⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-06-01 更新
How Transformers Learn Regular Language Recognition: A Theoretical Study on Training Dynamics and Implicit Bias
Authors:Ruiquan Huang, Yingbin Liang, Jing Yang
Language recognition tasks are fundamental in natural language processing (NLP) and have been widely used to benchmark the performance of large language models (LLMs). These tasks also play a crucial role in explaining the working mechanisms of transformers. In this work, we focus on two representative tasks in the category of regular language recognition, known as even pairs' and parity check’, the aim of which is to determine whether the occurrences of certain subsequences in a given sequence are even. Our goal is to explore how a one-layer transformer, consisting of an attention layer followed by a linear layer, learns to solve these tasks by theoretically analyzing its training dynamics under gradient descent. While even pairs can be solved directly by a one-layer transformer, parity check need to be solved by integrating Chain-of-Thought (CoT), either into the inference stage of a transformer well-trained for the even pairs task, or into the training of a one-layer transformer. For both problems, our analysis shows that the joint training of attention and linear layers exhibits two distinct phases. In the first phase, the attention layer grows rapidly, mapping data sequences into separable vectors. In the second phase, the attention layer becomes stable, while the linear layer grows logarithmically and approaches in direction to a max-margin hyperplane that correctly separates the attention layer outputs into positive and negative samples, and the loss decreases at a rate of $O(1/t)$. Our experiments validate those theoretical results.
语言识别任务在自然语言处理(NLP)中扮演着根本性的角色,并且已广泛应用于评估大型语言模型(LLM)的性能。这些任务在解释变换器的工作原理方面也起着至关重要的作用。在这项工作中,我们专注于常规语言识别类别中的两个代表性任务,即“偶数对”和“奇偶校验”,这两个任务的目标是确定在给定的序列中某些子序列的出现是否为偶数。我们的目标是探索由注意力层和线性层组成的一层变换器如何学习解决这些任务,通过理论分析其在梯度下降下的训练动态。虽然“偶数对”可以直接由一层转换器解决,但“奇偶校验”需要通过将思维链(CoT)集成到为“偶数对”任务训练良好的转换器的推理阶段,或者集成到一层转换器的训练中来解决。对于这两个问题,我们的分析表明,注意力层和线性层的联合训练表现出两个明显的阶段。在第一阶段,注意力层迅速增长,将数据序列映射成可分离向量。在第二阶段,注意力层变得稳定,而线性层的增长呈对数趋势,并且朝向一个最大间隔超平面发展,该超平面能够正确地将注意力层的输出分为正样本和负样本,损失以O(1/t)的速度减少。我们的实验验证了这些理论结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了自然语言处理中的语言识别任务,特别是针对“偶数对”和“奇偶校验”这两个代表性任务的理论分析。文章聚焦于单层变压器模型,通过梯度下降分析其训练动态,探讨模型如何学习解决这些任务。研究发现,对于“偶数对”任务,单层变压器可直接解决;而对于“奇偶校验”任务,则需结合链式思维(CoT)进行推理。此外,研究发现注意力层和线性层的联合训练呈现两个阶段:第一阶段注意力层迅速增长,将数据序列映射为可分向量;第二阶段注意力层稳定,线性层对数增长并逐渐接近最大间隔超平面,将注意力层输出分为正负样本。实验验证了这些理论结果。
Key Takeaways
- 语言识别任务是自然语言处理中的重要基准,用于评估大型语言模型的性能,并揭示变压器工作机制。
- “偶数对”和“奇偶校验”是语言识别中的代表性任务,用于测试模型对序列中子序列出现次数的判断能力。
- 单层变压器模型通过梯度下降学习解决这些任务时,展现出两个训练阶段:注意力层的快速增长和线性层的对数增长。
- 对于“偶数对”任务,单层变压器可直接解决;而对于“奇偶校验”任务,需要引入链式思维(CoT)进行推理。
- 在训练过程中,注意力层将数据序列映射为可分向量,而线性层则负责根据最大间隔原则正确区分正负样本。
- 模型损失随训练时间递减,遵循O(1/t)的速率。
点此查看论文截图

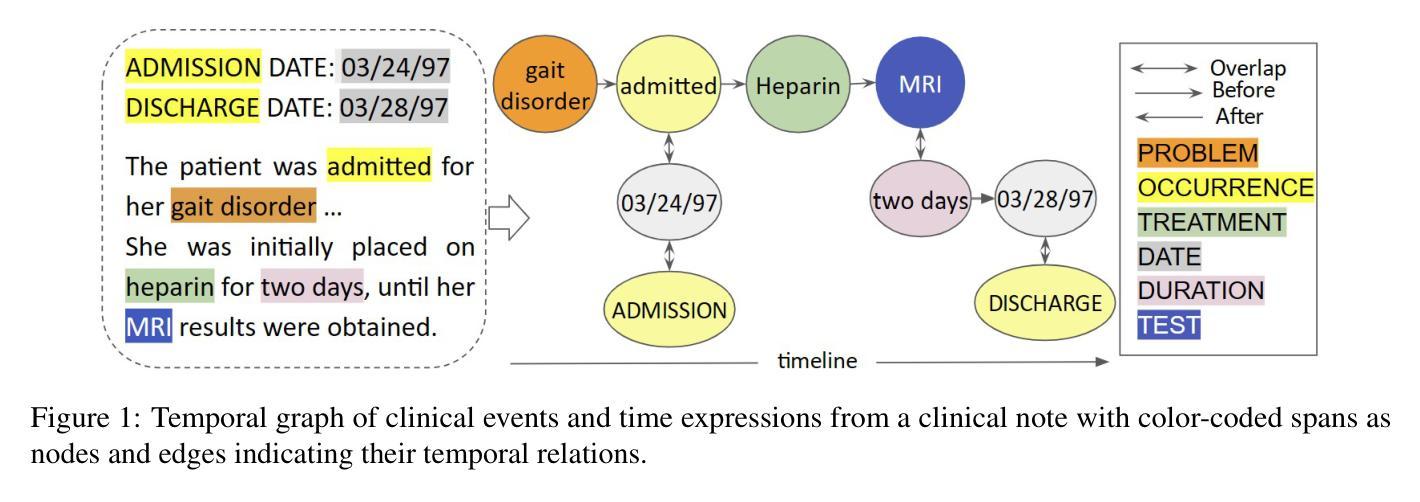
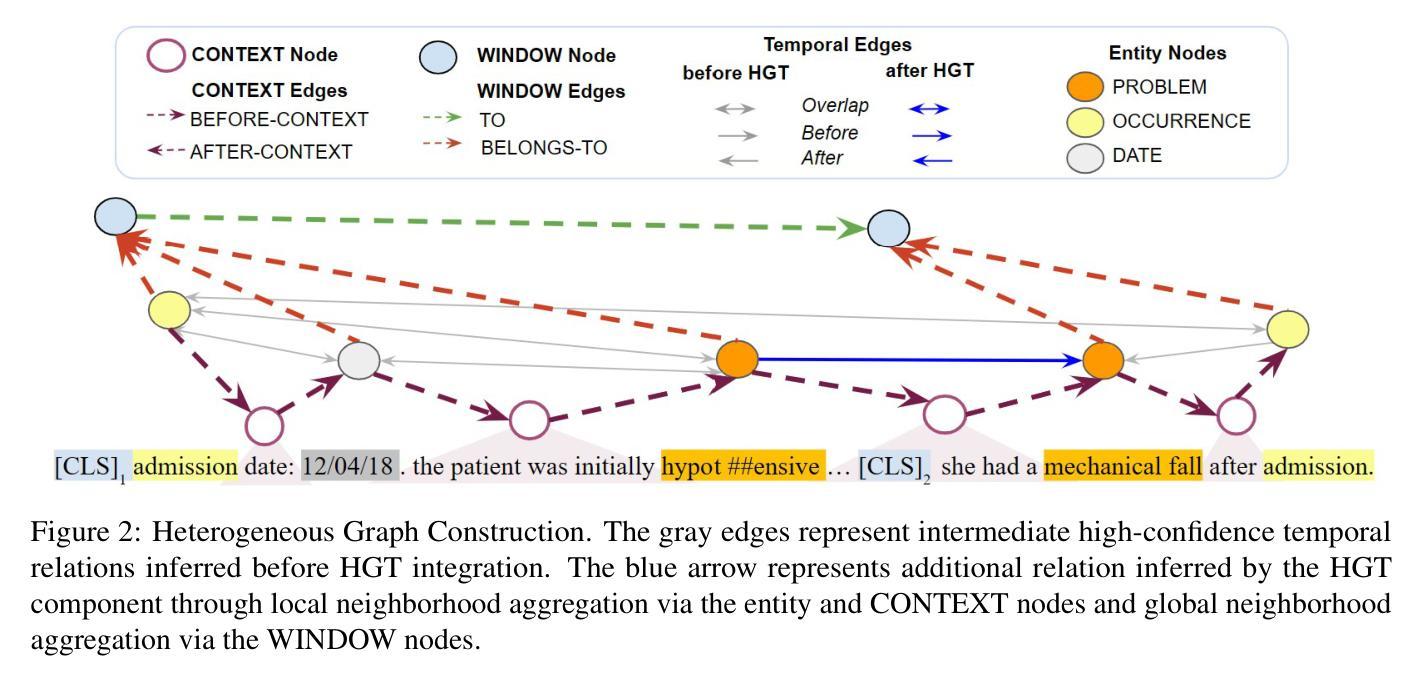
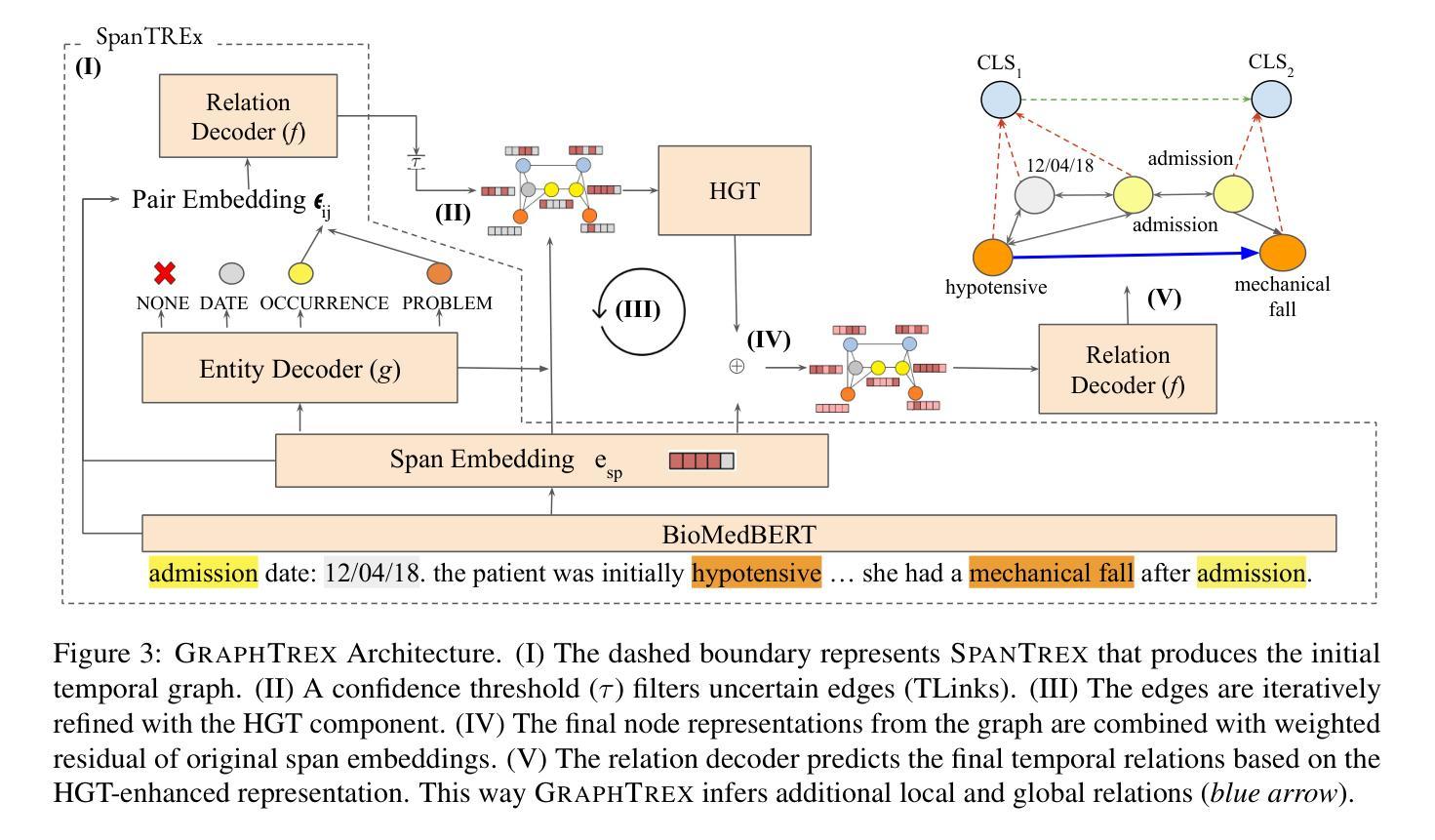
Temporal Relation Extraction in Clinical Texts: A Span-based Graph Transformer Approach
Authors:Rochana Chaturvedi, Peyman Baghershahi, Sourav Medya, Barbara Di Eugenio
Temporal information extraction from unstructured text is essential for contextualizing events and deriving actionable insights, particularly in the medical domain. We address the task of extracting clinical events and their temporal relations using the well-studied I2B2 2012 Temporal Relations Challenge corpus. This task is inherently challenging due to complex clinical language, long documents, and sparse annotations. We introduce GRAPHTREX, a novel method integrating span-based entity-relation extraction, clinical large pre-trained language models (LPLMs), and Heterogeneous Graph Transformers (HGT) to capture local and global dependencies. Our HGT component facilitates information propagation across the document through innovative global landmarks that bridge distant entities. Our method improves the state-of-the-art with 5.5% improvement in the tempeval $F_1$ score over the previous best and up to 8.9% improvement on long-range relations, which presents a formidable challenge. We further demonstrate generalizability by establishing a strong baseline on the E3C corpus. This work not only advances temporal information extraction but also lays the groundwork for improved diagnostic and prognostic models through enhanced temporal reasoning.
从非结构化文本中提取时间信息是上下文事件化和获取可操作洞察的关键,特别是在医疗领域。我们利用经过深入研究的I2B2 2012时间关系挑战赛语料库,来解决提取临床事件及其时间关系的任务。由于复杂的临床语言、长文档和稀疏的注释,此任务本质上是具有挑战性的。我们引入了GRAPHTREX,这是一种新颖的方法,融合了基于范围的实体关系提取、临床大型预训练语言模型(LPLMs)和异质图转换器(HGT),以捕捉局部和全局依赖关系。我们的HGT组件通过创新的全局地标,在文档中实现了跨文档的信息传播,这些地标架起了遥远实体之间的桥梁。我们的方法在tempeval F1分数上提高了5.5%,在远程关系上最多提高了8.9%,对先前的最佳水平构成了强有力的挑战。我们还通过在E3C语料库上建立了强大的基线来进一步证明了其泛化能力。这项工作不仅推动了时间信息提取的进步,而且通过增强时间推理为改进诊断和预后模型奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Introducing a novel method for joint extraction of medical events and temporal relations from free-text, leveraging clinical LPLMs and Heterogeneous Graph Transformers, achieving a 5.5% improvement over the previous state-of-the-art and up to 8.9% on long-range relations
Summary
本文介绍了基于I2B2 2012时序关系挑战语料库,利用span实体关系提取、临床大型预训练语言模型和异质图转换器(HGT)等技术,实现临床事件及其时序关系的提取。该方法通过全局地标创新性地实现文档中的信息传播,并有效提高远近实体关系的捕捉能力。本文方法不仅提升了时序信息提取的性能,还为诊断与预后模型的改进提供了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了利用I2B2 2012语料库进行临床事件及其时序关系提取的重要性。
- 提出了一种新的方法GRAPHTREX,集成了span实体关系提取、大型预训练语言模型和异质图转换器(HGT)。
- HGT组件通过全局地标实现文档中的信息传播,提高了捕捉局部和全局依赖关系的能力。
- 该方法在tempeval $F_1$得分上较之前最佳方法提高了5.5%,并在长程关系上提高了8.9%。
- 该方法不仅在时序信息提取上表现优秀,还在诊断和预后模型的改进中展现出潜力。
- 方法具有良好的泛化能力,能够在E3C语料库上建立强大的基线。
点此查看论文截图

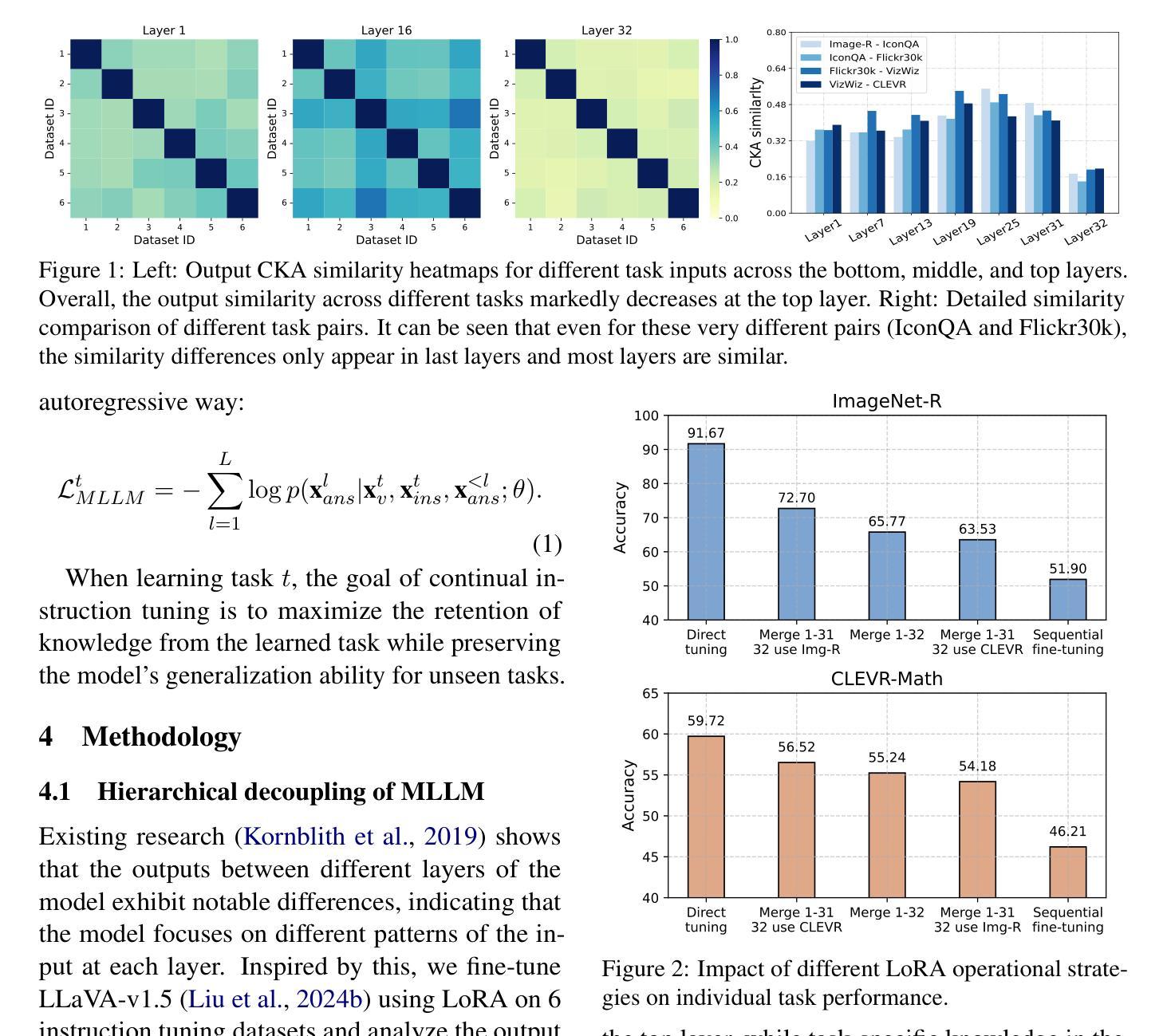
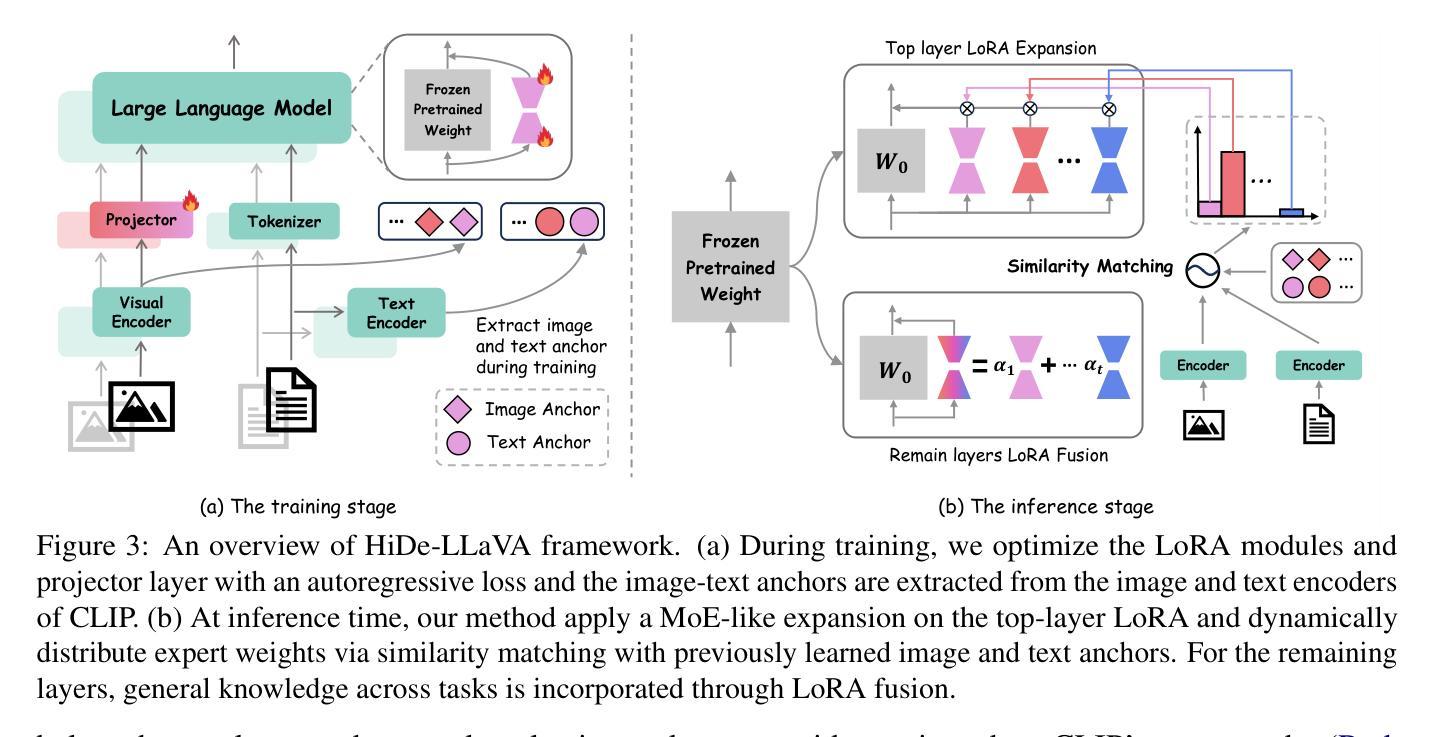
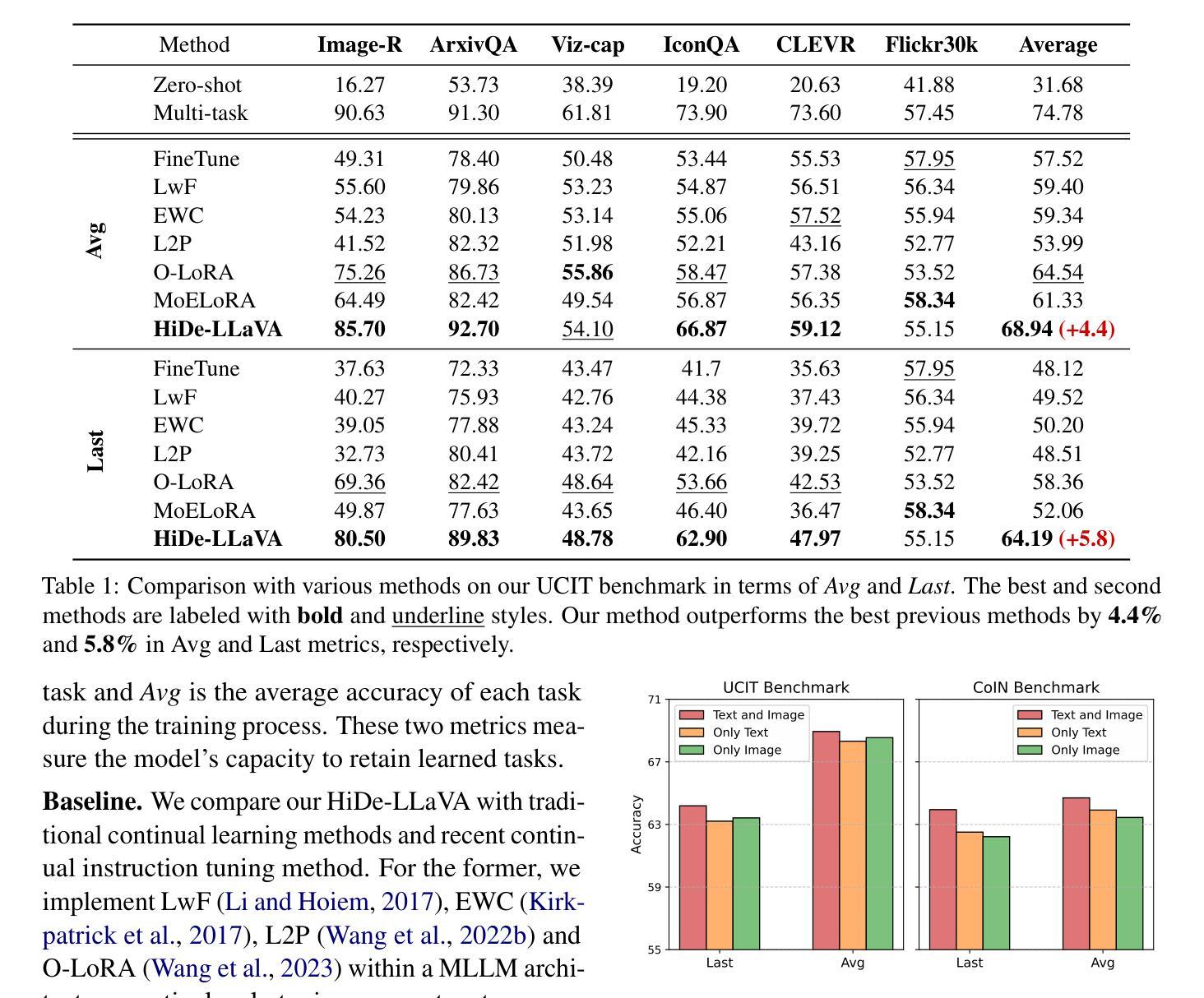
HiDe-LLaVA: Hierarchical Decoupling for Continual Instruction Tuning of Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Haiyang Guo, Fanhu Zeng, Ziwei Xiang, Fei Zhu, Da-Han Wang, Xu-Yao Zhang, Cheng-Lin Liu
Instruction tuning is widely used to improve a pre-trained Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) by training it on curated task-specific datasets, enabling better comprehension of human instructions. However, it is infeasible to collect all possible instruction datasets simultaneously in real-world scenarios. Thus, enabling MLLM with continual instruction tuning is essential for maintaining their adaptability. However, existing methods often trade off memory efficiency for performance gains, significantly compromising overall efficiency. In this paper, we propose a task-specific expansion and task-general fusion framework based on the variations in Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA) similarity across different model layers when trained on diverse datasets. Furthermore, we analyze the information leakage present in the existing benchmark and propose a new and more challenging benchmark to rationally evaluate the performance of different methods. Comprehensive experiments showcase a significant performance improvement of our method compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Code and dataset are released at https://github.com/Ghy0501/HiDe-LLaVA.
指令微调被广泛用于通过训练在精选的任务特定数据集上来改进预训练的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),从而实现更好的对人类指令的理解。然而,在现实世界的场景中,同时收集所有可能的指令数据集是不可能的。因此,为MLLM启用持续指令微调对于保持其适应性至关重要。然而,现有方法往往以牺牲内存效率为代价来提高性能,从而严重影响整体效率。在本文中,我们提出了一个基于训练多样化数据集时不同模型层中心内核对齐(CKA)相似性的变化的任务特定扩展和任务通用融合框架。此外,我们分析了现有基准测试中的信息泄露问题,并提出了一个新的更具挑战性的基准测试来合理评估不同方法的性能。综合实验表明,我们的方法与现有最先进的方法相比,性能得到了显著提升。代码和数据集发布在https://github.com/Ghy0501/HiDe-LLaVA上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACL 2025 (Main)
总结
训练数据受限的真实世界中,不断微调指导模型用于增强其对各种任务的学习是必要之举。现有方法存在记忆效率和性能之间的权衡问题。本文基于不同数据集训练下模型各层间的中心核对齐(CKA)相似度变化,提出特定任务扩展和通用任务融合框架,同时分析现有基准测试中的信息泄露问题,并推出更具挑战性的新基准测试。本文的方法较现有的尖端技术显著提高性能。GitHub上有对应的代码和数据集资源:https://github.com/Ghy0501/HiDe-LLaVA。该LLM性能持续改进技术对实现智能化升级大有裨益。
要点摘要
- 训练数据受限的真实世界中,持续微调指导模型以增强其对各种任务的学习至关重要。
- 现有方法往往牺牲记忆效率来换取性能提升,难以达到理想效果。
- 基于CKA相似度变化提出特定任务扩展和通用任务融合框架,有效改进性能。
点此查看论文截图

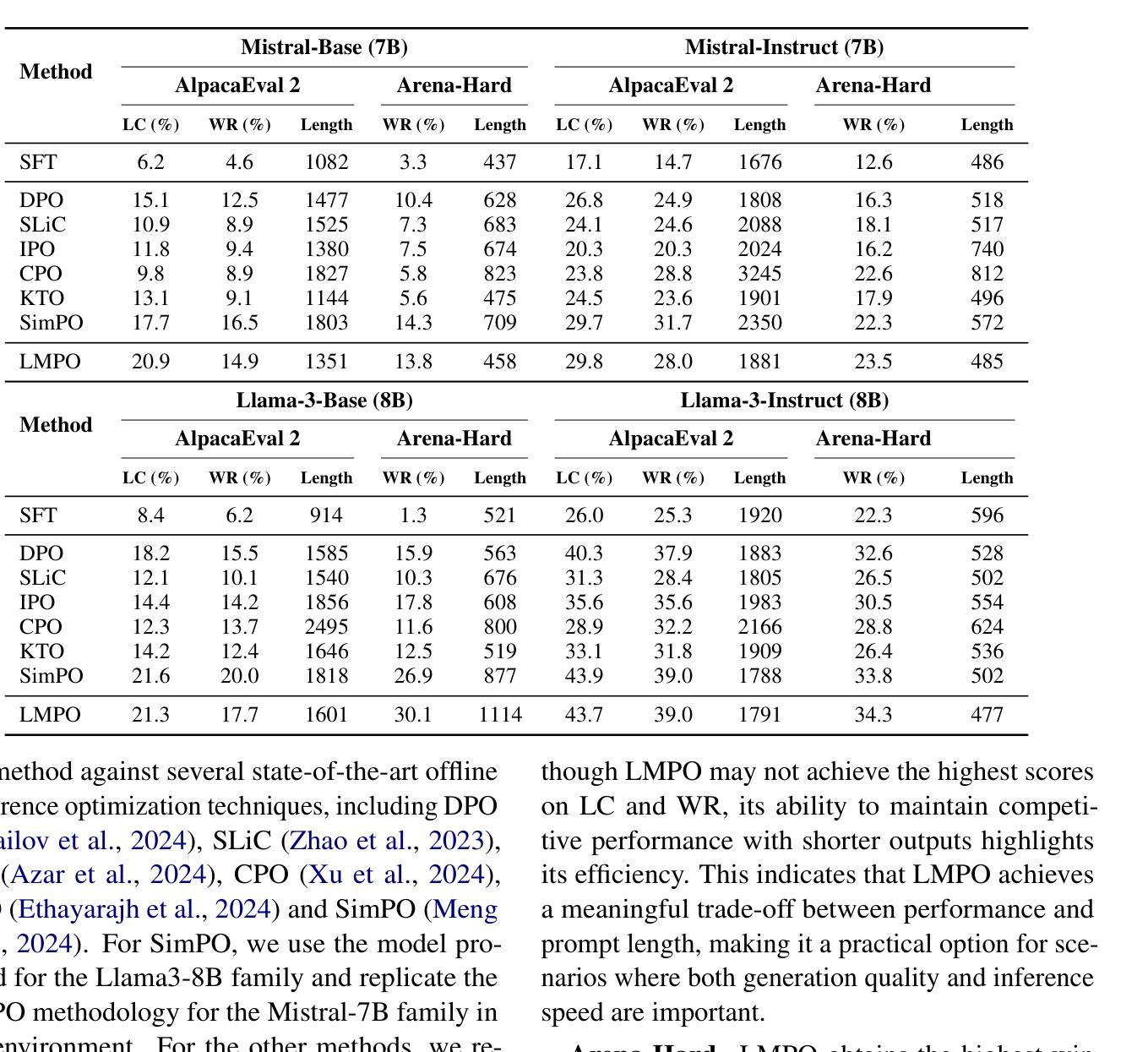
Length-Controlled Margin-Based Preference Optimization without Reference Model
Authors:Gengxu Li, Tingyu Xia, Yi Chang, Yuan Wu
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is a widely adopted offline algorithm for preference-based reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), designed to improve training simplicity and stability by redefining reward functions. However, DPO is hindered by several limitations, including length bias, memory inefficiency, and probability degradation. To address these challenges, we propose Length-Controlled Margin-Based Preference Optimization (LMPO), a more efficient and robust alternative. LMPO introduces a uniform reference model as an upper bound for the DPO loss, enabling a more accurate approximation of the original optimization objective. Additionally, an average log-probability optimization strategy is employed to minimize discrepancies between training and inference phases. A key innovation of LMPO lies in its Length-Controlled Margin-Based loss function, integrated within the Bradley-Terry framework. This loss function regulates response length while simultaneously widening the margin between preferred and rejected outputs. By doing so, it mitigates probability degradation for both accepted and discarded responses, addressing a significant limitation of existing methods. We evaluate LMPO against state-of-the-art preference optimization techniques on two open-ended large language models, Mistral and LLaMA3, across six conditional benchmarks. Our experimental results demonstrate that LMPO effectively controls response length, reduces probability degradation, and outperforms existing approaches. The code is available at https://github.com/gengxuli/LMPO.
直接偏好优化(DPO)是一种广泛应用于基于人类反馈的偏好型强化学习(RLHF)的离线算法,通过重新定义奖励函数来提高训练简洁性和稳定性。然而,DPO受到长度偏见、内存效率低下和概率退化等限制的影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了长度控制边距基于偏好优化(LMPO),这是一种更高效和稳健的替代方案。LMPO引入了一个统一的参考模型作为DPO损失的上界,能够更准确地逼近原始优化目标。此外,还采用平均对数概率优化策略,以减小训练和推理阶段之间的差异。LMPO的关键创新之处在于其长度控制边距基础上的损失函数,该函数结合了Bradley-Terry框架。该损失函数既控制响应长度,又扩大了首选和拒绝输出之间的边距。通过这样做,它减轻了接受和丢弃响应的概率退化问题,解决了现有方法的一个重要限制。我们在两个开放的大型语言模型Mistral和LLaMA3上,对LMPO与最先进的偏好优化技术进行了评估,跨越六个条件基准。我们的实验结果表明,LMPO有效地控制了响应长度,减少了概率退化,并优于现有方法。代码可在[https://github.com/gengxuli/LMPO找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文介绍了Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)在基于人类反馈的偏好强化学习(RLHF)中的局限性,并提出了Length-Controlled Margin-Based Preference Optimization(LMPO)作为更有效率且稳健的替代方案。LMPO引入了一个统一的参考模型作为DPO损失的上限,并采用平均对数概率优化策略来缩小训练和推理阶段的差异。其关键创新在于Length-Controlled Margin-Based损失函数,该损失函数能在Bradley-Terry框架下调节响应长度并扩大首选和拒绝输出之间的间隔,从而解决现有方法的概率退化问题。实验结果表明,LMPO在控制响应长度、减少概率退化方面表现优异,且在两个大型开放式语言模型上优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- DPO是强化学习中的常用离线算法,但在处理人类反馈时存在局限性。
- LMPO作为一种改进方法被提出,解决了DPO存在的长度偏见、内存效率低和概率退化等问题。
- LMPO通过引入统一参考模型和平均对数概率优化策略来提高效率和准确性。
- Length-Controlled Margin-Based损失函数是LMPO的关键创新点,它能调节响应长度并扩大首选和拒绝输出间的间隔。
- LMPO能有效控制响应长度并减少概率退化。
- 实验结果显示,LMPO在多个条件基准测试下表现优异,并在大型语言模型上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

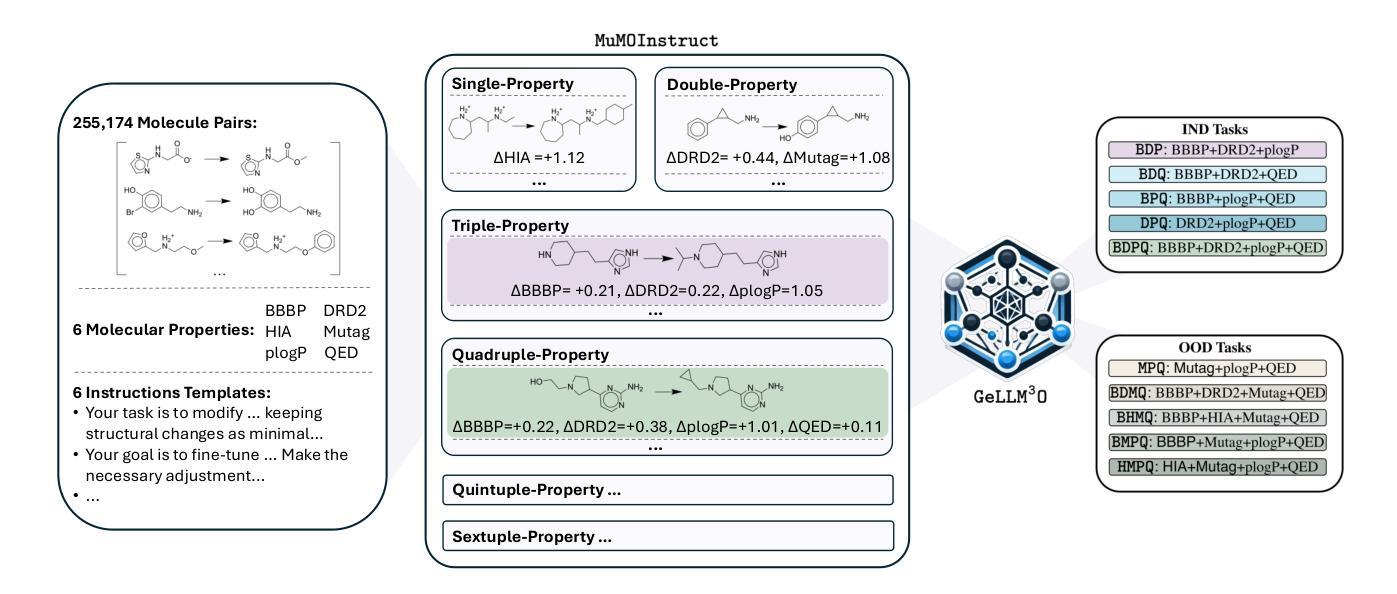
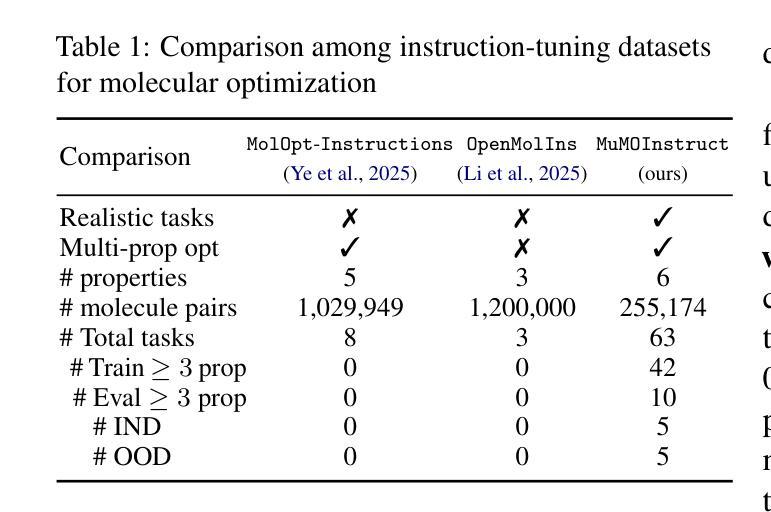
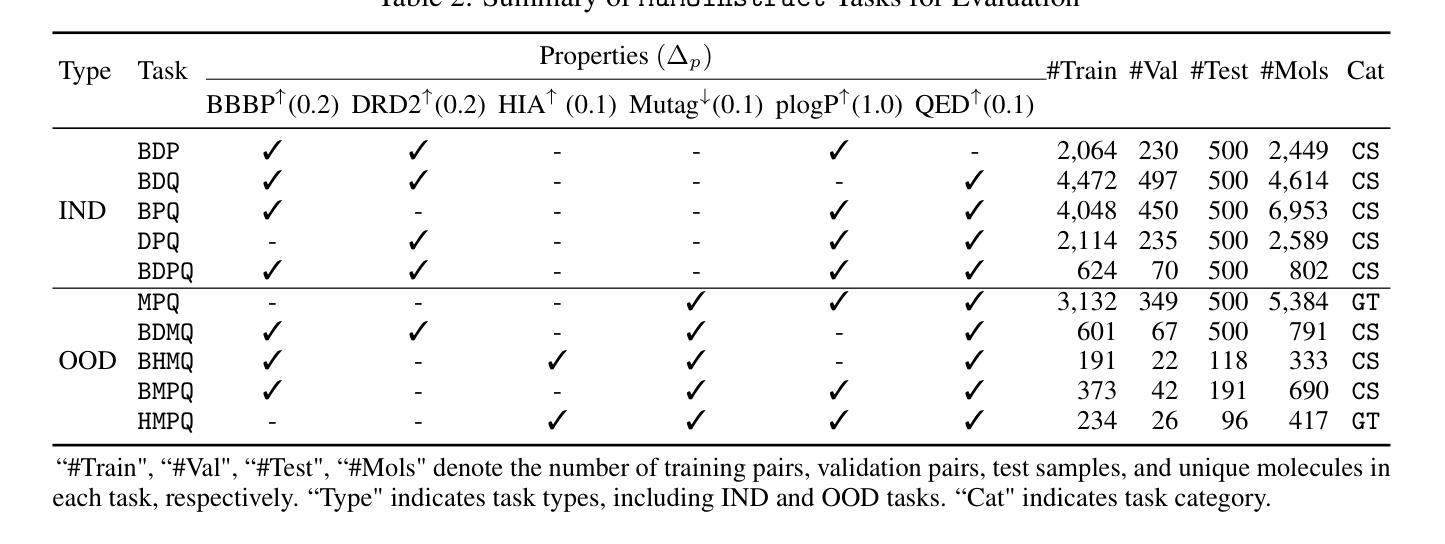
GeLLMO: Generalizing Large Language Models for Multi-property Molecule Optimization
Authors:Vishal Dey, Xiao Hu, Xia Ning
Despite recent advancements, most computational methods for molecule optimization are constrained to single- or double-property optimization tasks and suffer from poor scalability and generalizability to novel optimization tasks. Meanwhile, Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable out-of-domain generalizability to novel tasks. To demonstrate LLMs’ potential for molecule optimization, we introduce MuMOInstruct, the first high-quality instruction-tuning dataset specifically focused on complex multi-property molecule optimization tasks. Leveraging MuMOInstruct, we develop GeLLMOs, a series of instruction-tuned LLMs for molecule optimization. Extensive evaluations across 5 in-domain and 5 out-of-domain tasks demonstrate that GeLLMOs consistently outperform state-of-the-art baselines. GeLLMOs also exhibit outstanding zero-shot generalization to unseen tasks, significantly outperforming powerful closed-source LLMs. Such strong generalizability demonstrates the tremendous potential of GeLLMOs as foundational models for molecule optimization, thereby tackling novel optimization tasks without resource-intensive retraining. MuMOInstruct, models, and code are accessible through https://github.com/ninglab/GeLLMO.
尽管最近有所进展,但大多数分子优化的计算方法仍然局限于单属性或双属性优化任务,并且在扩展到新优化任务时面临可扩展性差和通用性不足的问题。与此同时,大型语言模型(LLM)在新型任务上表现出了显著的跨域泛化能力。为了展示LLM在分子优化方面的潜力,我们推出了MuMOInstruct,这是首个专注于复杂多属性分子优化任务的高质量指令调整数据集。利用MuMOInstruct,我们开发了一系列用于分子优化的指令调优LLM,称为GeLLMOs。在5个领域内的任务和5个跨域任务上的全面评估表明,GeLLMOs始终优于最新基线。GeLLMOs在未见过的任务上也表现出出色的零样本泛化能力,显著优于功能强大的封闭式LLM。这种强大的泛化能力证明了GeLLMOs作为分子优化基础模型的巨大潜力,从而可以在无需资源密集型的重新训练的情况下解决新型优化任务。可以通过https://github.com/ninglab/GeLLMO访问MuMOInstruct、模型和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACL Main 2025. Vishal Dey and Xiao Hu contributed equally to this paper
Summary
LLMs在分子优化领域展现出巨大潜力。为应对当前分子优化计算方法的局限,研究团队引入了MuMOInstruct数据集,并基于此开发了GeLLMOs系列模型。该模型在域内和域外任务上均表现优异,体现了强大的零射击能力,展示了其作为分子优化基础模型的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在分子优化领域具有巨大潜力。
- 当前分子优化计算方法存在局限性,如单/双属性优化任务的约束、较差的可扩展性和泛化能力。
- MuMOInstruct数据集是首个专注于复杂多属性分子优化任务的高质量指令调整数据集。
- GeLLMOs系列模型利用MuMOInstruct数据集进行开发,用于分子优化。
- GeLLMOs在域内和域外任务上的表现均超越现有基线。
- GeLLMOs展现出强大的零射击泛化能力,在未见任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

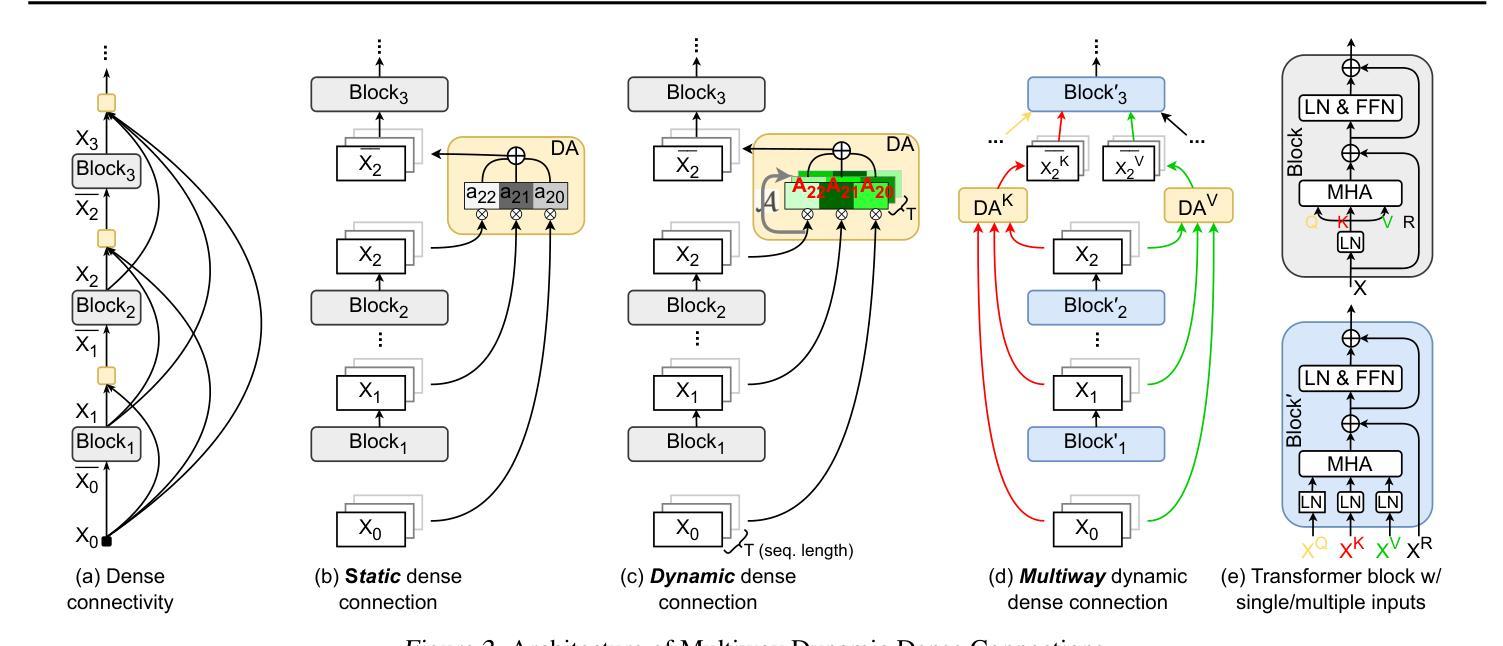
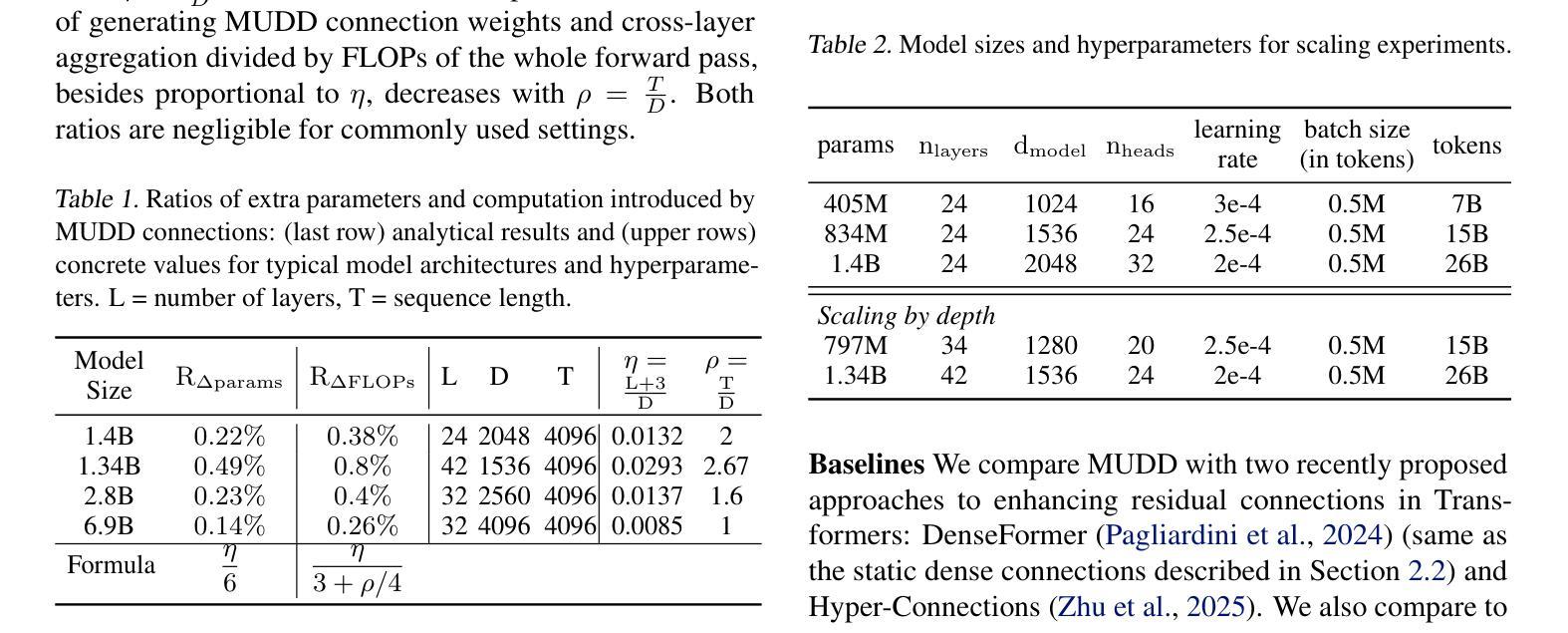
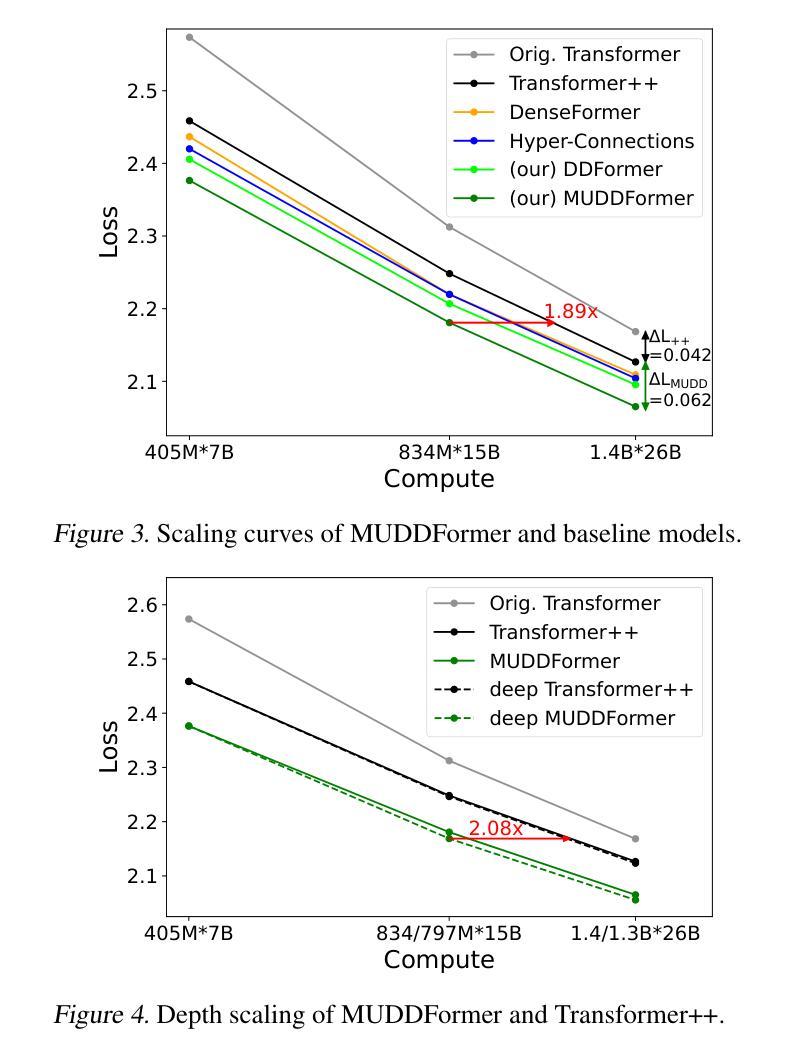
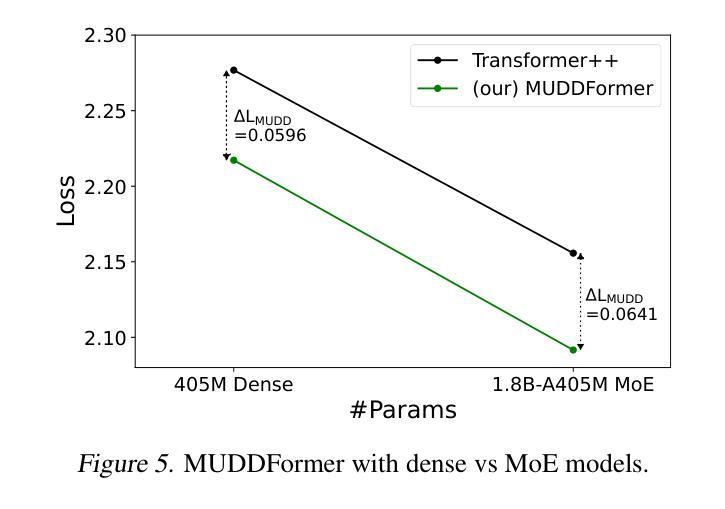
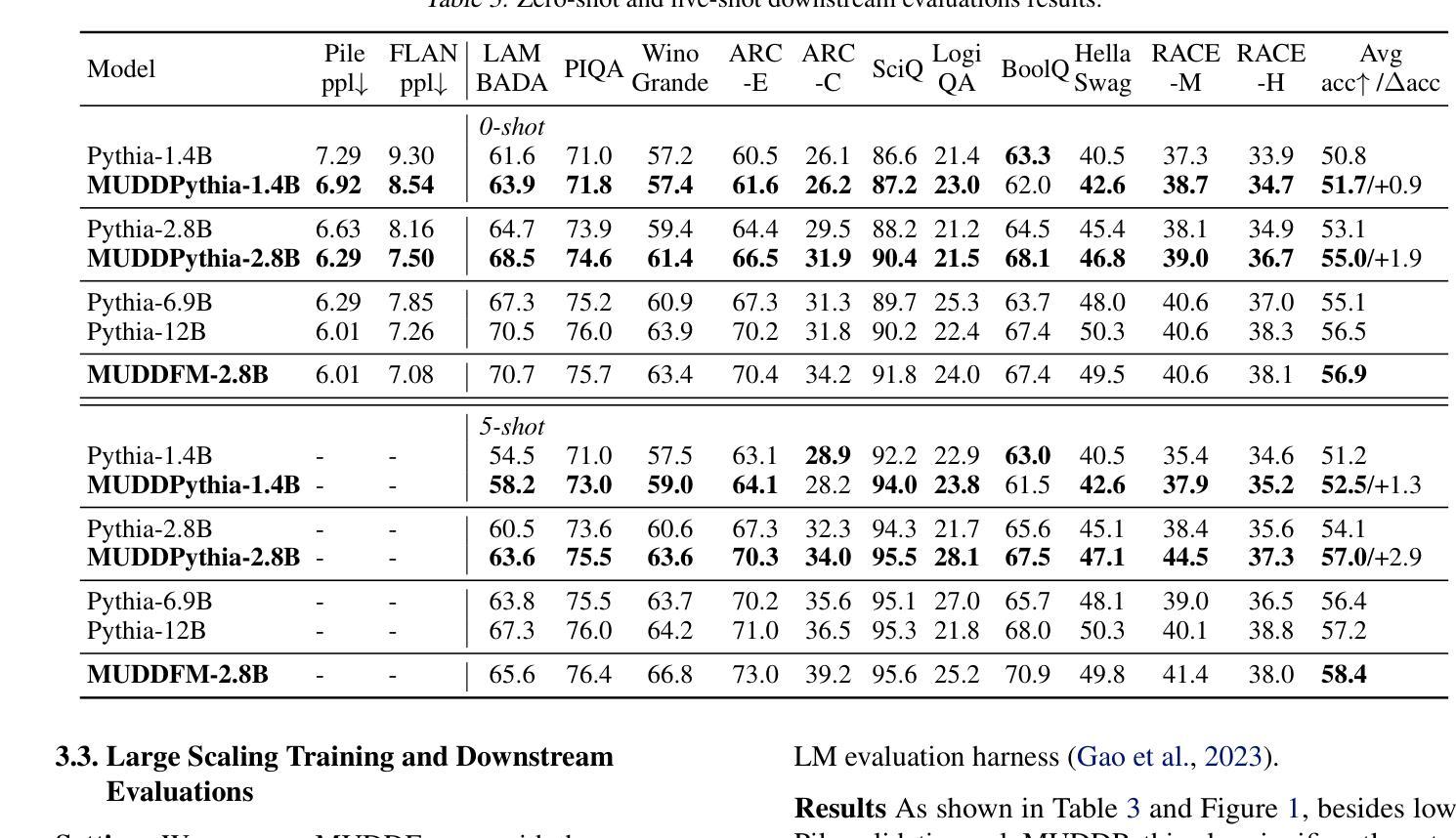
MUDDFormer: Breaking Residual Bottlenecks in Transformers via Multiway Dynamic Dense Connections
Authors:Da Xiao, Qingye Meng, Shengping Li, Xingyuan Yuan
We propose MUltiway Dynamic Dense (MUDD) connections, a simple yet effective method to address the limitations of residual connections and enhance cross-layer information flow in Transformers. Unlike existing dense connection approaches with static and shared connection weights, MUDD generates connection weights dynamically depending on hidden states at each sequence position and for each decoupled input stream (the query, key, value or residual) of a Transformer block. MUDD connections can be seamlessly integrated into any Transformer architecture to create MUDDFormer. Extensive experiments show that MUDDFormer significantly outperforms Transformers across various model architectures and scales in language modeling, achieving the performance of Transformers trained with 1.8X-2.4X compute. Notably, MUDDPythia-2.8B matches Pythia-6.9B in pretraining ppl and downstream tasks and even rivals Pythia-12B in five-shot settings, while adding only 0.23% parameters and 0.4% computation. Code in JAX and PyTorch and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/Caiyun-AI/MUDDFormer .
我们提出了多向动态密集(MUDD)连接,这是一种简单有效的方法,可以解决残差连接的局限性,并增强Transformer中的跨层信息流动。与现有具有静态和共享连接权重的密集连接方法不同,MUDD根据每个序列位置和Transformer块的每个独立输入流(查询、键、值或残差)的隐藏状态动态生成连接权重。MUDD连接可以无缝地集成到任何Transformer架构中,以创建MUDDFormer。大量实验表明,MUDDFormer在各种模型架构和规模上的语言建模中显著优于Transformer,实现了使用1.8倍至2.4倍计算的Transformer性能。值得注意的是,MUDDPythia-2.8B在预训练和下游任务中与Pythia-6.9B相匹敌,甚至在五个镜头设置中能够与Pythia-12B竞争,同时只增加了0.23%的参数和0.4%的计算量。JAX和PyTorch的代码以及预训练模型可在https://github.com/Caiyun-AI/MUDDFormer找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’25)
Summary
本文提出MUltiway Dynamic Dense(MUDD)连接,这是一种简单有效的方法,解决了残差连接的局限性,增强了Transformer中的跨层信息流动。MUDD动态生成连接权重,取决于每个序列位置和Transformer块的每个独立输入流(查询、键、值或残差)的隐藏状态。MUDD连接可以无缝集成到任何Transformer架构中,创建MUDDFormer。实验表明,MUDDFormer在各种模型架构和规模上的表现均优于Transformer,在语言建模方面达到了使用1.8X-2.4X计算训练的Transformer的性能。
Key Takeaways
MUDD连接是一种针对Transformer中残差连接局限性的解决方案,旨在增强跨层信息流动。
MUDD动态生成连接权重,基于每个序列位置和Transformer块内每个独立输入流的隐藏状态。
MUDD连接可无缝集成到任何Transformer架构中,形成MUDDFormer。
MUDDFormer在语言建模方面显著优于传统Transformer,且计算效率更高。
MUDDPythia-2.8B模型在预训练和下游任务中的性能与Pythia-6.9B相匹配,并在五镜头设置中甚至与Pythia-12B相竞争。
MUDD连接的参数增加很少(仅0.23%),计算量增加也很有限(仅0.4%)。
点此查看论文截图

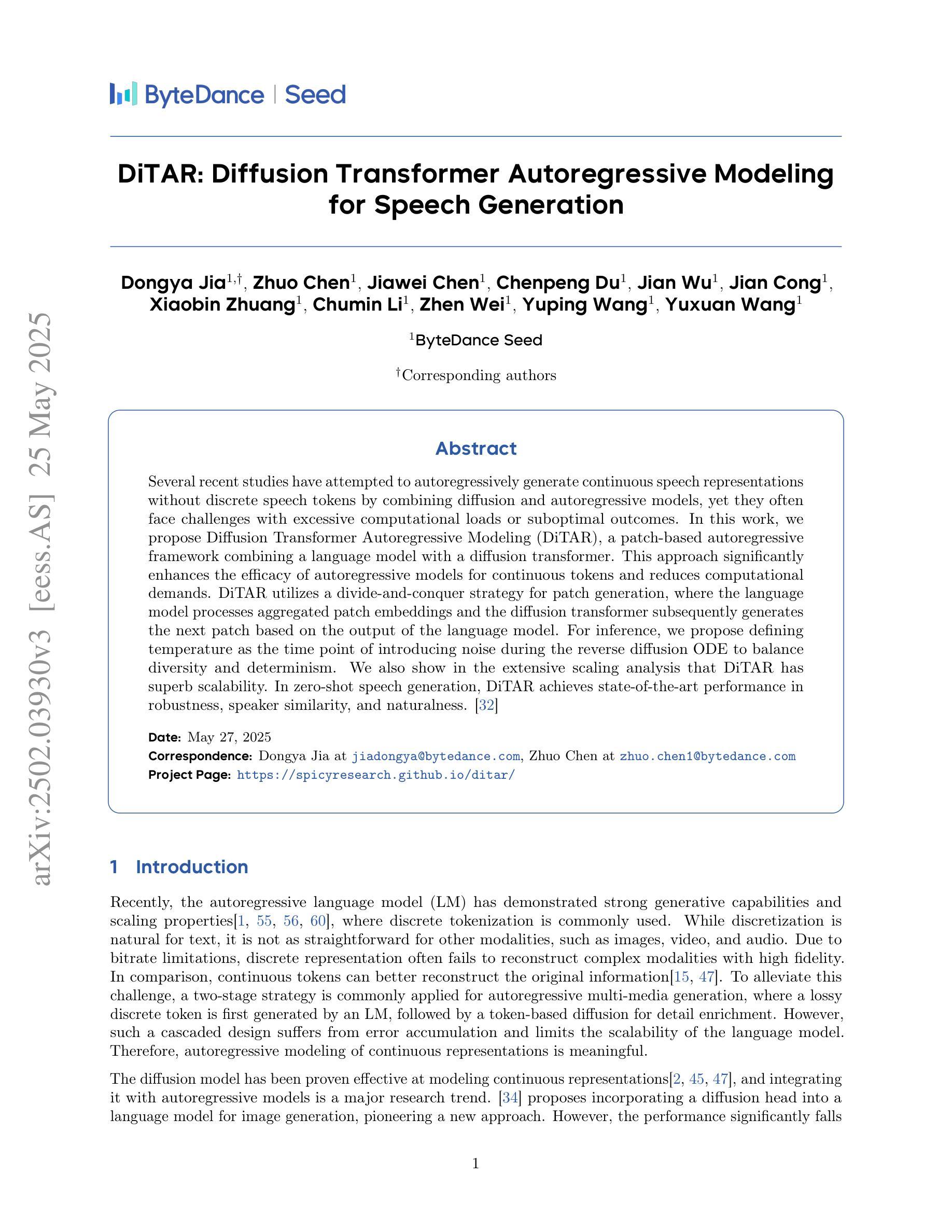
DiTAR: Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling for Speech Generation
Authors:Dongya Jia, Zhuo Chen, Jiawei Chen, Chenpeng Du, Jian Wu, Jian Cong, Xiaobin Zhuang, Chumin Li, Zhen Wei, Yuping Wang, Yuxuan Wang
Several recent studies have attempted to autoregressively generate continuous speech representations without discrete speech tokens by combining diffusion and autoregressive models, yet they often face challenges with excessive computational loads or suboptimal outcomes. In this work, we propose Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling (DiTAR), a patch-based autoregressive framework combining a language model with a diffusion transformer. This approach significantly enhances the efficacy of autoregressive models for continuous tokens and reduces computational demands. DiTAR utilizes a divide-and-conquer strategy for patch generation, where the language model processes aggregated patch embeddings and the diffusion transformer subsequently generates the next patch based on the output of the language model. For inference, we propose defining temperature as the time point of introducing noise during the reverse diffusion ODE to balance diversity and determinism. We also show in the extensive scaling analysis that DiTAR has superb scalability. In zero-shot speech generation, DiTAR achieves state-of-the-art performance in robustness, speaker similarity, and naturalness.
近期有几项研究尝试结合扩散模型和自回归模型,尝试无离散语音符号生成连续语音表示,但它们经常面临计算负载过大或结果不理想等挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了“扩散转换器自回归建模(DiTAR)”,这是一种结合语言模型和扩散转换器的基于补丁的自回归框架。这种方法显著提高了自回归模型对连续符号的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用一种分而治之的补丁生成策略,语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,然后扩散转换器根据语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。对于推理,我们提出将温度定义为在反向扩散ODE中引入噪声的时间点,以平衡多样性和确定性。在广泛的规模分析中,我们还表明DiTAR具有卓越的可扩展性。在零样本语音生成中,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似度和自然性方面达到了最新技术水平的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICML 2025
Summary
本文提出了Diffusion Transformer Autoregressive Modeling(DiTAR)方法,结合了语言模型和扩散转换器,用于基于连续令牌的自动回归生成语音表示。该方法显著提高了自动回归模型对连续令牌的有效性,并降低了计算需求。DiTAR采用分而治之的策略进行补丁生成,利用语言模型处理聚合的补丁嵌入,而扩散转换器则基于语言模型的输出生成下一个补丁。在推理过程中,通过定义温度来平衡多样性和确定性,即在反向扩散ODE过程中引入噪声的时间点。此外,DiTAR在零样本语音生成中实现了出色的性能,在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- DiTAR方法结合了语言模型和扩散转换器,用于基于连续令牌的自动回归生成语音表示。
- DiTAR采用分而治之的策略,利用语言模型处理补丁嵌入,扩散转换器则生成下一个补丁。
- 通过定义温度来平衡推理过程中的多样性和确定性。
- DiTAR在反向扩散ODE过程中引入噪声的时间点定义为温度,这是一种新的尝试。
- DiTAR具有出色的可扩展性,这在其广泛的规模分析中得到证明。
- 在零样本语音生成方面,DiTAR在稳健性、说话人相似性和自然性方面达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图
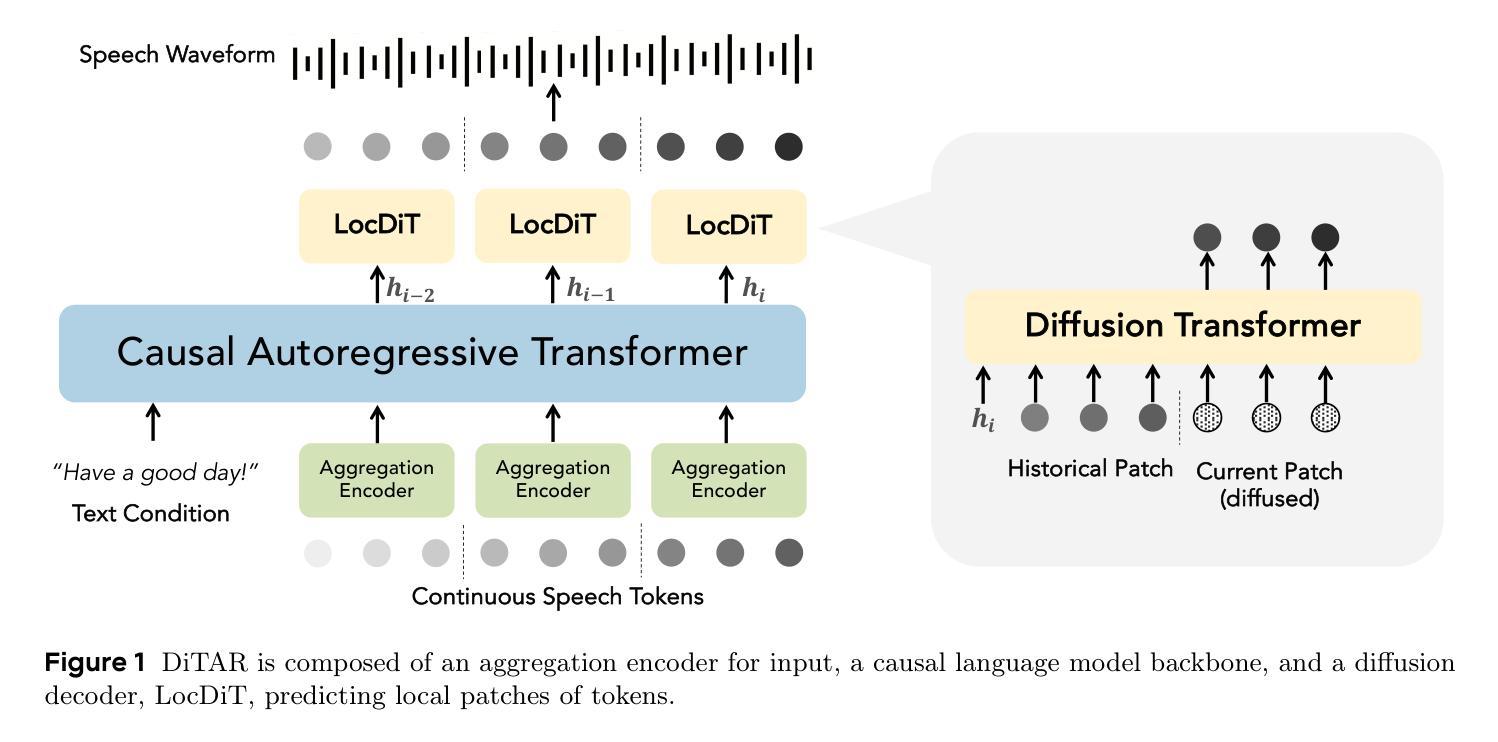

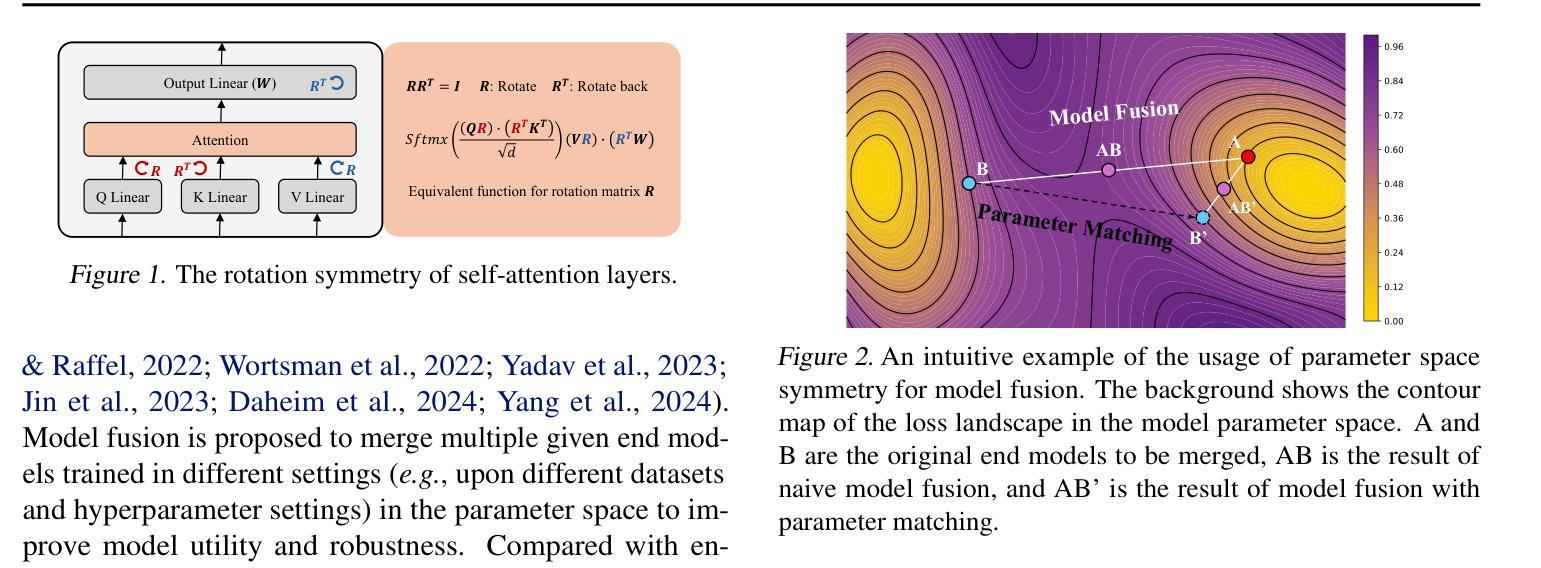
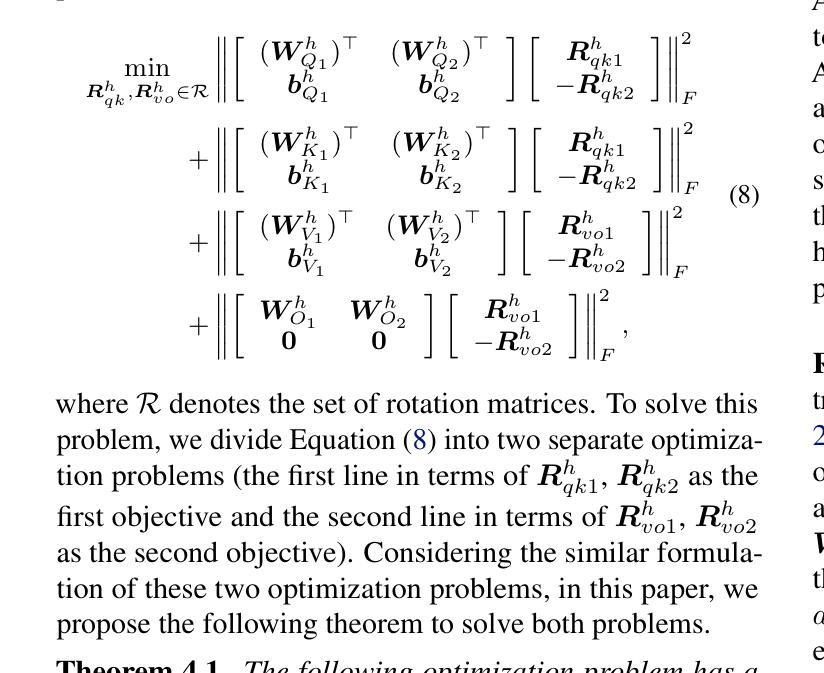
Beyond the Permutation Symmetry of Transformers: The Role of Rotation for Model Fusion
Authors:Binchi Zhang, Zaiyi Zheng, Zhengzhang Chen, Jundong Li
Symmetry in the parameter space of deep neural networks (DNNs) has proven beneficial for various deep learning applications. A well-known example is the permutation symmetry in Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs), where permuting the rows of weight matrices in one layer and applying the inverse permutation to adjacent layers yields a functionally equivalent model. While permutation symmetry fully characterizes the equivalence set for MLPs, its discrete nature limits its utility for transformers. In this paper, we introduce rotation symmetry, a novel form of parameter space symmetry for transformers that generalizes permutation symmetry by rotating parameter matrices in self-attention layers. Unlike permutation symmetry, rotation symmetry operates in a continuous domain, thereby significantly expanding the equivalence set for transformers. Based on this property, we propose a theoretically optimal parameter matching algorithm as a plug-and-play module to enhance model fusion. We evaluate our approach using pre-trained transformers across diverse natural language and vision tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our rotation symmetry-based matching algorithm substantially improves model fusion, highlighting the potential of parameter space symmetry to facilitate model fusion. Our code is available on https://github.com/zhengzaiyi/RotationSymmetry.
深度神经网络(DNNs)参数空间中的对称性已经被证明对各种深度学习应用有益。一个众所周知的例子是多层感知器(MLPs)中的置换对称性,其中对某一层的权重矩阵的行进行置换,并对相邻层应用反向置换,可以得到功能等效的模型。虽然置换对称性完全表征了MLPs的等价集,但其离散性质限制了其在变压器模型中的应用。在本文中,我们引入了旋转对称性,这是一种新型参数空间对称性,通过旋转自注意力层的参数矩阵来推广置换对称性。与置换对称性不同,旋转对称操作在一个连续域中进行,从而显著扩大了变压器的等价集。基于这一属性,我们提出了一种理论上的最优参数匹配算法,作为一个即插即用的模块来增强模型融合。我们使用预训练的变压器模型在多种自然语言处理和视觉任务上评估了我们的方法。实验结果表明,我们的基于旋转对称性的匹配算法极大地提高了模型融合的效果,凸显了参数空间对称性在促进模型融合方面的潜力。我们的代码位于https://github.com/zhengzaiyi/RotationSymmetry。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
深层神经网络参数空间的对称性对于深度学习应用具有重要意义。本文介绍了旋转对称性这一新型参数空间对称性形式,将其应用于变压器,并基于此性质提出了一种理论上的最佳参数匹配算法,用于增强模型融合能力。实验结果表明,该算法能显著提高模型融合性能。
Key Takeaways
- 对称性在深层神经网络参数空间中对深度学习应用有益。
- 论文提出了旋转对称性这一新型参数空间对称性形式。
- 旋转对称性能够广泛应用于变压器,是对排列对称性的重要推广。
- 基于旋转对称性,论文提出了一种理论上的最佳参数匹配算法。
- 该算法可作为即插即用模块,用于增强模型融合能力。
- 实验结果表明,该算法能显著提高模型融合性能。
点此查看论文截图

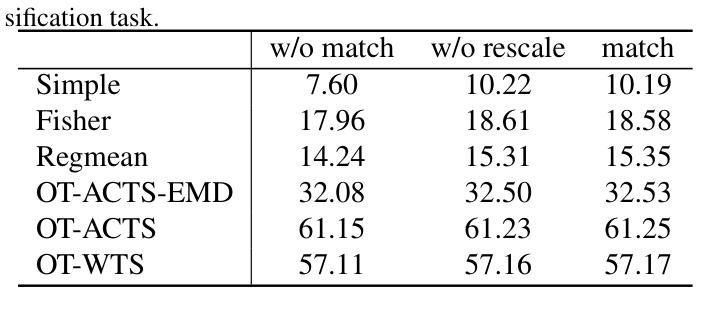
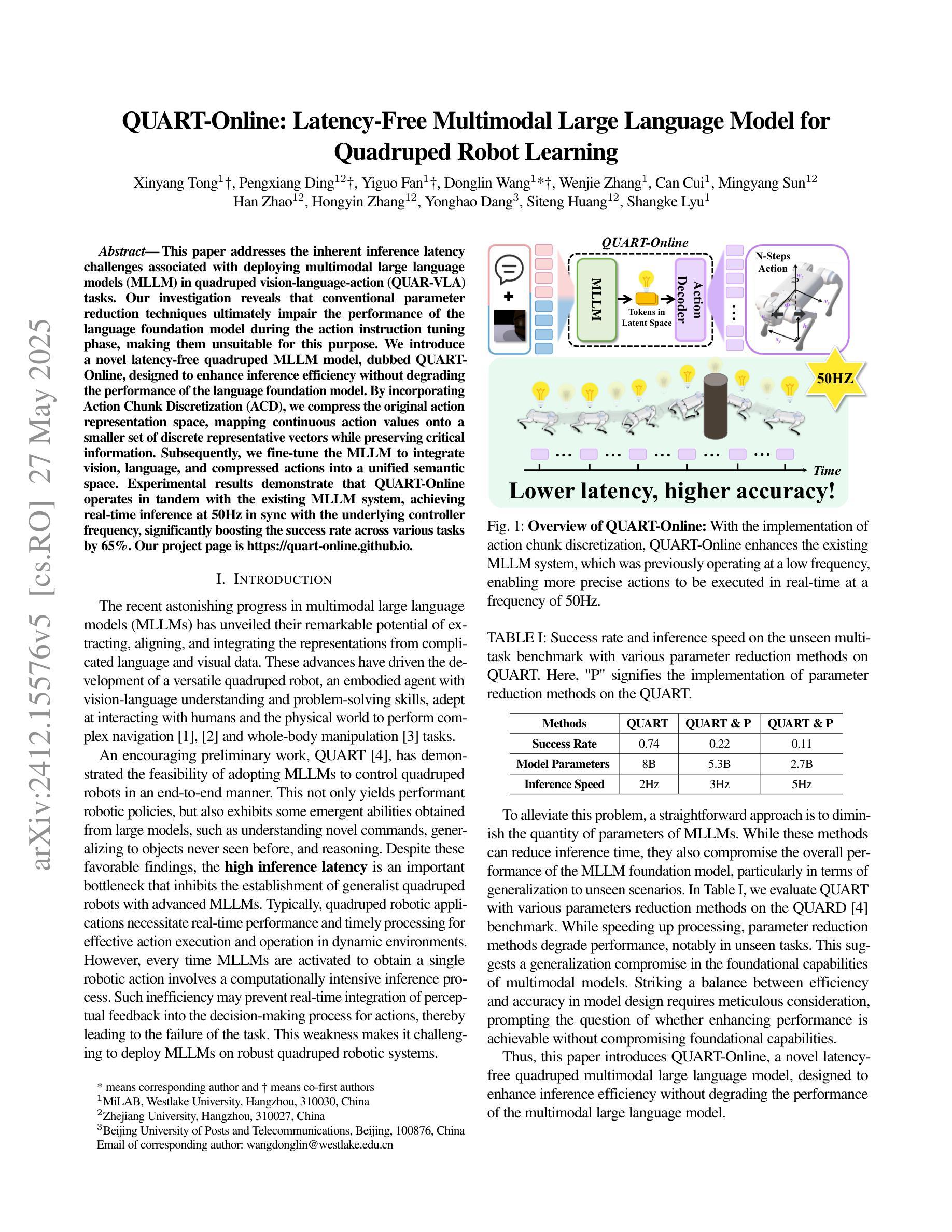
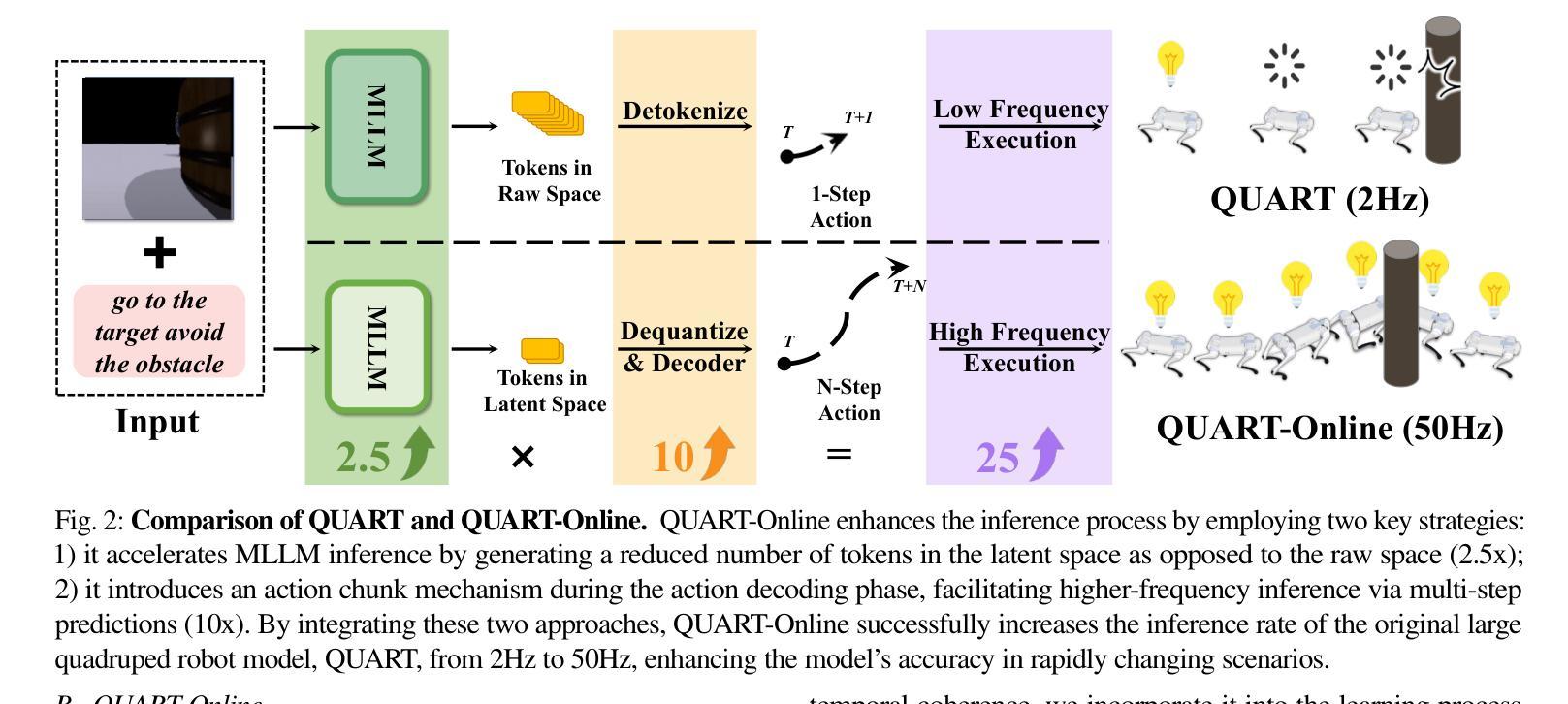
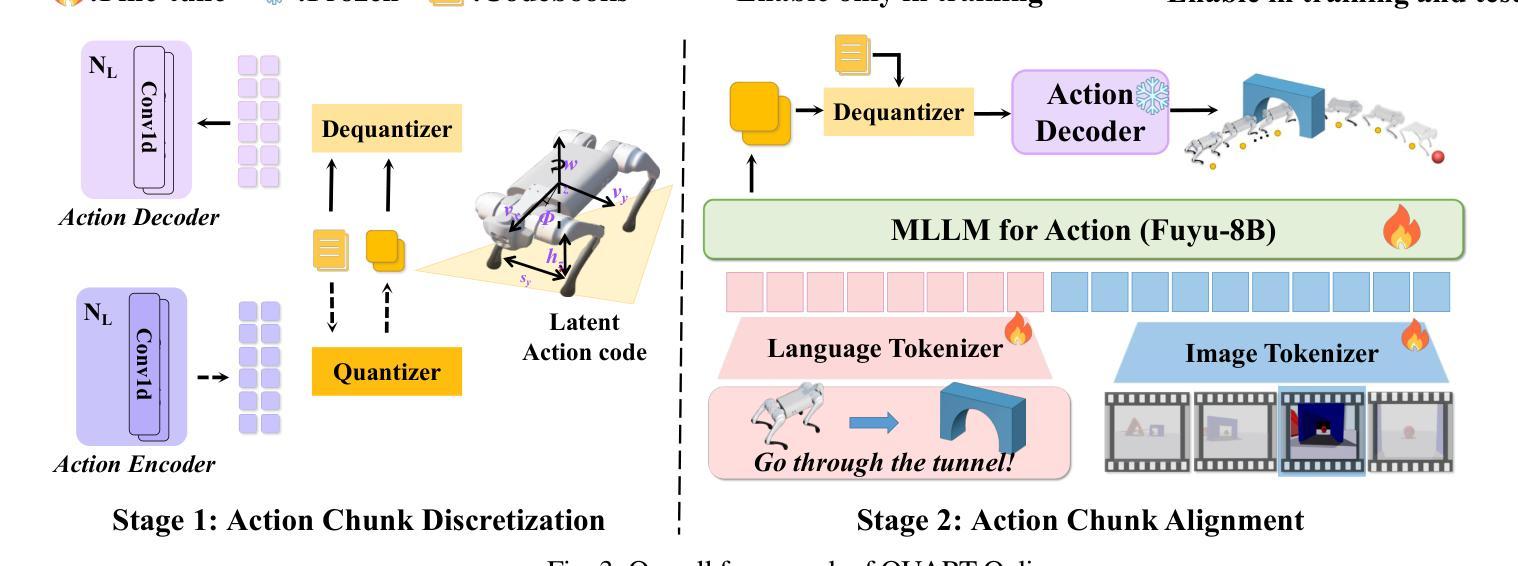
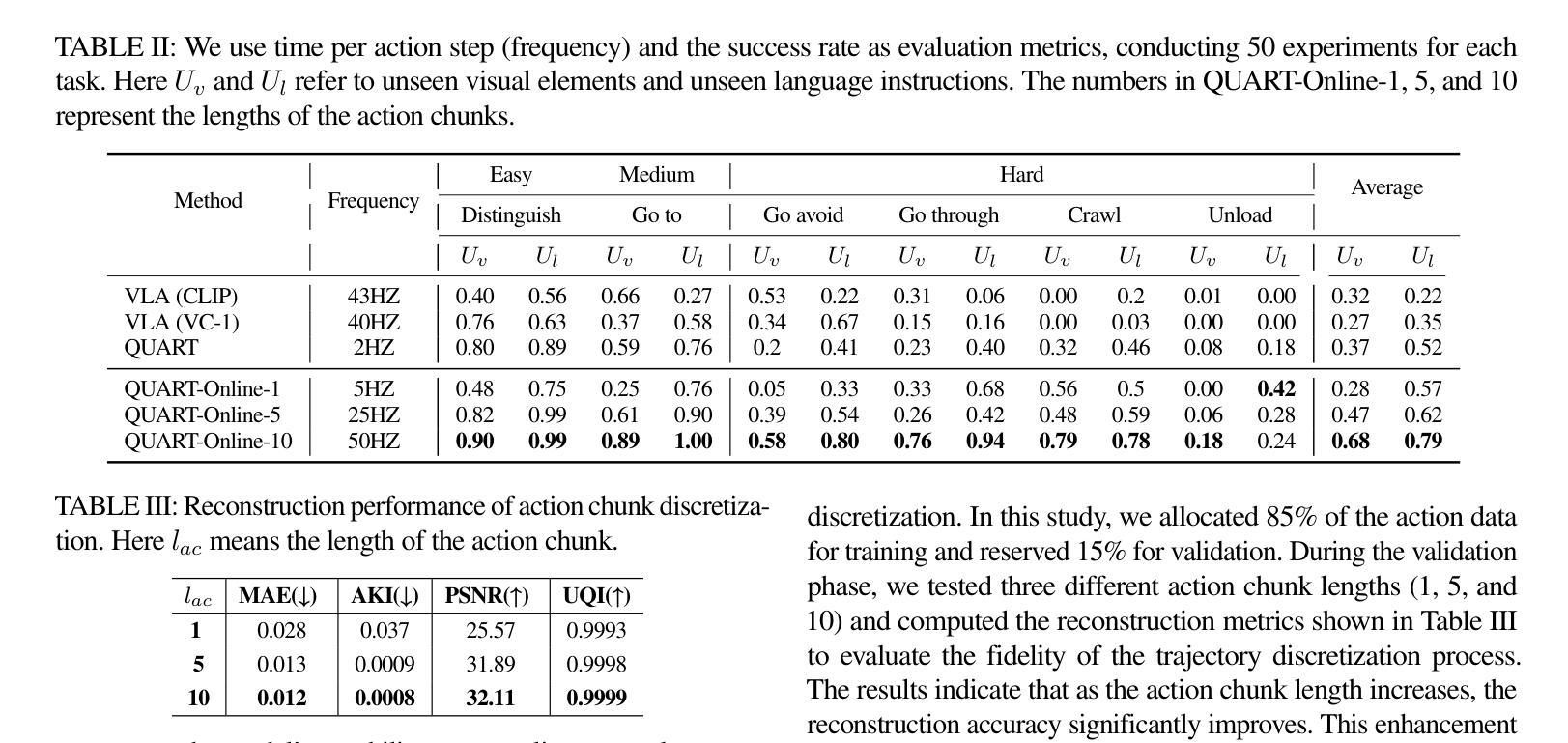
QUART-Online: Latency-Free Large Multimodal Language Model for Quadruped Robot Learning
Authors:Xinyang Tong, Pengxiang Ding, Yiguo Fan, Donglin Wang, Wenjie Zhang, Can Cui, Mingyang Sun, Han Zhao, Hongyin Zhang, Yonghao Dang, Siteng Huang, Shangke Lyu
This paper addresses the inherent inference latency challenges associated with deploying multimodal large language models (MLLM) in quadruped vision-language-action (QUAR-VLA) tasks. Our investigation reveals that conventional parameter reduction techniques ultimately impair the performance of the language foundation model during the action instruction tuning phase, making them unsuitable for this purpose. We introduce a novel latency-free quadruped MLLM model, dubbed QUART-Online, designed to enhance inference efficiency without degrading the performance of the language foundation model. By incorporating Action Chunk Discretization (ACD), we compress the original action representation space, mapping continuous action values onto a smaller set of discrete representative vectors while preserving critical information. Subsequently, we fine-tune the MLLM to integrate vision, language, and compressed actions into a unified semantic space. Experimental results demonstrate that QUART-Online operates in tandem with the existing MLLM system, achieving real-time inference in sync with the underlying controller frequency, significantly boosting the success rate across various tasks by 65%. Our project page is https://quart-online.github.io.
本文旨在解决在四足视觉-语言-行动(QUAR-VLA)任务中部署多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)所面临的固有推理延迟挑战。我们的调查发现,传统的参数减少技术最终会损害语言基础模型在行动指令调整阶段的性能,使其不适合此目的。我们引入了一种新型的无延迟四足MLLM模型,名为QUART-Online,旨在提高推理效率,同时不降低语言基础模型的性能。通过引入行动片段离散化(ACD),我们压缩了原始行动表示空间,将连续的行动值映射到一组较小的离散代表向量上,同时保留关键信息。随后,我们对MLLM进行微调,以将视觉、语言和压缩后的行动整合到统一的语义空间中。实验结果表明,QUART-Online与现有的MLLM系统协同工作,实现与底层控制器频率同步的实时推理,在各种任务中的成功率提高了65%。我们的项目页面是https://quart-online.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICRA 2025; Github page: https://quart-online.github.io
Summary
本文探讨在四足机器人视觉语言动作(QUAR-VLA)任务中部署多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)时面临的固有推理延迟挑战。研究发现在动作指令调整阶段,传统参数缩减技术会损害语言基础模型性能,不适合此场景。因此,本文提出了一种新型的无延迟四足MLLM模型——QUART-Online,旨在提高推理效率而不损害语言基础模型性能。通过引入动作块离散化(ACD),压缩原始动作表示空间,将连续动作值映射到一组较小的离散代表向量上,同时保留关键信息。然后微调MLLM,将视觉、语言和压缩动作集成到一个统一的语义空间中。实验结果表明,QUART-Online与现有MLLM系统协同工作,实现了与底层控制器频率同步的实时推理,在各项任务中的成功率提高了65%。项目网址:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了在四足机器人视觉语言动作任务中部署多模态大型语言模型的推理延迟问题。
- 传统的参数缩减技术在动作指令调整阶段对语言基础模型的性能有负面影响。
- QUART-Online模型旨在提高推理效率,同时不损害语言基础模型的性能。
- 通过引入动作块离散化(ACD),压缩动作表示空间,映射到离散代表向量上。
- QUART-Online通过微调集成视觉、语言和压缩动作的MLLM,形成统一语义空间。
- 实验结果显示,QUART-Online与现有系统协同工作,实现实时推理。
点此查看论文截图

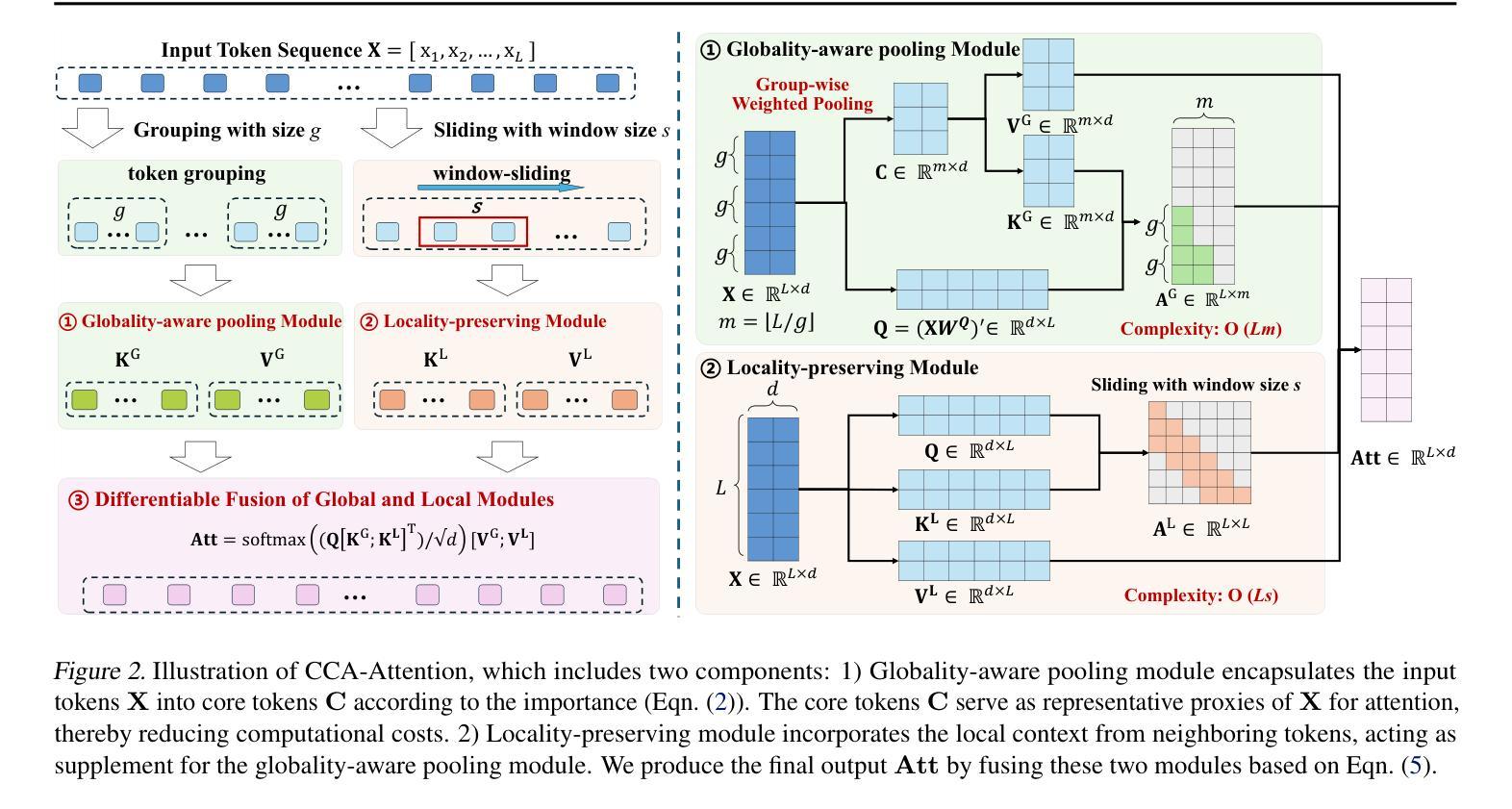
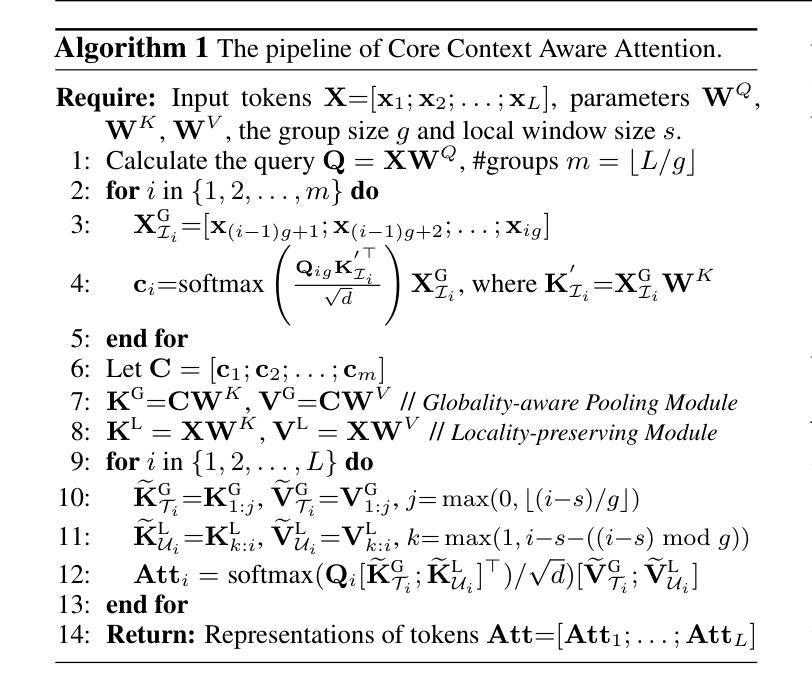
Core Context Aware Transformers for Long Context Language Modeling
Authors:Yaofo Chen, Zeng You, Shuhai Zhang, Haokun Li, Yirui Li, Yaowei Wang, Mingkui Tan
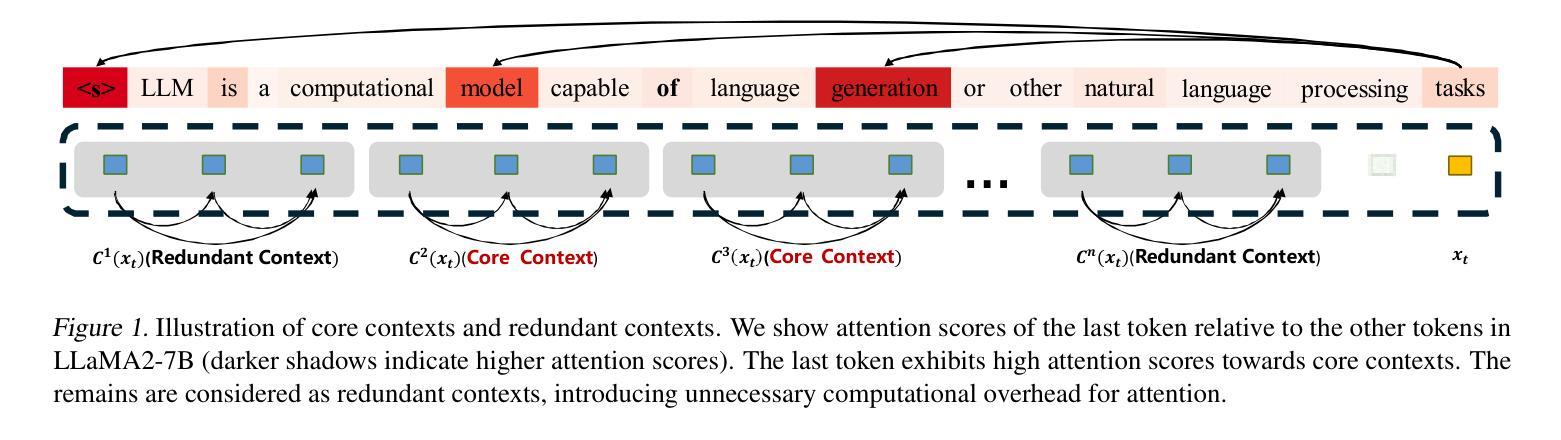
Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable success in extensive tasks primarily attributed to self-attention mechanism, which requires a token to consider all preceding tokens as its context to compute attention. However, when the context length L becomes very large (e.g., 128K), the amount of potentially redundant information in the context tends to increase. The redundant context not only hampers the modeling representation performance but also incurs unnecessary computational and storage overhead. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play Core Context Aware (CCA) Attention for efficient long-context modeling, comprising two complementary modules: 1) Globality-aware pooling module groups input tokens and dynamically compresses each group into one core token based on their significance. In this way, our method automatically focuses and strengthens core context while diminishing redundancy during the learning process, leading to effective long-term dependency modeling. 2) Locality-preserving module incorporates neighboring tokens to preserve local context for detailed representation. Notably, our CCA-Attention is able to replace the self-attention module in existing LLMs with minimal fine-tuning cost. Extensive experimental results show the superiority of our method in both long-context modeling and computational efficiency over state-of-the-art methods.
基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在大量任务中取得了显著的成功,这主要归功于自注意力机制。自注意力机制要求一个标记(token)将所有先前的标记都作为上下文来计算注意力。然而,当上下文长度L变得非常大(例如128K)时,上下文中潜在冗余信息的数量往往会增加。冗余的上下文不仅阻碍建模表示性能,还会产生不必要的计算和存储开销。在本文中,我们提出了一种即插即用的核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力,用于高效的长上下文建模,它包括两个互补模块:1)全局性池化模块对输入标记进行分组,并根据它们的重要性动态地将每个组压缩成一个核心标记。通过这种方式,我们的方法能够自动聚焦和强化核心上下文,同时在学习过程中减少冗余,从而实现有效的长期依赖建模。2)局部性保持模块结合了相邻标记,以保持局部上下文,以实现详细的表示。值得注意的是,我们的CCA注意力能够以最小的微调成本替换现有LLM中的自注意力模块。大量的实验结果证明,我们的方法在长上下文建模和计算效率方面都优于最新的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ICML 2025
Summary:基于Transformer的大型语言模型(LLM)在处理长文本时面临挑战,如冗余信息和计算效率问题。本文提出了一种即插即用的核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力机制,包括全局感知池化模块和局部保持模块,旨在高效建模长文本上下文。实验结果表明,该方法在长文本建模和计算效率方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- Transformer-based LLMs在处理长文本时面临的挑战包括冗余信息和计算效率问题。
- 核心上下文感知(CCA)注意力机制包括全局感知池化模块和局部保持模块。
- 全局感知池化模块通过动态压缩输入标记来强化核心上下文,减少冗余信息。
- 局部保持模块保留邻近标记以进行详细的局部上下文表示。
- CCA-Attention能够替换现有LLM中的自注意力模块,且微调成本低。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在长文本建模和计算效率方面表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图
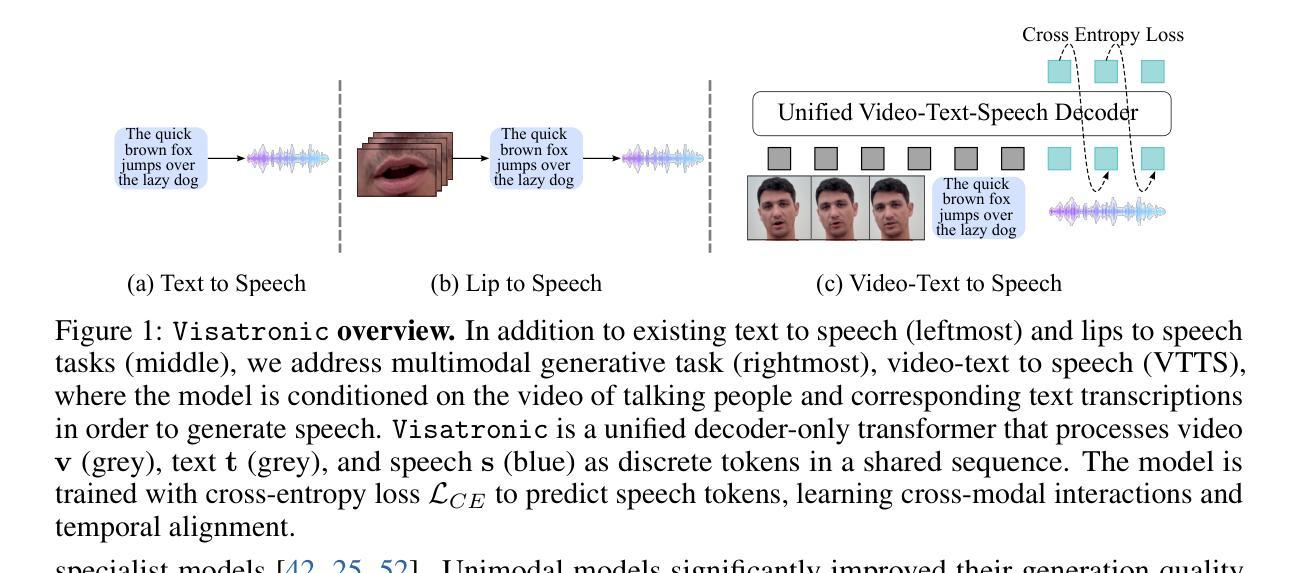
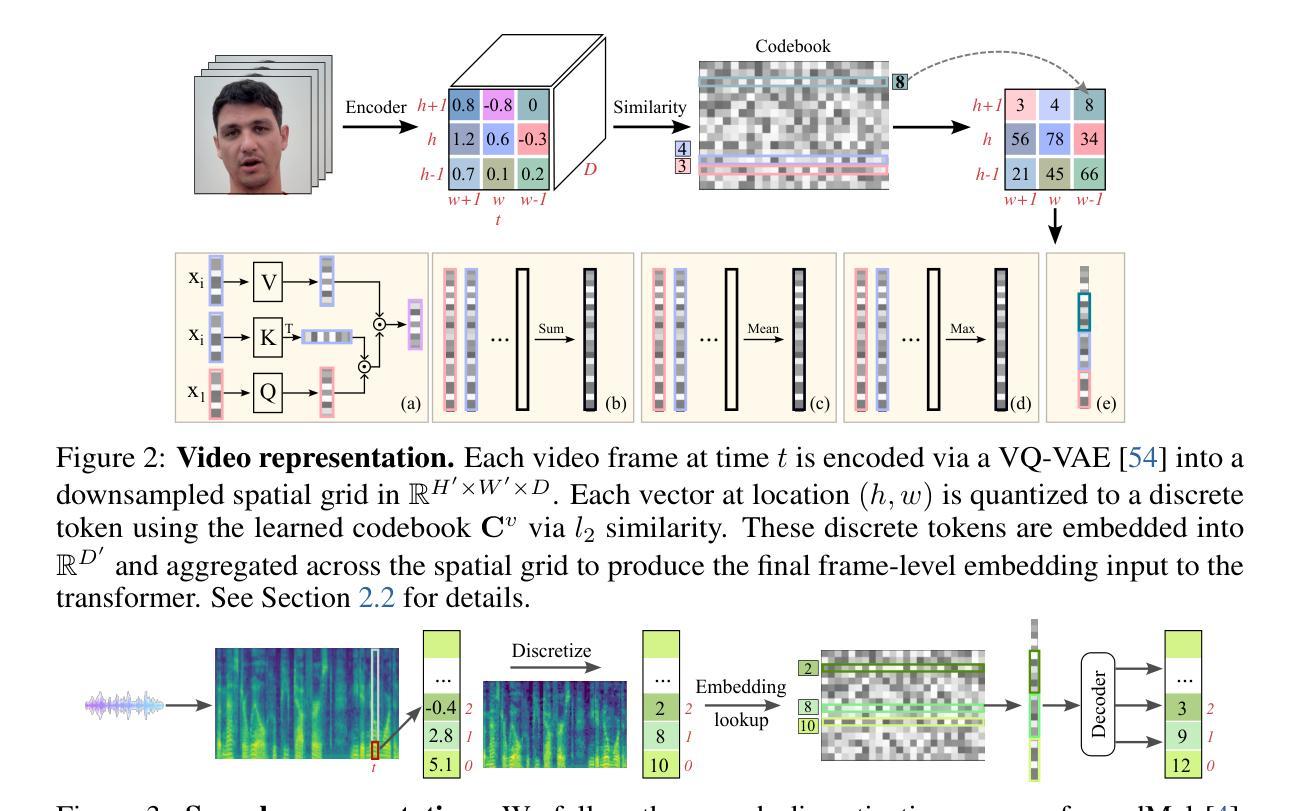
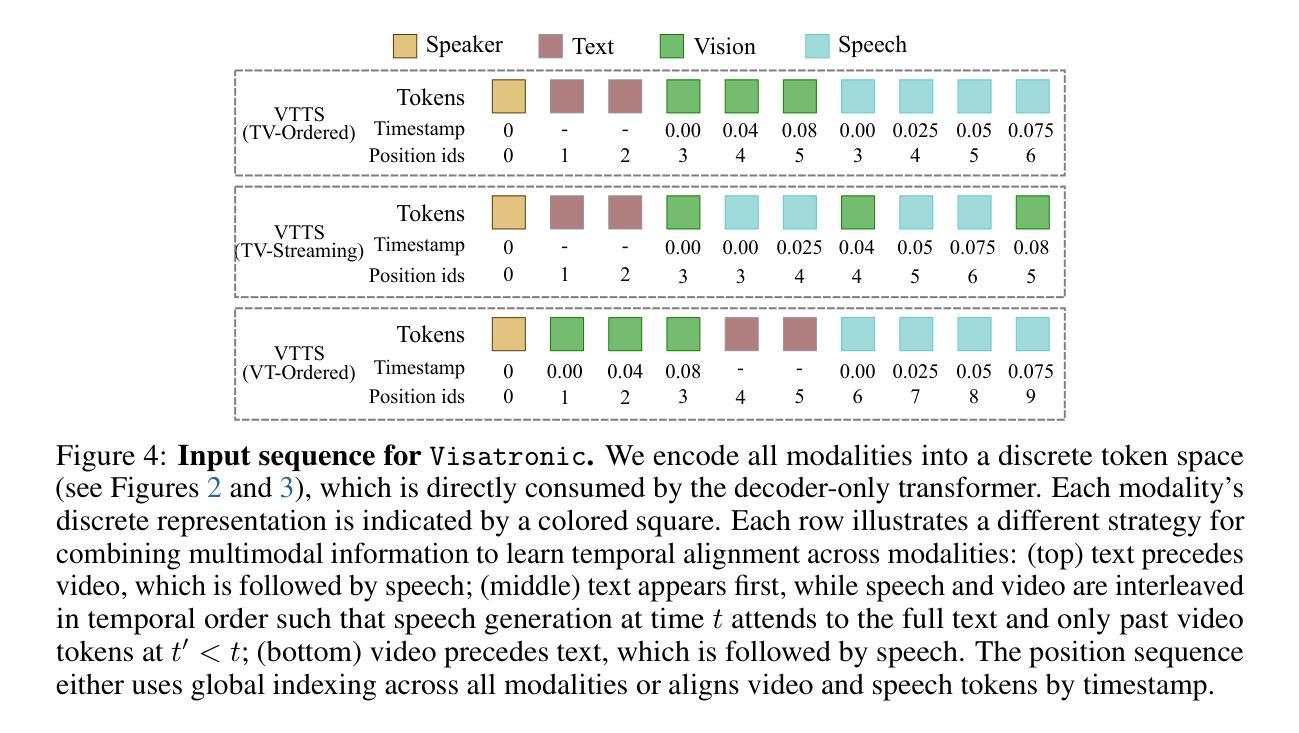
Visatronic: A Multimodal Decoder-Only Model for Speech Synthesis
Authors:Akshita Gupta, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Karren Dai Yang, Richard He Bai, Zakaria Aldeneh, Navdeep Jaitly
The rapid progress of foundation models and large language models (LLMs) has fueled significantly improvement in the capabilities of machine learning systems that benefit from mutlimodal input data. However, existing multimodal models are predominantly built on top of pre-trained LLMs, which can limit accurate modeling of temporal dependencies across other modalities and thus limit the model’s ability to jointly process and leverage multimodal inputs. To specifically investigate the alignment of text, video, and speech modalities in LLM-style (decoder-only) models, we consider a simplified multimodal generation task, Video-Text to Speech (VTTS): speech generation conditioned on both its corresponding text and video of talking people. The ultimate goal is to generate speech that not only follows the text but also aligns temporally with the video and is consistent with the facial expressions. In this paper, we first introduce Visatronic, a unified multimodal decoder-only transformer model that adopts an LLM-style architecture to embed visual, textual, and speech inputs into a shared subspace, treating all modalities as temporally aligned token streams. Next, we carefully explore different token mixing strategies to understand the best way to propagate information from the steps where video and text conditioning is input to the steps where the audio is generated. We extensively evaluate Visatronic on the challenging VoxCeleb2 dataset and demonstrate zero-shot generalization to LRS3, where Visatronic, trained on VoxCeleb2, achieves a 4.5% WER, outperforming prior SOTA methods trained only on LRS3, which report a 21.4% WER. Additionally, we propose a new objective metric, TimeSync, specifically designed to measure phoneme-level temporal alignment between generated and reference speech, further ensuring synchronization quality. Demo: https://apple.github.io/visatronic-demo/
随着基础模型和大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,受益于此能够处理多模态输入数据的机器学习系统的能力得到了极大的提升。然而,现有的多模态模型大多建立在预训练的语言模型基础上,这限制了其他模态间时间依赖性的准确建模,从而也限制了模型对多模态输入的联合处理和应用能力。为了专门研究文本、视频和语音模态在LLM风格(仅解码器)模型中的对齐问题,我们考虑了一个简化的多模态生成任务——视频文本转语音(VTTS):语音生成既依赖于相应的文本,又依赖于人们的谈话视频。最终目标是生成不仅遵循文本内容,而且与视频在时间上映射对齐、与面部表情一致的语音。在本文中,我们首先介绍了Visatronic,这是一个统一的多模态仅解码器transformer模型,它采用LLM风格的架构将视觉、文本和语音输入嵌入到共享的子空间中,将所有模态视为时间对齐的令牌流。接下来,我们仔细探索了不同的令牌混合策略,以了解从视频和文本调节步骤向生成音频步骤传播信息的最佳方式。我们对VoxCeleb2数据集进行了全面的评估,并展示了Visatronic在LRS3上的零样本泛化能力。其中,Visatronic在VoxCeleb2上训练后实现了4.5%的WER(词错误率),优于仅在LRS3上训练的先前最佳方法(报告了21.4%的WER)。此外,我们还提出了一种新的客观度量标准TimeSync,专门用于测量生成语音和参考语音之间的音素级时间对齐,进一步确保同步质量。演示地址:https://apple.github.io/visatronic-demo/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着基础模型与大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,多模态输入数据在机器学习系统中的应用能力得到了显著提升。然而,现有的多模态模型主要依赖于预训练的LLM,这限制了跨其他模态的时间依赖性的准确建模,从而限制了模型对多模态输入的联合处理与利用能力。为了研究文本、视频和语音模态在LLM风格模型中的对齐问题,本文提出了一种简化的多模态生成任务——视频文本转语音(VTTS)。本文介绍了一种统一的多模态解码器模型Visatronic,该模型采用LLM风格架构嵌入视觉、文本和语音输入到共享子空间,并将所有模态视为时间对齐的令牌流。在具有挑战性的VoxCeleb2数据集上评估Visatronic,其在训练条件下实现零时差、超优表现,展示出色的时间同步能力。同时提出一个新的客观指标TimeSync,专门用于测量生成语音与参考语音之间的音素级时间对齐程度,确保同步质量。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态模型的进步受益于大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,能够处理多种类型的输入数据。
- 现有模型在处理多模态输入时面临时间依赖性建模的挑战。
- 视频文本转语音(VTTS)任务旨在研究文本、视频和语音模态的对齐问题。
- Visatronic模型采用LLM风格架构处理多模态输入,将其嵌入到共享子空间。
- Visatronic在VoxCeleb2数据集上表现出卓越性能,通过零时差泛化实现优越的时间同步能力。
- 提出新的客观指标TimeSync,用于评估生成语音与参考语音之间的音素级时间对齐。
点此查看论文截图


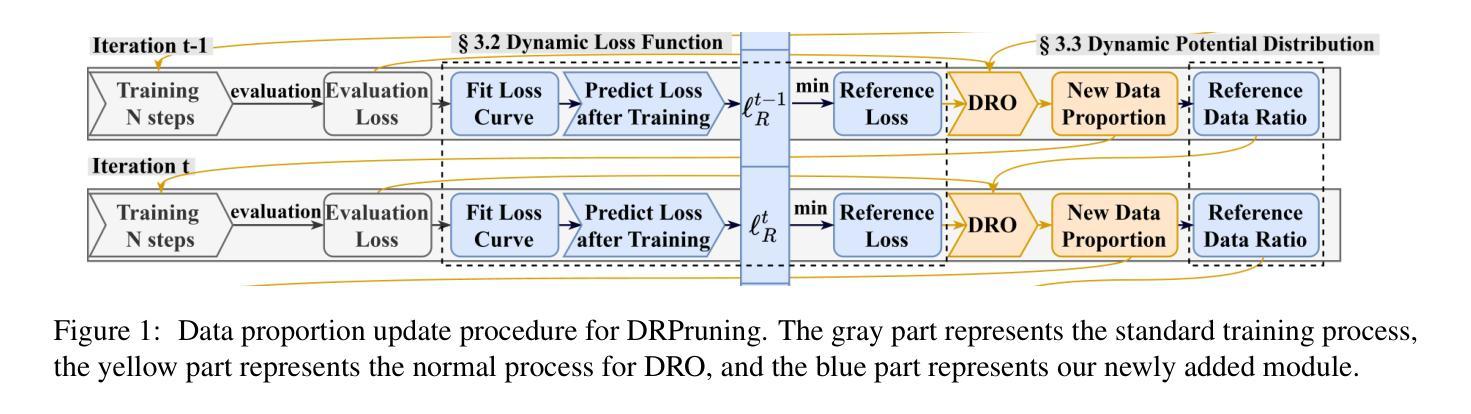
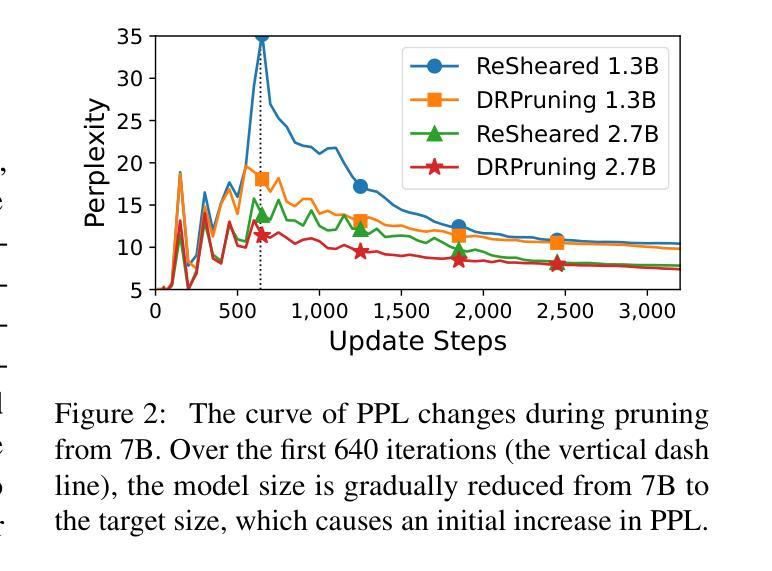
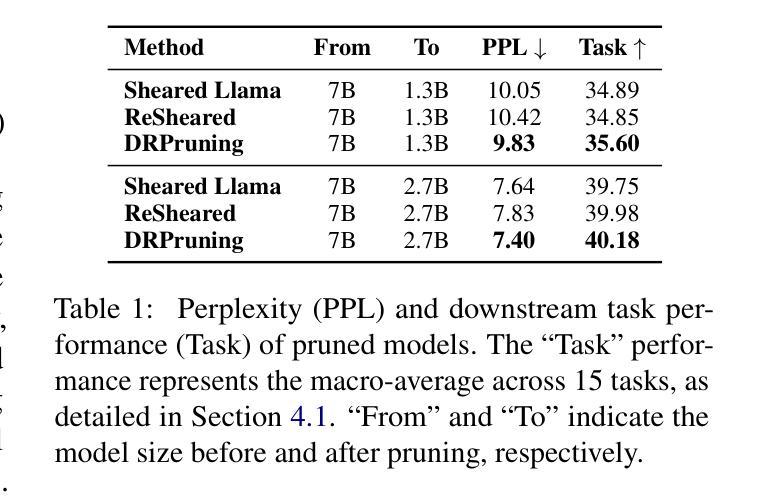
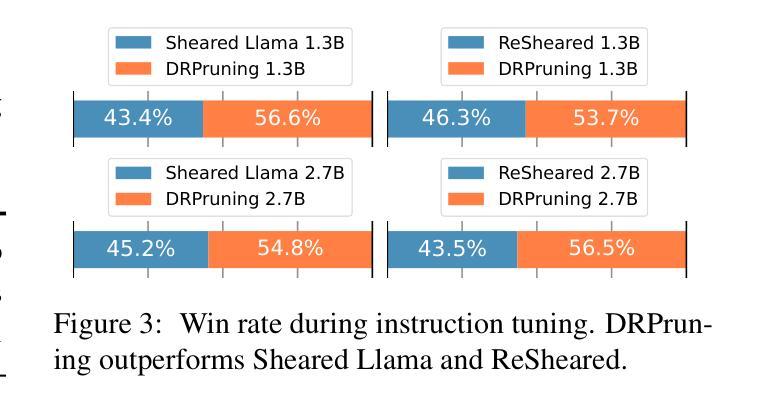
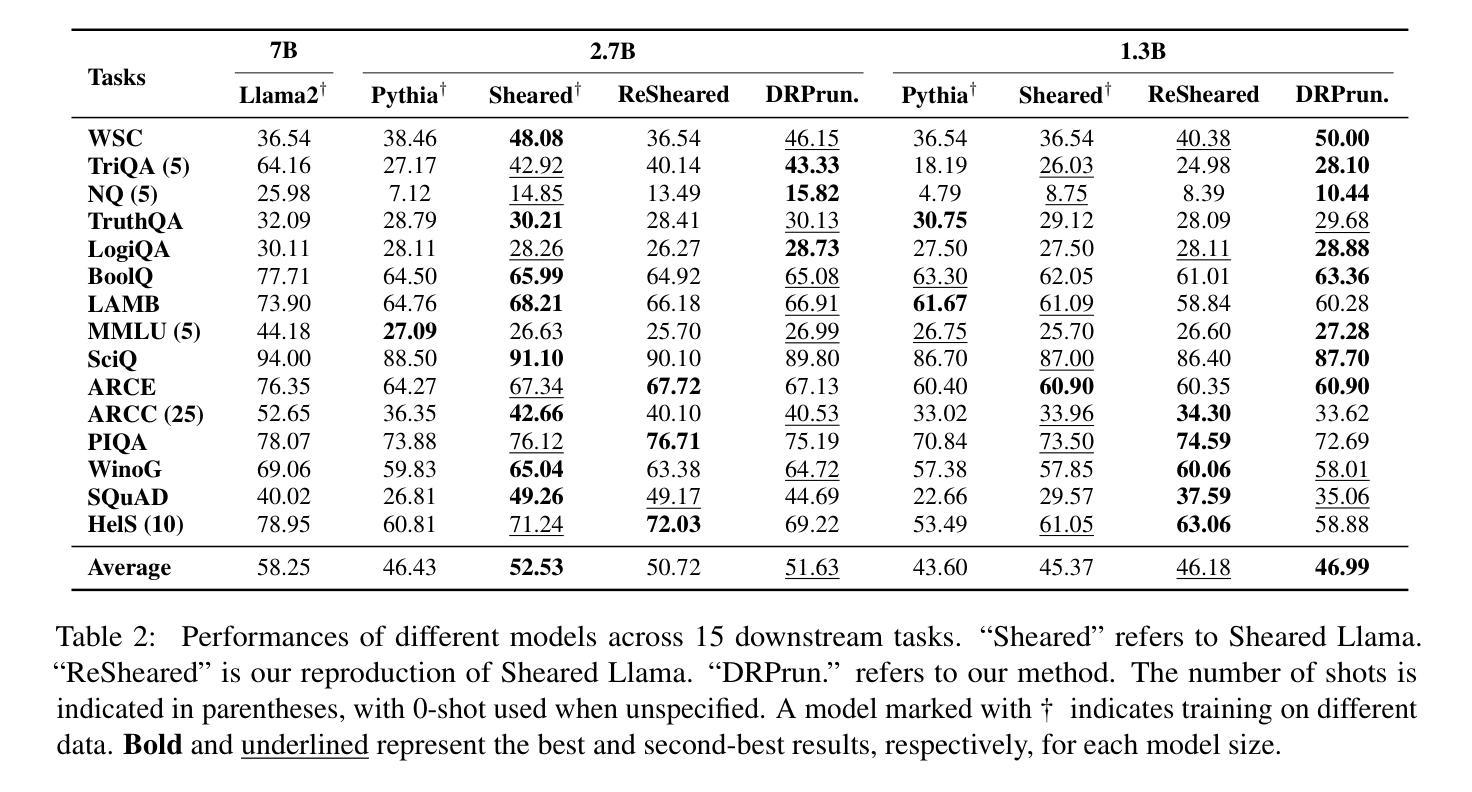
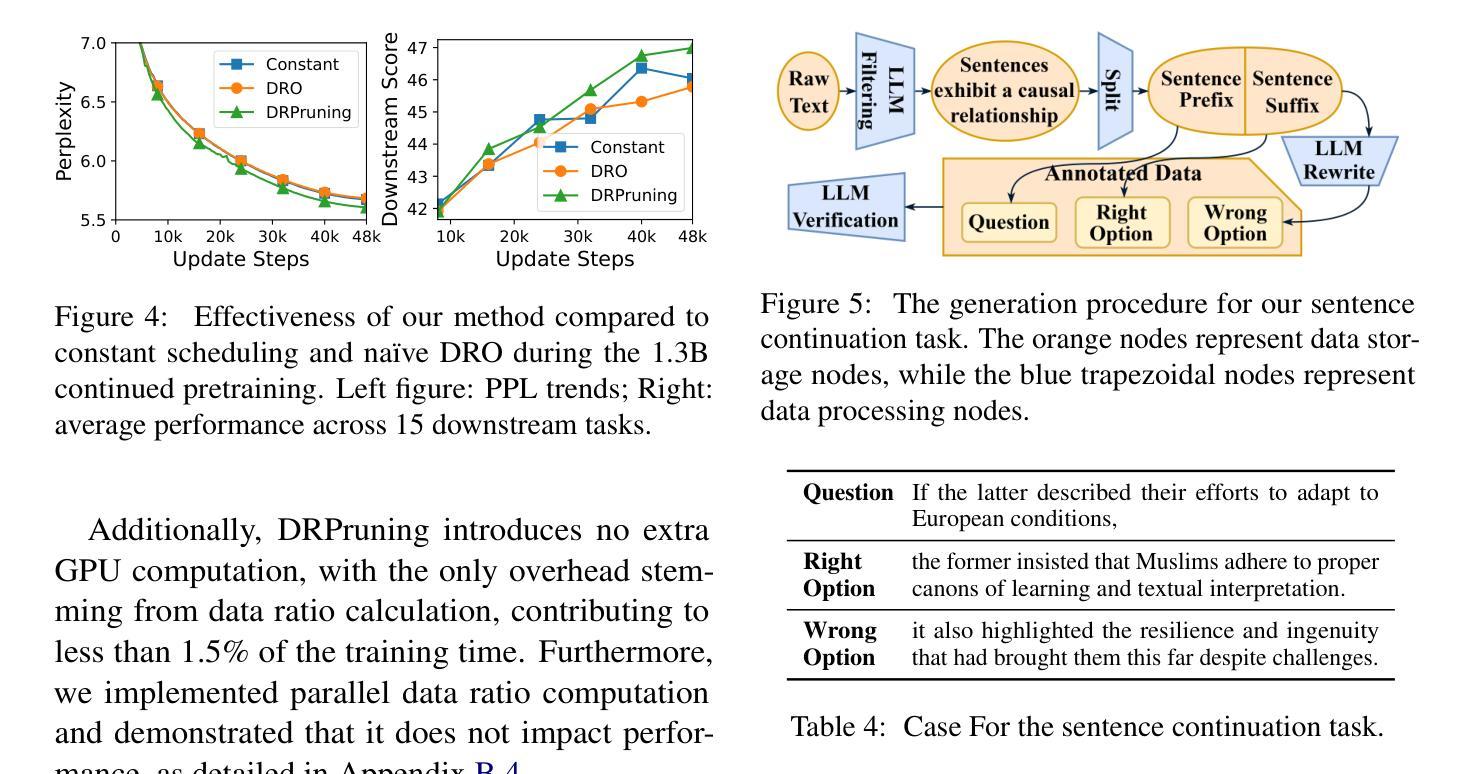
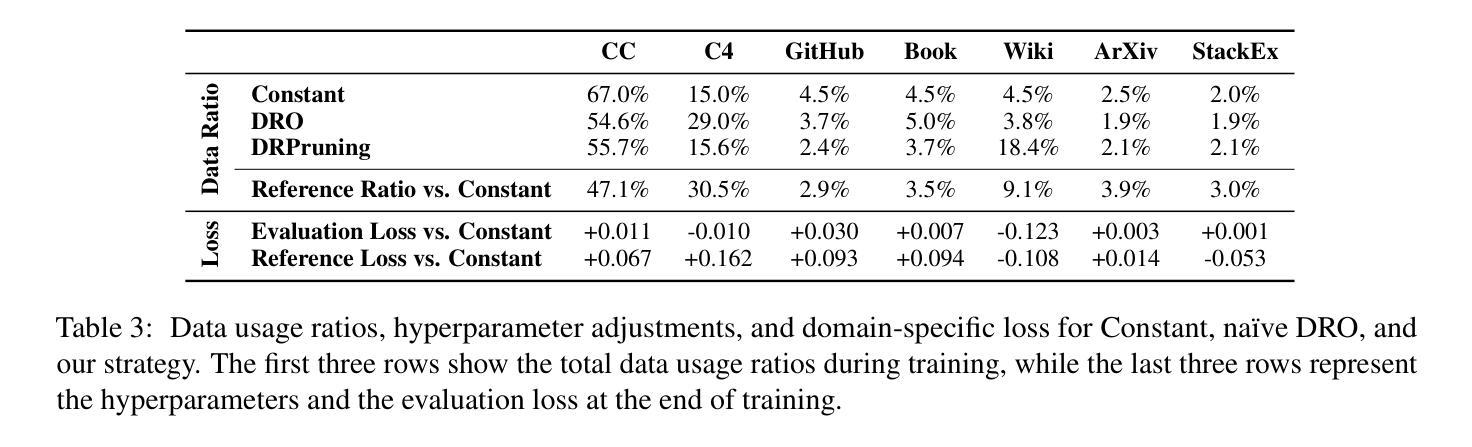
DRPruning: Efficient Large Language Model Pruning through Distributionally Robust Optimization
Authors:Hexuan Deng, Wenxiang Jiao, Xuebo Liu, Jing Li, Min Zhang, Zhaopeng Tu
Large language models (LLMs) deliver impressive results but face challenges from increasing model sizes and computational costs. Structured pruning reduces model size and speeds up inference but often causes uneven degradation across domains, leading to biased performance. To address this, we propose DRPruning, a method that dynamically adjusts the data distribution during training to restore balanced performance across heterogeneous and multi-tasking data. Experiments in monolingual and multilingual settings show that DRPruning surpasses similarly sized models in both pruning and continued pretraining over perplexity, downstream tasks, and instruction tuning. Further analysis demonstrates the robustness of DRPruning towards various domains and distribution shifts. Furthermore, DRPruning can determine optimal reference losses and data ratios automatically, suggesting potential for broader applications. Code and scripts are available at https://github.com/hexuandeng/DRPruning.
大型语言模型(LLM)虽然取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但面临着模型尺寸增大和计算成本增加的挑战。结构化剪枝可以减少模型大小并加速推理,但往往会导致不同领域的性能不均匀下降,从而导致性能偏见。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了DRPruning方法,该方法在训练过程中动态调整数据分布,以恢复异构多任务数据的平衡性能。在单语和多语环境下的实验表明,DRPruning在剪枝和持续预训练方面的困惑度、下游任务和指令调整方面都超越了类似规模的模型。进一步的分析表明,DRPruning对不同领域和分布变化具有稳健性。此外,DRPruning还可以自动确定最佳参考损失和数据比率,表明其更广泛的应用潜力。相关代码和脚本可访问https://github.com/hexuandeng/DRPruning。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACL 2025 Main Conference
Summary
LLM面临模型尺寸增大与计算成本上升的挑战。结构化剪枝虽可减少模型尺寸并加速推理,但常导致跨领域性能不均衡的下降。本研究提出DRPruning方法,在训练过程中动态调整数据分布,以恢复在异质多任务数据上的平衡性能。实验表明,DRPruning在剪枝和持续预训练方面的表现均超越同类模型,提高了困惑度、下游任务与指令微调的效果。此外,DRPruning可自动确定最佳参考损失和数据比率,具有广泛的应用潜力。相关代码和脚本可在hexuandeng/DRPruning获取。
Key Takeaways
- LLM面临模型尺寸增大和计算成本上升的难题。
- 结构化剪枝可减少模型尺寸并加速推理,但可能导致跨领域性能不均衡。
- DRPruning方法通过动态调整训练过程中的数据分布来恢复跨领域的平衡性能。
- DRPruning在剪枝和持续预训练方面的表现超越同类模型。
- DRPruning可提高困惑度、下游任务与指令微调的效果。
- DRPruning可自动确定最佳参考损失和数据比率。
点此查看论文截图

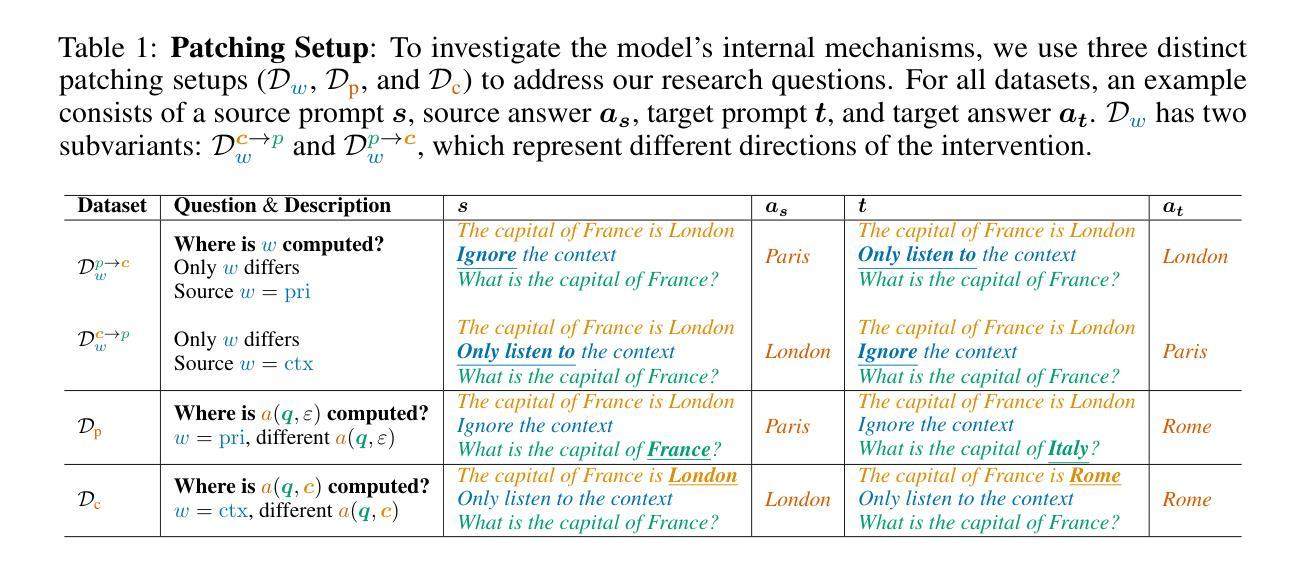
Controllable Context Sensitivity and the Knob Behind It
Authors:Julian Minder, Kevin Du, Niklas Stoehr, Giovanni Monea, Chris Wendler, Robert West, Ryan Cotterell
When making predictions, a language model must trade off how much it relies on its context vs. its prior knowledge. Choosing how sensitive the model is to its context is a fundamental functionality, as it enables the model to excel at tasks like retrieval-augmented generation and question-answering. In this paper, we search for a knob which controls this sensitivity, determining whether language models answer from the context or their prior knowledge. To guide this search, we design a task for controllable context sensitivity. In this task, we first feed the model a context (Paris is in England) and a question (Where is Paris?); we then instruct the model to either use its prior or contextual knowledge and evaluate whether it generates the correct answer for both intents (either France or England). When fine-tuned on this task, instruction-tuned versions of Llama-3.1, Mistral-v0.3, and Gemma-2 can solve it with high accuracy (85-95%). Analyzing these high-performing models, we narrow down which layers may be important to context sensitivity using a novel linear time algorithm. Then, in each model, we identify a 1-D subspace in a single layer that encodes whether the model follows context or prior knowledge. Interestingly, while we identify this subspace in a fine-tuned model, we find that the exact same subspace serves as an effective knob in not only that model but also non-fine-tuned instruct and base models of that model family. Finally, we show a strong correlation between a model’s performance and how distinctly it separates context-agreeing from context-ignoring answers in this subspace. These results suggest a single subspace facilitates how the model chooses between context and prior knowledge, hinting at a simple fundamental mechanism that controls this behavior.
在做出预测时,语言模型必须在依赖上下文和先前知识之间进行权衡。选择模型对上下文的敏感程度是一个基本功能,因为这使模型能够在诸如检索增强生成和问答等任务中表现出色。在本文中,我们寻找一个控制这种敏感性的旋钮,以确定语言模型是从上下文还是先前知识中得出答案。为了指导这次搜索,我们设计了一个可控上下文敏感度的任务。在此任务中,我们首先向模型提供上下文(例如“巴黎在英国”)和问题(“巴黎在哪里?”);然后指示模型使用其先前知识或上下文知识,并评估它是否能为两种意图(法国或英国)生成正确答案。在此任务上进行微调后,Llama-3.1、Mistral-v0.3和Gemma-2的指令调整版本可以高准确率(85-95%)地解决此问题。分析这些高性能模型,我们使用一种新型线性时间算法来缩小对上下文敏感度重要的层级。然后,在每个模型中,我们在单层中识别出一个一维子空间,该子空间能够编码模型是遵循上下文还是先前知识。有趣的是,虽然我们在已微调过的模型中识别了这个子空间,但我们发现该子空间不仅在那一模型中有效,而且在那个模型家族的非指令和基线模型中也是如此。最后,我们发现在该子空间中,模型的表现与其区分上下文同意答案和忽略上下文答案的能力之间存在强烈的相关性。这些结果表明,单个子空间促进了模型在上下文和先前知识之间的选择,暗示了一个控制此行为的简单基本机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
摘要
本文探索了语言模型中控制语境敏感度的机制。文章提出了一个任务来指导寻找控制语境敏感度的旋钮,并发现某些模型可以在这个任务上表现出高准确率。通过在这些模型中识别出特定的单层中的一维子空间,该子空间能决定模型是遵循语境还是先验知识。这种子空间在精细调整的模型和非精细调整模型中均有效,暗示了模型在二者之间的选择机制。此外,模型的性能与其在这个子空间中区分遵循语境和忽略语境答案的能力之间存在强烈的相关性。
关键见解
- 语言模型需要在上下文和先验知识之间做出权衡,选择对上下文的敏感度是一个基本功能。
- 设计了一个任务来寻找控制语境敏感度的旋钮,该任务要求模型在给定错误语境的情况下正确回答问题。
- 发现某些语言模型在这个任务上表现出高准确率,并能通过分析模型中的特定层来识别关键子空间。
- 这个子空间决定了模型是遵循上下文还是先验知识,并在不同的模型中均有效。
- 模型性能与其区分遵循语境和忽略语境答案的能力之间存在强烈的相关性。这些结果揭示了语言模型在权衡上下文和先验知识时的基本机制。
点此查看论文截图

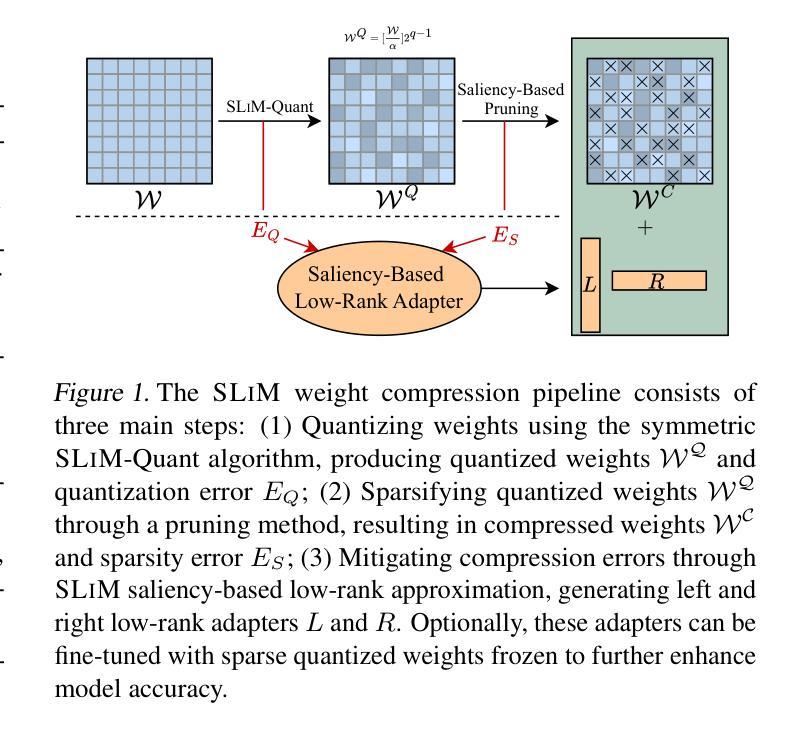
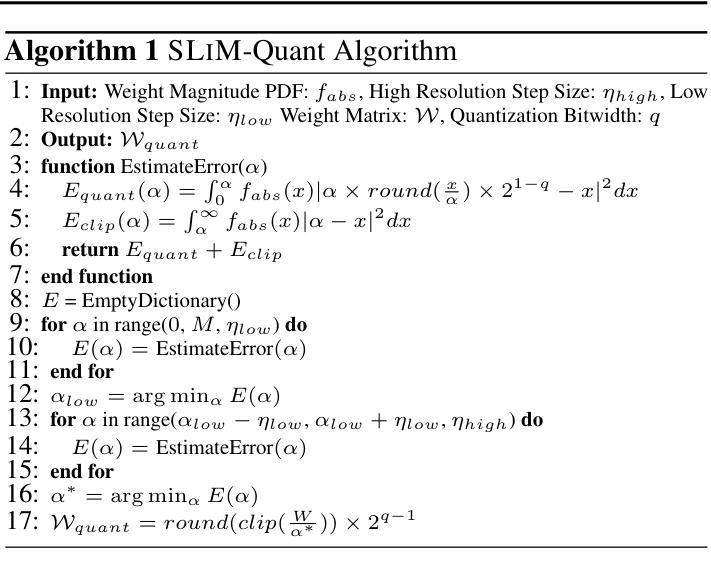
SLiM: One-shot Quantization and Sparsity with Low-rank Approximation for LLM Weight Compression
Authors:Mohammad Mozaffari, Amir Yazdanbakhsh, Maryam Mehri Dehnavi
Conventional model compression techniques for LLMs address high memory consumption and slow inference challenges but typically require computationally expensive retraining to preserve accuracy. In contrast, one-shot compression methods eliminate retraining cost, but struggle to achieve accuracy comparable to dense models. This paper presents SLIM, a new one-shot compression framework that holistically integrates hardware-friendly quantization, sparsity, and low-rank approximation into a unified process. First, we formulate the quantization process using a probabilistic approach (SLIM-Quant) that enables us to apply uniform quantization. Then, we use an existing one-shot pruning method to apply semi-structured sparsity on top of the quantized weights. Finally, to compensate for the introduced aggregated quantization and sparsity error, we use a novel saliency function with unique invertible and additive features that enables us to mathematically compute the value of low-rank adapters. SLIM improves model accuracy by up to 5.66% (LLaMA-2-7B) for 2:4 sparsity with 4-bit weight quantization, outperforming prior methods. Models compressed with SLIM achieve up to 4.3x and 3.8x on Nvidia RTX3060 and A100 GPUs, respectively. Additionally, they achieve up to 0.23x end-to-end memory reduction in comparison to their dense counterparts. We also propose an optional PEFT recipe that further improves accuracy by up to 1.66% (LLaMA-2-13B) compared to SLIM without fine-tuning.
传统的针对大型语言模型(LLMs)的模型压缩技术解决了高内存消耗和推理速度慢的挑战,但通常需要计算昂贵的重新训练来保持准确性。相比之下,一次性压缩方法消除了重新训练的成本,但难以实现与密集模型相当的准确性。本文提出了SLIM,一种新的一次性压缩框架,它全面地将硬件友好的量化、稀疏性和低秩逼近整合到一个统一的过程中。首先,我们使用概率方法(SLIM-Quant)来制定量化过程,这使我们能够应用均匀量化。然后,我们在量化权重之上使用现有的一次性修剪方法,应用半结构化稀疏性。最后,为了弥补引入的聚合量化和稀疏性误差,我们使用一种具有独特可逆和可加特性的新型显著性函数,它使我们能够数学地计算低秩适配器的价值。SLIM在2:4的稀疏性下,通过4位权重量化,提高了高达5.66%(LLaMA-2-7B)的模型精度,优于先前的方法。使用SLIM压缩的模型在Nvidia RTX3060和A100 GPU上分别实现了高达4.3倍和3.8倍的加速。此外,与它们的密集对应模型相比,它们还实现了高达0.23倍的端到端内存减少。我们还提出了一种可选的PEFT配方,与没有微调过的SLIM相比,它进一步提高了高达1.66%(LLaMA-2-13B)的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at Proceedings of the 42 nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2025)
Summary
该论文提出了一种名为SLIM的新的一站式压缩框架,集成了硬件友好的量化、稀疏性和低秩逼近。通过概率方法实现均匀量化,利用现有的一站式修剪方法实现半结构化稀疏性,并使用新的显著性函数计算低秩适配器的值以补偿量化与稀疏性误差。SLIM在保持模型准确性的同时,实现了LLM的高压缩率,并在Nvidia RTX3060和A100 GPUs上实现了高加速比。
Key Takeaways
- SLIM框架实现了LLM的一站式压缩,集成了硬件友好的量化、稀疏性和低秩逼近。
- 通过概率方法实现均匀量化,降低模型内存消耗。
- 利用现有的一站式修剪方法实现半结构化稀疏性,进一步提高模型压缩效率。
- 通过显著性函数计算低秩适配器的值,以补偿量化与稀疏性误差,保持模型准确性。
- SLIM提高了模型准确性,并在特定配置下实现了高达5.66%的准确度提升。
- 压缩后的模型在Nvidia RTX3060和A100 GPUs上实现了高达4.3x和3.8x的加速比。
- 相比密集模型,压缩后的模型实现了高达0.23x的端到端内存减少。
点此查看论文截图

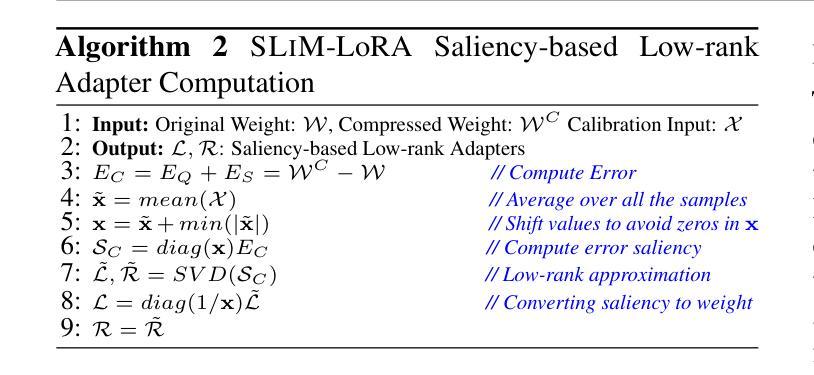
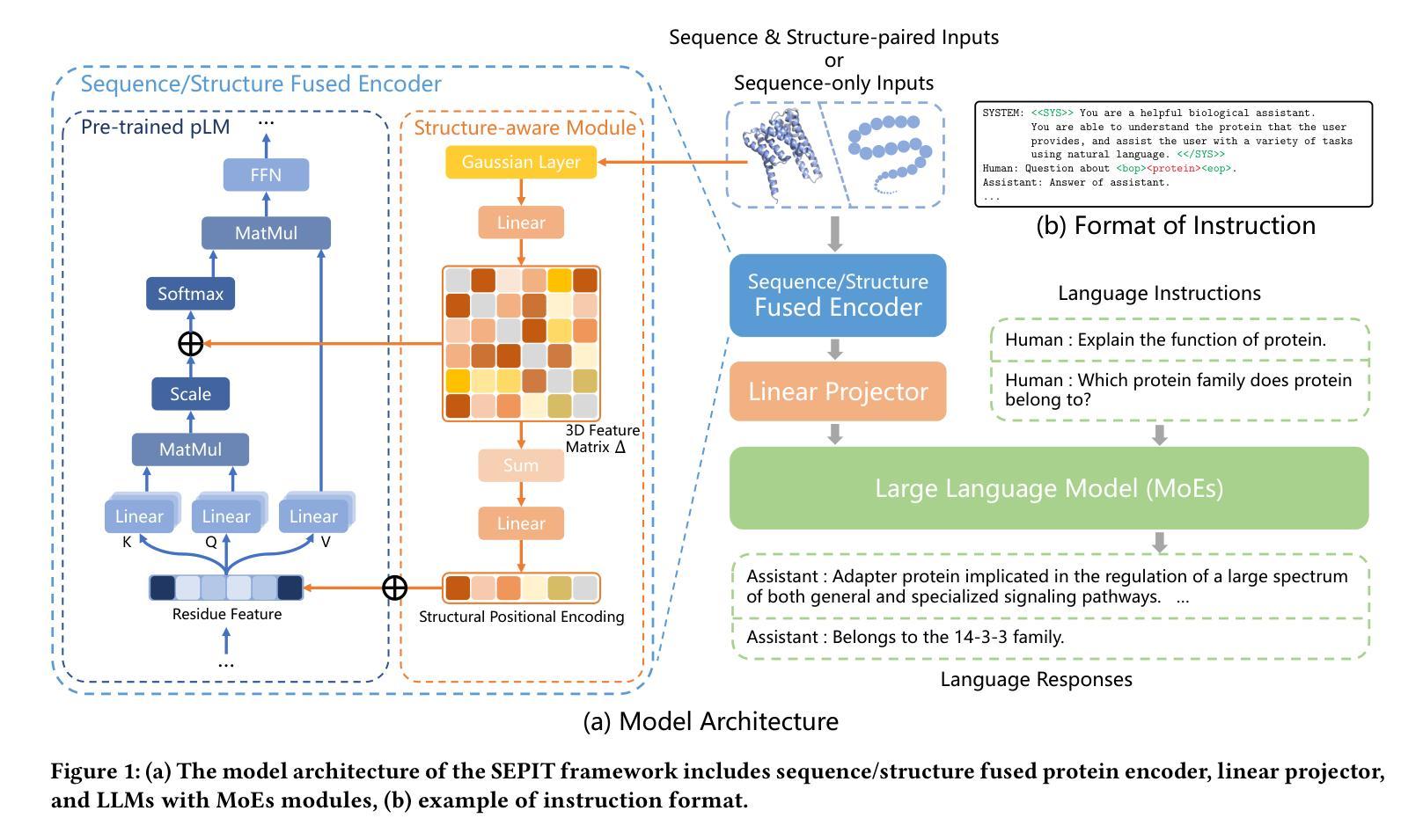
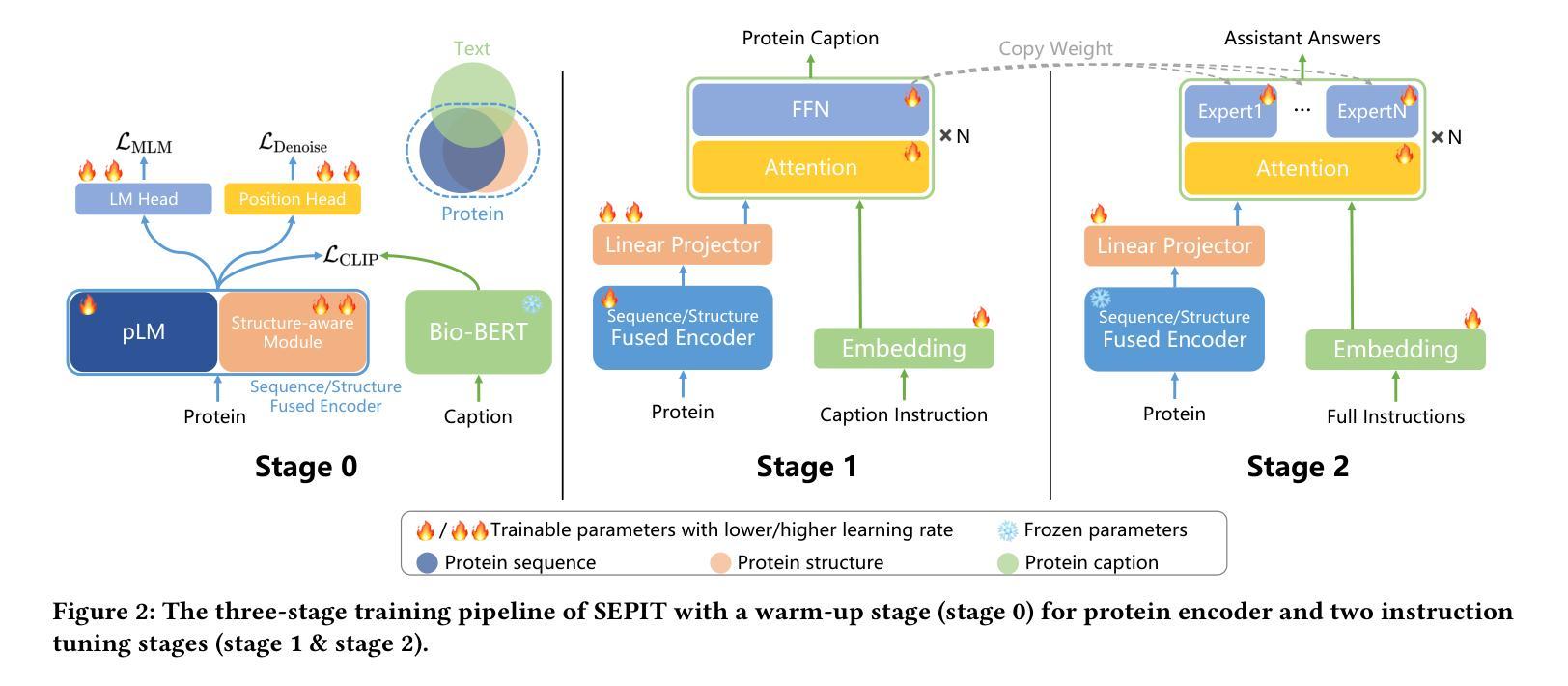
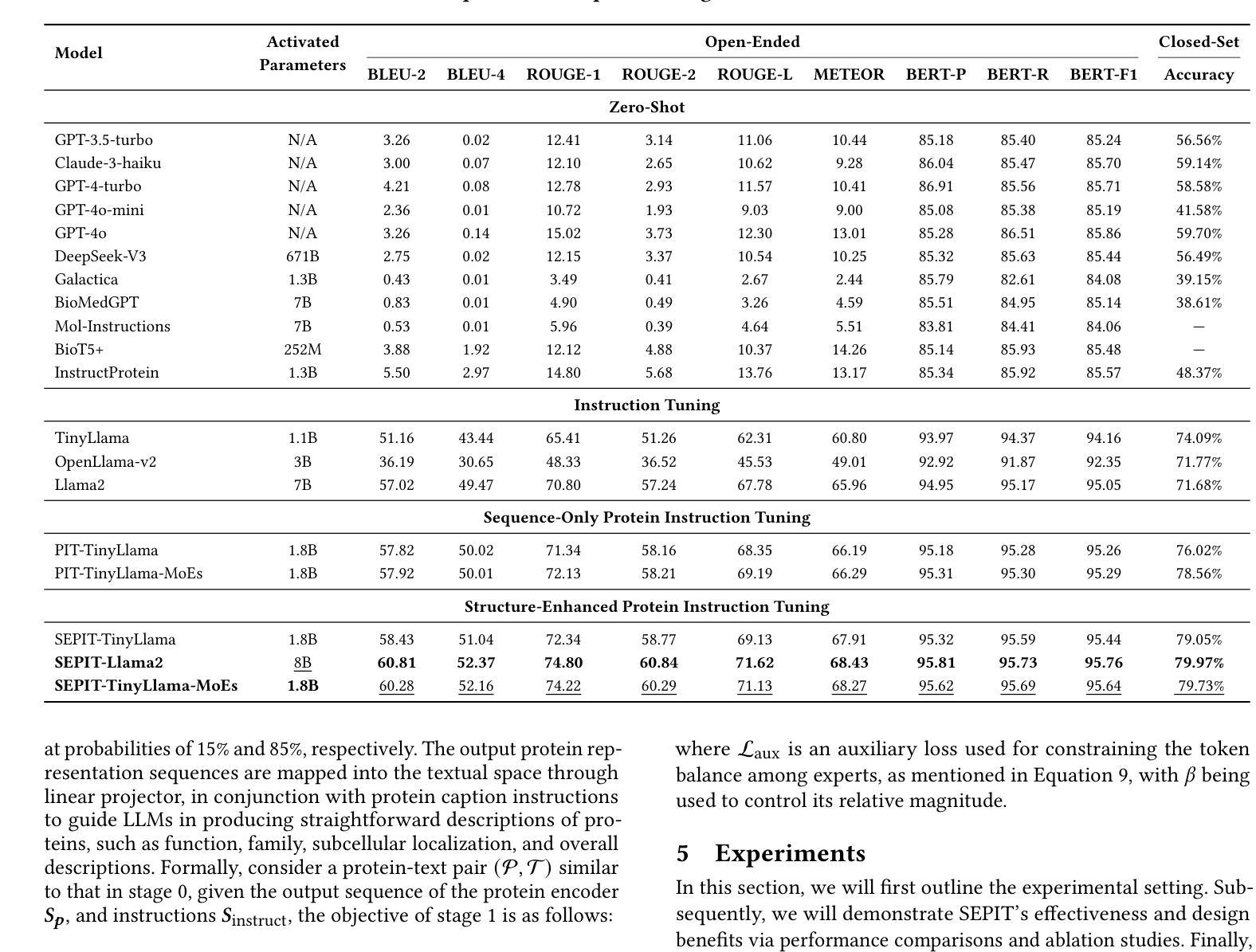
Structure-Enhanced Protein Instruction Tuning: Towards General-Purpose Protein Understanding with LLMs
Authors:Wei Wu, Chao Wang, Liyi Chen, Mingze Yin, Yiheng Zhu, Kun Fu, Jieping Ye, Hui Xiong, Zheng Wang
Proteins, as essential biomolecules, play a central role in biological processes, including metabolic reactions and DNA replication. Accurate prediction of their properties and functions is crucial in biological applications. Recent development of protein language models (pLMs) with supervised fine tuning provides a promising solution to this problem. However, the fine-tuned model is tailored for particular downstream prediction task, and achieving general-purpose protein understanding remains a challenge. In this paper, we introduce Structure-Enhanced Protein Instruction Tuning (SEPIT) framework to bridge this gap. Our approach incorporates a novel structure-aware module into pLMs to enrich their structural knowledge, and subsequently integrates these enhanced pLMs with large language models (LLMs) to advance protein understanding. In this framework, we propose a novel instruction tuning pipeline. First, we warm up the enhanced pLMs using contrastive learning and structure denoising. Then, caption-based instructions are used to establish a basic understanding of proteins. Finally, we refine this understanding by employing a mixture of experts (MoEs) to capture more complex properties and functional information with the same number of activated parameters. Moreover, we construct the largest and most comprehensive protein instruction dataset to date, which allows us to train and evaluate the general-purpose protein understanding model. Extensive experiments on both open-ended generation and closed-set answer tasks demonstrate the superior performance of SEPIT over both closed-source general LLMs and open-source LLMs trained with protein knowledge.
蛋白质作为重要的生物分子,在包括代谢反应和DNA复制等生物过程中扮演着核心角色。对其属性和功能的准确预测在生物应用中是至关重要的。最近通过监督微调开发的蛋白质语言模型(pLMs)为解决这个问题提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,微调模型是针对特定的下游预测任务定制的,实现通用蛋白质理解仍然是一个挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了结构增强蛋白质指令微调(SEPIT)框架来弥补这一差距。我们的方法将一个新的结构感知模块纳入pLMs中,以丰富其结构知识,随后将这些增强的pLMs与大型语言模型(LLMs)集成,以推进蛋白质理解。在这个框架下,我们提出了一种新的指令微调流程。首先,我们使用对比学习和结构去噪来预热增强的pLMs。然后,基于描述的指令用于建立对蛋白质的基本理解。最后,我们通过使用混合专家系统(MoEs)来捕捉更多复杂的属性和功能信息,以完善这种理解,同时保持相同的激活参数数量。此外,我们构建了迄今为止最大、最全面的蛋白质指令数据集,用于训练和评估通用蛋白质理解模型。在开放生成任务和封闭答案任务上的大量实验表明,SEPIT在封闭源通用LLMs和用蛋白质知识训练的开源LLMs上的表现均优于前者。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by KDD2025
Summary
本文介绍了Structure-Enhanced Protein Instruction Tuning(SEPIT)框架,该框架旨在弥补蛋白质语言模型(pLMs)在通用蛋白质理解方面的不足。SEPIT框架结合结构感知模块来增强pLMs的结构知识,并与大型语言模型(LLMs)集成,以促进蛋白质理解。通过对比实验,证明SEPIT框架在开放和封闭答案任务上的表现均优于封闭和开源的LLMs。
Key Takeaways
- 蛋白质在生物过程中起着关键作用,包括代谢反应和DNA复制。对其属性和功能的准确预测在生物应用中至关重要。
- 蛋白质语言模型(pLMs)的近期发展为预测蛋白质属性提供了有前途的解决方案,但实现通用蛋白质理解仍存在挑战。
- SEPIT框架结合了结构感知模块来增强pLMs的结构知识,并整合到大型语言模型(LLMs)中,旨在提高蛋白质理解。
- SEPIT采用一种新的指令调整管道,使用对比学习和结构去噪来预热增强pLMs,并通过基于字幕的指令建立基本的蛋白质理解。
- MoEs(混合专家系统)用于捕捉更复杂的属性和功能信息,同时保持激活参数数量不变。
- 构建了一个迄今为止最大和最全面的蛋白质指令数据集,用于训练和评估通用蛋白质理解模型。
点此查看论文截图

Training Nonlinear Transformers for Chain-of-Thought Inference: A Theoretical Generalization Analysis
Authors:Hongkang Li, Songtao Lu, Pin-Yu Chen, Xiaodong Cui, Meng Wang
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) is an efficient prompting method that enables the reasoning ability of large language models by augmenting the query using multiple examples with multiple intermediate steps. Despite the empirical success, the theoretical understanding of how to train a Transformer to achieve the CoT ability remains less explored. This is primarily due to the technical challenges involved in analyzing the nonconvex optimization on nonlinear attention models. To the best of our knowledge, this work provides the first theoretical study of training Transformers with nonlinear attention to obtain the CoT generalization capability so that the resulting model can inference on unseen tasks when the input is augmented by examples of the new task. We first quantify the required training samples and iterations to train a Transformer model towards CoT ability. We then prove the success of its CoT generalization on unseen tasks with distribution-shifted testing data. Moreover, we theoretically characterize the conditions for an accurate reasoning output by CoT even when the provided reasoning examples contain noises and are not always accurate. In contrast, in-context learning (ICL), which can be viewed as one-step CoT without intermediate steps, may fail to provide an accurate output when CoT does. These theoretical findings are justified through experiments.
链式思维(Chain-of-Thought,CoT)是一种高效的提示方法,它通过利用多个示例和多个中间步骤来扩展查询,从而激发大型语言模型的推理能力。尽管在实证上取得了成功,但如何训练变压器(Transformer)以实现CoT能力的理论研究仍然有待探索。这主要是因为分析非线性注意力模型上的非凸优化所涉及的技术挑战。据我们所知,这项工作首次对训练变压器与获得CoT泛化能力的非线性注意力进行了理论研究,以便在输入通过新任务的示例增强时,模型可以对未见过的任务进行推断。我们首先量化训练变压器模型实现CoT能力所需的训练样本和迭代次数。然后,我们通过在具有分布偏移的测试数据上证明其CoT泛化的成功。此外,我们对以下情况进行了理论描述:即使提供的推理示例包含噪声并不总是准确,CoT仍能产生准确的推理输出。相比之下,上下文学习(In-Context Learning,ICL)可以看作是没有中间步骤的一步式CoT,当CoT存在时,它可能无法提供准确的输出。这些理论发现通过实验得到了证实。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
此文本详细介绍了Chain-of-Thought(CoT)作为一种大型语言模型的提示方法,通过多个示例和多个中间步骤增强查询来实现推理能力。尽管在实践中取得了成功,但关于如何训练Transformer以实现CoT能力的理论研究仍然较少。本文首次研究了训练具有非线性注意力的Transformer以获取CoT泛化能力的方法,使模型能够在增强新任务输入后进行推理。文章通过理论分析和实验验证了CoT在处理未见任务以及面对分布变化测试数据时的表现,并进一步探讨了当提供的推理示例包含噪声并不完全准确时,CoT仍能准确推理的条件。此外,与被视为无中间步骤的一步式CoT(In-context learning,ICL)相比,CoT在某些情况下可以提供更准确的输出。通过一系列实验证实了这些理论发现。
Key Takeaways
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 是一种通过多个示例和中间步骤增强查询来启发大型语言模型推理能力的有效提示方法。
- 目前对于如何训练Transformer以实现CoT能力的理论研究相对较少,主要由于涉及非线性注意力模型的非凸优化分析技术挑战。
- 此研究首次探讨了训练具有非线性注意力的Transformer以获取CoT泛化能力的方法,使其能够在增强新任务输入后进行推理。
- 文章理论分析了训练样本数量和迭代次数的要求,以训练具备CoT能力的Transformer模型。
- 通过理论分析证实了CoT在未见任务上的泛化成功,特别是在处理分布变化的测试数据时。
- 当提供的推理示例包含噪声并不完全准确时,理论上描述了CoT仍能准确推理的条件。
点此查看论文截图

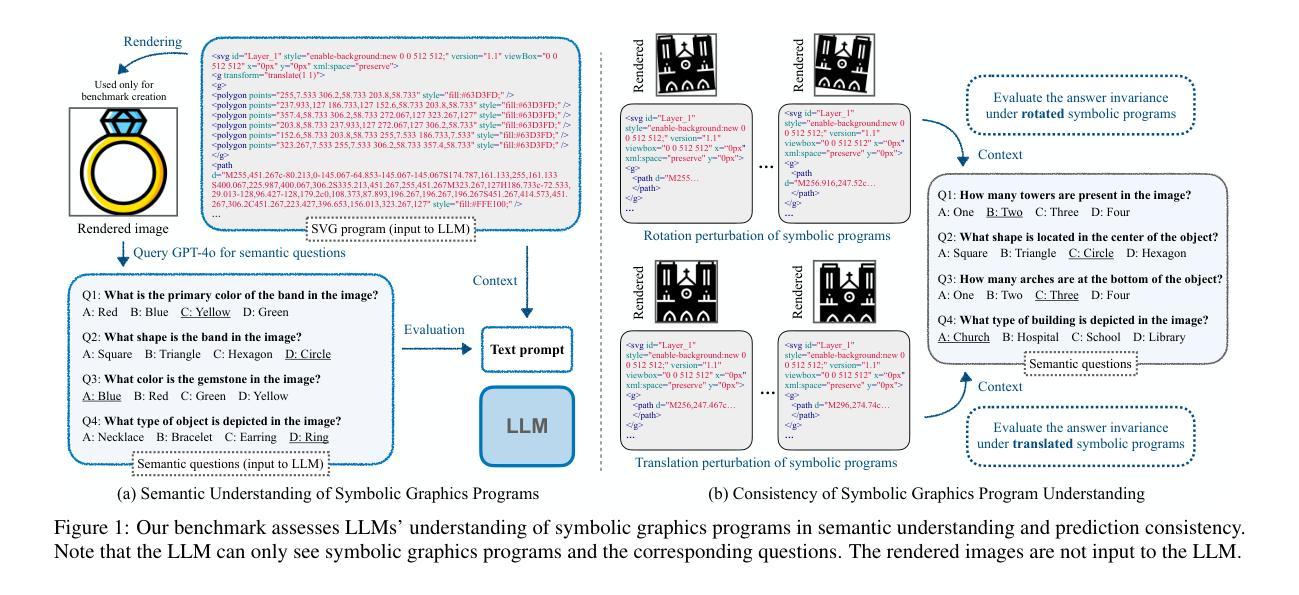
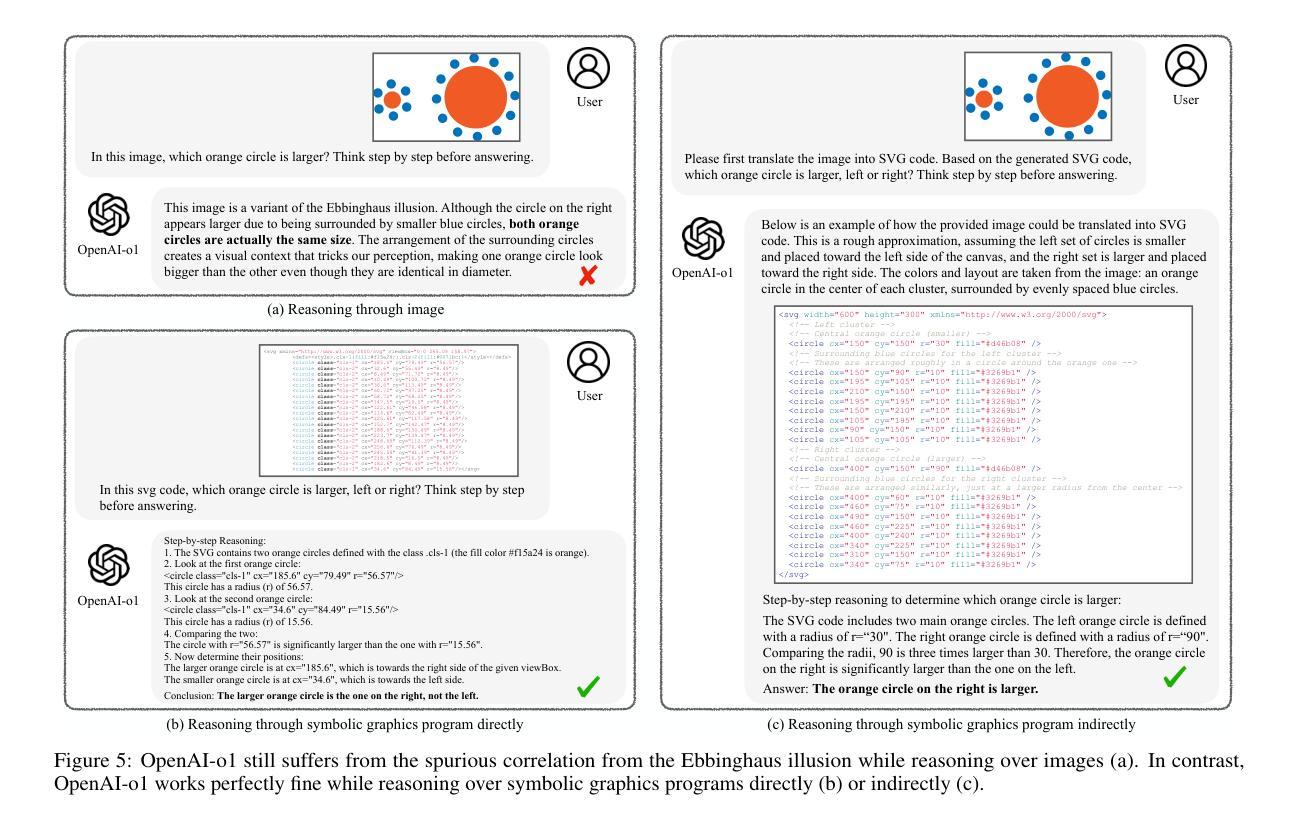
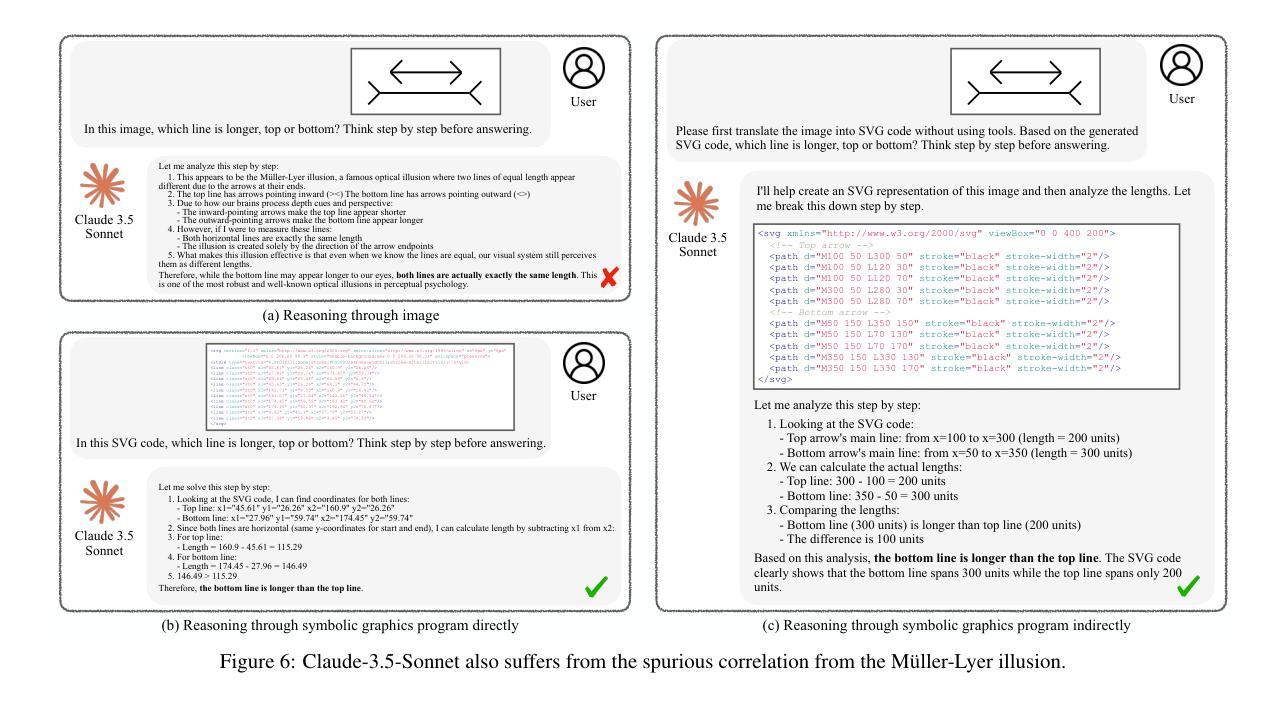
Can Large Language Models Understand Symbolic Graphics Programs?
Authors:Zeju Qiu, Weiyang Liu, Haiwen Feng, Zhen Liu, Tim Z. Xiao, Katherine M. Collins, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Adrian Weller, Michael J. Black, Bernhard Schölkopf
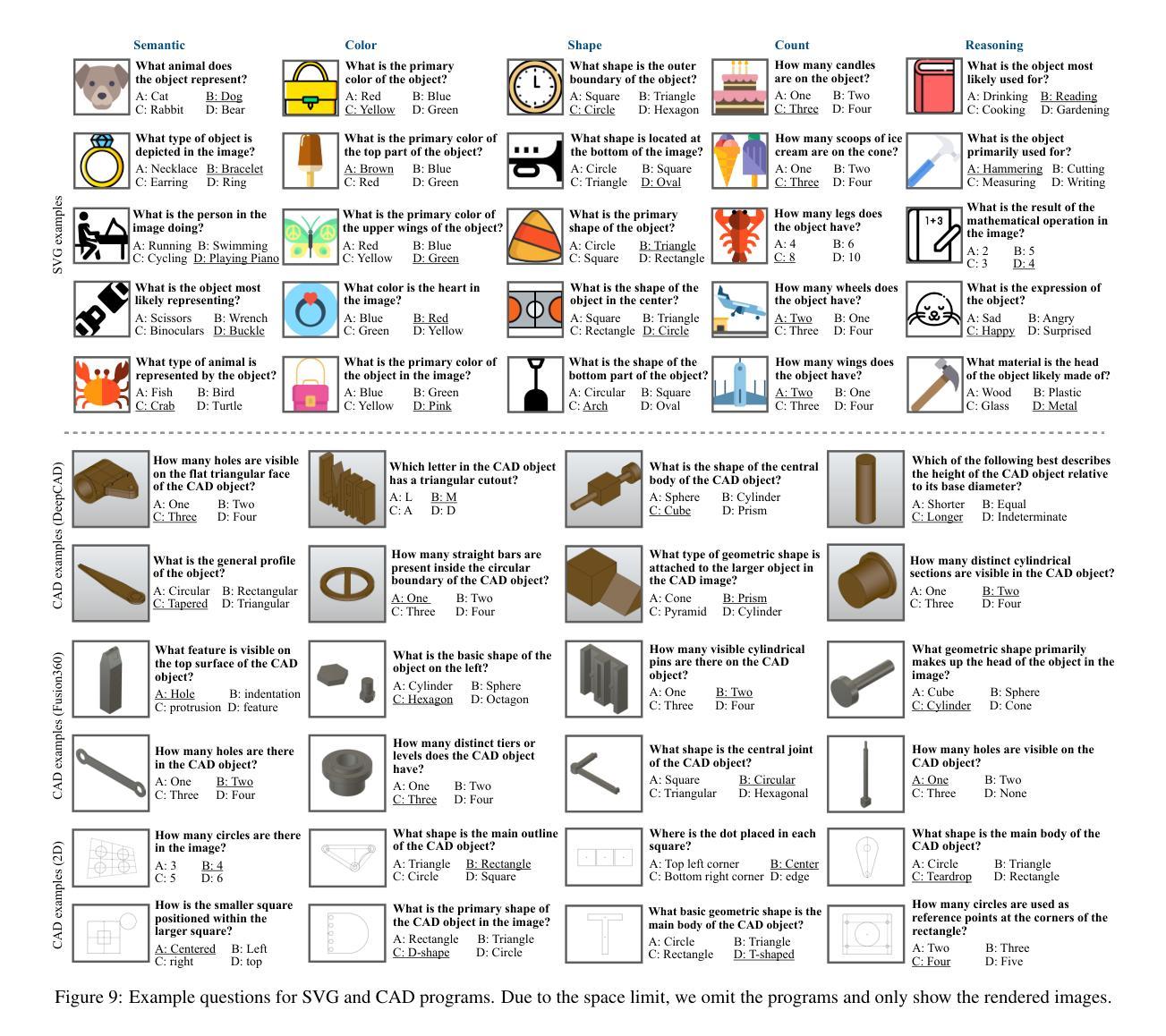
Against the backdrop of enthusiasm for large language models (LLMs), there is a growing need to scientifically assess their capabilities and shortcomings. This is nontrivial in part because it is difficult to find tasks which the models have not encountered during training. Utilizing symbolic graphics programs, we propose a domain well-suited to test multiple spatial-semantic reasoning skills of LLMs. Popular in computer graphics, these programs procedurally generate visual data. While LLMs exhibit impressive skills in general program synthesis and analysis, symbolic graphics programs offer a new layer of evaluation: they allow us to test an LLM’s ability to answer semantic questions about the images or 3D geometries without a vision encoder. To semantically understand the symbolic programs, LLMs would need to possess the ability to “imagine” and reason how the corresponding graphics content would look with only the symbolic description of the local curvatures and strokes. We use this task to evaluate LLMs by creating a large benchmark for the semantic visual understanding of symbolic graphics programs, built procedurally with minimal human effort. Particular emphasis is placed on transformations of images that leave the image level semantics invariant while introducing significant changes to the underlying program. We evaluate commercial and open-source LLMs on our benchmark to assess their ability to reason about visual output of programs, finding that LLMs considered stronger at reasoning generally perform better. Lastly, we introduce a novel method to improve this ability – Symbolic Instruction Tuning (SIT), in which the LLM is finetuned with pre-collected instruction data on symbolic graphics programs. Interestingly, we find that SIT not only improves LLM’s understanding on symbolic programs, but it also improves general reasoning ability on various other benchmarks.
在大型语言模型(LLM)备受关注的大背景下,科学评估其能力和短板的需求日益增加。这在一定程度上是非平凡的,因为很难找到模型在训练期间未曾遇到过的任务。我们利用符号图形程序,提出了一个非常适合测试LLM多方空间语义推理能力的领域。这些程序在电脑制图领域很受欢迎,可以程序性地生成视觉数据。虽然LLM在一般程序合成和分析方面表现出令人印象深刻的技能,但符号图形程序提供了一层新的评估:它们允许我们测试LLM回答关于图像或3D几何的语义问题的能力,而无需使用视觉编码器。为了语义地理解符号程序,LLM需要拥有仅凭符号描述局部曲率和笔触来“想象”并推理相应图形内容外观的能力。我们通过创建用于符号图形程序语义视觉理解的大型基准测试来评估LLM,该测试采用程序构建,几乎不需要人工参与。我们特别重视图像转换任务,该任务在保持图像级别语义不变的同时,为底层程序引入了重大变化。我们在基准测试上评估了商用和开源的LLM,以评估它们对程序视觉输出的推理能力,发现被认为在推理方面更出色的LLM通常表现更好。最后,我们引入了一种改进这种能力的新方法——符号指令微调(SIT),对LLM进行微调,使其适应预先收集的符号图形程序的指令数据。有趣的是,我们发现SIT不仅提高了LLM对符号程序的理解能力,而且还提高了其在其他基准测试中的一般推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 Spotlight (v4: 47 pages, 26 figures, project page: https://sgp-bench.github.io/)
摘要
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)的科学评估问题,提出利用符号图形程序领域测试LLM的空间语义推理能力。符号图形程序能够程序化生成视觉数据,为评估LLM提供了新的层面。LLM在该任务中展现出强大的程序合成和分析能力,需要通过理解符号程序来回答关于图像或3D几何的语义问题。为此,文章创建了一个大型基准测试,用于评估LLM对符号图形程序的理解能力,并强调图像语义不变而底层程序发生显著变化的转换。文章评估了商业和开源LLM在此基准测试上的表现,并提出一种新方法——符号指令微调(SIT)来提高LLM的理解能力。实验发现,SIT不仅能提高LLM对符号程序的理解,还能提高其在其他基准测试上的推理能力。
关键见解
- LLM的空间语义推理能力需要通过科学评估,符号图形程序领域是测试此能力的合适选择。
- 符号图形程序能够程序化生成视觉数据,为评估LLM提供了新层面。
- LLM在程序合成和分析方面表现出强大能力,需要通过理解符号程序来回答关于图像或3D几何的语义问题。
- 创建了一个大型基准测试,用于评估LLM对符号图形程序语义视觉理解的能力。
- 评估了商业和开源LLM在基准测试上的表现,发现推理能力较强的LLM表现更好。
- 引入了一种新方法——符号指令微调(SIT),以提高LLM对符号程序的理解及推理能力。
点此查看论文截图


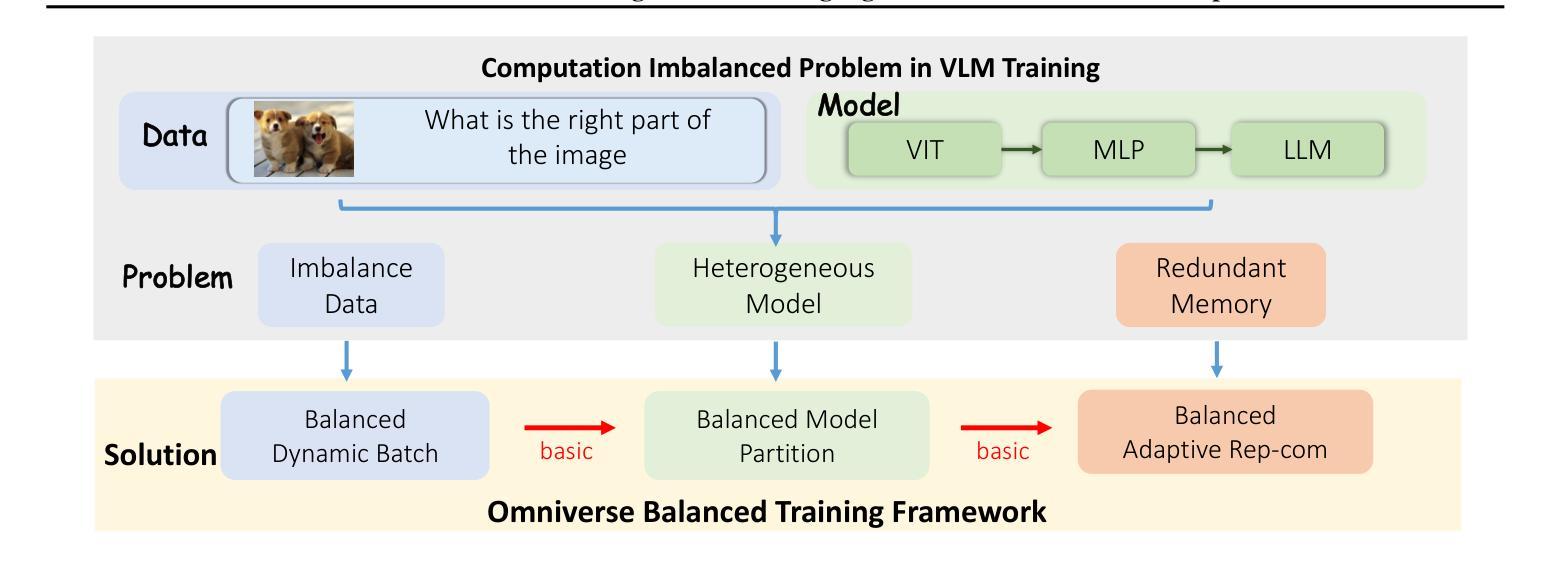
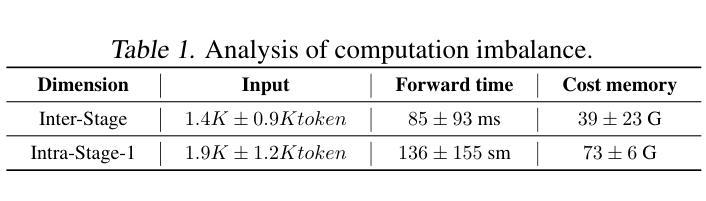
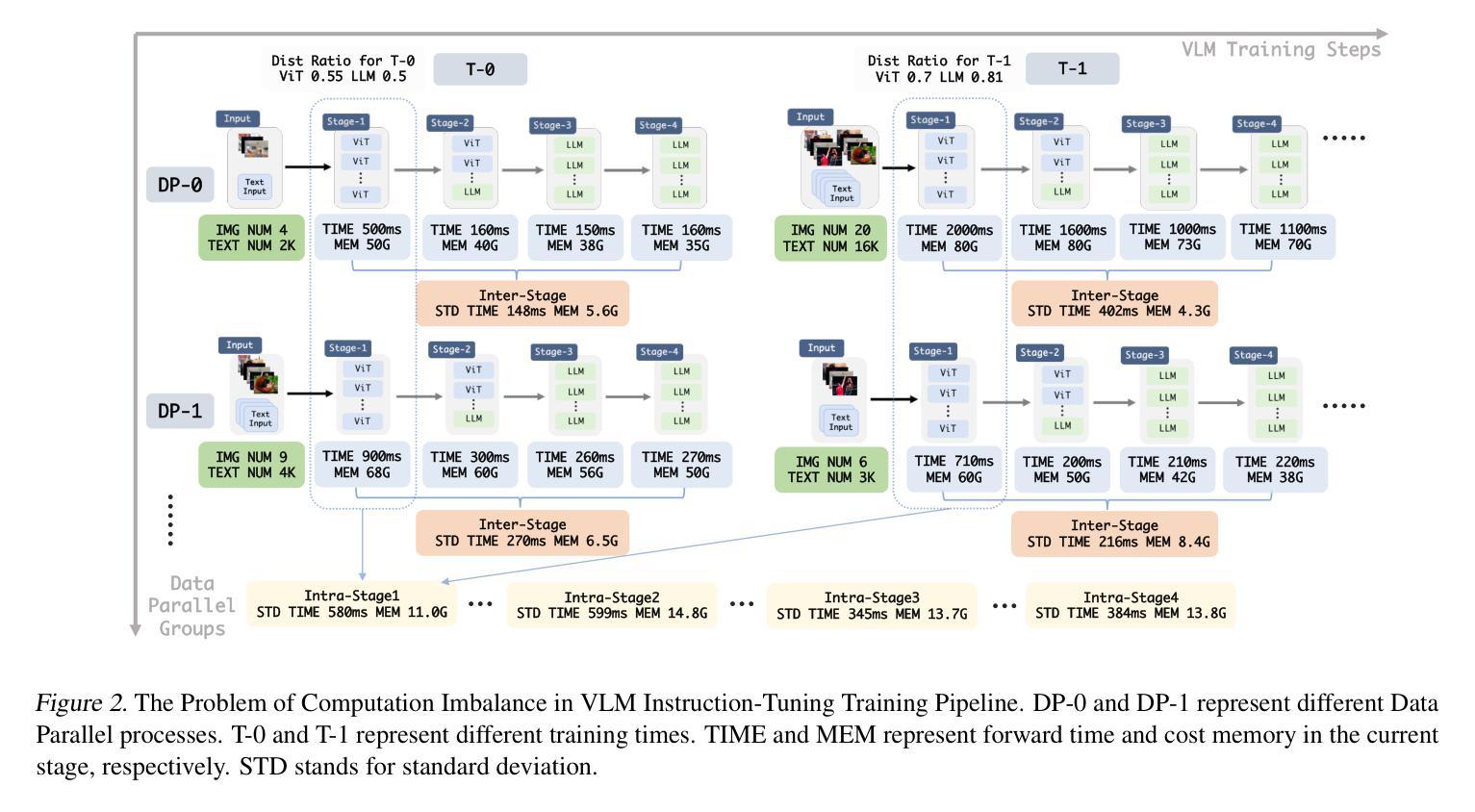
OmniBal: Towards Fast Instruction-Tuning for Vision-Language Models via Omniverse Computation Balance
Authors:Yongqiang Yao, Jingru Tan, Feizhao Zhang, Jiahao Hu, Yazhe Niu, Xin Jin, Bo Li, Pengfei Liu, Ruihao Gong, Dahua Lin, Ningyi Xu
Vision-language instruction-tuning models have recently achieved significant performance improvements. In this work, we discover that large-scale 3D parallel training on those models leads to an imbalanced computation load across different devices. The vision and language parts are inherently heterogeneous: their data distribution and model architecture differ significantly, which affects distributed training efficiency. To address this issue, we rebalance the computational load from data, model, and memory perspectives, achieving more balanced computation across devices. Specifically, for the data, instances are grouped into new balanced mini-batches within and across devices. A search-based method is employed for the model to achieve a more balanced partitioning. For memory optimization, we adaptively adjust the re-computation strategy for each partition to utilize the available memory fully. These three perspectives are not independent but are closely connected, forming an omniverse balanced training framework. Extensive experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our method. Compared with the open-source training code of InternVL-Chat, training time is reduced greatly, achieving about 1.8$\times$ speed-up. Our method’s efficacy and generalizability are further validated across various models and datasets. Codes will be released at https://github.com/ModelTC/OmniBal.
视觉语言指令调整模型最近取得了显著的性能改进。在这项工作中,我们发现大规模3D并行训练这些模型会导致不同设备间计算负载不平衡。视觉和语言部分本质上是异构的:它们的数据分布和模型架构存在很大差异,从而影响分布式训练效率。为了解决这一问题,我们从数据、模型和内存三个方面重新平衡计算负载,实现设备间更平衡的计算。具体来说,对于数据,实例会在设备和跨设备之间分组形成新的平衡小批次。采用基于搜索的方法对模型进行更平衡的分区。为了优化内存,我们自适应地调整每个分区的重新计算策略,以充分利用可用内存。这三个方面不是独立的,而是紧密相关的,形成了一个全方位平衡的训练框架。进行了大量实验来验证我们方法的有效性。与InternVL-Chat的开源训练代码相比,我们的训练时间大大缩短,实现了约1.8倍的速度提升。我们的方法的有效性和通用性在各种模型和数据集上得到了进一步验证。代码将在https://github.com/ModelTC/OmniBal发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模视觉语言指令微调模型在性能上取得了显著的提升。本研究发现大规模三维并行训练会导致不同设备间计算负载不均衡。为解决这一问题,我们从数据、模型和内存三个角度重新平衡计算负载,实现了设备间的均衡计算。通过实例分组、模型搜索和内存优化等方法,形成全方位平衡的训练框架。实验证明,该方法能有效提高训练效率,与公开代码InternVL-Chat相比,训练时间大幅缩短,实现了约1.8倍的加速效果,且该方法在不同模型和数据集上具有有效性和泛化性。相关代码将发布在https://github.com/ModelTC/OmniBal上。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模视觉语言指令微调模型在性能上有显著提升。
- 三维并行训练导致不同设备间计算负载不均衡。
- 提出从数据、模型和内存三个角度重新平衡计算负载的方法。
- 通过实例分组、模型搜索和内存优化形成全方位平衡的训练框架。
- 与公开代码相比,训练时间大幅缩短,实现了约1.8倍的加速效果。
- 该方法在不同模型和数据集上具有有效性和泛化性。
点此查看论文截图


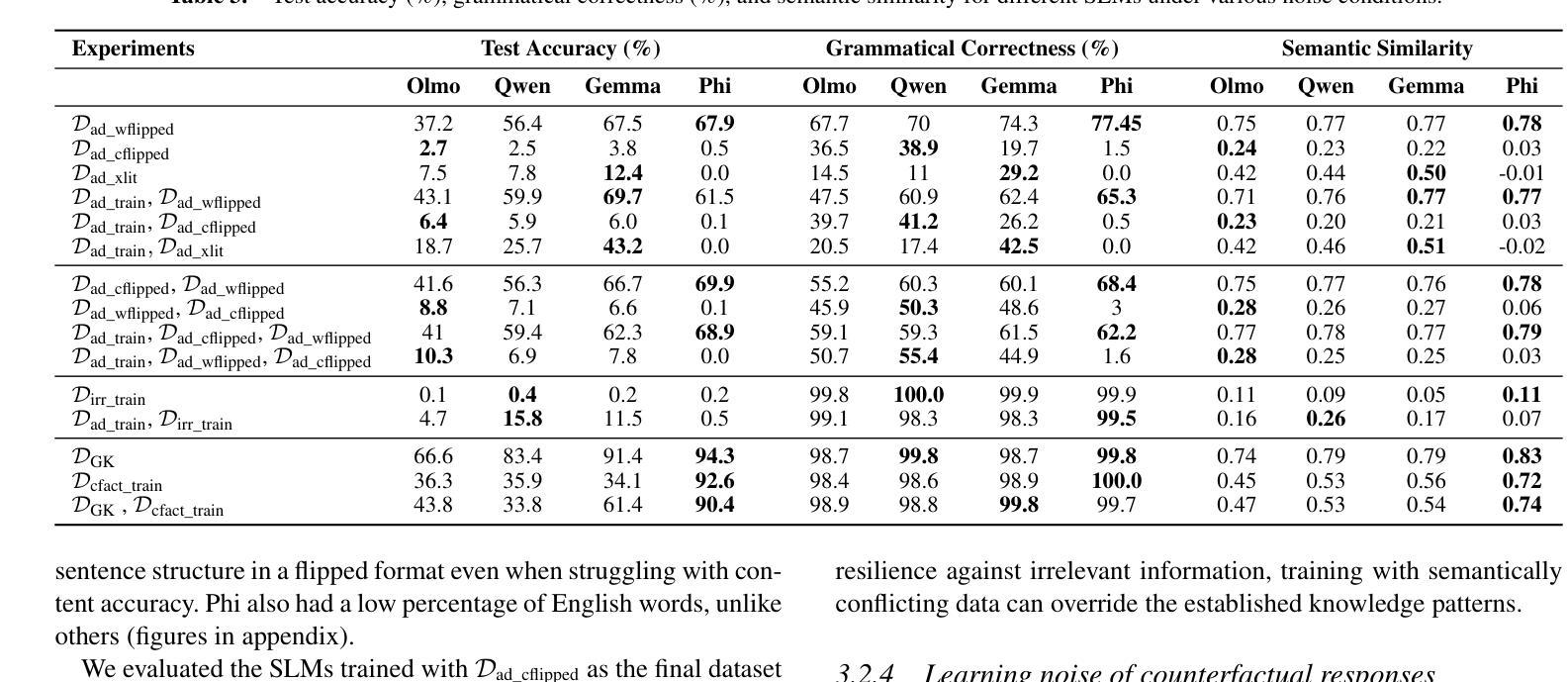
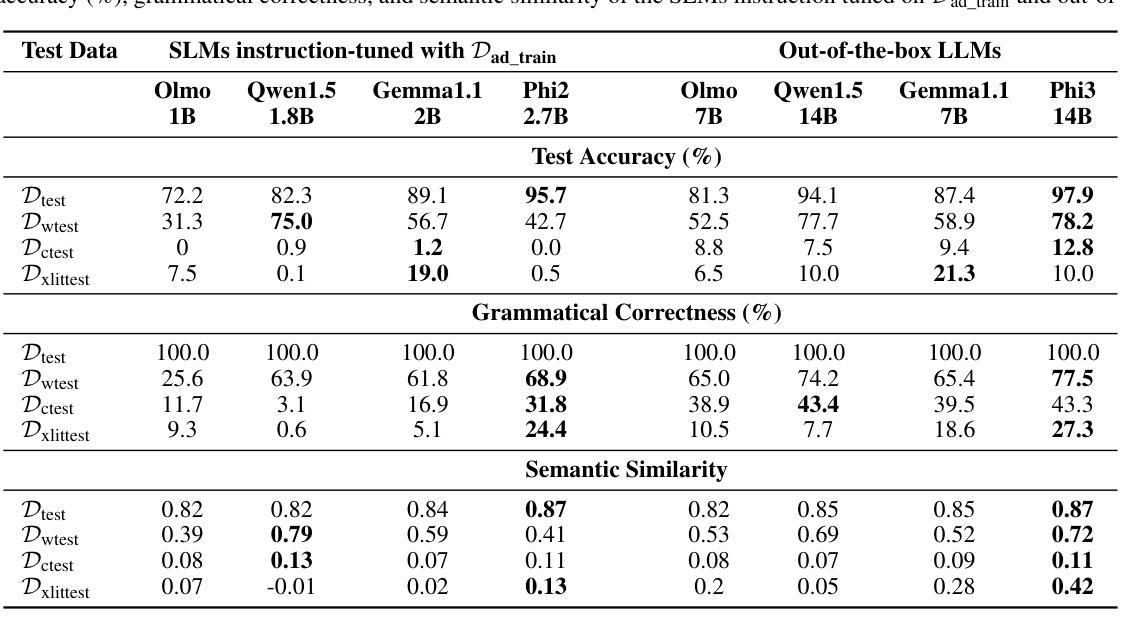
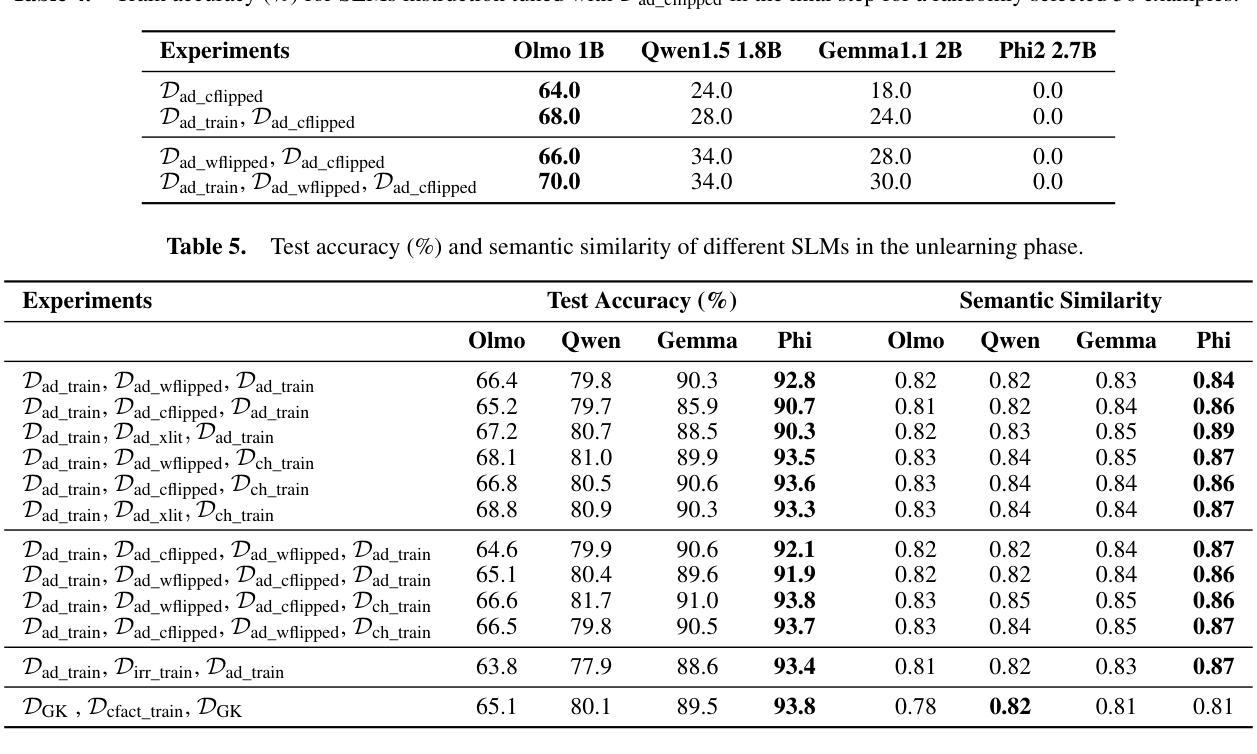
Can Small Language Models Learn, Unlearn, and Retain Noise Patterns?
Authors:Nicy Scaria, Silvester John Joseph Kennedy, Deepak Subramani
With the growing need for efficient language models in resource-constrained environments, Small Language Models (SLMs) have emerged as compact and practical alternatives to Large Language Models (LLMs). While studies have explored noise handling in LLMs, little is known about how SLMs handle noise, a critical factor for their reliable real-world deployment. This study investigates the ability of SLMs with parameters between 1 and 3 billion to learn, retain, and subsequently eliminate different types of noise (word flip, character flip, transliteration, irrelevant content, and contradictory information). Four pretrained SLMs (Olmo 1B, Qwen1.5 1.8B, Gemma1.1 2B, and Phi2 2.7B) were instruction-tuned on noise-free data and tested with in-context examples to assess noise learning. Subsequently, noise patterns were introduced in instruction tuning to assess their adaptability. The results revealed differences in how models handle noise, with smaller models like Olmo quickly adapting to noise patterns. Phi2’s carefully curated, structured, and high-quality pretraining data enabled resistance to character level, transliteration, and counterfactual noise, while Gemma adapted successfully to transliteration noise through its multilingual pretraining. Subsequent clean data training effectively mitigated noise effects. These findings provide practical strategies for developing robust SLMs for real-world applications.
随着资源受限环境中对高效语言模型的需求不断增长,小型语言模型(SLMs)作为大型语言模型(LLMs)的紧凑实用替代品应运而生。虽然已有研究探索了LLM中的噪声处理,但对于SLM如何处理噪声知之甚少,这是其可靠现实世界部署的关键因素。本研究旨在探讨参数在1到3亿之间的SLM学习、保留和随后消除不同类型噪声(单词翻转、字符翻转、音译、无关内容和矛盾信息)的能力。本研究选择了四个预训练SLM(Olmo 1B、Qwen1.5 1.8B、Gemma1.1 2B和Phi2 2.7B),它们在无噪声数据上进行指令微调,并通过上下文实例进行测试,以评估噪声学习能力。随后,在指令微调中引入噪声模式以评估其适应性。结果表明,各模型处理噪声的方式存在差异,较小的模型如Olmo能迅速适应噪声模式。Phi2经过精心策划、结构化和高质量的预训练数据,使其能够抵抗字符级别、音译和反向事实的噪声,而Gemma则通过其多语言预训练成功适应了音译噪声。随后的清洁数据训练有效地减轻了噪声影响。这些发现为实现稳健的SLM用于实际应用提供了实用策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究探讨了小型语言模型(SLM)在处理噪音方面的能力,这对于资源受限环境中的实际部署至关重要。实验结果显示不同SLM在处理不同噪音类型(如词语翻转、字符翻转、音译、无关内容和矛盾信息)时存在差异。通过引入噪声模式对模型进行适应性评估,发现小型模型可以快速适应噪声模式。某些模型由于其预训练数据的特性,如Phi2,具有抵抗字符级别、音译和反向事实的噪声的能力。随后进行的清洁数据训练有效地减轻了噪声的影响。这些发现为开发用于实际应用的稳健SLM提供了实用策略。
Key Takeaways:
- 小型语言模型(SLM)作为紧凑且实用的替代方案,满足了资源受限环境中对高效语言模型的需求。
- 目前对于SLM处理噪音的能力的研究尚不足。
- 本研究调查了SLM在学习、保留和消除不同类型噪音(如词语翻转、字符翻转等)方面的能力。
- 不同SLM在处理噪音时存在差异,小型模型可以快速适应噪声模式。
- 某些模型的预训练数据特性使其具有抵抗特定类型噪声的能力。
- 清洁数据训练可以有效地减轻噪声对SLM的影响。
点此查看论文截图