⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-01 更新
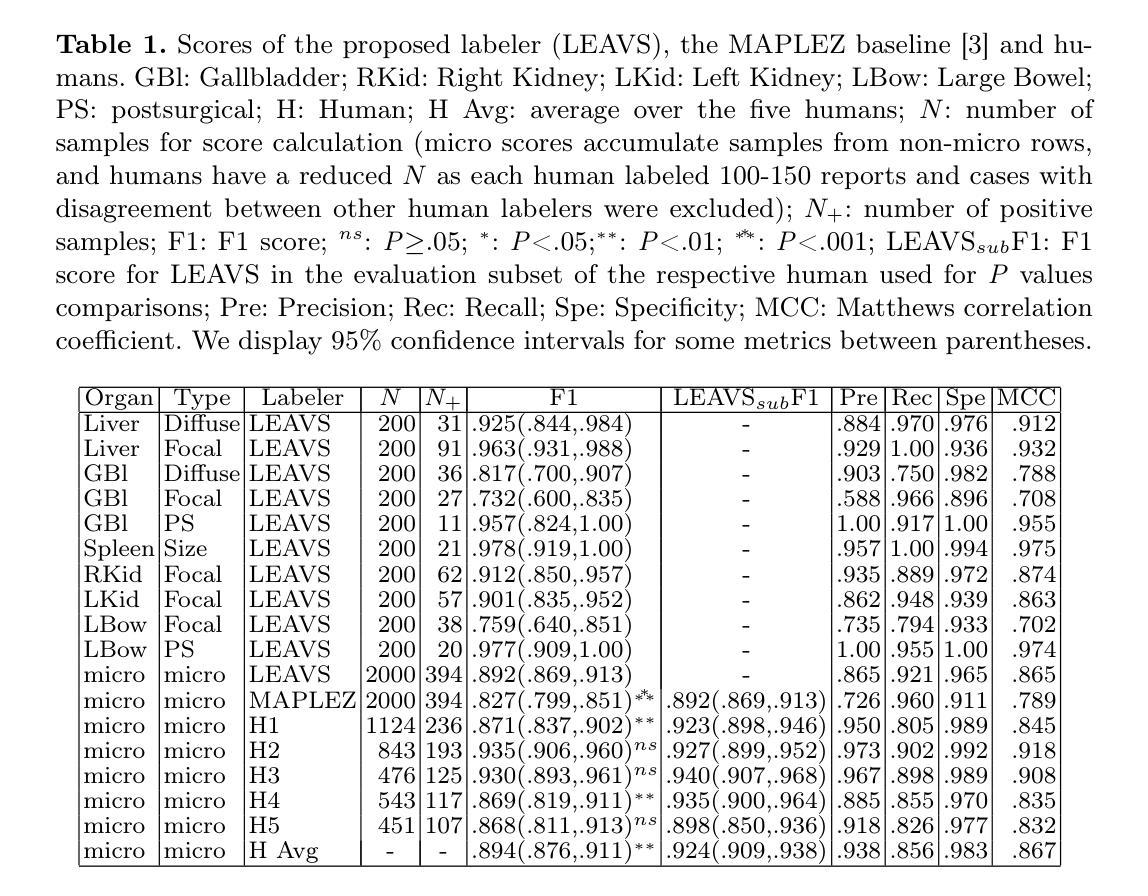
LEAVS: An LLM-based Labeler for Abdominal CT Supervision
Authors:Ricardo Bigolin Lanfredi, Yan Zhuang, Mark Finkelstein, Praveen Thoppey Srinivasan Balamuralikrishna, Luke Krembs, Brandon Khoury, Arthi Reddy, Pritam Mukherjee, Neil M. Rofsky, Ronald M. Summers
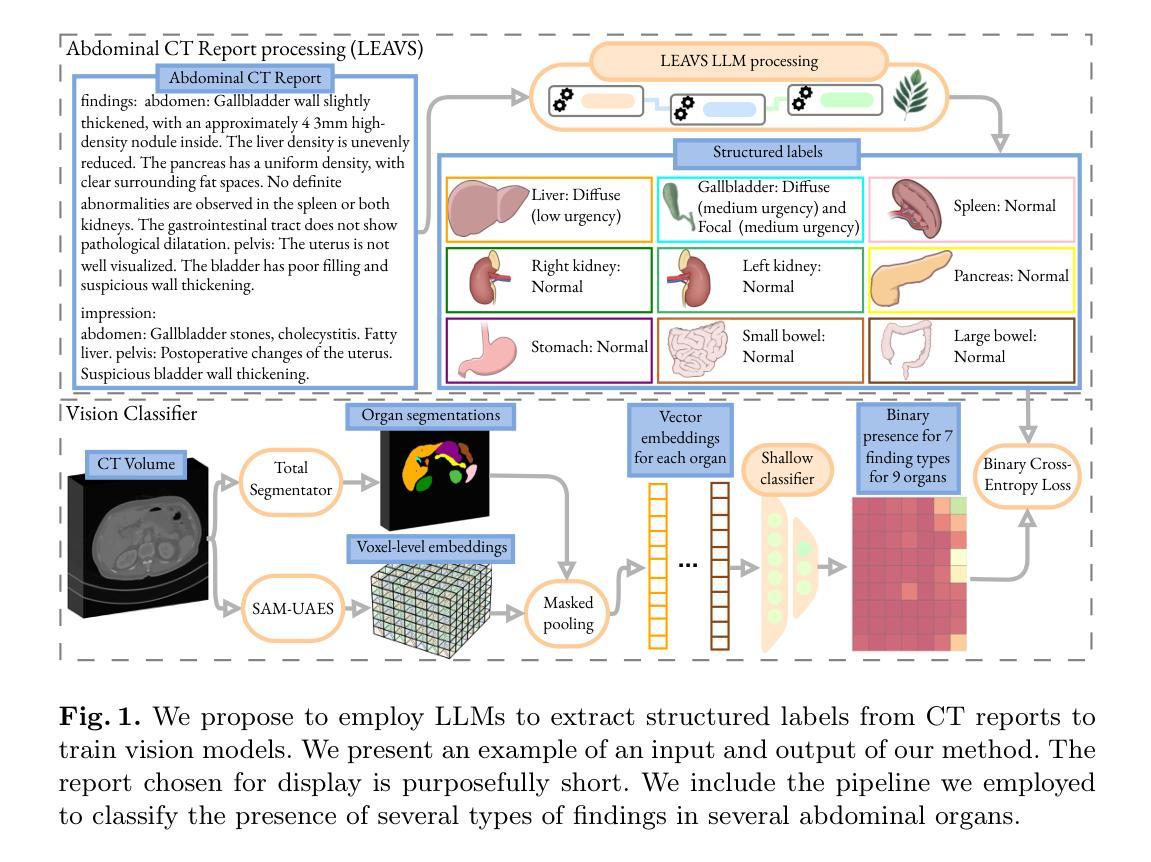
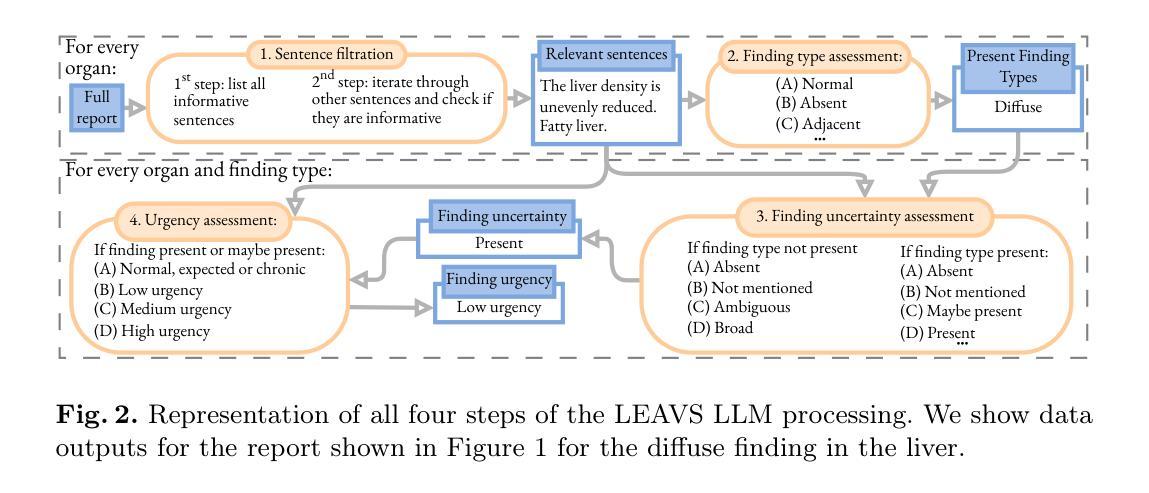
Extracting structured labels from radiology reports has been employed to create vision models to simultaneously detect several types of abnormalities. However, existing works focus mainly on the chest region. Few works have been investigated on abdominal radiology reports due to more complex anatomy and a wider range of pathologies in the abdomen. We propose LEAVS (Large language model Extractor for Abdominal Vision Supervision). This labeler can annotate the certainty of presence and the urgency of seven types of abnormalities for nine abdominal organs on CT radiology reports. To ensure broad coverage, we chose abnormalities that encompass most of the finding types from CT reports. Our approach employs a specialized chain-of-thought prompting strategy for a locally-run LLM using sentence extraction and multiple-choice questions in a tree-based decision system. We demonstrate that the LLM can extract several abnormality types across abdominal organs with an average F1 score of 0.89, significantly outperforming competing labelers and humans. Additionally, we show that extraction of urgency labels achieved performance comparable to human annotations. Finally, we demonstrate that the abnormality labels contain valuable information for training a single vision model that classifies several organs as normal or abnormal. We release our code and structured annotations for a public CT dataset containing over 1,000 CT volumes.
从放射学报告中提取结构化标签已被用于创建视觉模型,以同时检测多种异常类型。然而,现有工作主要集中在胸部区域。由于腹部解剖结构更为复杂且病理范围更广,对腹部放射学报告的研究工作很少。我们提出了LEAVS(腹部视觉监督大型语言模型提取器)。此标签器可以标注七种异常类型的存在确定性和腹部九个器官在CT放射学报告中的紧急程度。为确保广泛覆盖,我们选择了异常类型,涵盖了大多数来自CT报告的发现类型。我们的方法采用专用的一连串思考提示策略,使用句子提取和基于树形决策系统的多项选择题,适用于本地运行的大型语言模型。我们证明,大型语言模型能够在腹部器官中提取多种异常类型,平均F1分数为0.89,显著优于竞争对手标签器和人类。此外,我们还表明,提取的紧急程度标签的性能与人类注释相当。最后,我们证明异常标签包含有价值的信息,可用于训练单个视觉模型,将多个器官分类为正常或异常。我们公开了包含超过1000个CT体积的公共CT数据集的结构化注释和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Early acceptance (top 9% of submissions) for MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为LEAVS的大型语言模型腹部视觉监督标签器,能够从腹部CT报告中自动标注七种异常类型的存在和紧急程度,涵盖了大多数腹部器官的异常情况。该方法通过特定的思考链提示策略,利用本地运行的大型语言模型(LLM)进行句子提取和基于树形决策系统的多项选择题来实现。实验结果显示,LLM能够提取多个器官异常类型,平均F1分数达到0.89,显著优于竞争对手标签器和人类的表现。此外,该标签器还能用于训练单一视觉模型,用于分类器官的正常与否。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种名为LEAVS的大型语言模型腹部视觉监督标签器,专门用于标注腹部CT报告中的异常情况。
- 能够标注九种腹部器官中七种异常类型的存在和紧急程度。
- 通过特定的思考链提示策略实现高效标注。
- 实验结果显示LLM性能显著优于竞争对手标签器和人类的表现。
- 异常标签包含有价值的信息,可用于训练单一的视觉模型以分类器官的正常与否。
点此查看论文截图

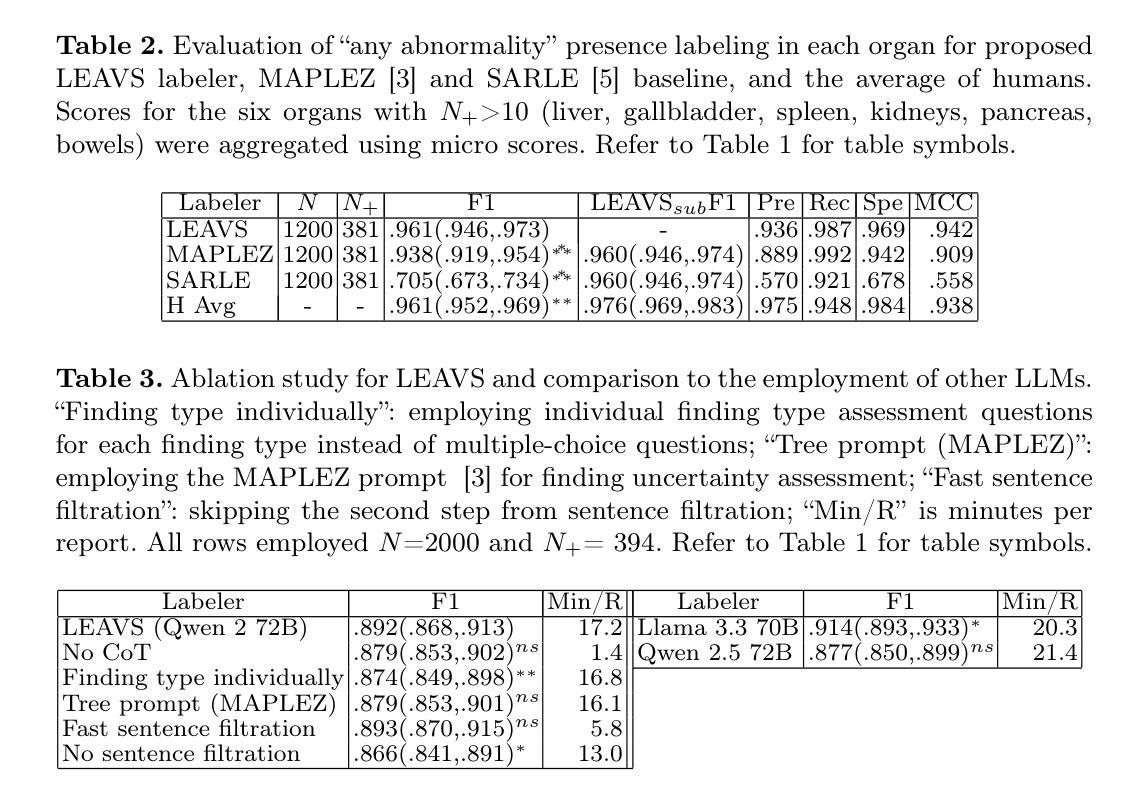
Safeguarding AI in Medical Imaging: Post-Hoc Out-of-Distribution Detection with Normalizing Flows
Authors:Dariush Lotfi, Mohammad-Ali Nikouei Mahani, Mohamad Koohi-Moghadam, Kyongtae Ty Bae
In AI-driven medical imaging, the failure to detect out-of-distribution (OOD) data poses a severe risk to clinical reliability, potentially leading to critical diagnostic errors. Current OOD detection methods often demand impractical retraining or modifications to pre-trained models, hindering their adoption in regulated clinical environments. To address this challenge, we propose a post-hoc normalizing flow-based approach that seamlessly integrates with existing pre-trained models without altering their weights. Our evaluation used a novel in-house built dataset, MedOOD, meticulously curated to simulate clinically relevant distributional shifts, alongside the MedMNIST benchmark dataset. On our in-house MedOOD dataset, our method achieved an AUROC of 84.61%, outperforming state-of-the-art methods like ViM (80.65%) and MDS (80.87%). Similarly, on MedMNIST, it reached an exceptional AUROC of 93.8%, surpassing leading approaches such as ViM (88.08%) and ReAct (87.05%). This superior performance, coupled with its post-hoc integration capability, positions our method as a vital safeguard for enhancing safety in medical imaging workflows. The model and code to build OOD datasets are publicly accessible at https://github.com/dlotfi/MedOODFlow.
在人工智能驱动的医学影像领域,无法检测出离群分布(OOD)数据给临床可靠性带来了严重风险,可能导致关键诊断错误。当前的OOD检测方法通常需要不切实际的重新训练或对预训练模型进行修改,阻碍了它们在受监管的临床环境中的采用。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种事后归一化流方法,该方法能够无缝集成到现有预训练模型中,无需更改其权重。我们的评估使用了一种新型内部构建数据集MedOOD,精心策划以模拟临床上相关的分布转移,以及MedMNIST基准数据集。在我们的内部MedOOD数据集上,我们的方法达到了84.61%的AUROC,优于ViM(80.65%)和MDS(80.87%)等最新方法。同样,在MedMNIST上,它达到了93.8%的惊人AUROC,超越了ViM(88.08%)和ReAct(87.05%)等领先方法。这种卓越性能,再加上其事后集成能力,使我们的方法在增强医学影像工作流程的安全性方面成为重要的保障。构建OOD数据集的模型和代码可在https://github.com/dlotfi/MedOODFlow公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于后处理标准化流的解决方案,旨在解决人工智能医学影像诊断中因未能检测到的离群数据而导致的潜在风险问题。该方法无需修改预训练模型,可直接集成现有模型,提高诊断的可靠性。实验结果显示,该方法在自定义数据集MedOOD上的表现优于其他先进方法,同时在MedMNIST基准数据集上也取得了良好的表现。
Key Takeaways
- AI医学影像诊断面临未能检测离群数据的风险,可能导致诊断错误。
- 提出一种基于后处理标准化流的解决方案,无需修改预训练模型即可提高诊断可靠性。
- 方法在自定义数据集MedOOD上的表现优于其他先进方法,AUROC达到84.61%。
- 在MedMNIST基准数据集上表现良好,AUROC达到93.8%。
- 模型和构建离群数据集的代码已公开分享。
点此查看论文截图

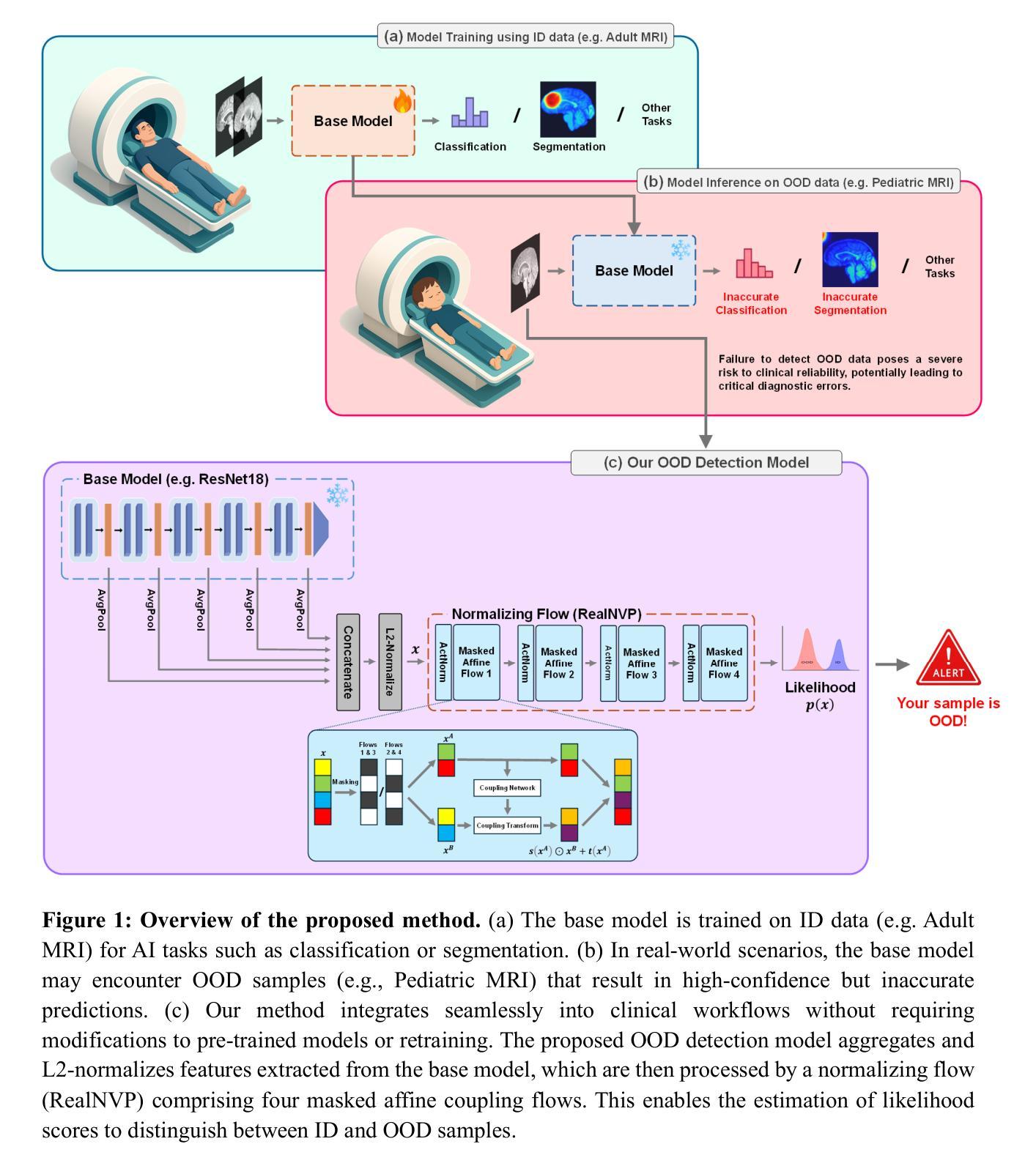
MedRAX: Medical Reasoning Agent for Chest X-ray
Authors:Adibvafa Fallahpour, Jun Ma, Alif Munim, Hongwei Lyu, Bo Wang
Chest X-rays (CXRs) play an integral role in driving critical decisions in disease management and patient care. While recent innovations have led to specialized models for various CXR interpretation tasks, these solutions often operate in isolation, limiting their practical utility in clinical practice. We present MedRAX, the first versatile AI agent that seamlessly integrates state-of-the-art CXR analysis tools and multimodal large language models into a unified framework. MedRAX dynamically leverages these models to address complex medical queries without requiring additional training. To rigorously evaluate its capabilities, we introduce ChestAgentBench, a comprehensive benchmark containing 2,500 complex medical queries across 7 diverse categories. Our experiments demonstrate that MedRAX achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both open-source and proprietary models, representing a significant step toward the practical deployment of automated CXR interpretation systems. Data and code have been publicly available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedRAX
胸部X光检查(CXRs)在疾病管理和患者护理中起着至关重要的决策作用。虽然最近的创新已经出现了针对各种CXR解读任务的专业模型,但这些解决方案往往独立运行,限制了它们在临床实践中的实用应用。我们推出了MedRAX,这是第一个将先进的CXR分析工具和多模态大型语言模型无缝集成到统一框架中的通用AI代理。MedRAX能够动态利用这些模型解决复杂的医学查询,无需额外的训练。为了严格评估其能力,我们推出了ChestAgentBench,这是一个包含2500个复杂医学查询的全面基准测试,涉及7个不同类别。我们的实验表明,与开源和专有模型相比,MedRAX达到了最先进的性能表现,朝着实际部署自动化CXR解读系统迈出了重要的一步。数据和代码已公开提供在https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedRAX。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 4 figures, 5 Tables
Summary
CXR在临床决策和病人护理中起到关键作用,尽管目前有许多专业模型用于CXR解读任务,但这些模型通常在实践中操作孤立。现在提出MedRAX统一框架,将最新CXR分析工具和多模态大型语言模型无缝集成。它可动态使用这些模型来解决复杂的医疗查询而无需额外训练。实验表明,与开源和专有模型相比,MedRAX在性能上达到最佳水平。这是向实用自动化CXR解读系统实际应用迈出的一步。具体详情参见GitHub链接。
Key Takeaways
- CXR在临床决策和护理中具有重要作用。
- 目前针对CXR的专业模型大多在操作中相互独立,缺乏实践效用。
- MedRAX作为首个集成的AI智能体,整合了最新的CXR分析工具和多模态大型语言模型。
- MedRAX能够动态利用这些模型来解决复杂的医疗查询,无需额外训练。
- ChestAgentBench是一个包含七种不同类别、总共含有2,500个复杂医疗查询的综合基准测试平台。
- MedRAX的性能已经达到最佳水平,超越了开源和专有模型。
点此查看论文截图


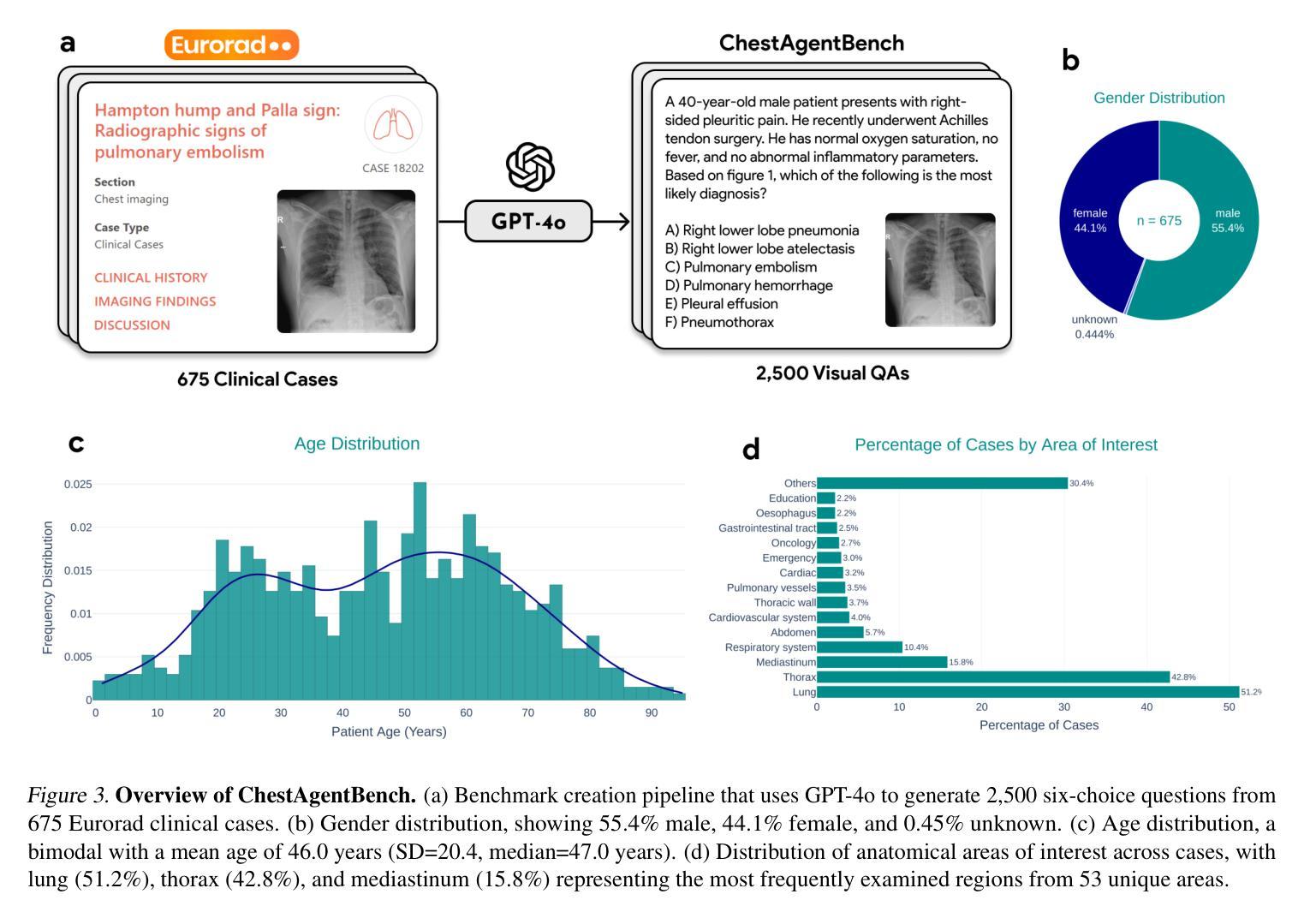
Distribution-aware Fairness Learning in Medical Image Segmentation From A Control-Theoretic Perspective
Authors:Yujin Oh, Pengfei Jin, Sangjoon Park, Sekeun Kim, Siyeop Yoon, Kyungsang Kim, Jin Sung Kim, Xiang Li, Quanzheng Li
Ensuring fairness in medical image segmentation is critical due to biases in imbalanced clinical data acquisition caused by demographic attributes (e.g., age, sex, race) and clinical factors (e.g., disease severity). To address these challenges, we introduce Distribution-aware Mixture of Experts (dMoE), inspired by optimal control theory. We provide a comprehensive analysis of its underlying mechanisms and clarify dMoE’s role in adapting to heterogeneous distributions in medical image segmentation. Furthermore, we integrate dMoE into multiple network architectures, demonstrating its broad applicability across diverse medical image analysis tasks. By incorporating demographic and clinical factors, dMoE achieves state-of-the-art performance on two 2D benchmark datasets and a 3D in-house dataset. Our results highlight the effectiveness of dMoE in mitigating biases from imbalanced distributions, offering a promising approach to bridging control theory and medical image segmentation within fairness learning paradigms. The source code will be made available. The source code is available at https://github.com/tvseg/dMoE.
确保医学图像分割的公平性是至关重要的,这是由于由人口统计学属性(如年龄、性别、种族)和临床因素(如疾病严重程度)导致的不平衡临床数据采集中的偏见。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了受最优控制理论启发的“分布感知专家混合(dMoE)”方法。我们对其内在机制进行了综合分析,并明确了dMoE在医学图像分割中适应异质分布的作用。此外,我们将dMoE集成到多种网络架构中,证明了其在不同医学图像分析任务中的广泛适用性。通过结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在两个2D基准数据集和一个3D内部数据集上达到了最先进的性能。我们的结果突出了dMoE在缓解不平衡分布中的偏见方面的有效性,为控制理论和医学图像分割在公平学习范式中的融合提供了一种有前途的方法。源代码将提供,可在[https://github.com/tvseg/dMoE获取。](https://github.com/tvseg/dMoE%E8%8E%B7%E5 TCTGMDSCDL%)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 spotlight, see https://openreview.net/forum?id=BUONdewsBa
摘要
确保医学图像分割中的公平性至关重要,这是因为由人口统计学特征(如年龄、性别、种族)和临床因素(如疾病严重程度)所导致的不均衡临床数据采集中存在的偏见。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了受最优控制理论启发的分布感知混合专家(dMoE)。我们对其内在机制进行了综合分析,并明确了dMoE在医学图像分割中适应异质分布的作用。此外,我们将dMoE集成到多种网络架构中,证明了其在不同医学图像分析任务中的广泛应用性。通过结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在两个二维基准数据集和一个三维内部数据集中实现了最佳性能。我们的结果突出了dMoE在缓解由不均衡分布引起的偏见方面的有效性,为控制理论与医学图像分割在公平性学习范式中的融合提供了有前景的方法。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割中的公平性至关重要,因不均衡临床数据导致的偏见是挑战。
- 引入分布感知混合专家(dMoE)解决此问题,受最优控制理论启发。
- dMoE能适应医学图像分割中的异质分布。
- dMoE集成到多种网络架构中,具有广泛的应用性。
- 结合人口统计学和临床因素,dMoE在多个数据集中实现最佳性能。
- dMoE有效缓解由不均衡分布引起的偏见。
- dMoE为控制理论与医学图像分割的公平性学习范式融合提供了前景。
点此查看论文截图

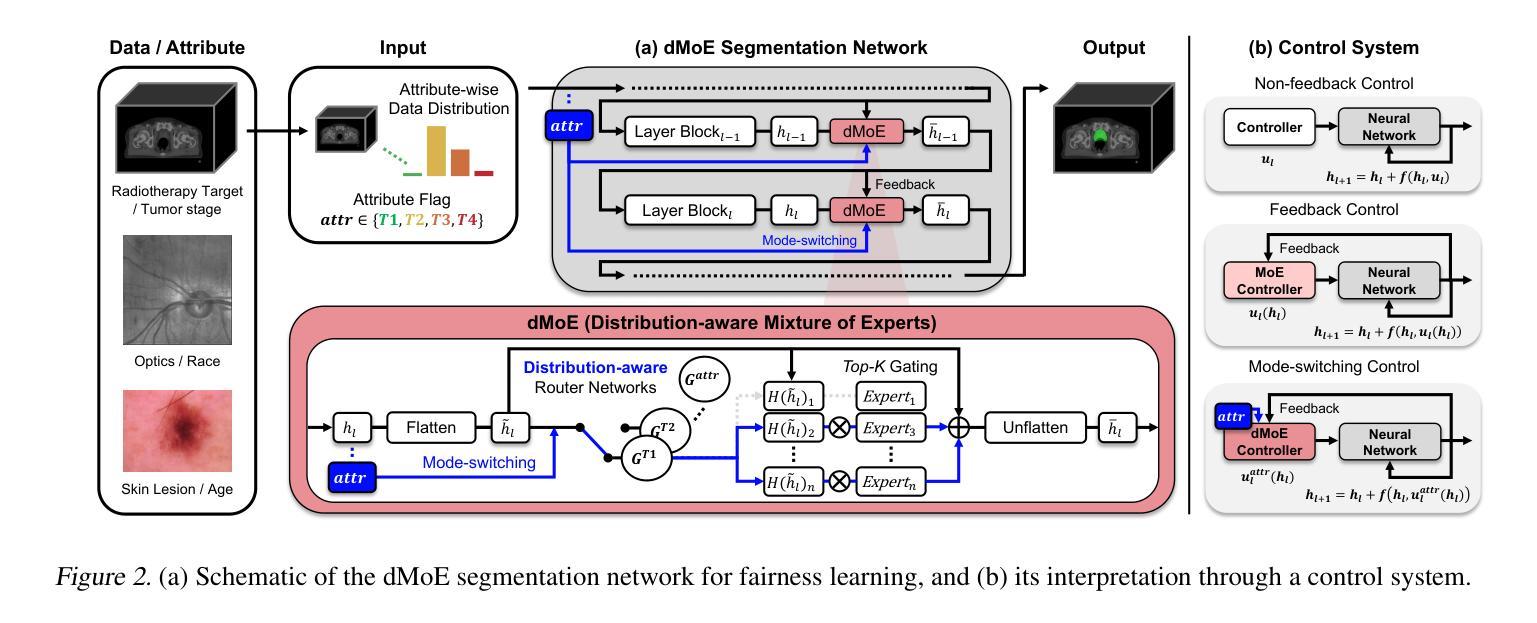
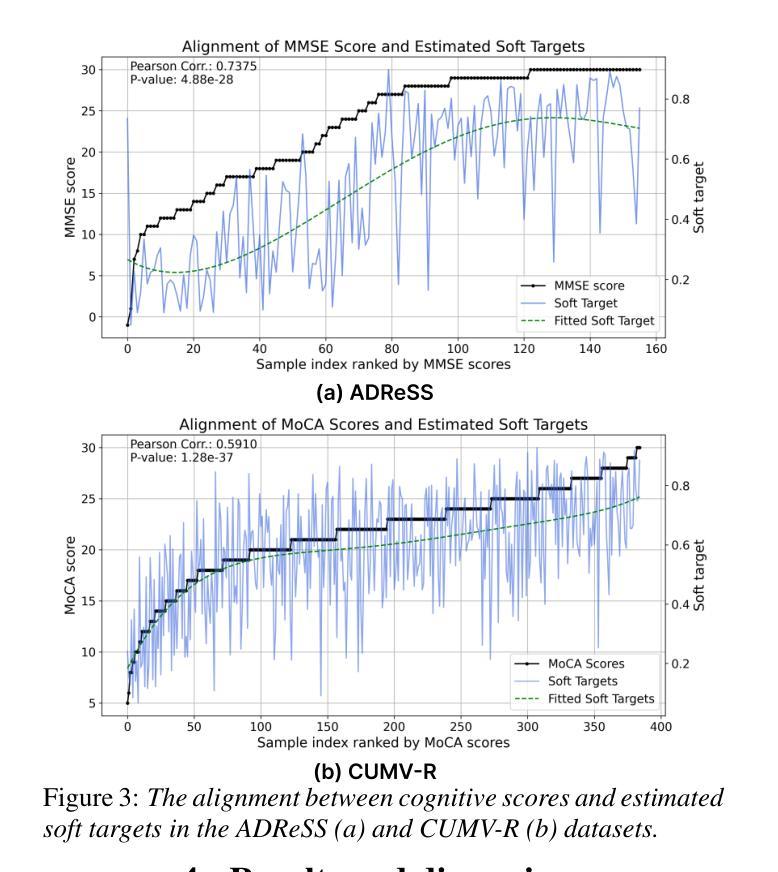
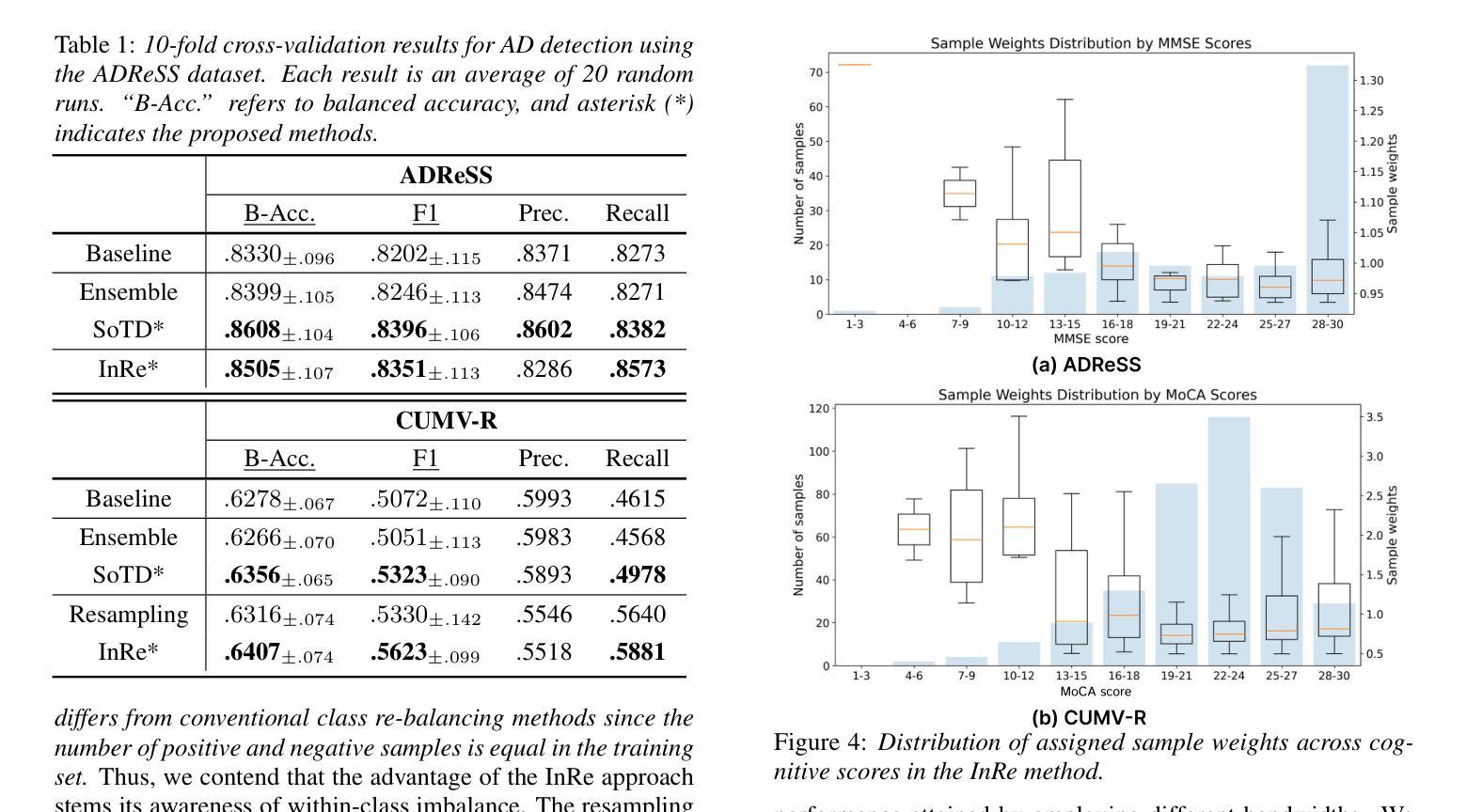
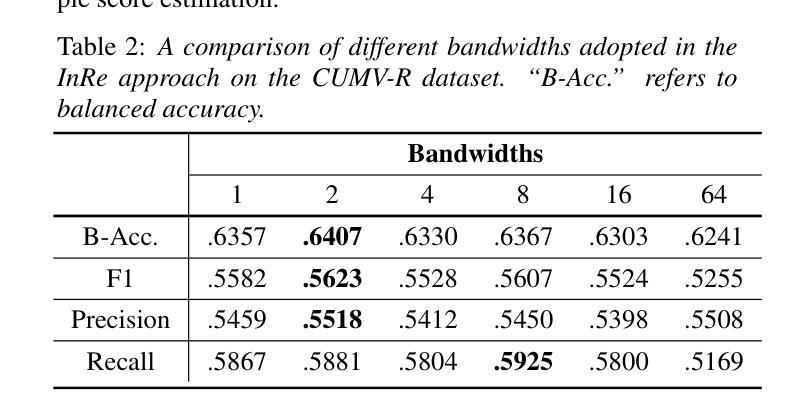
On the Within-class Variation Issue in Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Jiawen Kang, Dongrui Han, Lingwei Meng, Jingyan Zhou, Jinchao Li, Xixin Wu, Helen Meng
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) detection employs machine learning classification models to distinguish between individuals with AD and those without. Different from conventional classification tasks, we identify within-class variation as a critical challenge in AD detection: individuals with AD exhibit a spectrum of cognitive impairments. Therefore, simplistic binary AD classification may overlook two crucial aspects: within-class heterogeneity and instance-level imbalance. In this work, we found using a sample score estimator can generate sample-specific soft scores aligning with cognitive scores. We subsequently propose two simple yet effective methods: Soft Target Distillation (SoTD) and Instance-level Re-balancing (InRe), targeting two problems respectively. Based on the ADReSS and CU-MARVEL corpora, we demonstrated and analyzed the advantages of the proposed approaches in detection performance. These findings provide insights for developing robust and reliable AD detection models.
阿尔茨海默症(AD)检测利用机器学习分类模型来区分患有AD和无AD的个人。不同于传统的分类任务,我们认为类内变化是AD检测中的关键挑战:患有AD的个体表现出认知障碍的谱系。因此,简单的二元AD分类可能会忽略两个重要方面:类内异质性和实例级不平衡。在这项工作中,我们发现使用样本分数估计器可以生成与认知分数相对应的样本特定软分数。随后,我们提出了两种简单而有效的方法:软目标蒸馏(SoTD)和实例级再平衡(InRe),分别针对两个问题。基于ADReSS和CU-MARVEL语料库,我们展示并分析了所提出方法在检测性能方面的优势。这些发现对于开发稳健可靠的AD检测模型提供了启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by InterSpeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了利用机器学习分类模型进行阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测的挑战和方法。文章指出,不同于常规分类任务,AD检测面临的关键挑战是识别类内差异:患有AD的个体表现出多种程度的认知障碍。因此,简单的二元AD分类可能忽略两个重要因素:类内异质性和实例级不平衡。文章提出使用样本评分估算器生成与认知评分对齐的样本特定软评分,并针对这两个问题分别提出了两种简单有效的方法:软目标蒸馏(SoTD)和实例级再平衡(InRe)。基于ADReSS和CU-MARVEL语料库的实验分析,证明了所提方法在检测性能方面的优势,为开发稳健可靠的AD检测模型提供了启示。
Key Takeaways
- 阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测面临的关键挑战是识别类内差异,因为患者表现出多种程度的认知障碍。
- 简单的二元AD分类可能忽略类内异质性和实例级不平衡。
- 使用样本评分估算器可以生成与认知评分对齐的样本特定软评分。
- 针对类内差异和实例级不平衡问题,分别提出了软目标蒸馏(SoTD)和实例级再平衡(InRe)两种简单有效的方法。
- 基于ADReSS和CU-MARVEL语料库的实验分析证明了所提方法的优势。
点此查看论文截图
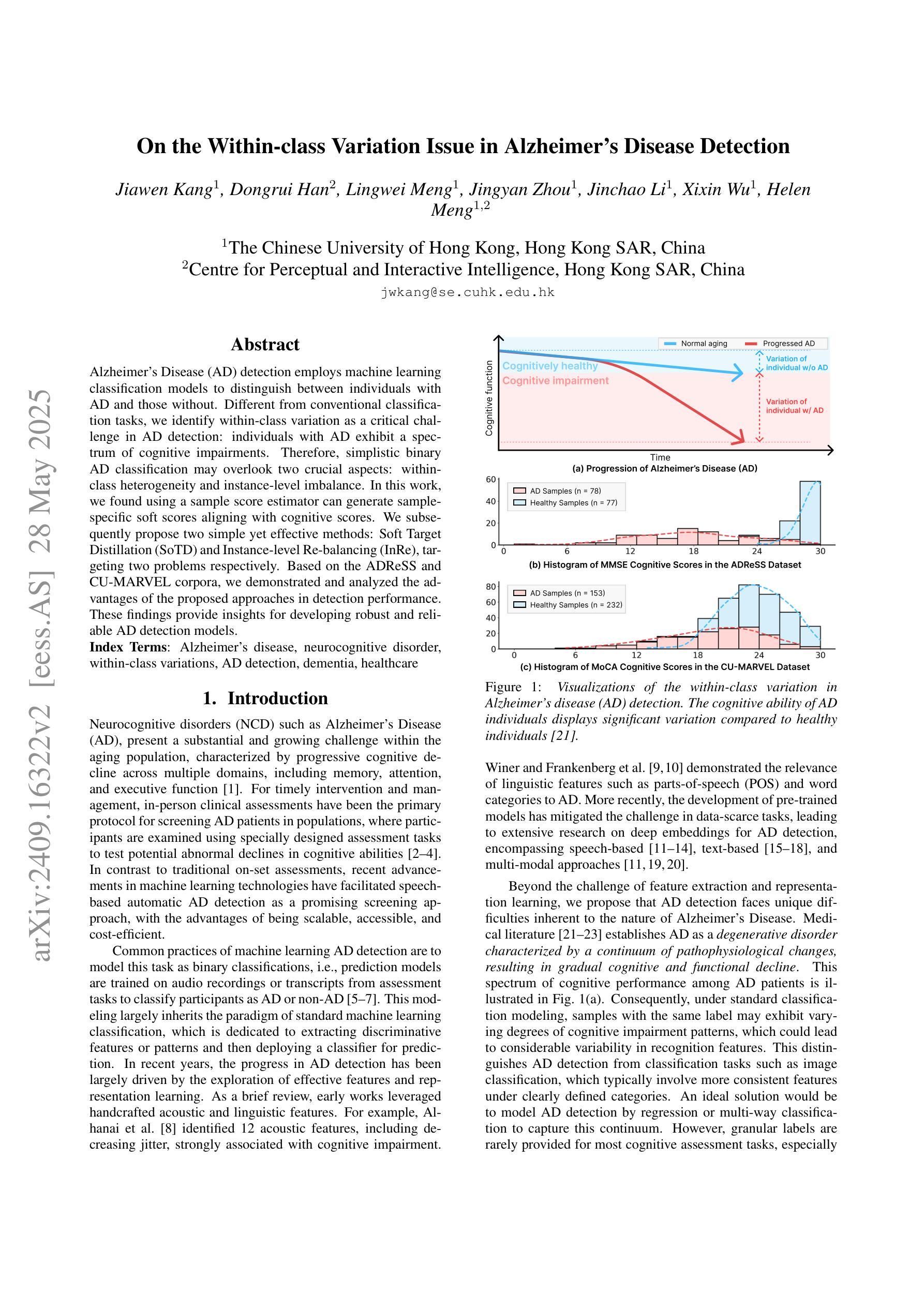
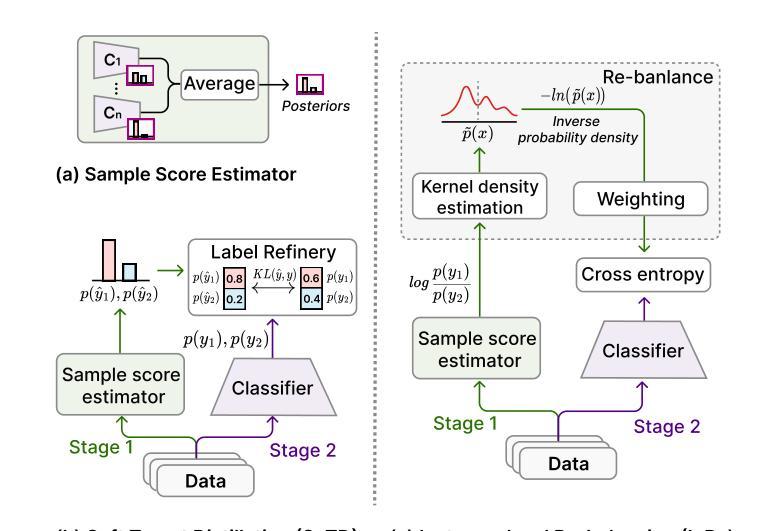
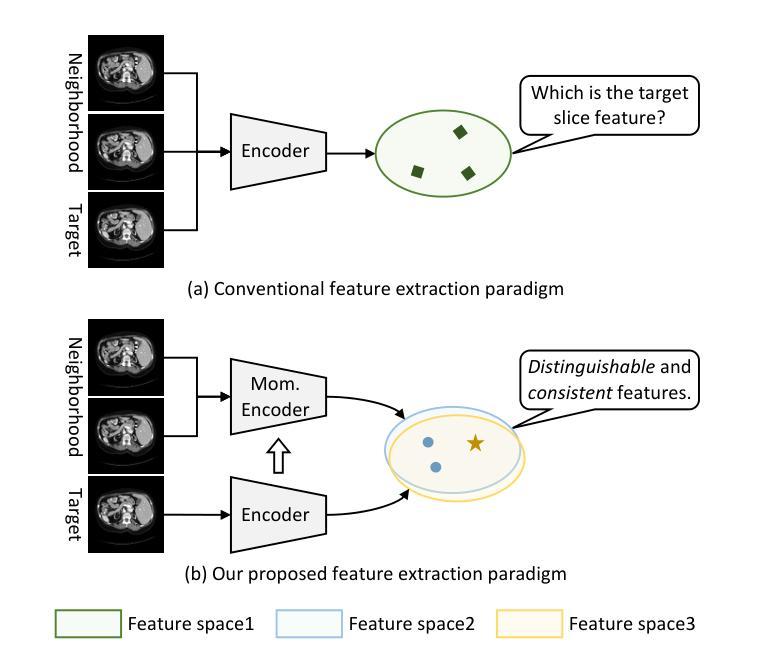
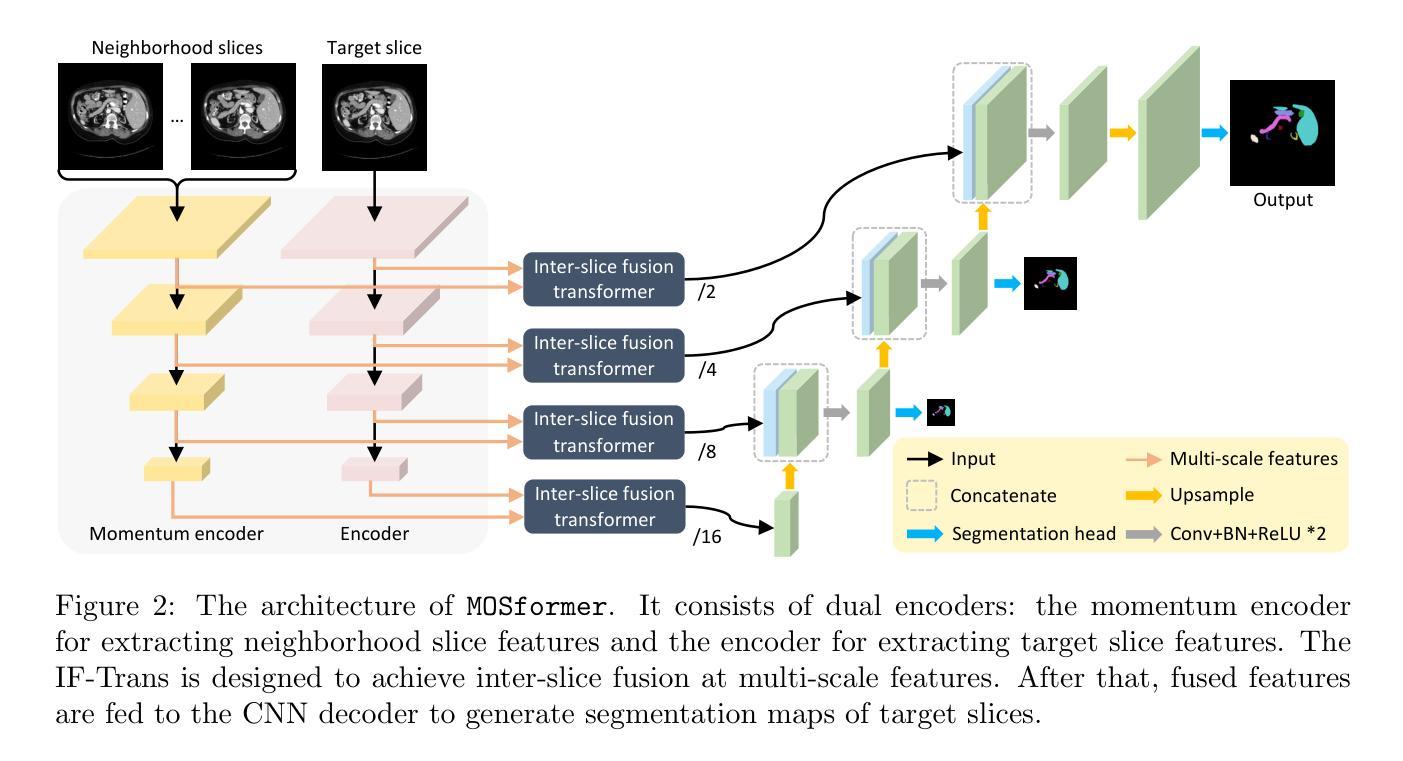
MOSformer: Momentum encoder-based inter-slice fusion transformer for medical image segmentation
Authors:De-Xing Huang, Xiao-Hu Zhou, Mei-Jiang Gui, Xiao-Liang Xie, Shi-Qi Liu, Shuang-Yi Wang, Zhen-Qiu Feng, Zeng-Guang Hou
Medical image segmentation takes an important position in various clinical applications. 2.5D-based segmentation models bridge the computational efficiency of 2D-based models with the spatial perception capabilities of 3D-based models. However, existing 2.5D-based models primarily adopt a single encoder to extract features of target and neighborhood slices, failing to effectively fuse inter-slice information, resulting in suboptimal segmentation performance. In this study, a novel momentum encoder-based inter-slice fusion transformer (MOSformer) is proposed to overcome this issue by leveraging inter-slice information at multi-scale feature maps extracted by different encoders. Specifically, dual encoders are employed to enhance feature distinguishability among different slices. One of the encoders is moving-averaged to maintain consistent slice representations. Moreover, an inter-slice fusion transformer (IF-Trans) module is developed to fuse inter-slice multi-scale features. The MOSformer is evaluated on three benchmark datasets (Synapse, ACDC, and AMOS), achieving a new state-of-the-art with 85.63%, 92.19%, and 85.43% DSC, respectively. These results demonstrate MOSformer’s competitiveness in medical image segmentation.
医学图像分割在各种临床应用中都扮演着重要角色。基于2.5D的分割模型融合了基于二维模型的计算效率和基于三维模型的感知能力。然而,现有的基于2.5D的模型主要使用单一编码器来提取目标和邻近切片特征,不能有效地融合切片间的信息,导致分割性能不够理想。本研究提出了一种新的动量编码器驱动的切片间融合转换器(MOSformer),通过利用不同编码器提取的多尺度特征图上的切片间信息来解决这一问题。具体来说,采用双编码器以增强不同切片特征的可分辨性。其中一个编码器进行移动平均以维持一致的切片表示。此外,还开发了一种切片融合转换器(IF-Trans)模块,用于融合切片多尺度特征。MOSformer在三个基准数据集(Synapse、ACDC和AMOS)上进行了评估,分别以85.63%、92.19%和85.43%的DSC达到了新的先进水平。这些结果证明了MOSformer在医学图像分割中的竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
摘要
本研究提出一种基于动量编码器(MOSformer)的跨切片融合转换器(IF-Trans),用于解决现有医学图像分割模型在跨切片信息融合方面的不足。通过利用不同编码器提取的多尺度特征映射上的跨切片信息,提高了特征区分度和模型性能。在三个基准数据集上的评估结果表明,MOSformer在医学图像分割方面达到了新的先进水平。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割在临床应用中的重要性。
- 现有基于2.5D的模型主要通过单一编码器提取目标及其邻近切片特征,但无法有效融合跨切片信息。
- 提出了一种新型的基于动量编码器的跨切片融合转换器(MOSformer),解决了上述问题。
- 通过利用不同编码器提取的多尺度特征映射上的跨切片信息,MOSformer显著提高了特征区分度和模型性能。
- 双编码器用于增强不同切片之间的特征区分度。其中,一个编码器进行移动平均处理以维持一致的切片表示。
- 开发了一种跨切片融合转换器(IF-Trans)模块来融合跨切片的多尺度特征。
点此查看论文截图