⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
PCA for Enhanced Cross-Dataset Generalizability in Breast Ultrasound Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Christian Schmidt, Heinrich Martin Overhoff
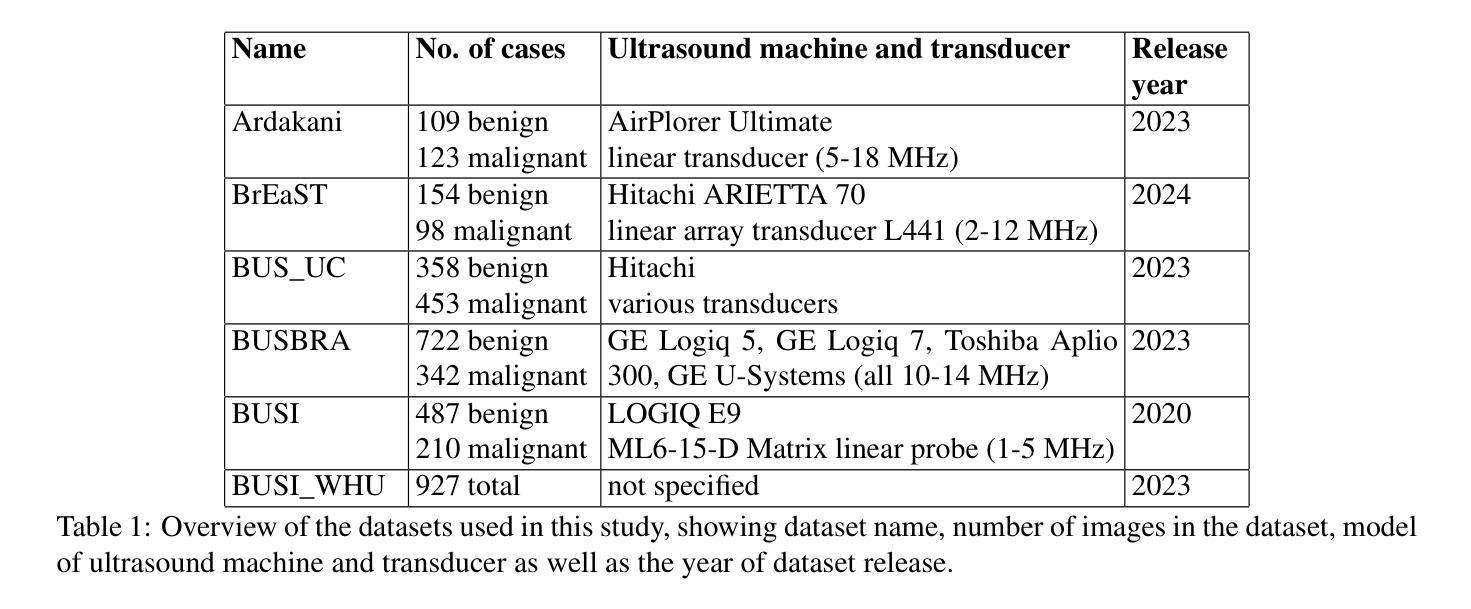
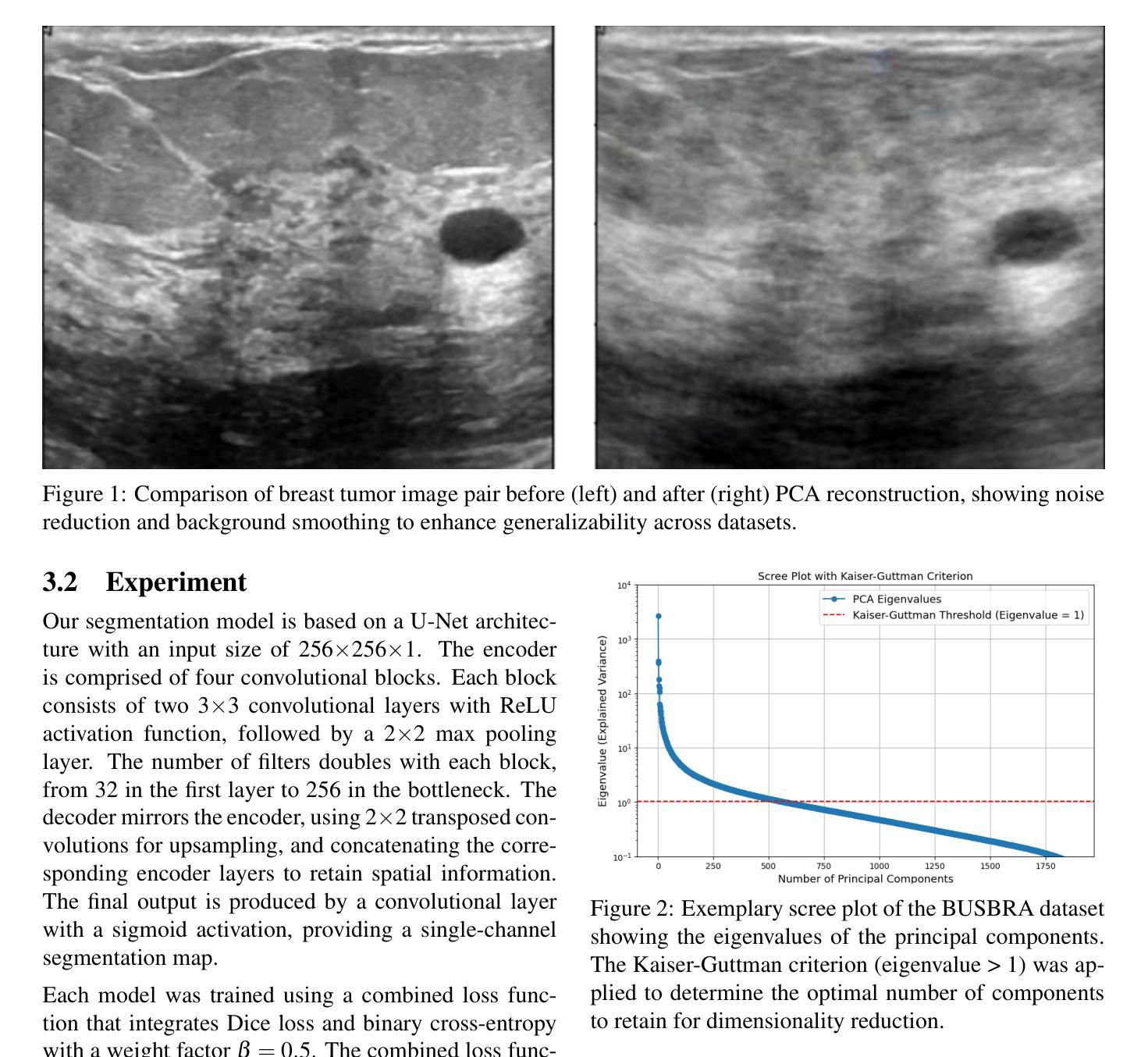
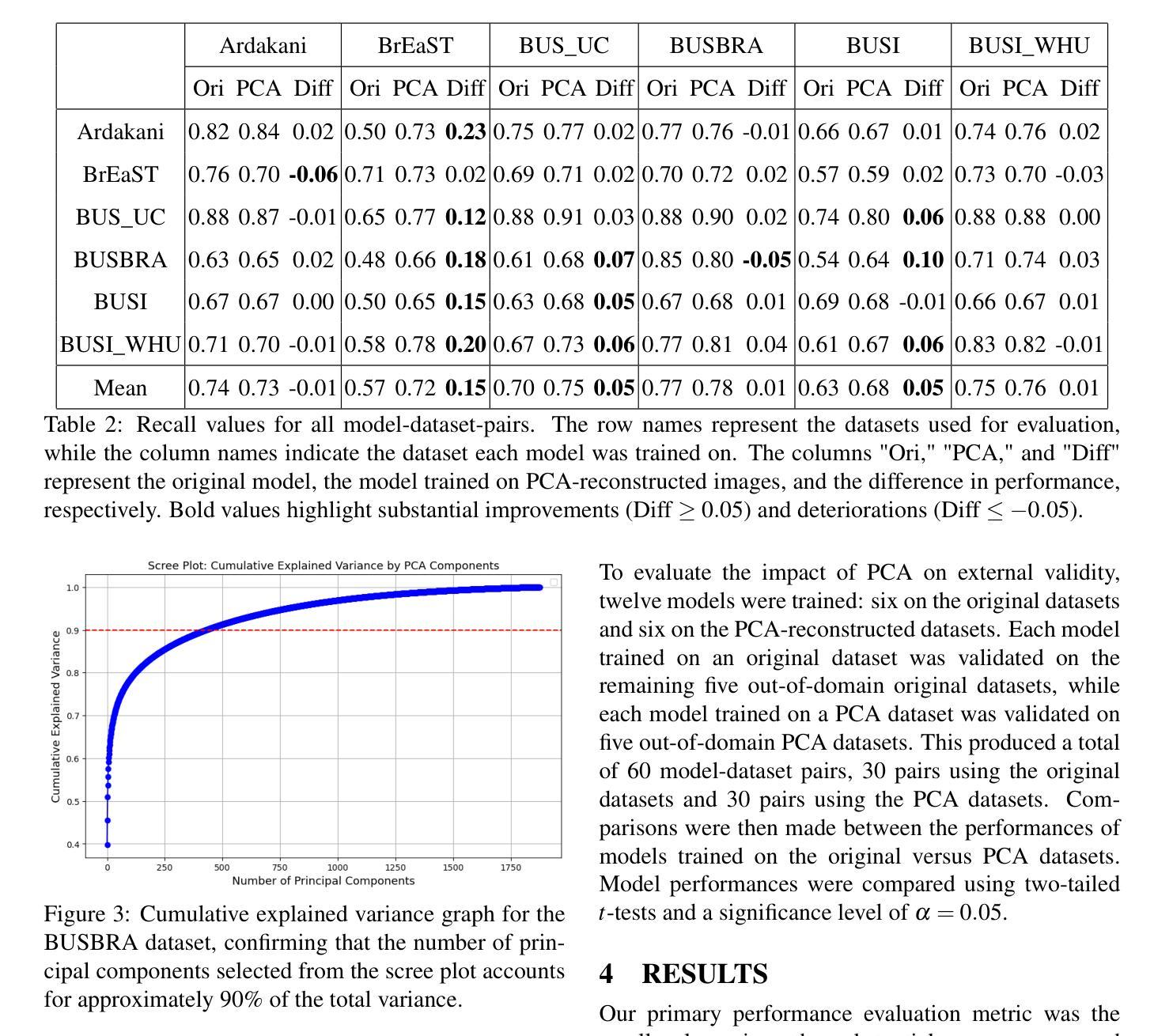
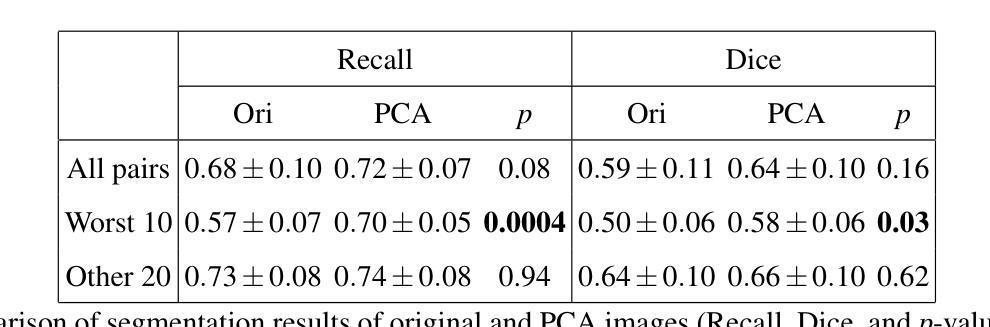
In medical image segmentation, limited external validity remains a critical obstacle when models are deployed across unseen datasets, an issue particularly pronounced in the ultrasound image domain. Existing solutions-such as domain adaptation and GAN-based style transfer-while promising, often fall short in the medical domain where datasets are typically small and diverse. This paper presents a novel application of principal component analysis (PCA) to address this limitation. PCA preprocessing reduces noise and emphasizes essential features by retaining approximately 90% of the dataset variance. We evaluate our approach across six diverse breast tumor ultrasound datasets comprising 3,983 B-mode images and corresponding expert tumor segmentation masks. For each dataset, a corresponding dimensionality reduced PCA-dataset is created and U-Net-based segmentation models are trained on each of the twelve datasets. Each model trained on an original dataset was inferenced on the remaining five out-of-domain original datasets (baseline results), while each model trained on a PCA dataset was inferenced on five out-of-domain PCA datasets. Our experimental results indicate that using PCA reconstructed datasets, instead of original images, improves the model’s recall and Dice scores, particularly for model-dataset pairs where baseline performance was lowest, achieving statistically significant gains in recall (0.57 $\pm$ 0.07 vs. 0.70 $\pm$ 0.05, $p = 0.0004$) and Dice scores (0.50 $\pm$ 0.06 vs. 0.58 $\pm$ 0.06, $p = 0.03$). Our method reduced the decline in recall values due to external validation by $33%$. These findings underscore the potential of PCA reconstruction as a safeguard to mitigate declines in segmentation performance, especially in challenging cases, with implications for enhancing external validity in real-world medical applications.
在医学图像分割领域,当模型部署在未见过的数据集上时,有限的外部有效性仍然是一个关键的障碍,这一问题在超声图像领域尤为突出。虽然现有的解决方案(如域自适应和基于GAN的风格转换)前景广阔,但在医学领域通常存在数据集小且多样的情况,这些方法往往难以达到预期效果。本文提出了一种主成分分析(PCA)的新应用来解决这一局限性。PCA预处理通过保留大约90%的数据集方差来减少噪声并强调重要特征。我们在包含3983张B模式图像和相应的专家肿瘤分割掩码的六个不同乳腺癌超声数据集上评估了我们的方法。对于每个数据集,创建一个相应的降维PCA数据集,并在每个十二个数据集上训练基于U-Net的分割模型。每个在原始数据集上训练的模型会在剩下的五个域外的原始数据集上进行推断(基线结果),而在PCA数据集上训练的模型会在五个域外的PCA数据集上进行推断。我们的实验结果表明,使用PCA重建的数据集而不是原始图像,可以提高模型的召回率和Dice得分,特别是在基线性能最低的模型-数据集对上,召回率(0.57±0.07 vs. 0.70±0.05,p=0.0004)和Dice得分(0.50±0.06 vs. 0.58±0.06,p=0.03)实现了统计学上的显著增长。我们的方法将由于外部验证而导致的召回值下降减少了33%。这些发现强调了PCA重建作为缓解分割性能下降的安全保障的潜力,特别是在复杂情况下,这对增强现实世界医学应用的外部有效性具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出将主成分分析(PCA)应用于医学图像分割领域,以解决模型在跨未见数据集部署时的外部有效性有限的问题。特别是在超声图像领域,现有解决方案如域适应和基于GAN的风格转换虽然前景广阔,但在医学领域通常难以实现,因为数据集通常较小且多样。PCA预处理可减少噪声并强调关键特征,保留约90%的数据集方差。实验结果表明,使用PCA重建的数据集相比原始图像提高了模型的召回率和Dice得分,特别是在模型与数据集基线性能最低的配对中。本研究结果强调PCA重建作为缓解分割性能下降的安全保障措施的潜力,特别是在具有挑战性的情况下,对增强实际医学应用的外部有效性具有意义。
Key Takeaways
- PCA被应用于医学图像分割领域,以提高模型的外部有效性。
- 在超声图像领域,现有解决方案面临数据集小且多样的挑战。
- PCA预处理可减少噪声并强调关键特征。
- 使用PCA重建的数据集可以提高模型的召回率和Dice得分。
- PCA重建对模型与数据集基线性能较低的配对效果更显著。
- PCA重建有助于提高模型在挑战性情况下的性能。
点此查看论文截图

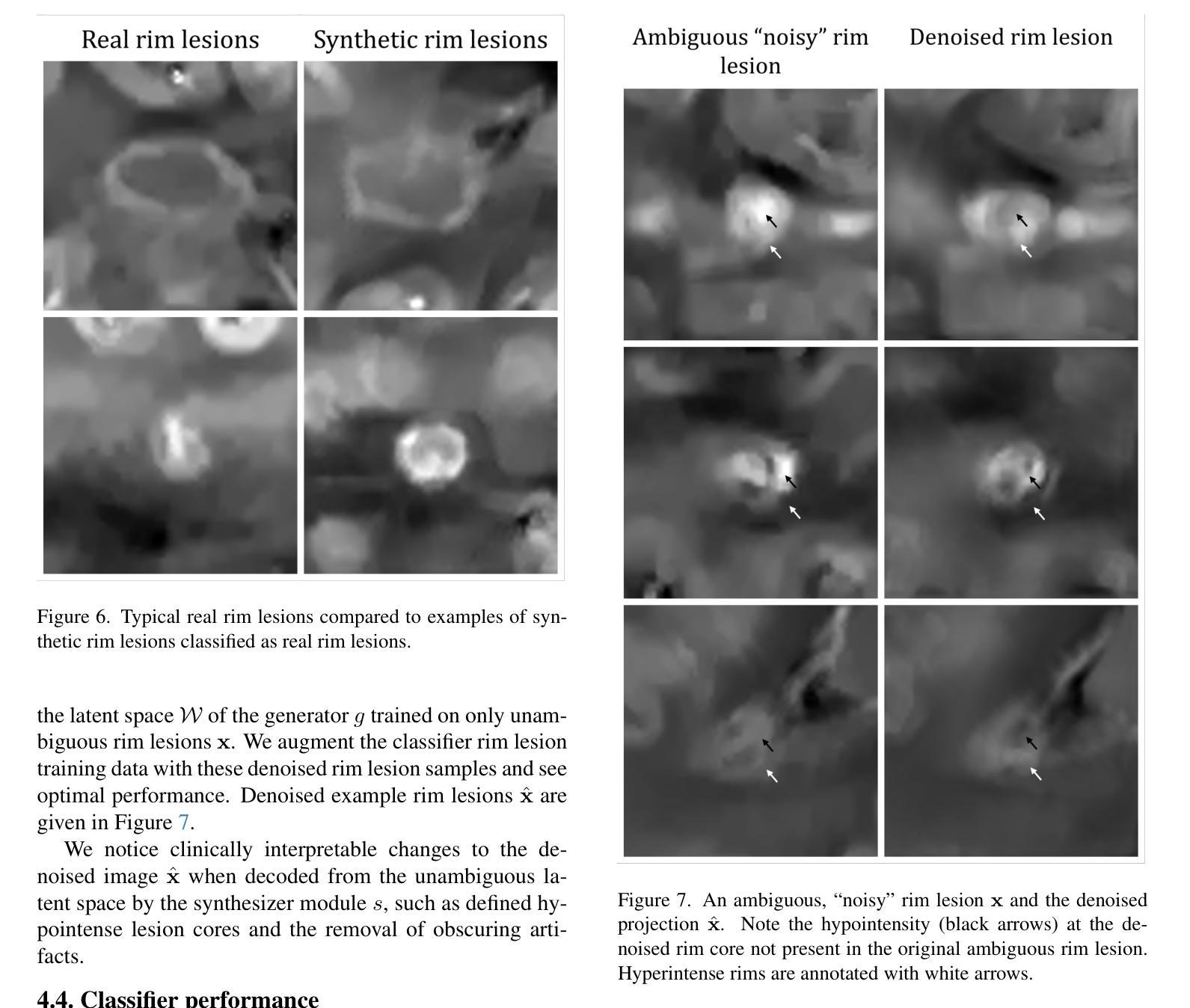
Synthetic Generation and Latent Projection Denoising of Rim Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis
Authors:Alexandra G. Roberts, Ha M. Luu, Mert Şişman, Alexey V. Dimov, Ceren Tozlu, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Susan A. Gauthier, Thanh D. Nguyen, Yi Wang
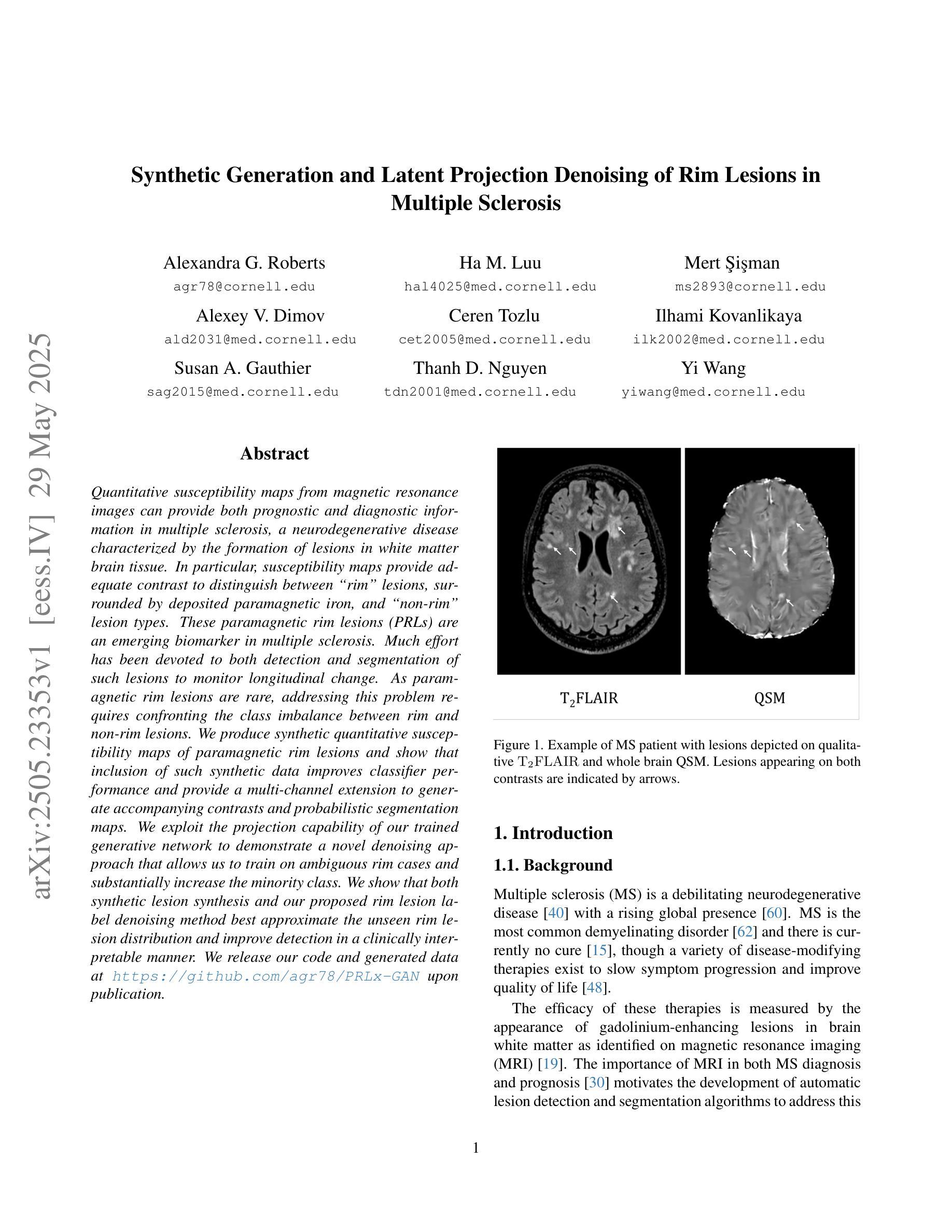
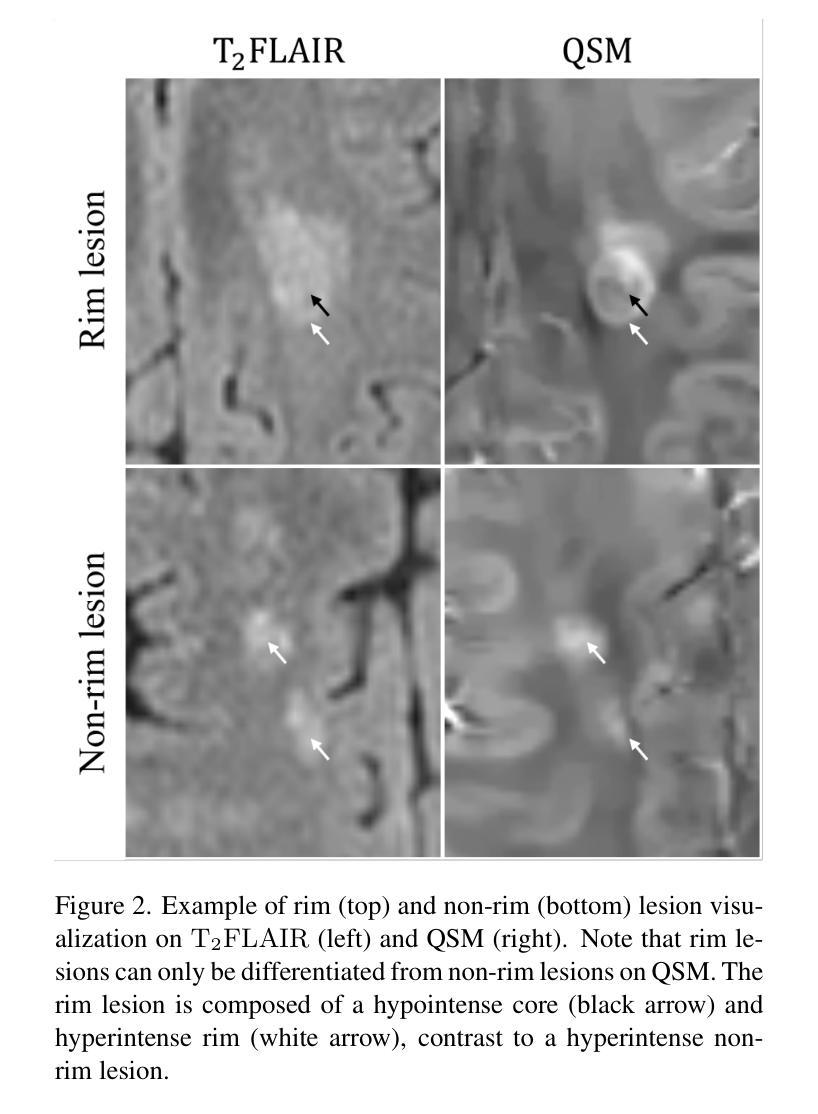
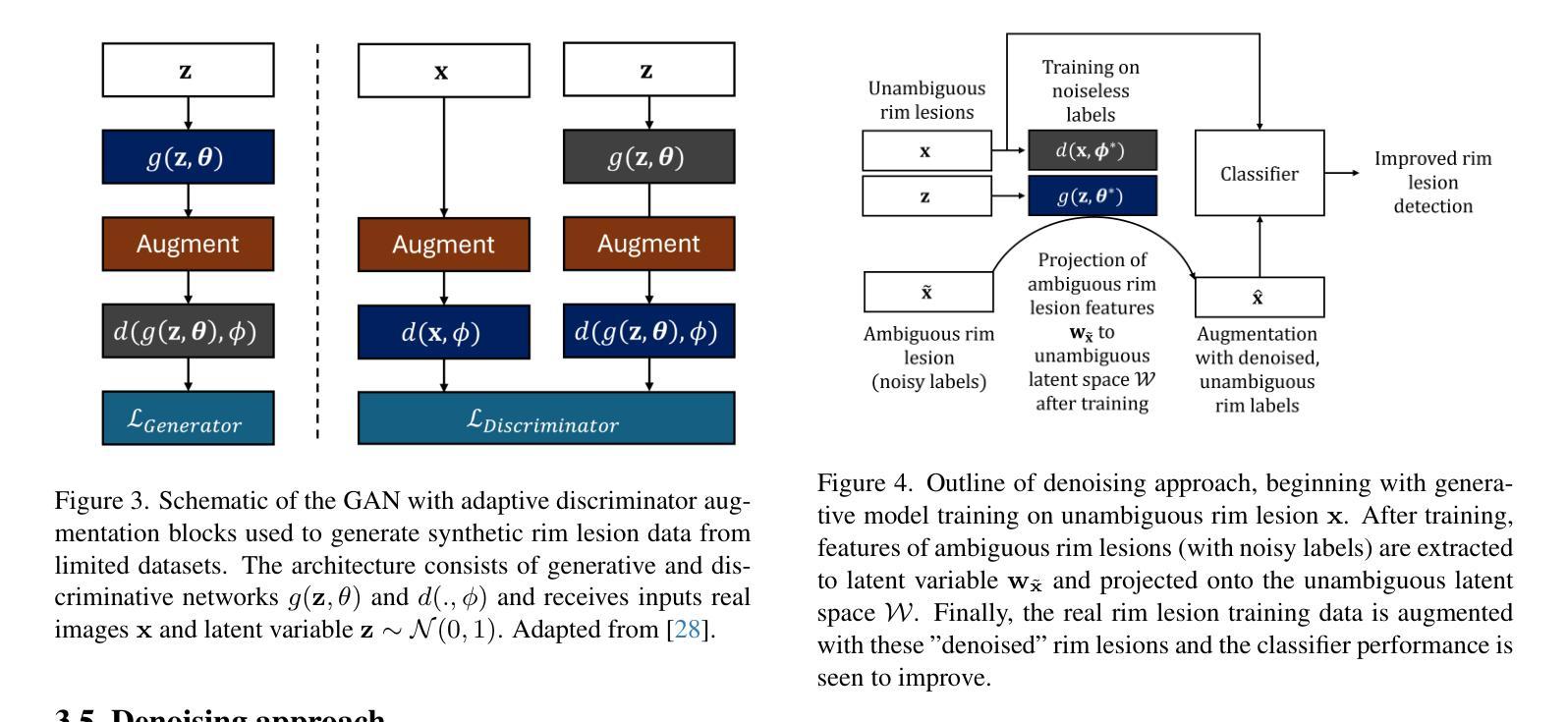
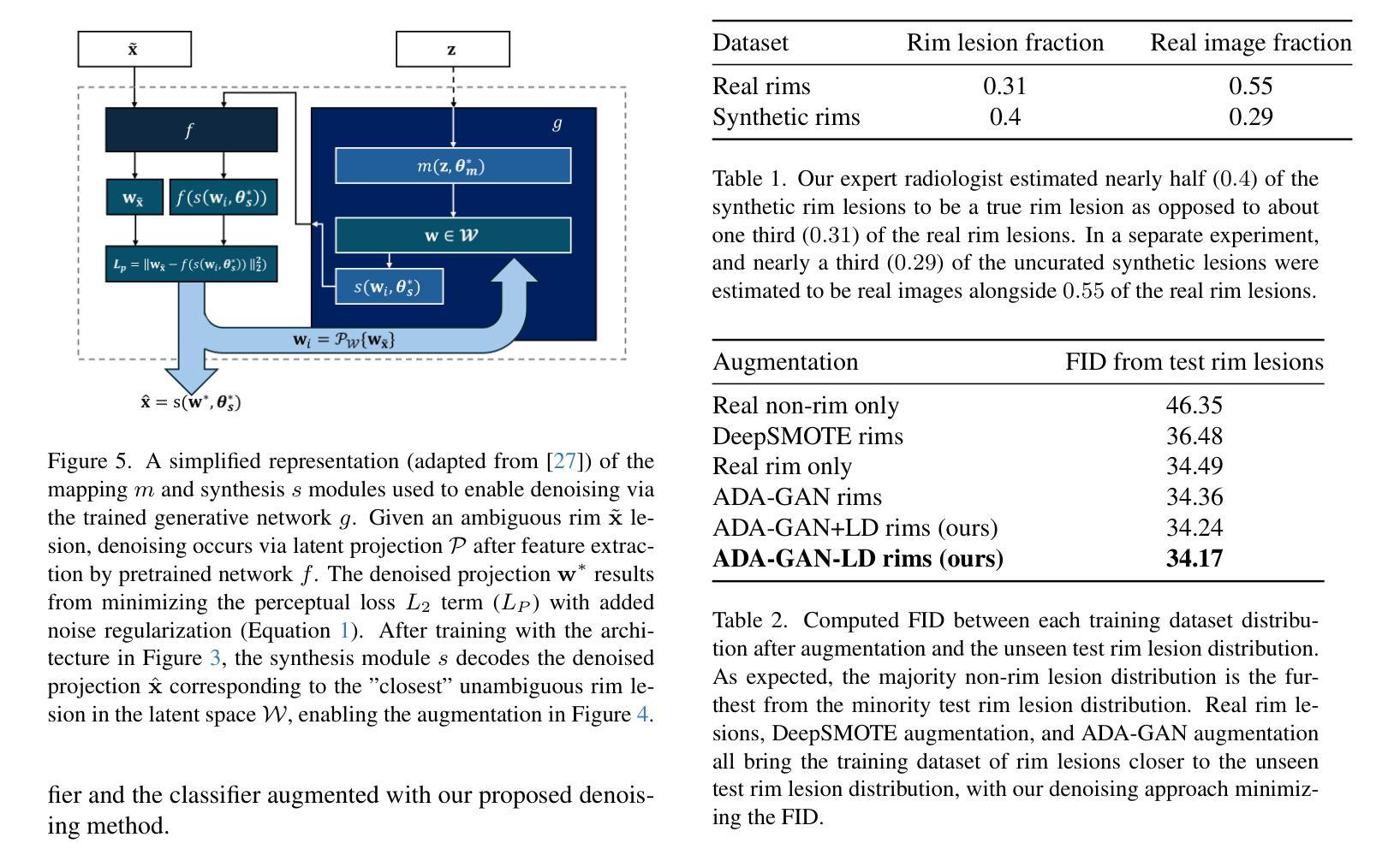
Quantitative susceptibility maps from magnetic resonance images can provide both prognostic and diagnostic information in multiple sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the formation of lesions in white matter brain tissue. In particular, susceptibility maps provide adequate contrast to distinguish between “rim” lesions, surrounded by deposited paramagnetic iron, and “non-rim” lesion types. These paramagnetic rim lesions (PRLs) are an emerging biomarker in multiple sclerosis. Much effort has been devoted to both detection and segmentation of such lesions to monitor longitudinal change. As paramagnetic rim lesions are rare, addressing this problem requires confronting the class imbalance between rim and non-rim lesions. We produce synthetic quantitative susceptibility maps of paramagnetic rim lesions and show that inclusion of such synthetic data improves classifier performance and provide a multi-channel extension to generate accompanying contrasts and probabilistic segmentation maps. We exploit the projection capability of our trained generative network to demonstrate a novel denoising approach that allows us to train on ambiguous rim cases and substantially increase the minority class. We show that both synthetic lesion synthesis and our proposed rim lesion label denoising method best approximate the unseen rim lesion distribution and improve detection in a clinically interpretable manner. We release our code and generated data at https://github.com/agr78/PRLx-GAN upon publication.
核磁共振图像的定量磁化率图可以为多发性硬化症提供预后和诊断信息。多发性硬化症是一种神经退行性疾病,其特点是脑白质组织形成病灶。特别是,磁化率图提供了足够的对比度,可以区分被沉积的顺磁性铁包围的“边缘”病灶和“无边缘”病灶类型。顺磁性边缘病灶(PRLs)是多发性硬化症中的一个新兴生物标志物。人们已经付出了很多努力来检测和分割这样的病灶,以监测纵向变化。由于顺磁性边缘病灶很少见,解决这个问题需要解决边缘病灶和非边缘病灶之间的类别不平衡问题。我们生成了顺磁性边缘病灶的合成定量磁化率图,并表明加入这种合成数据提高了分类器的性能,并提供了一个多通道扩展来生成伴随的对比度和概率分割图。我们利用训练有素的生成网络的投影能力,展示了一种新的去噪方法,该方法允许我们在模糊的边缘情况下进行训练,并大幅增加少数类。我们表明,无论是合成病灶的合成还是我们提出的边缘病灶标签去噪方法,都能最好地近似未见过的边缘病灶分布,并以临床可解释的方式提高检测效果。在发布时,我们将在https://github.com/agr78/PRLx-GAN上发布我们的代码和生成的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted full paper in Synthetic Data @ CVPR 2025 12 pages, 10 figures
Summary
定量磁化率图从磁共振图像中提取的信息对多发性硬化症具有重要的预后和诊断价值。磁化率图可以区分带有沉积顺磁性铁的边沿病灶和非边沿病灶类型,这些顺磁性边沿病灶是新兴的多发性硬化症生物标志物。研究者致力于检测和分割这类病灶以追踪纵向变化。合成定量磁化率图生成合成数据能提高分类器性能和生成伴随对比度和概率分割图。研究通过去噪方法解决顺磁性边沿病灶稀有问题,利用训练有素的生成网络的投影能力对模糊边沿病例进行训练并大幅增加少数类样本。合成病灶合成和边沿病灶标签去噪方法最符合未知边沿病灶分布并提高了检测的临床解读性。相关代码和数据发布在 https://github.com/agr78/PRLx-GAN 上。
Key Takeaways
- 定量磁化率图在多发性硬化症中具有预后和诊断价值。
- 磁化率图能够区分不同类型的病灶,特别是顺磁性边沿病灶(PRLs)是新兴的生物标志物。
- PRLs的检测和分割对于追踪多发性硬化症的纵向变化非常重要。
- 由于顺磁性边沿病灶的稀有性,解决类别不平衡问题至关重要。
- 合成定量磁化率图的生成有助于提高分类器性能和生成伴随的对比度和概率分割图。
- 利用生成网络的投影能力进行去噪训练,可以解决模糊边沿病例的问题并增加少数类样本。
点此查看论文截图
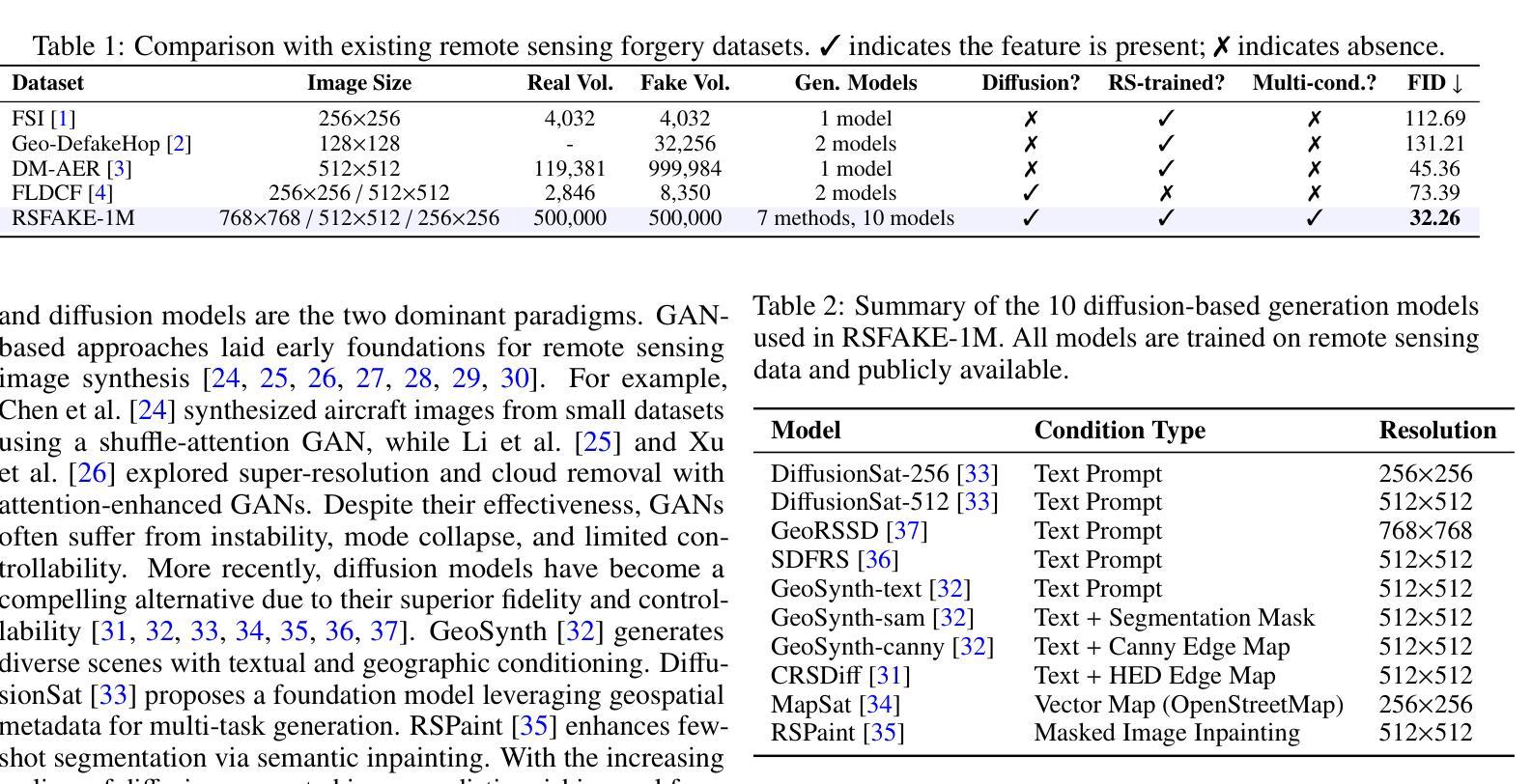
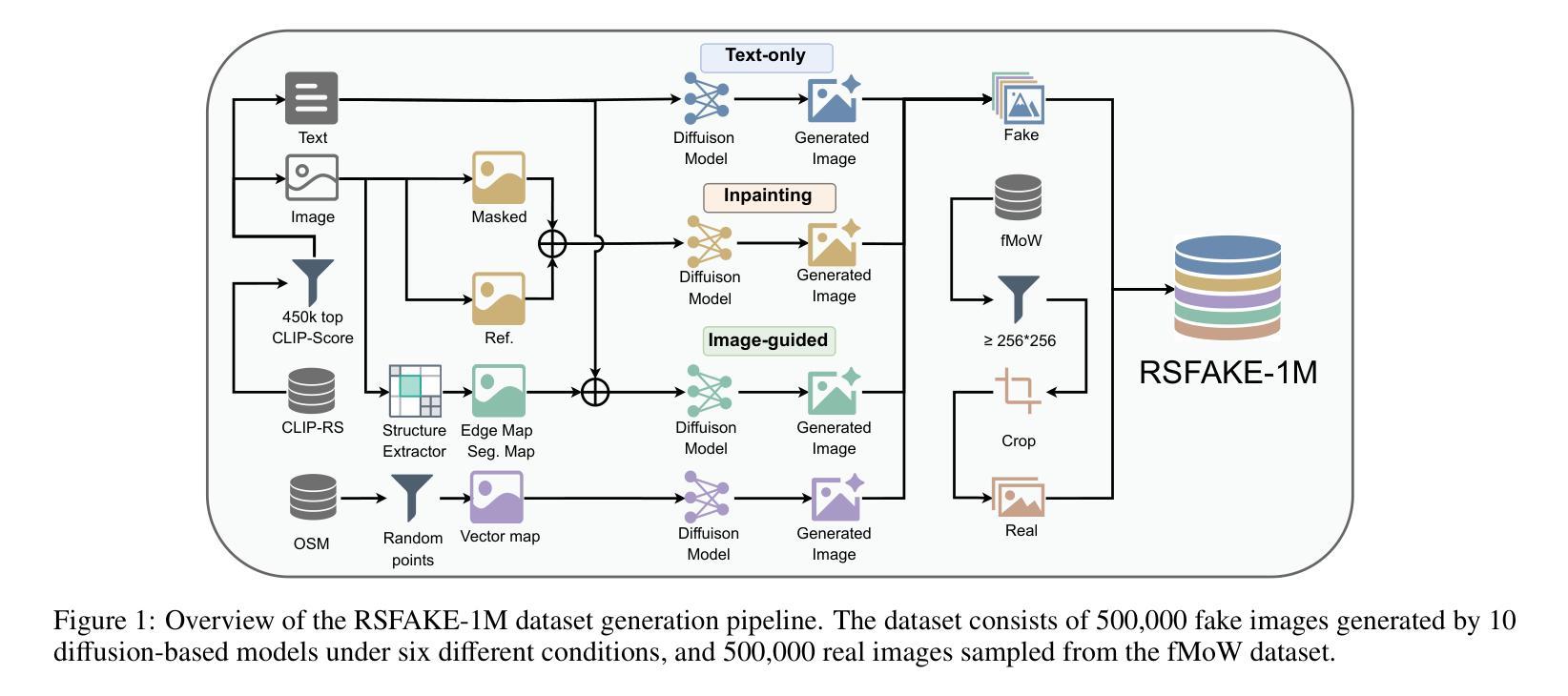
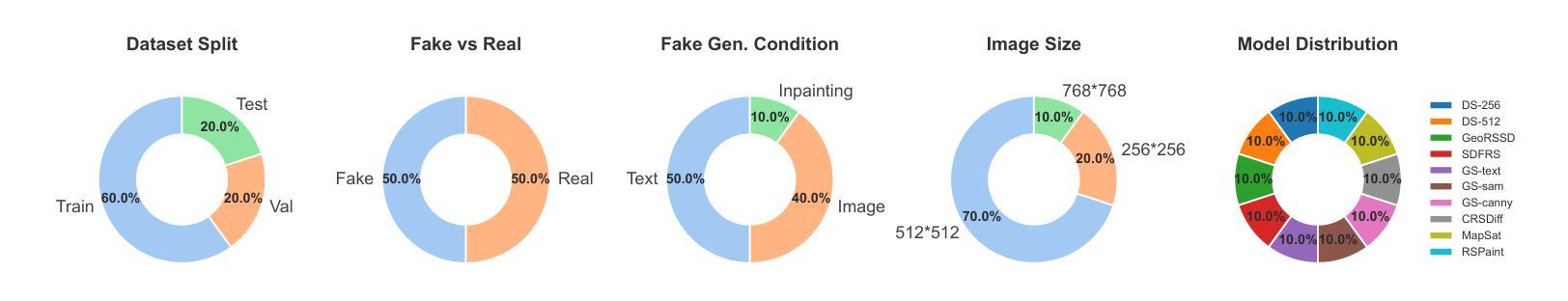
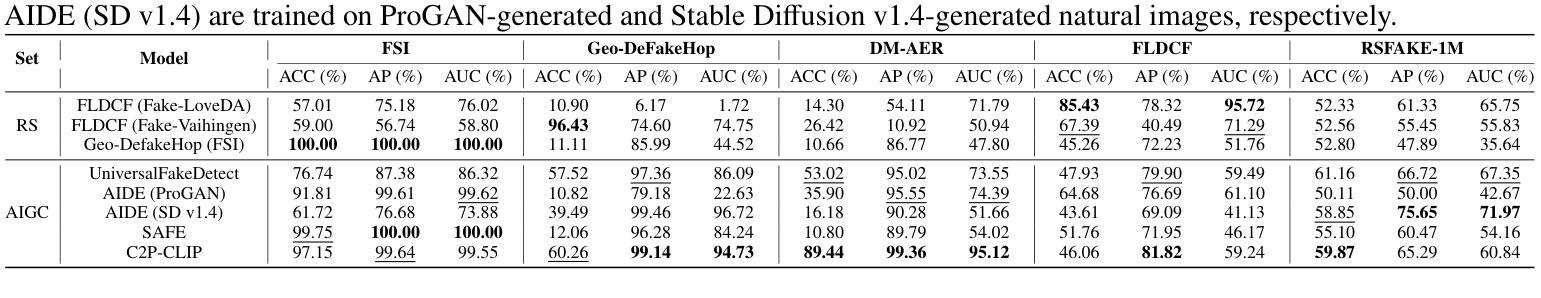
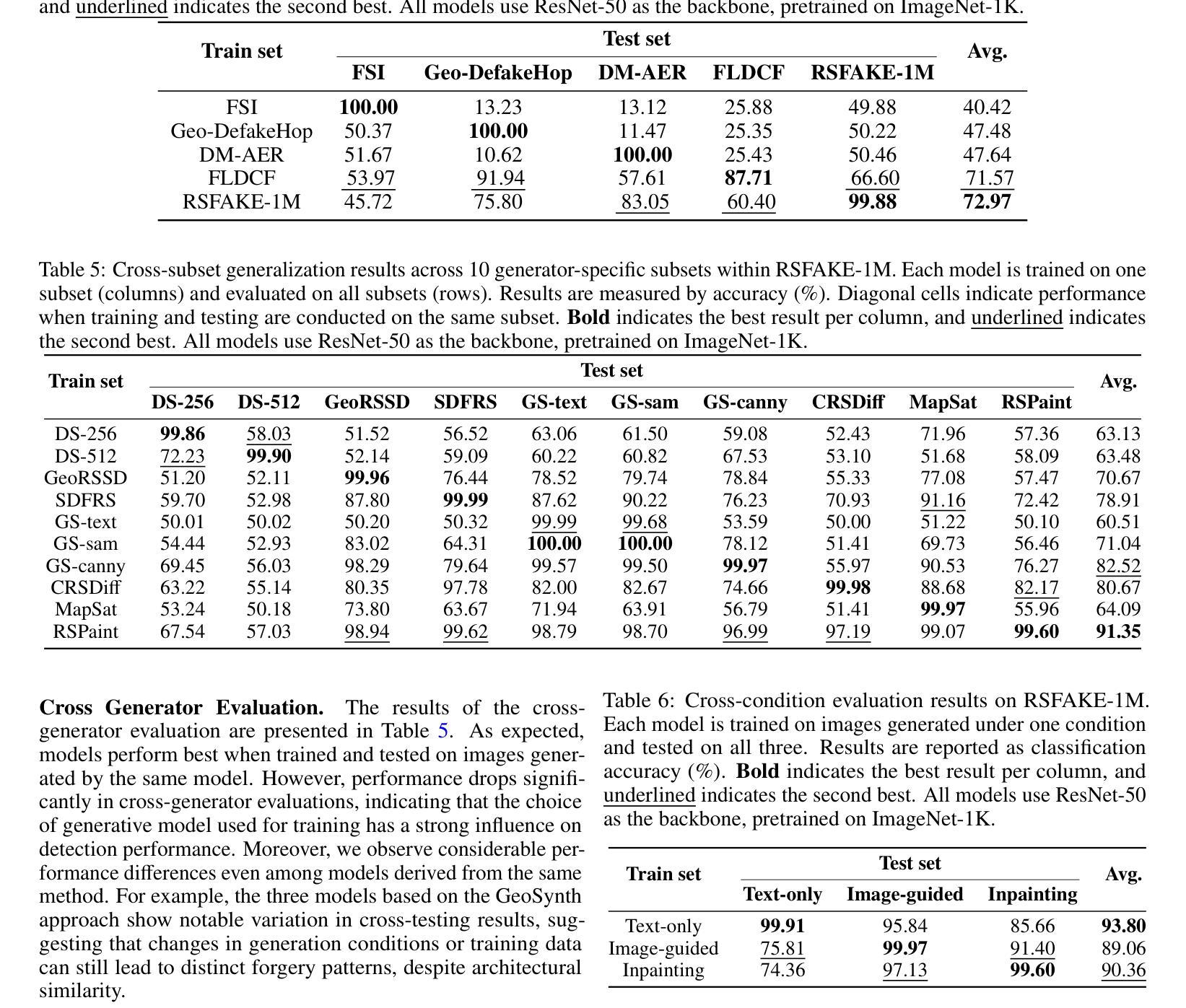
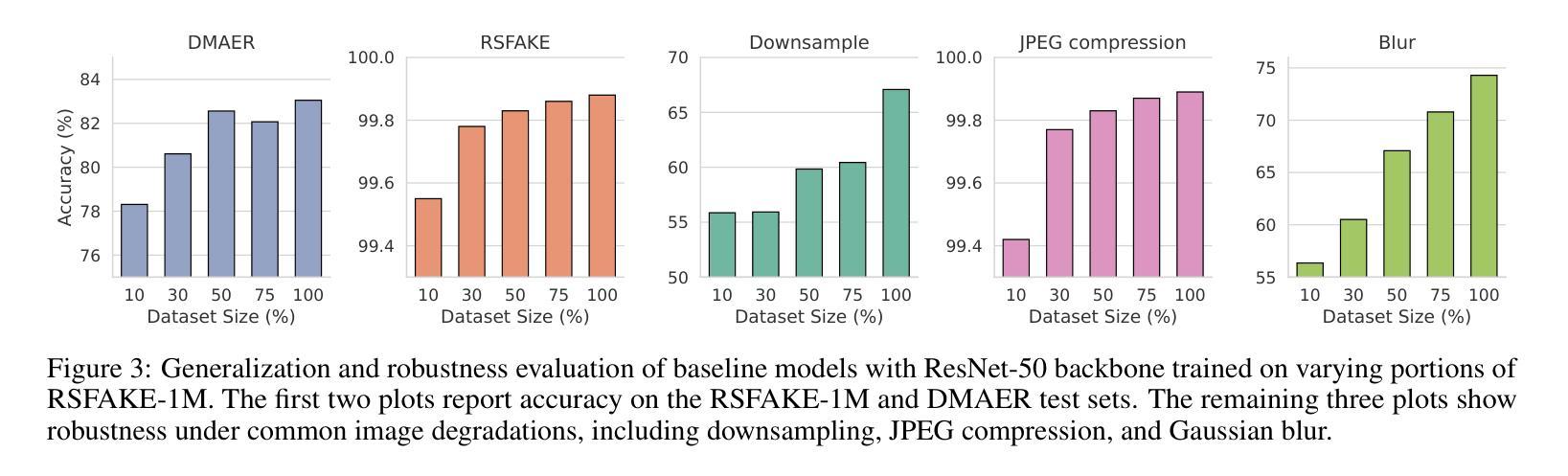
RSFAKE-1M: A Large-Scale Dataset for Detecting Diffusion-Generated Remote Sensing Forgeries
Authors:Zhihong Tan, Jiayi Wang, Huiying Shi, Binyuan Huang, Hongchen Wei, Zhenzhong Chen
Detecting forged remote sensing images is becoming increasingly critical, as such imagery plays a vital role in environmental monitoring, urban planning, and national security. While diffusion models have emerged as the dominant paradigm for image generation, their impact on remote sensing forgery detection remains underexplored. Existing benchmarks primarily target GAN-based forgeries or focus on natural images, limiting progress in this critical domain. To address this gap, we introduce RSFAKE-1M, a large-scale dataset of 500K forged and 500K real remote sensing images. The fake images are generated by ten diffusion models fine-tuned on remote sensing data, covering six generation conditions such as text prompts, structural guidance, and inpainting. This paper presents the construction of RSFAKE-1M along with a comprehensive experimental evaluation using both existing detectors and unified baselines. The results reveal that diffusion-based remote sensing forgeries remain challenging for current methods, and that models trained on RSFAKE-1M exhibit notably improved generalization and robustness. Our findings underscore the importance of RSFAKE-1M as a foundation for developing and evaluating next-generation forgery detection approaches in the remote sensing domain. The dataset and other supplementary materials are available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/TZHSW/RSFAKE/.
检测伪造遥感图像的工作变得越来越关键,因为此类图像在环境监测、城市规划和国家安全方面发挥着至关重要的作用。尽管扩散模型已经成为图像生成的主导范式,但它们对遥感伪造检测的影响仍被探索得不够充分。现有的基准测试主要面向基于GAN的伪造或自然图像,限制了这一关键领域的进展。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了RSFAKE-1M,这是一个包含50万张伪造的和50万张真实的遥感图像的大规模数据集。伪造图像是由10种经过遥感数据微调的扩散模型生成的,涵盖文本提示、结构指导、填充等六种生成条件。本文介绍了RSFAKE-1M的构建,以及使用现有检测器和统一基准进行的综合实验评估。结果表明,基于扩散的遥感伪造图像对当前方法来说仍然具有挑战性,而在RSFAKE-1M上训练的模型表现出显著改进的泛化能力和稳健性。我们的研究强调了RSFAKE-1M在遥感领域开发下一代伪造检测方法的评价工作中的重要性。数据集和其他辅助材料可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/TZHSW/RSFAKE/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文针对遥感图像伪造检测的重要性,提出了RSFAKE-1M数据集。该数据集包含50万张伪造的和50万张真实的遥感图像,由十种在遥感数据上微调过的扩散模型生成,涵盖六种生成条件。对现有检测器和统一基线进行的综合实验评估表明,基于扩散的遥感图像伪造仍对当前方法构成挑战,而在RSFAKE-1M上训练的模型表现出显著的提高。该数据集是开发下一代遥感领域伪造检测方法的基石。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像伪造检测的重要性在环境监控、城市规划和国家安全等领域中日益凸显。
- 扩散模型已成为图像生成的主导范式,但在遥感伪造检测领域的影响仍待探索。
- 现有基准测试主要关注GAN基础的伪造或自然图像,限制了遥感图像伪造检测的进展。
- 提出RSFAKE-1M数据集,包含50万张由十种扩散模型生成的伪造和真实遥感图像。
- 综合实验评估显示,基于扩散的遥感图像伪造对现行方法构成挑战。
- 在RSFAKE-1M上训练的模型表现出更好的泛化和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图