⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
Adaptive Spatial Augmentation for Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Lingyan Ran, Yali Li, Tao Zhuo, Shizhou Zhang, Yanning Zhang
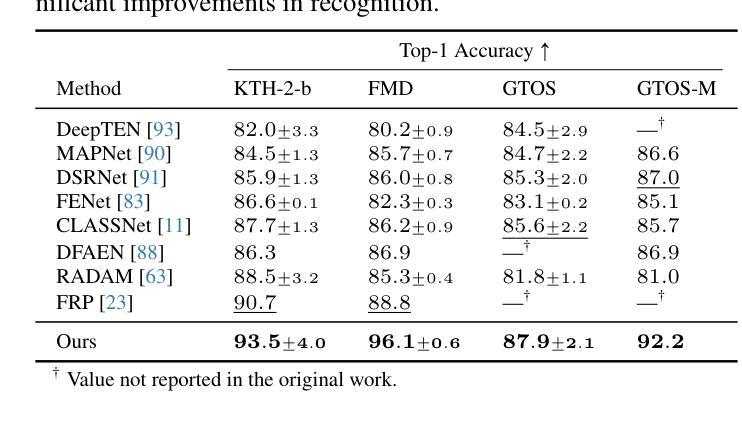
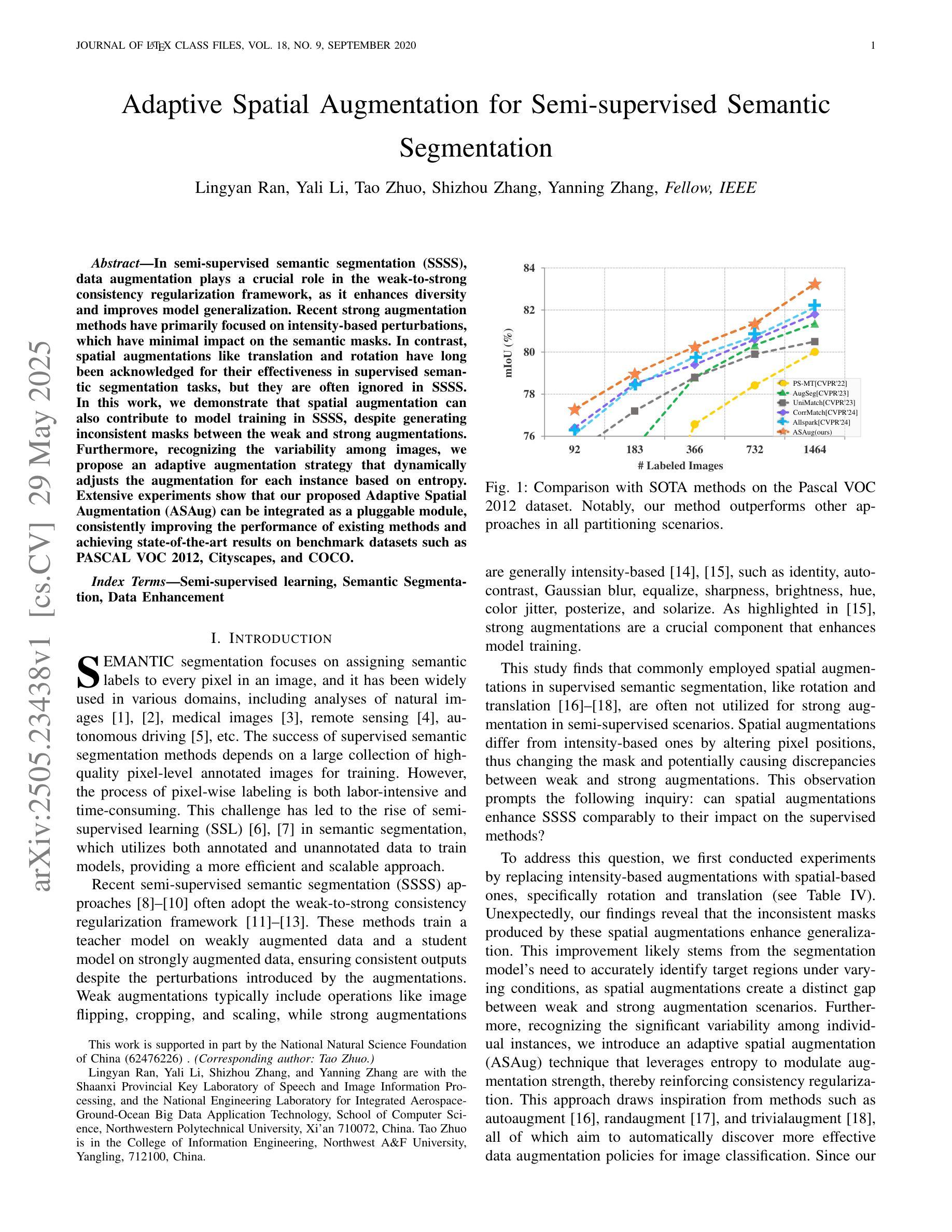
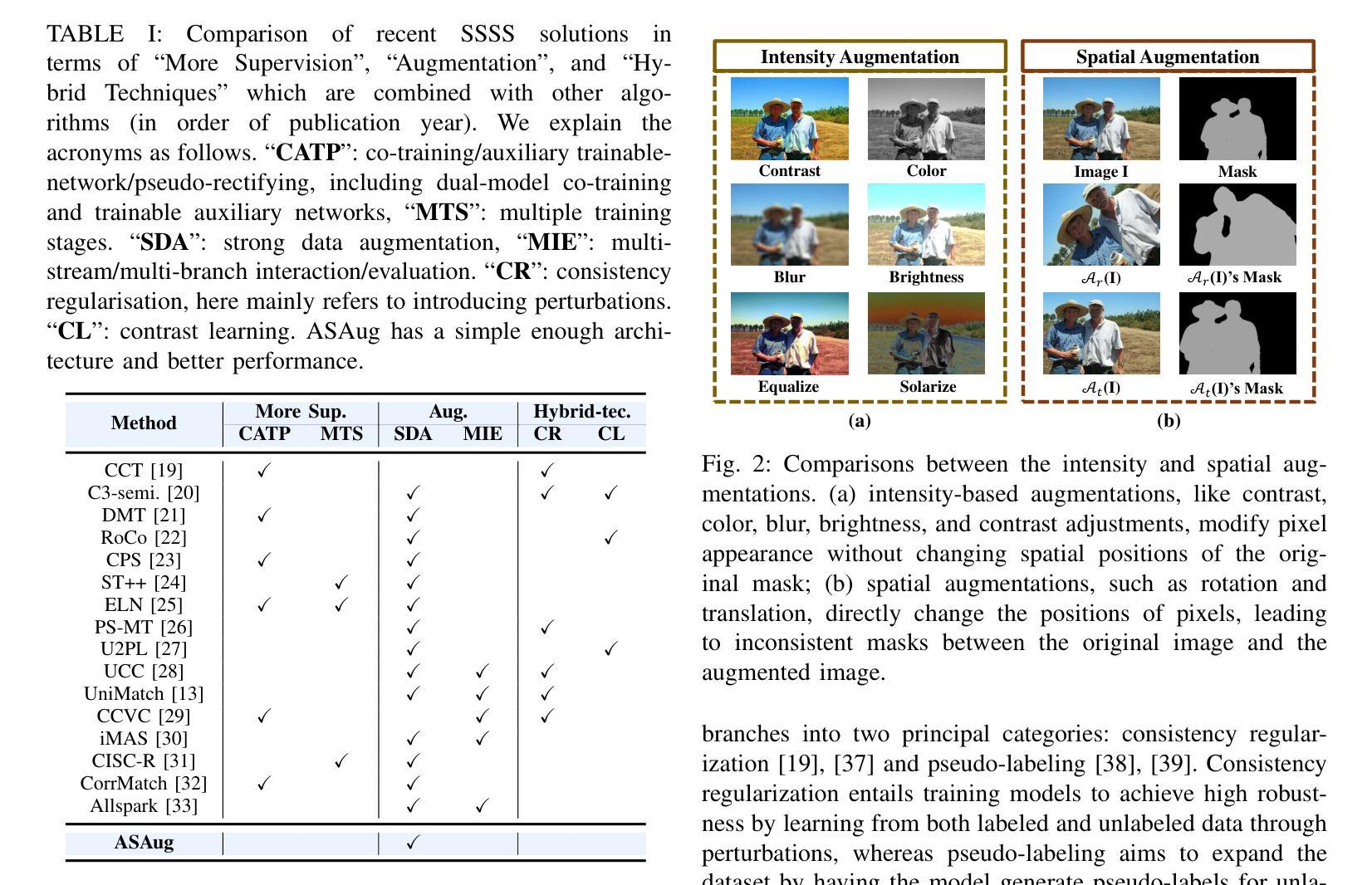
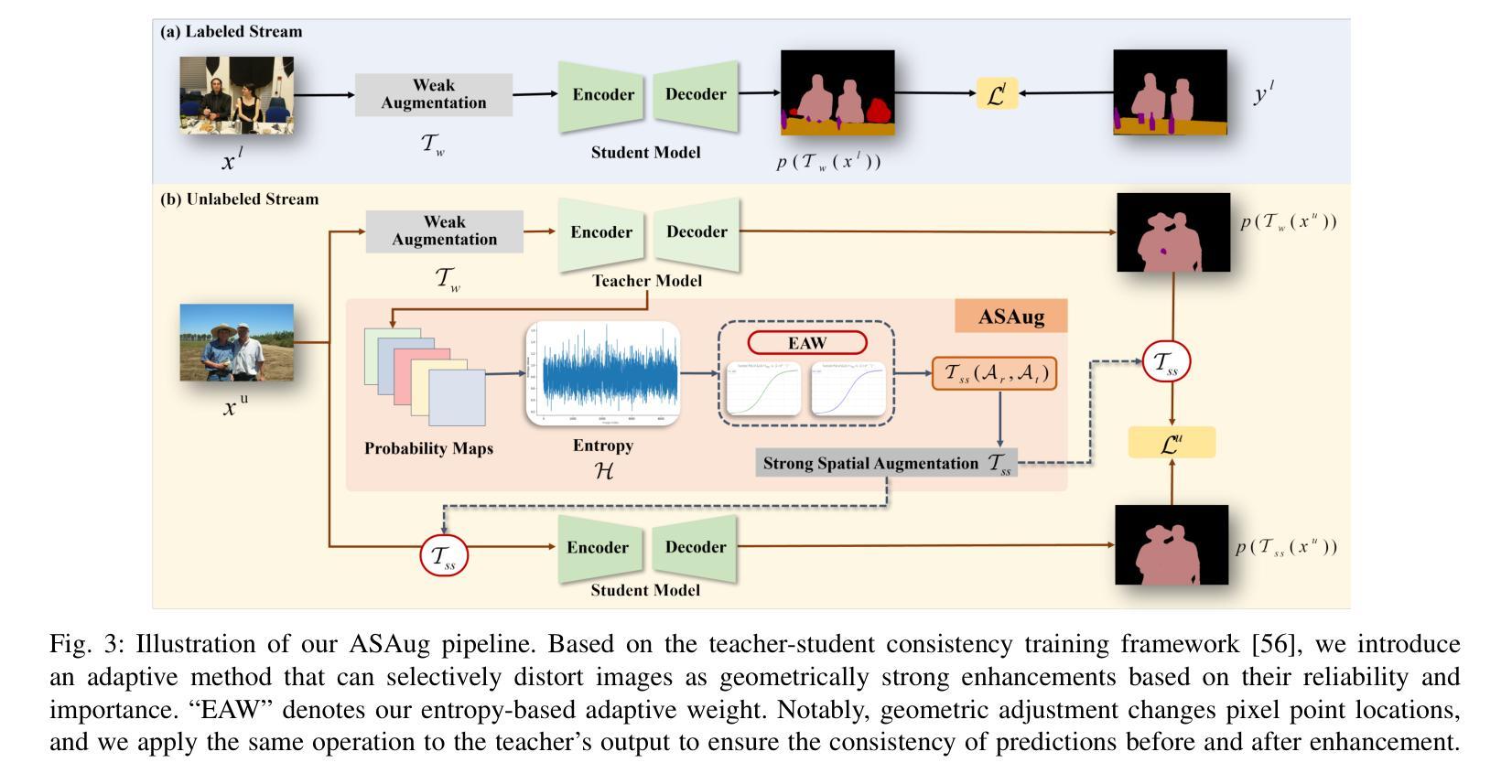
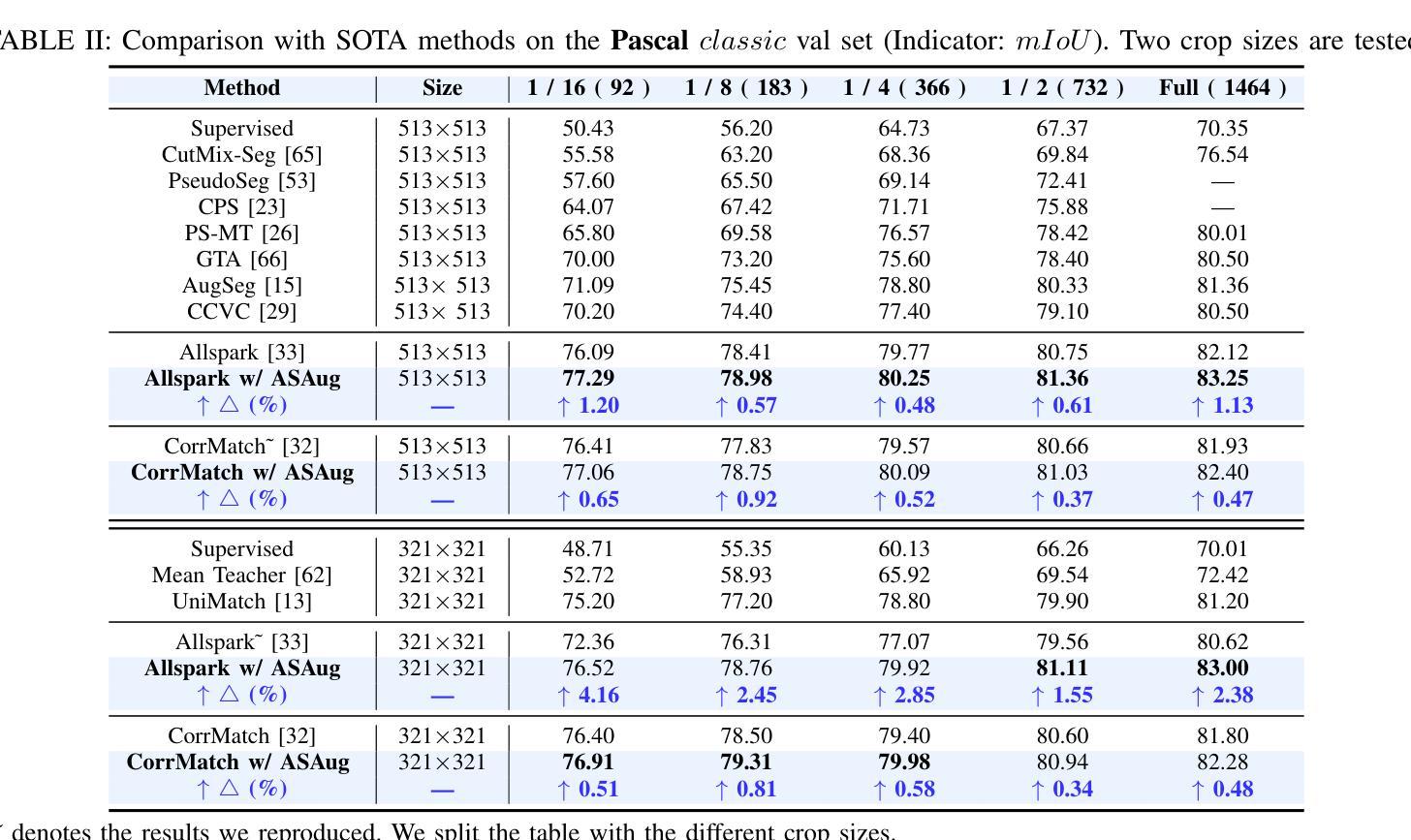
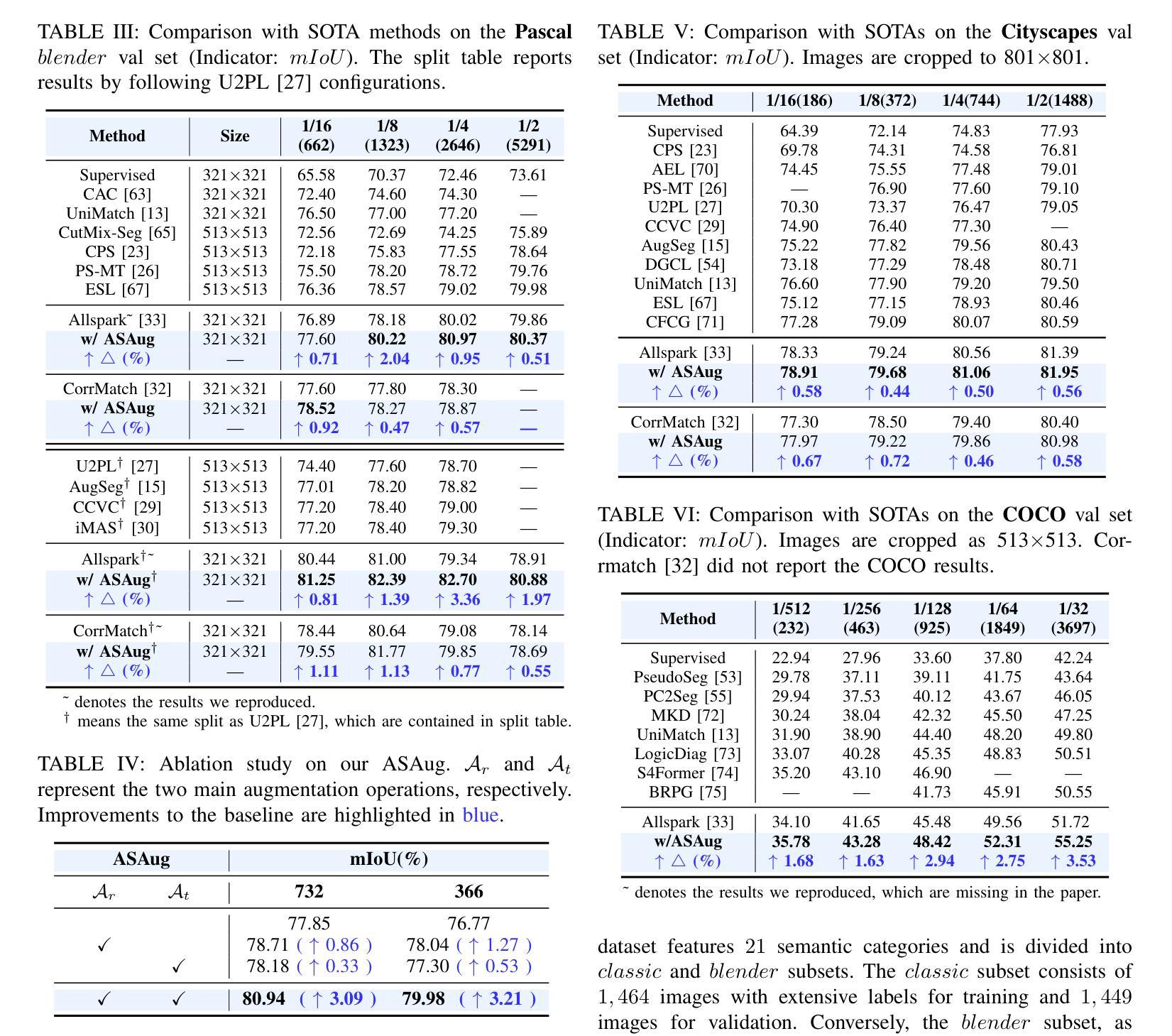
In semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS), data augmentation plays a crucial role in the weak-to-strong consistency regularization framework, as it enhances diversity and improves model generalization. Recent strong augmentation methods have primarily focused on intensity-based perturbations, which have minimal impact on the semantic masks. In contrast, spatial augmentations like translation and rotation have long been acknowledged for their effectiveness in supervised semantic segmentation tasks, but they are often ignored in SSSS. In this work, we demonstrate that spatial augmentation can also contribute to model training in SSSS, despite generating inconsistent masks between the weak and strong augmentations. Furthermore, recognizing the variability among images, we propose an adaptive augmentation strategy that dynamically adjusts the augmentation for each instance based on entropy. Extensive experiments show that our proposed Adaptive Spatial Augmentation (\textbf{ASAug}) can be integrated as a pluggable module, consistently improving the performance of existing methods and achieving state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets such as PASCAL VOC 2012, Cityscapes, and COCO.
在弱到强的半监督语义分割(SSSS)一致性正则框架中,数据增强起到了关键作用,增强了数据的多样性并提高了模型的泛化能力。最近的强增强方法主要集中在基于强度的扰动上,对语义掩膜的影响微乎其微。相比之下,空间增强(如平移和旋转)在监督语义分割任务中长期被认为是有效的,但在SSSS中往往被忽视。在这项工作中,我们证明了空间增强也可以对SSSS模型的训练做出贡献,尽管它在弱增强和强增强之间产生了不一致的掩膜。此外,为了识别图像之间的差异,我们提出了一种自适应增强策略,该策略会根据熵动态调整每个实例的增强方法。大量实验表明,我们提出的自适应空间增强(ASAug)可以作为一个插件模块进行集成,能够持续提高现有方法的效果,并在PASCAL VOC 2012、Cityscapes和COCO等基准数据集上实现最新成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 8 figures
Summary
半监督语义分割中数据增强对于弱到强一致性正则化框架至关重要,可以增强模型的多样性和泛化能力。本文提出自适应空间增强策略(Adaptive Spatial Augmentation),能根据图像熵动态调整每个实例的增强策略,提高现有方法的性能,并在PASCAL VOC 2012、Cityscapes和COCO等基准数据集上实现最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在半监督语义分割(SSSS)中的重要性。
- 弱到强一致性正则化框架通过数据增强提高模型性能。
- 空间增强(如平移和旋转)在SSSS中的有效性被忽视。
- 自适应空间增强策略(ASAug)能根据图像熵动态调整增强策略。
- ASAug可以集成到现有方法中,提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

Document-Level Text Generation with Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding using Optimal Transport
Authors:Yuu Jinnai
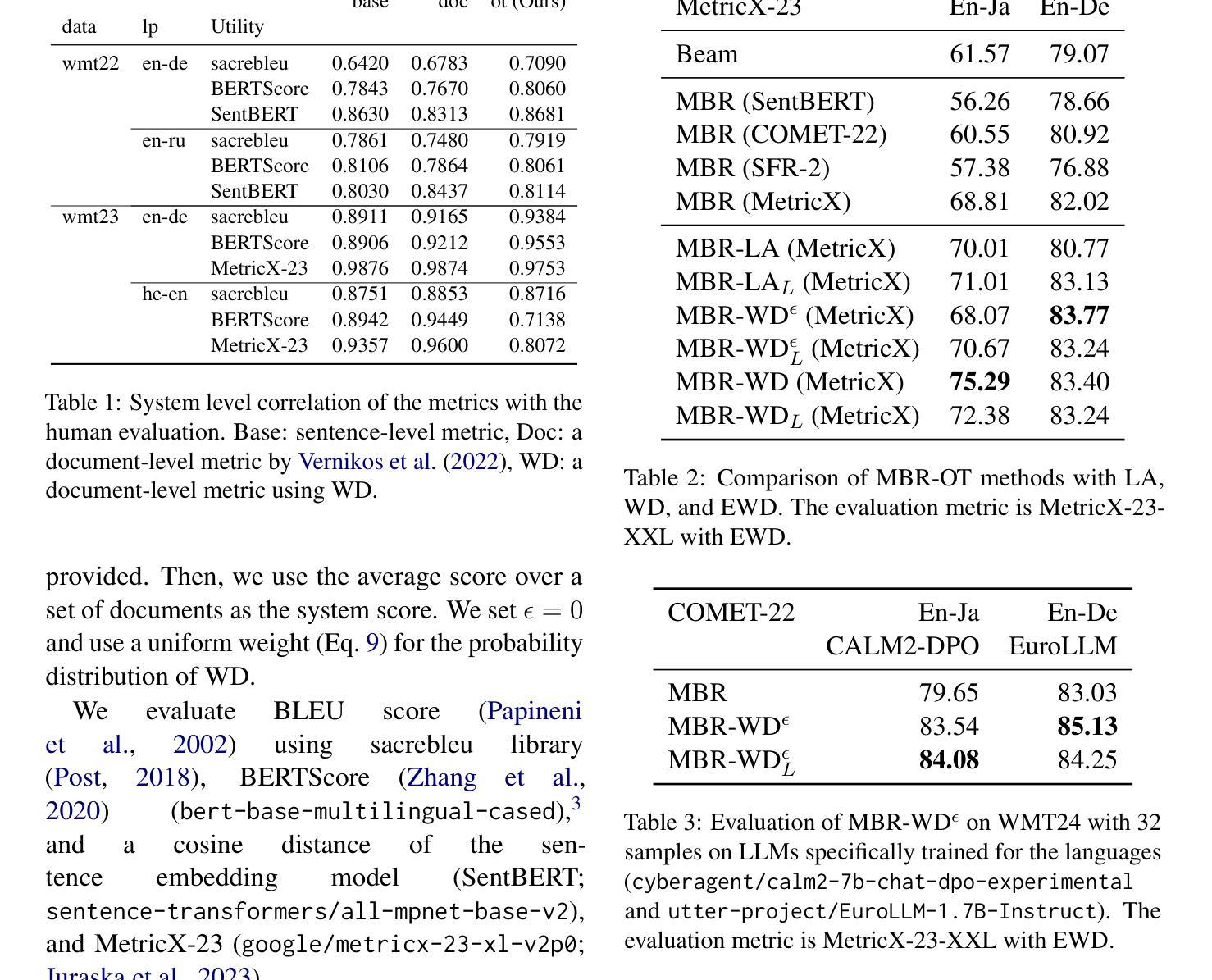
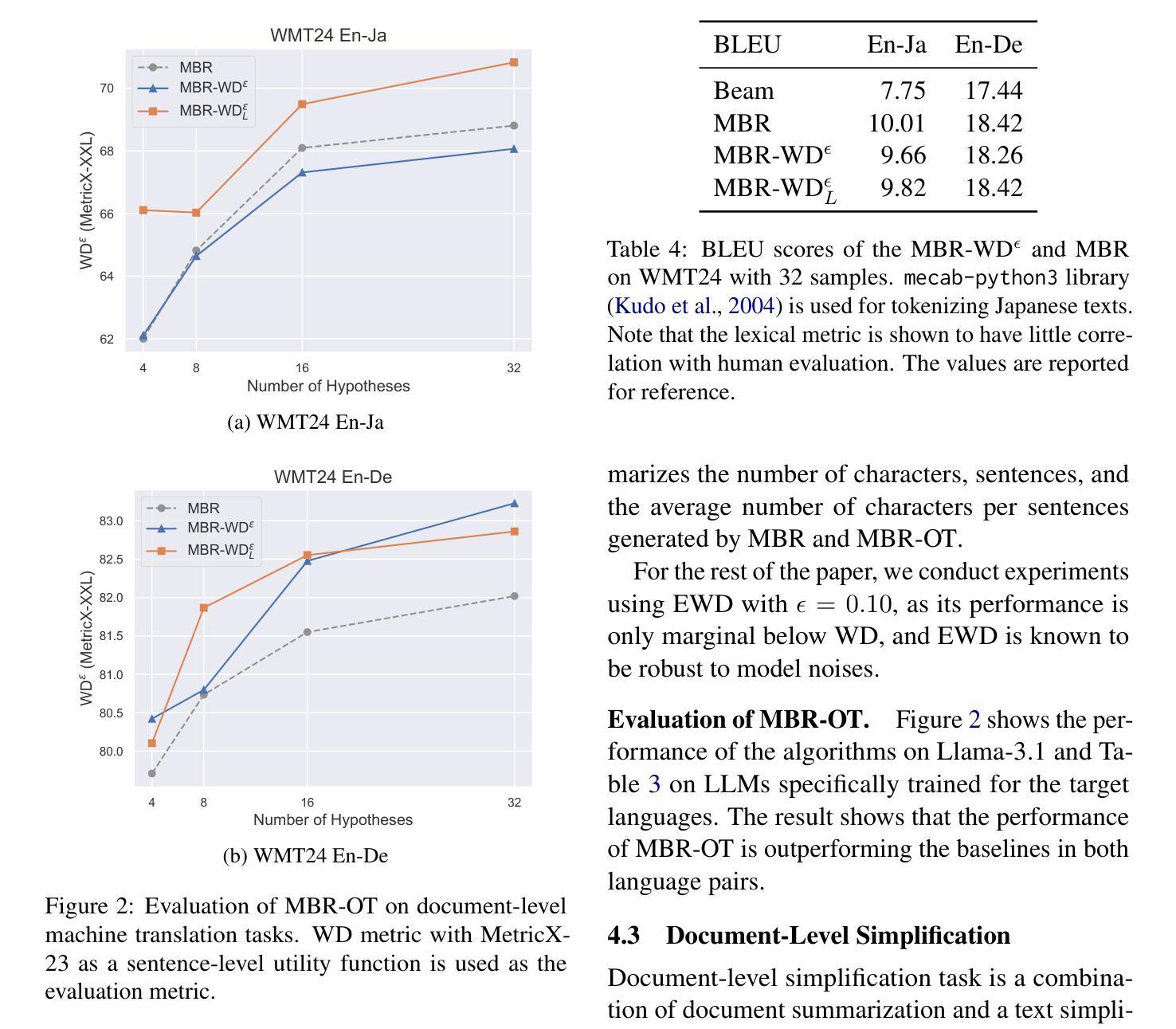
Document-level text generation tasks are known to be more difficult than sentence-level text generation tasks as they require the understanding of longer context to generate high-quality texts. In this paper, we investigate the adaption of Minimum Bayes Risk (MBR) decoding for document-level text generation tasks. MBR decoding makes use of a utility function to estimate the output with the highest expected utility from a set of candidate outputs. Although MBR decoding is shown to be effective in a wide range of sentence-level text generation tasks, its performance on document-level text generation tasks is limited as many of the utility functions are designed for evaluating the utility of sentences. To this end, we propose MBR-OT, a variant of MBR decoding using Wasserstein distance to compute the utility of a document using a sentence-level utility function. The experimental result shows that the performance of MBR-OT outperforms that of the standard MBR in document-level machine translation, text simplification, and dense image captioning tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/jinnaiyuu/mbr-optimal-transport
文档级别的文本生成任务比句子级别的文本生成任务更为困难,因为它们需要理解更长的上下文来生成高质量的文本。在本文中,我们研究了最小贝叶斯风险(MBR)解码在文档级别文本生成任务中的应用。MBR解码利用效用函数来估计一组候选输出中具有最高预期效用的输出。尽管MBR解码在多种句子级别的文本生成任务中被证明是有效的,但它在文档级别的文本生成任务上的表现受到限制,因为许多效用函数都是为评估句子的效用而设计的。为此,我们提出了MBR-OT,这是一种利用Wasserstein距离计算文档的效用的MBR解码的变体,使用句子级别的效用函数。实验结果表明,在文档级别的机器翻译、文本简化和密集图像描述任务中,MBR-OT的性能优于标准MBR。我们的代码可在https://github.com/jinnaiyuu/mbr-optimal-transport找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025
Summary
该文探讨了将最小贝叶斯风险(MBR)解码应用于文档级文本生成任务的适应性改进。MBR解码利用效用函数来估计一组候选输出中预期效用最高的输出。尽管MBR解码在句子级文本生成任务中表现有效,但在文档级文本生成任务中的性能受限,因为许多效用函数是为评估句子的效用而设计的。为此,我们提出了MBR-OT,这是MBR解码的一种变体,它使用Wasserstein距离来计算文档的效用,并使用句子级效用函数。实验结果表明,在文档级机器翻译、文本简化和密集图像描述任务中,MBR-OT的性能优于标准MBR。
Key Takeaways
- 文档级文本生成任务比句子级文本生成任务更为困难,需要理解更长的上下文来生成高质量的文本。
- MBR解码是一种利用效用函数来选择最佳输出的方法,已在多种句子级文本生成任务中证明有效。
- MBR解码在文档级文本生成任务中的性能受限,因为许多现有的效用函数是为句子设计的。
- 提出了MBR-OT,这是MBR解码的一种改进,采用Wasserstein距离来计算文档的效用。
- MBR-OT在文档级机器翻译、文本简化和密集图像描述任务中的性能优于标准MBR。
- 研究所提出的MBR-OT的源代码已公开分享在相关GitHub仓库中。
点此查看论文截图

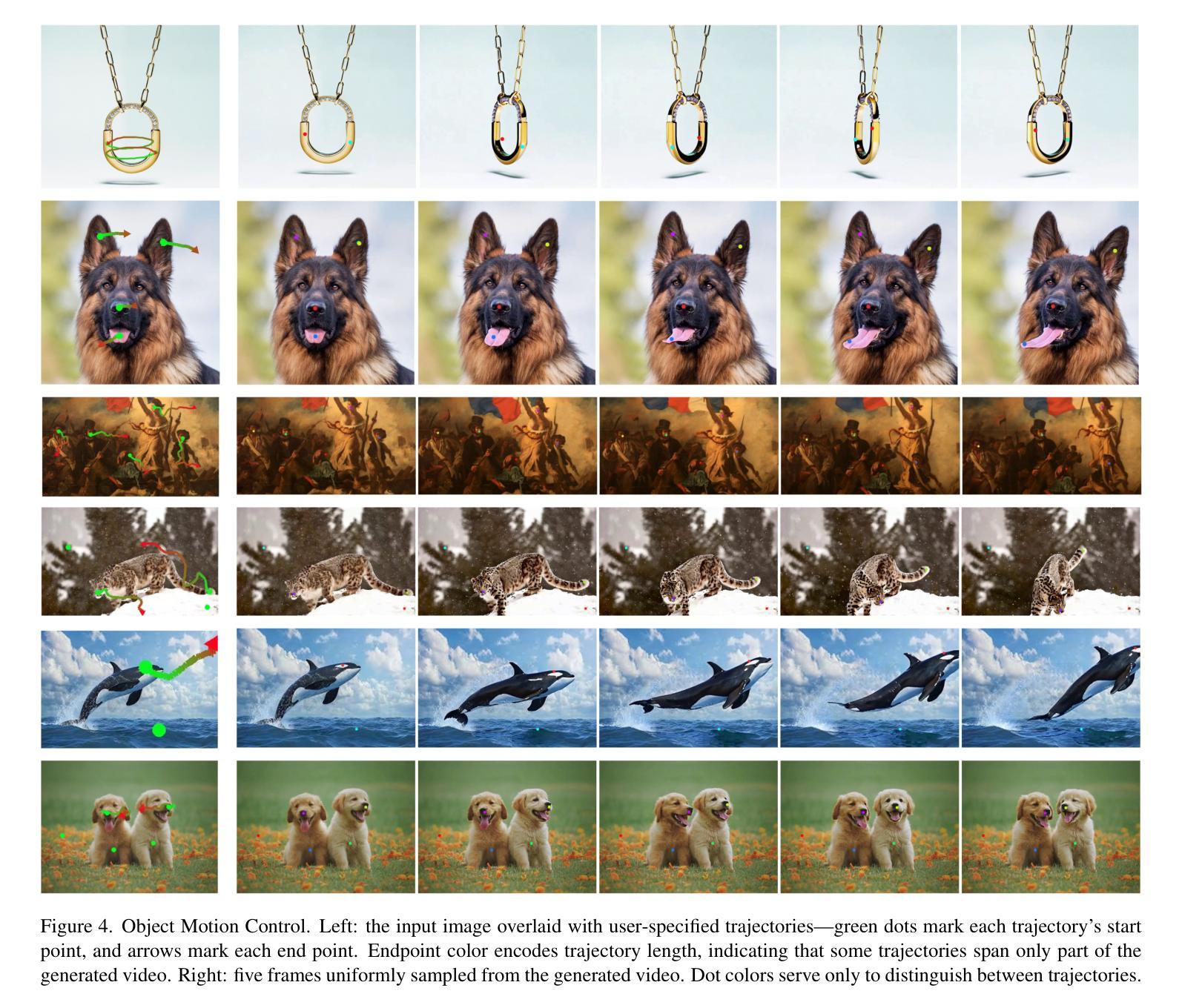
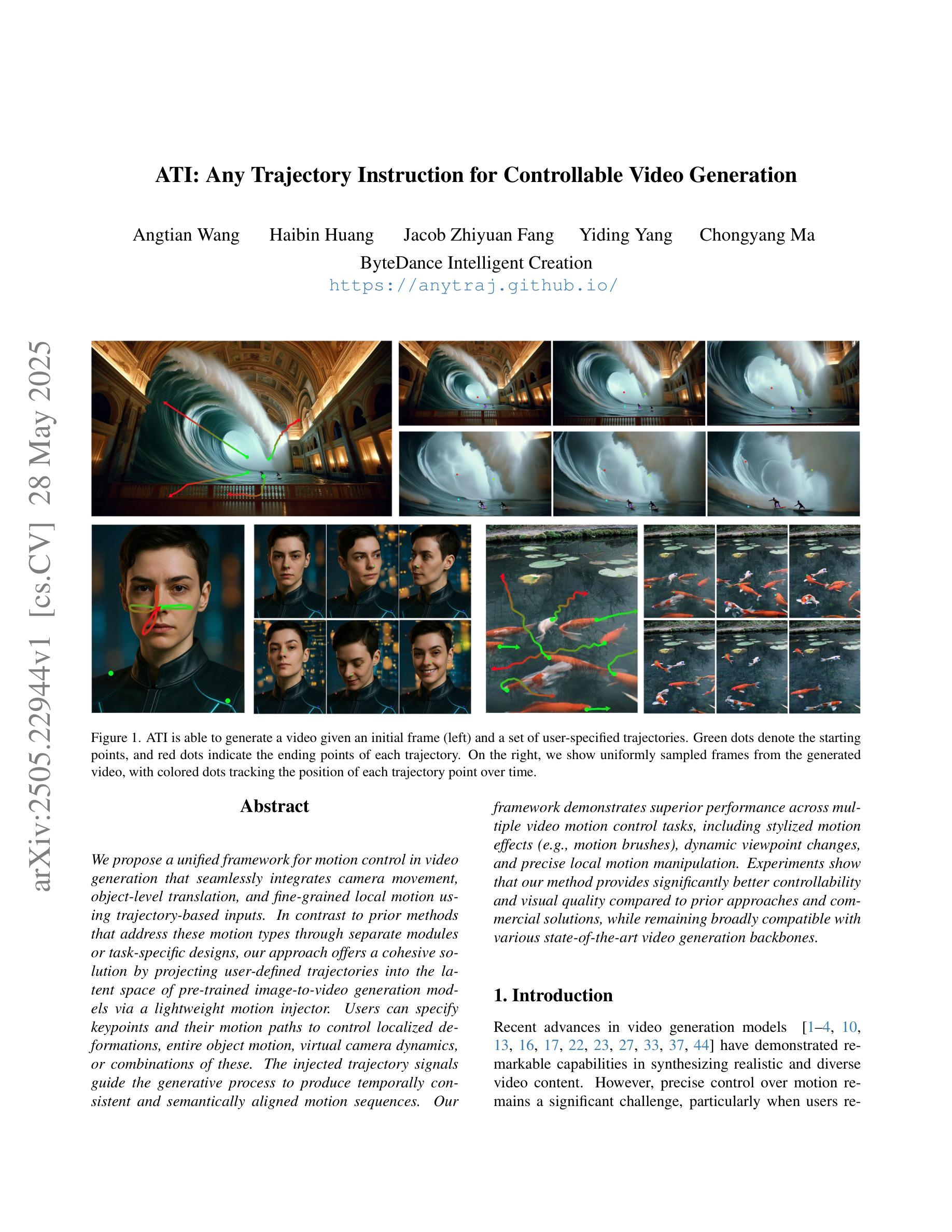
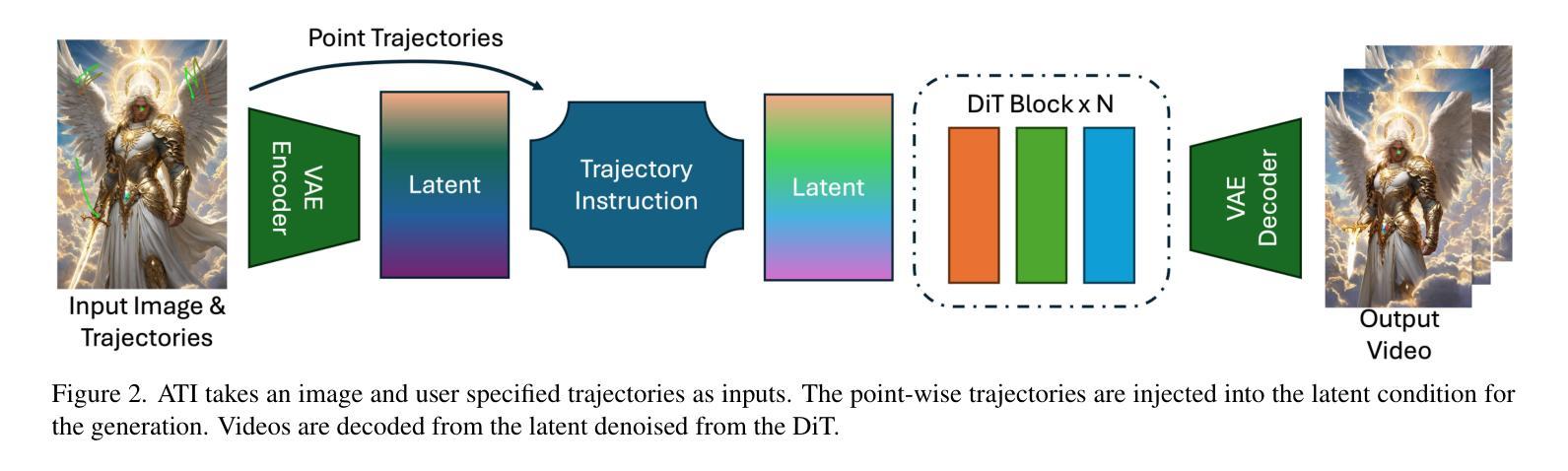
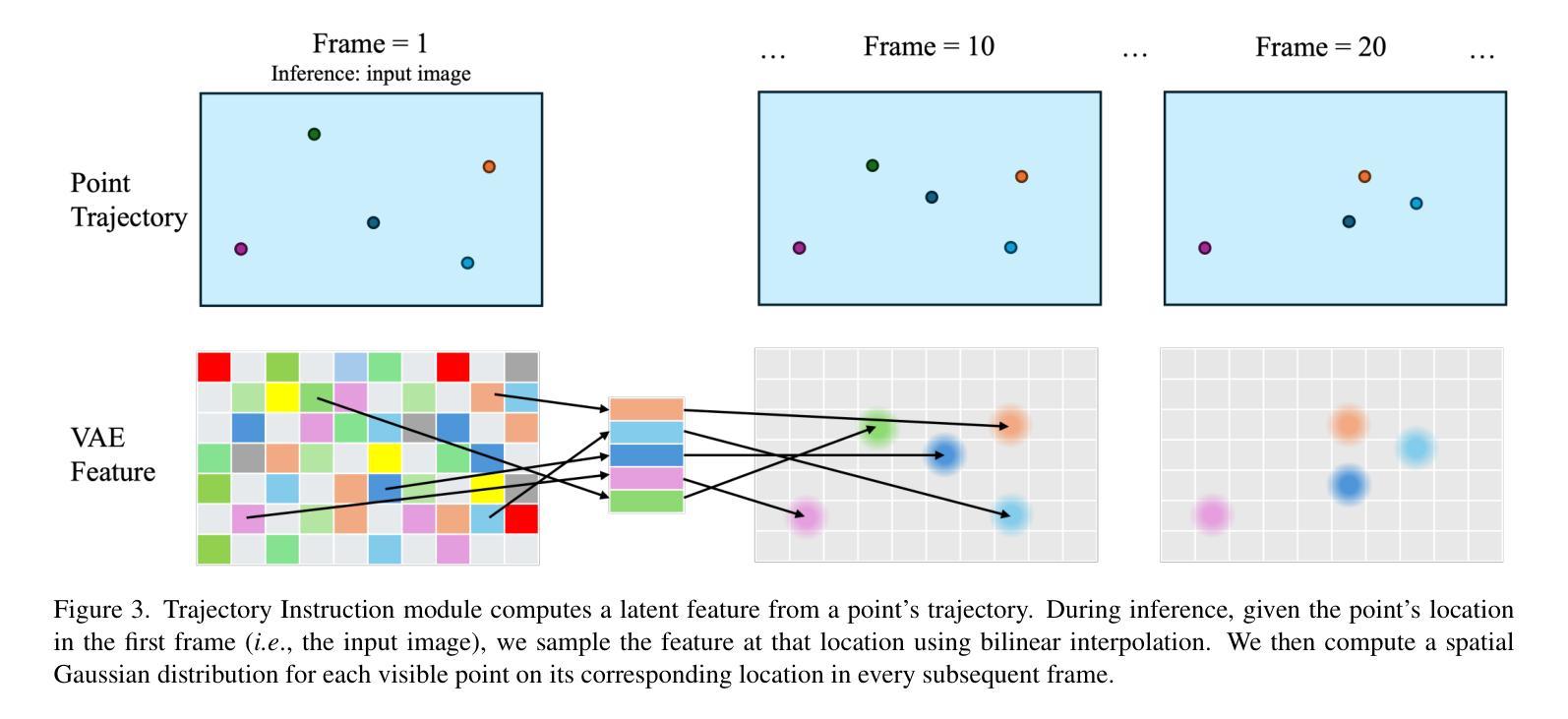
ATI: Any Trajectory Instruction for Controllable Video Generation
Authors:Angtian Wang, Haibin Huang, Jacob Zhiyuan Fang, Yiding Yang, Chongyang Ma
We propose a unified framework for motion control in video generation that seamlessly integrates camera movement, object-level translation, and fine-grained local motion using trajectory-based inputs. In contrast to prior methods that address these motion types through separate modules or task-specific designs, our approach offers a cohesive solution by projecting user-defined trajectories into the latent space of pre-trained image-to-video generation models via a lightweight motion injector. Users can specify keypoints and their motion paths to control localized deformations, entire object motion, virtual camera dynamics, or combinations of these. The injected trajectory signals guide the generative process to produce temporally consistent and semantically aligned motion sequences. Our framework demonstrates superior performance across multiple video motion control tasks, including stylized motion effects (e.g., motion brushes), dynamic viewpoint changes, and precise local motion manipulation. Experiments show that our method provides significantly better controllability and visual quality compared to prior approaches and commercial solutions, while remaining broadly compatible with various state-of-the-art video generation backbones. Project page: https://anytraj.github.io/.
我们提出一种视频生成中的运动控制统一框架,该框架无缝集成了摄像机移动、对象级别的平移和基于轨迹的输入进行精细局部运动。与之前通过单独模块或特定任务设计来解决这些运动类型的方法相比,我们的方法通过轻量级运动注入器将用户定义的轨迹投影到预训练图像到视频生成模型的潜在空间中,从而提供一种连贯的解决方案。用户可以通过指定关键点及其运动路径来控制局部变形、整个物体的运动、虚拟相机的动态或这些的组合。注入的轨迹信号引导生成过程,以产生时间上一致且语义上对齐的运动序列。我们的框架在多个视频运动控制任务中表现出卓越的性能,包括风格化的运动效果(例如运动刷)、动态视点变化和精确的局部运动操纵。实验表明,我们的方法与先前的方法和商业解决方案相比,在可控性和视觉质量方面提供了显著改善,同时与各种最先进的视频生成主干技术广泛兼容。项目页面:https://anytraj.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一个统一框架,通过轨迹输入无缝集成摄像机移动、物体级别翻译和精细局部运动,实现视频生成中的运动控制。该方法将用户定义的轨迹投影到预训练图像到视频生成模型的潜在空间中,通过轻量级运动注射器提供整体解决方案,可控制局部变形、整个物体运动、虚拟相机动态或这些的组合。注入的轨迹信号引导生成过程,产生时间一致和语义对齐的运动序列。该框架在多个视频运动控制任务中表现出卓越性能,包括风格化运动效果、动态视点变化和精确局部运动操纵。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一个统一框架用于视频生成中的运动控制,集成摄像机移动、物体级别翻译和精细局部运动。
- 通过轻量级运动注射器,将用户定义的轨迹投影到预训练模型的潜在空间。
- 用户可控制局部变形、整个物体运动、虚拟相机动态或这些的组合。
- 注入的轨迹信号产生时间一致和语义对齐的运动序列。
- 框架适用于多种视频运动控制任务,包括风格化运动效果、动态视点变化和精确局部运动操纵。
- 实验显示,该方法在性能上显著优于先前的方法和商业解决方案。
点此查看论文截图