⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
FMG-Det: Foundation Model Guided Robust Object Detection
Authors:Darryl Hannan, Timothy Doster, Henry Kvinge, Adam Attarian, Yijing Watkins
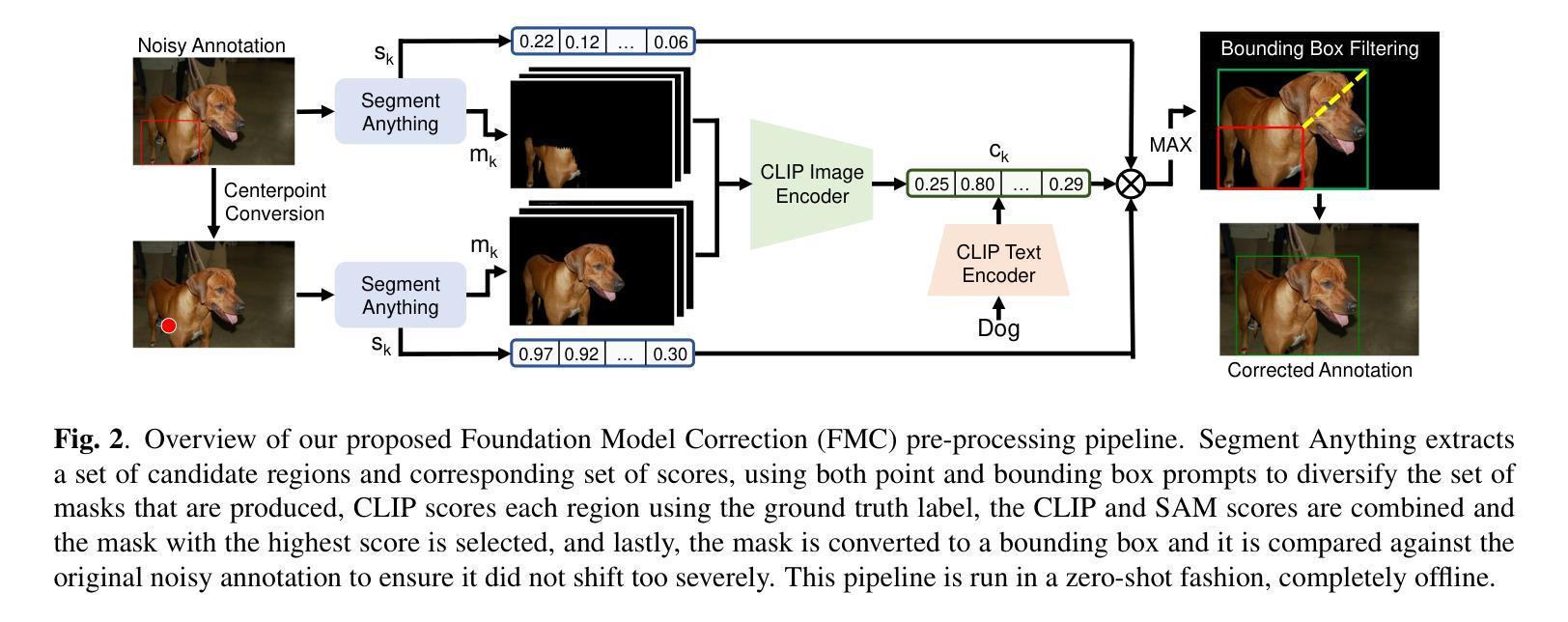
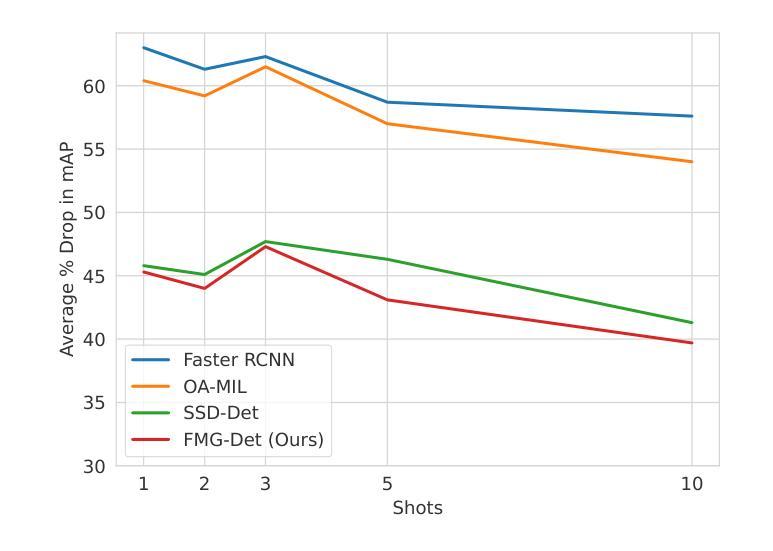
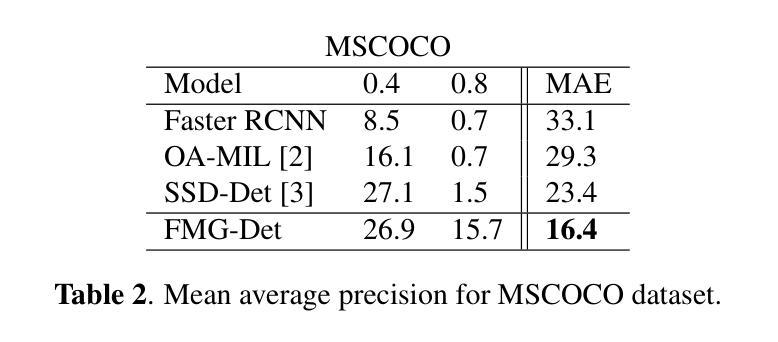
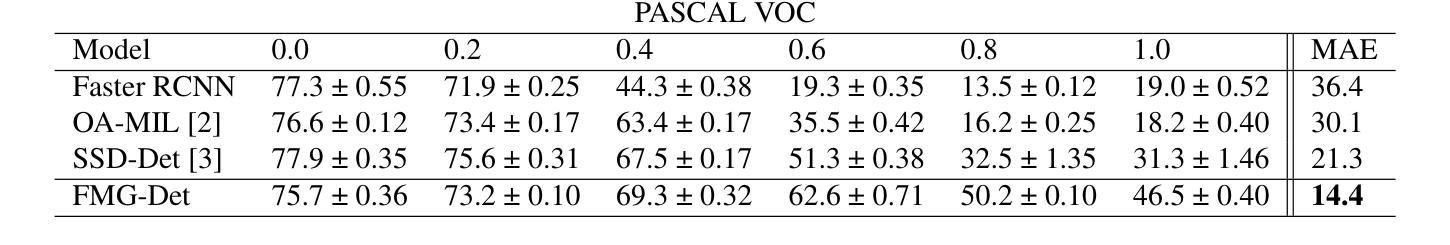
Collecting high quality data for object detection tasks is challenging due to the inherent subjectivity in labeling the boundaries of an object. This makes it difficult to not only collect consistent annotations across a dataset but also to validate them, as no two annotators are likely to label the same object using the exact same coordinates. These challenges are further compounded when object boundaries are partially visible or blurred, which can be the case in many domains. Training on noisy annotations significantly degrades detector performance, rendering them unusable, particularly in few-shot settings, where just a few corrupted annotations can impact model performance. In this work, we propose FMG-Det, a simple, efficient methodology for training models with noisy annotations. More specifically, we propose combining a multiple instance learning (MIL) framework with a pre-processing pipeline that leverages powerful foundation models to correct labels prior to training. This pre-processing pipeline, along with slight modifications to the detector head, results in state-of-the-art performance across a number of datasets, for both standard and few-shot scenarios, while being much simpler and more efficient than other approaches.
收集高质量的对象检测任务数据是一个挑战,因为标注对象边界存在固有的主观性。这导致不仅在数据集上收集一致的注释变得困难,而且验证它们也变得困难,因为两个注释者不太可能使用完全相同的坐标来标注同一对象。当对象边界部分可见或模糊时,这些挑战会进一步加剧,这在许多领域都可能是这种情况。在有噪声的注释上进行训练会显著降低检测器的性能,使其无法使用,特别是在小样本设置中,几个损坏的注释就会影响模型性能。在本工作中,我们提出了FMG-Det,这是一种用于在有噪声的注释上训练模型简单高效的方法。更具体地说,我们提议将多实例学习(MIL)框架与预处理管道相结合,该管道利用强大的基础模型在训练之前校正标签。该预处理管道与检测器头部的轻微修改相结合,在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,无论是标准场景还是小样本场景,同时比其他方法更简单、更高效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, ICIP 2025
Summary
本文提出一种简单高效的方法FMG-Det,用于在带有噪声标注的数据集上进行模型训练。该方法结合了多重实例学习(MIL)框架和一个预处理管道,利用强大的基础模型在训练前进行标签校正。此预处理管道与检测器头部的轻微修改相结合,可在多个数据集上实现标准与少样本场景的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 数据收集是目标检测任务中的一大挑战,标注对象边界具有主观性,导致跨数据集难以获得一致的注释并对其进行验证。
- 当对象边界部分可见或模糊时,挑战进一步加大,这在许多领域都可能是常态。
- 噪声标注会对检测器性能造成严重影响,特别是在少样本场景下,几个被损坏的标注就会影响模型性能。
- 提出了一种新的方法FMG-Det,结合多重实例学习(MIL)框架和预处理管道来解决噪声标注问题。
- 预处理管道利用强大的基础模型在训练前进行标签校正,可以提高模型对各种数据集的处理能力。
- FMG-Det在标准与少样本场景下的多个数据集上实现了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

Few-Shot Speech Deepfake Detection Adaptation with Gaussian Processes
Authors:Neta Glazer, David Chernin, Idan Achituve, Sharon Gannot, Ethan Fetaya
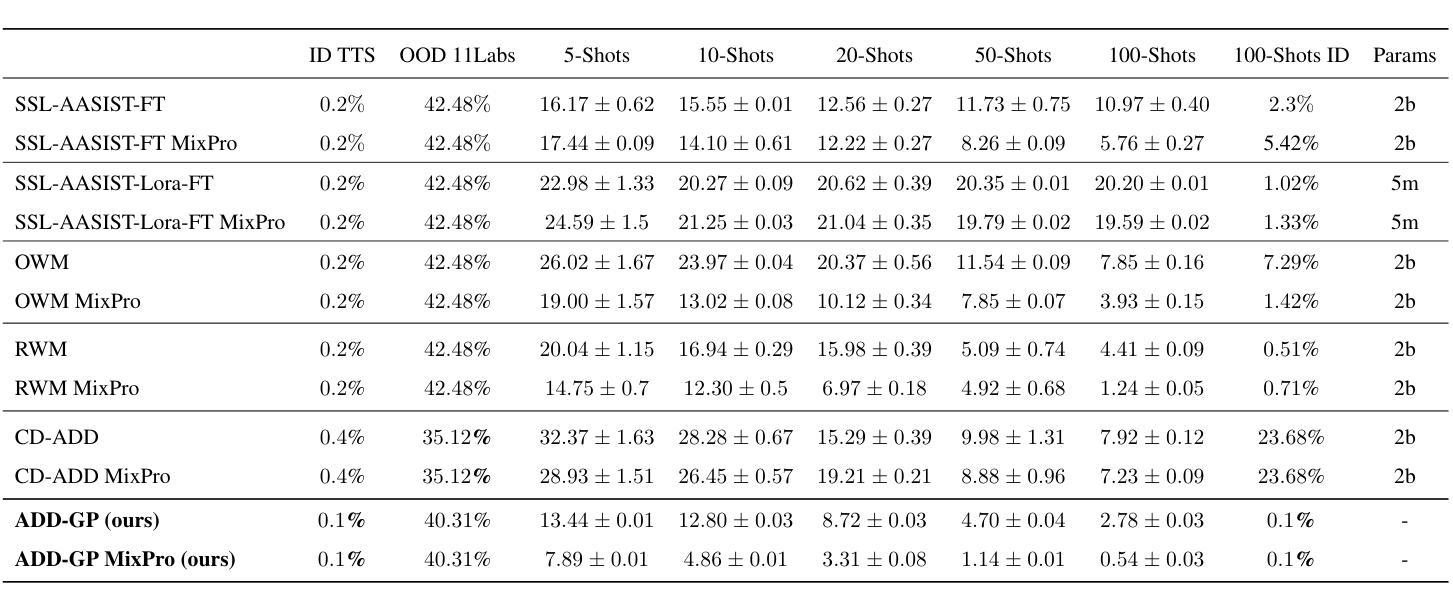
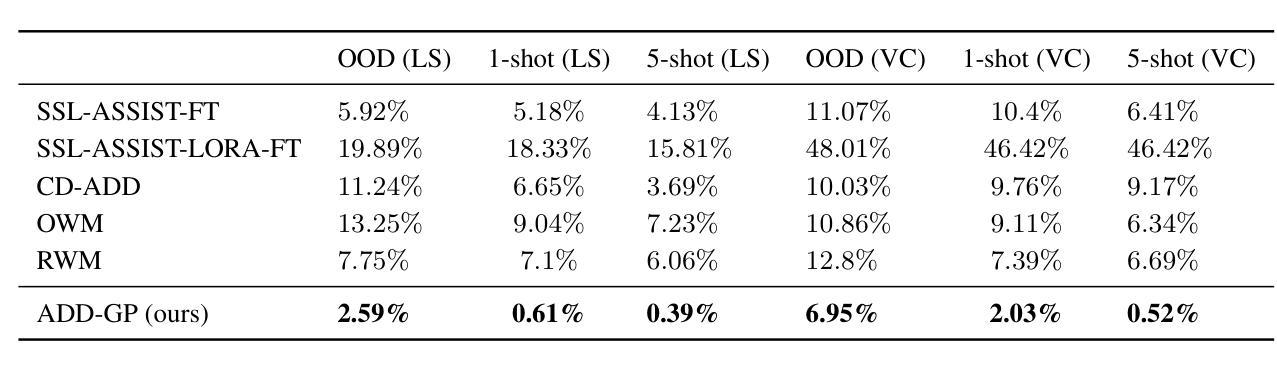
Recent advancements in Text-to-Speech (TTS) models, particularly in voice cloning, have intensified the demand for adaptable and efficient deepfake detection methods. As TTS systems continue to evolve, detection models must be able to efficiently adapt to previously unseen generation models with minimal data. This paper introduces ADD-GP, a few-shot adaptive framework based on a Gaussian Process (GP) classifier for Audio Deepfake Detection (ADD). We show how the combination of a powerful deep embedding model with the Gaussian processes flexibility can achieve strong performance and adaptability. Additionally, we show this approach can also be used for personalized detection, with greater robustness to new TTS models and one-shot adaptability. To support our evaluation, a benchmark dataset is constructed for this task using new state-of-the-art voice cloning models.
近期文本转语音(TTS)模型的进步,尤其是在语音克隆方面,进一步加剧了对自适应和高效深度伪造检测方法的需求。随着TTS系统的不断发展,检测模型必须能够以最小的数据量高效地适应以前未见过的生成模型。本文介绍了ADD-GP,这是一种基于高斯过程(GP)分类器的音频深度伪造检测(ADD)的少量自适应框架。我们展示了强大的深度嵌入模型与高斯过程的灵活性相结合如何实现强大的性能和适应性。此外,我们还展示了这种方法也可用于个性化检测,对新TTS模型的鲁棒性更强,并具有一次适应性。为了支持我们的评估,我们使用最新的语音克隆模型构建了用于此任务的标准数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期文本转语音(TTS)模型的进步,特别是语音克隆领域的发展,使得对适应性高且高效的深度伪造检测方法的呼声上升。文章提出了ADD-GP模型,该模型结合了高斯过程分类器和深度嵌入模型的特点,以实现高效而适应多变的音频深度伪造检测(ADD)。研究表明,ADD-GP框架具有良好的性能表现及对新模型的适应性,并支持个性化检测,尤其是对新出现的TTS模型的健壮性尤为突出,并能进行单例适应性。此外,该研究通过采用最新语音克隆模型构建基准数据集,对提出的方案进行了全面评估。
Key Takeaways
- TTS模型的最新进展推动了深度伪造检测方法的进化需求。
- ADD-GP模型结合了高斯过程分类器和深度嵌入模型的优势。
- ADD-GP框架表现出强大的性能和适应性,尤其是对新出现的TTS模型的健壮性突出。
- 该方法支持个性化检测并具有单例适应性。
- 采用最新语音克隆模型构建的基准数据集用于评估该方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Hierarchical Material Recognition from Local Appearance
Authors:Matthew Beveridge, Shree K. Nayar
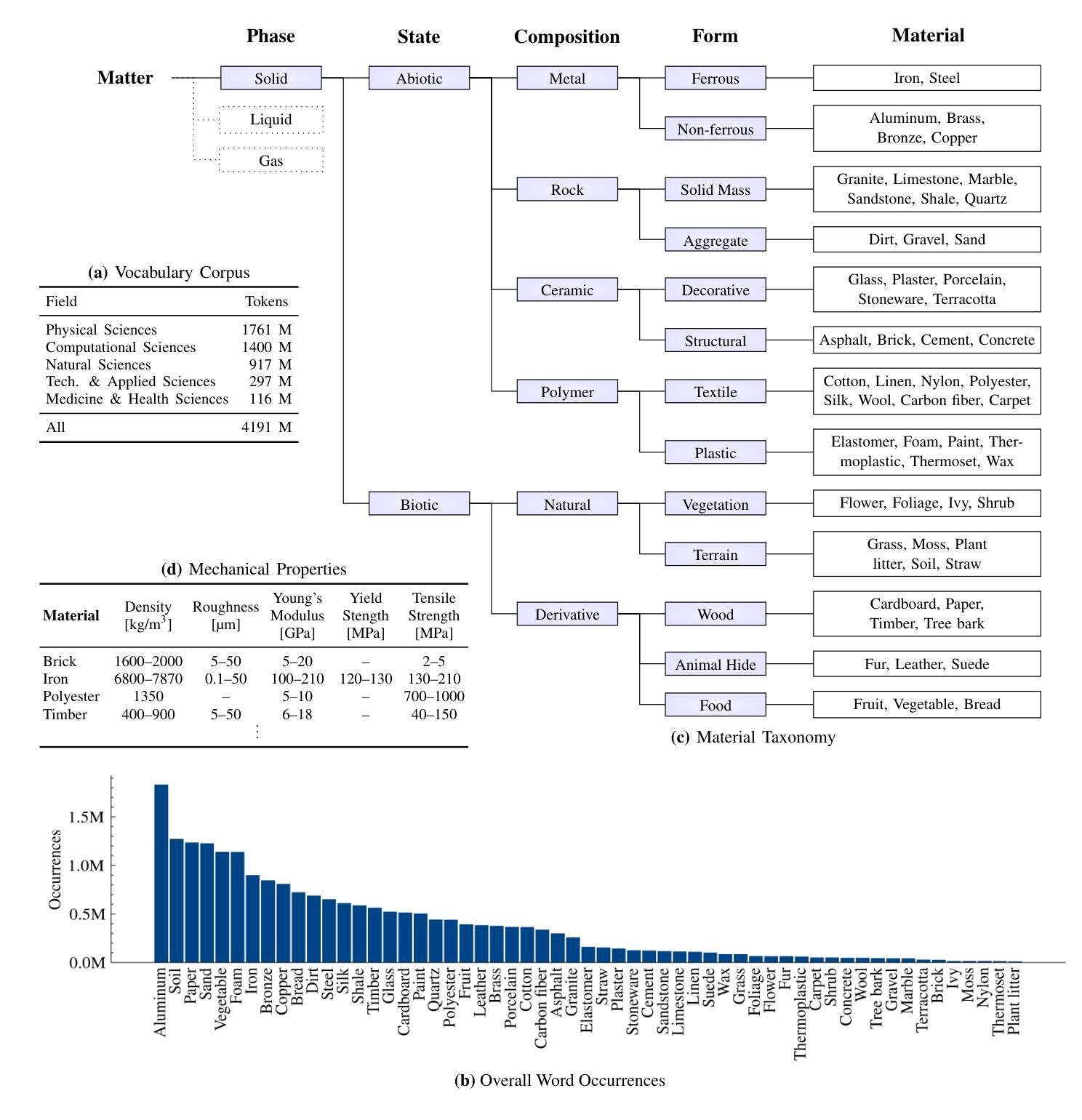
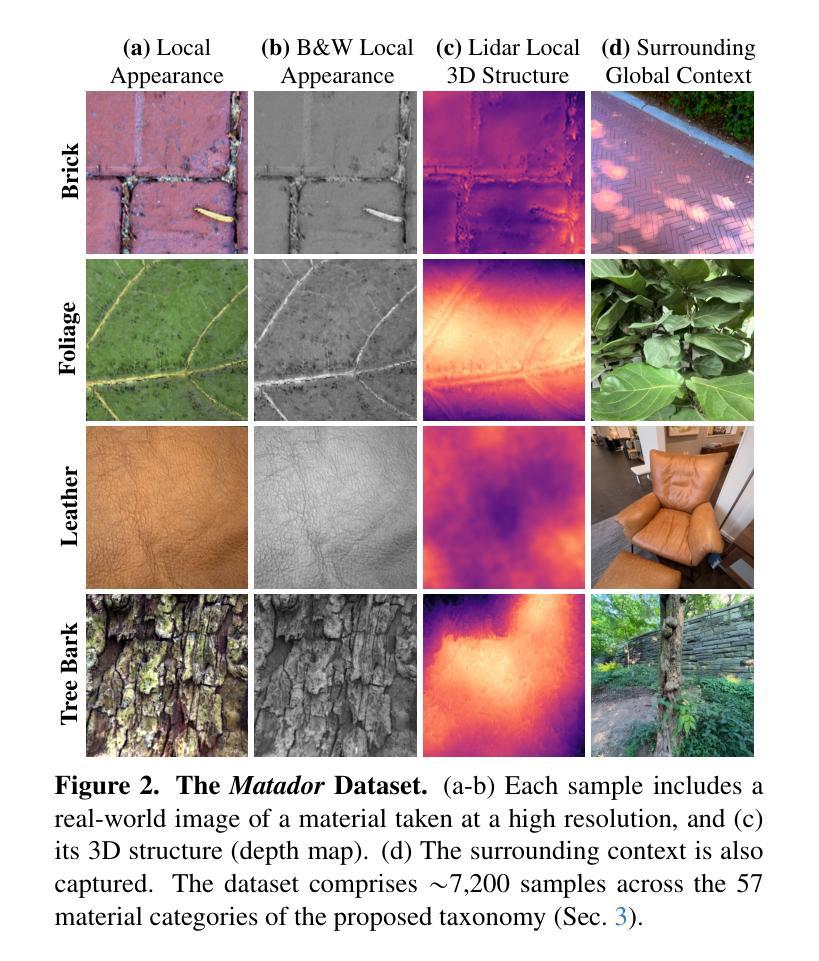
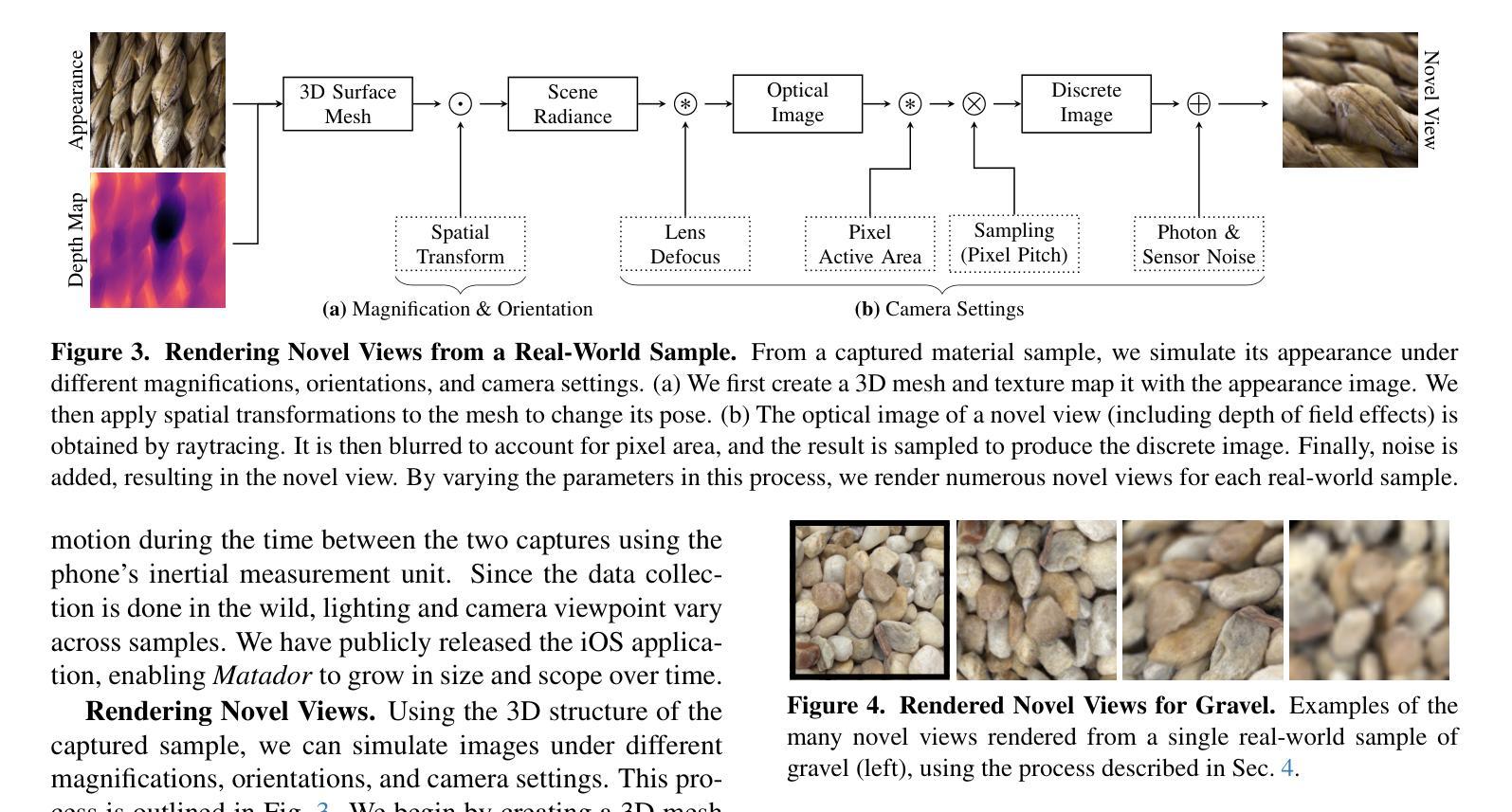
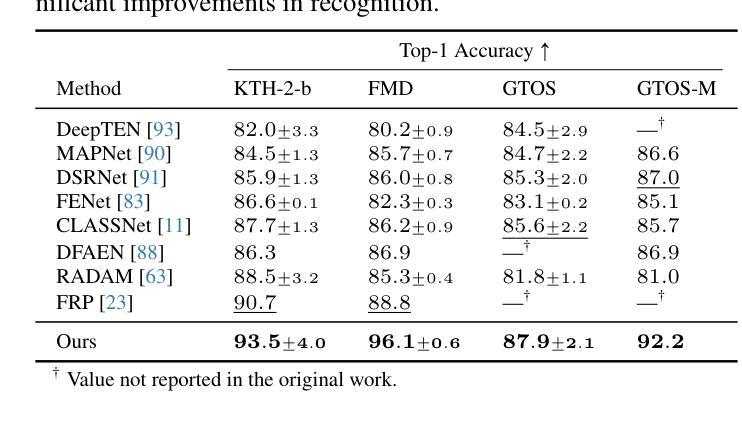
We introduce a taxonomy of materials for hierarchical recognition from local appearance. Our taxonomy is motivated by vision applications and is arranged according to the physical traits of materials. We contribute a diverse, in-the-wild dataset with images and depth maps of the taxonomy classes. Utilizing the taxonomy and dataset, we present a method for hierarchical material recognition based on graph attention networks. Our model leverages the taxonomic proximity between classes and achieves state-of-the-art performance. We demonstrate the model’s potential to generalize to adverse, real-world imaging conditions, and that novel views rendered using the depth maps can enhance this capability. Finally, we show the model’s capacity to rapidly learn new materials in a few-shot learning setting.
我们介绍了一种用于从局部外观进行层次识别的材料分类。我们的分类学受视觉应用的启发,根据材料的物理特征进行排列。我们贡献了一个包含分类图像和深度图的多样化野外数据集。利用分类和数据集,我们提出了一种基于图注意力网络的层次材料识别方法。我们的模型利用类之间的分类邻近性,实现了最先进的性能。我们证明了该模型在恶劣的、真实世界的成像条件下具有推广潜力,以及使用深度图呈现的新视角可以增强这一能力。最后,我们展示了该模型在少量学习环境中快速学习新材料的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于局部外观的用于层次识别的材料分类体系。该分类体系以视觉应用为动机,根据材料的物理特征进行排列。文章贡献了一个包含分类类别图像和深度图的野外数据集,并提出了一种基于图注意力网络的方法来进行层次材料识别。该方法利用类别之间的分类接近性,实现了最先进的性能。文章展示了该模型在恶劣现实成像条件下的泛化潜力,以及使用深度图渲染的新视角增强此能力的可能性。最后,展示了该模型在少量学习场景中的快速学习新材料的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于视觉应用的材料分类体系,该体系根据材料的物理特征进行分类。
- 提供了一个包含图像和深度图的野外数据集,用于层次材料识别研究。
- 提出了一种基于图注意力网络的层次材料识别方法,该方法利用类别之间的分类接近性。
- 该模型在恶劣现实成像条件下具有良好的泛化能力。
- 使用深度图渲染的新视角可以增强模型的识别能力。
- 模型具有快速学习新材料的能力,在少量学习场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

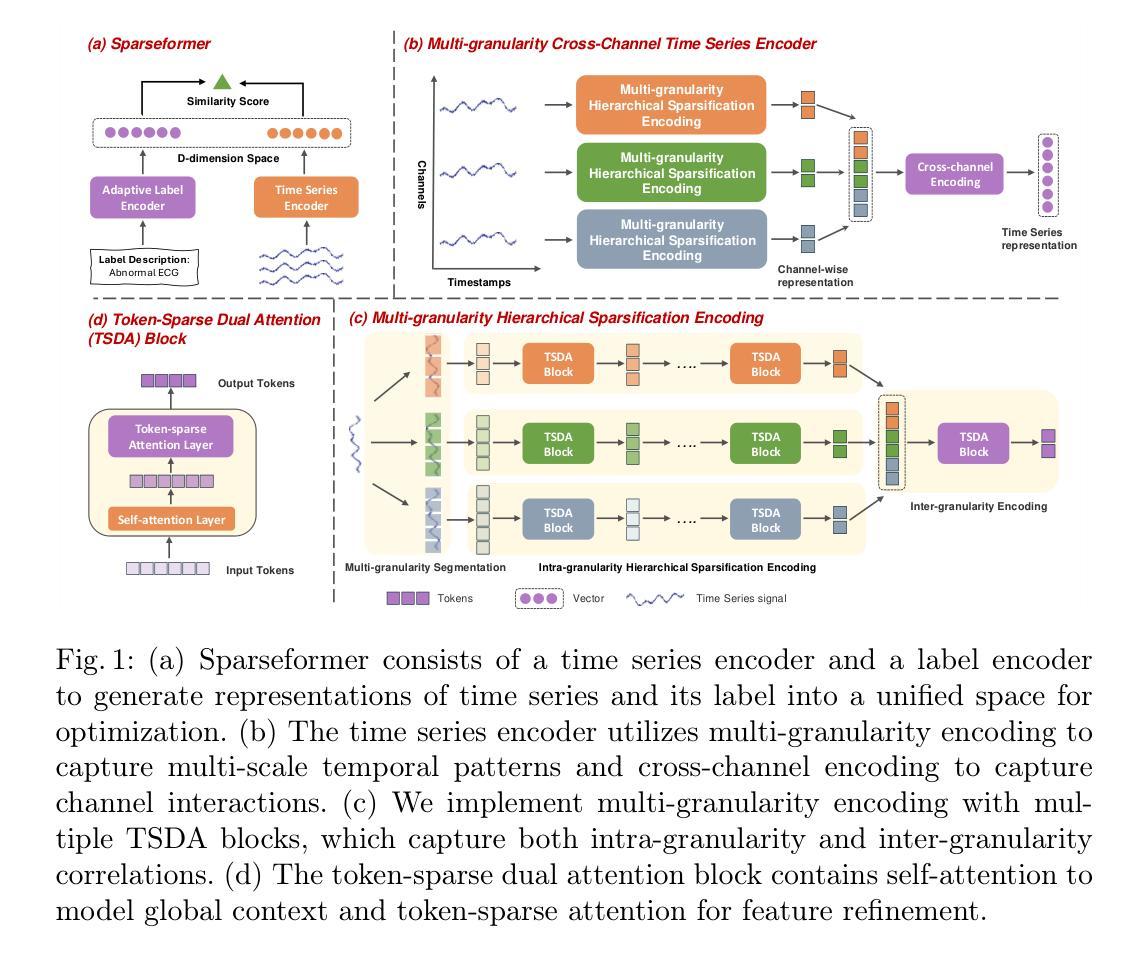
Sparseformer: a Transferable Transformer with Multi-granularity Token Sparsification for Medical Time Series Classification
Authors:Jiexia Ye, Weiqi Zhang, Ziyue Li, Jia Li, Fugee Tsung
Medical time series (MedTS) classification is crucial for improved diagnosis in healthcare, and yet it is challenging due to the varying granularity of patterns, intricate inter-channel correlation, information redundancy, and label scarcity. While existing transformer-based models have shown promise in time series analysis, they mainly focus on forecasting and fail to fully exploit the distinctive characteristics of MedTS data. In this paper, we introduce Sparseformer, a transformer specifically designed for MedTS classification. We propose a sparse token-based dual-attention mechanism that enables global modeling and token compression, allowing dynamic focus on the most informative tokens while distilling redundant features. This mechanism is then applied to the multi-granularity, cross-channel encoding of medical signals, capturing intra- and inter-granularity correlations and inter-channel connections. The sparsification design allows our model to handle heterogeneous inputs of varying lengths and channels directly. Further, we introduce an adaptive label encoder to address label space misalignment across datasets, equipping our model with cross-dataset transferability to alleviate the medical label scarcity issue. Our model outperforms 12 baselines across seven medical datasets under supervised learning. In the few-shot learning experiments, our model also achieves superior average results. In addition, the in-domain and cross-domain experiments among three diagnostic scenarios demonstrate our model’s zero-shot learning capability. Collectively, these findings underscore the robustness and transferability of our model in various medical applications.
医疗时间序列(MedTS)分类对于改进医疗保健中的诊断至关重要,然而由于模式的不同粒度、复杂的跨通道相关性、信息冗余和标签稀缺,它仍然是一个挑战。尽管现有的基于变压器的模型在时间序列分析中显示出希望,但它们主要侧重于预测,未能充分利用MedTS数据的特征。在本文中,我们介绍了Sparseformer,这是一个专为MedTS分类设计的变压器。我们提出了一种基于稀疏标记的双重注意力机制,能够实现全局建模和标记压缩,允许动态关注最具信息的标记,同时提炼冗余特征。然后,该机制应用于医疗信号的多粒度、跨通道编码,捕获粒度和跨粒度关联以及跨通道连接。稀疏化设计允许我们的模型直接处理不同长度和通道的异构输入。此外,我们引入了一种自适应标签编码器来解决数据集之间标签空间的不对齐问题,为我们的模型配备跨数据集的可转移性,以缓解医疗标签稀缺问题。我们的模型在七个医疗数据集的监督学习下超越了12个基准测试。在少量学习实验中,我们的模型也取得了优越的平均结果。此外,三个诊断场景中的域内和跨域实验证明了我们的模型的零样本学习能力。总的来说,这些发现凸显了我们的模型在各种医疗应用中的稳健性和可转移性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 3 figures, 16 pages, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出了一个专为医疗时间序列分类设计的Sparseformer模型。该模型采用稀疏标记的基于双注意力机制,实现全局建模和标记压缩,能够动态关注最具信息量的标记并过滤冗余特征。该模型应用于医疗信号的跨粒度、跨通道编码,捕捉内部和外部粒度的关联和通道间的连接。其稀疏设计可处理不同长度和通道的异质输入。此外,为解决标签空间跨数据集的对齐问题,模型引入了自适应标签编码器,赋予了其跨数据集迁移能力,以缓解医疗标签稀缺的问题。Sparseformer模型在七个医疗数据集上的监督学习表现优于十二个基线模型。在少量的学习中,我们的模型也取得了优异的平均结果。同时,跨三种诊断场景的实验表明,该模型还具备零样本学习能力。这些结果突显了模型在各种医疗应用中的稳健性和迁移能力。
Key Takeaways
- Sparseformer是一个专为医疗时间序列分类设计的变压器模型。
- 模型采用稀疏标记的基于双注意力机制,实现全局建模和标记压缩。
- 该模型能够处理不同长度和通道的异质输入。
- 引入自适应标签编码器以解决跨数据集的标签空间对齐问题。
- Sparseformer在多个医疗数据集上的监督学习表现优于其他模型。
- 在少量学习场景中,Sparseformer也表现出优异的性能。
- 模型具备零样本学习能力,突显了其稳健性和迁移能力。
点此查看论文截图

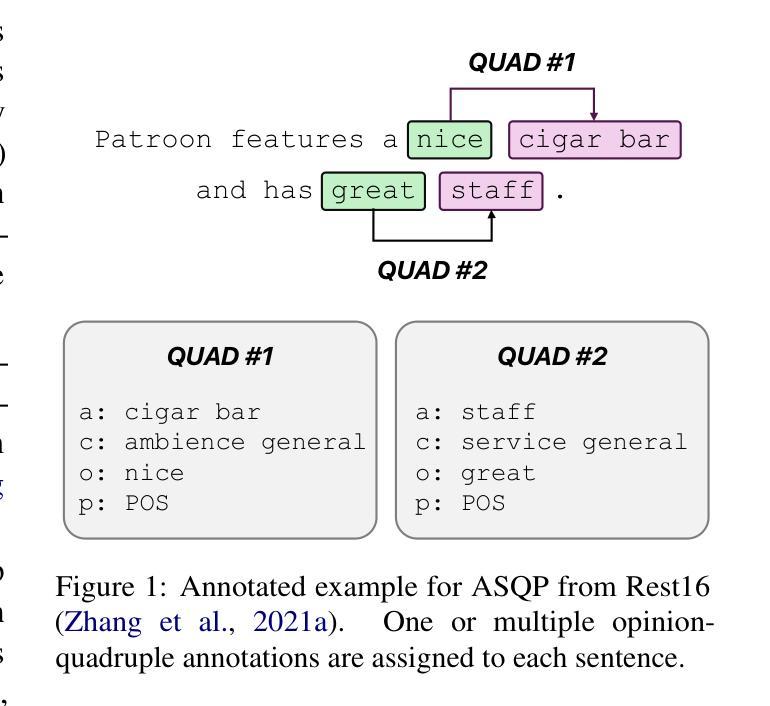
Do we still need Human Annotators? Prompting Large Language Models for Aspect Sentiment Quad Prediction
Authors:Nils Constantin Hellwig, Jakob Fehle, Udo Kruschwitz, Christian Wolff
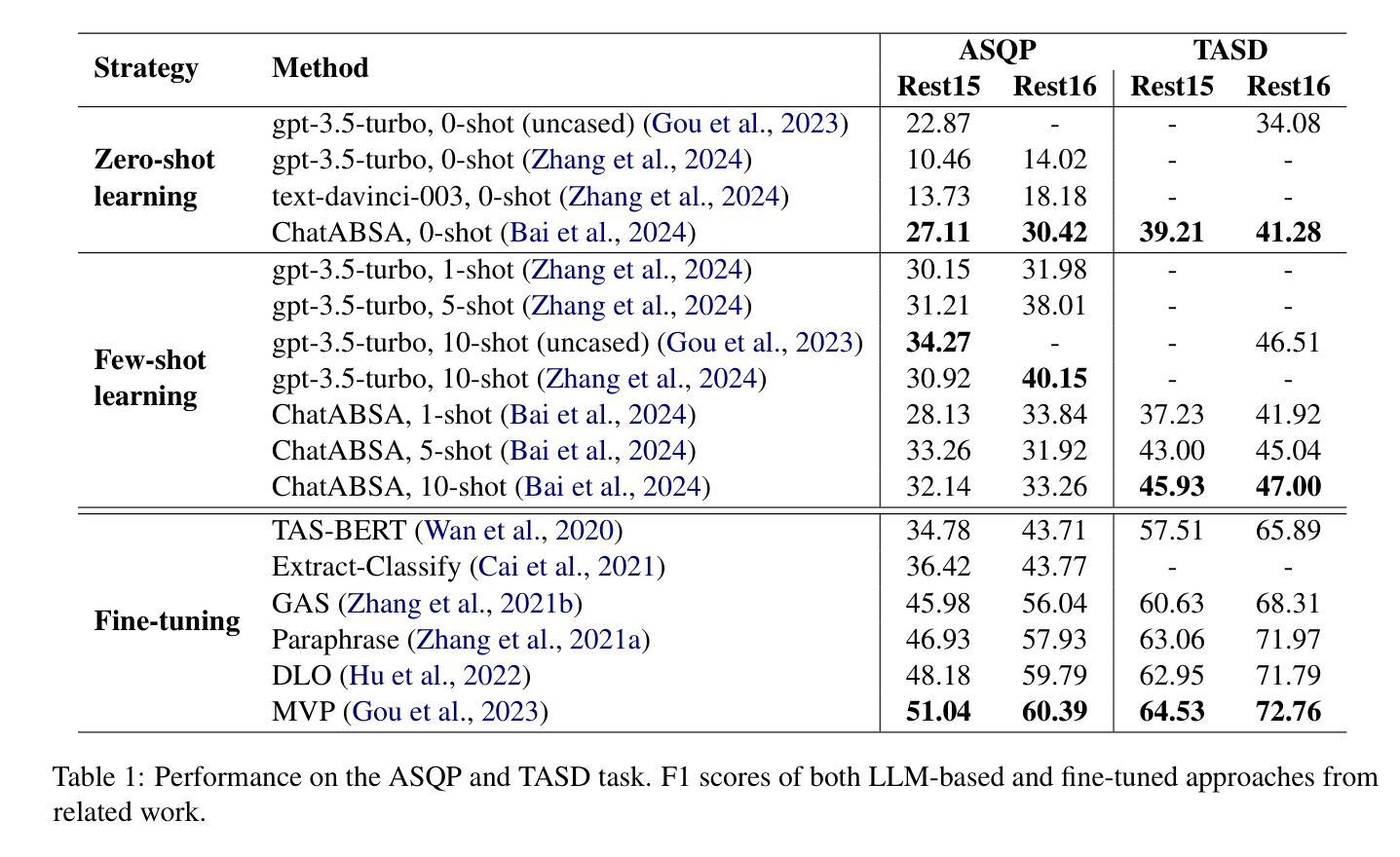
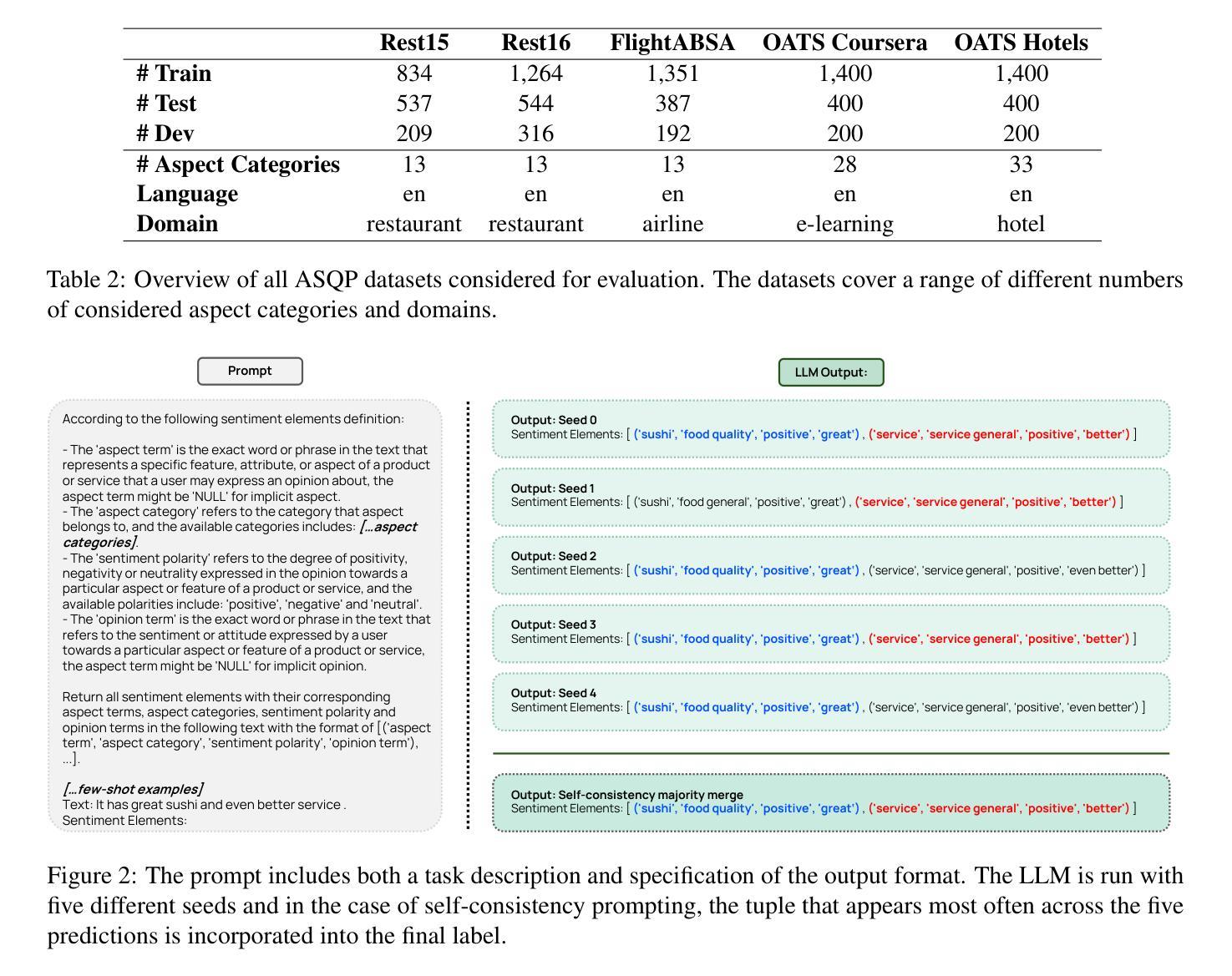
Aspect sentiment quad prediction (ASQP) facilitates a detailed understanding of opinions expressed in a text by identifying the opinion term, aspect term, aspect category and sentiment polarity for each opinion. However, annotating a full set of training examples to fine-tune models for ASQP is a resource-intensive process. In this study, we explore the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for zero- and few-shot learning on the ASQP task across five diverse datasets. We report F1 scores almost up to par with those obtained with state-of-the-art fine-tuned models and exceeding previously reported zero- and few-shot performance. In the 20-shot setting on the Rest16 restaurant domain dataset, LLMs achieved an F1 score of 51.54, compared to 60.39 by the best-performing fine-tuned method MVP. Additionally, we report the performance of LLMs in target aspect sentiment detection (TASD), where the F1 scores were close to fine-tuned models, achieving 68.93 on Rest16 in the 30-shot setting, compared to 72.76 with MVP. While human annotators remain essential for achieving optimal performance, LLMs can reduce the need for extensive manual annotation in ASQP tasks.
面向方面的情感四元预测(ASQP)通过识别每个意见的观点词、方面词、方面类别和情感极性,从而促进对文本中所表达意见的深度理解。然而,为ASQP任务标注全套训练样本以微调模型是一个资源密集型的流程。在本研究中,我们探索大型语言模型(LLM)在五个不同数据集上执行ASQP任务的零样本学习和少样本学习能力。我们报告的F1分数几乎与最先进经过微调模型的F1分数持平,并且超过了先前报告的零样本和少样本性能。在Rest16餐厅域数据集的20次实验中,LLMs取得了F1分数为51.54的分数,而表现最佳的经过训练的MVP方法取得的分数为60.39。此外,我们报告了目标方面情感检测(TASD)中LLMs的性能表现。在Rest16数据集上的多项实验中,其F1分数接近经过训练的模型,在30次实验中取得了68.93的分数,而MVP取得了的分数为72.76。虽然人类注释器对于实现最佳性能至关重要,但LLMs可以减少ASQP任务中对大量手动标注的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本和少样本学习方面展现出强大的能力,用于执行面向方面的情感四重预测(ASQP)任务。本研究展示了LLMs在五个不同数据集上的性能,并报告了在近乎小样本数据下的成绩已接近前沿微调模型。虽然LLMs在某些方面表现不如最佳微调模型,但它们显著减少了人工标注的需求。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具备零样本和少样本学习的能力,可以在面向方面的情感四重预测(ASQP)任务上展现强大的性能。
- 在五个不同的数据集上进行了实验,并报告了近乎小样本数据下的性能表现。
- LLMs的F1得分与最前沿的微调模型相当,并且在某些场景下超越了以往的零样本和少样本性能记录。
- 在Rest16餐厅领域数据集上进行的20次小样本实验中,LLMs的F1得分为51.54,而最佳微调模型MVP的得分为60.39。
- LLMs在目标方面情感检测(TASD)任务中的性能也接近微调模型,在Rest16数据集上的30次小样本实验中,其F1得分为68.93,而MVP的得分为72.76。
- 虽然人工标注对于实现最佳性能仍然至关重要,但LLMs显著减少了面向方面的情感预测任务中对大量人工标注的需求。
- 此研究证实了大型语言模型在解决自然语言处理任务时的潜在应用,尤其是资源有限的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

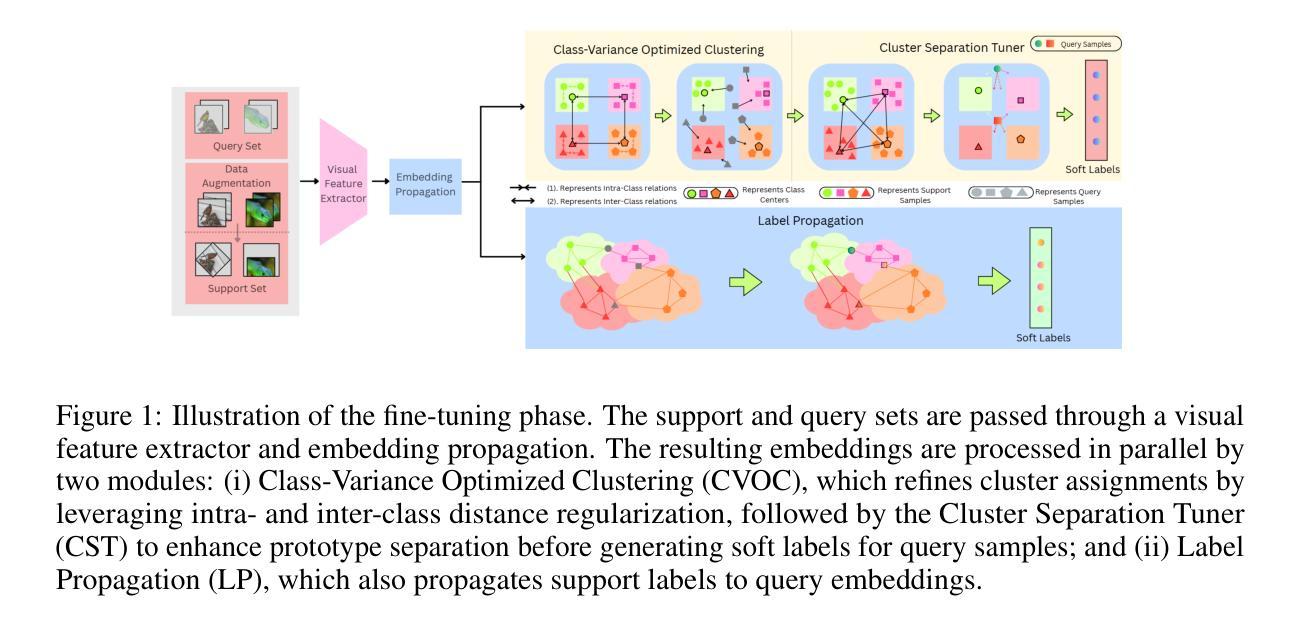
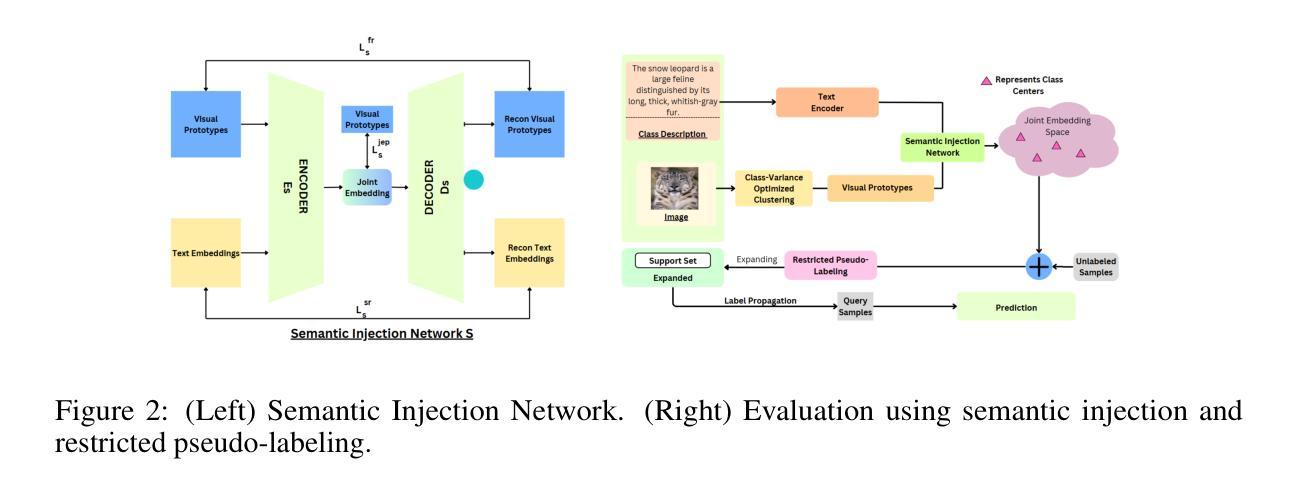
CVOCSemRPL: Class-Variance Optimized Clustering, Semantic Information Injection and Restricted Pseudo Labeling based Improved Semi-Supervised Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Souvik Maji, Rhythm Baghel, Pratik Mazumder
Few-shot learning has been extensively explored to address problems where the amount of labeled samples is very limited for some classes. In the semi-supervised few-shot learning setting, substantial quantities of unlabeled samples are available. Such unlabeled samples are generally cheaper to obtain and can be used to improve the few-shot learning performance of the model. Some of the recent methods for this setting rely on clustering to generate pseudo-labels for the unlabeled samples. Since the effectiveness of clustering heavily influences the labeling of the unlabeled samples, it can significantly affect the few-shot learning performance. In this paper, we focus on improving the representation learned by the model in order to improve the clustering and, consequently, the model performance. We propose an approach for semi-supervised few-shot learning that performs a class-variance optimized clustering coupled with a cluster separation tuner in order to improve the effectiveness of clustering the labeled and unlabeled samples in this setting. It also optimizes the clustering-based pseudo-labeling process using a restricted pseudo-labeling approach and performs semantic information injection in order to improve the semi-supervised few-shot learning performance of the model. We experimentally demonstrate that our proposed approach significantly outperforms recent state-of-the-art methods on the benchmark datasets.
小样本学习已经被广泛探索,以解决某些类别的标注样本数量非常有限的问题。在半监督小样本学习环境中,存在大量的未标注样本。这些未标注样本通常更容易获取,并可用于提高模型的少样本学习性能。最近的一些方法依赖于聚类来为未标注样本生成伪标签。由于聚类的有效性对未标注样本的标注有重要影响,因此它可能会显著影响小样本学习的性能。在本文中,我们专注于改进模型所学的表示,以提高聚类能力和模型性能。我们提出了一种半监督小样本学习方法,采用类方差优化聚类与聚类分离调节器相结合,以提高该环境中带标签和无标签样本的聚类效果。它还通过限制伪标签方法和执行语义信息注入来优化基于聚类的伪标签过程,以提高模型的半监督小样本学习性能。实验证明,我们提出的方法在基准数据集上显著优于最新的先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了半监督小样本学习问题,其中涉及对模型表示的改进以提高聚类效果。文章提出了一种半监督小样本学习方法,通过类方差优化聚类和集群分离调节器改进了聚类效果。同时,通过限制伪标签方法和语义信息注入优化了基于聚类的伪标签过程。实验证明,该方法在基准数据集上显著优于现有最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文章集中在改进模型表示以改善半监督小样本学习中的聚类效果。
- 提出了一种新的半监督小样本学习方法,包括类方差优化聚类和集群分离调节器。
- 限制伪标签方法和语义信息注入技术用于优化基于聚类的伪标签过程。
- 方法在基准数据集上显著优于现有最新方法。
- 未标注样本在半监督小样本学习中扮演重要角色,可以利用这些样本提升模型的性能。
- 聚类方法的优化直接影响模型对小样本学习的效果。
点此查看论文截图

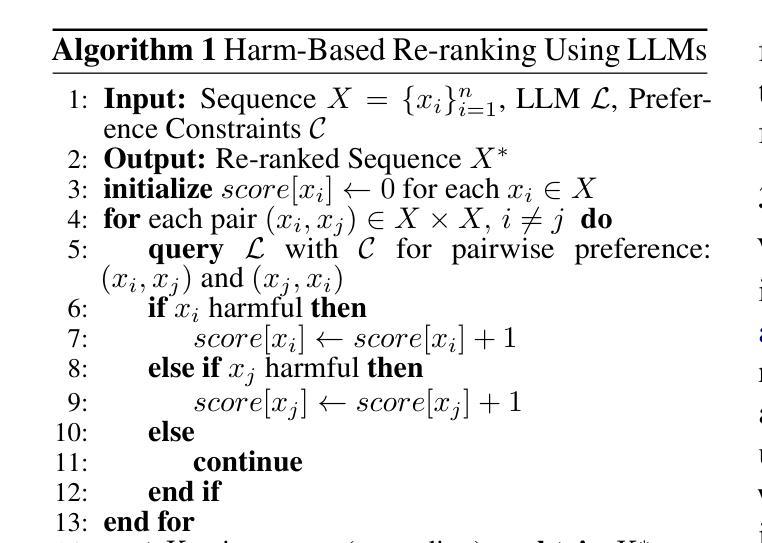
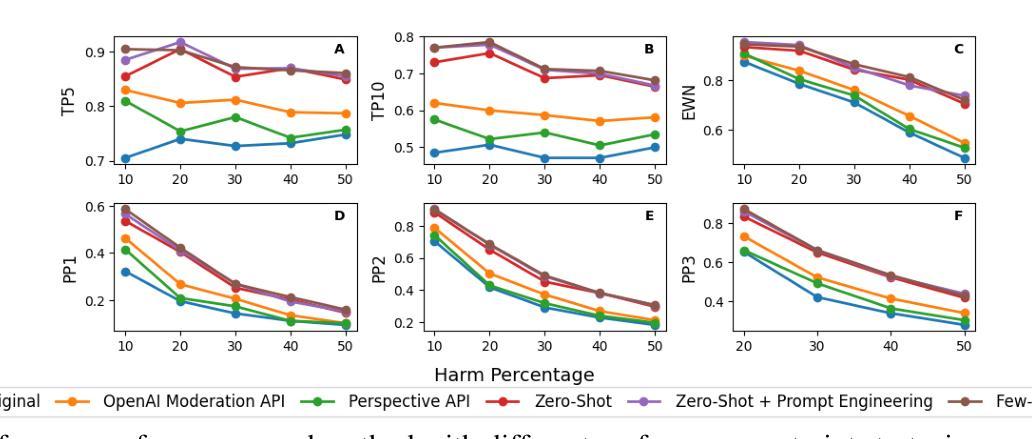
Re-ranking Using Large Language Models for Mitigating Exposure to Harmful Content on Social Media Platforms
Authors:Rajvardhan Oak, Muhammad Haroon, Claire Jo, Magdalena Wojcieszak, Anshuman Chhabra
Social media platforms utilize Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered recommendation algorithms to maximize user engagement, which can result in inadvertent exposure to harmful content. Current moderation efforts, reliant on classifiers trained with extensive human-annotated data, struggle with scalability and adapting to new forms of harm. To address these challenges, we propose a novel re-ranking approach using Large Language Models (LLMs) in zero-shot and few-shot settings. Our method dynamically assesses and re-ranks content sequences, effectively mitigating harmful content exposure without requiring extensive labeled data. Alongside traditional ranking metrics, we also introduce two new metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of re-ranking in reducing exposure to harmful content. Through experiments on three datasets, three models and across three configurations, we demonstrate that our LLM-based approach significantly outperforms existing proprietary moderation approaches, offering a scalable and adaptable solution for harm mitigation.
社交媒体平台利用机器学习和人工智能驱动的推荐算法来最大化用户参与度,这可能导致无意中接触到有害内容。当前的审核工作依赖于使用大量人工注释数据训练的分类器,面临着可扩展性和适应新形式的挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种在零样本和少样本环境下使用大型语言模型进行再排序的新方法。我们的方法动态地评估和重新排序内容序列,有效地减少接触有害内容的可能性,无需依赖大量的标记数据。除了传统的排名指标外,我们还引入了两种新指标来评估重新排序在减少接触有害内容方面的有效性。通过对三个数据集、三个模型以及三种配置的测试实验表明,我们基于大型语言模型的再排序方法显著优于现有的专有审核方法,为危害缓解提供了可扩展和可适应的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary:社交媒体平台利用机器学习和人工智能驱动的推荐算法来最大化用户参与度,这可能导致无意中接触到有害内容。为解决当前依赖大量人工标注数据训练的分类器在可扩展性和适应新形式危害方面的挑战,我们提出了一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行零样本和少样本设置的新型重新排序方法。该方法能够动态评估和重新排序内容序列,有效地减少有害内容的暴露,且无需大量标注数据。除了传统的排名指标外,我们还引入了两个新指标来评估重新排序在减少有害内容暴露方面的有效性。通过在三套数据集上进行的实验显示,基于LLM的方法显著优于现有的专有调节方法,为危害缓解提供了可扩展和可适应的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 社交媒体平台利用机器学习和人工智能推荐算法最大化用户参与度,可能无意中暴露用户于有害内容。
- 当前的内容调节方法面临可扩展性和适应新危害形式的挑战。
- 提出一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的重新排序方法,能在零样本和少样本设置下动态评估和重新排序内容序列。
- 该方法无需大量标注数据,即可有效减少有害内容的暴露。
- 除了传统排名指标外,还引入两个新指标来评估重新排序的效果。
- 实验表明,基于LLM的方法在减少有害内容暴露方面显著优于现有专有调节方法。
点此查看论文截图

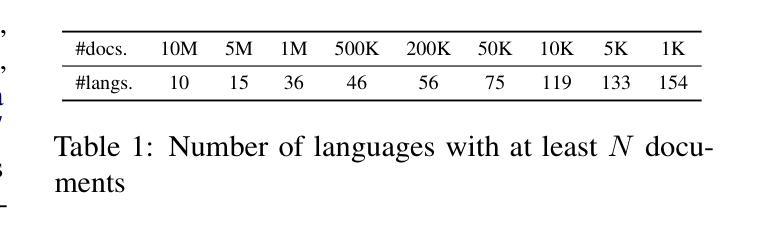
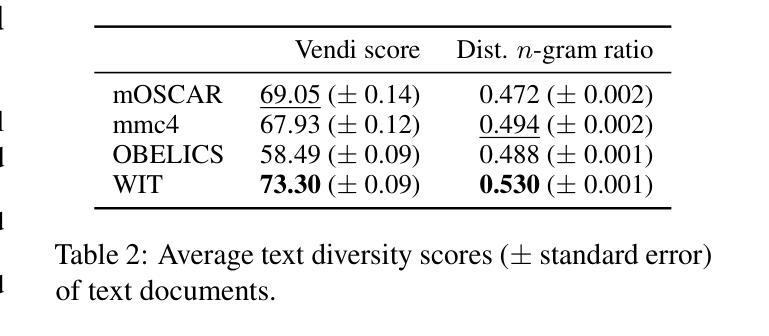
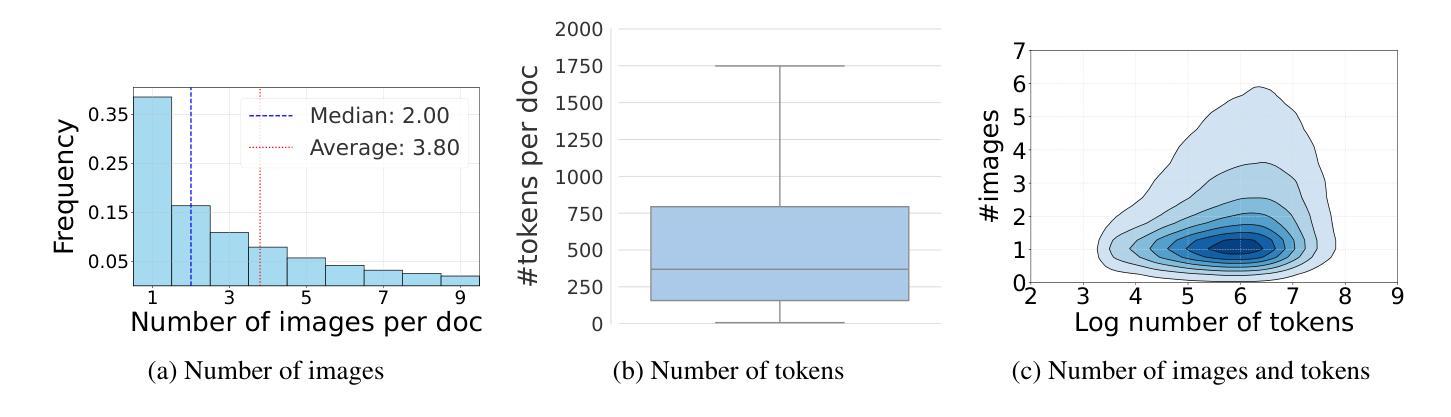
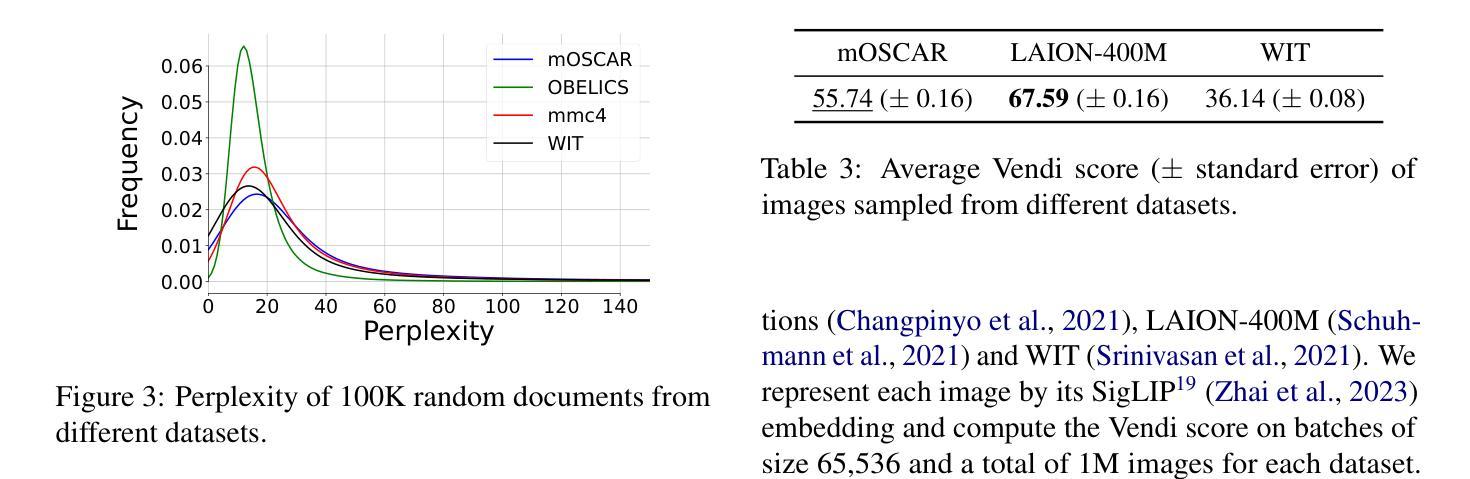
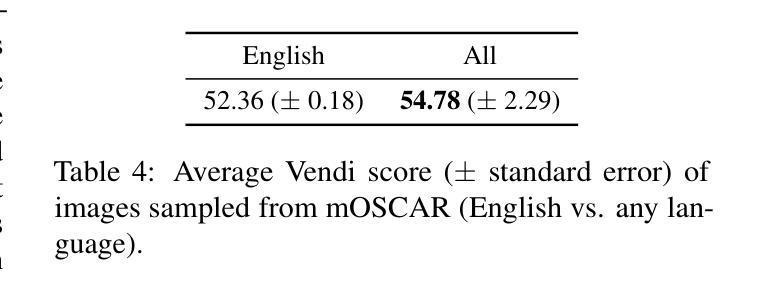
mOSCAR: A Large-scale Multilingual and Multimodal Document-level Corpus
Authors:Matthieu Futeral, Armel Zebaze, Pedro Ortiz Suarez, Julien Abadji, Rémi Lacroix, Cordelia Schmid, Rachel Bawden, Benoît Sagot
Multimodal Large Language Models (mLLMs) are trained on a large amount of text-image data. While most mLLMs are trained on caption-like data only, Alayrac et al. (2022) showed that additionally training them on interleaved sequences of text and images can lead to the emergence of in-context learning capabilities. However, the dataset they used, M3W, is not public and is only in English. There have been attempts to reproduce their results but the released datasets are English-only. In contrast, current multilingual and multimodal datasets are either composed of caption-like only or medium-scale or fully private data. This limits mLLM research for the 7,000 other languages spoken in the world. We therefore introduce mOSCAR, to the best of our knowledge the first large-scale multilingual and multimodal document corpus crawled from the web. It covers 163 languages, 303M documents, 200B tokens and 1.15B images. We carefully conduct a set of filtering and evaluation steps to make sure mOSCAR is sufficiently safe, diverse and of good quality. We additionally train two types of multilingual model to prove the benefits of mOSCAR: (1) a model trained on a subset of mOSCAR and captioning data and (2) a model trained on captioning data only. The model additionally trained on mOSCAR shows a strong boost in few-shot learning performance across various multilingual image-text tasks and benchmarks, confirming previous findings for English-only mLLMs. The dataset is released under the Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license and can be accessed here: https://huggingface.co/datasets/oscar-corpus/mOSCAR
多模态大型语言模型(mLLMs)是在大量的文本图像数据上训练的。虽然大多数mLLM仅在类似标题的数据上进行训练,但Alayrac等人(2022)的研究表明,通过在文本和图像的交错序列上进行额外训练,可以产生上下文学习能力。然而,他们使用的数据集M3W并非公开且仅适用于英语。尽管有人试图复制他们的结果,但发布的数据集都是英语版本的。相比之下,当前的多语种和多模态数据集要么仅包含类似标题的数据,要么是中规模或完全私有数据。这限制了全球其他7,000多种语言的多模态语言模型(mLLM)研究。因此,我们推出了mOSCAR,据我们所知,它是首个从网络爬虫中获取的大规模多语种多模态文档语料库。它涵盖163种语言、3.03亿份文档、20亿个令牌和1.15亿张图像。我们精心进行了一系列过滤和评估步骤,以确保mOSCAR足够安全、多样且质量良好。此外,我们还训练了两种多语种模型来证明mOSCAR的效益:(1)一种在mOSCAR子集和描述数据上训练的模型,(2)仅用于描述数据训练的模型。经过mOSCAR额外训练的模型在各种多语种图像文本任务和基准测试上的少样本学习能力得到了极大的提升,这证实了之前针对英语mLLM的发现。该数据集是在创意共享CC BY 4.0许可证下发布的,可从以下链接访问:https://huggingface.co/datasets/oscar-corpus/mOSCAR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 (Findings)
Summary
多模态大型语言模型(mLLM)训练时融合了海量的文本和图像数据。相较于仅使用描述性数据的训练方式,Alayrac等人展示了通过交替序列的文本和图像进行训练能够促使模型具备上下文学习能力。然而,其使用的数据集M3W并未公开且仅限于英语。尽管有尝试复制其成果,但发布的数据集同样仅限于英语。相较之下,现有的多语言多模态数据集要么是描述性的,要么是中等规模或封闭性的,这限制了全球其他七千种语言的mLLM研究。为此,推出mOSCAR这一据称首个大规模的多语言多模态文档语料库,涵盖163种语言、3.03亿文档、20亿词汇和1.1亿图像。经过严格的筛选和评估流程,确保语料库的优质和安全多样性。通过两种类型的多语种模型验证了mOSCAR的效益:在mOSCAR子集和描述数据上训练的模型以及在仅描述数据上训练的模型。额外在mOSCAR上训练的模型在多语种图像文本任务和基准测试中显示出强大的少样本学习能力提升,证实了英语mLLM的先前发现。该数据集以创意共享CC BY 4.0许可证发布,可在此访问:huggingface.co/datasets/oscar-corpus/mOSCAR。
Key Takeaways
- mOSCAR是首个大规模的多语言多模态文档语料库,涵盖多种语言。
- mOSCAR包含来自网络的文本和图像数据,文档数量庞大且覆盖面广。
- mOSCAR数据经过筛选和评估以确保质量、多样性和安全性。
- 通过多语种模型的训练验证了mOSCAR的效益,少样本学习能力有所提升。
- mOSCAR数据集具有创意共享CC BY 4.0许可证,便于访问和使用。
- mOSCAR的发布填补了多语言多模态数据集领域的空白,促进了全球其他语言的mLLM研究发展。
点此查看论文截图