⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
Few-Shot Speech Deepfake Detection Adaptation with Gaussian Processes
Authors:Neta Glazer, David Chernin, Idan Achituve, Sharon Gannot, Ethan Fetaya
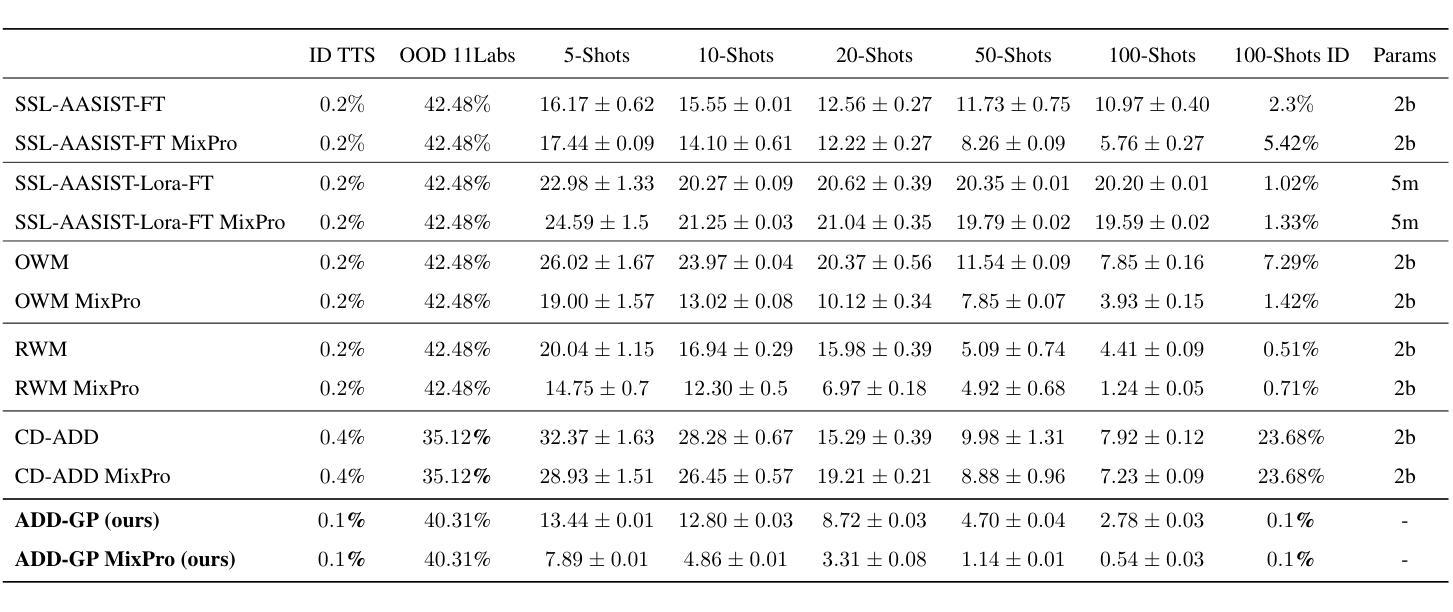
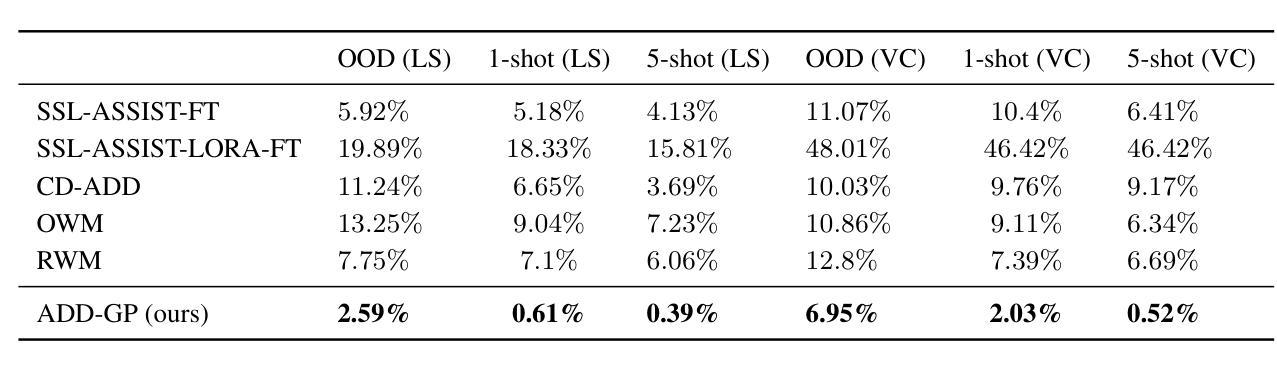
Recent advancements in Text-to-Speech (TTS) models, particularly in voice cloning, have intensified the demand for adaptable and efficient deepfake detection methods. As TTS systems continue to evolve, detection models must be able to efficiently adapt to previously unseen generation models with minimal data. This paper introduces ADD-GP, a few-shot adaptive framework based on a Gaussian Process (GP) classifier for Audio Deepfake Detection (ADD). We show how the combination of a powerful deep embedding model with the Gaussian processes flexibility can achieve strong performance and adaptability. Additionally, we show this approach can also be used for personalized detection, with greater robustness to new TTS models and one-shot adaptability. To support our evaluation, a benchmark dataset is constructed for this task using new state-of-the-art voice cloning models.
近期文本转语音(TTS)模型的进步,特别是在语音克隆方面,加剧了对自适应和高效的深度伪造检测方法的需求。随着TTS系统的不断发展,检测模型必须能够以最小的数据量高效地适应以前未见过的生成模型。本文介绍了ADD-GP,这是一种基于高斯过程(GP)分类器的音频深度伪造检测(ADD)的少量自适应框架。我们展示了强大的深度嵌入模型与高斯过程的灵活性如何结合,以实现强大的性能和适应性。此外,我们还证明该方法也可用于个性化检测,对新TTS模型具有更强的鲁棒性,并具备一次适应性。为了支持我们的评估,我们使用了最新的语音克隆模型构建了一个用于此任务的标准数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
随着文本转语音(TTS)模型的进步,特别是语音克隆技术的发展,对灵活且高效的声音深度伪造检测方法的需求愈发强烈。本文介绍了一个基于高斯过程(GP)分类器的ADD-GP少数自适应框架,用于音频深度伪造检测(ADD)。结合强大的深度嵌入模型与高斯过程的灵活性,该框架可实现出色的性能和适应性。此外,该框架还可用于个性化检测,对新TTS模型具有更强的鲁棒性,并具有一次适应性。
关键见解
- TTS模型的最新进展要求检测模型具有快速适应新生成模型的能力。
- ADD-GP框架结合了深度嵌入模型与高斯过程分类器,用于音频深度伪造检测。
- 该框架可实现强大的性能和适应性,尤其是针对新出现的TTS模型。
- 可以通过个性化检测增强框架的鲁棒性。
- 为支持评估,使用最新的语音克隆模型构建了针对此任务的标准数据集。
- 该框架具有一次适应性,即能够仅通过少量数据快速适应新的TTS模型。
- 这种自适应能力对于应对不断演变的TTS技术具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

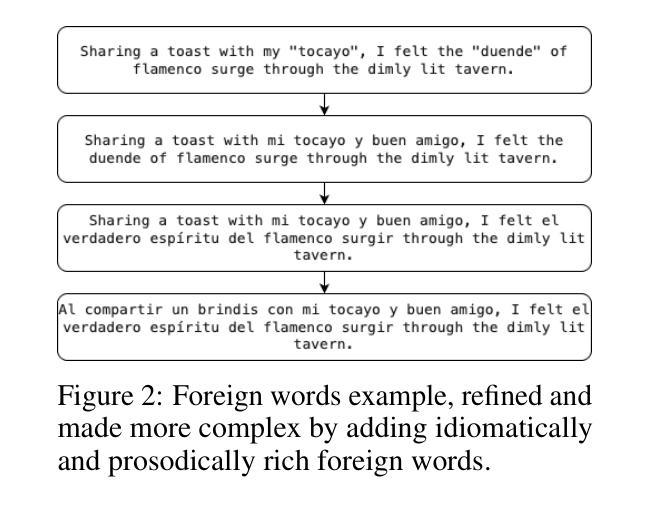
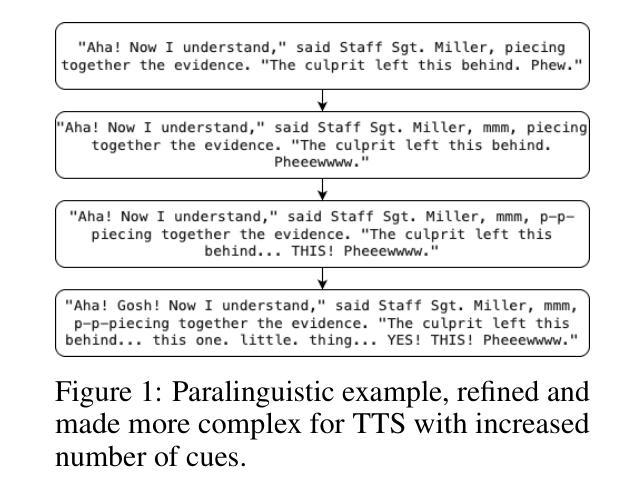
EmergentTTS-Eval: Evaluating TTS Models on Complex Prosodic, Expressiveness, and Linguistic Challenges Using Model-as-a-Judge
Authors:Ruskin Raj Manku, Yuzhi Tang, Xingjian Shi, Mu Li, Alex Smola
Text-to-Speech (TTS) benchmarks often fail to capture how well models handle nuanced and semantically complex text. Building on $\textit{EmergentTTS}$, we introduce $\textit{EmergentTTS-Eval}$, a comprehensive benchmark covering six challenging TTS scenarios: emotions, paralinguistics, foreign words, syntactic complexity, complex pronunciation (e.g. URLs, formulas), and questions. Crucially, our framework automates both test-case generation and evaluation, making the benchmark easily extensible. Starting from a small set of human-written seed prompts, we iteratively extend them using LLMs to target specific structural, phonetic and prosodic challenges, resulting in 1,645 diverse test cases. Moreover, we employ a model-as-a-judge approach, using a Large Audio Language Model (LALM) to assess the speech across multiple dimensions such as expressed emotion, prosodic, intonational, and pronunciation accuracy. We evaluate state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary TTS systems, such as 11Labs, Deepgram, and OpenAI’s 4o-mini-TTS, on EmergentTTS-Eval, demonstrating its ability to reveal fine-grained performance differences. Results show that the model-as-a-judge approach offers robust TTS assessment and a high correlation with human preferences. We open source the evaluation $\href{https://github.com/boson-ai/EmergentTTS-Eval-public}{code}$ and the $\href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/bosonai/EmergentTTS-Eval}{dataset}$.
文本转语音(TTS)基准测试通常无法捕捉模型处理微妙和语义复杂文本的能力。基于$\textit{EmergentTTS}$,我们推出了$\textit{EmergentTTS-Eval}$,这是一个涵盖六种具有挑战性TTS场景的全面基准测试:情感、副语言、外来词、句法复杂性、复杂发音(例如:URLs、公式)以及问题。我们的框架可以自动进行测试用例生成和评估,使得基准测试易于扩展。我们从一组人类写入的种子提示开始,通过迭代使用大型语言模型(LLMs)来针对特定的结构、语音和韵律挑战,从而生成了1645个多样化的测试用例。此外,我们采用模型作为法官的方法,使用大型音频语言模型(LALM)来评估语音的多个维度,如表达的情感、韵律、语调以及发音准确性等。我们在EmergentTTS-Eval上评估了先进的开源和专有TTS系统,如11Labs、Deepgram和OpenAI的4o-mini-TTS,展示了其揭示细微性能差异的能力。结果表明,模型作为法官的方法为TTS评估提供了稳健性,与人类偏好高度相关。我们公开了评估代码和数据集,分别位于$\href{https://github.com/boson-ai/EmergentTTS-Eval-public}{此处}$和$\href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/bosonai/EmergentTTS-Eval}{此处}$。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新兴TTS评测框架研究旨在克服现有TTS基准测试无法准确评估模型处理细微复杂文本的问题。该研究引入了EmergentTTS-Eval评测框架,涵盖情感、副语言、外来词、句法复杂性、复杂发音(如网址、公式)和问题等六个挑战场景。该框架实现了测试案例生成和评估的自动化,增强了可扩展性。通过使用大型音频语言模型评估语音的各种维度(如表达情感、语调等),其性能在评估顶尖开源和专有TTS系统时得到了验证。此研究为评估TTS性能提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
- EmergentTTS-Eval是一个全面的TTS评测框架,解决了现有基准测试无法充分评估模型处理复杂文本的问题。
- 该框架涵盖了六个挑战性的TTS场景,包括情感、副语言等。
- 通过自动化测试案例生成和评估,提高了基准测试的效率和可扩展性。
- 利用大型音频语言模型(LALM)作为评委,从多个维度评估语音质量。
- 在顶尖开源和专有TTS系统上的实验验证了EmergentTTS-Eval的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

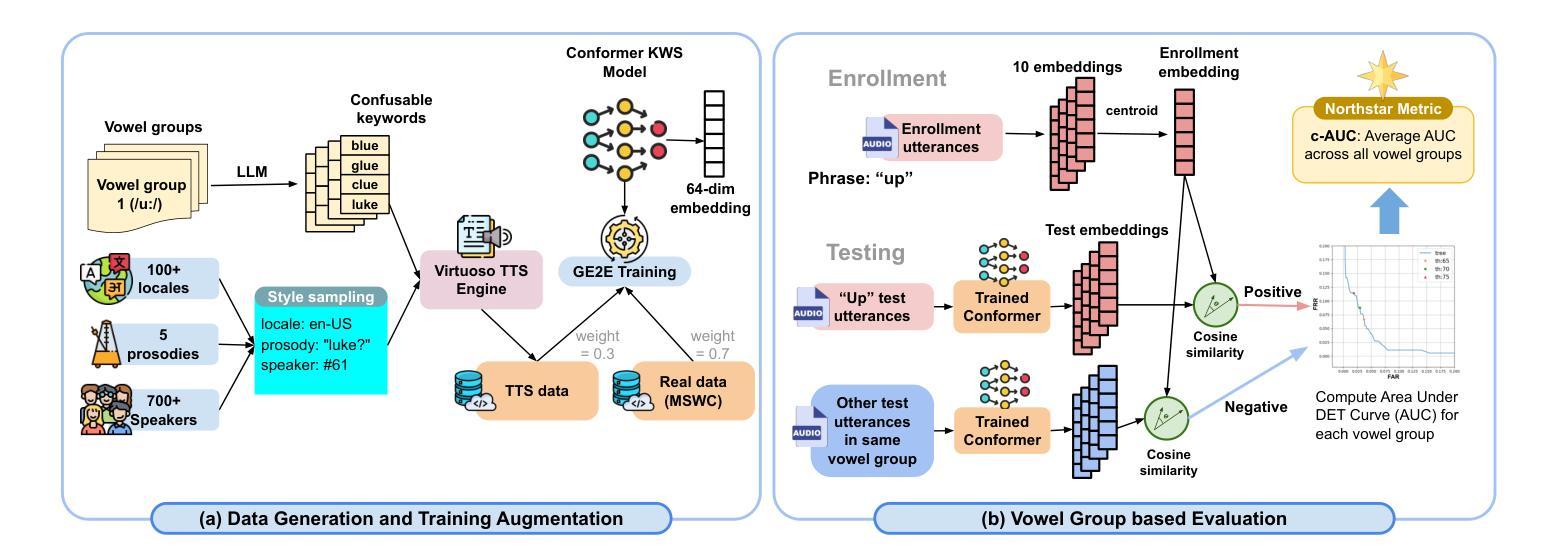
LLM-Synth4KWS: Scalable Automatic Generation and Synthesis of Confusable Data for Custom Keyword Spotting
Authors:Pai Zhu, Quan Wang, Dhruuv Agarwal, Kurt Partridge
Custom keyword spotting (KWS) allows detecting user-defined spoken keywords from streaming audio. This is achieved by comparing the embeddings from voice enrollments and input audio. State-of-the-art custom KWS models are typically trained contrastively using utterances whose keywords are randomly sampled from training dataset. These KWS models often struggle with confusing keywords, such as “blue” versus “glue”. This paper introduces an effective way to augment the training with confusable utterances where keywords are generated and grouped from large language models (LLMs), and speech signals are synthesized with diverse speaking styles from text-to-speech (TTS) engines. To better measure user experience on confusable KWS, we define a new northstar metric using the average area under DET curve from confusable groups (c-AUC). Featuring high scalability and zero labor cost, the proposed method improves AUC by 3.7% and c-AUC by 11.3% on the Speech Commands testing set.
自定义关键词识别(KWS)允许从流式音频中检测用户定义的语音关键词。这是通过比较语音注册和输入音频的嵌入来实现的。目前最先进的自定义KWS模型通常使用随机采样自训练数据集的语音来进行对比训练。这些KWS模型经常在与易混淆关键词对抗时遇到困境,例如“蓝色”与“胶水”。本文介绍了一种通过使用大型语言模型(LLM)生成并组合关键词,并用文本到语音(TTS)引擎合成具有不同说话风格的语音信号来增强训练的有效方法。为了更好地衡量用户对易混淆KWS的体验,我们使用来自混淆组的DET曲线平均面积(c-AUC)定义了一个新的北极星指标。该方法具有高度的可扩展性和零人工成本的特点,在Speech Commands测试集上提高了AUC 3.7%和c-AUC 11.3%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了通过合成语音信号和大型语言模型(LLM)生成混淆关键词来增强对比式训练关键词识别模型的方法。通过引入新的评估指标c-AUC,该方法提高了模型的性能,提高了AUC值3.7%,同时改善了模型在混淆关键词上的表现,提升了c-AUC值达11.3%。此方法具有高可扩展性和零人工成本的优势。
关键见解
- 介绍了通过对比语音嵌入进行自定义关键词识别(KWS)的方法。
- 训练先进的KWS模型时,通常使用随机采样的关键词训练集进行对比训练。
- 现有模型面临混淆关键词的挑战,如”蓝色”与”胶水”。
- 提出了一种通过大型语言模型(LLM)生成并分组关键词的合成语音信号的训练增强方法。
- 使用文本到语音(TTS)引擎合成不同说话风格的语音信号。
- 为了更好地衡量用户对混淆KWS的体验,引入了使用混淆组平均检测曲线下的面积(c-AUC)作为新的评估指标。
点此查看论文截图



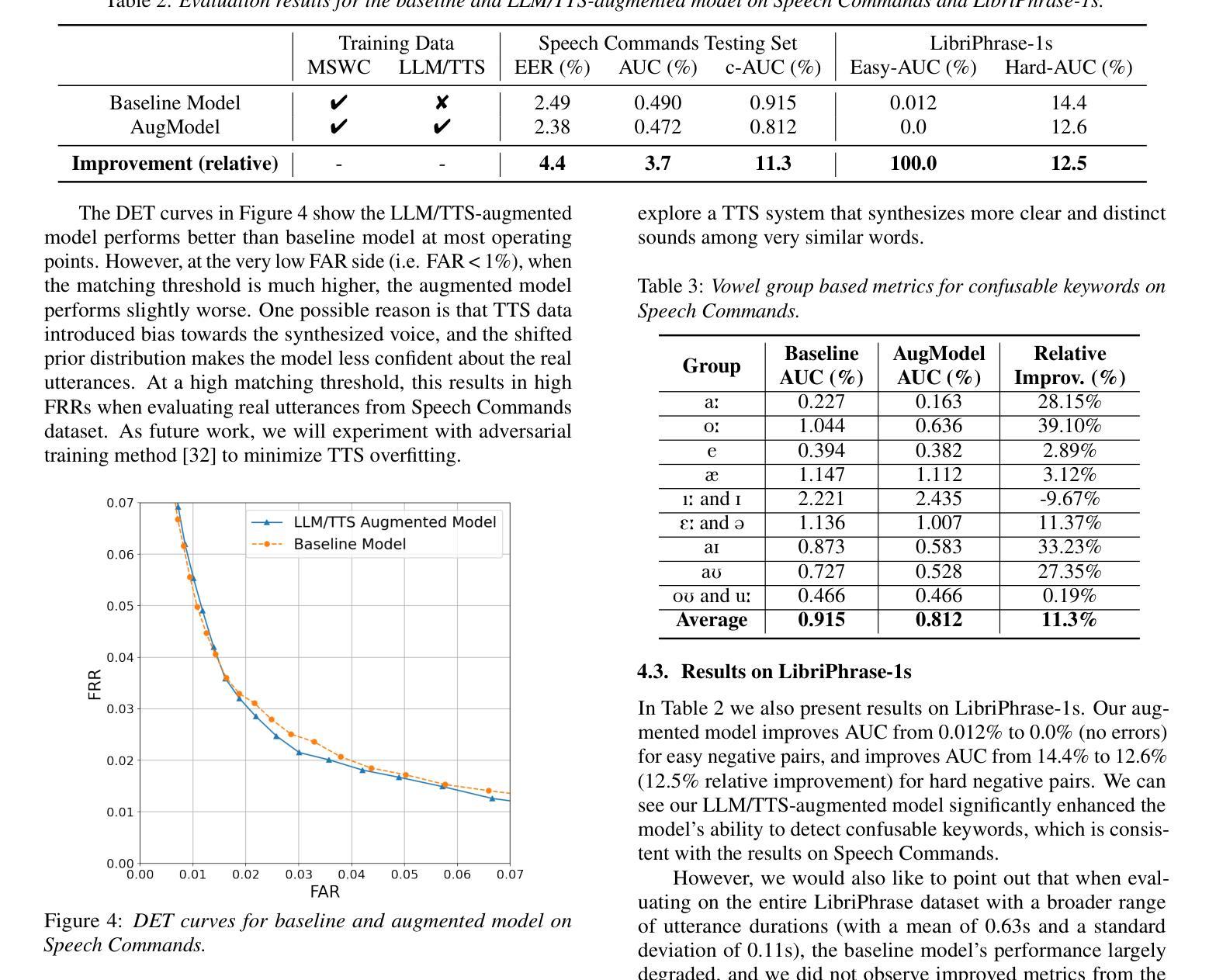
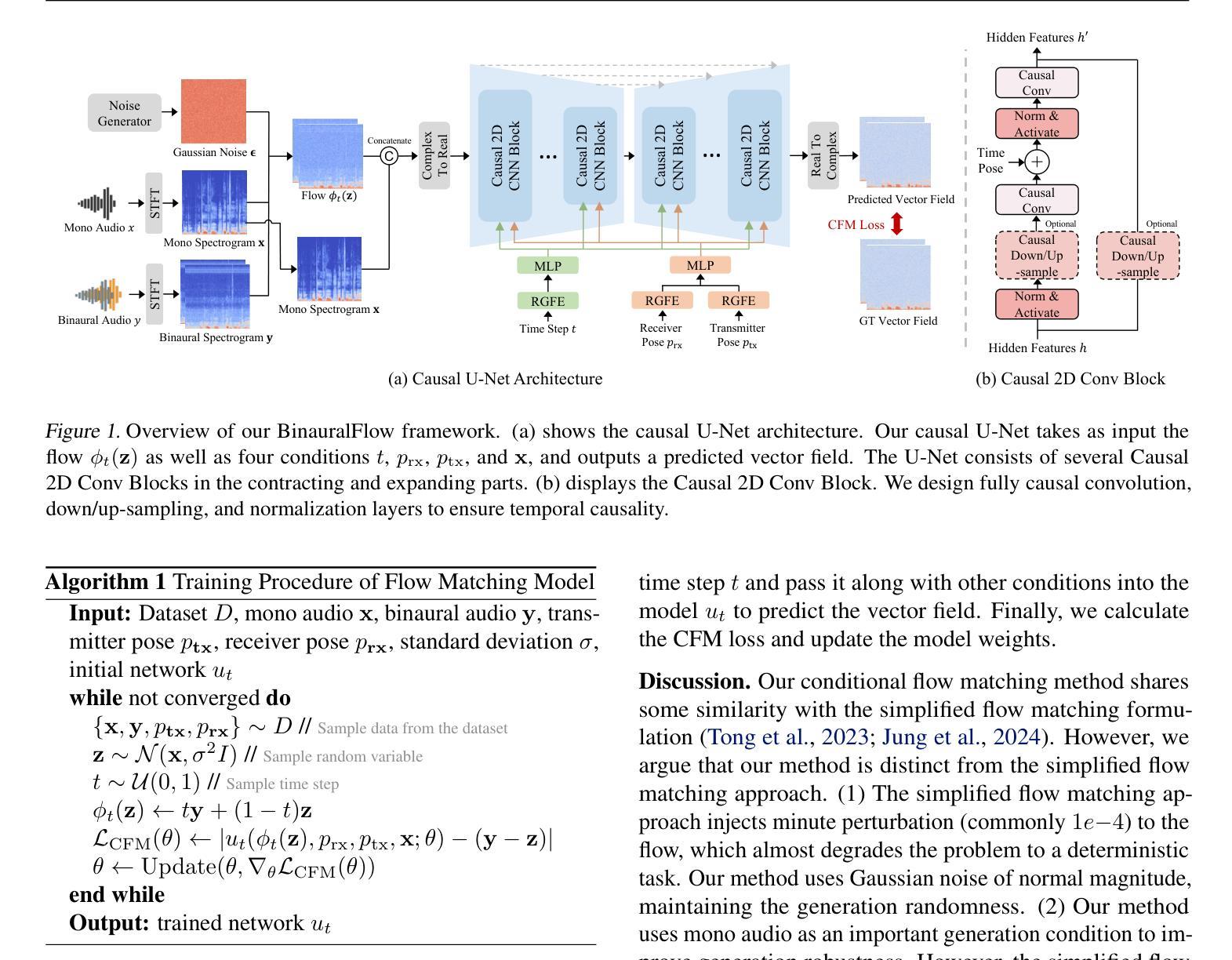
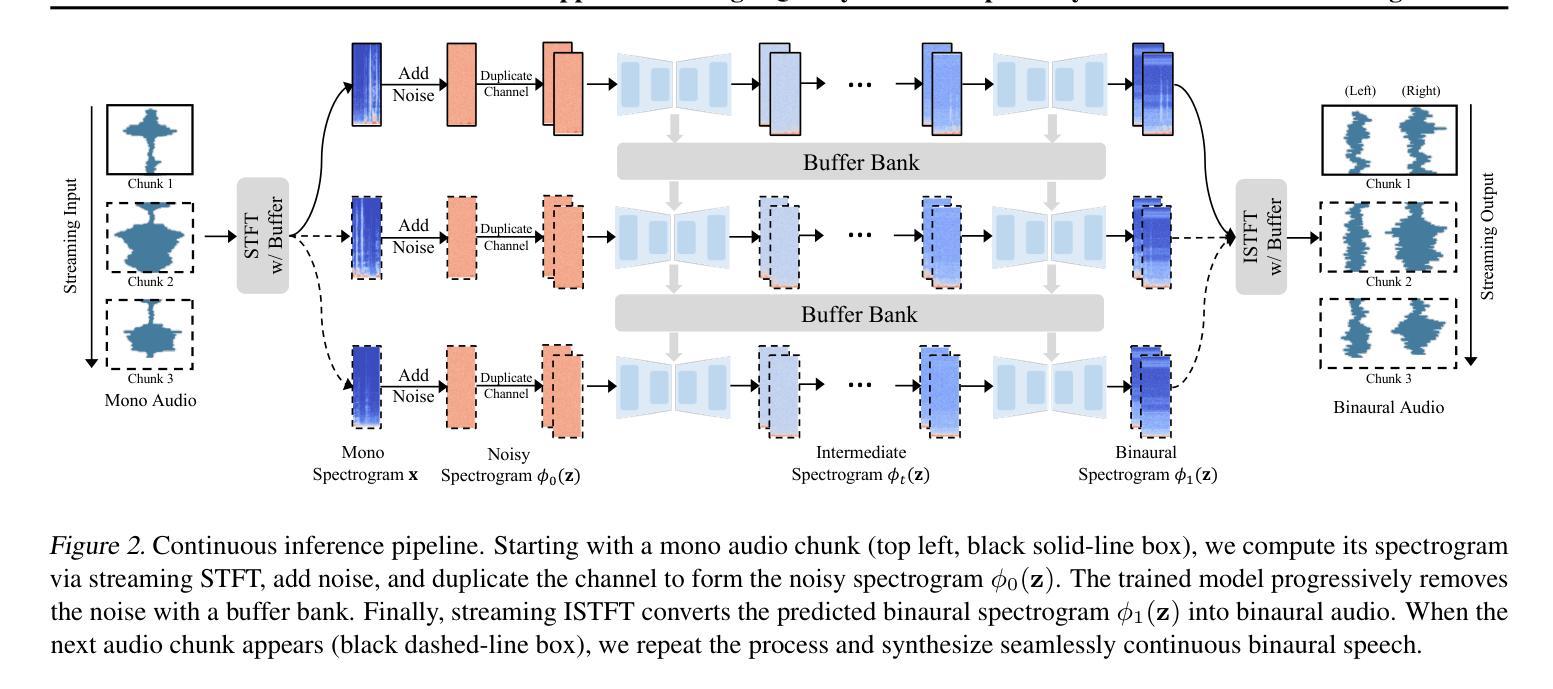
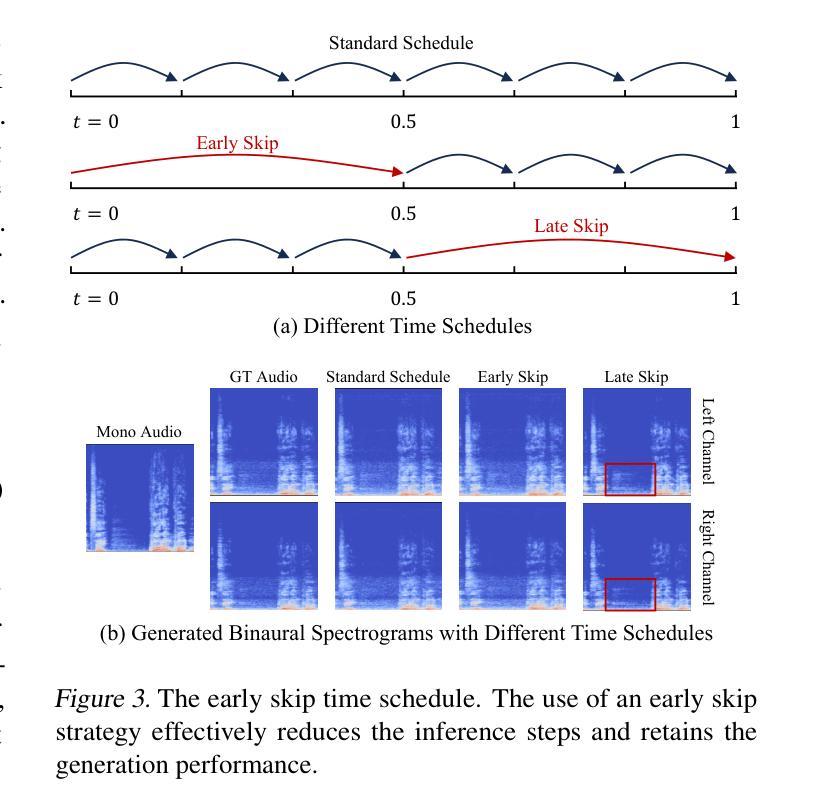
BinauralFlow: A Causal and Streamable Approach for High-Quality Binaural Speech Synthesis with Flow Matching Models
Authors:Susan Liang, Dejan Markovic, Israel D. Gebru, Steven Krenn, Todd Keebler, Jacob Sandakly, Frank Yu, Samuel Hassel, Chenliang Xu, Alexander Richard
Binaural rendering aims to synthesize binaural audio that mimics natural hearing based on a mono audio and the locations of the speaker and listener. Although many methods have been proposed to solve this problem, they struggle with rendering quality and streamable inference. Synthesizing high-quality binaural audio that is indistinguishable from real-world recordings requires precise modeling of binaural cues, room reverb, and ambient sounds. Additionally, real-world applications demand streaming inference. To address these challenges, we propose a flow matching based streaming binaural speech synthesis framework called BinauralFlow. We consider binaural rendering to be a generation problem rather than a regression problem and design a conditional flow matching model to render high-quality audio. Moreover, we design a causal U-Net architecture that estimates the current audio frame solely based on past information to tailor generative models for streaming inference. Finally, we introduce a continuous inference pipeline incorporating streaming STFT/ISTFT operations, a buffer bank, a midpoint solver, and an early skip schedule to improve rendering continuity and speed. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our method over SOTA approaches. A perceptual study further reveals that our model is nearly indistinguishable from real-world recordings, with a $42%$ confusion rate.
双耳渲染旨在根据单声道音频和说话人及听众的位置合成模仿自然听觉的双耳音频。尽管已经提出了许多方法来解决这一问题,但它们在处理渲染质量和流式推断方面遇到了困难。合成高质量的双耳音频,要求与真实世界录音无法区分,需要对双耳线索、房间回音和环境声音进行精确建模。此外,实际应用要求流式推理。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种基于流匹配的流式双耳语音合成框架,称为BinauralFlow。我们认为双耳渲染是一个生成问题,而不是一个回归问题,并设计了一个条件流匹配模型来渲染高质量音频。此外,我们设计了一种因果U-Net架构,该架构仅根据过去的信息来估计当前音频帧,以针对流式推断定制生成模型。最后,我们引入了一个连续的推理管道,结合了流式STFT/ISTFT操作、缓冲区银行、中点解算器和早期跳过调度,以提高渲染的连续性和速度。定量和定性评估表明,我们的方法优于最新方法。感知研究进一步表明,我们的模型与真实世界录音几乎无法区分,混淆率为42%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025, 18 pages
Summary
本文介绍了基于流的匹配流技术的双耳音频合成框架BinauralFlow。该方法将双耳渲染视为生成问题而非回归问题,通过设计条件流匹配模型来合成高质量音频。同时,采用因果U-Net架构实现流式推理,并引入连续推理管道提高渲染的连续性和速度。实验证明,该方法在音质和流式推理方面均优于现有方法,与真实录音的混淆率仅为42%。
Key Takeaways
- BinauralFlow是一个基于流的匹配流技术的双耳音频合成框架,旨在合成高质量的双耳音频。
- 该方法将双耳渲染视为生成问题,通过设计条件流匹配模型来合成高质量音频。
- 采用了因果U-Net架构来实现流式推理,适应实际应用的需求。
- 引入了连续推理管道,包括流式STFT/ISTFT操作、缓冲区银行、中点解算器和早期跳过调度,以提高渲染的连续性和速度。
- 定量和定性评估表明,BinauralFlow在音质和流式推理方面均优于现有方法。
- 感知研究表明,该模型的音频与真实录音的混淆率仅为42%,难以区分。
- BinauralFlow对于双耳音频合成领域的进步具有重要意义,有望在虚拟现实、增强现实等领域得到广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图

Nexus: An Omni-Perceptive And -Interactive Model for Language, Audio, And Vision
Authors:Che Liu, Yingji Zhang, Dong Zhang, Weijie Zhang, Chenggong Gong, Haohan Li, Yu Lu, Shilin Zhou, Yue Lu, Ziliang Gan, Ziao Wang, Junwei Liao, Haipang Wu, Ji Liu, André Freitas, Qifan Wang, Zenglin Xu, Rongjuncheng Zhang, Yong Dai
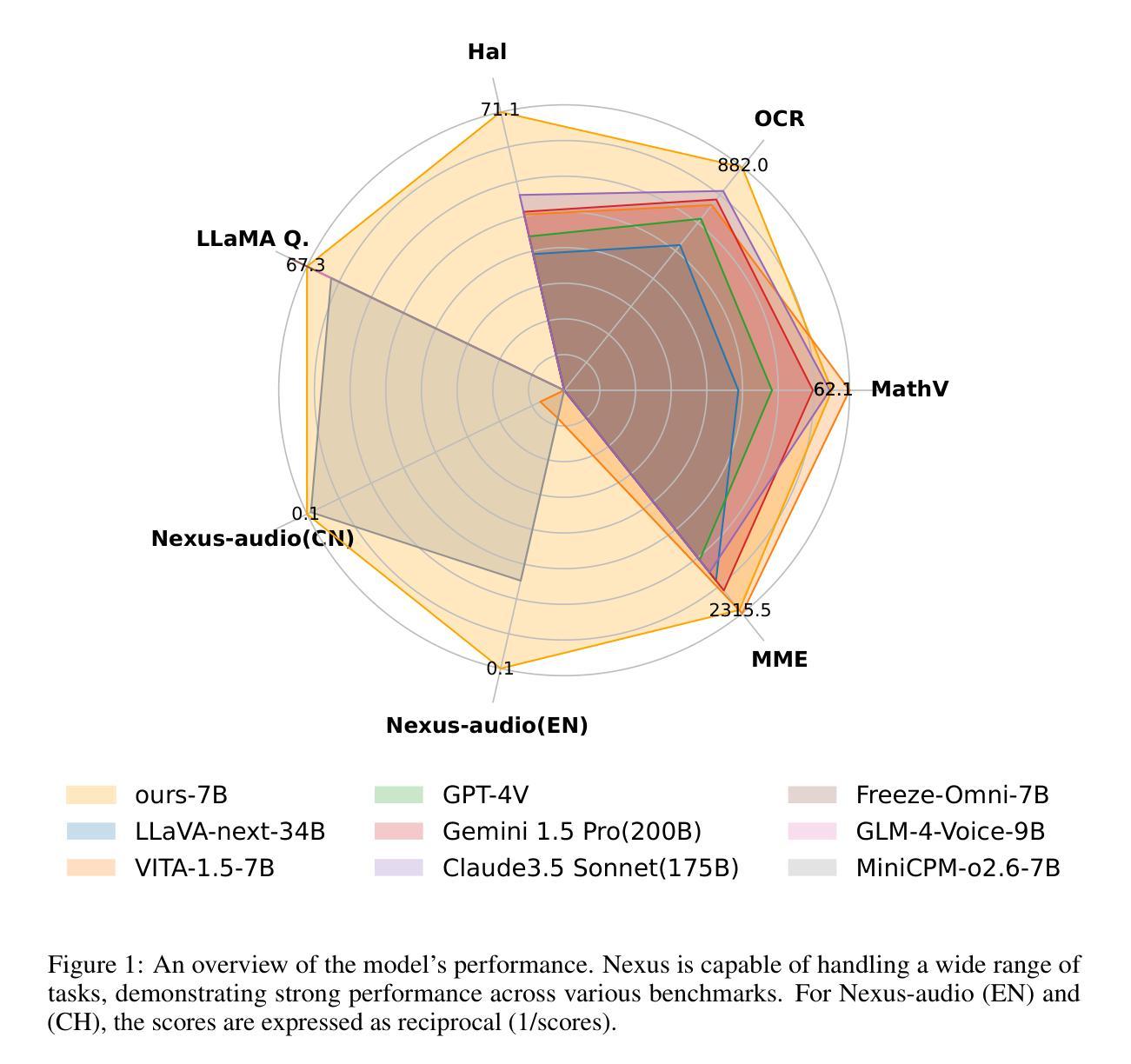
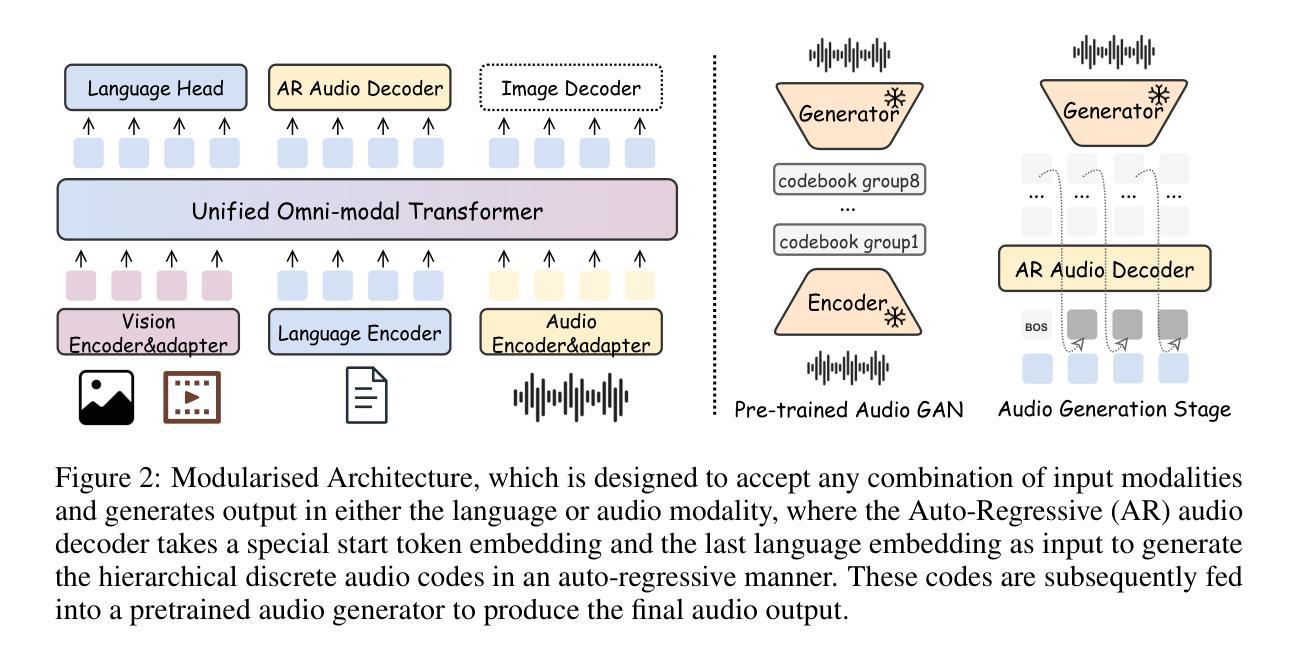
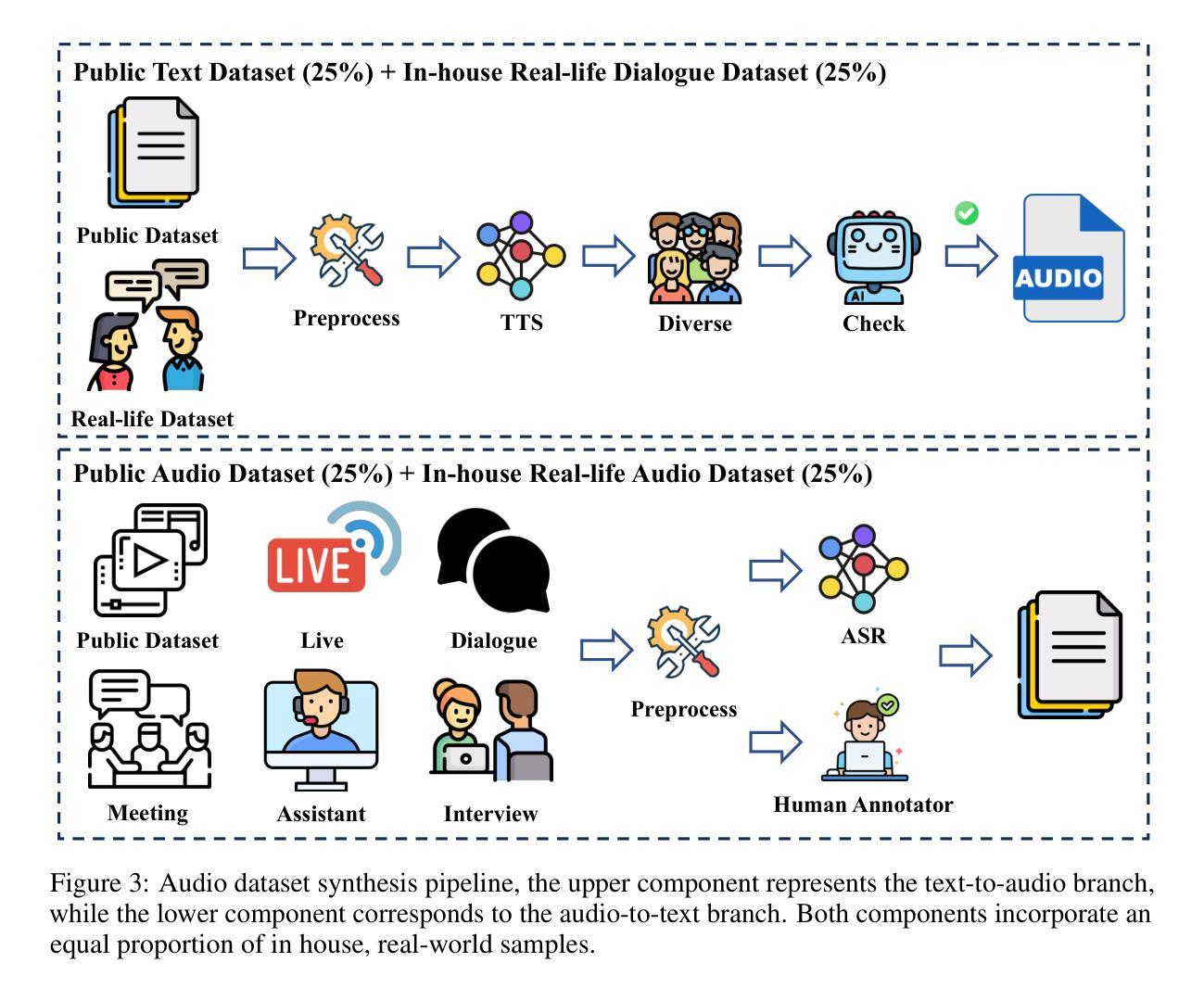
This work proposes an industry-level omni-modal large language model (LLM) pipeline that integrates auditory, visual, and linguistic modalities to overcome challenges such as limited tri-modal datasets, high computational costs, and complex feature alignments. Our pipeline consists of three main components: First, a modular framework enabling flexible configuration of various encoder-LLM-decoder architectures. Second, a lightweight training strategy that pre-trains audio-language alignment on the state-of-the-art vision-language model Qwen2.5-VL, thus avoiding the costly pre-training of vision-specific modalities. Third, an audio synthesis pipeline that generates high-quality audio-text data from diverse real-world scenarios, supporting applications such as Automatic Speech Recognition and Speech-to-Speech chat. To this end, we introduce an industry-level omni-modal LLM, Nexus. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of our pipeline, yielding the following key findings:(1) In the visual understanding task, Nexus exhibits superior performance compared with its backbone model - Qwen2.5-VL-7B, validating the efficiency of our training strategy. (2) Within the English Spoken Question-Answering task, the model achieves better accuracy than the same-period competitor (i.e, MiniCPM-o2.6-7B) in the LLaMA Q. benchmark. (3) In our real-world ASR testset, Nexus achieves outstanding performance, indicating its robustness in real scenarios. (4) In the Speech-to-Text Translation task, our model outperforms Qwen2-Audio-Instruct-7B. (5) In the Text-to-Speech task, based on pretrained vocoder (e.g., Fishspeech1.4 or CosyVoice2.0), Nexus is comparable to its backbone vocoder on Seed-TTS benchmark. (6) An in-depth analysis of tri-modal alignment reveals that incorporating the audio modality enhances representational alignment between vision and language.
本文提出了一种行业级的跨模态大型语言模型(LLM)管道,该管道融合了听觉、视觉和语言模式,以克服如有限的三模态数据集、高计算成本和复杂的特征对齐等挑战。我们的管道主要由三个部分组成:首先,一个模块化框架,能够灵活配置各种编码器-LLM-解码器架构。其次,一种轻量级的训练策略,通过在最先进的视觉语言模型Qwen2.5-VL上进行音频语言对齐的预训练,从而避免了针对特定视觉模式的昂贵预训练。最后,一个音频合成管道,用于从各种真实场景生成高质量音频文本数据,支持如自动语音识别和语音到语音聊天等应用。为此,我们引入了一种行业级的跨模态LLM,Nexus。大量实验验证了我们的管道的有效性,得出以下关键发现:(1)在视觉理解任务中,Nexus相较于其骨干模型Qwen2.5-VL-7B表现出卓越的性能,验证了我们的训练策略的有效性。(2)在英语口语问答任务中,该模型在LLaMA Q. benchmark上达到了比同期竞争对手(即MiniCPM-o2.6-7B)更高的准确性。(3)在我们的真实世界ASR测试集上,Nexus表现出卓越的性能,表明其在真实场景中的稳健性。(4)在语音到文本翻译任务中,我们的模型优于Qwen2-Audio-Instruct-7B。(5)在文本到语音任务中,基于预训练的vocoder(例如Fishspeech1.4或CosyVoice2.0),Nexus在Seed-TTS benchmark上的表现与其骨干vocoder相当。(6)对三模态对齐的深入分析表明,融入音频模式增强了视觉和语言之间的代表性对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种跨行业的多模态大型语言模型(LLM)管道,该管道融合了听觉、视觉和语言学三大模态,以应对如有限的三模态数据集、高计算成本和复杂特征对齐等挑战。该管道包括三个主要组件:一个支持各种编码器-LLM-解码器架构灵活配置的模块化框架;一种基于前沿视觉语言模型Qwen2.5-VL的轻量级训练策略,避免了昂贵的视觉特定模态预训练;以及一个从各种现实场景生成高质量音频文本数据的声音合成管道。引进的产业级多模态LLM Nexus经过广泛实验验证,在多项任务中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个多模态的大型语言模型(LLM)管道,集成听觉、视觉和语言学三大模态。
- 管道包含模块化框架、轻量级训练策略和音频合成管道三个主要组件。
- Nexus模型在视觉理解任务中表现出卓越性能,相较于其基础模型Qwen2.5-VL-7B有显著提升。
- 在英语口语问答任务中,Nexus模型达到同期竞品之上的准确性。
- 在实际场景的自动语音识别(ASR)测试集中,Nexus表现出出色性能,体现了其在真实场景中的稳健性。
- 在语音到文本翻译任务中,Nexus模型超越了Qwen2-Audio-Instruct-7B。
点此查看论文截图

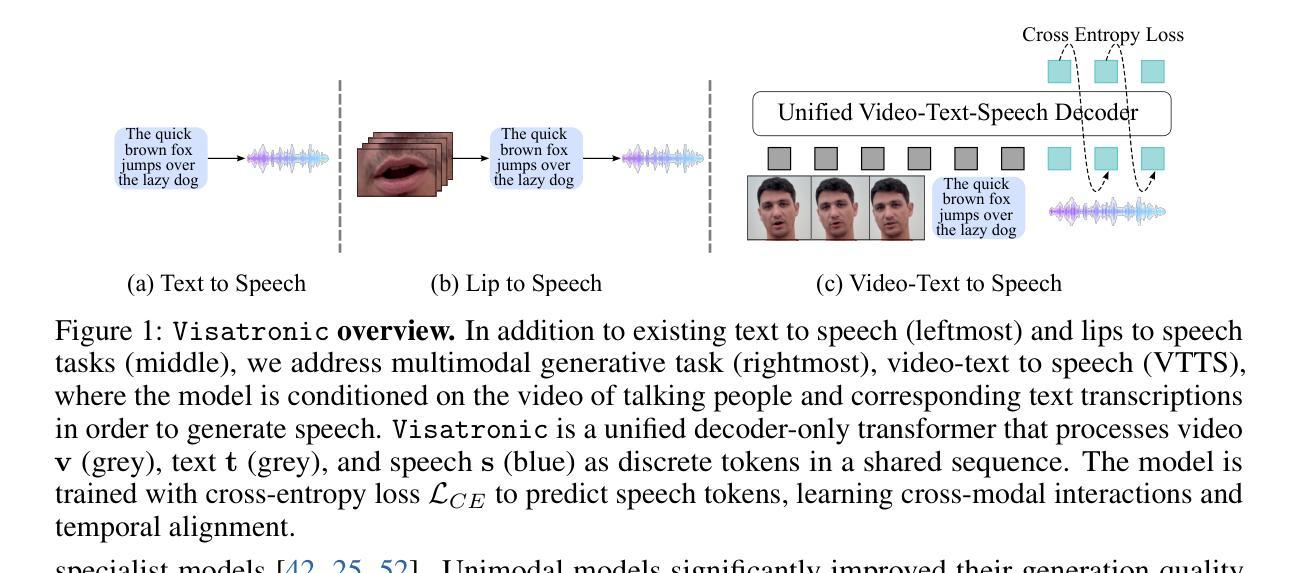
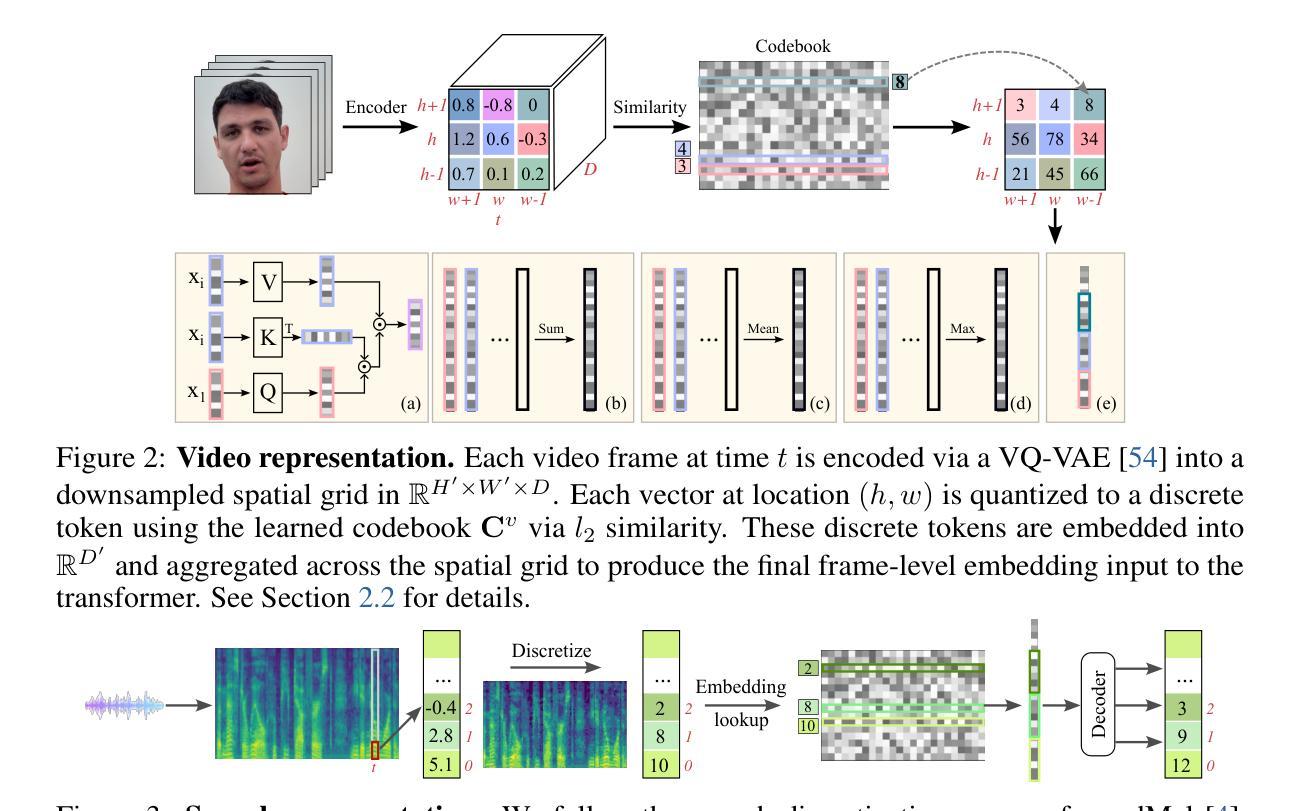
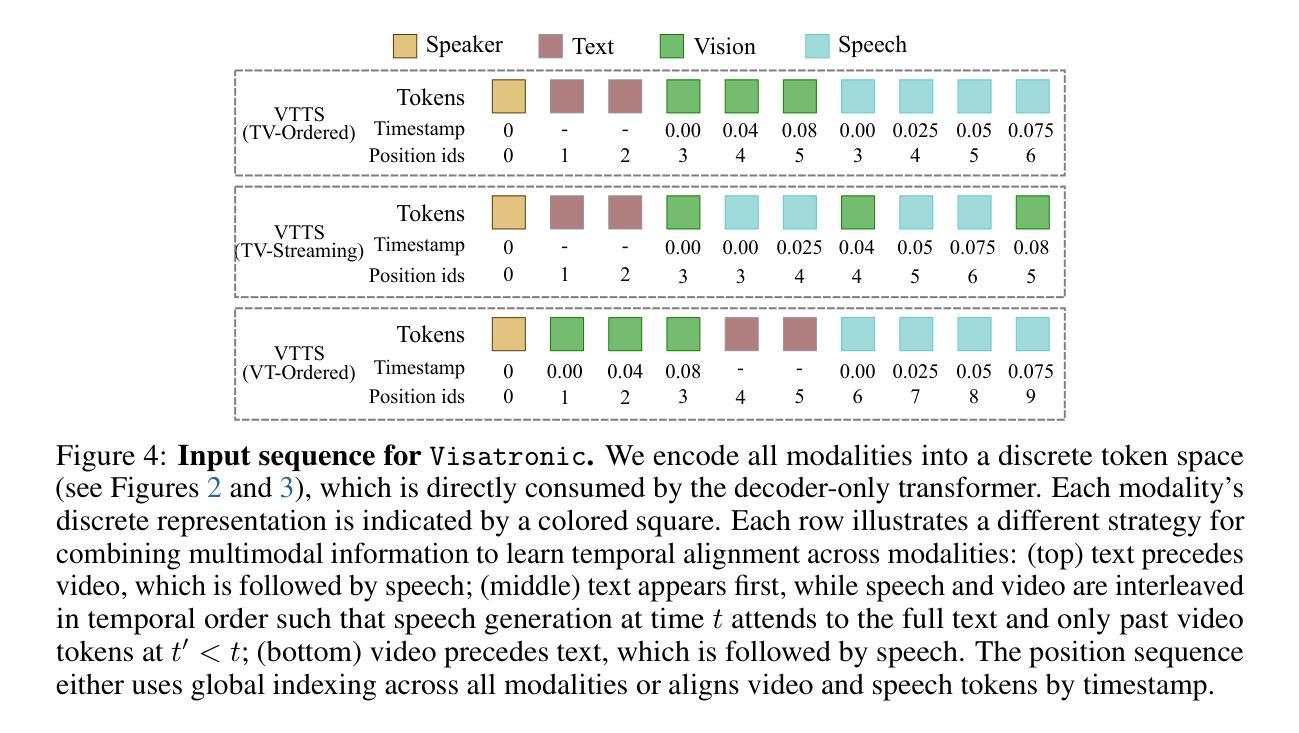
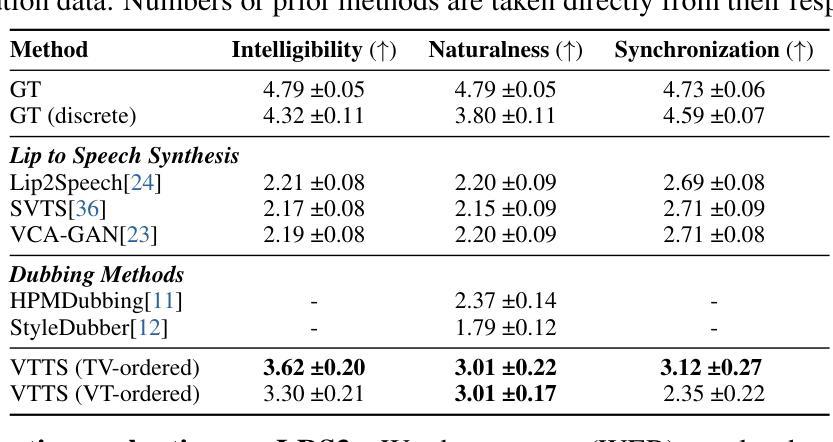
Visatronic: A Multimodal Decoder-Only Model for Speech Synthesis
Authors:Akshita Gupta, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Karren Dai Yang, Richard He Bai, Zakaria Aldeneh, Navdeep Jaitly
The rapid progress of foundation models and large language models (LLMs) has fueled significantly improvement in the capabilities of machine learning systems that benefit from mutlimodal input data. However, existing multimodal models are predominantly built on top of pre-trained LLMs, which can limit accurate modeling of temporal dependencies across other modalities and thus limit the model’s ability to jointly process and leverage multimodal inputs. To specifically investigate the alignment of text, video, and speech modalities in LLM-style (decoder-only) models, we consider a simplified multimodal generation task, Video-Text to Speech (VTTS): speech generation conditioned on both its corresponding text and video of talking people. The ultimate goal is to generate speech that not only follows the text but also aligns temporally with the video and is consistent with the facial expressions. In this paper, we first introduce Visatronic, a unified multimodal decoder-only transformer model that adopts an LLM-style architecture to embed visual, textual, and speech inputs into a shared subspace, treating all modalities as temporally aligned token streams. Next, we carefully explore different token mixing strategies to understand the best way to propagate information from the steps where video and text conditioning is input to the steps where the audio is generated. We extensively evaluate Visatronic on the challenging VoxCeleb2 dataset and demonstrate zero-shot generalization to LRS3, where Visatronic, trained on VoxCeleb2, achieves a 4.5% WER, outperforming prior SOTA methods trained only on LRS3, which report a 21.4% WER. Additionally, we propose a new objective metric, TimeSync, specifically designed to measure phoneme-level temporal alignment between generated and reference speech, further ensuring synchronization quality. Demo: https://apple.github.io/visatronic-demo/
随着基础模型和大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,受益于多模态输入数据的机器学习系统的能力得到了显著提升。然而,现有的多模态模型主要是建立在预训练LLM之上,这可能会限制跨其他模态的时间依赖性的准确建模,从而限制模型联合处理并利用多模态输入的能力。为了专门研究LLM风格(仅解码器)模型中文字、视频和语音模态的对齐问题,我们考虑了一个简化的多模态生成任务,即视频文本转语音(VTTS):语音生成既取决于相应的文本,又取决于人们讲话的视频。最终目标是生成不仅遵循文本而且与视频在时间上有对齐的语音,并与面部表情保持一致。在本文中,我们首先介绍了Visatronic,这是一个统一的多模态仅解码器transformer模型,它采用LLM风格架构将视觉、文本和语音输入嵌入到共享子空间中,将所有模态视为时间对齐的令牌流。接下来,我们仔细探索了不同的令牌混合策略,以了解从视频和文本调节步骤向生成音频步骤传播信息的最佳方式。我们在具有挑战性的VoxCeleb2数据集上对Visatronic进行了广泛评估,并展示了零样本泛化到LRS3的能力。在VoxCeleb2上训练的Visatronic在LRS3上实现了4.5%的WER(词错误率),优于仅针对LRS3进行训练的先前最佳方法(报告了21.4%的WER)。此外,我们还提出了一种新的客观指标TimeSync,专门用于测量生成语音和参考语音之间的音素级时间对齐,进一步确保同步质量。演示地址:https://apple.github.io/visatronic-demo/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着基础模型和大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,多模态输入数据对机器学习系统的能力提升显著。然而,现有的多模态模型主要依赖于预训练LLM,限制了跨其他模态的时间依赖性的准确建模以及多模态输入的联合处理。为此,我们研究文本、视频和语音模态的对齐问题,在LLM风格(仅解码器)模型中考虑简化的多模态生成任务——视频文本转语音(VTTS)。目标是生成不仅遵循文本还与时间视频对齐且符合面部表情的语音。本文介绍Visatronic模型,采用LLM风格架构嵌入视觉、文本和语音输入到共享子空间,将所有模态视为时间对齐的令牌流。通过探索不同的令牌混合策略,我们在VoxCeleb2数据集上评估Visatronic,并展示零样本泛化至LRS3数据集的能力。Visatronic在VoxCeleb2上训练的模型达到4.5%的WER,优于仅在LRS3上训练的先前最佳方法(报告为21.4%的WER)。我们还提出新的客观指标TimeSync,专门用于测量生成语音和参考语音之间的音素级时间对齐,以确保同步质量。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态模型的快速发展受益于基础模型和大语言模型(LLM)的进步。
- 当前多模态模型主要基于预训练LLM,存在对跨模态时间依赖性建模的限制。
- 研究聚焦于文本、视频和语音模态的对齐问题,引入视频文本转语音(VTTS)任务作为研究焦点。
- Visatronic模型采用LLM风格架构处理多模态输入,实现视觉、文本和语音的嵌入。
- 通过不同的令牌混合策略探索,优化了信息从视频和文本输入步骤到音频生成步骤的传播。
- 在VoxCeleb2数据集上的评估显示Visatronic模型性能优越,并实现了零样本泛化至LRS3数据集。
点此查看论文截图