⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
Adaptive Spatial Augmentation for Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Lingyan Ran, Yali Li, Tao Zhuo, Shizhou Zhang, Yanning Zhang
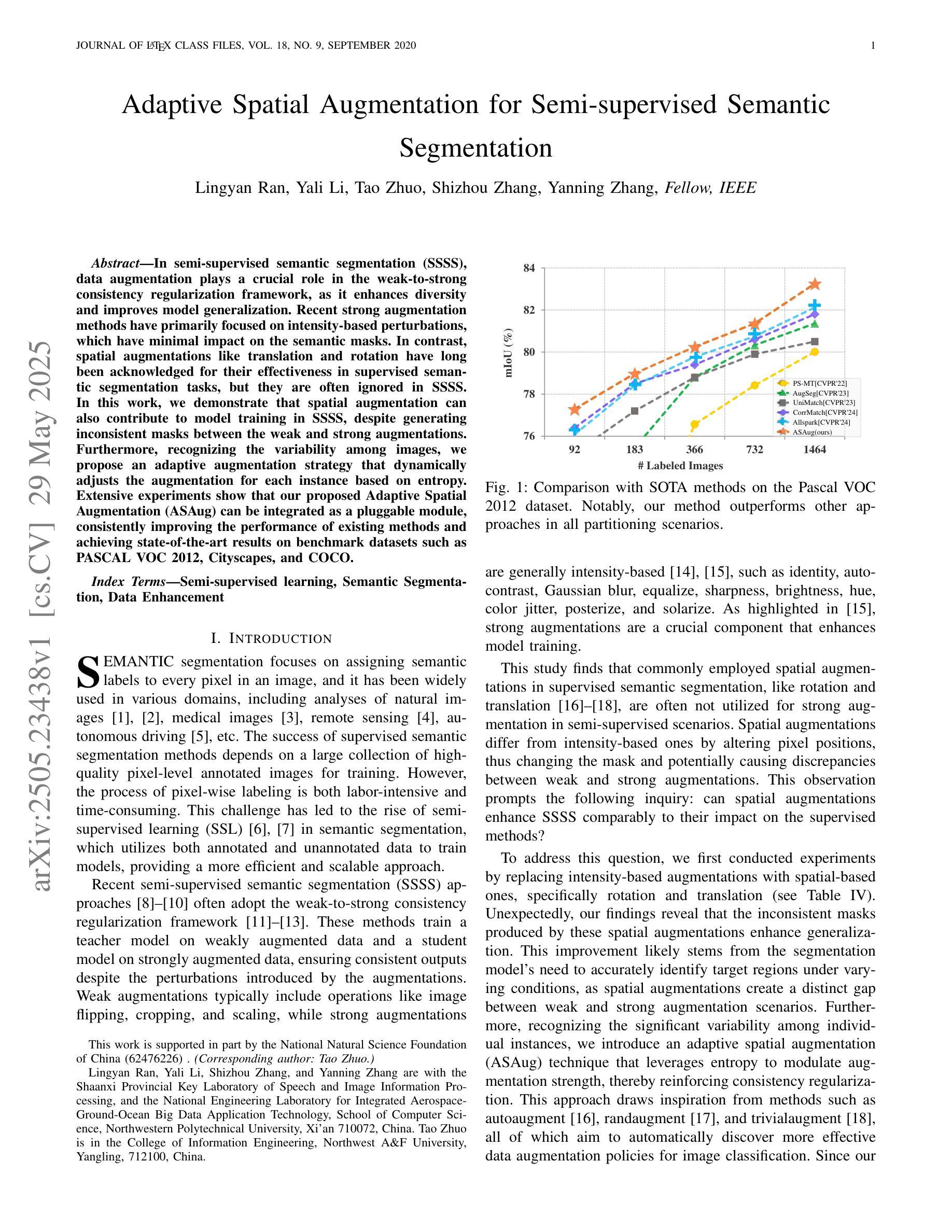
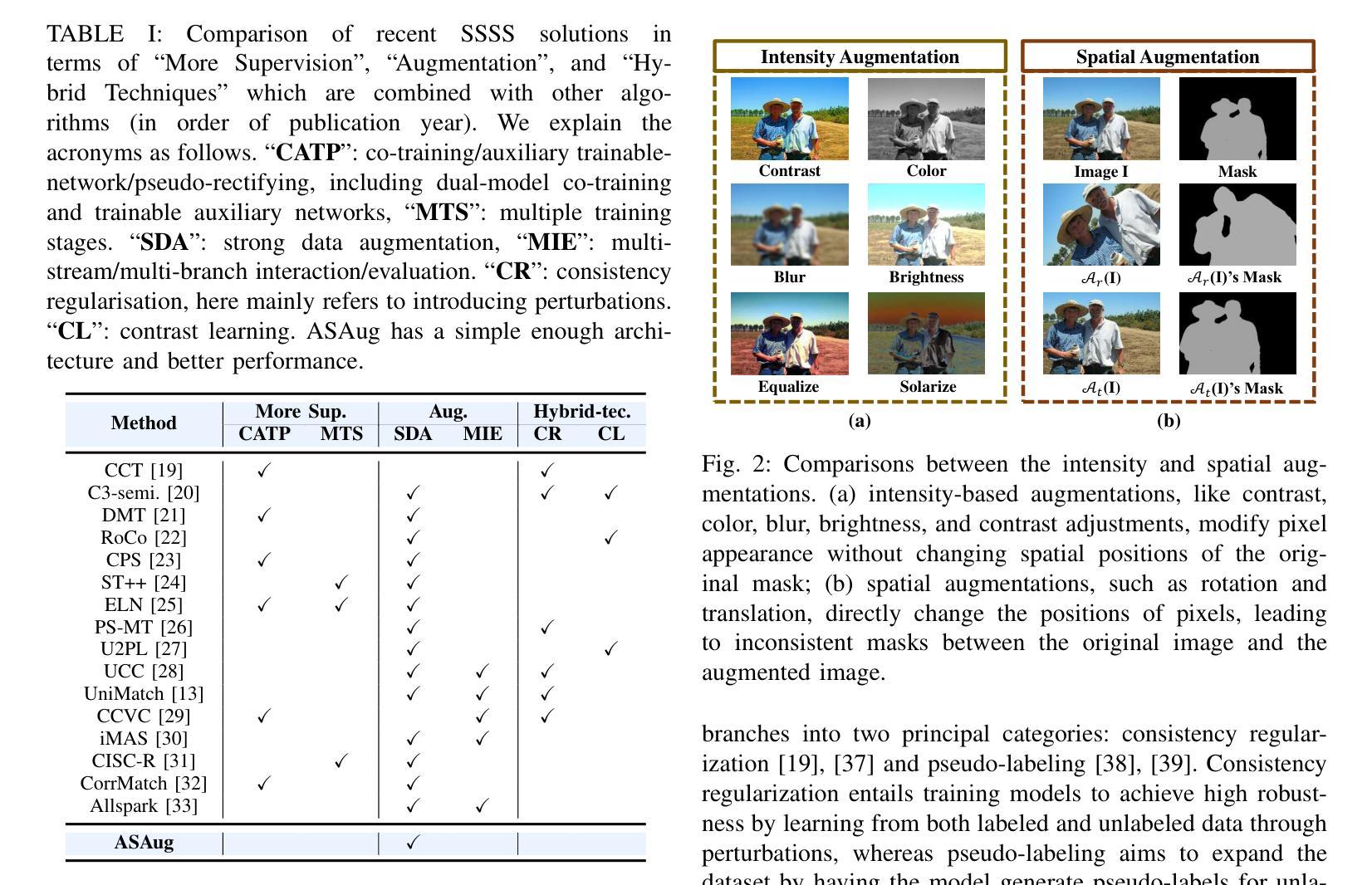
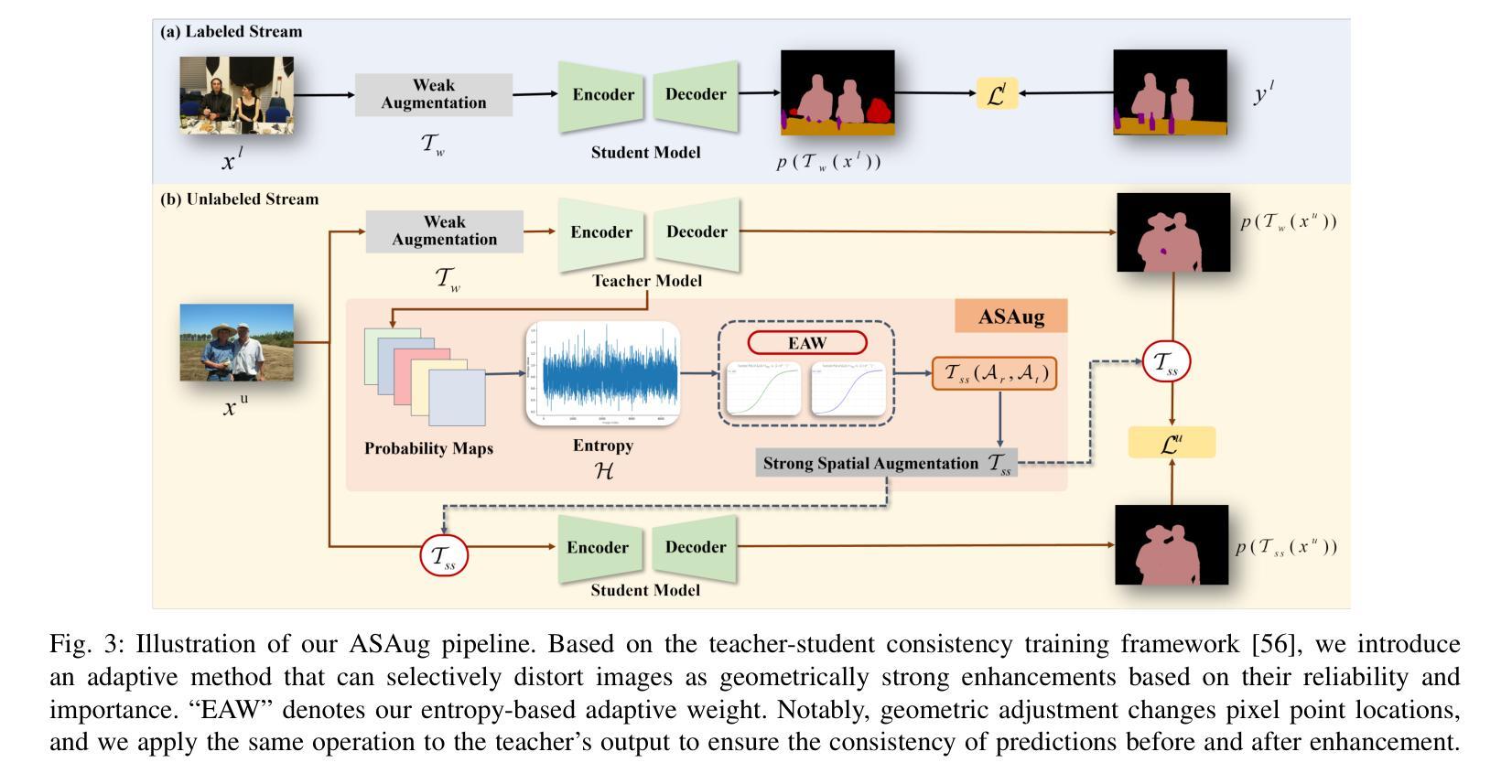
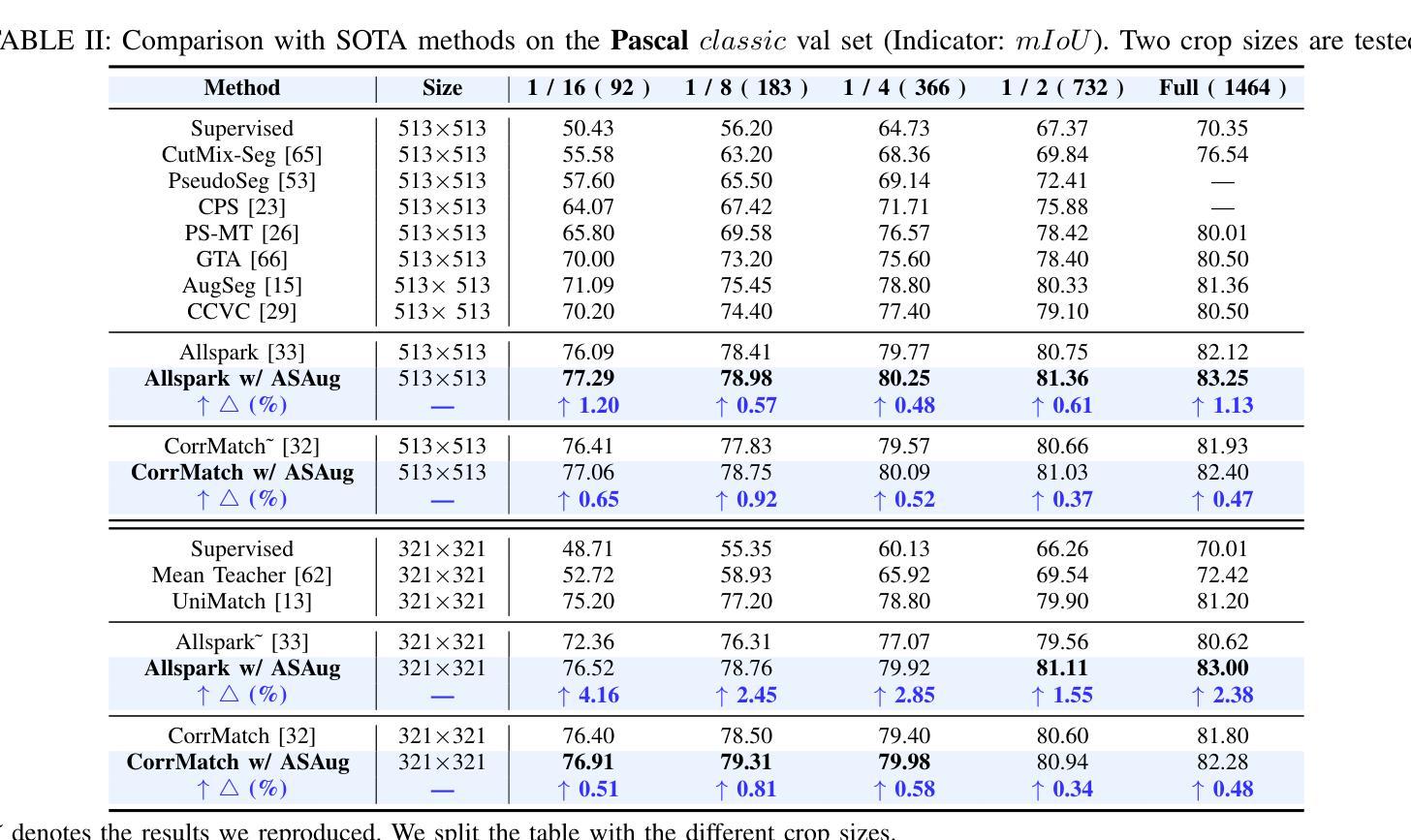
In semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS), data augmentation plays a crucial role in the weak-to-strong consistency regularization framework, as it enhances diversity and improves model generalization. Recent strong augmentation methods have primarily focused on intensity-based perturbations, which have minimal impact on the semantic masks. In contrast, spatial augmentations like translation and rotation have long been acknowledged for their effectiveness in supervised semantic segmentation tasks, but they are often ignored in SSSS. In this work, we demonstrate that spatial augmentation can also contribute to model training in SSSS, despite generating inconsistent masks between the weak and strong augmentations. Furthermore, recognizing the variability among images, we propose an adaptive augmentation strategy that dynamically adjusts the augmentation for each instance based on entropy. Extensive experiments show that our proposed Adaptive Spatial Augmentation (\textbf{ASAug}) can be integrated as a pluggable module, consistently improving the performance of existing methods and achieving state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets such as PASCAL VOC 2012, Cityscapes, and COCO.
在半监督语义分割(SSSS)中,数据增强在弱到强的一致性正则化框架中起着至关重要的作用,因为它增强了数据的多样性,提高了模型的泛化能力。近期强大的数据增强方法主要集中在基于强度的扰动上,而对语义掩膜的影响微乎其微。相反,如平移和旋转这样的空间增强方法在监督语义分割任务中长期被认为非常有效,但在SSSS中常常被忽略。在这项工作中,我们证明即使生成了弱增强和强增强之间的不一致掩膜,空间增强也可以对SSSS模型的训练做出贡献。此外,我们认识到了图像之间的变异性,因此提出了一种自适应增强策略,该策略根据熵动态调整每个实例的增强方法。大量实验表明,我们提出的自适应空间增强(\textbf{ASAug})可以作为一个可插拔的模块进行集成,一致地改进现有方法,并在PASCAL VOC 2012、Cityscapes和COCO等基准数据集上实现最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary
半监督语义分割中数据增强对弱到强一致性正则化框架至关重要,增强多样性和提高模型泛化能力。以前重视强度基础扰动,对语义蒙版影响甚微的空间增强,而本工作证明空间增强也可对半监督语义分割模型训练有所贡献,尽管会产生强弱蒙版间的不一致性。同时提出自适应增强策略,基于熵动态调整实例增强效果,经过广泛实验证明所提自适应空间增强可集成为一个插件模块,对现有方法进行持续改进并在基准数据集如PASCAL VOC 2012、Cityscapes和COCO上达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在弱到强一致性正则化框架的半监督语义分割中起到关键作用。
- 之前的研究主要关注强度扰动等轻微影响语义蒙版的方法。
- 空间增强如平移和旋转在监督语义分割任务中有效,但在半监督语义分割中常被忽视。
- 空间增强能对半监督语义分割模型训练有贡献,尽管会导致蒙版不一致性。
- 提出自适应增强策略,根据图像熵动态调整每个实例的增强效果。
点此查看论文截图

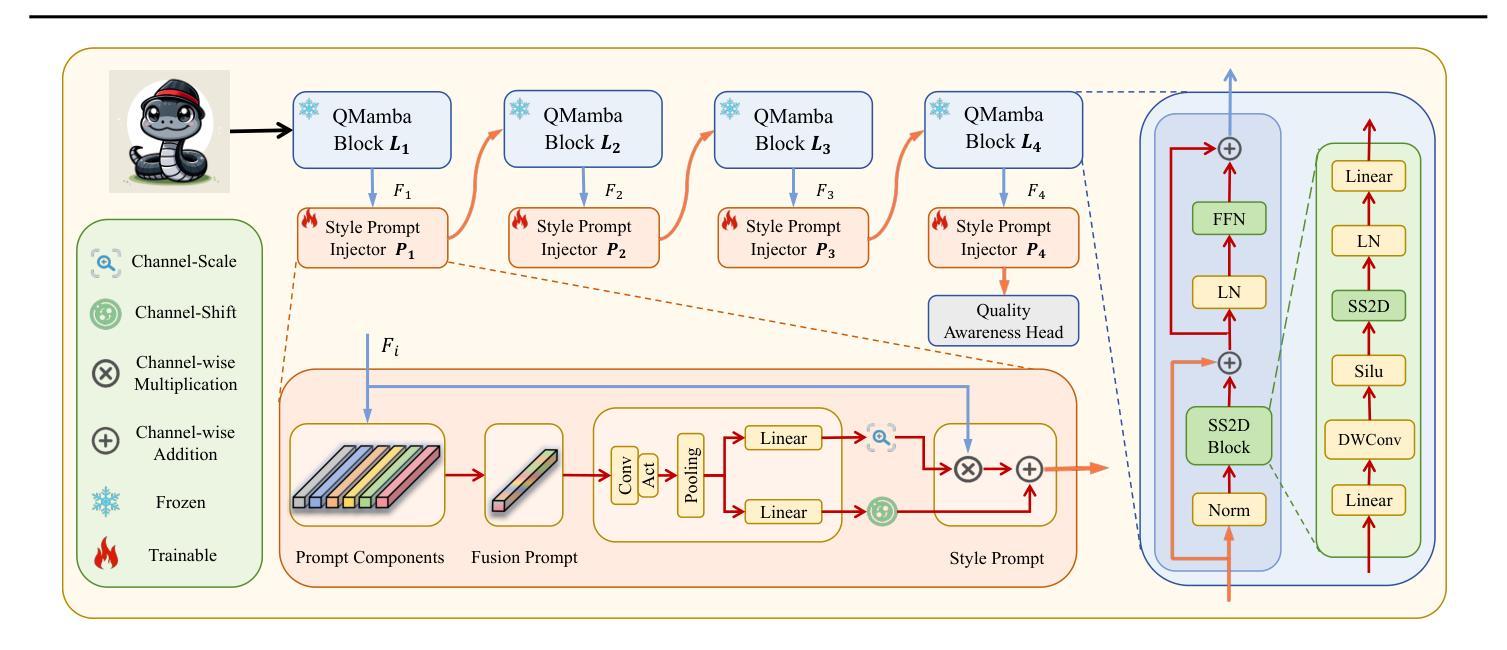
Federated Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Evangelos Charalampakis, Vasileios Mygdalis, Ioannis Pitas
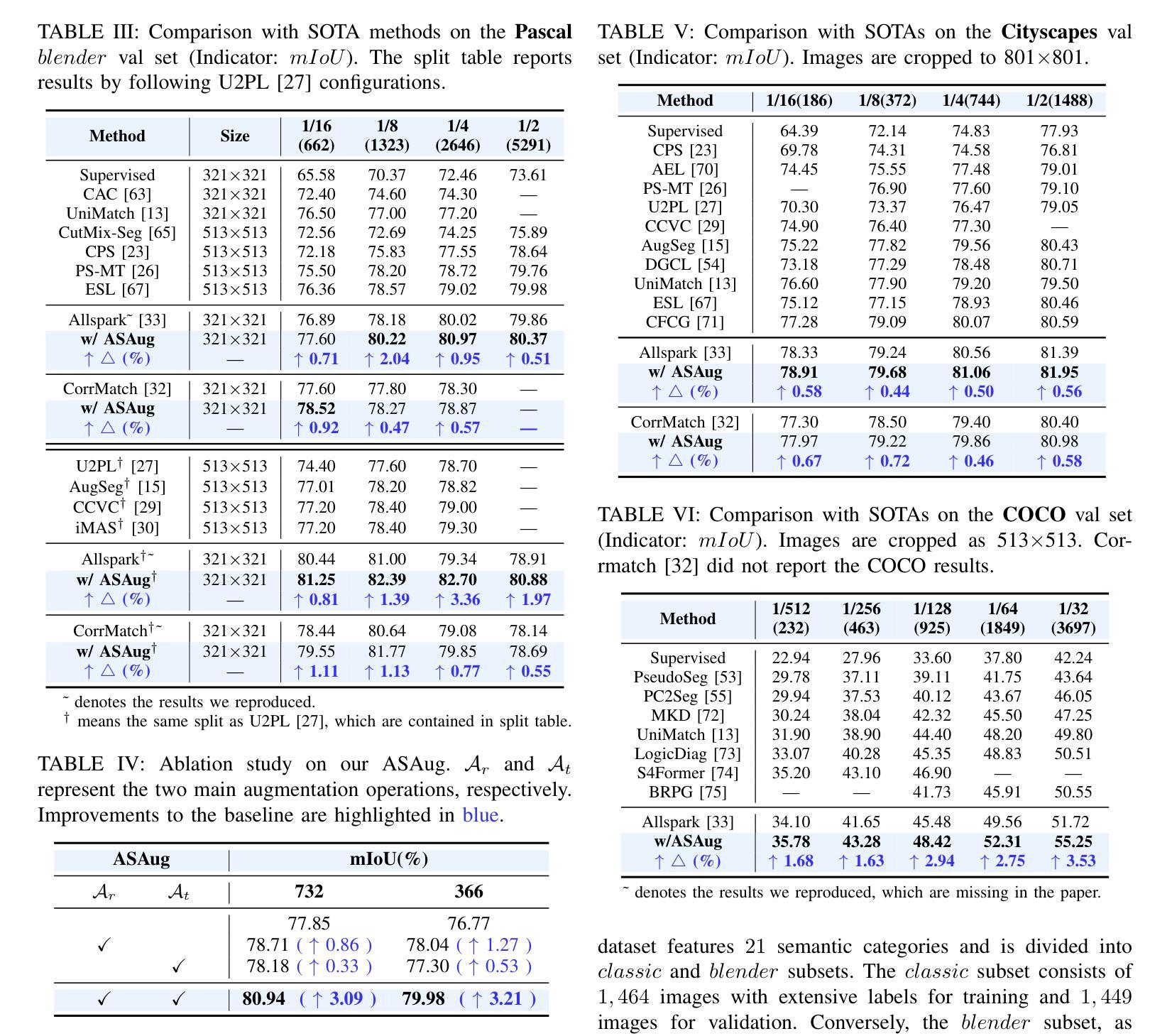
This work explores the application of Federated Learning (FL) in Unsupervised Semantic image Segmentation (USS). Recent USS methods extract pixel-level features using frozen visual foundation models and refine them through self-supervised objectives that encourage semantic grouping. These features are then grouped to semantic clusters to produce segmentation masks. Extending these ideas to federated settings requires feature representation and cluster centroid alignment across distributed clients – an inherently difficult task under heterogeneous data distributions in the absence of supervision. To address this, we propose FUSS Federated Unsupervised image Semantic Segmentation) which is, to our knowledge, the first framework to enable fully decentralized, label-free semantic segmentation training. FUSS introduces novel federation strategies that promote global consistency in feature and prototype space, jointly optimizing local segmentation heads and shared semantic centroids. Experiments on both benchmark and real-world datasets, including binary and multi-class segmentation tasks, show that FUSS consistently outperforms local-only client trainings as well as extensions of classical FL algorithms under varying client data distributions. To support reproducibility, full code will be released upon manuscript acceptance.
本文探讨了联邦学习(FL)在无监督语义图像分割(USS)中的应用。最近的USS方法使用冻结的视觉基础模型提取像素级特征,并通过自我监督目标进行细化,这些目标鼓励语义分组。然后,这些特征被分组到语义集群中,以产生分割掩膜。将这些思想扩展到联邦环境需要跨分布式客户端进行特征表示和聚类中心对齐——在缺乏监督的情况下,在异质数据分布中这是一项固有的困难任务。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FUSS(联邦无监督图像语义分割),据我们所知,这是第一个能够实现完全分散、无标签语义分割训练的框架。FUSS引入了新型联邦策略,促进特征和原型空间中的全局一致性,联合优化本地分割头和共享语义中心。在基准测试数据集和真实世界数据集上的实验,包括二元和多类分割任务,表明FUSS在各种客户端数据分布下,始终优于仅本地的客户端训练以及经典FL算法的扩展。为了支持可重复性,论文被接受后将公布完整的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了联邦学习(FL)在无监督语义图像分割(USS)中的应用。文章介绍了如何在联邦环境下扩展无监督语义图像分割的方法,提出FUSS(联邦无监督图像语义分割)框架,实现完全去中心化、无标签的语义分割训练。FUSS引入新型联邦策略,促进特征空间和原型空间的全局一致性,联合优化本地分割头和共享语义质心。实验结果表明,FUSS在不同客户端数据分布下,无论是基准数据集还是真实世界数据集,无论是二进制还是多类分割任务,都表现出出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本文将联邦学习(FL)应用于无监督语义图像分割(USS)。
- USS方法使用冻结的视觉基础模型提取像素级特征,并通过自监督目标进行细化,这些目标鼓励语义分组。
- 在联邦环境中扩展USS需要跨分布式客户端进行特征表示和聚类中心对齐,这是一项在缺乏监督的情况下具有异构数据分布的固有困难的任务。
- FUSS是首个实现完全去中心化、无标签的语义分割训练的框架。
- FUSS引入新型联邦策略,促进特征空间和原型空间的全球一致性。
- FUSS联合优化本地分割头和共享语义质心。
点此查看论文截图

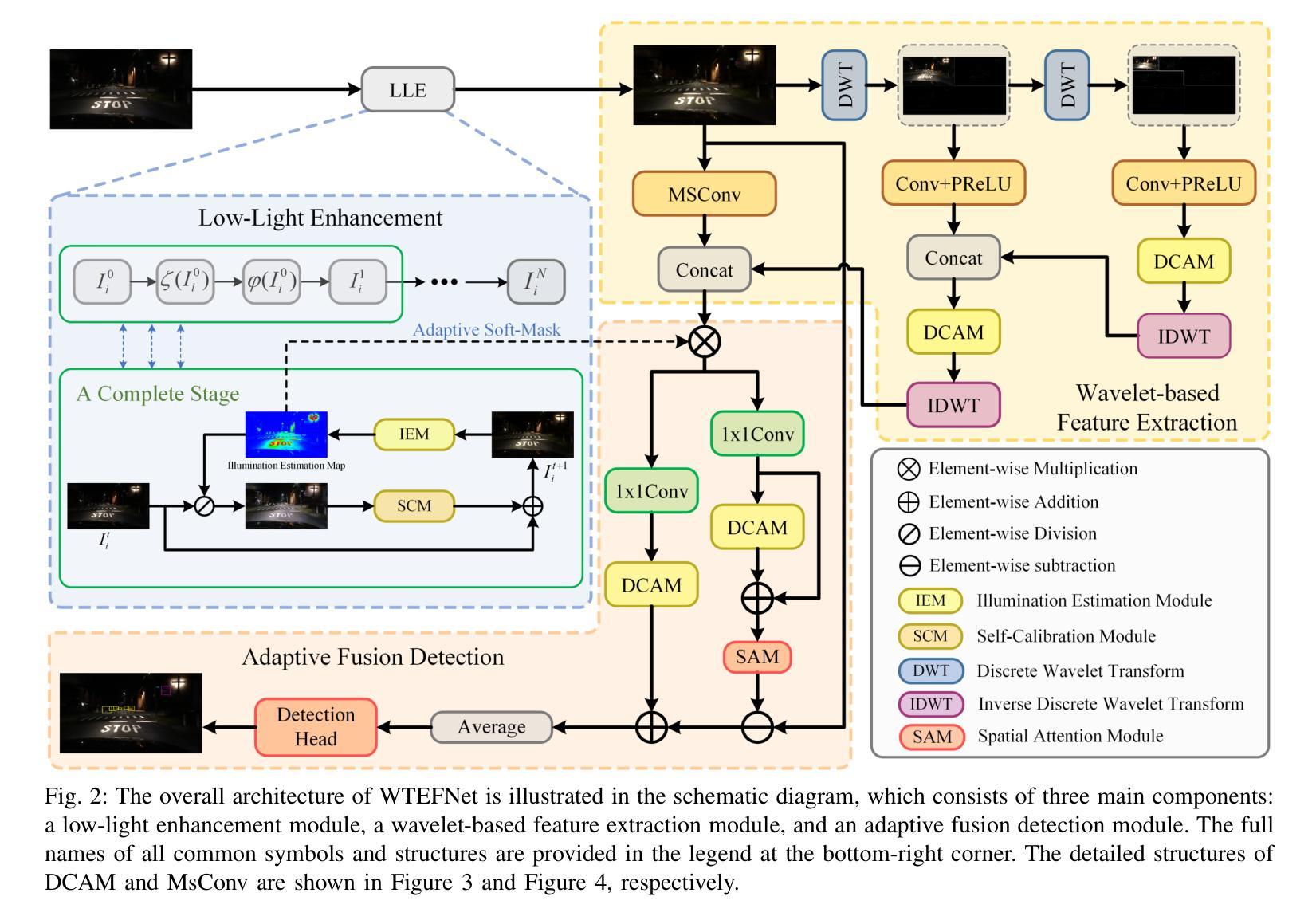
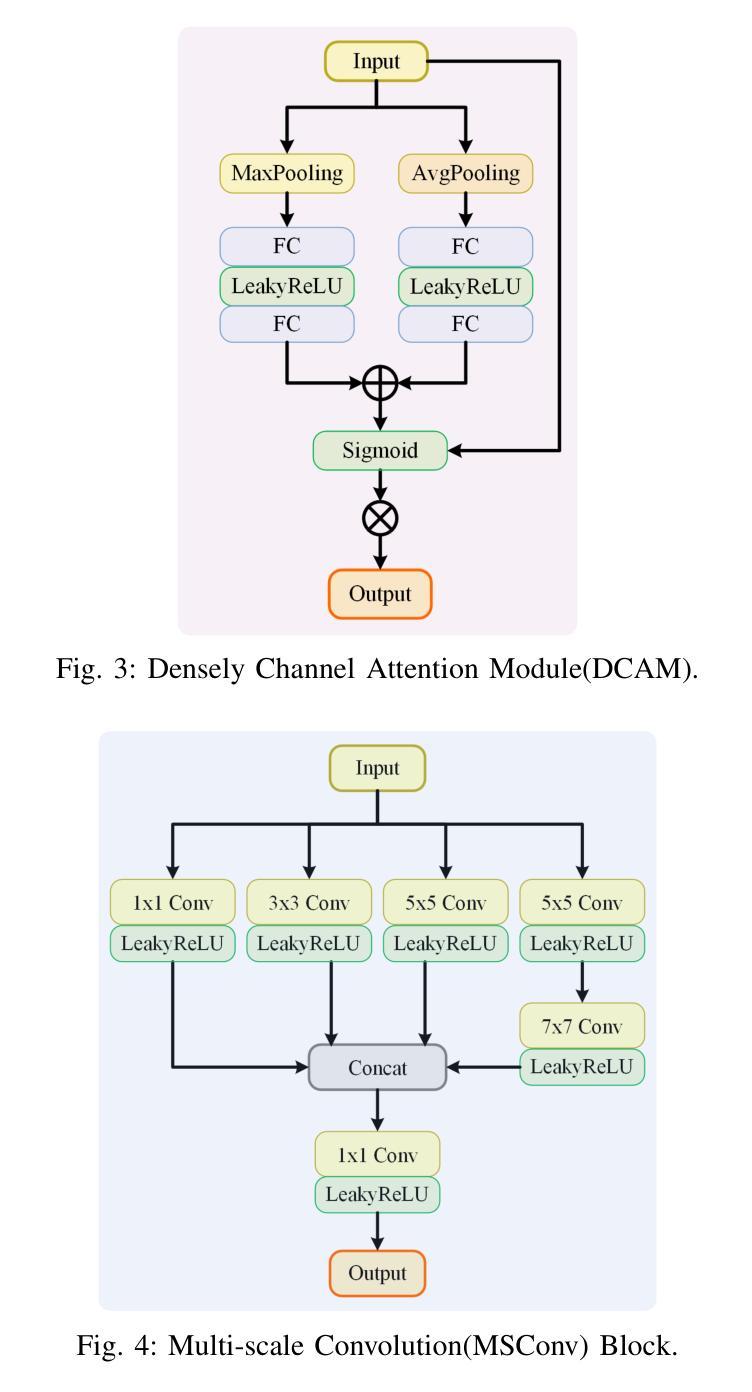
WTEFNet: Real-Time Low-Light Object Detection for Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems
Authors:Hao Wu, Junzhou Chen, Ronghui Zhang, Nengchao Lyu, Hongyu Hu, Yanyong Guo, Tony Z. Qiu
Object detection is a cornerstone of environmental perception in advanced driver assistance systems(ADAS). However, most existing methods rely on RGB cameras, which suffer from significant performance degradation under low-light conditions due to poor image quality. To address this challenge, we proposes WTEFNet, a real-time object detection framework specifically designed for low-light scenarios, with strong adaptability to mainstream detectors. WTEFNet comprises three core modules: a Low-Light Enhancement (LLE) module, a Wavelet-based Feature Extraction (WFE) module, and an Adaptive Fusion Detection (AFFD) module. The LLE enhances dark regions while suppressing overexposed areas; the WFE applies multi-level discrete wavelet transforms to isolate high- and low-frequency components, enabling effective denoising and structural feature retention; the AFFD fuses semantic and illumination features for robust detection. To support training and evaluation, we introduce GSN, a manually annotated dataset covering both clear and rainy night-time scenes. Extensive experiments on BDD100K, SHIFT, nuScenes, and GSN demonstrate that WTEFNet achieves state-of-the-art accuracy under low-light conditions. Furthermore, deployment on a embedded platform (NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin) confirms the framework’s suitability for real-time ADAS applications.
对象检测是先进驾驶辅助系统(ADAS)环境感知的基石。然而,大多数现有方法依赖于RGB相机,它们在低光条件下由于图像质量差而性能显著下降。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了WTEFNet,这是一个专为低光场景设计的实时对象检测框架,具有对主流检测器的强大适应性。WTEFNet包含三个核心模块:低光增强(LLE)模块、基于小波的特征提取(WFE)模块和自适应融合检测(AFFD)模块。LLE增强暗区同时抑制过曝区域;WFE应用多级离散小波变换以隔离高频和低频成分,从而实现有效的去噪和结构特征保留;AFFD融合语义和照明特征以实现稳健检测。为了支持训练和评估,我们引入了GSN,这是一个涵盖清晰和雨天夜间场景的手动注释数据集。在BDD100K、SHIFT、nuScenes和GSN上的大量实验表明,WTEFNet在低光条件下达到了最先进的准确性。此外,在嵌入式平台(NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin)上的部署证实了该框架适用于实时ADAS应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is expected to be submitted to IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement
Summary:
针对环境感知中的对象检测问题,特别是在低光照条件下的性能下降问题,提出了一种名为WTEFNet的实时对象检测框架。它包含三个核心模块:低光增强模块、基于小波的特征提取模块和自适应融合检测模块。为支持训练和评估,引入了GSN数据集。实验表明,WTEFNet在低光照条件下实现了最先进的准确性,并适用于嵌入式平台的实时应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 对象检测是ADAS环境感知的核心。
- 现有方法主要依赖RGB相机,在低光照条件下性能下降。
- WTEFNet框架专为低光照场景设计,具有主流检测器的强适应性。
- WTEFNet包含三个核心模块:低光增强模块、基于小波的特征提取模块和自适应融合检测模块。
- GSN数据集用于支持训练和评估,包含清晰和雨天夜间场景。
- 实验表明,WTEFNet在低光照条件下实现先进准确性。
点此查看论文截图

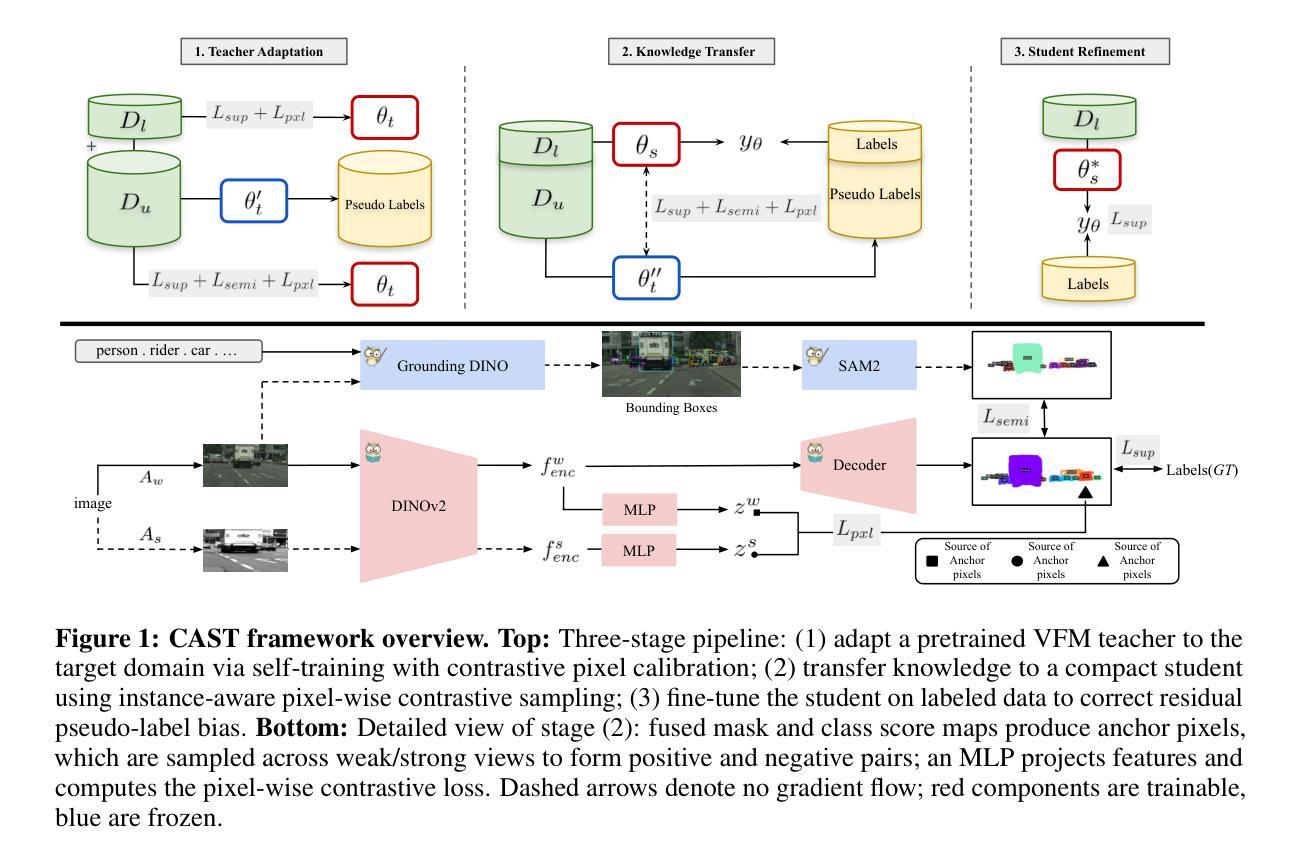
CAST: Contrastive Adaptation and Distillation for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
Authors:Pardis Taghavi, Tian Liu, Renjie Li, Reza Langari, Zhengzhong Tu
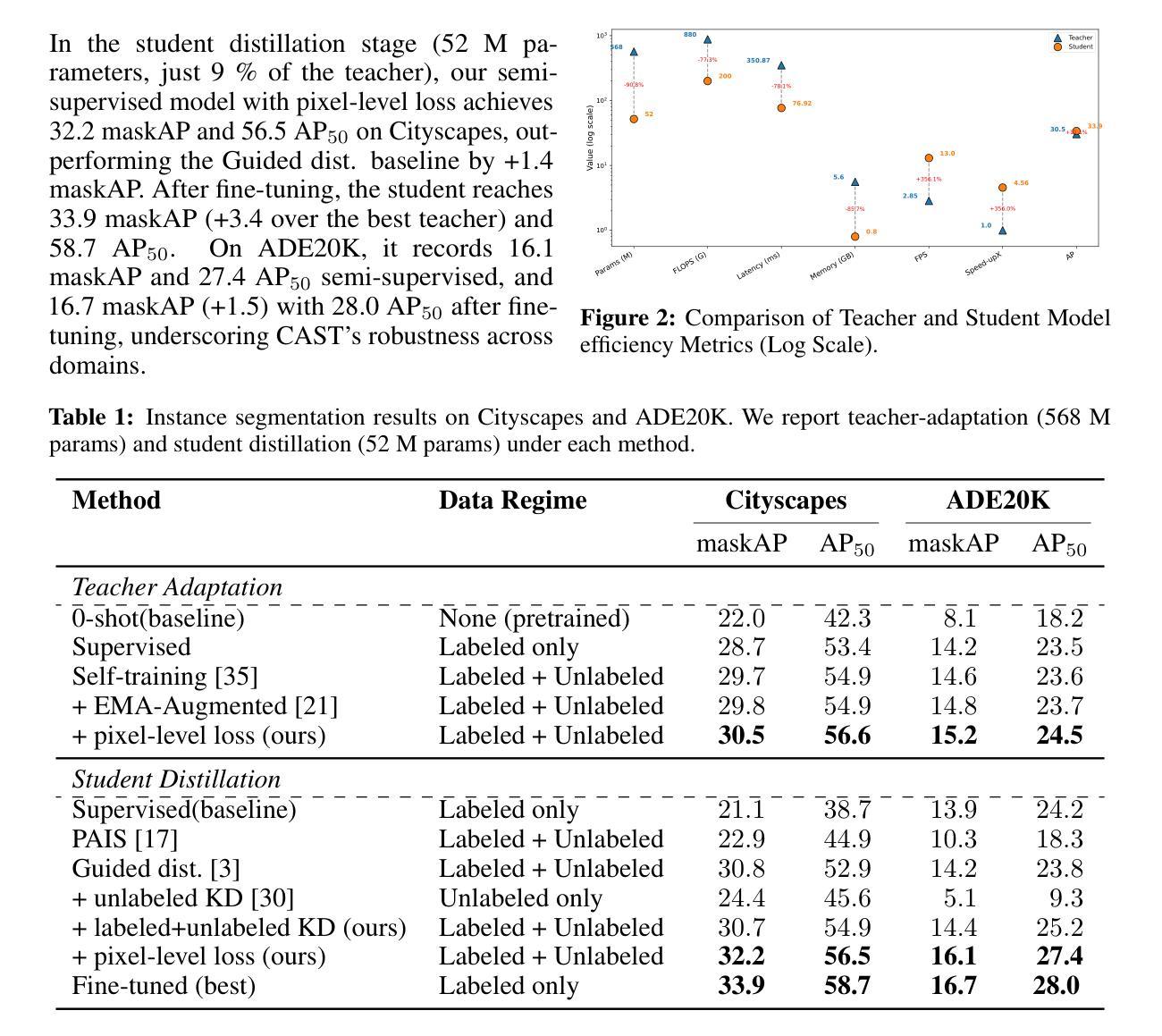
Instance segmentation demands costly per-pixel annotations and large models. We introduce CAST, a semi-supervised knowledge distillation (SSKD) framework that compresses pretrained vision foundation models (VFM) into compact experts using limited labeled and abundant unlabeled data. CAST unfolds in three stages: (1) domain adaptation of the VFM teacher(s) via self-training with contrastive pixel calibration, (2) distillation into a compact student via a unified multi-objective loss that couples standard supervision and pseudo-labels with our instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive term, and (3) fine-tuning on labeled data to remove residual pseudo-label bias. Central to CAST is an \emph{instance-aware pixel-wise contrastive loss} that fuses mask and class scores to mine informative negatives and enforce clear inter-instance margins. By maintaining this contrastive signal across both adaptation and distillation, we align teacher and student embeddings and fully leverage unlabeled images. On Cityscapes and ADE20K, our ~11X smaller student surpasses its adapted VFM teacher(s) by +3.4 AP (33.9 vs. 30.5) and +1.5 AP (16.7 vs. 15.2) and outperforms state-of-the-art semi-supervised approaches.
实例分割需要昂贵的像素级标注和大模型。我们引入了CAST,这是一种半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)框架,它利用有限的标记数据和大量的无标记数据,将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST分为三个阶段:(1)通过对比像素校准进行自我训练,对VFM教师进行域适应;(2)通过统一的多目标损失进行蒸馏,该损失将标准监督和伪标签与我们的实例感知像素级对比项相结合,形成一个紧凑的学生模型;(3)在标记数据上进行微调,以消除剩余的伪标签偏见。CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,它融合掩膜和类别分数来挖掘信息阴性样本并强制实施清晰的实例间边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持这种对比信号,我们对齐教师和学生嵌入,并充分利用无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K上,我们较小的~11倍学生模型超越了其适应的VFM教师模型,分别提高了+3.4 AP(33.9对30.5)和+1.5 AP(16.7对15.2),并优于最新的半监督方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了基于半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)的CAST框架,利用有限的标注数据和大量的无标签数据将预训练的视觉基础模型(VFM)压缩成紧凑的专家模型。CAST包括三个阶段:VFM教师的域自适应、通过统一的多目标损失蒸馏到紧凑的学生模型,以及在有标签数据上进行微调以消除残留的伪标签偏差。核心在于实例感知像素级对比损失,它融合了掩膜和类分数来挖掘信息性负样本并强制执行清晰的实例间边界。通过在整个适应和蒸馏过程中保持对比信号,我们使教师和学生嵌入对齐并充分利用无标签图像。在Cityscapes和ADE20K数据集上,我们的学生模型超过了其适应的VFM教师模型,并优于最新的半监督方法。
Key Takeaways:
- CAST是一个基于半监督知识蒸馏(SSKD)的框架,旨在利用有限的标注数据和大量的无标签数据。
- CAST包括三个阶段:VFM教师的域自适应、蒸馏到紧凑的学生模型,以及微调阶段以消除伪标签偏差。
- CAST的核心是实例感知像素级对比损失,能融合掩膜和类分数来挖掘信息性负样本并强制执行清晰的实例间边界。
- CAST通过在整个过程中保持对比信号,使教师和学生嵌入对齐,并充分利用无标签图像。
- 在Cityscapes和ADE20K数据集上,CAST框架表现优异,学生模型超越了其适应的VFM教师模型。
- CAST框架的性能优于现有的半监督方法。
点此查看论文截图

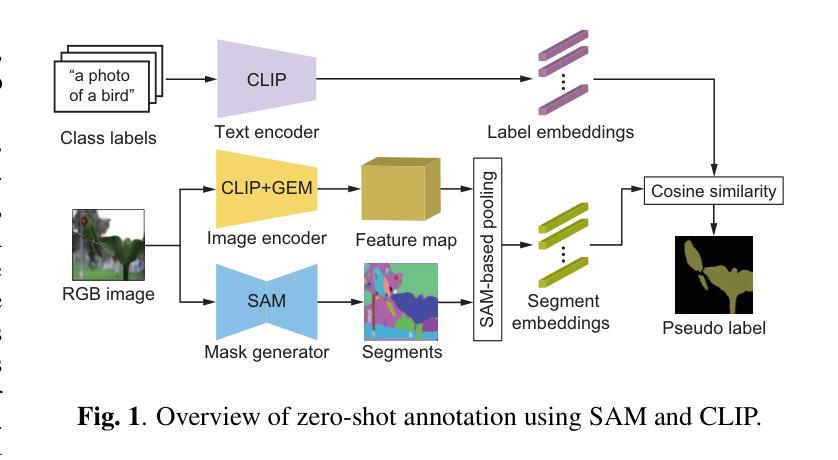
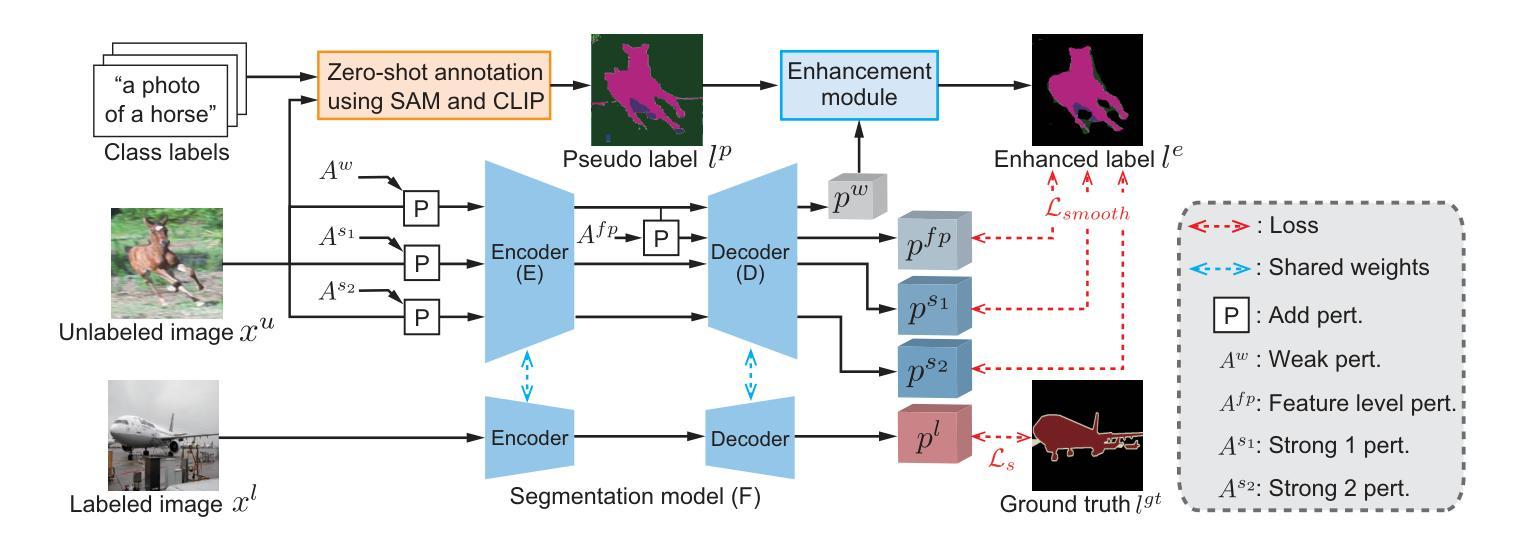
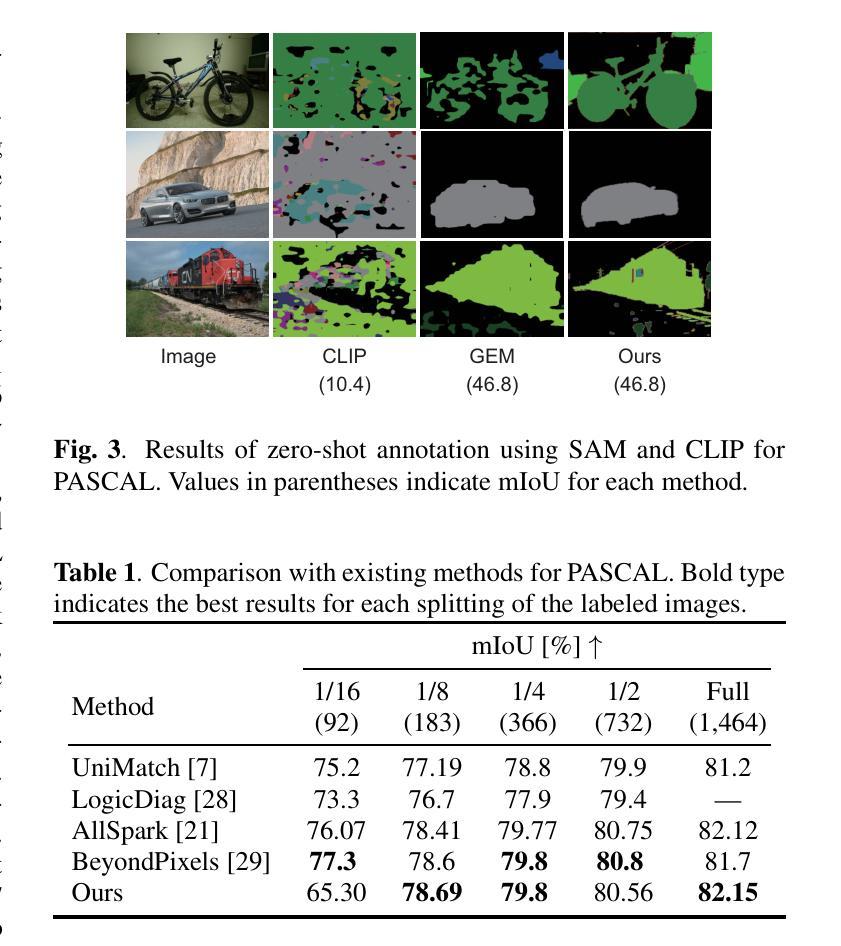
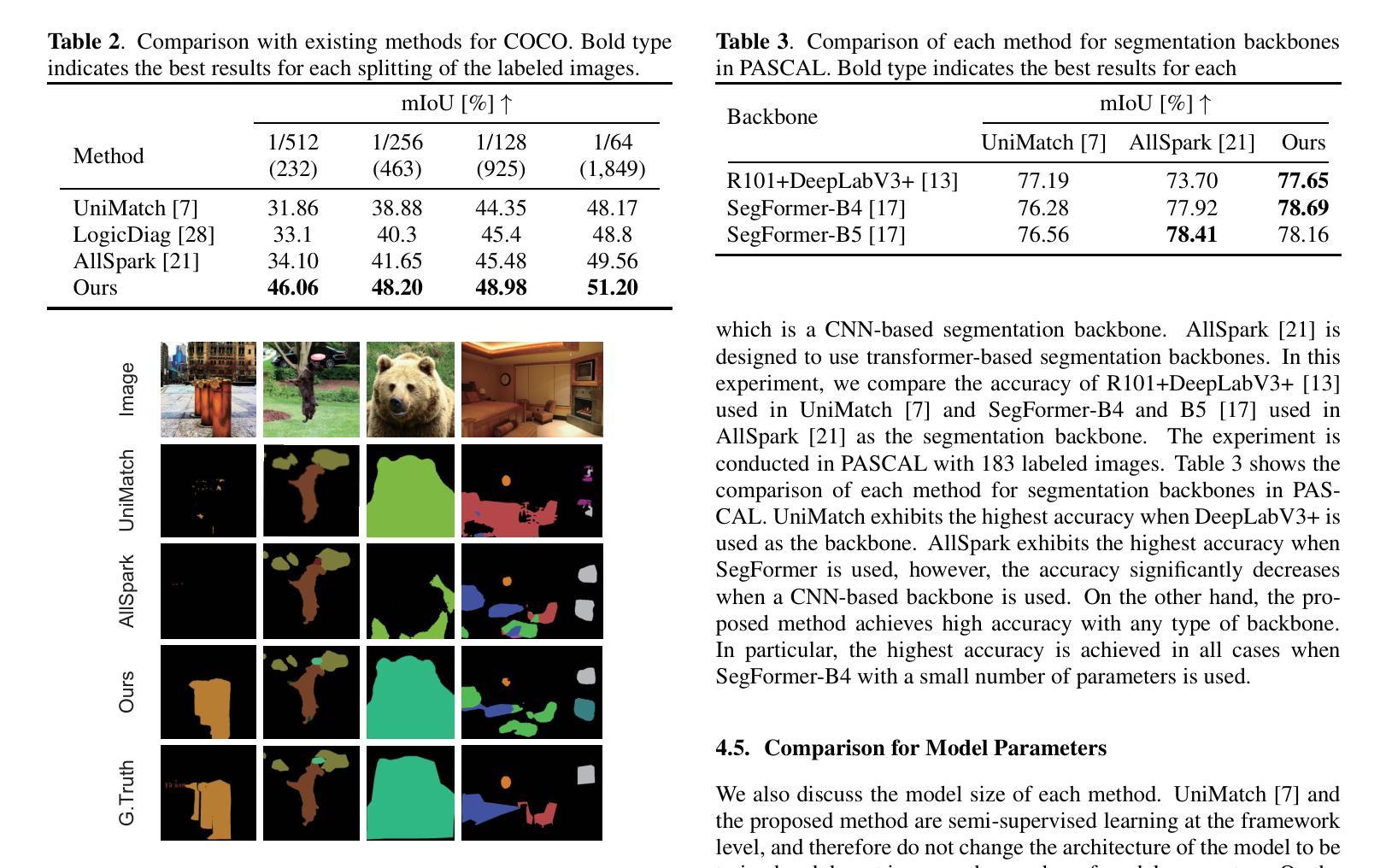
Zero-Shot Pseudo Labels Generation Using SAM and CLIP for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Nagito Saito, Shintaro Ito, Koichi Ito, Takafumi Aoki
Semantic segmentation is a fundamental task in medical image analysis and autonomous driving and has a problem with the high cost of annotating the labels required in training. To address this problem, semantic segmentation methods based on semi-supervised learning with a small number of labeled data have been proposed. For example, one approach is to train a semantic segmentation model using images with annotated labels and pseudo labels. In this approach, the accuracy of the semantic segmentation model depends on the quality of the pseudo labels, and the quality of the pseudo labels depends on the performance of the model to be trained and the amount of data with annotated labels. In this paper, we generate pseudo labels using zero-shot annotation with the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP), improve the accuracy of the pseudo labels using the Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach (UniMatch), and use them as enhanced labels to train a semantic segmentation model. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through the experiments using the public datasets: PASCAL and MS COCO. The project web page is available at: https://gsisaoki.github.io/ZERO-SHOT-PLG/
语义分割是医学图像分析和自动驾驶中的一项基本任务,并存在训练所需标签标注成本高昂的问题。为了解决这一问题,已经提出了基于少量标注数据的半监督学习的语义分割方法。例如,一种方法是通过带有标注标签和伪标签的图像来训练语义分割模型。该方法的语义分割模型的精度取决于伪标签的质量,而伪标签的质量又取决于待训练模型的性能以及标注标签的数据量。在本文中,我们使用零镜头注释(Zero-Shot Annotation)技术结合Segment Anything模型(SAM)和对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)生成伪标签,通过统一双流扰动方法(UniMatch)提高伪标签的准确性,并将它们作为增强标签来训练语义分割模型。该方法的有效性通过公共数据集PASCAL和MS COCO的实验得到了验证。项目网页位于:[https://gsisaoki.github.io/ZERO-SHOT-PLG/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对语义分割任务中高标注成本的问题,提出了一种基于半监督学习的方法,使用少量标注数据进行训练。通过结合Segment Anything Model (SAM)和Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP)生成伪标签,并采用Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach (UniMatch)提高伪标签的质量,最后使用这些增强的标签训练语义分割模型。实验在公共数据集PASCAL和MS COCO上进行,证明了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割是医疗图像分析和自动驾驶中的基础任务,但标注成本高昂。
- 提出了一种基于半监督学习的语义分割方法,仅使用少量标注数据进行训练。
- 结合Segment Anything Model (SAM)和Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP)生成伪标签。
- 采用Unified Dual-Stream Perturbations Approach (UniMatch)提高伪标签的质量。
- 使用增强的标签训练语义分割模型。
- 在公共数据集PASCAL和MS COCO上的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图