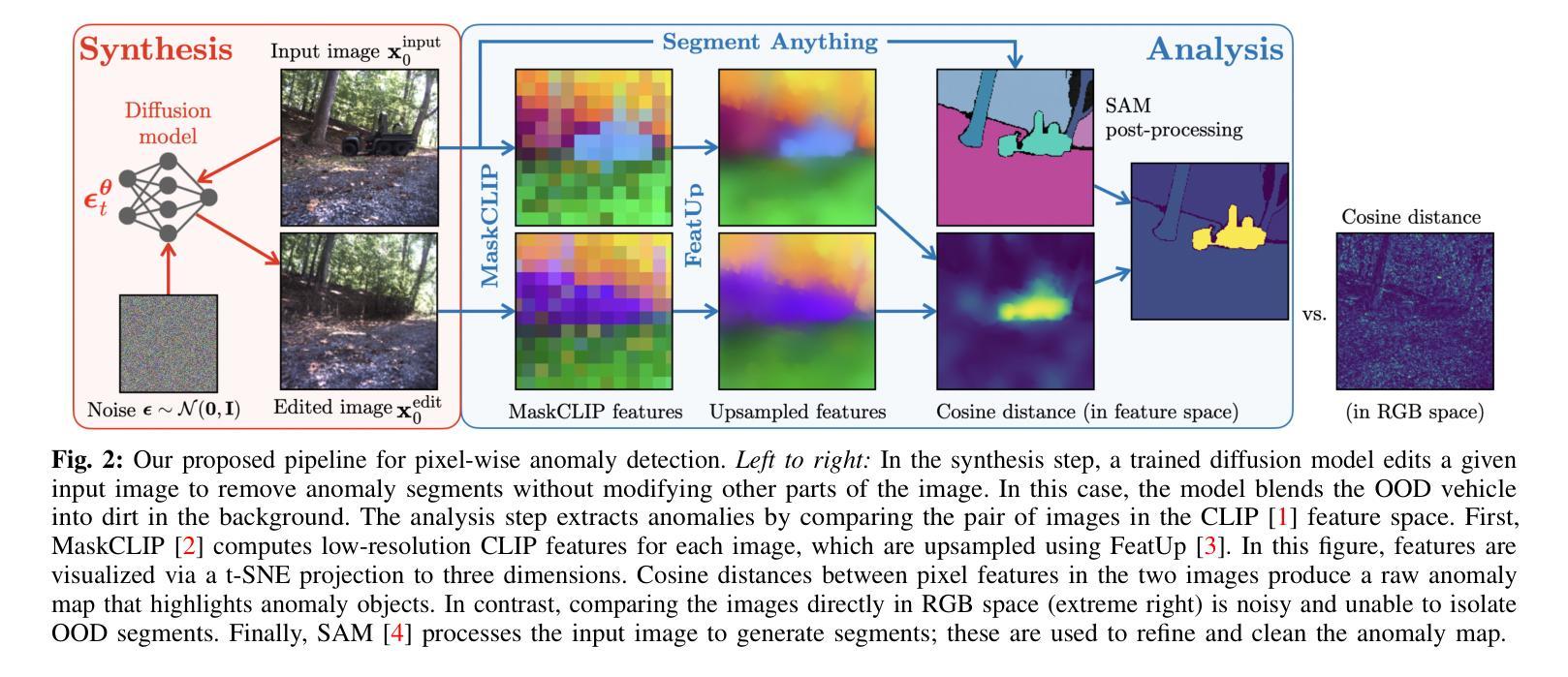
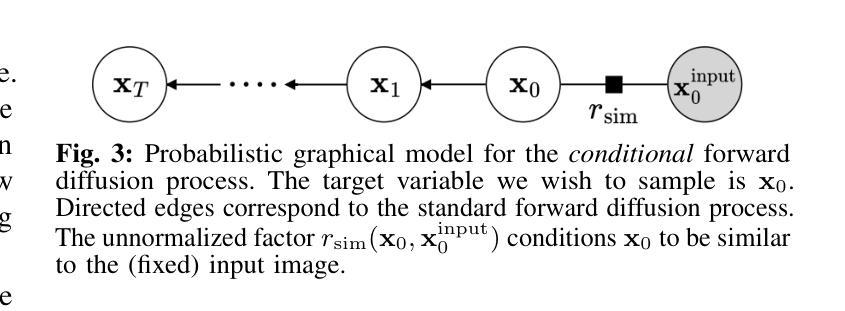
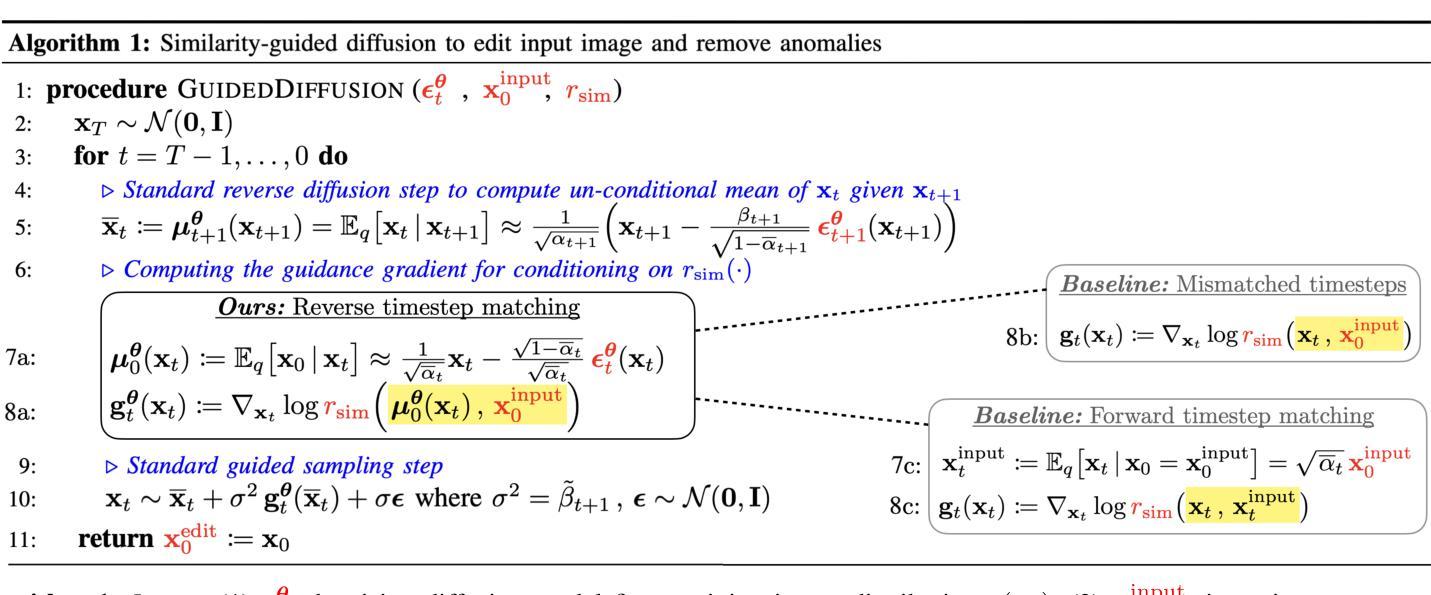
Anomalies by Synthesis: Anomaly Detection using Generative Diffusion Models for Off-Road Navigation
Authors:Siddharth Ancha, Sunshine Jiang, Travis Manderson, Laura Brandt, Yilun Du, Philip R. Osteen, Nicholas Roy
In order to navigate safely and reliably in off-road and unstructured environments, robots must detect anomalies that are out-of-distribution (OOD) with respect to the training data. We present an analysis-by-synthesis approach for pixel-wise anomaly detection without making any assumptions about the nature of OOD data. Given an input image, we use a generative diffusion model to synthesize an edited image that removes anomalies while keeping the remaining image unchanged. Then, we formulate anomaly detection as analyzing which image segments were modified by the diffusion model. We propose a novel inference approach for guided diffusion by analyzing the ideal guidance gradient and deriving a principled approximation that bootstraps the diffusion model to predict guidance gradients. Our editing technique is purely test-time that can be integrated into existing workflows without the need for retraining or fine-tuning. Finally, we use a combination of vision-language foundation models to compare pixels in a learned feature space and detect semantically meaningful edits, enabling accurate anomaly detection for off-road navigation. Project website: https://siddancha.github.io/anomalies-by-diffusion-synthesis/
为了在越野和非结构化环境中安全、可靠地导航,机器人必须检测与训练数据分布外的异常值(OOD)。我们提出了一种基于合成的像素级异常检测分析方法,无需对OOD数据的性质做出任何假设。给定输入图像,我们使用生成性扩散模型合成编辑后的图像,该图像移除了异常值,同时保持其余部分不变。然后,我们将异常检测表述为分析哪些图像段被扩散模型修改。我们提出了一种新型的引导扩散推理方法,通过分析理想引导梯度并推导出一种原则近似值,从而推动扩散模型预测引导梯度。我们的编辑技术是纯测试时间的,可以集成到现有工作流程中,无需进行再训练或微调。最后,我们结合视觉语言基础模型,在学习的特征空间中比较像素并检测语义上有意义的编辑,为实现越野导航中的精确异常检测提供了可能。项目网站地址为:[https://siddancha.github.io/anomalies-by-diffusion-synthesis/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at ICRA 2025
Summary
基于生成性扩散模型的分析合成方法,实现无需了解异常数据性质的像素级异常检测。通过合成编辑图像,移除异常同时保留原图像,将异常检测转化为分析哪些图像区域被扩散模型修改。提出新的引导扩散推理方法,通过理想引导梯度分析和推导原则近似值,使扩散模型预测引导梯度。编辑技术在测试阶段纯粹,可无缝集成现有工作流程,无需重新训练或微调。结合视觉语言基础模型,在学习的特征空间中比较像素,检测语义编辑,为越野导航提供准确的异常检测。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人需要在非道路和非结构化环境中安全可靠地导航,必须检测与训练数据分布外的异常。
- 提出一种分析合成方法,用于像素级的异常检测,无需假设异常数据的性质。
- 利用生成性扩散模型合成编辑图像,移除异常同时保留原图像。
- 将异常检测转化为分析图像中哪些区域被扩散模型修改。
- 提出新的引导扩散推理方法,通过理想引导梯度分析和原则近似值来预测指导梯度。
- 编辑技术在测试阶段纯粹,可轻松集成现有工作流程,无需重新训练或微调。
- 结合视觉语言基础模型检测语义编辑,为越野导航提供准确的异常检测。
点此查看论文截图


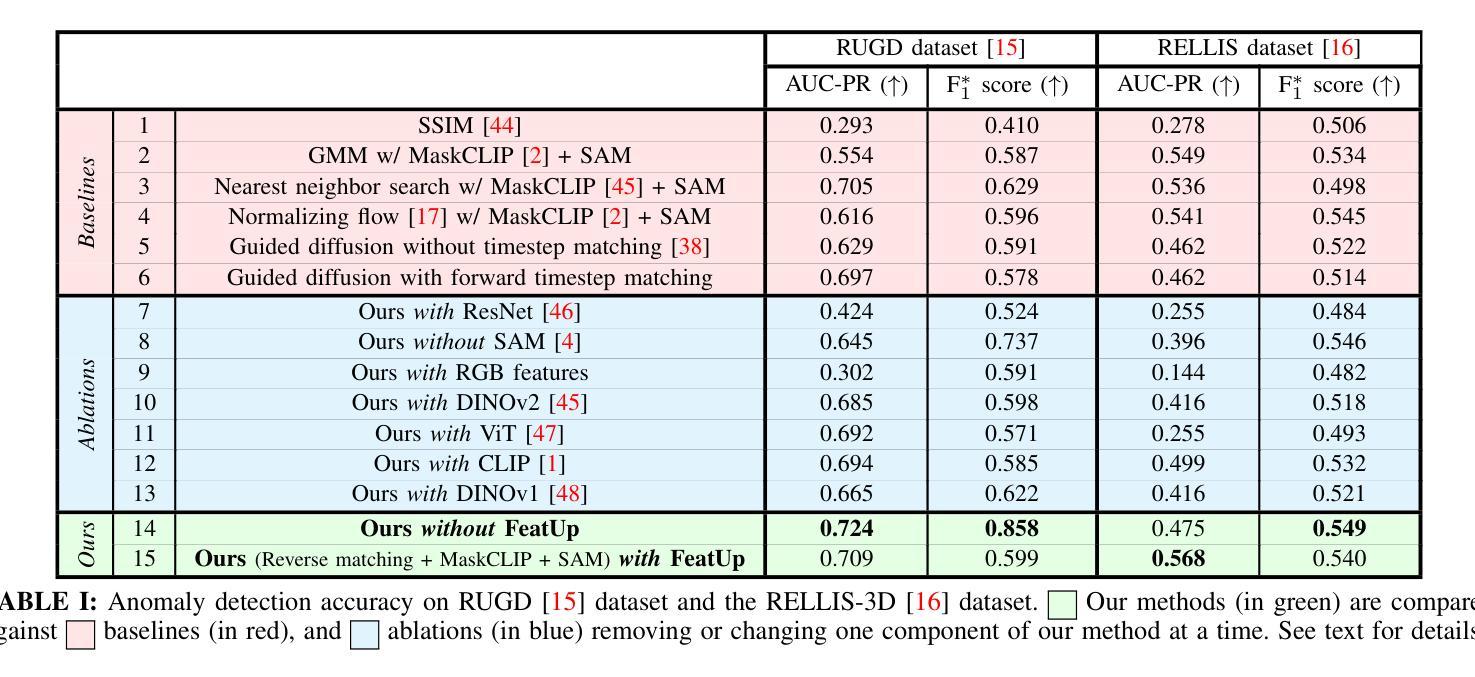
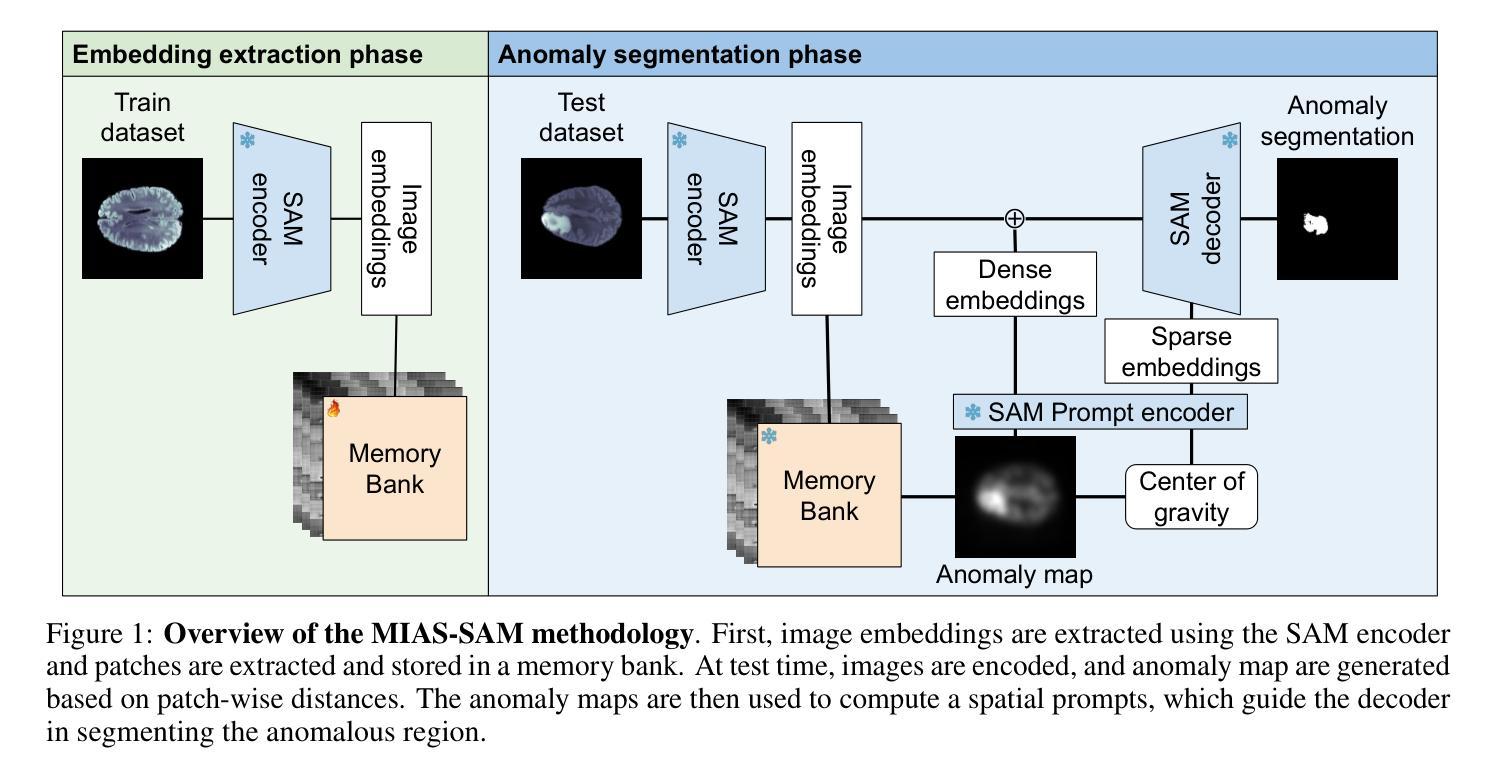
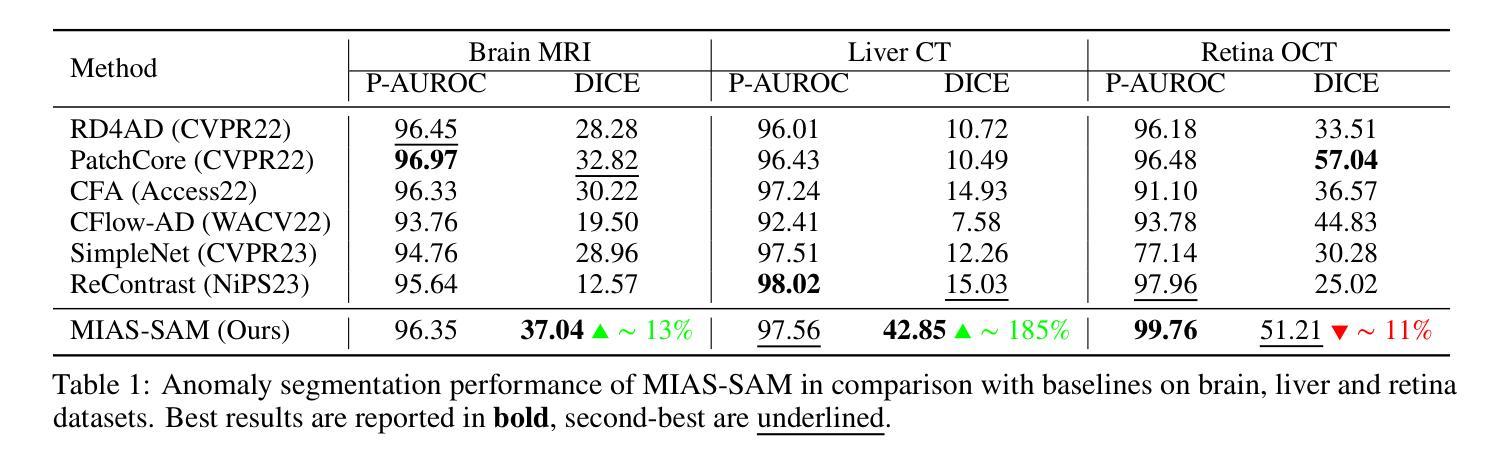
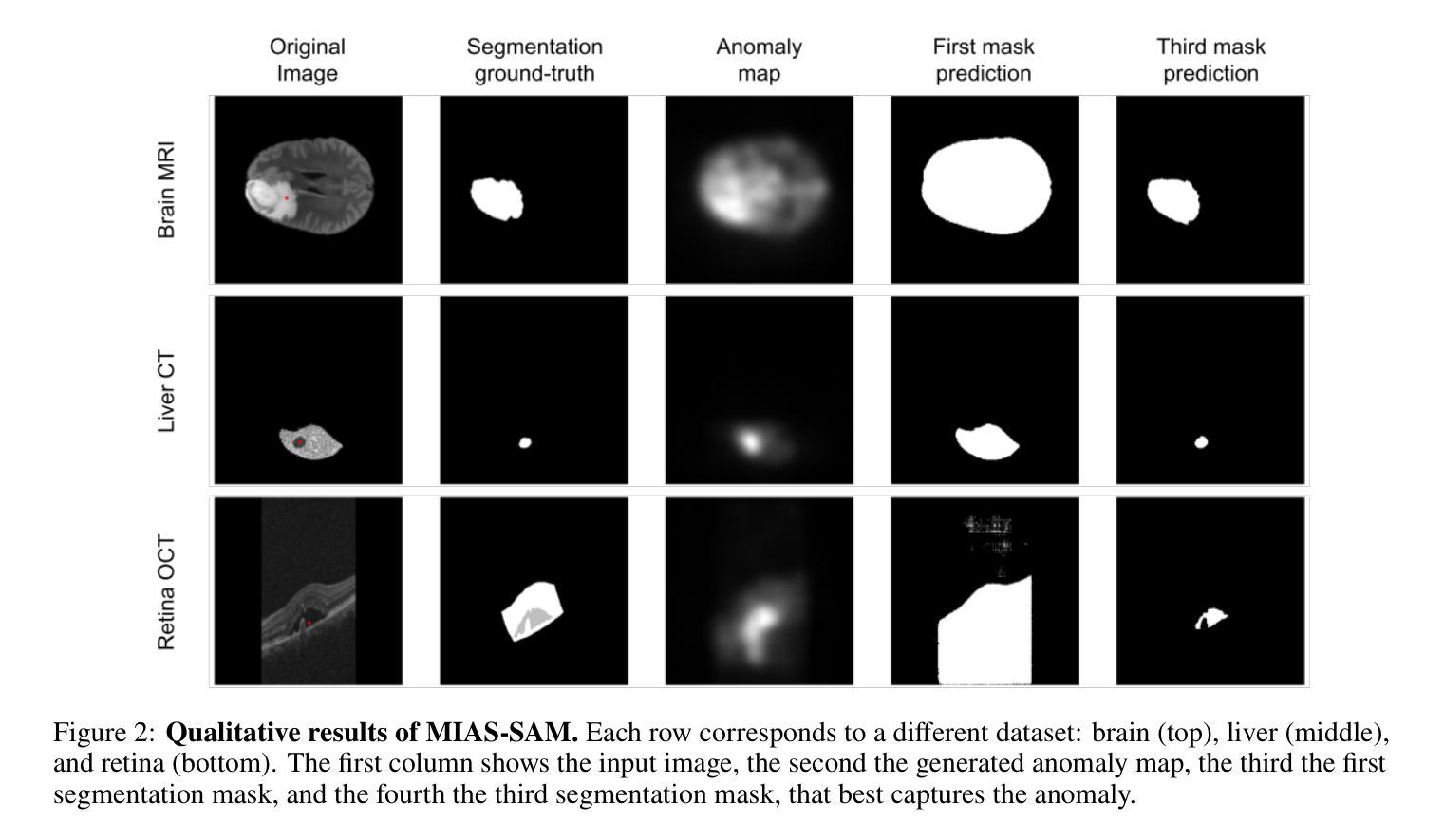
MIAS-SAM: Medical Image Anomaly Segmentation without thresholding
Authors:Marco Colussi, Dragan Ahmetovic, Sergio Mascetti
This paper presents MIAS-SAM, a novel approach for the segmentation of anomalous regions in medical images. MIAS-SAM uses a patch-based memory bank to store relevant image features, which are extracted from normal data using the SAM encoder. At inference time, the embedding patches extracted from the SAM encoder are compared with those in the memory bank to obtain the anomaly map. Finally, MIAS-SAM computes the center of gravity of the anomaly map to prompt the SAM decoder, obtaining an accurate segmentation from the previously extracted features. Differently from prior works, MIAS-SAM does not require to define a threshold value to obtain the segmentation from the anomaly map. Experimental results conducted on three publicly available datasets, each with a different imaging modality (Brain MRI, Liver CT, and Retina OCT) show accurate anomaly segmentation capabilities measured using DICE score. The code is available at: https://github.com/warpcut/MIAS-SAM
本文介绍了一种用于医学图像异常区域分割的新方法MIAS-SAM。MIAS-SAM使用基于补丁的内存库来存储从正常数据使用SAM编码器提取的相关图像特征。在推理阶段,将SAM编码器提取的嵌入补丁与内存库中的补丁进行比较,以获得异常映射。最后,MIAS-SAM计算异常映射的重心以提示SAM解码器,并从先前提取的特征中获得准确的分割。与之前的工作不同,MIAS-SAM不需要定义阈值即可从异常映射中获得分割。在三个公开数据集上进行的实验,每个数据集都有不同的成像模式(大脑MRI、肝脏CT和视网膜OCT),使用DICE得分衡量,显示出准确的异常分割能力。代码可在https://github.com/warpcut/MIAS-SAM处获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像异常区域分割新方法MIAS-SAM介绍。该方法利用基于补丁的内存库存储从正常数据中提取的特征,通过SAM编码器生成嵌入补丁并与内存库中的补丁进行比较,生成异常地图。计算异常地图的重心,引导SAM解码器获得准确分割。无需设定阈值,可在多种医学图像数据集上实现准确分割。
Key Takeaways
- MIAS-SAM是一种用于医学图像异常区域分割的新方法。
- 方法利用基于补丁的内存库存储正常图像的特征。
- 通过SAM编码器生成嵌入补丁,并与内存库中的补丁进行比较,生成异常地图。
- 计算异常地图的重心,以引导SAM解码器进行准确分割。
- 该方法无需设定阈值来获取分割结果。
- 在三种不同成像模态的公开数据集上进行了实验验证,包括Brain MRI、Liver CT和Retina OCT。
点此查看论文截图

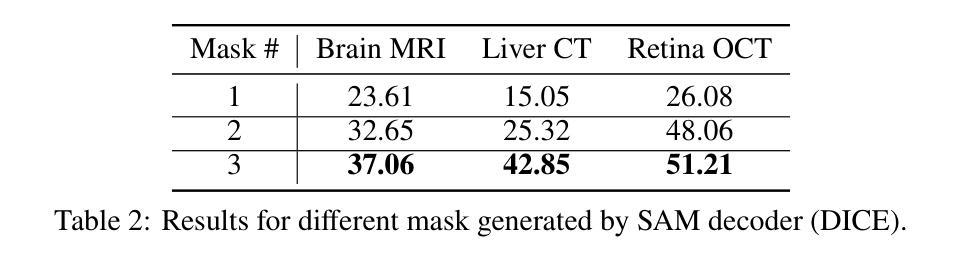
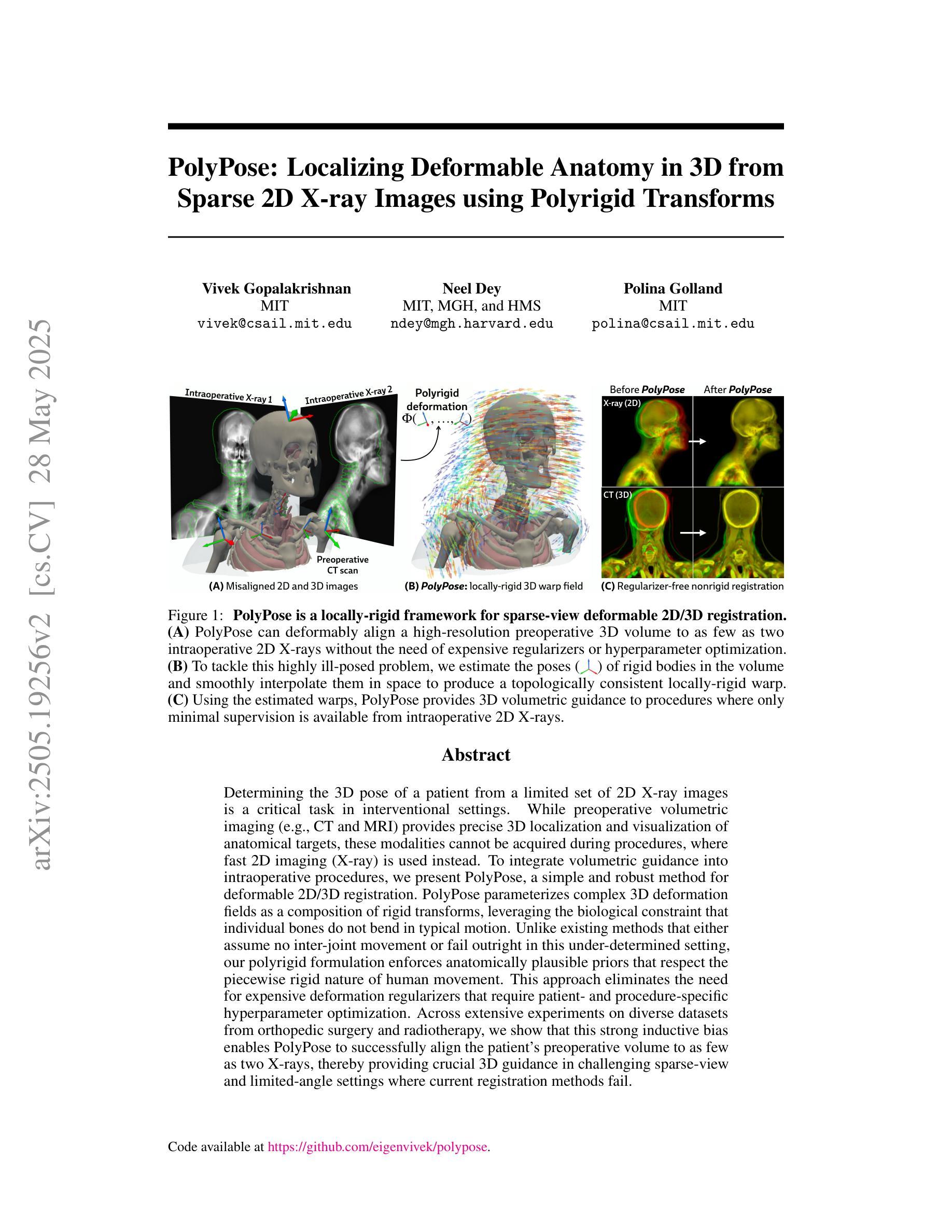
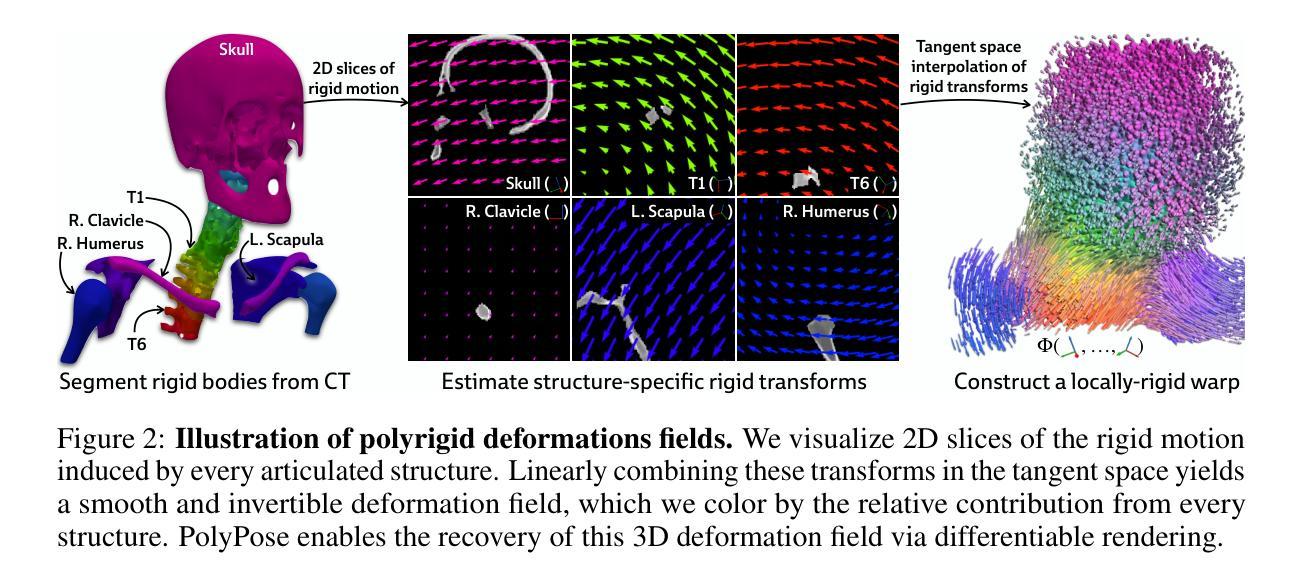
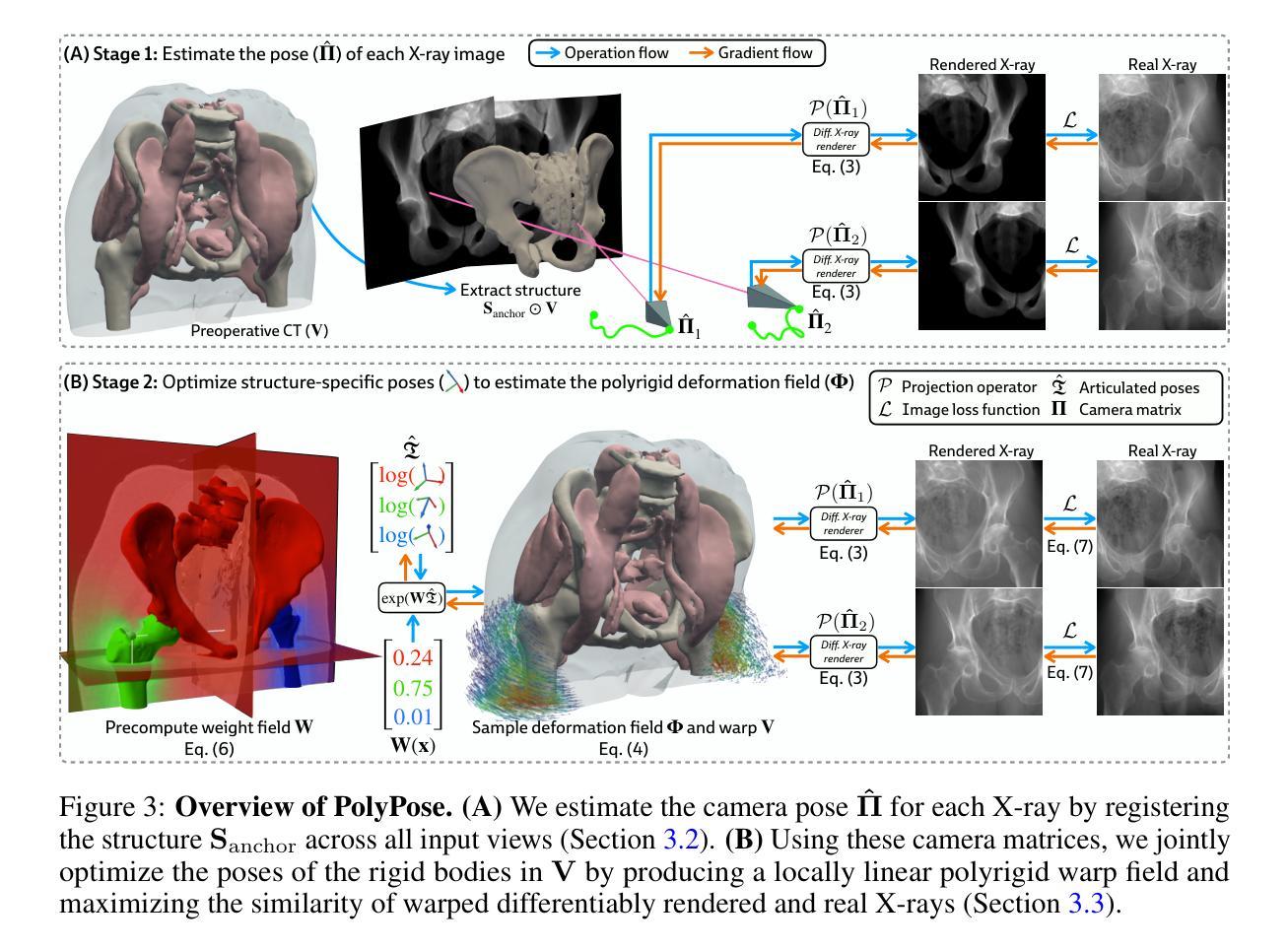
PolyPose: Localizing Deformable Anatomy in 3D from Sparse 2D X-ray Images using Polyrigid Transforms
Authors:Vivek Gopalakrishnan, Neel Dey, Polina Golland
Determining the 3D pose of a patient from a limited set of 2D X-ray images is a critical task in interventional settings. While preoperative volumetric imaging (e.g., CT and MRI) provides precise 3D localization and visualization of anatomical targets, these modalities cannot be acquired during procedures, where fast 2D imaging (X-ray) is used instead. To integrate volumetric guidance into intraoperative procedures, we present PolyPose, a simple and robust method for deformable 2D/3D registration. PolyPose parameterizes complex 3D deformation fields as a composition of rigid transforms, leveraging the biological constraint that individual bones do not bend in typical motion. Unlike existing methods that either assume no inter-joint movement or fail outright in this under-determined setting, our polyrigid formulation enforces anatomically plausible priors that respect the piecewise rigid nature of human movement. This approach eliminates the need for expensive deformation regularizers that require patient- and procedure-specific hyperparameter optimization. Across extensive experiments on diverse datasets from orthopedic surgery and radiotherapy, we show that this strong inductive bias enables PolyPose to successfully align the patient’s preoperative volume to as few as two X-ray images, thereby providing crucial 3D guidance in challenging sparse-view and limited-angle settings where current registration methods fail.
在介入环境中,从有限的2D X射线图像集中确定患者的3D姿态是一项关键任务。虽然术前体积成像(例如CT和MRI)可以提供精确的3D定位和解剖目标的可视化,但这些模式无法在手术过程中获取,此时使用的是快速的2D成像(X射线)。为了将体积引导整合到术中程序中,我们推出了PolyPose,这是一种简单而稳健的可变形2D/3D注册方法。PolyPose将复杂的3D变形场参数化为刚性变换的组合,利用个体骨骼在典型运动中的不弯曲的生物约束。与假设无关节间运动或在这个不确定环境中彻底失败的其他现有方法不同,我们的多刚性公式实施了符合人体运动分段刚性的解剖合理先验。这种方法消除了昂贵的变形调节器,这些调节器需要进行患者和手术特定的超参数优化。在骨科手术和放射治疗的不同数据集上的广泛实验表明,这种强烈的归纳偏见使PolyPose能够成功地将患者的术前体积与至少两张X射线图像对齐,从而在当前的注册方法失败的具有挑战性的稀疏视图和有限角度设置中提供关键的3D指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at https://github.com/eigenvivek/polypose
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为PolyPose的简易稳健方法,用于将体积引导集成到术中程序中,实现从有限的2D X光图像中确定患者的3D姿态。该方法将复杂的3D变形场参数化为刚性变换的组合,并利用人体骨骼在典型运动中的生物约束(即骨骼不会弯曲)。该方法无需昂贵的变形正则化器,后者需要针对患者和程序进行特定的超参数优化。在骨科手术和放射治疗的各种数据集上的实验表明,PolyPose能够在仅使用少数几张X光图像的情况下成功对齐患者的术前体积,为当前注册方法无法应对的挑战性稀疏视图和有限角度设置提供了关键的3D指导。
Key Takeaways
- PolyPose是一种用于术中确定患者三维姿态的方法,可从有限的二维X光图像中实现。
- PolyPose采用刚性变换的组合来参数化复杂的三维变形场。
- 利用人体骨骼的生物约束(骨骼在典型运动中不会弯曲),增强了方法的稳健性。
- 与现有方法不同,PolyPose可以在无关节间运动假设的场景中应用,并且能在缺乏足够的图像信息的情况下仍然有效。
- PolyPose方法具有强大的归纳偏见,能够成功对齐患者的术前体积,即使只使用少数几张X光图像。
- 该方法在骨科手术和放射治疗的多种数据集上进行了广泛实验验证。
点此查看论文截图
Non-rigid Motion Correction for MRI Reconstruction via Coarse-To-Fine Diffusion Models
Authors:Frederic Wang, Jonathan I. Tamir
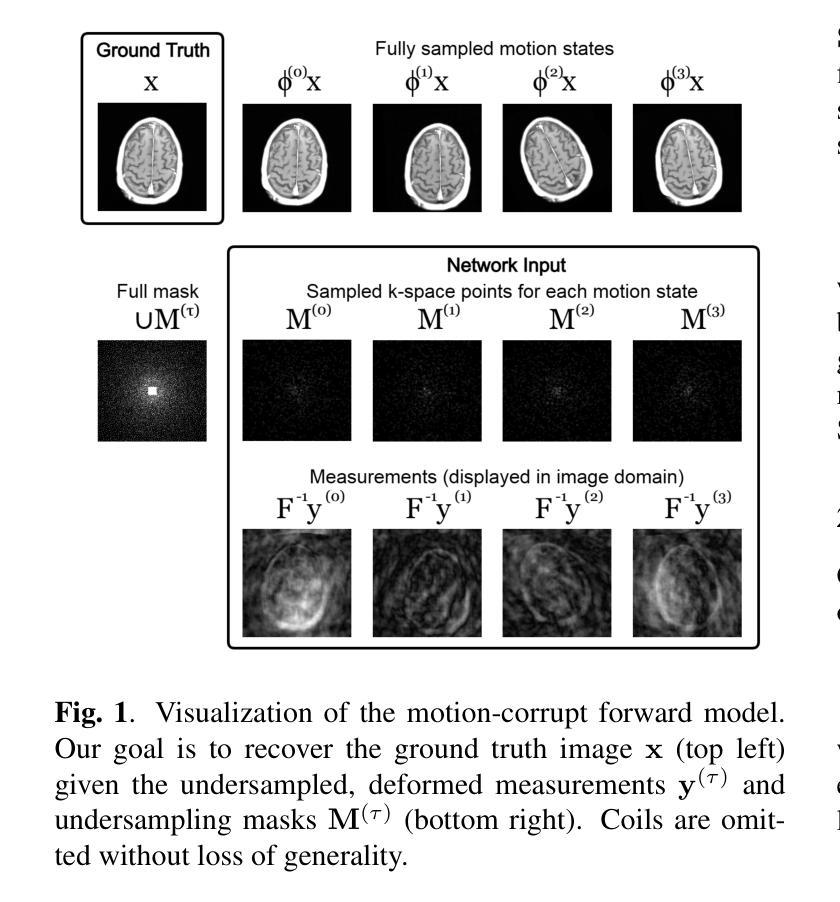
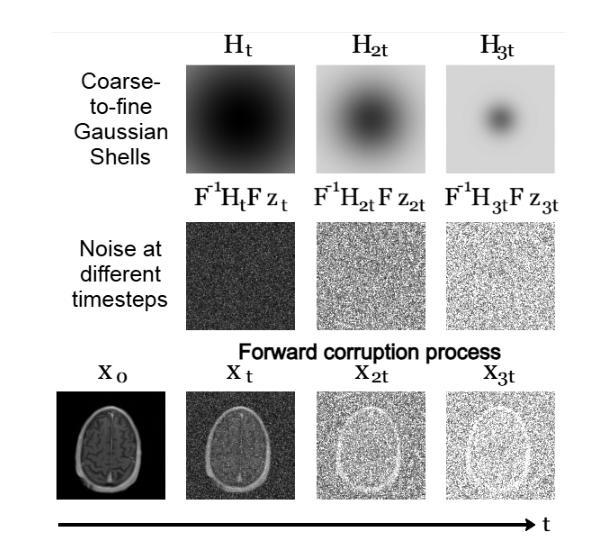
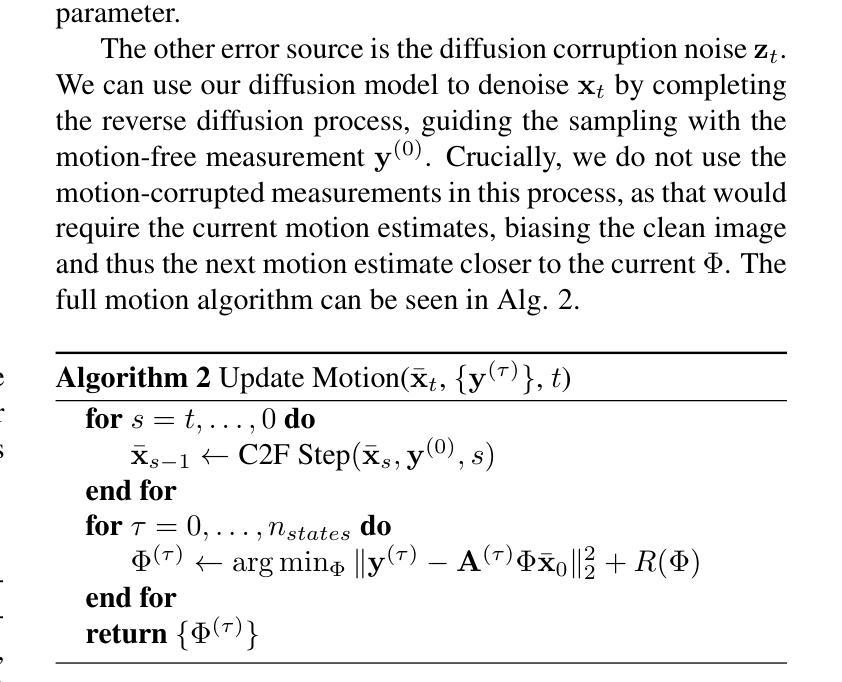
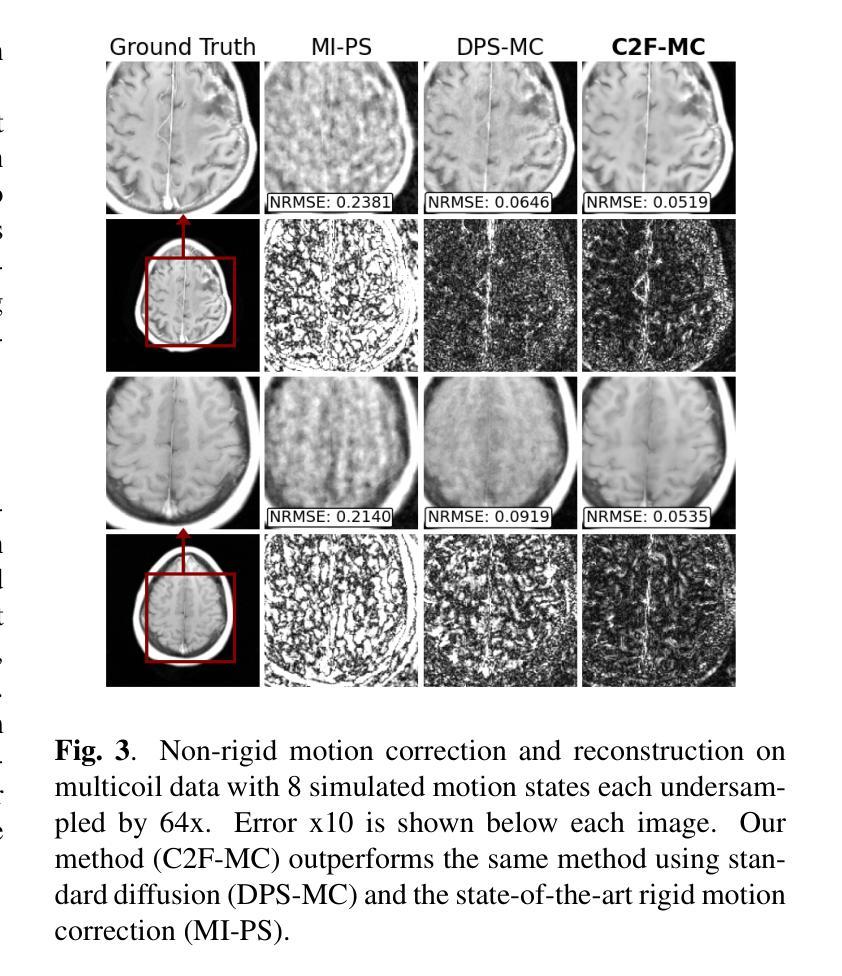
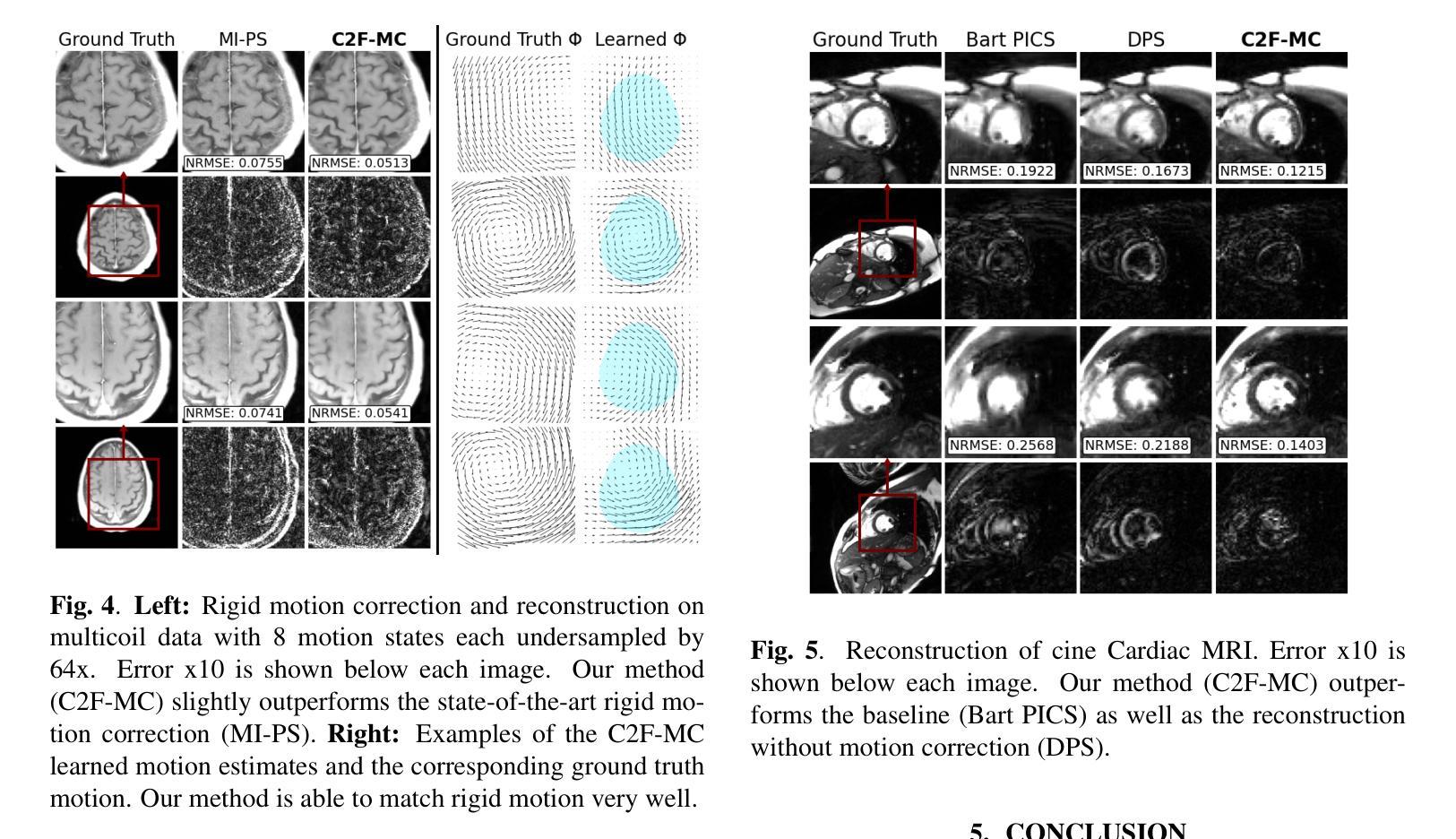
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is highly susceptible to motion artifacts due to the extended acquisition times required for k-space sampling. These artifacts can compromise diagnostic utility, particularly for dynamic imaging. We propose a novel alternating minimization framework that leverages a bespoke diffusion model to jointly reconstruct and correct non-rigid motion-corrupted k-space data. The diffusion model uses a coarse-to-fine denoising strategy to capture large overall motion and reconstruct the lower frequencies of the image first, providing a better inductive bias for motion estimation than that of standard diffusion models. We demonstrate the performance of our approach on both real-world cine cardiac MRI datasets and complex simulated rigid and non-rigid deformations, even when each motion state is undersampled by a factor of 64x. Additionally, our method is agnostic to sampling patterns, anatomical variations, and MRI scanning protocols, as long as some low frequency components are sampled during each motion state.
磁共振成像(MRI)由于k空间采样所需的延长采集时间而极易受到运动伪影的影响。这些伪影可能损害诊断效用,特别是在动态成像中。我们提出了一种新型的交替最小化框架,该框架利用专用扩散模型联合重建和纠正非刚性运动受干扰的k空间数据。该扩散模型采用由粗到细的降噪策略,首先捕获整体大运动并重建图像的低频部分,为运动估计提供更好的归纳偏置,优于标准扩散模型。我们在现实世界的电影心脏MRI数据集和复杂的模拟刚性和非刚性变形上展示了我们的方法性能,即使在每种运动状态下以64倍欠采样的情况下也是如此。此外,我们的方法对于采样模式、解剖变异和MRI扫描协议均保持不敏感性,只要在每个运动状态下采样一些低频成分即可。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICIP 2025
Summary
本文提出一种利用扩散模型解决磁共振成像中由于长时间采集引起的非刚性运动干扰问题的方法。通过粗到细的降噪策略,先重建图像的低频部分,估计整体运动,提高诊断效果。在真实的心脏MRI数据集和复杂的模拟刚性与非刚性变形上进行了验证,即使在每个运动状态下采样频率降低64倍,该方法依然有效。此方法对采样模式、解剖变异和MRI扫描协议具有通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)由于长时间的采集过程容易受到运动干扰的影响。
- 非刚性运动干扰会严重影响MRI的诊断效果。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的交替最小化框架来解决这一问题。
- 采用粗到细的降噪策略,首先重建图像的低频部分,用于估计整体运动。
- 该方法在真实和模拟数据上进行了验证,对多种类型的运动干扰有效。
- 即使在采样频率降低的情况下,该方法仍然具有高效性。
点此查看论文截图


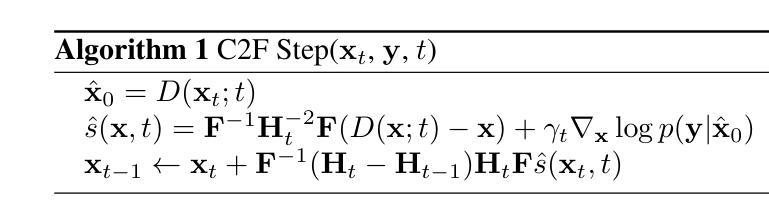
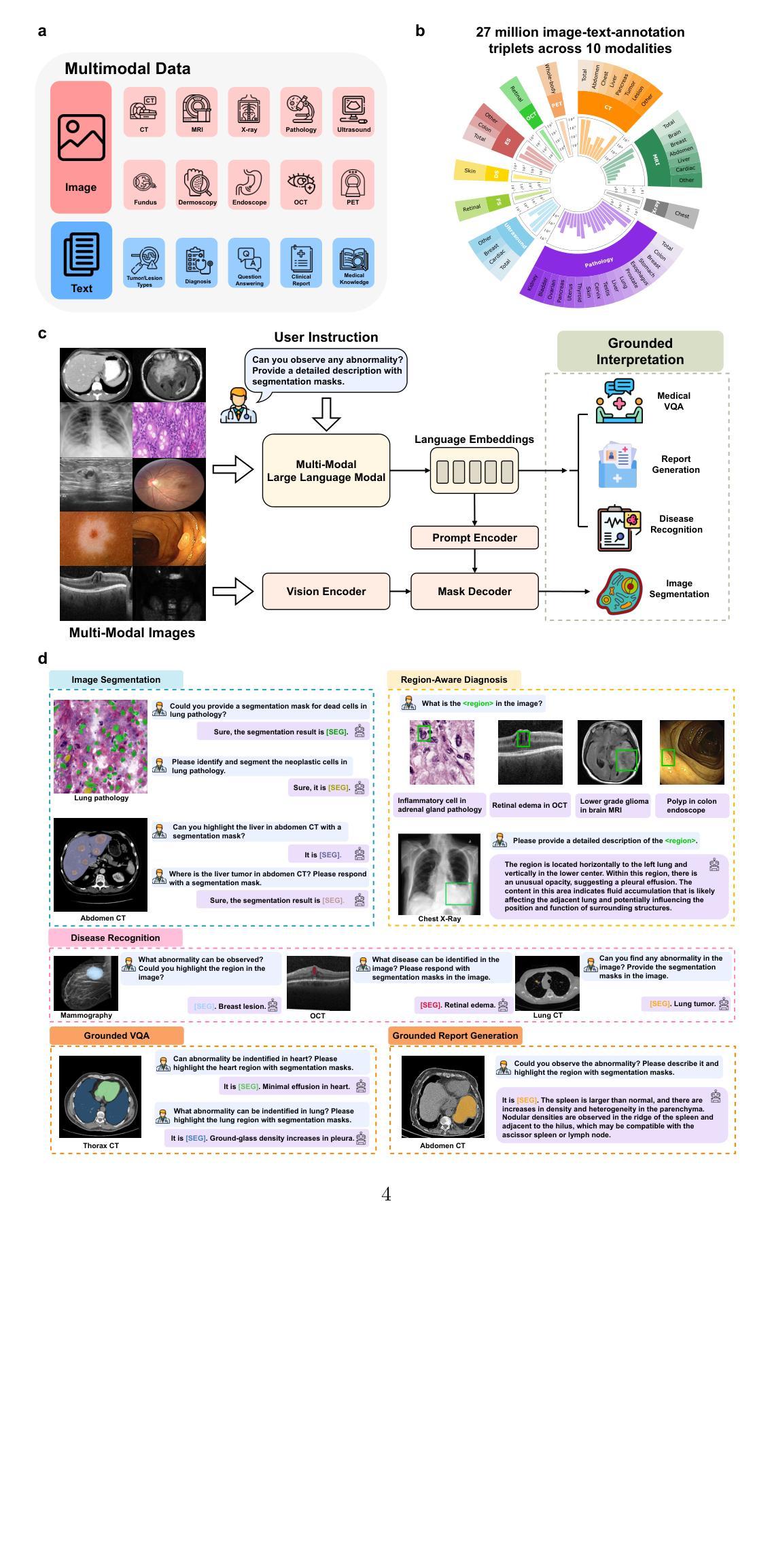
UniBiomed: A Universal Foundation Model for Grounded Biomedical Image Interpretation
Authors:Linshan Wu, Yuxiang Nie, Sunan He, Jiaxin Zhuang, Luyang Luo, Neeraj Mahboobani, Varut Vardhanabhuti, Ronald Cheong Kin Chan, Yifan Peng, Pranav Rajpurkar, Hao Chen
The integration of AI-assisted biomedical image analysis into clinical practice demands AI-generated findings that are not only accurate but also interpretable to clinicians. However, existing biomedical AI models generally lack the ability to simultaneously generate diagnostic findings and localize corresponding biomedical objects. This limitation makes it challenging for clinicians to correlate AI-generated findings with visual evidence (e.g., tiny lesions) in images and interpret the results of AI models. To address this challenge, we introduce UniBiomed, the first universal foundation model for grounded biomedical image interpretation, which is capable of generating accurate diagnostic findings and simultaneously segmenting the corresponding biomedical targets. UniBiomed is based on a novel integration of Multi-modal Large Language Model and Segment Anything Model, which can effectively unify diverse biomedical tasks in universal training for advancing grounded interpretation. To develop UniBiomed, we curate a large-scale dataset comprising over 27 million triplets of images, region annotations, and text descriptions across ten biomedical imaging modalities. Extensive validation on 70 internal and 14 external datasets demonstrated the state-of-the-art performance of UniBiomed in diverse biomedical tasks, including image segmentation, disease recognition, region-aware diagnosis, vision question answering, and report generation. In summary, UniBiomed is a powerful and versatile biomedical foundation model, unlocking the untapped grounded interpretation capability for optimizing AI-assisted biomedical image analysis.
将人工智能辅助生物医学图像分析整合到临床实践中的要求,是人工智能生成的发现不仅必须准确,而且必须能够让临床医生进行解读。然而,现有的生物医学人工智能模型通常缺乏同时生成诊断结果并定位相应生物医学对象的能力。这一局限性使得临床医生难以将人工智能生成的发现与图像中的视觉证据(例如微小病变)相关联,并解读人工智能模型的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first universal foundation model for grounded biomedical image interpretation
Summary
基于人工智能的生物医学图像分析在临床实践中的集成要求AI生成的发现不仅准确,而且临床医生可解释。然而,现有的生物医学AI模型通常缺乏同时生成诊断结果和定位相应生物医学对象的能力。为解决这一挑战,我们引入了UniBiomed,这是首个用于基于基础生物医学图像解释的通用基础模型,能够生成准确的诊断结果并同时分割相应的生物医学目标。它通过多模态大型语言模型和分段任何模型的全新整合,有效地统一了多样化的生物医学任务,以推动基于现实的解释。为开发UniBiomed,我们整理了一个大规模数据集,包含超过2700万张图像、区域注释和文本描述的三元组,跨越十种生物医学成像模式。在70个内部和14个外部数据集上的广泛验证表明,UniBiomed在多种生物医学任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括图像分割、疾病识别、区域感知诊断、视觉问答和报告生成。总的来说,UniBiomed是一个强大且通用的生物医学基础模型,解锁了基于现实解释的潜在能力,以优化人工智能辅助生物医学图像分析。
Key Takeaways
- AI在生物医学图像分析中的集成需要既准确又临床医生可解释的发现。
- 现有生物医学AI模型通常不能同时生成诊断结果和定位相应的生物医学对象,给临床医生带来挑战。
- UniBiomed是首个用于基于基础生物医学图像解释的通用模型,能够同时生成诊断结果并分割生物医学目标。
- UniBiomed通过整合多模态大型语言模型和分段任何模型,有效统一多样化的生物医学任务。
- UniBiomed的开发基于一个大规模数据集,包含图像、区域注释和文本描述的三元组。
- UniBiomed在多种生物医学任务中表现出卓越性能,包括图像分割、疾病识别、区域感知诊断、视觉问答和报告生成。
点此查看论文截图