⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
Boosting Domain Incremental Learning: Selecting the Optimal Parameters is All You Need
Authors:Qiang Wang, Xiang Song, Yuhang He, Jizhou Han, Chenhao Ding, Xinyuan Gao, Yihong Gong
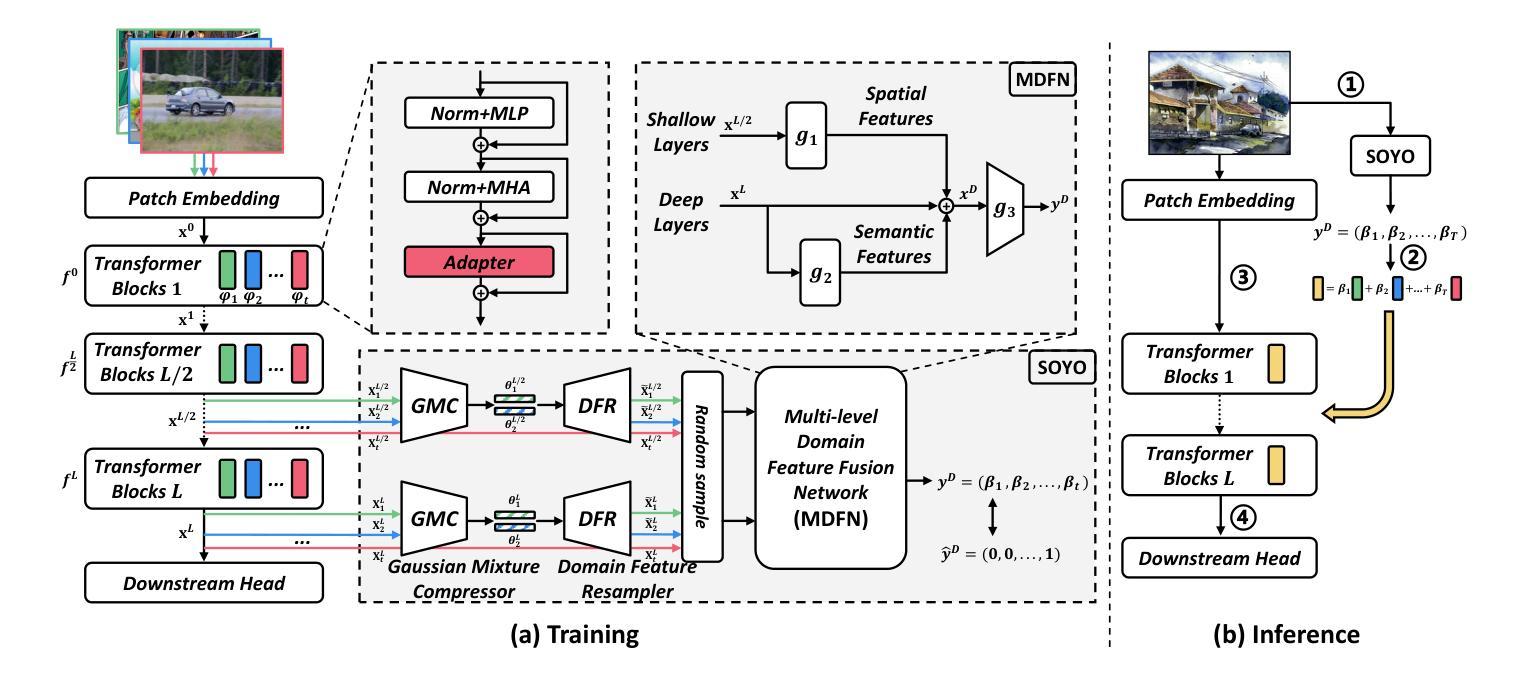
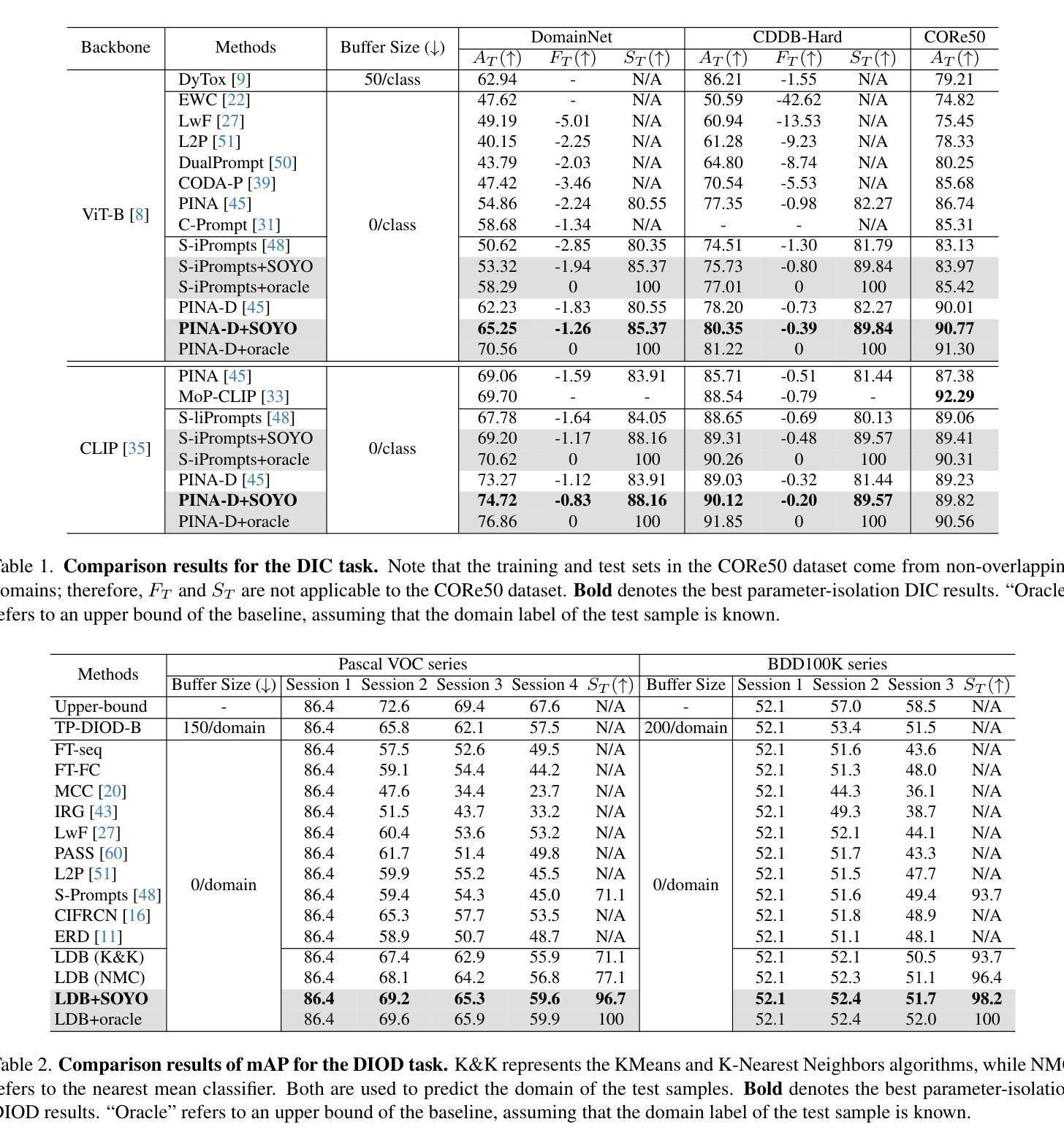
Deep neural networks (DNNs) often underperform in real-world, dynamic settings where data distributions change over time. Domain Incremental Learning (DIL) offers a solution by enabling continual model adaptation, with Parameter-Isolation DIL (PIDIL) emerging as a promising paradigm to reduce knowledge conflicts. However, existing PIDIL methods struggle with parameter selection accuracy, especially as the number of domains and corresponding classes grows. To address this, we propose SOYO, a lightweight framework that improves domain selection in PIDIL. SOYO introduces a Gaussian Mixture Compressor (GMC) and Domain Feature Resampler (DFR) to store and balance prior domain data efficiently, while a Multi-level Domain Feature Fusion Network (MDFN) enhances domain feature extraction. Our framework supports multiple Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods and is validated across tasks such as image classification, object detection, and speech enhancement. Experimental results on six benchmarks demonstrate SOYO’s consistent superiority over existing baselines, showcasing its robustness and adaptability in complex, evolving environments. The codes will be released in https://github.com/qwangcv/SOYO.
深度神经网络(DNNs)在现实世界中的动态环境中往往表现不佳,在这些环境中,数据分布会随时间发生变化。领域增量学习(DIL)通过实现持续模型自适应提供了解决方案,参数隔离型DIL(PIDIL)作为一种减少知识冲突的有前途的范式而出现。然而,现有的PIDIL方法在参数选择准确性方面面临挑战,尤其是随着领域和对应类别的数量增长时。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SOYO,这是一个改进的PIDIL领域选择的轻量级框架。SOYO引入了高斯混合压缩机(GMC)和领域特征重采样器(DFR)以有效地存储和平衡先前的领域数据,同时多级领域特征融合网络(MDFN)增强了领域特征的提取。我们的框架支持多种参数有效微调(PEFT)方法,并在图像分类、目标检测和语音增强等任务中得到了验证。在六个基准测试上的实验结果表明,与现有基准相比,SOYO具有持续的优越性,展示了其在复杂、不断发展的环境中的稳健性和适应性。代码将在https://github.com/qwangcv/SOYO发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CVPR 2025
Summary
面对随时间变化的动态环境,深度神经网络在真实世界中的表现常常不尽人意。域增量学习(DIL)通过持续模型自适应提供了解决方案,而参数隔离型域增量学习(PIDIL)成为减少知识冲突的有前途的范式。然而,随着域和相应类别的数量增长,现有的PIDIL方法在参数选择准确性方面遇到了挑战。为此,我们提出了SOYO框架,该框架改进了PIDIL中的域选择。SOYO引入了高斯混合压缩机(GMC)和域特征重采样器(DFR)以有效存储和平衡先前的域数据,同时多层次域特征融合网络(MDFN)增强了域特征的提取。该框架支持多种参数有效微调(PEFT)方法,并在图像分类、目标检测和语音增强等任务中进行了验证。在六个基准测试上的实验结果表明,SOYO相较于现有基线具有持续的优越性,展示了其在复杂、不断变化环境中的稳健性和适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在动态环境中面临性能挑战。
- 域增量学习(DIL)通过持续模型自适应为解决此挑战提供了方案。
- 参数隔离型域增量学习(PIDIL)是减少知识冲突的一种有前途的方法。
- SOYO框架改进了PIDIL中的域选择问题。
- SOYO引入了高斯混合压缩机(GMC)、域特征重采样器(DFR)和多层次域特征融合网络(MDFN)。
- SOYO框架支持多种参数有效微调(PEFT)方法。
- 在多个任务基准测试上,SOYO相较于现有方法表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

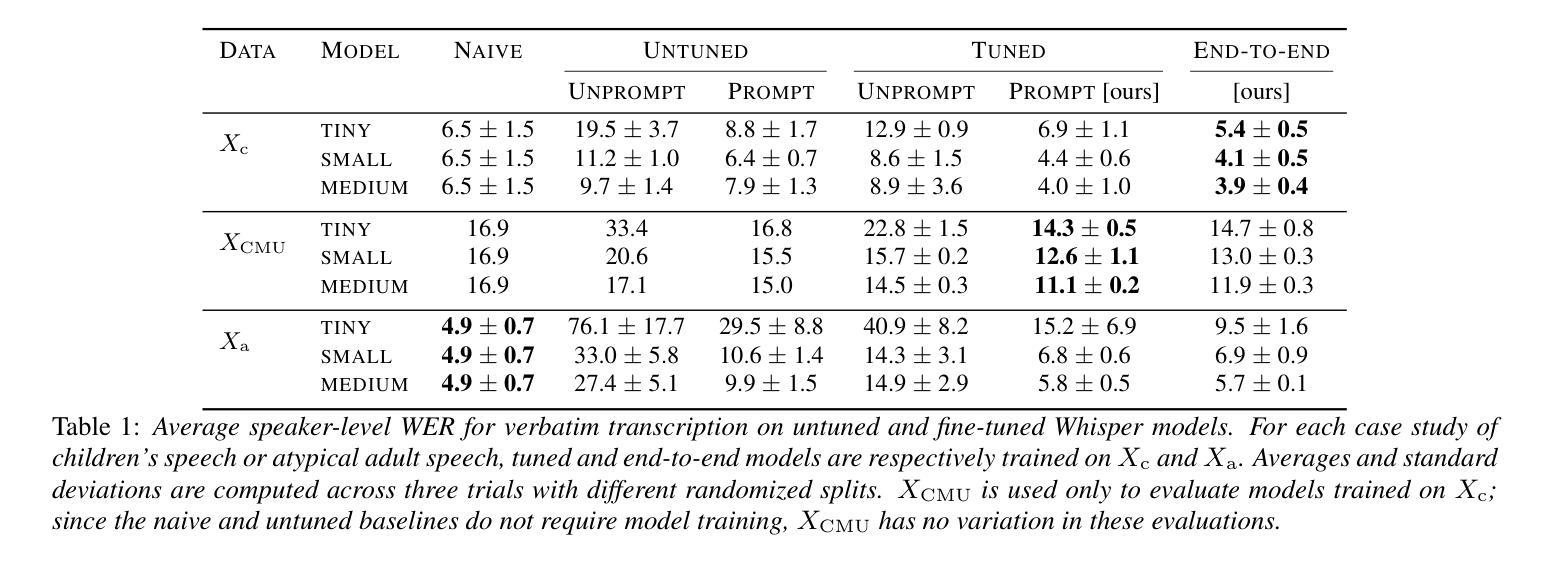
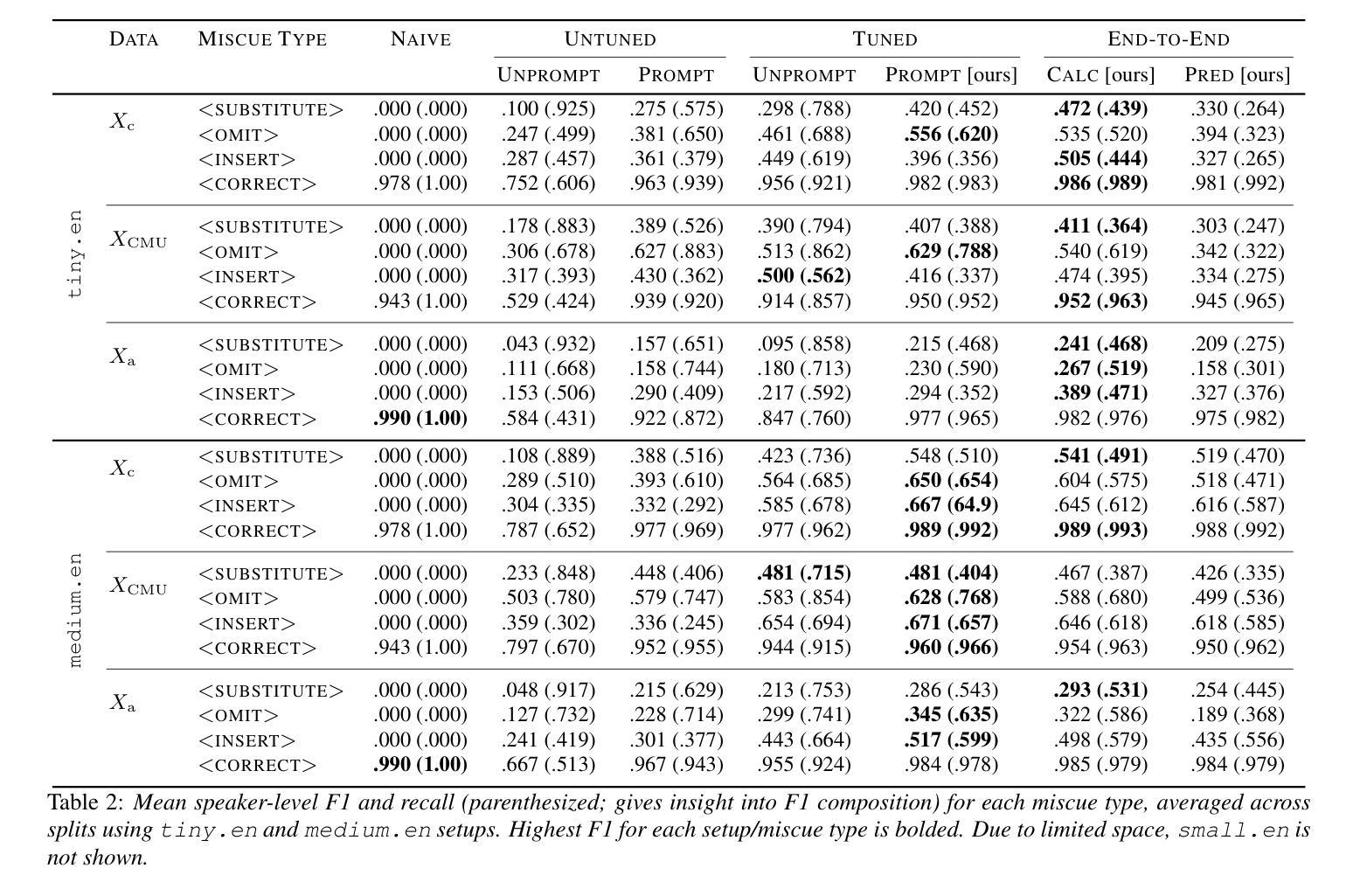
Prompting Whisper for Improved Verbatim Transcription and End-to-end Miscue Detection
Authors:Griffin Dietz Smith, Dianna Yee, Jennifer King Chen, Leah Findlater
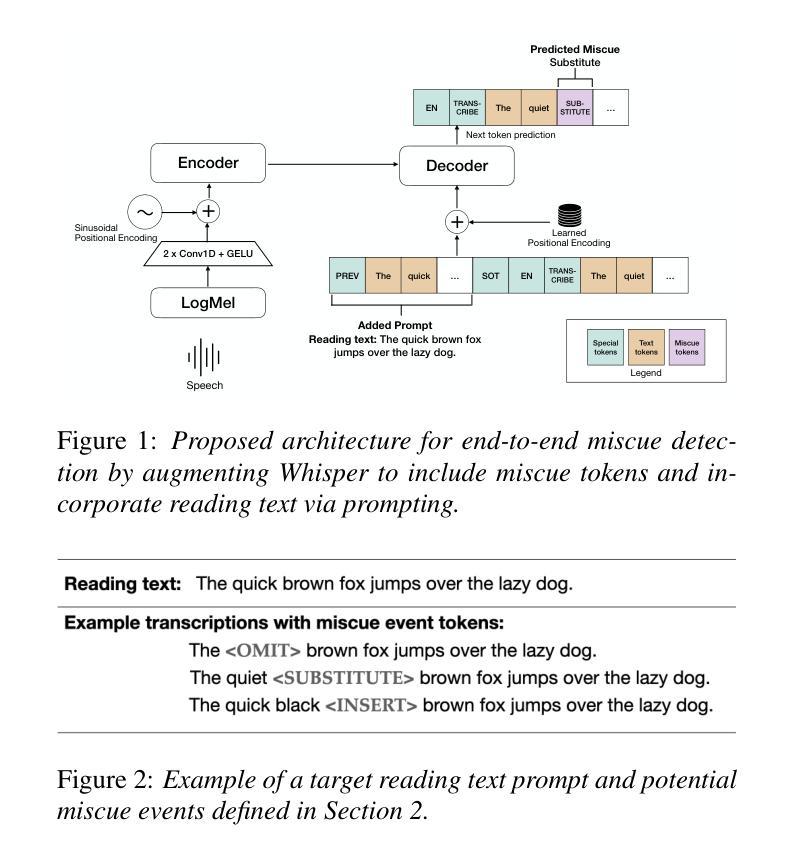
Identifying mistakes (i.e., miscues) made while reading aloud is commonly approached post-hoc by comparing automatic speech recognition (ASR) transcriptions to the target reading text. However, post-hoc methods perform poorly when ASR inaccurately transcribes verbatim speech. To improve on current methods for reading error annotation, we propose a novel end-to-end architecture that incorporates the target reading text via prompting and is trained for both improved verbatim transcription and direct miscue detection. Our contributions include: first, demonstrating that incorporating reading text through prompting benefits verbatim transcription performance over fine-tuning, and second, showing that it is feasible to augment speech recognition tasks for end-to-end miscue detection. We conducted two case studies – children’s read-aloud and adult atypical speech – and found that our proposed strategies improve verbatim transcription and miscue detection compared to current state-of-the-art.
识别朗读时出现的错误(即失误)通常是通过事后比较自动语音识别(ASR)转录与目标阅读文本进行的。然而,当ASR不准确转录原声语音时,事后方法的性能较差。为了改进当前的阅读错误注释方法,我们提出了一种新型端到端架构,该架构通过提示融入目标阅读文本,并经过训练,既能提高逐字转录质量,又能直接检测失误。我们的贡献包括:首先,证明通过提示融入阅读文本有助于提高逐字转录性能优于微调;其次,表明对端到端失误检测增强语音识别任务是可行的。我们进行了两项案例研究——儿童朗读和成人非典型语音,发现与当前最新技术相比,我们提出的策略改进了逐字转录和失误检测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Interspeech 2025
总结
本文提出了一种新的端到端架构,该架构通过提示目标阅读文本,改进了自动语音识别(ASR)的转录,提高了直接误读检测能力。该研究贡献在于证明通过提示阅读文本可以改善转录性能,并展示增强语音识别任务以实现端到端误读检测的可行性。在儿童朗读和成人非典型语音的两个案例研究中,该策略改进了转录和误读检测效果。
关键见解
- 现有方法使用自动语音识别(ASR)转录与目 标阅读文本对比来识别朗读时的错误,但当ASR转录不精确时表现不佳。
- 提出了一种新的端到端架构,该架构通过提示目标阅读文本改进了转录效果。
- 证明了通过提示阅读文本可以改善转录性能,相较于微调方式具有优势。
- 展示了对语音识别任务进行增强,以实现端到端的误读检测是可行的。
- 在儿童朗读和成人非典型语音的案例研究中,新策略提高了转录和误读检测的准确性,相较于当前最先进技术有所改进。
- 该方法对于提高语音识别系统的性能和准确性具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图


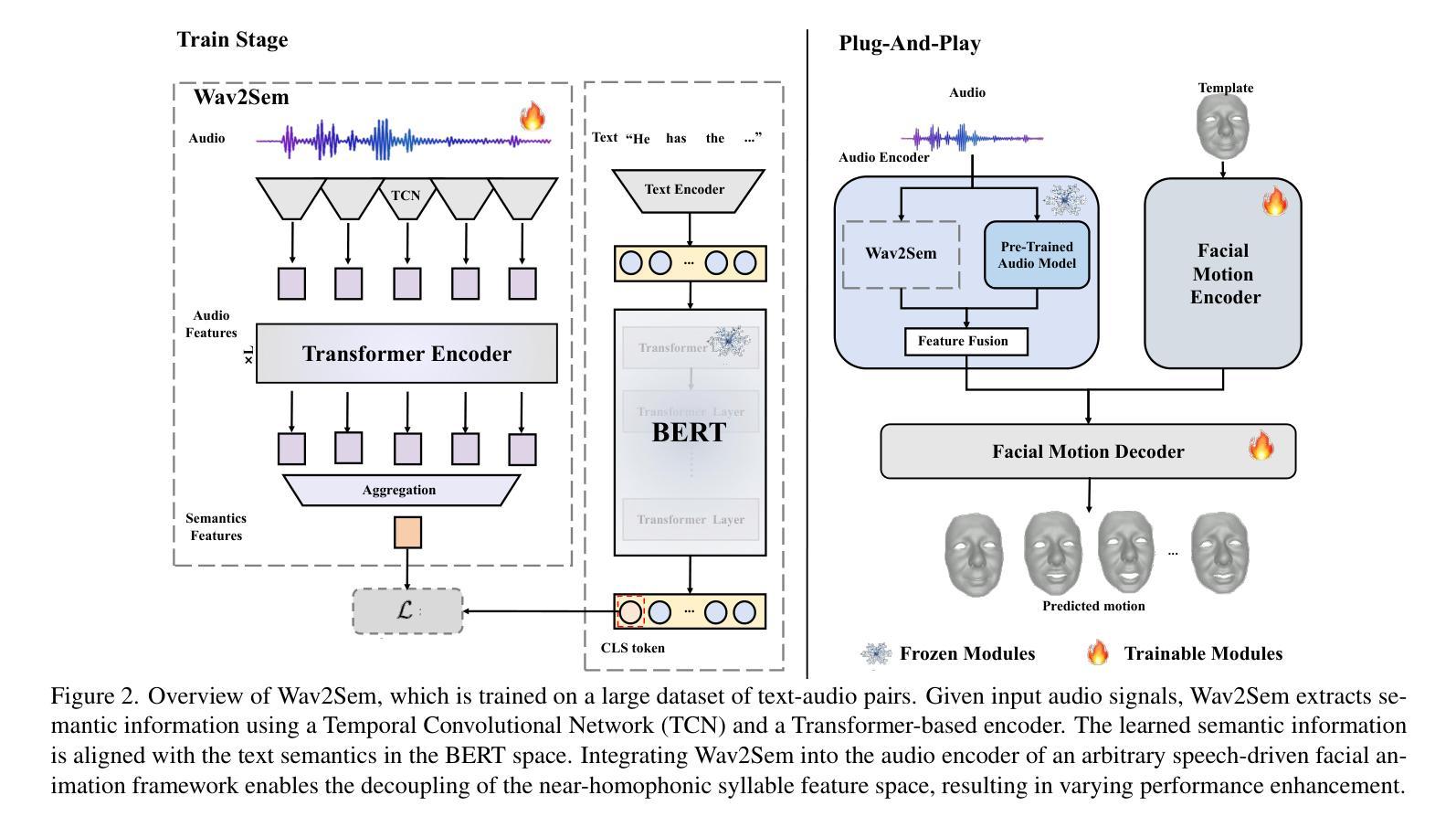
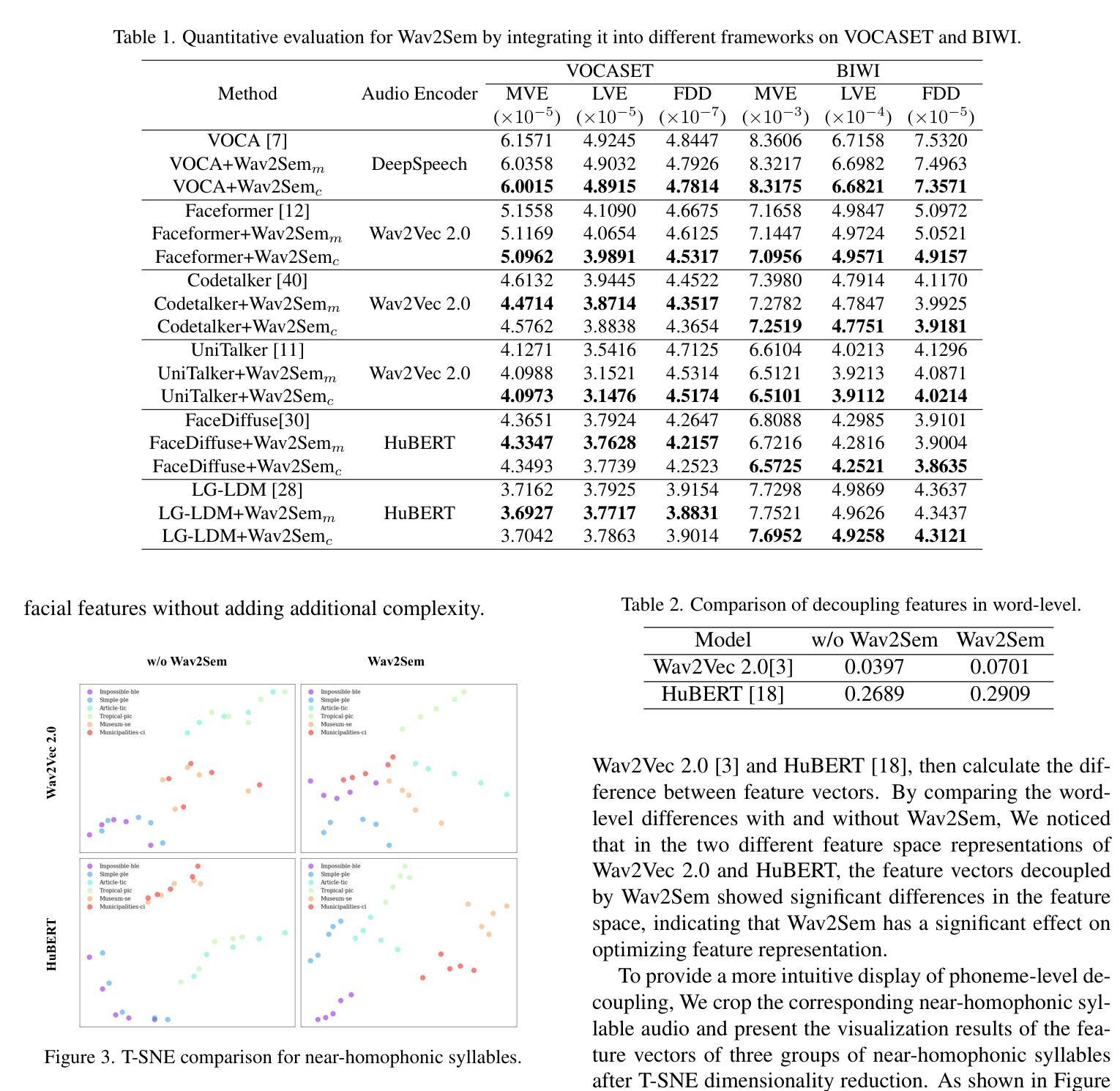
Wav2Sem: Plug-and-Play Audio Semantic Decoupling for 3D Speech-Driven Facial Animation
Authors:Hao Li, Ju Dai, Xin Zhao, Feng Zhou, Junjun Pan, Lei Li
In 3D speech-driven facial animation generation, existing methods commonly employ pre-trained self-supervised audio models as encoders. However, due to the prevalence of phonetically similar syllables with distinct lip shapes in language, these near-homophone syllables tend to exhibit significant coupling in self-supervised audio feature spaces, leading to the averaging effect in subsequent lip motion generation. To address this issue, this paper proposes a plug-and-play semantic decorrelation module-Wav2Sem. This module extracts semantic features corresponding to the entire audio sequence, leveraging the added semantic information to decorrelate audio encodings within the feature space, thereby achieving more expressive audio features. Extensive experiments across multiple Speech-driven models indicate that the Wav2Sem module effectively decouples audio features, significantly alleviating the averaging effect of phonetically similar syllables in lip shape generation, thereby enhancing the precision and naturalness of facial animations. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wslh852/Wav2Sem.git.
在3D语音驱动面部动画生成中,现有方法通常使用预训练的自我监督音频模型作为编码器。然而,由于语言中音位相似但唇形不同的音节普遍存在,这些近似同音节的音节在自我监督的音频特征空间中往往表现出显著的耦合,导致后续唇动生成中的平均效应。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种即插即用的语义去相关模块——Wav2Sem。该模块提取与整个音频序列对应的语义特征,利用添加的语义信息去相关特征空间中的音频编码,从而实现更具表现力的音频特征。在多个语音驱动模型上的广泛实验表明,Wav2Sem模块有效地解耦了音频特征,显著减轻了音位相似音节在唇形生成中的平均效应,从而提高了面部动画的精度和自然度。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/wslh852/Wav2Sem.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
语音驱动的三维面部动画生成中,现有方法常使用预训练的自我监督音频模型作为编码器。然而,由于语言中音位相似但唇形不同的音节普遍存在,这些近似的音节在自我监督的音频特征空间中往往表现出显著的耦合现象,导致后续的唇部运动生成出现平均效应。为解决这一问题,本文提出了即插即用的语义去相关模块——Wav2Sem。该模块提取整个音频序列的语义特征,利用额外的语义信息去相关音频编码特征空间中的编码,从而得到更富有表现力的音频特征。跨多个语音驱动模型的广泛实验表明,Wav2Sem模块有效地解除了音频特征的耦合,显著减轻了音位相似音节在唇形生成中的平均效应,从而提高了面部动画的精确性和自然性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有语音驱动面部动画方法主要使用预训练自我监督音频模型作为编码器。
- 近音节的普遍存在导致音频特征空间中的耦合现象。
- 耦合现象会引发唇部运动生成的平均效应。
- Wav2Sem模块旨在解决此问题,通过提取整个音频序列的语义特征来装饰相关音频编码。
- Wav2Sem利用额外语义信息去相关音频编码特征空间中的编码。
- Wav2Sem模块有效解除音频特征的耦合,减轻平均效应。
点此查看论文截图

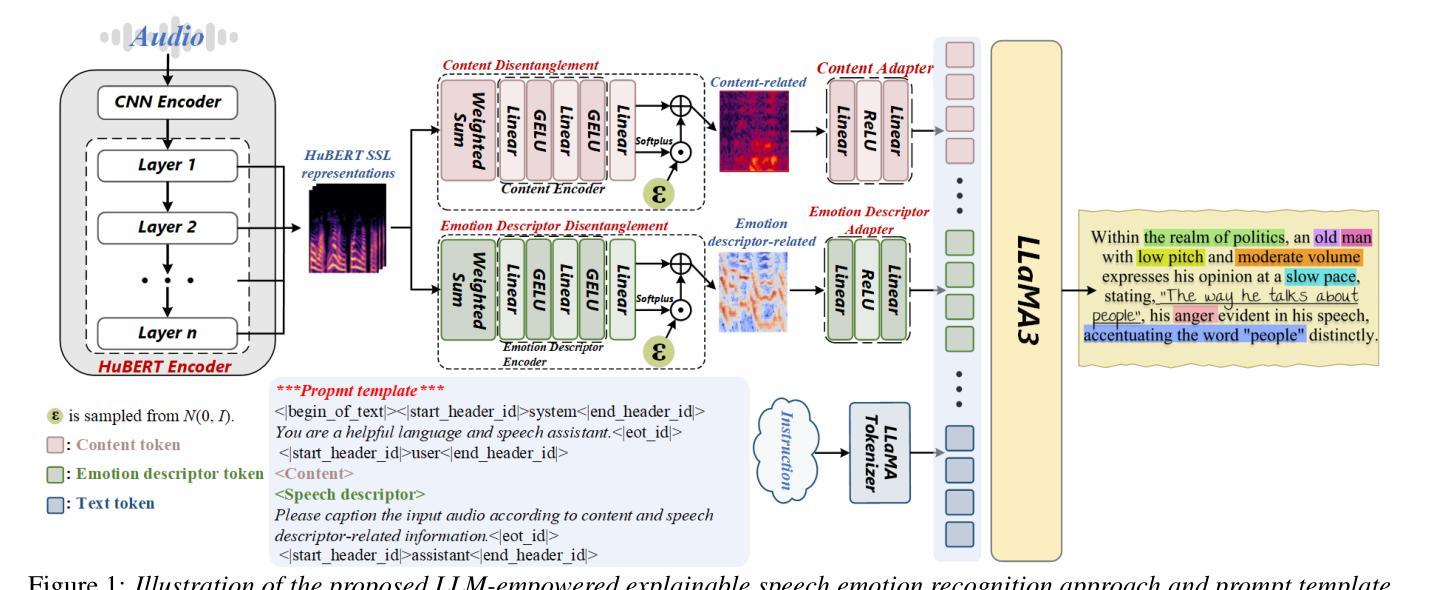
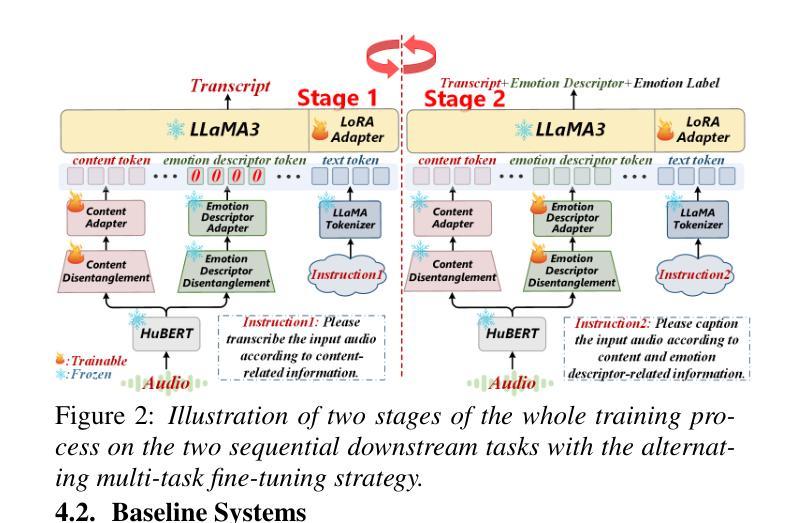
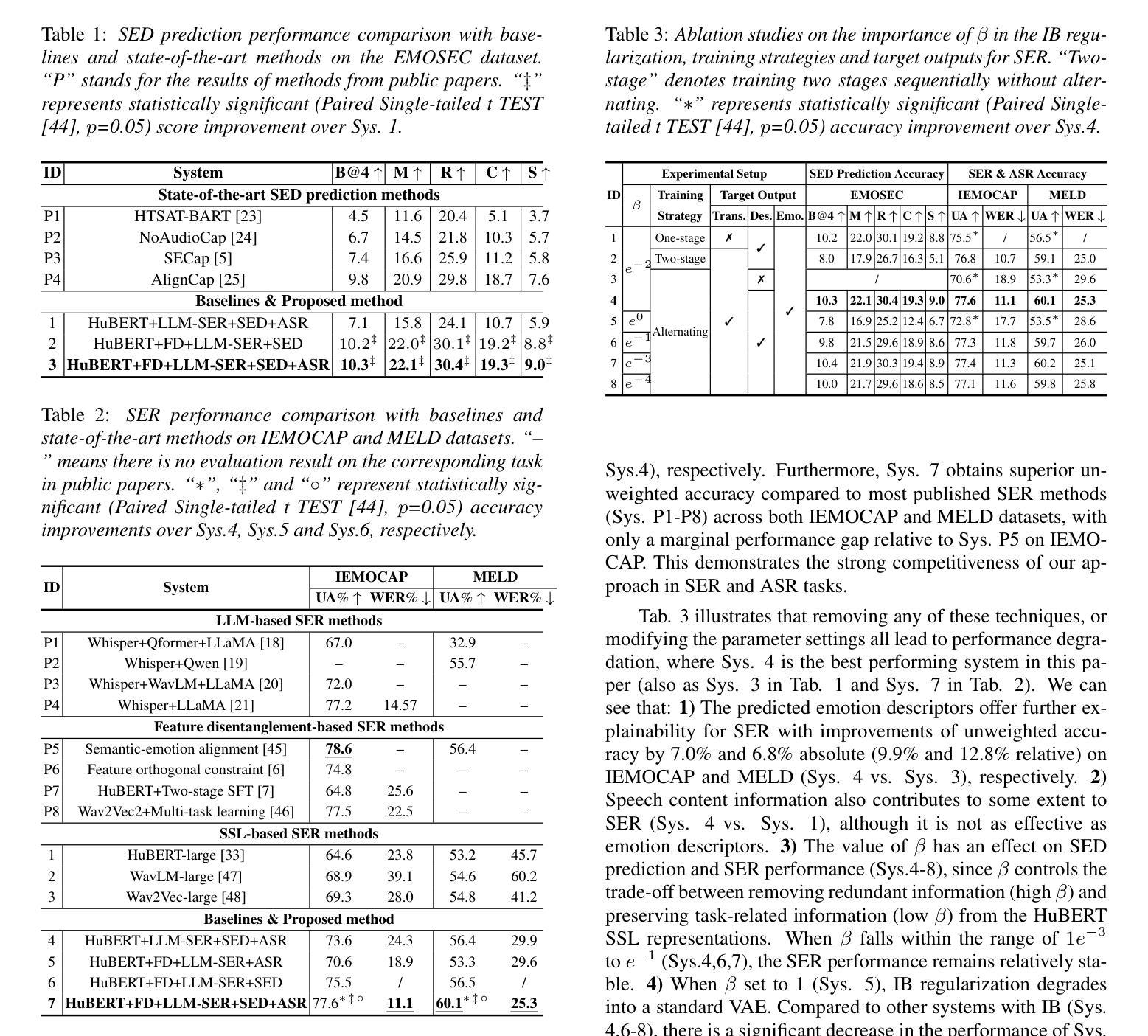
Towards LLM-Empowered Fine-Grained Speech Descriptors for Explainable Emotion Recognition
Authors:Youjun Chen, Xurong Xie, Haoning Xu, Mengzhe Geng, Guinan Li, Chengxi Deng, Huimeng Wang, Shujie Hu, Xunying Liu
This paper presents a novel end-to-end LLM-empowered explainable speech emotion recognition (SER) approach. Fine-grained speech emotion descriptor (SED) features, e.g., pitch, tone and emphasis, are disentangled from HuBERT SSL representations via alternating LLM fine-tuning to joint SER-SED prediction and ASR tasks. VAE compressed HuBERT features derived via Information Bottleneck (IB) are used to adjust feature granularity. Experiments on the IEMOCAP and MELD benchmarks demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms comparable LLaMA-based SER baselines, including those using either (a) alternating multi-task fine-tuning alone or (b) feature disentanglement only. Statistically significant increase of SER unweighted accuracy by up to 4.0% and 3.7% absolute (5.4% and 6.6% relative) are obtained. More importantly, emotion descriptors offer further explainability for SER.
本文提出了一种新型端到端的LLM赋能可解释语音情感识别(SER)方法。通过交替的LLM微调,从HuBERT SSL表示中分离出精细的语音情感描述符(SED)特征,如音调、音调和强调,以联合进行SER-SED预测和ASR任务。使用基于信息瓶颈(IB)的VAE压缩HuBERT特征来调整特征粒度。在IEMOCAP和MELD基准测试上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于类似的LLaMA基础的SER基线,包括那些(a)仅使用交替多任务微调或(b)仅使用特征分离的方法。在未经加权的SER准确率上获得了高达4.0%和3.7%的绝对增长(分别为5.4%和6.6%的相对增长)。更重要的是,情感描述符为SER提供了进一步的解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by INTERSPEECH2025
摘要
本文提出了一种新型端到端的LLM赋能的可解释语音情感识别(SER)方法。该方法通过交替的LLM微调,从HuBERT SSL表征中分离出精细的语音情感描述符(SED)特征,如音调、音调和强调等,然后进行联合SER-SED预测和ASR任务。通过信息瓶颈(IB)使用VAE压缩的HuBERT特征来调整特征粒度。在IEMOCAP和MELD基准测试上的实验表明,我们的方法始终优于类似的LLaMA基础的SER基线,包括那些只使用(a)交替多任务微调或(b)特征分离的方法。统计上,SER的无权重准确率绝对提高了4.0%和3.7%(相对提高了5.4%和6.6%)。更重要的是,情感描述符为SER提供了进一步的解释性。
关键见解
- 提出了端到端的LLM赋能语音情感识别新方法。
- 通过交替LLM微调,实现了从HuBERT SSL表征中分离出语音情感描述符特征。
- 结合SED特征和联合SER-SED预测及ASR任务,提高了性能。
- 使用VAE压缩的HuBERT特征,通过信息瓶颈调整特征粒度。
- 在IEMOCAP和MELD基准测试中表现优异,相对提高SER的无权重准确率达5.4%和6.6%。
- 情感描述符为SER提供了额外的解释性。
点此查看论文截图

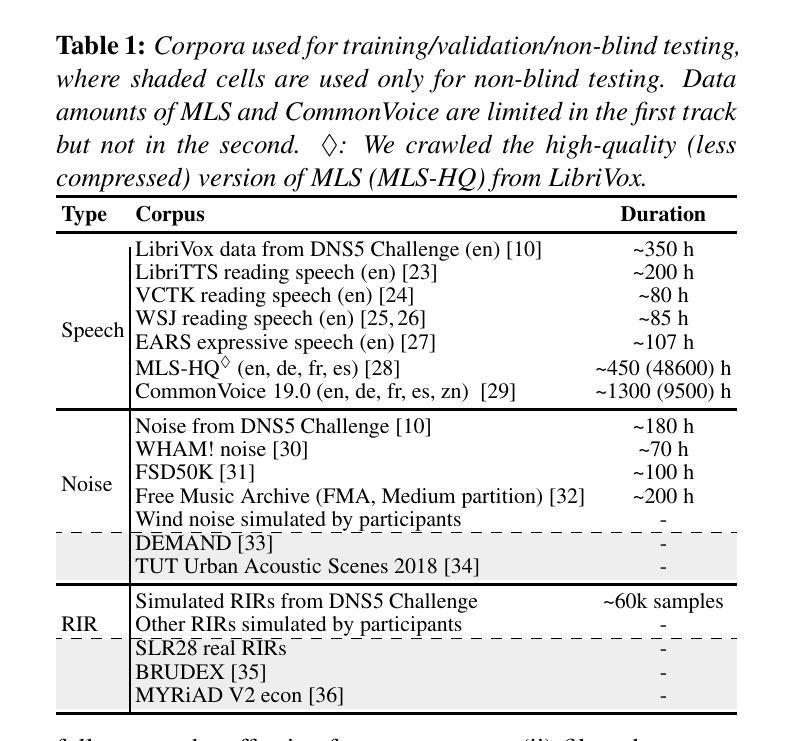
Interspeech 2025 URGENT Speech Enhancement Challenge
Authors:Kohei Saijo, Wangyou Zhang, Samuele Cornell, Robin Scheibler, Chenda Li, Zhaoheng Ni, Anurag Kumar, Marvin Sach, Yihui Fu, Wei Wang, Tim Fingscheidt, Shinji Watanabe
There has been a growing effort to develop universal speech enhancement (SE) to handle inputs with various speech distortions and recording conditions. The URGENT Challenge series aims to foster such universal SE by embracing a broad range of distortion types, increasing data diversity, and incorporating extensive evaluation metrics. This work introduces the Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge, the second edition of the series, to explore several aspects that have received limited attention so far: language dependency, universality for more distortion types, data scalability, and the effectiveness of using noisy training data. We received 32 submissions, where the best system uses a discriminative model, while most other competitive ones are hybrid methods. Analysis reveals some key findings: (i) some generative or hybrid approaches are preferred in subjective evaluations over the top discriminative model, and (ii) purely generative SE models can exhibit language dependency.
在开发能够处理各种语音失真和录音条件的通用语音增强(SE)方面,已经付出了越来越多的努力。URGENT Challenge系列旨在通过接纳广泛的失真类型、增加数据多样性和融入广泛的评估指标来促进这种通用SE的发展。这项工作介绍了Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge,即该系列的第二版,旨在探索迄今为止受到有限关注的几个方面:语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性、数据可扩展性以及使用带噪声训练数据的有效性。我们收到了32份提交,其中最佳系统使用的是判别模型,而其他大多数有竞争力的系统都是混合方法。分析揭示了一些关键发现:(i)在某些主观评价中,一些生成式或混合方法优于顶级判别模型;(ii)纯粹的生成式SE模型会表现出语言依赖性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Interspeech 2025
Summary
本段内容介绍了为了应对各种语音失真和录制条件而开发的通用语音增强技术(SE)。特别是介绍了Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge这一挑战系列的第二轮,该挑战旨在探讨语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性、数据可伸缩性和使用噪声训练数据的有效性等问题。同时提到了收到的一些重要发现和关键发现:主观评价中一些生成性或混合方法优于顶级判别模型,而纯粹的生成性SE模型可能会表现出语言依赖性。目前,最佳系统使用的是判别模型,而其他有竞争力的系统则多为混合方法。
Key Takeaways
- 通用语音增强技术(SE)正在不断发展,以应对各种语音失真和录制条件。
- Interspeech 2025 URGENT Challenge旨在探索语言依赖性、更多失真类型的普遍性等问题。
- 该挑战收到了32份提交,其中最佳系统使用的是判别模型。
- 分析发现一些生成性或混合方法在主观评价中优于顶级判别模型。
- 纯粹的生成性SE模型可能会表现出语言依赖性。
- 数据多样性和广泛评估指标对于通用SE的发展至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

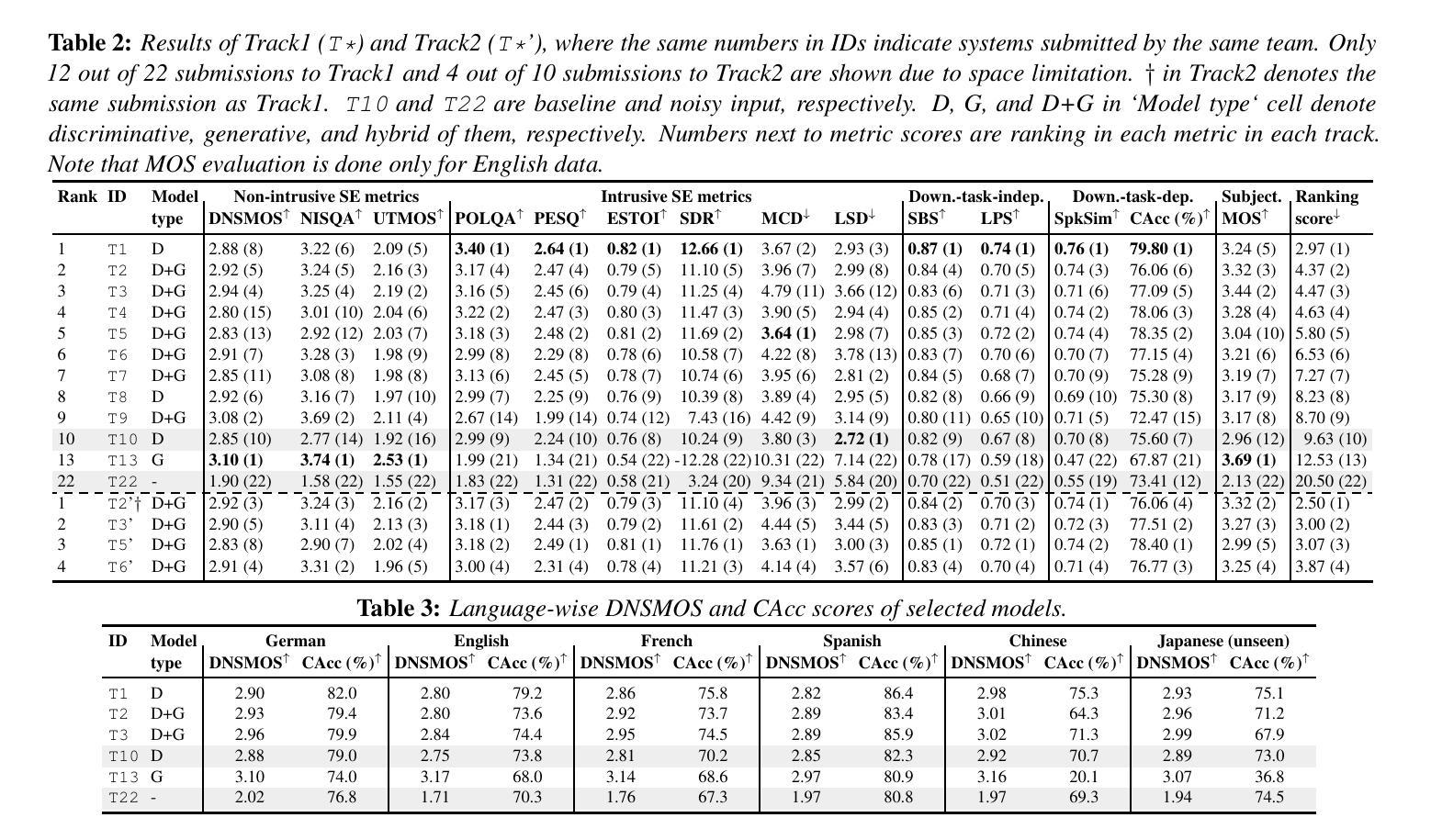
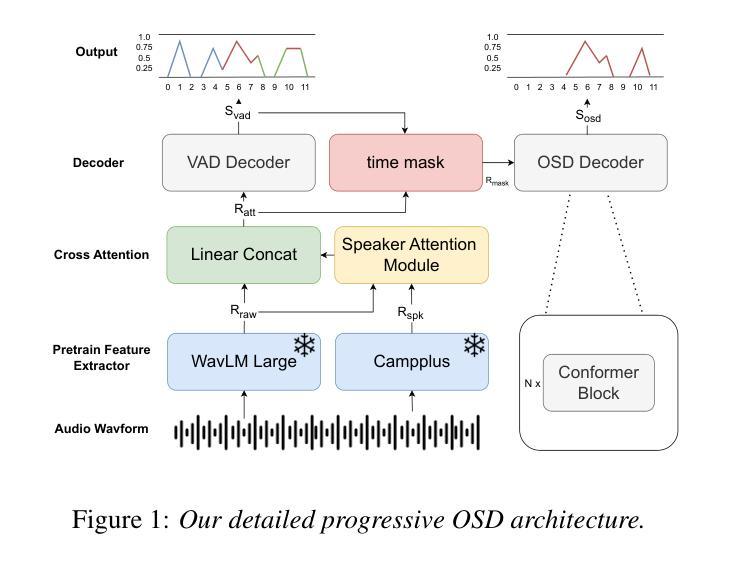
Towards Robust Overlapping Speech Detection: A Speaker-Aware Progressive Approach Using WavLM
Authors:Zhaokai Sun, Li Zhang, Qing Wang, Pan Zhou, Lei Xie
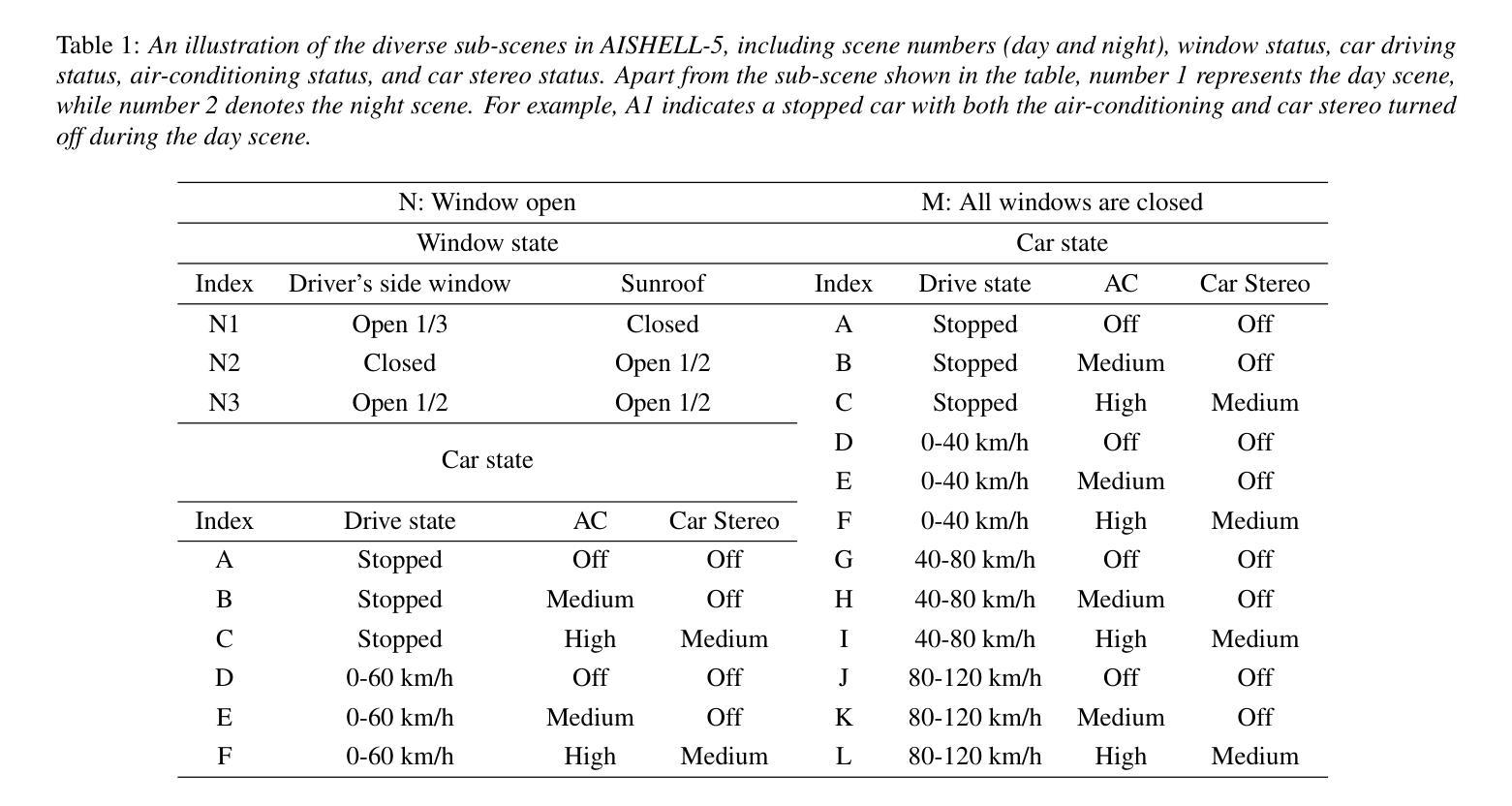
Overlapping Speech Detection (OSD) aims to identify regions where multiple speakers overlap in a conversation, a critical challenge in multi-party speech processing. This work proposes a speaker-aware progressive OSD model that leverages a progressive training strategy to enhance the correlation between subtasks such as voice activity detection (VAD) and overlap detection. To improve acoustic representation, we explore the effectiveness of state-of-the-art self-supervised learning (SSL) models, including WavLM and wav2vec 2.0, while incorporating a speaker attention module to enrich features with frame-level speaker information. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, with an F1 score of 82.76% on the AMI test set, demonstrating its robustness and effectiveness in OSD.
重叠语音检测(OSD)旨在识别对话中多个发言人重叠的区域,这是多方语音处理中的一项关键挑战。这项工作提出了一种基于发言人感知的渐进式OSD模型,该模型采用渐进式训练策略,以增强子任务(如语音活动检测(VAD)和重叠检测)之间的相关性。为了提高声音表示能力,我们探索了最先进的自监督学习(SSL)模型的有效性,包括WavLM和wav2vec 2.0,同时结合发言人注意力模块,以丰富帧级发言人信息的特征。实验结果表明,该方法达到了最先进的表现,在AMI测试集上的F1分数为82.76%,证明了其在OSD中的稳健性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于说话者感知的渐进式重叠语音检测模型,该模型采用渐进式训练策略,增强语音活动检测和重叠检测等子任务之间的相关性。为提高声学表现,本文探索了最前沿的自监督学习模型的有效性,如WavLM和wav2vec 2.0,同时结合说话者注意力模块,以丰富帧级别的说话者信息。实验结果表明,该方法在AMI测试集上取得了F1分数为82.76%的卓越性能,证明了其在重叠语音检测中的稳健性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 说话者感知的渐进式重叠语音检测模型被提出。
- 模型采用渐进式训练策略以增强语音活动检测和重叠检测等子任务的相关性。
- 通过使用最前沿的自监督学习模型(如WavLM和wav2vec 2.0),提高了声学表现。
- 结合说话者注意力模块,以丰富帧级别的说话者信息。
- 实验结果表明该模型在AMI测试集上取得了卓越性能。
- 模型具有稳健性和有效性,可用于多方的语音处理中的重叠语音检测。
点此查看论文截图


ZIPA: A family of efficient models for multilingual phone recognition
Authors:Jian Zhu, Farhan Samir, Eleanor Chodroff, David R. Mortensen
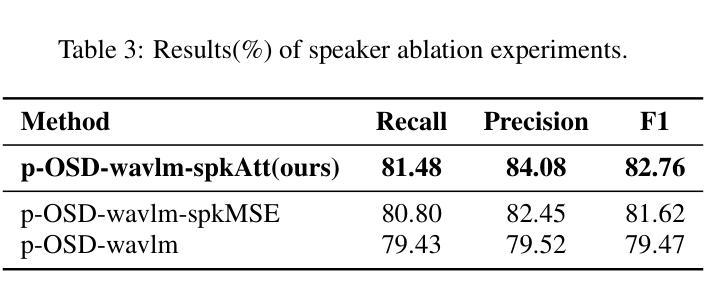
We present ZIPA, a family of efficient speech models that advances the state-of-the-art performance of crosslinguistic phone recognition. We first curated IPAPack++, a large-scale multilingual speech corpus with 17,132 hours of normalized phone transcriptions and a novel evaluation set capturing unseen languages and sociophonetic variation. With the large-scale training data, ZIPA, including transducer (ZIPA-T) and CTC-based (ZIPA-CR) variants, leverage the efficient Zipformer backbones and outperform existing phone recognition systems with much fewer parameters. Further scaling via noisy student training on 11,000 hours of pseudo-labeled multilingual data yields further improvement. While ZIPA achieves strong performance on benchmarks, error analysis reveals persistent limitations in modeling sociophonetic diversity, underscoring challenges for future research.
我们提出了ZIPA,这是一个高效的语音模型家族,它提高了跨语言语音识别的最新性能。我们首先整理了IPAPack++,这是一个大规模的多语言语音语料库,包含17,132小时的标准化语音转录和捕捉未见语言和语音社会差异的新型评估集。借助大规模训练数据,ZIPA包括转换器(ZIPA-T)和基于CTC的变体(ZIPA-CR),利用高效的Zipformer主干,以更少的参数超越现有语音识别系统。通过对11,000小时伪标记的多语言数据进行噪声学生训练,可以实现进一步的扩展和改进。虽然ZIPA在基准测试中表现出强大的性能,但误差分析显示,在模拟社会语音多样性方面仍存在持续的局限性,这突出了未来研究的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 Main
Summary
本文介绍了ZIPA这一高效语音模型家族,它提高了跨语言语音识别的最新性能。研究团队首先推出了IPAPack++,一个大型多语言语音语料库,包含17,132小时的标准化语音转录和捕捉未见语言和社音变异的新型评估集。利用大规模训练数据,ZIPA的转换器(ZIPA-T)和CTC(ZIPA-CR)变体借助高效的Zipformer主干,以更少的参数表现超过了现有语音识别系统。通过对超过一万小时的伪标签多语言数据进行噪声学生训练后进一步提高了性能。尽管ZIPA在基准测试中表现良好,但误差分析表明其在模拟社会语音多样性方面仍有局限,为未来的研究带来挑战。
Key Takeaways
- ZIPA是先进的语音模型家族,提高了跨语言语音识别的性能。
- IPAPack++是一个大型多语言语音语料库,包含标准化语音转录和新型评估集,用于捕捉未见语言和社音变异。
- ZIPA包括转换器(ZIPA-T)和CTC(ZIPA-CR)变体,利用Zipformer主干实现高效性能。
- ZIPA在基准测试中表现优于现有语音识别系统,使用更少的参数。
- 通过噪声学生训练和超过一万小时的伪标签多语言数据进行进一步性能提升。
- ZIPA在建模社会语音多样性方面存在局限性。
点此查看论文截图


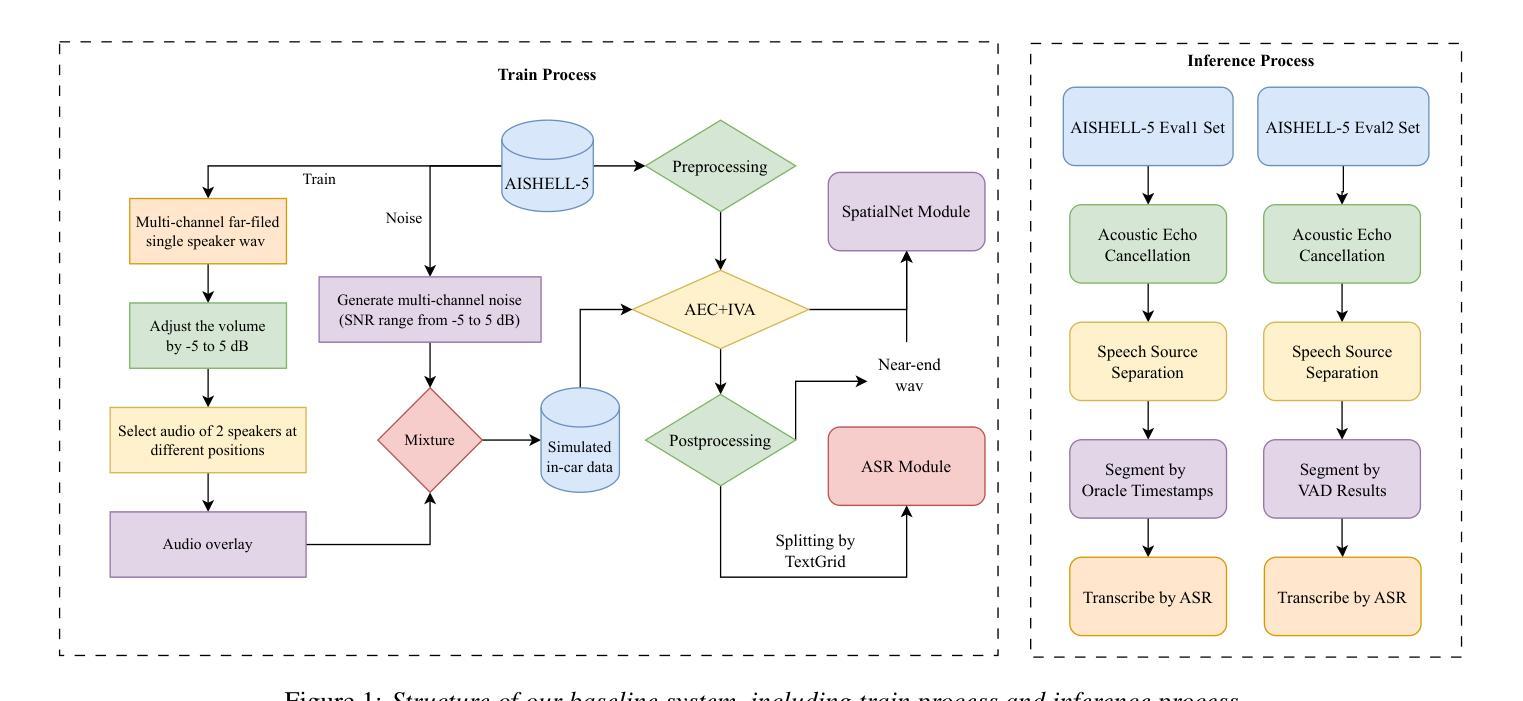
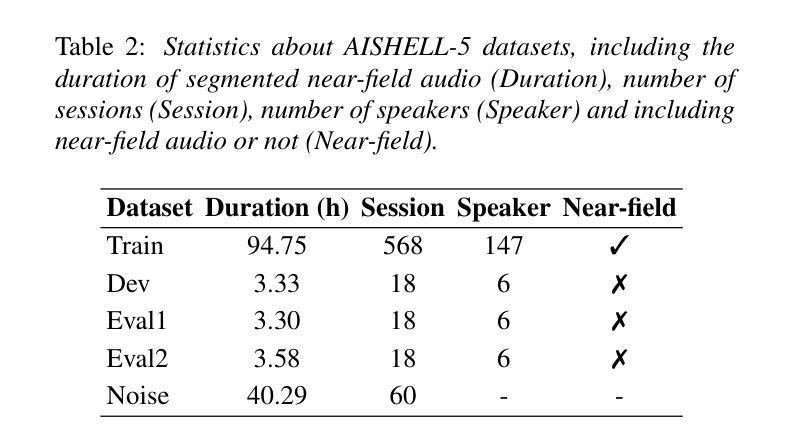
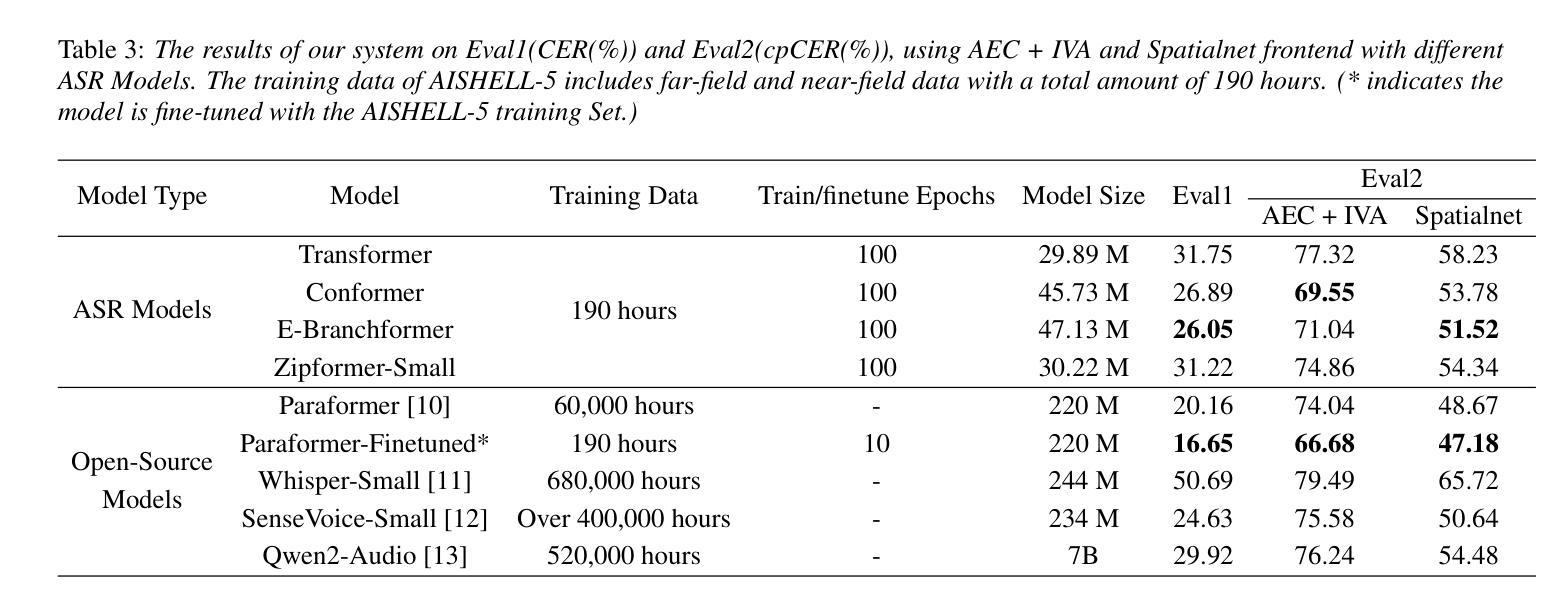
AISHELL-5: The First Open-Source In-Car Multi-Channel Multi-Speaker Speech Dataset for Automatic Speech Diarization and Recognition
Authors:Yuhang Dai, He Wang, Xingchen Li, Zihan Zhang, Shuiyuan Wang, Lei Xie, Xin Xu, Hongxiao Guo, Shaoji Zhang, Hui Bu, Wei Chen
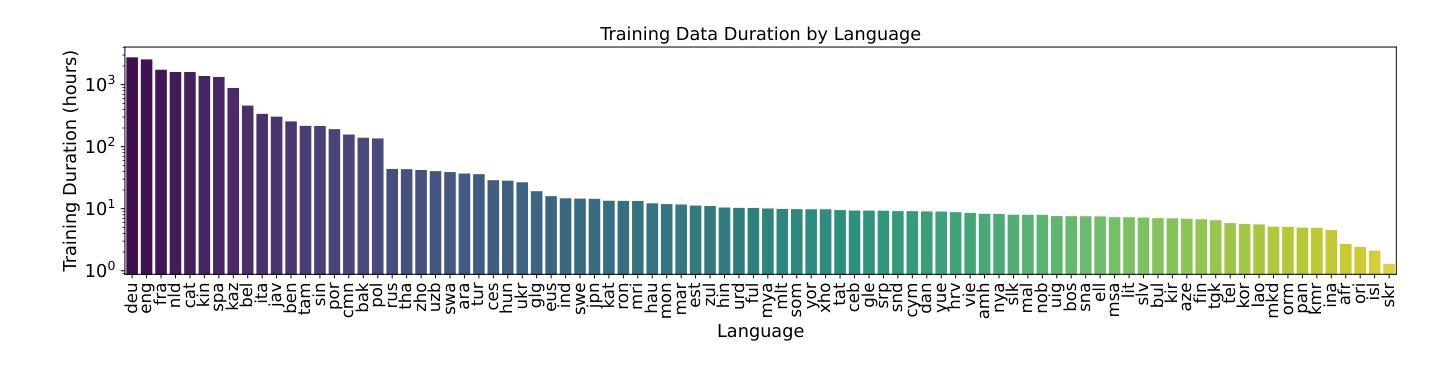
This paper delineates AISHELL-5, the first open-source in-car multi-channel multi-speaker Mandarin automatic speech recognition (ASR) dataset. AISHLL-5 includes two parts: (1) over 100 hours of multi-channel speech data recorded in an electric vehicle across more than 60 real driving scenarios. This audio data consists of four far-field speech signals captured by microphones located on each car door, as well as near-field signals obtained from high-fidelity headset microphones worn by each speaker. (2) a collection of 40 hours of real-world environmental noise recordings, which supports the in-car speech data simulation. Moreover, we also provide an open-access, reproducible baseline system based on this dataset. This system features a speech frontend model that employs speech source separation to extract each speaker’s clean speech from the far-field signals, along with a speech recognition module that accurately transcribes the content of each individual speaker. Experimental results demonstrate the challenges faced by various mainstream ASR models when evaluated on the AISHELL-5. We firmly believe the AISHELL-5 dataset will significantly advance the research on ASR systems under complex driving scenarios by establishing the first publicly available in-car ASR benchmark.
本文介绍了AISHELL-5,这是首个开源的车内多通道多说话者汉语自动语音识别(ASR)数据集。AISHELL-5包括两部分:(1)在超过60个真实驾驶场景中,在电动汽车中录制的超过100小时的多通道语音数据。该音频数据包括由每扇门上的麦克风捕捉到的四个远场语音信号,以及每个发言者佩戴的高保真头戴式麦克风获得的近场信号。(2)40小时真实世界环境噪声录音集,支持车内语音数据的模拟。此外,我们还提供了基于此数据集的开放访问、可重复使用的基线系统。该系统具有语音前端模型,采用语音源分离技术从远场信号中提取每个发言者的清洁语音,以及能够准确转录每个单独发言者内容的语音识别模块。实验结果证明了各种主流ASR模型在AISHELL-5上所面临的挑战。我们坚信,AISHELL-5数据集将通过建立首个公开可用的车内ASR基准,极大地推动复杂驾驶场景下的ASR系统研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figures, 3 tables, accepted by InterSpeech 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了AISHELL-5数据集,这是首个开源的车内多通道多说话者普通话语音识别(ASR)数据集。它包含两部分:一是超过100小时的在电动汽车中录制的多通道语音数据,涉及60多个真实驾驶场景;二是40小时的真实世界环境噪声录音,支持车内语音数据的模拟。此外,还提供了一个基于该数据集的开放可访问的基准系统,包括语音前端模型和语音识别模块。该数据集为复杂驾驶场景下的ASR系统研究带来了重要推进。
Key Takeaways:
- AISHELL-5是首个开源的车内多通道多说话者普通话语音识别(ASR)数据集。
- 数据集包含超过100小时的真实驾驶场景语音数据和40小时的环境噪声录音。
- 数据集支持车内语音数据的模拟。
- 提供了基于AISHELL-5数据集的开放可访问的基准系统。
- 基准系统包括语音前端模型和语音识别模块。
- 实验结果表明,主流ASR模型在AISHELL-5上面临挑战。
点此查看论文截图

EmotionTalk: An Interactive Chinese Multimodal Emotion Dataset With Rich Annotations
Authors:Haoqin Sun, Xuechen Wang, Jinghua Zhao, Shiwan Zhao, Jiaming Zhou, Hui Wang, Jiabei He, Aobo Kong, Xi Yang, Yequan Wang, Yonghua Lin, Yong Qin
In recent years, emotion recognition plays a critical role in applications such as human-computer interaction, mental health monitoring, and sentiment analysis. While datasets for emotion analysis in languages such as English have proliferated, there remains a pressing need for high-quality, comprehensive datasets tailored to the unique linguistic, cultural, and multimodal characteristics of Chinese. In this work, we propose \textbf{EmotionTalk}, an interactive Chinese multimodal emotion dataset with rich annotations. This dataset provides multimodal information from 19 actors participating in dyadic conversational settings, incorporating acoustic, visual, and textual modalities. It includes 23.6 hours of speech (19,250 utterances), annotations for 7 utterance-level emotion categories (happy, surprise, sad, disgust, anger, fear, and neutral), 5-dimensional sentiment labels (negative, weakly negative, neutral, weakly positive, and positive) and 4-dimensional speech captions (speaker, speaking style, emotion and overall). The dataset is well-suited for research on unimodal and multimodal emotion recognition, missing modality challenges, and speech captioning tasks. To our knowledge, it represents the first high-quality and versatile Chinese dialogue multimodal emotion dataset, which is a valuable contribution to research on cross-cultural emotion analysis and recognition. Additionally, we conduct experiments on EmotionTalk to demonstrate the effectiveness and quality of the dataset. It will be open-source and freely available for all academic purposes. The dataset and codes will be made available at: https://github.com/NKU-HLT/EmotionTalk.
近年来,情感识别在人机交互、心理健康监测和情感分析等领域的应用中发挥着至关重要的作用。虽然英语情感分析的数据集已经大量涌现,但仍迫切需要针对中文独特语言、文化和多模态特征的高质量、综合数据集。在这项工作中,我们提出了“EmotionTalk”这一交互式中文多模态情感数据集,包含丰富的注释。该数据集提供了来自19名演员在二元对话环境中的跨模态信息,融合了声音、视觉和文本模式。它包含23.6小时的语音(19,250句话),注释了7个话语级情感类别(快乐、惊讶、悲伤、厌恶、愤怒、恐惧和中性),5维情感标签(负面、轻微负面、中性、轻微正面和正面),以及4维语音字幕(说话者、说话风格、情感和总体评价)。该数据集适用于单模态和多模态情感识别研究、缺失模态挑战和语音字幕任务。据我们所知,它是第一个高质量且通用的中文对话多模态情感数据集,对跨文化情感分析和识别研究做出了宝贵的贡献。此外,我们在EmotionTalk上进行了实验,以证明数据集的有效性和质量。该数据集将开源并免费提供所有学术用途。数据集和代码将在以下网址提供:https://github.com/NKU-HLT/EmotionTalk。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为EmotionTalk的中文多模态情感数据集,该数据集包含来自19名参与者在对话环境中的多模态信息,包括声音、视频和文字。数据集包含丰富的标注信息,如情感类别、情感维度和语音字幕等。该数据集适用于单模态和多模态情感识别研究,缺失模态挑战和语音字幕任务等。这是首个高质量、多功能的中文对话多模态情感数据集,对跨文化情感分析和识别研究具有宝贵贡献。数据集将开源并免费提供给所有学术用途。
Key Takeaways
- EmotionTalk是一个针对中文的交互式多模态情感数据集,包含声音、视频和文字等多模态信息。
- 数据集包含来自19名参与者在对话环境中的丰富标注信息。
- 数据集适用于单模态和多模态情感识别研究,尤其适合处理缺失模态的挑战。
- 数据集包含情感类别、情感维度和语音字幕等多个维度的标注信息。
- EmotionTalk是首个高质量、多功能的中文对话多模态情感数据集,对跨文化情感分析具有宝贵贡献。
- 数据集将开源并免费提供给所有学术用途,方便研究者使用。
点此查看论文截图

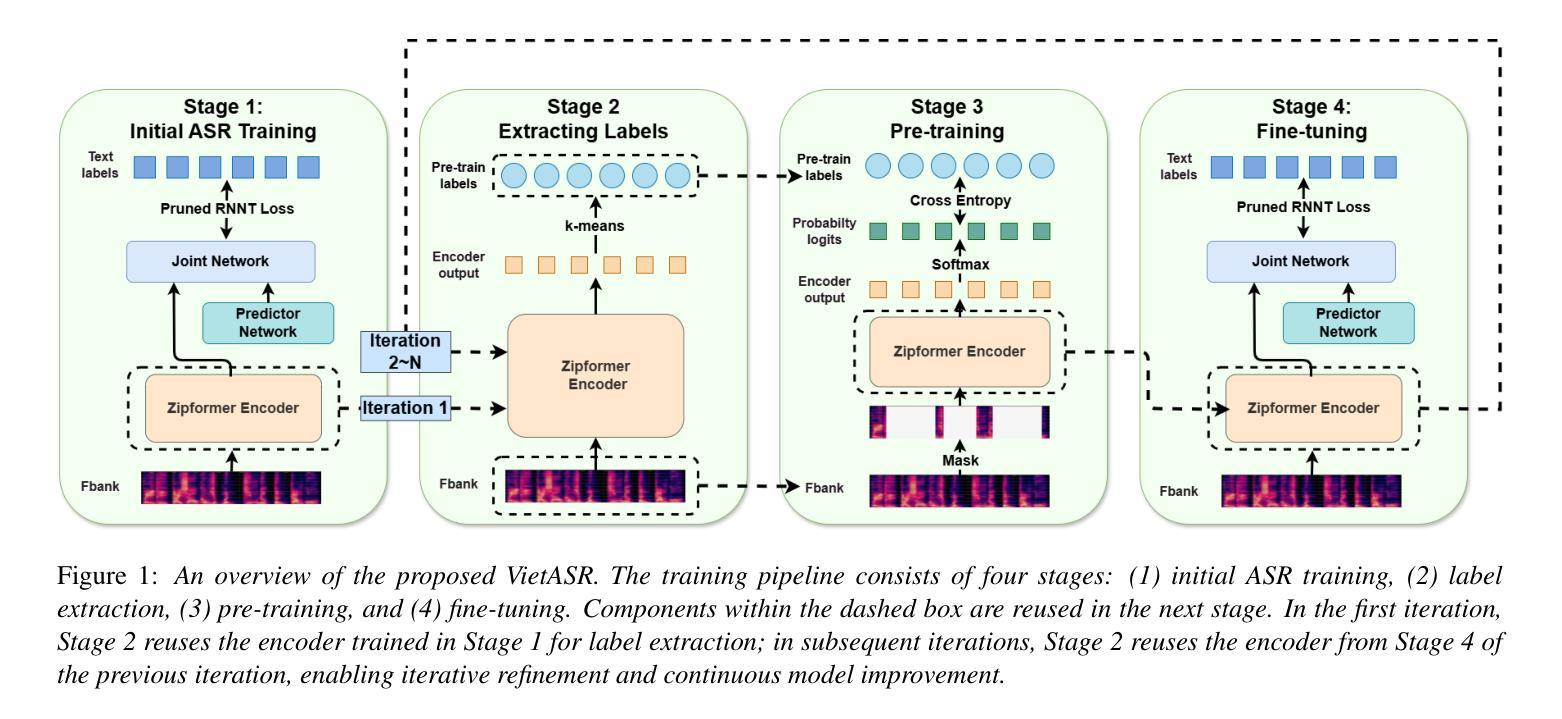
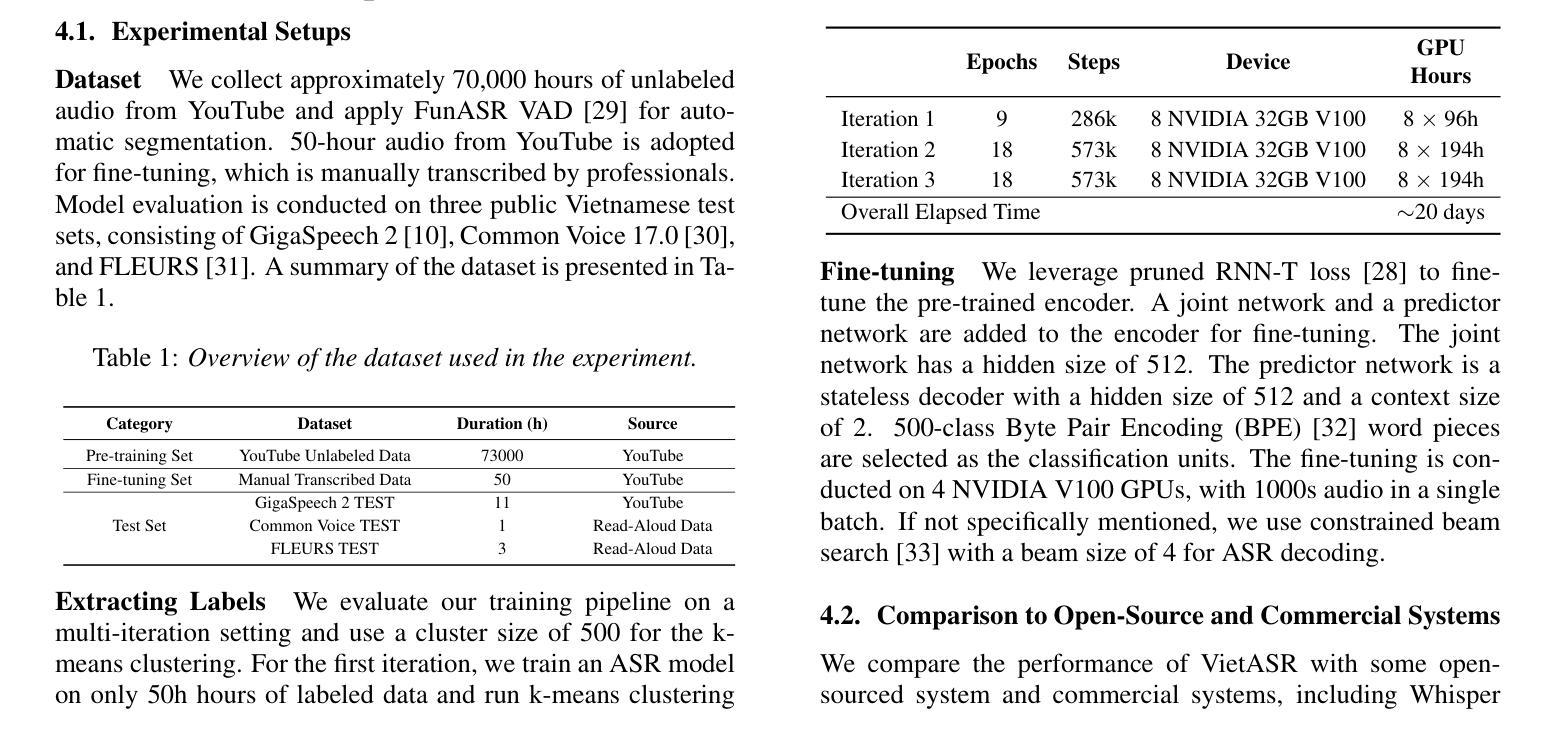
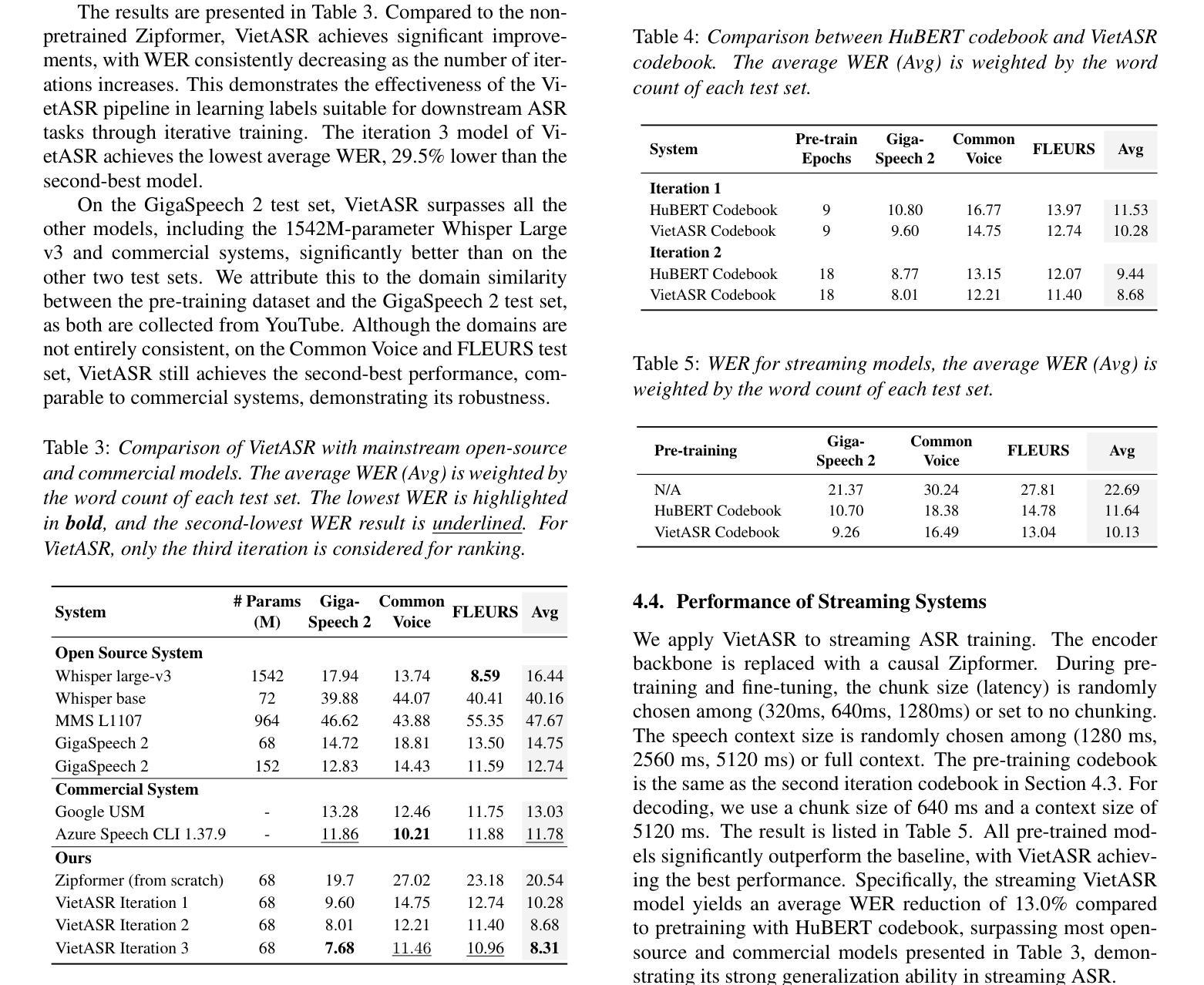
VietASR: Achieving Industry-level Vietnamese ASR with 50-hour labeled data and Large-Scale Speech Pretraining
Authors:Jianheng Zhuo, Yifan Yang, Yiwen Shao, Yong Xu, Dong Yu, Kai Yu, Xie Chen
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) has made remarkable progress but heavily relies on large-scale labeled data, which is scarce for low-resource languages like Vietnamese. While existing systems such as Whisper, USM, and MMS achieve promising performance, their efficacy remains inadequate in terms of training costs, latency, and accessibility. To address these issues, we propose VietASR, a novel ASR training pipeline that leverages vast amounts of unlabeled data and a small set of labeled data. Through multi-iteration ASR-biased self-supervised learning on a large-scale unlabeled dataset, VietASR offers a cost-effective and practical solution for enhancing ASR performance. Experiments demonstrate that pre-training on 70,000-hour unlabeled data and fine-tuning on merely 50-hour labeled data yield a lightweight but powerful ASR model. It outperforms Whisper Large-v3 and commercial ASR systems on real-world data. Our code and models will be open-sourced to facilitate research in low-resource ASR.
自动语音识别(ASR)已经取得了显著的进步,但严重依赖于大规模标注数据,对于像越南语这样的低资源语言,这些数据是稀缺的。虽然现有的系统如Whisper、USM和MMS表现良好,但在训练成本、延迟和可访问性方面仍存在不足。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了VietASR,这是一种新型的ASR训练管道,能够利用大量的无标签数据和一小部分有标签数据。VietASR通过在大规模无标签数据集上进行多次迭代的ASR偏向自监督学习,为增强ASR性能提供了经济高效且实用的解决方案。实验表明,在7万小时的无标签数据上进行预训练,仅在50小时的有标签数据上进行微调,可以生成一个轻便但强大的ASR模型。它在真实世界数据上的表现优于Whisper Large-v3和商业ASR系统。我们的代码和模型将开源,以促进低资源ASR的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文本介绍了针对越南语这类低资源语言存在的自动语音识别(ASR)问题,提出的一种新型的ASR训练管道VietASR。VietASR利用大量的无标签数据和少量的有标签数据,通过多轮ASR偏向的自监督学习,为解决高成本、延迟和可访问性问题提供了经济实用的解决方案。实验表明,在7万小时的无标签数据上进行预训练,仅在50小时的有标签数据上进行微调,即可获得一个轻便但功能强大的ASR模型,该模型在真实数据上的表现优于Whisper Large-v3和商用ASR系统。我们的代码和模型将开源,以促进低资源ASR的研究。
要点
- 自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源语言如越南语中面临挑战,需要大规模有标签数据。
- 现有系统如Whisper、USM和MMS在训练成本、延迟和可访问性方面存在不足。
3.VietASR是一种新型的ASR训练管道,利用大量的无标签数据和少量的有标签数据。 - 通过多轮ASR偏向的自监督学习,VietASR提高了ASR的性能。
- 实验表明,VietASR在真实数据上的表现优于其他系统。
6.VietASR的代码和模型将开源,以促进低资源ASR的研究。
点此查看论文截图

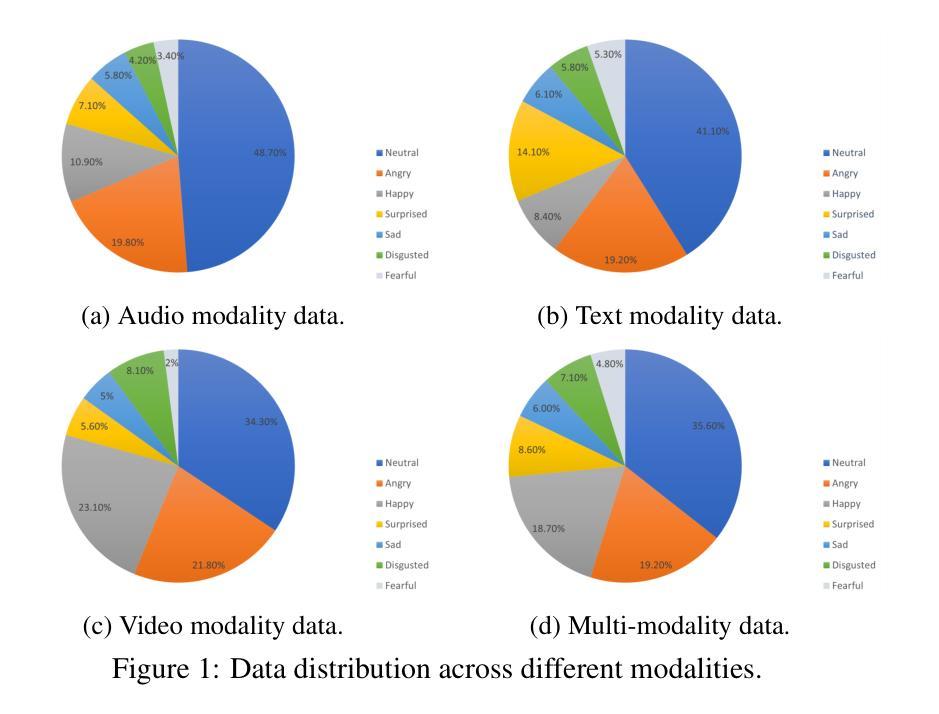
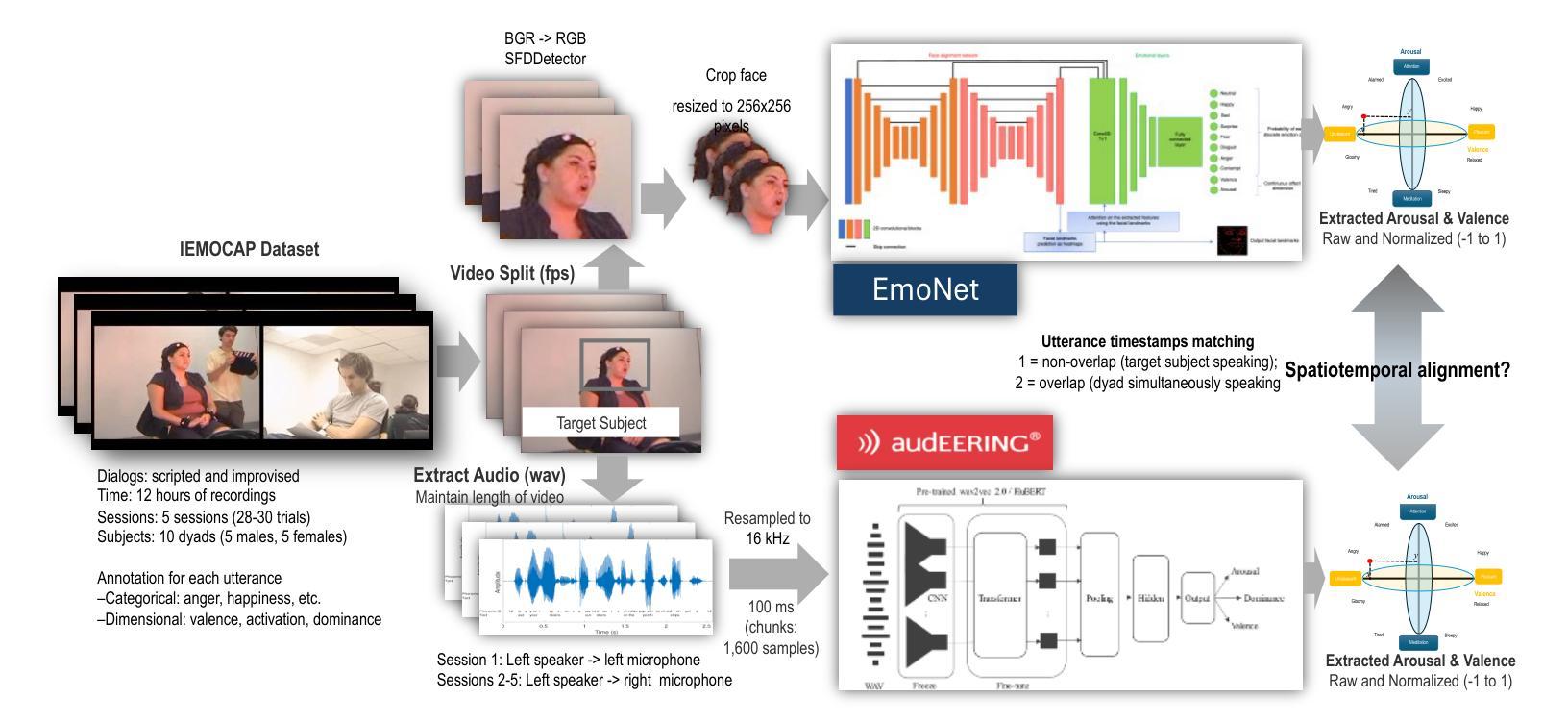
Exploring Spatiotemporal Emotional Synchrony in Dyadic Interactions: The Role of Speech Conditions in Facial and Vocal Affective Alignment
Authors:Von Ralph Dane Marquez Herbuela, Yukie Nagai
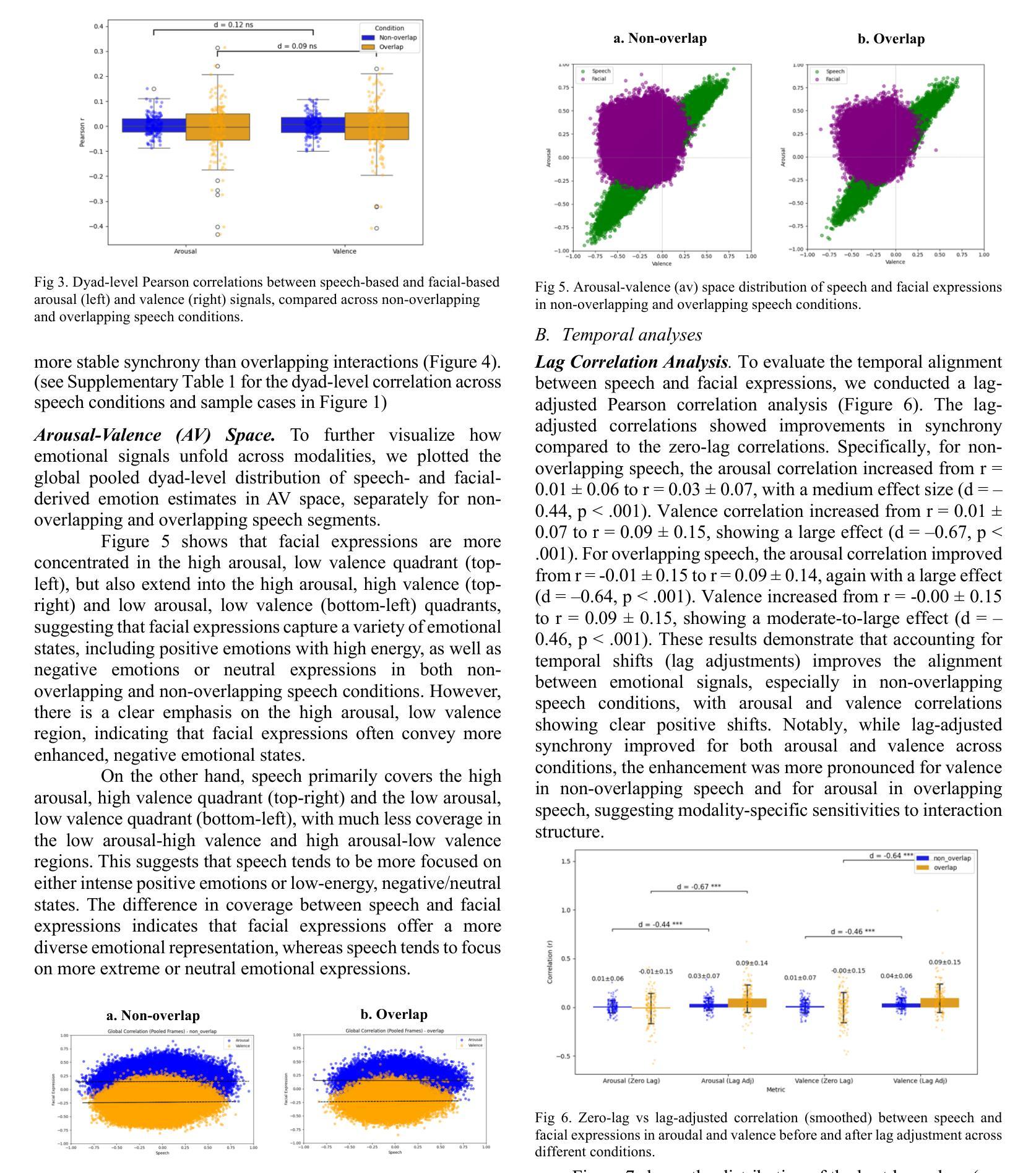
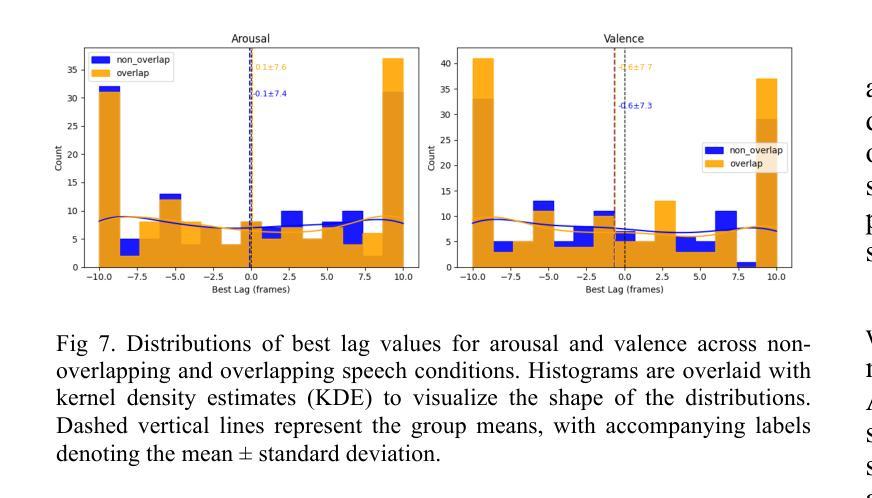
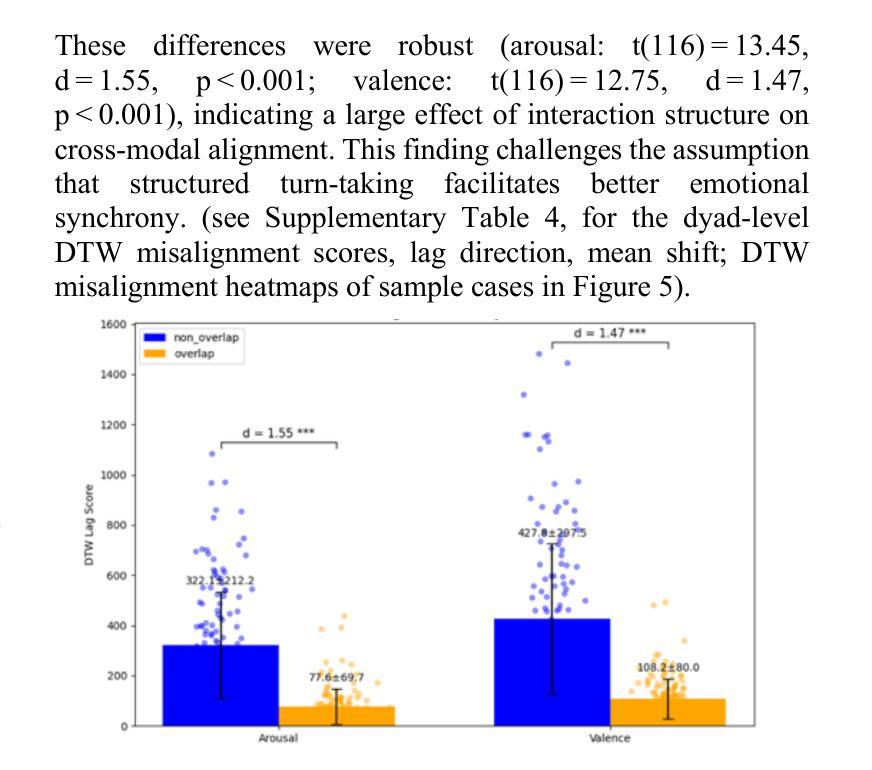
Understanding how humans express and synchronize emotions across multiple communication channels particularly facial expressions and speech has significant implications for emotion recognition systems and human computer interaction. Motivated by the notion that non-overlapping speech promotes clearer emotional coordination, while overlapping speech disrupts synchrony, this study examines how these conversational dynamics shape the spatial and temporal alignment of arousal and valence across facial and vocal modalities. Using dyadic interactions from the IEMOCAP dataset, we extracted continuous emotion estimates via EmoNet (facial video) and a Wav2Vec2-based model (speech audio). Segments were categorized based on speech overlap, and emotional alignment was assessed using Pearson correlation, lag adjusted analysis, and Dynamic Time Warping (DTW). Across analyses, non overlapping speech was associated with more stable and predictable emotional synchrony than overlapping speech. While zero-lag correlations were low and not statistically different, non overlapping speech showed reduced variability, especially for arousal. Lag adjusted correlations and best-lag distributions revealed clearer, more consistent temporal alignment in these segments. In contrast, overlapping speech exhibited higher variability and flatter lag profiles, though DTW indicated unexpectedly tighter alignment suggesting distinct coordination strategies. Notably, directionality patterns showed that facial expressions more often preceded speech during turn-taking, while speech led during simultaneous vocalizations. These findings underscore the importance of conversational structure in regulating emotional communication and provide new insight into the spatial and temporal dynamics of multimodal affective alignment in real world interaction.
理解人类如何在多个沟通渠道(尤其是面部表情和言语)上表达和同步情绪,对于情绪识别系统和人机交互有着重大启示。本研究受到非重叠性言语能够促进更清晰情感协调的观念的启发,同时重叠性言语会破坏同步性。本研究探讨了这些对话动态如何影响面部和声音模态的兴奋和价值的空间和时间对齐。我们使用了IEMOCAP数据集中的二元互动,通过EmoNet(面部视频)和基于Wav2Vec2的模型(语音音频)提取了连续的情绪估计值。根据语音重叠情况对片段进行分类,并使用Pearson相关性、滞后调整分析和动态时间弯曲(DTW)来评估情感对齐情况。在各种分析中,非重叠性言语在情绪同步方面表现得更稳定和可预测,相比之下,重叠性言语则表现出更高的可变性和较平坦的滞后分布。然而,DTW意外地显示出更紧密的对齐,表明存在不同的协调策略。值得注意的是,方向性模式显示,在轮流发言时,面部表情往往先于言语,而在同时发声时,则是言语领先。这些发现强调了对话结构在调节情感沟通中的重要性,并为现实互动中多模式情感对齐的空间和时间动态提供了新的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了人类在多通道沟通中如何表达和同步情绪,特别是在面部表情和言语方面。研究指出,非重叠的语音有助于更清晰的情感协调,而重叠的语音则会破坏同步性。通过对IEMOCAP数据集的双语互动进行研究,发现非重叠语音在情感同步方面表现更稳定且可预测。面部表情更常主导言语转换时的情绪表达,而同时发声时语音则更为主导。这些发现强调了对话结构在情感沟通中的重要性,并为真实互动中的多模态情感对齐的时空动态提供了新的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 人类在多通道沟通中表达和同步情绪的研究对情绪识别系统和人机交互有重要意义。
- 非重叠的语音有助于更清晰的情感协调,而重叠的语音可能导致情感同步的混乱。
- 通过IEMOCAP数据集的研究发现,非重叠语音在情感同步方面表现更稳定且可预测。
- 面部表情在言语转换时更常主导情绪表达,而同时发声时语音为主导。
- 零时间滞后相关性低,而非重叠语音降低了变异性,特别是觉醒度方面。
- 研究方向表明对话结构在情感沟通中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图


Nexus: An Omni-Perceptive And -Interactive Model for Language, Audio, And Vision
Authors:Che Liu, Yingji Zhang, Dong Zhang, Weijie Zhang, Chenggong Gong, Haohan Li, Yu Lu, Shilin Zhou, Yue Lu, Ziliang Gan, Ziao Wang, Junwei Liao, Haipang Wu, Ji Liu, André Freitas, Qifan Wang, Zenglin Xu, Rongjuncheng Zhang, Yong Dai
This work proposes an industry-level omni-modal large language model (LLM) pipeline that integrates auditory, visual, and linguistic modalities to overcome challenges such as limited tri-modal datasets, high computational costs, and complex feature alignments. Our pipeline consists of three main components: First, a modular framework enabling flexible configuration of various encoder-LLM-decoder architectures. Second, a lightweight training strategy that pre-trains audio-language alignment on the state-of-the-art vision-language model Qwen2.5-VL, thus avoiding the costly pre-training of vision-specific modalities. Third, an audio synthesis pipeline that generates high-quality audio-text data from diverse real-world scenarios, supporting applications such as Automatic Speech Recognition and Speech-to-Speech chat. To this end, we introduce an industry-level omni-modal LLM, Nexus. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of our pipeline, yielding the following key findings:(1) In the visual understanding task, Nexus exhibits superior performance compared with its backbone model - Qwen2.5-VL-7B, validating the efficiency of our training strategy. (2) Within the English Spoken Question-Answering task, the model achieves better accuracy than the same-period competitor (i.e, MiniCPM-o2.6-7B) in the LLaMA Q. benchmark. (3) In our real-world ASR testset, Nexus achieves outstanding performance, indicating its robustness in real scenarios. (4) In the Speech-to-Text Translation task, our model outperforms Qwen2-Audio-Instruct-7B. (5) In the Text-to-Speech task, based on pretrained vocoder (e.g., Fishspeech1.4 or CosyVoice2.0), Nexus is comparable to its backbone vocoder on Seed-TTS benchmark. (6) An in-depth analysis of tri-modal alignment reveals that incorporating the audio modality enhances representational alignment between vision and language.
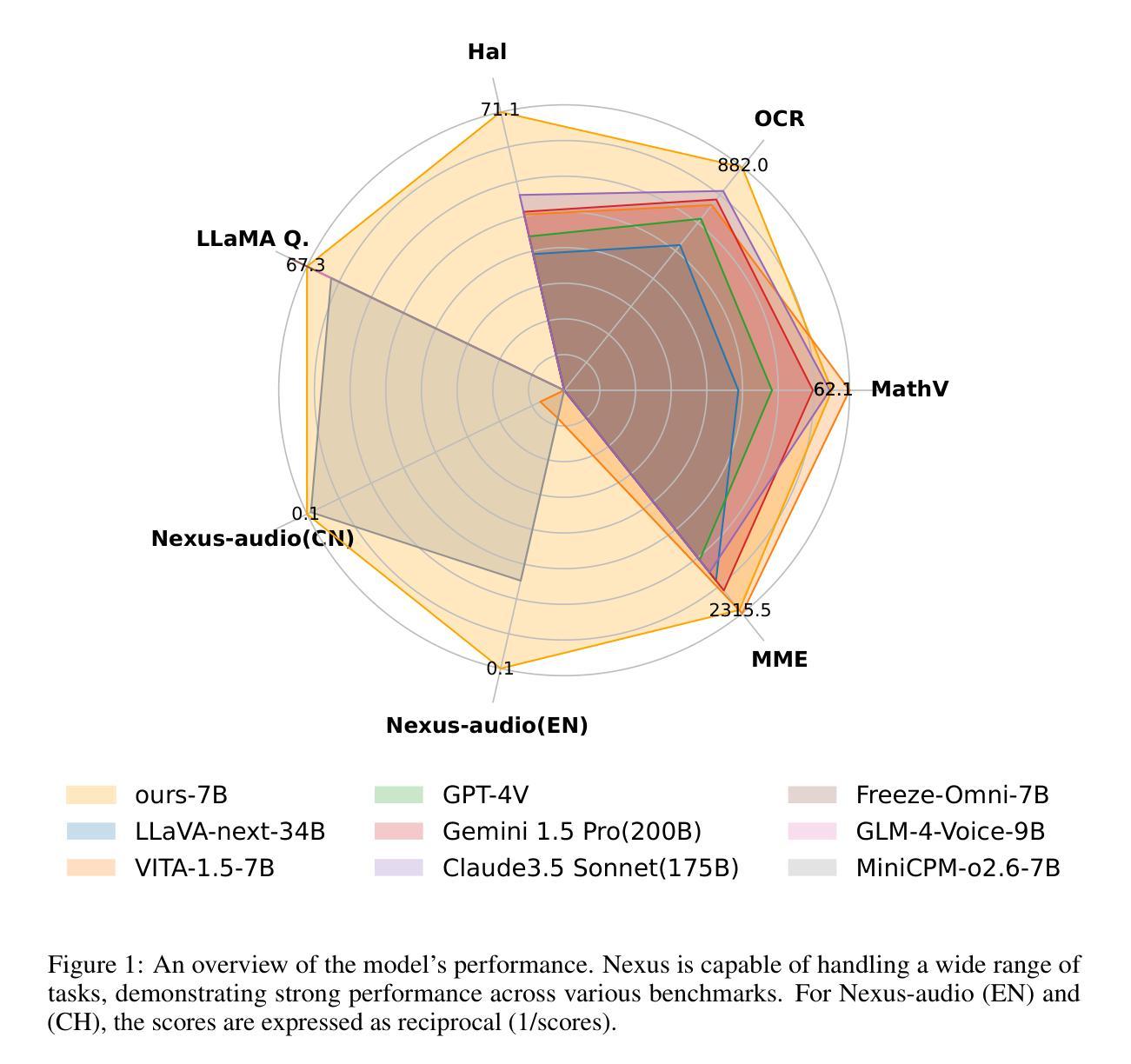
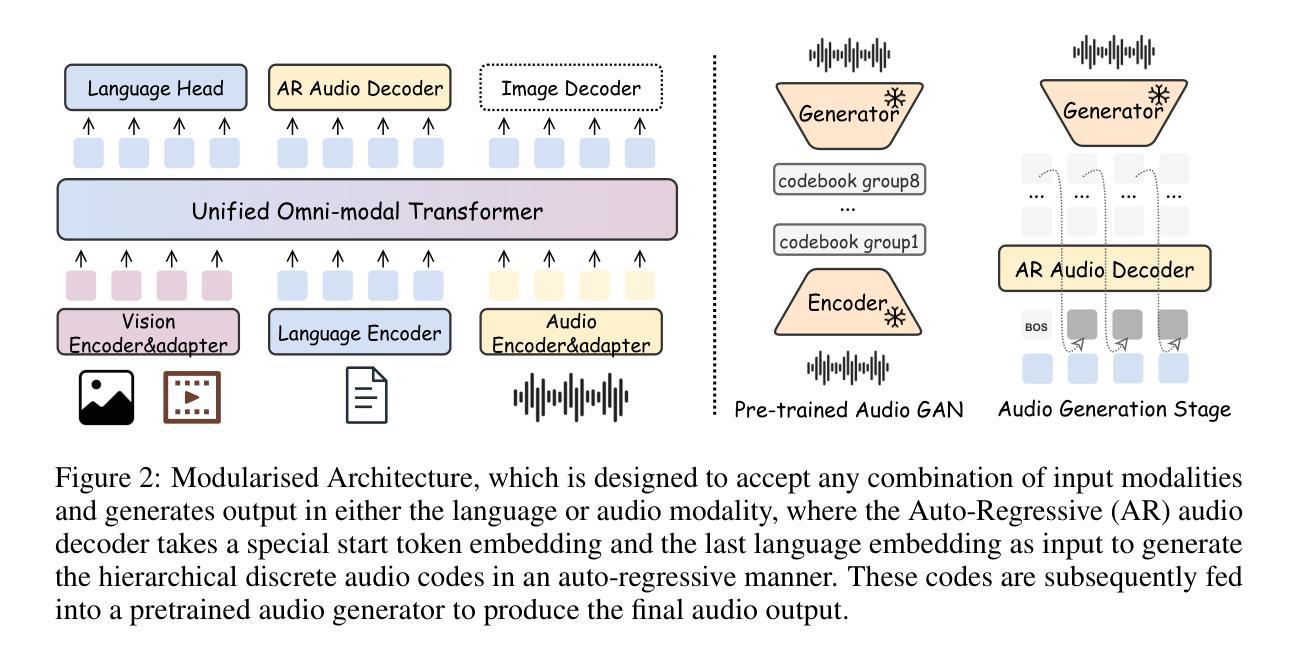
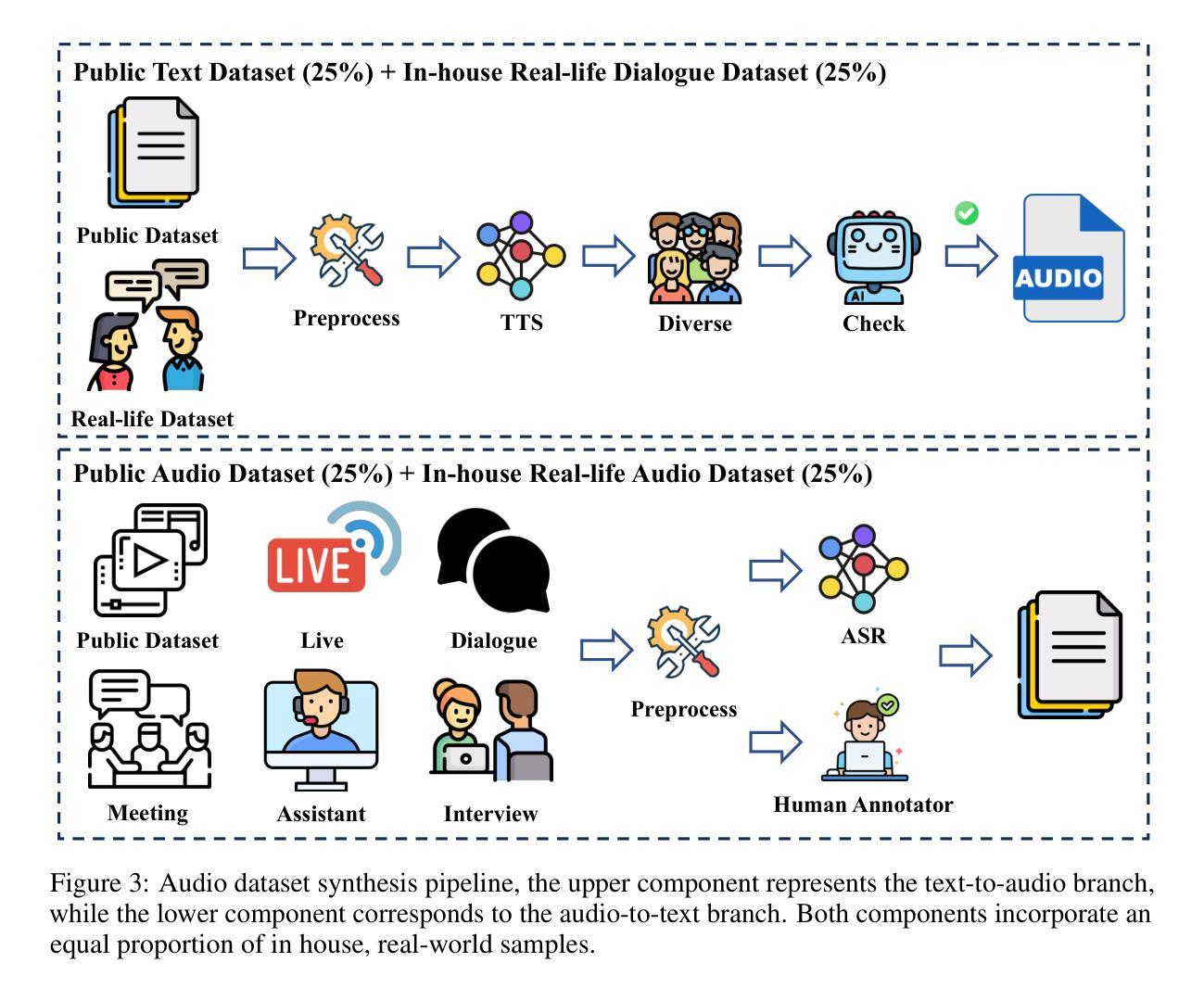
本文提出了一种跨行业的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)管道,该管道融合了听觉、视觉和语言学模态,以克服如有限的三模态数据集、高计算成本和复杂特征对齐等挑战。我们的管道主要由三个部分组成:首先,一个模块化框架,能够灵活配置各种编码器-LLM-解码器架构。其次,一种轻量级的训练策略,通过对最先进的视觉语言模型Qwen2.5-VL进行音频语言对齐的预训练,从而避免了针对特定视觉模态的昂贵预训练。最后,一个音频合成管道,从多样化的现实场景中生成高质量音频文本数据,支持如自动语音识别和语音到语音聊天等应用。为此,我们引入了一个跨行业的多模态LLM——Nexus。大量实验验证了我们管道的有效性,并产生了以下关键发现:(1)在视觉理解任务中,Nexus相较于其骨干模型Qwen2.5-VL-7B展现出卓越性能,验证了我们的训练策略的有效性。(2)在英语口语问答任务中,该模型在LLaMA Q. benchmark上的准确率高于同期竞争对手(即MiniCPM-o2.6-7B)。(3)在我们的现实ASR测试集中,Nexus表现出卓越性能,表明其在现实场景中的稳健性。(4)在语音到文本翻译任务中,我们的模型表现优于Qwen2-Audio-Instruct-7B。(5)在文本到语音任务中,基于预训练的vocoder(例如Fishspeech1.4或CosyVoice2.0),Nexus在Seed-TTS benchmark上的表现与其骨干vocoder相当。(6)对三模态对齐的深入分析表明,加入音频模态增强了视觉和语言之间的代表性对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种跨行业的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)管道,该管道融合了听觉、视觉和语言学三大模态,以克服如有限的三模态数据集、高昂的计算成本和复杂的特征对齐等挑战。本文的主要贡献包括一个模块化框架、一种轻量级训练策略和一个音频合成管道。模块化框架可灵活配置各种编码器-LLM-解码器架构;轻量级训练策略通过预训练音频语言对齐来避免昂贵的视觉特定模态的预训练;音频合成管道可生成高质量音频文本数据,支持如自动语音识别和语音聊天等应用。实验证明,该管道在多项任务中表现优异,包括视觉理解任务、英语口语问答任务等。该模型的音频模态融入进一步增强了视觉与语言的代表性对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 工作提出了一种融合听觉、视觉和语言三大模态的跨行业多模态大型语言模型(LLM)管道。
- 模块化框架提供灵活的架构配置。
- 轻量级训练策略通过预训练音频语言对齐来降低成本并提高效率。
- 音频合成管道支持自动生成高质量音频文本数据,适用于多种应用场景。
- 在视觉理解任务中,Nexus模型表现出比其骨干模型更优的性能。
- 在英语口语问答任务中,Nexus模型在LLaMA Q. benchmark上实现了较高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

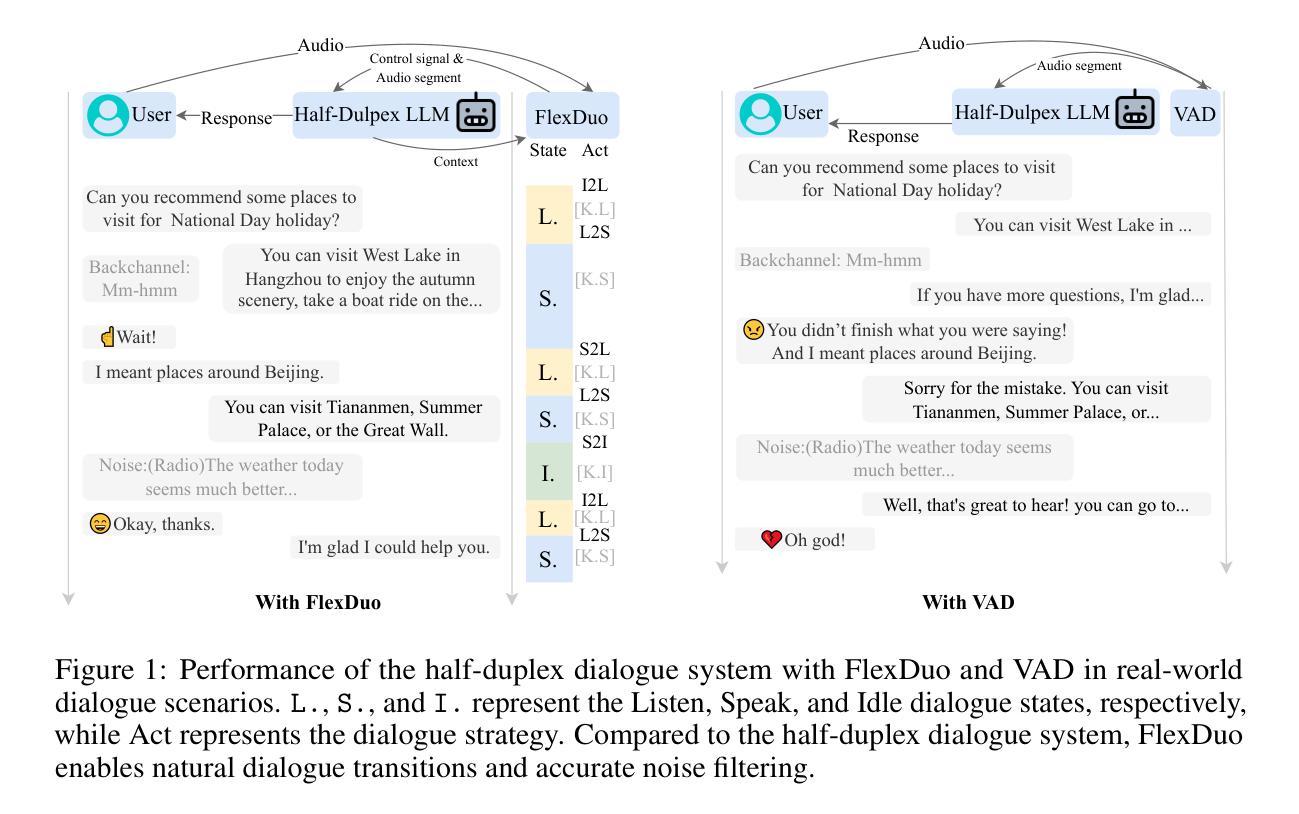
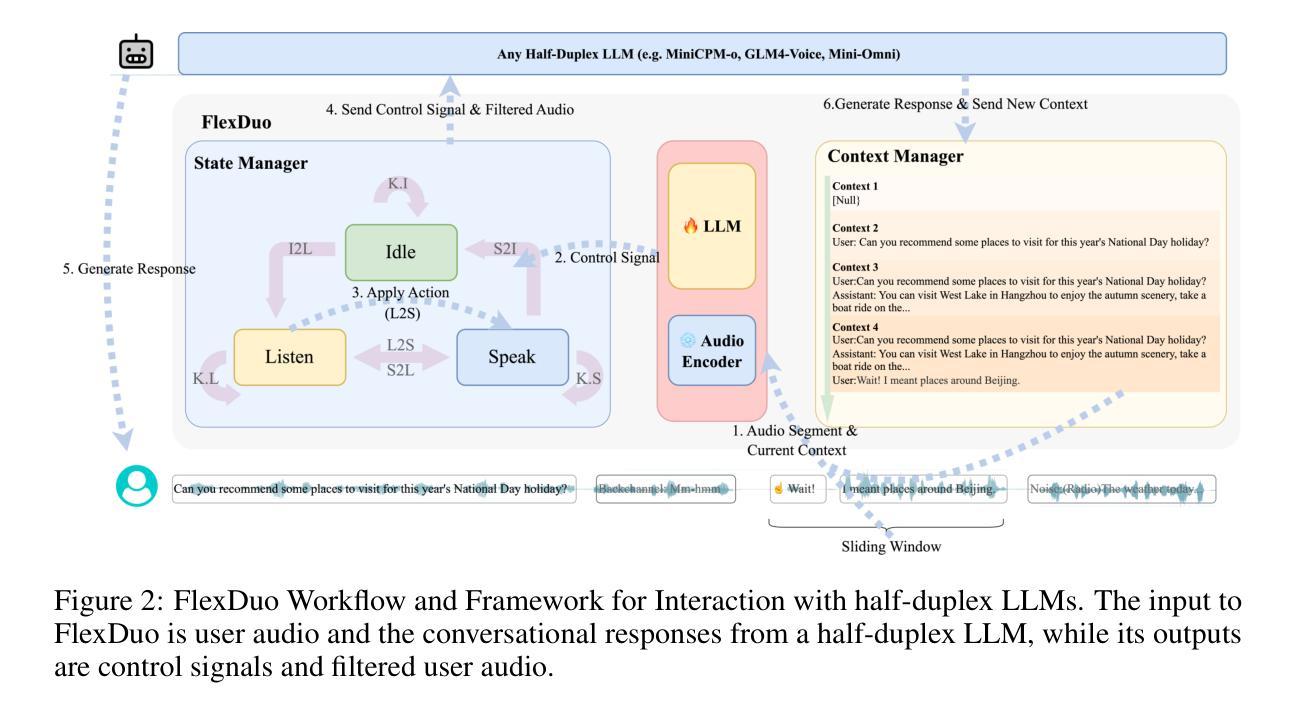
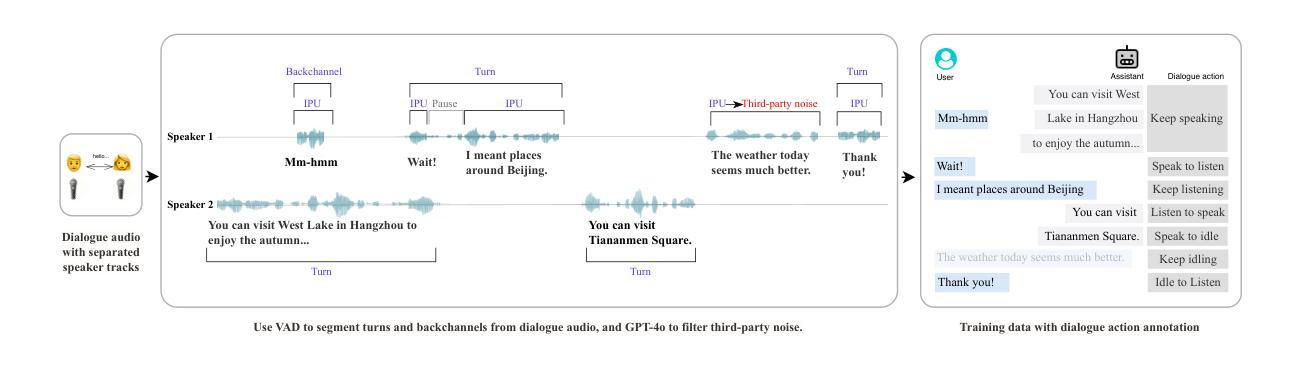
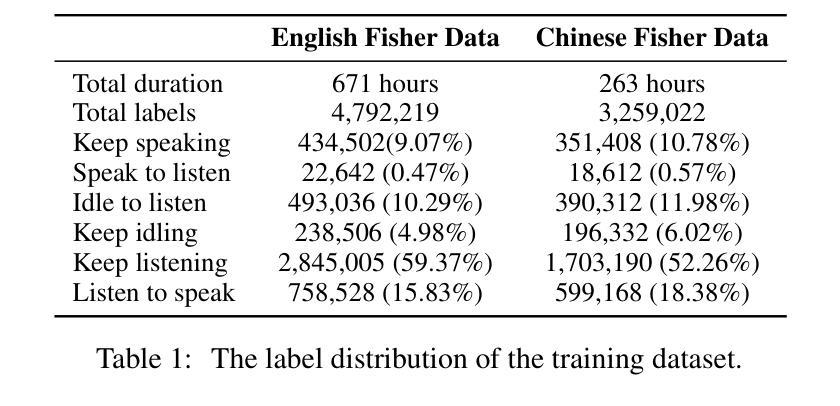
FlexDuo: A Pluggable System for Enabling Full-Duplex Capabilities in Speech Dialogue Systems
Authors:Borui Liao, Yulong Xu, Jiao Ou, Kaiyuan Yang, Weihua Jian, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang
Full-Duplex Speech Dialogue Systems (Full-Duplex SDS) have significantly enhanced the naturalness of human-machine interaction by enabling real-time bidirectional communication. However, existing approaches face challenges such as difficulties in independent module optimization and contextual noise interference due to highly coupled architectural designs and oversimplified binary state modeling. This paper proposes FlexDuo, a flexible full-duplex control module that decouples duplex control from spoken dialogue systems through a plug-and-play architectural design. Furthermore, inspired by human information-filtering mechanisms in conversations, we introduce an explicit Idle state. On one hand, the Idle state filters redundant noise and irrelevant audio to enhance dialogue quality. On the other hand, it establishes a semantic integrity-based buffering mechanism, reducing the risk of mutual interruptions while ensuring accurate response transitions. Experimental results on the Fisher corpus demonstrate that FlexDuo reduces the false interruption rate by 24.9% and improves response accuracy by 7.6% compared to integrated full-duplex dialogue system baselines. It also outperforms voice activity detection (VAD) controlled baseline systems in both Chinese and English dialogue quality. The proposed modular architecture and state-based dialogue model provide a novel technical pathway for building flexible and efficient duplex dialogue systems.
全双工语音对话系统(Full-Duplex SDS)通过实现实时双向通信,显著增强了人机交互的自然性。然而,现有方法面临诸多挑战,如因架构高度耦合和过于简化的二元状态建模而导致的独立模块优化困难和上下文噪声干扰等问题。本文提出了FlexDuo,这是一种灵活的全双工控制模块,它通过即插即用的架构设计,将双工控制从语音对话系统中解耦出来。此外,受人类对话中的信息过滤机制的启发,我们引入了明确的空闲状态。一方面,空闲状态可以过滤掉冗余的噪声和无关的音频,以提高对话质量。另一方面,它建立了一种基于语义完整性的缓冲机制,降低了相互干扰的风险,同时确保了准确的响应转换。在Fisher语料库上的实验结果表明,与集成全双工对话系统基线相比,FlexDuo将错误中断率降低了24.9%,响应准确率提高了7.6%。与语音活动检测(VAD)控制的基线系统相比,它在中文和英文对话质量方面也表现出色。所提出的模块架构和基于状态的对话模型为构建灵活高效的全双工对话系统提供了新颖的技术途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
全双工语音对话系统(Full-Duplex SDS)通过实现实时双向通信,显著提高了人机交互的自然性。然而,现有方法面临独立模块优化困难和上下文噪声干扰等挑战,这是由于高度耦合的架构设计以及简化的二元状态建模。本文提出FlexDuo,一种灵活的全双工控制模块,通过即插即用架构实现与口语对话系统的解耦。此外,受人类对话中的信息过滤机制的启发,引入了明确的空闲状态。一方面,空闲状态过滤冗余噪声和无关音频,提高对话质量。另一方面,它建立基于语义完整性的缓冲机制,降低相互干扰的风险,同时确保准确的响应转换。在Fisher语料库上的实验结果表明,FlexDuo与集成全双工对话系统基线相比,误中断率降低24.9%,响应准确率提高7.6%。它还优于基于语音活动检测(VAD)控制的基线系统在中文和英语对话质量方面的表现。所提出的模块化架构和基于状态的对话模型为构建灵活高效的全双工对话系统提供了新的技术途径。
Key Takeaways
- 全双工语音对话系统增强了人机交互的自然性,通过实时双向通信实现。
- 现有方法面临独立模块优化和上下文噪声干扰的挑战。
- FlexDuo通过即插即用架构实现与口语对话系统的解耦,提出灵活的全双工控制模块。
- 引入明确的空闲状态,提高对话质量,降低误中断风险。
- FlexDuo在Fisher语料库上的实验表现优于基线系统,误中断率降低24.9%,响应准确率提高7.6%。
- FlexDuo在中文和英语对话质量方面优于基于语音活动检测控制的基线系统。
点此查看论文截图