⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-31 更新
DA-VPT: Semantic-Guided Visual Prompt Tuning for Vision Transformers
Authors:Li Ren, Chen Chen, Liqiang Wang, Kien Hua
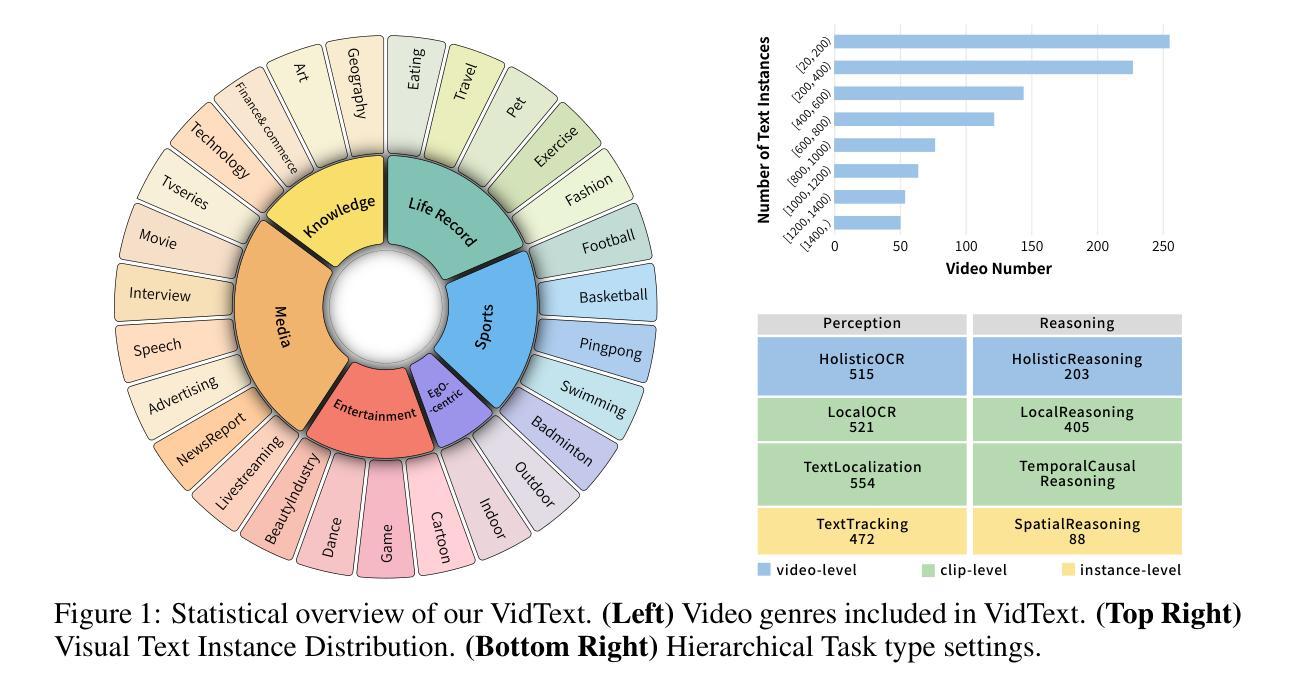
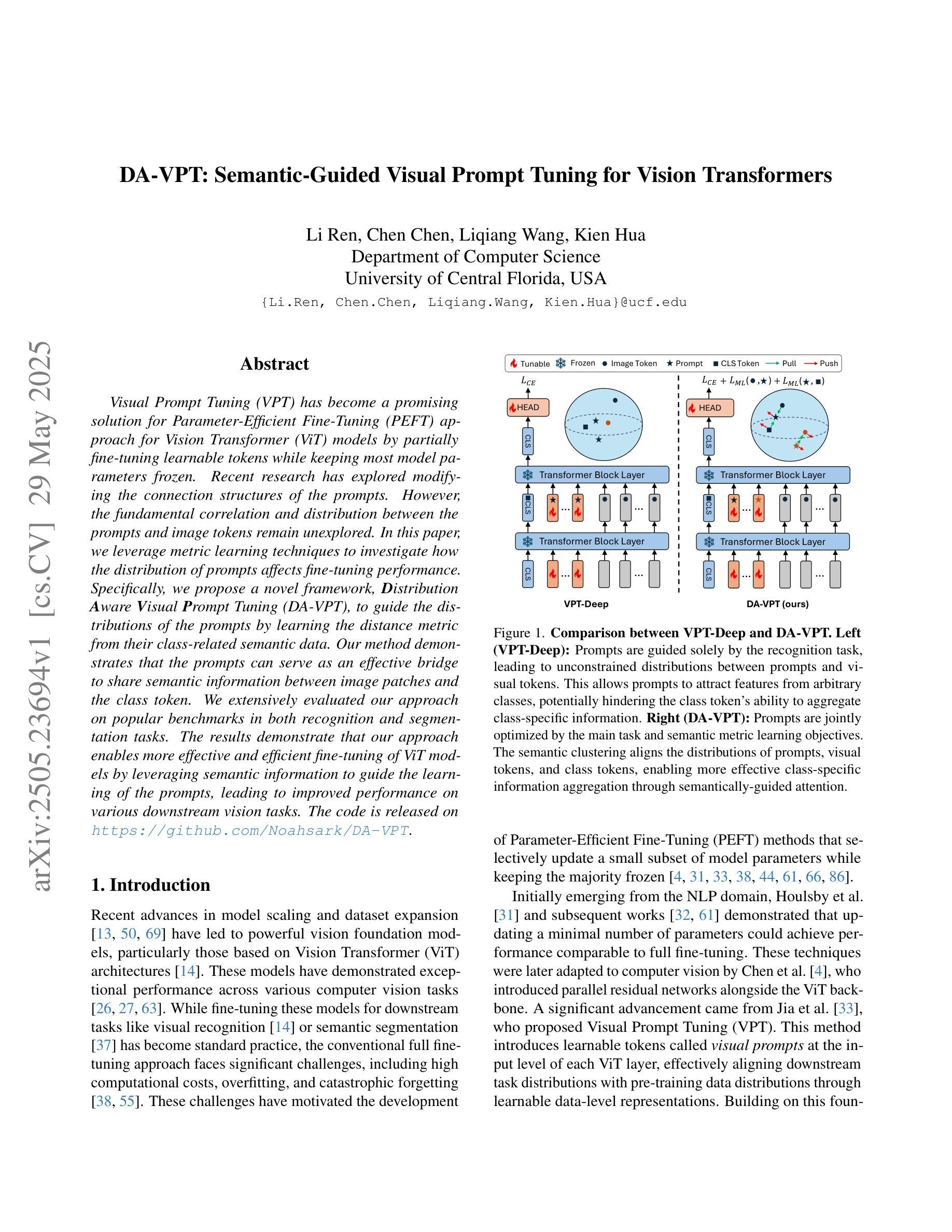
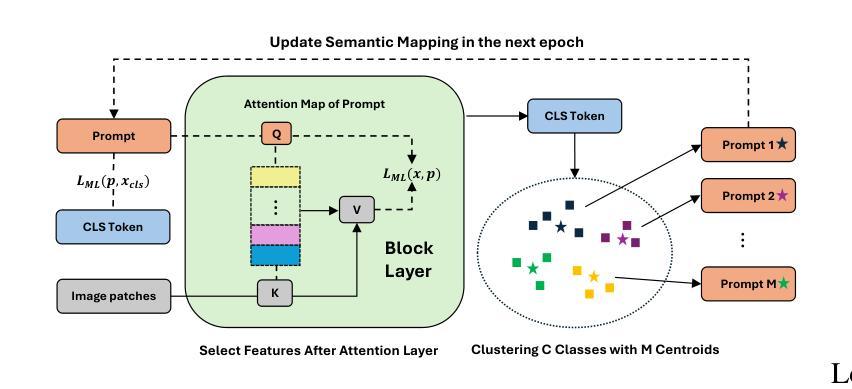
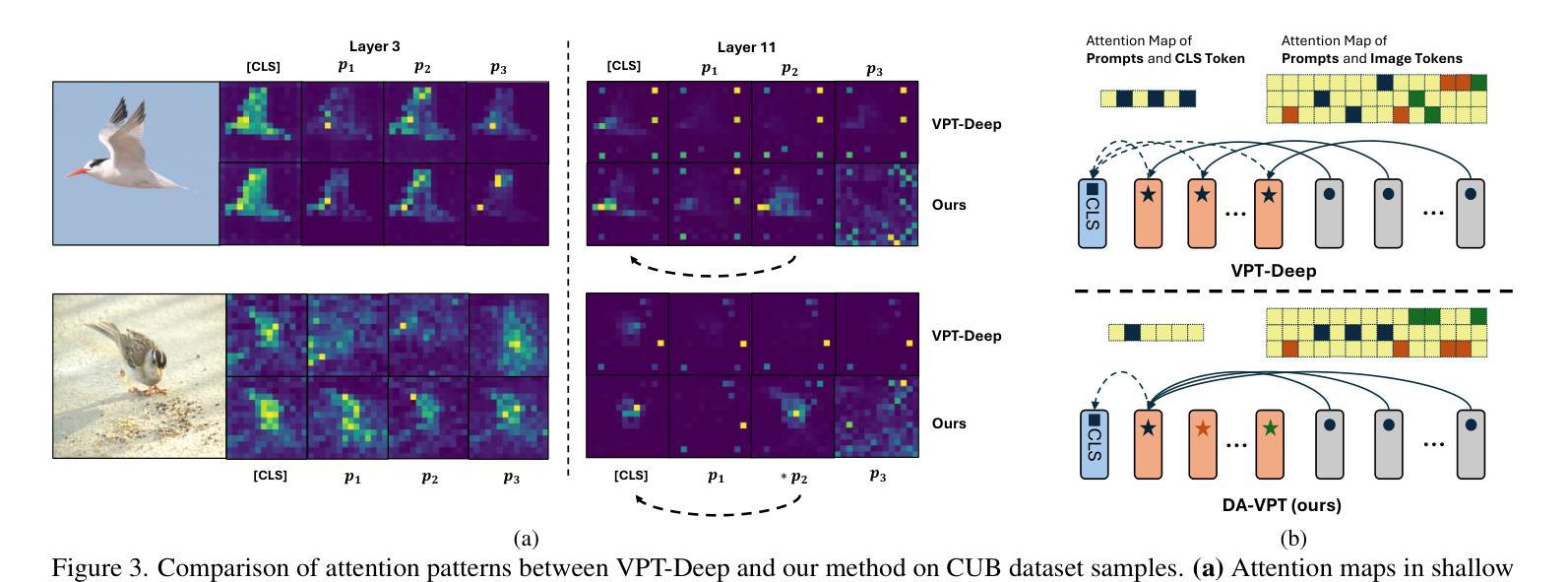
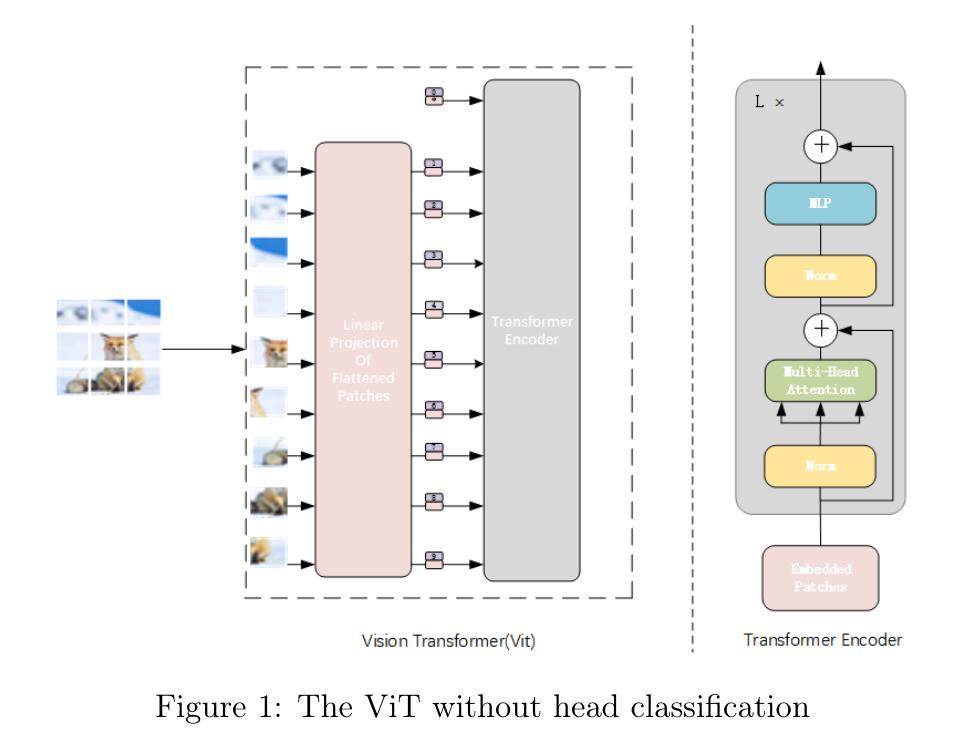
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) has become a promising solution for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) approach for Vision Transformer (ViT) models by partially fine-tuning learnable tokens while keeping most model parameters frozen. Recent research has explored modifying the connection structures of the prompts. However, the fundamental correlation and distribution between the prompts and image tokens remain unexplored. In this paper, we leverage metric learning techniques to investigate how the distribution of prompts affects fine-tuning performance. Specifically, we propose a novel framework, Distribution Aware Visual Prompt Tuning (DA-VPT), to guide the distributions of the prompts by learning the distance metric from their class-related semantic data. Our method demonstrates that the prompts can serve as an effective bridge to share semantic information between image patches and the class token. We extensively evaluated our approach on popular benchmarks in both recognition and segmentation tasks. The results demonstrate that our approach enables more effective and efficient fine-tuning of ViT models by leveraging semantic information to guide the learning of the prompts, leading to improved performance on various downstream vision tasks.
视觉提示微调(VPT)已成为一种有前景的解决方案,通过部分微调可学习令牌的同时保持大部分模型参数冻结,为视觉转换器(ViT)模型实现了参数高效的微调(PEFT)方法。最近的研究探索了修改提示的连接结构。然而,提示与图像令牌之间的基本关联和分布仍未被探索。在本文中,我们利用度量学习技术来研究提示分布对微调性能的影响。具体来说,我们提出了一种新型框架——分布感知视觉提示微调(DA-VPT),通过学习与其类别相关语义数据的距离度量来指导提示的分布。我们的方法表明,提示可以作为图像补丁和类别令牌之间共享语义信息的有效桥梁。我们在识别和分割任务的流行基准测试上全面评估了我们的方法。结果表明,通过利用语义信息来指导学习提示,我们的方法能够更有效地对ViT模型进行微调,并在各种下游视觉任务上实现性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
视觉提示微调(VPT)已成为一种有前景的解决方案,通过对学习标记进行部分微调来实现视觉变压器(ViT)模型的参数高效微调(PEFT)。本文利用度量学习技术,研究提示分布对微调性能的影响。提出了一种新的框架——分布感知视觉提示微调(DA-VPT),通过学习来自类相关语义数据的距离度量来指导提示分布。提示可以有效地作为图像补丁和类标记之间共享语义信息的桥梁。在识别和分割任务的流行基准测试中,该方法展示了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉提示微调(VPT)是一种针对Vision Transformer(ViT)模型的参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,通过部分微调学习标记来实现。
- 现有研究已探索了提示连接结构的修改,但提示与图像标记之间的基本关联和分布仍未被探索。
- 本文利用度量学习技术,提出了分布感知视觉提示微调(DA-VPT)框架,以指导与类相关语义数据的距离度量相关的提示分布。
- 提示可以有效地作为图像补丁和类标记之间共享语义信息的桥梁。
- 该方法通过在微调过程中利用语义信息来指导提示学习,实现了对ViT模型更有效的微调。
- 在多个下游视觉任务上的测试表明,该方法可以提高性能。
- 该研究为Visual Transformer模型的参数高效微调提供了新的视角和方法。
点此查看论文截图
Deep Modeling and Optimization of Medical Image Classification
Authors:Yihang Wu, Muhammad Owais, Reem Kateb, Ahmad Chaddad
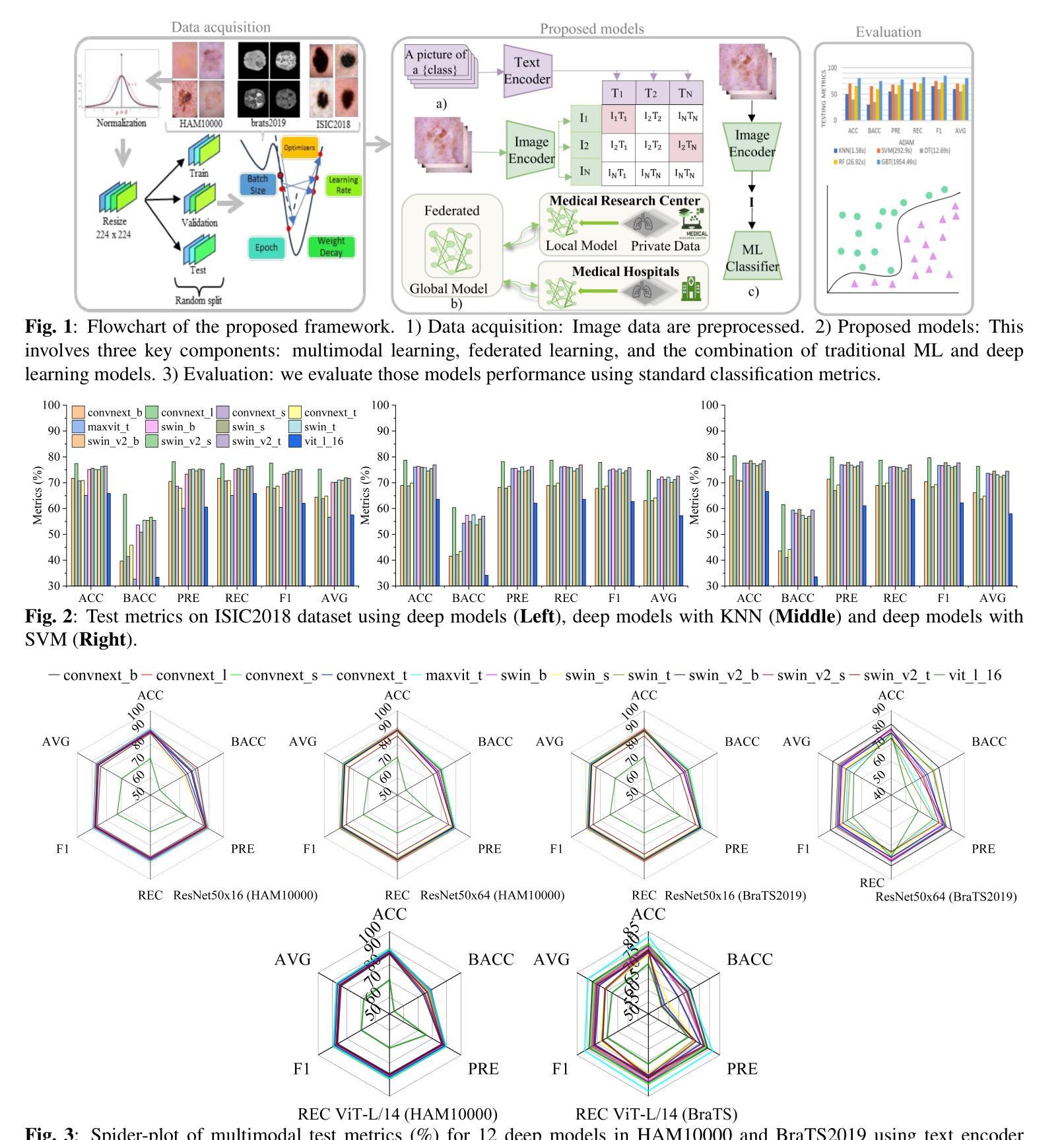
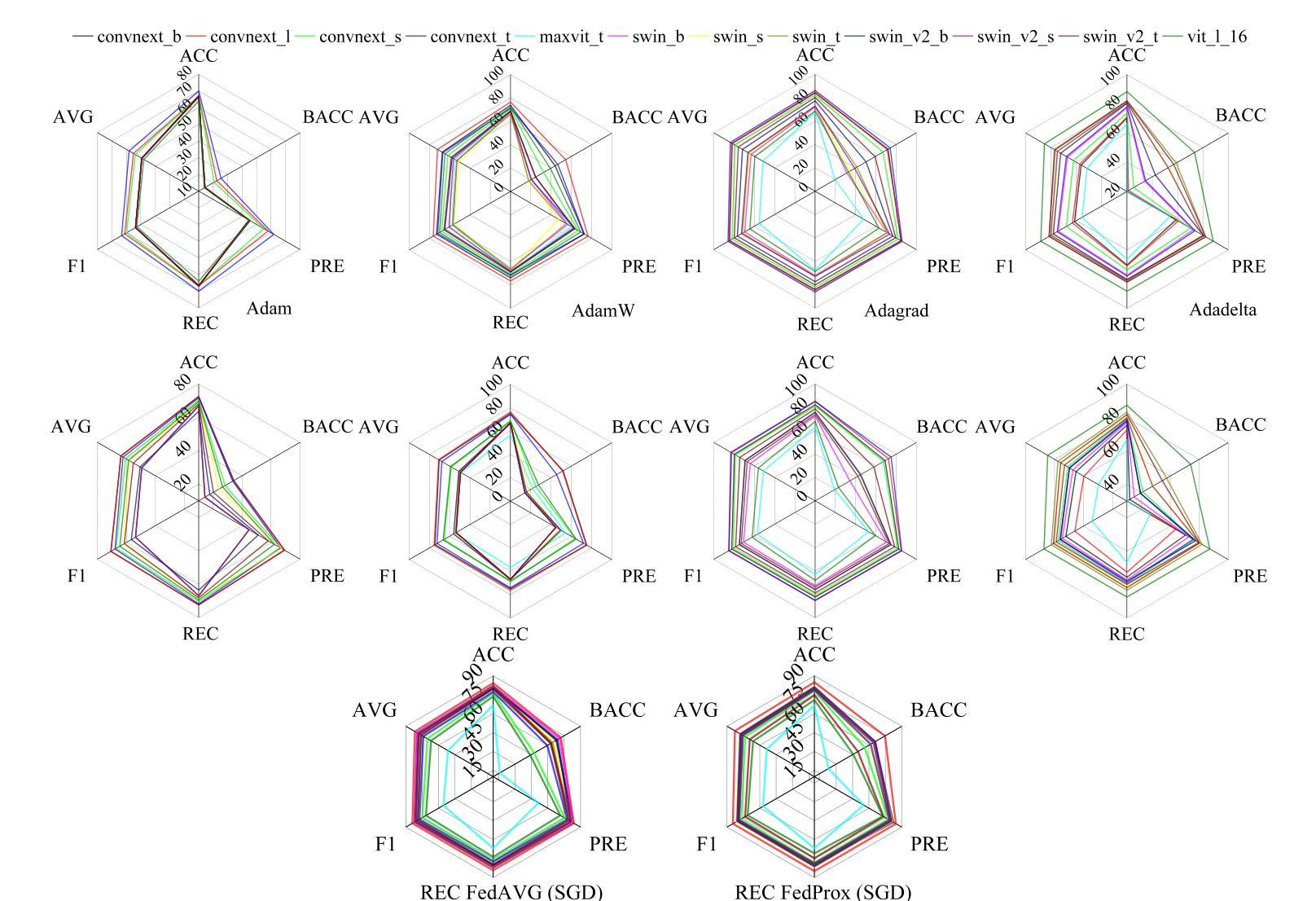
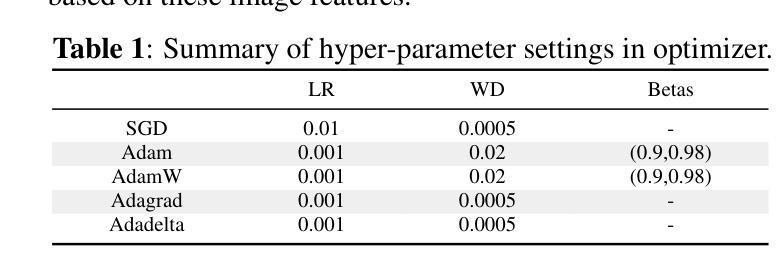
Deep models, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformer (ViT), demonstrate remarkable performance in image classification. However, those deep models require large data to fine-tune, which is impractical in the medical domain due to the data privacy issue. Furthermore, despite the feasible performance of contrastive language image pre-training (CLIP) in the natural domain, the potential of CLIP has not been fully investigated in the medical field. To face these challenges, we considered three scenarios: 1) we introduce a novel CLIP variant using four CNNs and eight ViTs as image encoders for the classification of brain cancer and skin cancer, 2) we combine 12 deep models with two federated learning techniques to protect data privacy, and 3) we involve traditional machine learning (ML) methods to improve the generalization ability of those deep models in unseen domain data. The experimental results indicate that maxvit shows the highest averaged (AVG) test metrics (AVG = 87.03%) in HAM10000 dataset with multimodal learning, while convnext_l demonstrates remarkable test with an F1-score of 83.98% compared to swin_b with 81.33% in FL model. Furthermore, the use of support vector machine (SVM) can improve the overall test metrics with AVG of $\sim 2%$ for swin transformer series in ISIC2018. Our codes are available at https://github.com/AIPMLab/SkinCancerSimulation.
深度模型,如卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT),在图像分类方面表现出卓越的性能。然而,这些深度模型需要大量数据进行微调,这在医学领域由于数据隐私问题并不实用。此外,尽管对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在自然领域表现出可行的性能,但其在医学领域的潜力尚未得到充分研究。为了应对这些挑战,我们考虑了以下三种情景:1)我们引入了一种新型的CLIP变体,使用四种CNN和八种ViT作为图像编码器,用于脑癌和皮肤癌的分类;2)我们将12种深度模型与两种联邦学习技术相结合,以保护数据隐私;3)我们引入传统机器学习(ML)方法来提高这些深度模型在未见领域数据中的泛化能力。实验结果表明,在HAM10000数据集上,maxvit的平均测试指标最高(AVG=87.03%),采用多模态学习时表现尤为突出;convnext_l在联邦学习(FL)模型中相对于swin_b的F1分数为83.98%,表现出优异的测试效果。此外,支持向量机(SVM)的使用可以提高swin transformer系列的总体测试指标,ISIC2018数据集上的平均提升约2%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/AIPMLab/SkinCancerSimulation获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ISBI2025
Summary
针对医学图像分类的挑战,研究提出了基于CLIP变体的新型模型,结合深度模型与联邦学习技术,并引入传统机器学习方法来提升模型的性能与泛化能力。在脑癌与皮肤癌分类上取得显著成效,代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对医学图像分类中的挑战,提出了基于CLIP变体的新型模型。
- 结合深度模型(如CNN和ViT)与联邦学习技术,以保护数据隐私。
- 引入传统机器学习方法,旨在提高模型的泛化能力。
- 在脑癌和皮肤癌分类任务上进行了实验,并取得显著成效。
- Maxvit在HAM10000数据集上表现最佳,平均测试指标达到87.03%。
- Convnext_l在联邦学习模型中表现出色,F1分数达到83.98%。
点此查看论文截图

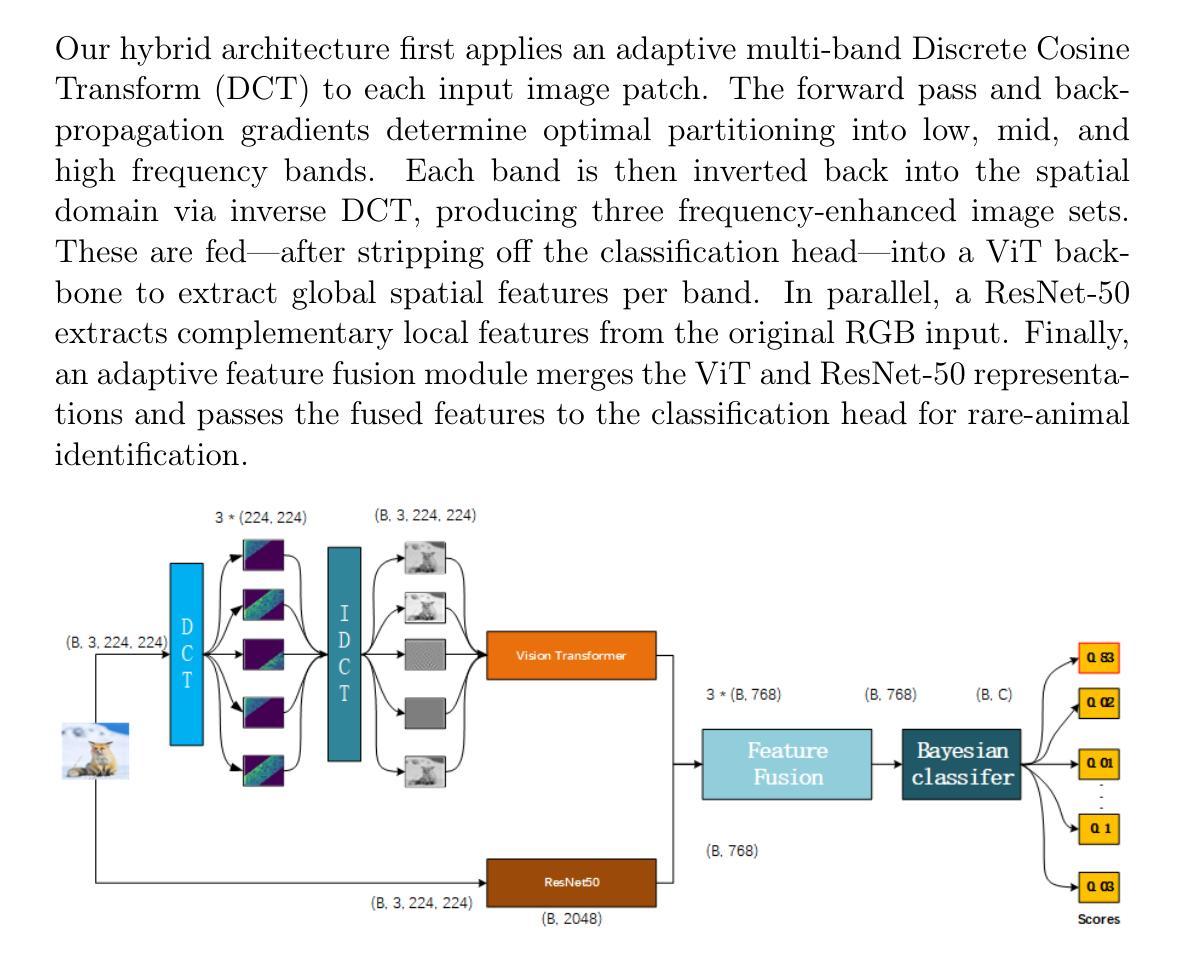
Frequency-Adaptive Discrete Cosine-ViT-ResNet Architecture for Sparse-Data Vision
Authors:Ziyue Kang, Weichuan Zhang
A major challenge in rare animal image classification is the scarcity of data, as many species usually have only a small number of labeled samples. To address this challenge, we designed a hybrid deep-learning framework comprising a novel adaptive DCT preprocessing module, ViT-B16 and ResNet50 backbones, and a Bayesian linear classification head. To our knowledge, we are the first to introduce an adaptive frequency-domain selection mechanism that learns optimal low-, mid-, and high-frequency boundaries suited to the subsequent backbones. Our network first captures image frequency-domain cues via this adaptive DCT partitioning. The adaptively filtered frequency features are then fed into ViT-B16 to model global contextual relationships, while ResNet50 concurrently extracts local, multi-scale spatial representations from the original image. A cross-level fusion strategy seamlessly integrates these frequency- and spatial-domain embeddings, and the fused features are passed through a Bayesian linear classifier to output the final category predictions. On our self-built 50-class wildlife dataset, this approach outperforms conventional CNN and fixed-band DCT pipelines, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy under extreme sample scarcity.
稀有动物图像分类面临的一个主要挑战是数据稀缺,因为许多物种通常只有少量标记样本。为了应对这一挑战,我们设计了一种混合深度学习框架,包括新型自适应DCT预处理模块、ViT-B16和ResNet50主干网,以及贝叶斯线性分类头。据我们所知,我们是首次引入自适应频域选择机制,学习适合后续主干的最佳低、中、高频边界。我们的网络首先通过自适应DCT分区捕获图像频域线索。然后,自适应滤波的频域特征输入ViT-B16,以建模全局上下文关系,而ResNet50则同时从原始图像中提取局部多尺度空间表示。跨级融合策略无缝集成了这些频域和空间域嵌入,融合的特征通过贝叶斯线性分类器输出最终的类别预测。在我们自建的50类野生动物数据集上,这种方法优于传统的CNN和固定频段DCT管道,在极端样本稀缺的情况下达到了最先进的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种混合深度学习框架,用于解决稀有动物图像分类中的数据稀缺问题。该框架包含自适应DCT预处理模块、ViT-B16和ResNet50骨干网,以及贝叶斯线性分类头。首次引入自适应频率域选择机制,学习适合后续骨干网的最佳低频、中频和高频边界。该网络首先通过自适应DCT分区捕获图像频率域线索,然后将过滤后的频率特征输入ViT-B16以建模全局上下文关系,同时ResNet50从原始图像中提取局部多尺度空间表示。通过跨级别融合策略无缝集成这些频率域和空间域嵌入,融合的特征通过贝叶斯线性分类器输出最终类别预测。在自建的50类野生动物数据集上,该方法优于传统的CNN和固定频段DCT管道,在极端样本稀缺的情况下达到最先进的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的混合深度学习框架旨在解决稀有动物图像分类中的数据稀缺问题。
- 框架包含自适应DCT预处理模块,能够学习最优的频率边界。
- 引入ViT-B16和ResNet50骨干网来分别建模全局和局部特征。
- 使用贝叶斯线性分类头进行类别预测。
- 自适应频率域选择机制能够提高在样本稀缺情况下的分类准确性。
- 跨级别融合策略集成频率域和空间域嵌入,提升性能。
- 在自建的50类野生动物数据集上,该方法达到最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

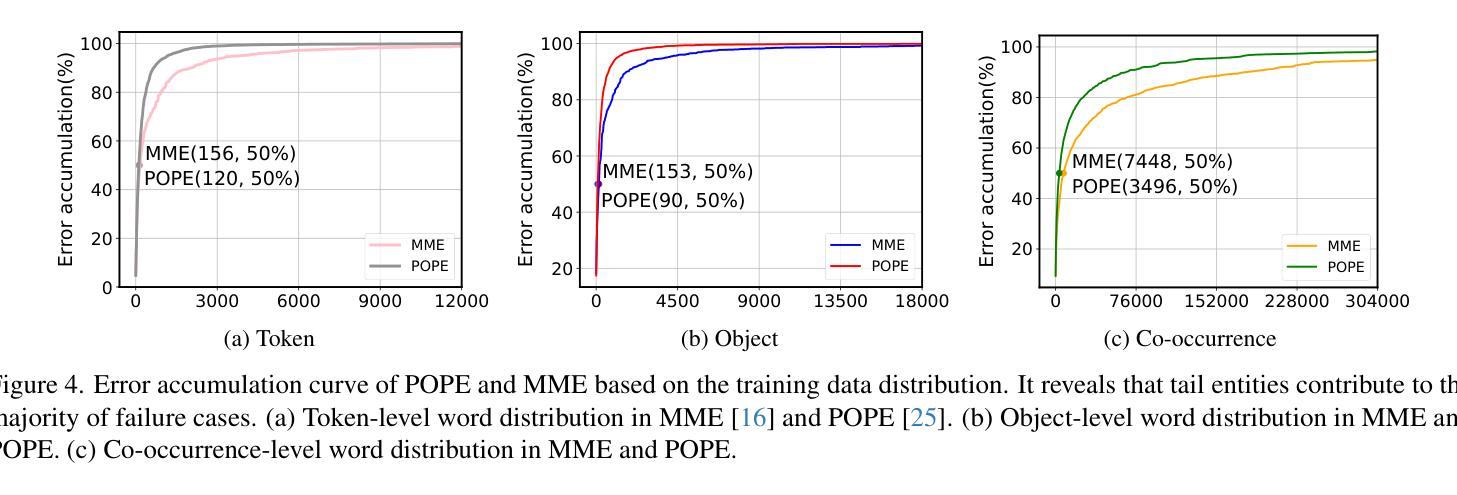
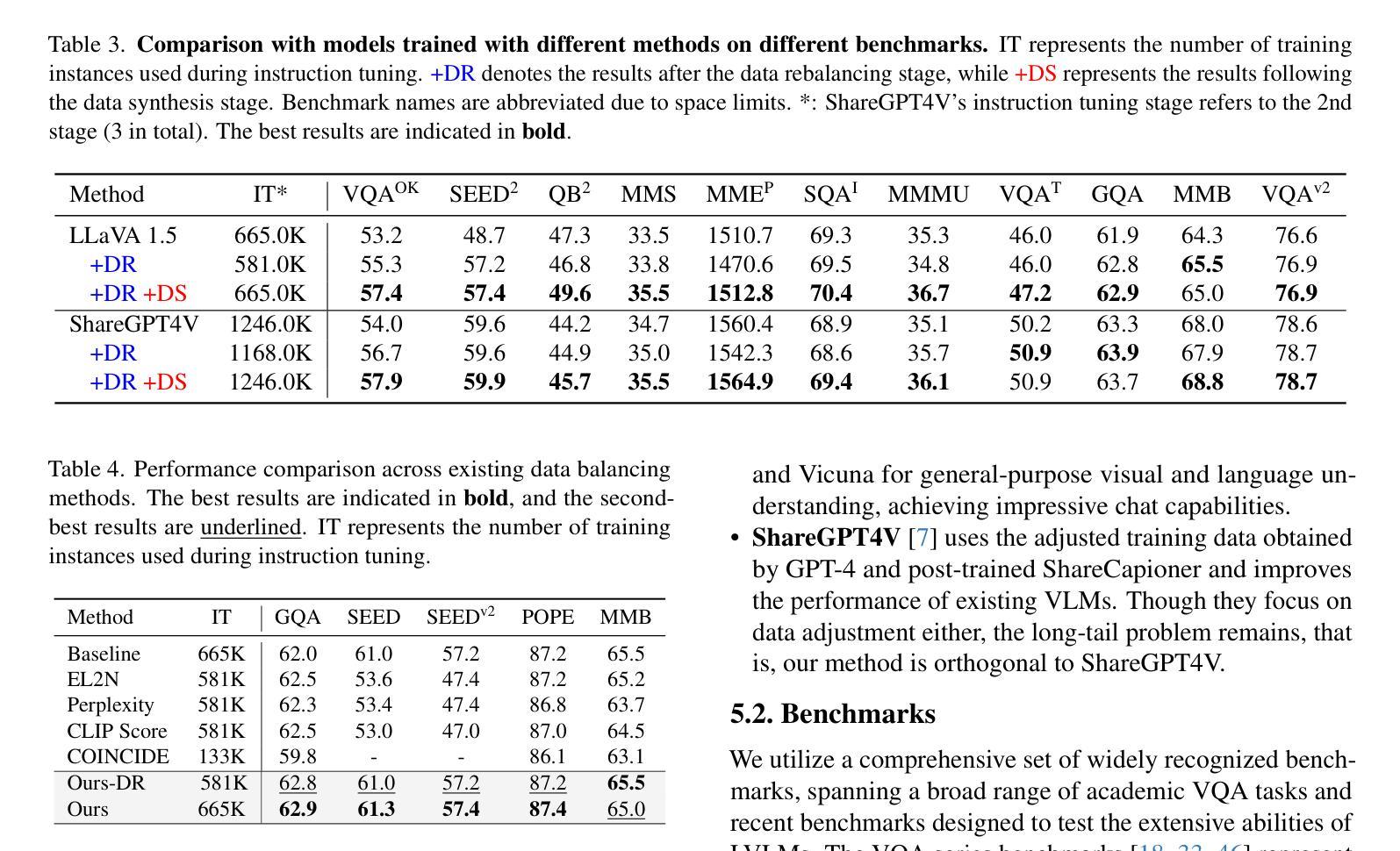
From Head to Tail: Towards Balanced Representation in Large Vision-Language Models through Adaptive Data Calibration
Authors:Mingyang Song, Xiaoye Qu, Jiawei Zhou, Yu Cheng
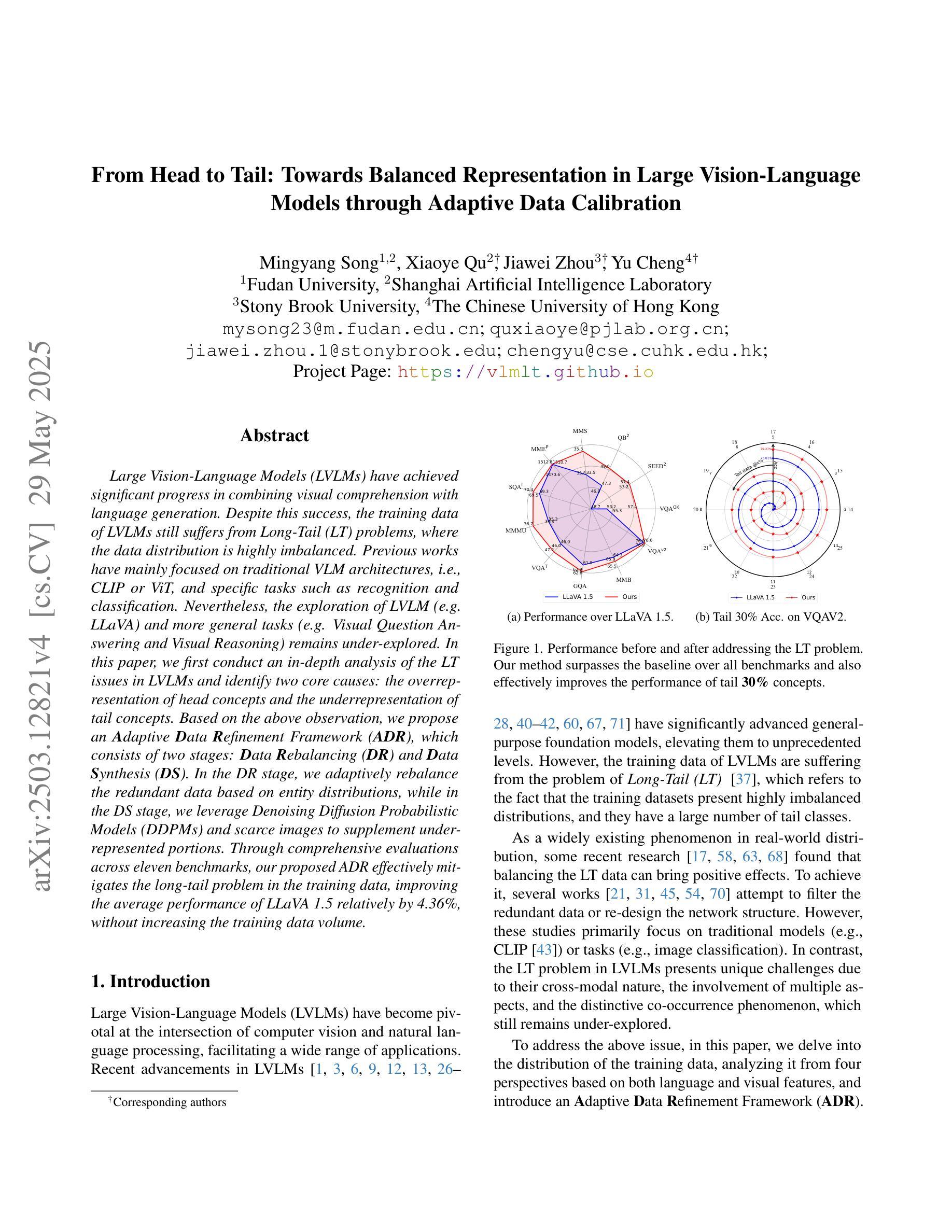
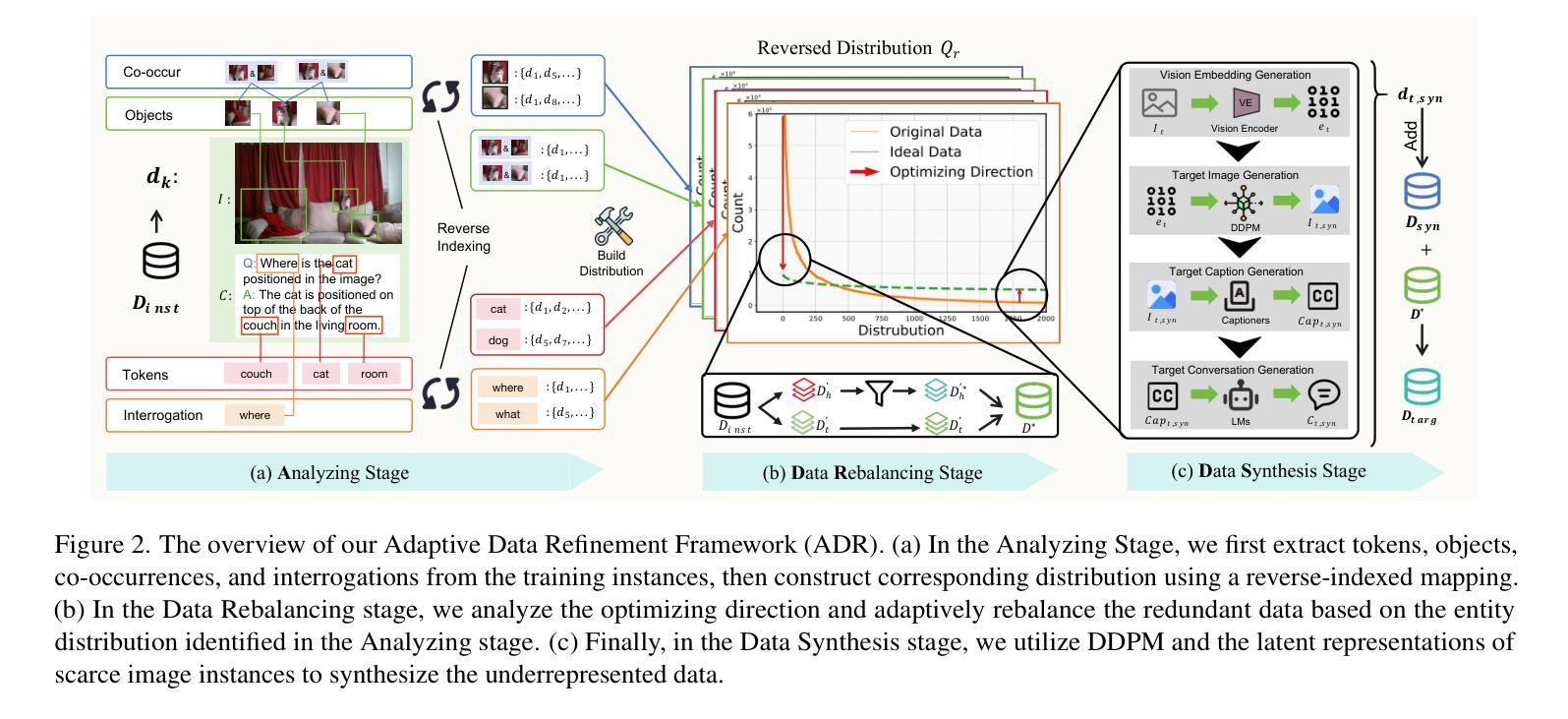
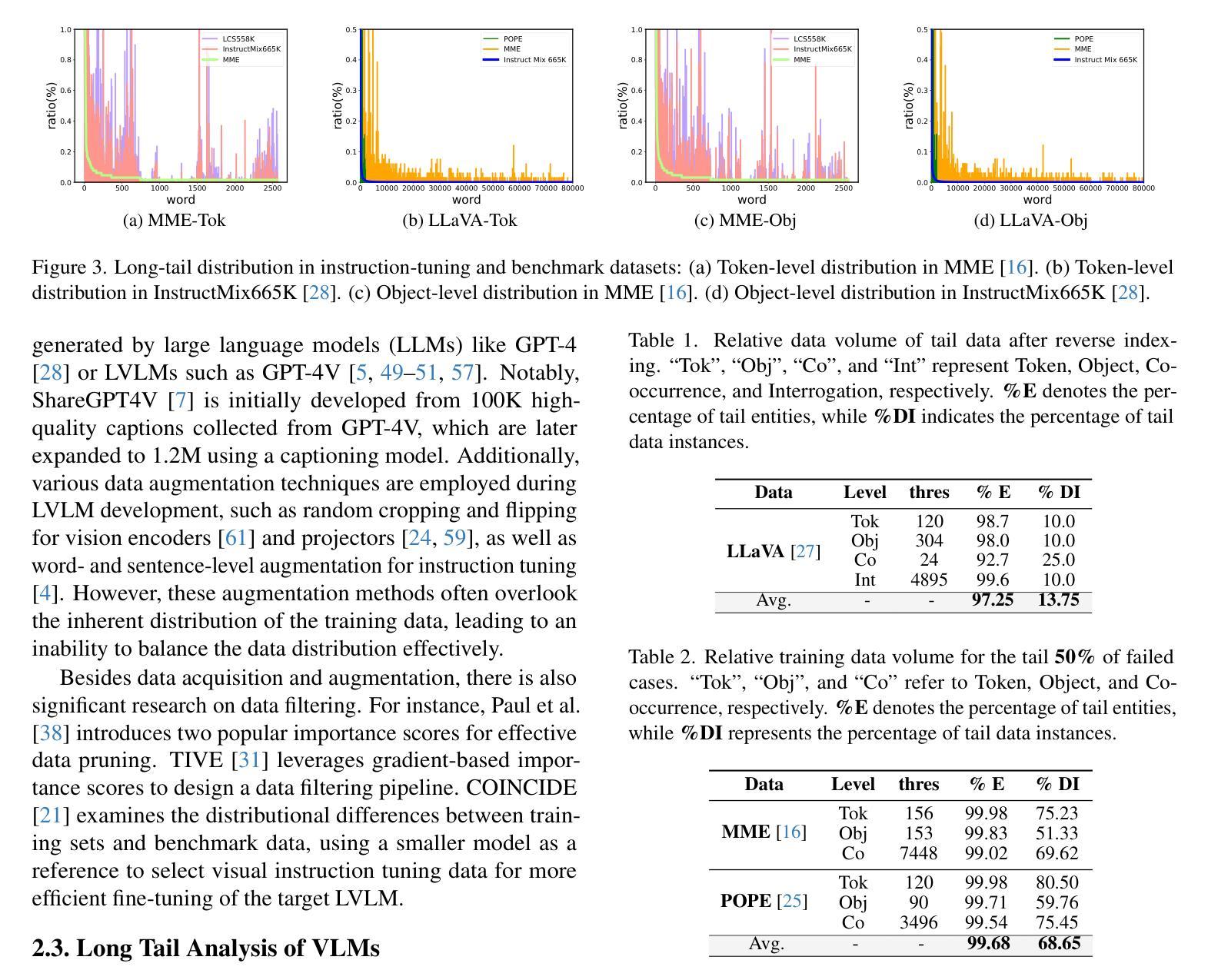
Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved significant progress in combining visual comprehension with language generation. Despite this success, the training data of LVLMs still suffers from Long-Tail (LT) problems, where the data distribution is highly imbalanced. Previous works have mainly focused on traditional VLM architectures, i.e., CLIP or ViT, and specific tasks such as recognition and classification. Nevertheless, the exploration of LVLM (e.g. LLaVA) and more general tasks (e.g. Visual Question Answering and Visual Reasoning) remains under-explored. In this paper, we first conduct an in-depth analysis of the LT issues in LVLMs and identify two core causes: the overrepresentation of head concepts and the underrepresentation of tail concepts. Based on the above observation, we propose an $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{R}$efinement Framework ($\textbf{ADR}$), which consists of two stages: $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{R}$ebalancing ($\textbf{DR}$) and $\textbf{D}$ata $\textbf{S}$ynthesis ($\textbf{DS}$). In the DR stage, we adaptively rebalance the redundant data based on entity distributions, while in the DS stage, we leverage Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) and scarce images to supplement underrepresented portions. Through comprehensive evaluations across eleven benchmarks, our proposed ADR effectively mitigates the long-tail problem in the training data, improving the average performance of LLaVA 1.5 relatively by 4.36%, without increasing the training data volume.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在结合视觉理解与语言生成方面取得了显著进展。然而,尽管取得了成功,LVLM的训练数据仍然面临长尾(LT)问题,即数据分布极度不平衡。之前的研究主要关注传统的VLM架构,例如CLIP或ViT,以及特定的任务,如识别和分类。然而,对于LVLM(例如LLaVA)和更一般的任务(例如视觉问答和视觉推理)的探索仍然不足。在本文中,我们首先对LVLM中的LT问题进行了深入分析,并确定了两个核心原因:头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。基于上述观察,我们提出了一个自适应数据精炼框架(ADR),该框架由两个阶段组成:数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)。在DR阶段,我们根据实体分布自适应地重新平衡冗余数据,而在DS阶段,我们利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和稀缺图像来补充表示不足的部分。通过跨越十一个基准点的全面评估,我们提出的ADR有效地缓解了训练数据中的长尾问题,相对提高了LLaVA 1.5的平均性能4.36%,且没有增加训练数据量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025. Project Page: https://vlmlt.github.io/
Summary
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)结合了视觉理解和语言生成技术,取得了显著进展。然而,其训练数据存在长尾(LT)问题,数据分布高度不平衡。本文深入分析了LVLM中的LT问题,并确定了两个核心原因:头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。针对这些问题,提出了自适应数据优化框架(ADR),包括数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)两个阶段。通过广泛的基准测试,ADR有效地缓解了训练数据中的长尾问题,提高了LLaVA 1.5的平均性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在视觉理解和语言生成方面取得了重要进展。
- LVLMs的训练数据存在长尾(LT)问题,即数据分布不平衡。
- 论文深入分析了LT问题的两个核心原因:头部概念的过度表示和尾部概念的表示不足。
- 为了解决这些问题,论文提出了自适应数据优化框架(ADR),包括数据再平衡(DR)和数据合成(DS)两个阶段。
- DR阶段通过自适应地再平衡数据来解决冗余数据问题。
- DS阶段利用去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)和稀缺图像来补充表示不足的部分。
点此查看论文截图
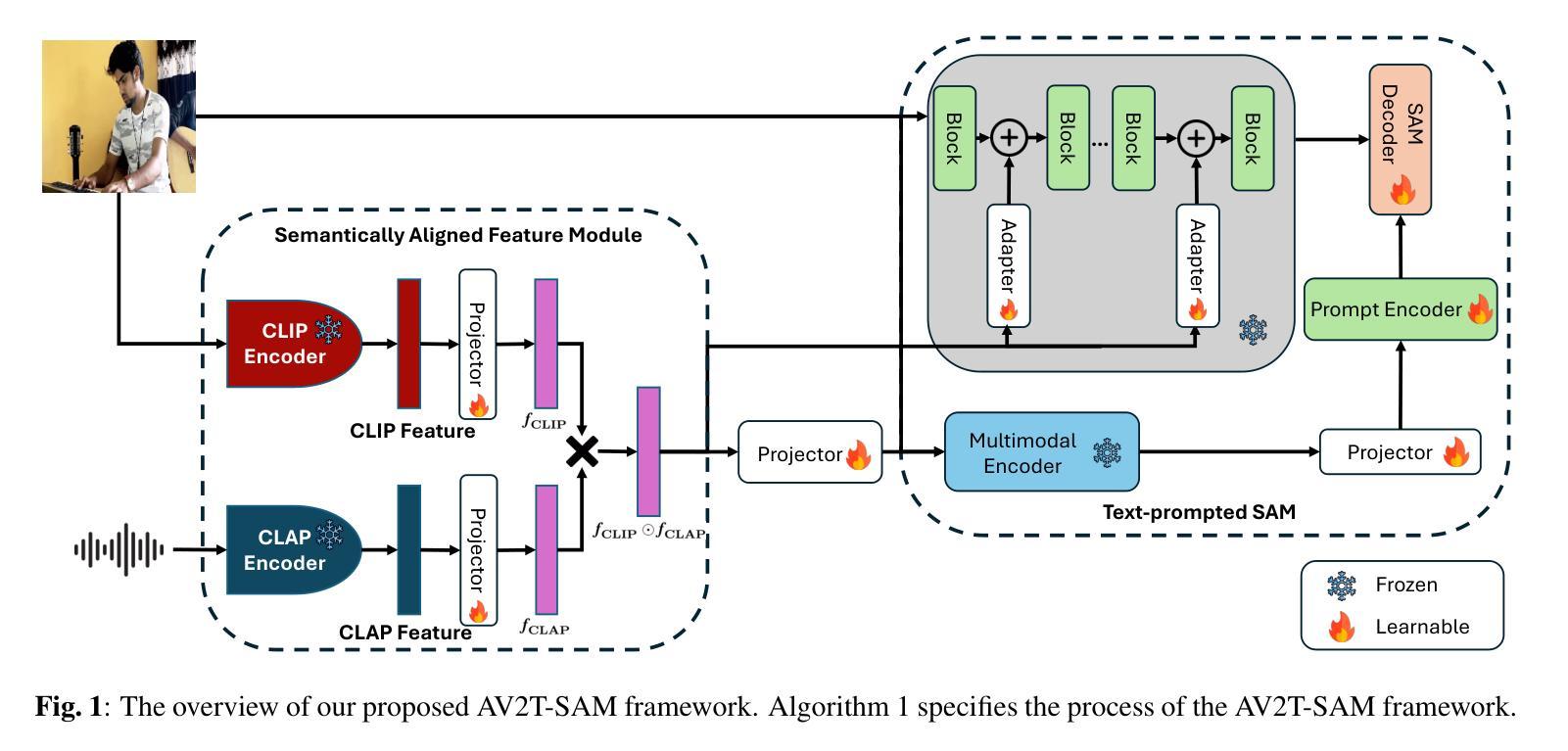
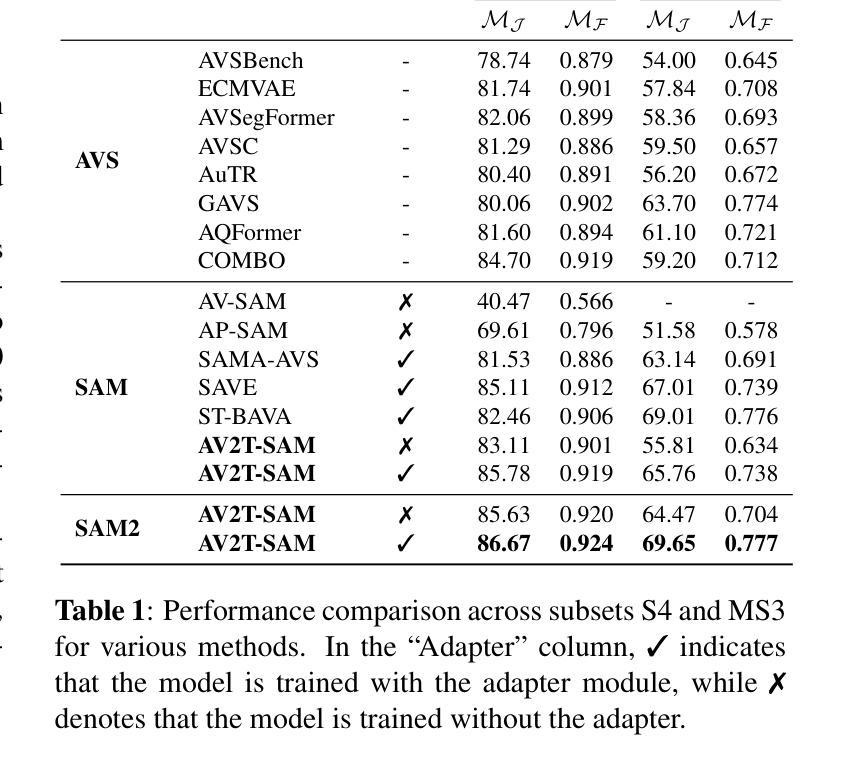
Audio Visual Segmentation Through Text Embeddings
Authors:Kyungbok Lee, You Zhang, Zhiyao Duan
The goal of Audio-Visual Segmentation (AVS) is to localize and segment the sounding source objects from video frames. Research on AVS suffers from data scarcity due to the high cost of fine-grained manual annotations. Recent works attempt to overcome the challenge of limited data by leveraging the vision foundation model, Segment Anything Model (SAM), prompting it with audio to enhance its ability to segment sounding source objects. While this approach alleviates the model’s burden on understanding visual modality by utilizing knowledge of pre-trained SAM, it does not address the fundamental challenge of learning audio-visual correspondence with limited data. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{AV2T-SAM}, a novel framework that bridges audio features with the text embedding space of pre-trained text-prompted SAM. Our method leverages multimodal correspondence learned from rich text-image paired datasets to enhance audio-visual alignment. Furthermore, we introduce a novel feature, $\mathbf{\textit{\textbf{f}}{CLIP} \odot \textit{\textbf{f}}{CLAP}}$, which emphasizes shared semantics of audio and visual modalities while filtering irrelevant noise. Our approach outperforms existing methods on the AVSBench dataset by effectively utilizing pre-trained segmentation models and cross-modal semantic alignment. The source code is released at https://github.com/bok-bok/AV2T-SAM.
音频视觉分割(AVS)的目标是定位视频帧中的发声源对象并将其分割出来。由于精细的手动标注成本高昂,AVS研究面临数据稀缺的问题。近期的研究工作试图通过利用视觉基础模型——分段任何事物模型(SAM)来克服数据量有限的挑战,并用音频来提示它以增强其分割发声源对象的能力。虽然这种方法通过利用预训练的SAM的知识减轻了模型对视觉模态理解的压力,但它并没有解决数据有限时学习视听对应关系的根本挑战。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种新的框架AV2T-SAM,它将音频特征与预训练的文本提示SAM的文本嵌入空间相结合。我们的方法利用从丰富的文本图像配对数据集中学习的多模态对应关系来增强视听对齐。此外,我们还引入了一种新的特征$\mathbf{\textit{\textbf{f}}{CLIP} \odot \textit{\textbf{f}}{CLAP}}$,它强调了音频和视觉模态的共享语义,同时过滤掉无关噪声。我们的方法通过在AVSBench数据集上有效地利用预训练的分割模型和跨模态语义对齐,实现了对现有方法的超越。源代码已发布在https://github.com/bok-bok/AV2T-SAM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频视觉分割(AVS)的目标是从视频帧中定位并分割声音源对象。研究AVS因精细粒度手动注释的高成本而面临数据稀缺的问题。最近的工作尝试通过利用视觉基础模型SAM和音频提示来增强其分割声音源对象的能力来克服数据有限的挑战。然而,这种方法并没有解决在有限数据下学习音频视觉对应关系的根本挑战。为解决此问题,本文提出了AV2T-SAM框架,该框架将音频特征与预训练文本提示SAM的文本嵌入空间相结合,利用丰富的文本图像配对数据集学习多模态对应关系以增强音频视觉对齐。此外,还引入了一种新特征fCLIP⊗fCLAP,强调音频和视觉模态的共享语义,同时过滤掉无关噪声。该方法在AVSBench数据集上优于现有方法,通过有效利用预训练分割模型和跨模态语义对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉分割(AVS)的目标是从视频帧中定位并分割声音源对象。
- 数据稀缺是AVS研究面临的挑战,因为精细粒度的手动注释成本高昂。
- 最近的研究尝试通过利用视觉基础模型SAM和音频提示来解决数据稀缺问题。
- 提出的AV2T-SAM框架结合音频特征与预训练文本提示SAM的文本嵌入空间,增强音频视觉对齐。
- AV2T-SAM利用丰富的文本图像配对数据集学习多模态对应关系。
- 引入新特征fCLIP⊗fCLAP,强调音频和视觉模态的共享语义,过滤无关噪声。
点此查看论文截图


QMamba: On First Exploration of Vision Mamba for Image Quality Assessment
Authors:Fengbin Guan, Xin Li, Zihao Yu, Yiting Lu, Zhibo Chen
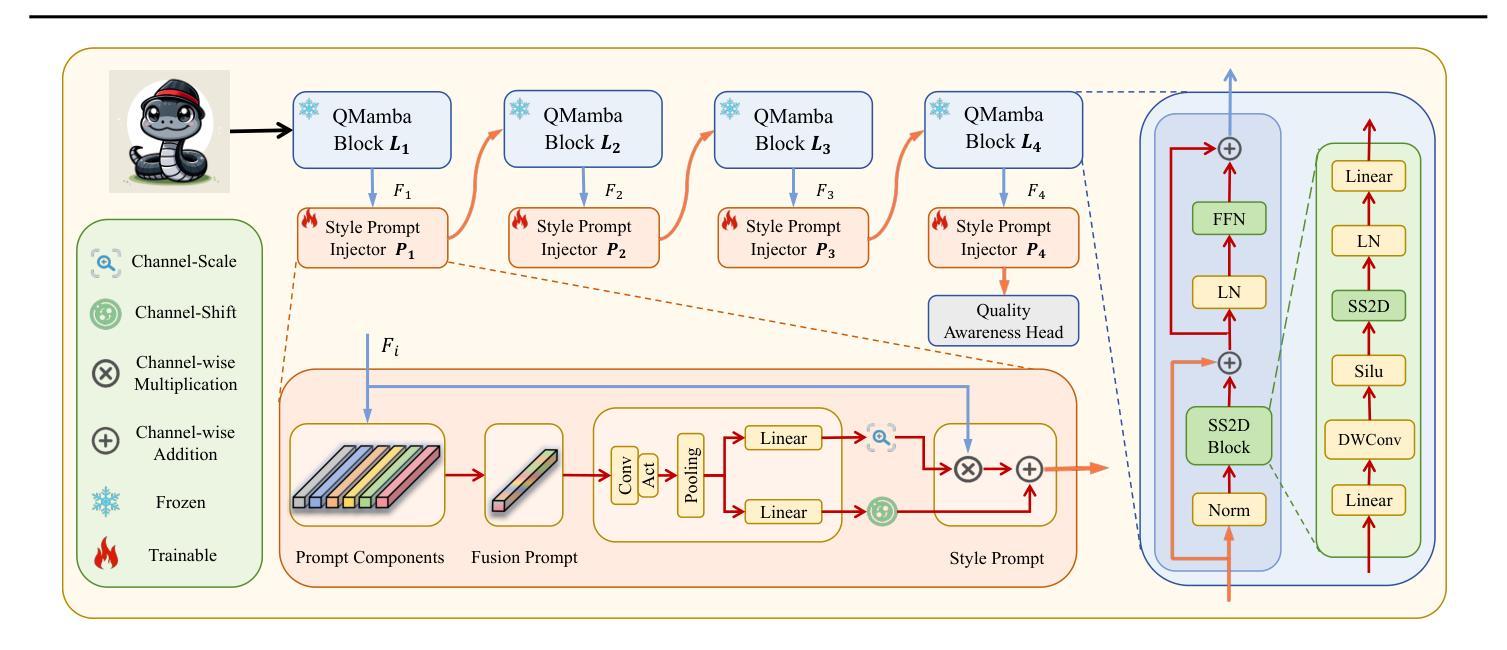
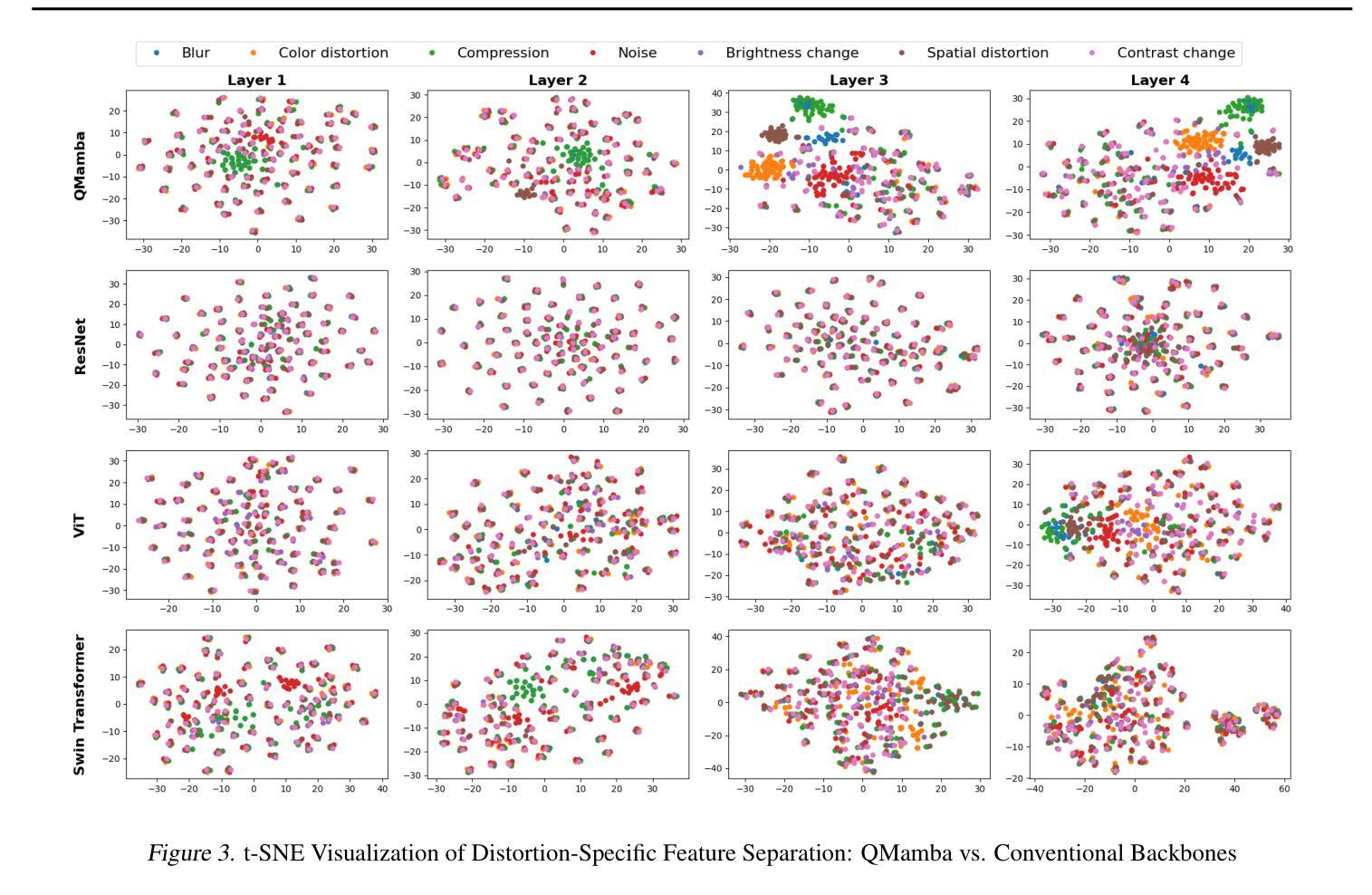
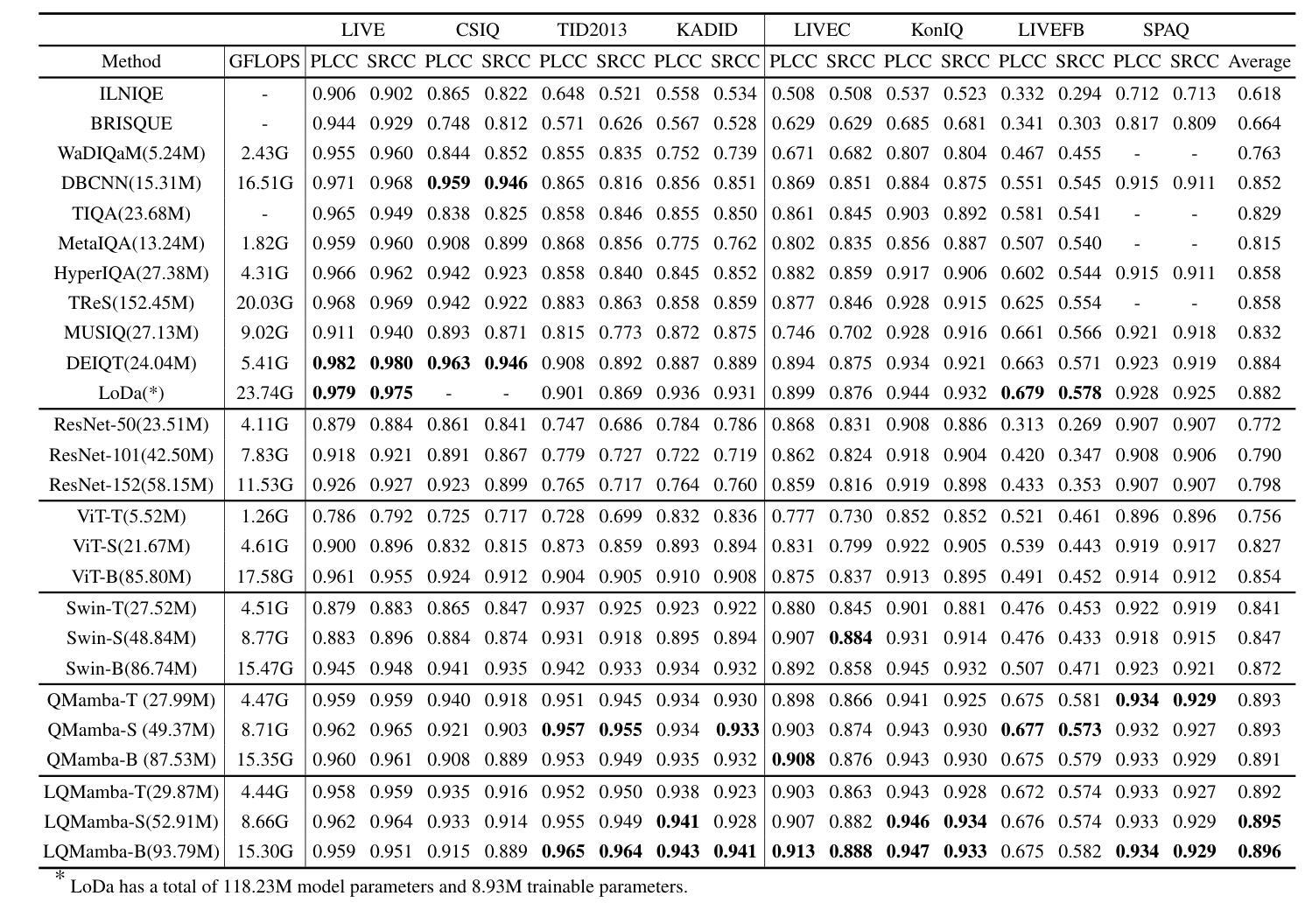
In this work, we take the first exploration of the recently popular foundation model, i.e., State Space Model/Mamba, in image quality assessment (IQA), aiming at observing and excavating the perception potential in vision Mamba. A series of works on Mamba has shown its significant potential in various fields, e.g., segmentation and classification. However, the perception capability of Mamba remains under-explored. Consequently, we propose QMamba by revisiting and adapting the Mamba model for three crucial IQA tasks, i.e., task-specific, universal, and transferable IQA, which reveals its clear advantages over existing foundational models, e.g., Swin Transformer, ViT, and CNNs, in terms of perception and computational cost. To improve the transferability of QMamba, we propose the StylePrompt tuning paradigm, where lightweight mean and variance prompts are injected to assist task-adaptive transfer learning of pre-trained QMamba for different downstream IQA tasks. Compared with existing prompt tuning strategies, our StylePrompt enables better perceptual transfer with lower computational cost. Extensive experiments on multiple synthetic, authentic IQA datasets, and cross IQA datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed QMamba. The code will be available at: https://github.com/bingo-G/QMamba.git
在这项工作中,我们首次探索了最近流行的基础模型,即状态空间模型(State Space Model)/Mamba在图像质量评估(IQA)中的应用,旨在观察挖掘视觉Mamba中的感知潜力。一系列关于Mamba的工作已经显示出它在各个领域的重要潜力,例如分割和分类。然而,Mamba的感知能力仍然没有得到充分的探索。因此,我们通过对Mamba模型进行回顾和适应,提出了QMamba,用于三项关键的IQA任务,即特定任务IQA、通用IQA和可迁移IQA。在感知和计算成本方面,QMamba显示出优于现有基础模型(如Swin Transformer、ViT和CNN)的明显优势。为了提高QMamba的可迁移性,我们提出了StylePrompt微调范式,通过注入轻量级均值和方差提示来辅助针对不同下游IQA任务的预训练QMamba的任务适应性迁移学习。与现有的提示调整策略相比,我们的StylePrompt能够以较低的计算成本实现更好的感知迁移。在多个合成、真实的IQA数据集和跨IQA数据集上的大量实验证明了所提出的QMamba的有效性。代码将在以下网址公开:https://github.com/bingo-G/QMamba.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文首次探索了近期流行的基础模型——状态空间模型/曼巴(State Space Model/Mamba)在图像质量评估(IQA)领域的应用,旨在挖掘曼巴在视觉领域的感知潜力。针对三种关键的IQA任务,作者提出了改进后的QMamba模型,并在多个数据集上验证了其在感知和计算成本方面的优势。为提高QMamba的迁移能力,作者还提出了StylePrompt微调范式,通过注入轻量级均值和方差提示来辅助预训练的QMamba对不同下游IQA任务的适应性转移学习。
Key Takeaways
- 文章首次将State Space Model/Mamba模型应用于图像质量评估(IQA),显示其在该领域的潜力。
- QMamba模型在任务特定、通用和可迁移的IQA任务上均表现出优于其他基础模型的感知和计算成本优势。
- 为提高QMamba的迁移能力,提出了StylePrompt微调范式。
- StylePrompt通过注入轻量级均值和方差提示,辅助预训练QMamba对不同下游IQA任务的适应性转移学习。
- StylePrompt相对于现有的提示调整策略,在较低的计算成本下实现了更好的感知迁移。
- 在多个合成、真实IQA数据集以及跨IQA数据集上的大量实验验证了QMamba模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图