⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
Argus: Vision-Centric Reasoning with Grounded Chain-of-Thought
Authors:Yunze Man, De-An Huang, Guilin Liu, Shiwei Sheng, Shilong Liu, Liang-Yan Gui, Jan Kautz, Yu-Xiong Wang, Zhiding Yu
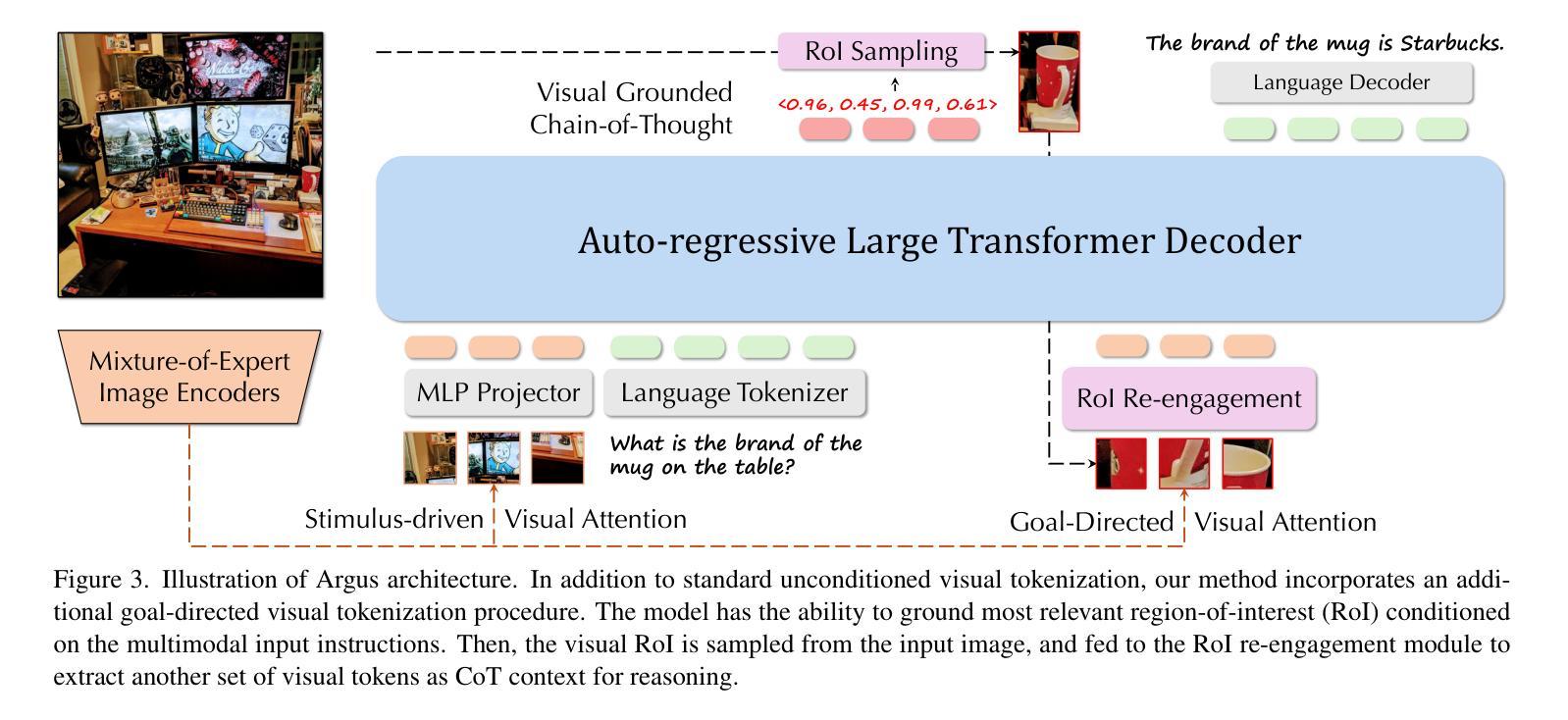
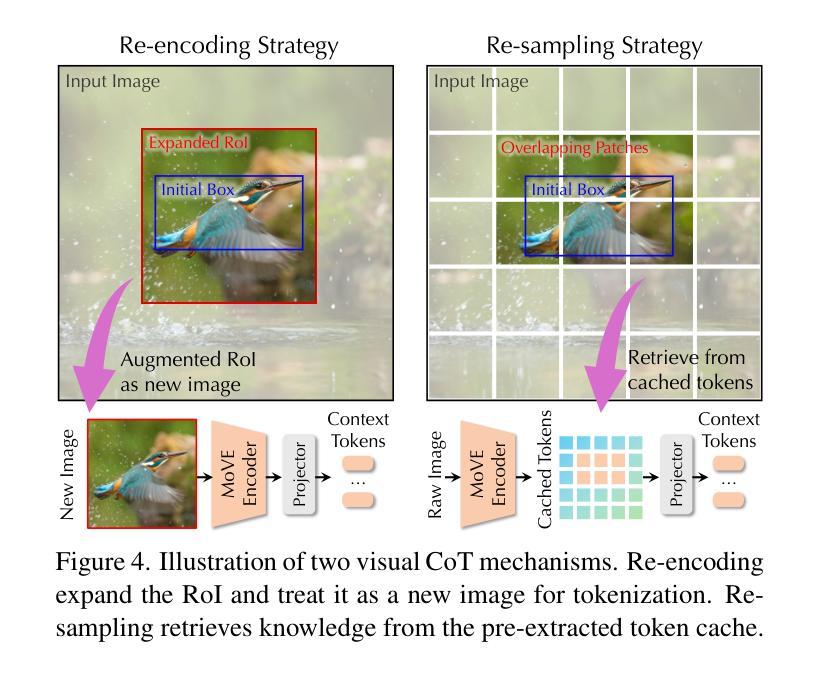
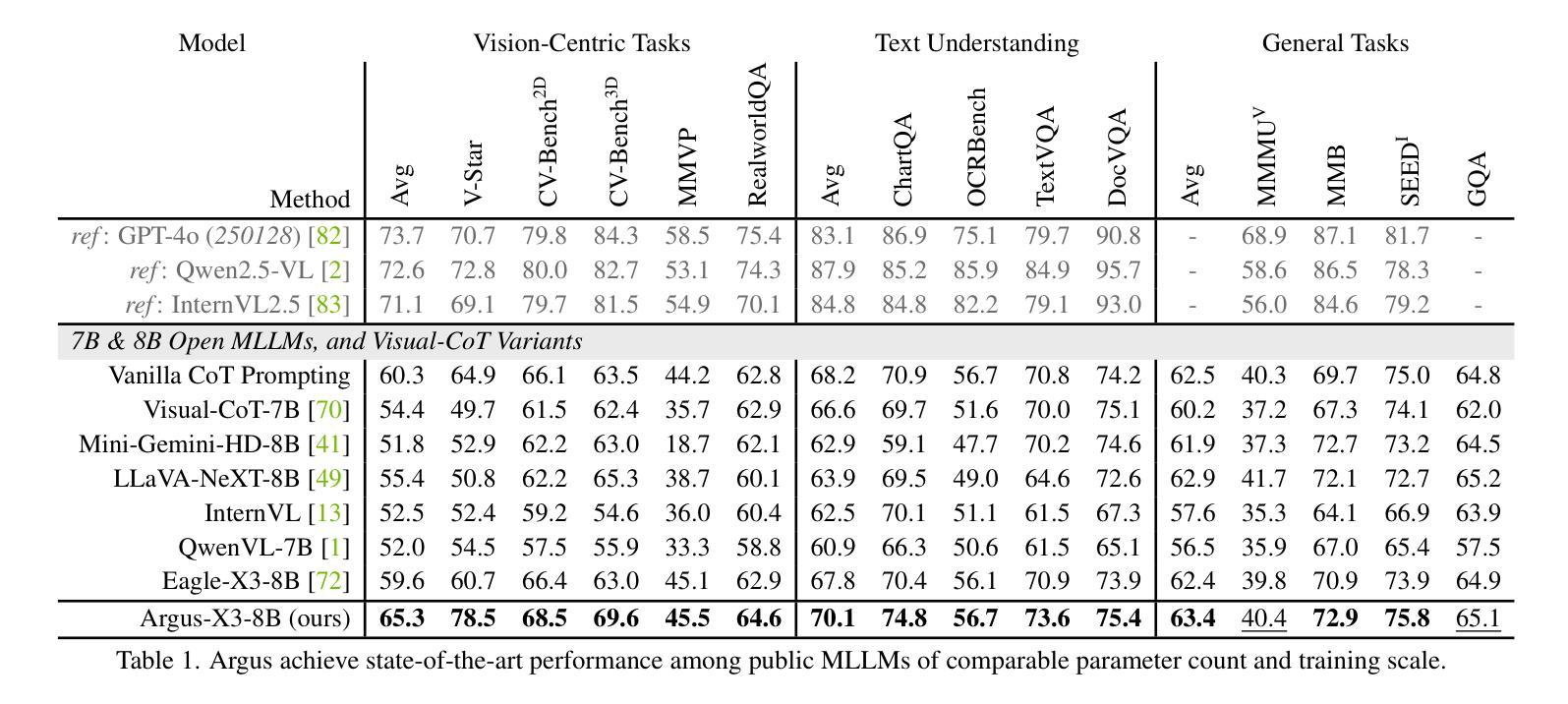
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in vision-language tasks, yet they often struggle with vision-centric scenarios where precise visual focus is needed for accurate reasoning. In this paper, we introduce Argus to address these limitations with a new visual attention grounding mechanism. Our approach employs object-centric grounding as visual chain-of-thought signals, enabling more effective goal-conditioned visual attention during multimodal reasoning tasks. Evaluations on diverse benchmarks demonstrate that Argus excels in both multimodal reasoning tasks and referring object grounding tasks. Extensive analysis further validates various design choices of Argus, and reveals the effectiveness of explicit language-guided visual region-of-interest engagement in MLLMs, highlighting the importance of advancing multimodal intelligence from a visual-centric perspective. Project page: https://yunzeman.github.io/argus/
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进步在视觉语言任务中表现出了显著的能力,然而,它们在以视觉为中心的场景中往往面临困难,这些场景需要精确的视觉焦点来进行准确推理。针对这些局限性,本文引入了Argus,通过一种新的视觉注意力定位机制来解决问题。我们的方法采用对象为中心的定位作为视觉思维链信号,使多模态推理任务期间的以目标为导向的视觉注意力更加有效。在多种基准测试上的评估表明,Argus在多模态推理任务和指代对象定位任务中都表现出色。进一步的分析验证了Argus的各种设计选择的有效性,并揭示了MLLM中明确的语言引导的视觉感兴趣区域参与的重要性,强调了从视觉中心视角发展多模态智能的重要性。项目页面:https://yunzeman.github.io/argus/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://yunzeman.github.io/argus/
Summary
近期多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言任务中展现出卓越的能力,但在需要精确视觉推理的以视觉为中心的场景中常面临挑战。本文提出Argus,通过新的视觉注意力定位机制来解决这些问题。Argus采用对象为中心的定位作为视觉思维信号,在多媒体推理任务中更有效地实现目标导向的视觉注意力。在不同基准测试上的评估表明,Argus在多模态推理任务和指代对象定位任务中都表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- Argus通过引入新的视觉注意力定位机制,解决了多模态大型语言模型在视觉为中心的场景中的挑战。
- Argus采用对象为中心的定位作为视觉思维信号,提升多媒体推理任务中的目标导向视觉注意力。
- Argus在多种基准测试上的表现优异,证明其有效性和实用性。
- 全面的分析验证了Argus各种设计选择的有效性。
- Argus强调了在多模态智能中明确语言引导的视觉区域兴趣点参与的重要性。
- Argus的引入为推进多模态智能从以视觉为中心的角度提供了有效手段。
点此查看论文截图


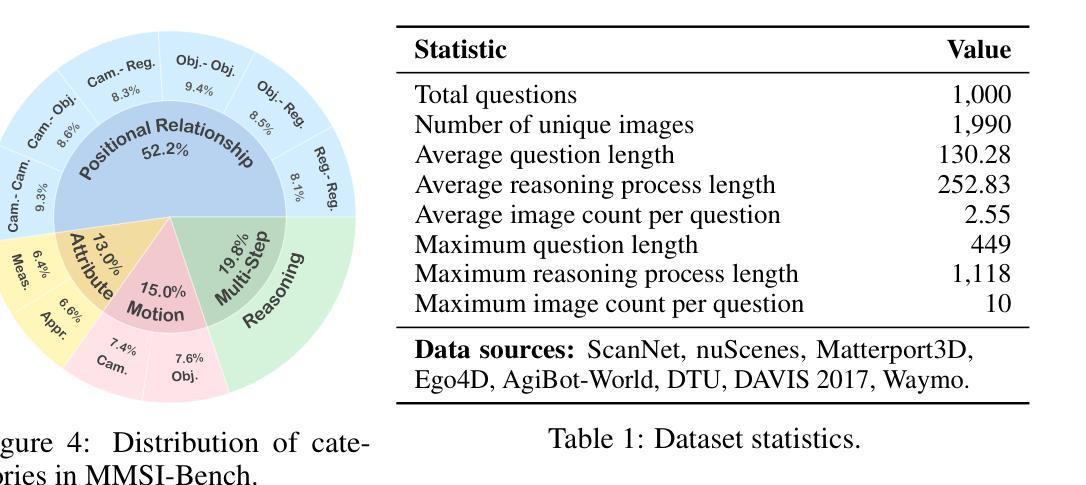
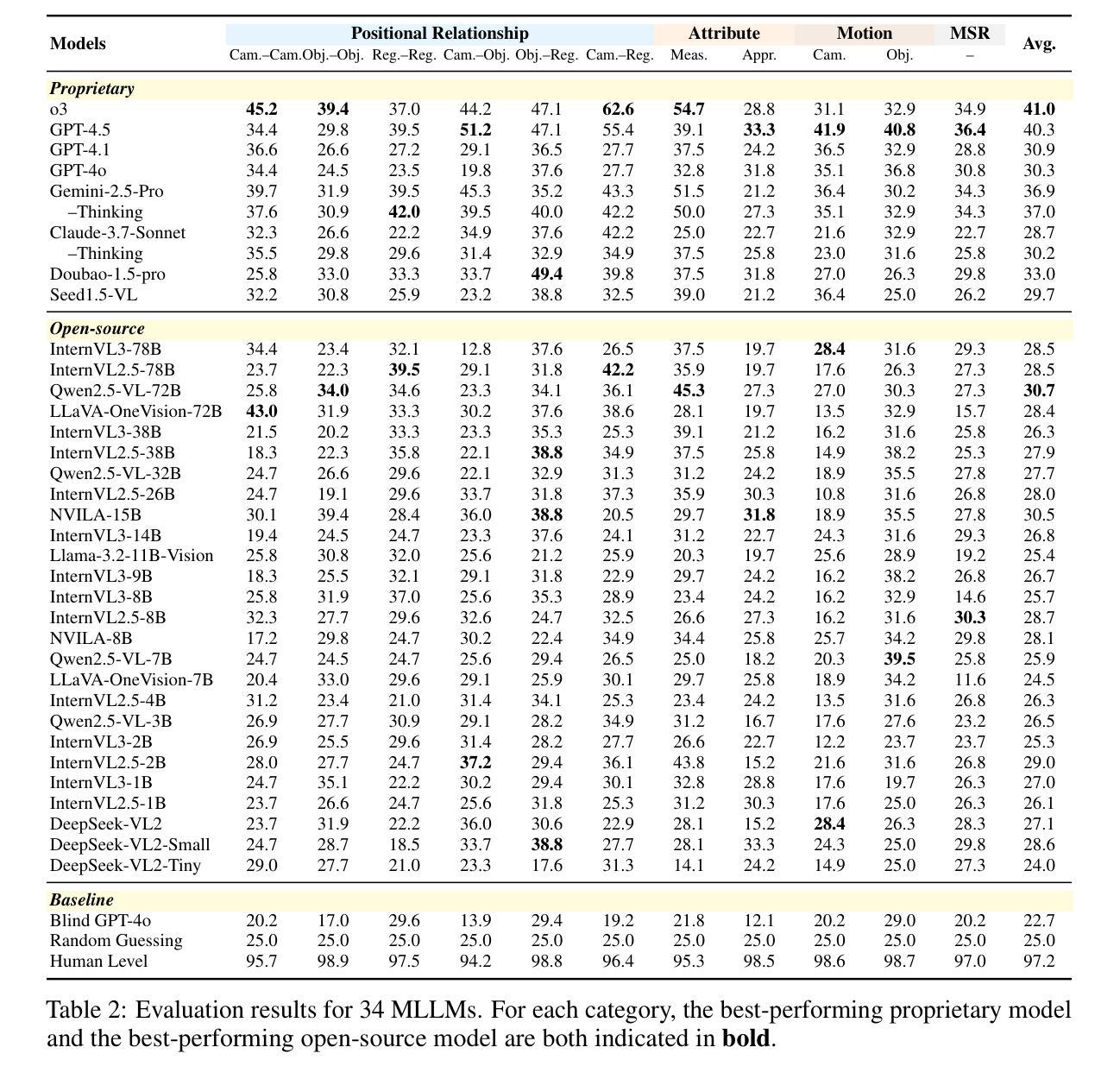
MMSI-Bench: A Benchmark for Multi-Image Spatial Intelligence
Authors:Sihan Yang, Runsen Xu, Yiman Xie, Sizhe Yang, Mo Li, Jingli Lin, Chenming Zhu, Xiaochen Chen, Haodong Duan, Xiangyu Yue, Dahua Lin, Tai Wang, Jiangmiao Pang
Spatial intelligence is essential for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) operating in the complex physical world. Existing benchmarks, however, probe only single-image relations and thus fail to assess the multi-image spatial reasoning that real-world deployments demand. We introduce MMSI-Bench, a VQA benchmark dedicated to multi-image spatial intelligence. Six 3D-vision researchers spent more than 300 hours meticulously crafting 1,000 challenging, unambiguous multiple-choice questions from over 120,000 images, each paired with carefully designed distractors and a step-by-step reasoning process. We conduct extensive experiments and thoroughly evaluate 34 open-source and proprietary MLLMs, observing a wide gap: the strongest open-source model attains roughly 30% accuracy and OpenAI’s o3 reasoning model reaches 40%, while humans score 97%. These results underscore the challenging nature of MMSI-Bench and the substantial headroom for future research. Leveraging the annotated reasoning processes, we also provide an automated error analysis pipeline that diagnoses four dominant failure modes, including (1) grounding errors, (2) overlap-matching and scene-reconstruction errors, (3) situation-transformation reasoning errors, and (4) spatial-logic errors, offering valuable insights for advancing multi-image spatial intelligence. Project page: https://runsenxu.com/projects/MMSI_Bench .
空间智能对于在复杂的物理世界中运行的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)至关重要。然而,现有的基准测试仅探讨单图像关系,因此无法评估现实世界部署所需的多图像空间推理能力。我们引入了MMSI-Bench,这是一个专门用于多图像空间智能的VQA基准测试。六位3D视觉研究人员花费了超过300小时的时间,从超过12万张图像中精心创作了1000个具有挑战性、无歧义的多项选择题,每个问题都配备了精心设计的干扰项和逐步推理过程。我们进行了广泛的实验,并对34个开源和专有MLLM进行了全面评估,观察到较大的差距:最强的开源模型准确率约为30%,OpenAI的o3推理模型达到40%,而人类得分为97%。这些结果强调了MMSI-Bench的挑战性,以及未来研究的巨大潜力。利用注释的推理过程,我们还提供了一个自动错误分析管道,诊断了四种主要的失败模式,包括(1)接地错误,(2)重叠匹配和场景重建错误,(3)情况转换推理错误,和(4)空间逻辑错误,为推进多图像空间智能提供了宝贵的见解。项目页面:https://runsenxu.com/projects/MMSI_Bench。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 34 pages. A comprehensive, fully human-curated, multi-image-based spatial intelligence benchmark with reasoning annotation for MLLMs. Project page: https://runsenxu.com/projects/MMSI_Bench
Summary
空间智能对于在复杂物理世界中运行的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)至关重要。然而,现有的基准测试仅探索单图像关系,无法评估多图像空间推理能力,与现实世界应用需求不符。本研究引入MMSI-Bench,专门面向多图像空间智能的视觉问答基准测试。研究团队耗时超过300小时,精心创作了超过1万道选择题,涵盖超过12万张图像,每个问题均配有精心设计干扰项和逐步推理过程。评估了多种开源和专有大型语言模型,发现表现参差不齐,表现最好的开源模型准确率约30%,OpenAI的o3推理模型达到40%,而人类准确率高达97%。此研究还提供了一个自动化错误分析管道,总结了四大失败模式。详情请访问项目主页。
Key Takeaways
- 空间智能在多模态大型语言模型中具有重要意义,尤其在复杂物理世界的应用背景下。
- 当前基准测试无法充分评估多图像空间推理能力。
- MMSI-Bench填补了这一空白,提供了专门面向多图像空间智能的视觉问答基准测试。
- 研究团队创建了大量的选择题来评估模型表现,涵盖了精心设计的干扰项和逐步推理过程。
- 模型评估结果显示存在巨大差异,表现出多图像空间智能的复杂性及提升空间。
- OpenAI的o3推理模型在评估中表现相对较好,但仍有提升空间。
- 人类在多图像空间智能任务中的表现远超过现有模型。
点此查看论文截图



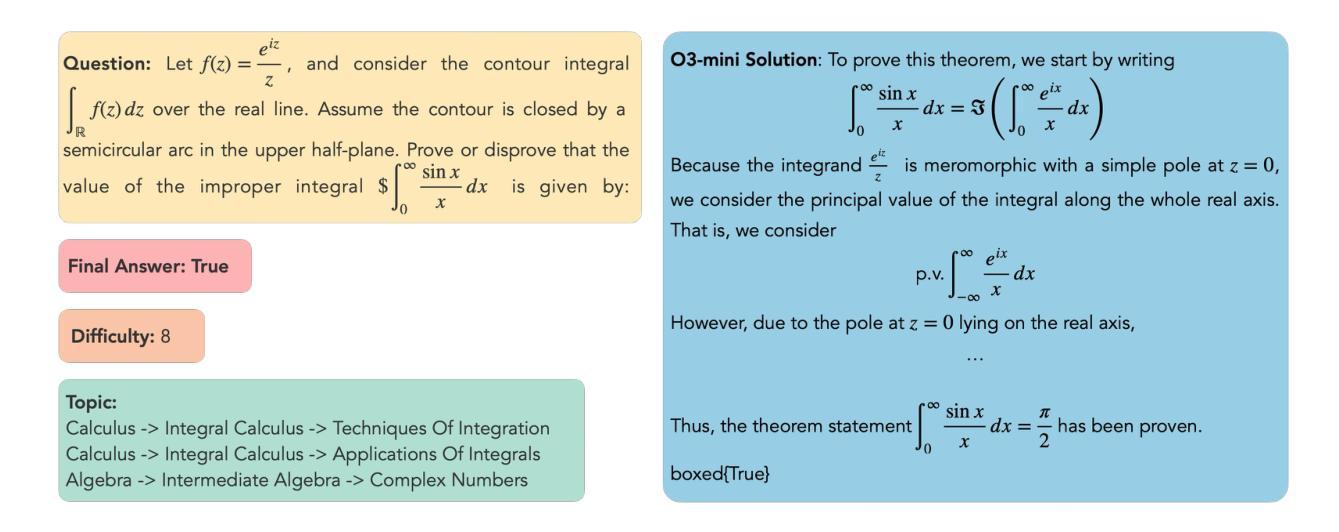
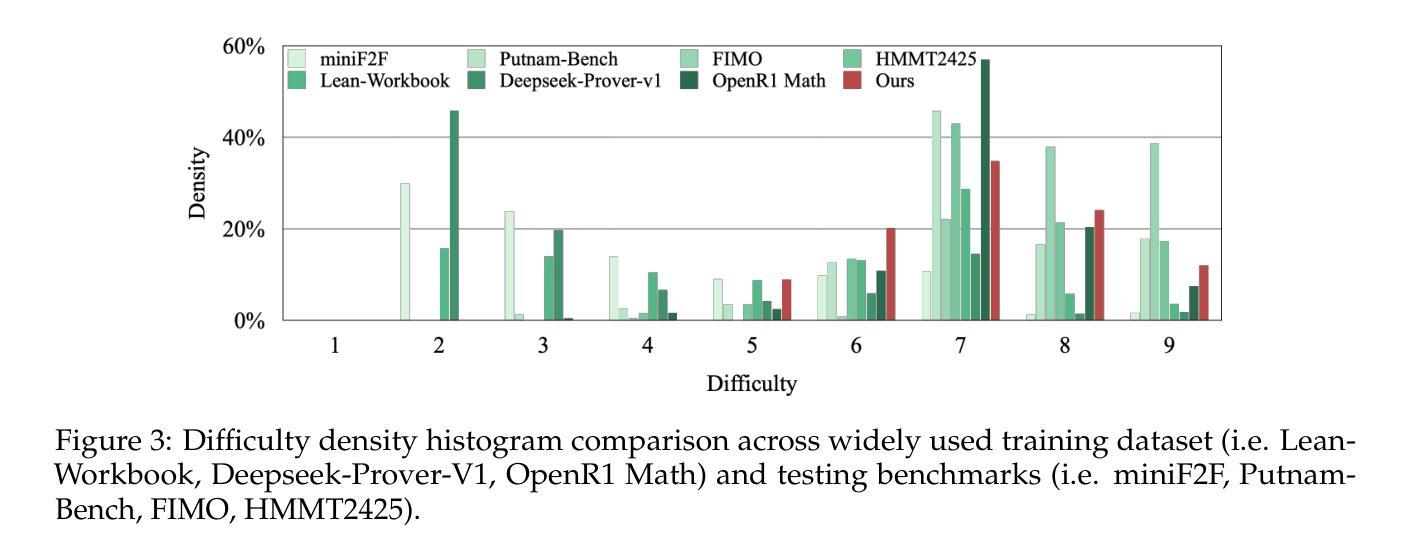
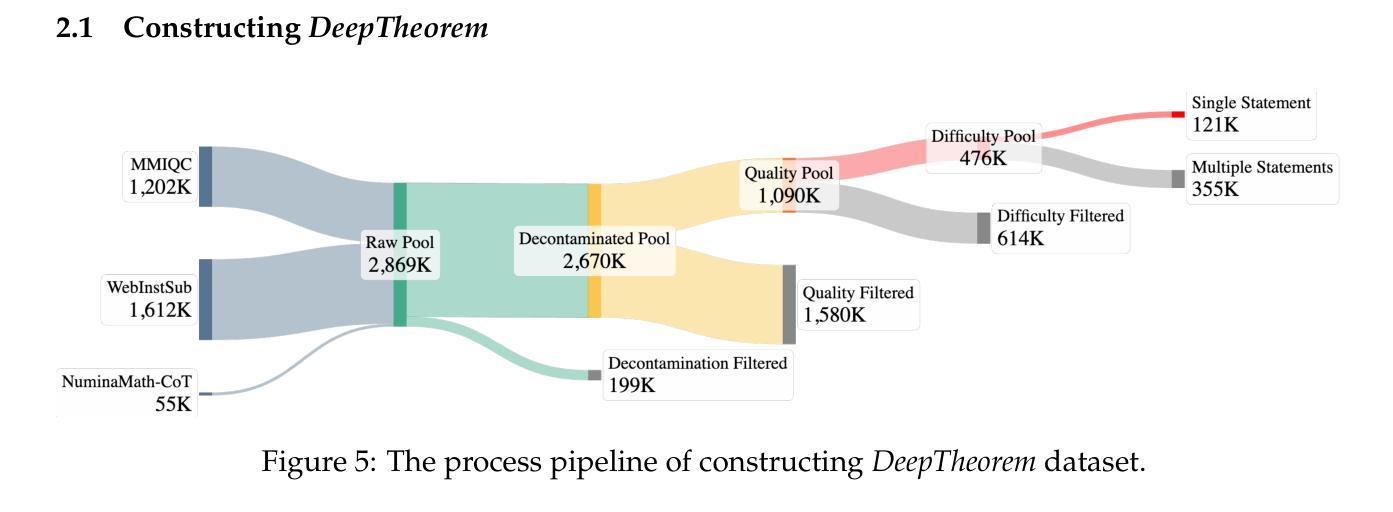
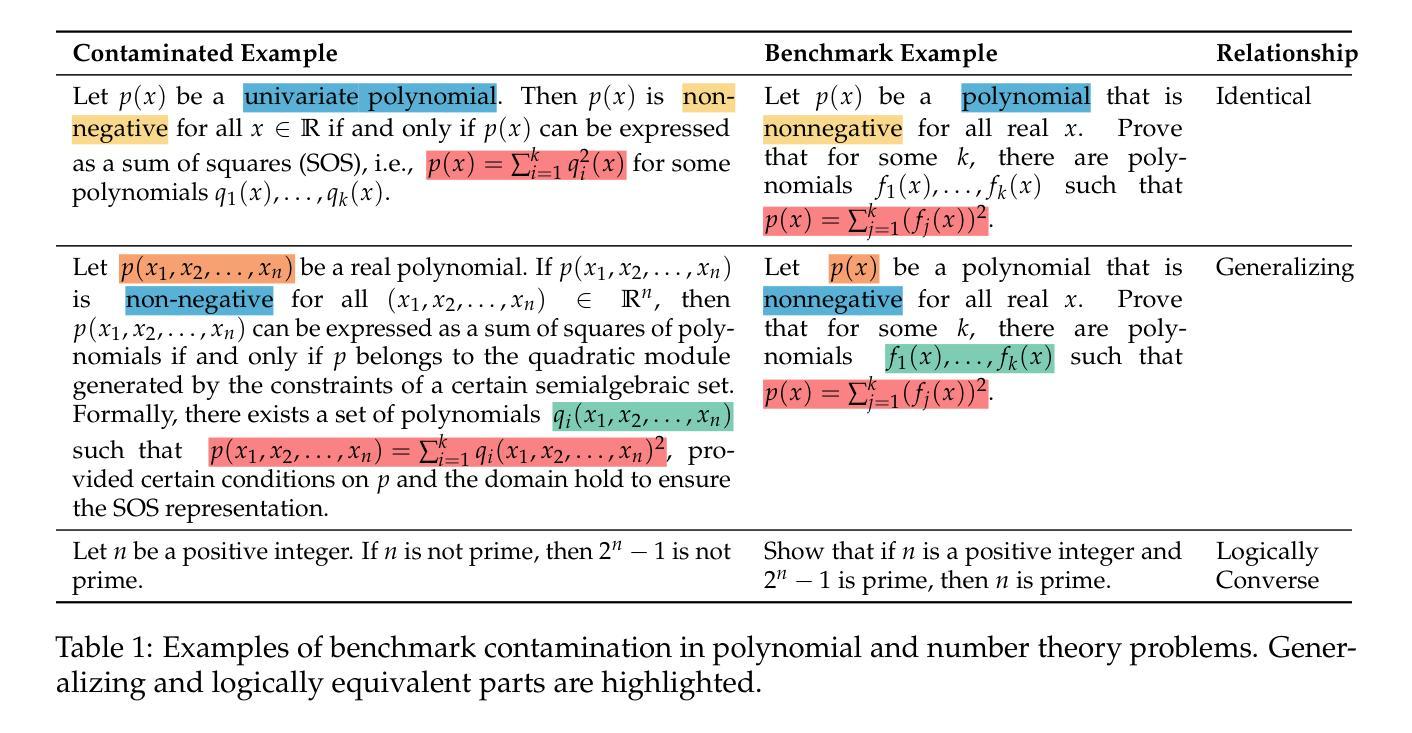
DeepTheorem: Advancing LLM Reasoning for Theorem Proving Through Natural Language and Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Ziyin Zhang, Jiahao Xu, Zhiwei He, Tian Liang, Qiuzhi Liu, Yansi Li, Linfeng Song, Zhengwen Liang, Zhuosheng Zhang, Rui Wang, Zhaopeng Tu, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
Theorem proving serves as a major testbed for evaluating complex reasoning abilities in large language models (LLMs). However, traditional automated theorem proving (ATP) approaches rely heavily on formal proof systems that poorly align with LLMs’ strength derived from informal, natural language knowledge acquired during pre-training. In this work, we propose DeepTheorem, a comprehensive informal theorem-proving framework exploiting natural language to enhance LLM mathematical reasoning. DeepTheorem includes a large-scale benchmark dataset consisting of 121K high-quality IMO-level informal theorems and proofs spanning diverse mathematical domains, rigorously annotated for correctness, difficulty, and topic categories, accompanied by systematically constructed verifiable theorem variants. We devise a novel reinforcement learning strategy (RL-Zero) explicitly tailored to informal theorem proving, leveraging the verified theorem variants to incentivize robust mathematical inference. Additionally, we propose comprehensive outcome and process evaluation metrics examining proof correctness and the quality of reasoning steps. Extensive experimental analyses demonstrate DeepTheorem significantly improves LLM theorem-proving performance compared to existing datasets and supervised fine-tuning protocols, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy and reasoning quality. Our findings highlight DeepTheorem’s potential to fundamentally advance automated informal theorem proving and mathematical exploration.
定理证明是评估大型语言模型(LLM)复杂推理能力的主要测试床。然而,传统的自动化定理证明(ATP)方法严重依赖于形式化证明系统,而这些系统并不能很好地与LLM在预训练期间获得的不正式的、自然语言知识相结合的优势相契合。在这项工作中,我们提出了DeepTheorem,这是一个全面的非正式定理证明框架,利用自然语言增强LLM的数学推理能力。DeepTheorem包括一个大规模基准数据集,包含12.1万个高质量的IMO级非正式定理和证明,涵盖多样化的数学领域,对正确性、难度和主题类别进行了严格的注释,并配有系统构建的可验证定理变体。我们设计了一种新型强化学习策略(RL-Zero),专门针对非正式定理证明,利用可验证的定理变体来激励稳健的数学推理。此外,我们提出了全面的结果和过程评估指标,以检查证明的正确性和推理步骤的质量。广泛的实验分析表明,与现有数据集和监督微调协议相比,DeepTheorem在定理证明性能上显著提高LLM的定理证明能力,实现了最先进的准确性和推理质量。我们的研究结果表明,DeepTheorem在自动化非正式定理证明和数学探索方面具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在数学推理方面展现出了潜力,但在定理证明上仍然面临挑战。传统自动定理证明方法主要依赖形式化证明系统,这与LLM的优势并不匹配。本研究提出了DeepTheorem框架,利用自然语言增强LLM的数学推理能力。该框架包括大规模基准数据集,包含高质量的非正式定理和证明,以及针对非正式定理证明定制的强化学习策略。实验证明,DeepTheorem显著提高了LLM的定理证明性能,有望推动非正式定理证明的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在定理证明上仍有挑战,传统方法依赖形式化证明系统,与LLM的优势不匹配。
- 本研究提出了DeepTheorem框架,结合自然语言增强LLM的数学推理能力。
- DeepTheorem包含大规模基准数据集,涵盖多样化数学领域的非正式定理和证明。
- 提出了针对非正式定理证明的强化学习策略RL-Zero。
- DeepTheorem显著提高LLM的定理证明性能,包括准确率和推理质量。
点此查看论文截图

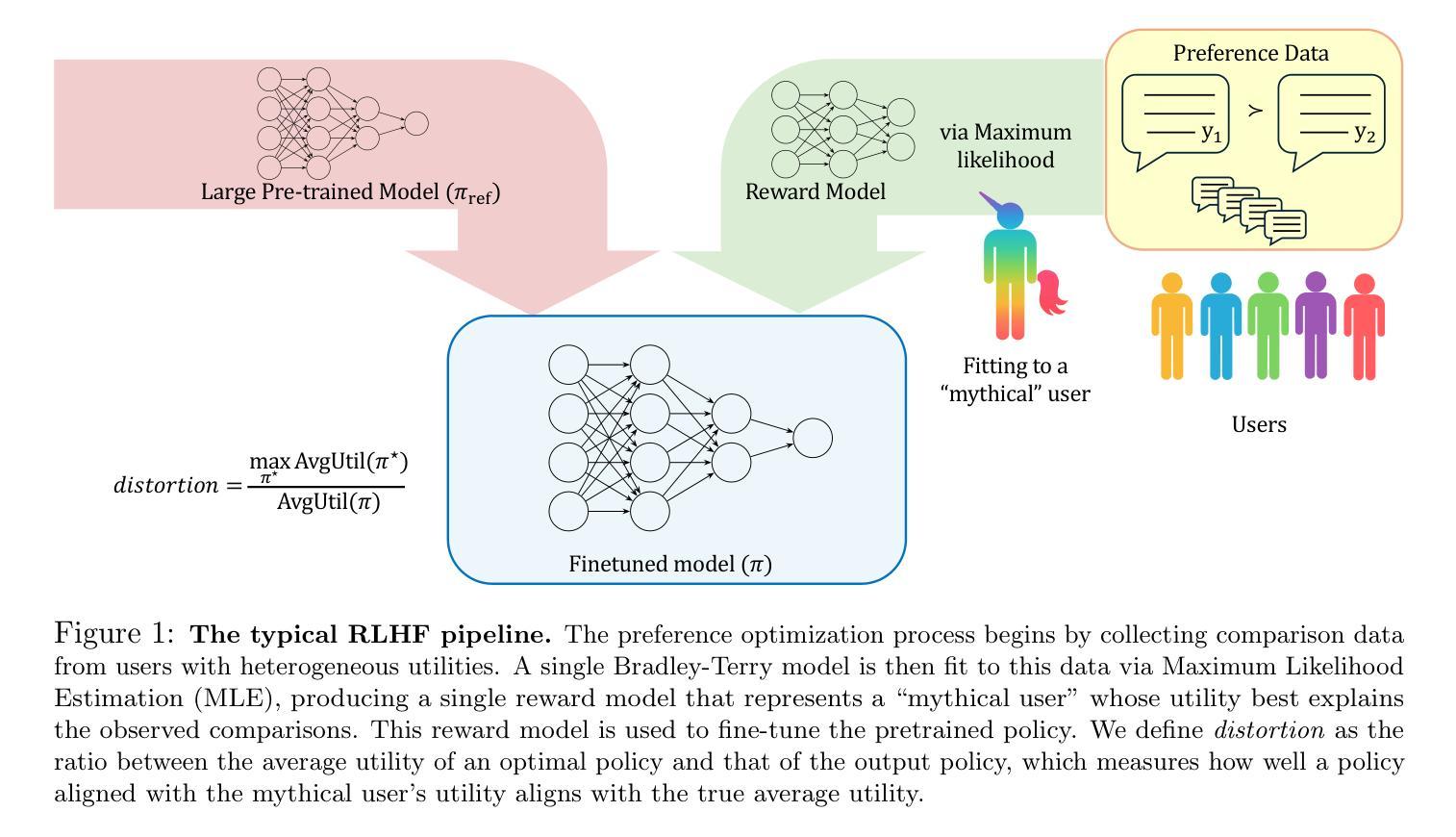
Distortion of AI Alignment: Does Preference Optimization Optimize for Preferences?
Authors:Paul Gölz, Nika Haghtalab, Kunhe Yang
After pre-training, large language models are aligned with human preferences based on pairwise comparisons. State-of-the-art alignment methods (such as PPO-based RLHF and DPO) are built on the assumption of aligning with a single preference model, despite being deployed in settings where users have diverse preferences. As a result, it is not even clear that these alignment methods produce models that satisfy users on average – a minimal requirement for pluralistic alignment. Drawing on social choice theory and modeling users’ comparisons through individual Bradley-Terry (BT) models, we introduce an alignment method’s distortion: the worst-case ratio between the optimal achievable average utility, and the average utility of the learned policy. The notion of distortion helps draw sharp distinctions between alignment methods: Nash Learning from Human Feedback achieves the minimax optimal distortion of $(\frac{1}{2} + o(1)) \cdot \beta$ (for the BT temperature $\beta$), robustly across utility distributions, distributions of comparison pairs, and permissible KL divergences from the reference policy. RLHF and DPO, by contrast, suffer $\geq (1 - o(1)) \cdot \beta$ distortion already without a KL constraint, and $e^{\Omega(\beta)}$ or even unbounded distortion in the full setting, depending on how comparison pairs are sampled.
预训练后,大型语言模型基于配对比较与人类偏好对齐。最先进的对齐方法(如基于PPO的RLHF和DPO)建立在与单一偏好模型对齐的假设之上,尽管它们部署在用户偏好多样的环境中。因此,这些对齐方法产生的模型是否满足用户的平均需求尚不清楚——这是多元对齐的最低要求。我们借鉴社会选择理论和通过个体Bradley-Terry(BT)模型对用户比较进行建模,引入了一种对齐方法的失真:最优可达平均效用与所学策略的平均效用之间的最坏情况比率。失真的概念有助于在对齐方法之间划出鲜明的界限:从人类反馈中学习纳什策略实现了最小最大最优失真(对于BT温度β的)($\frac{1}{2} + o(1)$)倍,在各种效用分布、对比对分布和参照策略的KL散度限制下都能稳健表现。相比之下,RLHF和DPO在不使用KL约束的情况下已经遭受了至少($1 - o(1)$)倍的失真,而在对比对采样完整的情况下,失真为$e^{\Omega(\beta)}$甚至更大。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型经过预训练后,基于成对比较与人类偏好对齐。现有的对齐方法(如基于PPO的RLHF和DPO)假设对齐单一偏好模型,但在用户偏好多样的环境中部署时存在局限性。为此,我们引入对齐方法的失真概念,即最优可实现的平均效用与学习政策的平均效用之间的最坏情况比率。Nash从人类反馈学习中实现对齐的方法获得最最优化的失真,而RLHF和DPO在没有KL约束的情况下就已经存在较大的失真。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型经过预训练后,可以通过成对比较与人类偏好对齐。
- 现有对齐方法(如RLHF和DPO)假设对齐单一偏好模型,但在实际中面临用户偏好多样性问题。
- 对齐方法的失真概念用于衡量最优可实现的平均效用与学习政策的平均效用之间的差距。
- Nash从人类反馈学习中实现对齐的方法具有最小的失真。
- RLHF和DPO在没有KL约束的情况下存在较大的失真问题。
- 对比样本的采集方式会影响对齐方法的失真。
点此查看论文截图

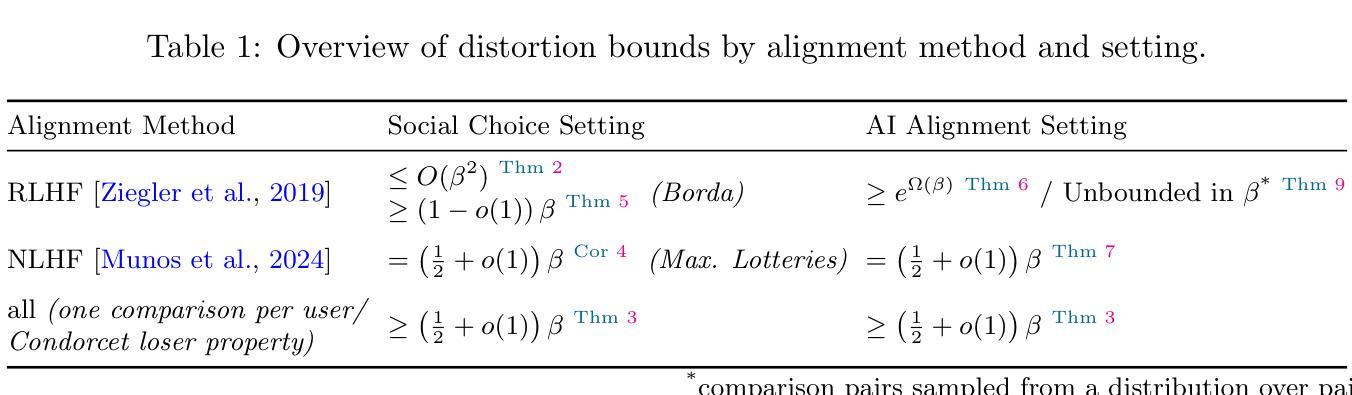
Spatial-MLLM: Boosting MLLM Capabilities in Visual-based Spatial Intelligence
Authors:Diankun Wu, Fangfu Liu, Yi-Hsin Hung, Yueqi Duan
Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced performance on 2D visual tasks. However, improving their spatial intelligence remains a challenge. Existing 3D MLLMs always rely on additional 3D or 2.5D data to incorporate spatial awareness, restricting their utility in scenarios with only 2D inputs, such as images or videos. In this paper, we present Spatial-MLLM, a novel framework for visual-based spatial reasoning from purely 2D observations. Unlike conventional video MLLMs which rely on CLIP-based visual encoders optimized for semantic understanding, our key insight is to unleash the strong structure prior from the feed-forward visual geometry foundation model. Specifically, we propose a dual-encoder architecture: a pretrained 2D visual encoder to extract semantic features, and a spatial encoder-initialized from the backbone of the visual geometry model-to extract 3D structure features. A connector then integrates both features into unified visual tokens for enhanced spatial understanding. Furthermore, we propose a space-aware frame sampling strategy at inference time, which selects the spatially informative frames of a video sequence, ensuring that even under limited token length, the model focuses on frames critical for spatial reasoning. Beyond architecture improvements, we construct the Spatial-MLLM-120k dataset and train the model on it using supervised fine-tuning and GRPO. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets demonstrate that our spatial-MLLM achieves state-of-the-art performance in a wide range of visual-based spatial understanding and reasoning tasks. Project page: https://diankun-wu.github.io/Spatial-MLLM/.
最近的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的进步在2D视觉任务上的表现显著提升。然而,提高它们的空间智能仍然是一个挑战。现有的3D MLLM总是依赖于额外的3D或2.5D数据来融入空间感知,这在只有2D输入的情境中(例如图像或视频)限制了它们的实用性。在本文中,我们提出了Spatial-MLLM,这是一个基于纯粹的2D观察进行视觉空间推理的新型框架。与传统的依赖于CLIP的视觉编码器优化的语义理解的视频MLLM不同,我们的关键见解是释放来自前馈视觉几何基础模型的强大结构先验。具体来说,我们提出了一种双编码器架构:一个预训练的2D视觉编码器来提取语义特征,以及一个从视觉几何模型主干初始化的空间编码器来提取3D结构特征。然后,一个连接器将这两种特征集成到统一的视觉令牌中,以增强空间理解。此外,我们在推理时提出了一种空间感知帧采样策略,该策略选择了视频序列中空间信息丰富的帧,确保即使在有限的令牌长度下,模型也能关注对空间推理至关重要的帧。除了架构改进外,我们还构建了Spatial-MLLM-120k数据集,并在其上使用有监督的微调策略和GRPO训练了模型。在多种真实世界数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的空间MLLM在基于视觉的空间理解和推理任务中达到了最先进的性能。项目页面:https://diankun-wu.github.io/Spatial-MLLM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Spatial-MLLM的新型框架,用于基于纯粹的二维观测进行视觉空间推理。该框架采用双编码器架构,结合预训练的二维视觉编码器和空间编码器,以提取语义特征和三维结构特征。此外,还提出了一种空间感知帧采样策略,以提高模型在有限令牌长度下的空间理解能力。通过Spatial-MLLM-120k数据集进行训练,并在多个真实世界数据集上进行广泛实验,证明了该模型在视觉基础空间理解和推理任务中的卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Spatial-MLLM框架成功地将二维视觉任务与空间推理相结合。
- 该框架采用双编码器架构,包括预训练的二维视觉编码器和空间编码器,以提取不同特征。
- 提出了空间感知帧采样策略,用于提高模型在有限令牌长度下的性能。
- Spatial-MLLM-120k数据集用于训练模型,涵盖丰富的空间信息。
- 广泛实验证明了该模型在多种真实世界数据集上的卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

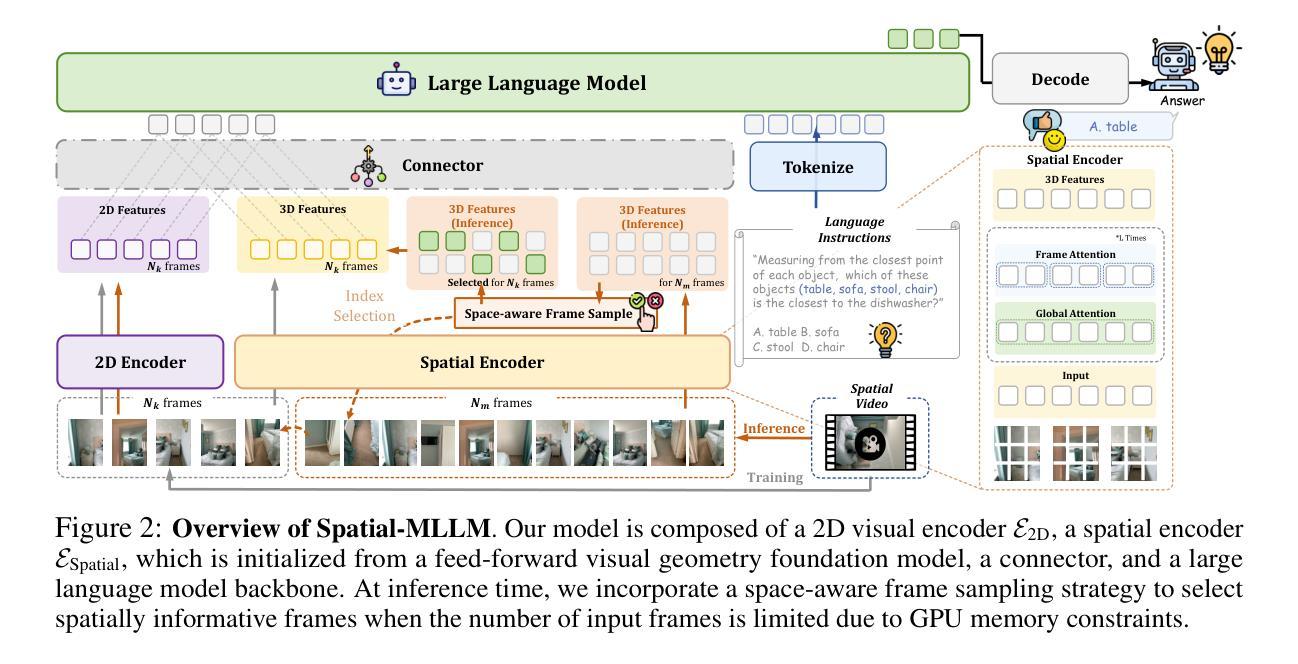
Bounded Rationality for LLMs: Satisficing Alignment at Inference-Time
Authors:Mohamad Chehade, Soumya Suvra Ghosal, Souradip Chakraborty, Avinash Reddy, Dinesh Manocha, Hao Zhu, Amrit Singh Bedi
Aligning large language models with humans is challenging due to the inherently multifaceted nature of preference feedback. While existing approaches typically frame this as a multi-objective optimization problem, they often overlook how humans actually make decisions. Research on bounded rationality suggests that human decision making follows satisficing strategies-optimizing primary objectives while ensuring others meet acceptable thresholds. To bridge this gap and operationalize the notion of satisficing alignment, we propose SITAlign: an inference time framework that addresses the multifaceted nature of alignment by maximizing a primary objective while satisfying threshold-based constraints on secondary criteria. We provide theoretical insights by deriving sub-optimality bounds of our satisficing based inference alignment approach. We empirically validate SITAlign’s performance through extensive experimentation on multiple benchmarks. For instance, on the PKU-SafeRLHF dataset with the primary objective of maximizing helpfulness while ensuring a threshold on harmlessness, SITAlign outperforms the state-of-the-art multi objective decoding strategy by a margin of 22.3% in terms of GPT-4 win-tie rate for helpfulness reward while adhering to the threshold on harmlessness.
将大型语言模型与人类对齐是一项具有挑战性的任务,这主要是由于偏好反馈的固有多元性质。尽管现有的方法通常将其构建为多目标优化问题,但它们往往忽视了人类实际如何做出决策。关于有限理性的研究表明,人类的决策制定遵循满意策略,即优化主要目标,同时确保其他目标达到可接受的阈值。为了弥合这一差距并落实满意对齐的概念,我们提出了SITAlign:一个推理时间框架,通过最大化主要目标并满足基于阈值的次要标准约束,来解决对齐的多元性质问题。我们通过推导基于满意的推理对齐方法的次优性界限,提供了理论见解。我们通过多个基准测试进行了广泛的实验,实证验证了SITAlign的性能。例如,在PKU-SafeRLHF数据集上,主要目标是最大化有益性,同时确保无害性的阈值,SITAlign在有益性奖励方面以22.3%的优势超越了最新的多目标解码策略,同时遵守无害性的阈值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型与人类对齐的挑战性,由于偏好反馈的多元性质,现有方法往往忽略人类实际决策过程。研究指出人类决策遵循满意策略,优化主要目标同时确保其他目标达到可接受阈值。为此,本文提出SATISFICING对齐框架(简称SATAlign),在推理阶段最大化主要目标的同时满足基于阈值的次要标准约束,以缩小人类与语言模型决策之间的差距。通过理论分析和在多个基准数据集上的实验验证,SATAlign表现出优异的性能。例如,在PKU-SafeRLHF数据集上,SATAlign在最大化有用性的同时确保无害性达到阈值,相较于当前的多目标解码策略,提升了22.3%的GPT-4友好性奖励win-tie率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型与人类对齐存在挑战,因为人类反馈具有多元性质。
- 现有方法往往忽略人类实际决策过程,而人类决策遵循满意策略。
- SATAlign框架旨在在推理阶段最大化主要目标,同时满足次要目标的阈值约束。
- SATAlign结合了理论分析和实证研究,展现出优异的性能。
- SATAlign通过优化有用性并确保无害性达到阈值,提升了语言模型的对人类友好的程度。
- SATAlign在PKU-SafeRLHF数据集上的表现优于当前的多目标解码策略。
点此查看论文截图

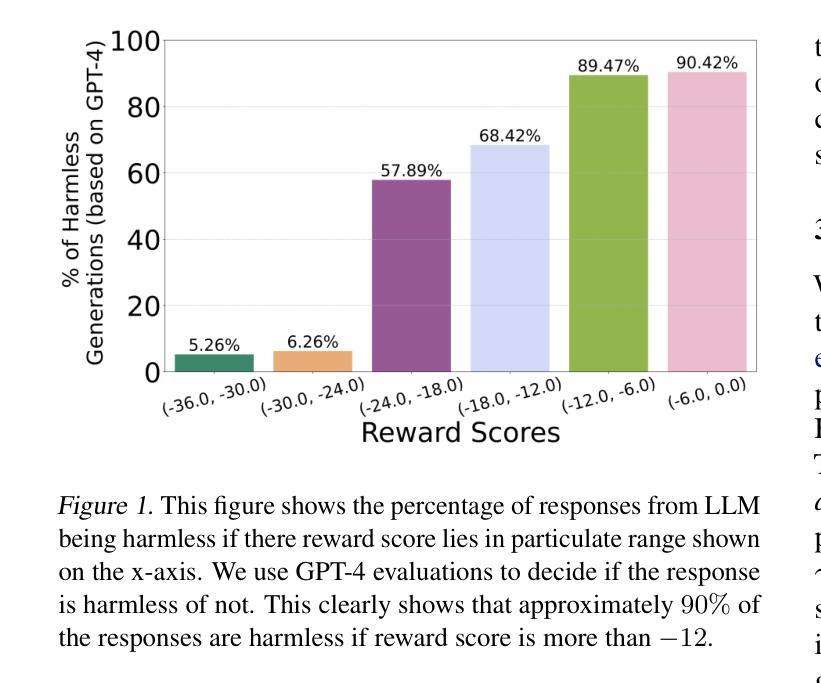
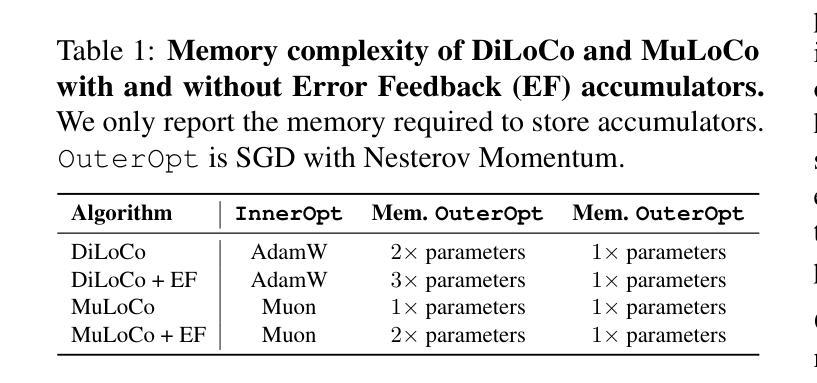
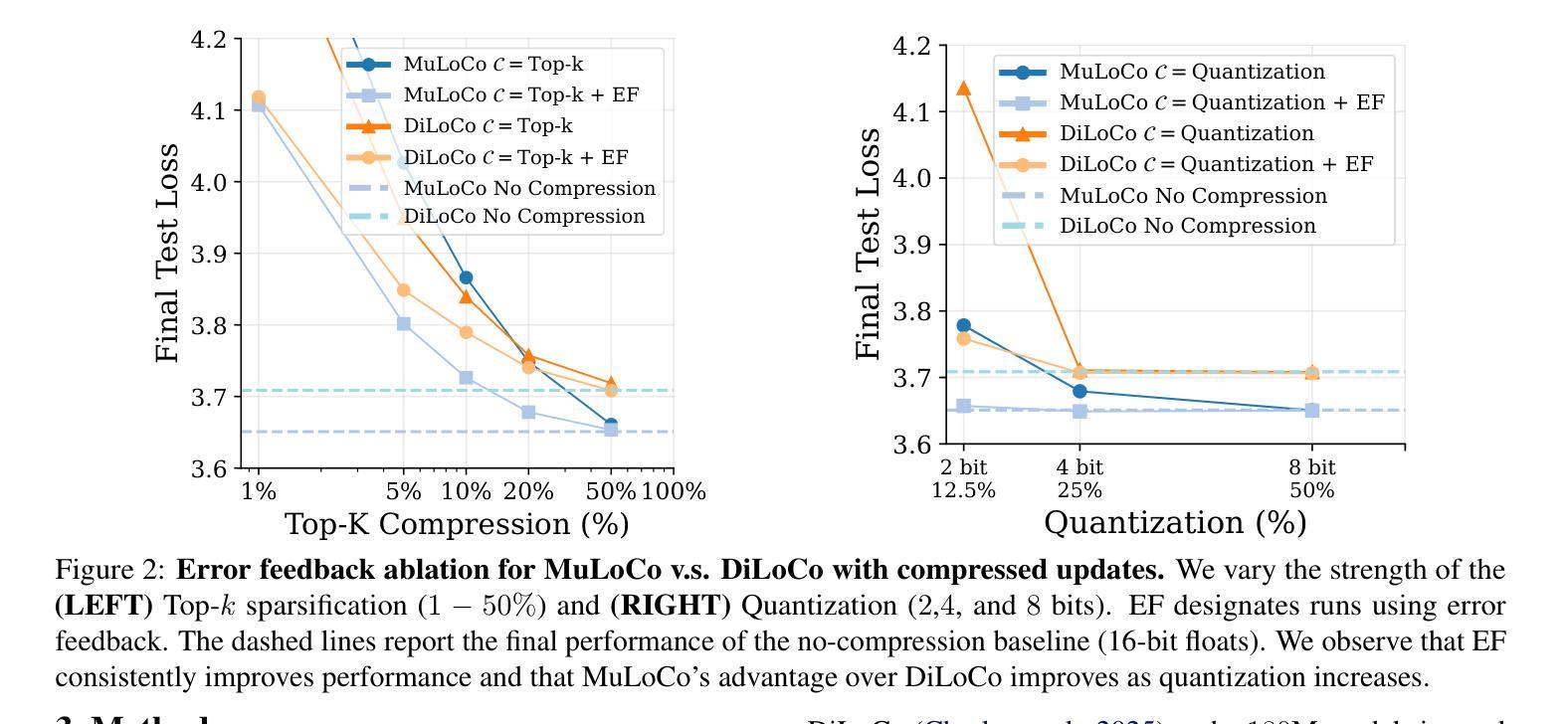
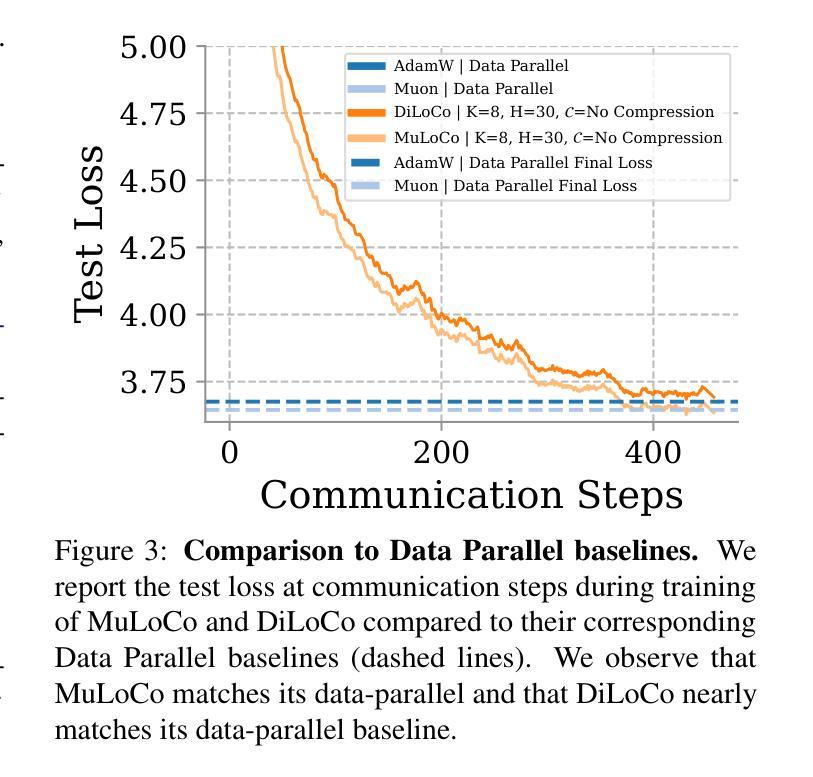
MuLoCo: Muon is a practical inner optimizer for DiLoCo
Authors:Benjamin Thérien, Xiaolong Huang, Irina Rish, Eugene Belilovsky
DiLoCo is a powerful framework for training large language models (LLMs) under networking constraints with advantages for increasing parallelism and accelerator utilization in data center settings. Despite significantly reducing communication frequency, however, DiLoCo’s communication steps still involve all-reducing a complete copy of the model’s parameters. While existing works have explored ways to reduce communication in DiLoCo, the role of error feedback accumulators and the effect of the inner-optimizer on compressibility remain under-explored. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of standard compression methods including Top-k sparsification and quantization for reducing the communication overhead of DiLoCo when paired with two local optimizers (AdamW and Muon). Our experiments pre-training decoder-only transformer language models (LMs) reveal that leveraging Muon as the inner optimizer for DiLoCo along with an error-feedback accumulator allows to aggressively compress the communicated delta to 2-bits with next to no performance degradation. Crucially, MuLoCo (Muon inner optimizer DiLoCo) significantly outperforms DiLoCo while communicating 8X less and having identical memory complexity.
DiLoCo是在网络约束下训练大型语言模型(LLM)的强大框架,其在数据中心环境中增加了并行性和加速器利用率的优点。尽管DiLoCo显著减少了通信频率,但其通信步骤仍然涉及所有模型参数的完整复制。虽然现有工作已经探索了减少DiLoCo通信的方法,但误差反馈累加器的作用以及内部优化器对压缩效果的影响仍然未被充分探索。在这项工作中,我们调查了标准压缩方法(包括Top-k稀疏化和量化)在结合两种本地优化器(AdamW和Muon)时,减少DiLoCo通信开销的有效性。我们的实验通过对仅解码器变压器语言模型(LM)进行预训练发现,利用Muon作为DiLoCo的内部优化器并结合误差反馈累加器,可以积极压缩通信的增量至2位,几乎不会对性能产生降级。关键的是,MuLoCo(Muon内部优化器的DiLoCo)在通信量减少8倍、内存复杂度相同的情况下,显著优于DiLoCo。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DiLoCo框架在数据中心环境下训练大型语言模型具有优势,能提高并行性和加速器利用率。本研究探讨了结合两种本地优化器(AdamW和Muon)时,使用Top-k稀疏化和量化等标准压缩方法减少DiLoCo通信开销的有效性。实验表明,使用Muon作为DiLoCo的内部优化器并结合误差反馈累加器,可以大幅度压缩通信量,同时几乎不影响性能。MuLoCo(使用Muon内部优化器的DiLoCo)在通信量减少8倍、内存复杂度相同的情况下,显著优于DiLoCo。
Key Takeaways
- DiLoCo框架适用于训练大型语言模型,在数据中心环境中可提高并行性和加速器利用率。
- 本研究探讨了标准压缩方法(如Top-k稀疏化和量化)在减少DiLoCo通信开销方面的效果。
- 结合Muon作为DiLoCo的内部优化器,可大幅度压缩通信量。
- 误差反馈累加器的使用在压缩通信中起到了关键作用。
- MuLoCo显著优于DiLoCo,在减少通信开销的同时保持相同的内存复杂度。
6.MuLoCo能够在大幅度压缩通信的情况下,几乎不影响模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图
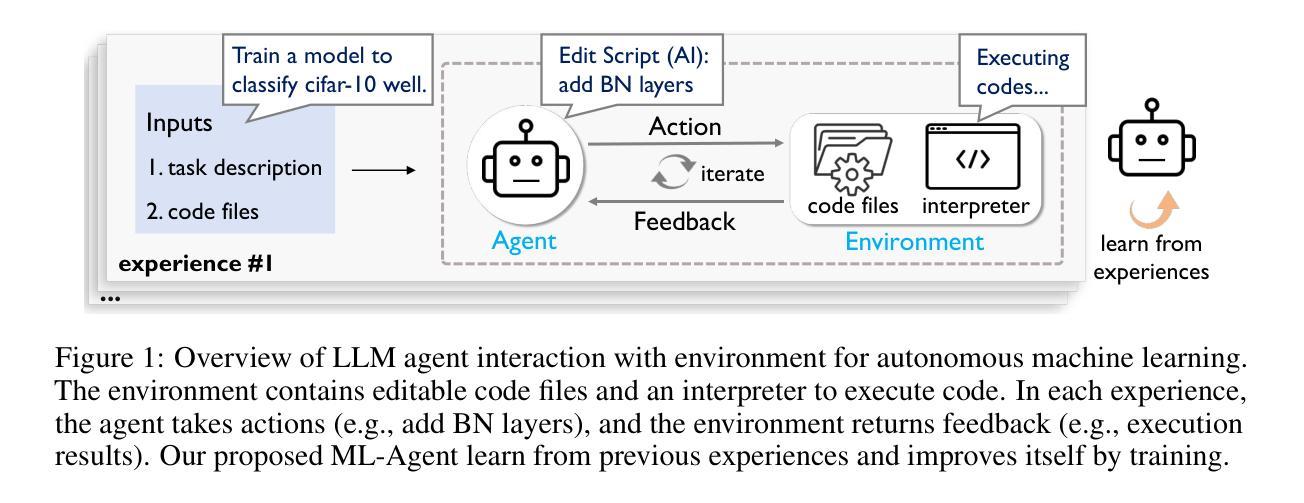
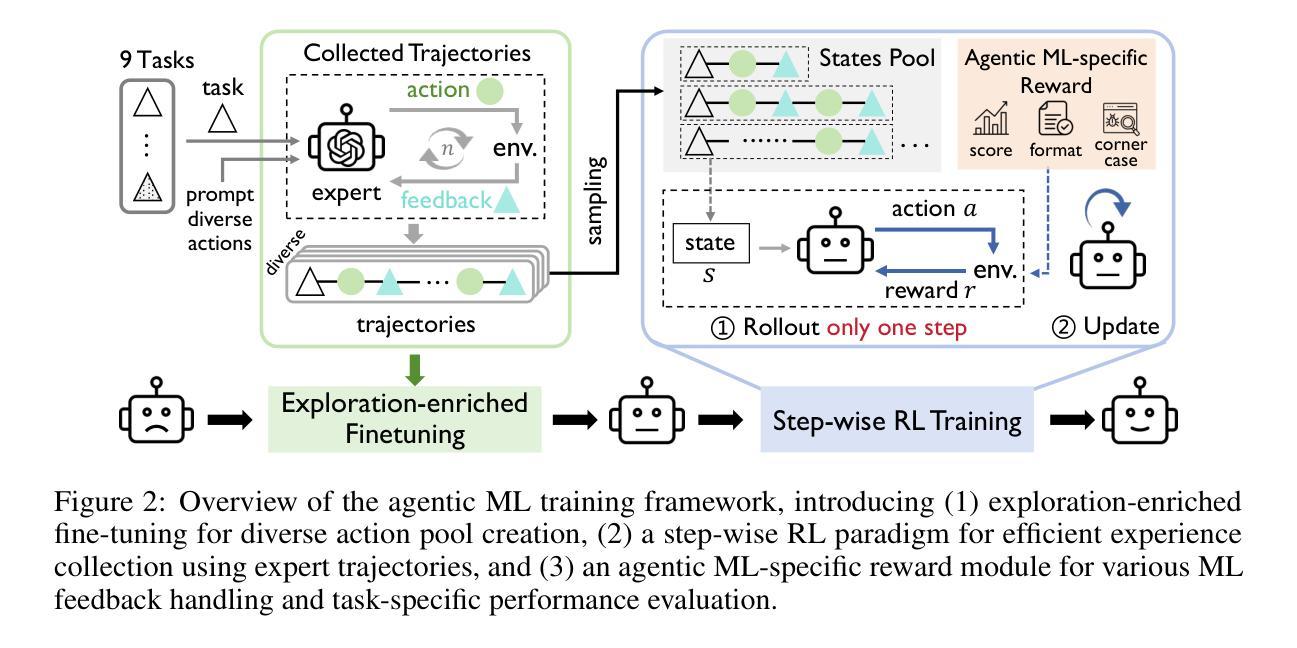
ML-Agent: Reinforcing LLM Agents for Autonomous Machine Learning Engineering
Authors:Zexi Liu, Jingyi Chai, Xinyu Zhu, Shuo Tang, Rui Ye, Bo Zhang, Lei Bai, Siheng Chen
The emergence of large language model (LLM)-based agents has significantly advanced the development of autonomous machine learning (ML) engineering. However, most existing approaches rely heavily on manual prompt engineering, failing to adapt and optimize based on diverse experimental experiences. Focusing on this, for the first time, we explore the paradigm of learning-based agentic ML, where an LLM agent learns through interactive experimentation on ML tasks using online reinforcement learning (RL). To realize this, we propose a novel agentic ML training framework with three key components: (1) exploration-enriched fine-tuning, which enables LLM agents to generate diverse actions for enhanced RL exploration; (2) step-wise RL, which enables training on a single action step, accelerating experience collection and improving training efficiency; (3) an agentic ML-specific reward module, which unifies varied ML feedback signals into consistent rewards for RL optimization. Leveraging this framework, we train ML-Agent, driven by a 7B-sized Qwen-2.5 LLM for autonomous ML. Remarkably, despite being trained on merely 9 ML tasks, our 7B-sized ML-Agent outperforms the 671B-sized DeepSeek-R1 agent. Furthermore, it achieves continuous performance improvements and demonstrates exceptional cross-task generalization capabilities.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人的出现,极大地推动了自主机器学习(ML)工程的发展。然而,大多数现有方法严重依赖于手动提示工程,无法根据丰富的实验经验进行适应和优化。基于此,我们首次探索了基于学习的人工智能ML范式,该范式中的LLM代理通过在线强化学习(RL)在ML任务上进行交互式实验进行学习。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种新型的人工智能ML训练框架,包含三个关键组件:(1)丰富探索的微调,使LLM代理能够生成多样化的行动,以增强RL的探索;(2)分步RL,使训练可以在单个行动步骤上进行,加快经验收集,提高训练效率;(3)针对人工智能ML的奖励模块,它将各种ML反馈信号统一为一致的奖励,用于RL优化。利用该框架,我们训练了由7B大小的Qwen-2.5 LLM驱动的ML-Agent进行自主ML。值得注意的是,尽管仅在9个ML任务上进行训练,我们7B大小的ML-Agent表现出优于671B大小的DeepSeek-R1代理的性能。此外,它实现了持续的性能改进,并表现出卓越的跨任务泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的出现极大地推动了自主机器学习(ML)工程的发展。然而,现有的大多数方法过于依赖手动提示工程,无法根据丰富的实验经验进行适应和优化。为此,本文首次探索了基于学习型的智能体机器学习范式,LLM智能体通过在线强化学习(RL)在机器学习任务上进行交互式实验学习。为此,我们提出了一个新型智能体机器学习训练框架,包含三个关键组件:(1)丰富探索的微调,使LLM智能体生成多样化行动以增强RL探索;(2)分步强化学习,实现单一行动步骤的训练,提高经验收集和训练效率;(3)智能体机器学习特定奖励模块,将各种机器学习反馈信号统一为一致的奖励用于RL优化。利用该框架,我们训练了ML-Agent,由7B规模的Qwen-2.5 LLM驱动进行自主机器学习。尽管仅在9个机器学习任务上进行训练,我们的7B规模ML-Agent表现出超越671B规模DeepSeek-R1代理的性能。此外,它实现了持续的性能改进,并显示出卓越的跨任务泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自主机器学习(ML)工程中起到重要作用。
- 现有方法过于依赖手动提示工程,缺乏对不同经验的适应和优化。
- 首次探索基于学习型的智能体机器学习范式,通过交互式实验学习。
- 提出新型智能体机器学习训练框架,包含丰富探索的微调、分步强化学习和特定奖励模块三个关键组件。
- 利用该框架训练的ML-Agent表现出卓越性能,超越其他代理。
- ML-Agent具有持续的性能改进和跨任务泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

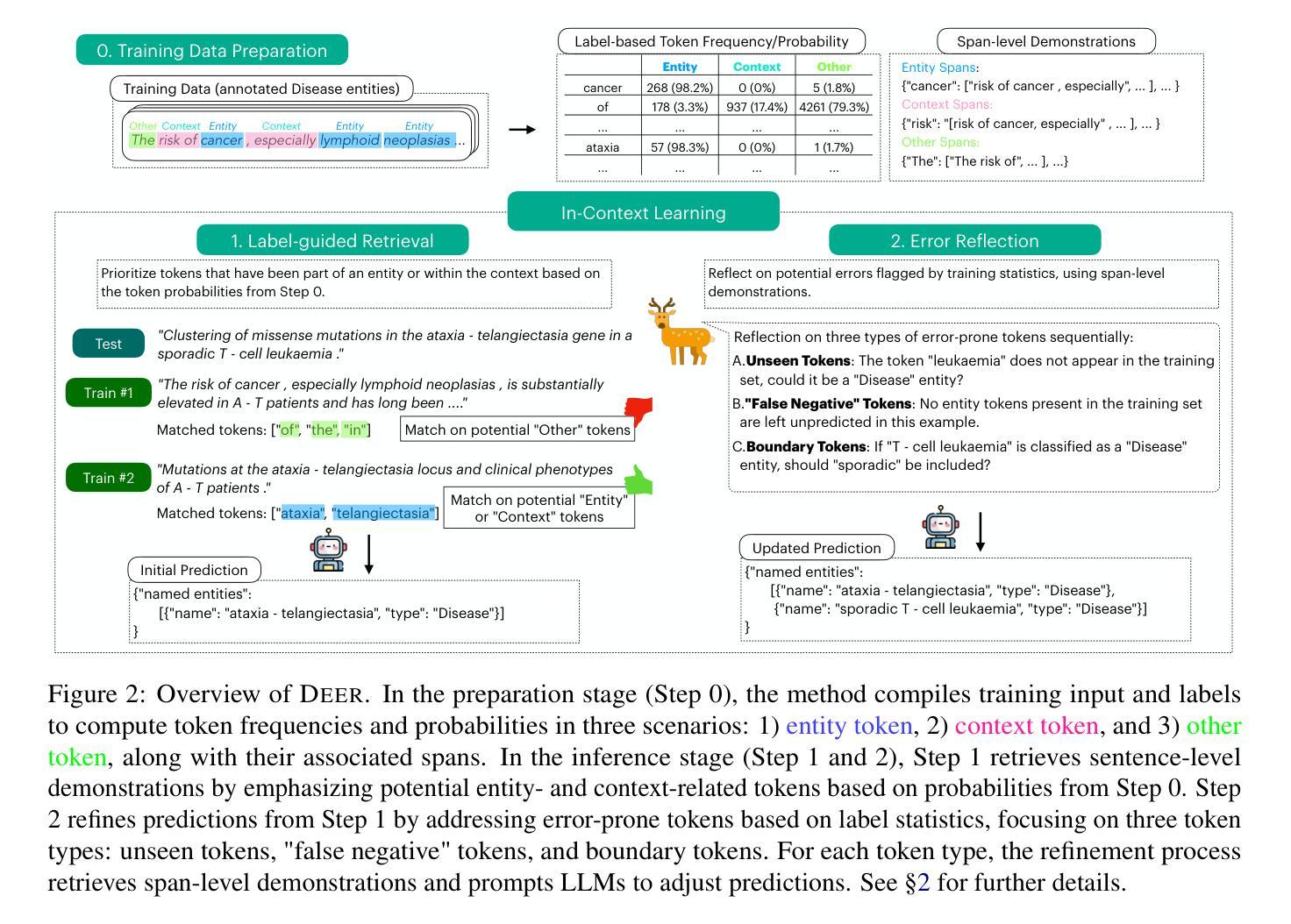
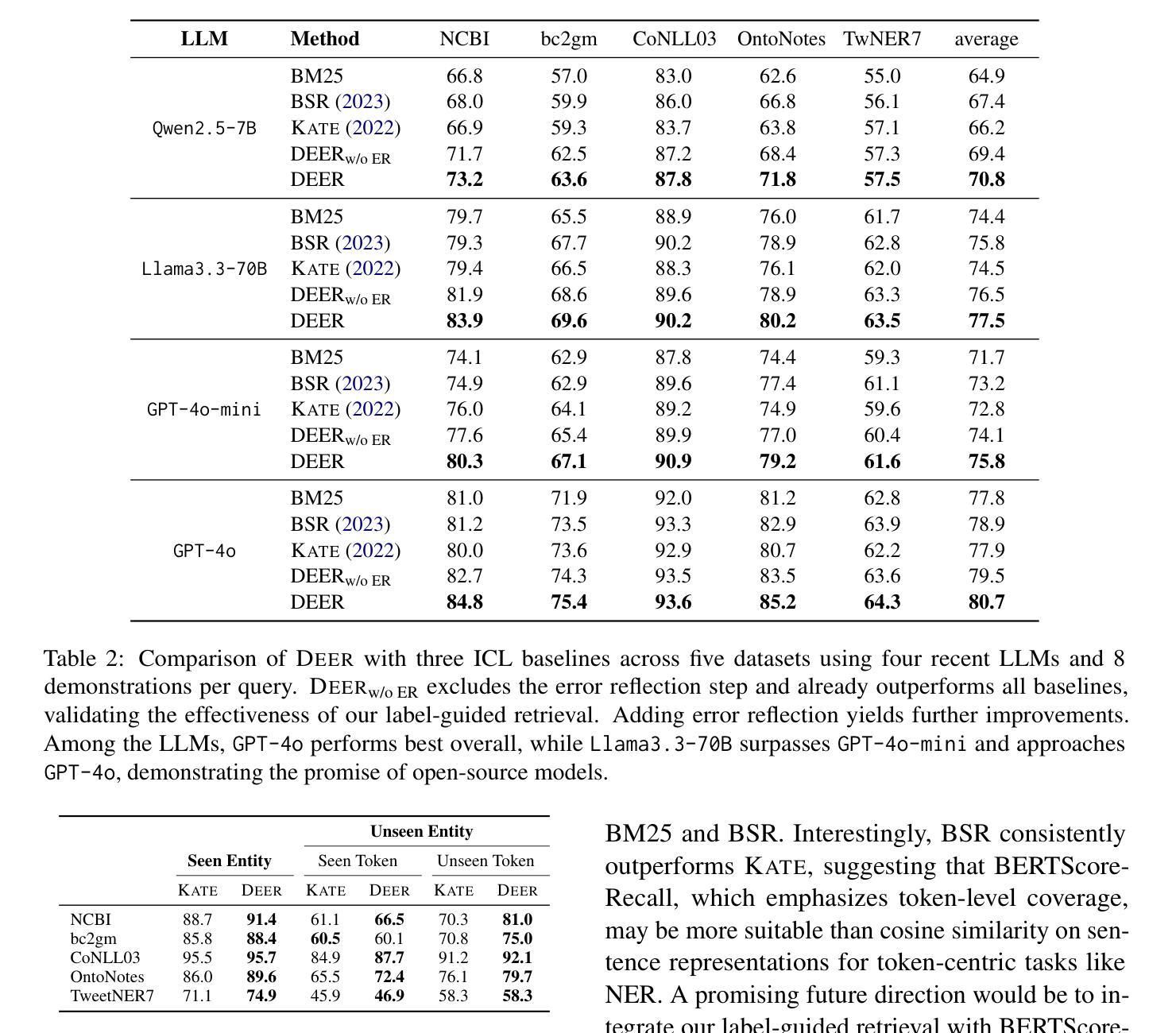
Label-Guided In-Context Learning for Named Entity Recognition
Authors:Fan Bai, Hamid Hassanzadeh, Ardavan Saeedi, Mark Dredze
In-context learning (ICL) enables large language models (LLMs) to perform new tasks using only a few demonstrations. In Named Entity Recognition (NER), demonstrations are typically selected based on semantic similarity to the test instance, ignoring training labels and resulting in suboptimal performance. We introduce DEER, a new method that leverages training labels through token-level statistics to improve ICL performance. DEER first enhances example selection with a label-guided, token-based retriever that prioritizes tokens most informative for entity recognition. It then prompts the LLM to revisit error-prone tokens, which are also identified using label statistics, and make targeted corrections. Evaluated on five NER datasets using four different LLMs, DEER consistently outperforms existing ICL methods and approaches the performance of supervised fine-tuning. Further analysis shows its effectiveness on both seen and unseen entities and its robustness in low-resource settings.
上下文学习(ICL)使大型语言模型(LLM)仅通过少数几个演示就能执行新任务。在命名实体识别(NER)中,演示通常基于与测试实例的语义相似性进行选择,忽略训练标签,从而导致性能不佳。我们引入了DEER,一种新方法,它通过令牌级统计利用训练标签来提高ICL的性能。DEER首先通过标签引导、基于令牌的检索器增强示例选择,该检索器优先处理对实体识别最有用的令牌。然后,它提示LLM重新访问易出错令牌,这些令牌也是通过标签统计确定的,并进行有针对性的更正。在五个NER数据集上使用四种不同的LLM进行评估,DEER始终优于现有的ICL方法,并接近监督微调的性能。进一步的分析表明,它在已知和未知实体上都很有效,并且在资源有限的环境中具有稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
在上下文学习(ICL)中,大型语言模型(LLM)仅通过少数示范即可执行新任务。在命名实体识别(NER)中,示范通常根据与测试实例的语义相似性来选择,忽略了训练标签,导致性能不佳。我们推出DEER新方法,利用训练标签通过标记级别的统计数据来提高ICL性能。DEER首先通过标签引导的基于标记的检索器增强示例选择,优先识别对实体识别最有用的标记。然后,它提示LLM重新检查错误倾向的标记(也通过标签统计进行识别),并进行有针对性的更正。在五个NER数据集上使用四种不同的LLM进行评估,DEER始终表现优于现有的ICL方法,并接近监督微调性能。进一步的分析表明,它在已知和未知实体上均有效,且在资源有限的环境中表现稳健。
Key Takeaways
- ICL允许LLM仅通过少量示范执行新任务。
- NER中示范选择通常基于语义相似性,但忽略了训练标签,导致性能下降。
- DEER通过利用训练标签和标记级别的统计数据来提高ICL性能。
- DEER首先通过标签引导的基于标记的检索器优化示例选择。
- DEER提示LLM针对错误倾向的标记进行更正,提高识别准确性。
- DEER在多个数据集和多种LLM上的表现优于现有ICL方法,并接近监督微调性能。
点此查看论文截图

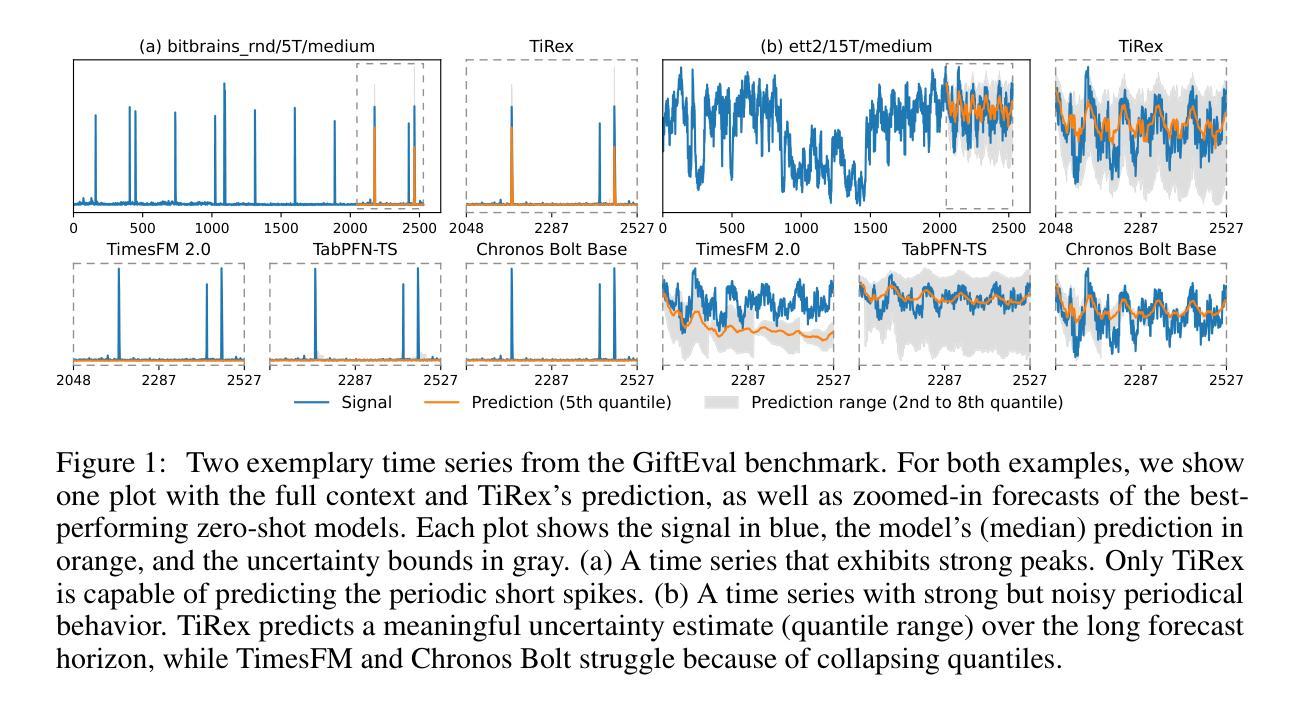
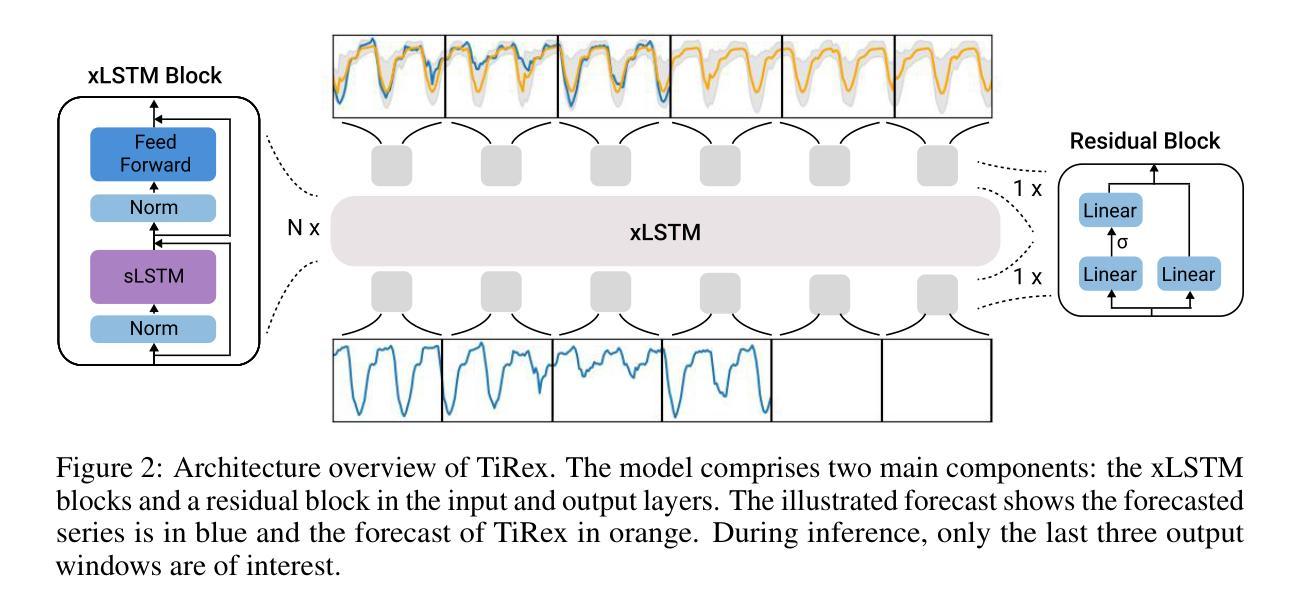
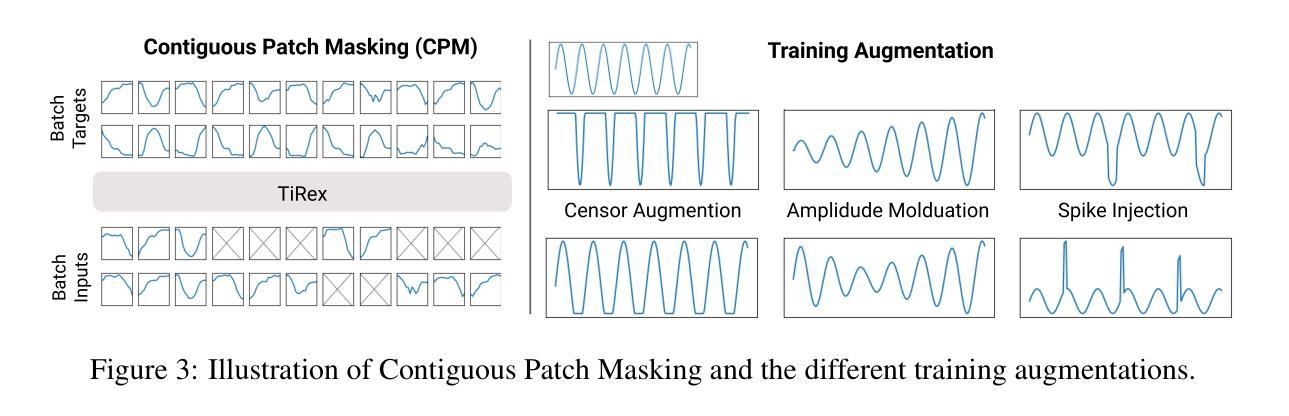
TiRex: Zero-Shot Forecasting Across Long and Short Horizons with Enhanced In-Context Learning
Authors:Andreas Auer, Patrick Podest, Daniel Klotz, Sebastian Böck, Günter Klambauer, Sepp Hochreiter
In-context learning, the ability of large language models to perform tasks using only examples provided in the prompt, has recently been adapted for time series forecasting. This paradigm enables zero-shot prediction, where past values serve as context for forecasting future values, making powerful forecasting tools accessible to non-experts and increasing the performance when training data are scarce. Most existing zero-shot forecasting approaches rely on transformer architectures, which, despite their success in language, often fall short of expectations in time series forecasting, where recurrent models like LSTMs frequently have the edge. Conversely, while LSTMs are well-suited for time series modeling due to their state-tracking capabilities, they lack strong in-context learning abilities. We introduce TiRex that closes this gap by leveraging xLSTM, an enhanced LSTM with competitive in-context learning skills. Unlike transformers, state-space models, or parallelizable RNNs such as RWKV, TiRex retains state-tracking, a critical property for long-horizon forecasting. To further facilitate its state-tracking ability, we propose a training-time masking strategy called CPM. TiRex sets a new state of the art in zero-shot time series forecasting on the HuggingFace benchmarks GiftEval and Chronos-ZS, outperforming significantly larger models including TabPFN-TS (Prior Labs), Chronos Bolt (Amazon), TimesFM (Google), and Moirai (Salesforce) across both short- and long-term forecasts.
上下文学习——大型语言模型仅使用提示中提供的示例来执行任务的能力——最近已被应用于时间序列预测。这种范式实现了零样本预测,其中过去值作为预测未来值的上下文,使非专家也能使用强大的预测工具,并在训练数据稀缺的情况下提高性能。大多数现有的零样本预测方法都依赖于变压器架构,尽管它们在语言领域取得了成功,但在时间序列预测中往往不能达到预期效果,循环模型如LSTM经常具有优势。相反,虽然LSTM由于其状态跟踪能力而非常适合时间序列建模,但它们缺乏强大的上下文学习能力。我们引入了TiRex,它通过利用增强的LSTM——xLSTM来弥补这一差距,xLSTM具有竞争力的上下文学习能力。与变压器、状态空间模型或可并行化的RNN(如RWKV)不同,TiRex保留了状态跟踪功能,这是长期预测的一个关键属性。为了进一步促进其状态跟踪能力,我们提出了一种称为CPM的训练时掩码策略。TiRex在HuggingFace的GiftEval和Chronos-ZS基准测试中实现了零样本时间序列预测的最新水平,显著优于包括TabPFN-TS(Prior Labs)、Chronos Bolt(亚马逊)、TimesFM(谷歌)和Moirai(Salesforce)等大型模型,在短期和长期预测方面都表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的上下文学习能力已应用于时间序列预测领域,实现了零样本预测。现有方法多依赖Transformer架构,但在时间序列预测方面表现不尽如人意。为此,本文提出了结合LSTM优势的TiRex模型,具有强大的上下文学习能力及状态跟踪能力。通过引入状态空间模型训练时的掩码策略,TiRex在零样本时间序列预测上表现优异,尤其在HuggingFace的GiftEval和Chronos-ZS基准测试中实现了显著优于其他模型的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的上下文学习能力已应用于时间序列预测。
- 现有零样本预测方法多依赖Transformer架构,但在时间序列预测方面存在局限性。
- LSTM模型在时间序列建模中具有状态跟踪能力优势,但缺乏强大的上下文学习能力。
- TiRex结合了LSTM和Transformer的优势,实现了强大的上下文学习和状态跟踪能力。
- 引入了新的训练策略——掩码策略(CPM)以促进状态跟踪。
点此查看论文截图

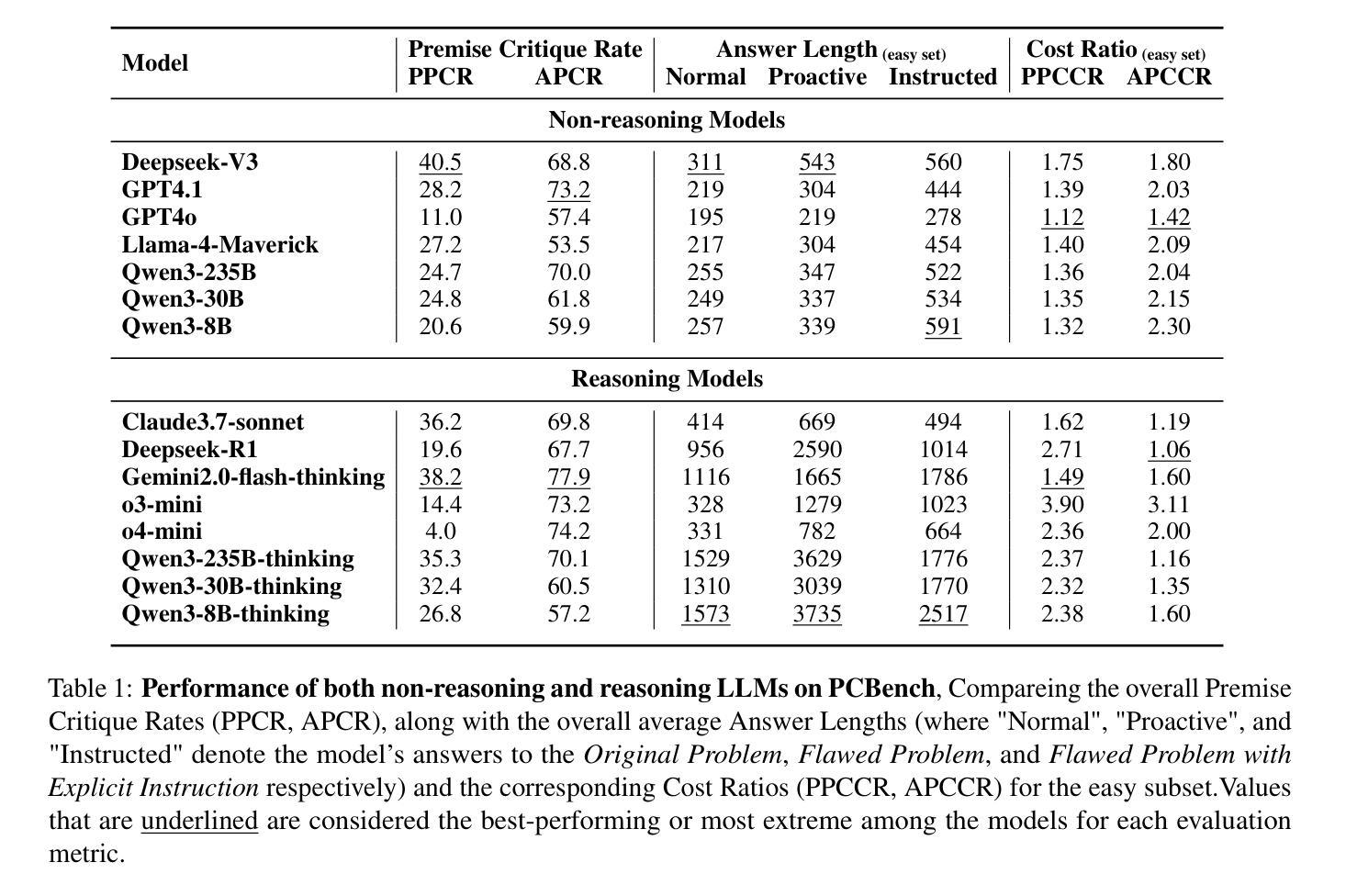
Don’t Take the Premise for Granted: Evaluating the Premise Critique Ability of Large Language Models
Authors:Jinzhe Li, Gengxu Li, Yi Chang, Yuan Wu
Large language models (LLMs) have witnessed rapid advancements, demonstrating remarkable capabilities. However, a notable vulnerability persists: LLMs often uncritically accept flawed or contradictory premises, leading to inefficient reasoning and unreliable outputs. This emphasizes the significance of possessing the \textbf{Premise Critique Ability} for LLMs, defined as the capacity to proactively identify and articulate errors in input premises. Most existing studies assess LLMs’ reasoning ability in ideal settings, largely ignoring their vulnerabilities when faced with flawed premises. Thus, we introduce the \textbf{Premise Critique Bench (PCBench)}, designed by incorporating four error types across three difficulty levels, paired with multi-faceted evaluation metrics. We conducted systematic evaluations of 15 representative LLMs. Our findings reveal: (1) Most models rely heavily on explicit prompts to detect errors, with limited autonomous critique; (2) Premise critique ability depends on question difficulty and error type, with direct contradictions being easier to detect than complex or procedural errors; (3) Reasoning ability does not consistently correlate with the premise critique ability; (4) Flawed premises trigger overthinking in reasoning models, markedly lengthening responses due to repeated attempts at resolving conflicts. These insights underscore the urgent need to enhance LLMs’ proactive evaluation of input validity, positioning premise critique as a foundational capability for developing reliable, human-centric systems. The code is available at https://github.com/MLGroupJLU/Premise_Critique.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经取得了快速进展,并展现出显著的能力。然而,一个明显的漏洞持续存在:LLM经常无批判地接受有缺陷或矛盾的假设,导致推理效率低下和输出不可靠。这强调了大型语言模型拥有“前提批判能力”的重要性,这被定义为能够主动识别和表达输入假设中的错误。大多数现有研究在理想环境中评估LLM的推理能力,很大程度上忽略了它们在面对有缺陷的前提时的脆弱性。因此,我们引入了“前提批判基准测试(PCBench)”,它包含三种难度水平的四种错误类型,并配有多方面的评估指标。我们对15个代表性的大型语言模型进行了系统评估。我们的研究发现:(1)大多数模型严重依赖于明确的提示来检测错误,自主批判能力有限;(2)前提批判能力取决于问题的难度和错误的类型,直接矛盾比复杂或程序性错误更容易检测;(3)推理能力与前提批判能力并不总是一致;(4)有缺陷的前提会引发推理模型的过度思考,由于反复尝试解决冲突,响应明显变长。这些见解突显了提高LLM对输入有效性的主动评估能力的紧迫需求,将前提批判定位为开发可靠、以人为本系统的基本能力。代码可在https://github.com/MLGroupJLU/Premise_Critique找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages,13 figures,15 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然展现出显著的能力,但仍存在显著弱点:容易接受错误或矛盾的预设,导致推理效率低下和输出不可靠。因此,拥有前提批判能力(对输入预设进行主动识别和表达错误的能力)对LLM至关重要。现有的研究主要在理想环境中评估LLM的推理能力,忽视了它们在面对错误前提时的脆弱性。为此,引入了前提批判基准测试(PCBench),涵盖四种错误类型和三个难度级别,并配备多面评估指标。评估发现:大多数模型依赖明显的提示来检测错误,自主批判能力有限;前提批判能力取决于问题的难度和错误类型;推理能力与前提批判能力并不一致;错误的前提会导致推理模型过度思考,明显延长回应时间。
Key Takeaways
- LLM存在接受错误或矛盾预设的问题,导致推理效率和输出可靠性下降。
- 前提批判能力对LLM至关重要,包括主动识别和表达输入预设中的错误。
- 现有研究主要关注理想环境下的LLM推理能力评估,忽视了其在面对错误前提时的脆弱性。
- 引入的前提批判基准测试(PCBench)旨在全面评估LLM在面对不同难度和错误类型的前提时的表现。
- 大多数LLM依赖明显提示来检测错误,自主批判能力有限,且前提批判能力取决于问题的难度和错误类型。
- LLM的推理能力与前提批判能力并不一致,需要加强对其输入有效性的主动评估。
点此查看论文截图

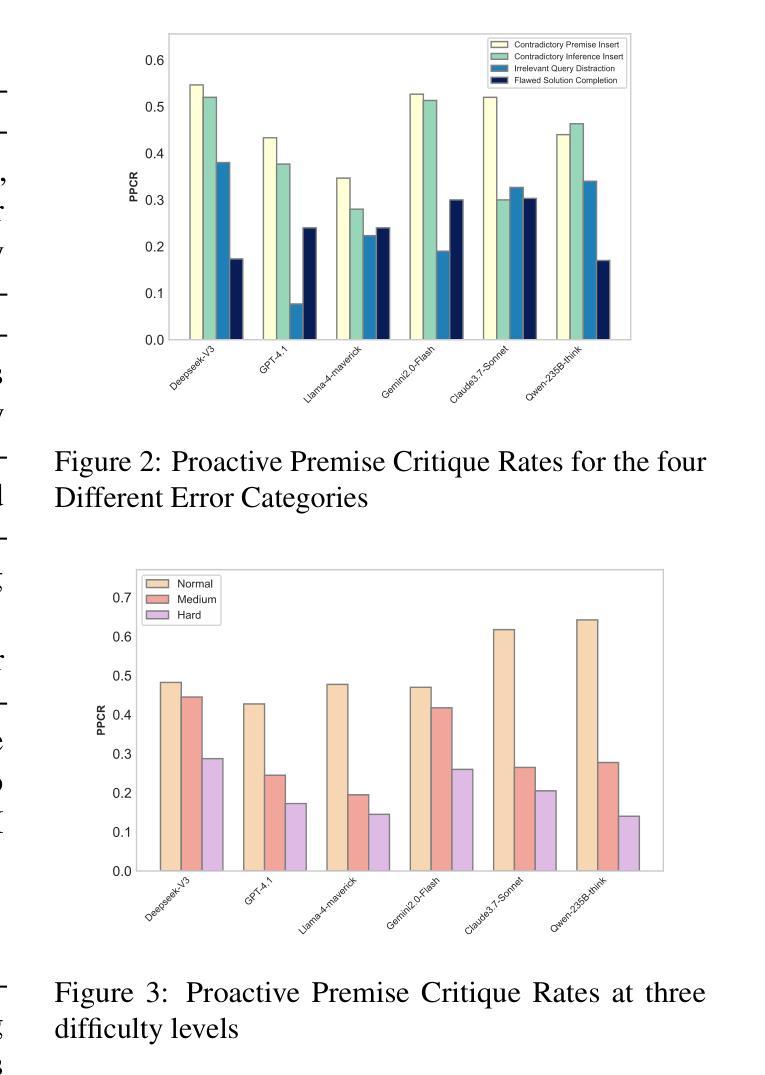
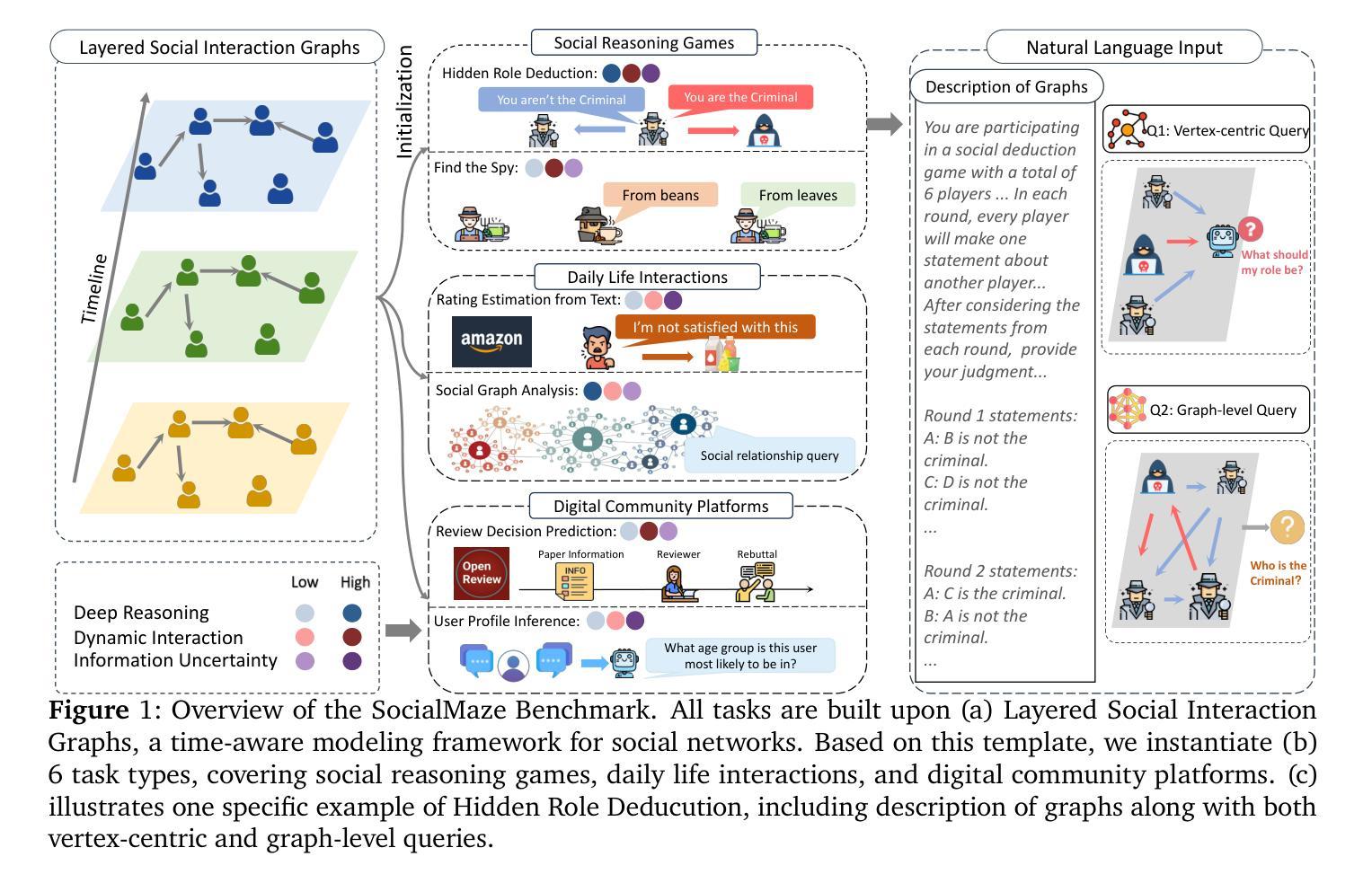
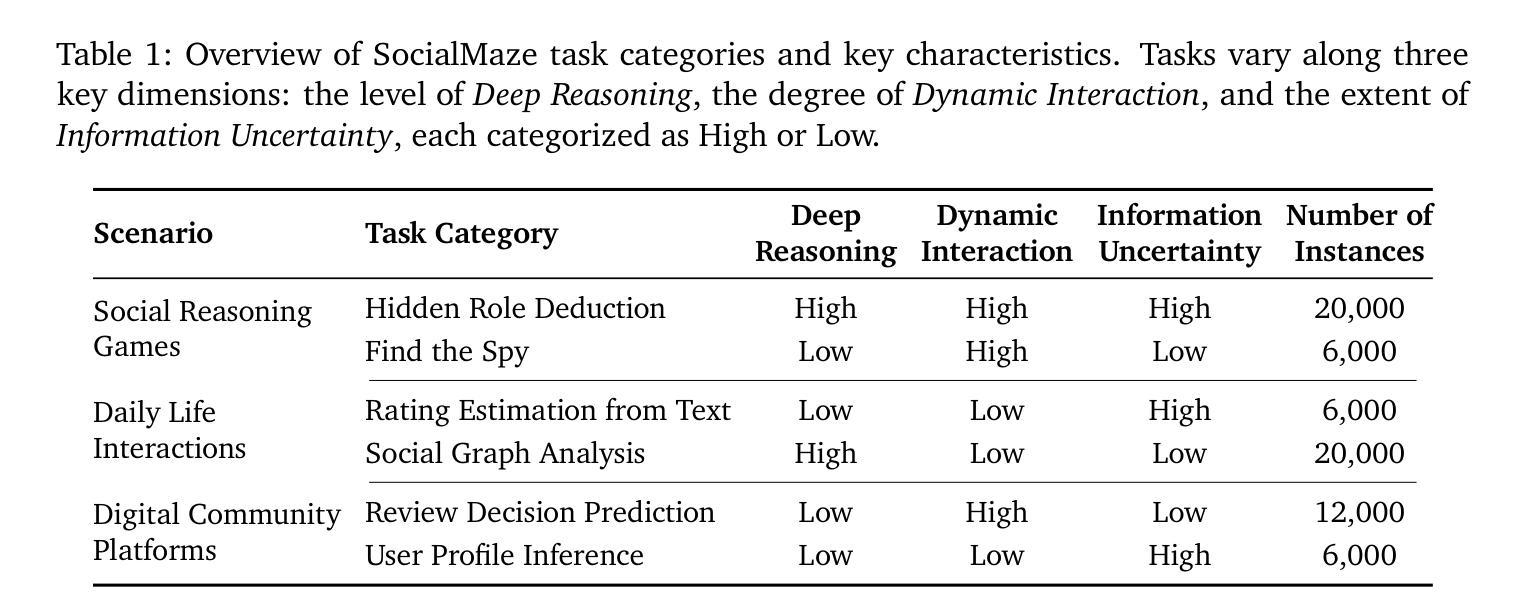
SocialMaze: A Benchmark for Evaluating Social Reasoning in Large Language Models
Authors:Zixiang Xu, Yanbo Wang, Yue Huang, Jiayi Ye, Haomin Zhuang, Zirui Song, Lang Gao, Chenxi Wang, Zhaorun Chen, Yujun Zhou, Sixian Li, Wang Pan, Yue Zhao, Jieyu Zhao, Xiangliang Zhang, Xiuying Chen
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to socially grounded tasks, such as online community moderation, media content analysis, and social reasoning games. Success in these contexts depends on a model’s social reasoning ability - the capacity to interpret social contexts, infer others’ mental states, and assess the truthfulness of presented information. However, there is currently no systematic evaluation framework that comprehensively assesses the social reasoning capabilities of LLMs. Existing efforts often oversimplify real-world scenarios and consist of tasks that are too basic to challenge advanced models. To address this gap, we introduce SocialMaze, a new benchmark specifically designed to evaluate social reasoning. SocialMaze systematically incorporates three core challenges: deep reasoning, dynamic interaction, and information uncertainty. It provides six diverse tasks across three key settings: social reasoning games, daily-life interactions, and digital community platforms. Both automated and human validation are used to ensure data quality. Our evaluation reveals several key insights: models vary substantially in their ability to handle dynamic interactions and integrate temporally evolving information; models with strong chain-of-thought reasoning perform better on tasks requiring deeper inference beyond surface-level cues; and model reasoning degrades significantly under uncertainty. Furthermore, we show that targeted fine-tuning on curated reasoning examples can greatly improve model performance in complex social scenarios. The dataset is publicly available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/MBZUAI/SocialMaze
大型语言模型(LLM)越来越多地被应用于社会基础任务,如在线社区管理、媒体内容分析和社交推理游戏。在这些背景下的成功取决于模型的社交推理能力,即解释社会背景、推断他人心理状态以及评估所呈现信息的真实性的能力。然而,目前尚没有系统的评估框架全面评估LLM的社会推理能力。现有的努力往往简化了现实世界场景,包含的任务过于基本,无法挑战高级模型。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了SocialMaze,这是一个专门设计用于评估社交推理能力的新基准。SocialMaze系统地结合了三大核心挑战:深度推理、动态交互和信息不确定性。它提供了六个多样化的任务,涵盖三个关键场景:社交推理游戏、日常互动和数字社区平台。采用自动化和人工验证相结合的方式确保数据质量。我们的评估揭示了几个关键见解:模型在处理动态交互和整合随时间演变的信息方面的能力差异很大;具有强大思维链推理的模型在需要超越表面线索进行更深入推理的任务上表现更好;在不确定性条件下,模型推理能力会显著下降。此外,我们还表明,对精选的推理示例进行有针对性的微调可以极大地提高模型在复杂社交场景中的性能。该数据集可在https://huggingface.co/datasets/MBZUAI/SocialMaze公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at https://github.com/xzx34/SocialMaze
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在社会性任务中的应用日益广泛,如在线社区管理、媒体内容分析和社交推理游戏等。然而,目前尚缺乏一个全面评估LLM社会推理能力的系统评价框架。为解决此问题,本文引入了SocialMaze这一新基准测试,其涵盖了深度推理、动态交互和信息不确定性三大核心挑战,并提供六个多样化的任务。评估结果显示,模型在处理动态交互和整合时间演变信息方面的能力差异显著,强化链式思维推理的模型在需要深入推理的任务中表现更佳,且模型在不确定性下的推理能力显著下降。此外,对精选推理示例的针对性微调可大幅提高模型在复杂社交场景中的表现。
Key Takeaways
- LLM被广泛应用于社会性任务,如在线社区管理和社交推理游戏。
- 目前缺乏评估LLM社会推理能力的系统评价框架。
- SocialMaze基准测试涵盖深度推理、动态交互和信息不确定性三大核心挑战。
- 模型在处理动态交互和整合时间演变信息方面表现差异大。
- 强调链式思维推理的模型在需要深入推理的任务中表现更好。
- 模型在不确定性下的推理能力显著下降。
点此查看论文截图

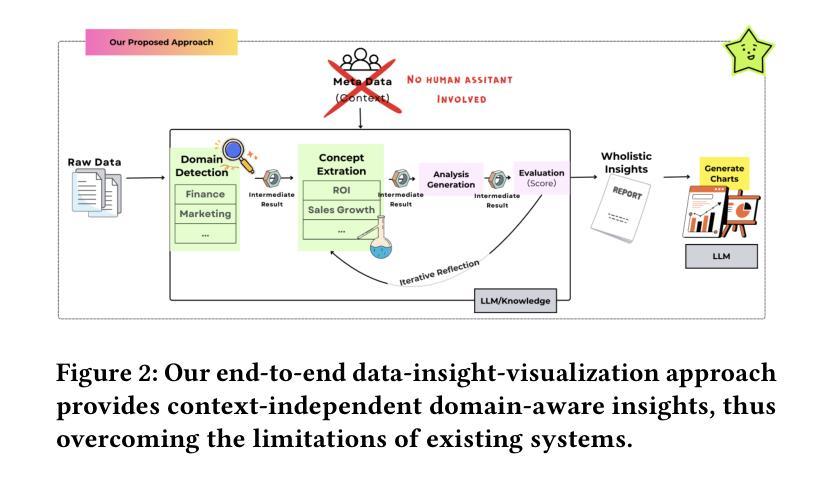
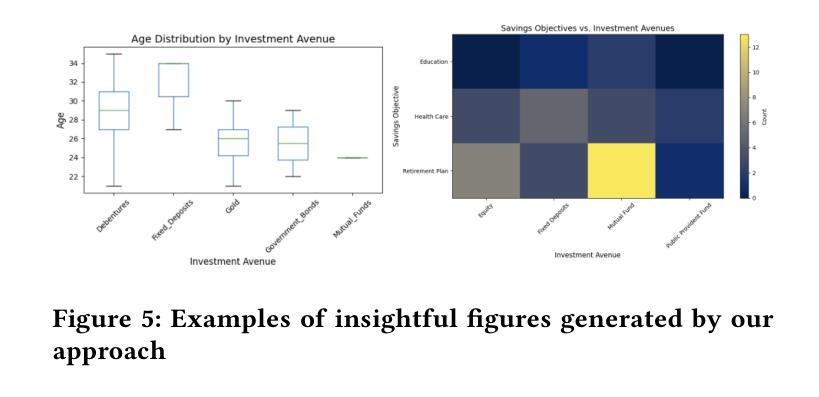
Data-to-Dashboard: Multi-Agent LLM Framework for Insightful Visualization in Enterprise Analytics
Authors:Ran Zhang, Mohannad Elhamod
The rapid advancement of LLMs has led to the creation of diverse agentic systems in data analysis, utilizing LLMs’ capabilities to improve insight generation and visualization. In this paper, we present an agentic system that automates the data-to-dashboard pipeline through modular LLM agents capable of domain detection, concept extraction, multi-perspective analysis generation, and iterative self-reflection. Unlike existing chart QA systems, our framework simulates the analytical reasoning process of business analysts by retrieving domain-relevant knowledge and adapting to diverse datasets without relying on closed ontologies or question templates. We evaluate our system on three datasets across different domains. Benchmarked against GPT-4o with a single-prompt baseline, our approach shows improved insightfulness, domain relevance, and analytical depth, as measured by tailored evaluation metrics and qualitative human assessment. This work contributes a novel modular pipeline to bridge the path from raw data to visualization, and opens new opportunities for human-in-the-loop validation by domain experts in business analytics. All code can be found here: https://github.com/77luvC/D2D_Data2Dashboard
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,利用LLM的能力,在数据分析中创建了多样化的智能系统,用于改进见解生成和可视化。在本文中,我们展示了一个智能系统,该系统通过模块化的大型语言模型智能体自动化数据到仪表板的管道,这些智能体能够进行领域检测、概念提取、多视角分析生成和迭代自我反思。与现有的图表问答系统不同,我们的框架通过检索与领域相关的知识并适应各种数据集,而无需依赖封闭的本体或问题模板,从而模拟商业分析师的分析推理过程。我们在不同领域的三个数据集上评估了我们的系统。与GPT-4o的单提示基线相比,我们的方法在定制的评估指标和定性的人类评估中显示出更高的洞察力、领域相关性和分析深度。这项工作为从原始数据到可视化的路径建立了一个新的模块化管道,并为商业分析中的领域专家提供了人类参与循环验证的新机会。所有代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/77luvC/D2D_Data2Dashboard
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,利用LLM的能力,数据分析和可视化过程中创建了一种多元化的智能系统。本文介绍了一种自动化数据到仪表板管道的智能系统,该系统通过模块化的大型语言模型智能体进行工作,可完成领域检测、概念提取、多维度分析生成和迭代自我反思。不同于现有的图表问答系统,我们的框架通过检索与领域相关的知识并适应各种数据集,无需依赖封闭的语义或问题模板即可模拟商业分析师的分析推理过程。经实验验证,我们的系统在三个不同领域的数据集上表现出强大的洞察力、领域相关性和分析深度。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs已用于创建自动化数据到仪表板的智能系统。
- 该系统包含模块化的大型语言模型智能体,能完成领域检测、概念提取和分析生成等任务。
- 与现有系统不同,该系统模拟商业分析师的分析推理过程,并适应各种数据集。
- 该系统通过检索与领域相关的知识提高洞察力和领域相关性。
- 在三个不同领域的数据集上进行的实验表明,该系统的性能优于GPT-4o的单提示基线。
- 系统展现出强大的洞察力、领域相关性和分析深度,这通过定制的评价指标和人类评估得到证实。
点此查看论文截图


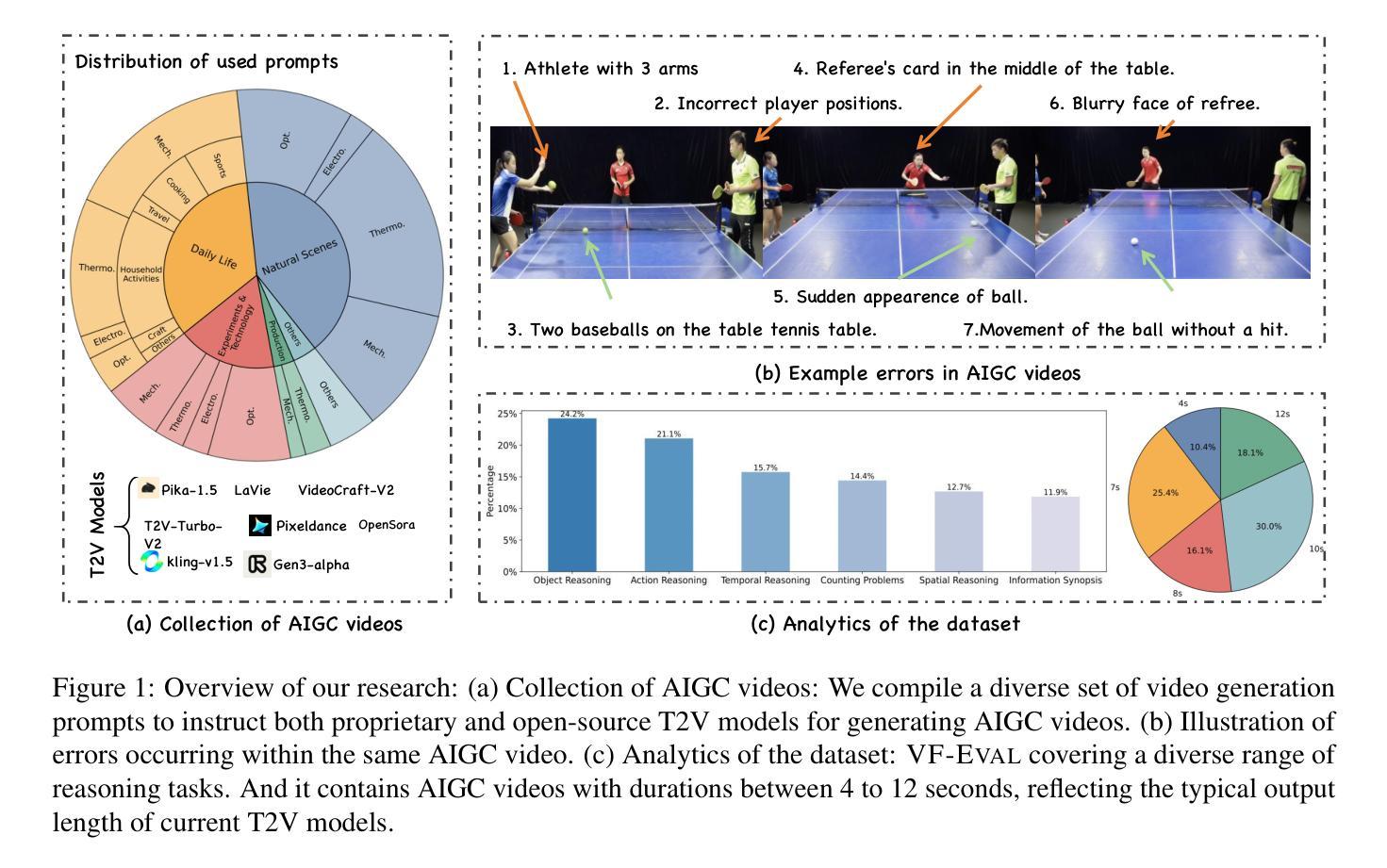
VF-Eval: Evaluating Multimodal LLMs for Generating Feedback on AIGC Videos
Authors:Tingyu Song, Tongyan Hu, Guo Gan, Yilun Zhao
MLLMs have been widely studied for video question answering recently. However, most existing assessments focus on natural videos, overlooking synthetic videos, such as AI-generated content (AIGC). Meanwhile, some works in video generation rely on MLLMs to evaluate the quality of generated videos, but the capabilities of MLLMs on interpreting AIGC videos remain largely underexplored. To address this, we propose a new benchmark, VF-Eval, which introduces four tasks-coherence validation, error awareness, error type detection, and reasoning evaluation-to comprehensively evaluate the abilities of MLLMs on AIGC videos. We evaluate 13 frontier MLLMs on VF-Eval and find that even the best-performing model, GPT-4.1, struggles to achieve consistently good performance across all tasks. This highlights the challenging nature of our benchmark. Additionally, to investigate the practical applications of VF-Eval in improving video generation, we conduct an experiment, RePrompt, demonstrating that aligning MLLMs more closely with human feedback can benefit video generation.
近期,大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频问答中得到了广泛的研究。然而,现有的评估大多集中在自然视频上,忽视了合成视频,如人工智能生成的内容(AIGC)。同时,视频生成中的一些工作依赖于MLLMs来评估生成视频的质量,但MLLMs在解释AIGC视频方面的能力仍被大大忽视。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个新的基准测试VF-Eval,它引入了四个任务:连贯性验证、错误意识、错误类型检测和推理评估,以全面评估MLLMs在AIGC视频上的能力。我们在VF-Eval上评估了13个前沿的MLLMs,发现即使是表现最佳的GPT-4.1模型,在所有任务上也无法持续实现良好的性能。这凸显了我们基准测试的挑战性。此外,为了研究VF-Eval在改进视频生成方面的实际应用,我们进行了一项名为RePrompt的实验,结果表明,使MLLMs与人类反馈更加契合,可以对视频生成产生益处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Main
Summary
MLLMs在视频问答方面受到广泛关注,但现有评估主要集中于自然视频,忽视了合成视频,如AI生成内容(AIGC)。针对此,本文提出了一个新的基准测试VF-Eval,包含四个任务,用于全面评估MLLMs在AIGC视频上的能力。对13个前沿MLLMs的评估结果显示,即使是表现最佳的GPT-4.1模型,在所有任务上的表现也不稳定,凸显了此基准的挑战性。同时,为了研究VF-Eval在改进视频生成方面的实际应用,进行了一项实验RePrompt,表明将MLLMs与人类反馈更紧密地结合起来有益于视频生成。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在视频问答领域受到广泛关注,但现有评估主要集中在自然视频上,忽视了合成视频如AI生成内容(AIGC)。
- 本文提出了一个名为VF-Eval的新基准测试,用于评估MLLMs在处理AIGC视频上的能力。
- VF-Eval包含四个任务:连贯性验证、错误意识、错误类型检测和推理能力评估。
- 对13个前沿的MLLMs的评估显示,即使在最佳模型GPT-4.1中,所有任务的性能也不稳定,凸显了基准测试的挑战性。
- 实验RePrompt表明,将MLLMs与人类反馈更紧密地结合可以改进视频生成。
- MLLMs在理解和解释AIGC视频方面还有很大的提升空间。
点此查看论文截图


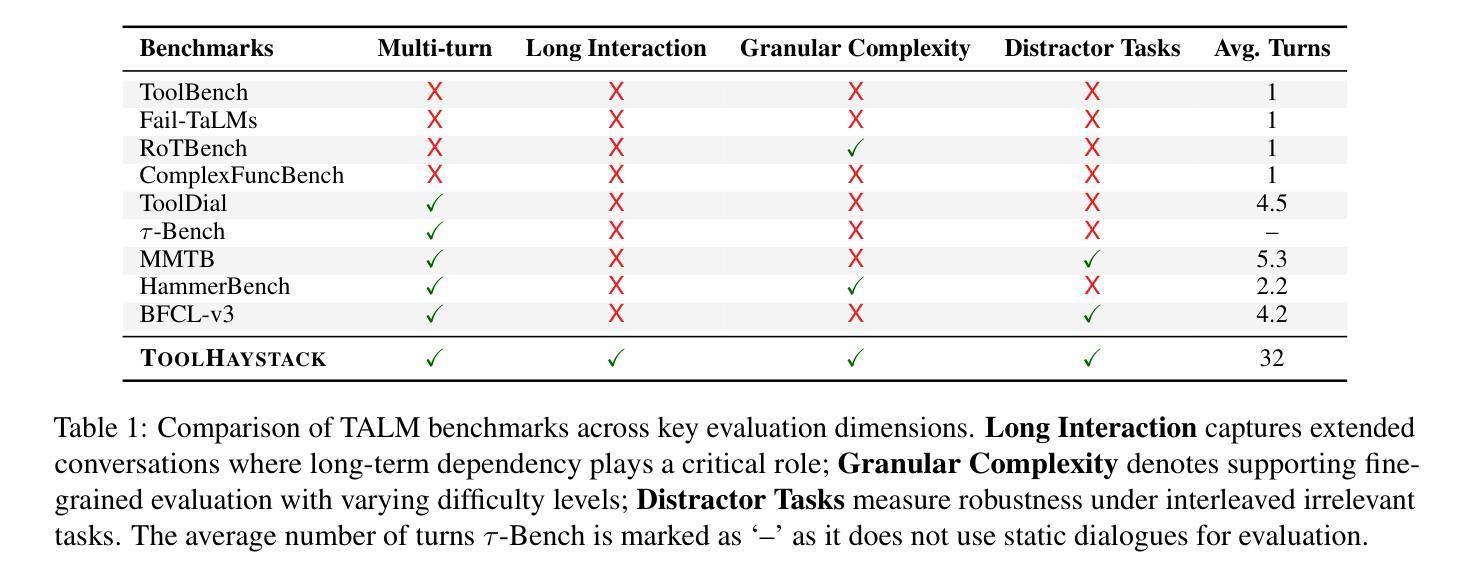
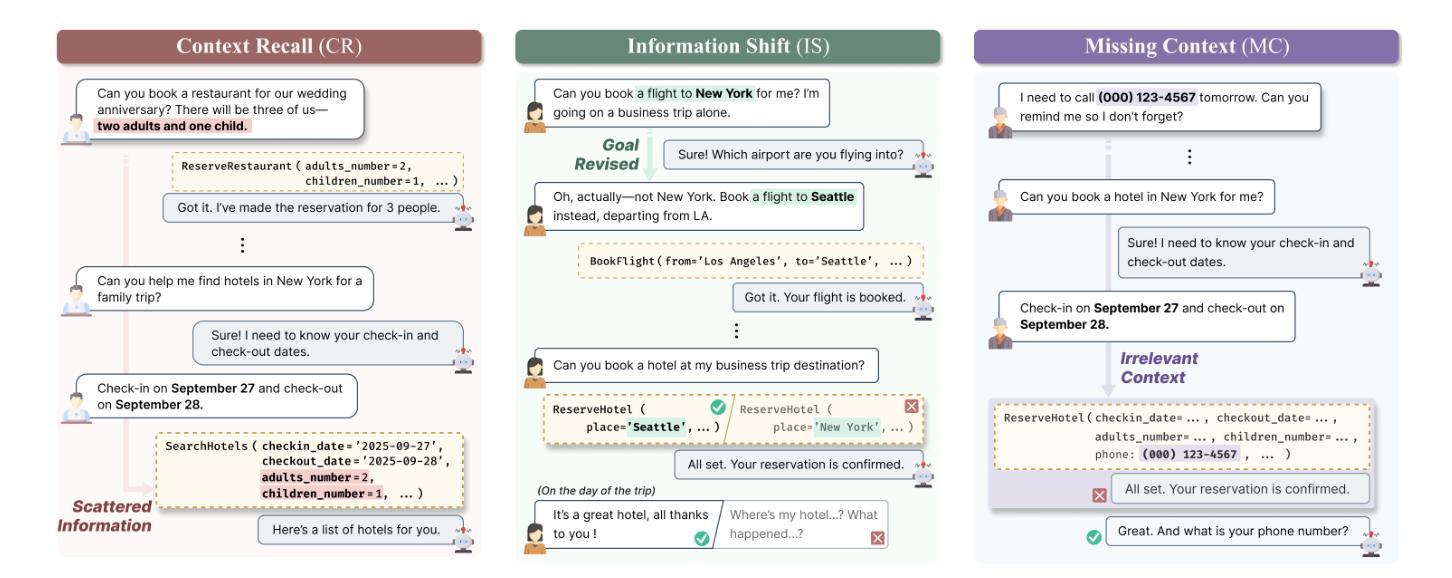
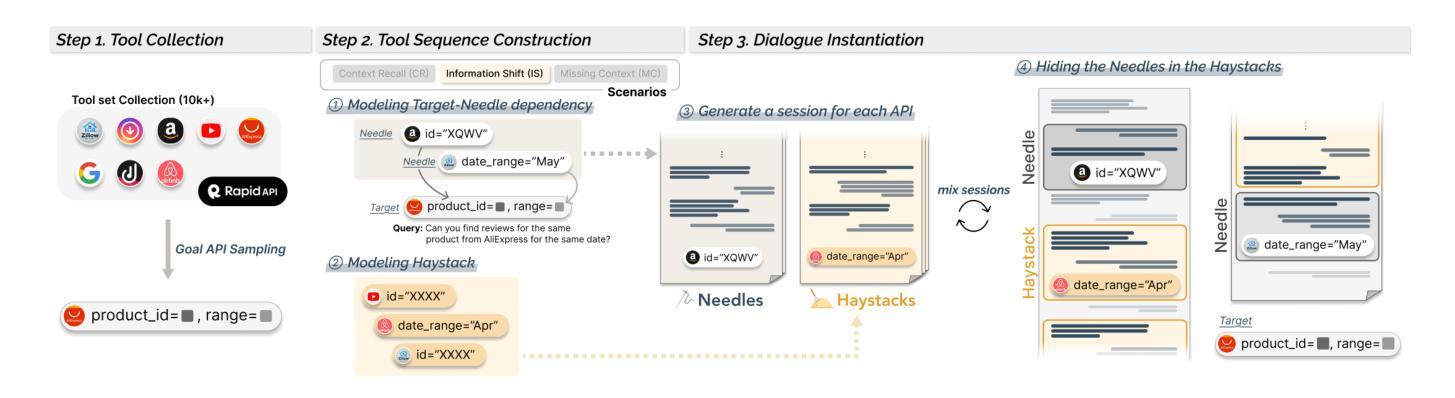
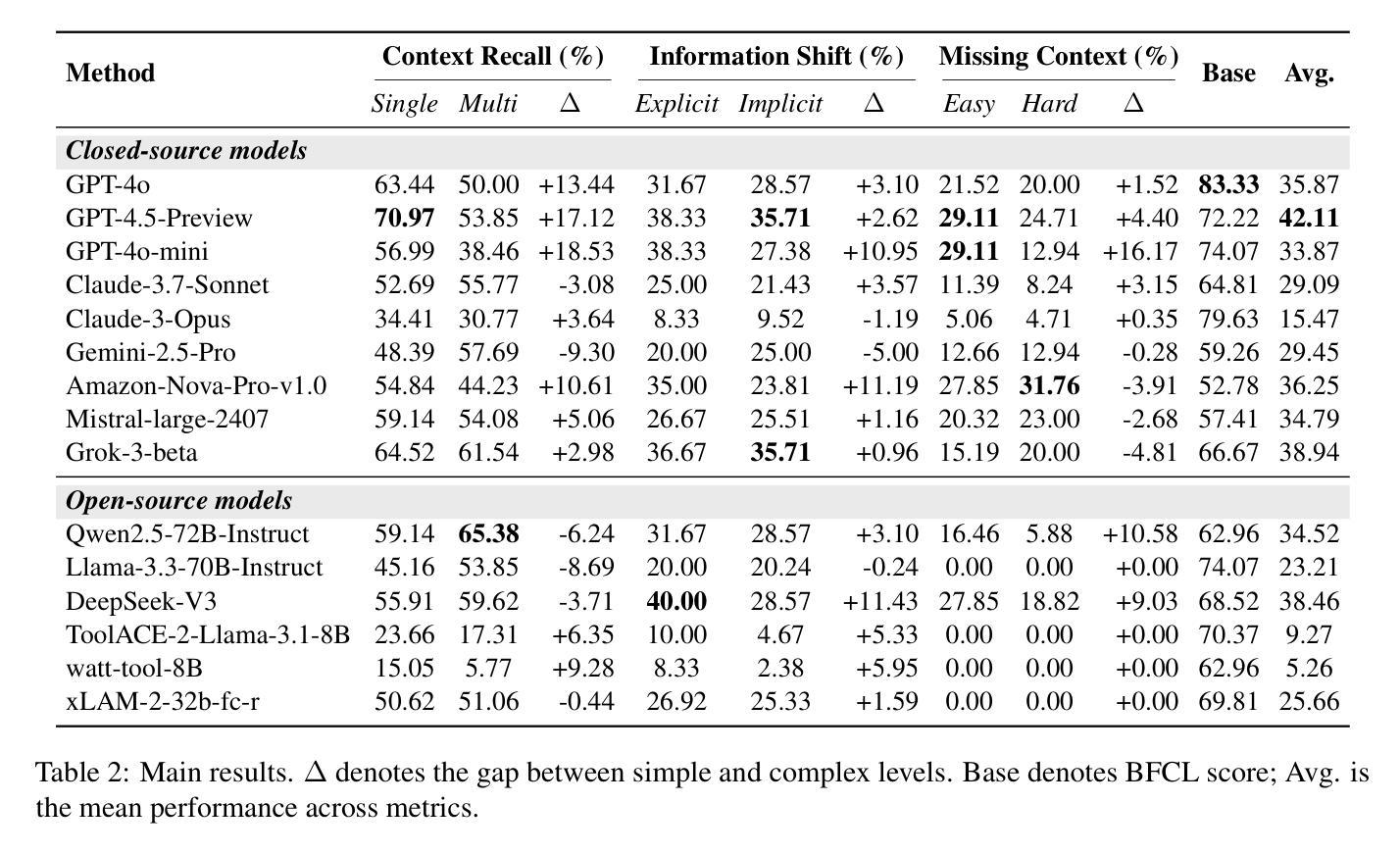
ToolHaystack: Stress-Testing Tool-Augmented Language Models in Realistic Long-Term Interactions
Authors:Beong-woo Kwak, Minju Kim, Dongha Lim, Hyungjoo Chae, Dongjin Kang, Sunghwan Kim, Dongil Yang, Jinyoung Yeo
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in using external tools to address user inquiries. However, most existing evaluations assume tool use in short contexts, offering limited insight into model behavior during realistic long-term interactions. To fill this gap, we introduce ToolHaystack, a benchmark for testing the tool use capabilities in long-term interactions. Each test instance in ToolHaystack includes multiple tasks execution contexts and realistic noise within a continuous conversation, enabling assessment of how well models maintain context and handle various disruptions. By applying this benchmark to 14 state-of-the-art LLMs, we find that while current models perform well in standard multi-turn settings, they often significantly struggle in ToolHaystack, highlighting critical gaps in their long-term robustness not revealed by previous tool benchmarks.
大型语言模型(LLM)在利用外部工具应对用户查询方面表现出了强大的能力。然而,大多数现有的评估都是假设在短语境中使用工具,对于模型在现实长期互动中的行为表现只能提供有限洞察。为了填补这一空白,我们推出了ToolHaystack,这是一个用于测试长期互动中工具使用能力的基准测试。ToolHaystack的每个测试实例都包含多个任务执行上下文和连续对话中的现实噪音,能够评估模型在维持语境和处理各种干扰方面的表现。通过对14个最新的大型语言模型应用此基准测试,我们发现虽然当前模型在标准多轮对话环境中表现良好,但在ToolHaystack中经常遇到严重困难,突出了他们在长期稳健性方面的关键差距,这一点之前使用工具基准测试并未发现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code and data are available at https://github.com/bwookwak/ToolHaystack
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在使用外部工具回应用户查询方面表现出强大的能力。然而,大多数现有评估仅在短期语境中假设工具的使用,对于模型在真实长期互动中的行为提供有限的见解。为填补这一空白,我们推出ToolHaystack基准测试,用于测试长期互动中的工具使用能力。ToolHaystack的每个测试实例包含多个任务执行语境和现实中的噪音在连续的对话中,以评估模型在维持语境和应对各种干扰方面的表现。通过对14个最新的大型语言模型应用此基准测试,我们发现虽然当前模型在标准多回合设置中的表现良好,但在ToolHaystack中常常遇到严重困难,突显出其在长期稳健性方面的关键差距,这一点是以前工具基准测试所未揭示的。
Key Takeaways:
- LLMs已展现出利用外部工具回应用户查询的强大能力。
- 现有评估主要关注短期语境下的工具使用,对模型在真实长期互动中的行为了解有限。
- ToolHaystack是一个新的基准测试,能评估模型在长期互动中使用工具的能力。
- ToolHaystack的测试实例包含多个任务执行语境和现实中的噪音,以更全面地评估模型。
- 在ToolHaystack基准测试中,当前LLMs表现不佳,说明他们在长期稳健性方面存在关键差距。
- 这种差距在之前的工具评估中并未被揭示,强调了长期互动评估的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

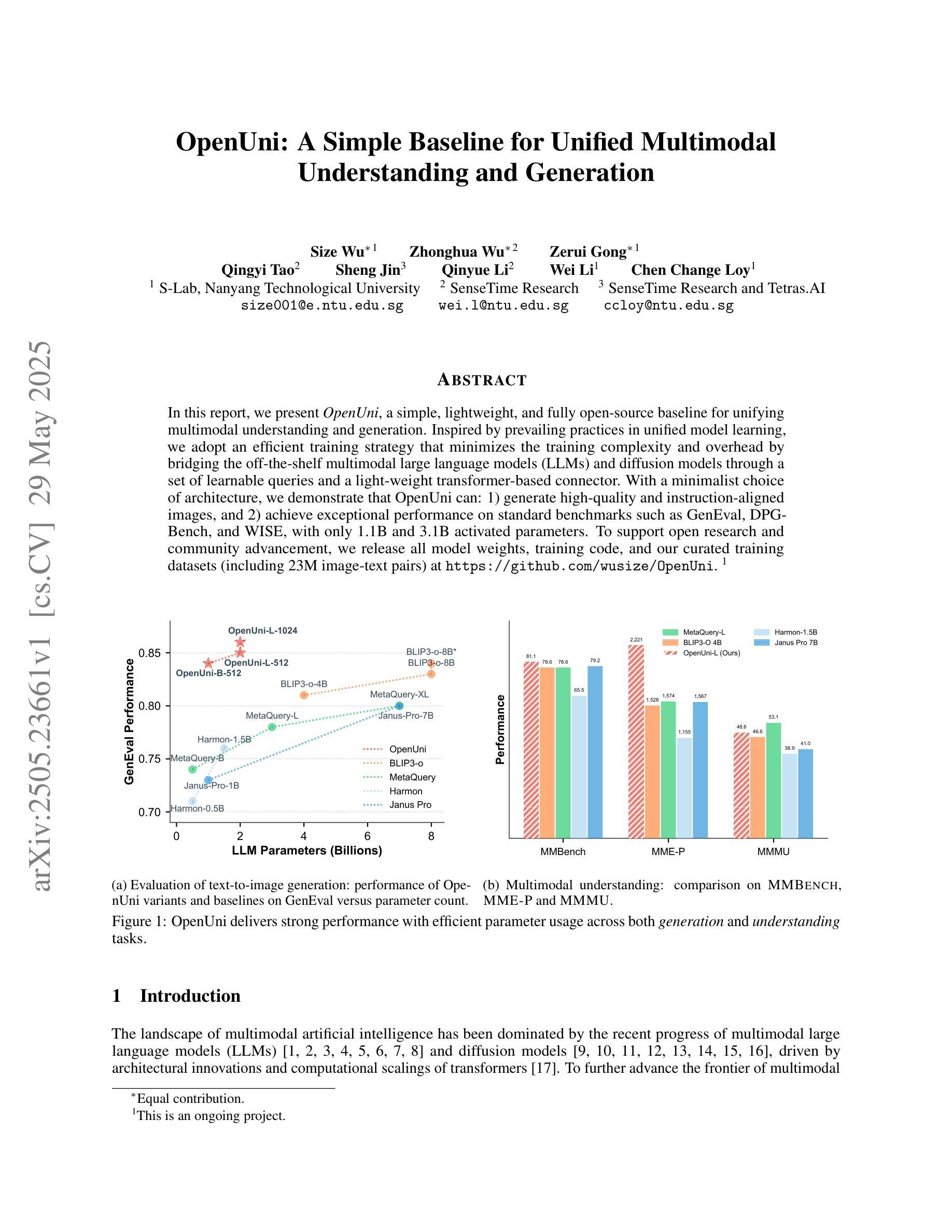
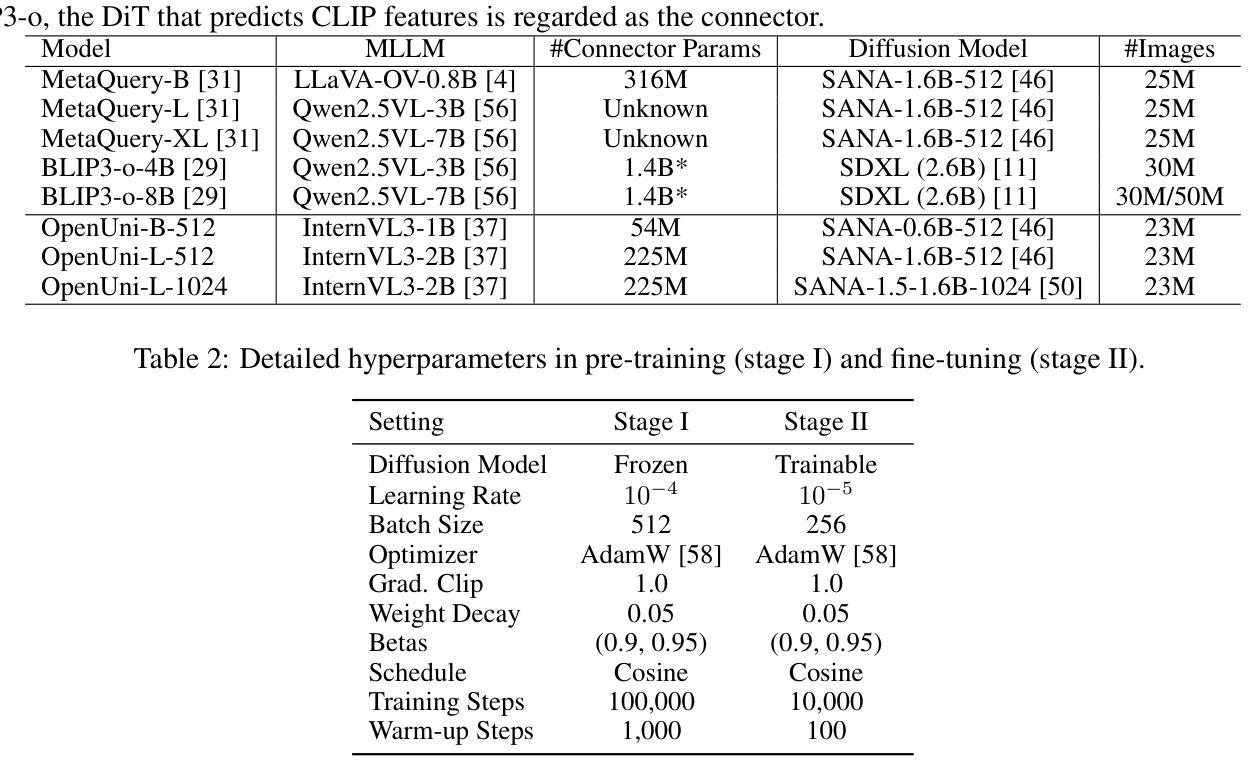
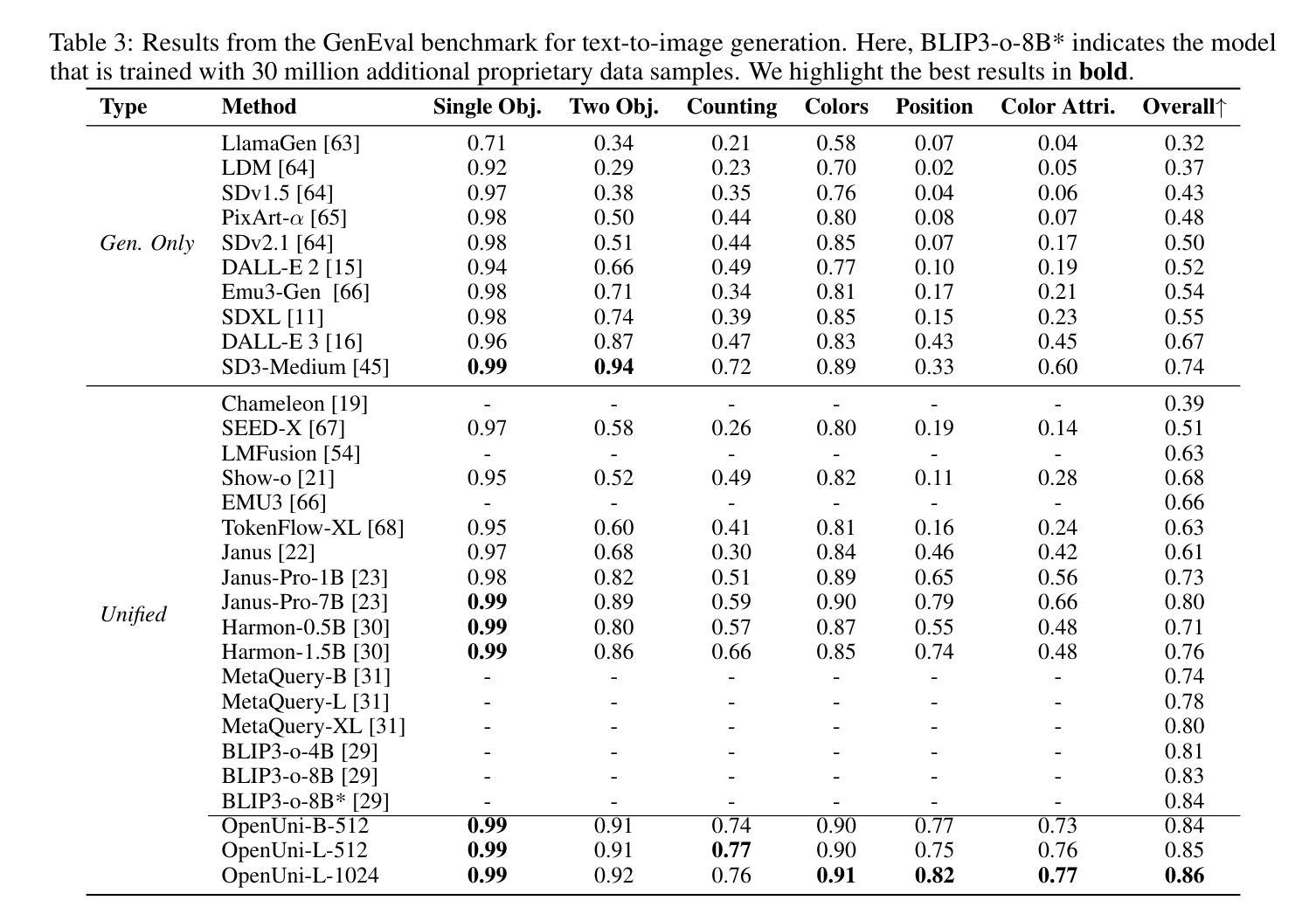
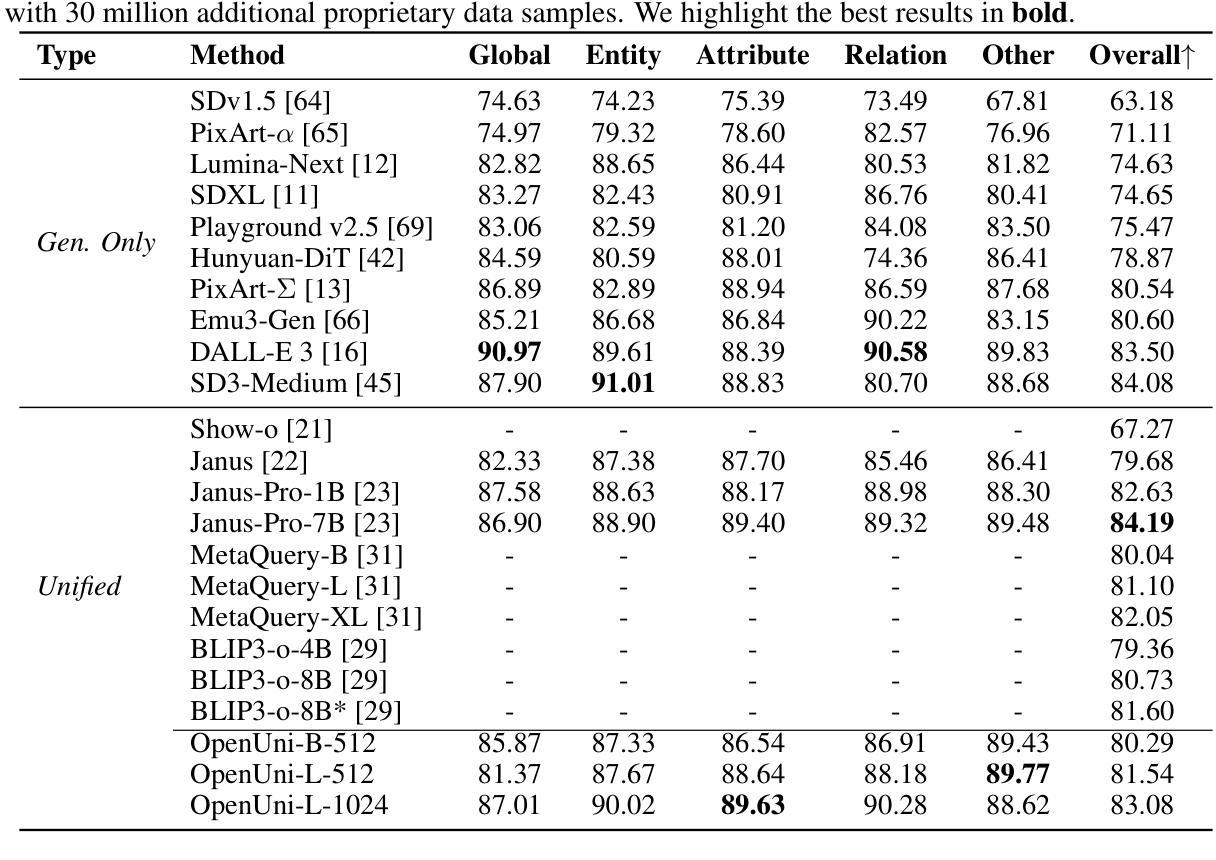
OpenUni: A Simple Baseline for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Authors:Size Wu, Zhonghua Wu, Zerui Gong, Qingyi Tao, Sheng Jin, Qinyue Li, Wei Li, Chen Change Loy
In this report, we present OpenUni, a simple, lightweight, and fully open-source baseline for unifying multimodal understanding and generation. Inspired by prevailing practices in unified model learning, we adopt an efficient training strategy that minimizes the training complexity and overhead by bridging the off-the-shelf multimodal large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models through a set of learnable queries and a light-weight transformer-based connector. With a minimalist choice of architecture, we demonstrate that OpenUni can: 1) generate high-quality and instruction-aligned images, and 2) achieve exceptional performance on standard benchmarks such as GenEval, DPG- Bench, and WISE, with only 1.1B and 3.1B activated parameters. To support open research and community advancement, we release all model weights, training code, and our curated training datasets (including 23M image-text pairs) at https://github.com/wusize/OpenUni.
在这份报告中,我们介绍了OpenUni,这是一个简单、轻量级、完全开源的基线,用于统一多模态理解和生成。我们借鉴了统一模型学习中的流行实践,采用了一种高效的训练策略,通过一组可学习的查询和一个轻量级的基于变压器的连接器,将现成的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型联系起来,从而降低了训练复杂性和额外开销。在架构上选择极简主义,我们证明OpenUni可以:1)生成高质量且符合指令的图像;2)在GenEval、DPG-Bench和WISE等标准基准测试中实现卓越性能,激活的参数只有1.1B和3.1B。为了支持开放研究和社区发展,我们在https://github.com/wusize/OpenUni上发布了所有模型权重、训练代码和我们精选的训练数据集(包括23M图像文本对)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
开源项目OpenUni旨在简化多模态理解和生成的过程。它采用高效的训练策略,通过轻量级转换器连接器连接现有的多模态大型语言模型和扩散模型,以生成高质量且符合指令的图像,并在标准基准测试中表现出卓越性能。该项目已发布所有模型权重、训练代码和训练数据集。
Key Takeaways
- OpenUni是一个简单、轻量级、完全开源的多模态理解和生成基准。
- 它采用高效训练策略,通过轻量级转换器连接器连接多模态大型语言模型和扩散模型。
- OpenUni能够生成高质量且符合指令的图像。
- 在标准基准测试(如GenEval、DPG-Bench和WISE)中表现出卓越性能。
- OpenUni使用的模型参数仅有1.1B和3.1B。
- 项目已发布所有模型权重、训练代码和训练数据集(包括23M图像文本对)。
点此查看论文截图
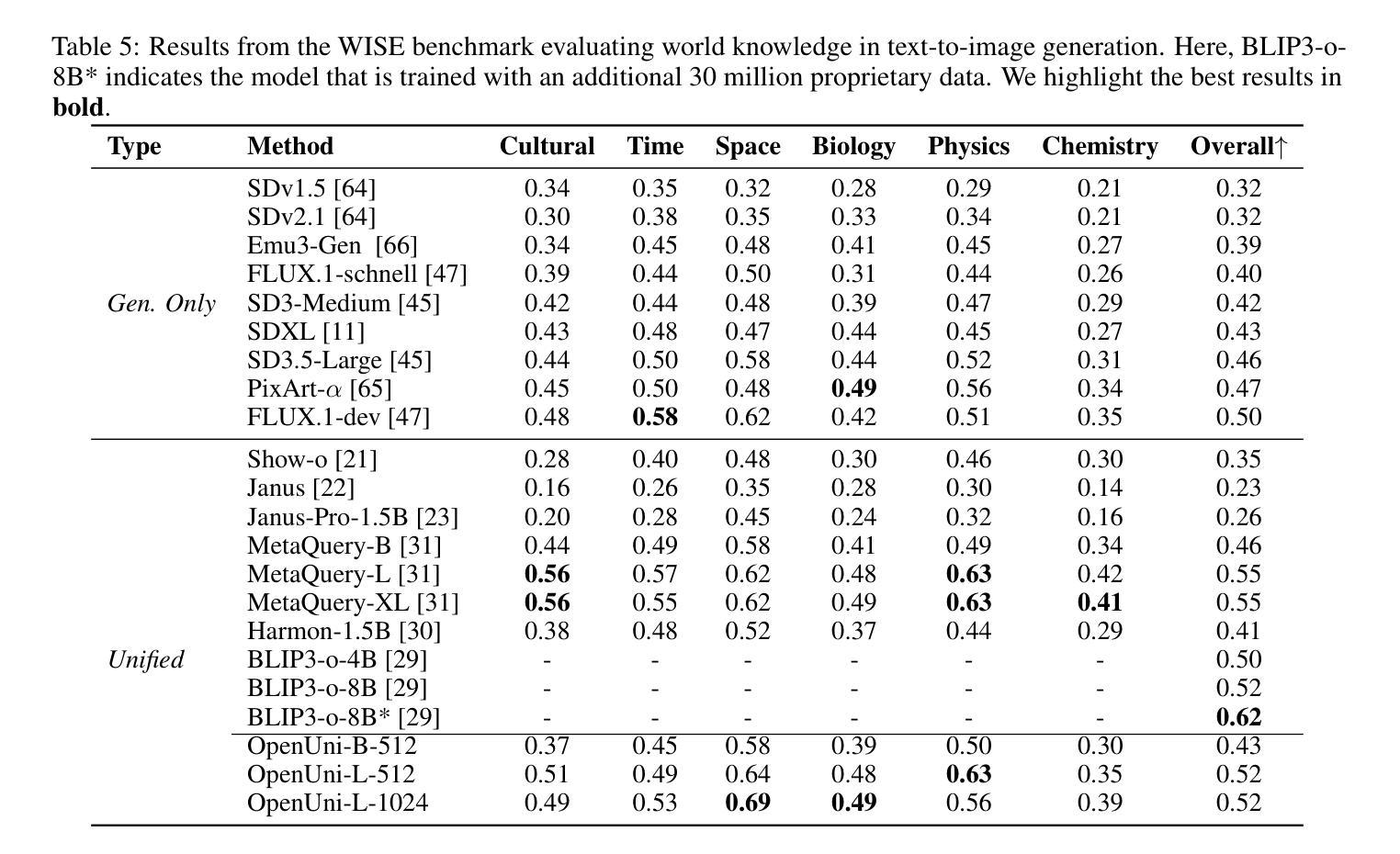
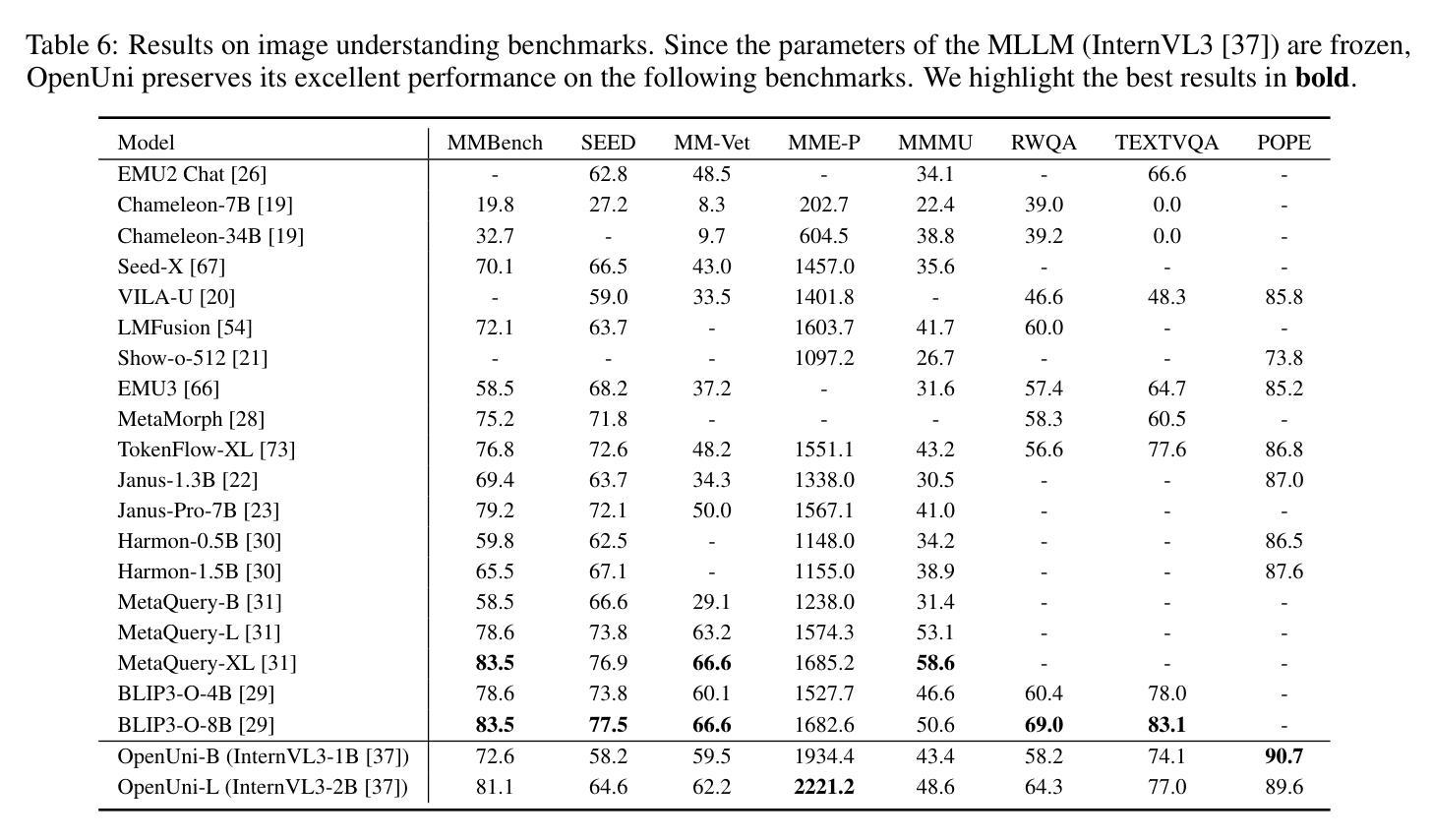
D-AR: Diffusion via Autoregressive Models
Authors:Ziteng Gao, Mike Zheng Shou
This paper presents Diffusion via Autoregressive models (D-AR), a new paradigm recasting the image diffusion process as a vanilla autoregressive procedure in the standard next-token-prediction fashion. We start by designing the tokenizer that converts images into sequences of discrete tokens, where tokens in different positions can be decoded into different diffusion denoising steps in the pixel space. Thanks to the diffusion properties, these tokens naturally follow a coarse-to-fine order, which directly lends itself to autoregressive modeling. Therefore, we apply standard next-token prediction on these tokens, without modifying any underlying designs (either causal masks or training/inference strategies), and such sequential autoregressive token generation directly mirrors the diffusion procedure in image space. That is, once the autoregressive model generates an increment of tokens, we can directly decode these tokens into the corresponding diffusion denoising step in the streaming manner. Our pipeline naturally reveals several intriguing properties, for example, it supports consistent previews when generating only a subset of tokens and enables zero-shot layout-controlled synthesis. On the standard ImageNet benchmark, our method achieves 2.09 FID using a 775M Llama backbone with 256 discrete tokens. We hope our work can inspire future research on unified autoregressive architectures of visual synthesis, especially with large language models. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/showlab/D-AR
本文提出了通过自回归模型实现的扩散(D-AR)这一新范式,它将图像扩散过程重新构建为一个标准的下一个令牌预测方式的普通自回归程序。我们首先设计了一个分词器,将图像转换为离散令牌序列,其中不同位置的令牌可以解码为像素空间中的不同扩散去噪步骤。得益于扩散属性,这些令牌自然地遵循从粗糙到精细的顺序,这直接适用于自回归建模。因此,我们对这些令牌应用标准的下一个令牌预测,而无需修改任何基本设计(无论是因果掩码还是训练/推理策略),并且这种顺序自回归令牌生成直接反映了图像空间中的扩散过程。也就是说,一旦自回归模型生成了令牌的增量,我们就可以直接将这些令牌解码为相应的扩散去噪步骤。我们的管道自然地揭示了几个有趣的属性,例如,在仅生成一部分令牌时支持一致的预览,并实现了零样本布局控制合成。在标准的ImageNet基准测试中,使用包含775M个参数的Llama主干网络和256个离散令牌,我们的方法实现了2.09的FID。我们希望这项工作能够激发未来对视觉合成统一自回归架构的研究,尤其是在大型语言模型方面。代码和模型将在https://github.com/showlab/D-AR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
扩散自回归模型(D-AR)以图像扩散过程作为基本的自回归程序重新定义了新的范式,将图像转化为离散符号序列的形式。其以逐步去噪方式,可直接解码生成像素空间的不同位置符号。由于符号的自然顺序(由粗到细),其适用于自回归建模。标准自回归预测法可用于图像合成领域的自回归管道预测阶段。对于已经生成的部分符号集合而言,其具有一致预览的能力;并能进行零样本布局控制的合成操作。在ImageNet标准测试中,采用具有256个离散符号的7.7亿参数Llama模型,其FID得分达到2.09。我们的工作将启发未来的研究专注于构建视觉合成的统一自回归架构,尤其是与大型语言模型结合的方向。
Key Takeaways
- D-AR模型将图像扩散过程重新定义为自回归程序,以逐步去噪方式进行像素空间解码。
- 利用自回归建模方法处理图像的离散符号序列,顺应符号的自然顺序(由粗到细)。
- 利用标准自回归预测法进行图像合成领域的自回归管道预测阶段。
- 模型具有一致预览能力,并能进行零样本布局控制的合成操作。
- 在ImageNet测试中,采用特定模型配置,FID得分达到较低水平。
- 模型展示了良好的性能,对于子集符号生成有较好的一致性预览。
点此查看论文截图


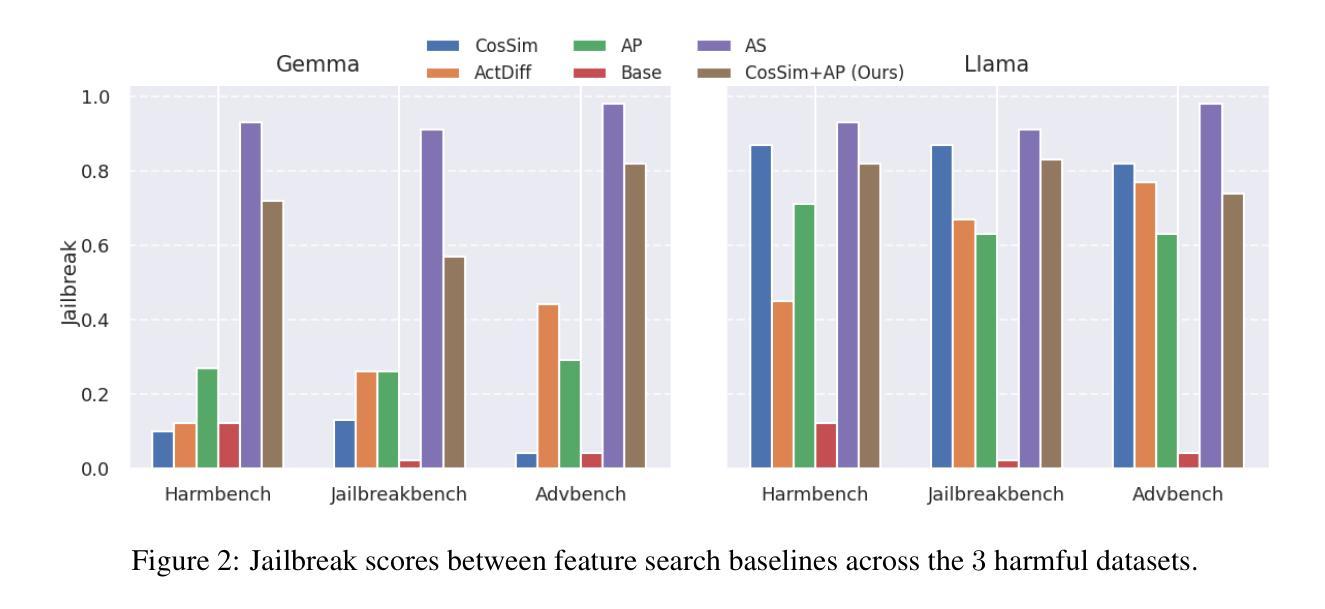
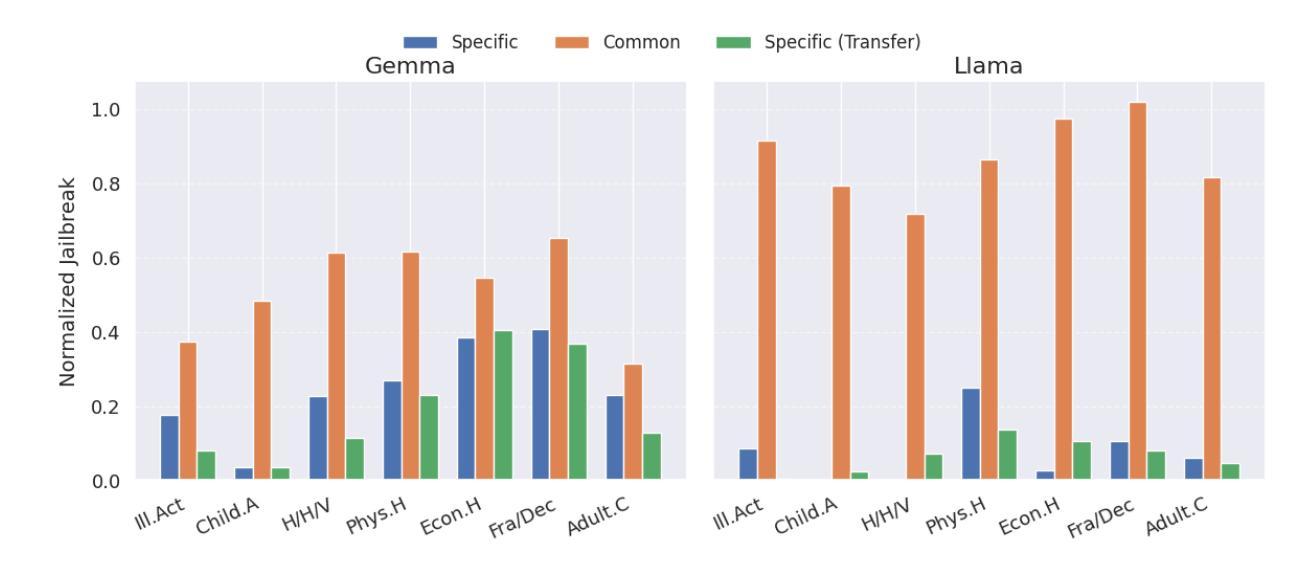
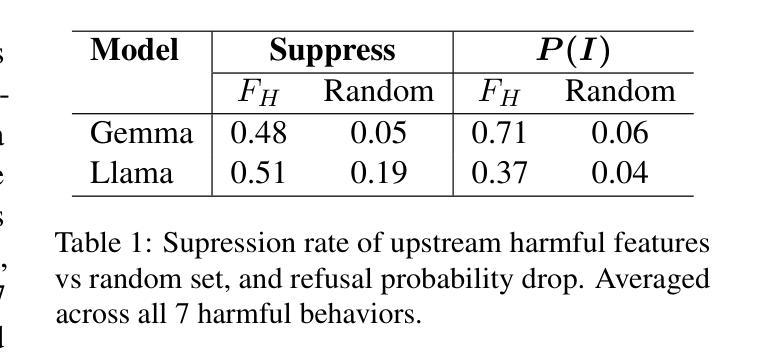
Understanding Refusal in Language Models with Sparse Autoencoders
Authors:Wei Jie Yeo, Nirmalendu Prakash, Clement Neo, Roy Ka-Wei Lee, Erik Cambria, Ranjan Satapathy
Refusal is a key safety behavior in aligned language models, yet the internal mechanisms driving refusals remain opaque. In this work, we conduct a mechanistic study of refusal in instruction-tuned LLMs using sparse autoencoders to identify latent features that causally mediate refusal behaviors. We apply our method to two open-source chat models and intervene on refusal-related features to assess their influence on generation, validating their behavioral impact across multiple harmful datasets. This enables a fine-grained inspection of how refusal manifests at the activation level and addresses key research questions such as investigating upstream-downstream latent relationship and understanding the mechanisms of adversarial jailbreaking techniques. We also establish the usefulness of refusal features in enhancing generalization for linear probes to out-of-distribution adversarial samples in classification tasks. We open source our code in https://github.com/wj210/refusal_sae.
拒绝是语言模型对齐中的关键安全行为,然而驱动拒绝的内部机制仍然不明确。在这项工作中,我们使用稀疏自动编码器对指令调整的LLM中的拒绝行为进行机制性研究,以识别因果中介拒绝行为的潜在特征。我们将该方法应用于两个开源聊天模型,并对与拒绝相关的特征进行干预,以评估它们对生成的影响,在多个有害数据集上验证其行为影响。这使我们能够精细地检查拒绝如何在激活层面表现,并解决关键的研究问题,例如调查上游和下游的潜在关系以及了解对抗性越狱技术的机制。我们还确定了拒绝特征在增强分类任务中对超出分布的对抗样本的通用性方面的作用。我们的代码已公开在https://github.com/wj210/refusal_sae。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
拒绝是指令对齐语言模型中的关键安全行为,但其内部机制仍不明确。本研究利用稀疏自动编码器对拒绝行为在指令微调大型语言模型(LLM)中的机制进行研究,以识别因果拒绝行为的潜在特征。我们将该方法应用于两个开源聊天模型,并对拒绝相关特征进行干预,以评估它们对生成的影响,在多个有害数据集上验证其行为影响。这使我们可以细致地检查拒绝如何在激活层面表现出来,并解决关键研究问题,例如调查上游和下游潜在关系以及了解对抗性越狱技术的机制。我们还建立了拒绝特征在增强分类任务中对超出分布的对抗样本的泛化能力方面的实用性。我们的代码已公开在https://github.com/wj210/refusal_sae。
Key Takeaways
- 拒绝是指令对齐大型语言模型中的重要安全行为。
- 利用稀疏自动编码器研究拒绝行为的内部机制。
- 方法应用于两个开源聊天模型,通过干预拒绝相关特征评估其对生成的影响。
- 在多个有害数据集上验证了拒绝行为的影响。
- 拒绝机制的研究有助于细致地了解其在激活层面的表现。
- 研究解决了关于上游和下游潜在关系以及对抗性越狱技术的关键研究问题。
点此查看论文截图

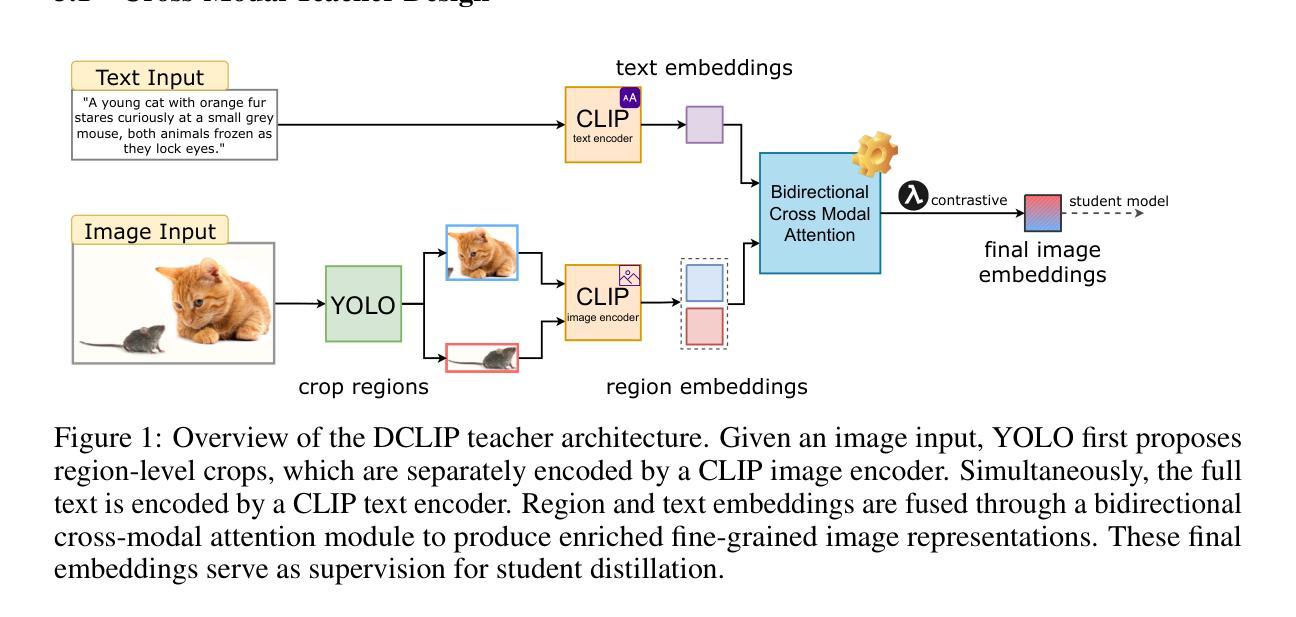
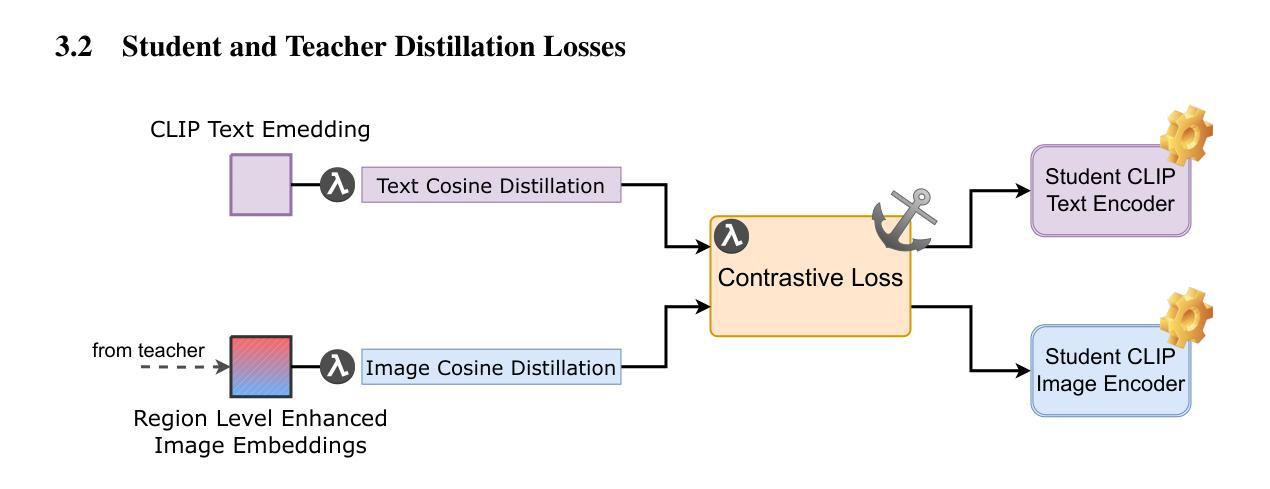
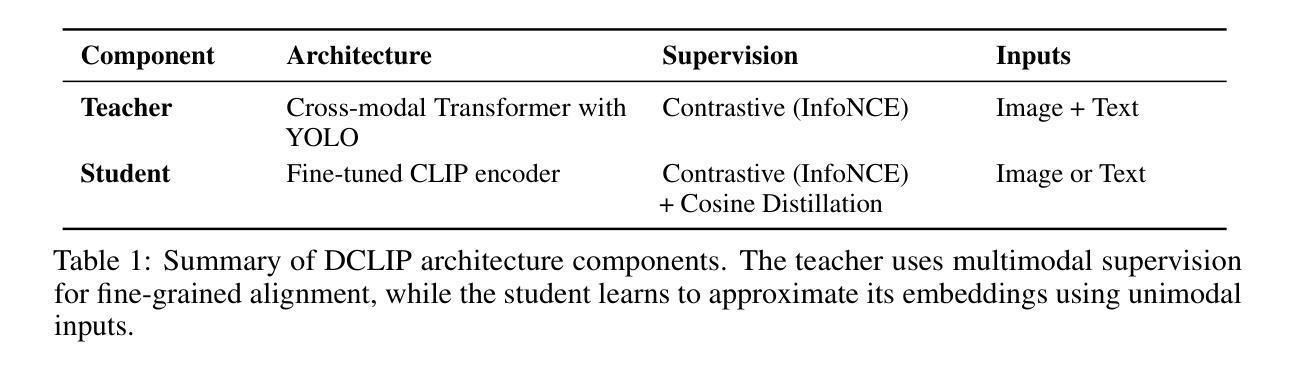
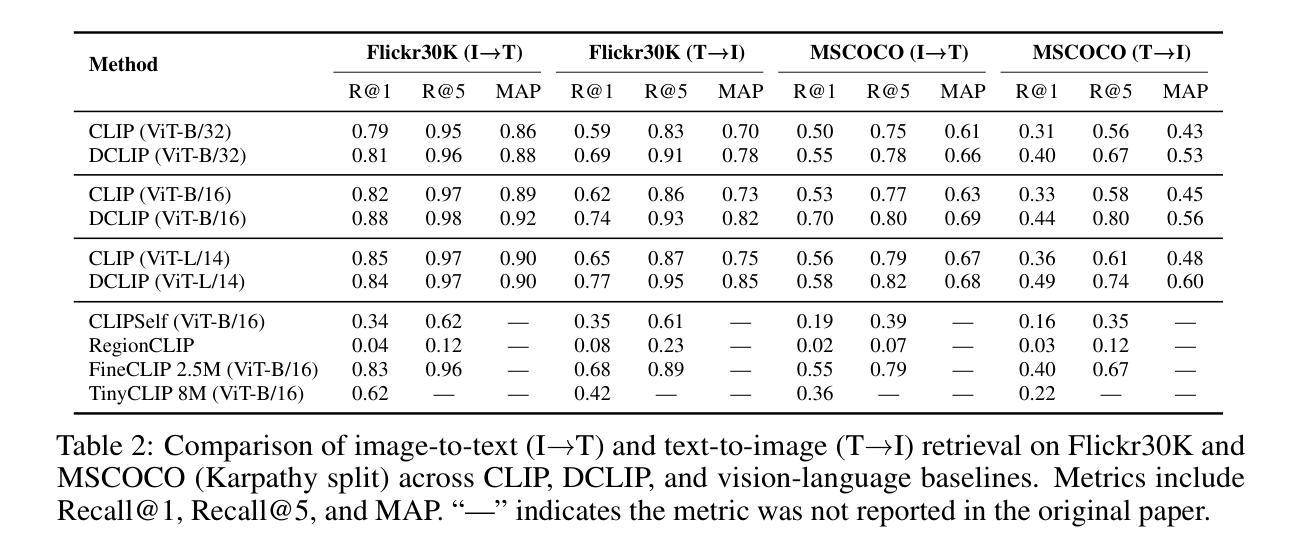
Distill CLIP (DCLIP): Enhancing Image-Text Retrieval via Cross-Modal Transformer Distillation
Authors:Daniel Csizmadia, Andrei Codreanu, Victor Sim, Vighnesh Prabhu, Michael Lu, Kevin Zhu, Sean O’Brien, Vasu Sharma
We present Distill CLIP (DCLIP), a fine-tuned variant of the CLIP model that enhances multimodal image-text retrieval while preserving the original model’s strong zero-shot classification capabilities. CLIP models are typically constrained by fixed image resolutions and limited context, which can hinder their effectiveness in retrieval tasks that require fine-grained cross-modal understanding. DCLIP addresses these challenges through a meta teacher-student distillation framework, where a cross-modal transformer teacher is fine-tuned to produce enriched embeddings via bidirectional cross-attention between YOLO-extracted image regions and corresponding textual spans. These semantically and spatially aligned global representations guide the training of a lightweight student model using a hybrid loss that combines contrastive learning and cosine similarity objectives. Despite being trained on only ~67,500 samples curated from MSCOCO, Flickr30k, and Conceptual Captions-just a fraction of CLIP’s original dataset-DCLIP significantly improves image-text retrieval metrics (Recall@K, MAP), while retaining approximately 94% of CLIP’s zero-shot classification performance. These results demonstrate that DCLIP effectively mitigates the trade-off between task specialization and generalization, offering a resource-efficient, domain-adaptive, and detail-sensitive solution for advanced vision-language tasks. Code available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md.
我们提出了Distill CLIP(DCLIP),它是CLIP模型的一种微调变体,增强了多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留了原始模型强大的零样本分类能力。CLIP模型通常受到固定图像分辨率和有限上下文的限制,这可能会阻碍它们在需要精细跨模态理解的任务中的有效性。DCLIP通过元教师学生蒸馏框架来解决这些挑战,其中跨模态变压器教师经过微调,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力产生丰富的嵌入。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过使用结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标的混合损失来指导轻量级学生模型的训练。尽管仅在MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions等数据集中精心挑选的约67,500个样本上进行训练,仅占CLIP原始数据集的一部分,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K,MAP),同时保留了CLIP约94%的零样本分类性能。这些结果表明,DCLIP有效地缓解了任务特化与通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCLIP-B772/README.md找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Distill CLIP(DCLIP)是CLIP模型的精细调整变体,旨在增强多模态图像文本检索功能,同时保留原始模型的强大零样本分类能力。DCLIP通过元教师-学生蒸馏框架解决CLIP模型在图像分辨率和上下文方面的局限性,通过跨模态变压器教师模型产生丰富的嵌入,通过YOLO提取的图像区域和相应文本跨度之间的双向交叉注意力进行双向交叉注意力处理。这些语义和空间对齐的全局表示通过使用结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标的混合损失来训练轻量级学生模型。尽管仅在MSCOCO、Flickr30k和Conceptual Captions等数据集的部分样本上进行训练,但DCLIP显著提高了图像文本检索指标(Recall@K、MAP),同时保留CLIP的零样本分类性能的约94%。结果证明,DCLIP有效缓解了任务专业化和通用化之间的权衡,为高级视觉语言任务提供了资源高效、领域自适应和细节敏感的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- DCLIP是CLIP模型的改进版本,专注于增强多模态图像文本检索功能。
- DCLIP通过教师-学生蒸馏框架解决CLIP模型的局限性。
- 教师模型通过双向交叉注意力处理图像区域和文本跨度,产生丰富的嵌入。
- DCLIP使用混合损失来训练轻量级学生模型,结合对比学习和余弦相似性目标。
- DCLIP在有限的样本集上训练,但显著提高了图像文本检索性能。
- DCLIP保留了CLIP的零样本分类性能的约94%。
点此查看论文截图

Multilingual Question Answering in Low-Resource Settings: A Dzongkha-English Benchmark for Foundation Models
Authors:Md. Tanzib Hosain, Rajan Das Gupta, Md. Kishor Morol
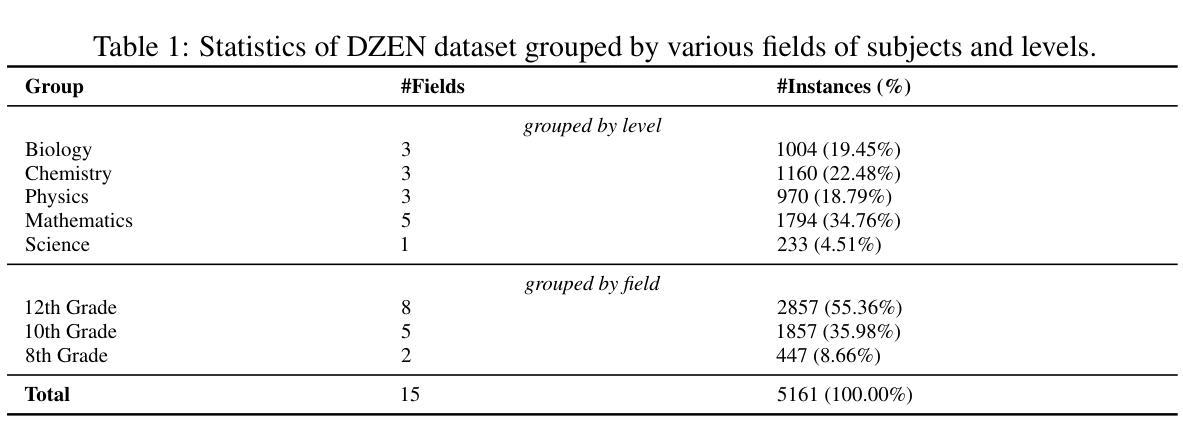
In this work, we provide DZEN, a dataset of parallel Dzongkha and English test questions for Bhutanese middle and high school students. The over 5K questions in our collection span a variety of scientific topics and include factual, application, and reasoning-based questions. We use our parallel dataset to test a number of Large Language Models (LLMs) and find a significant performance difference between the models in English and Dzongkha. We also look at different prompting strategies and discover that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting works well for reasoning questions but less well for factual ones. We also find that adding English translations enhances the precision of Dzongkha question responses. Our results point to exciting avenues for further study to improve LLM performance in Dzongkha and, more generally, in low-resource languages. We release the dataset at: https://github.com/kraritt/llm_dzongkha_evaluation.
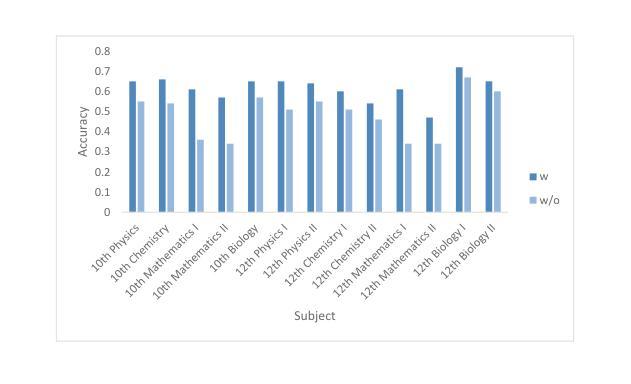
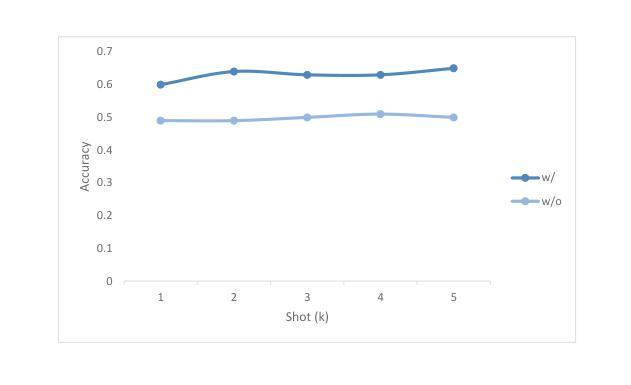
在这项工作中,我们提供了DZEN数据集,这是一组用于不丹中学和高中生的藏语和英语平行测试问题。我们的收藏中超过5000个问题涵盖了各种科学主题,包括事实、应用和基于推理的问题。我们使用平行数据集测试了大量的大型语言模型(LLM),并发现英语和藏语模型之间的性能存在显著差异。我们还研究了不同的提示策略,发现链式思维提示对于推理问题效果很好,但对事实问题效果较差。我们还发现添加英语翻译可以提高藏语问题回答的准确性。我们的结果指出了进一步研究以改善藏语乃至低资源语言环境中LLM性能的激动人心的途径。我们在以下地址发布数据集:https://github.com/kraritt/llm_dzongkha_evaluation 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 20 figures
Summary:本研究提供了名为DZEN的平行数据集,其中包含超过五千道面向不丹中学和高年级学生的Dzongkha语和英语的测试问题。这些问题涵盖了多个科学领域,包括事实、应用和推理问题。研究使用此数据集测试了多个大型语言模型(LLM),发现不同语言模型中英语和Dzongkha语的表现差异显著。研究还探讨了不同的提示策略,发现链式思维提示对推理问题有效但对事实问题效果较差。此外,添加英语翻译能提高Dzongkha问题的回答准确性。研究指出进一步改善LLM在Dzongkha和低资源语言表现的研究方向。数据集已在相关链接发布。
Key Takeaways:
- 提供了一个包含超过五千道测试问题的平行数据集DZEN,面向不丹中学和高年级学生,涵盖多个科学领域。
- 通过数据集测试了多种大型语言模型(LLM),发现英语和Dzongkha语表现存在差异。
- 研究了不同的提示策略,发现链式思维提示对推理问题效果好但对事实问题效果差。
- 添加英语翻译能够提高DzongKwa问题的回答准确性。
- 此研究展示了改进大型语言模型在低资源语言如DzongKwa中表现的研究方向。
- 数据集已在指定链接发布,便于公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图